- 1HBN Research Institute and Biological Laboratory, Shenzhen Hujia Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China
- 2Hubei Shizhen Laboratory, Hubei Key Laboratory of Resources and Chemistry of Chinese Medicine, College of Pharmacy, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China
- 3Western Herbs (Hubei) Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China
- 4College of Food Science, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
Introduction: Selaginella species hold a traditional place in medicine and cosmetics, but their potential to extend lifespan and the underlying bioactive compounds remain inadequately investigated. This study aims to systematically evaluate the anti-aging properties of diverse Selaginella extracts and to identify the key bioactive components and mechanisms involved.
Methods: We collected 23 Selaginella samples from 13 different provinces across China to assess their geographical influence. Two representative methanol extracts, S4 (high in amentoflavone) and S16 (low in amentoflavone), were selected for in-depth evaluation using the Caenorhabditis elegans model. We employed lifespan assays, stress resistance tests, and comparative transcriptomics to analyze the effects on longevity, and pathway modulation.
Results: Both S4 and S16 extracts significantly extended the lifespan of C. elegans under normal conditions and modulated conserved longevity pathways, including MAPK and FOXO signaling, with daf-16 and egl-8 emerging as key hub genes. Amentoflavone was identified and validated as a critical bioactive component, which alone extended lifespan by 63.81% and enhanced stress resistance. Mechanistically, amentoflavone promoted the nuclear translocation of DAF-16 and up-regulated the expression of antioxidant genes (e.g., sod-3, gst-3/4, hsp-16.48/12.6), leading to a significant reduction in intracellular ROS levels.
Discussion: Our findings demonstrate that Selaginella extract and its key component, amentoflavone, delay aging primarily by activating the DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor and bolstering the antioxidant defense system. This study not only highlights amentoflavone as a major contributor to the lifespan-extending effects of Selaginella but also underscores the potential of these natural compounds as promising agents for healthy aging.
1 Introduction
Advancements in living standards and medical technology have markedly increased human life expectancy, resulting in a global demographic transition towards an aging population (Piggott and Woodland, 2016). The World Health Organization estimates that by 2050, adults aged 65 and above will account for 16% of the global population (Padeiro et al., 2023). Aging is associated with a progressive deterioration of physiological functions and mobility, compromising the body’s capacity to maintain homeostasis and recover from stress (Guo et al., 2022). This decline elevates the risk of numerous age-related diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and Parkinson’s disease (Guo et al., 2022). This functional decline significantly elevates the susceptibility to age-related pathologies, including diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson’s disease (Guo et al., 2022). The escalating prevalence of these diseases imposes substantial societal and economic burdens, underscoring the urgent need for effective strategies to delay aging and enhance healthspan (Jarzebski et al., 2021). Consequently, identifying interventions that mitigate aging and improve quality of life in the elderly has emerged as a paramount research objective worldwide.
In recent years, Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) has attracted growing interest for its potential lifespan extension benefits (Zhao et al., 2020). Numerous medicinal plants—such as Psoralea corylifolia (Wang et al., 2022), Salsola collina (Wang et al., 2024), and Salvia haenkei (Zumerle et al., 2024)—along with their bioactive constituents, including corylin, luteolin, quercetin, β-sitosterol, and salicylic acid, have demonstrated efficacy in extending lifespan and attenuating aging-related decline. Among these, the genus Selaginella has garnered particular attention due to its abundance of biflavonoids, especially amentoflavone and its derivatives, which exhibit broad applications in traditional medicine and cosmetics (Křížkovská et al., 2020; Kumar et al., 2021; Bailly, 2021). For instance, S. tamariscina is extensively utilized in Asian traditional medicine for treating hemorrhage, inflammation, immune dysregulation, cancer, oxidative stress, hyperglycemia, and hypercholesterolemia (Bailly, 2021). Additionally, S. rossii has been shown to confer protection against skin aging and UVB-induced wrinkling via its antioxidant activity (Lee et al., 2022). Despite these documented therapeutic effects, a systematic evaluation of the lifespan-extending potential of Selaginella species and the underlying molecular mechanisms remains lacking. This gap highlights the need for comprehensive investigations into the lifespan extension properties of Selaginella.
Caenorhabditis elegans has become an important biological model for studying the lifespan extension mechanisms of CHMs, including Lonicera japonica, Lycium barbarum, Ganoderma lucidum, Astragalus membranaceus, and S. collina (Wan et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024). Over the past few decades, numerous genes (e.g., daf-2, daf-15, daf-16, daf-18, let-363, egl-8, lin-45, etc.), genetic pathways (e.g., the insulin/insulinlike growth factor-1(IIS), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathways, etc.), as well as many environmental factors (e.g., temperature, ultraviolet, oxidation exposures, etc.) contributing to the aging process, have been identified from studies using C. elegans (Cho and Park, 2024). In parallel, network pharmacology has emerged as a powerful tool in the study of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and functional foods, providing insights into the interactions between bioactive compounds and human biological systems (Zhang et al., 2023; Sha et al., 2024). It has been applied in various studies to investigate immune and aging regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic effects, such as in research on different rice varieties (Sha et al., 2024) and on Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Bisht et al., 2024). Combining C. elegans models with network pharmacology offers a promising approach to uncovering the mechanisms by which Selaginella and its bioactive components influence aging and longevity.
In this study, we collected 23 Selaginella samples from 13 provinces across China to assess their effects on aging and lifespan in C. elegans. Using comparative transcriptomics, we explored how geographical origin influences metabolic profiles and aging-related transcriptomic changes, while also identifying key bioactive compounds. Our results indicate that amentoflavone is a major contributor to the lifespan extension effects of Selaginella, likely through enhancing antioxidant defense via activation of the DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor. We further demonstrate that both Selaginella methanol extracts and purified amentoflavone extend lifespan and ameliorate aging in C. elegans by bolstering antioxidant mechanisms.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Selaginella plant materials were collected from 13 provinces in China and cultivated at the understory resource nursery at Hubei University of Chinese Medicine. Details of the collection sites were listed in Supplementary Table S1 and Supplementary Figure S1, and morphological characteristics of select Selaginella specimens were shown in Supplementary Figure S2. Wild-type C. elegans (N2 strain), DAF-16 mutant worms (CF1038), DAF-16GFP (TJ356) and Escherichia coli OP50 were generously provided by Dr. Pan Li from South China Agricultural University.
For molecular experiments, the Total RNA Kit (RC112-01), and HiScript III first Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (R312-01) were obtained from Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). Astaxanthin (catalog number: SA8730), and amentoflavone (catalog number: 1,617-53-4) were sourced from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.2 Preparation of Selaginella methanolic extracts (SMEs)
The aerial parts of Selaginella were harvested and dried at 60 °C until a constant weight was obtained. The dried plant material was then finely ground and passed through a 65-mesh sieve. For extraction, 100 mg of the powdered sample was soaked in 10 mL of methanol (HPLC Grade, ≥99.9%, FTSCI Hubei) for 40 min. This was followed by ultrasonic extraction using an SB-4200DT ultrasonic cleaner (SCIENTZ, China) at 55 °C for 30 min. The mixture was then filtered through a 0.45 µm membrane (XingYa, Shanghai) to obtain crude extracts, designated as MEs, at a final concentration of 10 mg mL-1. This ME solution was used as the stock solution and further diluted to 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mg mL-1 for subsequent experiments.
2.3 Preparation of amentoflavone monomer
Twenty milligrams of amentoflavone monomer were dissolved in methanol and diluted to a final concentration of 1 mg mL-1 to prepare a stock solution. This stock solution was then further diluted to concentrations of 25, 50, and 100 μg mL-1 for use in subsequent experiments. Astaxanthin was prepared separately by diluting in chloroform to a final concentration of 0.64 µM. All solutions were filtered using a 0.45 µm organic filter membrane, aliquoted into 500 µL portions, and stored at −80 °C until further use.
2.4 Culture and physiological indices of C. elegans
The C. elegans strains were cultured at 20 °C on solid Nematode Growth Medium (NGM) agar plates seeded with Escherichia coli OP50.
