- 1State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, National Clinical Research Center for Infectious Diseases, China-Singapore Belt and Road Joint Laboratory on Infection Research and Drug Development, National Medical Center for Infectious Diseases, Collaborative Innovation Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 2Yuhang Institute of Medical Science Innovation and Transformation, Hangzhou, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedical Research of Zhejiang Province, Stomatology Hospital, School of Stomatology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Zhejiang Provincial Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Cancer Center of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
- 4College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
- 5Jinan Microecological Biomedicine Shandong Laboratory, Jinan, China
- 6College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a significant global health challenge affecting approximately 25% of adults worldwide. Given the limited efficacy of existing therapies, there is an urgent need for novel treatment strategies. Flavonoids, a diverse class of natural polyphenolic compounds, exhibit significant potential in ameliorating MAFLD by modulating hepatic lipid metabolism and immune-inflammatory responses via gut-liver axis. This review systematically explores the interactions between flavonoids and gut microbiota, elucidating their role in MAFLD progression. We highlight how flavonoid structural diversity and microbial biotransformation modulate multiple key pathways, such as PPARα, PPARγ, ERβ, Nrf2, NF-κB, and FXR signalling. These multi-target mechanisms underpin the therapeutic potential of flavonoids in reducing lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in MAFLD. We also discuss innovative strategies, including flavonoid-probiotic synergies, nanotechnology-enhanced delivery systems, and personalized nutrition strategies. By integrating evidence from preclinical models and clinical trials, we highlight the translational potential of flavonoid-based interventions for MAFLD management. Our analysis underscores flavonoids as multi-target, safe and effective solutions for MAFLD management, warranting further clinical studies to translate these findings into routine clinical practice.
1 Introduction
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a global health challenge affecting an estimated 25% of the adult, with its prevalence rising due to the increasing rates of obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome (Younossi et al., 2023; Man et al., 2023). Its severe form, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (Huang et al., 2021; Paik et al., 2022). Despite this significant burden, effective drug therapies for MAFLD are lacking, as many anticipated drugs have failed in clinical trials (Rong et al., 2023; Piero et al., 2024). Diet is a critical factor in MAFLD pathogenesis, with diets rich in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and low in essential micronutrients exacerbating its progression (Francesca et al., 2022). Of particular interest is the role of flavonoid-rich diets, such as the Mediterranean diet, which has been consistently linked to a reduced risk of developing MAFLD (Ilaria et al., 2020; Riazi et al., 2022). Epidemiological studies have demonstrated that individuals with diets deficient in flavonoids are at an increased risk of developing MAFLD (Iino et al., 2022), further emphasizing the importance of dietary interventions in MAFLD management (Sherouk and Joseph, 2023).
Flavonoids, a diverse group of natural polyphenolic compounds, have garnered attention as “food-derived medicine” therapeutic potential. These compounds exhibit remarkable structural diversity, characterized by their C6-C3-C6 backbone (Figure 1), which allows for a wide range of substitution patterns and bioactive properties (Dias et al., 2021; Kaushal et al., 2022). Flavonoids are abundant in citrus fruits, soy, tea, and medicinal herbals such as snow lotus (Saussurea eriocephala Franch), Chinese skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi), Dendrobium officinale Kimura and Migo, Dragon’s blood (Dracaena draco (L.) L.) and Ficus hirta (Ficus simplicissima Lour) (Dias et al., 2021; Shen et al., 2022; Yi et al., 2012; Yi et al., 2009a; Chen et al., 2017; Xue et al., 2017; Yi et al., 2009b) (Table 1). Pharmacologically, flavonoids show potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties by modulating oxidative stress pathways (e.g., Nrf2, CYP2E1, ROS) and inhibiting pro-inflammatory signalling pathways (e.g., NF-κB, TNF-α, TLR4) (Kaushal et al., 2022; Shen et al., 2022). As estrogen analogs, flavonoids may modulate diseases associated with estrogen abnormalities with low toxicity and low side effects (Kiyama, 2023). As food-derived medicine, flavonoids were found to modulate intestinal microbiota, which in turn affect host metabolism and immune function (Kuziel et al., 2025). After being ingested by the body, the metabolic fate of flavonoids is influenced by their structural characteristics and their interactions with the intestinal microbiota (Kuziel et al., 2025; Li C. et al., 2023). A major challenge lies in their typically low bioavailability and extensive first-pass metabolism, which severely limits the flavonoid concentration in systemic circulation and target tissues. Furthermore, the diverse metabolic transformations by gut microbiota and host enzymes can lead to varied, making their precise in vivo effects difficult to predict and standardize across individuals. Therefore, how to enhance the bioavailability of flavonoids within the context of gut-liver crosstalk is crucial for alleviating liver diseases such as MAFLD. In summary, flavonoids’ structural diversity, rich dietary sources, and broad spectrum of pharmacological activities position them as promising candidates for developing novel therapeutic strategies of MAFLD (Kaushal et al., 2022; Li C. et al., 2023; Xiaopeng et al., 2022).
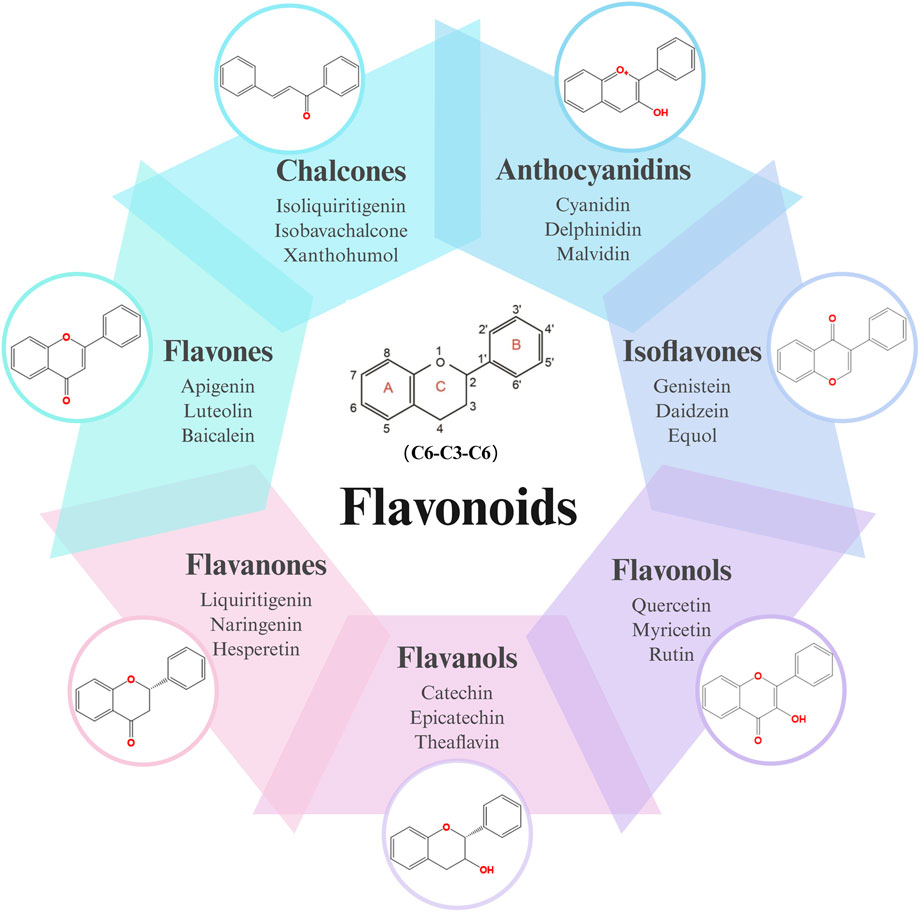
Figure 1. Skeletal structure of flavonoids and their seven subclassifications. Original image drawn for this review using Biorender software.
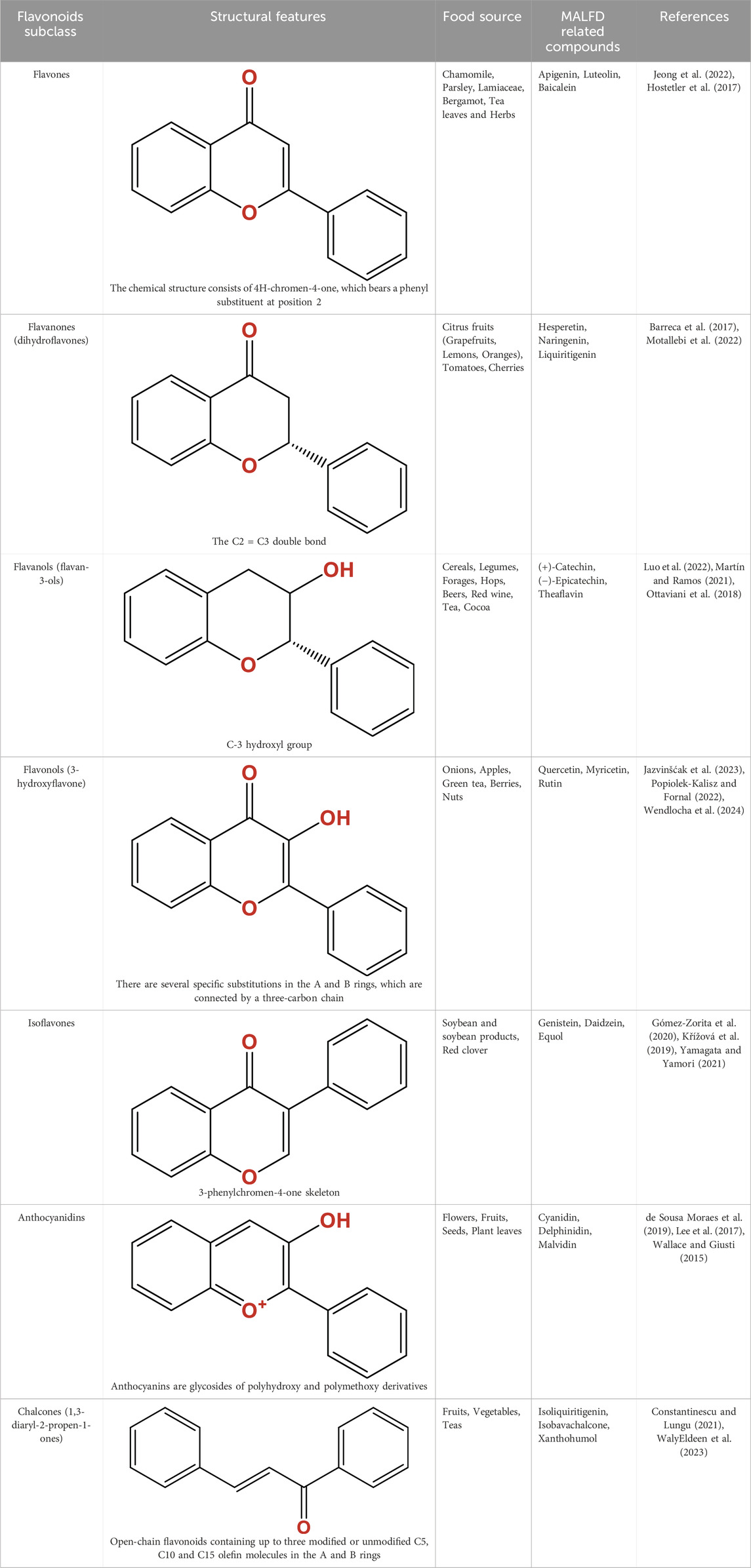
Table 1. Structure, characteristics, food sources and representative molecules of the seven subclasses of flavonoids.
Recent studies highlight the central role of the gut-liver axis in MAFLD pathogenesis through oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipid dysregulation (De Cól et al., 2024; Fianchi et al., 2021; Hu Y. et al., 2025; Peng et al., 2024). This communication system between the gut microbiota, the gastrointestinal tract, and the liver underpins MAFLD development (Kuziel et al., 2025; Luo et al., 2023; Martín-Mateos and Albillos, 2021). For instance, microbiota dysbiosis can cause translocation of microbial products like lipopolysaccharides (LPS), triggering endotoxemia, systemic inflammation, and liver injury (Luo et al., 2023; Peiseler et al., 2022). Microbial metabolites also have emerged as important modulators in the development of hepatic steatosis. Altered bile acid (BA) profile resulting from microbiome imbalances contributes to hepatic steatosis by affecting both BA signalling and lipid metabolism, reinforcing the gut-liver interaction and advancing the pathogenesis of MAFLD (De Cól et al., 2024; Luo et al., 2023).Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), produced by gut microbiota fermentation, enhance the intestinal barrier and modulate liver fatty acid (FA) metabolism. SCFAs decrease hepatic triglyceride accumulation, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce inflammation, mitigating MAFLD progression (Fianchi et al., 2021; Barber et al., 2023).
Metabolite of dietary flavonoids by gut bacteria, such as S-equol, which improve liver health by modulating oxidative stress and inflammation (Rao et al., 2021; Qi et al., 2025). The interaction between gut metabolism and flavonoid bioavailability also provides an important basis to understands flavonoid’s role to intervene MAFLD development (Cheng et al., 2024). Studies have shown that gut dysbiosis, which is often associated with MAFLD, can impair the metabolic conversion of flavonoids, reducing their protective effects on liver health (Long et al., 2024; Fang et al., 2024).
Given the structural diversity of flavonoid and their complex interaction with gut microbial community, this review aims to summarize how flavonoids target the gut-liver axis to mitigate MAFLD. It emphasizes microbiota-dependent and -independent mechanisms to provide novel therapeutic strategies for MAFLD management through medical or dietary interventions.
2 Flavonoid, and their metabolism by gut microbiota
Flavonoids represent the principal bioactive constituents in a wide array of medicinal plants and have been employed in the management of numerous diseases, including MAFLD. Owing to their multi-targeted biological activity, minimal toxicity, and dietary origin, flavonoids have garnered increasing scientific interest for their therapeutic potential in mitigating MAFLD. This growing interest is substantiated by findings from evidence-based medicine derived from population-level data. For instance, analyses of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database have highlighted the hepatoprotective properties of dietary flavonoids in reducing the risk of MAFLD (Tong et al., 2022). Moreover, a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials has indicated that flavonoids—such as quercetin, epicatechin, naringenin, apigenin, among others—ameliorate MAFLD by enhancing hepatic metabolic function, attenuating inflammatory responses, and modulating gut microbiota composition (Li et al., 2023b).
Actually, the intricate interplay between flavonoids and gut microbiota constitutes a bidirectional relationship that profoundly influences host physiology. Emerging evidence highlights the gut microbiome’s role in modulating flavonoid bioavailability and bioactivity, while flavonoids reciprocally reshape microbial ecology and metabolic output (Murota et al., 2018; Shabbir et al., 2021; Pei et al., 2020). This dynamic interaction forms a critical axis for understanding the therapeutic potential of flavonoids in metabolic diseases, including MAFLD (Figure 2), as will be elaborated upon in subsequent sections.
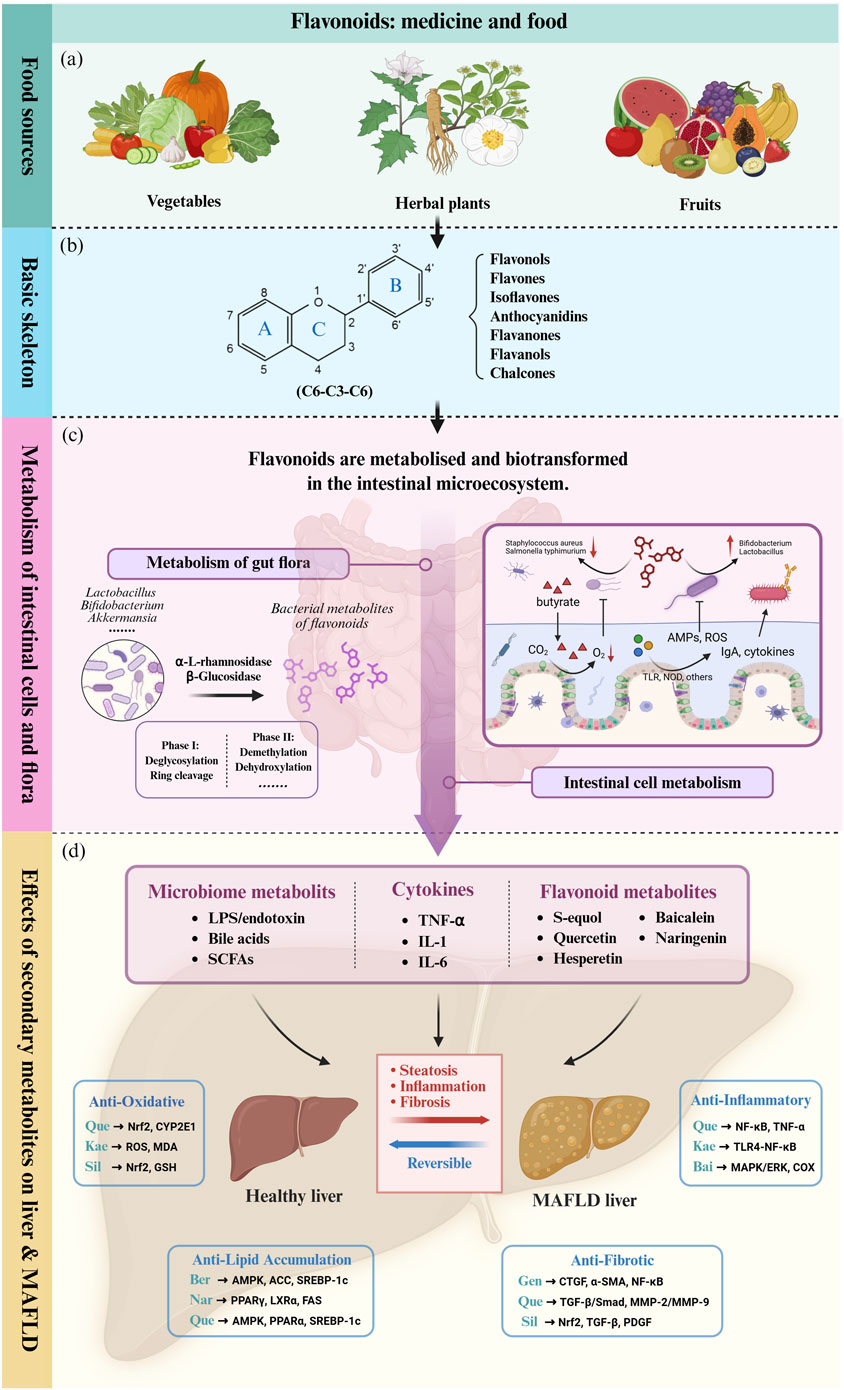
Figure 2. Flavonoids influence liver metabolism and MALFD progression directly or indirectly through the gut-liver axis. (a) Flavonoids are widely distributed in the natural diet and are abundant in various medicinal plants, vegetables and fruits. (b) The basic skeletal structure and seven subclasses of flavonoids. (c) The intestinal microenvironment and its role in flavonoid metabolism and biotransformation. (d) Flavonoids and intestinal secondary metabolites ultimately act on the liver and affect pathophysiological processes of MAFLD such as hepatic inflammatory cascade, oxidative stress and lipid accumulation through complex molecular mechanisms (In the image, upstream and downstream pathways use the same color to distinguish signaling pathways driven by different bioactive molecules). TLR: Toll-like Receptor. TLR4: Toll-like Receptor 4. NOD: Nucleotide-binding Oligomerization Domain-containing protein. ROS: Reactive Oxygen Species. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide. SCFA: Short-Chain Fatty Acid. TNF-α: Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha. IL-1: Interleukin-1. IL-6: Interleukin-6. Nrf-2: Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2. CYP2E1: Cytochrome P450 Family 2 Subfamily E Member 1. MDA: Malondialdehyde. GSH: Glutathione. AMPK: AMP-activated Protein Kinase. ACC: Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase. SREBP-1c: Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Protein 1c. PPARα: Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor Alpha. PPARγ: Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor Gamma. LXRα: Liver X Receptor Alpha. FAS: Fatty Acid Synthase. CTGF: Connective Tissue Growth Factor. α-SMA: Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin. NF-κB: Nuclear Factor-kappa B. TGF-β: Transforming Growth Factor-beta. Smad: Homolog of the Caenorhabditis elegans protein SMA and Drosophila protein MAD. MMP-2: Matrix Metalloproteinase-2. MMP-9: Matrix Metalloproteinase-9. MAPK: Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. COX: Cyclooxygenase. ERK: Extracellular Regulated Protein Kinase. ApoB: Apolipoprotein B. Bid: BH3 interacting-domain death agonist. SIRT1: Sirtuin 1. UQ: Ubiquinone. Que: Quercetin. Kae: Kaempferol. Bai: Baicalein. Sil: Silymarin. Gen: Genistein. Nar: Naringenin. Ber: Berberine. Original image drawn for this review using Biorender software.
