- 1School of Pharmacy, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 2Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Drugability and Preparation Modification of TCM, Changsha, China
- 3Hunan Hengyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hengyang, Hunan, China
Polygonatum spp., encompassing various species within the genus, is a traditional Chinese botanical drug. It is known for its pharmacological effects, including qi tonification, yin nourishment, spleen invigoration, lung moistening, and kidney tonification. Polygonatum contains abundant bioactive metabolites, such as polysaccharides, steroidal saponins, flavonoids, volatile metabolites, and alkaloids. Recent research primarily revolves around its anti-inflammatory, anti-ageing, and glycaemic regulatory properties, while its antitumor potential remains comparatively underexplored. Malignant tumors represent a considerable global public health obstacle and are now a leading contributor to the global disease burden. The identification of effective antitumor agents and therapeutic strategies is urgent. Bioactive metabolites in Polygonatum have shown strong cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic impacts in vitro and in vivo. However, current research mostly focuses on isolated metabolites, lacking comprehensive narrative analysis. This review endeavors to narratively summarize recent advances on the antitumor activity and underlying mechanisms of Polygonatum, critically evaluate existing research gaps, and proposes future directions to facilitate the development of Polygonatum as a potential novel anticancer agent.
1 Introduction
Cancer, as a major class of diseases that seriously threaten human health, has long been a research priority in the global medical field. In recent years, due to environmental changes, lifestyle shifts and the accelerated ageing of the population, the incidence and mortality rates of cancer have shown a sustained upward trend (Łaniewski et al., 2020). According to the World Health Organization, there were as many as 19.3 million new instances of cancer globally in 2020, resulting in nearly 10 million deaths (Chhikara and Parang, 2023). In China alone, there were 4.57 million new cancer diagnoses and 3 million cancer-related deaths in 2020, with morbidity and mortality rates among the highest globally. Currently, clinical therapies for cancer primarily include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. While these approaches have improved survival rates and quality of life for cancer sufferers to some extent, challenges remain, such as limited applicability to certain populations, drug resistance, and high toxicity and significant side effects (Liu et al., 2024a). These challenges are closely related to the multifactorial nature of tumorigenesis, which involves genetic mutations, epigenetic changes, dysregulated signaling pathways, and tumor–immune interactions. Tumor development generally proceeds through initiation, promotion, progression, and metastasis (Testa et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2024), with immune cells such as regulatory T cells, macrophages, and NK cells playing important roles (Lei et al., 2020). This complexity highlights the need for therapies that can target multiple pathways simultaneously, consistent with the principles of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
TCM has a long-standing history and extensive practical experience in cancer treatment, owing to its multi-metabolites, multi-target, and holistic regulatory properties (Chan, 1995). Polygonatum spp., a traditional medicinal and edible substance, has been used in China for over 2,000 years. As recorded in the Compendium of Materia Medica, it “nourishes the middle and benefits the qi, removes wind-dampness, pacifies the five viscera, lightens the body, and prolongs life when taken for a long time”. This botanical drug is characterized by its sweet taste and neutral nature, and it is attributed to the spleen, lung, and kidney meridians. It is renowned for its capacity to replenish qi, nourish yin, enhance spleen function, moisten the lungs, and support kidney health. Modern research has identified numerous chemical metabolites in Polygonatum spp., such as polysaccharides, steroidal saponins, flavonoids, and amino acids, which exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic, and immunomodulatory effects (Zhao et al., 2018). Recent studies also suggest that Polygonatum spp. May inhibit tumor cell proliferation, induce apoptosis, and enhance immunity (Liu et al., 2024b). However, most investigations have focused on single metabolite, and its mechanisms remain insufficiently clarified. Therefore, this paper aims to summarize the main antitumor metabolites of Polygonatum spp. and their mechanisms of action, analyze current research progress, and identify existing challenges, thereby providing a foundation for its further development and application as a natural anticancer agent.