For the heat stress resistance assay, 60-69 worms were divided into each experimental group, with each group distributed across three NGM plates (20-23 worms per plate). The plates were supplemented with either 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mg mL-1 of Selaginella methanol extracts (SME) or 50 μg mL-1 of amentoflavone monomer. The worms were incubated at 37 °C, and the number of survivors was recorded at 1-hour intervals until all the worms perished.
Similarly, in the ultraviolet (UV) stress resistance assay, 60-69 worms were distributed into groups on three NGM plates (20-23 worms per plate), supplemented with either 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mg mL-1 of SME or 50 μg mL-1 of the monomer. The worms were then exposed to UV irradiation (8 W) for six additional days. Survival rates were recorded at 12-hour intervals until all the worms perished.
For lifespan analysis of wild-type C. elegans (N2 strain) or daf-16 mutant worms (CF1038), the assay were performed following previously described methods (Wang et al., 2024). Worms were synchronized and lysed, then cultured on NGM plates at 20 °C until reaching the L4 larval stage. The L4 larvae were exposed to SME or the monomer to evaluate lifespan. Worms treated with 100% methanol served as the negative control. To prevent progeny development, 5-fluorodeoxyuridine (10 μg mL-1) was administered from day 0 to day 5. The number of surviving worms was recorded daily, and the worms were transferred to fresh plates every 24 h. Survival curves were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9 software.
2.5 Transcriptome sequencing analysis
Synchronized L4 C. elegans (N2 strain) were transferred to NGM plates containing the SMEs (0.5, 1.0, 2.0 mg mL-1) or monomer amentoflavone (50 μg mL-1). Worms were transferred to fresh NGM plates daily throughout the 5-day treatment period. Afterward, approximately 200 worms were harvested for RNA sequencing analysis.
Total RNA extraction followed the protocol of the R6834 Total RNA Kit I. Libraries were then prepared and sequenced using the DNBSEQ high-throughput sequencing platform (BENAGEN, China). The trimmed sequencing reads were aligned to the C. elegans reference genome (Yoshimura et al., 2019) using STAR software (version 2.7.9a). For transcript assembly, StringTie (version 2.1.4; default parameters) was employed, and the assembled transcripts were merged using StringTie’s “merge” function. The merged transcripts were compared with known genome annotations using gffcompare (version 0.12.1; parameters: R-C-K) to identify novel transcripts and genes, thereby complementing the existing annotations. Transcript abundance and gene quantification were calculated using RSEM software.
Transcript levels were quantified by calculating Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads (FPKM), with an FPKM value of 1 as the threshold for transcript expression. Differentially expressed transcripts (DGTs) were identified based on the criteria |logFC| > 1 and p < 0.05. Data visualization and functional enrichment analyses, including volcano plots, heatmaps, GO term enrichment, KEGG pathway analysis, and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA), were performed using the clusterProfiler package.
To explore the interactions among the significant transcripts (p < 0.05), a PPI network was constructed. The PPI network was built using the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes (STRING) database (https://www.string-db.org/) and visualized using Cytoscape software.
2.6 High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis
The HPLC analysis was carried out using an Agilent 1,260 Infinity II LC system (Agilent Technologies Inc.) equipped with an Agilent 5 TC-C18 (2) column (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm). The chromatographic conditions were as follows: solution A: 0.1% phosphoric acid water, solution B: 100% methanol (high performance liquid phase grade); Column temperature: 30 °C; Detection wavelength: 330 nm; Injection volume: 10 μL; Flow rate: 1 mL min-1; Gradient conditions: 0.0 min, 40% B; 14.0 min, 50% B; 19.0 min, 60% B; 24.0 min, 70% B; 29.0 min, 80% B; 49.0 min, 90% B; 51.0 min, 40% B; 53.0 min, 40% B.
2.7 Pharyngeal aspiration, body bending and fertility indices
Nematodes were maintained under the same culture conditions as described in the lifespan assay. The pharyngeal pumping rate was assessed following a previously reported method (Ding et al., 2024), with slight modifications. Briefly, on days 3 and 7 of cultivation, relaxation and contraction cycles of the pharyngeal pump were observed and counted over a 30-second interval under a microscope. In addition, body bending frequency was evaluated on days 3, 7, and 12 of culture, during which body bends were recorded within a 30-second observation window (Yu et al., 2021).
For the fertility assay, synchronized nematodes were individually transferred to NGM plates—either blank control or amentoflavone (50 μg mL-1) treatment groups—with three replicates per group. Of note, 5-FU was not included in the NGM plates during this experiment. Every 24 h, the nematodes were transferred to fresh corresponding NGM plates. The number of eggs was recorded once the offspring had developed to the L2 or L3 larval stage, and counting continued until the end of the egg-laying period.
2.8 Quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis
RNA was extracted from three biological replicates, each consisting of approximately 200 worms. Total RNA was isolated using Trizol reagent, and cDNA was synthesized with SuperScript® II Reverse Transcriptase. RT-qPCR was performed using TB Green® Premix Ex Taq™ II (Tli RNaseH Plus) on a StepOnePlus™ Real-Time PCR System, in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The housekeeping gene pmp-3 (GenBank accession number NM_001269678.3) was used as an internal control. Primer sequences are provided in Supplementary Table S2.
2.9 Measurement of ROS levels in C. elegans
Intracellular ROS levels were detected according to the method described by Li et al. (2022). N2 wild-type worms were treated with methanol or amentoflavone for 5 days. Subsequently, the worms were collected into 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes using M9 buffer and washed three times. The nematodes were then incubated with 2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCF-DA; 1 μM, Sigma) at 20 °C for 4 h. After incubation, the worms were washed with M9 buffer, anesthetized with 5 mM levamisole, transferred onto glass slides, and visualized under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX73, Tokyo, Japan) at an excitation wavelength of 485 nm and an emission wavelength of 535 nm. Fluorescence intensity was quantified using ImageJ software (NIH, Bethesda, MD). Each experiment was performed in triplicate with 30 worms per treatment group.
2.10 Analysis of DAF-16 nuclear localization
The subcellular localization of DAF-16 was examined as previously reported (Lin et al., 2019). The transgenic strain TJ356 was employed to monitor DAF-16GFP localization. After treatment, worms were washed with M9 buffer and anesthetized using 5 mM levamisole. Images were acquired with a fluorescence microscope and analyzed using ImageJ. DAF-16GFP localization patterns were classified into three categories: cytosolic, intermediate, and nuclear. Assays were conducted in triplicate, with 30 worms analyzed per treatment.
2.11 Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9.0. The Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was employed for survival analysis, while comparisons between two groups were performed using a two-sided Student’s t-test. For multiple comparisons, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction was applied. Results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, and p < 0.0001.
3 Results
3.1 Collection and analysis of Selaginella resources
Selaginella has been widely utilized in traditional medicine and cosmetics due to its bioactive properties, which include promoting blood circulation, regulating menstruation, and enhancing skin whitening (Bailly, 2021; Lee et al., 2022). However, its potential effect on lifespan extension remains unexplored. To address this, we collected 23 Selaginella samples from 14 different provinces across China (Figure 1A; Supplementary Figures S1–S2; Supplementary Table S1), designated as S1 to S23. HPLC analysis revealed substantial variation in the concentration of amentoflavone—a key bioactive biflavonoid and an established chemical marker in Selaginella (Zhang et al., 2022)—across species and geographic origins (Figure 1B; Supplementary Table S3). Based on amentoflavone content, the samples were classified into three groups: high (≥23.92 μg g-1), medium (11.15–23.49 μg g-1), and low (≤10.39 μg g-1) (Figure 1B).
