Abstract
Globally, colorectal cancer (CRC) ranked third in cancer prevalence and emerged as the primary contributor to cancer-related fatalities in 2022, with projections indicating substantial escalation by 2040. The malignant progression of healthy colonic cells involves complex interactions among multiple cellular pathways over extended periods (typically exceeding 10 years), influenced by dietary patterns, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions. In addition, marked disparities in CRC incidence and mortality appear to show large differences across geographic regions, demographic groups, and biological sexes, suggesting that there are traces of CRC. Therefore, timely intervention or regression of the development of CRC, particularly targeting high-risk populations, may be an excellent strategy to reduce CRC burden in forthcoming decades. Natural derived small molecule compounds (NDSMCs) exhibit significant advantages, including structural diversity, unique biological activities, low toxicity and multi-target effects. Increasing evidence suggests that NDSMCs demonstrate therapeutic potential against CRC through multi-target mechanisms, such as modulation of gut microbiota, induction of ferroptosis, and regulation of programmed cell death pathways (apoptosis/autophagy), thereby offering promising avenues for CRC treatment. However, comprehensive reviews in this field remain scarce. Consequently, this study systematically summarizes the research advancements over the past 5 years regarding the mechanisms of NDSMCs in combating CRC, aiming to provide valuable insights for therapeutic strategies, preventive measures, and novel drug development. Furthermore, the clinical progress and limitations of certain NDSMCs in CRC treatment are also discussed.

1 Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common malignancy and a major contributor to cancer-related mortality worldwide (Wu et al., 2025). Global estimates for 2020 indicated over 1.9 million newly reported CRC cases alongside approximately 930,000 fatalities attributed to this disease (Morgan et al., 2023). Projections suggest a good deal of escalation in CRC prevalence by 2040, with anticipated annual figures reaching 3.2 million incident cases (marking a 63% surge) and 1.6 million deaths (reflecting a 73% rise) (Olfatifar et al., 2025).
The incidence and mortality of CRC appear to exhibit significant disparities across gender, geographic regions, and age groups, suggesting that CRC incidence has a track record. Data (Figure 1) from https://gco.iarc.fr/today/en/dataviz reveal Asian and European populations collectively responsible for 78.10% of global cases and 78.55% of mortality figures. Given substantial demographic variations between these regions, age-standardized rates (ASR) per 100,000 population provide more accurate comparisons of CRC burden. This statistical method normalizes population age structures, enabling meaningful cross-regional analysis. Epidemiologic data demonstrates striking continental variations, with Oceania (31.1), Europe (30.5), and North America (27.2) showing incidence ASRs 2-3 times higher than other continents. Mortality patterns mirror this distribution, with Europe demonstrating the highest mortality ASR at 12.1, followed by Oceania (9.2) and North America (8.2). For individuals aged above 50 years, Oceania exhibited the highest age-standardized incidence rates (137.4), followed by Europe (127.9) and North America (105.6). Mortality patterns showed Europe leading with 56.4 age-standardized mortality per 100,000 population, trailed by Oceania (42.3) and Latin America (36.4). Notably, over nine-tenths of total CRC cases and fatalities occurred in this older demographic cohort. In addition, male populations demonstrated 24.79% higher incidence rates and 23.63% elevated mortality compared to females.
FIGURE 1
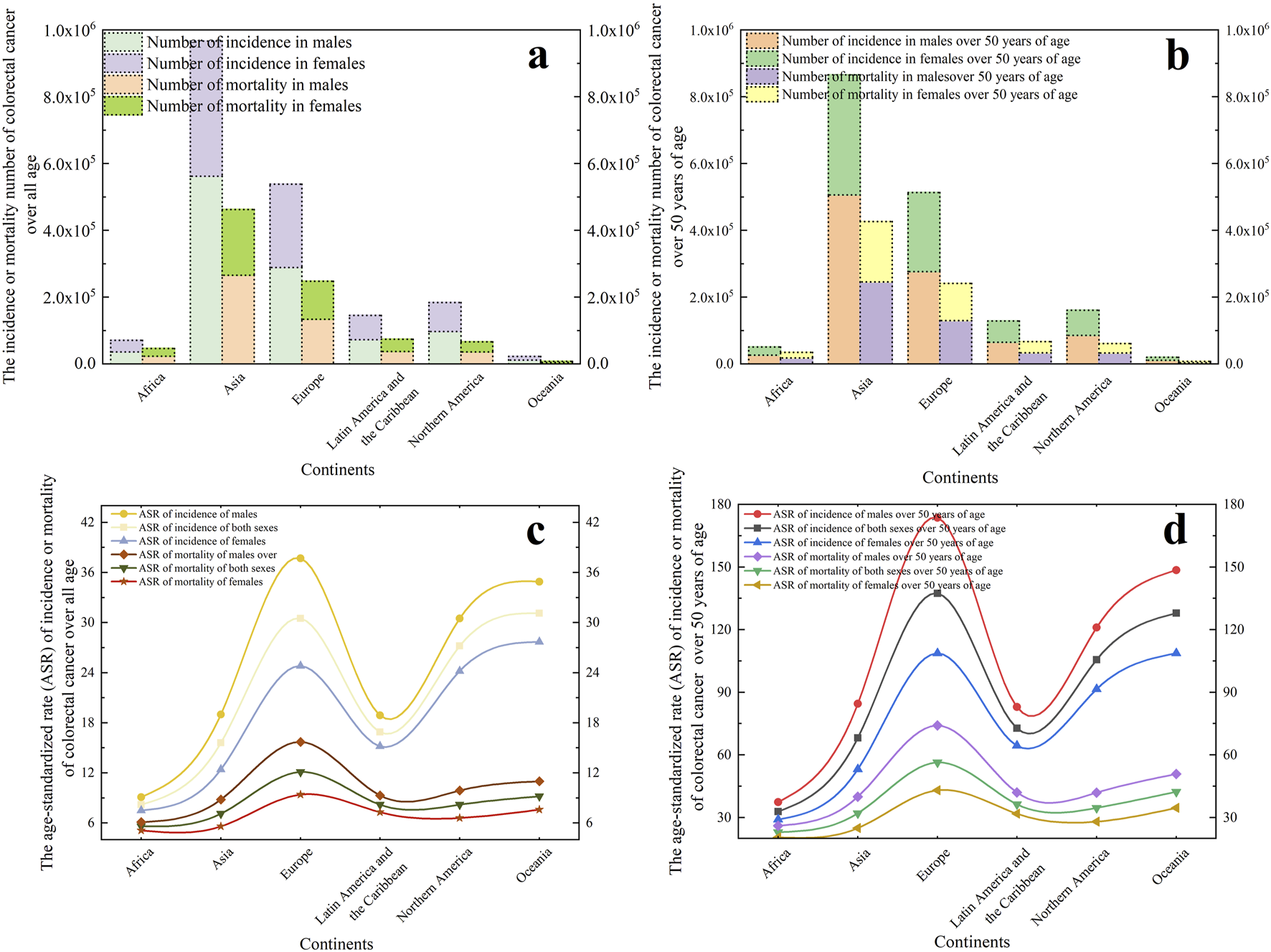
In 2022, global colorectal cancer statistics across six continents, presenting case counts and age-standardized rates (ASR) for both incidence and mortality. (a) The incidence or mortality number of colorectal cancer over all age. (b) The incidence or mortality number of colorectal cancer r focusing on individuals over 50 years old. (c) The ASR of incidence or mortality of colorectal cancer over all age. (d) The ASR of incidence or mortality of colorectal cancer focusing on individuals over 50 years old.
The observed variations primarily stem from CRC’s multifactorial etiology, which encompasses hereditary predisposition, dietary patterns, and lifestyle choice (Cañellas-Socias et al., 2024). From a genetic perspective, individuals with familial histories of colorectal polyps-including specific syndromes like familial adenomatous polyposis, Lynch syndrome and mutY DNA glycosylase-associated polyposis-demonstrate elevated susceptibility to CRC development. Nutritional and behavioral factors such as insufficient dietary fiber consumption coupled with excessive consumption of animal-derived proteins and lipids, along with sedentary behaviors, tobacco use, and chronic alcohol abuse, collectively contribute to heightened disease risk (Chan et al., 2025). Furthermore, chronic gastrointestinal inflammatory conditions including persistent ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and other prolonged inflammatory states have been clinically identified as significant risk factors for colorectal carcinogenesis (Shahgoli et al., 2024).
The progression from healthy colonic epithelial cells to advanced adenocarcinomas typically spans over 10 years, involving complex interactions among multiple biological mechanisms that respond to nutritional factors, behavioral patterns, and genetic pressures, which process evolves through precancerous adenomatous polyps before manifesting the morphological and functional transformations characteristic of malignant tumors (Zheng et al., 2023). Implementing intervention or regression (prevention) of CRC development timely, especially targeting key areas, age ranges, and genders, could emerge as a promising approach for substantially decreasing CRC-related incidence and mortality in forthcoming years.
Contemporary clinical management of CRC primarily involves multimodal therapeutic approaches including surgical intervention, radiation treatment, systemic chemotherapy, combination regimen (Kumar et al., 2023) or molecularly targeted agents (Zheng et al., 2023; Feng et al., 2024). Despite these interventions, patient outcomes remain suboptimal, with survival statistics demonstrating marked disparity across disease stages. Epidemiological data reveals stage I CRC patients achieve approximately 90% 5-year survival probability, contrasting sharply with the dismal 10% survival rate observed in stage IV cases, underscoring the limitations of existing therapeutic paradigms (Xie et al., 2020). Furthermore, chronic treatment administration imposes substantial socioeconomic burdens while inducing multisystem adverse effects spanning gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, emesis, diarrheal episodes), mucosal complications (oral ulceration), organ-specific toxicities (hepatic impairment), and hematological sequelae including myelosuppression and immune dysfunction (Miao et al., 2025).
During recent years, a growing number of studies have confirmed that natural derived small molecular compounds (NDSMCs) exhibit multiple mechanisms of action in the prevention and treatment CRC by regulating the intestinal microbiota (Lu et al., 2022; Weng and Goel, 2022), ferroptosis (Wu et al., 2023a), apoptosis (Li et al., 2023), autophagy (Secme et al., 2023) by not only stopping cancer progression or reversing carcinogenic effects in the precancerous stage, but also significantly restrain the proliferation activity of CRC cells, induce programmed death, hinder the metastasis process and inhibit angiogenesis. Therefore, this study systematically summarizes the research progress of NDSMCs in the fight against CRC in the past 5 years, including intestinal microbiota regulation, ferroptosis induction, apoptosis activation and autophagy regulation, to establish causation theories for clinical treatment strategy optimization and innovative drug development. In addition, clinical advances and shortcomings in the treatment of CRC with some NDSMCs have also been reported. The chemical structures of all the NDSMCs mentioned in this article has been shown in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2
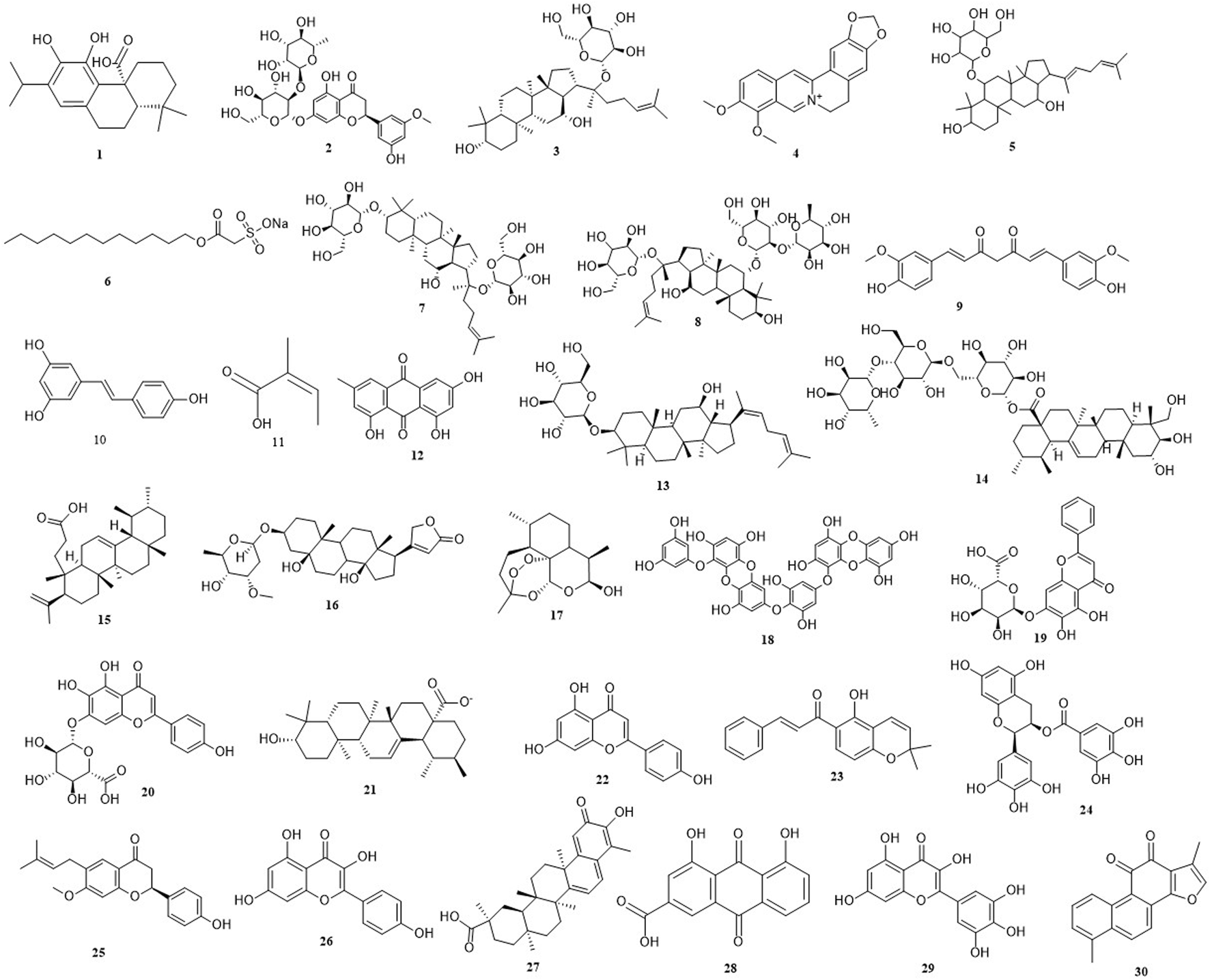
The chemical structures of all the natural derived small molecule compounds mentioned in this article. (1) Carnosic acid. (2) Neohesperidin. (3) Ginsenoside compound K. (4) Berberine. (5) Rare ginsenoside Rh4. (6) New Houttuynia sodium folate. (7) Ginsenoside-F2. (8) Ginsenoside-Re. (9) Curcumin. (10) Resveratrol. (11) Angelic acid. (12) Emodin. (13) Ginsenoside Rh3. (14) Asiaticoside. (15) Roburic acid. (16) Periplocymarin. (17) Dihydroartemisinin. (18) Dieckol. (19) Baicalin. (20) Scutellarin. (21) Ursolic acid. (22) Apigenin. (23) Lonchocarpin. (24) (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate. (25) Bavachin. (26) Kaempferol. (27) Celastrol. (28) Rhein. (29) Myricetin. (30) Tanshinone.