2 Traditional uses of Polygonatum spp.
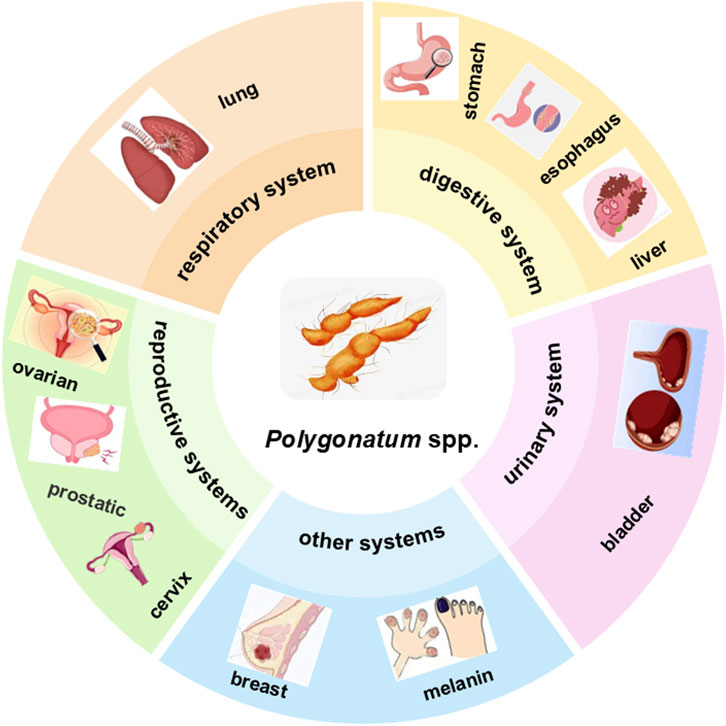
Polygonatum spp(Huangjing) has a documented history of over 2,000 years in China, and is classified as a superior botanical drug for tonifying qi, nourishing yin, and strengthening the spleen, lungs, and kidneys. These properties were first described in ancient texts such as the Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica and later elaborated in the Compendium of Materia Medica (Xu et al., 2021). Subsequent materia medica also consistently emphasized its use in “deficiency syndromes,” a concept encompassing fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, and weakness of the immune system—symptoms that closely resemble those frequently observed in cancer patients (Su et al., 2023). Polygonatum preparations were prescribed for the management of sores, ulcers, and protracted wounds, conditions that may reflect chronic inflammation and tumor-related complications. Such long-recognized applications suggest potential anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and restorative activities (Wang et al., 2022).
Modern pharmacological investigations have increasingly corroborated these traditional claims. Recent studies have identified polysaccharides, flavonoids, and saponins as the main bioactive metabolites, which exert notable antitumor effects via diverse mechanisms, including enhancement of immune responses, induction of cancer cell apoptosis, and suppression of tumor proliferation. Thus, the convergence of traditional knowledge with modern pharmacological evidence highlights Polygonatum spp. as a promising candidate for integrative cancer therapy.