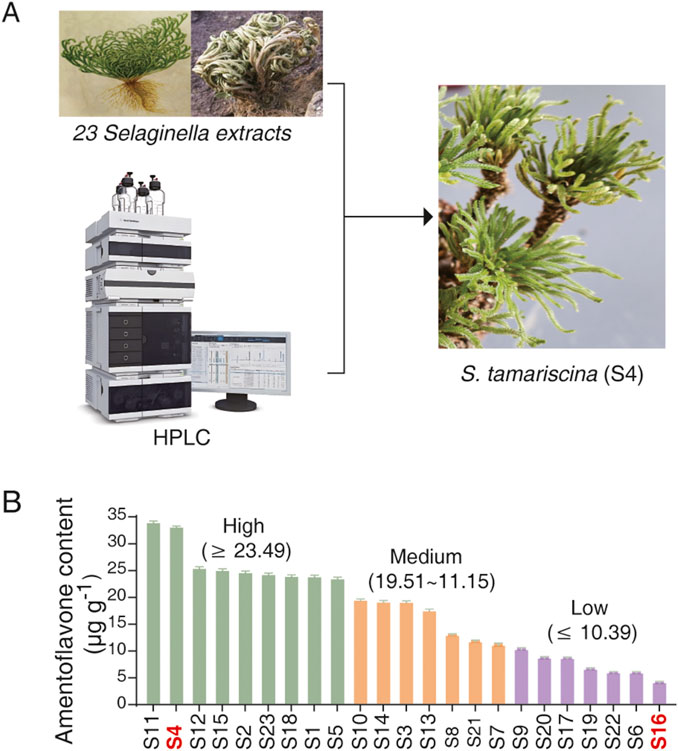
Figure 1. Collection and phytochemical profiling of Selaginella samples. (A) Geographic distribution of the 23 Selaginella samples collected from 14 provinces across China. (B) Amentoflavone content (µg g-1) in the 23 Selaginella samples as quantified by HPLC. Samples are categorized into three groups based on amentoflavone levels: high (≥23.92 μg g-1), medium (11.15–23.49 μg g-1), and low (≤10.39 μg g-1). S4 (high) and S16 (low) were selected for further study.
For subsequent lifespan analysis, two representative samples with contrasting amentoflavone levels were selected: S4, which had the second-highest content (33.07 μg g-1) from the high group, and S16, which had the lowest (4.24 μg g-1) from the low group. This comparative approach, based on divergent phytochemical profiles, allows for a more precise assessment of the potential role of Selaginella extract and its constituent amentoflavone in modulating lonevity.
3.2 Selaginella extract extends C. elegans lifespan
As lifespan is a primary biomarker of aging, we evaluated the lifespan extension potential of two distinct Selaginella extracts S4 and S16—in the C. elegans model using a concentration-gradient experiment (0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mg mL-1). By day 21, lifespan curves for S4-treated worms exhibited significant rightward shifts compared to the methanol-treated control, corresponding to average lifespan extensions of 8.56%–17.19% (Figure 2A; Table 1). Similarly, by day 27, S16-treated groups showed rightward shifts relative to the control; however, these were less pronounced than those observed with S4, suggesting potential concentration-dependent toxicity in this specific geographical variant (Figure 2B; Table 1). These results demonstrate that Selaginella extracts significantly extend lifespan in wild-type C. elegans, with efficacy varying according to geographic origin and associated phytochemical composition.
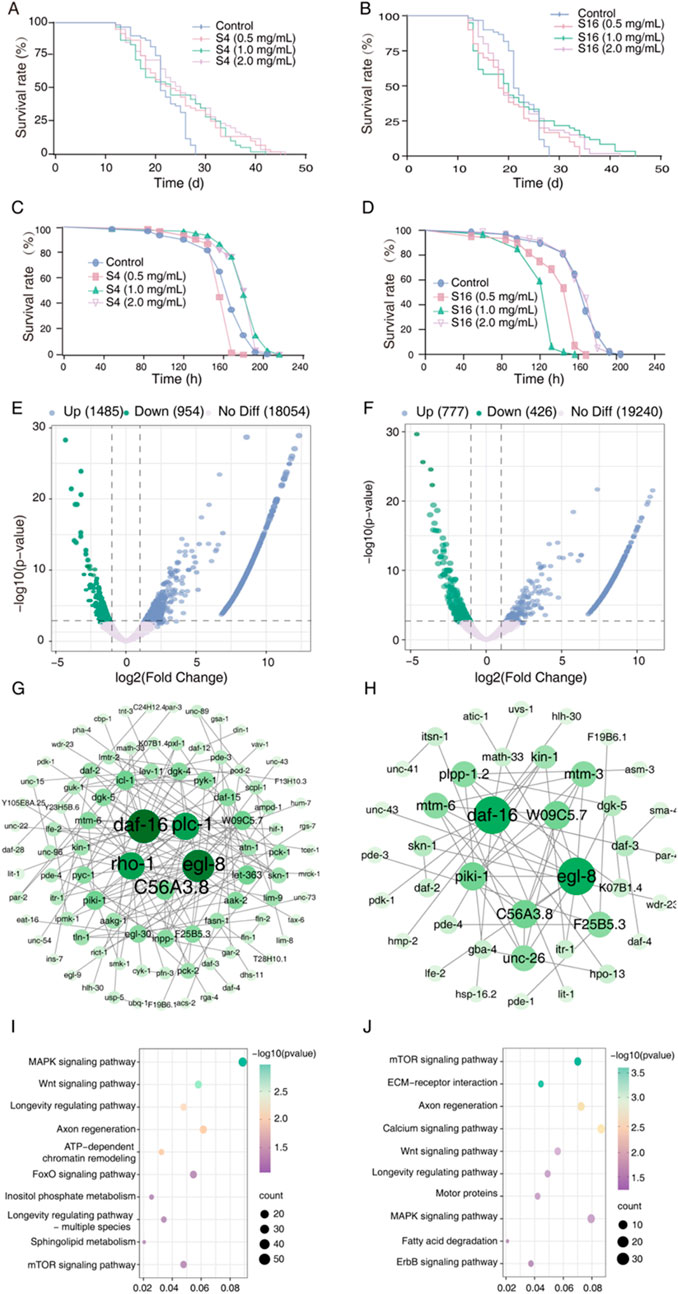
Figure 2. Effects of Selaginellae herba extracts on C. elegans lifespan and transcriptomic profiles. (A,B) Survival curves of nematodes treated with Selaginellae herba methanol extracts (SME) at indicated concentrations. BC: Blank control (methanol); S4L: 0.5 mg mL-1 S4 extract; S4M: 1 mg mL-1 S4; S4H: 2 mg mL-1 S4; S16L: 0.5 mg mL-1 S16; S16M: 1 mg mL-1 S16; S16H: 2 mg mL-1 S16. (C,D) Survival curves under UV stress following SME treatment (concentrations as in A, B). (E,F) Volcano plots of transcriptomic changes in S4 SEM-treated (E) and S16 SEM-treated (F) worms versus untreated controls. Genes with |log2FC| > 1 and p < 0.05 are highlighted (blue: upregulated; green: downregulated; pink: non-DEGs). (G,H) Protein-protein interaction networks of top differentially expressed transcripts (DETs) in control vs. S4 SEM (G) and S16 SEM (H) groups. (I,J) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of significant DETs from S4 SEM (I) and S16 SEM (J) treatments. Statistical significance vs. methanol-treated control determined by one-way ANOVA with log-rank test (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, p < 0.0001).
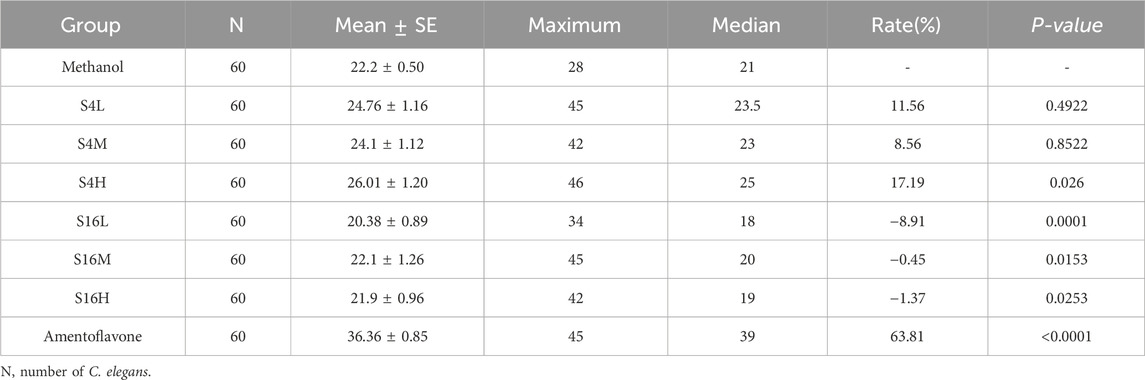
Table 1. Lifespan extension in C. elegans treated with Selaginella extracts (S4 and S16) and amentoflavone under standard culture conditions.
