- 1Department of Pharmacy, Shaoxing Campus, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Shaoxing, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, Yangzhou, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Qingchun Campus, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
- 4Department of Pharmacy, Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
- 5Research Center for Clinical Pharmacy, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Background: The concomitant use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole is generally contraindicated in clinical practice because of drug‒drug interactions (DDIs). However, emerging clinical data suggest that this DDI is complicated and that the concomitant use of these two drugs may be feasible.
Methods: This was a multicenter retrospective study. Hospitalized patients who were diagnosed with COVID-19 in 2023 and who received concomitant nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and voriconazole were retrospectively included according to preset criteria. Personal information, medication records and voriconazole plasma levels were obtained from the hospital information system. The voriconazole concentrations were analyzed.
Results: A total of 13 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and 16 voriconazole trough concentrations were included from 4 centers. Half of the patients (8 patients, 50.0%) had voriconazole plasma concentrations within the therapeutic range. The remaining 8 cases (50.0%) fell outside the therapeutic range, including 1 case (12.5%) with subtherapeutic levels and 7 cases (87.5%) with supratherapeutic concentrations.
Conclusion: The concomitant use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole might be feasible, but the dosing of voriconazole needs further study.
1 Introduction
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir is an oral antiviral formulation for COVID-19 treatment that has been designated by the World Health Organization as the prefer therapeutic option for high-risk populations susceptible to severe disease progression (Agarwal et al., 2020). Ritonavir is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor that can also induce CYP2C19; therefore, concomitant use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir may lead to clinically significant drug‒drug interactions (DDIs). Fungal infection, such as invasive aspergillosis, is common in patients with severe COVID-19 (White et al., 2020). Voriconazole is one of the first-line options for severe fungal infections (Douglas et al., 2021). However, coadministration of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir with voriconazole is contraindicated in product labeling and widely discouraged in therapeutic guidelines (Merck, 2022). The pharmacokinetic interaction between nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole exhibits significant mechanistic complexity. Expected interactions stem from ritonavir’s potent inhibition of CYP3A4, which may theoretically induce significant increases in systemic exposure. Unexpected interactions arise from ritonavir-induced CYP2C19 enzyme induction during prolonged use (>7 days), leading to unanticipated late-phase concentration reductions, combined with nirmatrelvir’s competitive inhibition that exacerbates nonlinear pharmacokinetics (Wang et al., 2024). Although the interaction between nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole is rather complex, recent evidence suggests that their combination is feasible (Wang et al., 2023). Thus, we performed this multicenter retrospective study to assess the plasma level of voriconazole under the concomitant use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in patients with COVID-19.
2 Methods
2.1 Patient inclusion
This study was a multicenter retrospective study. Inpatients meeting the following criteria were included in the study: (1) hospitalized patients due to COVID-19 infection in 2023; (2) patients aged over 18 years; (3) patients receiving concomitant nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and voriconazole; and (4) patients with available voriconazole plasma levels during concomitant use. Owing to the irreversible inhibitory effect of ritonavir on CYP3A4, patients receiving voriconazole treatment within 5 days of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir withdrawal were also considered to have potential DDI risk and were included.
2.2 Data collection and analysis
The following personnel information and drug administration information were extracted from the hospital information system: patient age, sex, body weight and height; admission to the ICU or receiving organ support, such as CRRT and ECMO; laboratory test results indicating renal and hepatic function; formulation, dose, dosing frequency and treatment length of both drugs; and therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of voriconazole.
A voriconazole concentration of 1–5.5 mg/g was considered the therapeutic range (Ashbee et al., 2014). The data are descriptively presented. Continuous data are shown as medians and IQRs, and categorical data are shown as numbers and percentages. The voriconazole concentrations were stratified by dose, formulation, and other meaningful variables.