3 Antitumor active metabolites of Polygonatum spp.
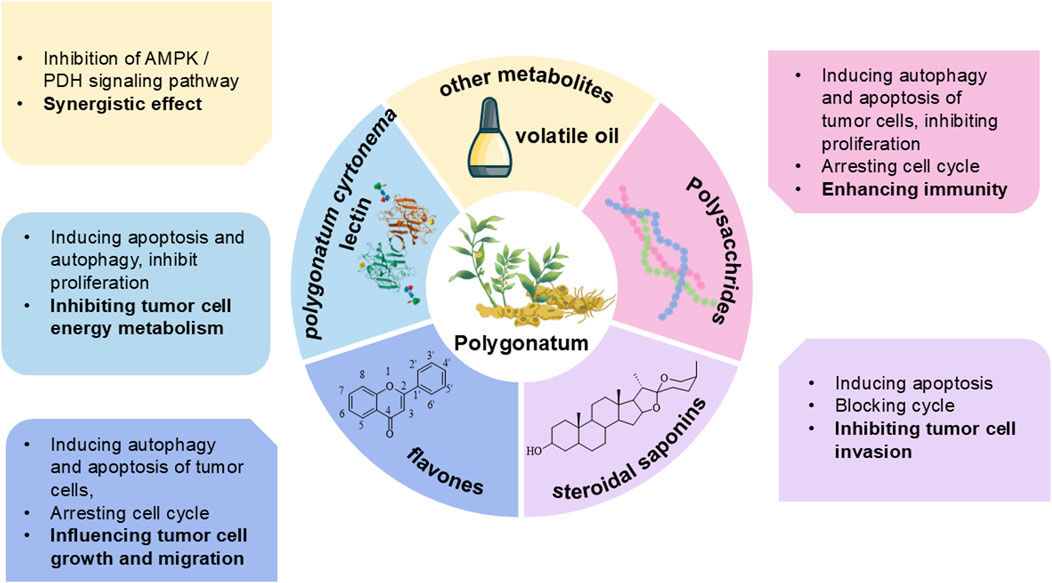
As a traditional Chinese botanical drug, Polygonatum spp. (Huangjing) is characterized by complex metabolites, with its principal active metabolites including polysaccharides, saponins, flavonoids, anthraquinones, alkaloids, amino acids, and volatile oils (Ren et al., 2020). Modern research indicates that the metabolites primarily responsible for its antitumor activity include polysaccharides, steroidal saponins, flavonoids, and Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin. The active antitumor metabolites of Polygonatum spp. and the different molecular mechanisms through which they exert their effects in cancer treatment are illustrated in Figure 1.
3.1 Polygonatum polysaccharide
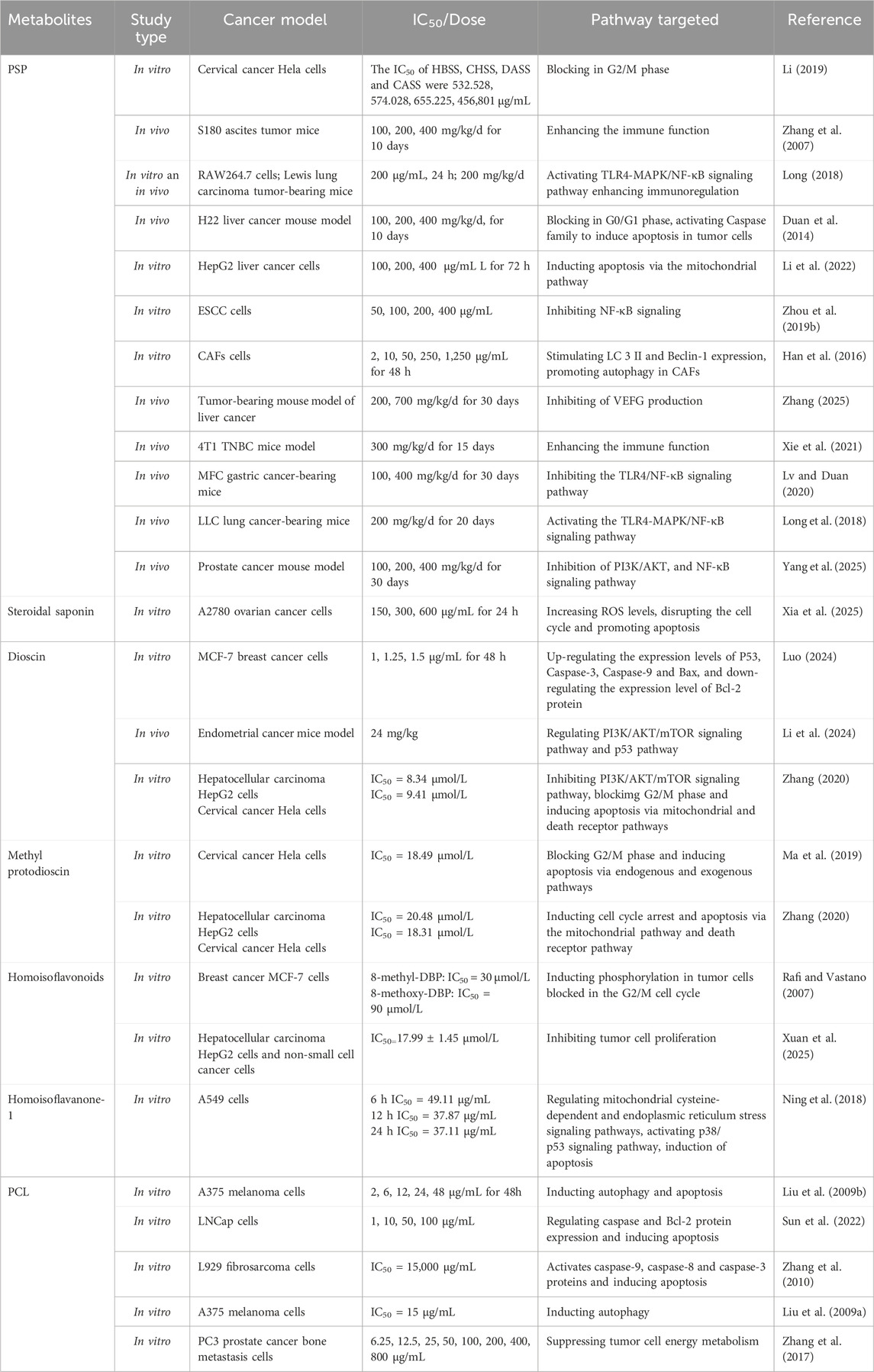
Polygonatum polysaccharide (PSP) is the most abundant and pharmacologically active metabolites in Polygonatum spp., serving as both a quality marker and the primary active metabolite. It demonstrates abundant biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-aging, glucose and lipid metabolism regulation, immunomodulation and anti-tumor effects (Hu et al., 2023). Recent research has indicated that PSP can inhibit the growth of extensive types of tumors, like liver, lung, gastric, breast, and cervical cancers. Its mechanisms of action involve inducing tumor cell apoptosis, inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, blocking the cell cycle, and activating the immune response (Lai et al., 2024). In cervical cancer HeLa cells, PSP fractions suppressed proliferation and induced apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner, with concentrated alkali-soluble solids (CASS) displaying the strongest effect by regulating apoptosis-related gene expression (Li, 2019). PSP also prolonged the survival of S180 ascitic tumor-bearing mice, and inhibited H22 solid tumors (Zhang et al., 2007). Moreover, PSP enhanced immune function by activating the TLR4–MAPK/NF-κB pathway, thereby promoting cytokine secretion and facilitating tumor cell clearance (Long, 2018).
