- 1Research Institute of Marine Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Qingdao, China
- 2Qingdao Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Qingdao, China
- 3Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 4College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
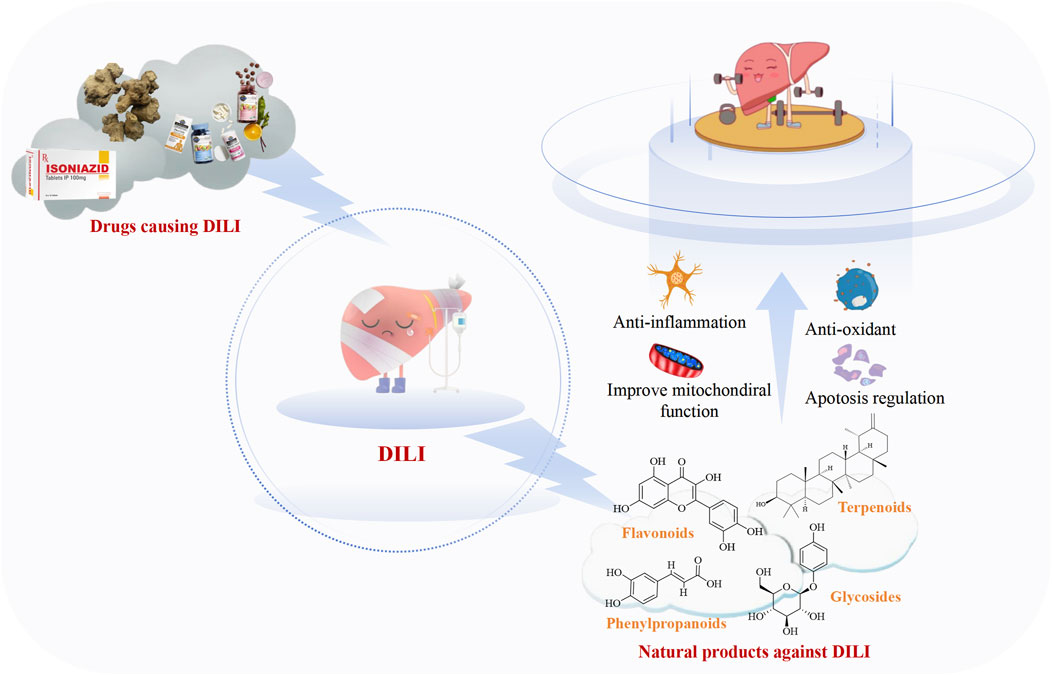
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a major cause of drug development failure and post-marketing restrictions. To date, over 1,000 drugs have been reported to cause liver damage, such as acetaminophen, isoniazid, methotrexate, triptolide and so on. However, there are currently no effective therapies for DILI. Plant-derived natural products including flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, terpenoids, and glycosides have been used for the treatment of DILI due to their low toxicity and strong bioactivity. These anti-DILI compounds involve multiple mechanisms, such as reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, restoring mitochondrial function, and suppressing apoptosis. This review primarily summarizes the recent advances over the past 5 years in the therapeutic potential of natural products against a range of commonly used hepatotoxic drugs rather than focusing on a specific hepatotoxic agent. The insights will provide a cue for further research and promote the development of novel and effective drugs for treating DILI.
1 Introduction
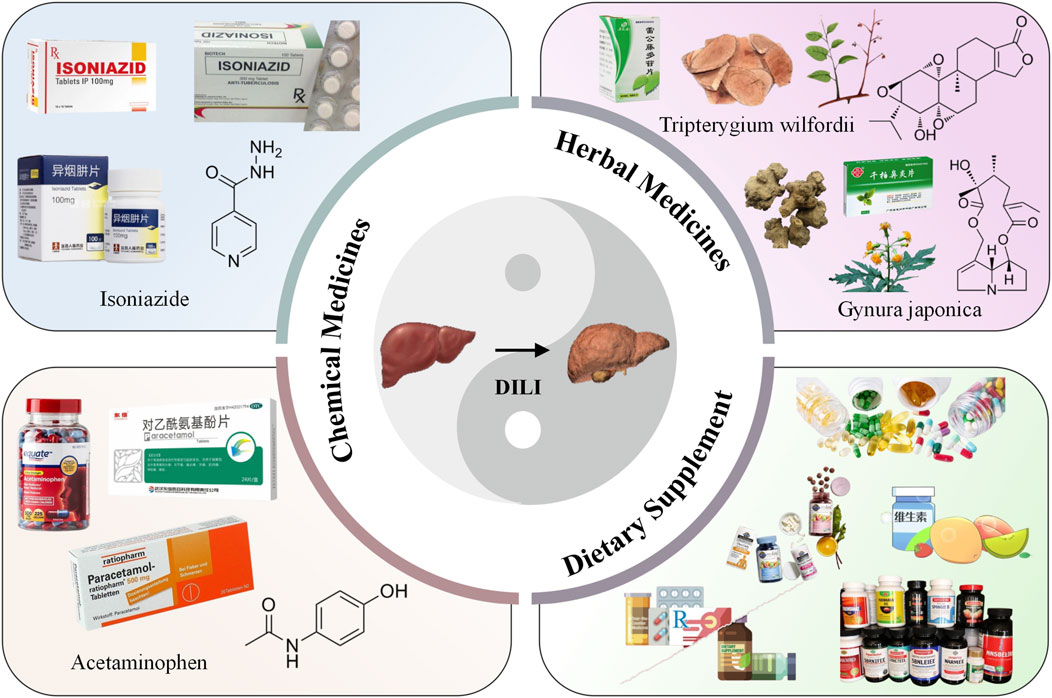
The liver accounts for approximately 2% of the human body weight, and it performs many vital functions including metabolism, synthesis, detoxification, immunity, hematopoiesis, blood storage, blood volume regulation, and coagulation (Berasain et al., 2023; Li J. et al., 2024). However, many commonly used medications pose a high risk of causing liver injury, which is an uncommon but challenging clinical problem with respect to both diagnosis and treatment (Hoofnagle and Björnsson, 2019). Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) remains a leading cause of drug development termination and post-marketing warnings and restriction of use. To date, over 1,000 drugs have been reported to cause liver injury, which can develop into necrosis, cirrhosis, liver failure and cancer, or even death (Ma et al., 2023; Neshat et al., 2021). Both prescription and non-prescribed drugs may harm the liver, including medications, herbal medicines, and dietary supplements (Garcia-Cortes et al., 2020; Real et al., 2019; Figure 1). According to the statistics, the incidence of DILI is 14–19/100,000 people in Western countries, and it is the most common cause of acute liver failure (Hosack et al., 2023; Björnsson and Björnsson, 2022; European Association for the Study of the Liver, 2019). Meanwhile, in China, it is estimated that the annual occurrence in the general population is approximately 23.80/100,000, which is higher than that reported in Western countries (Ma et al., 2023). It has a low incidence among the general population, but DILI has become more prevalent in hospitalized patients, especially among patients with unexplained liver conditions (Hosack et al., 2023; Li et al., 2022). In addition, smoking, alcohol consumption, viral infections, and drug–drug interactions can exacerbate DILI (Rani et al., 2024). Although the past decade has witnessed major efforts in the prevention and treatment of other liver diseases, progress on these fronts has been modest in the case of DILI (Devarbhavi et al., 2023).
Natural products derived from diverse sources, including plants, animals, microorganisms, fermentation products, and marine organisms, exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activities and chemical structures. These compounds hold significant potential as alternative or adjunctive therapeutic agents (Rao et al., 2019; Atanasov et al., 2021). The medicinal application of natural products can be tracked to the origins of traditional Chinese medicine. In recent years, with the increasing scientific interest in natural products among researchers, an increasing number of natural products have been identified as having beneficial effects on liver diseases (Aboelez et al., 2024; Abouzed et al., 2024). Plant-derived flavonoids, terpenoids, phenylpropanoids, and glycosides have validated hepatoprotective properties (Sahu et al., 2023; Xu G. B. et al., 2018; Guo C. et al., 2024; Thilagavathi et al., 2023). For instance, silymarin, a phenylpropanoid from Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn., has been utilized in alcoholic or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and drug-induced liver injury (Gillessen and Schmidt, 2020). Similarly, schizandrin A and B from Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., have been shown to exert hepatoprotective effects, particularly in the prevention and treatment of liver diseases (Zhang X. et al., 2020). However, despite the fact that natural products and their derivatives accounted for over one-third of all FDA-approved new molecular entities in the past 5 years (Luo et al., 2024), few natural products have been approved specifically for combating DILI by FDA. In this review, we comprehensively summarized the recent advances in the field of hepatoprotective effects of natural products, aiming to provide valuable insights for future research and facilitate the development of novel, effective therapeutics against DILI.
2 The classification and pathogenesis characteristics of DILI
Based on the pathogenesis, DILI is typically classified into two types: intrinsic (direct) and idiosyncratic. However, indirect injury has been increasingly recognized as a third type. The characteristics of DILI pathogenesis are shown in Table 1 (Hoofnagle and Björnsson, 2019; Ma et al., 2023). Intrinsic liver injury is caused by medications or substances that are intrinsically toxic to the liver. Common causative agents include acetaminophen, nicotinic acid, aspirin, cocaine, amiodarone, methotrexate, certain chemotherapeutic drugs, and traditional Chinese medicines containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids. This type of liver injury is common, predictable, and dose-dependent. It typically has a short latency period and presents clinically as acute hepatitis (Garcia-Cortes et al., 2020; Maris et al., 2025). In contrast, idiosyncratic DILI is often described as being unpredictable and not dose-related (Ma et al., 2023). Although idiosyncratic liver injury is not considered dose-dependent, such injury is more commonly associated with orally administered drugs at daily doses ≥50 mg or with agents capable of triggering immune-mediated reactions (Björnsson and Björnsson, 2022). Unlike the above two types of liver injury, indirect drug-induced liver injury arises from the effects of a drug rather than from intrinsic hepatotoxicity or an idiosyncratic reaction to the medication. For example, protein kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies can induce immune-mediated liver injury. Additionally, indirect injury may manifest as the onset of a new liver condition or exacerbation of a pre-existing condition (Hoofnagle and Björnsson, 2019).
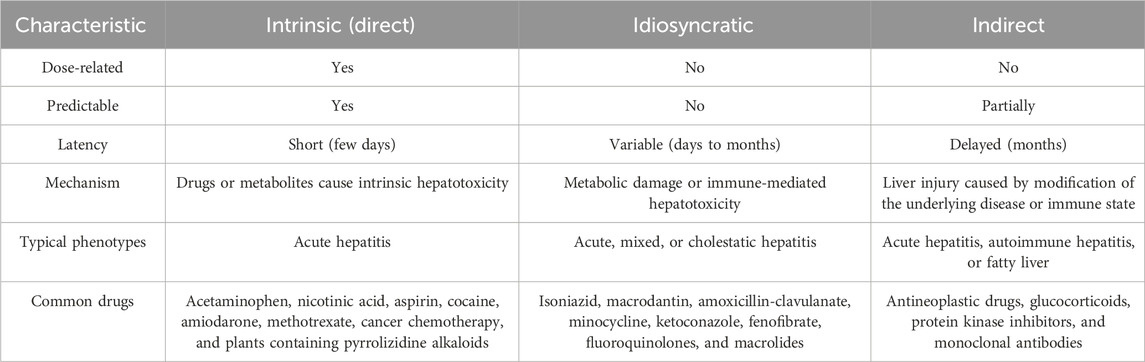
Table 1. Characteristics of DILI pathogenesis (Ma et al., 2023).
3 Plant-derived natural anti-DILI products
3.1 Flavonoids
Flavonoids are natural polyphenolic compounds, characterized by a general structure consisting of two benzene rings (Shen et al., 2022). At present, more than 5,000 flavonoids have been identified in different sources, mainly from the Compositae, Lamiaceae, Rutaceae, and Scrophulariaceae families, which show extensive bioactivities (Wen et al., 2021; Li C. H. et al., 2023). Both in vivo and in vitro studies exhibited the potential effect of flavonoids in preventing and treating liver diseases.