2.1 Introduction of diverse flavonoid structures
Flavonoids are a diverse group of plant-derived polyphenolic compounds, characterized by a common 15-carbon skeleton comprising two aromatic rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C), forming a C6–C3–C6 structure (Kumar and Pandey, 2013; Latos-Brozio and Masek, 2019). This core structure serves as the foundation of flavonoids subclasses, each distinguished by specific modifications that influence their biological activities and physicochemical properties (Dias et al., 2021; Shen et al., 2022). Through extensive modification, it yields >8,000 species across seven major subclasses (Figure 1): flavones characterized by a 2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone (e.g., luteolin, apigenin), flavonols which are 3-hydroxylated flavones (e.g., quercetin, kaempferol) flavanones that lack the C2 = C3 double bond (e.g., naringenin, hesperetin), flavanols that lack the C2 = C3 double bond and C4 = O carboxyl group, but have C3-hydroxyl group (e.g., catechins, epicatechins), isoflavones with B ring attached to C3 (e.g., genistein, daidzein), anthocyanidins with C1 oxonium ion and C3-hydroxyl group (e.g., cyanidin, delphinidin), chalcones which are open-chain flavonoids serving as precursors in flavonoid biosynthesis (e.g., phloretin, isoliquiritigenin) (Shen et al., 2022; Kumar and Pandey, 2013).
Beyond these core structures, flavonoids undergo various modifications through hydroxylation, methylation (mainly O-methylation), glycosylation, and polymerization, that enhance their structural diversity and functional properties (Wang et al., 2020). Additional hydroxylation increases polarity and antioxidant capacity, while methoxylation enhances lipophilicity and membrane permeability, facilitating absorption and bioavailability. Glycosylation, the attachment of sugar moieties, improves water solubility and stability, and can substantially influence their bioactivity. Polymerization leads to the formation of oligomeric compounds, such as proanthocyanidins, which exhibit unique antioxidant properties (Cao et al., 2015).
These structural features and modifications not only define the chemical nature of flavonoids but also underpin their vast array of biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. Understanding the structural diversity of flavonoids is crucial for elucidating their mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications.
2.2 Flavonoid metabolism by gut microbiota
2.2.1 Two-stage microbial biotransformation of flavonoids
The gut microbiota mediates the structural modification and metabolism of dietary flavonoids through a complex enzymatic network, including phase I (deglycosylation, ring cleavage) and phase II (demethylation, dehydroxylation) reactions (Loo et al., 2020; Liu C. et al., 2024; Tian et al., 2019). In the first stage, key bacterial enzymes (e.g., β-glucosidase, α-rhamnosidase, and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases) and host intestinal lactase convert β-glycosylated flavonoids to more easily absorbed aglycone compounds (Loo et al., 2020; Liu Z. et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Following absorption, these flavonoid aglycones undergo further biotransformation through phase II reactions. These reactions, predominantly mediated by the gut microbiota, include critical modifications such as glycosylation, hydroxylation, O-methylation and depolymerization. Microbial metabolites derived from flavonoids exhibit different bioactivity compared to their parent compounds. These metabolites often survive hepatic first-pass metabolism, achieving higher systemic concentrations and longer half-lives (Liu C. et al., 2024).
2.2.2 Impact of flavonoid structure on microbial metabolism
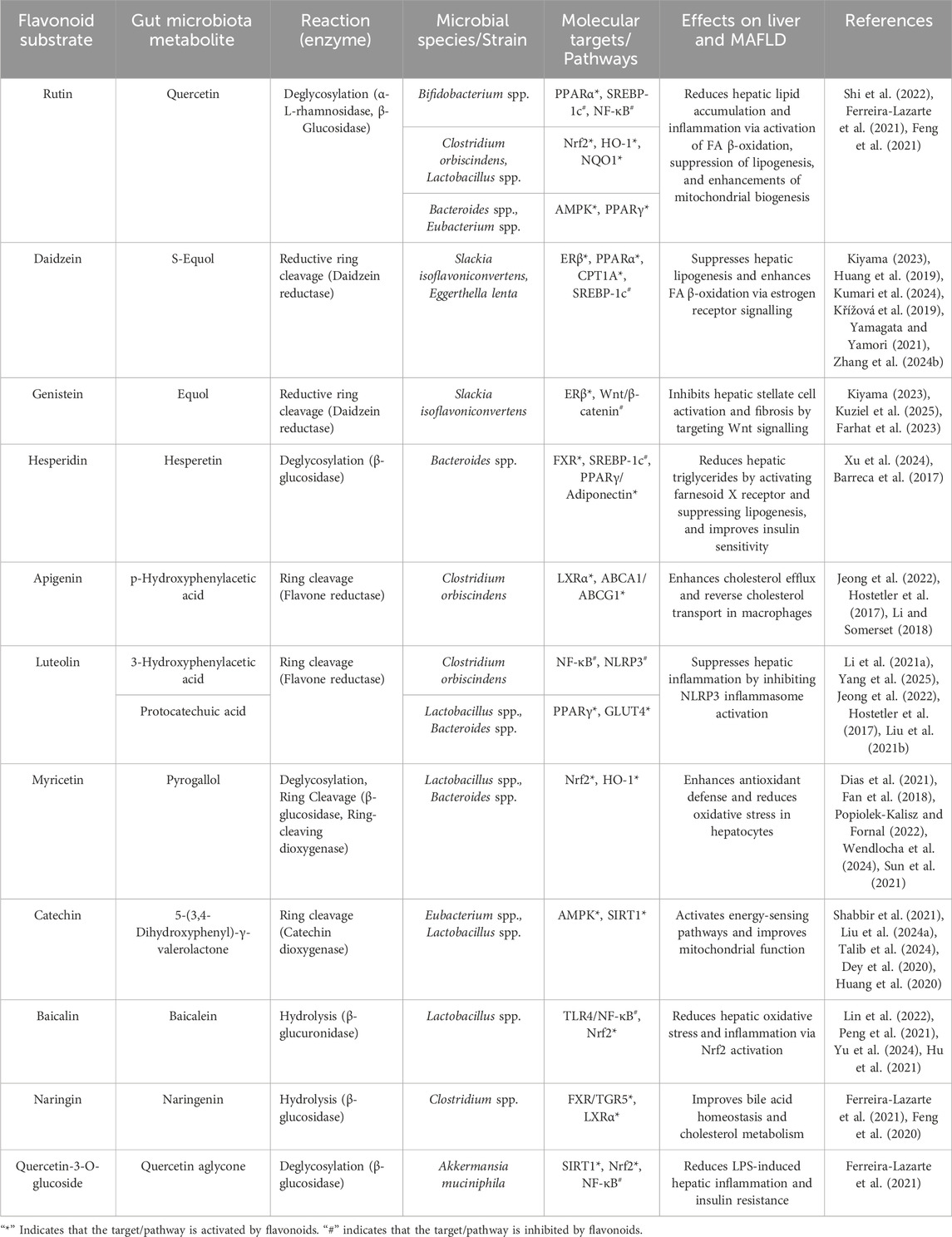
The structure of flavonoids not only dictates their biological activities and target interactions but also profoundly influences their metabolic fate within the gut microbiota. We summarised the metabolic transformations of selected flavonoids based on gut flora and their targets of action regarding MAFLD treatment (Table 2).
2.2.2.1 Glycosylation
Glycosylation significantly impacts flavonoid bioavailability and target engagement (Zeng et al., 2020; Shi et al., 2022). C-linked glycosides (e.g., vitexin), resistant to hydrolysis by mammalian digestive enzymes, require microbial glycoside hydrolases (e.g., C-glycoside hydrolases contained in Enterococcus faecalis) for deglycosylation (Braune and Blaut, 2011). The resulting aglycones can directly interact with cellular targets, including nuclear receptors such as ER, FXR (Tian et al., 2019; Kiriyama et al., 2024). In addition, O-glycosylated flavonoids like rutin (quercetin-3-O-rutinoside) are hydrolyzed by intestinal α-L-rhamnosidases (e.g., from Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus), generating quercetin aglycone (Murota et al., 2018; Liu C. et al., 2024; Liu Z. et al., 2021; Fan et al., 2018). Flavonols with 3-O-glycone are preferentially hydrolyzed by Lactobacillus strains, which express β-glucosidases (Wang et al., 2023; Chen-Chen et al., 2024; Li B. et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2024). Reciprocally, unique glycan constituents of flavonoids also affect microbial ecology. For instance, the rutin glycoside moiety acts as a prebiotic, selectively promoting Bifidobacterium growth and enhancing SCFA production, which in turn activates G-protein-coupled receptor 43 (GPR43) to improve hepatic energy metabolism (Shi et al., 2022; Ferreira-Lazarte et al., 2021).
2.2.2.2 Hydroxylation
The number and position of hydroxyl groups on the flavonoid skeleton also dictate substrate specificity for microbial enzymes and target binding affinity. For instance, flavones possessing a 5,7-dihydroxy configuration, such as apigenin, are recognized substrates for gut microbes like Flavonifractor plautii. A key initial step in the intestinal catabolism of apigenin is the hydrogenation of its C2-C3 double bond. This reaction is catalysed by a flavone reductase (FLR) from F. plautii, which stereospecifically reduces apigenin to naringenin (a dihydroflavone), an essential intermediate for further degradation into phenolic acids (Yang et al., 2021). The activity of FLR is a critical gateway to the breakdown of dietary flavones.
Importantly, the specific hydroxylation pattern of a flavonoid can enable it to selectively modulate inflammatory responses. In the case of kaempferol, the 4′-hydroxyl group on its B-ring is crucial for the inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which suppresses the production of inflammatory cytokines by downregulating ERK1/2 phosphorylation (Niziński et al., 2025; Li N. et al., 2023). Furthermore, the 3,5,7-trihydroxy arrangement of kaempferol facilitates its interaction with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), thereby blocking lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced NF-κB activation and attenuating liver inflammation (Niziński et al., 2025; Qu et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2024). Therefore, the anti-inflammatory properties of flavonoids can be modified by gut microbiome.
2.2.2.3 O-methylation (methoxylation) and O-demethylation
Structural alkyl modifications of flavonoids, particularly O-methylation (forming methoxyl groups, -OCH3), critically determine their metabolic fate and bioactivity (Kim et al., 2014). Polymethoxyflavones (PMFs) like nobiletin, confers unique biological activities by enhancing membrane permeability and membrane receptor binding (Xu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2020). Increasing evidence highlights the significant impact of gut microbiota on flavonoid methylation status. Although direct microbe-mediated O-methylation of flavonoids has been less extensively studied, specific microbial enzymes, such as DnrK from Streptomyces peucetius, have been shown to perform O-methylation in vitro on various flavonoids, including apigenin and genistein, typically at the C7 hydroxyl group (Kim et al., 2007). This suggests a potential for similar activities within the complex gut microbiome, even if not yet fully characterized in situ.
Conversely, microbial O-demethylation of many methoxylated flavonoids is relatively well documented. For instance, PMFs often undergo extensive O-demethylation by gut bacteria, particularly at positions like C-3′ and C-4′ on the B ring (Cao et al., 2015; Braune and Blaut, 2016). This may exhibit different bioactivities, absorption profiles, and targets in the host compared to their parent compounds. For example, Aspergillus niger strains have been shown to regioselectively O-demethylate tangeretin and 3-hydroxytangeretin into their 4′-O-demethylated metabolites, demonstrating a microbial capacity for targeted demethylation similar to some mammalian P450 systems (Murota et al., 2018; Buisson et al., 2007).
2.2.2.4 Depolymerization
Flavonoid polymers such as oligomeric proanthocyanidins, polymeric rutin, and condensation complexes of catechin exhibit significantly delayed microbial catabolism compared to their monomers (Latos-Brozio and Masek, 2019; Patanè et al., 2023). Specifically, crosslinked rutin shows a 5.6-fold prolonged intestinal retention time relative to its monomeric form due to reduced passive diffusion across enterocytes (Latos-Brozio and Masek, 2019). This kinetic property allows sustained release of bioactive metabolites in the distal colon (Liu C. et al., 2024; Shi et al., 2021). Due to their complex structures and high molecular weights, polymeric flavonoids like proanthocyanidins are poorly absorbed in the small intestine and a substantial portion reaches the colon largely intact (Braune and Blaut, 2016; Niwano et al., 2022). Here, the diverse enzymatic machinery of the gut microbiota plays a vital role in their breakdown. This microbial processing is initiated by depolymerization, a critical prerequisite for their biological activity where gut bacteria cleave the interflavan bonds (C-C and C-O-C linkages) holding the monomers together (Murota et al., 2018; Braune and Blaut, 2016). For instance, glycoside hydrolases from Lactobacillus and Bacteroides species target the glycosidic bonds in proanthocyanidins. These enzymes are induced by flavonoid exposure and show higher activity toward oligomers (DP 2–4) than high-molecular-weight polymers (Xiong et al., 2023). In addition, proanthocyanidin polymers (DP > 20) show limited depolymerization within the gastrointestinal tract, but their partial degradation by Bifidobacterium species produces metabolites (e.g., 5-(hydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone) that modulate hepatic lipid metabolism via the gut-liver axis (Niwano et al., 2022; Shoji et al., 2023; Déprez et al., 2000). These differences in kinetics and bioactivity place the gut microbiota in a unique position in the gut-liver axis regulation of polymeric flavonoids.
However, despite the well-established enzymatic framework we outlined in 2.2, a critical translational gap remains between identifying microbial metabolic capabilities and confirming their physiological relevance in MAFLD. For instance, while bacterial β-glucosidases from Lactobacillus spp. are known to hydrolyze rutin to quercetin, and F. plautii can hydrogenate apigenin to naringenin, the functional outcomes of these transformations are often inferred rather than definitively proven. Meanwhile, the field suffers from significant quantification deficit, the inadequate characterization and quantification of the terminal active metabolites: despite knowing that microbial metabolites like equol exhibit potent bioactivities in vitro (e.g., activating AMPK or FXR), their actual concentrations achieved in human portal circulation or hepatic tissue following dietary flavonoid intake are scarcely measured. It is therefore plausible that many proposed mechanisms operate at pharmacologically irrelevant concentrations. If the intrinsic concentrations fall substantially below these thresholds, the proposed mechanisms and physiological significance of flavonoid-derived metabolites become questionable.
Furthermore, the immense inter-individual variability in gut microbiota composition means that the metabolic pathways detailed herein—such as the production of S-equol from daidzein by Slackia isoflavoniconvertens—may be absent or inefficient in a substantial proportion of the MAFLD population. Consequently, the promising effects observed in preclinical models may not consistently translate to human patients. Future research must prioritize absolute quantification of microbial flavonoid metabolites in human biospecimens using advanced techniques—such as targeted metabolomics, and in vivo imaging—to accurately quantify and spatially resolve the distribution of these metabolites in target tissues, thereby moving beyond correlative associations to establish causative links, and finally distinguish truly impactful metabolic pathways from mere observational curiosities.
2.3 Modulation of microbiota by flavonoid
As mentioned previously, flavonoids and gut microbiota engage in dynamic, reciprocal interactions that transcend mere metabolism, influencing both microbial composition and host physiology. Many flavonoids exert prebiotic-like effects by selectively enriching beneficial symbionts while suppressing pathobionts (Shabbir et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2024; Naudhani et al., 2021).
For instance, theabrownin and quercetin increases symbionts Bifidobacterium and Akkermansia muciniphila abundances, while concurrently decrease the abundance of detrimental bacteria, such as Proteobacteria, Bacteroides, Escherichia-Shigella, and Escherichia_coli in murine models (Huang et al., 2019; Yuan et al., 2024). Importantly, these shifts in microbial community structure are often accompanied by significant alterations in overall microecological diversity. Studies have indeed reported that quercetin can modulate both alpha and beta diversity, leading to a more balanced and diverse gut microbiota composition, which is generally associated with improved gut health outcomes (e.g., increased Shannon, Simpson and Chao1 indices for alpha diversity, and PCoA and weighted UniFrac tree analysis for beta diversity) (Mi et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024a). Furthermore, these microecological changes translate into tangible physiological improvements in the host. Quercetin has been shown to reverse gut microbiota dysbiosis and inhibit the endotoxemia-mediated TLR-4 pathway, thereby ameliorating lipid metabolism abnormalities and mitigating systemic inflammation (Yuan et al., 2024; Porras et al., 2017; Cai et al., 2024). Compared to quercetin, isoquercetin exhibits a stronger ability to improve the MAFLD phenotype in mice induced by high-fat diet-fed (HFD). Isoquercetin significantly increases the abundance of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Akkermansia, leading to the production of more SCFAs and indole metabolites, which leads to a reduction in hepatic steatosis in HFD mice (Tan et al., 2018). Similarly, luteolin and kaempferol increase the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio through upregulation of mucin-degrading A. muciniphila, which enhances gut barrier integrity (Li B. et al., 2021; Qu et al., 2021). This effect is partially mediated by flavonoid-induced inhibition of bile salt hydrolases (BSH), which alters intraluminal BA profiles. Specifically, BSH inhibition generally leads to an increase in conjugated BAs and a decrease in deconjugated BAs, thereby creating a microenvironment less favourable for certain pathogenic bacteria and more conducive to the growth of probiotic bacteria (Xu et al., 2024; Collins et al., 2023; Sayin et al., 2013).