3 Results
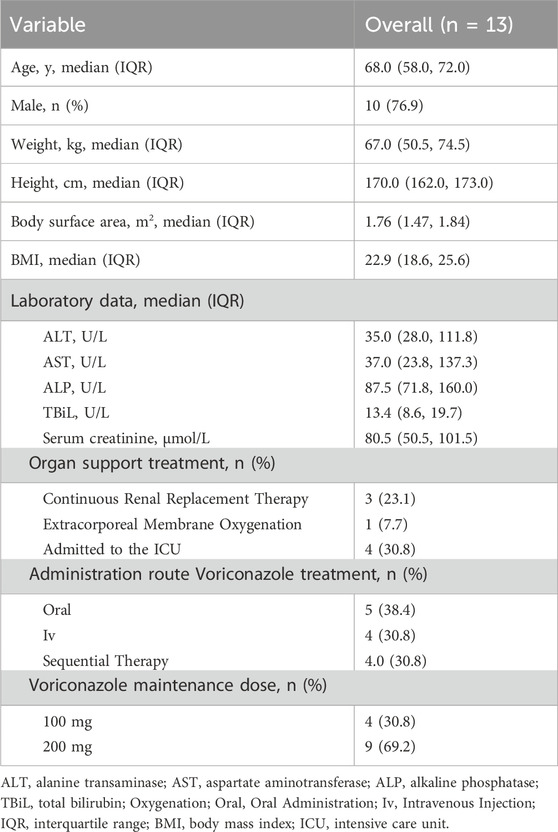
A total of 13 hospitalized patients were included from four centers. The demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. Most patients were old, and four were admitted to the ICU. All the patients received voriconazole at 12-h intervals, but only four patients received a reduced maintenance dose. Among these patients, 5 (38.4%) received oral voriconazole, 4 (30.8%) received intravenous voriconazole, and 4 (30.8%) underwent sequential therapy during nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment. Nine patients (69.2%) received a maintenance voriconazole dose of 200 mg every 12 h, whereas 4 (30.8%) received a reduced dose of 100 mg every 12 h.
A total of 16 voriconazole plasma concentration values were obtained. Six of these concentrations were used concomitantly, and 10 were used after nirmatrelvir/ritonavir withdrawal. All post-use plasma concentrations were measured within 3 days. Half of the voriconazole concentrations were within the reference range. One patient even had a low voriconazole concentration during concomitant use. The detailed voriconazole concentrations are shown in Table 2. The rate of achieving the therapeutic window for intravenous voriconazole was 60% (3/5), and for oral administration, it was 40% (2/5); for the 100 mg dose of voriconazole, the rate within the therapeutic window was 50% (2/4), and for the 200 mg dose, it was 50% (6/12); the rate within the therapeutic window during nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment was 66.7% (4/6); and after nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment, it was 40% (4/10).
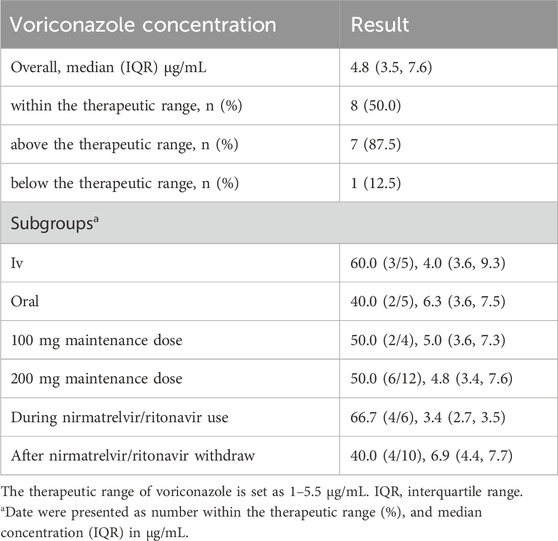
Table 2. Concentration distribution of voriconazole under the concomitant use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir.
4 Discussion
This study provides multicenter clinical evidence of voriconazole concentration distributions under the concomitant use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir. Half of the concentrations were within the therapeutic range. These findings may support the feasibility of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole coadministration, which may be important during epidemics and for source-limiting settings. Moreover, ritonavir is a common CYP booster in many combinations, and the results of this study would also be useful for handling DDI between voriconazole and other ritonavir containing formulations.