3.1.1 Quercetin
Quercetin, a well-known natural antioxidant, is widely present in vegetables, fruits, and medicinal plants (Andres et al., 2018). Rats were given quercetin (25 mg/kg or 50 mg/kg p.o.) for 14 days, which decreased vincristine-induced liver injury via modulating the levels of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1), SIRT1/PGC-1α, and NF-kB/STAT3 (Çomaklı et al., 2023). These results suggested that the liver-protective activities are closely related to its potent antioxidant properties and multi-pathway regulatory capacity.
3.1.2 Baicalin
Baicalin is the main compound from the Chinese medicinal plant Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, which possess various pharmacological activities such anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, and antioxidant activities (Hou et al., 2024). Furthermore, several studies showed that baicalin plays an important therapeutic role in liver disease, including DILI (Hu M. L. et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021). Baicalin promotes hepatocyte proliferation after acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury (Shi et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2024). It can induce the accumulation of Nrf2 (Shi et al., 2018; 2020), subsequently activating the NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome (Shi et al., 2020). Furthermore, baicalin mediates the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway, thereby promoting liver repair in APAP-induced liver injury (Zhang et al., 2024). Taken together, these findings suggest that liver regeneration is likely the primary mechanism by which baicalin exerts its protective effects against DILI.
3.1.3 Kaempferol
Kaempferol, a flavonoid predominantly isolated from the rhizome of Kaempferia galanga L., is also ubiquitously distributed in various vegetables and fruits. It has been extensively studied for its various biological activities such as anti-oxidation, cancer prevention, neuroprotection, and hepatoprotection (Amjad et al., 2022; Dong et al., 2023; Bangar et al., 2023). Rats were orally administered 250 mg/kg kaempferol for 7 days, which activated the silent information regulator 1 and decreased the acetylation of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ), forkhead transcription factors-1 (FOXO-1), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and p53 in the APAP-induced liver injury model (BinMowyna and AlFaris, 2021). Additionally, Li et al. showed that kaempferol mediated the Nrf2 pathway and upregulated the levels of glutathione peroxidase 4 (Gpx4) in mouse liver and L02 cells to inhibit ferroptosis induced by APAP (Li Y. G. et al., 2023). Similar to other flavonoids, the role of kaempferol in DILI is related to its antioxidant capacity, which may be attributed to the presence of phenolic hydroxyl groups in its structure.
3.1.4 Hyperoside
As a quercetin-derived flavonol galactoside, hyperoside, also known as quercetin-3-O-galactoside, is extensively found in Hypericaceae, Rosaceae, Campanulaceae, and Lamiaceae members. It exhibits multiple pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective effects (Xu et al., 2022). Notably, hyperoside attenuated liver damage caused by APAP, pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs), and the chemotherapeutic agent cisplatin (Xie et al., 2016a; Hu C. et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2023a; Niu et al., 2017). Xie and Hu et al.’s studies suggested that hyperoside protects APAP-induced liver injury by regulating the glutathione pathway and suppressing the activity of Cyp2e1 in mice (Xie et al., 2016a; Hu F. F. et al., 2020). Furthermore, it has also been shown to exert a protective effect against PA-induced liver injury by ameliorating transcription factor EB-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction (Xu et al., 2023a). Although hyperoside was beneficial for various DILI models, its in vitro and in vivo mechanism still needs to be further explored.
3.1.5 Naringin
Naringin is a dihydroflavonoid that is mainly found in the Rue family, such as grapefruits and oranges. It is also a main component of traditional Chinese medicine, including Drynariae Rhizoma, Aurantii Fructus, Aurantii Fructus Immaturus, and Citri Grandis Exocarpium (Yang et al., 2022). Naringin has been reported to exert various biological and pharmacological effects (Chen J. et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2024; Heidary et al., 2020; Ahmed et al., 2019). Growing evidence suggests that naringin exerts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects that are effective in the treatment of liver diseases (Zhu et al., 2024; Shirani et al., 2020). Recent studies have shown that naringin can also ameliorate multi drug-induced hepatotoxicity, particularly against chemotherapeutic agents. A prominent example is doxorubicin, a highly effective anticancer drug whose clinical application is significantly constrained by severe dose-dependent organ toxicity, including hepatotoxicity, cardiotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and neurotoxicity (Pugazhendhi et al., 2018). Xi et al. found that naringin attenuates doxorubicin-induced liver injury by upregulating the expression levels of sirtuin (SIRT1) and inhibiting the downstream inflammatory, apoptotic, and oxidative stress signaling pathways in mice and in alpha mouse liver 12 (AML-12) cells (Xi et al., 2023). In addition, naringin alleviates gefitinib-, methotrexate-, and oxaliplatin-induced liver injury through anti-oxidation and inhibition of autophagy and apoptosis (Liu et al., 2024; Elsawy et al., 2020; Ileriturk et al., 2024); however, the specific molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways require further investigation. Moreover, naringin was found to upregulate the expression of cation transport regulator-like protein 2 (CHAC2) and activate the Nrf2 pathway, thereby exerting a protective effect against APAP-induced liver injury (Zhai et al., 2022). Collectively, these findings highlight the potential of naringin as a natural therapeutic agent for the prevention or treatment of DILI.
3.1.6 Other flavonoids
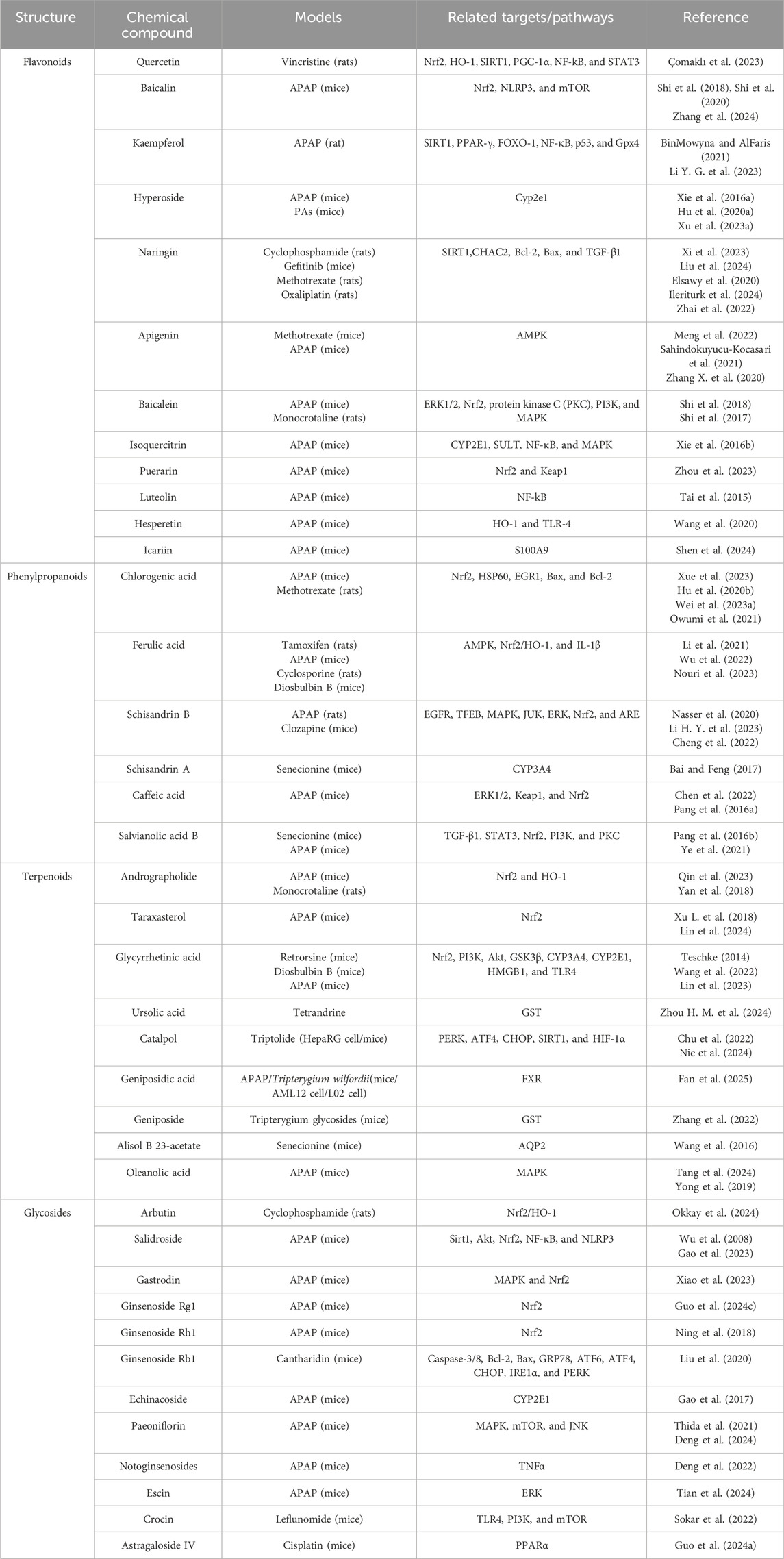
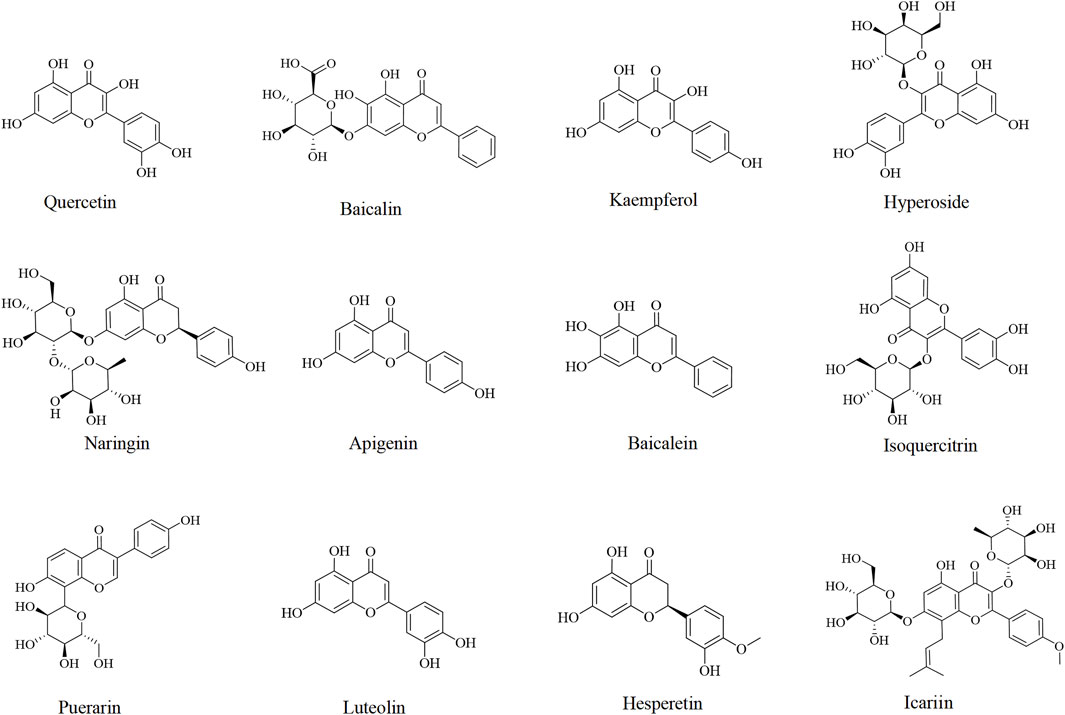
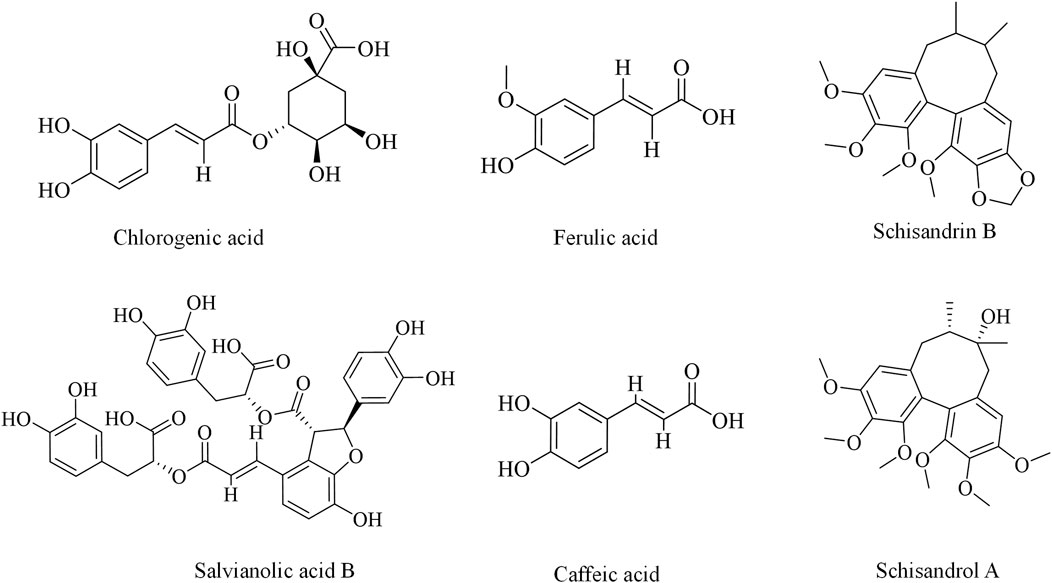
Other flavonoids including apigenin (Meng et al., 2022; Sahindokuyucu-Kocasari et al., 2021; Zhang W. et al., 2020), baicalein (Shi et al., 2017), isoquercitrin (Xie et al., 2016b), puerarin (Zhou et al., 2023), luteolin (Tai et al., 2015), hesperetin (Wang et al., 2020), and icariin (Shen et al., 2024) have also been studied for their potential in the prevention and treatment of DILI, which are listed in Table 2 and Figure 2.
