- 1Department of Korean Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Sangji University, Wonju, Republic of Korea
- 3Division of Allergy, Immune and Respiratory System, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Background: Yukgunja-tang (YGJT), also known as Liujunzi Decoction or Rikkunshito, is a traditional East Asian herbal formula widely used to manage symptoms associated with cancer and chemotherapy. This study aimed to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of modified YGJT combined with standard antitumor therapy in patients with lung cancer.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in 10 databases through March 2025. Randomized controlled trials comparing modified YGJT plus antitumor therapy versus antitumor therapy alone or placebo were included. Studies involving other herbal combinations or East Asian therapies were excluded. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool. A random-effects model was used for meta-analysis.
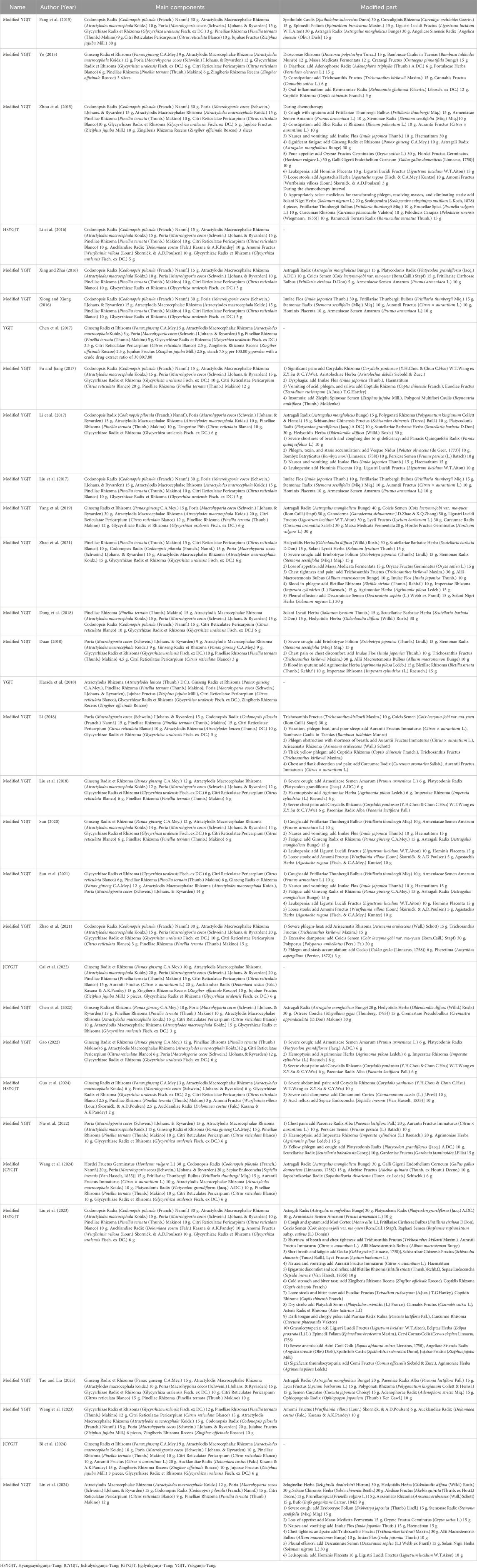
Results: Thirty-one trials involving 2,496 participants were included. Modified YGJT significantly improved the objective response rate (ORR; RR 1.69, 95% CI 1.41–2.04), disease control rate (DCR; RR 1.21, 95% CI 1.11–1.31), and Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS; RR 1.79, 95% CI 1.23–2.60; MD 8.62, 95% CI 3.86–13.38). Symptom relief was observed (RR 1.52, 95% CI 1.25–1.85; MD -10.87, 95% CI -12.51 to −9.22), along with improvements in immune markers (CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD4+/CD8+ ratio) and reductions in tumor markers (CEA, CYFRA 21-1, NSE, SCC, CA19-9) and adverse events (myelosuppression, leukopenia, gastrointestinal reactions).
Conclusion: Modified YGJT may offer clinical benefits as an adjuvant to standard lung cancer therapy by improving treatment outcomes and reducing toxicity. Large-scale, high-quality trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024619038, identifier CRD42024619038.
1 Introduction
Globally, lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths (Leiter et al., 2023). Although considerable advances have been made in its treatment, including surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and cellular therapies (Lee et al., 2023; Riely et al., 2024), challenges persist in the management of advanced lung cancer (Lee et al., 2023; Riely et al., 2024). Consequently, various complementary and alternative medicine therapies, including traditional herbal medicines, are increasingly being used not only to alleviate cancer-associated symptoms but also to enhance the efficacy of standard treatments and reduce adverse effects, with growing interest and supporting evidence (Guerra-Martin et al., 2021; Li et al., 2021).
Yukgunja-tang (YGJT, also known as Liujunzi Decoction in Chinese and Rikkunshito in Japanese) is a widely used herbal formula in Asia for improving gastrointestinal symptoms, including functional dyspepsia. YGJT was first documented in 1345 during the Yuan dynasty in the classical medical text Shi Yi De Xiao Fang (Efficacious Remedies of Physicians), authored by Yilin (2009). It comprises six primary medicinal herbs: Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma (Panax ginseng C.A.Mey.), Atractylodis macrocephalae Rhizoma (Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.), Poria (Macrohyporia cocos (Schwein.) I.Johans. & Ryvarden), Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. ex DC.), Pinelliae Rhizoma (Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Makino), and Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium (Citrus reticulata Blanco) (Inokuchi et al., 2021). In traditional East Asian medicine, YGJT is believed to tonify qi, strengthen the spleen, and eliminate dampness, primarily for treating spleen and stomach qi deficiency accompanied by dampness (Wu et al., 2022). This pattern presents with symptoms such as dyspepsia, fatigue, and weakness, which frequently occur in individuals receiving conventional cancer treatments.
In traditional East Asian medicine, the principle of reinforcing healthy qi to eliminate pathogenic factors constitutes a core therapeutic rationale in the management of cancer (Liu et al., 2018). Lung cancer is defined as a pattern of qi deficiency of the spleen and lung with concomitant phlegm-damp accumulation and secondary impairment of spleen function (You, 2016). Therapeutic strategies focus on strengthening the spleen, supplementing qi, transforming phlegm, and eliminating stasis, and also address chemotherapy-induced impairment of vital qi and gastrointestinal function by reinforcing healthy qi and restoring spleen-stomach integrity (Zhou et al., 2015).
YGJT and its modified formulations are widely prescribed during cancer treatment in East Asian countries (Iwase et al., 2012; Li et al., 2018). A systematic review published in 2023 identified YGJT as the most frequently used herbal intervention for cancer-related anorexia, reflecting its traditional indication for spleen-stomach deficiency and its capacity to address qi deficiency (Park et al., 2023). Moreover, in patients with lung cancer, the adjunctive use of YGJT alongside standard therapies has been associated with improved prognosis, delayed disease progression, and prolonged survival (Liu et al., 2020; Xi et al., 2025). These clinical benefits are consistent with traditional medical theory, which attributes lung cancer to qi deficiency of the spleen and lung and recommends reinforcing qi and resolving phlegm (Li et al., 2017). Through this mechanism, YGJT supports its role as an effective adjunct to standard therapy in lung cancer management.
Although several systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have examined the efficacy of YGJT and its modified formulations in gastrointestinal disorders, no review has specifically focused on its role in lung cancer (Ko et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). In lung cancer management, YGJT may alleviate cancer- and chemotherapy-related symptoms and improve the effectiveness of anticancer therapies. Therefore, a systematic evaluation of its efficacy and safety is warranted to guide its appropriate integration into clinical practice. This review aims to assess the efficacy and safety of YGJT as an adjunct therapy for individuals with lung cancer and to provide evidence supporting its clinical use.
2 Materials and methods
This systematic review was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; registration number: CRD42024619038) to ensure transparency and alignment with established review standards. No amendments have been made since registration. The review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Page et al., 2021), the PRISMA extension for Chinese Herbal Medicines 2020 (Zhang et al., 2020), and the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins et al., 2024) to maintain methodological rigor. The PRISMA Checklist is provided in Supplementary Table S1.
2.1 Search strategy
The final systematic literature search was completed on 3 March 2025, across the following electronic databases: MEDLINE via PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Oriental Medicine Advanced Searching Integrated System, Korean Studies Information Service System, Research Information Sharing Service, ScienceON, Korean Medical Database, China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database, and Citation Information by Nii. No language restrictions were applied to minimize selection bias and ensure comprehensive inclusion. The search terms included “lung cancer,” “Yukgunja-Tang,” and “RCT,” along with their synonyms. The comprehensive search strategy, including the exact search strings with all keywords and Boolean operators for each of the 10 databases, is provided in Supplementary Table S2.
2.2 Eligibility criteria
2.2.1 Participants
Eligible studies included patients diagnosed with lung cancer. No restrictions were applied regarding baseline characteristics such as age or sex.
2.2.2 Intervention and control
Interventions comprised studies investigating YGJT and its modified formulations. The original formulation included Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma (P. ginseng C. A. Mey.), Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma (A. macrocephala Koidz.), Poria (M. cocos (Schwein.) I.Johans. & Ryvarden), Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma (G. uralensis Fisch. ex DC.), Pinelliae Rhizoma (P. ternata (Thunb.) Makino), and Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium (C. reticulata Blanco). Commonly used herbal substitutes in traditional East Asian medicine were also considered; for example, Codonopsis Radix (Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf.) or Pseudostellariae Radix (Pseudostellaria heterophylla (Miq.) Pax) may replace Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma, and Atractylodis Rhizoma (Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC.) may substitute Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma.
Modified YGJT was defined as any prescription that included the six core herbs of YGJT (or their accepted substitutes) plus one or more additional herbs. Variants included modified Hyangsayukgunja-tang (HSYGJT), modified Jigilyukgunja-tang (JGYGJT), and modified Jichulyukgunja-tang (JCYGJT).
The intervention group received modified YGJT, described as “Yukgunja,” “Liujunzi,” or “Rikkunshi,” in combination with antitumor therapies such as surgery, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or cellular therapies, with or without symptom management medications. The control group received either a placebo version of modified YGJT in addition to antitumor therapy or antitumor therapy alone, with symptom management medications, as applicable. Studies using other herbal medicines or traditional East Asian therapies in either group were excluded.
2.2.3 Outcomes
Primary outcomes included objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) scores. ORR was defined as the proportion of patients achieving complete or partial response, and DCR as the proportion achieving complete response, partial response, or stable disease, based on the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (Wilson et al., 2015). KPS was assessed on a scale from 100 (normal functioning) to 0 (death) in 10-point intervals (Karnofsky, 1949). Changes in KPS were categorized as follows: improvement (≥10-point increase), deterioration (≥10-point decrease), and stable (±10-point change). The improvement rate was calculated as the proportion of patients with improved KPS out of the total. Secondary outcomes included clinical symptom scores; immune function indicators (CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, and natural killer cells); tumor markers (including carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), cytokeratin 19 fragment 21-1 (CYFRA 21-1), neuron-specific enolase (NSE), squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC), and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9)); and adverse events such as myelosuppression, leukopenia, and digestive tract reactions. Clinical symptom scores were evaluated as both dichotomous and continuous variables. The dichotomous outcome was measured using the total effective rate, calculated as the percentage of participants categorized as cured, markedly effective, or improved, divided by the total number of participants. The continuous outcome was assessed using the Traditional East Asian Medicine Symptom Score, in accordance with the Guidelines for Clinical Research on New Chinese Medicine published by the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China (Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, 2002). For digestive tract reactions reported as separate symptoms (e.g., nausea and vomiting), the maximum reported prevalence was used as a conservative estimate to avoid overestimation due to symptom overlap (Stewart et al., 2020). A meta-analysis of adverse events was conducted when at least two studies reported data for the same outcome. All outcomes were evaluated at the earliest available post-treatment time point. No restrictions were applied regarding the timing of outcome assessment.
2.2.4 Study design
Only RCTs with a parallel design were included. Studies without full-text availability, case reports, case series, reviews, observational studies, non-RCTs, animal studies, and in vitro studies were excluded. This restriction to RCTs was implemented to ensure the highest level of evidence on therapeutic efficacy and to minimize the significant risk of confounding and selection bias inherent in other study designs.
2.3 Study selection and data extraction
Search results were imported into EndNote 21 (Clarivate, Philadelphia, PA, USA) for reference management. Duplicate records were initially removed using the built-in deduplication feature. Two independent reviewers (KSW and HSJ) screened the titles and abstracts of retrieved studies against predefined inclusion criteria. Full texts of potentially eligible articles were subsequently assessed to determine final eligibility. Reasons for exclusion after full-text review are provided in Supplementary Table S3. Discrepancies between reviewers were resolved through discussion with a third reviewer (LBJ). The complete selection process was documented using a PRISMA flow diagram.
Data extraction was independently performed by the same two reviewers (KSW and HSJ), who collected information on the following variables: study title, first author, publication year, patient age and sex, sample sizes in the experimental and control groups, lung cancer type, TNM stage, intervention characteristics (herbal medicine components and dosing frequency), treatment duration, and outcome measures. All extracted data were cross-checked for accuracy, and inconsistencies were resolved in consultation with the third reviewer (LBJ).