Anthocyanins, which derived from black rice and blackcurrant (Ribes nigrum L.), was shown to enhance the proportion of SCFA-producing microbiota by promoting the growth of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and A. muciniphila, while suppressing pro-inflammatory pathogenic taxa such as Helicobacter and Desulfovibrio. Concurrently, these anthocyanins activate the PPARα, FXR, and AMPK signalling pathways and downregulate the expression of SREBP-1c, thereby contributing to improved hepatic lipid metabolism (Song et al., 2021a; Song et al., 2021b).
2.4 MAFLD evidence: based on the gut-liver axis
Accumulating clinical evidence positions flavonoids as promising therapeutics for MAFLD through microbiota-dependent mechanisms. Notably, fecal microbiota transplantation from flavonoid-treated mice recapitulates these metabolic benefits, confirming the functionality of flavonoid-trained microbial community (Fang et al., 2021). Moreover, flavonoids also mitigate MAFLD through multiple microbial-triggered pathways, including the inhibition of TLR4-NF-κB signalling to dampen hepatic inflammation (Qu et al., 2021; Porras et al., 2017; Huiru et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024b; Ting et al., 2022), activation of AMPK to promote FA β-oxidation (Song et al., 2021b; Li X. et al., 2021), and regulation of SCFA production to improve energy metabolism, among others (Kiriyama et al., 2024). These observations highlight the gut microbiota as a central hub through which flavonoids exert their hepatoprotective effects, underscoring the therapeutic potential of microbiota-targeted flavonoid interventions in MAFLD. Obviously, further exploration of the specific mechanisms is a great temptation for researchers in this field.
3 Mechanism of flavonoids action in MAFLD via the gut-liver axis
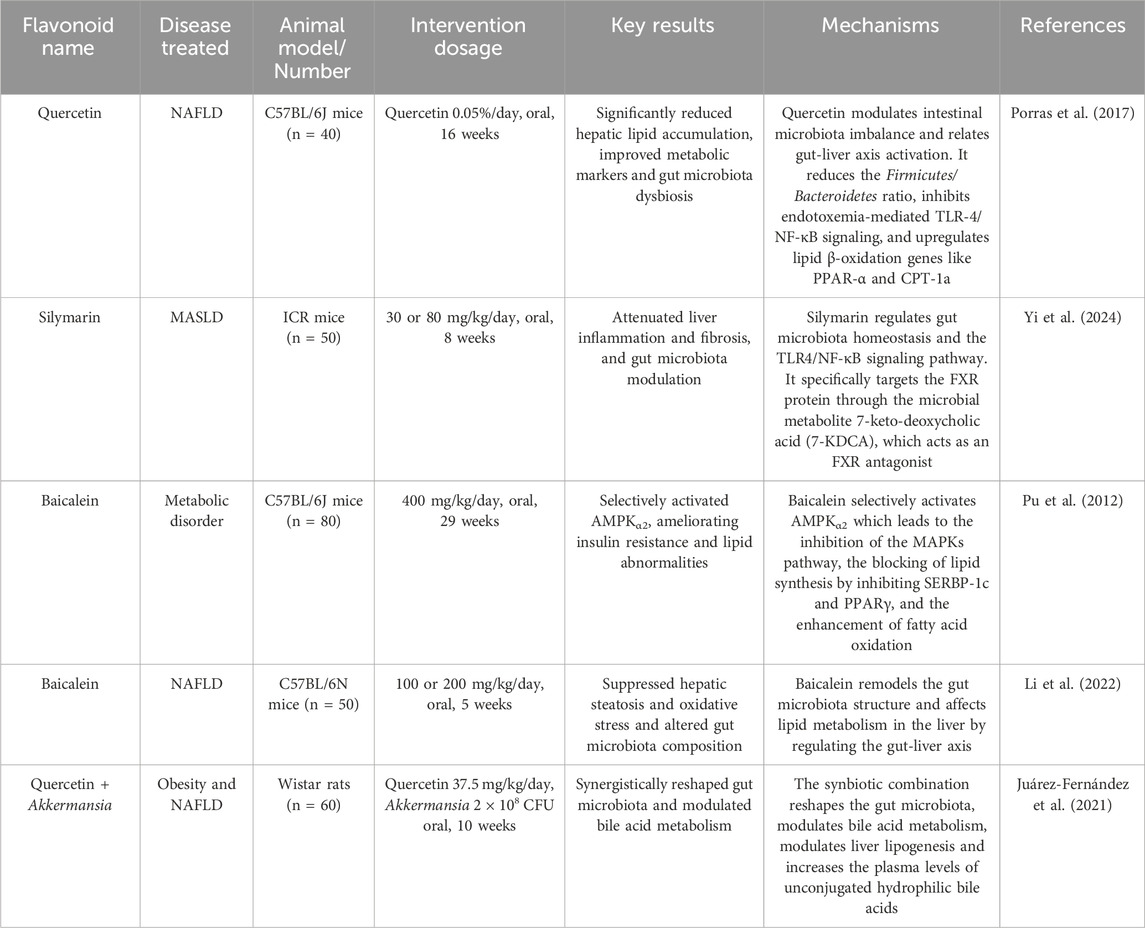
In recent years, a growing number of meta-analyses and systematic reviews with high-quality of evidence-based medicine evidence have pointed to flavonoid supplementation as a promising pharmacological option for the management of MAFLD and its associated complications (Li et al., 2023b; Liu H. et al., 2024). Their therapeutic efficacy is largely attributed to their ability to modulate the gut-liver axis: flavonoids can act directly on the liver after modification by the gut microbiota, or they can work synergistically with microbial metabolites to accomplish cooperative signalling (Figure 3). These findings are supported by a large body of animal studies, which have elucidated the diverse mechanisms by which flavonoids exert their therapeutic effects on MAFLD (Table 3). However, these promising results must be interpreted with caution due to significant translational limitations inherent in current animal models. The widely used HFD model effectively recapitulates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance, but often fails to fully replicate the profound inflammatory component and fibrotic progression characteristic of human MASH. Conversely, while the methionine-choline deficient (MCD) diet model rapidly induces steatohepatitis and fibrosis, its accompanying weight loss paradoxically contradicts the typical obese phenotype observed in most human MASH patients. Furthermore, the pharmacological doses employed in many animal studies (e.g., baicalein at 400 mg/kg/day) vastly exceed achievable human dietary intake levels—when converted to human equivalent doses, these doses fall far beyond reasonable supplementation ranges, and raise legitimate concerns about potential toxicity. Therefore, considerable challenges still remain in translating these findings into clinically relevant, dietary achievable interventions for human MAFLD.
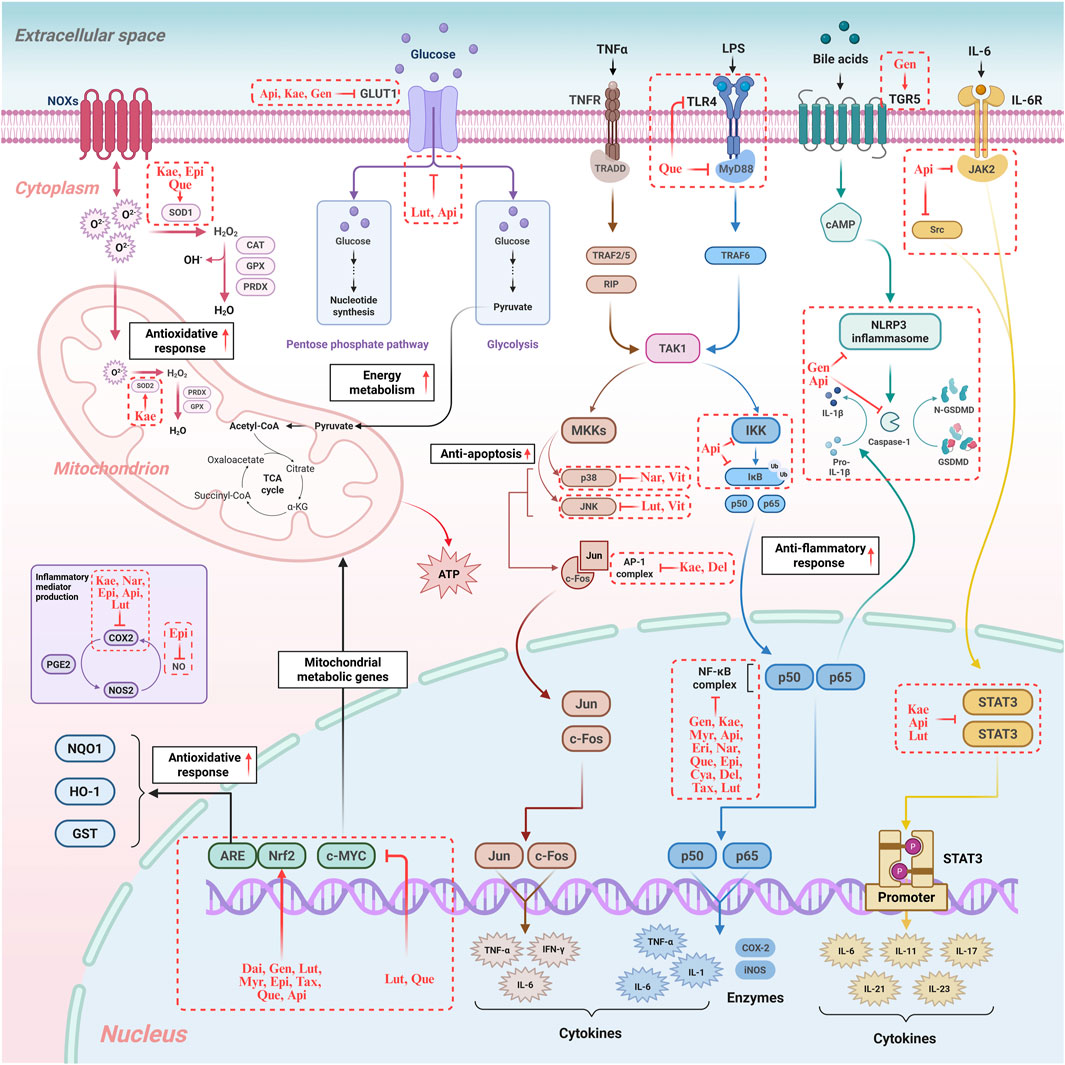
Figure 3. Regulatory mechanisms of flavonoids in hepatocyte oxidative stress, inflammation, immunity, and energy metabolism. The diagram illustrates how flavonoids modulate crucial signalling pathways, including those regulating oxidative stress (e.g., Nrf2 activation), inflammation (e.g., NF-κB inhibition), and energy metabolism (e.g., TCA cycle), highlighting their multi-target therapeutic potential. NOXS: NADPH Oxidases. SOD1: Superoxide Dismutase 1. SOD2: Superoxide Dismutase 2. CAT: Catalase. GPX: Glutathione Peroxidase. PRDX: Peroxiredoxin. GLUT1: Glucose Transporter 1. ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate. PGE2: Prostaglandin E2. COX2: Cyclooxygenase-2. iNOS: Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase. NOS2: Nitric Oxide Synthase 2. NQO1: NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1. IDH1: Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 1. ME1: Malic Enzyme 1. MAF: Musculoaponeurotic Fibrosarcoma Proteins. Nrf2: Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2. c-MYC: cellular myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog. TNFR: Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor. TRADD: TNF Receptor-Associated Death Domain. TRAF2/5: TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2/5. TRAF6: TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6. RIP: Receptor-Interacting Protein. TAK1: TGF-β-Activated Kinase 1. MKKs: Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinases. p38: p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. p50: NF-κB subunit p50. p65: NF-κB subunit p65. JNK: c-Jun N-terminal Kinase. c-Fos: FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog. Jun: Transcription factor Jun. AP-1: Activator Protein-1. TNF-α: Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha. IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma. IL-1: Interleukin-1. IL-1β: Interleukin-1 beta. IL-6: Interleukin-6. IL-11: Interleukin-11. IL-17: Interleukin-17. IL-21: Interleukin-21. IL-23: Interleukin-23. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide. TLR4: Toll-like Receptor 4. MyD88: Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response 88. IKK: IκB Kinase. IκB: Inhibitor of κB. NF-κB: Nuclear Factor-kappa B. TGR5: G Protein-coupled Bile Acid Receptor 1. cAMP: Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate. NLRP3: NLR Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3. GSDMD: Gasdermin D. IL-6R: Interleukin-6 Receptor. JAK2: Janus Kinase 2. Src: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src. STAT3: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3. Kae: Kaempferol. Epi: Epigallocatechin. Que: Quercetin. Api: Apigenin. Gen: Genistein. Lut: Luteolin. Nar: Naringenin. Dai: Daidzein. Myr: Myricetin. Tax: Taxifolin. Eri: Eriodictyol. Cya: Cyanidin. Del: Delphinidin. Vit: Vitexin. Original image drawn for this review using Biorender software.
3.1 Direct hepatic effects of microbiota-modified flavonoids
The human gut-liver axis is increasingly recognized as a key regulator of hepatic metabolic health, and in addition to its direct involvement in hepatic physiology (e.g., BA metabolism), it can affect the liver through its ability to alter bioactive compounds. The gut microbiota converts dietary flavonoids into metabolites that directly modulate hepatic signalling. This is expected to address the lipid dysregulation, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response that are core pathological features of MAFLD.
3.1.1 Regulation of lipid metabolism
Flavonoids can inhibit de novo lipogenesis via key transcription factors like Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 1c (SREBP-1c) and lipogenic enzymes. In some cases, they also promote fatty acid oxidation by activating master regulators like PPARα, rate-limiting enzymes such as Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), and enhancing alternative oxidation pathways like ω-oxidation. In brief, flavonoids contribute to systemic remodelling of lipid, improving circulating lipid profiles and influencing BA synthesis and excretion.
3.1.1.1 Inhibition of hepatic lipogenesis
The synthesis process of new fatty acids and triglycerides in the liver is known as de novo lipogenesis (DNL), which is a critical contributor to hepatic steatosis in MAFLD (Gnoni et al., 2022; Ponugoti et al., 2010). A primary molecular target in this process is SREBP-1c, a master transcriptional regulator of hepatic lipogenesis (Ponugoti et al., 2010; Yoon et al., 2009). Flavonoids such as quercetin and baicalin have been shown to significantly reduce the expression of SREBP-1c and lipogenic genes (Gnoni et al., 2022; Jiang L. et al., 2025). Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) and Fatty Acid Synthase (FASN) are key rate-limiting enzymes in fatty acid synthesis (Yoon et al., 2009; Jiang L. et al., 2025; Mu et al., 2020; Dong et al., 2025). Quercetin exerts its anti-lipogenic effect by phosphorylating Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Alpha (ACACA), a key player that catalyses the committing step in the DNL pathway (Gnoni et al., 2022; Wan et al., 2025). Furthermore, baicalin suppresses DNL by inhibiting the AMPK/acetyl-CoA carboxylase pathway and downregulating FASN (Dai et al., 2018). Licorice chalcone and luteolin also inhibit adipogenesis by activating the Sirtuin1/AMPK pathway (Tan et al., 2022). The consistent targeting of SREBP-1c, ACC, and FASN by various flavonoids indicates a convergent therapeutic strategy to suppress the core DNL pathway. However, the distinct upstream mechanisms, such as quercetin’s action on the ACACA/AMPK/PP2A axis versus licorice chalcone/luteolin’s SIRT1/AMPK activation, reveal diverse molecular effect points to achieve this common outcome.
3.1.1.2 Promotion of hepatic fatty acid oxidation
Flavonoids enhance the breakdown of fatty acids for energy, thereby reducing intrahepatic fat levels (Aneta et al., 2024; Ipsen et al., 2018). Fatty acid oxidation (FAO), which is crucial for maintaining lipid homeostasis (Ipsen et al., 2018), is mainly regulated by hepatic Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor alpha (PPARα), particularly during fasting, that orchestrate the transcription of numerous FAO genes (Ipsen et al., 2018; Silva and Peixoto, 2018). Flavonoids (including quercetin, naringenin and baicalin) have been shown to ameliorate hepatic fat accumulation by targeting PPARα/γ (Jiang L. et al., 2025; Dong et al., 2025; Dai et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2023).
Another critical molecular target is CPT1, a rate-limiting enzyme that facilitates lipid influx into mitochondria for FAO (Jiang L. et al., 2025; Dai et al., 2018). Baicalin directly activates hepatic CPT1, accelerating this process (Dai et al., 2018). Quercetin enhances CPT1A expression, and increases hepatic lipid ω-oxidation, leading to lowered circulating lipid levels (Jiang L. et al., 2025; Hoek-van den Hil et al., 2013). The consistent promotion of FAO by flavonoids via PPARα and CPT1 directly addresses the insufficiency of compensatory FAO often observed in MAFLD, which can otherwise lead to oxidative stress and disease progression (Ipsen et al., 2018). The ability of quercetin to increase ω-oxidation provides an additional, distinct pathway for fatty acid disposal, which is particularly important when mitochondrial β-oxidation is overwhelmed or compromised. This suggests that flavonoids may protect against lipotoxicity not merely by reducing fat production, but by enhancing the liver’s capacity to safely process excess fatty acids, thereby preventing the “second hit” of oxidative stress and inflammation (Zhang S. et al., 2025).
3.1.2 Regulation of BA Enterohepatic metabolism
Flavonoids act on FXR in the liver and intestine to regulate BA synthesis, excretion and reabsorption. This modulation of BA metabolism is one of the key axes influencing the pathological processes associated with MAFLD. By inhibiting intestinal FXR signalling, compounds like theabrownin from Pu-erh tea increase hepatic BA synthesis and fecal excretion, reducing hepatic cholesterol accumulation (Huang et al., 2019; Liang et al., 2024). Quercetin, a paradigmatic flavonol which alleviates hepatic steatosis in HFD mice, maintains lipid homeostasis and attenuates hepatic fat accumulation mainly by regulating intestinal BA metabolism and activating FXR and TGR5 in the liver (Yuan et al., 2024; Porras et al., 2017; Cai et al., 2024). S-equol, as previously noted, binds estrogen receptors with higher affinity than precursor daidzein, which not only exerts stronger anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects, (Farhat et al., 2023), but also activates hepatic FXR to regulate BA synthesis (Kumari et al., 2024). Moreover, naringenin enhances the production of secondary BAs (e.g., lithocholic acid) by inducing BSH activity in Bacteroides ovatus. These BAs activate FXR in the ileum and stimulate fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) secretion (Katafuchi and Makishima, 2022). Hepatic FGF19 receptor (FGFR4) activation inhibits cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1), the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of bile acids, and activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which phosphorylates and inhibits carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP), reducing hepatic gluconeogenesis (Huang et al., 2019). At another metabolic node, flavonoids modulate BA metabolism by inhibiting BSH activity in Clostridium and Bacteroides, thereby increasing conjugated BA that antagonize intestinal FXR signalling (Zhang et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2022). Concurrently, altered BA profiles feedback on gut microbiota, suppressing BSH-positive pathogens and promoting beneficial bacteria (Xu et al., 2024). This bidirectional crosstalk targeting dysregulated BA metabolism that contributes to hepatic steatosis and inflammation holds key to the development of novel therapy for MAFLD (Xu et al., 2024; Huang et al., 2019).