3.2 Phenylpropanoids
Phenylpropanoids, which include phenylpropionic acid, phenylpropenes, phenylpropanols, phenylpropionaldehydes, coumarins, lignans, and lignins, are characterized by a core C6–C3 carbon skeleton (Li et al., 2025). As a major class of phenolic compounds, phenylpropanoids are widely distributed in plants and exhibit a broad range of biological activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammation, anti-cancer, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, and hepatoprotective effects (Neelam et al., 2020).
3.2.1 Chlorogenic acid
Chlorogenic acid, a typical phenolic acid, is formed by a conjugation between the hydroxy group of quinic acid and the carboxyl group of caffeic acid. It is commonly derived from the Caprifoliaceae family plants such as Lonicera japonica Thunb. (Nguyen et al., 2024). Previous studies have demonstrated that chlorogenic acid exerts protective effects against DILI both in vitro and in vivo (Pang et al., 2015; Zheng et al., 2016; Xue et al., 2023). Nrf2 plays a key role in the hepatoprotective effects of chlorogenic acid, which alleviates APAP-induced liver injury by regulating heat shock protein 60 (HSP60)-initiated liver inflammation (Hu F. F. et al., 2020). Another study showed that chlorogenic acid promotes liver regeneration and repair in APAP-intoxicated mice by transcriptionally activating the early growth response-1 (EGR1) (Wei M. J. et al., 2023). Furthermore, chlorogenic acid has been reported to alleviate tamoxifen- and methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats by mitigating inflammation and apoptosis and enhancing the antioxidant defense (Owumi et al., 2021; Ali et al., 2017). However, the underlying mechanisms of these effects have not yet been fully elucidated.
3.2.2 Ferulic acid
Ferulic acid is widely found in plants of the Umbelliferae, Ranunculaceae, and Liliaceae families, such as Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort., Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels., and Cimicifuga heracleifolia Kom. (Zhang and Gao, 2020). It possesses multiple bioactivities, with particularly notable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (Li et al., 2021). Ferulic acid holds great potential in alleviating DILI due to its characteristics. Treatment with 25 mg/kg ferulic acid three times per 12 h is shown to restore liver function to normal levels in mice with APAP-induced liver injury, along with the upregulation of hepatic specific markers and AMPK phosphorylation. Additionally, ferulic acid ameliorated APAP-induced mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in hepatocytes (Wu et al., 2022). It also activated the Nrf2/hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1) signaling axis and decreased the expressions of inflammatory cytokines including NF-kB, TNFα, and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) (Nouri et al., 2023). These findings demonstrated that the hepatoprotective effects of ferulic acid are closely related to its antioxidant capacity. Moreover, Chen et al. reported that ferulic acid mitigated diosbulbin B-induced hepatotoxicity by reducing the formation of reactive metabolite protein adducts (Chen et al., 2023).
3.2.3 Schisandrin B
Schisandrin B is one of the main lignan compounds isolated from the traditional Chinese medicine Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. Numerous studies have shown that schisandrin B plays an essential role in liver protection (Nasser et al., 2020). Li et al. found that schisandrin B inhibited the production of TNF-α and IL-1β; upregulated the expression levels of beclin-1, transcription factor EB (TFEB), and LC-3; and downregulated the expressions of autophagy-related protein 3 (ATG3) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in APAP-treated HepG2 cells (Li H. Y. et al., 2023). It has also been reported that schisandrin B can not only activate the pentose phosphate pathway but also suppress the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway in an APAP-induced liver cell line (HHL-5 cells) (Cheng et al., 2022). In addition, schisandrin B was found to have protective effects against clozapine-induced liver injury via the activation of the Nrf2/antioxidant response element (ARE) signal pathway (Bai and Feng, 2017). Although these studies suggested that schisandrin B can alleviate DILI, its in vivo mechanism of action remains unclear.
3.2.4 Other phenylpropanoids
Other phenylpropanoids including schisandrin A (Chen et al., 2022), caffeic acid (Pang et al., 2016a; Pang et al., 2016b), and salvianolic acid B (Ye et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2015) have also been reported to possess significant potential in the prevention and treatment of DILI, as summarized in Table 2 and illustrated in Figure 3.
3.3 Terpenoids
Terpenoids are a class of active natural products characterized by a complex structure and diverse biological activities. Based on the number of isoprene units in their chemical structure, terpenoids are classified into several subclasses, including hemiterpenoids, monoterpenoids, sesquiterpenoids, diterpenoids, sesterterpenes, triterpenoids, tetraterpenes, and polyterpenes (Kuang, 2017). The hepatoprotective potential of terpenoids in the prevention and treatment of liver diseases has attracted considerable attention (Wei J. R. et al., 2023; Yao and Liu, 2022).
3.3.1 Andrographolide
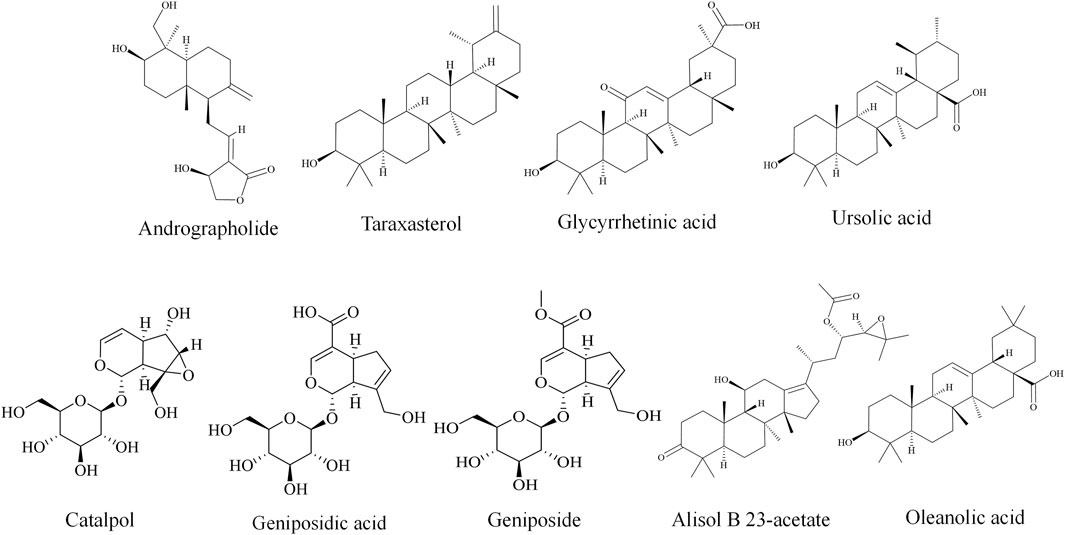
Andrographolide is a diterpenoid compound isolated from Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees, and it has been clinically used for the treatment of upper respiratory tract infection (Hossain et al., 2021; Zeng et al., 2022). Recent studies have showed that andrographolide exerts a curative effect in liver diseases (Qin et al., 2023). Long-term ingestion of APAP can induce liver fibrosis, while andrographolide has been shown to alleviate APAP-induced liver fibrosis in mice by activating Nrf2 and upregulating the expression of downstream genes glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCLC and GCLM) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) (Yan et al., 2018). These results suggested that the hepatoprotective effect of andrographolide was closely associated with its antioxidant capacity. Additionally, Huang et al. indicated that andrographolide can attenuate monocrotaline-induced hepatotoxicity by modulating Nrf2-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant responses (Huang et al., 2023).
3.3.2 Taraxasterol
Taraxasterol is a pentacyclic triterpenoid compound with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities derived from Taraxacum mongolicum (Jiao et al., 2022). Previous studies have indicated that taraxasterol exhibits protective effects in various liver diseases (Sang et al., 2019; Xu L. et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2024; Ge et al., 2023). In APAP-treated mice and cell models, taraxasterol was shown to restore the expression of Nrf2 and alleviate APAP-induced cellular injury. In addition, Lin et al. further revealed that taraxasterol decreases CYP1A1 expression and increases UGT1A1 expression (Lin et al., 2024). In another study, Ge et al. reported that taraxasterol markedly suppresses APAP-induced liver oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and apoptosis. The underlying mechanisms were related to the modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and JNK phosphorylation (Ge et al., 2023).
3.3.3 Glycyrrhetinic acid
Glycyrrhetinic acid, a hydrolyzed metabolite of glycyrrhizic acid in vivo, is one of the prominent active compounds of Glycyrrhiza uralensis (Pastorino et al., 2018). It is also a pentacyclic triterpenoid with hepatoprotective, antioxidant, and anti-tumor effects, which have attracted considerable attention among scientists (Chen Y. et al., 2024). Owing to the well-documented liver-protective properties of Glycyrrhiza uralensis, numerous studies have suggested that glycyrrhetinic acid may contribute significantly to its hepatoprotective potential (Wu et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2024). Traditional Chinese medicine containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids or diosbulbin B are recognized as causes of DILI (Liu et al., 2024; Teschke, 2014). Wang et al. showed that glycyrrhetinic acid exerts protective effects against PA-induced liver injury in rats by potentiating the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant system through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β) pathway (Wang et al., 2022). In addition, glycyrrhetinic acid can inhibit the metabolic activation of diosbulbin B, thereby reducing its hepatotoxic effects in mice (Lin et al., 2023). Additionally, pretreatment with glycyrrhetinic acid significantly downregulated the expression of CYP2e1 and the high mobility group box 1(HMGB1)-toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) in APAP-exposed mice (Yang et al., 2017). Collectively, these studies suggested that glycyrrhetinic acid may have great potential in the prevention and treatment of DILI.