Although data from 4 centers were retrospectively analyzed, only 13 patients were included. These findings indicate that the DDI between nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole were well known and avoided in clinical practice (Marzolini et al., 2022). However, ritonavir has irreversible inhibitory effects on CYP3A4, and the DDI risk can last several days after nirmatrelvir/ritonavir withdrawal. In this study, 10 of the 16 plasma concentrations were obtained after the withdrawal of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, which indicated that this post-use DDI risk was neglected in clinical practice (Han et al., 2025). This study revealed that among 13 COVID-19 patients coadministered nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole, 50% (8/16) of the monitored voriconazole plasma concentrations remained within the therapeutic range (1–5.5 μg/mL). A large cohort including 597 trough concentrations in Chinese patients found that 65.0% of the concentrations are within the target therapeutic range (1–5 μg/mL), while the proportions <1 mg/L and >5 mg/L were 11.7% and 23.3%, respectively (Wang et al., 2022). Another retrospective study in US analyzing the target achievement of voriconazole had included 250 concentrations, and found that 54% of concentration are therapeutic (reference range 1–5 μg/mL), 26% were subtherapeutic and 20% were super therapeutic (Yi et al., 2017). Although it is difficult to make a statistical comparison, we can find that patients with concomitant nirmatrelvir/ritonavir had similar percentages in therapeutic range achievement, but higher in percentages in super therapeutic concentrations. And this needs further validation. These findings indicate that the concomitant use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole may be feasible, which is different from current label information and clinical guidelines. Although numerous studies have reported adverse outcomes when nirmatrelvir/ritonavir is combined with drugs metabolized by CYP3A4, this phenomenon is a reasonable explanation (Haque et al., 2023; Qin et al., 2023). As a pharmacokinetic booster, ritonavir inhibits CYP3A4 to slow the metabolism of nirmatrelvir, as do other drugs metabolized by CYP3A4. This effect is always overlooked in clinical practice. Notably, concomitant use of voriconazole should be avoided on its label because of the concern of a low concentration of voriconazole. A previous study focusing on the influence of a single dose of ritonavir also revealed that the concentrations of voriconazole were elevated (Mikus et al., 2006). Wang et al. reported that the voriconazole concentration may be greater or lower in patients with COVID-19 when coadministered with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, and the difference may be attributed to polymorphisms of the CYP2C19 genotype (Wang et al., 2023). Although the evidence of DDI between voriconazole and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in COVID-19 patients is limited, the DDI between voriconazole and ritonavir (or its combination with other antiviral drugs) has been reported. Zhu et al. reported that when coadministered with atazanavir-ritonavir in healthy subjects, voriconazole exposure decreased in CYP2C19 extensive metabolizers but increased in CYP2C19 poor metabolizers (Zhu et al., 2017). Liu et al. reported that after a 10-day duration of ritonavir treatment, voriconazole exposure decreased to different extents, depending on the ritonavir dose (López-Hernández et al., 2025).
Additionally, we investigated voriconazole plasma concentrations among different subgroups, which were stratified on the basis of formulation, maintenance dose and concomitant course. Intravenous voriconazole demonstrated a 60% probability (3/5) of concentrations within the therapeutic range versus 40% (2/5) for oral administration. This is very reasonable, as oral voriconazole has high bioavailability (Harada et al., 2021). The observed reduction in therapeutic attainment with the oral formulation (40% vs 60% IV) aligns with established pharmacokinetic properties of voriconazole: Significantly reduced oral bioavailability attributable to CYP450-mediated metabolism in the gut/liver. The dose significantly influences voriconazole exposure; however, both the 100 mg and 200 mg maintenance regimens yielded 50% therapeutic target attainment (2/4 and 6/12, respectively) and similar concentrations. This similar therapeutic target attainments between different dosing may be attributed to high inter-individual viability of voriconazole pharmacokinetic in patients and the limited sample size. A recent physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling study suggested that ritonavir could increase voriconazole exposure to CYP2C19 intermediate and poor metabolizers rather than decrease it (Wang et al., 2024). Our results were in accordance with these studies. When we focused on the voriconazole plasma concentrations after discontinuation of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, the concentrations were still high. CYP3A4 activity may need approximately 4 days to be restored, according to recent reports (Wang and Chan, 2022). Thus, the post-use DDI risk should be considered with caution.
The main limitation of this study is the small sample size. The genotypes of CYP3A4 and 2C19 in the included patients were unknown. Voriconazole concentrations when it is used alone were not collected and it is unable to make a direct comparison. The DDI was not quantified by advanced models, such as physiological-based pharmacokinetic models, which should be evaluated in the future.
In conclusion, the concomitant use of voriconazole and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir may be feasible, but the dosing of voriconazole under concomitant use needs further study.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The ethics committee of Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because Informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of study.
