- 1California Northstate University College of Medicine, Elk Grove, CA, United States
- 2Howard University College of Medicine, Washington, DC, United States
- 3VA Northern California HealthCare System, Dermatology Section, Mather, CA, United States
- 4VA Northern California Health Care System, Podiatry Section, Mather, CA, United States
- 5Department of Dermatology, University of California, Davis, CA, United States
Introduction: Chronic wounds are a significant source of patient morbidity, and ineffective treatment can lead to complications that are difficult and costly to manage. Given the limitations of current therapies, repurposing medications with well-studied safety and accessibility profiles offers a promising strategy for advancing wound care.
Methods: A comprehensive review of the existing literature was conducted to evaluate the role of serotonin-modulating pharmacotherapy in wound healing.
Results: Serotonergic signaling plays a multifaceted role in wound healing and evidence increasingly supports serotonin-modulating pharmacotherapy as having favorable angio-regulatory, immunomodulatory, and antimicrobial wound healing effects. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that topical administration of serotonin-modulating pharmacotherapy may improve wound healing outcomes.
Discussion: findings of this study provide support for the use of serotonin-modulating pharmacotherapy, with a special focus on topical application, as an adjunctive treatment for chronic, non-healing wounds and highlight the need for further translational clinical investigation.
1 Introduction
Chronic non-healing wounds, such as neuropathic and vascular ulcers, cause significant disability and increase the risk of pain, infection, sepsis, amputation, and other morbidities (Zhao et al., 2016). In the United States, chronic wounds affect nearly 2.5% of the population and contribute to an economic burden surpassing $50 billion annually (Sen, 2019; Sen, 2021). Serotonin also known as 5-hyrdoxytryptamine (5-HT) is an extensively studied monoamine neurotransmitter that is also synthesized and used by peripheral cells (Malinin et al., 2004; Alstergren et al., 1999; Laberge et al., 1996; Nguyen et al., 2019). Tryptophan hydroxylase 1, a key peripheral serotonin-synthesizing enzyme, is expressed in lymphocytes, macrophages, mast cells, and T cells, while serotonin transporter (SERT) and 5-HT receptors are also present in macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes (Shah and Amini-Nik, 2017). In response to peripheral inflammation, both 5-HT and its receptors are upregulated, promoting key angiogenic and cellular wound healing pathways (Malinin et al., 2004; Alstergren et al., 1999; Laberge et al., 1996; Nguyen et al., 2019). At present, 5-HT is underappreciated in the wound healing literature, but its developing multifaceted involvement positions 5-HT signaling as a promising target for advanced wound care therapeutics.
2 Mechanistic basis and therapeutic rational for Serotonin/SSRIs in wound healing
2.1 Overview and clinical framing
5-HT plays regulatory roles in the four progressive, overlapping stages of wound healing: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling (Figure 1) (Enoch and Leaper, 2008; Eskeland et al., 2017). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), including fluoxetine, citalopram, escitalopram, sertraline, and paroxetine, inhibit 5-HT reuptake at the synaptic cleft and are increasingly used across a broadening range of clinical applications including dermatologic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, and psoriasis, partially due to their well-documented downregulation of various proinflammatory cytokine signatures (Brody and Gu, 2020; Eskeland et al., 2017; Kiecka and Szczepanik, 2022; Shah and Amini-Nik, 2017). Emerging evidence supports the use of SSRIs to improve wound healing outcomes via angio-regulatory, immunomodulatory, and antimicrobial mechanisms, which remain under-characterized and have not yet been comprehensively contextualized for cutaneous wound healing (Eskeland et al., 2017).
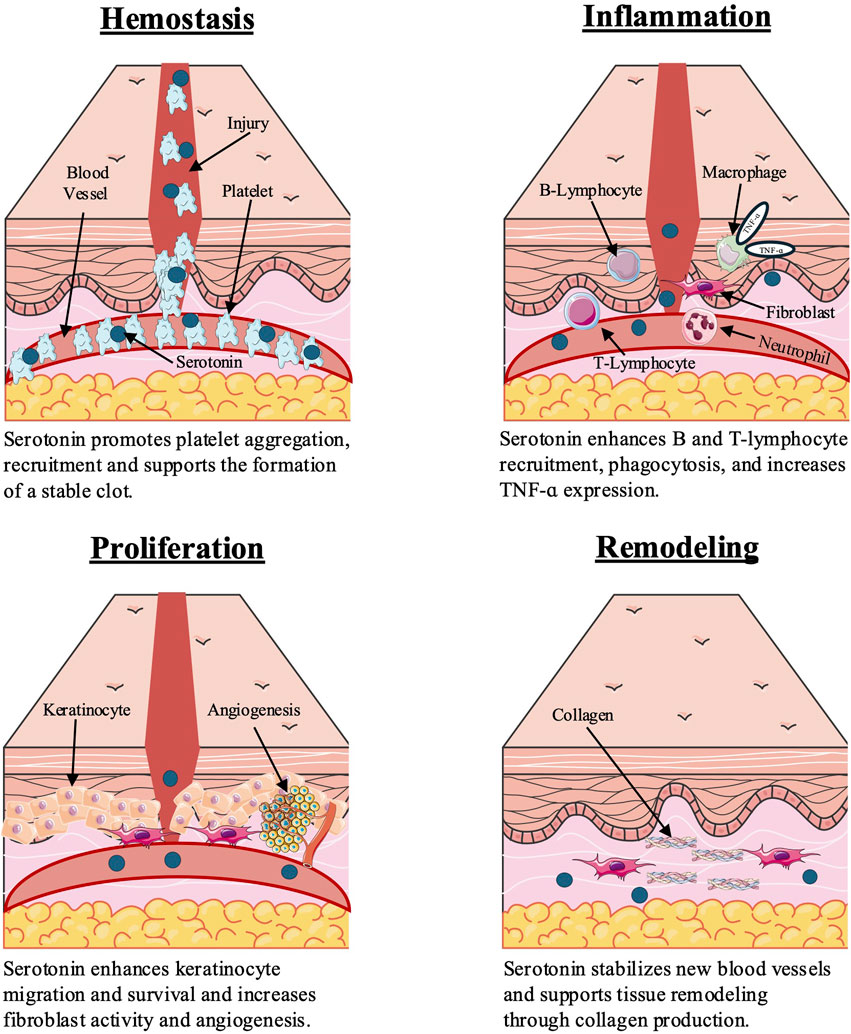
Figure 1. Serotonin influences wound healing stages through effects on platelets, immune cells, fibroblasts, and keratinocytes. Figure created by the authors based on findings from Enoch and Leaper (2008), Opneja et al. (2019), and Shah and Amini-Nik (2017).