3.3.4 Ursolic acid
Ursolic acid is a pentacyclic triterpenoid compound that is widely distributed in a variety of plants belonging to the Oleaceae, Lamiaceae, Rosaceae, and Scrophulariaceae families (Zhang and Zhu, 2011). It shows hepatoprotective effects in several liver injury models (Zheng et al., 2024; Zhou L. F. et al., 2024). Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), as an important phase II enzyme, play a crucial role in mediating the protective effect of ursolic acid against tetrandrine-induced hepatotoxicity. Specifically, ursolic acid was found to alleviate tetrandrine-induced oxidative stress injury by competitively binding to the GST H-site pockets, thereby blocking the interaction between tetrandrine and glutathione S-transferase Mu 1 (GSTM1) (Chu et al., 2022). Although these findings suggest a novel mechanism and a potential therapeutic target for improving tetrandrine-induced hepatotoxicity, further studies are required to validate these observations and explore their clinical relevance.
3.3.5 Catalpol
Catalpol is an iridoid monosaccharide found in several plants, including Rehmanniae Radix, and it exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic capacities. Growing evidence supports its protective effects against DILI. Zhang et al. and Fu et al. demonstrated that catalpol suppresses excessive autophagy through the PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway and synergistically activates phase-I and phase-II detoxifying enzymes via the CAR and NRF2 pathways, ultimately attenuating triptolide-induced liver toxicity (Zhang et al., 2022; Fu et al., 2020). Furthermore, based on metabolomics analyses, catalpol was found to alleviate triptolide-induced hepatic injury in mice by regulating the SIRT1/HIF-1α signaling pathway, which contributed to the restoration of hepatic glucose metabolism disorder and oxidative stress (Nie et al., 2024). These findings highlighted the therapeutic anti-DILI potential of catalpol, particularly through mechanisms related to metabolic dysfunction and oxidative stress.
3.3.6 Geniposidic acid
Geniposidic acid, a natural iridoid glycoside, is a major active constituent of Gardeniae Fructus, which has been reported to alleviate liver injury through regulating bile acid and cholesterol metabolism (Song et al., 2022). As a farnesoid X receptor (FXR)-specific agonist, geniposidic acid could influence bile acid homeostasis in multiple DILI models, such as APAP-acute DILI, Tripterygium wilfordii-acute DILI, and Tripterygium wilfordii-chronic DILI. Moreover, geniposidic acid has been shown to enhance CYP-mediated bile acid metabolism and inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis via miR-19a-3p regulation (Fan et al., 2025). This dual regulatory action contributed to the restoration of hepatic metabolic balance and underscored its therapeutic potential in the treatment of DILI.
3.3.7 Other terpenoids
Other terpenoids including geniposide (Wang et al., 2016), alisol B 23-acetate (Tang et al., 2024), and oleanolic acid (Yong et al., 2019; Wang and Liu, 2024) have therapeutic potential against DILI, as listed in Table 2 and Figure 4.
3.4 Glycosides
Glycosides are widely distributed in plants due to their unique structural characteristics. They represent an important class of active ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine and have a wide range of biological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antibacterial, anticancer, antiaging, and hepatoprotective effects (Shah et al., 2022; Alizadeh and Ebrahimzadeh, 2022; Li J. et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2020).
3.4.1 Arbutin
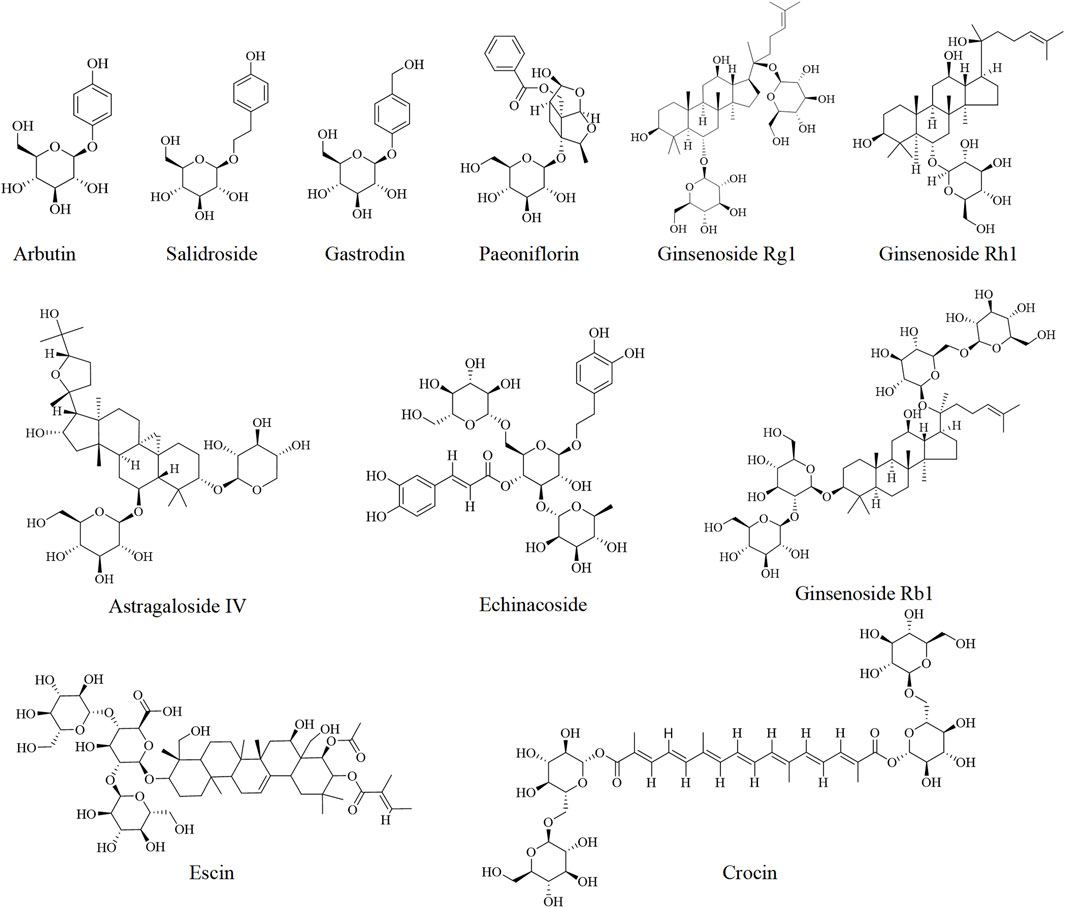
Arbutin is a naturally occurring glucoside extracted from plants, and it exhibits various pharmacological activities. It is a bioactive polyphenol composed of a hydroquinone moiety bound to a D-glucose molecule, and it is commonly used in cosmetics and herbal dietary supplements (Wang Q. L. et al., 2024). Arbutin has shown protective effects against liver diseases (Jiang et al., 2023; Okkay et al., 2024). Administration of arbutin (25 and 50 mg/kg) for 2 weeks markedly alleviated cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Furthermore, arbutin could suppress inflammatory markers and hepatocyte apoptosis and increase antioxidant capacity. These effects are associated with the activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway (Alruhaimi, 2023). However, the underlying mechanisms through which arbutin attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced liver injury remain to be elucidated.
3.4.2 Salidroside
Salidroside, a phenolic glycoside compound extracted from Rhodiola crenulata, used in traditional Chinese medicine, is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-hypoxia effects (Zhang et al., 2021; Liang et al., 2024). Several studies have suggested that salidroside exerts protective effects in liver disease models (Hu Q. C. et al., 2021; Zhang J. Q. et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2008). Salidroside promoted sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) expression, activated the Akt/Nrf2 pathway, and inhibited the NF-kB/nucleotide-binding domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome axis in APAP-treated L02 cells and in mice (Gao et al., 2023). Furthermore, Xu et al. found that salidroside alleviates APAP-induced liver injury via activating the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway, which is associated with the inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated ferroptosis in the activating transcription factor 4 (AFT4)-cation transport regulator homolog 1 (CHAC1) axis (Xu et al., 2023b). In conclusion, these findings indicated that salidroside has great potential for protecting and alleviating liver damage.
3.4.3 Gastrodin
Gastrodin is the major active phenolic glycoside extracted from Gastrodia elata Bl., which has been widely used in the clinic. It exhibits extensive pharmacological activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular protective, neuroprotective, and hepatoprotective effects (Wang Y. L. et al., 2024; Xiao et al., 2023). Intraperitoneal injection of gastrodin (at concentrations ranging from 15 mg/kg to 45 mg/kg) significantly attenuated APAP-induced liver injury in mice. Gastrodin could reduce the production and release of inflammatory factors (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) and oxidative stress. The results showed that the hepatoprotective effect of gastrodin is closely related to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, potentially involving the activation of the ERK/JUK/MAPK and Nrf2 signaling pathways (Liao et al., 2022).
3.4.4 Ginsenosides
Ginsenosides, characterized by their triterpenoid glycoside structure, are the principal active components of Panax ginseng. To date, more than 100 types of ginsenosides have been identified and isolated from P. ginseng (Li Q. et al., 2024). These compounds exhibit a broad range of pharmacological activities that include, but are not limited to, anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation, immune regulation, and anticancer effects (Yu et al., 2019; Cai et al., 2022). In various pathological models of liver disease, ginsenosides have been found to show hepatoprotective effects (Yi, 2024; Li X. K. et al., 2023; Zhou H. M. et al., 2024; Guo J. A. et al., 2024). For instance, continuous treatment with ginsenoside Rg1 for 3 days enhanced the antioxidant and detoxification capacities in mice with APAP-induced liver injury, which was related to the activation of the antioxidant defense system through the Nrf2 signaling pathway (Ning et al., 2018). In addition, Bi et al. reported that ginsenoside Rg1 not only markedly decreases the levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β but also regulates those of apoptosis-related proteins such as Bax and Bcl-2 in APAP-treated mice. Similarly, ginsenoside Rh1 also exerted comparable hepatoprotective effects (Bi et al., 2021). Cantharidin, the active compound of Mylabris, is used as an anticancer agent. However, its clinical use is mainly limited due to hepatotoxicity (Liu et al., 2020). Research has found that ginsenoside Rb1 mitigates cantharidin-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Ginsenoside Rb1 could downregulate the expression of glucose-regulating protein 78 (GRP78) and inhibit the pancreatic ER kinase (PERK)-activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), thus activating inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha (IRE1α) and the transcription factor 6 (ATF6) pathway (Xiong et al., 2024). Nevertheless, only a few studies have explored the protective effects of Rb1 against cantharidin-induced liver injury, and its underlying mechanisms are yet to be fully elucidated. Given their chemical diversity and potent hepatoprotective effects (Wu et al., 2025; Gao et al., 2017), ginsenosides provide a promising new insight into the development of natural products for the treatment of DILI.
3.4.5 Other glycosides
Other glycosides including echinacoside (Thida et al., 2021), paeoniflorin (Deng et al., 2024; 2022), notoginsenosides (Tian et al., 2024), escin (Lee et al., 2019), crocin (Sokar et al., 2022), and astragaloside IV (Guo Y. T. et al., 2024) have shown effectiveness in the prevention and treatment of DILI, which are listed in Table 2 and Figure 5.
4 Discussion and perspectives
DILI is an infrequent but serious adverse reaction to drugs or other xenobiotics. It may occur either as a predictable event when an individual is exposed to toxic doses of some drugs or as an unpredictable event with many commonly used medications (Andrade et al., 2019). DILI is a significant issue that needs to be taken seriously during the development and application of drugs. Although the concept of DILI was proposed several decades ago (Allison et al., 2023), more efforts are still needed for its investigation. Natural products, as the primary ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine, have become valuable resources for the development of novel pharmaceuticals due to their low toxicity and side effects, extensive and strong bioactivities, and abundant availability.