2.4 Quality assessment
The risk of bias for each included RCT was assessed independently by two reviewers (KSW and HSJ) using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool (Higgins et al., 2024). The assessment covered five domains: the randomization process, deviations from intended interventions, missing outcome data, outcome measurement, and selection of the reported results. Disagreements were resolved through discussion with a third reviewer (LBJ).
2.5 Certainty of evidence
The certainty of evidence for each outcome was independently evaluated by two reviewers (KSW and HSJ) using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach. In cases of disagreement, consensus was achieved through discussion with a third reviewer (LBJ). A Summary of Findings table was generated using the GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool (GRADEpro GDT, 2025). The certainty of evidence was categorized as very low, low, moderate, or high, based on considerations including risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and publication bias.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Meta-analyses were conducted using Review Manager version 5.4 (Cochrane Collaboration), R software version 4.4.0 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria), and the “metafor” package version 4.6.0 (Viechtbauer, 2010). Risk ratios (RRs) were calculated for dichotomous outcomes, and mean differences (MDs) for continuous outcomes, both with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). All included studies provided complete and extractable data; thus, no imputation or transformation of summary statistics was necessary. For outcomes reported in 10 or more studies, potential publication bias was assessed through visual inspection of funnel plots generated using Review Manager 5.4, and formally with Egger’s test, which was conducted using the “metafor” package in R. A random-effects model was applied for all meta-analyses. This choice was made a priori due to the anticipated clinical heterogeneity stemming from variations in the modified YGJT, patient populations, and treatment durations across studies. This model was therefore considered more appropriate for providing a conservative estimate of the overall treatment effect. Forest plots were generated using Review Manager 5.4.
2.7 Subgroup analysis and assessment of heterogeneity
Pre-specified subgroup analyses were conducted based on the type of anti-tumor therapy, YGJT formulation, comparator group (placebo vs. no additional treatment), cancer stage (early vs. advanced), and lung cancer type (non-small cell lung cancer [NSCLC] vs. small cell lung cancer [SCLC]). Subgroup analyses were performed only when at least two studies were available for a given comparison. Heterogeneity was assessed by visual inspection of forest plots and quantified using the I2 statistic (Higgins et al., 2003).
2.8 Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analyses were conducted to evaluate the robustness of the overall findings. Specifically, we examined outcomes in studies involving patients with advanced-stage lung cancer. An additional sensitivity analysis was performed for studies that applied pattern identification as a diagnostic criterion to assess whether this approach influenced treatment outcomes.
3 Results
3.1 Retrieval results
A total of 147 studies were retrieved from the 10 databases. Following the removal of duplicates and screening of titles and abstracts, full-text reviews were conducted for 39 studies to determine eligibility. Eight studies were excluded due to inappropriate study design, non-compliance with the review criteria for the intervention, or lack of original research content. Ultimately, 31 RCTs involving 2,496 participants were included (Figure 1; Supplementary Table S3).
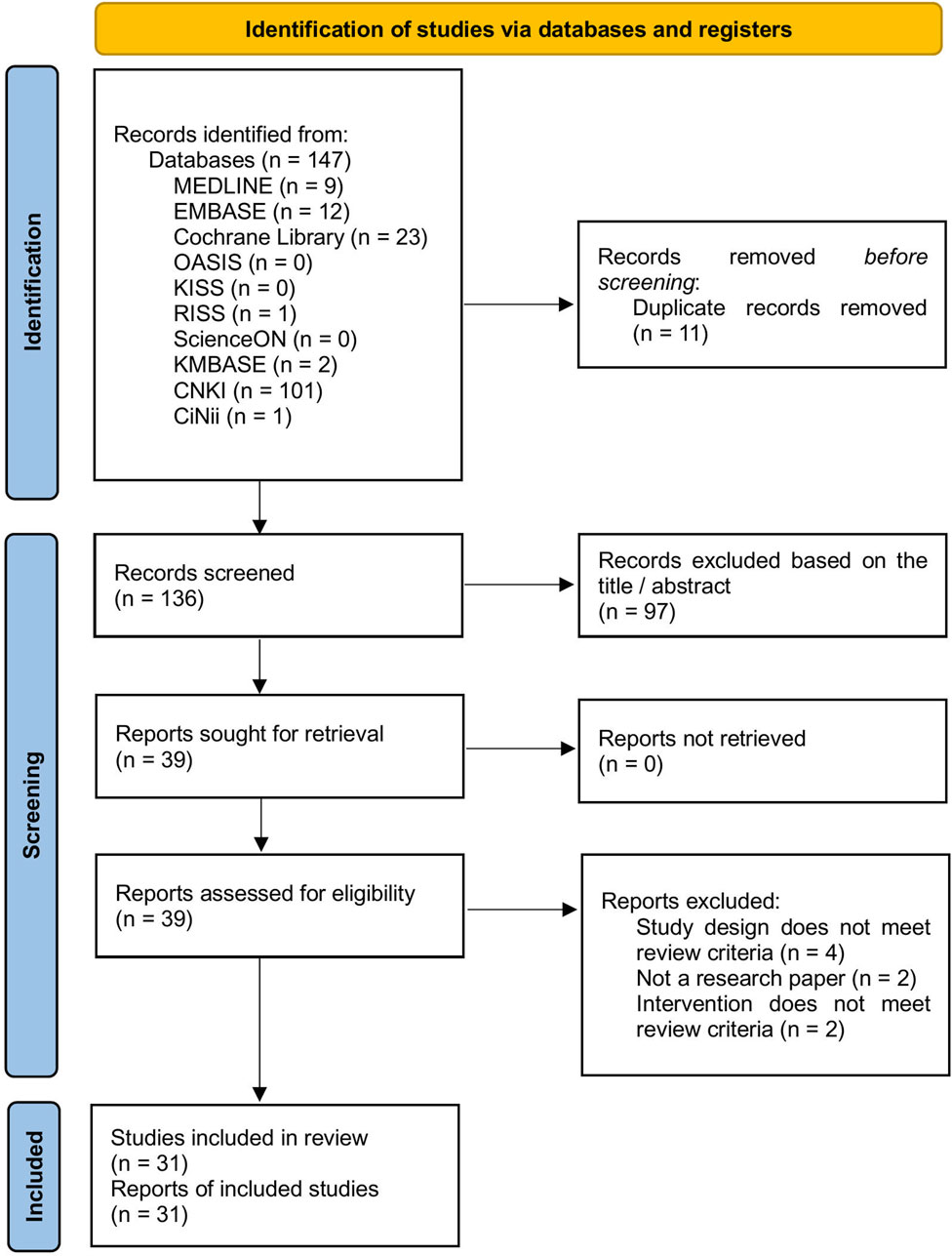
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram. CiNii, Citation Information by Nii; CNKI, China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database; KISS, Korean Studies Information Service System; KMBASE, Korean Medical Database; OASIS, Oriental Medicine Advanced Searching Integrated System; RISS, Research Information Sharing Service.
3.2 Characteristics of included studies
Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of the included studies, including first author, publication year, sex, age, sample size, type of lung cancer, TNM stage, intervention details, treatment duration, and outcome measures Table 2; Supplementary Table S4 list the names of the herbal medicines, authors, publication years, principal components, and any modifications.
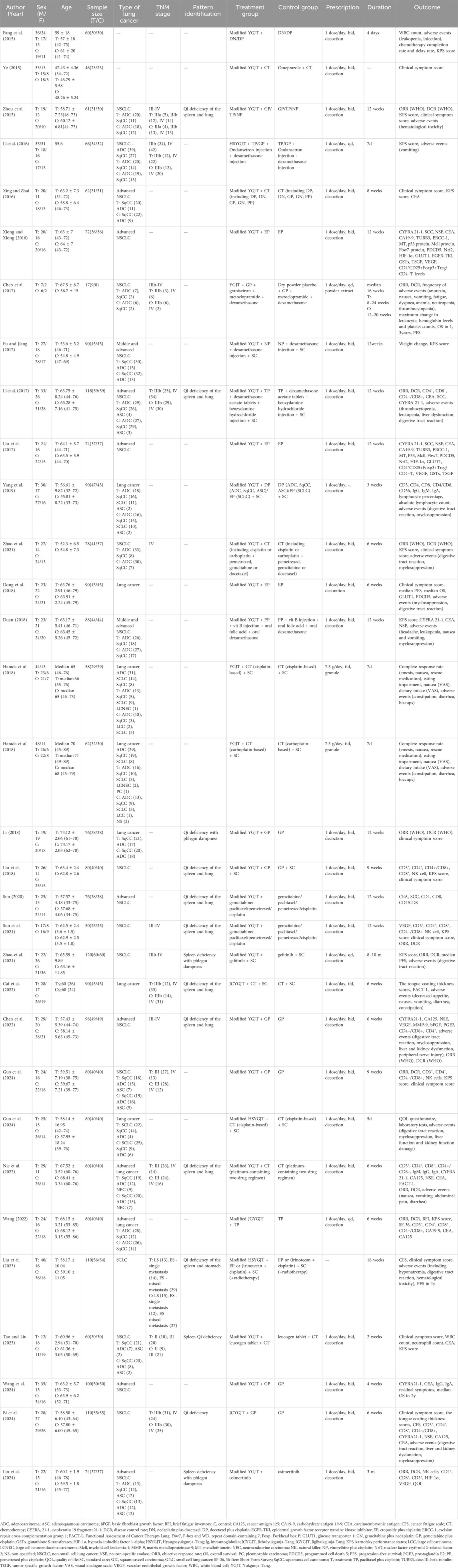
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the 31 randomized controlled trials included in the systematic review.
The 31 RCTs enrolled a total of 2,496 patients: 1,256 in the treatment group and 1,240 in the control group. Harada et al. (2018) were analyzed as two separate entries Harada et al. (2018), as they reported outcomes separately for cisplatin- and carboplatin-based chemotherapy. The studies by Harada et al. (2018) were conducted in Japan, while all other studies were conducted in China, with publication years ranging from 2015 to 2024. Sample sizes ranged from 17 to 120 participants, and treatment durations varied from 4 to 10 months.
The modified YGJT formulations included YGJT, HSYGJT, JGYGJT, JCYGJT, and several variants of these formulations. In 29 studies, both groups received chemotherapy, while two studies used EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in both groups (Zhao et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2024). Of the 31 studies, 29 compared modified YGJT combined with antitumor therapy against antitumor therapy alone. One study by Ye (2015) compared modified YGJT plus chemotherapy with omeprazole plus chemotherapy, while another by Chen et al. (2017) compared modified YGJT plus chemotherapy with placebo plus chemotherapy. These two studies were excluded from the meta-analysis due to the absence of comparable study designs. Accordingly, only studies directly comparing modified YGJT plus antitumor therapy with antitumor therapy alone were included to maintain methodological consistency and allow reliable meta-analysis.
Fifteen studies incorporated traditional East Asian pattern identification as a diagnostic criterion. Qi deficiency was reported across all studies. The distribution of specific syndromes was as follows:
• Qi deficiency of the spleen and lung: eight studies (Zhou et al., 2015; Li et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2018; Sun, 2020; Sun et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2022; Nie et al., 2022; Wang, 2022),
• Spleen deficiency with phlegm dampness: two studies (Zhao et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2024),
• Qi deficiency with phlegm dampness: two studies (Li, 2018; Bi et al., 2024),
• Spleen Qi deficiency: one study (Tao and Liu, 2023),
• Qi deficiency of the spleen and stomach: one study (Liu et al., 2023), and Qi deficiency (unspecified): one study (Cai et al., 2022).
3.3 Risk of bias
All 31 RCTs were evaluated for the risk of bias (Figure 2).
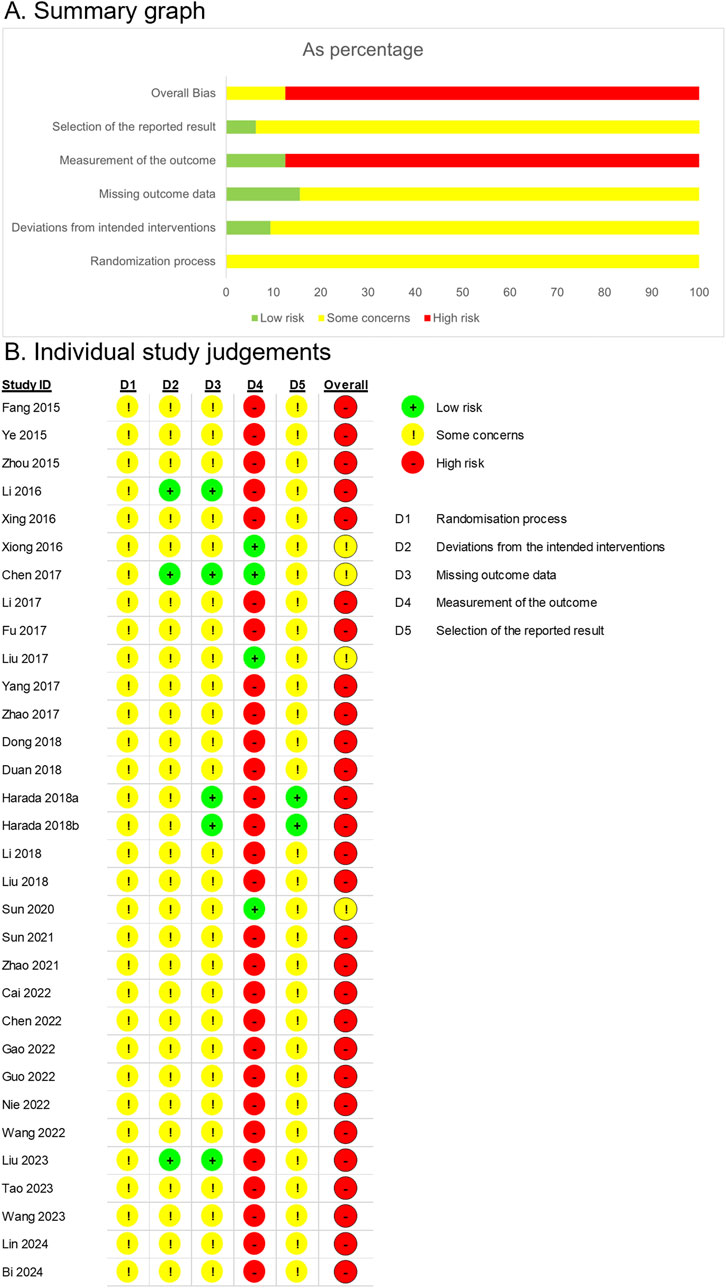
Figure 2. Risk of bias assessment based on the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool. (A) Summary graph. (B) Individual study judgements.