2.2 Hemostasis and angiogenesis
Within minutes of cutaneous injury in the hemostasis stage, thrombin triggers 5-HT release from platelets and endothelial cells, activating 5-HT receptors on the same cell types and initiating G-protein–mediated extracellular signal–regulated kinases 1 and 2 phosphorylation in the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway (Iwabayashi et al., 2012; Raote et al., 2007; Machida et al., 2013; Qin et al., 2013; Olszewska-Pazdrak and Carney, 2013; Gonzalez de Valdivia et al., 2017; Guo et al., 2022; Flaumenhaft and De Ceunynck, 2017; Huang et al., 2015; Tsopanoglou and Maragoudakis, 1999; Duerschmied et al., 2013). This early 5-HT autocrine signaling amplifies downstream pro-angiogenic cascades by upregulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors and promoting release of VEGF, CXCL12, and matrix metalloproteinases, to sustain VEGF and nitric oxide–driven neovascularization (Almalki and Agrawal, 2017; Lin et al., 2023; Olszewska-Pazdrak and Carney, 2013; Guo et al., 2022; Flaumenhaft and De Ceunynck, 2017; Yang et al., 2005; Ceradini et al., 2004). SSRIs may be leveraged to attenuate dysregulated 5-HT signaling and to modulate the aberrant platelet and vascular responses in pathologic chronic wounds. For example, systemic SSRIs block SERT on platelets, preventing 5-HT uptake and causing a dose-dependent decrease, often exceeding 80%, in platelet 5-HT with greater effects seen after 6–12 weeks (Maguire et al., 1993; Kubera et al., 2001; Serebruany et al., 2001). Additionally, SSRIs lower plasma 5-HT, reduce key aggregation glycoproteins, and inhibit platelet signaling proteins involved in calcium mobilization release, which is a key step in platelet activation (Maguire et al., 1993; Kubera et al., 2001; Serebruany et al., 2001; Malinin et al., 2004). In contrast to CNS neurons which can synthesize 5-HT de novo via tryptophan hydroxylase, an enzyme which has enhanced expression in response to SSRIs, platelets cannot synthesize 5-HT and experience a depletion of intracellular stores to less than 2% of baseline after SSRI treatment (Shah and Amini-Nik, 2017). Relevant for poorly perfusing wounds, preliminary animal model studies have shown SSRIs may increase endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity and nitric oxide bioavailability (Pereira et al., 2015; Ofek et al., 2012). The platelet-inhibitory SSRI effects may also be particularly useful for targeting venous stasis ulcer disease processes as all classes of chronic venous insufficiency are linked to pathogenic platelet hyperactivity and increased platelet-monocyte and platelet-neutrophil aggregates, independent of whether a wound is present (Malinin et al., 2004).
2.3 Inflammation phase immunomodulation
The downregulatory effects of SSRIs on platelet 5-HT signaling may also modulate the inflammatory stage of wound healing where platelet-secreted 5-HT enhances recruitment and activation of neutrophils and macrophages, leading to unfavorable upregulation of key pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-ɑ) and interleukin-12 (IL-12) in chronic wounds (Maguire et al., 1993; Kubera et al., 2001; Serebruany et al., 2001; Shah and Amini-Nik, 2017). Synergistically, in vitro SSRI exposure has been shown to increase natural killer cell, a negative regulator of wound-microenvironment pro-inflammatory signaling, activity thereby reducing inflammation via two converging, complementary mechanisms (Frank et al., 1999; Brubaker et al., 2011). Dendritic cells are also involved in the inflammatory stage and sequester 5-HT via SERT from activated T lymphocytes, subsequently presenting it to naïve T cells to promote their activation and adaptive immune response (Shah and Amini-Nik, 2017). In pathologic nonhealing wounds, T lymphocytes are elevated and exhibit dysfunctional signaling unresponsive to stimulation (Raziyeva et al., 2021; Havran and Jameson, 2010; Shah and Amini-Nik, 2017). SSRIs may reduce T lymphocyte proliferation, cytokine production, and induce apoptosis in unresponsive, constitutively activated T lymphocytes preferentially compared to mature naïve T lymphocytes (Shenoy et al., 2013; Di Rosso et al., 2016; Pállinger and Csaba, 2007; Gobin et al., 2013). A persistent inflammatory phase may be associated with dysregulated monopoiesis and sustained elevation of proinflammatory macrophages, a key cell-type for transition to the proliferative stage which has upregulated phagocytosis and TNF-a in response to 5-HT (Li et al., 2021; Malinin et al., 2004). In an ex-vivo study, SSRIs significantly reduced the expression of CXCR4, CD4, and CCR5 on both monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells compared to control, suggesting an inhibitory role of SSRIs for macrophage proinflammatory signaling (Greeson et al., 2016). Other studies have demonstrated SSRI-associated reductions in MDM proinflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen species, and antigen presentation to immune cells, which may be dysregulated in pathologic wound healing (Nazimek et al., 2017).