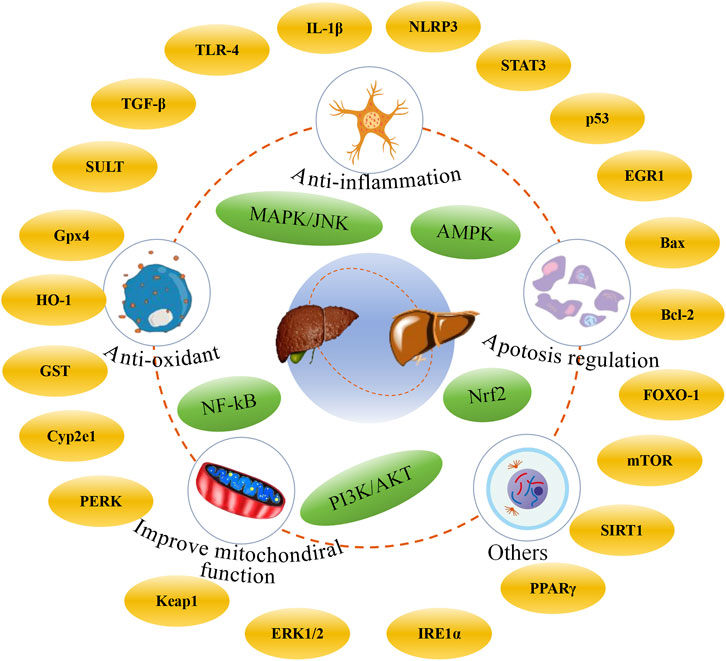
In this review, we systematically summarized the recent advances in natural products with potential anti-DILI effects (including flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, terpenoids, and glycosides) over the past 5 years, and the mechanisms of hepatoprotective effects were also discussed. It is widely recognized that these compounds exhibit significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which alleviate the symptoms of DILI, such as cellular inflammation and cholestasis, which frequently occur in the clinic (Björnsson and Björnsson, 2022). The mechanisms involve multiple pathways and targets, such as anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation, improvement of mitochondrial function, and inhibition of apoptosis (Figure 6). However, the application of natural products in the prevention and treatment of DILI is associated with several notable limitations and challenges. First, it should be noted that many studies have only been conducted in preclinical animal models, and the clinical evidence remains limited. Moreover, the intricate signaling pathways involved in natural products for the prevention and treatment of DILI require further exploration to fully understand the mechanism of action of natural products. Second, compared with other liver diseases, researchers have conducted relatively fewer studies on DILI in recent years. The emergence of such phenomena might be related to public awareness, supervision of market, and policies. DILI is a complex condition and is influenced by multiple risk factors, especially idiosyncratic DILI. These factors include, but are not limited to, age, gender, genetic, environment, and disease state (Allison et al., 2023). As the liver is the primary site of medications metabolism, DILI still represents an inescapable and potentially fatal challenge in the evaluation of drug safety. Although APAP cannot exclusively cause liver damage, we found that APAP-induced liver injury with reproducibility, stability, and clinical relevance is one of the most common models to evaluate the potential of natural products against DILI (Jaeschke and Ramachandran, 2024; Stravitz and Lee, 2019; Jaeschke et al., 2013). Nevertheless, it is noteworthy that hepatotoxic drugs, including anti-cancer drugs such as doxorubicin, tamoxifen, and methotrexate, and traditional Chinese medicines containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids, tetrandrine, and diosbulbin B, are attracting increasing attention in the fields of toxicology, public health, nutrition, and food science. In addition, it is crucial to focus not only on the intrinsic effects of the drugs themselves but also on their potential interactions.
Therefore, based on the above discussion, we should (1) increase the screening of bioactive compounds and the investigation of their mechanisms against DILI; (2) establish stable and mature animal models for a variety of DILIs and investigate the individual differences in DILIs by diverse genetic models to explore the genetic variability; (3) enhance collaboration between clinical application and fundamental research to bridge the gap between them; (4) study the biomarkers of DILI patients for future research on natural products-based hepatoprotection.
5 Conclusion
In summary, while natural products have considerable potential in the prevention and treatment of DILI, overcoming the limitations and challenges still requires sustained research efforts and collaborative endeavors. With continued in-depth research, it is possible to develop more natural products and their derivatives that are effective, efficient, cheaper, and have low side-effects for the prevention and treatment of DILI and other diseases.
Author contributions
YC: Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YM: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. LH: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. KL: Validation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF (grant number GZC20231506), the Youth Project of Scientific Research Foundation of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (grant number KYZK2024Q31), and the Central Government’s Special Program for Guiding Local Science and Technology Development Science and Technology Plan for the Benefit of the People Special Project (Science and Technology Cooperation) (grant Number 24-1-4-3zyyd-nsh).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aboelez, M. O., Ezelarab, H. A. A., Alotaibi, G., and Abouzed, D. E. E. (2024). Inflammatory setting, therapeutic strategies targeting some pro-inflammatory cytokines and pathways in mitigating ischemia/reperfusion-induced hepatic injury: a comprehensive review. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 397 (9), 6299–6315. doi:10.1007/s00210-024-03074-y
Abouzed, D. E. A., Ezelarab, H. A. A., Selim, H. M. R. M., Elsayed, M. M. A., Hamd, M. A. E., and Aboelez, M. O. (2024). Multimodal modulation of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury by phytochemical agents: a mechanistic evaluation of hepatoprotective potential and safety profiles. Int. Immunopharmacol. 138, 112445. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112445
Ahmed, S., Khan, H., Aschner, M., Hasan, M. M., and Hassan, S. T. S. (2019). Therapeutic potential of naringin in neurological disorders. Food Chem. Toxicol. 132, 110646. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2019.110646
Ali, M., Rashid, S., Nafees, S., Hasan, S. K., Shahid, A., Majed, F., et al. (2017). Protective effect of chlorogenic acid against methotrexate induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rat liver: an experimental approach. Chem. Biol. Interact. 272, 80–91. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2017.05.002
Alizadeh, S. R., and Ebrahimzadeh, M. A. (2022). O-Glycoside quercetin derivatives: biological activities, mechanisms of action, and structure-activity relationship for drug design, a review. Phytother. Res. 36 (2), 778–807. doi:10.1002/ptr.7352
Allison, R., Guraka, A., Shawa, I. T., Tripathi, G., Moritz, W., and Kermanizadeh, A. (2023). Drug induced liver injury-a 2023 update. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 26 (8), 442–467. doi:10.1080/10937404.2023.2261848
Alruhaimi, R. S. (2023). Protective effect of arbutin against cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and hepatotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 30 (26), 68101–68110. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-27354-x
Amjad, E., Sokouti, B., and Asnaashari, S. (2022). A systematic review of anti-cancer roles and mechanisms of kaempferol as a natural compound. Cancer Cell Int. 22 (1), 260. doi:10.1186/s12935-022-02673-0
Andrade, R. J., Chalasani, N., Björnsson, E. S., Suzuki, A., Kullak-Ublick, G. A., Watkins, P. B., et al. (2019). Drug-induced liver injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 5 (1), 58. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0105-0
Andres, S., Pevny, S., Ziegenhagen, R., Bakhiya, N., Schäfer, B., Hirsch-Ernst, K. I., et al. (2018). Safety aspects of the use of quercetin as a dietary supplement. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 62 (1), 1700447. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201700447
Atanasov, A. G., Zotchev, S. B., Dirsch, V. M., and Supuran, C. T. (2021). Natural products in drug discovery: advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20 (3), 200–216. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-00114-z
Bai, H. Y., and Feng, S. (2017). Protection effects of schizandrin B against liver injury induced by clozapine in mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. 52 (3), 390–396.
Bangar, S. P., Chaudhary, V., Sharma, N., Bansal, V., Ozogul, F., and Lorenzo, J. M. (2023). Kaempferol: a flavonoid with wider biological activities and its applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 63 (28), 9580–9604. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2067121
Berasain, C., Arechederra, M., Argemí, J., Fernández-Barrena, M. G., and Avila, M. A. (2023). Loss of liver function in chronic liver disease: an identity crisis. J. Hepatol. 78 (2), 401–414. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.09.001
Bi, Y. F., Li, Q. Y., Tao, W. M., Tang, J. X., You, G. F., and Yu, L. (2021). Ginsenoside Rg1 and ginsenoside Rh1 prevent liver injury induced by acetaminophen in mice. J. Food Biochem. 45, e13816. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13816
BinMowyna, M. N., and AlFaris, N. A. (2021). Kaempferol suppresses acetaminophen-induced liver damage by upregulation/activation of SIRT1. Pharm. Biol. 59 (1), 146–156. doi:10.1080/13880209.2021.1877734
Björnsson, H. K., and Björnsson, E. S. (2022). Drug-induced liver injury: pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, and practical management. Eur. J. Intern Med. 97, 26–31. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2021.10.035
Cai, J. S., Huang, K. L., Han, S. N., Chen, R. H., Li, Z. J., Chen, Y., et al. (2022). A comprehensive system review of pharmacological effects and relative mechanisms of ginsenoside re: recent advances and future perspectives. Phytomedicine 102, 154119. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154119
Chen, Y., Jia, X. L., Xiong, A. Z., Wang, C. H., Yang, L., and Wang, Z. T. (2022). The protective effect of schisandrol A against senecionine-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. 57 (12), 3626–3633. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.2022-0858
Chen, H. L., Liu, C. C., Li, M., Zhang, Y. D., Wang, Z. D., Jiang, Q. Y., et al. (2023). Ferulic acid prevents diosbulbin B-induced liver injury by inhibiting covalent modifications on proteins. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 50, 100507. doi:10.1016/j.dmpk.2023.100507
Chen, J., Qin, X., Chen, M. Y., Chen, T. Z., Chen, Z., and He, B. H. (2024a). Biological activities, molecular mechanisms, and clinical application of naringin in metabolic syndrome. Pharmacol. Res. 202, 107124. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107124
Chen, Y., Li, Y., Yang, Q., She, L., Huang, X. Y., and Peng, C. (2024b). Research progress on biological activity and application of glycyrrhetinic acid. Chin. Tra Herb. Drugs 55 (21), 7507–7518.