3.2 Steroidal saponins
Steroidal saponins are synthesized through the combination of steroidal saponin aglycones with sugars, which mainly include D-glucose, D-galactose, D-xylose, L-rhamnose, and L-arabinose. Recent research has shown that steroidal saponins are the principal bioactive metabolite of Polygonatum spp., exhibiting a wide range of pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and lipid-lowering effects, as well as notable antitumor activity (Xu et al., 2023). Recent research has demonstrated that metabolites such as flavnoide B, polygonum saponin, and diosgenin in Polygonatum spp. Exhibit potent therapeutic efficacy against various cancers, including lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, melanoma, and cervical cancer. These metabolites primarily restrain tumor cell proliferation, trigger apoptosis, and curb tumor invasion (Zhou et al., 2019a; Sharma et al., 2021; Xie and Chen, 2021). Diosgenin demonstrated inhibitory effects on human epidermoid carcinoma cells, showing an activity comparable to adriamycin, as determined by the thiazolyl blue method (Zhang et al., 2007). Purified steroidal saponins have been reported to suppress A2780 ovarian cancer cell proliferation by promoting apoptosis, disrupting the cell cycle, modulating intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and regulating pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins, achieving an inhibition rate of 66.76% (Xia et al., 2025). Spirosteroidal saponins from Polygonatum spp., including Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté [Asparagaceae; Polygonati rhizoma] saponin B and dioscin, exhibited notable activity against various tumor cell lines, such as HL-60, 7901, A549, KB, and HeLa. Among these metabolites, diosgenin demonstrated the strongest activity, significantly inhibiting the growth of murine sarcoma S180 and murine hepatocellular carcinoma HAC (Yang, 1999).