In all the studies, the allocation sequence was either random or not reported, and no baseline differences were observed between the intervention groups. However, due to insufficient information on allocation concealment, the randomization process was rated as having some concerns.
For bias due to deviations from intended interventions, both participants and intervention providers were aware of the interventions assigned in the studies by Li et al. (2016) and Liu et al. (2023). However, the authors explicitly reported no dropouts, and all randomized participants were analyzed according to their allocated groups, suggesting that an intention-to-treat approach was likely followed. As there were no apparent deviations from the intended interventions, these studies were assessed to have a low risk of bias. Chen et al. (2017) employed a placebo, which likely ensured blinding of participants and intervention providers. The study explicitly stated that no dropouts occurred, and all randomized participants were included in the follow-up. Given these conditions, intention-to-treat analysis appeared to have been conducted, and the study was evaluated as having a low risk of bias. In contrast, Harada et al. (2018) reported one dropout outside the clinical trial context, where participants and intervention providers were aware of the assigned interventions. A per-protocol analysis was performed, and a single deviation was deemed unlikely to substantially affect the results. Consequently, this study was rated as having certain limitations. Zhao et al. (2021) conducted a study under conditions where both participants and intervention providers were aware of the assigned interventions. In the treatment group, there were instances of loss to follow-up, while in the control group, some participants discontinued the treatment, suggesting the possibility of deviation within the clinical trial context. Although no information was provided on whether these deviations influenced the outcomes, they appeared balanced between the two groups, and a per-protocol analysis, which excluded less than 5% of the participants, indicated a minimal likelihood of a significant impact on the results. Consequently, the study was rated as having concerns regarding risk of bias. In other studies, participants and intervention providers were aware of the assigned interventions; however, information on deviations and intention-to-treat analysis was not reported. All studies reported the results for all randomized participants; therefore, no substantial impact on the outcomes was evident. Thus, these studies were rated as having some concerns regarding the risk of bias.
Regarding missing outcome data, Li et al. (2016), Chen et al. (2017), Harada et al. (2018), and Liu et al. (2023) explicitly reported no dropouts, indicating a low risk of bias. Harada et al. (2018) reported a missing outcome due to disease progression before treatment initiation. Since this dropout rate was unlikely to be related to the true outcome value, the study was rated as having a low risk of bias. Zhao et al. (2021) reported dropouts in both groups, resulting in missing outcomes. However, the dropout rates and reasons were similar between the intervention and control groups, leading to some concerns. For the remaining studies, information on missing data was unavailable. Nonetheless, there were no indications of imbalanced dropout rates or differing reasons between the groups, and the results were reported for the full number of randomized participants. Consequently, these studies were rated as having some concerns regarding the risk of bias.
In Chen et al. (2017), the study was rated low risk due to the use of a placebo-controlled design. In Xiong and Xiong (2016), Liu et al. (2017), and Sun (2020), it is unlikely that the assessment of outcomes such as tumor response, immune markers, and tumor markers was influenced by awareness of the intervention received, resulting in a low rating of bias in the measurement of the outcome. In other studies, a modified YGJT was administered as an add-on therapy, and outcomes included subjective measures, leading to a high risk of bias in the outcome measurement.
Thirty studies were rated as having some concerns due to the lack of protocols. However, the study by Harada et al. (2018) was assessed as low risk, as it was conducted based on a predefined protocol.
3.4 Modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus anti-tumor therapy alone
3.4.1 ORR (primary outcome)
Seven RCTs, comprising 657 participants, reported the ORR. The modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy group showed a statistically significant improvement in ORR compared to the anti-tumor therapy alone group (RR 1.69, 95% CI 1.41 to 2.04, p < 0.00001) (Figure 3A). No significant heterogeneity was detected (p = 0.91, I2 = 0%). Subgroup analysis based on the type of anti-tumor therapy yielded results consistent with the main findings for both chemotherapy (RR 1.71, 95% CI 1.36 to 2.15; 5 RCTs; 468 participants) and EGFR-TKI (RR 1.66, 95% CI 1.20 to 2.30; 2 RCTs; 189 participants).
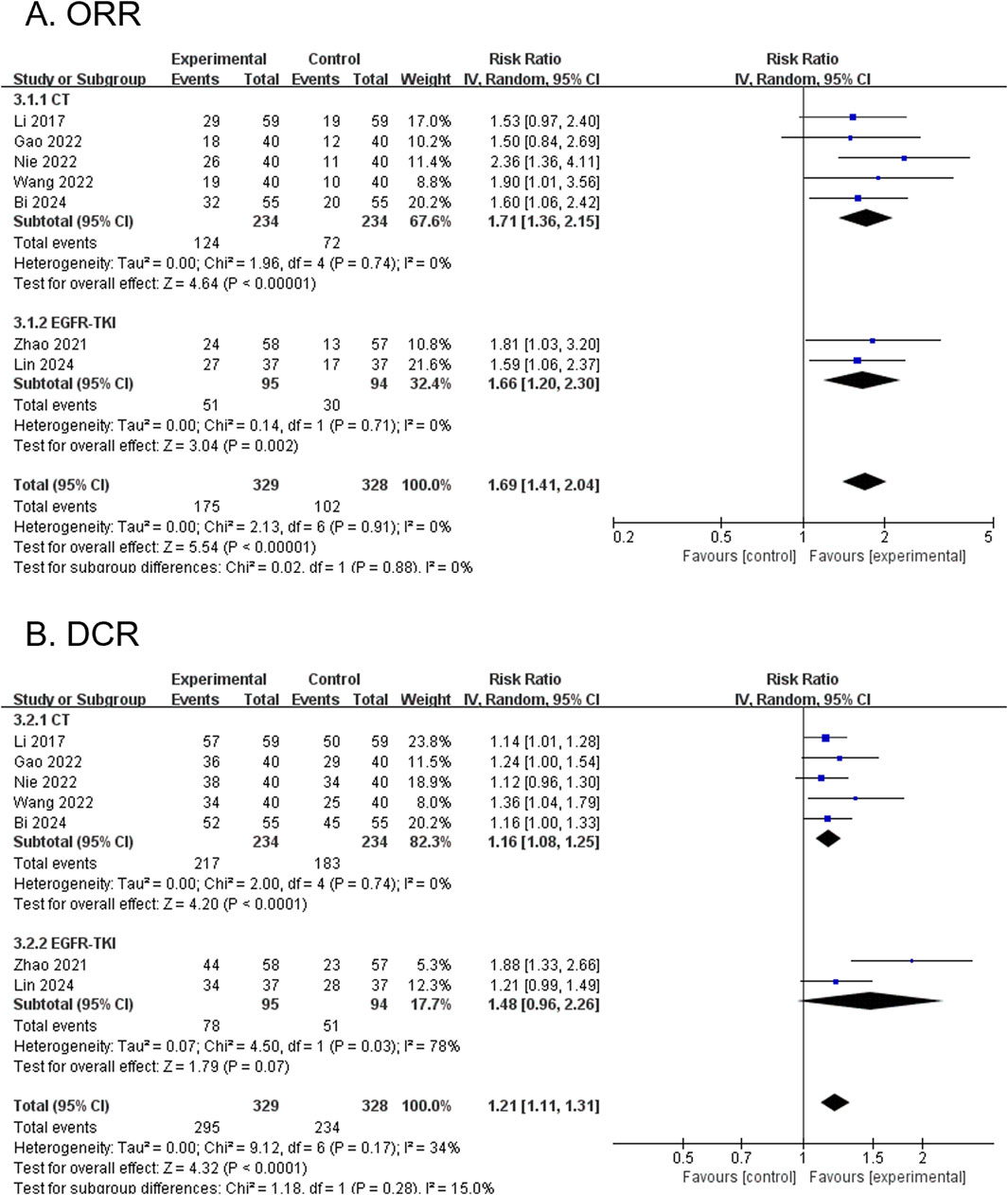
Figure 3. Forest plots comparing the effect of modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus anti-tumor therapy alone on tumor response outcomes. (A) Objective response rate (ORR). (B) Disease control rate (DCR). CI, confidence interval; CT, chemotherapy; EGFR-TKI, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor; IV, inverse variance; YGJT, Yukgunja-tang.
3.4.2 DCR (primary outcome)
Seven RCTs, comprising 657 participants, reported the DCR. The modified YGJT intervention group demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in DCR compared to the control group (RR 1.21, 95% CI 1.11 to 1.31, p < 0.0001) (Figure 3B). Low heterogeneity was detected (p = 0.17, I2 = 34%). In the subgroup analysis by type of anti-tumor therapy, a significant effect was observed in the chemotherapy group (RR 1.16, 95% CI 1.08 to 1.25; 5 RCTs; 468 participants), whereas the EGFR-TKI group did not show a statistically significant result (RR 1.48, 95% CI 0.96 to 2.26; 2 RCTs; 189 participants).
3.4.3 KPS score (dichotomous) (primary outcome)
Six RCTs, comprising 470 participants, reported dichotomous outcomes for KPS scores. The modified YGJT intervention group showed a significant improvement in KPS scores compared to the control group (RR 1.79, 95% CI 1.23 to 2.60, p = 0.002) (Figure 4A). Moderate heterogeneity was observed (p = 0.04, I2 = 56%). Subgroup analysis was not performed due to fewer than two studies per subgroup.
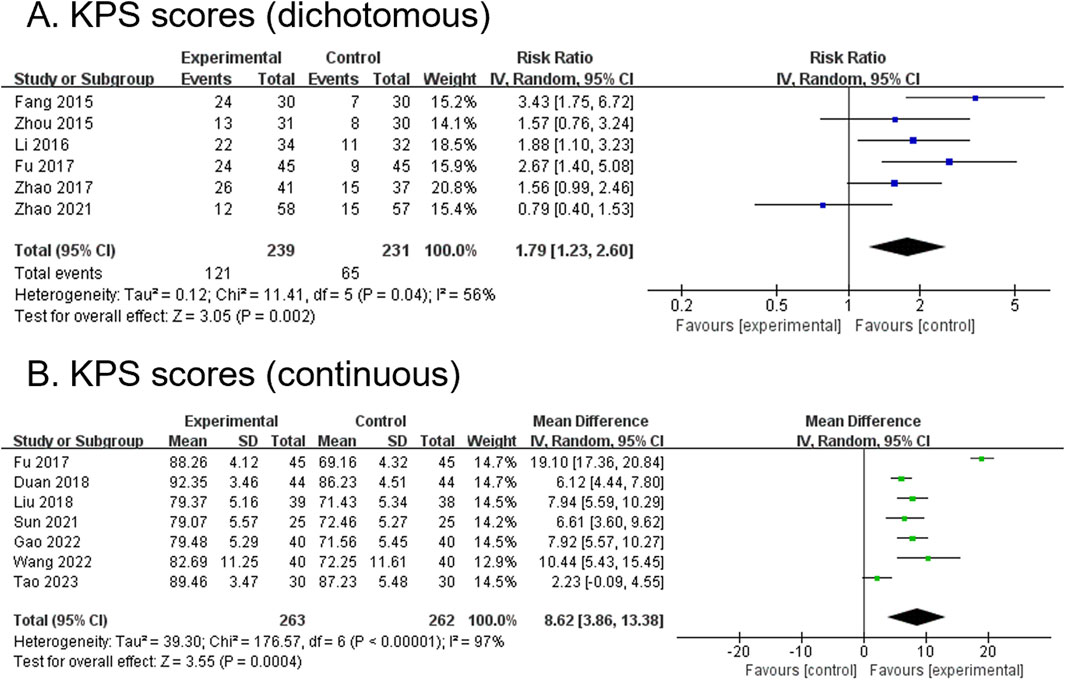
Figure 4. Forest plots comparing the effect of modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus anti-tumor therapy alone on Karnofsky Performance Status scores. (A) Dichotomous. (B) Continuous. CI, confidence interval; IV, inverse variance; SD, standard deviation; YGJT, Yukgunja-tang.
3.4.4 KPS score (continuous) (primary outcome)
Seven RCTs, comprising 525 participants, reported continuous outcomes for the KPS score. The modified YGJT intervention group demonstrated a significant increase in KPS scores compared to the control group (MD 8.62, 95% CI 3.86 to 13.38, p = 0.0004) (Figure 4B). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.00001, I2 = 97%). Subgroup analysis could not be performed because fewer than two studies were available for each subgroup.