2.4 Proliferation: keratinocyte and fibroblast responses
In regard to proliferative phase keratinocytes, topical 5-HT has been shown to enhance survival, migration, and wound area reduction in a dose-dependent manner, accelerating closure in both in vitro and in vivo models (Polanski et al., 1995; Sternberg et al., 1987; Nguyen et al., 2019; Sadiq et al., 2018; Lenz et al., 2001; Malinin et al., 2004; Seuwen et al., 1988; Rodriguez-Barucg et al., 2024). Improved keratinocyte scratch closure rates due to increased proliferation were reversed following treatment with ketanserin, a 5-HT receptor antagonist, supporting SSRI dependance on 5-HT keratinocyte signaling (Rodriguez-Barucg et al., 2024). This study also identified improved phosphorylation profiles and 350 differentially expressed genes in SSRI-treated keratinocytes with reactome analysis suggesting altered mitochondrial and ribonucleotide metabolism and thermogenesis (Rodriguez-Barucg et al., 2024). In fibroblasts, 5-HT promotes survival, activity, proliferation, and collagen production, while also synergizing with FGF-2 to enhance tissue proliferation (Polanski et al., 1995; Sternberg et al., 1987; Nguyen et al., 2019; Sadiq et al., 2018; Lenz et al., 2001; Malinin et al., 2004; Seuwen et al., 1988). These effects involve active transport, increased oxygen formation, protein phosphorylation, and 5-HT receptor–mediated mitogenesis, adhesion, and multiplication in culture (Polanski et al., 1995; Sternberg et al., 1987; Nguyen et al., 2019; Sadiq et al., 2018; Lenz et al., 2001; Malinin et al., 2004; Seuwen et al., 1988). The effects of SSRIs on certain chronic wound mechanism which have implicated 5-HT signaling remain unassessed; these include 5-HT-induced B-lymphocyte proliferation, afferent nerve ending stimulation and pain response and the potential of SSRIs to alter β-receptor function in wound cells, similar to SSRI-induced postsynaptic β-receptor downregulation in the brain (Malinin et al., 2004).
2.5 Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and wound microbiome
Recurrent or chronic infection is a known contributor to impaired wound healing and, in a retrospective analysis of 2963 patients, it was found that the predominant bacterial species in chronic wounds were S. epidermidis, S. aureus, Corynebacterium, and Pseudomonadaceae (Kiecka and Szczepanik, 2022). Biofilms, which hinder antibiotic treatment by using extracellular polymeric substance barriers and efflux pumps, are associated with delayed healing and increased infection risk in chronic wounds (Gompelman et al., 2016; Wall et al., 2019; Pereira et al., 2021). Polymicrobial interactions, involving species like Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa may enhance biofilm pathogenicity via exchange of antibiotic resistance genes, like those producing antibiotic-degrading enzymes (Ponde et al., 2021; Cheong et al., 2021; Orazi and O'Toole, 2019).
Among SSRIs, fluoxetine and sertraline have the strongest antimicrobial effects; these SSRIs are more hydrophobic than others and may diffuse more easily across the phospholipid membrane to interact with cellular machinery (Kiecka and Szczepanik, 2022). These SSRIs, at sub-minimum inhibitory concentrations, have been shown to prevent biofilm production via ALS3 protein-binding and reduce mature biofilm metabolism (Oliveira et al., 2018; Costa Silva et al., 2017; Rodrigues et al., 2023). Fluoxetine has been shown to have in vitro effect against multi-resistant S. aureus, E. faecalis, S. epidermidis, E. coli and P. aeruginosa and decreases biofilm formation of S. aureus clinical isolate UAMS-1 (Dafinone et al., 2025). There is also evidence suggesting fluoxetine synergizes polymyxin B bactericidal effects in 80% of gram-negative isolates, outperforming fosfomycin and meropenem combinations (Ahmed et al., 2024). Fluoxetine topical application to infected wounds may also decrease purulence and hinder hematogenous bacterial invasion (Dafinone et al., 2025). Fluoxetine has also shown effectiveness against fluconazole-resistant Candida strains, and its administration leads to significant dose-dependent reductions in biofilm metabolism, 96% for C. krusei, and biomass, 82% for C. glabrata (Costa Silva et al., 2017). Sertraline inhibits the growth of S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and other Gram-positive bacteria such as S. epidermidis and E. faecalis, and shows synergy with antibiotics, including reductions in mimimum inhibitory concentration of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin against C. urealyticum and quinolone-resistant strains (Dafinone et al., 2025). While generally less effective against Gram-negative species, it demonstrates activity against H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, C. jejuni, Acinetobacter spp., and can inhibit biofilm production in coagulase-negative staphylococci (Dafinone et al., 2025). In addition to the immunomodulatory properties of SSRIs, the antimicrobial properties of SSRIs make them promising adjuncts for difficult-to-treat wound bacterial and fungal infection.