2 Natural derived small molecule compounds treat colorectal cancer by regulating intestinal flora composition and metabolites
The gut microbiota, comprising diverse microbial populations inhabiting the human digestive system’s gastrointestinal tract, undergoes dynamic modulation through various determinants including host genetics, aging processes, nutritional patterns, daily habits, pathological conditions, and pharmacological interventions (Barko et al., 2018; Ma et al., 2022). A well-regulated gut microbial ecosystem enhances immune function and inhibits CRC progression, whereas microbial dysbiosis characterized by pathogenic bacterial overgrowth facilitates CRC initiation and advancement (Wang J. et al., 2024). In recent years, numerous reports have indicated that NDSMCs exert significant anti-CRC effects by interacting with the intestinal microbiota to alter the abundance of the overall microbiota or specific bacteria, or influencing microbiota-derived metabolic byproducts (Table 1). Of course, gut microbiota actively participating in modifying NDSMCs' biotransformation processes and nutrient assimilation, consequently impacting their anticancer efficacy (Fujisaka et al., 2023).
TABLE 1
| Compounds | Model | Changes in the gut microbiota | Related mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carnosic acid | JGpt-Apcem1Cin(min)/Gpt (ApcMin/+) mice | ↓Bacteroide, ↓Bifidobacterium, ↓Alistipe, ↓Desulfovibrio, ↑Faecalibacterium, ↑Subdoligranulum | ↓NF-κB/STAT3 signaling, ↓IL-1β, ↓IL-6, ↓CXCL1, ↓IL-17, ↓DL-lactate, ↓citric acid | Li et al. (2022) |
| Neohesperidin | APC (min/+) transgenic mouse model | ↓Bacteroidetes, ↑Firmicutes, ↑ Proteobacteria | — | Gong et al. (2019) |
| Ginsenoside compound K | HCT-116, HT-29 and LOVO cells | ↑Akkermansia spp., ↓Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group | — | Shao et al. (2022) |
| Berberine | AOM/dss-induced CRC model mice fed with HFD | ↑Akkermansia, ↑Parabacteroides | ↓IL-6/STAT3, ↓Wnt signaling pathways | Chen et al. (2023) |
| Rare ginsenoside Rh4 | AOM/DSS-induced mouse model of CRC | ↑Akkermansia muciniphila | ↑7α-hydroxy-steroid dehydrogenase activity, ↑UDCA ↑FXR, ↓ TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway | Bai et al. (2024) |
| New Houttuynia sodium folate | Fn load in the CRC-cells-derived mice xenografts | ↓F. nucleatum | ↓FadA, ↓cancer-driven inflammation | Jia et al. (2022) |
| Panax notoginseng saponin | AOM/DSS induced colon tumorigenesis mouse | ↑Akkermansia spp | ↑the richness and diversity of intestinal flora | Chen et al. (2020) |
| Pien Tze Huang | AOM/dss-induced CRC model mice | ↑Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans, ↑Eubacterium ↓limosum, ↓Aeromonas veronii, ↓Campylobacter jejuni, ↓Collinsella aerofaciens, ↓ Peptoniphilus harei | ↑taurine, ↑hypotaurine, ↑bile acids, ↑ unsaturated fatty acids, ↓IL-17, ↓TNF, ↓ cytokine-chemokine | Gou et al. (2023) |
| Curcumin | The AOM/DSS-induced CRC model mice | ↓Ileibacterium, Monoglobus, ↓Desulfovibri, ↑ Clostridia_UCG-014, ↑Bifidobacterium, ↑ Lactobacillus | ↑the richness and diversity of intestinal flora | Deng et al. (2024) |
Natural derived small molecule compounds treat and improve colorectal cancer by regulating intestinal microbiota and its mechanism of action.
Some bacterial species (B. fragilis, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Porphyromonas asaccharolytica)) demonstrate higher abundance in CRC and the classified as detrimental microorganisms (Torres-Maravilla et al., 2021), conversely, microbial strains including Clostridium butyricum, Streptococcus thermophilus, and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei exhibit protective effects against CRC development (Doo et al., 2024). A primary mechanism through which NDSMCs counteract CRC progression involves mitigating inflammatory processes and immune activation triggered by pathogenic bacterial interactions with host tissues (Yang and Cong, 2021). For example, the components or secretions of certain intestinal microorganisms, such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS), short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (Hou et al., 2022), probile acids (Kuhls et al., 2022) and azoxymethane (Dzhalilova et al., 2023), have been identified as mediators of chronic intestinal inflammation and immune dysregulation, significantly contributing to CRC pathogenesis, while other metabolites, including ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) (Zhang et al., 2021a) and butyrate (Mann et al., 2024), exhibit therapeutic advantages and counteract tumorigenesis and disease progression.
Here, a brief introduction to the effects of some star molecules on CRC were introduced. SCFAs, microbial-derived metabolites synthesized through bacterial breakdown of dietary fibers in anaerobic intestinal environment (Liu Y. et al., 2023). The three predominant SCFAs, butyrate, propionate and acetate, exhibit protective properties against CRC through distinct mechanisms (Blaak et al., 2020). Butyrate serves as the primary energy substrate for colonic epithelial cells, enhancing cellular differentiation processes while mitigating inflammatory responses, which barrier-strengthening effects manifest through upregulated tight junction protein synthesis, stimulated mucin 2 secretion, and HIF-1 pathway stabilization (Zhang et al., 2025). Propionate can inhibit malignant transformation and induces apoptosis in precancerous CRC, although it is less effective (compared with butyrate) and less abundant in CRC (Cheong and Trefely, 2025). Acetate undergoes metabolic conversion by specific colonic microbiota including Roseburia spp., Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, and Coprococcus species, functioning as the terminal product in this fermentation cascade and concentrated to butyrate by the action of butyryl-coa: acetate transferase (Hosmer et al., 2024). Elevated lactate levels within tissue microenvironments serve as a hallmark of neoplastic progression and inflammatory conditions (Dai et al., 2024). Citrate present in extracellular spaces may act as a danger-associated molecular pattern, stimulating inflammatory responses via NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation and subsequent nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) (Parkinson et al., 2021). The bidirectional relationship between bile acid metabolism and gut microbiota exerts both protective and pathogenic influences on host physiology (Collins et al., 2023). Specific bile acids including Cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) demonstrate carcinogenic potential in CRC through modulation of NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling cascade (Fuchs and Trauner, 2022). Conversely, UDCA exhibits preventive properties by activating farnesoid X receptor signaling while suppressing TLR4-mediated pathways.
In addition, reducing the production of metabolites that promote CRC development and elevating beneficial metabolites is another important mechanism (González et al., 2024). As a recognized contributor to CRC, F. nucleatum secretes the virulence factor FadA that interacts with E-cadherin on intestinal epithelial cells, activating the Wnt-β-catenin signaling cascade which upregulates cyclin D1 expression and accelerates cellular proliferation (Ou et al., 2022). The bacterial component LPS additionally stimulates Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) receptors, initiating MYD88-dependent NF-κB activation that elevates miRNA-21 levels while suppressing RASA1 expression and molecular cascade subsequently triggers RAS-MAPK signaling, leading to S-phase cell cycle arrest and consequent enhancement of malignant cell multiplication in CRC (Sulit et al., 2023).
Carnosic acid (Figure 2, 1), a phenolic diterpene predominantly extracted from rosemary, exhibits notable anti-inflammatory characteristic (Li et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022) found that the abundance of Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, Alistipes and Desulfovibrio were downregulated by carnosic acid, while enhancing beneficial anti-inflammatory genera such as Faecalibacterium and Subdoligranulum, which relies on the degradation of acetic acid to produce butyric acid and anti-inflammatory properties by effectively control pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, CXCL1, and IL-17, thus showing anti-CRC properties, particularly, Faecalibacterium, which further reduces the production of DL-lactate and citric acid.
Neohesperidin (Figure 2, 2) derived from citrus fruits was discovered by Akhter et al. (2024) that the CRC would be inhibited and angiogenesis would be blocked by neohesperidin. However, interestingly, subsequent investigations demonstrated that neohesperidin’s protective effects operate independently of direct tumor cell interaction or Wnt/β-catenin pathway modulation, which is through microbial population shifts, specifically decreasing Bacteroidetes while elevating Firmicutes and Proteobacteria abundance at the phylum level. Instead, it exerts its anti-CRC effect by reducing, at the phylum level, the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes and increasing the abundances of Firmicutes and Proteobacteria. Critical validation through fecal microbiota transfer trials and antibiotic-mediated reversal of neohesperidin’s CRC suppression conclusively established gut microbiome modification as the principal mechanism underlying neohesperidin’s preventive action against colorectal tumor formation.
Ginsenoside compound K (Figure 2, 3), a dammarane-type tetracyclic triterpene, is derived from Panax ginseng, demonstrating diverse therapeutic properties including hypoglycemic, anti-aging, anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory and CRC-suppressing activities (Shao et al., 2022; Shao et al., 2022) found that ginsenoside compound K exerts anti-CRC effects through gut microbiota modulation, specifically enhancing populations of Akkermansia species (mucin-degrading commensals) while suppressing pathogenic Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group populations in AOM/DSS-induced colitis models.
High-fat diet (HFD) is positively correlated with the risk of CRC (Tang et al., 2024). Berberine (BBR) (Figure 2, 4), a bioactive isoquinoline alkaloid derived from Coptis chinensis, exhibits antimicrobial properties and has been widely employed in managing gastrointestinal infections including bacterial enteritis and dysentery (Huang and Huang, 2025; Chen et al., 2023) demonstrated that BBR inhibits CRC progression in HFD-fed mice with AOM/DSS-induced carcinogenesis through dual pathway modulation (IL-6/STAT3 and Wnt signaling pathways) thereby suppressing cell proliferation by increasing the abundance of beneficial gut microbiota, including Akkermansia and Parabacteroides in mice with AOM/DSS-induced CRC models fed with HFD. At the same time, BBR treatment notably decreased the incidence of colonic polyps while restoring intestinal barrier integrity and ameliorating microbial imbalance. In addition, glycerophospholipid metabolism is often significantly altered in the progression of CRC associated with HFD in mice. In this study, BBR treatment was found can reverse these changes in glycerophospholipid metabolites, especially reducing the concentration of lysophosphatidylcholine, proven to stimulate CRC cell growth and exacerbate cellular junction impairments. Notably, the anti-tumor efficacy of BBR was not observed in CRC models with depleted intestinal flora from HFD-fed mice, though transplanting the gut microbiota from BBR-treated mice via fecal microbiota transplantation restored the tumor-suppressing effects on both CRC development and lysophosphatidylcholine regulation, emphasizing gut microbiome’s crucial role in countering HFD-induced CRC. In AOM/DSS-induced CRC models, BBR administration enhanced the abundance of SCFA-producing bacteria including Prevotellaceae and Alloprevotella, consequently elevating concentrations of acetate, propionate, and butyrate while suppressing pathogenic strains such as Odoribacter and LPS-producing Marinifilaceae, thereby mitigating inflammatory responses and CRC progression (Yan et al., 2022).
Rare ginsenoside Rh4 (Figure 2, 5), a crucial active component in ginseng, has been stated to possess the capability of inducing apoptosis in tumor cells and ameliorating antibiotic-induced intestinal dysbiosis and inflammation (Wu et al., 2018; Bai et al., 2024) discovered that 7α-hydroxy-steroid dehydrogenas activity and UDCA production were enhanced by rare ginsenoside Rh4 by enriching Akkermansia muciniphila, a bile acid metabolism probiotic, in AOM/DSS-induced mouse model, which subsequently activated the farnesoid X receptor while modulating the TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory cascade, effectively restoring intestinal barrier integrity, suppressing colonic inflammatory processes and impeding CRC progression.
New Houttuynia sodium folate (Figure 2, 6), originating from the herb Houttuynia cordata (Jia et al., 2022), exhibits potent antimicrobial effects against F. nucleatum (Jia et al., 2022). found that new Houttuynia sodium folate reduced F. nucleatum load in tumor tissue and suppressed tumor progression in F. nucleatum mouse xenografts by targeting membrane-associated FadA and modulation of F. nucleatum-associated inflammatory pathways, while the damaged intestinal barrier was also improved.