3.3 Selaginella extract modulates stress resilience in C. elegans
To further assess the survival benefits of S4 and S16, we examined their effects on C. elegans under UV stress. S4 treatment resulted in significant rightward shifts in survival curves, increasing lifespan by 1.47%–10.81% under UV exposure (Figure 2C; Table 1). In contrast, low and medium concentrations of S16 caused leftward shifts in the survival curve. The high-concentration S16 group showed no difference from the control under UV stress (Figure 2D; Table 1). These findings indicate that S4 not only extends lifespan under normal conditions but also enhances resilience to UV stress, supporting its lifespan extension potential. Conversely, S16 failed to improve lifespan under UV stress.
3.4 Transcriptomic analysis reveals lifespan extension mechanisms of Selaginella
To investigate the lifespan extension mechanisms of Selaginella derivatives, we performed RNA-seq analysis on C. elegans treated with S4 or S16. S4 treatment induced 2,439 differentially expressed transcripts (DETs), significantly enriched in MAPK, FOXO, mTOR, and longevity-regulating pathways (Figure 2E; Supplementary Tables S3-S5). S16 treatment altered 1,203 DETs, predominantly enriched in MAPK, Wnt, ErbB, and longevity-regulating pathways (Figure 2F; Supplementary Tables S6-S8). Although S4 induced approximately twofold more DETs than S16, both treatments shared enrichment in MAPK and longevity-regulating pathways, suggesting a common lifespan extension mechanism. This result indicates that Selaginella derivatives extend lifespan through coordinated modulation of evolutionarily conserved longevity pathways and compound-specific metabolic interventions.
Protein interaction network analysis identified five hub genes per treatment, with daf-16, egl-8, and C56A3.8 common to both groups (Figures 2G,H). Functional studies confirmed their critical roles: DAF-16 mediates insulin/IGF-1 signaling in lifespan regulation; egl-8 (typically associated with nicotine dependence studies) encodes a protein that activates 1-phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase and participates in phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthesis. These findings suggest both samples converge on FOXO signaling activation (Figures 2I,J).
To identify potential bioactive components, we conducted network pharmacology and molecular docking analyses (Supplementary Figure S3-S6; Supplementary Table S9-S12). The results revealed ten key candidate compounds: andromedotoxin, asebotoxin, beta-caryophyllene, isocembrol, hinokiflavone, isocryptomerin, amentoflavone, selaginellin, hinokinin, and tremetone. Combined with HPLC analysis identifying the amentoflavone as primary active substance in Selaginella, we selected amentoflavone for further mechanistic study (Figure 1A).
3.5 Amentoflavone extend C. elegans lifespan
In pre-experimental tests, amentoflavone was evaluated at concentrations of 25, 50, and 100 μg mL-1. The 50 μg mL-1 concentration demonstrated the most pronounced lifespan extension without any adverse effects, such as alterations in feeding behavior, and was therefore chosen for further mechanistic investigation. Lifespan analysis of C. elegans treated with 50 μg mL-1 amentoflavone revealed a significant extension of 63.81% (Figure 3B; Table 1). This represents a 3.7-fold greater increase compared to the group treated with S4 SME, identifying amentoflavone as a key contributor to the lifespan-extending properties of Selaginella.
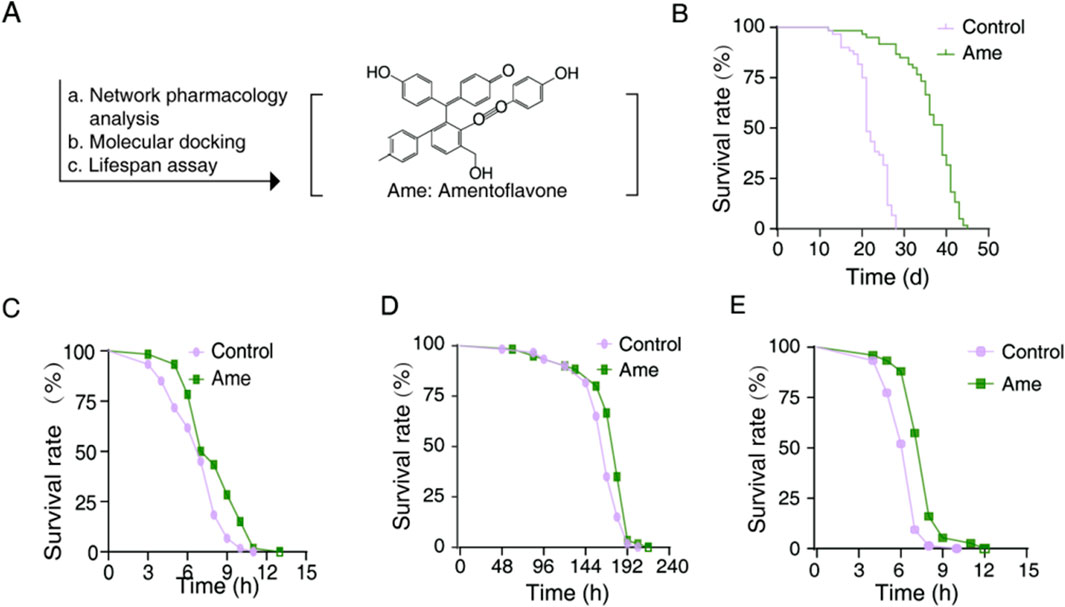
Figure 3. Amentoflavone extend lifespan and enhance the resilience to environmental stress of C. elegans. (A) Flow diagram of lifespan extension compositions from amentoflavone; (B) Survival curve of amentoflavone-treatment; (C) Survival of heat stress of amentoflavone-treatment (D) Survival of ultraviolet stress of amentoflavone-treatment (E) Survival of Oxidative Stress of amentoflavone-treatment. Ame, amentoflavone; The treated concentration of amentoflavone is 50 μg mL-1, compared to the mock-treated control by one-way ANOVA following log-rank test.
Further assessment under UV, thermal and oxidative stress conditions showed that amentoflavone induced rightward survival curve shifts (Wang et al., 2020; Hou et al., 2023). Lifespan enhancements ranged from 1.47% under UV stress, 18.29% under thermal stress and 19.75% under oxidative stress (Figures 3C–E; Tables 2-4). Notably, the improvement in both thermal and oxidative stress resistances were significantly greater than under UV stress, suggesting this amentoflavone may primarily extend lifespan by enhancing resistance to thermal and oxidative damage.
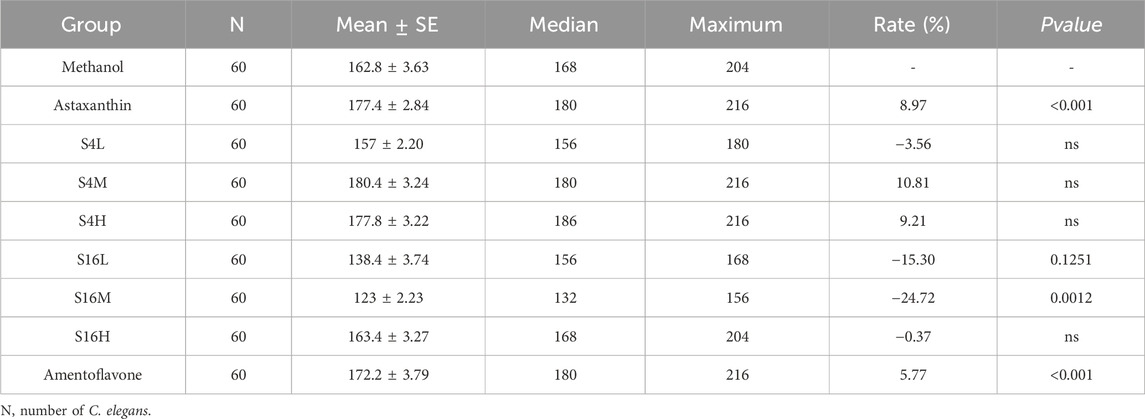
Table 2. Survival of C. elegans under ultraviolet (UV) stress following treatment with Selaginella extracts and amentoflavone.