3.1.3 Modulation of oxidative stress
Various Flavonoids such as citrus-enriched naringenin exhibited potent anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties. Demethylation of naringin by microorganisms produces naringenin, which undergoes further ring cleavage to produce phenolic acids (e.g., 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid). These metabolites activate nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), promoting its translocation to the nucleus and binding to antioxidant response elements (AREs) in the promoters of HO-1 (Heme Oxygenase-1), NQO1 (NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1) and GCLC (glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit) (Dias et al., 2021). In HFD-induced MAFLD mice, naringenin supplementation increased hepatic glutathione (GSH) levels by 60%, reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) by 40%, and attenuated cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1)-mediated oxidative damage (Shi et al., 2022).
3.1.4 Regulation of inflammatory via Kupffer cells (KCs)
Kupffer cells (KCs), the liver’s resident macrophages, their critical functions include recognizing and clearing foreign materials (such as bacterial products like LPS), and endogenous danger signals (Baffy, 2009). Activated KCs are significant contributors to hepatic inflammation and the progression of MAFLD to steatohepatitis. They release a variety of pro-inflammatory mediators, including cytokines, chemokines, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Baffy, 2009).
Flavonoids exert their anti-inflammatory effects on the liver through a dual approach. First, they can directly interact with KCs, as in case of bergamot polyphenols that shown to decrease hepatic inflammation by the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-6 (IL-6) while increasing the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 (Parafati et al., 2018). This effect correlated with fewer KCs and lower inflammatory foci scores in the liver, suggesting a direct immunomodulatory action (Parafati et al., 2018). Second, flavonoids modulate the inflammatory response via gut-liver axis by influencing the production and translocation of key microbial metabolites. In MAFLD, an impaired gut barrier allows the translocation of bacterial components like LPS from the intestinal lumen to the liver, that activate KCs via the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signalling pathway and subsequently the MyD88/NF-κB cascade, a central driver of pro-inflammatory gene expression. Flavonoids can directly inhibit this cascade, but they also have an indirect effect by modulating the gut microbiota to increase the production of anti-inflammatory metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate. These SCFAs can then reach the liver via the portal vein and directly interact with KCs to suppress their inflammatory response. This multi-pronged approach is further facilitated by the fact that specific flavonoids, such as quercetin and luteolin, can modulate broader inflammatory networks. For example, they can affect the production of cytokines such as IL-17, which in turn influences KC activation and the subsequent inflammatory cascade (Jiang L. et al., 2025; Ma et al., 2020; Meng et al., 2012; Kelepouri et al., 2018).
3.1.5 Regulation of inflammatory via hepatic T-cell
Beyond their influence on KCs, flavonoids exert a direct immunomodulatory effect on hepatic T-cells, which is crucial for managing liver inflammation and fibrosis. Specific flavonoids, such as curcumin and quercetin, have been shown to regulate T-cell activity by modulating key signalling pathways. For instance, curcumin suppresses T-cell activation by inhibiting calcium mobilization and the NFAT (Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells) signalling pathway, leading to a dose-dependent reduction in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-2 and IFN-γ (Kliem et al., 2012). This effect is further supported by evidence that curcumin inhibits the proliferation of CD4+ T-cells (Kim et al., 2013). Similarly, quercetin has been found to modulate the balance between pro-inflammatory Th17 cells and anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells (Tregs), promoting an anti-inflammatory state within the liver (Jiang Z. et al., 2025).
Furthermore, flavonoids can induce apoptosis in activated T-cells, a mechanism essential for resolving inflammation. For example, baicalein selectively promotes apoptosis in activated lymphocytes, which helps to mitigate hepatitis by removing excessive inflammatory cells (Zhang et al., 2013). The anti-inflammatory actions of these compounds are often mediated by their ability to inhibit central signalling pathways such as NF-κB, MAPK, and the NLRP3 inflammasome, all of which are critical for T-cell activation and cytokine production (Jiang Z. et al., 2025; Martinez et al., 2019). These findings provide a cellular and molecular basis for how flavonoids can directly modulate hepatic immune responses, offering a promising therapeutic approach for MAFLD and other liver inflammatory conditions (Li et al., 2018; Wu and Wang, 2025).
3.1.6 Regulation of fibrosis via hepatic stellate cells (HSCs)
Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSCs) play pivotal roles in the development and progression of liver fibrosis in chronic inflammation conditions such as in MAFLD. The activated HSCs are the primary producers of excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, which leads to the accumulation of fibrotic tissue (Zhang Y. et al., 2024). The activation of HSCs is driven by the dysregulation of multiple signalling pathways, including TGF-β/Smads, MAPK (ERK, JNK, p38), PI3K/AKT, Wnt, NF-κB, and AMPK (Zhang Y. et al., 2024). Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) is a particularly potent activator of HSCs, promoting fibrosis through the Smad2/3 signalling pathway (Zhang Y. et al., 2024).
Flavonoids are recognized as promising natural compounds for alleviating or reversing hepatic fibrosis (Tauil et al., 2024). For example, quercetin, hydrolyzed from rutin by Lactobacillus β-glucosidases, can work with butyrate (a SCFA) to suppress TGF-β/Smad signalling in HSCs (Feng et al., 2021). Quercetin blocks TGF-β type I receptor (ALK5) phosphorylation, preventing Smad2/3 nuclear translocation and reducing COL1A1 and α-SMA transcription, while butyrate enhances this effect by inhibiting histone deacetylases (HDACs), increasing acetylation of the TGF-β promoter and reducing its expression (Wang S. et al., 2022). Genistein, a soy isoflavone, and urolithin A (derived from ellagitannins by Enterococcus and Gordonella spp) cooperate to inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, a key driver of HSCs activation (Farhat et al., 2023). Genistein binds to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6 (LRP5/6), blocking Wnt ligand binding and β-catenin stabilization, while urolithin A enhances this effect by promoting β-catenin ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, reducing nuclear β-catenin levels and downstream fibrosis-related genes (e.g., CTGF, VEGFA) (Liu et al., 2025). Specific flavonoids have demonstrated clear anti-fibrotic effects.
3.1.7 Flavonoids act on MAFLD via liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs)
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) play a pivotal role in the development and progression of MAFLD. As a specialized cell type lining the liver sinusoids, LSECs are essential for maintaining liver homeostasis, regulating blood flow, and facilitating the bidirectional exchange of nutrients, hormones, and immune signals between the portal blood and hepatocytes. LSEC dysfunction, which can precede the development of inflammation and fibrosis, is now recognized as an early and critical event in MAFLD pathogenesis (Hammoutene et al., 2020; Velliou et al., 2023; Hammoutene and Rautou, 2019). This dysfunction is mechanistically characterized by several key changes, including the loss of fenestrations (defenestration) and the formation of a continuous basement membrane (capillarization). These structural alterations hinder the metabolic exchange between the bloodstream and hepatocytes, leading to lipotoxicity and a subsequent pro-inflammatory state. At the molecular level, this pathological process is exacerbated by a defect in endothelial autophagy, which has been observed in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and contributes to inflammation and fibrosis by allowing the accumulation of damaged cellular components (Hammoutene et al., 2020). Furthermore, MAFLD-associated inflammation drives the overexpression of adhesion molecules, such as vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), on the surface of LSECs. This promotes the recruitment and adhesion of inflammatory cells, such as macrophages, to the liver, thereby accelerating the inflammatory cascade and the progression of fibrosis (Guo et al., 2022). By targeting these specific pathways—such as by protecting LSEC integrity, enhancing endothelial autophagy, or modulating adhesion molecule expression—flavonoids offer a promising therapeutic avenue for mitigating MAFLD progression.
3.2 Indirect effects of flavonoids on the MALFD via the gut-liver axis
In addition to direct effects on the liver, flavonoids also mediate synergistic signalling via intestinal epithelial cells and immune cells, which can significantly affect liver metabolism and disease progression. Such synergistic signalling networks amplify their effects on liver inflammation, fibrosis and metabolic homeostasis.
3.2.1 Flavonoids act on MAFLD via intestinal epithelial cells (IECs)
Intestinal epithelial cells form a critical component of the gut barrier, regulating nutrient absorption and playing a significant role in metabolic signalling. Flavonoids have a multifaceted effect on these cells, particularly on regulating intestinal barrier function.
Dysregulation of the gut microbiota and subsequent intestinal barrier dysfunction are recognized contributors to the pathogenesis of MAFLD (Sun et al., 2025). Research shows that flavonoids can inhibit the loss of tight junction proteins such as ZO-1 and occludin, thereby improving intestinal barrier function. This protective action is attributed to the flavonoids’ ability to modulate the gut microbiota and an increased production of beneficial SCFAs (Dong et al., 2025; Aneta et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024). These SCFAs then exert protective effects on IECs, including the upregulation or maintenance of tight junction proteins like ZO-1 and occluding (Vancamelbeke and Vermeire, 2017). This sequence of events results in enhanced intestinal barrier function, a reduction in the translocation of bacterial endotoxins (such as LPS) to the liver, and ultimately, an attenuation of hepatic inflammation and MAFLD progression. This pathway highlights a crucial indirect mechanism by which flavonoids contribute to liver protection. For instance, total flavonoids derived from Dracocephalum moldavica L. have been shown to alleviate HFD rats by enhancing the intestinal barrier, alongside their anti-inflammatory and lipid metabolism-regulating effects (Sun et al., 2025).
3.2.2 Flavonoids act on MAFLD via intestinal immune cells
The liver functions as a central immunological organ, and its susceptibility to inflammatory responses is particularly evident in chronic liver diseases such as MAFLD. The balance of intestinal T-cell responses, notably the Th17/Treg axis, further influences liver inflammation (Hammerich et al., 2011). Flavonoids exhibit immunomodulatory effects that can influence this delicate balance of intestinal T cell, impacting hepatic lipid inflammation.
The balance between Th17 cells and T regulatory (Treg) cells is crucial, as Tregs secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines and can mitigate the Th17 response, such as produce pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-17 and IL-22 (Hammerich et al., 2011; Olveira et al., 2023; Abdelnabi et al., 2024; Pan et al., 2014). Levels of IL-17 have been correlated with the progression from MAFLD to steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma (Hammerich et al., 2011; Olveira et al., 2023; Chackelevicius et al., 2016). In contrast, IL-22 is a pleiotropic cytokine that abrogates MASH-related inflammation and fibrosis development by inducing antioxidant and anti-apoptotic factors (Abdelnabi et al., 2024; Pan et al., 2014). This differentiation in function suggests that effective therapeutic strategies for MAFLD should aim to suppress the detrimental effects of IL-17 while potentially enhancing the beneficial actions of IL-22.
Previous studies have shown that flavonoids can significantly affect the release of IL-17 and IL-22 by regulating immune cell function and signalling pathways. For example, in the LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophage model, luteolin blocked the NF-κB signalling pathway, reduced the p65 binding activity in the promoter region of the IL-17A gene by 40%, led to downregulation of IL-17A mRNA expression, and inhibited the secretion of IL-17 (Gendrisch et al., 2021). In addition, a variety of flavonoids such as quercetin and naringenin have been shown to regulate the Th17/Treg cell ratio and affect IL-17/IL-22 levels in intestinal tissue (Yang et al., 2018; Ke et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2018).
In addition to influence key molecular pathways such as NF-κB, MAPK and PPARγ directly, flavonoids can also affect the Th17/Treg balance by improving the composition of intestinal flora (Kelepouri et al., 2018; Fu et al., 2025). A commensal bacterium, Bacteroides fragilis, could inhibit IL-17 production and enhance intestinal Treg cell activity by producing polysaccharide A (PSA) with anti-inflammatory effects (Jin et al., 2012; Round et al., 2011). PSA is an immunomodulatory molecule present in the pod membrane of B. fragilis, which mediates the conversion of CD4+ T cells into Treg cells via toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) (Round et al., 2011). In addition, PSA is recognized by dendritic cells (DCs) in the intestine and then causes IL-10 production by DC cells, thus promoting Treg production (Chu et al., 2016). Quercetin and luteolin can both decrease the abundance of B. fragilis, thereby regulating Th17/Treg balance and cytokine secretion (Yuan et al., 2024; Kelepouri et al., 2018; Fu et al., 2025; Liu et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2025).
Currently, it is still unclear how flavonoids regulate the cytokine profile to make the Th17/Treg axis more balanced in the MAFLD model, such as reducing pro-inflammatory IL-17 and supporting protective IL-22. Future studies should focus on specific flavonoid metabolites and their direct effects on immune cell differentiation and cytokine production within the gut-liver axis to fully characterize these complex interactions. In summary, the synergistic actions of flavonoids with enterocyte and microbial metabolites represent a complex and dynamic regulatory network that can significantly impact hepatic health. By modulating key metabolic pathways and inflammatory responses, these cooperative interactions offer promising therapeutic avenues for the management of MAFLD and its associated complications.
However, while the mechanistic pathways delineated in this section present a compelling framework, the evidence supporting these mechanisms remains largely correlative and derived from imperfect model systems. For instance, the proposed anti-fibrotic effects of quercetin and urolithin A are primarily founded on preclinical models that may not fully recapitulate human disease pathophysiology. A critical, unresolved question is whether the observed microbial shifts (e.g., enrichment of A. muciniphila or Bacteroides spp.) are related to consequence of improved liver health by flavonoids. This requires causal validation in germ-free or antibiotic depletion animal models to tell whether the absence of gut microbiota abrogates the hepatoprotective effects of flavonoids like naringenin or baicalein. Faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) studies could also establish whether microbiota from flavonoid-treated donors is sufficient to transfer metabolic benefits. Future research must prioritise these approaches to transcend correlation and establish causality, ensuring that the compelling narrative of flavonoid action via the gut-liver axis is robustly anchored in definitive experimental evidence.
4 Clinical evidence and trials
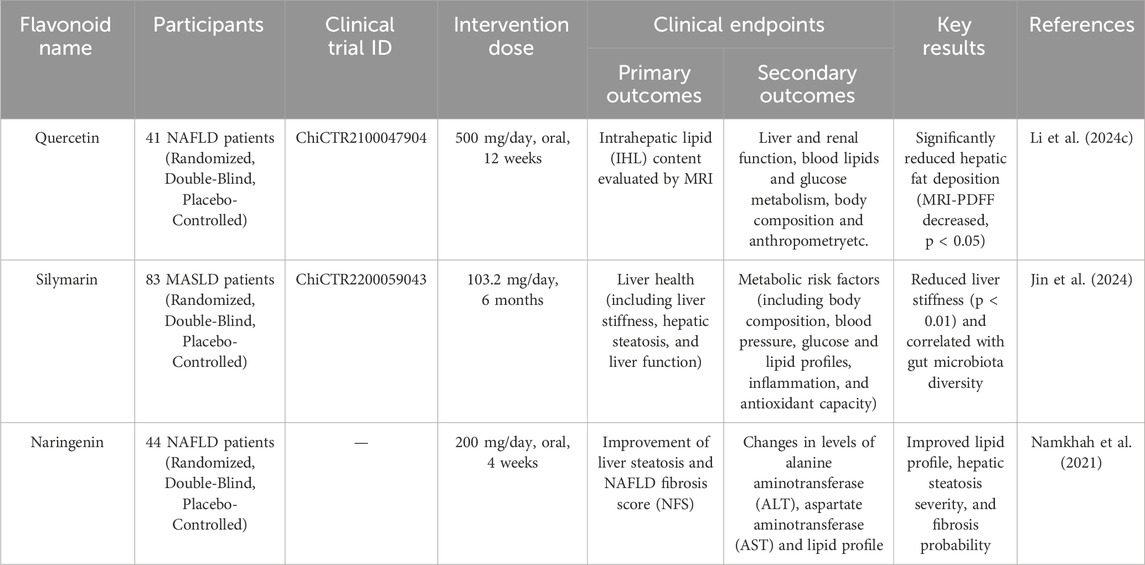
Flavonoids have been explored as potential modulators of the gut-liver axis in the context of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Animal studies have shown that flavonoids can modulate the gut microbiota and its metabolites to alleviate MAFLD. Other than preclinical studies in animal models as discussed in previous sections and summarized in Table 3, several clinical studies have documented the efficacy of flavonoids for MALFD management (Table 4).
A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover clinical trial assessed the impact of quercetin supplementation on intrahepatic lipid content in patients with MAFLD. In this trial, 41 patients were randomised to receive either quercetin (500 mg) or placebo capsules for 12 weeks, followed by a 4-week washout period and subsequent intervention crossover. The primary outcome was intrahepatic lipid content evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) estimated proton density fat fraction. Secondary outcomes included liver function measurements and safety assessments. The results showed that quercetin intervention moderately decreased intrahepatic lipid contents from 11.5% ± 6.4%–9.6% ± 5.8%, compared with a minimal decrease of 0.1% ± 2.6% in the placebo group (P = 0.013). Body weight and body mass index (BMI) were also mildly reduced after quercetin intervention (P < 0.05 and adjusted P values of 0.038), while the placebo group experienced much smaller reductions. The reduction in intrahepatic lipid content was positively associated with body weight loss after both interventions. No significant differences were found in other secondary and safety outcomes, and no adverse events were associated with the study intervention. This trial demonstrated that 12 weeks of quercetin treatment could reduce intrahepatic lipid content in MAFLD patients. However, the trial was limited by its relatively small sample size and crossover design, which may have introduced carryover effects despite the washout period. Further trials with larger cohorts and longer intervention durations are needed to confirm these clinical findings and to explore the long-term safety and efficacy of quercetin in MAFLD management (Li N. et al., 2024).
Another randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial registered at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2200059043) investigated the potential efficacy of silymarin in improving MAFLD indicators and the underlying mechanisms related to gut microbiota. In this 24-week trial, 83 patients with MAFLD were randomised to either placebo (n = 41) or silymarin (103.2 mg/d, n = 42). Liver stiffness and hepatic steatosis were assessed using FibroScan at 0, 12, and 24 weeks, while blood samples were collected for biochemical detection and faecal samples were gathered at 0 and 24 weeks for 16S rRNA sequencing. The results showed that silymarin supplementation significantly reduced liver stiffness (LSM, −0.21 ± 0.17 vs. 0.41 ± 0.17, P = 0.015) and serum levels of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT, −8.21 ± 3.01 vs. 1.23 ± 3.16, P = 0.042), but had no significant effect on other biochemical indicators, physical measurements or fibrosis indices (AST to Platelet Ratio Index and Fibrosis-4 Index). Gut microbiota analysis revealed increased species diversity and enrichment of Oscillospiraceae in the silymarin group. These clinical findings suggest that silymarin supplementation could improve liver stiffness in MAFLD patients, possibly by modulating gut microbiota. The trial was limited by its relatively small sample size and the lack of long-term follow-up to assess the sustainability of the observed effects. Further trials are needed to confirm these results and to explore the optimal dosing and duration of silymarin treatment in MAFLD management Meanwhile, the specific mechanism linking gut microbiota changes to liver stiffness was not directly elucidated. Therefore, the findings may have limited generalizability, and future research should focus on confirming these results in larger, more diverse cohorts and exploring the causality of the proposed mechanism (Jin et al., 2024).