3.3 Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a category of natural organic metabolites characterized by a C6-C3-C6 structure, with a basic nucleus of 2-phenylchromone. Based on the degree of oxidation of the central three-carbon chain, the attachment of the B ring (at the 2 - or 3 - position) and whether the three-carbon chain is ring-forming and other characteristics, flavonoids can be classified into flavonoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonoids, isoflavonoids, chalcones, and other types of metabolites (Taldaev et al., 2022). Flavonoid metabolites display a broad spectrum of biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulation, and cardiovascular protection. Among these metabolites, high-isoflavonoids, chalcones, dihydroflavonoids, and flavonoid glycosides have demonstrated significant anticancer activities (Tao et al., 2018). These metabolites inhibit tumor development by interfering with the cell cycle, inducing apoptosis and autophagy, and modulating related signaling pathways, thereby impacting the development and metastasis of tumor cells (Ye et al., 2025). Two high-isoflavonoids were isolated from Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce [Asparagaceae; Polygonati rhizoma] and were found to induce Bcl-2 phosphorylation, trigger apoptosis, and arrest the G2/M phase of the cell cycle in breast tumor cells (Rafi and Vastano, 2007). Chemical metabolites from the rhizomes of Polygonatum kingianum Collett & Hemsl. [Asparagaceae; Polygonati rhizoma] were isolated and characterized, revealing four novel high-isoflavones that effectively suppressed the growth of HepG2 cells and non-small cell carcinoma cells associated with hepatocellular carcinoma, and their findings revealed that four novel high-isoflavones effectively suppressed the growth of HepG2 cells and non-small cell lung cancer cells associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Notably, the metabolite (3R)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-methyl-3-(2′-hydroxy-4′-methoxybenzyl)-chroman-4-one demonstrated significant inhibitory activity against mouse tumor cells. Additionally, the IC50 value of this metabolite for mouse macrophages was determined to be 17.99 ± 1.45 μmol/L (Xuan et al., 2025).
3.4 Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin
Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin (PCL) is a mannose/sialic acid-binding lectin isolated from the rhizome of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua [Asparagaceae; Polygonati rhizoma], which has been shown to possess multiple anti-tumor properties, such as inducing apoptosis and autophagy, and inhibiting migration (Liu et al., 2016). Studies indicate that PCL can induce tumor cell apoptosis through activation of the caspase and mitochondrial ROS-p38-p53 signaling pathways. Meanwhile, it inhibits the Ras-Raf and PI3K-AKT pathways to enhance autophagy and promote cancer cell death (Wang et al., 2011). Lectins isolated from Polygonatum multiflorum (L.) All. [Asparagaceae; Polygonati rhizoma] were reported to significantly inhibit the malignant progression of A375 melanoma cells by simultaneously modulating autophagy and apoptosis pathways (Liu et al., 2009b). Mechanistic analysis revealed that PCL family member PCL-2 promoted apoptosis by enhancing ROS production, upregulating the expression of pro-apoptotic genes (Bax, Caspase-3, and Caspase-9) at both mRNA and protein levels, and downregulating the expression of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2, thereby suppressing tumor cell proliferation (Sun et al., 2022).