3.4.5 Clinical symptom score (dichotomous) (secondary outcome)
Four RCTs, comprising 277 participants, reported dichotomous outcomes for clinical symptom scores. The modified YGJT group showed a significant improvement in clinical symptom scores compared to the control group (RR 1.52, 95% CI 1.25 to 1.85, p < 0.0001) (Figure 5A). No significant heterogeneity was observed (p = 0.84, I2 = 0%). Subgroup analysis was not conducted due to insufficient data across the groups.
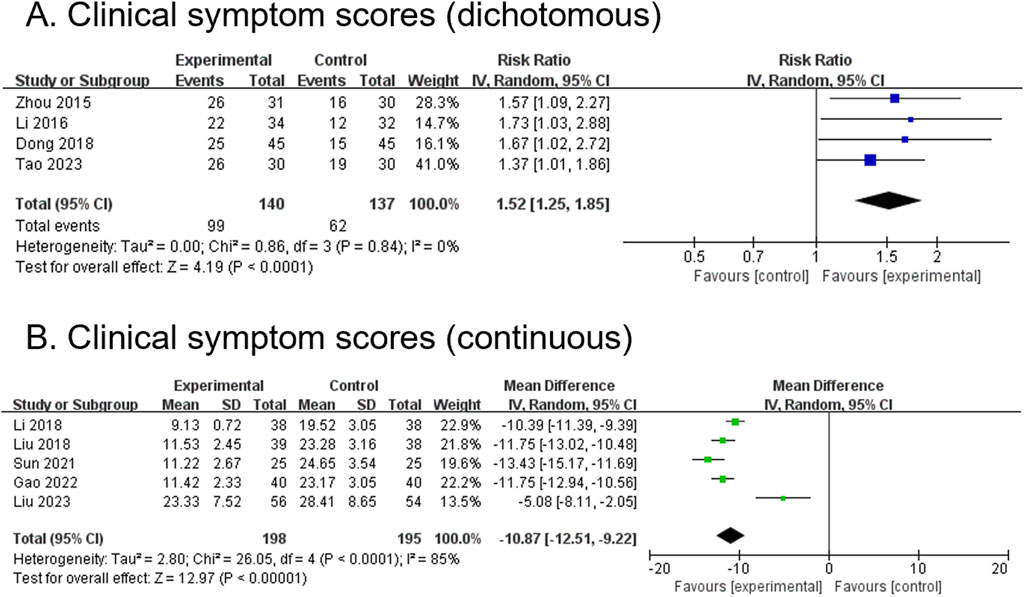
Figure 5. Forest plots comparing the effect of modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus anti-tumor therapy alone on clinical symptom scores. (A) Dichotomous. (B) Continuous. CI, confidence interval; IV, inverse variance; SD, standard deviation; YGJT, Yukgunja-tang.
3.4.6 Clinical symptom score (continuous) (secondary outcome)
Five RCTs, comprising 393 participants, reported continuous outcomes for clinical symptom scores. The modified YGJT group showed a significant reduction in clinical symptoms compared to the control group (MD -10.87, 95% CI -12.51 to −9.22, p < 0.00001) (Figure 5B). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.0001, I2 = 85%). Subgroup analysis was not performed due to insufficient data.
3.4.7 CD3+ (secondary outcome)
A total of 8 RCTs, comprising 641 participants, reported CD3+ levels. The modified YGJT group showed a significant increase in CD3+ levels compared to the control group (MD 8.38, 95% CI 4.47 to 12.28, p < 0.0001) (Figure 6A). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.00001, I2 = 96%). Subgroup analysis was not feasible due to limited data within the relevant groups.
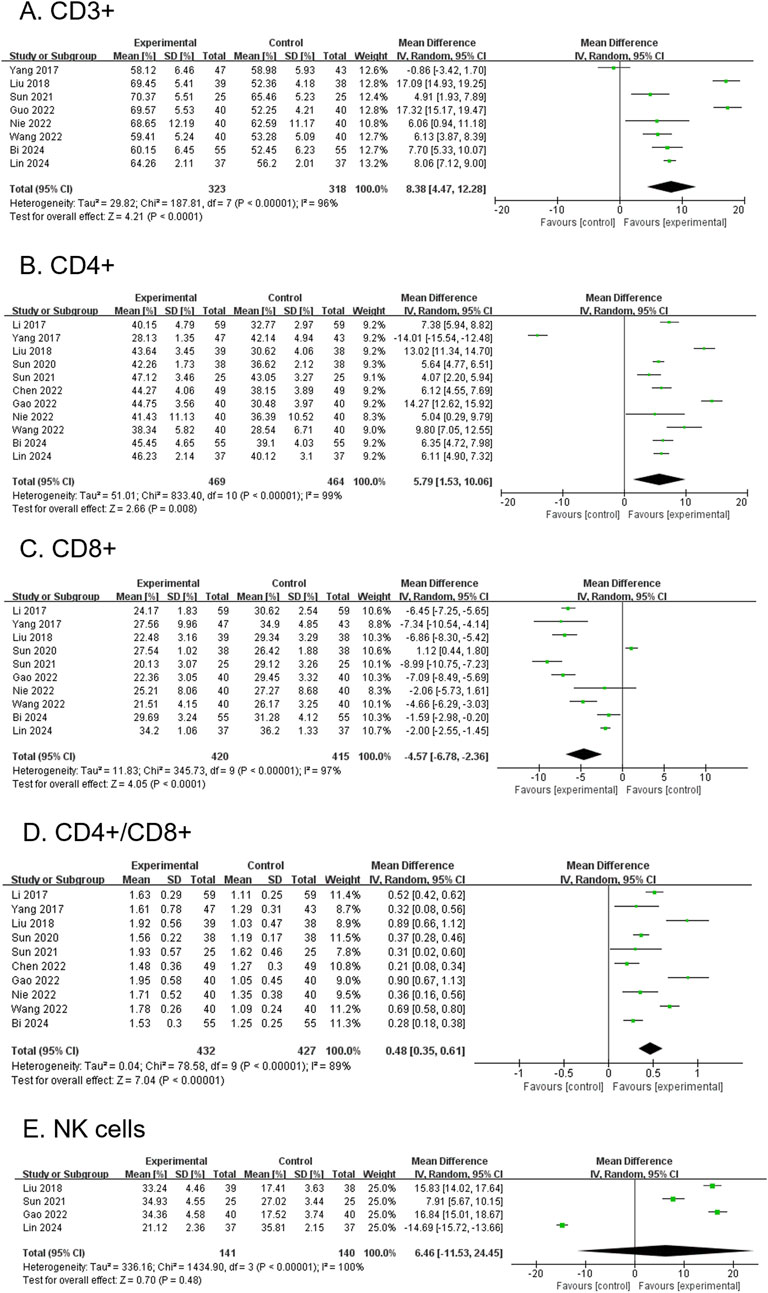
Figure 6. Forest plots comparing the effect of modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus anti-tumor therapy alone on immune function markers. (A) CD3+. (B) CD4+. (C) CD8+. (D) CD4+/CD8+. (E) NK Cells. CI, confidence interval; IV, inverse variance; SD, standard deviation; YGJT, Yukgunja-tang.
3.4.8 CD4+ (secondary outcome)
A total of 11 RCTs, involving 933 participants, reported CD4+ levels. The modified YGJT group showed a significant increase in CD4+ levels compared to the control group (MD 5.79, 95% CI: 1.53–10.06, p = 0.008) (Figure 6B). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.00001, I2 = 99%). The funnel plot suggested a potential publication bias; however, Egger’s test revealed no evidence of bias, with a regression intercept (bias) of 5.0421 (p = 0.8679) (Supplementary Figure S1A). Subgroup analysis was not feasible due to limited data across the relevant groups.
3.4.9 CD8+ (secondary outcome)
Ten RCTs, involving 835 participants, reported CD8+ levels. The modified YGJT group showed a significant reduction in CD8+ levels compared to the control group (MD -4.57, 95% CI: −6.78 to −2.36, p < 0.0001) (Figure 6C). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.00001, I2 = 97%). The funnel plot showed no clear evidence of publication bias, and Egger’s test did not suggest significant publication bias or a small-study effect (Egger’s regression intercept = −3.2948, p = 0.4843) (Supplementary Figure S1B). Subgroup analysis was not possible due to insufficient data across the relevant groups.
3.4.10 CD4+/CD8+ (secondary outcome)
Ten RCTs, involving 859 participants, reported CD4+/CD8+ ratios. The modified YGJT group showed a significant increase in the CD4+/CD8+ ratio compared to the control group (MD 0.48, 95% CI: 0.35 to 0.61, p < 0.00001) (Figure 6D). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.00001, I2 = 89%). The funnel plot showed no clear evidence of publication bias, and Egger’s test did not detect significant publication bias or a small-study effect (Egger’s regression intercept = 0.3616, p = 0.5395) (Supplementary Figure S1C). A subgroup analysis was not performed due to insufficient data across the study groups.
3.4.11 NK cell (secondary outcome)
Four RCTs, involving 281 participants, reported NK cell levels. The modified YGJT group exhibited an increase in NK cell levels compared to the control group; however, this was not statistically significant (MD 6.46, 95% CI: −11.53 to 24.45, p = 0.48) (Figure 6E). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.00001, I2 = 100%). Subgroup analysis was not feasible due to limited data.
3.4.12 CEA (secondary outcome)
Eleven RCTs, involving 920 participants, reported CEA levels. The modified YGJT group showed a significant reduction in CEA levels compared to the control group (MD -6.53, 95% CI: −8.72 to −4.33, p < 0.00001) (Figure 7A). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.00001, I2 = 97%). The funnel plot suggested potential publication bias or a small-study effect, as confirmed by Egger’s test (Egger’s regression intercept (bias) = −2.2596, p = 0.0025) (Supplementary Figure S1D). Subgroup analysis was not conducted due to limited subgroup data.
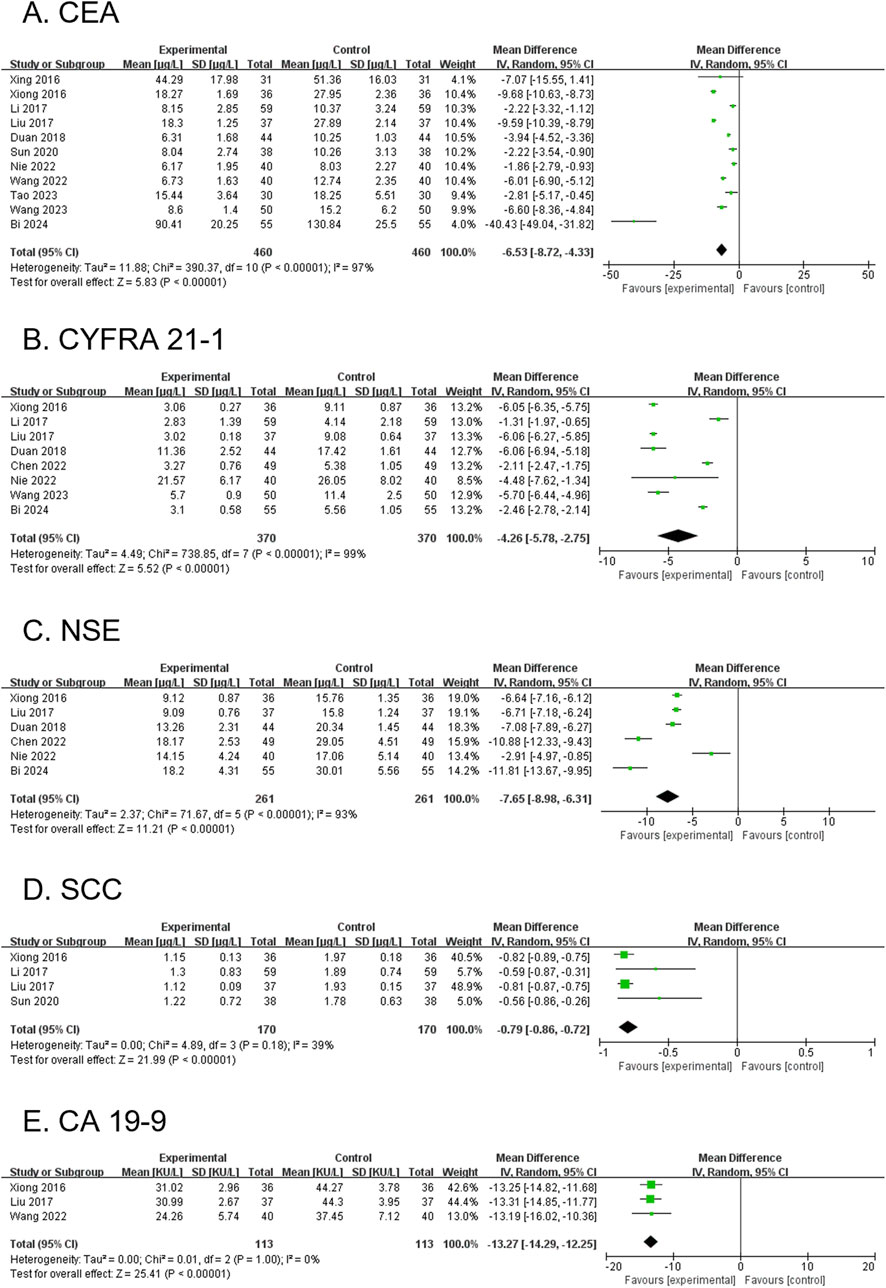
Figure 7. Forest plots comparing the effect of modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus anti-tumor therapy alone on tumor markers. (A) CEA. (B) CYFRA 21-1. (C) NSE. (D) SCC. (E) CA 19-9. CI, confidence interval; IV, inverse variance; SD, standard deviation; YGJT, Yukgunja-tang.