Author contributions
HS: Project administration, Methodology, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. XZ: Writing – review and editing, Data curation. QK: Writing – review and editing, Data curation. LY: Supervision, Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. ZY: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Conceptualization, Resources, Validation, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Agarwal, A., Hunt, B., Stegemann, M., Rochwerg, B., Lamontagne, F., Siemieniuk, R. A., et al. (2020). A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. BMJ 370, m3379. doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379
Ashbee, H. R., Barnes, R. A., Johnson, E. M., Richardson, M. D., Gorton, R., and Hope, W. W. (2014). Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of antifungal agents: guidelines from the British society for medical mycology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69, 1162–1176. doi:10.1093/jac/dkt508
Douglas, A. P., Smibert, O. C., Bajel, A., Halliday, C. L., Lavee, O., McMullan, B., et al. (2021). Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of invasive aspergillosis, 2021. Intern Med. J. 51, 143–176. doi:10.1111/imj.15591
Han, Y., Gou, Y., Liu, J., Yu, L., Zhao, Y., and Yu, Z. (2025). Potential drug interaction after withdrawal of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist 42, 151–153. doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2024.12.014
Haque, O. I., Mahar, S., Hussain, S., and Sloane, P. (2023). Pharmacokinetic interaction between verapamil and ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir: implications for the management of COVID-19 in patients with hypertension. BMJ Case Rep. 16, e252677. doi:10.1136/bcr-2022-252677
Harada, S., Niwa, T., Hoshino, Y., Fujibayashi, A., and Suzuki, A. (2021). Influence of switching from intravenous to oral administration on serum voriconazole concentration. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 46, 780–785. doi:10.1111/jcpt.13352
López-Hernández, J., Guisado-Gil, A. B., Mejías-Trueba, M., Herrera-Hidalgo, L., Reina-Martínez, F. J., and Gil-Navarro, M. V. (2025). Unexpected voriconazole toxicity due to nirmatrelvir/ritonavir: a case report on drug-drug interaction and the role of therapeutic drug monitoring. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1616061. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1616061
Marzolini, C., Kuritzkes, D. R., Marra, F., Boyle, A., Gibbons, S., Flexner, C., et al. (2022). Recommendations for the management of drug-drug interactions between the COVID-19 antiviral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (paxlovid) and comedications. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 112, 1191–1200. doi:10.1002/cpt.2646
Mikus, G., Schöwel, V., Drzewinska, M., Rengelshausen, J., Ding, R., Riedel, K. D., et al. (2006). Potent cytochrome P450 2C19 genotype-related interaction between voriconazole and the cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitor ritonavir. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 80, 126–135. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2006.04.004
Qin, F., Wang, H., Li, M., Zhuo, S., and Liu, W. (2023). Drug–drug interaction of nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and tacrolimus: a potential risk disproportionality analysis of nephrotoxicity from COVID-19 reports in FAERS. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 22, 1321–1327. doi:10.1080/14740338.2023.2239156
Wang, Z., and Chan, E. C. Y. (2022). Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling-guided dose management of oral anticoagulants when initiating nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (paxlovid) for COVID-19 treatment. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 112, 803–807. doi:10.1002/cpt.2687
Wang, T., Miao, L., Shao, H., Wei, X., Yan, M., Zuo, X., et al. (2022). Voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring and hepatotoxicity in critically ill patients: a nationwide multi-centre retrospective study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 60 (5-6), 106692. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2022.106692
Wang, P., Xing, H., Zhang, X., and Yang, J. (2023). Complexity interactions between nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and voriconazole in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 76, 2209–2210. doi:10.1093/cid/ciad159
Wang, P., Liu, S., and Yang, J. (2024). Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to investigate the disease-Drug–Drug interactions between voriconazole and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in COVID-19 patients with CYP2C19 phenotypes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 116, 363–371. doi:10.1002/cpt.3222
White, P. L., Dhillon, R., Hughes, H., Wise, M. P., and Backx, M. (2020). COVID-19 and fungal infection: the need for a strategic approach. Lancet Microbe 1, e196. doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30127-0
Yi, W. M., Schoeppler, K. E., Jaeger, J., Mueller, S. W., MacLaren, R., Fish, D. N., et al. (2017). Voriconazole and posaconazole therapeutic drug monitoring: a retrospective study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 16 (1), 60. doi:10.1186/s12941-017-0235-8
Keywords: nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, voriconazole, drug interaction, therapeutic drug monitoring, CYP = cytochrome P450
Citation: Shi H, Zhang X, Kong Q, Yu L and Yu Z (2025) Plasma concentration of voriconazole under concomitant use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in patients with COVID-19: a multicenter retrospective study. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1654671. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1654671
Received: 26 June 2025; Accepted: 31 July 2025;
Published: 15 August 2025.
Edited by:
Allen W. Tsang, Wake Forest University, United StatesReviewed by:
Cyprian Onyeji, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, NigeriaChangcheng Shi, Westlake University, China
Copyright © 2025 Shi, Zhang, Kong, Yu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lingyan Yu, bGluZ3lhbnl1QHpqdS5lZHUuY24=; Zhenwei Yu, eXp3X3NycnNoQHpqdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hao Shi1†
Hao Shi1† Xuan Zhang
Xuan Zhang Qihui Kong
Qihui Kong Lingyan Yu
Lingyan Yu Zhenwei Yu
Zhenwei Yu