Also eligible for randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled a clinical trial of naringenin included 44 eligible overweight/obese patients with MAFLD. This study assessed the effect of naringenin supplementation on lipid profile, transaminase levels, severity of steatosis and probability of fibrosis. Participants were randomised to receive naringenin capsules (100 mg) or identical placebo capsules twice daily for 4 weeks. The primary outcomes were improvement of liver steatosis and MAFLD fibrosis score (NFS), while secondary outcomes included changes in ALT, AST and lipid profile. The results showed that naringenin consumption significantly reduced the percentages of MAFLD grades (P < 0.001), as well as serum levels of triglyceride (TG) (P < 0.001), total cholesterol (TC) (P = 0.01), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) (P = 0.02), and increased serum levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) (P = 0.02) compared with the control group. However, no significant changes were observed in AST, ALT and NFS. The trial concluded that daily intake of 200 mg of naringenin for 4 weeks had beneficial effects on lipid profile and MAFLD grades as an indicator for the severity of hepatic steatosis (Namkhah et al., 2021).
The aforementioned clinical trials, while providing foundational evidence for the therapeutic potential of flavonoids in MAFLD, are subject to several limitations that warrant careful consideration. A primary and common limitation is the relatively small sample size in all trials (n = 41, n = 83, and n = 44, respectively), with insufficient statistical power to detect smaller, yet clinically meaningful effects, thereby increasing the risk of Type II errors (false negatives), such as failing to identify significant changes in fibrosis scores or other metabolic parameters. Furthermore, the short intervention durations (4, 12, and 24 weeks) are a significant constraint, as meaningful improvements in hepatic fibrosis or metabolic outcomes needs long-term observation, and the reversal of fibrosis typically requires extended periods beyond these timeframes, limiting the ability to capture true therapeutic effects. For instance, the lack of significant change in transaminases and fibrosis scores in the naringenin trial is likely a reflection of its extremely short 4-week duration rather than a true absence of effect, as these markers typically require a longer period to respond to interventions.
Additionally, the reliance on non-invasive surrogate endpoints (e.g., MRI-PDFF for steatosis and FibroScan for stiffness) instead of liver biopsy introduces uncertainty in accurately evaluating the severity of MAFLD and the full extent of histological improvement, as these imaging and biochemical markers may not fully correlate with pathological changes. The crossover design of the quercetin trial, despite its washout period, introduces the potential for carryover effects, where the influence of the initial treatment may persist and confound the results of the subsequent treatment period, a bias that can only be definitively ruled out with a longer washout period or a parallel-group design. The silymarin trial did not establish a direct causal link between the observed changes in Oscillospiraceae enrichment and the reduction in liver stiffness. The use of 16S rRNA sequencing also provides only a taxonomic snapshot of the microbiota, lacking the functional insights that could be provided by shotgun metagenomics or metabolomics to track specific flavonoid-derived metabolites. Moreover, these trials did not account for individual variability in flavonoid bioavailability, which is profoundly influenced by gut microbiota composition and genetic background (e.g., polymorphisms in drug-metabolizing enzymes or bile acid receptors); the absence of patient stratification based on enterotypes or genetic markers may obscure subgroup effects and contribute to inconsistent outcomes across studies.
These methodological constraints significantly limit the generalizability of the findings to the broader, heterogeneous MAFLD population, as the specific patient characteristics and baseline disease severity are likely to influence treatment response. Future research must, therefore, be guided by more robust methodologies. This includes large-scale, multi-center, parallel-group randomized controlled trials with intervention periods of at least 6 months to 1 year to properly evaluate sustained efficacy and long-term safety. The inclusion of more definitive clinical endpoints, such as a histological response (via liver biopsy) or significant and sustained changes in liver stiffness (FibroScan) and metabolic markers, will be essential. Furthermore, future studies should incorporate a multi-omics approach to thoroughly investigate the mechanistic link between flavonoids, gut microbiota, and hepatic pathology, moving beyond basic sequencing to measure microbial metabolites and host-derived signalling molecules in the gut-liver axis. Establishing optimal dosing regimens through dose-ranging studies and exploring the therapeutic efficacy in specific patient subgroups (e.g., by genetic polymorphisms or gut enterotypes) will be critical for translating these promising preclinical and preliminary clinical findings into personalized, effective clinical practice.
5 Beyond monotherapy: nanotechnology and probiotic Co-administration
5.1 Synbiotics: flavonoid-probiotic combinations
As discussed previously, the gut microbiota plays a crucial role in mediating the physiological effects of flavonoids via the gut-liver axis. Probiotics, defined as live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts, can interact synergistically with flavonoids, which are potential prebiotics, to form synbiotics. The combination of dietary flavonoids with specific probiotic strains has emerged as an innovative approach to address gut-liver axis dysregulation in the context of MAFLD (Jazvinšćak et al., 2023). Probiotic enzymatic activity activates flavonoid precursors into bioactive metabolites, while flavonoids selectively modulate the gut microbiota and microbial composition, creating a self-amplifying loop that enhances MAFLD management. This positive feedback loop targets multiple pathological mechanisms and exerts beneficial effects on oxidative stress, inflammation, and the gut microbiome (Zhu et al., 2022). In this section, we review several studies investigating the combined effects of flavonoids and probiotics on MAFLD, elucidating their therapeutic potential.
5.1.1 Quercetin and Akkermansia muciniphila
Akkermansia muciniphila is a prominent gut bacterium that has shown potential in improving metabolic diseases, including obesity and MAFLD. In a landmark study involving HFD-induced obese mice, researchers demonstrated that the synbiotic combination of A. muciniphila with quercetin was superior in reducing hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance compared to either intervention alone. This combination restored intestinal barrier integrity, as evidenced by upregulation of tight junction proteins, such as Claudin-1 and Occludin, while decreasing LPS translocation (Le Barz et al., 2019). Moreover, the combination reshaped the microbiota by enriching Roseburia and Faecalibacterium, bacteria that produce butyrate, a SCFA with anti-inflammatory properties. Notably, the quercetin-A. muciniphila synergy also modulated BA metabolism with enhanced FXR signalling, which suppressed hepatic lipogenesis by downregulating SREBP-1c and activated mitochondrial β-oxidation by upregulating PGC-1α. Co-administration of quercetin (50 mg/kg/day) with A. muciniphila (1 × 109 CFU/day) resulted in a 38% greater reduction in hepatic TG content compared to either treatment alone. This highlights the potential of flavonoid-probiotic combinations to modulate multiple metabolic pathways and improve liver health in MAFLD (Juárez-Fernández et al., 2021).
5.1.2 Grapeseed flour and Lactobacillus acidophilus
Grapeseed flour (GSF) is rich in flavonoids, particularly proanthocyanidins, which possess potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (Cho et al., 2018). In a 24-week clinical trial, a synbiotic combination of GSF and kefir-derived probiotics L. acidophilus LA-5 was showed to reduced liver fat content, as measured by the controlled attenuation parameter, by 22% compared to the use of probiotics alone. Additionally, this combination downregulated hepatic SREBP-1c (62%) and ACC (55%) expression through AMPK phosphorylation, as validated by CRISPR-Cas9 knockout models. The synbiotic treatment also reversed HFD-induced gut barrier dysfunction, which is crucial for preventing endotoxemia and inflammation in MAFLD. Moreover, Lactobacillus acidophilus enhanced the absorption of procyanidins by degrading mucus-bound glycoproteins in the intestine, thereby improving their bioavailability. These clinical findings suggest that combining flavonoid-rich GSF with probiotics can significantly ameliorate hepatic steatosis and related metabolic disturbances (Kwon et al., 2019; Seo et al., 2020).
5.1.3 Green tea EGCG and Lactobacillus fermentum
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a flavonoid extracted from green tea, has been extensively studied for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, both of which are essential for the management of MAFLD (Carrasco-Pozo et al., 2019; Talib et al., 2024). In a study involving aged C57BL/6 mice with diet-induced MAFLD, a synbiotic combination of EGCG and the probiotic L. fermentum was tested for its protective effects against oxidative stress and inflammation (Sharma et al., 2019). The synbiotic was found to increase hepatic glutathione peroxidase activity by 40%, decrease malondialdehyde (a marker of lipid peroxidation) level by 35%, and suppress CD8+ T-cell hepatic infiltration, which is indicative of liver inflammation. Transcriptome analysis revealed upregulation of antioxidant genes (HO-1, NQO1) and downregulation of Th17-related cytokines, suggesting that the synbiotic combination modulated both oxidative stress and immune responses (Ting et al., 2022). The EGCG component inhibited JNK phosphorylation, a key pathway in oxidative stress, while Lactobacillus fermentum promoted T-regulatory cell proliferation, further supporting the anti-inflammatory effects (Dey et al., 2020). The strong upregulation of hepatic Nrf2 expression exclusively in the synbiotic-fed animals provides additional evidence of the robust antioxidant defence induced by EGCG-L. fermentum combination (Sharma et al., 2019). These results highlight the potential of flavonoid-probiotic synbiotics as a therapeutic strategy for MAFLD, particularly in populations prone to oxidative stress, such as the elderly (Sharma et al., 2019; Huang et al., 2020).
5.1.4 Flavonoid-probiotic synbiotics: challenges and future
In conclusion, flavonoid-probiotic combinations represent a promising avenue for the treatment of MAFLD. The synergistic effects of these bioactive compounds, targeting multiple pathways such as gut microbiota modulation, bile acid metabolism, and hepatic lipid metabolism, provide a multifaceted cutting-edge strategy to managing this increasingly prevalent liver disease (Axling et al., 2012; Xiong et al., 2023; Thilakarathna and Rupasinghe, 2024; Peng et al., 2020). However, existing studies highlight several challenges, most notably the critical issue of strain-specificity where effects observed with particular bacterial strains (e.g., Lactobacillus or B. spp.) cannot be extrapolated to the entire species, yet many studies fail to adequately characterize or report the specific strains utilised, rendering results difficult to interpret and replicate. Other challenges include the need for optimal strain selection, biosafety evaluation, and the impact of patient variability, including genetic predisposition, individual microbiome composition, and dietary habits, on therapeutic outcomes (DiStefano, 2023; Oh et al., 2023; Wang M. et al., 2022; Ribeiro et al., 2018). Furthermore, there is a conspicuous lack of standardisation in formulations and dosages across studies, with highly variable flavonoid-to-probiotic ratios, delivery formats, and intervention regimens creating significant obstacles for comparing outcomes and establishing reproducible therapeutic protocols. Future research must focus on strain-specific screening, pharmacokinetic modelling, and long-term safety assessments to ensure the clinical translation of these promising preclinical findings (Palencia-Argel et al., 2024).
Genetic polymorphisms have also been identified as crucial determinants of the therapeutic response to flavonoid-based treatments, such as silibinin. For instance, Lrp6(+/−) mice exhibited less severe liver injury in response to MCD, but a reduced treatment response to silibinin, compared to Lrp6(+/+) mice, suggesting that Lrp6 may serve as a target for silibinin’s therapeutic action (Chen et al., 2021). This highlights the need for personalized treatment approaches based on genetic variations, as individual susceptibility to MAFLD may be modulated by specific genetic factors, including Lrp6 polymorphisms (Chen et al., 2021). Addressing these issues will be critical in ensuring that flavonoid-probiotic combinations can be successfully used as personalized therapeutic strategies for MAFLD.
Despite the compelling preclinical evidence, the clinical translation of flavonoid-probiotic synbiotics encounters substantial hurdles. A particularly significant barrier is the regulatory gap whereby these combinations are typically classified as dietary supplements or probiotics rather than pharmaceuticals, subjecting them to considerably less stringent requirements for demonstrating efficacy, safety, and quality control compared to medicinal products—this permissive and inconsistent regulatory landscape contributes to variable product quality and weakened clinical evidence. A primary unmet need lies in establishing standardized formulations and dosages, given the immense diversity of flavonoid compounds and probiotic strains, which contributes to highly variable synergistic effects in vivo (Palencia-Argel et al., 2024). The intricate interplay among distinct flavonoid types, specific probiotic strains, individual host microbiomes, and dietary factors necessitates extensive and rigorous clinical trials to ascertain consistent efficacy and safety in MAFLD patients. Furthermore, the evolving regulatory requirement for synbiotic products presents additional challenges for their widespread clinical adoption and therapeutic standardization. Therefore, while these combinations hold considerable promise, achieving clinical readiness mandates overcoming these multifaceted translational gaps through meticulously designed, large-scale clinical studies and the establishment of clearer regulatory frameworks.
5.2 Nanotechnology for targeted delivery
Flavonoids exhibit broad-spectrum biological and pharmacological properties, but many of their key constituents is limited by physicochemical constraints such as poor dispersibility, and instability, as well as extensive gastrointestinal degradation, liver first-pass metabolism, and restricted membrane transport, all collectively contributing to reduced oral bioavailability (Bhia et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). Nanotechnology, including flavonoid-loaded nanoparticles like chitosan, nanoliposomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles, has been developed to enhance the bioavailability, stability, solubility, and delivery of flavonoids such as EGCG (Hu L. et al., 2025; Prananda et al., 2025; Shi et al., 2018).
Chitosan nanoparticles, in particular, have been widely used to encapsulate flavonoids due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and mucoadhesive properties (Prananda et al., 2025; Seyam et al., 2020). These nanoparticles can be designed to provide controlled and sustained release of encapsulated flavonoids, ensuring a gradual and prolonged delivery to target cells or tissues (Stevens Barron et al., 2023). For example, one study focused on the effect of chitosan-modified, silymarin-loaded lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles (CS-LPNs) in enhancing the oral bioavailability of silymarin and improving its lipid-lowering efficacy for NAFLD treatment. The results showed that the relative bioavailability of CS-LPNs was 14.38 times higher than that of silymarin suspension, and it enhanced the uptake of the nanocarriers by fat-emulsion-treated HepG2 and Caco-2 cells. Meanwhile, the study confirmed that CS-LPNs inhibited lipid accumulation in the mouse liver and enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of silymarin in a transgenic mouse model of NAFLD. These clinical findings suggest that the improved uptake of CS-LPNs could be achieved in vivo, potentially increasing the oral bioavailability of silymarin (Talib et al., 2024; Liang et al., 2018). Also, in the field of lipid reduction, a recent study explored a novel strategy for obesity treatment by using hydroxy-α-sanshool-loaded adipose-targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) to specifically induce the browning of white adipose tissue (WAT). This research demonstrated that the nanocarriers activate the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channel, providing a potential therapeutic approach for MAFLD patients with hepatic lipid accumulation (Zhang Q. et al., 2025).
Nanoliposomes have also been used to encapsulate flavonoids, such as EGCG, to improve their bioavailability and stability (Talib et al., 2024; Hu L. et al., 2025). These nanoparticles can be designed to provide targeted delivery of flavonoids to specific tissues, such as the myocardium or vascular endothelium, via endocytotic mechanisms (Prananda et al., 2025). Additionally, nanoliposomes have been shown to improve the therapeutic efficacy of flavonoids by enhancing their absorption and distribution in the body (Talib et al., 2024; Hu L. et al., 2025; Kasem et al., 2025).
While nanotechnology presents significant promise for overcoming the inherent limitations of flavonoid delivery, its clinical translation is fraught with several critical caveats and unmet needs. The vast majority of existing research remains confined to pre-clinical stages, with the long-term biosafety profile of these nanocarriers (including CS-LPNs and MSNs) representing a formidable “area of unknown” in clinical translation. Comprehensive assessments of their potential for long-term accumulation, immunogenicity, and unanticipated organ toxicity following chronic administration are notably lacking, necessitating extensive in vivo investigations to preclude unanticipated adverse effects, particularly with chronic administration (Bhia et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022; Hu L. et al., 2025). Furthermore, the challenges pertaining to reproducible synthesis, scalable manufacturing, and cost-effectiveness of nano formulations must be rigorously addressed for viable clinical applications (Shi et al., 2018). Most current protocols remain at the proof-of-concept stage, with little consideration given to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance or industrial scalability, whilst stability issues during storage and transport present additional hurdles for real-world implementation. Meanwhile, the formidable biological barriers and complex in vivo interactions imply that targeted delivery, though conceptually appealing, is often less efficient than in vitro results. This disparity underscores the need for more sophisticated targeting strategies and meticulous preclinical validation.
6 Future perspective
The growing body of evidence highlights flavonoids as potential therapeutic agents for MAFLD, but significant challenges remain in translating these findings into effective clinical practice (Qian et al., 2024; Nie et al., 2025). A critical hurdle is addressing the significant inter-individual variability in response to flavonoid interventions. The complex interplay between flavonoids and the gut microbiota, shaped by host genetics, dictates their metabolism and bioavailability. Future research must move beyond a one-size-fits-all approach to investigate these genetic and microbial factors to develop more personalized strategies.
Another important caveat in developing flavonoid-based MAFLD drugs is that many natural flavonoids fall into the category of Pan-Assay Interference Compounds (PAINS) (Baell, 2016). These compounds often contain problematic motifs, such as redox-active catechols or aggregatory structures, which require cautious interpretation of data from high-throughput in vitro or cell-based assays. Therefore, structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies should aim to optimize flavonoids toward improved drug-like properties by reducing polyphenolic character while maintaining efficacy. Ultimately, demonstrating target engagement in physiologically relevant animal models is critical to distinguish true pharmacology from assay artifacts. Only rigorous, evidence-based approaches ensure that promising flavonoids advance as bona fide therapeutic candidates rather than as PAINS-misleading hits.
The translation of flavonoid-based therapies from bench to bedside for MAFLD management is primarily hampered by two interconnected barriers: the scarcity of robust long-term clinical evidence and the inherent challenges of bioavailability and consistent efficacy. The considerable inter-individual variation in flavonoid metabolism, heavily influenced by unique host genetics and gut microbial composition, necessitates a fundamental shift away from universal dosing regimens towards personalized, biomarker-guided approaches. Future clinical trials must therefore be larger, longer, and integratively designed to incorporate multi-omics analyses (metagenomics, metabolomics, genomics), enabling patient stratification and the identification of predictive biomarkers for treatment response.
To overcome the bioavailability barrier, innovative delivery systems such as nanotechnology and synbiotic formulations present promising avenues. However, their clinical translation mandates a critical focus on overcoming hurdles related to long-term safety, reproducible large-scale manufacturing, and the establishment of standardized regulatory frameworks. Ultimately, the future of flavonoid therapy lies in leveraging advanced delivery technologies and precision nutrition principles to transform the gut-liver axis paradigm into tangible, effective, and personalized clinical strategies for MAFLD.