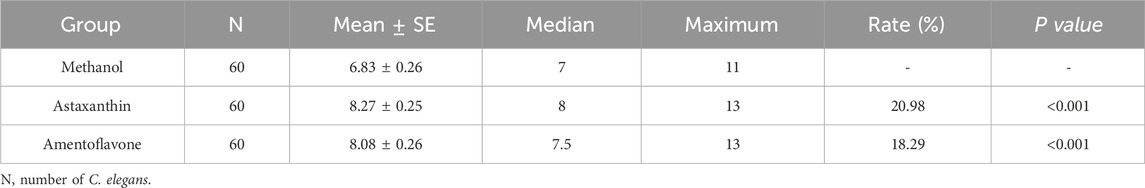
Table 3. Lifespan of C. elegans under heat stress after treatment with amentoflavone and astaxanthin.
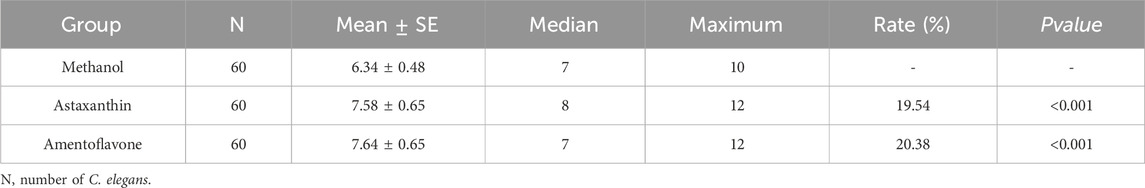
Table 4. Lifespan of C. elegans under oxidative stress after treatment with amentoflavone and astaxanthin.
Collectively, these findings demonstrate that amentoflavone significantly extend C. elegans lifespan and improve thermal and oxidative stress resistances, confirming its role as a key active compound in Selaginella for lifespan extension.
3.6 Amentoflavone increases lifespan of C. elegans by activating the DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor
To further explore the mechanisms by which Selaginella polyphenols extend lifespan, we performed RNA sequencing to analyze differentially expressed transcripts (DETs) in C. elegans treated with amentoflavone. We identified 693 DETs (372 upregulated, 267 downregulated) in amentoflavone-treated worms (Supplementary Table S13). Volcano plots and heatmaps of these DETs (FPKM >1, p < 0.05) are presented in Figures 4A,B.
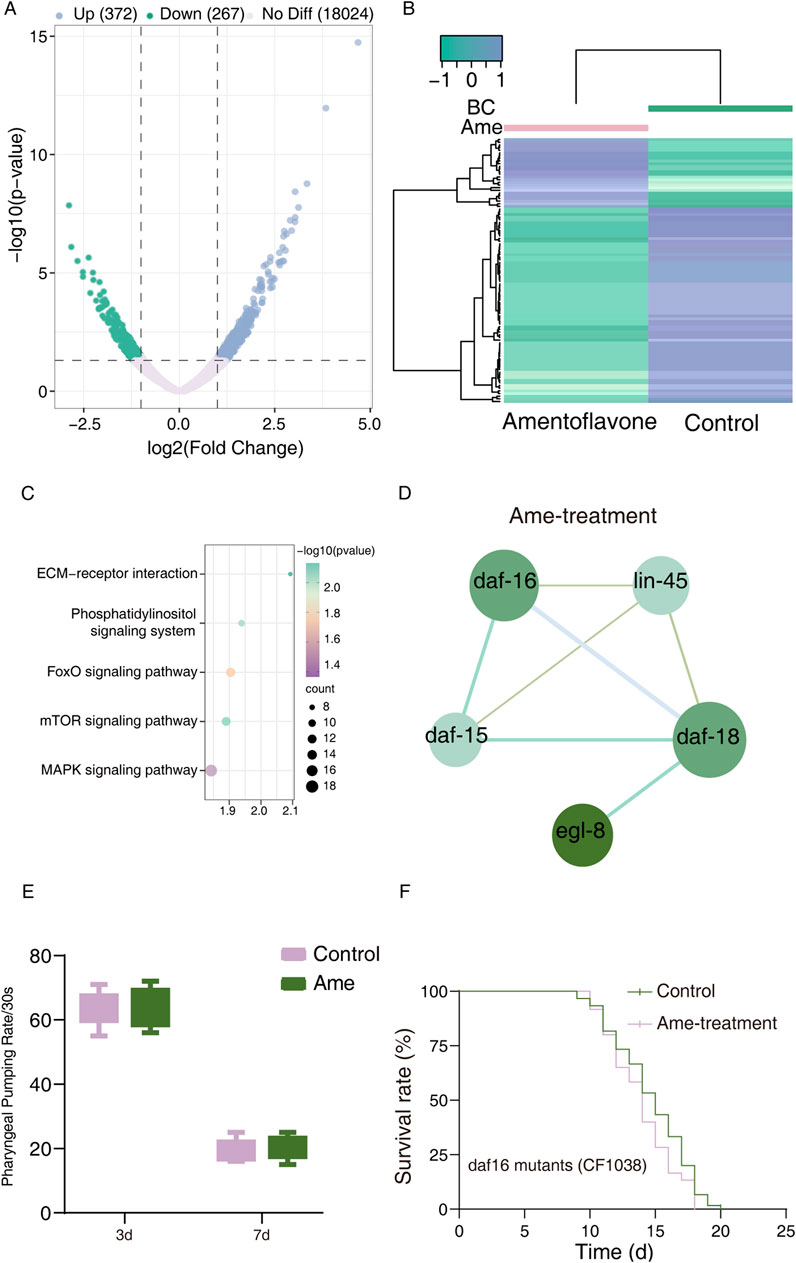
Figure 4. Transcriptomes of amentoflavone-treated C. elegans. (A) Volcano plot in control vs amentoflavone-treatment. Each point represents a single transcript. Plotted along the x-axis is the log2 (FC) of each transcript (transcript expression with or without amentoflavone-treated worms). The y-axis represents the negative logarithm of the corresponding p-value of that transcript. Up- and downregulated transcripts with p < 0.05 and log2FCI >1 are shown in red and green, respectively, whereas transcripts showing no differential expression are shown in grey; (B) Heatmap of significantly changed expression amounts of transcripts in control vs amentoflavone-treatment; (C) Amentoflavone significant KEGG pathways identified by enrichment analyses. (D) PPI network of top 5 DETs in control vs amentoflavone-treated C. elegans; (E) The effect of amentoflavone on the pharyngeal pumping frequency in N2 wild-type C. elegans. (F) The lifespan analysis of DF-16 mutant worms with amentoflavone compared to Control by one-way ANOVA following log-rank test.
Subsequent Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis categorized these DETs into 3,214 terms, encompassing 2,161 biological processes (BPs), 402 cellular components (CCs), and 651 molecular functions (MFs) (Supplementary Table S14). The top 10 enriched terms for each category are shown in Supplementary Figure S9. The DETs were predominantly associated with BPs including regulation of biological process, cellular process, and response to stimulus. Key CCs included supramolecular complex and cell junction, while primary MFs involved metal ion binding and protein binding (Supplementary Figure S9; Supplementary Table S15).
KEGG pathway analysis revealed significant enrichment (p < 0.05) of these DETs in 8 pathways, among which 5 signaling pathways—MAPK, FOXO, Phosphatidylinositol, mTOR, and ECM-receptor interaction—were relevant to our study objectives (Figure 4C; Supplementary Table S16,S17). Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) indicated upregulation of all these signaling pathways (Supplementary Table S18).