3 Topical selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and wound healing studies
3.1 Pre-clinical studies
Evidence from preclinical studies suggest topical SSRI application may improve wound healing. An in vivo study of diabetic mouse wound models revealed topical fluoxetine treatment promoted re-epithelialization, with significant decreases in wound area and exudate. Topical fluoxetine treatment also increased angiogenesis, suggested by higher CD31+ endothelial cell counts and visible small vessels, while reducing inflammatory macrophages and shifting their phenotype towards a pro-reparative state (Nguyen et al., 2019). In another study where wounds were created in rats, chronic topical fluoxetine administration improved mean wound lengths compared to acute administration in the initial 4 days; wounds in both chronic and acute fluoxetine treatment groups healed completely by day 10, while the placebo group did not fully heal by the study’s conclusion (Farahani et al., 2007) In rats subjected to stress which decreased wound healing rate, topical fluoxetine treatment increased healing rate, leukocyte healing response, and normalized epithelialization and epithelial cell structure (Farahani et al., 2007). Bioelectronic delivery of topical fluoxetine in a murine punch wound model increased re-epithelialization by nearly 40% compared to control; this was accompanied by anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage infiltration without pro-inflammatory M1 presence, leading to a reduced M1/M2 ratio over time, indicative of accelerated transition to the reparative phase of wound healing (Li et al., 2024; Asefifeyzabadi et al., 2024). In a porcine model also using bioelectronic delivery, topical fluoxetine produced similar re-epithelialization improvements, also with corresponding improvements in the wound macrophage and cytokine profile (Li et al., 2025).There is an advantage to topical, as opposed to systemic, administration: preclinical data indicate that topical fluoxetine application leads to plasma fluoxetine concentrations that are twofold lower than those achieved with oral fluoxetine at therapeutic neurological doses. Importantly, topical fluoxetine treatment does not affect plasma levels of 5-HT, highlighting its potential for localized therapy with minimal systemic impact (Nguyen et al., 2019).
3.2 Clinical studies
In view of the pro-reparative outcomes noted with agonists of the 5-HT receptors, it may be counterintuitive to propose that antagonists may have a similar result. However, existing clinical studies have investigated ketanserin. Although ketanserin does not increase serotonin levels, its wound healing effects are thought to result from its antiplatelet properties and ability to improve microvascular perfusion, rather than through direct serotonergic signaling (Malinin et al., 2004; Hedner and Persson, 1988). Separately, iproniazid (an irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor that limits the breakdown of serotonin) may promote reparative effects by increasing extracellular 5-HT and enhancing downstream receptor activation (Gillman, 2005). There are no ongoing or previous clinical trials investigating topical SSRIs for the treatment of chronic wounds (ClinicalTrials.gov).
In a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of various chronic wounds, topical ketanserin 2% BID application was associated with greater re-epithelialization, granulation tissue formation, and wound area reduction rate (Janssen et al., 1989). Other studies of topical ketanserin 2% BID for VLUs and DFUs showed similar improvements in wound healing measures in addition to reductions in transudate and erythema (Roelens, 1989). In a double-blind intra-individual comparative study, diabetic participants with ≥2 chronic leg ulcers were randomized to receive topical 2% ketanserin BID on one ulcer and placebo on another ulcer for 8 weeks, in adjunct to SOC. The mean weekly reduction in wound area was significantly greater for ketanserin-treated ulcers (10.25%) compared to placebo-treated ulcers (2.5%) (Quatresooz et al., 2006). One trial investigating topical 10% iproniazid BID for 2 weeks for the treatment of chronic ulcers showed significantly increased rates of healing throughout the trial compared to placebo control (Goldstein et al., 1962). These studies are summarized in Table 1.
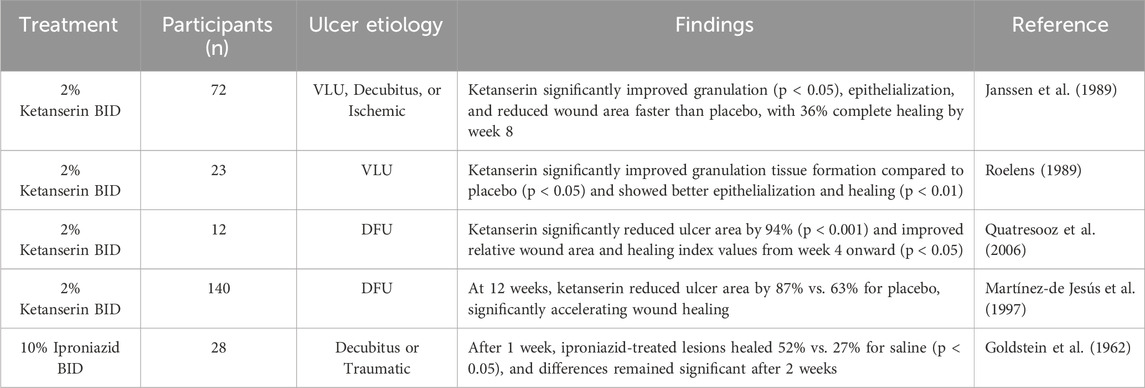
Table 1. Clinical studies investigating topical serotonin-modulating medications and chronic wound healing.
4 Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor-associated cutaneous adverse drug reactions
Oral SSRI-associated cutaneous adverse drug reactions (CADRs) have been reported in the literature. One systematic review of 173 cases found fluoxetine is the most commonly reported SSRI with CADRs, followed by sertraline and paroxetine. CADRs were frequently petechiae, ecchymoses, alopecia, and photo-dermatoses (Masuka et al., 2022). SSRI-related petechiae and ecchymoses may be attributed to SSRI-induced platelet inhibition; however, a study of oral fluoxetine found no significant difference in cutaneous microcirculation compared to control (Andrade et al., 2010; Edinoff et al., 2022; Mück-Weymann and Rechlin, 1996). Notably, there are no reports of adverse drug reactions for topical SSRI administration. Therefore, topical delivery of SSRIs for the treatment of chronic wounds or wound infections is preferred, to maximize concentrations of the drug at the wound while minimizing systemic absorption. Indeed, these approaches are under investigation, including delivery via hydrogels, microparticles, nano capsules, or bioelectronic delivery devices (Josino et al., 2021; Dos Santos et al., 2020). Topical use would be expected to minimize serotonergic effects; although, patients on dual antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulation should still be monitored clinically.