To effectively translate these findings into clinical practice, a shift in perspective is required for both healthcare providers and researchers. Clinicians must move toward a personalized approach, using advanced diagnostic tools to screen for genetic predispositions and gut microbiome composition to identify which patients will benefit most. Researchers, in turn, should prioritize developing standardized, reproducible methods for assessing flavonoid bioavailability and metabolism in humans through well-powered, long-term randomized controlled trials. These efforts should focus on understanding dose-response relationships and developing safe, effective delivery systems. By overcoming these barriers, flavonoids could provide a novel, multi-targeted strategy to manage the complex pathophysiology of MAFLD/MASH, potentially revolutionizing treatment options.
Author contributions
MH: Investigation, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Visualization. ZW: Investigation, Writing – original draft. LW: Writing – original draft, Investigation. AY: Writing – review and editing. XS: Writing – review and editing. MZ: Writing – review and editing, Resources. XL: Writing – review and editing. QZ: Writing – review and editing. ZS: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Supervision, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (2022YFA1303801, 2023YFC2506004), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2025ZFJH03), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82370612), Independent Project Fund of the State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases (zz202311), Shandong Provincial Laboratory Project (SYS202202), Research Project of Jinan Microecological Biomedicine Shandong Laboratory (JNL-2025002B), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LTGC24C050002) and National Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Programme Projects (202410335058). The funders had no role in study design, data collection or analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdelnabi, M. N., Hassan, G. S., and Shoukry, N. H. (2024). Role of the type 3 cytokines IL-17 and IL-22 in modulating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Front. Immunol. 15, 1437046. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437046
Aneta, S., Sara, J.-C., and Rafał, F. (2024). Flavonoids and their role in preventing the development and progression of MAFLD by modifying the microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 11187. doi:10.3390/ijms252011187
Axling, U., Olsson, C., Xu, J., Fernandez, C., Larsson, S., Ström, K., et al. (2012). Green tea powder and Lactobacillus plantarum affect gut microbiota, lipid metabolism and inflammation in high-fat fed C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Metab. (Lond). 9, 105. doi:10.1186/1743-7075-9-105
Baell, J. B. (2016). Feeling nature's PAINS: natural products, natural product drugs, and pan assay interference compounds (PAINS). J. Nat. Prod. 79, 616–628. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00947
Baffy, G. (2009). Kupffer cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the emerging view. J. Hepatol. 51, 212–223. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.008
Barber, T. M., Hanson, P., and Weickert, M. O. (2023). Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and the gut microbiota. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 52, 485–496. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2023.01.004
Barreca, D., Gattuso, G., Bellocco, E., Calderaro, A., Trombetta, D., Smeriglio, A., et al. (2017). Flavanones: citrus phytochemical with health-promoting properties. BioFactors 43, 495–506. doi:10.1002/biof.1363
Bhia, M., Motallebi, M., Abadi, B., Zarepour, A., Pereira-Silva, M., Saremnejad, F., et al. (2021). Naringenin nano-delivery systems and their therapeutic applications. Pharmaceutics 13, 291. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13020291
Braune, A., and Blaut, M. (2011). Deglycosylation of puerarin and other aromatic C-glucosides by a newly isolated human intestinal bacterium. Environ. Microbiol. 13, 482–494. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02352.x
Braune, A., and Blaut, M. (2016). Bacterial species involved in the conversion of dietary flavonoids in the human gut. Gut Microbes 7, 216–234. doi:10.1080/19490976.2016.1158395
Buisson, D., Quintin, J., and Lewin, G. (2007). Biotransformation of polymethoxylated flavonoids: access to their 4'-O-demethylated metabolites. J. Nat. Prod. 70, 1035–1038. doi:10.1021/np070084q
Cai, T., Song, X., Xu, X., Dong, L., Liang, S., Xin, M., et al. (2024). Effects of plant natural products on metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and the underlying mechanisms: a narrative review with a focus on the modulation of the gut microbiota. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 14, 1323261. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2024.1323261
Cao, H., Chen, X., Jassbi, A. R., and Xiao, J. (2015). Microbial biotransformation of bioactive flavonoids. Biotechnol. Adv. 33, 214–223. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.10.012
Carrasco-Pozo, C., Cires, M. J., and Gotteland, M. (2019). Quercetin and epigallocatechin gallate in the prevention and treatment of obesity: from molecular to clinical studies. J. Med. Food 22, 753–770. doi:10.1089/jmf.2018.0193
Chackelevicius, C. M., Gambaro, S. E., Tiribelli, C., and Rosso, N. (2016). Th17 involvement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 22, 9096–9103. doi:10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9096
Chen, Q. L., Zhu, L., Tang, Y. N., Kwan, H. Y., Zhao, Z. Z., Chen, H. B., et al. (2017). Comparative evaluation of chemical profiles of three representative 'snow lotus' herbs by UPLC-DAD-QTOF-MS combined with principal component and hierarchical cluster analyses. Drug Test. Anal. 9 (9), 1105–1115. doi:10.1002/dta.2123
Chen, L. J., Lin, X. X., Guo, J., Xu, Y., Zhang, S. X., Chen, D., et al. (2021). Lrp6 genotype affects individual susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and silibinin therapeutic response via Wnt/β-catenin-Cyp2e1 signaling. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17, 3936–3953. doi:10.7150/ijbs.63732
Chen-Chen, J., Yue, R., Wenwen, X., Yiduo, H., Xin, L., and Feng-Jie, W. (2024). Effect of modified xiaoyao powder on intestinal barrier and intestinal flora in mice with metabolic associated fatty liver disease based on gut-liver axis. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240506.401
Cheng, Z., Chen, Y., Schnabl, B., Chu, H., and Yang, L. (2024). Bile acid and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: molecular insights and therapeutic targets. J. Adv. Res. 59, 173–187. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2023.06.009
Cho, Y. J., Lee, H. G., Seo, K. H., Yokoyama, W., and Kim, H. (2018). Antiobesity effect of prebiotic polyphenol-rich grape seed flour supplemented with probiotic kefir-derived lactic acid bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66, 12498–12511. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03720
Chu, H., Khosravi, A., Kusumawardhani, I. P., Kwon, A. H., Vasconcelos, A. C., Cunha, L. D., et al. (2016). Gene-microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Science. 352, 1116–1120. doi:10.1126/science.aad9948
Collins, S. L., Stine, J. G., Bisanz, J. E., Okafor, C. D., and Patterson, A. D. (2023). Bile acids and the gut microbiota: metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. #N/A 21, 236–247. doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00805-x
Constantinescu, T., and Lungu, C. N. (2021). Anticancer activity of natural and synthetic chalcones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 11306. doi:10.3390/ijms222111306
Dai, J., Liang, K., Zhao, S., Jia, W., Liu, Y., Wu, H., et al. (2018). Chemoproteomics reveals baicalin activates hepatic CPT1 to ameliorate diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, E5896–E905. doi:10.1073/pnas.1801745115
De Cól, J. P., de Lima, E. P., Pompeu, F. M., Cressoni Araújo, A., de Alvares Goulart, R., Bechara, M. D., et al. (2024). Underlying mechanisms behind the brain-gut-liver axis and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): an update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 3694. doi:10.3390/ijms25073694
de Sousa Moraes, L. F., Sun, X., Peluzio, M., and Zhu, M. J. (2019). Anthocyanins/Anthocyanidins and colorectal cancer: what is behind the scenes? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 59, 59–71. doi:10.1080/10408398.2017.1357533
Déprez, S., Brezillon, C., Rabot, S., Philippe, C., Mila, I., Lapierre, C., et al. (2000). Polymeric proanthocyanidins are catabolized by human colonic microflora into low-molecular-weight phenolic acids. J. Nutr. 130, 2733–2738. doi:10.1093/jn/130.11.2733
Dey, P., Olmstead, B. D., Sasaki, G. Y., Vodovotz, Y., Yu, Z., and Bruno, R. S. (2020). Epigallocatechin gallate but not catechin prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice similar to green tea extract while differentially affecting the gut microbiota. #N/A 84, 108455. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108455
Dias, M. C., Pinto, D., and Silva, A. M. S. (2021). Plant flavonoids: Chemical characteristics and biological activity. Molecules 26, 5377. doi:10.3390/molecules26175377
DiStefano, J. K. (2023). The role of choline, soy isoflavones, and probiotics as adjuvant treatments in the prevention and management of NAFLD in postmenopausal women. Nutrients 15 (12), 2670. doi:10.3390/nu15122670
Dong, L., Lou, W., Xu, C., and Wang, J. (2025). Naringenin cationic lipid-modified nanoparticles mitigate MASLD progression by modulating lipid homeostasis and gut microbiota. J. Nanobiotechnology 23, 168. doi:10.1186/s12951-025-03228-x
Fan, L., Zhao, X., Tong, Q., Zhou, X., Chen, J., Xiong, W., et al. (2018). Interactions of dihydromyricetin, a flavonoid from Vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata) with gut microbiota. J. Food Sci. 83, 1444–1453. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.14128
Fang, Y., Zhang, J., Zhu, S., He, M., Ma, S., Jia, Q., et al. (2021). Berberine ameliorates ovariectomy-induced anxiety-like behaviors by enrichment in equol generating gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 165, 105439. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105439
Fang, Z., Shen, G., Wang, Y., Hong, F., Tang, X., Zeng, Y., et al. (2024). Elevated kallistatin promotes the occurrence and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9, 66. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01781-9
Farhat, E. K., Sher, E. K., Džidić-Krivić, A., Banjari, I., and Sher, F. (2023). Functional biotransformation of phytoestrogens by gut microbiota with impact on cancer treatment. #N/A 118, 109368. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109368
Feng, W., Chengying, Z., Guifang, T., Xue, W., Zihan, M., Jiefen, C., et al. (2020). Naringin alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE–/– mice by regulating cholesterol metabolism involved in gut microbiota remodeling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 12651–12660. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.0c05800
Feng, X. H., Xu, H. Y., Wang, J. Y., Duan, S., Wang, Y. C., and Ma, C. M. (2021). In vivo hepatoprotective activity and the underlying mechanism of chebulinic acid from Terminalia chebula fruit. Phytomedicine 83, 153479. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153479
Ferreira-Lazarte, A., Plaza-Vinuesa, L., de Las Rivas, B., Villamiel, M., Muñoz, R., and Moreno, F. J. (2021). Production of α-rhamnosidases from Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 and their role in deglycosylation of dietary flavonoids naringin and rutin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 193, 1093–1102. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.053
Fianchi, F., Liguori, A., Gasbarrini, A., Grieco, A., and Miele, L. (2021). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) as model of gut-liver axis interaction: from pathophysiology to potential target of treatment for personalized therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 6485. doi:10.3390/ijms22126485
Francesca, L., Stefano, G., Elisabetta, D. A., Alessandra, S., Josè Alberto, D. A., Pierluigi, M., et al. (2022). Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease from childhood to adulthood: state of art and future directions. World J. Hepatology 14, 1087–1098. doi:10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1087
Fu, J., Zhao, Z., Zhou, D., and Liu, S. (2025). Therapeutic potential of polyphenols in targeting Th17/Treg balance for intestinal barrier maintenance. Food Sci. Nutr. 13, e70400. doi:10.1002/fsn3.70400
Gendrisch, F., Esser, P. R., Schempp, C. M., and Wölfle, U. (2021). Luteolin as a modulator of skin aging and inflammation. BioFactors 47, 170–180. doi:10.1002/biof.1699
Gnoni, A., Di Chiara Stanca, B., Giannotti, L., Gnoni, G. V., Siculella, L., and Damiano, F. (2022). Quercetin Reduces Lipid Accumulation in a Cell Model of NAFLD by Inhibiting de novo Fatty Acid Synthesis through the Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 1/AMPK/PP2A Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 1044. doi:10.3390/ijms23031044
Gómez-Zorita, S., González-Arceo, M., Fernández-Quintela, A., Eseberri, I., Trepiana, J., and Portillo, M. P. (2020). Scientific evidence supporting the beneficial effects of isoflavones on human health. #N/A, 12. doi:10.3390/nu12123853
Guo, Q., Furuta, K., Islam, S., Caporarello, N., Kostallari, E., Dielis, K., et al. (2022). Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell expressed vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promotes liver fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 13, 983255. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.983255
Hammerich, L., Heymann, F., and Tacke, F. (2011). Role of IL-17 and Th17 cells in liver diseases. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 345803. doi:10.1155/2011/345803
Hammoutene, A., and Rautou, P. E. (2019). Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 70, 1278–1291. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.012
Hammoutene, A., Biquard, L., Lasselin, J., Kheloufi, M., Tanguy, M., Vion, A. C., et al. (2020). A defect in endothelial autophagy occurs in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and promotes inflammation and fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 72, 528–538. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.028
Hoek-van den Hil, E. F., Keijer, J., Bunschoten, A., Vervoort, J. J., Stankova, B., Bekkenkamp, M., et al. (2013). Quercetin induces hepatic lipid omega-oxidation and lowers serum lipid levels in mice. PLoS One 8, e51588. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051588
Hostetler, G. L., Ralston, R. A., and Schwartz, S. J. (2017). Flavones: food sources, bioavailability, metabolism, and bioactivity. Adv. Nutr. 8, 423–435. doi:10.3945/an.116.012948
Hu, Q., Zhang, W., Wu, Z., Tian, X., Xiang, J., Li, L., et al. (2021). Baicalin and the liver-gut system: pharmacological bases explaining its therapeutic effects. Pharmacol. Res. 165, 105444. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105444
Hu, Y., Hu, X., Jiang, L., Luo, J., Huang, J., Sun, Y., et al. (2025a). Microbiome and metabolomics reveal the effect of gut microbiota on liver regeneration of fatty liver disease. EBioMedicine 111, 105482. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105482
Hu, L., Luo, Y., Yang, J., and Cheng, C. (2025b). Botanical flavonoids: efficacy, absorption, metabolism and advanced pharmaceutical technology for improving bioavailability. Molecules 30, 1184. doi:10.3390/molecules30051184
Huang, F., Zheng, X., Ma, X., Jiang, R., Zhou, W., Zhou, S., et al. (2019). Theabrownin from Pu-erh tea attenuates hypercholesterolemia via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Nat. Commun. 10, 4971. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12896-x
Huang, J., Li, W., Liao, W., Hao, Q., Tang, D., Wang, D., et al. (2020). Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and ameliorates intestinal immunity in mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 11, 9924–9935. doi:10.1039/d0fo02152k
Huang, D. Q., El-Serag, H. B., and Loomba, R. (2021). Global epidemiology of NAFLD-Related HCC: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 223–238. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-00381-6
Huiru, L., Wenwen, M., Dongsheng, Z., Zhen, M., Wenguang, Z., Zhi, C., et al. (2023). Study on mechanism of action of total flavonoids from cortex juglandis mandshuricae against alcoholic liver disease based on “gut-liver axis”. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1074286. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1074286
Iino, C., Endo, T., Iino, K., Tateda, T., Sato, S., Igarashi, G., et al. (2022). Reduced equol production and gut microbiota features in men with lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Mens. Health 16, 15579883221115598. doi:10.1177/15579883221115598
Ilaria, B., Flavia Agata, C., and Maria Gisella, C. (2020). Vitamin D and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): an update. #N/A 12, 3302. doi:10.3390/nu12113302
Ipsen, D. H., Lykkesfeldt, J., and Tveden-Nyborg, P. (2018). Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 75, 3313–3327. doi:10.1007/s00018-018-2860-6
Jazvinšćak, J. M., Oršolić, N., Karlović, D., and Peitl, V. (2023). Flavonols in action: targeting oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in major depressive disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24. doi:10.3390/ijms24086888
Jeong, S. H., Kim, H. H., Ha, S. E., Park, M. Y., Bhosale, P. B., Abusaliya, A., et al. (2022). Flavones: six selected flavones and their related signaling pathways that induce apoptosis in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 10965. doi:10.3390/ijms231810965
Jiang, L., Yi, R., Chen, H., and Wu, S. (2025a). Quercetin alleviates metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by tuning hepatic lipid metabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation. Anim. Biotechnol. 36, 2442351. doi:10.1080/10495398.2024.2442351
Jiang, Z., Lhamo, G., Ma, M., Ye, X., Chen, J., He, Y., et al. (2025b). Quercetin as a therapeutic agent for acute pancreatitis: a comprehensive review of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1587314–2025. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1587314
Jin, B., Sun, T., Yu, X. H., Yang, Y. X., and Yeo, A. E. (2012). The effects of TLR activation on T-cell development and differentiation. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 836485. doi:10.1155/2012/836485
Jin, Y., Wang, X., Chen, K., Chen, Y., Zhou, L., Zeng, Y., et al. (2024). Silymarin decreases liver stiffness associated with gut microbiota in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lipids Health Dis. 23, 239. doi:10.1186/s12944-024-02220-y
Juárez-Fernández, M., Porras, D., Petrov, P., Román-Sagüillo, S., García-Mediavilla, M. V., Soluyanova, P., et al. (2021). The synbiotic combination of Akkermansia muciniphila and quercetin ameliorates early obesity and NAFLD through gut microbiota reshaping and bile acid metabolism modulation. Antioxidants (Basel), 10. doi:10.3390/antiox10122001
Kasem, E. A., Hamza, G., El-Shafai, N. M., Ghanem, N. F., Mahmoud, S., Sayed, S. M., et al. (2025). Thymoquinone-loaded chitosan nanoparticles combat testicular aging and oxidative stress through SIRT1/FOXO3a activation: an in vivo and in vitro study. Pharmaceutics 17, 210. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics17020210
Katafuchi, T., and Makishima, M. (2022). Molecular basis of bile Acid-FXR-FGF15/19 signaling axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 6046. doi:10.3390/ijms23116046
Kaushal, N., Singh, M., and Singh Sangwan, R. (2022). Flavonoids: food associations, therapeutic mechanisms, metabolism and nanoformulations. Food Res. Int. 157, 111442. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111442
Ke, X., Chen, Z., Wang, X., Kang, H., and Hong, S. (2023). Quercetin improves the imbalance of Th1/Th2 cells and Treg/Th17 cells to attenuate allergic rhinitis. Autoimmunity 56, 2189133. doi:10.1080/08916934.2023.2189133
Kelepouri, D., Mavropoulos, A., Bogdanos, D. P., and Sakkas, L. I. (2018). The role of flavonoids in inhibiting Th17 responses in inflammatory arthritis. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 9324357. doi:10.1155/2018/9324357
Kim, N. Y., Kim, J. H., Lee, Y. H., Lee, E. J., Kim, J., Lim, Y., et al. (2007). O-methylation of flavonoids using DnrK based on molecular docking. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 17 (12), 1991–1995.