3.4.13 CYFRA 21-1 (secondary outcome)
Eight RCTs, involving 740 participants, reported CYFRA 21-1 levels. The modified YGJT group showed a significant reduction in CYFRA 21-1 levels compared to the control group (MD -4.26, 95% CI: −5.78 to −2.75, p < 0.00001) (Figure 7B). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.00001, I2 = 99%). Planned subgroup analysis could not be performed due to limited subgroup data.
3.4.14 NSE (secondary outcome)
Six RCTs, involving 522 participants, reported NSE levels. The modified YGJT group exhibited a significant reduction in NSE levels compared to the control group (MD -7.65, 95% CI: −8.98 to −6.31, p < 0.00001) (Figure 7C). Substantial heterogeneity was observed (P < 0.00001, I2 = 93%). A subgroup analysis was not conducted due to insufficient data within the subgroups.
3.4.15 SCC (secondary outcome)
Four RCTs, involving 340 participants, reported SCC antigen levels. The modified YGJT group showed a significant reduction in SCC levels compared to the control group (MD -0.79, 95% CI: −0.86 to −0.72, p < 0.00001) (Figure 7D). Moderate heterogeneity was observed (p = 0.18, I2 = 39%). A subgroup analysis was not performed due to data limitations.
3.4.16 CA19-9 (secondary outcome)
Three RCTs, involving 226 participants, reported CA19-9 levels. The modified YGJT group showed a significant reduction in CA19-9 levels compared to the control group (MD -13.27, 95% CI: −14.29 to −12.25, p < 0.00001) (Figure 7E). No significant heterogeneity was observed (p = 1.00, I2 = 0%). A subgroup analysis was not performed due to limited data across groups.
3.4.17 Myelosuppression (secondary outcome)
Seven RCTs, involving 634 participants, reported myelosuppression. The modified YGJT group showed a marginally significant reduction in myelosuppression compared to the control group (RR 0.63, 95% CI: 0.43–0.92, p = 0.02) (Figure 8A). Substantial heterogeneity was observed (p = 0.003, I2 = 69%). A subgroup analysis was not feasible due to limited data across groups.
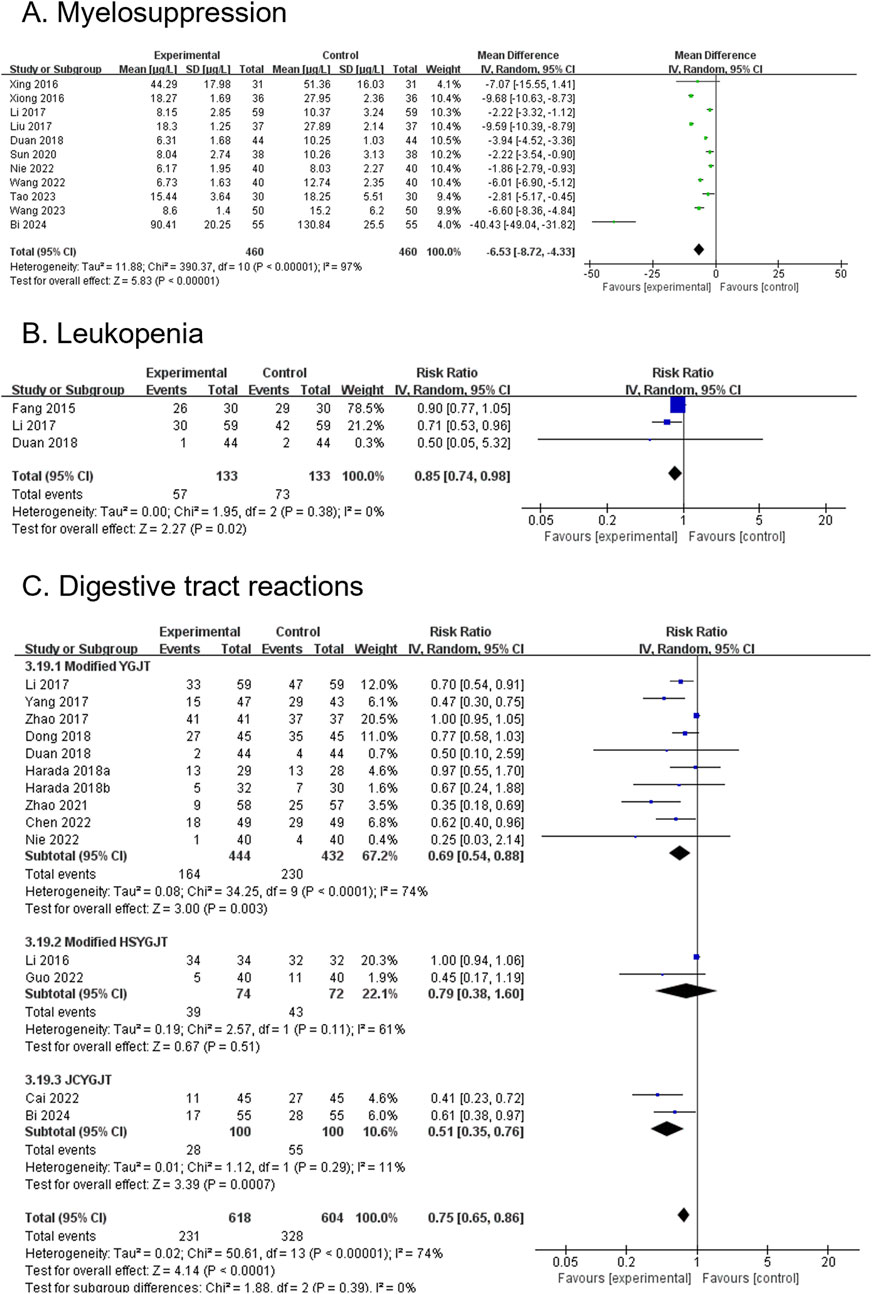
Figure 8. Forest plots comparing the effect of modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus anti-tumor therapy alone on adverse events. (A) Myelosuppression. (B) Leukopenia. (C) Digestive tract reactions. CI, confidence interval; IV, inverse variance; YGJT, Yukgunja-tang.
3.4.18 Leukopenia (secondary outcome)
Six RCTs, involving 266 participants, reported leukopenia. The modified YGJT group showed a significant reduction in leukopenia compared to the control group (RR 0.85, 95% CI: 0.74–0.98, p = 0.02) (Figure 8B). No significant heterogeneity was observed (p = 0.38, I2 = 0%). A subgroup analysis was not performed due to insufficient data.
3.4.19 Digestive tract reaction (secondary outcome)
Fourteen RCTs, involving 1,222 participants, reported digestive tract reactions. The modified YGJT group showed a significant reduction in digestive tract reactions compared to the control group (RR 0.75, 95% CI: 0.65–0.86, p < 0.0001) (Figure 8C). Substantial heterogeneity was observed (P < 0.00001, I2 = 74%). Subgroup analysis based on the type of YGJT showed results consistent with the main findings for modified YGJT (RR 0.69, 95% CI: 0.54–0.88; 10 RCTs; 876 participants) and JCYGJT (RR 0.51, 95% CI: 0.35–0.76; 2 RCTs; 200 participants). However, the effect in the modified HSYGJT group was no longer significant (RR 0.79, 95% CI: 0.38–1.60; 2 RCTs; 146 participants). The funnel plot suggested potential publication bias, and Egger’s test indicated a significant publication bias or small study effect (Egger’s regression intercept (bias) 0.0512, p < 0.0001) (Supplementary Figure S1E).
3.5 Modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus placebo plus anti-tumor therapy
Chen et al. (2017) conducted a study comparing YGJT dry powder extract with a dry powder placebo in patients with advanced NSCLC receiving gemcitabine plus cisplatin therapy. After a median treatment duration of 16 weeks, no significant differences were observed between the YGJT and placebo groups in tumor response or adverse events.
3.6 Modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus active control plus anti-tumor therapy
Ye (2015) compared modified YGJT with omeprazole in patients with lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy. The modified YGJT group showed a significantly greater improvement in clinical symptom scores compared to the omeprazole group (p < 0.05).
3.7 Sensitivity analysis
For advanced-stage lung cancer, the sensitivity analysis demonstrated the same ORR (RR 1.69, 95% CI:1.41–2.04) and DCR (RR 1.21, 95% CI: 1.11–1.31) as the primary analysis, as the studies included in both analyses were identical. Improvements were confirmed in KPS score (RR 1.43, 95% CI: 1.01–2.03; MD 7.79, 95% CI: 6.05–9.52) and clinical symptom score (RR 1.62, 95% CI: 1.20–2.19; MD -12.47, 95% CI: −14.09 to −10.84). Immune function markers, including CD3+ (MD 7.11, 95% CI: 5.90–8.32), CD4+ (MD 7.25, 95% CI: 5.36–9.13), and CD4+/CD8+ ratio (MD 0.45, 95% CI: 0.31–0.59), continued to show benefits, with a reduction in CD8+ levels (MD -3.97, 95% CI: −6.41 to −1.54). Among tumor markers, CEA (MD -7.29, 95% CI: −10.38 to −4.20), CYFRA 21-1 (MD -3.64, 95% CI: −5.59 to −1.70), NSE (MD -8.10, 95% CI: −11.27 to −4.93), SCC (MD -0.70, 95% CI: −0.88 to −0.52), and CA19-9 (MD -13.28, 95% CI: −14.63 to −11.93) all showed consistent reductions in sensitivity analysis. The analysis also found reductions in myelosuppression (RR 0.63, 95% CI: 0.33–1.21), leukopenia (RR 0.71, 95% CI: 0.53–0.96), and digestive tract reactions (RR 0.79, 95% CI: 0.68–0.92). In contrast, the effect on NK cells (MD 3.34, 95% CI: −18.12–24.80) was less conclusive due to wide confidence intervals.
In studies that incorporated pattern differentiation as part of the diagnostic criteria, the results demonstrated a slightly higher ORR (RR 1.72, 95% CI 1.41–2.09) and a comparable DCR (RR 1.21, 95% CI 1.10–1.33) compared to the primary analysis and the sensitivity analysis for advanced cancer. Improvements in the KPS score were maintained; however, the effect weakened in the continuous analysis (MD 6.48, 95% CI 3.10–9.86) and became statistically non-significant in the dichotomous analysis (RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.56–2.16). Similarly, clinical symptom scores retained their directionality but showed a reduced effect size (RR 1.45, 95% CI 1.14 to 1.83; MD -10.51, 95% CI -12.73 to −8.29). Immune function markers, including CD3+ (MD 8.46, 95% CI 5.08–11.84), CD4+ (MD 7.10, 95% CI 5.46–8.73), and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (MD 0.45, 95% CI 0.31–0.59), continued to demonstrate benefits. CD8+ levels still decreased but with a reduced magnitude (MD -3.94, 95% CI -6.36 to −1.53), while NK cell levels showed a significant reduction (MD -5.17, 95% CI -6.00 to −4.34). For tumor markers, such as CEA (MD -5.56, 95% CI -8.32 to −2.80), CYFRA 21-1 (MD -2.10, 95% CI -2.65 to −1.54), NSE (MD -8.57, 95% CI -13.61 to −3.52), SCC (MD -0.58, 95% CI -0.78 to −0.37), and CA19-9 (MD -13.19, 95% CI -16.02 to −10.36), the results remained consistent or showed a slight attenuation compared to the primary analysis and the advanced cancer sensitivity analysis. Regarding adverse events, studies incorporating pattern differentiation demonstrated greater reductions in myelosuppression (RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.27–0.74), leukopenia (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.53–0.96), and digestive tract reactions (RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.46–0.72). A comprehensive summary comparing the results of these sensitivity analyses with the main analysis for all outcomes is presented in Table 3.
3.8 Certainty of evidence
The certainty of the evidence was assessed using the GRADE approach, with detailed results presented in Table 4. The outcomes assessed included ORR, DCR, and clinical symptom score (dichotomous), rated as high; SCC and CA19-9, rated as moderate; NK cell, CEA, and digestive tract reactions, rated as very low; and the remaining outcomes, rated as low.