5 Conclusion
With their immunomodulatory and antimicrobial properties, repurposing 5-HT modulating pharmacotherapy, including SSRIs, for topical administration may offer significant benefits in treating chronic wounds, as supported by both preclinical and clinical evidence. Further clinical research and pharmacokinetic studies are essential to fully evaluate the potential of SSRIs in improving wound healing outcomes and to establish their role as a viable adjunctive therapeutic option in chronic wound care.
Author contributions
AB: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Methodology. AM: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. JG-K: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. JDP: Writing – review and editing. CH-V: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. LA: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. SD: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. RRI: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
This manuscript includes adapted and modified versions of the following icons by Servier Medical Art: “skin-normal,” “platelet-2,” “b-lymphocyte,” “macrophage,” “neutrophil-granulocyte-1,” “lymphoid-stem-cell,” “fibroblast-1,” “keratinocyte-1,” “angiogenesis,” and “collagen-3d.” All original images are available at https://smart.servier.com and are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (CC BY 3.0). The modified versions are published under the same license, with appropriate attribution.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmed, S. A., Jordan, R. L., Isseroff, R. R., and Lenhard, J. R. (2024). Potential synergy of fluoxetine and antibacterial agents against skin and soft tissue pathogens and drug-resistant organisms. Antibiot. (Basel) 13, 1165. doi:10.3390/antibiotics13121165
Almalki, S. G., and Agrawal, D. K. (2017). ERK signaling is required for VEGF-A/VEGFR2-induced differentiation of porcine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 8, 113. doi:10.1186/s13287-017-0568-4
Alstergren, P., Ernberg, M., Kopp, S., Lundeberg, T., and Theodorsson, E. (1999). TMJ pain in relation to circulating neuropeptide Y, serotonin, and interleukin-1 beta in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Orofac. Pain 13, 49–55.
Andrade, C., Sandarsh, S., Chethan, K. B., and Nagesh, K. S. (2010). Serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants and abnormal bleeding: a review for clinicians and a reconsideration of mechanisms. J. Clin. Psychiatry 71, 1565–1575. doi:10.4088/JCP.09r05786blu
Asefifeyzabadi, N., Nguyen, T., Li, H., Zhu, K., Yang, H. Y., Baniya, P., et al. (2024). A pro-reparative bioelectronic device for controlled delivery of ions and biomolecules. Wound Repair Regen. 32, 709–719. doi:10.1111/wrr.13191
Brody, D. J., and Gu, Q. (2020). Antidepressant use among adults: united States, 2015-2018 NCHS data brief. MD: Hyattsville. code data-end=”628” data-start=”611.
Brubaker, A. L., Schneider, D. F., and Kovacs, E. J. (2011). Neutrophils and natural killer T cells as negative regulators of wound healing. Expert Rev. Dermatol 6, 5–8. doi:10.1586/edm.10.66
Ceradini, D. J., Kulkarni, A. R., Callaghan, M. J., Tepper, O. M., Bastidas, N., Kleinman, M. E., et al. (2004). Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat. Med. 10, 858–864. doi:10.1038/nm1075
Cheong, J. Z. A., Johnson, C. J., Wan, H., Liu, A., Kernien, J. F., Gibson, A. L. F., et al. (2021). Priority effects dictate community structure and alter virulence of fungal-bacterial biofilms. ISME J. 15, 2012–2027. doi:10.1038/s41396-021-00901-5
Costa Silva, R. A., Da Silva, C. R., De Andrade Neto, J. B., Da Silva, A. R., Campos, R. S., Sampaio, L. S., et al. (2017). In vitro anti-candida activity of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors against fluconazole-resistant strains and their activity against biofilm-forming isolates. Microb. Pathog. 107, 341–348. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2017.04.008
Dafinone, M. E., Lyle, R. E., Lee, C., Mehta, A., Dahle, S. E., and Isseroff, R. R. (2025). Non-antibiotic approaches to mitigating wound infections: potential for SSRIs and adrenergic antagonists as emerging therapeutics. Wound Repair Regen. 33, e13240. doi:10.1111/wrr.13240
Di Rosso, M. E., Palumbo, M. L., and Genaro, A. M. (2016). Immunomodulatory effects of fluoxetine: a new potential pharmacological action for a classic antidepressant drug? Pharmacol. Res. 109, 101–107. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2015.11.021
Dos Santos, S. B. F., Pereira, S. A., Rodrigues, F. A. M., Da Silva, A. C. C., De Almeida, R. R., Sousa, A. C. C., et al. (2020). Antibacterial activity of fluoxetine-loaded starch nanocapsules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 164, 2813–2817. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.184
Duerschmied, D., Suidan, G. L., Demers, M., Herr, N., Carbo, C., Brill, A., et al. (2013). Platelet serotonin promotes the recruitment of neutrophils to sites of acute inflammation in mice. Blood 121, 1008–1015. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-06-437392
Edinoff, A. N., Raveendran, K., Colon, M. A., Thomas, B. H., Trettin, K. A., Hunt, G. W., et al. (2022). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and associated bleeding risks: a narrative and clinical review. Health Psychol. Res. 10, 39580. doi:10.52965/001c.39580
Enoch, S., and Leaper, D. J. (2008). “Basic science of wound healing,”, 26. Oxford, 31–37. doi:10.1016/j.mpsur.2007.11.005Surgery
Eskeland, S., Halvorsen, J. A., and Tanum, L. (2017). Antidepressants have anti-inflammatory effects that may be relevant to dermatology: a systematic review. Acta Derm. Venereol. 97, 897–905. doi:10.2340/00015555-2702