Cheng, L., Wang, T. T., Gao, Z. L., Wu, W. K., Cao, Y. Z., Wang, L. H., et al. (2022). Study on the protective effect of schizandrin B against acetaminophen induced cytotoxicity in human hepatocyte. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 45 (5), 596–604. doi:10.1248/bpb.b21-00965
Chu, S. M., Lu, Y. J., Liu, W. J., Ma, X. Y., Peng, J. M., Wang, X. Y., et al. (2022). Ursolic acid alleviates tetrandrine-induced hepatotoxicity by competitively binding to the substrate-binding site of glutathione S-transferases. Phytomedicine 104, 154325. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154325
Çomaklı, S., Özdemir, S., Küçükler, S., and Kandemir, F. M. (2023). Beneficial effects of quercetin on vincristine-induced liver injury in rats: modulating the levels of Nrf2/HO-1, NF-kB/STAT3, and SIRT1/PGC-1α. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 37 (5), e23326. doi:10.1002/jbt.23326
Deng, X. Y., Li, Y. B., Li, X., Zhang, Z. P., Dai, S., Wu, H. F., et al. (2022). Paeoniflorin protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via JNK signaling pathway. Molecules 27 (23), 8534. doi:10.3390/molecules27238534
Deng, X. Y., Li, Y. B., Chen, Y., Hu, Q. C., Zhang, W. W., Chen, L. S., et al. (2024). Paeoniflorin protects hepatocytes from APAP-Induced damage through launching autophagy via the MAPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 29 (1), 119. doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00631-4
Devarbhavi, H., Asrani, S. K., Arab, J. P., Nartey, Y. A., Pose, E., and Kamath, P. S. (2023). Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 79 (2), 516–537. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017
Dong, X. Y., Zhou, S. Y., and Nao, J. F. (2023). Kaempferol as a therapeutic agent in Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from preclinical studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 87, 101910. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2023.101910
Elsawy, H., Algefare, A., Alfwuaires, M., Khalil, M., Elmenshawy, O. M., Sedky, A., et al. (2020). Naringin alleviates methotrexate-induced liver injury in Male albino rats and enhances its antitumor efficacy in HepG2 cells. Biosci. Rep. 40 (6), BSR20193686. doi:10.1042/BSR20193686
European Association for the Study of the Liver (2019). EASL clinical practice guidelines: drug-induced liver injury. J. Hepatol. 70, 1222–1261. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.014
Fan, M. Q., Xu, Y. H., Wu, B. X., Long, J. C., Liu, C. H., Liang, Z. H., et al. (2025). Geniposidic acid targeting FXR “S332 and H447” mediated conformational change to upregulate CYPs and miR-19a-3p to ameliorate drug-induced liver injury. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 12 (15), e2409107. doi:10.1002/advs.202409107
Fu, L., Zhou, L. L., Geng, S., Li, M., Lu, W., Lu, Y., et al. (2020). Catalpol coordinately regulates phase I and II detoxification enzymes of triptolide through CAR and NRF2 pathways to reduce triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 129, 110379. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110379
Gao, Y., Chu, S. F., Zhang, Z., and Chen, N. H. (2017). Hepataprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1-a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 206, 178–183. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.04.012
Gao, Z. S., Zhan, H. H., Zong, W., Sun, M. M., Linghu, L., Wang, G. W., et al. (2023). Salidroside alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via Sirt1-mediated activation of Akt/Nrf2 pathway and suppression of NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Life Sci. 327, 121793. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121793
Garcia-Cortes, M., Robles-Diaz, M., Stephens, C., Ortega-Alonso, A., Lucena, M. I., and Andrade, R. J. (2020). Drug induced liver injury: an update. Arch. Toxicol. 94 (10), 3381–3407. doi:10.1007/s00204-020-02885-1
Ge, B. J., Sang, R., Wang, W., Yan, K. X., Yu, Y. F., Kong, L., et al. (2023). Protection of taraxasterol against acetaminophen-induced liver injury elucidated through network pharmacology and in vitro and in vivo experiments. Phytomedicine 16, 154872. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154872
Gillessen, A., and Schmidt, H. H. J. (2020). Silymarin as supportive treatment in liver diseases: a narrative review. Adv. Ther. 37 (4), 1279–1301. doi:10.1007/s12325-020-01251-y
Guo, C., Lai, L. Y., Ma, B. Y., Huang, Q., and Wang, Z. R. (2024a). Notoginsenoside R1 targets PPAR-γ to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation and ameliorates liver fibrosis. Exp. Cell Res. 437 (1), 113992. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.113992
Guo, J. A., Le, Y. F., Yuan, A. N., Liu, J., Chen, H., Qiu, J. N., et al. (2024b). Astragaloside IV ameliorates cisplatin-induced liver injury by modulating ferroptosis-dependent pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 328, 118080. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118080
Guo, Y. T., Sun, Q. S., Wang, S. J., Zhang, M. D., Lei, Y. Y., Wu, J. J., et al. (2024c). Corydalis saxicola Bunting total alkaloids improve NAFLD by suppressing de novo lipogenesis through the AMPK-SREBP1 axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 1), 117162. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117162
Heidary, M. R., Samimi, Z., Moradi, S. Z., Moradi, S. Z., Little, P. J., Xu, S. W., et al. (2020). Naringenin and naringin in cardiovascular disease prevention: a preclinical review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 887, 173535. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173535
Hoofnagle, J. H., and Björnsson, E. S. (2019). Drug-induced liver injury-types and phenotypes. N. Engl. J. Med. 381 (3), 264–273. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1816149
Hosack, T., Damry, D., and Biswas, S. (2023). Drug-induced liver injury: a comprehensive review. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 16, 17562848231163410. doi:10.1177/17562848231163410
Hossain, S., Urbi, Z., Karuniawati, H., Mohiuddin, R. B., Qrimida, A. M., Allzrag, A. M. M., et al. (2021). Andrographis paniculata (burm. F.) wall. Ex nees: an updated review of phytochemistry, antimicrobial pharmacology, and clinical safety and efficacy. Life (Basel) 11 (4), 348. doi:10.3390/life11040348
Hou, X. J., Zhang, J. F., Hou, C. Z., Zhou, L. J., Dai, H., Zhang, S. Y., et al. (2024). Research progress of pharmacological effects and mechanism of baicalin. Drug Evalu Res. 47 (11), 2688–2696.
Hu, C., Chen, Y., Cao, Y. Y., Jia, Y. Q., and Zhang, J. Q. (2020a). Metabolomics analysis reveals the protective effect of quercetin-3-O-galactoside (hyperoside) on liver injury in mice induced by acetaminophen. J. Food Biochem. 44 (10), e13420. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13420
Hu, F. F., Guo, Q., Wei, M. J., Huang, Z. L., Shi, L., Sheng, Y. C., et al. (2020b). Chlorogenic acid alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via regulating Nrf2-mediated HSP60-initiated liver inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 883, 173286. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173286
Hu, M. L., Zhang, D. R., Xu, H. Y., Zhang, Y., Shi, H., Huang, X., et al. (2021a). Salidroside activates the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway to suppress nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 74 (6), 3056–3073. doi:10.1002/hep.32066
Hu, Q. C., Zhang, W. W., Wu, Z., Tian, X., Xiang, J. B., Li, L. X., et al. (2021b). Baicalin and the liver-gut system: pharmacological bases explaining its therapeutic effects. Pharmacol. Res. 165, 105444. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105444
Huang, Z. L., Wu, Z. Q., Zhang, J. N., Wang, K. K., Zhao, Q., Chen, M. W., et al. (2023). Andrographolide attenuated MCT-Induced HSOS via regulating NRF2-initiated mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant response. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 39 (6), 3269–3285. doi:10.1007/s10565-023-09832-7
Ileriturk, M., Ileriturk, D., Kandemir, O., Akaras, N., Simsek, H., Erdogan, E., et al. (2024). Naringin attenuates oxaliplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity: a molecular, biochemical, and histopathological approach in a rat model. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 38 (1), e23604. doi:10.1002/jbt.23604
Jaeschke, H., and Ramachandran, A. (2024). Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: paradigm for understanding mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 19, 453–478. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-051122-094016
Jaeschke, H., Williams, C. D., McGill, M. R., Xie, Y., and Ramachandran, A. (2013). Models of drug-induced liver injury for evaluation of phytotherapeutics and other natural products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 55, 279–289. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.12.063
Jiang, T. Y., Xiao, Y., Zhou, J. F., Luo, Z. P., Yu, L., Liao, Q. C., et al. (2023). Arbutin alleviates fatty liver by inhibiting ferroptosis via FTO/SLC7A11 pathway. Redox Biol. 68, 102963. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102963
Jiang, J. Z., Zhou, X. T., Chen, H., Wang, X., Ruan, Y. B., Liu, X. H., et al. (2024). 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid protects against deoxynivalenol-induced liver injury via modulating ferritinophagy and mitochondrial quality control. J. Hazard Mater 471, 134319. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134319
Jiao, F. J., Tan, Z. Y., Yu, Z. H., Zhou, B. J., Meng, L. Y., and Shi, X. T. (2022). The phytochemical and pharmacological profile of taraxasterol. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 927365. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.927365
Kuang, H. X. (2017). Chinese medicine chemistry. Beijing, China: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press.
Lee, H. C., Yu, H. P., Liao, C. C., Chou, A. H., and Liu, F. C. (2019). Escin protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via attenuating inflammatory response and inhibiting ERK signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (8), 5170–5182.
Li, C. H., Dai, T. T., Chen, J., Chen, M. S., Liang, R. H., Liu, C. M., et al. (2023). Modification of flavonoids: methods and influences on biological activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 63 (31), 10637–10658. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2083572
Li, D., Rui, Y. X., Guo, S. D., Luan, F., Liu, R., and Zeng, N. (2021). Ferulic acid: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and derivatives. Life Sci. 284, 119921. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119921
Li, X. Y., Tang, J. T., and Mao, Y. M. (2022). Incidence and risk factors of drug-induced liver injury. Liver Int. 42 (9), 1999–2014. doi:10.1111/liv.15262
Li, K. W., Zhuang, Y. B., Tang, J., Fan, X. G., Bi, H. P., and Liu, T. (2025). Research progress on the biosynthesis of plant phenylpropanoids. Sci. Sin. Vitae 55 (4), 647–660. doi:10.1360/ssv-2024-0029
Li, H. Y., Weng, Q. Q., Gong, S., Zhang, W. X., Wang, J. Q., Huang, Y. Q., et al. (2023). Kaempferol prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury by suppressing hepatocyte ferroptosis via Nrf2 pathway activation. Food Funct. 14 (4), 1884–1896. doi:10.1039/d2fo02716j
Li, J., Zhao, J. R., Wang, X. H., Lin, Z., Lin, H., and Lin, Z. (2024). Ginsenoside-a promising natural active ingredient with steroidal hormone activity. Food Funct. 15 (4), 1825–1839. doi:10.1039/d3fo05484e
Li, Q., Wang, S. Y., Fu, J., Chen, Y., Xu, J., Wei, W. J., et al. (2024). Liver regeneration after injury: mechanisms, cellular interactions and therapeutic innovations. Clin. Transl. Med. 14 (8), e1812. doi:10.1002/ctm2.1812
Li, X. K., Zhao, Y., Gong, S. H., Song, T. B., Ge, J. M., Li, J. R., et al. (2023). Schisandrin B ameliorates acute liver injury by regulating EGFR-Mediated activation of autophagy. Bioorg Chem. 130, 106272. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106272
Li, Y. G., Yu, P., Fu, W. W., Wang, S., Zhao, W. J., Ma, Y., et al. (2023). Ginsenoside Rd inhibited ferroptosis to alleviate CCl4-Induced acute liver injury in mice via cGAS/STING pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 51 (1), 91–105. doi:10.1142/S0192415X23500064
Liang, K. K., Ma, S. H., Luo, K., Wang, R. J., Xiao, C. R., Zhang, X. X., et al. (2024). Salidroside: an overview of its promising potential and diverse applications. Pharm. (Basel) 17 (12), 1703. doi:10.3390/ph17121703
Liao, C. C., Yu, H. P., Chou, A. H., Lee, H. C., Hu, L. M., and Liu, F. C. (2022). Gastrodin alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury in a mouse model through inhibiting MAPK and enhancing Nrf2 pathways. Inflammation 45 (4), 1450–1462. doi:10.1007/s10753-021-01557-1
Lin, M. S., Zhai, X. H., Wang, G. Z., Tian, X. F., Gao, D. Y., Shi, L., et al. (2015). Salvianolic acid B protects against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity by inducing Nrf2 and phase II detoxification gene expression via activation of the PI3K and PKC signaling pathways. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 127 (2), 203–210. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2014.12.010
Lin, D. J., Liu, J., Chang, X. J., Yang, B. F., Gu, X. F., and Li, W. W. (2023). Glycyrrhetinic acid ameliorates diosbulbin B-induced hepatotoxicity in mice by modulating metabolic activation of diosbulbin B. J. Appl. Toxicol. 43 (8), 1139–1147. doi:10.1002/jat.4450
Lin, W. L., Gu, B. J., Gu, Y. Y., Zhao, R., Huang, Y. M., Fan, R., et al. (2024). Taraxasterol protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by reducing liver inflammatory response and ameliorating oxidative stress in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 138, 112580. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112580
Liu, C. H. (2024). Research advances and challenges in herb-induced liver injury. J. Clin. Hepatol. 40 (8), 1505–1511.
Liu, F., Wang, X. N., Duan, C. C., Zhang, J. Y., and Li, X. F. (2020). Hepatoxicity mechanism of cantharidin-induced liver LO2 cells by LC-MS metabolomics combined traditional approaches. Toxicol. Lett. 333, 49–61. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.07.024
Liu, D., Zhen, C. L., He, X. Z., Chen, W. S., Pan, J., Yin, M. Y., et al. (2024). Naringin alleviates gefitinib-induced hepatotoxicity through anti-oxidation, inhibition of apoptosis, and autophagy. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 27 (10), 1309–1316. doi:10.22038/ijbms.2024.76852.16623
Luo, Z. W., Yin, F. C., Wang, X. B., and Kong, L. Y. (2024). Progress in approved drugs from natural product resources. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 22 (3), 195–211. doi:10.1016/S1875-5364(24)60582-0
Ma, S. W., Liu, C. H., Liu, X. Y., Su, M. H., Li, D. L., Li, Y. L., et al. (2023). Chinese guideline for diagnosis and management of drug-induced liver injury (2023 version). Chin. J. Gastroenterol. 28 (7), 397–431.