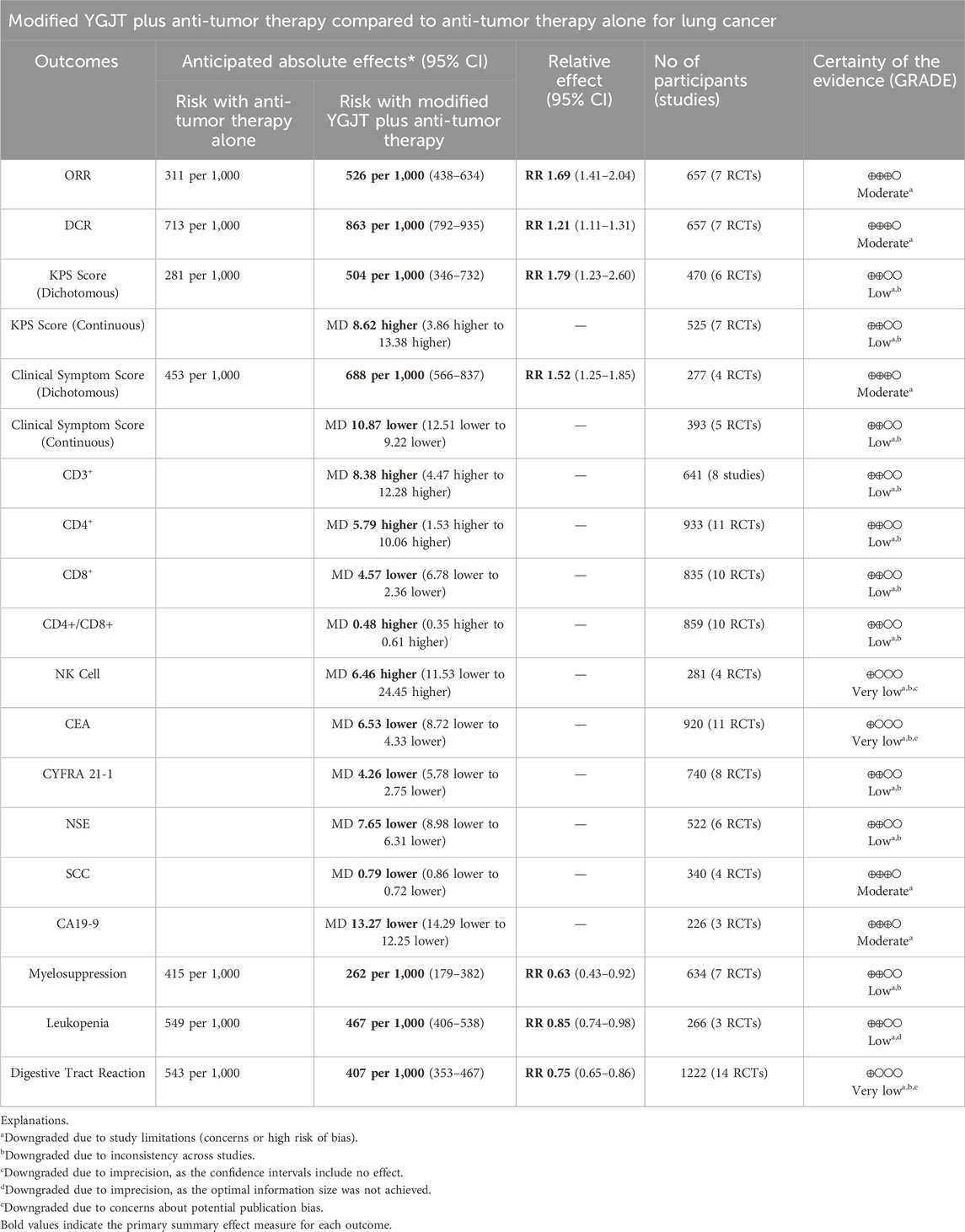
Table 4. GRADE summary of findings for the comparison of modified YGJT plus anti-tumor therapy versus anti-tumor therapy alone.
All outcomes were downgraded due to the risk of bias. The KPS score, clinical symptom score (continuous), CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, NK cells, CEA, CYFRA 21-1, NSE, myelosuppression, and digestive tract reaction were further downgraded by one level due to inter-study inconsistencies. NK cell levels were additionally downgraded by one level for imprecision because the confidence interval included the null effect (0). Leukopenia was downgraded by one level for imprecision because the optimal information size criterion was not met. The digestive tract reaction was downgraded by one level due to indications of potential publication bias.
4 Discussion
This systematic review included 31 RCTs with 2,496 participants who met the inclusion criteria. Modified YGJT combined with antitumor therapy improved both ORR and DCR compared to antitumor therapy alone. Furthermore, YGJT significantly enhanced patients’ quality of life and immune function, while reducing tumor markers and treatment-related adverse events.
Lung cancer has the highest incidence and mortality of all cancers worldwide, with an estimated annual incidence of 2.48 million cases and 1.82 million deaths (Bray et al., 2024). Significant advancements have been made in standard treatment modalities, surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and immune checkpoint inhibition, along with recent progress in nano-drug delivery systems, molecular targeted therapies, photothermal approaches, and immunotherapy, all contributing to incremental improvements in survival rates (Thai et al., 2021; Li et al., 2023). Nevertheless, the 5-year survival rate remains alarmingly low, highlighting persistent challenges in disease management (Li et al., 2023). As a result, the therapeutic potential of traditional herbal medicine is increasingly recognized as a promising complementary strategy to enhance efficacy and alleviate patient burden.
In traditional East Asian medicine, the pathology of lung cancer is attributed to root deficiency with excess tip, where an underlying Qi deficiency in the spleen and lung leads to the formation of byproducts, such as blood stasis or phlegm dampness (Liu et al., 2018). This imbalance is often exacerbated during anti-tumor therapy, as patients frequently experience physical weakness manifesting as symptoms of Qi deficiency and phlegm dampness, including nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and malaise. These symptoms ultimately reduce treatment adherence and patient quality of life. To address these issues, traditional East Asian medicine applies the primary principles of “strengthening the body” and “eliminating evil,” which refer to enhancing immune defenses against tumors and inhibiting tumor growth, proliferation, and metastasis in terms of Western medicine (Li et al., 2021).
YGJT is a representative prescription for the treatment of spleen Qi deficiency and phlegm dampness. YGJT exerts effects such as tonifying the spleen and lung, benefiting Qi and nourishing blood, and expelling dampness: Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma strengthens the spleen and benefits the lung, replenishes Yuan-primordial Qi, nourishes blood, and generates fluids; Poria strengthens the spleen, calms the mind, and drains dampness; Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma tonifies the spleen and benefits the lung, dries dampness, and promotes urination; Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium harmonizes the middle jiao, circulates Qi, disperses nodules, and dries dampness; Pinelliae Rhizoma downregulates Qi, resolves masses, transforms phlegm, and dries dampness; and Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma tonifies the spleen, nourishes blood, and coordinates medicines (Nie et al., 2022).
Originally recorded in the classical text Shi Yi De Xiao Fang (Efficacious Remedies of the Physicians) as a prescription for treating symptoms such as loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, and indigestion, YGJT has since been widely used for gastrointestinal disorders (Yilin, 2009). Building on this traditional application, it has been investigated for its potential in lung cancer to manage gastrointestinal symptoms caused by the disease itself and by anticancer treatments (Wu et al., 2022). Both preclinical and clinical studies have reported that YGJT increases appetite, protects gastric mucosa, and promotes digestive fluid secretion, thereby addressing appetite loss in individuals with cancer (Sun et al., 2020; Dai et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2022). YGJT prevents anorexia and gastrointestinal dysmotility by antagonizing 5-HT2b/2c receptors in the stomach and hypothalamus, activating the ghrelin receptor GHS-R1a, and inhibiting deacylating enzymes to enhance ghrelin activity (Fujitsuka and Uezono, 2014; Yamada et al., 2021). Additionally, YGJT has demonstrated efficacy in the gastrointestinal system by improving stress-induced gastric hypersensitivity through NO-mediated pathways, promoting gastric accommodation, reducing gastric dysmotility, and inhibiting adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol (Inokuchi et al., 2021). In particular, its mechanisms in cancer-induced and chemotherapy-induced anorexia involve activation of ghrelin signaling pathways, antagonism of 5-HT2B/2C receptors, and protection of the gastrointestinal mucosal barrier (Wu et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2024). Through these mechanisms, YGJT has been shown in animal and clinical studies to prevent cancer cachexia and increase food intake following chemotherapy (Fujitsuka and Uezono, 2014; Yamada et al., 2021). This anti-cachectic effect is of high translational value, as cancer-associated cachexia is a major contributor to morbidity and mortality in lung cancer. By improving nutritional status, YGJT may help break the cycle of weight loss and functional decline that limits patients’ tolerance to aggressive anticancer therapies. Previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses have primarily examined the effects of YGJT on upper gastrointestinal symptoms, such as functional dyspepsia and chemotherapy-induced anorexia (Mogami and Hattori, 2014; Hoshino et al., 2019; Ko et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). These findings align with the present study, which demonstrated a reduction in digestive tract reactions, further supporting the effectiveness of YGJT in managing gastrointestinal symptoms in lung cancer treatment.
In the subgroup analysis, JCYGJT exhibited greater efficacy against digestive tract reactions than modified YGJT or HSYGJT. This could be explained by its focus on benefiting Qi and strengthening the spleen through the increased proportion of Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma as a primary component, combined with the addition of Aurantii Fructus, which regulates Qi and transforms phlegm, and Aucklandiae Radix, which regulates Qi and resolves masses (Bi et al., 2024). These combined effects likely enhanced its digestive properties, enabling better management of gastrointestinal side effects. However, the small number of available studies makes it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the relative superiority of these formulations. As the synergistic use of herbs is a fundamental principle of traditional East Asian medicine (Wang et al., 2012), further research is needed to better differentiate the effects of YGJT and its modified decoctions and assess their clinical implications.
This study indicates that YGJT may also enhance the effectiveness of antitumor therapy, an area that has been relatively underexplored. This effect is reflected in the observed improvements in ORR and DCR. From a clinical standpoint, the magnitude of this synergy is meaningful. Applying our pooled risk ratio of 1.69 to the baseline control group response rate of 31.1% yields an absolute improvement in ORR of approximately 21.5%. This level of benefit is noteworthy, as more modest improvements in ORR have been considered clinically significant in pivotal lung cancer trials (Cho et al., 2022). There is substantial evidence from preclinical studies that YGJT has antitumor effects. For example, YGJT has been reported to exert antitumor effects in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting the miR-34a/STAT3/IL-6R pathway and enhancing antitumor immune responses by inhibiting PD-1, thereby restoring T-cell cytotoxicity (Han et al., 2023). In liver cancer, YGJT was observed to downregulate UBE2I and the NF-κB/PD-L1 pathway via miR-122-3p (Guo et al., 2024). In NSCLC, YGJT has been suggested to modulate several genes associated with neutrophils in ways that enhance immune responses or mitigate inflammatory side effects, with RNA-induced gene silencing potentially contributing to its anticancer effects (Chen et al., 2017; Xin et al., 2022).
From the perspective of traditional East Asian medicine, the principle of “strengthening the body” and “eliminating evil” suggests that YGJT could potentiate cancer treatment by tonifying Qi, mitigating pathological byproducts such as phlegm dampness, and directly contributing to tumor suppression. Sensitivity analysis using Qi deficiency-related patterns as diagnostic criteria showed improved ORR while reducing the occurrence of adverse events, supporting the clinical relevance of these principles. However, the results for other outcomes were inconsistent, likely because most studies using pattern identification were conducted on advanced lung cancer cases, and the limited number of studies reduced statistical power. Future studies using pattern identification could facilitate robust comparisons between patterns and clarify those most suitable for YGJT in lung cancer treatment.
Furthermore, YGJT resulted in a higher tumor response rate when combined with chemotherapy than when combined with EGFR-TKIs. Although this suggests that YGJT enhances the cytotoxic effects of conventional agents, it is more likely attributable to the more advanced cancer stage in the EGFR-TKI group, possibly related to the indication criteria for EGFR-TKI use. Additional studies examining possible synergistic or antagonistic interactions between YGJT and other Western therapies, such as immunotherapy and radiotherapy, which remain largely unexplored, are warranted. Such research is essential to validate YGJT as a viable adjunct to standard oncological treatments.
A key effect of YGJT in cancer treatment may be its immunomodulatory activity. The role of lymphocyte subsets in cancer prognosis remains incompletely understood, with studies reporting varied results. While CD4+ T cells enhance immune responses, CD8+ T cells can suppress immune activity and are associated with tumor progression and growth (Wang et al., 2013). CD4+ T cells are believed to play a critical role in anti-tumor immunity by directly killing cancer cells, with decreased CD4+ levels linked to lower survival rates in patients with lung cancer (Oh and Fong, 2021; Eberst et al., 2022; Malyshkina et al., 2023). The CD4+/CD8+ ratio reflects immune function balance and is an important prognostic biomarker for assessing immune competence in patients with cancer (Xu et al., 2018). Additionally, patients with NSCLC who respond well to anti-PD-1 treatment show increased levels of CD4+ T cells and a higher CD4+/CD8+ ratio (Zhuang et al., 2024). Our analysis aligns with these principles, revealing that YGJT significantly increased total T cells (CD3+) and CD4+ T cells, leading to an elevated CD4+/CD8+ ratio. These findings suggest that YGJT enhances systemic immune function. This enhancement is of high translational value, as it suggests YGJT may counteract the profound T-cell exhaustion and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment that are key features of lung cancer pathophysiology, potentially restoring the patient’s capacity to respond to both conventional and immune-based therapies.
The decrease in CD8+ cell levels observed in this study is controversial, as research on its prognostic significance in lung cancer remains inconclusive. Some studies have indicated that an increase in CD8+ T cells is an independent prognostic factor for poor survival in patients with malignant mesothelioma or advanced NSCLC (McCoy et al., 2013), while a systematic review reported that CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ cells are all positively associated with improved overall survival in patients with NSCLC (Yan et al., 2024). These results suggest that while YGJT may boost immune function and demonstrate anticancer efficacy, the changes in CD8+ levels and their effects on prognosis require further investigation through clinical trials.