Kim, G., Jang, M. S., Son, Y. M., Seo, M. J., Ji, S. Y., Han, S. H., et al. (2013). Curcumin inhibits CD4+ T cell activation, but augments CD69 expression and TGF-β1-Mediated generation of regulatory T cells at late phase. PLoS One 8, e62300. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062300
Kim, M., Kim, N., and Han, J. (2014). Metabolism of Kaempferia parviflora polymethoxyflavones by human intestinal bacterium bautia sp. MRG-PMF1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 12377–12383. doi:10.1021/jf504074n
Kiriyama, Y., Tokumaru, H., Sadamoto, H., Kobayashi, S., and Nochi, H. (2024). Effects of phenolic acids produced from food-derived flavonoids and amino acids by the gut microbiota on health and disease. Molecules 29, 5102. doi:10.3390/molecules29215102
Kiyama, R. (2023). Estrogenic flavonoids and their molecular mechanisms of action. #N/A 114, 109250. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109250
Kliem, C., Merling, A., Giaisi, M., Köhler, R., Krammer, P. H., and Li-Weber, M. (2012). Curcumin suppresses T cell activation by blocking Ca2+ mobilization and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) activation. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 10200–10209. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.318733
Křížová, L., Dadáková, K., Kašparovská, J., and Kašparovský, T. (2019). Isoflavones. Molecules 24, 1076. doi:10.3390/molecules24061076
Kumar, S., and Pandey, A. K. (2013). Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: an overview. ScientificWorldJournal 2013, 162750. doi:10.1155/2013/162750
Kumari, N., Kumari, R., Dua, A., Singh, M., Kumar, R., Singh, P., et al. (2024). From gut to hormones: unraveling the role of gut microbiota in (phyto)Estrogen modulation in health and disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 68, e2300688. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202300688
Kuziel, G. A., Lozano, G. L., Simian, C., Li, L., Manion, J., Stephen-Victor, E., et al. (2025). Functional diversification of dietary plant small molecules by the gut microbiome. Cell 188, 1967–83.e22. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2025.01.045
Kwon, J. H., Lee, H. G., Seo, K. H., and Kim, H. (2019). Combination of whole grapeseed flour and newly isolated kefir lactic acid bacteria reduces high-fat-induced hepatic steatosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 63, e1801040. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201801040
Latos-Brozio, M., and Masek, A. (2019). Structure-activity relationships analysis of monomeric and polymeric polyphenols (quercetin, rutin and catechin) obtained by various polymerization methods. Chem. Biodivers. 16, e1900426. doi:10.1002/cbdv.201900426
Le Barz, M., Daniel, N., Varin, T. V., Naimi, S., Demers-Mathieu, V., Pilon, G., et al. (2019). In vivo screening of multiple bacterial strains identifies Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lb102 and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. Lactis Bf141 as probiotics that improve metabolic disorders in a mouse model of obesity. FASEB J. 33, 4921–4935. doi:10.1096/fj.201801672R
Lee, Y. M., Yoon, Y., Yoon, H., Park, H. M., Song, S., and Yeum, K. J. (2017). Dietary anthocyanins against obesity and inflammation. #N/A 9, 1089. doi:10.3390/nu9101089
Li, L., and Somerset, S. (2018). Associations between flavonoid intakes and gut microbiota in a group of adults with cystic fibrosis. #N/A 10, 1264. doi:10.3390/nu10091264
Li, X., Jin, Q., Yao, Q., Xu, B., Li, L., Zhang, S., et al. (2018). The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates liver inflammation and fibrosis by regulating hepatic macrophages activation and polarization in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 72. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00072
Li, B., Du, P., Du, Y., Zhao, D., Cai, Y., Yang, Q., et al. (2021a). Luteolin alleviates inflammation and modulates gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis rats. Life Sci. 269, 119008. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.119008
Li, X., Yang, L., Li, J., Lin, L., and Zheng, G. (2021b). A flavonoid-rich smilax China L. extract prevents obesity by upregulating the adiponectin-receptor/AMPK signalling pathway and modulating the gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 12, 5862–5875. doi:10.1039/d1fo00282a
Li, P., Hu, J., Zhao, H., Feng, J., and Chai, B. (2022). Multi-omics reveals inhibitory effect of baicalein on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 925349. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.925349
Li, C., Dai, T., Chen, J., Chen, M., Liang, R., Liu, C., et al. (2023a). Modification of flavonoids: methods and influences on biological activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 63, 10637–10658. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2083572
Li, L., Ji, K., Du, F., Jin, N., Boesch, C., Farag, M. A., et al. (2023b). Does flavonoid supplementation alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 67, e2300480. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202300480
Li, N., Yin, L., Shang, J., Liang, M., Liu, Z., Yang, H., et al. (2023c). Kaempferol attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetic mice via the Sirt1/AMPK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165, 115113. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115113
Li, B., Yan, Y., Zhang, T., Xu, H., Wu, X., Yao, G., et al. (2024a). Quercetin reshapes gut microbiota homeostasis and modulates brain metabolic profile to regulate depression-like behaviors induced by CUMS in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1362464. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1362464
Li, B., Jiang, X. F., Dong, Y. J., Zhang, Y. P., He, X. L., Zhou, C. L., et al. (2024b). The effects of Atractylodes macrocephala extract BZEP self-microemulsion based on gut-liver axis HDL/LPS signaling pathway to ameliorate metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 175, 116519. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116519
Li, N., Cui, C., Xu, J., Mi, M., Wang, J., and Qin, Y. (2024c). Quercetin intervention reduced hepatic fat deposition in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 120, 507–517. doi:10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.07.013
Liang, J., Liu, Y., Liu, J., Li, Z., Fan, Q., Jiang, Z., et al. (2018). Chitosan-functionalized lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for oral delivery of silymarin and enhanced lipid-lowering effect in NAFLD. J. Nanobiotechnology 16, 64. doi:10.1186/s12951-018-0391-9
Liang, A., Leonard, W., Beasley, J. T., Fang, Z., Zhang, P., and Ranadheera, C. S. (2024). Anthocyanins-gut microbiota-health axis: a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 7563–7588. doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2187212
Lin, Y., Wang, Z. Y., Wang, M. J., Jiang, Z. M., Qin, Y. Q., Huang, T. Q., et al. (2022). Baicalin attenuate diet-induced metabolic syndrome by improving abnormal metabolism and gut microbiota. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 925, 174996. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174996
Liu, W., Zhou, Y., Qin, Y., Yu, L., Li, R., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). Quercetin intervention alleviates offspring's oxidative stress, inflammation, and tight junction damage in the colon induced by maternal fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure through the reduction of bacteroides. Nutrients 12 (10), 3095. doi:10.3390/nu12103095
Liu, Z., de Bruijn, W. J. C., Bruins, M. E., and Vincken, J. P. (2021a). Microbial metabolism of Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate and its gut microbiota composition modulatory effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 232–245. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06622
Liu, X., Sun, R., Li, Z., Xiao, R., Lv, P., Sun, X., et al. (2021b). Luteolin alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via restoration of intestinal mucosal barrier damage and microbiota imbalance involving in gut-liver axis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 711, 109019. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2021.109019
Liu, C., Gan, R. Y., Chen, D., Zheng, L., Ng, S. B., and Rietjens, I. (2024a). Gut microbiota-mediated metabolism of green tea catechins and the biological consequences: an updated review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 7067–7084. doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2180478
Liu, H., Li, Y., Jin, Y., Li, X., Wang, D., Yu, X., et al. (2024b). Effects of different natural products in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 38, 3801–3824. doi:10.1002/ptr.8182
Liu, J., Liu, Y., Huang, C., He, C., Yang, T., Ren, R., et al. (2025). Quercetin-driven Akkermansia muciniphila alleviates obesity by modulating bile acid metabolism via an ILA/m(6)A/CYP8B1 signaling. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 12, e2412865. doi:10.1002/advs.202412865
Long, J., Xu, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, B., and Wang, C. (2024). Role of FXR in the development of NAFLD and intervention strategies of small molecules. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 757, 110024. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2024.110024
Loo, Y. T., Howell, K., Chan, M., Zhang, P., and Ng, K. (2020). Modulation of the human gut microbiota by phenolics and phenolic fiber-rich foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 19 (4), 1268–1298. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12563
Luo, Y., Jian, Y., Liu, Y., Jiang, S., Muhammad, D., and Wang, W. (2022). Flavanols from nature: a phytochemistry and biological activity review. Molecules 27, 719. doi:10.3390/molecules27030719
Luo, L., Chang, Y., and Sheng, L. (2023). Gut-liver axis in the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from the microbial derivatives-centered perspective. Life Sci. 321, 121614. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121614
Ma, H. Y., Yamamoto, G., Xu, J., Liu, X., Karin, D., Kim, J. Y., et al. (2020). IL-17 signaling in steatotic hepatocytes and macrophages promotes hepatocellular carcinoma in alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 72, 946–959. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.12.016
Man, S., Deng, Y., Ma, Y., Fu, J., Bao, H., Yu, C., et al. (2023). Prevalence of liver steatosis and fibrosis in the general population and various high-risk populations: a nationwide study with 5.7 million adults in China. Gastroenterology 165, 1025–1040. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.053
Martín, M., and Ramos, S. (2021). Impact of dietary flavanols on microbiota, immunity and inflammation in metabolic diseases. N/A 13, 850. doi:10.3390/nu13030850
Martín-Mateos, R., and Albillos, A. (2021). The role of the gut-liver axis in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Front. Immunol. 12, 660179. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.660179
Martinez, G., Mijares Tussaint, M. R., and De Sanctis, J. (2019). Effects of flavonoids and its derivatives on immune cell responses. Recent Pat. Inflamm. and Allergy Drug Discov. 13, 84–104. doi:10.2174/1872213X13666190426164124
Meng, F., Wang, K., Aoyama, T., Grivennikov, S. I., Paik, Y., Scholten, D., et al. (2012). Interleukin-17 signaling in inflammatory, kupffer cells, and hepatic stellate cells exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice. Gastroenterology 143, 765–776. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.05.049
Mi, W., Hu, Z., Xu, L., Bian, X., Lian, W., Yin, S., et al. (2022). Quercetin positively affects gene expression profiles and metabolic pathway of antibiotic-treated mouse gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 13, 983358. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.983358
Motallebi, M., Bhia, M., Rajani, H. F., Bhia, I., Tabarraei, H., Mohammadkhani, N., et al. (2022). Naringenin: a potential flavonoid phytochemical for cancer therapy. Life Sci. 305, 120752. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120752
Mu, H., Zhou, Q., Yang, R., Zeng, J., Li, X., Zhang, R., et al. (2020). Naringin attenuates high fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and gut bacterial dysbiosis in mice. Front. Microbiol. 11, 585066. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.585066
Murota, K., Nakamura, Y., and Uehara, M. (2018). Flavonoid metabolism: the interaction of metabolites and gut microbiota. #N/A 82, 600–610. doi:10.1080/09168451.2018.1444467
Namkhah, Z., Naeini, F., Mahdi Rezayat, S., Mehdi, Y., Mansouri, S., and Javad Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M. (2021). Does naringenin supplementation improve lipid profile, severity of hepatic steatosis and probability of liver fibrosis in overweight/obese patients with NAFLD? A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 75, e14852. doi:10.1111/ijcp.14852
Naudhani, M., Thakur, K., Ni, Z. J., Zhang, J. G., and Wei, Z. J. (2021). Formononetin reshapes the gut microbiota, prevents progression of obesity and improves host metabolism. Food Funct. 12, 12303–12324. doi:10.1039/d1fo02942h
Nie, W. Y., Ye, Y., Tong, H. X., and Hu, J. Q. (2025). Herbal medicine as a potential treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 31, 100273. doi:10.3748/wjg.v31.i9.100273
Niwano, Y., Kohzaki, H., Shirato, M., Shishido, S., and Nakamura, K. (2022). Metabolic fate of orally ingested proanthocyanidins through the digestive tract. Antioxidants (Basel) 12, 17. doi:10.3390/antiox12010017
Niziński, P., Krajewska, A., Oniszczuk, T., Polak, B., and Oniszczuk, A. (2025). Hepatoprotective effect of Kaempferol-A review. Molecules 30, 1913. doi:10.3390/molecules30091913
Oh, K. K., Gupta, H., Ganesan, R., Sharma, S. P., Won, S. M., Jeong, J. J., et al. (2023). The seamless integration of dietary plant-derived natural flavonoids and gut microbiota May ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a network pharmacology analysis. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 51, 217–232. doi:10.1080/21691401.2023.2203734
Olveira, A., Augustin, S., Benlloch, S., Ampuero, J., Suárez-Pérez, J. A., Armesto, S., et al. (2023). The essential role of IL-17 as the pathogenetic link between psoriasis and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Life (Basel) 13, 419. doi:10.3390/life13020419
Ottaviani, J. I., Heiss, C., Spencer, J. P. E., Kelm, M., and Schroeter, H. (2018). Recommending flavanols and procyanidins for cardiovascular health: revisited. Mol. Asp. Med. 61, 63–75. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2018.02.001
Paik, J. M., Kabbara, K., Eberly, K. E., Younossi, Y., Henry, L., and Younossi, Z. M. (2022). Global burden of NAFLD and chronic liver disease among adolescents and young adults. Hepatology 75, 1204–1217. doi:10.1002/hep.32228
Palencia-Argel, M., Rodríguez-Villamil, H., Bernal-Castro, C., Díaz-Moreno, C., and Fuenmayor, C. A. (2024). Probiotics in anthocyanin-rich fruit beverages: research and development for novel synbiotic products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 110–126. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2104806
Pan, C. X., Tang, J., Wang, X. Y., Wu, F. R., Ge, J. F., and Chen, F. H. (2014). Role of interleukin-22 in liver diseases. Inflamm. Res. 63, 519–525. doi:10.1007/s00011-014-0727-3
Parafati, M., Lascala, A., La Russa, D., Mignogna, C., Trimboli, F., Morittu, V. M., et al. (2018). Bergamot polyphenols boost therapeutic effects of the diet on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) induced by “Junk Food”: evidence for anti-inflammatory activity. Nutrients 10 (11), 1604. doi:10.3390/nu10111604
Patanè, G. T., Putaggio, S., Tellone, E., Barreca, D., Ficarra, S., Maffei, C., et al. (2023). Catechins and proanthocyanidins involvement in metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 9228. doi:10.3390/ijms24119228
Pei, R., Liu, X., and Bolling, B. (2020). Flavonoids and gut health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 61, 153–159. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2019.12.018
Peiseler, M., Schwabe, R., Hampe, J., Kubes, P., Heikenwälder, M., and Tacke, F. (2022). Immune mechanisms linking metabolic injury to inflammation and fibrosis in fatty liver disease - novel insights into cellular communication circuits. J. Hepatol. 77, 1136–1160. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.012
Peng, M., Tabashsum, Z., Anderson, M., Truong, A., Houser, A. K., Padilla, J., et al. (2020). Effectiveness of probiotics, prebiotics, and prebiotic-like components in common functional foods. #N/A 19, 1908–1933. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12565
Peng, L. Y., Shi, H. T., Tan, Y. R., Shen, S. Y., Yi, P. F., Shen, H. Q., et al. (2021). Baicalin inhibits APEC-Induced lung injury by regulating gut microbiota and SCFA production. Food Funct. 12, 12621–12633. doi:10.1039/d1fo02407h
Peng, W., He, C. X., Li, R. L., Qian, D., Wang, L. Y., Chen, W. W., et al. (2024). Zanthoxylum bungeanum amides ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver via regulating gut microbiota and activating AMPK/Nrf2 signaling. J. Ethnopharmacol. 318, 116848. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116848
Piero, P., Mohamad, K., Laura, M., Valeria, P., Valeria, I., Annarita, G., et al. (2024). Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease: from pathogenesis to current therapeutic options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 5640. doi:10.3390/ijms25115640
Ponugoti, B., Kim, D. H., Xiao, Z., Smith, Z., Miao, J., Zang, M., et al. (2010). SIRT1 deacetylates and inhibits SREBP-1C activity in regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 33959–33970. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.122978
Popiolek-Kalisz, J., and Fornal, E. (2022). The impact of flavonols on cardiovascular risk. #N/A 14, 1973. doi:10.3390/nu14091973
Porras, D., Nistal, E., Martínez-Flórez, S., Pisonero-Vaquero, S., Olcoz, J. L., Jover, R., et al. (2017). Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 102, 188–202. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.037
Prananda, A. T., Halim, P., and Syahputra, R. A. (2025). Targeting miRNA with flavonoids: unlocking novel pathways in cardiovascular disease management. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1532986. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1532986
Pu, P., Wang, X. A., Salim, M., Zhu, L. H., Wang, L., Chen, K. J., et al. (2012). Baicalein, a natural product, selectively activating AMPKα(2) and ameliorates metabolic disorder in diet-induced mice. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 362, 128–138. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2012.06.002
Qi, W., Cao, X., Chen, Y., Chen, H., Zhang, N., Liu, R., et al. (2025). JiGuCao capsule formula alleviates metabolic fatty liver disease by regulating the gut-liver axis and lipid metabolism. Phytomedicine 140, 156559. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156559
Qian, D., Zhang, Q., He, C. X., Guo, J., Huang, X. T., Zhao, J., et al. (2024). Hai-honghua medicinal liquor is a reliable remedy for fracture by promotion of osteogenic differentiation via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 330, 118234. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118234
Qu, Y., Li, X., Xu, F., Zhao, S., Wu, X., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Kaempferol alleviates murine experimental colitis by restoring gut microbiota and inhibiting the LPS-TLR4-NF-κB axis. Front. Immunol. 12, 679897. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.679897
Rao, Y., Kuang, Z., Li, C., Guo, S., Xu, Y., Zhao, D., et al. (2021). Gut Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease by regulating the metabolism of L-aspartate via gut-liver axis. Gut Microbes 13, 1–19. doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.1927633
Riazi, K., Azhari, H., Charette, J. H., Underwood, F. E., King, J. A., Afshar, E. E., et al. (2022). The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 851–861. doi:10.1016/s2468-1253(22)00165-0
Ribeiro, A. E., Monteiro, N. E. S., Moraes, A. V. G., Costa-Paiva, L. H., and Pedro, A. O. (2018). Can the use of probiotics in association with isoflavone improve the symptoms of genitourinary syndrome of menopause? Results from a randomized controlled trial. #N/A 26, 643–652. doi:10.1097/gme.0000000000001279
Rong, L., Junyan, Z., Ran, W., Xinming, Q., Yaokai, C., Hongjuan, C., et al. (2023). Advancements in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 1087260. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1087260