To identify key molecular events, we conducted protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis on DETs related to aging and longevity. Five central hub genes were identified: daf-16, daf-18, daf-15, egl-8, and lin-45 (Figure 4D; Supplementary Table S10). DAF-16, a key transcription factor downstream of insulin/IGF-1 signaling, regulates lifespan (Murphy et al., 2003). DAF-15 deficiency-induced longevity requires intestinal DAF-16/FOXO activity (Zang et al., 2024), while DAF-18 promotes DAF-16 nuclear translocation by inhibiting PIP3 and the PI3K-Akt pathway and is linked to antioxidant activity (Berman and Kenyon, 2006). Furthermore, other hub genes (egl-8, lin-45) are functionally connected to the FOXO pathway: EGL-8 acts upstream of DAF-16 to regulate lifespan in a DAF-16-dependent manner (Mack et al., 2022); LIN-45 (ERK signaling) influences DAF-2/DAF-16 insulin-like signaling via SKN-1 (Okuyama et al., 2010). These findings collectively suggest that amentoflavone extends lifespan by activating the DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor and upregulating the FOXO signaling pathway (Figures 4A–D).
3.7 Amentoflavone extends lifespan via DAF-16/FOXO-dependent antioxidant gene regulation in C. elegans
To exclude potential confounding effects of dietary restriction on the IIS signaling pathway in C. elegans, we measured the pharyngeal pumping rate of wild-type worms following amentoflavone treatment. As shown in Figure 4E, a slight increase in pharyngeal pumping frequency was observed in amentoflavone-treated worms compared to the control group, indicating that amentoflavone does not reduce feeding behavior. Moreover, we also assessed the healthspan of C. elegans following amentoflavone treatment, specifically focusing on body bending ability and reproductive capacity. However, the results revealed no significant differences in either body bending or fertility between the amentoflavone-treated group and the blank control group (Supplementary Figure S8).
To further validate the pivotal role of DAF-16, we treated daf-16 knockout C. elegans mutants with amentoflavone (50μg mL-1). No significant alterations in survival curves were observed compared to wild-type controls (Figure 4F), confirming that DAF-16 is essential for the anti-aging effects of this compound. Since nuclear translocation is necessary for DAF-16 function, we used the DAF-16GFP (TJ356) strain to examine whether amentoflavone influences DAF-16 subcellular localization. As illustrated in Figures 5A,B, amentoflavone treatment significantly enhanced nuclear accumulation of DAF-16 by 48.85% compared to the control, supporting the involvement of this transcription factor in lifespan extension.
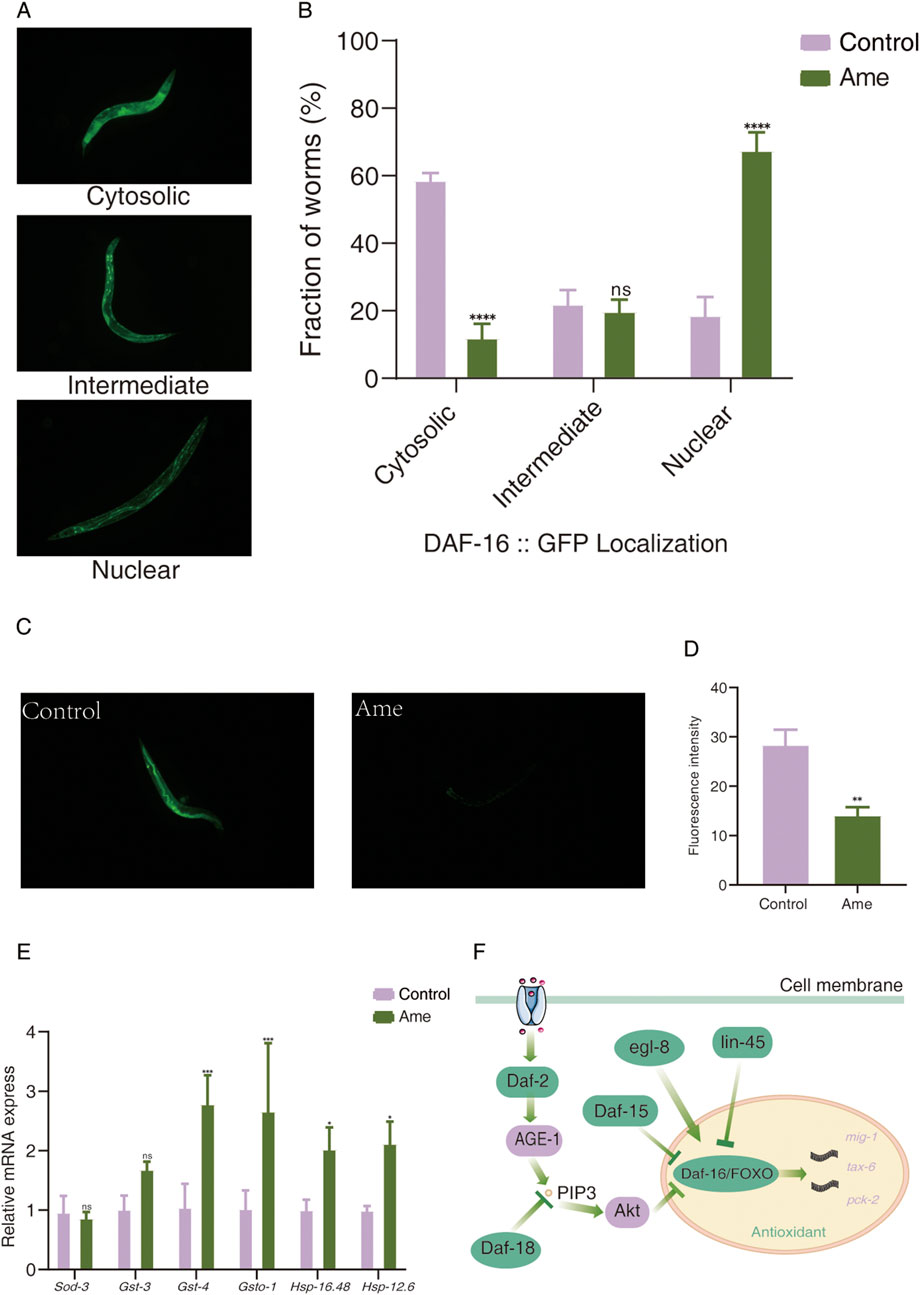
Figure 5. Exploration of the antioxidant mechanism of amentoflavone from Selaginella in delaying aging in C. elegans. (A) Representative fluorescence images showing three typical subcellular distributions of DAF-16 in transgenic strain TJ356: cytosolic localization, intermediate localization, and nuclear localization. (B) Effect of amentoflavone treatment on the subcellular localization of DAF-16 in TJ356 worms. P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.001 compared with the control group. (C) Fluorescence microscopy images of reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation. (D) Quantitative analysis of ROS fluorescence intensity. (E) mRNA expression levels of antioxidant-related genes in C. elegans after treatment with amentoflavone. (F) Proposed pathways involved in longevity regulation mediated by DAF-16/FOXO in amentoflavone-treated C. elegans. Ame, amentoflavone.
We next assessed intracellular ROS levels in C. elegans, as reduced ROS is indicative of enhanced antioxidant capacity. Amentoflavone administration resulted in a 50.22% decrease in ROS content compared to controls (Figures 5C,D).
Given the well-established association between FOXO signaling and antioxidant defense (Kim et al., 2014), we investigated DAF-16-interacting genes within protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks (Supplementary Figure S10). Our analysis revealed that DAF-16 interacts with three antioxidant-related genes: mig-1, tax-6, and pck-2 (Supplementary Table S19). Expression analysis indicated that nearly all of these genes (with the exception of mig-1) were significantly upregulated (p < 0.05) following amentoflavone treatment.
To further assess the impact on antioxidant gene expression downstream of FOXO, we performed RT-qPCR on key genes, including Sod-3, Gst-3, Gst-4, Gsto-1, Hsp-16.48, and Hsp-12.6 (Figure 5E). While Sod-3 expression was only mildly increased, members of the Hsp and Gst families showed significant upregulation compared to the control group. These results suggest that amentoflavone enhances antioxidant defenses primarily through the induction of these gene families.
In conclusion, our findings indicate that amentoflavone extends lifespan and improves antioxidant capacity in C. elegans mainly by activating DAF-16/FOXO and upregulating its downstream antioxidant pathway. DAF-16/FOXO-mediated gene regulation appears crucial for the observed longevity phenotype (Figure 5F).