Farahani, R. M., Sadr, K., Rad, J. S., and Mesgari, M. (2007). Fluoxetine enhances cutaneous wound healing in chronically stressed wistar rats. Adv. Skin. Wound Care 20, 157–165. doi:10.1097/01.ASW.0000262710.59293.6b
Flaumenhaft, R., and De Ceunynck, K. (2017). Targeting PAR1: now what? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 38, 701–716. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2017.05.001
Frank, M. G., Hendricks, S. E., Johnson, D. R., Wieseler, J. L., and Burke, W. J. (1999). Antidepressants augment natural killer cell activity: in vivo and in vitro. Neuropsychobiology 39, 18–24. doi:10.1159/000026555
Gillman, P. K. (2005). Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, opioid analgesics and serotonin toxicity. Br. J. Anaesth. 95, 434–441. doi:10.1093/bja/aei210
Gobin, V., Van Steendam, K., Fevery, S., Tilleman, K., Billiau, A. D., Denys, D., et al. (2013). Fluoxetine reduces murine graft-versus-host disease by induction of t cell immunosuppression. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 8, 934–943. doi:10.1007/s11481-013-9463-7
Goldstein, H. S., Wolcott, M. W., and Rosenstein, I. N. (1962). Iproniazid in healing of chronic topical ulcers. Arch. Surg. 85, 1011–1015. doi:10.1001/archsurg.1962.01310060147026
Gompelman, M., Van Asten, S. A. V., and Peters, E. J. G. (2016). Update on the role of infection and biofilms in wound healing: pathophysiology and treatment. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 138, 61S-70S–70S. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000002679
Gonzalez De Valdivia, E., Broselid, S., Kahn, R., Olde, B., and Leeb-Lundberg, L. M. F. (2017). G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER1)/GPR30 increases ERK1/2 activity through PDZ motif-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 9932–9943. doi:10.1074/jbc.M116.765875
Greeson, J. M., Gettes, D. R., Spitsin, S., Dubé, B., Benton, T. D., Lynch, K. G., et al. (2016). The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram decreases human immunodeficiency virus receptor and coreceptor expression in immune cells. Biol. Psychiatry 80, 33–39. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.11.003
Guo, P., Tai, Y., Wang, M., Sun, H., Zhang, L., Wei, W., et al. (2022). Gα12 and Gα13: versatility in physiology and pathology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 809425. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.809425
Havran, W. L., and Jameson, J. M. (2010). Epidermal T cells and wound healing. J. Immunol. 184, 5423–5428. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902733
Hedner, T., and Persson, B. (1988). Effects of a new serotonin antagonist, ketanserin, in experimental and clinical hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1, 317S-323S–323S. doi:10.1093/ajh/1.3.317s
Huang, Z., Miao, X., Luan, Y., Zhu, L., Kong, F., Lu, Q., et al. (2015). PAR1-stimulated platelet releasate promotes angiogenic activities of endothelial progenitor cells more potently than PAR4-stimulated platelet releasate. J. Thrombosis Haemostasis 13, 465–476. doi:10.1111/jth.12815
Iwabayashi, M., Taniyama, Y., Sanada, F., Azuma, J., Iekushi, K., Kusunoki, H., et al. (2012). Role of serotonin in angiogenesis: induction of angiogenesis by sarpogrelate via endothelial 5-HT1B/Akt/eNOS pathway in diabetic mice. Atherosclerosis 220, 337–342. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.10.042
Janssen, P. A. J., Janssen, H., Cauwenbergh, G., Doncker, P. D., Beule, K. D., Lewi, P., et al. (1989). Use of topical ketanserin in the treatment of skin ulcers: a double-blind study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatology 21, 85–90. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70153-5
Josino, M. A. A., Rocha Da Silva, C., De Andrade Neto, J. B., Barroso, F. D. D., Juvêncio Da Silva, L., Cavalcanti, B. C., et al. (2021). Development and in vitro evaluation of microparticles of fluoxetine in galactomannan against biofilms of S. aureus methicilin resistant. Carbohydr. Polym. 252, 117184. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117184
Kiecka, A., and Szczepanik, M. (2022). The potential action of SSRIs in the treatment of skin diseases including atopic dermatitis and slow-healing wounds. Pharmacol. Rep. 74, 947–955. doi:10.1007/s43440-022-00423-7
Kubera, M., Lin, A. H., Kenis, G., Bosmans, E., Van Bockstaele, D., and Maes, M. (2001). Anti-inflammatory effects of antidepressants through suppression of the interferon-gamma/interleukin-10 production ratio. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 21, 199–206. doi:10.1097/00004714-200104000-00012
Laberge, S., Cruikshank, W. W., Beer, D. J., and Center, D. M. (1996). Secretion of IL-16 (lymphocyte chemoattractant factor) from serotonin-stimulated CD8+ T cells in vitro. J. Immunol. 156, 310–315. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.156.1.310
Lenz, G., Gonçalves, D., Luo, Z., Avruch, J., Rodnight, R., and Neary, J. T. (2001). Extracellular ATP stimulates an inhibitory pathway towards growth factor-induced cRaf-1 and MEKK activation in astrocyte cultures. J. Neurochem. 77, 1001–1009. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00299.x
Li, M., Hou, Q., Zhong, L., Zhao, Y., and Fu, X. (2021). Macrophage related chronic inflammation in non-healing wounds. Front. Immunol. 12, 681710. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.681710
Li, H., Yang, H.-Y., Asefifeyzabadi, N., Baniya, P., Lopez, A. M., Gallegos, A., et al. (2024). Programmable delivery of fluoxetine via wearable bioelectronics for wound healing in vivo. Adv. Mater. Technol. 9, 2301115. doi:10.1002/admt.202301115
Li, H., Asefifeyzabadi, N., Schorger, K., Baniya, P., Yang, H.-Y., Tebyani, M., et al. (2025). Remote-controlled wireless bioelectronics for fluoxetine therapy to promote wound healing in a porcine model. Adv. Mater. Technol. 10, 70039. n/a. doi:10.1002/admt.202500040