3.5 Other metabolites
To further complement the antitumor profile of Polygonatum spp., beyond the primary bioactive metabolites discussed above, various secondary metabolites such as phenolic acids, alkaloids, volatile oils, and lignans have also been shown to exert immunomodulatory and antitumor effects through multi-target regulation of key signaling pathways (Song et al., 2024; Wan et al., 2024). Volatile oils extracted from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua demonstrated significant cytotoxic activity against NCI-H460 human lung cancer cells in vitro, achieving an inhibition rate of 98.08% at a concentration of 100 μg/mL (Yu et al., 2008). The anticancer potential of various solvent fractions of Polygonatum verticillatum (L.) All. [Asparagaceae; Polygonati rhizoma] was assessed, indicating that dichloromethane, chloroform, and aqueous extracts exhibited dose-dependent cytotoxicity against cancer cells at concentrations ranging from 25 to 400 μg/mL, with the chloroform extract showing the most potent cytotoxic effect (Singh and Patra, 2018). Further studies have highlighted the synergistic interactions among multiple phytochemicals within Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté extracts. The identified metabolites were shown to inhibit the AMPK/PDH signaling pathway, suppress mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in M2 macrophages, impede M2 polarization, and facilitate the phenotypic switch to the M1 macrophage subtype. These actions collectively inhibit tumor cell migration and enhance immune surveillance (Hou, 2023). Additionally, UPLC-Q-Exactive-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular docking were applied to analyze the chemical metabolite of Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté leaves, identifying 56 metabolites, three core bioactives, 11 major targets, and 30 KEGG pathways related to antitumor effects. This integrative study elucidated the multi-metabolites, multi-target, and multi-pathway mechanisms underlying the antitumor activity of the extracts (Chen et al., 2023).
4 Mechanisms of antitumor effects of active metabolites in Polygonatum spp.
Recent studies indicate that the anti-tumor mechanisms of the bioactive metabolites of Polygonatum spp. are multifaceted and synergistic, involving cell cycle arrest, stimulation of tumor cell apoptosis, promotion of autophagy, modulation of the tumor microenvironment, and immune system regulation. These pathways collectively facilitate the suppression of tumor development and progression, as shown in Figure 2. The specific metabolites and their corresponding mechanisms are summarized in Table 1.
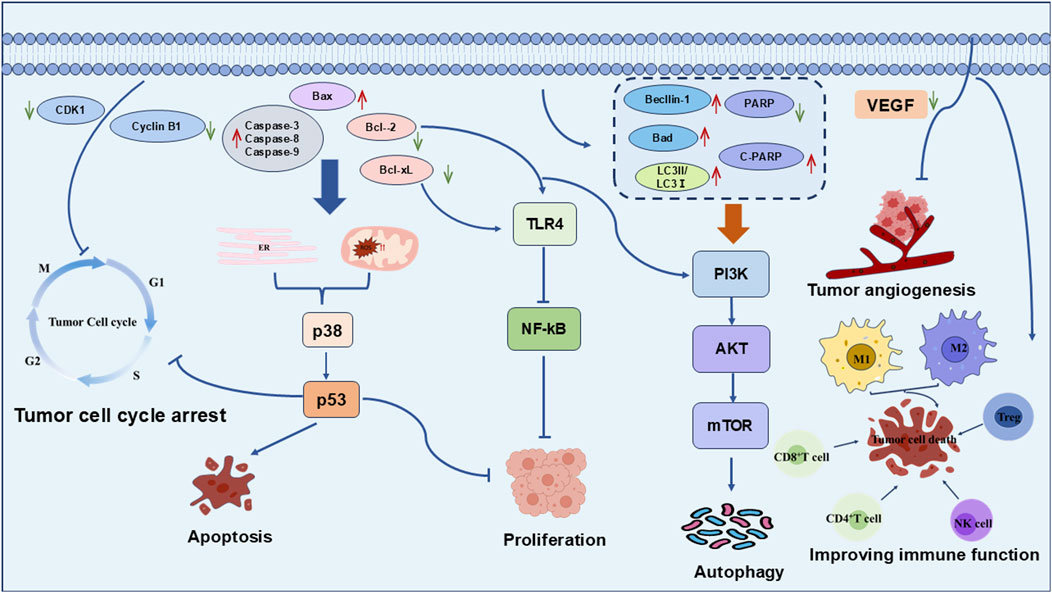
Figure 2. Antitumor mechanism of the active metabolites of Polygonatum spp. The antitumor mechanisms of Polygonatum spp. Mainly involve cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction, proliferation inhibition, angiogenesis suppression, autophagy promotion, and immune modulation.