Panax notoginseng saponin, recognized as the primary bioactive constituent derived from P. notoginseng extracts, comprises ginsenoside Rb1, Rg1 and notoginsenoside R1 as its principal components (Zhang H. et al., 2024). Colon tumorigenesis and development was alleviated by P. notoginseng saponin via restoring the richness and diversity of intestinal flora, in particularly, by increasing the abundance of Akkermansia spp, which is inversely associated with CRC progression. Furthermore, gut microbiota biotransformation analysis revealed ginsenoside compound K (Figure 2, 3) as the principal microbial metabolite of P. notoginseng saponin, exhibiting potent antiproliferative effects against human CRC cell lines through distinct molecular mechanisms (Chen et al., 2020).
Pien Tze Huang, a well-established traditional medicinal formulation, has been proven to prevent and treat CRC through microbial-dependent and non-microbial-dependent mechanisms (Chen et al., 2022). As a microbial-dependent mechanism, Pien Tze Huang enhances intestinal barrier integrity by modulating gut microbial composition, notably elevating beneficial strains like Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans and Eubacterium limosum while suppressing pathogenic species including Aeromonas veronii, Campylobacter jejuni, Collinsella aerofaciens, and Peptoniphilus harei. Concurrently, this herbal preparation elevates protective metabolites such as taurine derivatives, bile acids, and unsaturated fatty acids. Through non-microbial pathways, PZH downregulates oncogenic signaling cascades including PI3K-Akt activation and pro-inflammatory mediators like IL-17, TNF, and chemokine networks. Experimental evidence reveals that specific bioactive constituents [ginsenoside-F2 (Figure 2, 7) and ginsenoside-Re (Figure 2, 8)] exhibit anti-proliferative effects against CRC cell lines and patient-derived organoids, with additional efficacy observed in AOM/DSS-induced CRC models (Gou et al., 2023).
Curcumin (Figure 2, 9), a primary polyphenolic compound derived from turmeric rhizomes (Anas et al., 2024). Curcumin treatment has been shown can effectively reverses microbial dysbiosis in CRC mice by restoring core microbiota diversity and abundance, this treatment suppresses pathogenic genera including Ileibacterium, Monoglobus and Desulfovibrio while enhancing beneficial bacterial populations such as Clostridia_UCG-014, Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus (Deng et al., 2024). 13 different metabolites were identified, and curcumin reduced levels of ethylsuximine, xanthine, and 17-β-estradiol 3-sulfate-17 - (β-D-glucuronide), which were augmented in the CRC model group. In contrast, glutamylleucine, γ-glutamylleucine, liquiritin, ubenimex, 5'-deoxy-5 ′-fluoruridine, 7, 8-dihydroterophenic acid, ribenzapril, heterosin A, and 7,4'-dihydroxy-8-methylflavane were reduced in the CRC group, but were significantly upregulated by curcumin. However, the therapeutic mechanisms and clinical relevance of these biochemical alterations in CRC pathogenesis demand more comprehensive exploration.
3 Natural derived small molecule compounds treat colorectal cancer by promoting ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is a recently identified type of regulated cell death which is triggered through iron-mediated lipid peroxidation processes, showing therapeutic potential for CRC management (Li et al., 2020). This cell death pathway primarily involves catalytic oxidation of membrane-bound polyunsaturated fatty acids by ferrous iron or lipoxygenases, generating lipid peroxides that culminate in cellular demise (Dixon et al., 2024). As a crucial component in ferroptosis regulation, glutathione (GSH) plays dual roles in supporting immune homeostasis and combating oxidative stress. Serving as the primary cofactor for GPX4 (glutathione peroxidase 4), this tripeptide enables the enzyme’s lipid repair capabilities by reducing oxidized membrane components (Weaver and Skouta, 2022). Depletion of GSH reserves incapacitates GPX4’s redox-regulatory functions, precipitating lethal lipid peroxidation in CRC cells (Niu et al., 2021). The cystine/glutamate antiporter (System XC-), functioning as the principal antioxidant pathway in mammalian cells, has emerged as a critical ferroptosis modulator through its cystine transport activity (Parker et al., 2021). The reverse transport function of xCT regulates the synthesis of GSH by exchanging glutamate for cysteine, thereby helping to balance excessive hydrogen peroxide (Lim et al., 2019). Within ferroptosis mechanisms, solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) serves as a crucial regulatory component (Liu Z. et al., 2022). Functioning as a ferroptosis suppressor, this protein operates within the System XC- complex by controlling cellular cystine absorption (Lee and Roh, 2022). Disruption of the XC- system diminishes cystine availability, subsequently halting GSH biosynthesis and initiating iron-dependent cell death pathways (Sun K. et al., 2023). There are many reports NDSMs treat CRC by promoting ferroptosis (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3
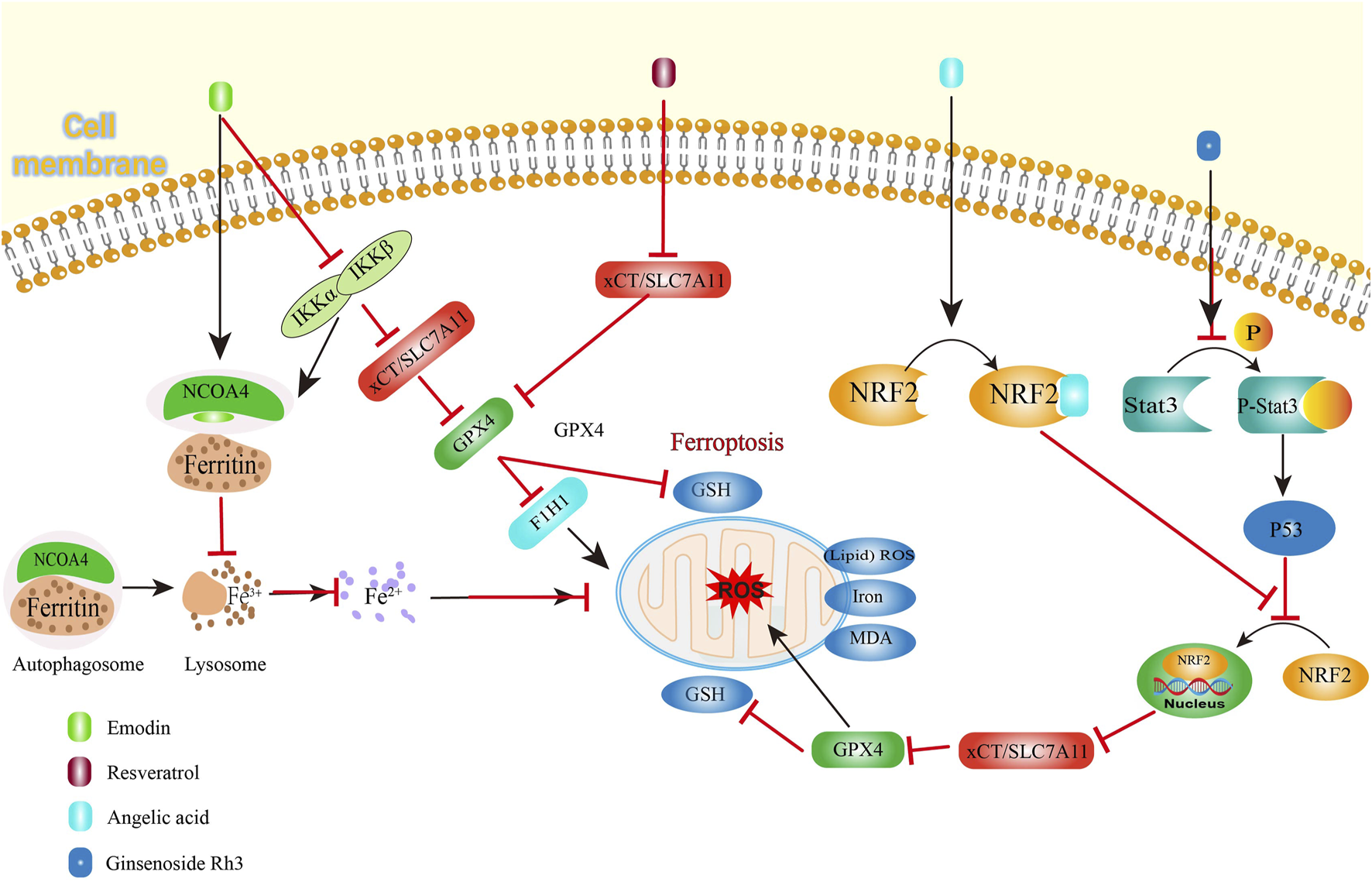
Natural derived small molecule compounds treat colorectal cancer by promoting ferroptosis.
Resveratrol (Figure 2, 10), a plant-derived non-flavonoid polyphenol, functions as a phytoalexin with demonstrated therapeutic potential in cancer treatment (Vikal et al., 2024). This bioactive compound, naturally present in wine and grape products, exhibits multifaceted biological activities including oxidative stress reduction, inflammation control, and cardioprotective effects. Resveratrol potentiates ferroptosis through dual inhibition of SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression, thereby amplifying reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and lipid peroxidation in CRC cells (Zhang Z. et al., 2022).
Angelic acid (Figure 2, 11), a bioactive constituent derived from the rhizomes of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, has been identified as a ferroptosis inducer in CRC cell (Wen et al., 2025; Cao et al., 2024) found angelic acid destabilizes nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), a crucial regulator of oxidative stress responses, through protein degradation mechanisms, as evidenced including elevated malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, enhanced lipid peroxidation, and increased expression of CHAC1 and PTGS2 -effects that were reversed upon administration of the ferroptosis inhibitor Fer-1. Mechanistically, no significant changes in the mRNA levels of GPX4 and NRF2 were detected after angelic acid treatment, but the expression of NRF2 was weakened in a concentration-dependent manner. The cellular thermal shift assay and cycloheximide chase assay demonstrated that that angelic acid affected NRF2 stability by increasing the K48-ubiquitination level of NRF2. The reversal of NRF2-mediated suppression on CRC cell viability through genetic overexpression further confirms that angelic acid physically interacts with NRF2 to accelerate its proteasomal breakdown, consequently initiating ferroptotic cell death mechanisms in CRC cells. Additionally, the syngeneic mouse model revealed that the sensitivity of CRC cells to ferroptosis inducers, sulfasalazine, was enhanced by angelic acid and no toxicity in vivo showed, basically, demonstrating the promising feasibility of angelic acid as a dietary therapeutic agent for CRC treatment.
Ferroptosis represents an iron-dependent oxidative cell death mechanism driven by Fenton reaction-generated reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) (Zhang X. et al., 2024). Malignant cells exhibit heightened iron demands to support their rapid proliferation, making them particularly vulnerable to iron-mediated cytotoxicity (Li et al., 2025). During iron deficiency, cells release ferritin, their primary iron storage complex, through regulated pathways. Iron storage protein, ferritin, is usually released by the cell when it urgently needs iron. Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) is an important transcriptional regulatory factor (Yin et al., 2024). The NCOA4-mediated degradation pathway, termed ferritinophagy, involves selective recognition of ferritin by autophagic vesicles for lysosomal breakdown (Santana-Codina et al., 2021). This process elevates intracellular iron concentrations, exacerbating oxidative damage through lipid peroxidation cascades that initiate ferroptotic cell death (Hoelzgen et al., 2024).
Emodin (Figure 2, 12), a bioactive compound exhibiting significant anticancer, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, is widely present in various medicinal herbs including Rheum palmatum, and Polygonum multiflorum (Hassan et al., 2024; Shen et al., 2024) demonstrated that this phytochemical triggers ferroptosis in CRC cells through dual mechanisms involving NCOA4-regulated ferritinophagy and suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway. After emodin treatment, ROS generation, lipid peroxidation levels, MDA levels, iron levels, and the expressions of NCOA4 and transferrin receptor (TFRC) increased in CRC, while GSH/GSSG ratio, System Xc-, GPX4 and ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1) expression decreased. Crucially, genetic ablation of NCOA4 reversed emodin-induced iron overload, confirming ferritinophagy’s essential role in mediating iron accumulation during this process. The study further established a mechanistic link between NF-κB pathway inhibition and ferroptosis induction, with emodin treatment significantly downregulating components of this inflammatory signaling cascade. This indicates that coordinated regulation of ferroptosis and inflammatory pathways underlies emodin’s therapeutic potential against CRC. Experimental data revealed downregulation of NF-κB and IKK signaling pathway components, indicating emodin-mediated suppression of NF-κB activation. Pharmacological activation of NF-κB using PMA significantly counteracted emodin’s effects on critical regulators including antioxidant proteins (SLC7A11, GPX4), autophagy markers (LC3B, P62), and iron metabolism proteins (NCOA4, FTH1) in CRC cells and PMA partially reversed cytoplasmic iron accumulation, as well as MDA and lipid peroxidation. These findings collectively demonstrate that NF-κB pathway inhibition plays a pivotal role in mediating emodin-triggered ferroptosis in CRC through modulation of iron homeostasis and oxidative stress mechanisms.