Maris, B. R., Grama, A., and Pop, T. L. (2025). Drug-induced liver injury-pharmacological spectrum among children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26 (5), 2006. doi:10.3390/ijms26052006
Meng, Z. Q., Zhu, B. M., Gao, M., Wang, G., Zhou, H. J., Lu, J., et al. (2022). Apigenin alleviated PA-induced pyroptosis by activating autophagy in hepatocytes. Food Funct. 13 (10), 5559–5570. doi:10.1039/d1fo03771d
Nasser, M. I., Zhu, S. J., Chen, C., Zhao, M. Y., Huang, H. L., and Zhu, P. (2020). A comprehensive review on schisandrin B and its biological properties. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2172740. doi:10.1155/2020/2172740
Neelam, , Khatkar, A., and Sharma, K. K. (2020). Phenylpropanoids and its derivatives: biological activities and its role in food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 60 (16), 2655–2675. doi:10.1080/10408398.2019.1653822
Neshat, S. Y., Quiroz, V. M., Wang, Y., Tamayo, S., and Doloff, J. C. (2021). Liver disease: induction, progression, immunological mechanisms, and therapeutic interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (13), 6777. doi:10.3390/ijms22136777
Nguyen, V., Taine, E. G., Meng, D. H., Cui, T. X., and Tan, W. B. (2024). Chlorogenic acid: a systematic review on the biological functions, mechanistic actions, and therapeutic potentials. Nutrients 16 (7), 924. doi:10.3390/nu16070924
Nie, W. J., Zhu, H., Sun, X., Zhou, J., Xu, H., Yu, Z. C., et al. (2024). Catalpol attenuates hepatic glucose metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in triptolide-induced liver injury by regulating the SIRT1/HIF-1α pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 20 (10), 4077–4097. doi:10.7150/ijbs.97362
Ning, C. Q., Gao, X. G., Wang, C. Y., Kong, Y. L., Liu, Z. H., Sun, H. J., et al. (2018). Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury via activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 98, 58–68. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.07.012
Niu, C. W., Ma, M., Han, X., Wang, Z. M., and Li, H. Y. (2017). Hyperin protects against cisplatin-induced liver injury in mice. Acta Cir. Bras. 32 (8), 633–640. doi:10.1590/s0102-865020170080000005
Nouri, A., Ghatreh-Samani, K., Amini-Khoei, H., Najafi, M., and Heidarian, E. (2023). Ferulic acid exerts a protective effect against cyclosporine-induced liver injury in rats via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling, suppression of oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and halting the apoptotic cell death. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 37 (10), e23427. doi:10.1002/jbt.23427
Okkay, I. F., Famurewa, A., Bayram, C., Okkay, U., Mendil, A. S., Sezen, S., et al. (2024). Arbutin abrogates cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity via upregulating Nrf2/HO-1 and suppressing genotoxicity, NF-κB/iNOS/TNF-α and caspase-3/Bax/Bcl2 signaling pathways in rats. Toxicol. Res. (Camb) 13 (3), tfae075. doi:10.1093/toxres/tfae075
Owumi, S. E., Olusola, J. K., Arunsi, U. O., and Oyelere, A. K. (2021). Chlorogenic acid abates oxido-inflammatory and apoptotic responses in the liver and kidney of Tamoxifen-treated rats. Toxicol. Res. (Camb) 10 (2), 345–353. doi:10.1093/toxres/tfab002
Pang, C., Sheng, Y. C., Jiang, P., Wei, H., and Ji, L. L. (2015). Chlorogenic acid prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury: the involvement of CYP450 metabolic enzymes and some antioxidant signals. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 16 (7), 602–610. doi:10.1631/jzus.B1400346
Pang, C., Shi, L., Sheng, Y. C., Zheng, Z. Y., Wei, H., Wang, Z. T., et al. (2016a). Caffeic acid attenuated acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting ERK1/2-mediated early growth response-1 transcriptional activation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 260, 186–195. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2016.10.009
Pang, C., Zheng, Z. Y., Shi, L., Sheng, Y. C., Wei, H., Wang, Z. T., et al. (2016b). Caffeic acid prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating the Keap1-Nrf2 antioxidative defense system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 91, 236–246. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.12.024
Pastorino, G., Cornara, L., Soares, S., Rodrigues, F., and Oliveira, M. B. P. P. (2018). Liquorice (glycyrrhiza glabra): a phytochemical and pharmacological review. Phytother. Res. 32 (12), 2323–2339. doi:10.1002/ptr.6178
Pugazhendhi, A., Edison, T. N. J. I., Velmurugan, B. K., Jacob, J. A., and Karuppusamy, I. (2018). Toxicity of doxorubicin (dox) to different experimental organ systems. Life Sci. 200, 26–30. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.023
Qin, X. Y., Wang, X., Tian, M. Y., Dong, Z. W., Wang, J., Wang, C., et al. (2023). The role of andrographolide in the prevention and treatment of liver diseases. Phytomedicine 109, 154537. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154537
Rani, J., Dhull, S. B., Rose, P. K., and Kidwai, M. K. (2024). Drug-induced liver injury and anti-hepatotoxic effect of herbal compounds: a metabolic mechanism perspective. Phytomedicine 122, 155142. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155142
Rao, T., Tan, Z. R., Peng, J. B., Guo, Y., Chen, Y., Zhou, H. H., et al. (2019). The pharmacogenetics of natural products: a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic perspective. Pharmacol. Res. 146, 104283. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104283
Real, M., Barnhill, M. S., Higley, C., Rosenberg, J., and Lewis, J. H. (2019). Drug-induced liver injury: highlights of the recent literature. Drug Saf. 42 (3), 365–387. doi:10.1007/s40264-018-0743-2
Sahindokuyucu-Kocasari, F., Akyol, Y., Ozmen, O., Erdemli-Kose, S. B., and Garli, S. (2021). Apigenin alleviates methotrexate-induced liver and kidney injury in mice. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 40 (10), 1721–1731. doi:10.1177/09603271211009964
Sahu, R., Goswami, S., Narahari, S. G., and Rawal, R. K. (2023). The preventive and therapeutic potential of the flavonoids in liver cirrhosis: current and future perspectives. Chem. Biodivers. 20 (2), e202201029. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202201029
Sang, R., Yu, Y. F., Ge, B. J., Xu, L., Wang, Z., and Zhang, X. M. (2019). Taraxasterol from taraxacum prevents concanavalin A-induced acute hepatic injury in mice via modulating TLRs/NF-κB and Bax/Bc1-2 signalling pathways. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47 (1), 3929–3937. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1671433
Shah, K., Chhabra, S., and Chauhan, N. S. (2022). Chemistry and anticancer activity of cardiac glycosides: a review. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 100 (3), 364–375. doi:10.1111/cbdd.14096
Shen, N., Wang, T. F., Gan, Q., Liu, S., Wang, L., and Jin, B. (2022). Plant flavonoids: classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 383, 132531. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132531
Shen, P., Xue, M., Hu, Z. S., Han, L., and Deng, X. (2024). Direct targeting of S100A9 with icariin counteracted acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 136, 112296. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112296
Shi, J. Q., Sheng, Y. C., Shi, L., Zheng, Z. Y., Chen, M. W., Lu, B., et al. (2017). Quercetin and baicalein suppress monocrotaline-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 795, 160–168. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.12.015
Shi, L., Hao, Z. X., Zhang, S. B., Wei, M. J., Lu, B., Wang, Z. T., et al. (2018). Baicalein and baicalin alleviate acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating Nrf2 antioxidative pathway: the involvement of ERK1/2 and PKC. Biochem. Pharmacol. 150, 9–23. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.026
Shi, L., Zhang, S. B., Huang, Z. L., Hu, F. F., Zhang, T. Y., Wei, M. J., et al. (2020). Baicalin promotes liver regeneration after acetaminophen-induced liver injury by inducing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 160, 163–177. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.05.012
Shirani, K., Yousefsani, B. S., Shirani, M., and Karimi, G. (2020). Protective effects of naringin against drugs and chemical toxins induced hepatotoxicity: a review. Phytother. Res. 34 (8), 1734–1744. doi:10.1002/ptr.6641
Sokar, S. S., Alkabbani, M. A., Akool, E. S., and Abu-Risha, S. E. S. (2022). Hepatoprotective effects of carvedilol and crocin against leflunomide-induced liver injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 113 (Pt A), 109297. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109297
Song, M., Chen, Z. J., Qiu, R. A., Zhi, T. W., Xie, W. M., Zhou, Y. Y., et al. (2022). Inhibition of NLRP3-mediated crosstalk between hepatocytes and liver macrophages by geniposidic acid alleviates cholestatic liver inflammatory injury. Redox Biol. 55, 102404. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102404
Stravitz, R. T., and Lee, W. M. (2019). Acute liver failure. Lancet 394 (10201), 869–881. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31894-X
Tai, M. H., Zhang, J. Y., Song, S. D., Miao, R. C., Liu, S. S., Pang, Q., et al. (2015). Protective effects of luteolin against acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure in mouse. Int. Immunopharmacol. 27 (1), 164–170. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2015.05.009
Tang, Y. Y., Jia, X. L., Wang, J. Y., Dong, K., Chen, Y., Ding, L. L., et al. (2024). Effects of alisol B 23-acetate on water-liquid balance in mice with senecionine-induced acute liver injury. Acta Pharm. Sin. 59 (7), 1982–1992. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.2024-0077
Teschke, R. (2014). Traditional Chinese medicine induced liver injury. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2 (2), 80–94. doi:10.14218/JCTH.2014.00003
Thida, M., Li, B., Zhang, X. Y., Chen, C., and Zhang, X. Y. (2021). Echinacoside alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in mice. J. Appl. Biome 19 (2), 105–112. doi:10.32725/jab.2021.011
Thilagavathi, R., Begum, S. S., Varatharaj, S. D., Balasubramaniam, A. K., George, J. S., and Selvam, C. (2023). Recent insights into the hepatoprotective potential of medicinal plants and plant-derived compounds. Phytother. Res. 37 (5), 2102–2118. doi:10.1002/ptr.7821
Tian, Y. G., Fan, J. J., Wang, R. S., Ding, R., Zhao, C. X., Xu, J., et al. (2024). Triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Panax notoginseng with protective effects against APAP-Induced liver injury. Fitoterapia 178, 106159. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106159
Wang, Y. X., and Liu, K. (2024). Therapeutic potential of oleanolic acid in liver diseases. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 397 (7), 4537–4554. doi:10.1007/s00210-024-02959-2
Wang, J. M., Miao, M. S., Qu, L. B., Cui, Y., and Zhang, Y. Y. (2016). Protective effects of geniposide against tripterygium glycosides (TG)-Induced liver injury and its mechanisms. J. Toxicol. Sci. 41 (1), 165–173. doi:10.2131/jts.41.165
Wang, J. Y., Kuang, G., Zhang, L., Jiang, R., Chen, Y. T., He, Z., et al. (2020). Hesperetin attenuated acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting hepatocyte necrosis and apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response via upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression. Int. Immunopharmacol. 83, 106435. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106435
Wang, Z., Ma, J., He, Y. S., Miu, K. K., Yao, S., Tang, C. P., et al. (2022). Nrf2-mediated liver protection by 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid against pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced toxicity through PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Phytomedicine 102, 154162. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154162
Wang, Q. L., Zhang, P. X., Shen, R., Xu, M., Han, L., Shi, X., et al. (2024a). Determination of arbutin in vitro and in vivo by LC-MS/MS: pre-Clinical evaluation of natural product arbutin for its early medicinal properties. J. Ethnopharmacol. 330, 118232. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118232
Wang, Y. L., Bai, M. T., Wang, X., Peng, Z. L., Cai, C. Y., Xi, J. J., et al. (2024b). Gastrodin: a comprehensive pharmacological review. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 397 (6), 3781–3802. doi:10.1007/s00210-023-02920-9