4 Discussion
Our study provides comprehensive evidence that Selaginella extracts, particularly those rich in the biflavonoid amentoflavone, significantly extend lifespan and enhance stress resilience in C. elegans. By integrating phytochemical analysis, transcriptomics, network pharmacology, and functional genetics, we demonstrate that amentoflavone is a key bioactive component responsible for these effects, primarily through the activation of the DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor and subsequent enhancement of antioxidant defense mechanisms.
The substantial variability in amentoflavone content across different Selaginella species and geographic origins—and its strong correlation with longevity promotion—highlights this compound as a critical mediator of the observed anti-aging effects. The high-amentoflavone extract S4 extended lifespan under both standard and UV-stress conditions, whereas the low-amentoflavone S16 exhibited reduced efficacy and signs of potential toxicity at higher concentrations. These findings underscore the importance of phytochemical standardization in herbal medicine research.
Notably, purified amentoflavone alone extended median lifespan by 63.81%—significantly surpassing the effect of the crude extract and exceeding the efficacy of several well-known longevity compounds such as resveratrol (28.6%) and ginsenosides (34.1%) (Li et al., 2023), as well as the average lifespan extension reported for most traditional Chinese medicine ingredients (15.3%–31.3%) (Wang et al., 2021). This remarkable effect underscores the strong potential of amentoflavone for commercial development in nutraceuticals and cosmeceuticals (Wang et al., 2024). Moreover, amentoflavone conferred greater resistance to thermal and oxidative stress than to UV stress, suggesting that its mechanisms are particularly associated with mitigating oxidative damage and proteotoxic stress.
Transcriptomic and network pharmacology analyses revealed that both S4 extract and amentoflavone modulate evolutionarily conserved longevity pathways, including MAPK, mTOR, and FOXO signaling. The convergence of both treatments on FOXO pathway activation—supported by enrichment analyses and hub gene identification—emphasizes the importance of insulin/IGF-1 signaling (IIS) modulation in Selaginella-induced longevity. Specifically, amentoflavone promoted nuclear translocation of DAF-16 and upregulated the expression of antioxidant genes such as gst-4, sod-3, and heat shock protein family members. The potent antioxidant activity of amentoflavone and other Selaginella polyphenols is consistent with previous reports (Křížkovská et al., 2020; Kumar et al., 2021; Bailly, 2021; Muema et al., 2022). It is also noteworthy that amentoflavone did not reduce pharyngeal pumping rate, ruling out dietary restriction as a confounding factor. Instead, its effects are clearly linked to enhanced antioxidant capacity, as evidenced by significantly reduced ROS levels in treated worms. These findings align with existing literature on the role of DAF-16 in regulating oxidative stress response and longevity (Rodriguez-Colman et al., 2024; Cho and Park, 2024).
While our work clearly establishes amentoflavone as a key longevity-promoting compound in Selaginella, several questions remain. For instance, the broader ecological and genetic factors influencing amentoflavone accumulation in Selaginella species merit further investigation. Moreover, the precise molecular interactions through which amentoflavone activates DAF-16—whether through direct modulation of upstream regulators like DAF-2 or through alternative pathways—require deeper mechanistic inquiry. The potential synergy between amentoflavone and other phytochemicals in Selaginella also warrants additional study (Wang et al., 2024).
Beyond C. elegans, the conservation of the IIS/FOXO pathway across metazoans suggests that amentoflavone may offer therapeutic potential for aging-related disorders in mammals. Future studies should validate these findings in murine models and explore possible applications in delaying age-related decline or treating oxidative-stress-related pathologies (Chen et al., 2021).
In conclusion, our results position Selaginella and its constituent amentoflavone as promising candidates for developing natural interventions aimed at promoting healthy aging. By elucidating the genetic and pharmacological mechanisms underlying their effects, this work bridges traditional herbal medicine and contemporary molecular gerontology, offering a robust foundation for future research and application.
Data availability statement
The transcriptome data presented in the study are deposited in the The Genome Sequence Archive (GSA), accession number CRA031806. The raw contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: https://figshare.com/s/98776ec4c63aaf336209.
Ethics statement
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
XC: Validation, Writing – review and editing. BY: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. YiW: Supervision, Writing – original draft. WQ: Validation, Writing – original draft. YuL: Validation, Writing – original draft. YH: Software, Writing – original draft. YS: Supervision, Writing – original draft. YuW: Supervision, Writing – original draft. QZ: Supervision, Writing – original draft. YiL: Supervision, Writing – original draft. SL: Supervision, Writing – original draft. JW: Supervision, Writing – original draft. PL: Writing – original draft, Resources. ZS: Writing – original draft, Supervision. PS: Resources, Writing – review and editing. JG: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by research grants from Shenzhen Hujia Technology Co., Ltd., Technological Research Foundation of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine (2023ZDXM007), the Hubei Provincial Science and Technology Plan for 2024 (2024BCA002, 2024BBB091), Open Fund of Hubei Key Laboratory of Resources and Chemistry of Chinese Medicine (KLRCCM2405), the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (NATCM) Special TCM Science and Technology Research Project (GZY-KJS-2025-005).
Acknowledgements
We thank the Core Facilities at College of Plant Science and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural University for assistance with metabolite detection and we would be grateful to Fengfeng Li for her help of analyzing polyphenol metabolites and Yi Zhang (Shenzhen Hujia Technology Co., Ltd.) for her help of beautification of diagrams.
Conflict of interest
Authors XC, YW, QZ, and PS were employed by Shenzhen Hujia Technology Co., Ltd. Author JW was employed by Western Herbs (Hubei) Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that this study received funding from Shenzhen Hujia Technology Co., Ltd. The funder had the following involvement in the study: decision-making regarding project article writing, data analysis, and submission of manuscripts.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1658991/full#supplementary-material
References
Bailly, C. (2021). The traditional and modern uses of Selaginella tamariscina (P. Beauv.) spring, in medicine and cosmetic: applications and bioactive ingredients. J. Ethnopharmacol. 280, 114444. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114444
Berman, J. R., and Kenyon, C. (2006). Germ-cell loss extends C. elegans life span through regulation of DAF-16 by kri-1 and lipophilic-hormone signaling. Cell 124 (5), 1055–1068. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.039
Bisht, A., Tewari, D., Kumar, S., and Chandra, S. (2024). Network pharmacology-based approach to investigate the molecular targets and molecular mechanisms of Rosmarinus officinalis L. for treating aging-related disorders. Biogerontology 25, 793–808. doi:10.1007/s10522-024-10122-w
Chen, M., Liu, Y., and Yang, W. (2021). Skin permeation and antioxidant efficacy of topically applied resveratrol. Archives Dermatological Res. 313, 879–891. doi:10.1007/s00403-021-02209-y
Cho, J., and Park, Y. (2024). Development of aging research in Caenorhabditis elegans: from molecular insights to therapeutic application for healthy aging. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 9, 100809. doi:10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100809
Ding, J., Liu, J., Guo, Q., and Zhang, N. (2024). Transcriptomic approaches to investigate the anti-aging effects of blueberry anthocyanins in a Caenorhabditis elegans aging model. Antioxidants (Basel) 14 (1), 35. doi:10.3390/antiox14010035
Guo, J., Huang, X., Dou, L., Yan, M., Shen, T., Tang, W., et al. (2022). Aging and aging-related diseases: from molecular mechanisms to interventions and treatments. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 391. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01251-0