Tumor markers are closely associated with the disease stage of lung cancer and are widely used for screening, clinical diagnosis, and prognostic assessment (Kumar et al., 2006; Arya and Bhansali, 2011). Specifically, CEA, NSE, SCC, CYFRA 21-1, and CA19-9 have become established indicators for evaluating prognosis in lung cancer, with reductions in these markers often correlating with extended survival (Holdenrieder et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2019; Trulson and Holdenrieder, 2024). In this study, YGJT was shown to reduce these tumor markers. However, due to the high heterogeneity of the included studies, relatively small sample sizes, and lack of data on combination therapy with EGFR-TKIs, further research is required to elucidate the relationship between YGJT and tumor markers.
KPS is one of the most critical prognostic factors affecting the outcomes of patients with cancer, including those with lung cancer (Buccheri et al., 1996; West and Jin, 2015). Therefore, maintaining a high KPS score is crucial in lung cancer treatment. Adding YGJT to conventional therapy resulted in relatively greater improvements in both KPS and symptom scores, suggesting that YGJT not only synergizes with antitumor treatments but also improves patient symptoms, enhances quality of life, and increases treatment tolerability, thereby supporting the overall goals of cancer therapy. The ability of adjunctive YGJT to significantly improve KPS suggests its benefits translate to a tangible enhancement in patients’ functional status and daily life. The mean improvement of 8.62 points observed in our analysis substantially exceeds the 3.83-point threshold empirically identified as the minimal clinically important difference for a noticeable improvement in KPS (Ringash et al., 2007). This indicates that the observed change is not only statistically significant but also represents a highly meaningful clinical benefit for patients.
Another major aspect of the therapeutic effects of YGJT is its reduction of adverse effects associated with cancer treatment. These adverse effects, primarily bone marrow suppression and gastrointestinal toxicity, often lead to a decline in quality of life. YGJT effectively reduced these side effects while improving patients’ quality of life. YGJT’s ability to mitigate a spectrum of adverse events, including both myelosuppression and gastrointestinal toxicity, contrasts with standard supportive care, which often requires the administration of multiple single-target agents. This suggests a potential role for YGJT as a broad-spectrum supportive care intervention, capable of simplifying patient management. In vivo studies have reported that YGJT and its modified formulations prevent cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity through antioxidant effects, regulation of mitochondrial function, and alleviation of paclitaxel-induced neuropathy and leukopenia (Chiou et al., 2018; Shiah et al., 2023). Consistent with its immune-balancing properties, YGJT also reduced myelosuppression and leukopenia in this study, suggesting an improvement in immune function that contributes to its anti-tumor effects. Further research on the immunomodulatory effects of YGJT may provide stronger evidence of its potential synergistic effects with current anticancer agents.
The strengths of this study are as follows: To our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis examining the synergistic effects of YGJT and antitumor therapy in lung cancer patients. This review encompasses a broad range of outcomes, including ORR, DCR, KPS score, clinical symptom score, immune function markers, tumor markers, and treatment-related adverse events, providing a comprehensive assessment of the efficacy and safety of YGJT. This study used a robust data extraction process conducted by multiple independent reviewers to ensure high reliability and minimize bias. Sensitivity analyses specific to advanced-stage lung cancer further reinforced the robustness of the results, while publication bias assessments using funnel plots and Egger’s test added an additional layer of validation. We also conducted an extensive database search without restrictions on language, publication year, or publication type.
Despite its strengths, this review has several limitations. First, a primary limitation of this review is the inability to perform our pre-specified comparative subgroup analyses, particularly for cancer stage and histological subtype. This was due to an insufficient number of included studies representing certain key subgroups (e.g., early-stage or SCLC), which prevented a direct meta-analytic comparison. However, as pre-specified in our protocol, we conducted a sensitivity analysis on the cohort of studies involving advanced-stage cancer, which largely confirmed the robustness of our overall findings for this population. Second, the generalizability of the findings is limited as most studies were conducted in China. This geographical concentration raises questions about the applicability of these results to other ethnic populations. Third, our search strategy, while extensive across published literature databases, did not include a specific search of clinical trial registries or other sources of grey literature. This could have resulted in the omission of relevant unpublished or ongoing trials, representing a potential source of publication bias. Additionally, the majority of the included RCTs were rated as having a “high” or “some concerns” for risk of bias, primarily due to inadequate blinding and unclear randomization methods. This high risk of bias substantially tempers confidence in the observed effect sizes and may have led to an overestimation of the treatment benefit. Furthermore, the substantial clinical heterogeneity, driven by the wide variability in modified YGJT interventions, complicates the attribution of the observed effects to a single, standardized intervention. Future research should aim to address these limitations by including high-quality multicenter RCTs with detailed protocols to validate the findings and explore the application of YGJT in broader, more diverse populations.
5 Conclusion
This systematic review provides evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of modified YGJT as an adjuvant therapy for lung cancer. The findings indicate that YGJT improves ORR and DCR, enhances KPS scores and clinical symptoms, boosts immune function, and reduces tumor markers and treatment-related adverse events. Despite these promising results, the overall quality of the included studies was low, with limitations such as small sample sizes, potential biases, and high heterogeneity. These challenges underscore the need for well-designed, large-scale, multicenter RCTs to confirm these findings and further investigate the underlying mechanisms of the effects of YGJT. Future research should aim to address these limitations and explore the interactions between YGJT and contemporary cancer treatments, including immunotherapy and radiotherapy, to fully unlock its potential in comprehensive cancer care.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
S-WK: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Resources, Investigation, Conceptualization, Methodology. SH: Writing – review and editing, Resources. K-IK: Writing – review and editing. H-JJ: Writing – review and editing. B-JL: Conceptualization, Resources, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: RS-2022-KH127464).
Acknowledgments
This study was based on the Ph.D. dissertation of S-WK. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.co.kr) for English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1657423/full#supplementary-material
References
Arya, S. K., and Bhansali, S. (2011). Lung cancer and its early detection using biomarker-based biosensors. Chem. Rev. 111 (11), 6783–6809. doi:10.1021/cr100420s
Bi, W., Li, C., and Chen, M. (2024). Effect of zhizhu liujunzi decoction combined with GP regimen on cancer-related fatigue in non-small cell lung cancer patients. New Chin. Med. 56 (18), 185–189. doi:10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2024.18.038
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74 (3), 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Buccheri, G., Ferrigno, D., and Tamburini, M. (1996). Karnofsky and ECOG performance status scoring in lung cancer: a prospective, longitudinal study of 536 patients from a single institution. Eur. J. Cancer 32 (7), 1135–1141. doi:10.1016/0959-8049(95)00664-8
Cai, R., Sun, J., Liu, J., Bai, M., and Liang, B. (2022). Effect of zhizhu liujunzi decotion in the treatment of lung cancer patients with Qi-deficiency syndrome during chemotherapy and its influence on the tongue coating thickness and the gastrointestinal reaction. China Mod. Med. 29 (23), 137–140. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4721.2022.23.036
Chen, Y. C., Lin, A. S., Hung, Y. C., Chen, K. D., Wu, C. Y., Lie, C. H., et al. (2017). Whole genome gene expression changes and hematological effects of rikkunshito in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving first line chemotherapy. Exp. Ther. Med. 14 (3), 2040–2052. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4773
Chen, Y., Sun, L., and Hu, L. (2022). Study on the mechanism of modified liujunzi decoction in the treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients of lung-spleen Qi deficiency pattern undergoing GP regimen. West. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 35 (01), 119–123. doi:10.12174/j.issn.2096-9600.2022.01.29
Chiou, C.-T., Wang, K.-C., Yang, Y.-C., Huang, C.-L., Yang, S.-H., Kuo, Y.-H., et al. (2018). Liu Jun Zi Tang—A potential, multi-herbal complementary therapy for chemotherapy-induced neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (4), 1258. doi:10.3390/ijms19041258
Cho, B. C., Abreu, D. R., Hussein, M., Cobo, M., Patel, A. J., Secen, N., et al. (2022). Tiragolumab plus atezolizumab versus placebo plus atezolizumab as a first-line treatment for PD-L1-selected non-small-cell lung cancer (CITYSCAPE): primary and follow-up analyses of a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 23 (6), 781–792. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00226-1
Dai, Y., Chen, S., Li, Y., Zhang, G., Bi, P., and Nie, K. (2022). Liujunzi decoction ameliorated cisplatin-induced anorexia by inhibiting the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and coordinating anorexigenic and orexigenic neuropeptides in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 285, 114840. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114840
Dong, X., Jia, R., Ye, X., and Liu, M. (2018). Observation on the clinical efficacy of Liu Jun Zi Tang combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of lung cancer. Shenzhen J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med. 28 (05), 36–37. doi:10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2018.05.016
Duan, Y. (2018). Study on the clinical value of Liu Jun Zi Tang combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of middle and advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Pract. Clin. J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med. 18 (06), 104–105. doi:10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2018.06.053
Eberst, G., Vernerey, D., Laheurte, C., Meurisse, A., Kaulek, V., Cuche, L., et al. (2022). Prognostic value of CD4+ T lymphopenia in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 22 (1), 529. doi:10.1186/s12885-022-09628-8
Fang, X., Yan, S., Lu, W., Xu, S., and Lu, W. (2015). Clinical observation of treatment of Leucopenia after chemotherapy for lung cancer by modified liujunzi decoction. J. Shandong Univ. Traditional Chin. Med. 39 (05), 418–420. doi:10.16294/j.cnki.1007-659x.2015.05.046
Fu, B., and Jiang, S. (2017). The clinical observation on liujunzi decoction combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. Med. Mod. Distance Educ. China 15 (09), 84–85. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2017.09.037
Fujitsuka, N., and Uezono, Y. (2014). Rikkunshito, a ghrelin potentiator, ameliorates anorexia-cachexia syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 5, 271. doi:10.3389/fphar.2014.00271
Gao, S. (2022). Effect of Liujunzi decoction on patients with non-small cell lung cancer after chemotherapy. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 14 (18), 127–129. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2022.18.040
GRADEpro GDT (2025). GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool [Software]. Hamilton, ON: McMaster University and Evidence Prime. Available online at: https://gradepro.org (Accessed September 20, 2025).
Guerra-Martin, M. D., Tejedor-Bueno, M. S., and Correa-Casado, M. (2021). Effectiveness of complementary therapies in cancer patients: a systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 (3), 1017. doi:10.3390/ijerph18031017
Guo, Z., Wang, Y., Qin, W., Heng, Y., Chen, X., Liu, N., et al. (2024). miR-122-3p targets UBE2I to regulate the immunosuppression of liver cancer and the intervention of liujunzi formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 329, 118081. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118081
Han, Y., Fan, X., Fan, L., Wu, Y., Zhou, Z., Wang, G., et al. (2023). Liujunzi decoction exerts potent antitumor activity in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting miR-34a/STAT3/IL-6R feedback loop, and modifies antitumor immunity. Phytomedicine 111, 154672. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154672
Harada, T., Amano, T., Ikari, T., Takamura, K., Ogi, T., Fujikane, T., et al. (2018). Rikkunshito for preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in lung cancer patients: results from 2 prospective, randomized phase 2 trials. Front. Pharmacol. 8 (JAN), 972. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00972
Higgins, J. P., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J., and Altman, D. G. (2003). Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj 327 (7414), 557–560. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Higgins, J. P. T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M. J., et al. (2024). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.5. Chichester, UK: Cochrane. Available online at: https://www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (Accessed September 20, 2025).
Holdenrieder, S., Wehnl, B., Hettwer, K., Simon, K., Uhlig, S., and Dayyani, F. (2017). Carcinoembryonic antigen and cytokeratin-19 fragments for assessment of therapy response in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 116 (8), 1037–1045. doi:10.1038/bjc.2017.45
Hoshino, N., Nishizaki, D., Hida, K., Obama, K., and Sakai, Y. (2019). Rikkunshito for upper gastrointestinal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 42, 255–263. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2018.11.025
Inokuchi, K., Masaoka, T., and Kanai, T. (2021). Rikkunshito as a therapeautic agent for functional dyspepsia and its prokinetic and non-prokinetic effects. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 640576. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.640576
Iwase, S., Yamaguchi, T., Miyaji, T., Terawaki, K., Inui, A., and Uezono, Y. (2012). The clinical use of kampo medicines (traditional Japanese herbal treatments) for controlling cancer patients' symptoms in Japan: a national cross-sectional survey. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 12, 222. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-12-222
Karnofsky, D. A. (1949). The clinical evaluation of chemotherapeutic agents in cancer. Eval. Chemother. agents, 191–205.