Ginsenoside Rh3 (Figure 2, 13), a bioactive triterpenoid compound derived from Panax ginseng C. A. Mey roots, demonstrates significant anticancer properties (Xu et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2023a) revealed ginsenoside Rh3 can effectively eliminate CRC cells through both pyroptosis and ferroptosis. Pyroptosis involves Caspase-1-mediated activation of Gasdermin proteins, particularly Gasdermin D, which manifests through cellular membrane perforation and subsequent release of inflammatory mediators into the extracellular environment (Shi et al., 2017). The STAT protein family, particularly STAT3, serves as critical regulators of cellular signaling networks, coordinating essential biological functions ranging from cell cycle progression to angiogenesis. Under physiological conditions, STAT3 undergoes transient phosphorylation to mediate cytokine-induced transcriptional responses, maintaining strict regulation of cellular processes (Kim et al., 2018). Ginsenoside Rh3 modulates oncogenic signaling pathways by interfering with nuclear translocation of redox regulators. While STAT3 demonstrates constitutive activation across numerous malignancies, pharmacological intervention with ginsenoside Rh3 specifically attenuated tyrosine-phosphorylated Stat3 levels while elevating total p53 tumor suppressor expression. Although whole-cell analyses showed minimal alterations in total Stat3 and NRF2 concentrations, nuclear fractionation revealed substantial suppression of NRF2 nuclear accumulation following ginsenoside Rh3 exposure. This impaired nuclear localization consequently diminished HO-1 transcriptional activity, thereby enhancing NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and caspase-1 activation. The activated caspase-1 protease cleaves Gasdermin D to execute pyroptotic cell death. Concurrently, ginsenoside Rh3-mediated nuclear exclusion of NRF2 disrupts xCT/SLC7A11-dependent glutathione synthesis, precipitating iron overload, lipid peroxidation (evidenced by MDA accumulation), and catastrophic GSH depletion - hallmark events culminating in ferroptotic cell death (Wu et al., 2023a).
4 Natural derived small molecule compounds treat colorectal cancer by promoting apoptosis
Apoptosis is defined by distinct cellular changes including nuclear condensation, chromatin fragmentation, membrane blebbing, and reduced MMP activity (Bertheloot et al., 2021). The mitochondrial apoptotic pathway is primarily regulated through interactions between Bcl-2 family members and caspase activation (Czabotar and Garcia-Saez, 2023). As opposing regulators within this protein family, Bcl-2 demonstrates anti-apoptotic properties by maintaining mitochondrial membrane integrity and preventing cytochrome C release (Czabotar and Garcia-Saez, 2023). Conversely, the pro-apoptotic Bax protein promotes mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, facilitating cytoplasmic release of cytochrome C and apoptotic activators to initiate cell death cascades (Wolf et al., 2022). Bax increases apoptosis by binding to Bcl-2, disrupting the protective effect of Bcl-2 on apoptosis (Edlich, 2018) Concurrently, dysregulated cell cycle progression contributes to malignant proliferation, with cyclin D1 overexpression being frequently observed in cancerous growth patterns (Wang et al., 2023b). Many NDSMCs have been shown to exert therapeutic effects through multifaceted pathways, including modulation of Bcl-2 protein clusters, Caspase enzyme systems, and cyclin D1 expression. These biochemical interventions demonstrate capacity to control mitotic progression, activate programmed cell death pathways, and suppress CRC.
4.1 Natural derived small molecules induce apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting nuclear factor kappa-beta (NF-κB) signaling pathway
The NF-κB signaling cascade serves as a central modulator in numerous biological functions including immune regulation, inflammatory responses, and cellular homeostasis (Mao et al., 2025). This molecular pathway exhibits responsiveness to diverse stimuli encompassing inflammatory mediators, oxidative stressors, radiation exposure, and microbial pathogens, subsequently governing transcriptional activation of multiple genetic targets (Guo et al., 2024).
NF-κB represents an umbrella term for dimeric transcription factor complexes predominantly composed of structural subunits (Yu et al., 2020). In unactivated state, NF-κB is located in the cytoplasm and binds to the inhibitory protein IκB, thus remaining in an inactive state (Mitchell and Carmody, 2018). Cellular activation triggered by specific stimuli induces IκB phosphorylation followed by proteasomal degradation, thereby liberating NF-κB complexes (Guo et al., 2024). The liberated dimers subsequently translocate to the nuclear compartment where they initiate the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines and survival factors, processes critically involved in inflammatory pathogenesis and oncogenic development (Guo et al., 2024).
Asiaticoside (Figure 2, 14), the primary bioactive component derived from Centella asiatica (Umbelliferae family), demonstrates notable anti-inflammatory properties as documented in prior research (Bandopadhyay et al., 2023). I-κBα phosphorylation was found diminished by Asiaticoside in human CRC cell lines (HCT116, SW480, LoVo) concentration-dependently, which effectively blocks the nuclear translocation of the P65 subunit, indicating its potential to suppress colorectal tumor progression and stimulate apoptotic mechanisms through NF-κB pathway inhibition. Concurrently, researchers observed marked downregulation of CDK4 and Cyclin D1 expression alongside enhanced caspase-9 and caspase-3 activation. These cellular changes, coupled with a reduced Bcl-2/Bax mRNA ratio, collectively contribute to G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest and programmed cell death induction (Figure 3) (Zhou et al., 2020).
The TNF-activated NF-κB signaling pathway serves as a critical mediator in cancer pathogenesis and represents a promising therapeutic target for pharmacological intervention (Zhang T. et al., 2021). Roburic acid (Figure 2, 15), a recently identified tetracyclic triterpene compound extracted from oak galls, exhibits notable anti-inflammatory properties (Wang L. et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2022) reveals roburic acid’s capacity to suppress IKKα/β phosphorylation, inhibit IκBα degradation, and prevent p65 nuclear translocation in TNF-stimulated systems. This molecular mechanism was observed in both in vitro models using CRC cells and in vivo studies with xenografted nude mice, demonstrating roburic acid’s ability to downregulate NF-κB-regulated survival proteins such as XIAP, Mcl-1, and Survivin. These findings collectively establish RA roburic acid’s anti-proliferative effects on CRC cells through NF-κB pathway inhibition roburic acid was found inhibited the phosphorylation of IKKα/β, IκBα and p65, degradation of IκBα, nuclear translocation of p65 and expression of NF-κB target gene, including that of XIAP, Mcl-1, and Survivin, in TNF-induced CRC cells and xenografted nude mice, indicated that inhibited the growth of human CRC cells was inhibited by roburic acid via inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway (Figure 4) (Xu et al., 2022).
FIGURE 4
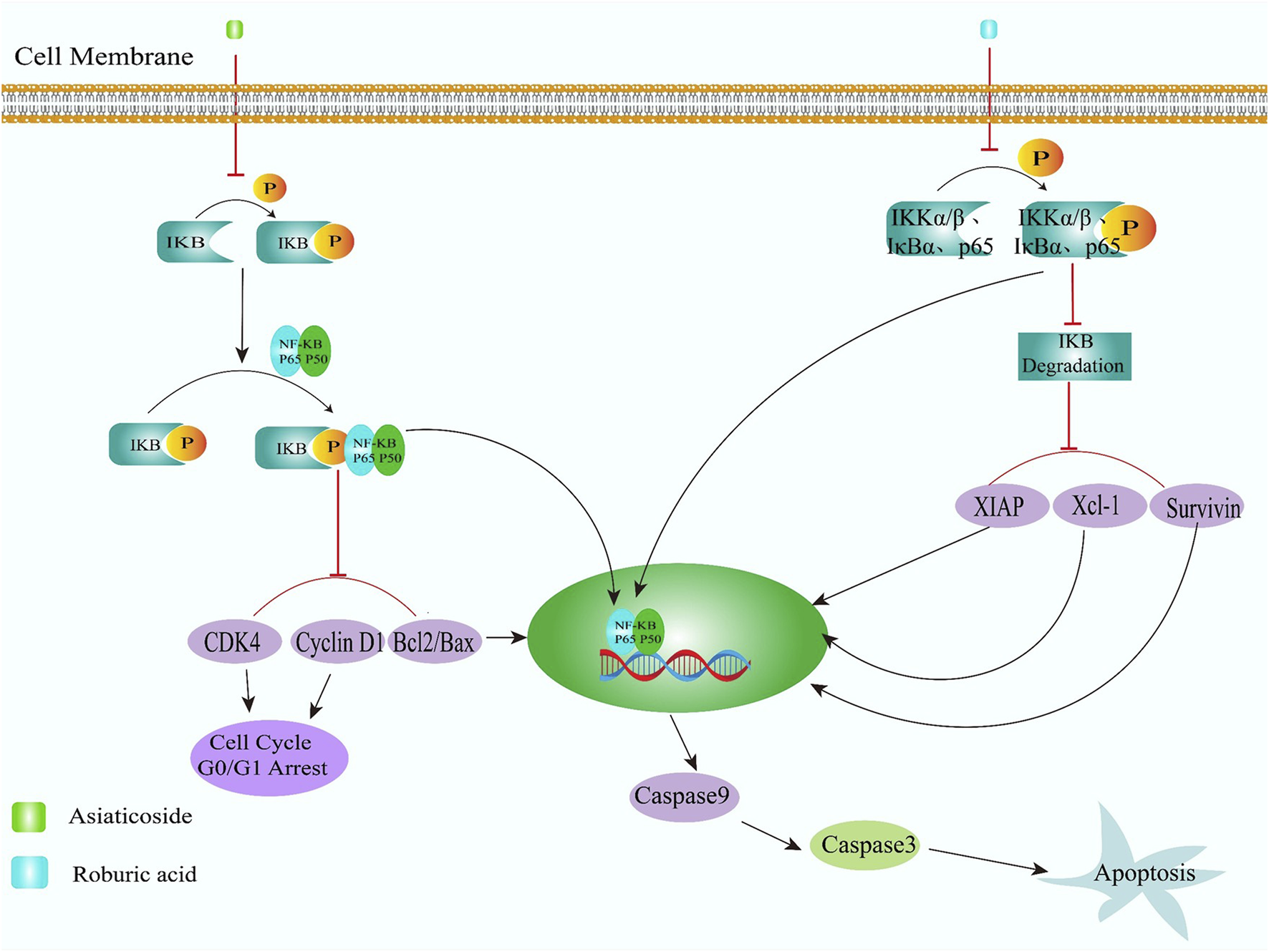
Natural derived small molecules induce apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting nuclear factor kappa-beta (NF-κB) signaling pathway.
4.2 Natural derived small molecules induce apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
The Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase-B (PI3K/Akt) cascade represents a crucial intracellular signaling mechanism activated by numerous oncogenic factors and receptor tyrosine kinases (Thapa et al., 2020). This pathway’s core components include PI3K and the serine-threonine kinase Akt, with the latter serving as PI3K’s primary downstream effector that directly mediates its activation signals (Khezri et al., 2022). Research across various malignancies has demonstrated that dysregulation of this signaling axis drives oncogenic processes through sustained activation, facilitating tumor cell proliferation, metabolic adaptation, and survival signaling networks (Khezri et al., 2022).
Periplocymarin (Figure 2, 16), a cardiac glycoside derived from Periploca sepium, exhibits potential anticancer properties (Cheng Y. et al., 2021; Cheng et al., 2021b) demonstrated that this compound exerts therapeutic effects against CRC through impairment of PI3K/AKT pathway functionality, which mechanism involves triggering apoptotic processes and inducing cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase, achieved through suppression of IRS1 expression and phosphorylation of PI3K/AKT proteins. Additionally, periplocymarin modulates the expression levels of Bcl-2 family members, survivin, p21, and cyclin D1 proteins, which collectively contribute to its anticancer efficacy.
Dihydroartemisinin (Figure 2, 17), a derivative of artemisinin, demonstrates potent antitumor effects through inducing programmed cell death, suppressing neoplastic growth, and impeding cellular proliferation and motility (Olatunde et al., 2023; Chen and Yao, 2023) found that dihydroartemisinin effectively curtailed CRC RKO cell proliferation and migration while stimulating apoptosis through G2/M phase cell cycle arrest, which mechanism involves suppression of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway activation, evidenced by reduced phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, PI3K, and AKT proteins. The treatment concurrently downregulated AKT expression while elevating MMP-9 protein levels and Caspase-3/9 mRNA concentrations. Notably, dihydroartemisinin administration increased cleaved Caspase-9/Caspase-9 ratios and elevated Bax/Bcl-2 protein expression proportions. In animal models, dihydroartemisinin outperformed cisplatin by enhancing body mass and substantially decreasing serum TNF-α concentrations, tumor mass, and volumetric dimensions with 41.45% tumor growth inhibition. Parallel in vitro experiments confirmed dihydroartemisinin capacity to suppress malignant cell proliferation/migration, induce apoptotic processes, and mediate G2/M phase cycle arrest in cultured cells.
Dieckol (Figure 2, 18) is a polyphenol extracted from brown algae Ecklonia cava (Rajan et al., 2021). Dieckol successfully inhibited the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by significantly reducing the expression and protein levels of Cyclin-D1, PCNA, Bcl-2, p-P13K, AKT, mTOR and other apoptosis-related genes, thereby inducing the apoptosis of HCT-116 cells (Dai et al., 2023). Notably, dieckol also significantly increased the concentration of ROS in HCT-116 cells, which are molecules with unpaired valence shell electrons, also known as free radicals. ROS are incredibly active and inflict a large amount of oxidative damage to the organism, which is considered as the main factor of apoptosis.
4.3 Natural derived small molecules induce apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting hedgehog signaling pathway
Hedgehog (HH) signaling pathway is a classical signaling pathway that controls embryonic development and maintains crucial functions in embryonic development and cell growth and proliferation after embryo formation (Martelli et al., 2023).
The HH signaling pathway consists of HH ligands (SHH, DHH, IHH), 2 cell membrane receptors Patched (Ptc) and Smoothened (Smo), and Glioma 2/3 (Glioma-associated oncogene) homolog, serine/threonine protein kinase Fused (Fu), negative regulatory protein Suppressor of Fused (SuFu), microtubule associated protein Kinesin family member 7(KIF7), protein kinase A (PKA), etc. (Jing et al., 2023). HH receptor patch 1 (PTCH1) and HH receptor patch 2 (PTCH2) encode the negative regulatory proteins Patched1 and Patched2 in the Hedgehog signaling pathway, respectively (Zhong and Wang, 2022). Smo encodes the positive regulatory protein Smoothened in the HH signaling pathway. The transcription factors Gli (1, 2 and 3) are the main downstream executive factors of HH activation and key final outputs of HH (Lou et al., 2020). Gli1 is an HH response gene product, which only acts as a transcriptional activator and participates in the formation of positive feedback loops during pathway activation (Sigafoos et al., 2021). Gli2 and Gli3 are the major transcriptional activators and suppressors, respectively (Yoshida and Yoshida, 2025). Under ligand-deficient conditions, PTCH1 actively suppresses Smo activity by blocking its translocation into primary cilia (Cong et al., 2025). When HH ligand binds to Ptc, this mutual inhibition is relieved and Smo signal is excite (Jing et al., 2023). Ligand-receptor interaction between HH and Ptc disrupts this mutual antagonism, triggering Smo signal transduction (Li et al., 2018). Aberrant activation of this signaling cascade is frequently observed in multiple malignancies. Emerging evidence confirms the Hedgehog pathway’s regulatory involvement in CRC, particularly through SHH-mediated stimulation of neovascularization, cellular multiplication, and metastatic progression, while IHH downregulation emerges as a precursor event in CRC pathogenesis (Wang et al., 2023a).