Hou, Z., Zhu, D., Gao, X., Zhao, L., Yang, H., Wang, Q., et al. (2023). Antiaging and antioxidative effects of water extract of Zizyphus jujuba mill on Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Funct. Foods 110, 105829. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2023.105829
Jarzebski, M. P., Elmqvist, T., Gasparatos, A., Fukushi, K., Eckersten, S., Haase, D., et al. (2021). Ageing and population shrinking: implications for sustainability in the urban century. npj Urban Sustain. 1, 17. doi:10.1038/s42949-021-00023-z
Kim, J., Ishihara, N., and Lee, T. R. (2014). A DAF-16/FoxO3a-dependent longevity signal is initiated by antioxidants. Biofactors 40, 247–257. doi:10.1002/biof.1146
Křížkovská, B., Kumar, R., Řehořová, K., Sýkora, D., Dobiasová, S., Kučerová, D., et al. (2020). Comparison of chemical composition and biological activities of eight selaginella species. Pharmaceuticals 14, 16. doi:10.3390/ph14010016
Kumar, R., Viktorova, J., Krizkovska, B., Lipov, J., and Ruml, T. (2021). Structural diversity and biological activities of secondary metabolites isolated from the genus selaginella. Phytochem. Rev. 20, 1209–1243. doi:10.1007/s11101-021-09743-7
Lee, H., Kim, S. Y., Lee, S. W., Kwak, S., Li, H., Piao, R., et al. (2022). Amentoflavone-enriched Selaginella rossii protects against ultraviolet- and oxidative stress-induced aging in skin cells. Life 12, 2106. doi:10.3390/life12122106
Li, H., Zeng, L., Wang, C., Shi, C., Li, Y., Peng, Y., et al. (2022). Review of the toxicity and potential molecular mechanisms of parental or successive exposure to environmental pollutants in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Pollut. 311, 119927. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119927
Li, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, Q., and Wang, H. (2023). Comparative analysis of lifespan extension by resveratrol, ginsenosides, and novel polyphenols in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Gerontology Lifesp. Ext. Res. 12 (3), 123–135. doi:10.1000/jgaar.2023.0045
Lin, C., Zhang, X., Su, Z., Xiao, J., Lv, M., Cao, Y., et al. (2019). Carnosol improved lifespan and healthspan by promoting antioxidant capacity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 5958043. doi:10.1155/2019/5958043
Lin, Y., Lin, C., Cao, Y., and Chen, Y. (2023). Caenorhabditis elegans as an in vivo model for the identification of natural antioxidants with anti-aging actions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 167, 115594. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115594
Mack, H. I. D., Buck, L. G., Skalet, S., Kremer, J., Li, H., and Mack, E. K. M. (2022). Further extension of lifespan by Unc-43/CaMKII and Egl-8/PLCβ mutations in germline-deficient Caenorhabditis elegans. Cells 11 (22), 3527. doi:10.3390/cells11223527
Muema, F. W., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Chen, G., and Guo, M. (2022). Flavonoids from Selaginella doederleinii hieron and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. Antioxidants 11, 1189. doi:10.3390/antiox11061189
Murphy, C. T., McCarroll, S. A., Bargmann, C. I., Fraser, A., Kamath, R. S., Ahringer, J., et al. (2003). Genes that act downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 424 (6946), 277–283. doi:10.1038/nature01789
Okuyama, T., Inoue, H., Ookuma, S., Satoh, T., Kano, K., Honjoh, S., et al. (2010). The ERK-MAPK pathway regulates longevity through SKN-1 and insulin-like signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biol. Chem. 285 (39), 30274–30281. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.146274
Padeiro, M., Santana, P., and Grant, M. (2023). Global aging and health determinants in a changing world. Aging, 3–30. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-823761-8.00021-5
Piggott, J., and Woodland, A. D. (2016). Handbook of the economics of population aging. Book 1, 1–1046.
Rodriguez-Colman, M. J., Dansen, T. B., and Burgering, B. M. T. (2024). FOXO transcription factors as mediators of stress adaptation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 25 (1), 46–64. doi:10.1038/s41580-023-00649-0
Sha, H., Ma, Y., Li, J., Zhao, J., Xu, Y., and Su, D. (2024). The mechanism exploration of different colored rice for immunomodulation based on UPLC-Q-TOF, network pharmacology, and cell experiments. Food Res. Int. 192, 114850. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114850
Wan, F., Zhi, D., Liu, D., Xian, J., Li, M., AbuLizi, A., et al. (2014). Lifespan extension in caenorhabiditis elegans by several traditional Chinese medicine formulas. Biogerontology 15, 377–387. doi:10.1007/s10522-014-9508-1
Wang, J., Deng, N., Wang, H., Li, T., Chen, L., Zheng, B., et al. (2020). Effects of Orange extracts on longevity, healthspan, and stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 25, 351. doi:10.3390/molecules25020351
Wang, L., Zuo, X., Ouyang, Z., Qiao, P., and Wang, F. (2021). A systematic review of antiaging effects of 23 traditional Chinese medicines. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 15, 5591573. doi:10.1155/2021/5591573
Wang, T. H., Tseng, W. C., Leu, Y. L., Chen, C. Y., Lee, W. C., Chi, Y. C., et al. (2022). The flavonoid corylin exhibits lifespan extension properties in mouse. Nat. Commun. 13, 1238. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28908-2
Wang, J., Liu, W., Huang, Y., Wang, G., Guo, X., Shi, D., et al. (2024). A senomorphlytic three-drug combination discovered in Salsola collina for delaying aging phenotypes and extending healthspan. Adv. Sci. 29, e2401862. doi:10.1002/advs.202401862
Yoshimura, J., Ichikawa, K., Shoura, M. J., Artiles, K. L., Gabdank, I., Wahba, L., et al. (2019). Recompleting the Caenorhabditis elegans genome. Genome Res. 29, 1009–1022. doi:10.1101/gr.244830.118
Yu, X., Li, H., Lin, D., Guo, W., Xu, Z., Wang, L., et al. (2021). Ginsenoside prolongs the lifespan of C. elegans via lipid metabolism and activating the stress response signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 9668. doi:10.3390/ijms22189668
Zang, X., Wang, Q., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Wu, Z., et al. (2024). Knockdown of neuronal DAF-15/Raptor promotes healthy aging in C. elegans. J. Genet. Genomics 51 (5), 507–516. doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2023.11.002
Zhang, S., Li, F., Zhou, T., Wang, G., and Li, Z. (2020). Caenorhabditis elegans as a useful model for studying aging mutations. Front. Endocrinol. 11, 554994. doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.554994
Zhang, W., Li, W., Zou, H., Xu, K., Long, H., Li, J., et al. (2022). Screening and characterizing the quality markers of Selaginella tamariscina (P. Beauv.) spring using metabonomics and molecular networking. Arabian J. Chem. 15, 104281. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104281
Zhang, P., Zhang, D., Zhou, W., Wang, L., Wang, B., Zhang, T., et al. (2023). Network pharmacology: towards the artificial intelligence-based precision traditional Chinese medicine. Briefings Bioinforma. 25, bbad518. doi:10.1093/bib/bbad518
Zhao, J., Lan, X., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Xian, Y., Lin, Z., et al. (2020). Anti-aging role of Chinese herbel medicine: an overview of scientific evidence from 2008 to 2018. Ann. Palliat. Med. 9, 1230–1248. doi:10.21037/apm.2020.04.09
Keywords: amentoflavone, Caenorhabditis elegans, DAF-16/FOXO pathway, lifespan, selaginella tamariscina, transcriptome
Citation: Chen X, Yan B, Wu Y, Quan W, Liu Y, Huang Y, Shao Y, Wang Y, Zhou Q, Liu Y, Liu S, Wang J, Li P, Shi Z, Shu P and Gou J (2025) Selaginella extracts extend lifespan and mitigate oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1658991. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1658991
Received: 03 July 2025; Accepted: 29 September 2025;
Published: 25 November 2025.
Edited by:
Uraiwan Panich, Mahidol University, ThailandReviewed by:
Newman Osafo, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, GhanaHang Shi, Zhangjiagang Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Yan, Wu, Quan, Liu, Huang, Shao, Wang, Zhou, Liu, Liu, Wang, Li, Shi, Shu and Gou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junbo Gou, anVuYm9nb3VAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Peng Shu, c2h1cGVuZ0BoYm4uY24=; Zhaohua Shi, emhzaGk3OEBoYnVjbS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xueqing Chen
Xueqing Chen Bingjian Yan
Bingjian Yan Yingmei Wu2†
Yingmei Wu2† Yifei Liu
Yifei Liu Pan Li
Pan Li Junbo Gou
Junbo Gou