Ko, S. J., Park, J., Kim, M. J., Kim, J., and Park, J. W. (2021). Effects of the herbal medicine rikkunshito, for functional dyspepsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 36 (1), 64–74. doi:10.1111/jgh.15208
Kumar, S., Mohan, A., and Guleria, R. (2006). Biomarkers in cancer screening, research and detection: present and future: a review. Biomarkers 11 (5), 385–405. doi:10.1080/13547500600775011
Lee, J. H., Saxena, A., and Giaccone, G. (2023). Advancements in small cell lung cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 93, 123–128. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.05.008
Leiter, A., Veluswamy, R. R., and Wisnivesky, J. P. (2023). The global burden of lung cancer: current status and future trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 20 (9), 624–639. doi:10.1038/s41571-023-00798-3
Li, Y. (2018). Clinical observation of modified liu Jun Zi tang in the treatment of elderly lung cancer patients with Qi deficiency and phlegm-dampness syndrome. Guide China Med. 16 (01), 175–176. doi:10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2018.01.140
Li, L., Fang, C., Zhang, H., Liu, L., Meng, J., Kuang, W., et al. (2016). Clinical study of modified xiangsha liu Jun Zi Tang for treating chemotherapy-induced vomiting in 34 cases of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Pract. Clin. J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med. 16 (09), 34–35. doi:10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2016.09.017
Li, D., Sun, C., and Fan, H. (2017). Clinical observation of modified liujunzi decoction in adjuvant chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. China Pharm. 28 (36), 5068–5071. doi:10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2017.36.08
Li, T. M., Yu, Y. H., Tsai, F. J., Cheng, C. F., Wu, Y. C., Ho, T. J., et al. (2018). Characteristics of Chinese herbal medicine usage and its effect on survival of lung cancer patients in Taiwan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 213, 92–100. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.031
Li, Z., Feiyue, Z., and Gaofeng, L. (2021). Traditional Chinese medicine and lung cancer--From theory to practice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 137, 111381. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111381
Li, Y., Yan, B., and He, S. (2023). Advances and challenges in the treatment of lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 169, 115891. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115891
Lin, Y., Chen, W., and Cai, G. (2024). Clinical study of modified liujunzi decoction combined with ohitinib tablets in the treatment of advanced spleen deficiency phlegm-Dampness type non-small cell lung cancer. Med. Innovation China 21 (16), 53–57. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2024.16.011
Liu, Q., Li, Y., Cui, W., and Liang, Q. (2017). Liunzi decoction combined with EP chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer for 37 cases. Chin. Med. Mod. Distance Educ. China 15 (05), 98–99. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2017.05.041
Liu, Y., Wang, B., and Sun, Q. (2018). The effect of modified liu Jun Zi tang on immune function in chemotherapy patients with lung and spleen Qi deficiency type non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 11 (12), 107–109. doi:10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2018.12.055
Liu, D., Jiang, S., Wu, Y., and He, Q. (2020). Research progress on the application and therapeutic mechanism of liujunzi decoction in the treatment of tumor diseases. Chin. Med. Mod. Distance Educ. China 18 (05), 132–134. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2020.05.054
Liu, Y., Guo, Y., Liang, J., Wang, Y., Yuan, Y., Yao, J., et al. (2023). Effect of xiangsha Liujunzi decoction on the improvement of related traditional Chinese medicine symptoms in small cell lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Mod. Chin. Med. 43 (02), 54–58. doi:10.13424/j.cnki.mtcm.2023.02.012
Malyshkina, A., Brüggemann, A., Paschen, A., and Dittmer, U. (2023). Cytotoxic CD4(+) T cells in chronic viral infections and cancer. Front. Immunol. 14, 1271236. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1271236
McCoy, M. J., Nowak, A. K., van der Most, R. G., Dick, I. M., and Lake, R. A. (2013). Peripheral CD8+ T cell proliferation is prognostic for patients with advanced thoracic malignancies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 62, 529–539. doi:10.1007/s00262-012-1360-z
Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China (2002). Guidelines for clinical research on new Chinese medicine. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press.
Mogami, S., and Hattori, T. (2014). Beneficial effects of rikkunshito, a Japanese kampo medicine, on gastrointestinal dysfunction and anorexia in combination with Western drug: a systematic review. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 519035. doi:10.1155/2014/519035
Nie, D., Liu, Z., Dong, J., Li, D., and Zhang, F. (2022). Protective effect of modified liujunzi Tang on immunity in elderly patients with advanced lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy. West. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 35 (08), 97–100. doi:10.12174/j.issn.2096-9600.2022.08.23
Oh, D. Y., and Fong, L. (2021). Cytotoxic CD4(+) T cells in cancer: expanding the immune effector toolbox. Immunity 54 (12), 2701–2711. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.11.015
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372, n71. doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Park, S. B., Yoon, J. H., Kim, E. H., Jin, H., and Yoon, S. W. (2023). Traditional herbal medicine for anorexia in patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1203137. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1203137
Riely, G. J., Wood, D. E., Ettinger, D. S., Aisner, D. L., Akerley, W., Bauman, J. R., et al. (2024). Non-Small cell lung cancer, version 4.2024, NCCN Clinical practice Guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 22 (4), 249–274. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2204.0023
Ringash, J., O'Sullivan, B., Bezjak, A., and Redelmeier, D. A. (2007). Interpreting clinically significant changes in patient-reported outcomes. Cancer 110 (1), 196–202. doi:10.1002/cncr.22799
Shiah, H.-S., Lee, C.-J., Lee, F.-Y., Tseng, S.-H., Chen, S.-H., and Wang, C.-C. (2023). Chemopreventive effects of Xiang Sha Liu Jun Zi Tang on paclitaxel-induced leucopenia and neuropathy in animals. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1106030. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1106030
Stewart, S., Yang, K. C. K., Atkins, K., Dalbeth, N., and Robinson, P. C. (2020). Adverse events during oral colchicine use: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Arthritis Res. Ther. 22 (1), 28. doi:10.1186/s13075-020-2120-7
Sun, Y. (2020). Effects of modified Liujunzi decoction on tumor marker levels and immune function in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving chemotherapy. Acta Med. Sin. 33 (03), 22–25. doi:10.19296/j.cnki.1008-2409.2020-03-007
Sun, L. L., Lai, H. Z., Chen, Z. Z., Zhu, X. S., and Lin, L. Z. (2020). Modified liujunzi decoction alleviates chemotherapy-induced anorexia in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a propensity Score matched case-control Study. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 26 (4), 256–262. doi:10.1007/s11655-020-3185-5
Sun, Y.-h., Long, P.-f., Zhang, Y.-m., and Huang, M.-r. (2021). Effects of modified Liujunzi decoction on angiogenesis and immune function in the treatment of lung-spleen Qi deficiency type of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Logist. Univ. PAP Medical Sci. 30 (11), 75–77. doi:10.16548/j.2095-3720.2021.11.051
Sun, Z., Deng, H., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., and Xu, C. (2024). A systematic review and meta-analysis of Xiangsha Liujunzi decoction in the treatment of chronic gastritis. Comb. Chem. High. Throughput Screen 27 (3), 386–399. doi:10.2174/0113862073252121230925103843
Tao, C., and Liu, J. (2023). Effect of modified Liujunzi decoction combined with leucogen tablets in the treatment of patients with leukopenia after NSCLC chemotherapy. Chin. Foreign Med. Res. 21 (36), 132–135. doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2023.36.032
Thai, A. A., Solomon, B. J., Sequist, L. V., Gainor, J. F., and Heist, R. S. (2021). Lung cancer. Lancet 398 (10299), 535–554. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00312-3
Trulson, I., and Holdenrieder, S. (2024). Prognostic value of blood-based protein biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer: a critical review and 2008-2022 update. Tumour Biol. 46 (s1), S111–s161. doi:10.3233/tub-230009
Viechtbauer, W. (2010). Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 36 (3), 1–48. doi:10.18637/jss.v036.i03
Wang, Y. (2022). Clinical effect of Zhiju Liu Jun Zi Tang in treating tumor-related fatigue in patients with advanced lung cancer. Mod. Med. Health Res. Electron. J. 6 (08), 7–10.
Wang, S., Hu, Y., Tan, W., Wu, X., Chen, R., Cao, J., et al. (2012). Compatibility art of traditional Chinese medicine: from the perspective of herb pairs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 143 (2), 412–423. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.07.033
Wang, W.-J., Tao, Z., Gu, W., and Sun, L.-H. (2013). Variation of blood T lymphocyte subgroups in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. cancer Prev. 14 (8), 4671–4673. doi:10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.8.4671
Wang, Y., Zhang, N., Li, H., and Lian, Y. (2023). Clinical value of liujunzi decoction with addition and subtraction as an adjunct to chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Syst. Med. 8 (04), 41–44. doi:10.19368/j.cnki.2096-1782.2023.04.041
Wang, L., Ding, X., Yao, X., Li, P., Zhang, F., Wang, F., et al. (2024). Efficacy and safety of Xiangsha liujunzi decoction for functional dyspepsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1356899. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1356899
West, H. J., and Jin, J. O. (2015). JAMA oncology patient page. Performance status in patients with cancer. JAMA Oncol. 1 (7), 998. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.3113
Wilson, M. K., Karakasis, K., and Oza, A. M. (2015). Outcomes and endpoints in trials of cancer treatment: the past, present, and future. Lancet Oncol. 16 (1), e32–e42. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(14)70375-4
Wu, X., Dai, Y., and Nie, K. (2022). Research progress of liujunzi decoction in the treatment of tumor-associated Anorexia. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 16, 1731–1741. doi:10.2147/dddt.S365292
Xi, Z., Dai, R., Ze, Y., Jiang, X., Liu, M., and Xu, H. (2025). Traditional Chinese medicine in lung cancer treatment. Mol. Cancer 24 (1), 57. doi:10.1186/s12943-025-02245-6
Xin, X. L., Wang, G. D., Han, R., Jiang, Y., Liu, C., Liu, L. S., et al. (2022). Mechanism underlying the effect of Liujunzi decoction on advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer in patients after first-line chemotherapy. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 42 (1), 108–115. doi:10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.01.007
Xing, Y., and Zhai, J. (2016). Clinical observation of modified Liu Jun Zi Tang combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Sichuan Traditional Chin. Med. 34 (11), 81–82.
Xiong, X.-j., and Xiong, L.-j. (2016). Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of Liu Jun Zi Tang combined with the EP chemotherapy regimen in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hainan Med. Univ. 22 (15), 1714–1717+1721. doi:10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20160308.006
Xu, J., Jiang, L., Cao, H., Jia, Y., Wu, S., Jiang, C., et al. (2018). Predictive value of CD4(+)/CD8(+) ratio in patients with breast cancer receiving recombinant human thrombopoietin. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 38 (5), 213–220. doi:10.1089/jir.2017.0146
Yamada, C., Hattori, T., Ohnishi, S., and Takeda, H. (2021). Ghrelin enhancer, the latest evidence of Rikkunshito. Front. Nutr. 8, 761631. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.761631
Yan, Q., Li, S., He, L., and Chen, N. (2024). Prognostic implications of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 15, 1476365. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1476365
Yang, G., Xiao, Z., Tang, C., Deng, Y., Huang, H., and He, Z. (2019). Recent advances in biosensor for detection of lung cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 141, 111416. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2019.111416
Ye, R. (2015). Study on the treatment of gastrointestinal reactions induced by chemotherapy in patients with lung cancer using traditional Chinese medicine. For all Health 9 (13), 31–32.
Yilin, W. (2009). Shi Yi De Xiao Fang (Efficacious Remedies of the Physicians). Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press.
You, J. (2016). Clinical effect of Liujun Qutan Jiedu decoction combined with GP chemotherapy regimen on non-small cell lung cancer and the impact on serum VEGF level. Pract. J. Cardiac Cereb. Pneumal Vasc. Dis. 24 (01), 88–91. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2016.01.026
Zhang, X., Tan, R., Lam, W. C., Yao, L., Wang, X., Cheng, C. W., et al. (2020). PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) extension for Chinese Herbal Medicines 2020 (PRISMA-CHM 2020). Am. J. Chin. Med. 48 (06), 1279–1313. doi:10.1142/s0192415x20500639
Zhao, L.-C., Li, L.-Z., Yuan, J.-H., Zhuang, J.-N., Chen, T., and Fang, C.-T. (2021). Clinical Study on treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with spleen deficiency and phlegm-damp syndrome by modified Liujunzi decoction combined with gefitinib tablets. J. Guangzhou Univ. Traditional Chin. Med. 38 (02), 250–256. doi:10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2021.02.006
Zhou, B., Shan, Z., Fang, M., Chen, Y., Wu, X., and Xiao, L. (2015). Clinical observation on modified liujunzi decoction in combination with chemotherapy in treatment of 31 advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 56 (03), 219–222. doi:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2015.03.011
Keywords: Yukgunja-tang, Liujunzi Decoction, Rikkunshito, herbal medicine, lung cancer, systematic review
Citation: Kang S-W, Ha S, Kim K-I, Jung H-J and Lee B-J (2025) Therapeutic potential of modified Yukgunja-tang (Liujunzi Decoction, Rikkunshito) as an adjuvant treatment for lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1657423. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1657423
Received: 01 July 2025; Accepted: 10 September 2025;
Published: 01 October 2025.
Edited by:
Olu Israel Oyewole, Osun State University, NigeriaReviewed by:
Oluwaseyi Emilola Okoro, Ministry of Health and Wellness, JamaicaOlaide Awosanya, University of Ibadan, Nigeria
Copyright © 2025 Kang, Ha, Kim, Jung and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Beom-Joon Lee, ZnJhbmNoaXNqdW5AbmF2ZXIuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Sung-Woo Kang
Sung-Woo Kang Seojung Ha
Seojung Ha Kwan-Il Kim
Kwan-Il Kim Hee-Jae Jung1,3
Hee-Jae Jung1,3 Beom-Joon Lee
Beom-Joon Lee