Round, J. L., Lee, S. M., Li, J., Tran, G., Jabri, B., Chatila, T. A., et al. (2011). The toll-like receptor 2 pathway establishes colonization by a commensal of the human microbiota. Science 332, 974–977. doi:10.1126/science.1206095
Sayin, S. I., Wahlström, A., Felin, J., Jäntti, S., Marschall, H. U., Bamberg, K., et al. (2013). Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab. 17, 225–235. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.01.003
Seo, K. H., Jeong, J., and Kim, H. (2020). Synergistic effects of heat-killed kefir paraprobiotics and flavonoid-rich prebiotics on Western diet-induced obesity. #N/A 12, 2465. doi:10.3390/nu12082465
Seyam, S., Nordin, N. A., and Alfatama, M. (2020). Recent progress of chitosan and chitosan derivatives-based nanoparticles: pharmaceutical perspectives of oral insulin delivery. Pharm. (Basel) 13, 307. doi:10.3390/ph13100307
Shabbir, U., Rubab, M., Daliri, E. B., Chelliah, R., Javed, A., and Oh, D. H. (2021). Curcumin, quercetin, catechins and metabolic diseases: the role of gut microbiota. #N/A 13, 206. doi:10.3390/nu13010206
Sharma, R., Kumari, M., Kumari, A., Sharma, A., Gulati, A., Gupta, M., et al. (2019). Diet supplemented with phytochemical epigallocatechin gallate and probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum confers second generation synbiotic effects by modulating cellular immune responses and antioxidant capacity in aging mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 58, 2943–2957. doi:10.1007/s00394-018-01890-6
Shen, N., Wang, T., Gan, Q., Liu, S., Wang, L., and Jin, B. (2022). Plant flavonoids: classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 383, 132531. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132531
Sherouk, F., and Joseph, M. P. (2023). Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: a disastrous human health challenge. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 52. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2023.03.001
Shi, M., Shi, Y. L., Li, X. M., Yang, R., Cai, Z. Y., Li, Q. S., et al. (2018). Food-grade encapsulation systems for (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate. Molecules 23, 445. doi:10.3390/molecules23020445
Shi, P. Z., Wang, J. W., Wang, P. C., Han, B., Lu, X. H., Ren, Y. X., et al. (2021). Urolithin a alleviates oxidative stress-induced senescence in nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells through SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway. World J. Stem Cells 13, 1928–1946. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v13.i12.1928
Shi, Z., Zhang, C., Lei, H., Chen, C., Cao, Z., Song, Y., et al. (2022). Structural insights into amelioration effects of quercetin and its glycoside derivatives on NAFLD in mice by modulating the gut microbiota and host metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70, 14732–14743. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06212
Shoji, T., Masumoto, S., and Miura, T. (2023). Mechanism of procyanidins for health functionality by improving the intestinal environment. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 88, 345–351. doi:10.1093/bbb/zbad174
Silva, A. K. S., and Peixoto, C. A. (2018). Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease inflammation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 75, 2951–2961. doi:10.1007/s00018-018-2838-4
Song, H., Shen, X., Wang, F., Li, Y., and Zheng, X. (2021a). Black current anthocyanins improve lipid metabolism and modulate gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced Obese mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 65, e2001090. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202001090
Song, H., Shen, X., Zhou, Y., and Zheng, X. (2021b). Black rice anthocyanins alleviate hyperlipidemia, liver steatosis and insulin resistance by regulating lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in Obese mice. Food Funct. 12, 10160–10170. doi:10.1039/d1fo01394g
Stevens Barron, J. C., Chapa Gonzalez, C., Alvarez Parrilla, E., and De la Rosa, L. A. (2023). Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of flavonoids: impact on proinflammatory cytokine production: a systematic review. Biomolecules 13, 1158. doi:10.3390/biom13071158
Sun, W. L., Li, X. Y., Dou, H. Y., Wang, X. D., Li, J. D., Shen, L., et al. (2021). Myricetin supplementation decreases hepatic lipid synthesis and inflammation by modulating gut microbiota. Cell Rep. 36, 109641. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109641
Sun, X., Ge, N., Liang, Q., Wang, Q., Yu, H., and Jin, M. (2025). Effect of the total flavonoids of Dracocephalum moldavica L. on metabolic associated fatty liver disease in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1549515. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1549515
Talib, W. H., Awajan, D., Alqudah, A., Alsawwaf, R., Althunibat, R., Abu AlRoos, M., et al. (2024). Targeting cancer hallmarks with epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG): mechanistic basis and therapeutic targets. Molecules 29, 1373. doi:10.3390/molecules29061373
Tan, S., Caparros-Martin, J. A., Matthews, V. B., Koch, H., O'Gara, F., Croft, K. D., et al. (2018). Isoquercetin and inulin synergistically modulate the gut microbiome to prevent development of the metabolic syndrome in mice fed a high fat diet. Sci. Rep. 8, 10100. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-28521-8
Tan, P., Jin, L., Qin, X., and He, B. (2022). Natural flavonoids: potential therapeutic strategies for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1005312. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1005312
Tauil, R. B., Golono, P. T., de Lima, E. P., de Alvares Goulart, R., Guiguer, E. L., Bechara, M. D., et al. (2024). Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: the influence of oxidative stress, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunctions, and the role of polyphenols. Pharm. (Basel). 17, 1354. doi:10.3390/ph17101354
Thilakarathna, W., and Rupasinghe, H. P. V. (2024). Proanthocyanidins-based synbiotics as a novel strategy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) risk reduction. Molecules 29, 709. doi:10.3390/molecules29030709
Tian, L., Tan, Y., Chen, G., Wang, G., Sun, J., Ou, S., et al. (2019). Metabolism of anthocyanins and consequent effects on the gut microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 59, 982–991. doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1533517
Ting, X., Liyong, L., Yan, L., Kang, S., Liyong, L., and Liang, Z. (2022). Hawk tea flavonoids as natural hepatoprotective agents alleviate acute liver damage by reshaping the intestinal microbiota and modulating the Nrf2 and NF-κB signaling pathways. N/A 14, 3662. doi:10.3390/nu14173662
Tong, J., Zeng, Y., Xie, J., Xiao, K., Li, M., and Cong, L. (2022). Association between flavonoid and subclasses intake and metabolic associated fatty liver disease in U.S. adults: results from national health and nutrition examination survey 2017-2018. Front. Nutr. 9, 1074494. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1074494
Vancamelbeke, M., and Vermeire, S. (2017). The intestinal barrier: a fundamental role in health and disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11, 821–834. doi:10.1080/17474124.2017.1343143
Velliou, R. I., Legaki, A. I., Nikolakopoulou, P., Vlachogiannis, N. I., and Chatzigeorgiou, A. (2023). Liver endothelial cells in NAFLD and transition to NASH and HCC. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 80, 314. doi:10.1007/s00018-023-04966-7
Wallace, T. C., and Giusti, M. M. (2015). Anthocyanins. Adv. Nutr. 6, 620–622. doi:10.3945/an.115.009233
WalyEldeen, A. A., Sabet, S., El-Shorbagy, H. M., Abdelhamid, I. A., and Ibrahim, S. A. (2023). Chalcones: promising therapeutic agents targeting key players and signaling pathways regulating the hallmarks of cancer. Chem-Biol. Interact. 369, 110297. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110297
Wan, X., Ma, J., Bai, H., Hu, X., Ma, Y., Zhao, M., et al. (2025). Drug advances in NAFLD: individual and combination treatment strategies of natural products and small-synthetic-molecule drugs. Biomolecules 15, 140. doi:10.3390/biom15010140
Wang, H. K., Yeh, C. H., Iwamoto, T., Satsu, H., Shimizu, M., and Totsuka, M. (2012). Dietary flavonoid naringenin induces regulatory T cells via an Aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediated pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 2171–2178. doi:10.1021/jf204625y
Wang, J., Niu, X., Wu, C., and Wu, D. (2018). Naringenin modifies the development of lineage-specific effector CD4(+) T cells. Front. Immunol. 9, 2267. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02267
Wang, J. F., Liu, S. S., Song, Z. Q., Xu, T. C., Liu, C. S., Hou, Y. G., et al. (2020). Naturally occurring flavonoids and isoflavonoids and their microbial transformation: a review. Molecules 25, 5112. doi:10.3390/molecules25215112
Wang, S., Li, X. Y., Ji, H. F., and Shen, L. (2022a). Modulation of gut microbiota by glycyrrhizic acid May contribute to its anti-NAFLD effect in rats fed a high-fat diet. Life Sci. 310, 121110. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121110
Wang, M., Zhang, Z., Sun, H., He, S., Liu, S., Zhang, T., et al. (2022b). Research progress of anthocyanin prebiotic activity: a review. Phytomedicine 102, 154145. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154145
Wang, M., Lu, Y., Wu, Q., Chen, G., Zhao, H., Ho, C. T., et al. (2023). Biotransformation and gut microbiota-mediated bioactivity of flavonols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 8317–8331. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01087
Wendlocha, D., Kubina, R., Krzykawski, K., and Mielczarek-Palacz, A. (2024). Selected flavonols targeting cell death pathways in cancer therapy: the latest achievements in research on apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and. Cuproptosis. #N/A, 16. doi:10.3390/nu16081201
Wu, C., and Wang, G. (2025). Research progress on the mechanism of baicalein in Scutellaria baicalensis against liver fibrosis. J. Contemp. Med. Pract. 7 (7), 1–5. doi:10.53469/jcmp.2025.07(04).01
Wu, H. T., Lin, X. X., Yang, X. L., Ding, Y., Wang, J. L., Liu, C. L., et al. (2024). Kaempferol attenuates inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced gallbladder epithelial cells by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 103, e14519. doi:10.1111/cbdd.14519
Xiaopeng, Z., Mingfeng, X., and Xin, G. (2022). Update on genetics and epigenetics in metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metabolism 13, 20420188221132138. doi:10.1177/20420188221132138
Xiong, H.-H., Lin, S.-Y., Chen, L.-L., Ouyang, K.-H., and Wang, W.-J. (2023). The interaction between flavonoids and intestinal microbes: a review. Foods 12, 320. doi:10.3390/foods12020320
Xu, H., Yuan, M., Niu, K., Yang, W., Jiang, M., Zhang, L., et al. (2024). Involvement of bile acid metabolism and gut microbiota in the amelioration of experimental metabolism-associated fatty liver disease by nobiletin. Molecules 29, 976. doi:10.3390/molecules29050976
Xue, Y., Zhu, L., and Yi, T. (2017). Fingerprint analysis of resina draconis by ultra-performance liquid chromatography. Chem. Cent. J. 11, 67. doi:10.1186/s13065-017-0299-8
Yamagata, K., and Yamori, Y. (2021). Potential effects of soy isoflavones on the prevention of metabolic syndrome. Molecules 26, 5863. doi:10.3390/molecules26195863
Yang, Y., Zhang, X., Xu, M., Wu, X., Zhao, F., and Zhao, C. (2018). Quercetin attenuates collagen-induced arthritis by restoration of Th17/Treg balance and activation of heme oxygenase 1-mediated anti-inflammatory effect. Int. Immunopharmacol. 54, 153–162. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.013
Yang, G., Hong, S., Yang, P., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, P., et al. (2021). Discovery of an ene-reductase for initiating flavone and flavonol catabolism in gut bacteria. Nat. Commun. 12, 790. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-20974-2
Yang, S., Duan, H., Yan, Z., Xue, C., Niu, T., Cheng, W., et al. (2025). Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by modulating gut microbiota and plasma metabolism. #N/A 17, 203. doi:10.3390/nu17020203
Yi, T., Chen, H.-B., Zhao, Z.-Z., Jiang, Z.-H., Cai, S.-Q., and Wang, T.-M. (2009a). Comparative analysis of the major constituents in the traditional Tibetan medicinal plants Saussurea laniceps and S. medusa by LC–DAD–MS. #N/A 70, 957–962. doi:10.1365/s10337-009-1240-7
Yi, T., Chen, H.-B., Zhao, Z.-Z., Jiang, Z.-H., Cai, S.-Q., and Wang, T.-M. (2009b). Identification and determination of the major constituents in the traditional uighur medicinal plant Saussurea involucrata by LC-DAD-MS. #N/A 69, 537–542. doi:10.1365/s10337-008-0923-9
Yi, T., Tang, Y., Zhang, J., Zhao, Z., Yang, Z., and Chen, H. (2012). Characterization and determination of six flavonoids in the ethnomedicine “Dragon's Blood” by UPLC-PAD-MS. Chem. Cent. J. 6, 116. doi:10.1186/1752-153x-6-116
Yi, M., Manzoor, M., Yang, M., Zhang, H., Wang, L., Zhao, L., et al. (2024). Silymarin targets the FXR protein through microbial metabolite 7-keto-deoxycholic acid to treat MASLD in Obese mice. Phytomedicine 133, 155947. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155947
Yoon, Y. S., Seo, W. Y., Lee, M. W., Kim, S. T., and Koo, S. H. (2009). Salt-inducible kinase regulates hepatic lipogenesis by controlling SREBP-1c phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 10446–10452. doi:10.1074/jbc.M900096200
Younossi, Z. M., Golabi, P., Paik, J. M., Henry, A., Van Dongen, C., and Henry, L. (2023). The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a systematic review. Hepatology 77, 1335–1347. doi:10.1097/hep.0000000000000004
Yu, Z., Xiaojia, L., Wei, Z., Jian, Z., Aiting, W., Jing, W., et al. (2024). Baicalin circumvents anti-PD-1 resistance by regulating the gut microbiota metabolite short-chain fatty acids. Pharmacol. Res. 199, 107033. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2023.107033
Yuan, M., Sun, T., Zhang, Y., Guo, C., Wang, F., Yao, Z., et al. (2024). Quercetin alleviates insulin resistance and repairs intestinal barrier in Db/Db mice by modulating gut microbiota. #N/A 16, 1870. doi:10.3390/nu16121870
Zeng, S. L., Li, S. Z., Xiao, P. T., Cai, Y. Y., Chu, C., Chen, B. Z., et al. (2020). Citrus polymethoxyflavones attenuate metabolic syndrome by regulating gut microbiome and amino acid metabolism. Sci. Adv. 6, eaax6208. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aax6208
Zhang, Y., Shan, L., Hua, Y., Wang, D., Zeng, H., Liu, R., et al. (2013). Baicalein selectively induces apoptosis in activated lymphocytes and ameliorates concanavalin A-Induced hepatitis in mice. PLoS One 8, e69592. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069592
Zhang, Y., Bobe, G., Revel, J. S., Rodrigues, R. R., Sharpton, T. J., Fantacone, M. L., et al. (2020). Improvements in metabolic syndrome by xanthohumol derivatives are linked to altered gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 64, e1900789. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201900789
Zhang, Z., Li, X., Sang, S., McClements, D. J., Chen, L., Long, J., et al. (2022). A review of nanostructured delivery systems for the encapsulation, protection, and delivery of silymarin: an emerging nutraceutical. Food Res. Int. 156, 111314. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111314
Zhang, Y., Ren, L., Tian, Y., Guo, X., Wei, F., and Zhang, Y. (2024a). Signaling pathways that activate hepatic stellate cells during liver fibrosis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 11, 1454980. doi:10.3389/fmed.2024.1454980
Zhang, H., Liang, S., Yin, K., Mo, Y., Li, Y., Lv, Y., et al. (2024b). Urinary equol and equol-predicting microbial genera are favorably associated with body fat measures among Chinese adults. J. Nutr. 154, 2843–2851. doi:10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.07.024
Zhang, S., Shen, C., Di, H., Wang, Y., and Guan, F. (2025a). Regulatory mechanisms of phenolic acids in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a review. Antioxidants 14, 760. doi:10.3390/antiox14070760
Zhang, Q., He, C., Guo, J., Tang, D., Qian, D., Zheng, C., et al. (2025b). Hydroxy-α-sanshool-loaded adipose-targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles induce white adipose browning and reduce obesity by activating TRPV1. Bio-Design Manuf. 8, 288–309. doi:10.1631/bdm.2400248
Zhao, J., Sun, Y., Yuan, C., Li, T., Liang, Y., Zou, H., et al. (2023). Quercetin ameliorates hepatic fat accumulation in high-fat diet-induced Obese mice via PPARs. Food Funct. 14, 1674–1684. doi:10.1039/d2fo03013f
Zhou, M., Ma, J., Kang, M., Tang, W., Xia, S., Yin, J., et al. (2024). Flavonoids, gut microbiota, and host lipid metabolism. Eng. Life Sci. 24, 2300065. doi:10.1002/elsc.202300065
Zhu, H., Guo, L., Yu, D., and Du, X. (2022). New insights into immunomodulatory properties of lactic acid bacteria fermented herbal medicines. Front. Microbiol. 13, 1073922. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.1073922
Zhu, X., Dai, X., Zhao, L., Li, J., Zhu, Y., He, W., et al. (2024). Quercetin activates energy expenditure to combat metabolic syndrome through modulating gut microbiota-bile acids crosstalk in mice. Gut Microbes 16, 2390136. doi:10.1080/19490976.2024.2390136
Glossary
ACACA Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Alpha
ACC Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
ALK5 TGF-β type I receptor
AREs antioxidant response elements
BA bile acid
BMI body mass index
BSH bile salt hydrolases
ChREBP carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein
CPT1 Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1
CS-LPNs chitosan-modified, silymarin-loaded lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles
CYP2E1 cytochrome P450 2E1
CYP7A1 cytochrome P450 7A1
DNL de novo lipogenesis
ECM extracellular matrix
EGCG Epigallocatechin gallate
FA fatty acid
FAO fatty acid oxidation
FASN Fatty Acid Synthase
FGF19 fibroblast growth factor 19
FGFR4 FGF19 receptor
FLR flavone reductase
GCLC glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit
GGT γ-glutamyl transpeptidase
GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors
GSH glutathione
GSF Grapeseed flour
HCC hepatocellular carcinoma
HDACs histone deacetylases
HDL high-density lipoprotein
HFD high-fat diet-fed
HO-1 Heme Oxygenase-1
HSCs Hepatic Stellate Cells
IECs Intestinal Epithelial Cells
IL-6 interleukin-6
JNK c-Jun N-terminal kinase
KCs Kupffer cells
LDL low-density lipoprotein
LPS lipopolysaccharides
LRP5/6 low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6
MAFLD Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase
MASH Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
MDA malondialdehyde
MRI magnetic resonance imaging
NFS MAFLD fibrosis score
NHANES National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
NQO1 NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1
Nrf2 nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
PMFs Polymethoxyflavones
PPARs peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
PPARα Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor alpha
PSA polysaccharide A
ROS reactive oxygen species
SCFAs Short-chain fatty acids
SFB Segmentous filamentous bacteria
SREBP-1c Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 1c
TC total cholesterol
TG triglyceride
TGF-β Transforming growth factor-beta
TLR2 Toll-like receptor 2
TLR4 Toll-like receptor 4
Treg T regulatory
Keywords: MAFLD, flavonoids, gut-liver axis, gut microbial modulation, natural herbal products
Citation: Hao M, Wang Z, Wang L, Yimamu A, Su X, Zhang M, Li X, Zhang Q and Sun Z (2025) Flavonoids as modulators of gut-liver axis: emerging therapeutic strategies for MAFLD. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1657751. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1657751
Received: 01 July 2025; Accepted: 30 September 2025;
Published: 16 October 2025.
Edited by:
Wei Peng, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Qianliang Ming, The 74th Army Hospital of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, ChinaYan Cao, Second Military Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Hao, Wang, Wang, Yimamu, Su, Zhang, Li, Zhang and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zeyu Sun, emV5dXN1bkB6anUuZWR1LmNu; Quanlong Zhang, enFsMjAxNjEwNjVAemNtdS5lZHUuY24=
 Mengxuan Hao
Mengxuan Hao Zihui Wang
Zihui Wang Liren Wang4
Liren Wang4 Aidiya Yimamu
Aidiya Yimamu Quanlong Zhang
Quanlong Zhang Zeyu Sun
Zeyu Sun