Sun et al. (2023b) demonstrated that BBR (Figure 2, 4) effectively suppresses the HH signaling pathway in both in vitro models and HCT116 xenograft tumors. This inhibition manifests through downregulation of SHH, Ptch1, SMO, Gli1, and c-Myc expression while elevating SUFU levels in CRC cells. Furthermore, experimental evidence reveals BBR’s capacity to trigger programmed cell death and arrest the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase. The compound concurrently diminishes G2/M and S phase distribution through modulation of Bcl-2 and Bax expression levels, accompanied by reduced mitochondrial membrane potential and decreased cyclin D1 production in CRC cells.
Baicali (Figure 2, 19), a naturally occurring flavonoid compound extracted from the medicinal herb Scutellariabaicalensis Georgi (Ibrahim et al., 2022), demonstrates regulatory effects on inflammatory cytokines and Hedgehog pathway components. Experimental studies reveal BC downregulates mRNA and protein expression of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, SHH, SMO, and Gli1 while upregulating SUFU expression in SW620 CRC cells. In CRC models, BC administration significantly reduces tissue levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) and modulates Hedgehog signaling markers - suppressing SHH, SMO, and Gli1 protein expression while enhancing SUFU protein production. These findings suggest baicali anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on CRC cells may operate through Hedgehog pathway inhibition (Lin, 2023).
Scutellarin (Figure 2, 20) is the another active ingredient of Scutellariabaicalensis Georgi (Liao et al., 2021). Scutellarin inhibited the activity of the HH signaling pathway in CRC tissues and SW480 cells, reducing the expression of SHH, Ptch1, Smo, and Gli1, while increasing the level of SUFU. At the same time, scutellarin treatment could inhibit the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 in response to TNF-α stimulation in IEC-6 cells to exert anti-inflammatory effects. The literature confirms that NF-κB can induce the expression of SHH and IL-1β and IL-6 by activating the HH signaling pathway. Activated NF-κB can induce overexpression of SHH, activating the HH signaling pathway. Therefore, the blockade of NF-κB signaling may inhibit the expression of SHH and thus the HH signaling axis (Zeng et al., 2022). Future research directions should prioritize mechanistic studies exploring SL’s regulatory effects on the HH-NF-κB crosstalk in CRC.
4.4 Natural derived small molecules induce apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
In the majority of CRC cases, upregulated expression of key genes within the Wnt/β-catenin pathway contributes to cell cycle disruption in malignant cells, promoting accelerated invasion and metastatic progression (Liu J. et al., 2022). The nuclear accumulation of β-catenin directly correlates with pathway activation intensity, making its intracellular concentration regulation fundamental for controlling this signaling cascade (Liu J. et al., 2022). Under normal physiological conditions without Wnt stimulation, cytoplasmic β-catenin undergoes phosphorylation through the APC/Axin/GSK3β destruction complex, subsequently targeted for proteasomal degradation to maintain subthreshold concentrations (Maurice and Angers, 2025). When Wnt signaling is triggered by ligand binding to membrane receptors, GSK3β undergoes phosphorylation-induced functional impairment, enabling β-catenin stabilization and cytoplasmic accumulation (Shah and Kazi, 2022). This stabilized signaling molecule subsequently transports into nuclear compartments, initiating transcriptional activation of oncogenic targets including CD133, CD44, ALDH isoforms, c-Myc proto-oncogenes, and cyclin-dependent kinase regulators (Chen et al., 2012). Numerous studies have demonstrated that constitutive activation of this pathway represents a central driver in CRC.
Ursolic acid (Figure 2, 21), a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpene compound, is widely distributed in numerous edible plants, herbal medicines, and culinary spices (Arulnangai et al., 2025). Ursolic acid was found greatly inhibited the proliferation, migration, and clonality of SW620 cells; induced apoptosis; and arrest the cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase, accompanied by decreased activity of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Furthermore, in vivo investigations revealed ursolic acid administration markedly inhibited tumor progression in xenograft models, ameliorated histopathological characteristics, enhanced programmed cell death, and induced cell cycle blockade in CRC tissues through downregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling components (Zhao et al., 2023).
Apigenin (Figure 2, 22), a flavonoid, is abundantly present in various fruits and vegetables from tropical regions, with celery being a particularly rich source (Yan et al., 2014). Zhao et al. (2023) reveals that apigenin counteracts LiCl-induced activation of β-catenin/T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor signaling cascades, showing concentration-dependent efficacy against this Wnt pathway activator. This action prevents nuclear translocation of β-catenin, consequently blocking the transcriptional activation of Wnt-regulated target genes.
Lonchocarpin (Figure 2, 23) was initially extracted from Lonchocarpus sericeus (synonymously termed Derris sericeus) through the pioneering work of Baudrenghien’s research group in 1949 (do Nascimento and Mors, 1972). Subsequent investigations by Predes et al. (2019) identified lonchocarpin as a novel Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor that disrupts β-catenin nuclear translocation, thereby decreasing its nuclear accumulation. This compound additionally demonstrated inhibitory effects on the constitutively active TCF4 variant dnTCF4-VP16. In vivo, Xenopus laevis embryology assays showed that lonchocarpin acts at the transcriptional level. Embryological studies using X. laevis models revealed lonchocarpin’s transcriptional-level activity. Experimental evaluations using colorectal carcinoma cell lines (HCT116, SW480, DLD-1) demonstrated lonchocarpin’s capacity to suppress both cellular migration and proliferation, while showing no cytotoxic effects on the non-malignant intestinal IEC-6 cell line. Furthermore, in vivo testing using AOM/DSS-induced murine CRC models confirmed lonchocarpin’s tumor-suppressive properties. Notably, multiple solid malignancies including colorectal carcinomas contain cancer stem cells-a distinct cellular subgroup demonstrating self-renewal capacity and multilineage differentiation potential. These neoplastic stem cells significantly contribute to tumor maintenance and progression through their unique biological properties.
The initiation, progression, metastatic spread, chemoresistance, and relapse of malignancies are closely associated with CRC stem cells (CRCSCs), making these cells a promising therapeutic target for impeding metastasis and recurrence in CRC (Chu et al., 2024). As the primary bioactive compound in green tea, (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) (Figure 2, 24) has been shown to suppress CRCSCs proliferation and promote apoptotic cell death through modulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade (Chen et al., 2017). The expression levels of CD133, CD44, ALDHA1, which are CRC markers in CRC, as well as the protein and mRNA levels of cell cycle protein D1 and PCNA were observed to be downregulated with EGCG treatment. At the same time, EGCG treatment led to a downregulation of Bcl-2 expression and an upregulation of Bax, caspases (3, 8, and 9) levels.
4.5 Natural derived small molecules induce apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting MAPK signaling pathway
Extensive research has demonstrated that Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) serves as a central mediator in translating external signals into diverse biological responses such as cellular development, motility, multiplication, specialization, and programmed cell death (Braicu et al., 2019). The mammalian MAPK family includes ERK, JNK and P38, etc. (Wu et al., 2023b). Gadd45a protein, characterized by its acidic nature and spherical conformation, belongs to a conserved group of molecules associated with growth suppression and genomic instability (Rostami et al., 2025). This multifunctional regulator participates in critical cellular operations encompassing genetic material restoration, division cycle control, cell death mechanisms, neoplastic transformation, and blood vessel formation. Research indicates that Gadd45a’s apoptosis-promoting effects frequently operate through activation pathways involving both p38 and JNK kinases (Yue and López, 2020).
Bavachin (Figure 2, 25), a dihydroflavonoid derived from Psoralea species, exhibits diverse pharmacological propertie (Wang et al., 2025). It was found that bavachin’s capacity to stimulate phosphorylation of p38, JNK, and ERK kinases in both HCT 116/HT-29 cell lines and murine xenograft models. This biochemical activation coincided with upregulated Gadd45a expression, consequently triggering MAPK pathway activation that suppresses CRC cell proliferation while promoting apoptotic mechanisms (Wang M. et al., 2023).
HIF-1 is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of target genes related to oxygen homeostasis under hypoxic conditions, thereby promoting tumor development and progression,and he overexpression of HIF-1α is closely associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients (Pandey et al., 2025). Kaempferol (Figure 2, 26) is a naturally occurring flavonoid compound found in various fruits and vegetables, and it has attracted attention due to its potential anti-cancer effects. Mechanistic studies have shown that kaempferol can dual regulate the transcriptional activity of HIF-1α and MAPK signaling (p-ERK/p-38), as well as ROS-induced DNA damage and intrinsic cell apoptosis (cleaved caspase-3/9 and Bcl-2 protein expression), effecting on angiogenesis, EMT, and survival pathways significantly reduce the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis abilities of hypoxic colon cancer cells, indicating that kaempferol can serve as an innovative multi-pathway inhibitor (Haroon and Kang, 2025).
5 Natural derived small molecule compounds treat colorectal cancer by promoting autophagy
Autophagy is a degradative metabolic pathway, mainly relies on lysosomes to clear damaged or aged cellular organelle (Liu S. et al., 2023). Among autophagy-regulating proteins, ATG7 represents a crucial molecular player that primarily facilitates autophagosome biogenesis through its enzymatic functions (Liu et al., 2024).
Celastrol (Figure 2, 27) is a bioactive component extracted from Tripterygium wilfordii, and has shown may induce autophagy in CRC by targeting Nur77 which is a pro-cancer regulator and upregulating ATG7 (Zhang W. et al., 2022), which offers novel perspectives on celastrol’s antitumor potential in CRC. Celastrol administration effectively suppressed tumor progression in mice bearing CRC xenografts, potentially mediated through Nur77 downregulation-induced ATG7 upregulation. Notably, celastrol-treated human CRC cell lines (HCT-116 and SW480) exhibited diminished clonogenic capacity alongside elevated pro-apoptotic Bax and cleaved PARP levels, coupled with reduced anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 expression. Concurrently, autophagy markers showed significant alterations: decreased p62 protein levels contrasted with increased Beclin-1 expression, while crucially impairing the Bcl-1/Bcl-2 interaction required for autophagy initiation. Additionally, celastrol promoted the conversion of LC3-I to lipidated LC3-II in CRC cells, which is essential for the formation of autophagosomes.
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), an atypical serine/threonine kinase, serves as a pivotal regulator of cellular processes including proliferation, programmed cell death, autophagy, and metabolic regulation (Panwar et al., 2023). Aberrant activation of this signaling molecule stimulates cellular proliferation and metastatic potential, establishing its central role in pathway modulation (Holroyd and Michie, 2018). Dysregulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis frequently occurs in various malignancies. Rhein (Figure 2, 28), a bioactive anthraquinone compound derived from rhubarb species (Cheng L. et al., 2021) demonstrates significant antitumor effects through mTOR interaction. Zhang et al. (2021b) revealed that rhein administration effectively suppresses CRC cell proliferation and metastatic behavior through direct mTOR binding and subsequent pathway inhibition. Mechanistically, this natural compound induces G1 phase arrest by modulating cell cycle regulators including cyclin A1, E1, D1, and CDK2 expression. Concurrent elevation of apoptotic mediators (p53, phosphorylated p53, activated caspase 3 and Bax) confirms rhein’s pro-apoptotic capacity in malignant colon cells. The critical role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition processes in tumor progression further underscores Rhein suppressed CRC cell motility and metastatic potential through modulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers, including increased E-cadherin production and decreased expression of N-cadherin and vimentin. The influence of rhein on the mTOR signal transduction pathway in CRC cells is reflected in the fact that it can directly bind to mTOR and downregulate mTOR expression. mTOR is crucial for the activation of HSF1 and the synthesis of HSP90, and the activation of HSF1 and the synthesis of HSP90 in many cancers are significantly associated with tumor metastasis and death. The protein levels of HSF1 and HSP90 in CRC cells were downregulated by RE treatment. Furthermore, the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway plays an important role in protein degradation, and RE can promote the degradation of mTOR via the ubiquitin-proteasome. Similarly, RE showed significant tumor growth inhibition in xenografted mouse models without significant toxicity. RE is, therefore, a potent anticancer agent that may help prevent and treat CRC.
Myriceti (Figure 2, 29), a flavonoid pigment abundant in fruits, herbs, and nuts (Zhu et al., 2020). Studies (Zhu et al., 2020) reveals that myriceti modulates programmed cell death mechanisms through PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibition. Myriceti diminishes Bcl-2/Bax protein ratios while promoting apoptosis in HCT116 and SW620 cell lines. Morphological changes observed under optical microscopy after 48-h exposure to 50–100 μmol/L myriceti included cellular rounding, membrane blebbing, and cytoplasmic autophagic vacuoles. The autophagy process was evidenced by LC3-I to LC3-II transformation, with immunoblotting showing increased LC3-II/β-actin ratios. Concurrent elevation of Beclin-1/β-actin expression, indicative of autophagosome formation, was observed alongside these molecular changes. Exposure to myriceti triggered a dose-responsive escalation in autophagic activity within HCT116 and SW620 cell lines, with microscopic analysis revealing enhanced autophagic vesicle formation compared to control groups. Phospho-PI3K, phospho-Akt, and phospho-mTOR levels showed dose-dependent reductions in both cell models, while total protein levels of these signaling molecules remained statistically comparable across treatment conditions. Notably, the phosphorylation ratios of Akt and mTOR relative to their total forms were markedly diminished. These collective findings indicate that myriceti administration activates autophagic processes in CRC cells through modulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling axis.