Lin, P. K., Koller, G. M., and Davis, G. E. (2023). Elucidating the morphogenic and signaling roles of defined growth factors controlling human endothelial cell lumen formation versus sprouting behavior. Am. J. Pathol. 193, 2203–2217. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.08.009
Machida, T., Iizuka, K., and Hirafuji, M. (2013). 5-hydroxytryptamine and its receptors in systemic vascular walls. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 36, 1416–1419. doi:10.1248/bpb.b13-00344
Maguire, K., Tuckwell, V., Pereira, A., Dean, B., and Singh, B. (1993). Significant correlation between 14C-5-HT uptake by and 3H-paroxetine binding to platelets from healthy volunteers. Biol. Psychiatry 34, 356–360. doi:10.1016/0006-3223(93)90179-h
Malinin, A., Oshrine, B., and Serebruany, V. (2004). Treatment with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for enhancing wound healing. Med. Hypotheses 63, 103–109. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2003.10.021
Martínez-De Jesús, F. R., Morales-Guzmán, M., Castañeda, M., Pérez-Morales, A., García-Alonso, J., and Mendiola-Segura, I. (1997). Randomized single-blind trial of topical ketanserin for healing acceleration of diabetic foot ulcers. Arch. Med. Res. 28, 95–99.
Masuka, J. T., Mchunu, N., Mkhize, Z., Thandar, Y., and Mosam, A. (2022). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor associated cutaneous adverse drug reactions: a systematic review of case reports and case series. Australas. J. Dermatol 63, e13–e20. doi:10.1111/ajd.13780
Mück-Weymann, M., and Rechlin, T. (1996). Reflexes of the cutaneous microcirculation in amitriptyline and in fluoxetine treated patients. Psychopharmacol. Berl. 124, 241–244. doi:10.1007/BF02246663
Nazimek, K., Strobel, S., Bryniarski, P., Kozlowski, M., Filipczak-Bryniarska, I., and Bryniarski, K. (2017). The role of macrophages in anti-inflammatory activity of antidepressant drugs. Immunobiology 222, 823–830. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2016.07.001
Nguyen, C. M., Tartar, D. M., Bagood, M. D., So, M., Nguyen, A. V., Gallegos, A., et al. (2019). Topical fluoxetine as a novel therapeutic that improves wound healing in diabetic mice. Diabetes 68, 1499–1507. doi:10.2337/db18-1146
Ofek, K., Schoknecht, K., Melamed-Book, N., Heinemann, U., Friedman, A., and Soreq, H. (2012). Fluoxetine induces vasodilatation of cerebral arterioles by co-modulating NO/muscarinic signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 16, 2736–2744. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01596.x
Oliveira, A. S., Martinez-De-Oliveira, J., Donders, G. G. G., Palmeira-De-Oliveira, R., and Palmeira-De-Oliveira, A. (2018). Anti-candida activity of antidepressants sertraline and fluoxetine: effect upon pre-formed biofilms. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 207, 195–200. doi:10.1007/s00430-018-0539-0
Opneja, A., Kapoor, S., and Stavrou, E. X. (2019). Contribution of platelets, the coagulation and fibrinolytic systems to cutaneous wound healing. Thromb. Res. 179, 56–63. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2019.05.001
Olszewska-Pazdrak, B., and Carney, D. H. (2013). Systemic administration of thrombin peptide TP508 enhances VEGF-stimulated angiogenesis and attenuates effects of chronic hypoxia. J. Vasc. Res. 50, 186–196. doi:10.1159/000348250
Orazi, G., and O'toole, G. A. (2019). It takes A village: mechanisms underlying antimicrobial recalcitrance of polymicrobial biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 202, e00530-19. doi:10.1128/JB.00530-19
Pállinger, E., and Csaba, G. (2007). Effect of serotonin-acting agents on the serotonin content of immune cells. A peculiar observation. Cell Biochem. Funct. 25, 581–583. doi:10.1002/cbf.1329
Pereira, C. A., Ferreira, N. S., Mestriner, F. L., Antunes-Rodrigues, J., Evora, P. R., Resstel, L. B., et al. (2015). Chronic fluoxetine treatment increases NO bioavailability and calcium-sensitive potassium channels activation in rat mesenteric resistance arteries. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 765, 375–383. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.09.002
Pereira, R., Dos Santos Fontenelle, R. O., De Brito, E. H. S., and De Morais, S. M. (2021). Biofilm of candida albicans: formation, regulation and resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 131, 11–22. doi:10.1111/jam.14949
Polanski, M., Vermeulen, M. W., Wu, J., and Karnovsky, M. L. (1995). Muramyl dipeptide mimicry in the regulation of murine macrophage activation by serotonin. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 17, 225–232. doi:10.1016/0192-0561(94)00097-8
Ponde, N. O., Lortal, L., Ramage, G., Naglik, J. R., and Richardson, J. P. (2021). Candida albicans biofilms and polymicrobial interactions. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 47, 91–111. doi:10.1080/1040841X.2020.1843400
Qin, L., Zhao, D., Xu, J., Ren, X., Terwilliger, E. F., Parangi, S., et al. (2013). The vascular permeabilizing factors histamine and serotonin induce angiogenesis through TR3/Nur77 and subsequently truncate it through Thrombospondin-1. Blood 121, 2154–2164. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-07-443903
Quatresooz, P., Kharfi, M., Paquet, P., Vroome, V., Cauwenbergh, G., and Piérard, G. E. (2006). Healing effect of ketanserin on chronic leg ulcers in patients with diabetes. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatology Venereol. 20, 277–281. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2006.01422.x
Raote, I., Bhattacharya, A., and Panicker, M. M. (2007). “Serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptor function: ligand-dependent mechanisms and pathways,” in Serotonin receptors in neurobiology. Editor C. Amitabha (Boca Raton, FL: Taylor & Francis).