4.1 Arresting the tumor cell cycle
The cell cycle of tumor cells resembles that of normal cells, comprising the G1, S, G2, and M phases; however, its regulatory mechanisms are frequently disrupted by genetic mutations and other factors, resulting in uncontrolled proliferation (Matthews et al., 2022). Transitions from G1 to S phase and G2 to M phase involve complex molecular events that are sensitive to environmental stimuli and currently represent key targets in tumor therapy (Liu et al., 2022). PSPs, flavonoids, and steroidal saponins found in Polygonatum spp. have been shown to disrupt tumor cell cycle regulation, promoting cytotoxicity and inducing apoptosis.
In the H22 hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft model, flavonoids and steroidal saponins can induce G0/G1 phase arrest in tumor cells, thereby preventing DNA replication in the S phase and inhibiting cell proliferation (Duan et al., 2014). Studies have shown that PSP effectively induces G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in HeLa cells by downregulating the expression of CDK1 and Cyclin B1 (Li et al., 2020). Additionally, research indicated that dioscin, another bioactive metabolite of Polygonati rhizoma, arresting the G2/M phase of tumor cells through the upregulation of p53, Caspase-3, Caspase-9, and Bax, concomitant with the downregulation of Bcl-2 (Luo, 2024). Furthermore, investigations have revealed that methylprotodioscin, a major saponin metabolite, significantly restrained the proliferation of HeLa cells via multiple mechanisms, including the induction of G2/M phase arrest, the enhancement of intracellular ROS accumulation, and the activation of the death receptor pathway (Ma et al., 2019).
4.2 Induction of tumor cell apoptosis
In oncology, apoptosis is an essential procedure of programmed cell death that inhibits tumor progression and maintains tissue homeostasis (Nagata, 2018). Three major apoptotic pathways have been characterized: the extrinsic pathway (death receptor-mediated), the intrinsic pathway (mitochondria-mediated), and the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Within these pathways, the caspase protease family and the Bcl-2 protein family serve as crucial regulators of tumor cell apoptosis (Qian et al., 2022; Sahoo et al., 2023).
Water-soluble PSP derived from Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté could efficiently induce apoptosis in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells, mediated by activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, characterized by stimulation of Bax, suppression of Bcl-2, and increased activities of caspase-3 and caspase-9. These molecular changes ultimately led to DNA fragmentation and nuclear damage (Li et al., 2022). Methylprotodioscin isolated from Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté elicited apoptosis in HeLa cervical cancer cells via dual mechanisms involving the mitochondrial pathway and the death receptor pathway (Zhang, 2020). Homoisoflavanone-1, purified via ethanol extraction, significantly reduced the proliferation of tumor cells and induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner in A549 cells (Ning et al., 2018). This effect was attributed to several mechanisms, including the intervention of mitochondrial cysteine-associated pathways and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signaling, the activation of the p38/p53 signaling axis, and which ultimately led to the induction of apoptosis in A549 cells. Similarly, PLC has been proved to induce apoptosis in L929 murine fibrosarcoma cells, with an IC50 value of 15 μg/mL. This process was primarily mediated through the activation of caspase-9, caspase-8, and caspase-3 (Zhang et al., 2010).