The Aurora kinase family, comprising three subtypes (Aurora A, B, and C), consists of serine/threonine kinases essential for regulating mitotic progression (Kolli, 2025). Elevated Aurora gene expression through amplification and increased mRNA/protein production has been documented across multiple malignancies including prostate, breast, pancreatic, and ovarian cancers. Aurora A demonstrates specific localization at mitotic spindle poles and centrosomes (Lin et al., 2020), positioning it as a promising therapeutic target in oncology due to its functional interaction with p53 through phosphorylation-mediated degradation (Magnaghi-Jaulin et al., 2019). Derived from the traditional Chinese medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen), Tanshinone (Figure 2, 30) represents a bioactive constituent (Naz et al., 2020) with demonstrated anticancer properties. Studies (Lu et al., 2016) have shown that the mechanism by which Aurora A-p53 axis may inhibit the growth of CRC cells may differ depending on the intrinsic characteristics of the tumor cells. In HCT116 cancer cells, after 24 h of treatment, tanshinone significantly increased the proportion of G2/M and 4N cells, decreased the proportion of S and G0/G1 cells, and reduced the expression levels of CDK4, cyclin D1, c-PARP, Bax, and Bcl-2 proteins, indicating cell cycle arrest and increased cell apoptosis.
6 Progress in clinical research of natural derived small molecules
The finally goal of basic research on NDSMCs is the successful application of safe and effective drugs to clinical patients. Through clinical research network station (https://clinicaltrials.gov/) to retrieve the data about the NDSMCs against CRC clinical research data (Table 2). Lots and quality NDSMCs have been studied against CRC, which undoubtedly confirms the reproducibility and translational potential of their anti-CRC effects.
TABLE 2
| Project title | Compound | Status | Registration no. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 2 Study with Abraxane (Nab®Paclitaxel) in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | Paclitaxel | Phase 2 | NCT02103062 |
| Curcumin Biomarkers | Curcumin | Phase 1 | NCT01333917 |
| Clinical Study Evaluating the Anticancer Effect of Pentoxiphylline in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC - PTX) | Pentoxiphylline | Phase 1 | NCT06115174 |
| Safety and Effectiveness Study of Pre-operative Artesunate in Stage II/III Colorectal Cancer (NeoART-V) (NeoART-V) | Artesunat | Phase 2 | NCT03093129 |
| Ursodiol, Combination Chemotherapy, and Bevacizumab in Treating Patients with Stage IV Colorectal Cancer | Ursodiol | Phase 3 | NCT00873275 |
| Effect of Silymarin in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients | Silymarin | Phase 3 | NCT05631041 |
| Genistein in Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | Genistein | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
NCT01985763 |
| Resveratrol for Patients with Colon Cancer | Resveratrol | Phase 1 | NCT00256334 |
| Cancer Associated Thrombosis and Isoquercetin | Isoquercetin | Phase 2 Phase 3 |
NCT02195232 |
Clinical trial of colorectal cancer with natural derived small molecule compounds.
7 Conclusion
Over the past decade, the occurrence and fatality rates of CRC have shown a marked escalation, primarily attributed to the interplay of detrimental lifestyle patterns, dietary modifications, and additional contributing elements. Current investigations have highlighted the therapeutic potential of NDSMCs in the prevention and treatment of CRC, with this comprehensive review analyzing recent advancements in past 5 years. The analysis encompasses four critical biological mechanisms: gut microbiome regulation, ferroptosis modulation, and programmed cell death pathways (apoptosis and autophagy). Notably, phytochemical constituents including ginsenosides, berberine alkaloids, and curcuminoids have demonstrated promising outcomes in both preclinical studies and translational research, emerging as viable complementary approaches for CRC intervention strategies.
Nevertheless, certain limitations persist regarding the application of NDSMCs in nutritional supplementation and biomedical research. Primarily, NDSMCs are usually derived from natural resources such as animals, plants, and microorganisms, and their yields are easily affected by factors such as origin, season, and growth environment, and the scarcity of resources may limit large-scale research and application. Therefore, new sources should be actively explored, such as artificial breeding and cultivation raw materials, chemical synthesis and biosynthesis, etc. To enhance predictive accuracy regarding therapeutic potential and toxicological profiles while minimizing clinical trial complexities, integration of cutting-edge biotechnological tools becomes imperative. Genomic sequencing platforms, proteomic profiling systems, and metabolic pathway analyses, when synergized with computer-aided molecular modeling, could elucidate precise molecular targets and mechanistic pathways of NDSMCs. Many NDSMCs have problems such as low oral bioavailability, short half-life, fast metabolism, and unsatisfactory distribution in vivo, which affect their efficacy in vivo. The use of new formulation technologies, such as nanoparticles, liposomes, microcapsules, etc., to improve the pharmacokinetic properties of NDSMCs, improve bioavailability, prolong the time of action of drugs in vivo. Illustrating this trend, researchers have engineered various advanced curcumin delivery systems such as liposomal encapsulation, nanoparticle formulations, phospholipid complexes, and structural analogs to optimize its bioavailability. During preclinical evaluation phases, implementing rigorous safety assessment protocols-encompassing cytotoxicity analyses, chronic toxicity studies in animal models, and hypersensitivity assessments-is crucial for developing robust adverse event surveillance frameworks capable of promptly identifying and mitigating potential risks.
Statements
Author contributions
M-JL: Writing – original draft. H-YD: Writing – original draft. GC: Data curation, Writing – original draft. W-WL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. G-FL: Resources, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the grants from the Health and Medical Scientific Research Project of Shenzhen Baoan Medical Association (No. BAYXH2024040).
Acknowledgments
We extend our sincere thanks to all our colleagues in the project for their contribution and time. We thank the editorial team and the expert reviewers for their professional advice.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Akhter S. Arman M. S. I. Tayab M. A. Islam M. N. Xiao J. (2024). Recent advances in the biosynthesis, bioavailability, toxicology, pharmacology, and controlled release of citrus neohesperidin. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr.64 (15), 5073–5092. 10.1080/10408398.2022.2149466
2
Anas M. Falak A. Khan A. Khattak W. A. Nisa S. G. Aslam Q. et al (2024). Therapeutic potential and agricultural benefits of curcumin: a comprehensive review of health and sustainability applications. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci.10.1007/s43994-024-00200-7
3
Arulnangai R. Asia Thabassoom H. Vajiha Banu H. Thirugnanasambandham K. Ganesamoorthy R. (2025). Recent developments on ursolic acid and its potential biological applications. Toxicol. Rep.14, 101900. 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101900
4
Bai X. Duan Z. Deng J. Zhang Z. Fu R. Zhu C. et al (2024). Ginsenoside Rh4 inhibits colorectal cancer via the modulation of gut microbiota-mediated bile acid metabolism. J. Adv. Res.72, 37–52. 10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.028
5
Bandopadhyay S. Mandal S. Ghorai M. Jha N. K. Kumar M. Radha et al (2023). Therapeutic properties and pharmacological activities of asiaticoside and madecassoside: a review. J. Cell. Mol. Med.27 (5), 593–608. 10.1111/jcmm.17635
6
Barko P. C. McMichael M. A. Swanson K. S. Williams D. A. (2018). The gastrointestinal microbiome: a review. J. Vet. Intern. Med.32 (1), 9–25. 10.1111/jvim.14875
7
Bertheloot D. Latz E. Franklin B. S. (2021). Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol. Immunol.18 (5), 1106–1121. 10.1038/s41423-020-00630-3
8
Blaak E. E. Canfora E. E. Theis S. Frost G. Groen A. K. Mithieux G. et al (2020). Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes.11 (5), 411–455. 10.3920/bm2020.0057
9
Braicu C. Buse M. Busuioc C. Drula R. Gulei D. Raduly L. et al (2019). A comprehensive review on MAPK: a promising therapeutic target in cancer. Cancers (Basel)11 (10), 1618. 10.3390/cancers11101618
10
Cañellas-Socias A. Sancho E. Batlle E. (2024). Mechanisms of metastatic colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.21 (9), 609–625. 10.1038/s41575-024-00934-z
11
Cao Y. Wang Y. Li Y. Liu S. Wang L. Zhou L. et al (2024). Angelic acid triggers ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells via targeting and impairing NRF2 protein stability. J. Nat. Med.79, 82–94. 10.1007/s11418-024-01849-4
12
Chan O. Y. A. Tao L. Chen G. Kong L. (2025). The association of dietary fiber intake with colorectal cancer and related risks: a literature review of recent research. J. Agric. Food Chem.21, 101999. 10.1016/j.jafr.2025.101999
13
Chen J. Yao G. (2023). Herbal medicine dihydroartemisinin inhibits colorectal cancer by regulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Oncol.3. 10.52768/2692-563X/1080
14
Chen H.-J. Hsu L.-S. Shia Y.-T. Lin M.-W. Lin C.-M. (2012). The β-catenin/TCF complex as a novel target of resveratrol in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol.84 (9), 1143–1153. 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.08.011
15
Chen Y. Wang X.-Q. Zhang Q. Zhu J.-Y. Li Y. Xie C.-F. et al (2017). (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate inhibits colorectal cancer stem cells by suppressing Wnt/β-Catenin pathway. Nutrients9 (6), 572. 10.3390/nu9060572
16
Chen L. Chen M.-Y. Shao L. Zhang W. Rao T. Zhou H.-H. et al (2020). Panax notoginseng saponins prevent colitis-associated colorectal cancer development: the role of gut microbiota. Chin. J. Nat. Med.18 (7), 500–507. 10.1016/S1875-5364(20)30060-1
17
Chen Q. Hong Y. Weng S. Guo P. Li B. Zhang Y. et al (2022). Traditional Chinese medicine pien-tze-huang inhibits colorectal cancer growth and immune evasion by reducing β-catenin transcriptional activity and PD-L1 expression. Front. Pharmacol.13, 828440. 10.3389/fphar.2022.828440
18
Chen H. Ye C. Wu C. Zhang J. Xu L. Wang X. et al (2023). Berberine inhibits high fat diet-associated colorectal cancer through modulation of the gut microbiota-mediated lysophosphatidylcholine. Int. J. Biol. Sci.19 (7), 2097–2113. 10.7150/ijbs.81824
19
Cheng L. Chen Q. Pi R. Chen J. (2021a). A research update on the therapeutic potential of rhein and its derivatives. Eur. J. Pharmacol.899, 173908. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173908
20
Cheng Y. Wang G. Zhao L. Dai S. Han J. Hu X. et al (2021b). Periplocymarin induced colorectal cancer cells apoptosis via impairing PI3K/AKT pathway. Front. Oncol.11, 753598. 10.3389/fonc.2021.753598
21
Cheong Y. J. Trefely S. (2025). Divergent roles for propionate and butyrate in colorectal cancer epigenetics. Nat. Metab.7, 11–13. 10.1038/s42255-024-01186-6
22
Chu X. Tian W. Ning J. Xiao G. Zhou Y. Wang Z. et al (2024). Cancer stem cells: advances in knowledge and implications for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.9 (1), 170. 10.1038/s41392-024-01851-y
23
Collins S. L. Stine J. G. Bisanz J. E. Okafor C. D. Patterson A. D. (2023). Bile acids and the gut microbiota: metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.21 (4), 236–247. 10.1038/s41579-022-00805-x
24
Cong G. Zhu X. Chen X. R. Chen H. Chong W. (2025). Mechanisms and therapeutic potential of the hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer. Cell Death Discov.11 (1), 40. 10.1038/s41420-025-02327-w
25
Czabotar P. E. Garcia-Saez A. J. (2023). Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.24 (10), 732–748. 10.1038/s41580-023-00629-4
26
Dai W. Dai Y. g. Ren D. f. Zhu D. w. (2023). Dieckol, a natural polyphenolic drug, inhibits the proliferation and migration of Colon cancer cells by inhibiting PI3K, AKT, and mTOR phosphorylation. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol.37 (5), e23313. 10.1002/jbt.23313
27
Dai E. Wang W. Li Y. Ye D. Li Y. (2024). Lactate and lactylation: behind the development of tumors. Cancer Lett.591, 216896. 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216896
28
Deng W. Xiong X. Lu M. Huang S. Luo Y. Wang Y. et al (2024). Curcumin suppresses colorectal tumorigenesis through restoring the gut microbiota and metabolites. BMC Cancer24 (1), 1141. 10.1186/s12885-024-12898-z
29
Dixon S. J. Olzmann J. A. (2024). The cell biology of ferroptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.25 (6), 424–442. 10.1038/s41580-024-00703-5
30
do Nascimento M. C. Mors W. B. (1972). Chalcones of the root bark of Derris sericea. Phytochemistry11 (10), 3023–3028. 10.1016/0031-9422(72)80097-9
31
Doo H. Kwak J. Keum G. B. Ryu S. Choi Y. Kang J. et al (2024). Lactic acid bacteria in Asian fermented foods and their beneficial roles in human health. Food Sci. Biotechnol.33 (9), 2021–2033. 10.1007/s10068-024-01634-9
32
Dzhalilova D. Zolotova N. Fokichev N. Makarova O. (2023). Murine models of colorectal cancer: the azoxymethane (AOM)/Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) model of colitis-associated cancer. Peer. J.11, e16159. 10.7717/peerj.16159
33