Raziyeva, K., Kim, Y., Zharkinbekov, Z., Kassymbek, K., Jimi, S., and Saparov, A. (2021). Immunology of acute and chronic wound healing. Biomolecules 11, 700. doi:10.3390/biom11050700
Rodrigues, D. S., Cabral, V. P. F., Barbosa, A. D., Sá, L. G. D. A., Moreira, L. E. A., De Andrade Neto, J. B., et al. (2023). Sertraline has in vitro activity against both mature and forming biofilms of different candida species. J. Med. Microbiol. 72. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.001664
Rodriguez-Barucg, Q., Garcia, A. A., Garcia-Merino, B., Akinmola, T., Okotie-Eboh, T., Francis, T., et al. (2024). Environmental fluoxetine promotes skin cell proliferation and wound healing. Environ. Pollut. 362, 124952. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2024.124952
Roelens, P. (1989). Double-blind placebo-controlled study with topical 2% ketanserin ointment in the treatment of venous ulcers. Dermatologica 178, 98–102. doi:10.1159/000248400
Sadiq, A., Shah, A., Jeschke, M. G., Belo, C., Qasim Hayat, M., Murad, S., et al. (2018). The role of serotonin during skin healing in post-thermal injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1034. doi:10.3390/ijms19041034
Sen, C. K. (2019). Human wounds and its burden: an updated compendium of estimates. Adv. Wound Care 8, 39–48. doi:10.1089/wound.2019.0946
Sen, C. K. (2021). Human wound and its burden: updated 2020 compendium of estimates. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 10, 281–292. doi:10.1089/wound.2021.0026
Serebruany, V. L., Gurbel, P. A., and O'connor, C. M. (2001). Platelet inhibition by sertraline and N-desmethylsertraline: a possible missing link between depression, coronary events, and mortality benefits of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 43, 453–462. doi:10.1006/phrs.2001.0817
Seuwen, K., Magnaldo, I., and Pouysségur, J. (1988). Serotonin stimulates DNA synthesis in fibroblasts acting through 5-HT1B receptors coupled to a Gi-protein. Nature 335, 254–256. doi:10.1038/335254a0
Shah, A., and Amini-Nik, S. (2017). The role of serotoninergic system in skin healing. Int. J. Drug Res. Technol. 7, 80–106.
Shenoy, A. R., Dehmel, T., Stettner, M., Kremer, D., Kieseier, B. C., Hartung, H. P., et al. (2013). Citalopram suppresses thymocyte cytokine production. J. Neuroimmunol. 262, 46–52. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.06.006
Sternberg, E. M., Wedner, H. J., Leung, M. K., and Parker, C. W. (1987). Effect of serotonin (5-HT) and other monoamines on murine macrophages: modulation of interferon-gamma induced phagocytosis. J. Immunol. 138, 4360–4365. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.138.12.4360
Tsopanoglou, N. E., and Maragoudakis, M. E. (1999). On the mechanism of thrombin-induced angiogenesis. Potentiation of vascular endothelial growth factor activity on endothelial cells by up-regulation of its receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23969–23976. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.34.23969
Wall, G., Montelongo-Jauregui, D., Vidal Bonifacio, B., Lopez-Ribot, J. L., and Uppuluri, P. (2019). Candida albicans biofilm growth and dispersal: contributions to pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 52, 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2019.04.001
Yang, S. X., Chen, J. H., Jiang, X. F., Wang, Q. L., Chen, Z. Q., Zhao, W., et al. (2005). Activation of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in malignant glioma cells promotes the production of vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 335, 523–528. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.113
Keywords: wound healing, chronic wounds, serotonin, selective-serotonin reuptake inhibitor, serotonin-modulating pharmacotherapy
Citation: Budhiraja A, Mehta A, Ghebrehiwet-Kuflom J, Patel JD, How-Volkman C, Ali L, Dahle S and Isseroff RR (2025) Serotonin-modulating therapies for the management of chronic wounds. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1656302. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1656302
Received: 29 June 2025; Accepted: 27 August 2025;
Published: 22 September 2025.
Edited by:
Sujata Mohanty, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaReviewed by:
Igor Prudovsky, Maine Medical Center, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Budhiraja, Mehta, Ghebrehiwet-Kuflom, Patel, How-Volkman, Ali, Dahle and Isseroff. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Roslyn Rivkah Isseroff, cnJpc3Nlcm9mZkB1Y2RhdmlzLmVkdQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Anuj Budhiraja1†
Anuj Budhiraja1† Alisha Mehta
Alisha Mehta Roslyn Rivkah Isseroff
Roslyn Rivkah Isseroff