Wei, M. J., Gu, X. N., Li, H., Zheng, Z. Y., Qiu, Z. M., Sheng, Y. C., et al. (2023a). EGR1 is crucial for the chlorogenic acid-provided promotion on liver regeneration and repair after APAP-Induced liver injury. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 39 (6), 2685–2707. doi:10.1007/s10565-023-09795-9
Wei, J. R., Chen, Y. Q., Zhong, H. Y., Sun, Y., Zhang, Y. Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2023b). Research progress on the mechanism of antagonistic liver fibrosis by terpenoids in traditional Chinese medicine. J. Liaoning Uni TCM 25 (9), 107–112. doi:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2023.09.022
Wen, K. M., Fang, X. C., Yang, J. L., Yao, Y. F., Nandakumar, K. S., Salem, M. L., et al. (2021). Recent research on flavonoids and their biomedical applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 28 (5), 1042–1066. doi:10.2174/0929867327666200713184138
Wu, Y. L., Piao, D. M., Han, X. H., and Nan, J. X. (2008). Protective effects of salidroside against acetaminophen-induced toxicity in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 31 (8), 1523–1529. doi:10.1248/bpb.31.1523
Wu, L. P., Georgiev, M. I., Cao, H., Nahar, L., El-Seedi, H. R., Sarker, S. D., et al. (2020). Therapeutic potential of phenylethanoid glycosides: a systematic review. Med. Res. Rev. 40 (6), 2605–2649. doi:10.1002/med.21717
Wu, S. Y., Wang, W. J., Dou, J. H., and Gong, L. K. (2021). Research progress on the protective effects of licorice-derived 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid against liver injury. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 42 (1), 18–26. doi:10.1038/s41401-020-0383-9
Wu, J. Z., Zhou, F., Fan, G. F., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Xue, X. Y., et al. (2022). Ferulic acid ameliorates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by promoting AMPK-Mediated protective autophagy. IUBMB Life 74 (9), 880–895. doi:10.1002/iub.2625
Wu, M. Y., Li, K., Wu, J. B., Ding, Y. X., Ma, X. T., Wang, W. H., et al. (2025). Ginsenoside Rg1: a bioactive therapeutic agent for diverse liver diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 212, 107571. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107571
Xi, Y., Chi, Z. C., Tao, X. F., Zhai, X. H., Zhao, Z. R., Ren, J. Q., et al. (2023). Naringin against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity in mice through reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis via the up-regulation of SIRT1. Environ. Toxicol. 38 (5), 1153–1161. doi:10.1002/tox.23755
Xiao, G. R., Tang, R., Yang, N., and Chen, Y. H. (2023). Review on pharmacological effects of gastrodin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 46 (9-10), 744–770. doi:10.1007/s12272-023-01463-0
Xie, W. Y., Jiang, Z. H., Wang, J., Zhang, X. Y., and Melzig, M. F. (2016a). Protective effect of hyperoside against acetaminophen (APAP) induced liver injury through enhancement of APAP clearance. Chem. Biol. Interact. 246, 11–19. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2016.01.004
Xie, W. Y., Wang, M., Chen, C., Zhang, X. Y., and Melzig, M. F. (2016b). Hepatoprotective effect of isoquercitrin against acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Life Sci. 152, 180–189. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2016.04.002
Xiong, L. J., Lin, K. X., He, T. M., Liu, X. Y., Yuan, R., Li, X. F., et al. (2024). A novel approach combining network pharmacology and experimental validation to study the protective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 against cantharidin-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 134 (5), 737–749. doi:10.1111/bcpt.13999
Xu, S. J., Chen, S. P., Xia, W. X., Sui, H., and Fu, X. Y. (2022). Hyperoside: a review of its structure, synthesis, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicity. Molecules 27 (9), 3009. doi:10.3390/molecules27093009
Xu, J., Chen, Y. L., Ruan, D. Q., Zhnag, Y. M., Wang, X. J., Ding, L. L., et al. (2023a). Effect and mechanism of hyperoside on acute liver injury induced by pyrrolizidine alkaloids in mice. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 57 (12), 80–87.
Xu, J., Zhao, L. Y., Zhang, X. T., Ying, K. L., Zhou, R. R., Cai, W. M., et al. (2023b). Salidroside ameliorates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury through the inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated ferroptosis by activating the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 262, 115331. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115331
Xu, G. B., Xiao, Y. H., Zhang, Q. Y., Zhou, M., and Liao, S. G. (2018). Hepatoprotective natural triterpenoids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 145, 691–716. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.01.011
Xu, L., Yu, Y. F., Sang, R., Li, J. X., Ge, B. J., and Zhang, X. M. (2018). Protective effects of taraxasterol against ethanol-induced liver injury by regulating CYP2E1/Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways in mice. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 8284107. doi:10.1155/2018/8284107
Xue, H. Y., Wei, M. J., and Ji, L. L. (2023). Chlorogenic acids: a pharmacological systematic review on their hepatoprotective effects. Phytomedicine 118, 154961. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154961
Yan, H. Y., Huang, Z. L., Bai, Q. Y., Sheng, Y. C., Hao, Z. X., Wang, Z. T., et al. (2018). Natural product andrographolide alleviated APAP-Induced liver fibrosis by activating Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Toxicology 396-397, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2018.01.007
Yang, G. L., Zhang, L., Ma, L., Jiang, R., Kuang, G., Li, K., et al. (2017). Glycyrrhetinic acid prevents acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via the inhibition of CYP2E1 expression and HMGB1-TLR4 signal activation in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 50, 186–193. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.06.027
Yang, J. Y., Li, M., Zhang, C. L., and Liu, D. (2021). Pharmacological properties of baicalin on liver diseases: a narrative review. Pharmacol. Rep. 73 (5), 1230–1239. doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00227-1
Yang, X. R., Dou, X., Li, G. F., Song, Q. J., Li, X. W., Wu, H. W., et al. (2022). Research progress on pharmacological effects and mechanism of naringin. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 53 (10), 3226–3240.
Yao, P. Y., and Liu, Y. J. (2022). Terpenoids: natural compounds for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) therapy. Molecules 28 (1), 272. doi:10.3390/molecules28010272
Ye, X. L., Jiang, K. Y., Yang, L., Xiong, A. Z., and Wang, Z. T. (2021). The protective effect of salvianolic acid B against senecionine induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. 56 (4), 1079–1085.
Yi, Y. S. (2024). Pharmacological potential of ginseng and ginsenosides in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Ginseng Res. 48 (2), 122–128. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2023.11.003
Yong, Y. X., Zhang, Y. G., Li, H. J., Zhao, Y., Cai, E. B., Zhu, H. Y., et al. (2019). Triterpenoids from fruits of sorbus pohuashanensis inhibit acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 109, 493–502. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.160
Yu, S. E., Mwesige, B., Yi, Y. S., and Yoo, B. C. (2019). Ginsenosides: the need to move forward from bench to clinical trials. J. Ginseng Res. 43 (3), 361–367. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2018.09.001
Zeng, B., Wei, A. L., Zhou, Q., Yuan, M. H., Lei, K. L., Liu, Y. S., et al. (2022). Andrographolide: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches. Phytother. Res. 36 (1), 336–364. doi:10.1002/ptr.7324
Zhai, X. H., Dai, T. T., Chi, Z. C., Zhao, Z. R., Wu, G. L., Yang, S. L., et al. (2022). Naringin alleviates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by activating Nrf2 via CHAC2 upregulation. Environ. Toxicol. 37 (6), 1332–1342. doi:10.1002/tox.23487
Zhang, X., and Gao, Z. P. (2020). Research progress in ferulic acid. Mod. Chin. Med. 22 (1), 138–147. doi:10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20190311005
Zhang, X. H., and Zhu, X. (2011). Recent advances in pharmacology of ursolic acid. Chin. J. Integ Med. 31 (9), 1285–1289.
Zhang, X. M., Xie, L., Long, J. Y., Xie, Q. X., Zheng, Y., Liu, K., et al. (2021). Salidroside: a review of its recent advances in synthetic pathways and pharmacological properties. Chem. Biol. Interact. 339, 109268. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109268
Zhang, L. L., Li, C. Q., Fu, L., Yu, Z. C., Xu, G. R., Zhou, J., et al. (2022). Protection of catalpol against triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting excessive autophagy via the PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway. PeerJ 10, e12759. doi:10.7717/peerj.12759
Zhang, J., Sun, W. Y., Wang, C. B., and Bai, Q. Y. (2024). Effect of baicalin on liver repair after acetaminophen-induced liver injury based on mTOR signaling pathway. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 55 (13), 4399–4410.
Zhang, J. Q., Liang, X. Q., Li, J. C., Yin, H., Liu, F. C., Hu, C., et al. (2020). Apigenin attenuates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by activating AMP-Activated protein kinase/carnitine palmitoyltransferase I pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 549057. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.549057
Zhang, W., Zhu, Y. D., Zhang, Q. Y., Ma, L. J., Yang, L., Guo, W. Z., et al. (2020). Research progress in application and mechanism of schisandrae chinensis fructus for prevention and treatment of liver disease. Chin. J. Chin. Mat. Med. 45 (16), 3759–3769. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200513.601
Zhang, X., Kuang, G., Wan, J. Y., Jiang, R., Ma, L., Gong, X., et al. (2020). Salidroside protects mice against CCl4-induced acute liver injury via down-regulating CYP2E1 expression and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 85, 106662. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106662
Zheng, Z. Y., Shi, L., Sheng, Y. C., Zhang, J. Q., Lu, B., and Ji, L. L. (2016). Chlorogenic acid suppresses monocrotaline-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome: the potential contribution of NFB, Egr1, Nrf2, MAPKs and PI3K signals. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 46, 80–89. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2016.07.002
Zheng, Y. Y., Zhao, L. N., Xiong, Z. K., Huang, C. Y., Yong, Q. H., Fang, D., et al. (2024). Ursolic acid targets secreted phosphoprotein 1 to regulate Th17 cells against metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 30 (3), 449–467. doi:10.3350/cmh.2024.0047
Zhou, W. H., He, H., Wei, Q., Che, L. T., Zhao, X., Liu, W. W., et al. (2023). Puerarin protects against acetaminophen-induced oxidative damage in liver through activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Food Sci. Nutr. 11 (10), 6604–6615. doi:10.1002/fsn3.3609
Zhou, H. M., Liu, Y., Su, Y., Ji, P. M., Kong, L. L., Sun, R., et al. (2024). Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced chronic liver damage by activating Nrf2 signaling and inhibiting inflammasomes in hepatic cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 324, 117794. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117794
Zhou, L. F., Xiao, M., Li, Y. X., Chitrakar, B., Sheng, Q. H., and Zhao, W. (2024). Ursolic acid ameliorates alcoholic liver injury through attenuating oxidative stress-mediated ferroptosis and modulating gut microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72 (38), 21181–21192. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c04762
Keywords: flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, terpenoids, glycosides, drug-induced liver injury, mechanism
Citation: Chen Y, Mei Y-Q, Hou L and Li K-J (2025) Therapeutic potential of plant-derived natural products against drug-induced liver injury. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1652860. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1652860
Received: 24 June 2025; Accepted: 28 July 2025;
Published: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Hua Li, Air Force Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Chen, Mei, Hou and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Chen, Y2hlbnk5MTBAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Lin Hou, aG91bGluNTAyN0AxNjMuY29t; Ke-Jian Li, cWxsa2oyMDIwQDEyNi5jb20=
 Yan Chen
Yan Chen Yu-Qi Mei3
Yu-Qi Mei3