Edlich F. (2018). BCL-2 proteins and apoptosis: recent insights and unknowns. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.500 (1), 26–34. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.190
34
Feng L. Wang X. Guo X. Shi L. Su S. Li X. et al (2024). Identification of novel target DCTPP1 for colorectal cancer therapy with the natural small-molecule inhibitors regulating metabolic reprogramming. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.63 (47), e202402543. 10.1002/anie.202402543
35
Fuchs C. D. Trauner M. (2022). Role of bile acids and their receptors in gastrointestinal and hepatic pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.19 (7), 432–450. 10.1038/s41575-021-00566-7
36
Fujisaka S. Watanabe Y. Tobe K. (2023). The gut microbiome: a core regulator of metabolism. J. Endocrinol.256 (3), e220111. 10.1530/joe-22-0111
37
Gong Y. Dong R. Gao X. Li J. Jiang L. Zheng J. et al (2019). Neohesperidin prevents colorectal tumorigenesis by altering the gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res.148, 104460. 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104460
38
González A. Fullaondo A. Odriozola I. Odriozola A. (2024). Microbiota and beneficial metabolites in colorectal cancer. Adv. Genet.112, 367–409. 10.1016/bs.adgen.2024.08.002
39
Gou H. Su H. Liu D. Wong C. C. Shang H. Fang Y. et al (2023). Traditional medicine Pien Tze Huang suppresses colorectal tumorigenesis through restoring gut microbiota and metabolites. Gastroenterology165 (6), 1404–1419. 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.052
40
Guo Q. Jin Y. Chen X. Ye X. Shen X. Lin M. et al (2024). NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther9 (1), 53. 10.1038/s41392-024-01757-9
41
Haroon M. Kang S. C. (2025). Kaempferol promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation and migration by suppressing HIF-1α/VEGF and Wnt/β-catenin activation under hypoxic condition in colon cancer. J. Appl. Biol. Chem.68 (1), 19. 10.1186/s13765-025-00992-0
42
Hassan H. M. Hamdan A. M. Alattar A. Alshaman R. Bahattab O. Al-Gayyar M. M. H. (2024). Evaluating anticancer activity of emodin by enhancing antioxidant activities and affecting PKC/ADAMTS4 pathway in thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Redox Rep.29 (1), 2365590. 10.1080/13510002.2024.2365590
43
Hoelzgen F. Nguyen T. T. P. Klukin E. Boumaiza M. Srivastava A. K. Kim E. Y. et al (2024). Structural basis for the intracellular regulation of ferritin degradation. Nat. Commun.15 (1), 3802. 10.1038/s41467-024-48151-1
44
Holroyd A. K. Michie A. M. (2018). The role of mTOR-mediated signaling in the regulation of cellular migration. Immunol. Lett.196, 74–79. 10.1016/j.imlet.2018.01.015
45
Hosmer J. McEwan A. G. Kappler U. (2024). Bacterial acetate metabolism and its influence on human epithelia. Emergi. Top. Life Sci.8 (1), 1–13. 10.1042/ETLS20220092
46
Hou H. Chen D. Zhang K. Zhang W. Liu T. Wang S. et al (2022). Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and colorectal cancer: ready for clinical translation?Cancer Lett.526, 225–235. 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.11.027
47
Huang S. Huang G. (2025). The delivery carriers and applications for Xiaobojian. Discov. Nano20 (1), 56. 10.1186/s11671-025-04239-1
48
Ibrahim A. Nasr M. El-Sherbiny I. M. (2022). Baicalin as an emerging magical nutraceutical molecule: emphasis on pharmacological properties and advances in pharmaceutical delivery. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Tec.70, 103269. 10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103269
49
Jia F. Yu Q. Zhao L. Shen Y. Guo H. He F. (2022). Sodium new houttuyfonate inhibits cancer-promoting Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn) to reduce colorectal cancer progression. Cancers14 (24), 6111. 10.3390/cancers14246111
50
Jing J. Wu Z. Wang J. Luo G. Lin H. Fan Y. et al (2023). Hedgehog signaling in tissue homeostasis, cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther8 (1), 315. 10.1038/s41392-023-01559-5
51
Khezri M. R. Jafari R. Yousefi K. Zolbanin N. M. (2022). The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in cancer: molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic interventions. Exp. Mol. Pathol.127, 104787. 10.1016/j.yexmp.2022.104787
52
Kim M. Morales L. D. Jang I. S. Cho Y. Y. Kim D. J. (2018). Protein tyrosine phosphatases as potential regulators of STAT3 signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19 (9), 2708. 10.3390/ijms19092708
53
Kolli R. (2025). Dawning aurora: TPXL3 activates α-Aurora kinase and regulates mitotic spindle morphogenesis. Plant Cell37 (4), koaf074. 10.1093/plcell/koaf074
54
Kuhls S. Osswald A. Ocvirk S. (2022). Bile acids, bile pigments and colorectal cancer risk. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol.38 (2), 173–178. 10.1097/mog.0000000000000820
55
Kumar A. Gautam V. Sandhu A. Rawat K. Sharma A. Saha L. (2023). Current and emerging therapeutic approaches for colorectal cancer: a comprehensive review. World J. Gastrointest. Surg.15 (4), 495–519. 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.495
56
Lee J. Roh J.-L. (2022). SLC7A11 as a gateway of metabolic perturbation and ferroptosis vulnerability in cancer. Antioxidants11 (12), 2444. 10.3390/antiox11122444
57
Li S. Li S. Wang B. Jiang J. (2018). Hedgehog reciprocally controls trafficking of Smo and ptc through the smurf family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. Sci. Signal.11 (516), eaan8660. 10.1126/scisignal.aan8660
58
Li J. Cao F. Yin H.-l. Huang Z.-j. Lin Z.-t. Mao N. et al (2020). Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis.11 (2), 88. 10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
59
Li S. Yang H. Li L. Wang W. Tan H.-Y. Qu Y. et al (2022). The involvement of gut microbiota in the anti-tumor effect of carnosic acid via IL-17 suppression in colorectal cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact.365, 110080. 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110080
60
Li S. Y. Shi C. J. Fu W. M. Zhang J. F. (2023). Berberine inhibits tumour growth in vivo and in vitro through suppressing the lincROR-Wnt/β-catenin regulatory axis in colorectal cancer. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.75 (1), 129–138. 10.1093/jpp/rgac067
61
Li B. Zhang B. Cheng Z. Lou Y. Chen S. (2025). Nanomaterials targeting iron homeostasis: a promising strategy for cancer treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol.13, 1511197. 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1511197
62
Liao H. Ye J. Gao L. Liu Y. (2021). The main bioactive compounds of Scutellaria baicalensis georgi. For alleviation of inflammatory cytokines: a comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother.133, 110917. 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110917
63
Lim J. K. M. Delaidelli A. Minaker S. W. Zhang H.-F. Colovic M. Yang H. et al (2019). Cystine/Glutamate antiporter xCT (SLC7A11) facilitates oncogenic RAS transformation by preserving intracellular redox balance. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. Usa.116 (19),9433–9442. 10.1073/pnas.1821323116
64
Lin H. (2023). Mechanism of baicalin against colitis-associated colorectal cancer based on hedgehog signal pathway. Nat. Prod. Res.35 (5), 741–749.
65
Lin X. Xiang X. Hao L. Wang T. Lai Y. Abudoureyimu M. et al (2020). The role of Aurora-A in human cancers and future therapeutics. Am. J. Cancer Res.10 (9), 2705–2729.
66
Liu J. Xiao Q. Xiao J. Niu C. Li Y. Zhang X. et al (2022a). Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther7 (1), 3. 10.1038/s41392-021-00762-6
67
Liu Z. Wang H. Larsen M. Gunewardana S. Cendali F. I. Reisz J. A. et al (2022b). The solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) is regulated by LH/androgen and required for cystine/glutathione homeostasis in mouse sertoli cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.549, 111641. 10.1016/j.mce.2022.111641
68
Liu S. Yao S. Yang H. Liu S. Wang Y. (2023a). Autophagy: regulator of cell death. Cell Death and Dis.14 (10), 648. 10.1038/s41419-023-06154-8
69
Liu Y. Pei Z. Pan T. Wang H. Chen W. Lu W. (2023b). Indole metabolites and colorectal cancer: gut microbial tryptophan metabolism, host gut microbiome biomarkers, and potential intervention mechanisms. Microbiol. Res.272, 127392. 10.1016/j.micres.2023.127392
70
Liu J. Xiao Y. Cao L. Lu S. Zhang S. Yang R. et al (2024). Insights on E1-like enzyme ATG7: functional regulation and relationships with aging-related diseases. Commun. Biol.7 (1), 382. 10.1038/s42003-024-06080-1
71
Lou H. Li H. Huehn A. R. Tarasova N. I. Saleh B. Anderson S. K. et al (2020). Genetic and epigenetic regulation of the smoothened gene (SMO) in cancer cells. Cancers (Basel)12 (8), 2219. 10.3390/cancers12082219
72
Lu M. Wang C. Wang J. (2016). Tanshinone I induces human colorectal cancer cell apoptosis: the potential roles of Aurora A-p53 and survivin-mediated signaling pathways. Int. J. Oncol.49 (2), 603–610. 10.3892/ijo.2016.3565
73
Lu L. Dong J. Liu Y. Qian Y. Zhang G. Zhou W. et al (2022). New insights into natural products that target the gut microbiota: effects on the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. Front. Pharmacol.13, 964793. 10.3389/fphar.2022.964793
74
Ma J. Piao X. Mahfuz S. Long S. Wang J. (2022). The interaction among gut microbes, the intestinal barrier and short chain fatty acids. Anim. Nutr.9, 159–174. 10.1016/j.aninu.2021.09.012
75
Magnaghi-Jaulin L. Eot-Houllier G. Gallaud E. Giet R. (2019). Aurora A protein kinase: to the centrosome and beyond. Biomolecules9 (1), 28. 10.3390/biom9010028
76
Mann E. R. Lam Y. K. Uhlig H. H. (2024). Short-chain fatty acids: linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol.24 (8), 577–595. 10.1038/s41577-024-01014-8
77
Mao H. Zhao X. Sun S.-c. (2025). NF-κB in inflammation and cancer. Cell Mol. Immunol.22, 811–839. 10.1038/s41423-025-01310-w
78
Martelli A. M. Paganelli F. Truocchio S. Palumbo C. Chiarini F. McCubrey J. A. (2023). Understanding the roles of the hedgehog signaling pathway during T-Cell lymphopoiesis and in T-Cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (3), 2962. 10.3390/ijms24032962
79
Maurice M. M. Angers S. (2025). Mechanistic insights into Wnt–β-catenin pathway activation and signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.26, 371–388. 10.1038/s41580-024-00823-y
80
Miao H. Fang Y. Pan C. Yang H. Wang Z. Qi Y. et al (2025). Transforming the landscape of cancer treatment with seven promising novel therapies: evolution and future perspectives. Med2 (2), 100087. 10.1016/j.medp.2025.100087
81
Mitchell J. P. Carmody R. J. (2018). NF-κB and the transcriptional control of inflammation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol.335, 41–84. 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.07.007
82
Morgan E. Arnold M. Gini A. Lorenzoni V. Cabasag C. J. Laversanne M. et al (2023). Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut72 (2), 338–344. 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327736
83
Naz I. Merarchi M. Ramchandani S. Khan M. R. Malik M. N. Sarwar S. et al (2020). An overview of the anti-cancer actions of tanshinones, derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza (danshen). Explor. target. anti-tumor Ther.1 (3), 153–170. 10.37349/etat.2020.00010
84
Niu B. Liao K. Zhou Y. Wen T. Quan G. Pan X. et al (2021). Application of glutathione depletion in cancer therapy: enhanced ROS-Based therapy, ferroptosis, and chemotherapy. Biomaterials277, 121110. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121110
85
Olatunde O. Z. Yong J. Lu C. (2023). An overview of dihydroartemisinin as a promising lead compound for development of anticancer agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem.23 (3), 265–289. 10.2174/1389557522666220425124923
86
Olfatifar M. Rafiei F. Sadeghi A. Ataei E. Habibi M. A. Pezeshgi Modarres M. et al (2025). Assessing the colorectal cancer landscape: a comprehensive exploration of future trends in 216 countries and territories from 2021 to 2040. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health15 (1), 5. 10.1007/s44197-025-00348-3
87
Ou S. Wang H. Tao Y. Luo K. Ye J. Ran S. et al (2022). Fusobacterium nucleatum and colorectal cancer: from phenomenon to mechanism. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol.12, 1020583. 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1020583
88
Pandey P. Lakhanpal S. Mahmood D. Baldaniya L. Kang H. N. Hwang S. et al (2025). Recent update of natural compounds as HIF-1α inhibitors in colorectal carcinoma. Drug Des. Dev. Ther.19, 2017–2034. 10.2147/dddt.S511406
89
Panwar V. Singh A. Bhatt M. Tonk R. K. Azizov S. Raza A. S. et al (2023). Multifaceted role of mTOR (Mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther8 (1), 375. 10.1038/s41392-023-01608-z
90
Parker J. L. Deme J. C. Kolokouris D. Kuteyi G. Biggin P. C. Lea S. M. et al (2021). Molecular basis for redox control by the human cystine/glutamate antiporter system xc. Nat. Commun.12 (1), 7147. 10.1038/s41467-021-27414-1
91
Parkinson E. K. Adamski J. Zahn G. Gaumann A. Flores-Borja F. Ziegler C. et al (2021). Extracellular citrate and metabolic adaptations of cancer cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev.40 (4), 1073–1091. 10.1007/s10555-021-10007-1
92
Predes D. Oliveira L. F. S. Ferreira L. S. S. Maia L. A. Delou J. M. A. Faletti A. et al (2019). The chalcone lonchocarpin inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin signaling and suppresses colorectal cancer proliferation. Cancers11 (12), 1968. 10.3390/cancers11121968
93
Rajan D. K. Mohan K. Zhang S. Ganesan A. R. (2021). Dieckol: a brown algal phlorotannin with biological potential. Dieckol a brown algal phlorotannin Biol. potential142, 111988. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111988
94
Rostami A. Palomer X. Pizarro-Delgado J. Peña L. Zamora M. Montori-Grau M. et al (2025). GADD45A suppression contributes to cardiac remodeling by promoting inflammation, fibrosis and hypertrophy. Cell Mol. Life Sci.82 (1), 189. 10.1007/s00018-025-05704-x
95
Santana-Codina N. Gikandi A. Mancias J. D. (2021). The role of NCOA4-Mediated ferritinophagy in ferroptosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.1301, 41–57. 10.1007/978-3-030-62026-4_4
96
Secme M. Mutlu D. Elmas L. Arslan S. (2023). Assessing effects of caffeic acid on cytotoxicity, apoptosis, invasion, GST enzyme activity, oxidant, antioxidant status and micro-RNA expressions in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. S. Afr. J. Bot.157, 19–26. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy. 10.1016/j.sajb.2023.03.046
97
Shah K. Kazi J. U. (2022). Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of WNT/Beta-Catenin signaling. Front. Oncol.12, 858782. 10.3389/fonc.2022.858782
98
Shahgoli V. K. Noorolyai S. Ahmadpour Youshanlui M. Saeidi H. Nasiri H. Mansoori B. et al (2024). Inflammatory bowel disease, colitis, and cancer: unmasking the chronic inflammation link. Int. J. Colorectal Dis.39 (1), 173. 10.1007/s00384-024-04748-y
99
Shao L. Guo Y.-P. Wang L. Chen M.-Y. Zhang W. Deng S. et al (2022). Effects of ginsenoside compound K on colitis-associated colorectal cancer and gut microbiota profiles in mice. Ann. Transl. Med.10 (7), 408. 10.21037/atm-22-793
100
Shen Z. Zhao L. Yoo S.-a. Lin Z. Zhang Y. Yang W. et al (2024). Emodin induces ferroptosis in colorectal cancer through NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy and NF-κb pathway inactivation. Apoptosis29 (9), 1810–1823. 10.1007/s10495-024-01973-2
101
Shi J. Gao W. Shao F. (2017). Pyroptosis: gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends. biochem. Sci.42 (4), 245–254. 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.004
102
Sigafoos A. N. Paradise B. D. Fernandez-Zapico M. E. (2021). Hedgehog/GLI signaling pathway: transduction, regulation, and implications for disease. Cancers (Basel)13 (14), 3410. 10.3390/cancers13143410
103
Sulit A. K. Daigneault M. Allen-Vercoe E. Silander O. K. Hock B. McKenzie J. et al (2023). Bacterial lipopolysaccharide modulates immune response in the colorectal tumor microenvironment. npj Biofilms Microbiomes9 (1), 59. 10.1038/s41522-023-00429-w
104
Sun K. Zhi Y. Ren W. Li S. Zhou X. Gao L. et al (2023a). The mitochondrial regulation in ferroptosis signaling pathway and its potential strategies for cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother.169, 115892. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115892
105
Sun Q. Tao Q. Ming T. Tang S. Zhao H. Liu M. et al (2023b). Berberine is a suppressor of hedgehog signaling Cascade in colorectal cancer. Phytomedicine114, 154792. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154792
106
Tang Q. Huang H. Xu H. Xia H. Zhang C. Ye D. et al (2024). Endogenous coriobacteriaceae enriched by a high-fat diet promotes colorectal tumorigenesis through the CPT1A-ERK axis. npj Biofilms Microbiomes10 (1), 5. 10.1038/s41522-023-00472-7
107
Thapa N. Chen M. Horn H. T. Choi S. Wen T. Anderson R. A. (2020). Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signalling is spatially organized at endosomal compartments by microtubule-associated protein 4. Nat. Cell Biol.22 (11), 1357–1370. 10.1038/s41556-020-00596-4
108
Torres-Maravilla E. Boucard A. S. Mohseni A. H. Taghinezhad S. S. Cortes-Perez N. G. Bermúdez-Humarán L. G. (2021). Role of gut microbiota and probiotics in colorectal cancer: onset and progression. Microorganisms9 (5), 1021. 10.3390/microorganisms9051021
109
Vikal A. Maurya R. Bhowmik S. Khare S. Raikwar S. Patel P. et al (2024). Resveratrol: a comprehensive review of its multifaceted health benefits, mechanisms of action, and potential therapeutic applications in chronic disease. Pharmacol. Res.3, 100047. 10.1016/j.prenap.2024.100047
110
Wang J. Cui B. Li X. Zhao X. Huang T. Ding X. (2023a). The emerging roles of hedgehog signaling in tumor immune microenvironment. Front. Oncol.13, 1171418. 10.3389/fonc.2023.1171418
111
Wang J. Su W. Zhang T. Zhang S. Lei H. Ma F. et al (2023b). Aberrant cyclin D1 splicing in cancer: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation. Cell Death Dis.14 (4), 244. 10.1038/s41419-023-05763-7
112
Wang M. Tian B. Shen J. Xu S. Liu C. Guan L. et al (2023c). Bavachin induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells through Gadd45a via the MAPK signaling pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med.21 (1), 36–46. 10.1016/s1875-5364(23)60383-8
113
Wang J. He M. Yang M. Ai X. (2024a). Gut microbiota as a key regulator of intestinal mucosal immunity. Life Sci.345, 122612. 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122612
114
Wang L. Chen H. Deng L. Hu M. Wang Z. Zhang K. et al (2024b). Roburic acid inhibits lung cancer metastasis and triggers autophagy as verified by network pharmacology, molecular docking techniques and experiments. Front. Oncol.14, 1449143. 10.3389/fonc.2024.1449143
115
Wang Z. Chen Y. Dai X. (2025). Bavachin ameliorates HFD-Induced obesity through enhancing gut microbiota-regulated adipose thermogenesis. Food Biosci.66, 106212. 10.1016/j.fbio.2025.106212
116
Weaver K. Skouta R. (2022). The selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase 4: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Biomedicines10 (4), 891. 10.3390/biomedicines10040891
117
Wen H. Li S. Zhang Y. (2025). Phthalide mono- and dimers from the rhizomes of Angelica sinensis and their anti-inflammatory activities. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect.15 (1), 26. 10.1007/s13659-025-00512-z
118
Weng W. Goel A. (2022). Curcumin and colorectal cancer: an update and current perspective on this natural medicine. Semin. Cancer Biol.80, 73–86. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.02.011
119
Wolf P. Schoeniger A. Edlich F. (2022). Pro-apoptotic complexes of BAX and BAK on the outer mitochondrial membrane. BBA-MOL. CELL Res.1869 (10), 119317. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2022.119317
120
Wu Q. Deng J. Fan D. Duan Z. Zhu C. Fu R. et al (2018). Ginsenoside Rh4 induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death through activation of the ROS/JNK/p53 pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol.148, 64–74. 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.004
121
Wu Y. Pi D. Zhou S. Yi Z. Dong Y. Wang W. et al (2023a). Ginsenoside Rh3 induces pyroptosis and ferroptosis through the Stat3/p53/NRF2 axis in colorectal cancer cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin.55 (4), 587–600. 10.3724/abbs.2023068
122
Wu Y. Zhao X. Xiang Y. Guo M. Li C. (2023b). Evolution of mitogen-activated protein kinase family and their immune function in Apostichopus japonicus. Dev. Comp. Immunol.139, 104586. 10.1016/j.dci.2022.104586
123
Wu Q. Zhao J. Sun Z. Jiang H. Qiao G. Zhao K. et al (2025). Advances and emerging trends in the tumor microenvironment of colorectal cancer liver metastasis: a bibliometric analysis. Discov. Oncol.16 (1), 1503. 10.1007/s12672-025-03292-7
124
Xie Y.-H. Chen Y.-X. Fang J.-Y. (2020). Comprehensive review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther5 (1), 22. 10.1038/s41392-020-0116-z
125
Xu H. Liu T. Li J. Chen F. Xu J. Hu L. et al (2022). Roburic acid targets TNF to inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway and suppress human colorectal cancer cell growth. Front. Immunol.13, 853165. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.853165
126
Xu W. Lyu W. Duan C. Ma F. Li X. Li D. (2023). Preparation and bioactivity of the rare ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2: an updated review. Fitoterapia167, 105514. 10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105514
127
Yan J. Yu L. Xu S. Gu W. Zhu W. (2014). Apigenin accumulation and expression analysis of apigenin biosynthesis relative genes in celery. Sci. Hortic.165, 218–224. 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.11.018
128
Yan S. Chang J. Hao X. Liu J. Tan X. Geng Z. et al (2022). Berberine regulates short-chain fatty acid metabolism and alleviates the colitis-associated colorectal tumorigenesis through remodeling intestinal flora. Phytomedicine102, 154217. 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154217
129
Yang W. Cong Y. (2021). Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in the regulation of host immune responses and immune-related inflammatory diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol.18 (4), 866–877. 10.1038/s41423-021-00661-4
130
Yin Z. Lv Z. Yang L. Li C. Teng F. Liang W. (2024). The nuclear receptor coactivator 4 regulates ferritinophagy induced by Vibrio splendidus in coelomocytes of Apostichopus japonicus. Fish. Shellfish Immunol.151, 109745. 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109745
131
Yoshida S. Yoshida K. (2025). Regulatory mechanisms governing GLI proteins in hedgehog signaling. Anat. Sci. Int.100 (2), 143–154. 10.1007/s12565-024-00814-1
132
Yu H. Lin L. Zhang Z. Zhang H. Hu H. (2020). Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther5 (1), 209. 10.1038/s41392-020-00312-6
133
Yue J. López J. M. (2020). Understanding MAPK signaling pathways in apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci.21 (7), 2346. 10.3390/ijms21072346
134
Zeng S. Tan L. Sun Q. Chen L. Zhao H. Liu M. et al (2022). Suppression of colitis-associated colorectal cancer by scutellarin through inhibiting hedgehog signaling pathway activity. Phytomedicine98, 153972. 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153972
135
Zhang H. Xu H. Zhang C. Tang Q. Bi F. (2021a). Ursodeoxycholic acid suppresses the malignant progression of colorectal cancer through TGR5-YAP axis. Cell Death Discov.7 (1), 207. 10.1038/s41420-021-00589-8
136
Zhang H. Yi J.-K. Huang H. Park S. Park S. Kwon W. et al (2021b). Rhein suppresses colorectal cancer cell growth by inhibiting the mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cancers13 (9), 2176. 10.3390/cancers13092176
137
Zhang T. Ma C. Zhang Z. Zhang H. Hu H. (2021c). NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. MedComm2 (4), 618–653. 10.1002/mco2.104
138
Zhang W. Wu Z. Qi H. Chen L. Wang T. Mao X. et al (2022a). Celastrol upregulated ATG7 triggers autophagy via targeting Nur77 in colorectal cancer. Phytomedicine104, 154280. 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154280
139
Zhang Z. Ji Y. Hu N. Yu Q. Zhang X. Li J. et al (2022b). Ferroptosis-induced anticancer effect of resveratrol with a biomimetic nano-delivery system in colorectal cancer treatment. Asian J. Pharm. Sci.17 (5), 751–766. 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.07.006
140
Zhang H. Li J. Diao M. Li J. Xie N. (2024a). Production and pharmaceutical research of minor saponins in Panax notoginseng (sanqi): current status and future prospects. Phytochemistry223, 114099. 10.1016/j.phytochem.2024.114099
141
Zhang X. Hu Y. Wang B. Yang S. (2024b). Ferroptosis: iron-Mediated cell death linked to disease pathogenesis. J. Biomed. Res.38 (5), 413–435. 10.7555/jbr.37.20230224
142
Zhang H. Sun J. Xie A. Yang H. Li Y. Mei Y. et al (2025). Enhancing butyrate synthesis and intestinal epithelial energy supply through mixed probiotic intervention in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Food Biosci.63, 105727. 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.105727
143
Zhao H. Tang S. Tao Q. Ming T. Lei J. Liang Y. et al (2023). Ursolic acid suppresses colorectal cancer by down-regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway activity. J. Agric. Food Chem.71 (9), 3981–3993. 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06775
144
Zheng S. Schrijvers J. J. A. Greuter M. J. W. Kats-Ugurlu G. Lu W. de Bock G. H. (2023). Effectiveness of colorectal cancer (CRC) screening on all-cause and CRC-specific mortality reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel)15 (7), 1948. 10.3390/cancers15071948
145
Zhong C. Wang B. (2022). Regulation of cholesterol binding to the receptor Patched1 by its interactions with the ligand sonic hedgehog (shh). Front. Mol. Biosci.9, 831891. 10.3389/fmolb.2022.831891
146
Zhou X. Ke C. Lv Y. Ren C. Lin T. Dong F. et al (2020). Asiaticoside suppresses cell proliferation by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med.46 (4), 1525–1537. 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4688
147
Zhu M.-l. Zhang P.-m. Jiang M. Yu S.-w. Wang L. (2020). Myricetin induces apoptosis and autophagy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling in human Colon cancer cells. BMC Complement. Med.20 (1), 209. 10.1186/s12906-020-02965-w
Summary
Keywords
colorectal cancer, natural derived small molecule compounds, mechanism of action, gut microbiota, ferroptosis, apoptosis, autophagy
Citation
Liao M-J, Dong H-Y, Chen G, Li W-W and Li G-F (2025) Mechanisms and advantages of natural derived small molecule compounds in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1658493. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1658493
Received
02 July 2025
Accepted
25 August 2025
Published
10 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Shang-Gao Liao, Guizhou Medical University, China
Reviewed by
Ashok Kumar Pandurangan, B. S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology, India
Zhixing Wu, Texas A and M University, United States
Pratibha Pandey, Chitkara University, India
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Liao, Dong, Chen, Li and Li.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guo-Feng Li, doctorlgf@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.