4.3 Inhibition of tumor cell proliferation
Tumor cell proliferation refers to an abnormal and rapid process of cell division that bypasses normal growth regulatory mechanisms. It is characterized by autonomy, an accelerated cell cycle, evasion of growth inhibition, metabolic reprogramming, spatial heterogeneity, clonal evolution, and the ability to invade and metastasize, ultimately resulting in tumor formation and progression (Keibler et al., 2016). PSP has been explored for its effects on the human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell line Eca109 using in vitro assays at gradient concentrations of 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL. This substantially attenuated the proliferative capacity of Eca109 cells by regulating TLR4 expression and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway (Zhou et al., 2019b). Moreover, PCL significantly modulated the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, specifically increasing Bax levels while diminishing Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 expression. This alteration led to the excessive accumulation of ROS within the mitochondrial pathway, subsequently activating key signaling molecules such as p38 and p53. The resulting signaling cascade effectively suppressed the proliferation of human melanoma A375 cells, with an IC50 value of 15 μg/mL observed within 24 h (Liu et al., 2009a).
4.4 Induction of tumor cell autophagy
Autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved intracellular catabolic mechanism characterized by the formation of double-membraned autophagosomes, which engulf defective organelles and aggregated proteins and subsequently fuse with lysosomes to enable their degradation and recycling. This tightly regulated process is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis, as it removes impaired cellular metabolites and helps to sustain energy equilibrium, especially during periods of nutrient scarcity (Debnath et al., 2023). Flavonoid polysaccharides have been shown to specifically target the proliferation of prostate cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), inducing apoptosis, while exerting minimal effects on normal fibroblasts. This effect was associated with elevated levels of Beclin-1 and LC3-II, key autophagy-related proteins, which in turn enhanced autophagic activity and stimulated programmed cell death in cancer cells. A dose-dependent relationship between PSP concentration and autophagy induction was observed, with maximal autophagic activity at 1,250 μg/mL (Han et al., 2016). Moreover, dioscin has been shown to induce autophagy by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and p53 signaling pathways, through downregulation of PARP and Bcl-2, upregulation of cleaved c-PARP and Bad, and an increased LC3-II/LC3-I ratio, thereby demonstrating significant antitumor activity in endometrial cancer (Li et al., 2024).
4.5 Antitumor angiogenesis
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a crucial modulator of tumor angiogenesis, exerting its effects primarily through interactions with vascular endothelial cells. It stimulates the proliferation and migration of these cells, facilitating the development of new blood vessels. This process is crucial for providing tumors with the necessary nutrients and oxygen to support their growth and metastatic potential (Geindreau et al., 2021). Studies have shown that the polysaccharide from Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté can efficiently suppress the expression and activity of VEGF in a dose-dependent manner. Specifically, at a concentration of 100 μg/mL, PSP significantly reduced VEGF secretion compared to the control group. This finding suggested that PSP could effectively inhibit VEGF production by hepatocellular carcinoma cells, ultimately leading to the suppression of tumor angiogenesis (Zhang, 2025).
4.6 Regulation of immune function
The immune system plays a crucial role in defending against tumor development by identifying and eliminating abnormally proliferating tumor cells, while maintaining internal homeostasis. Therefore, enhancing immune function is considered a key strategy in cancer treatment (Petroni et al., 2021). Polygonatum spp. Exhibits remarkable immunomodulatory properties, enhancing the functionality of immune cells such as NK cells and macrophages, thereby bolstering the body’s antitumor immune responses.
Crude polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua have been shown to prolong the survival of mice bearing S180 ascitic tumors by enhancing immune function, with dosages of 200 mg/kg and 400 mg/kg exceeding the efficacy thresholds defined in traditional Chinese medicine (Ye et al., 2008). Further studies demonstrated that PSP could inhibit the proliferation of hematopoietic cells in the spleen induced by triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), and significantly increase the number of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) as well as common lymphocytes in the bone marrow (Xie et al., 2021). PSP also significantly restrained tumor expansion in a murine model of gastric cancer, likely via the suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. This suppression enhanced the immunoregulatory balance of cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-2, and IL-6, thereby impeding tumor progression (Lv and Duan, 2020). Additionally, PSP stimulated the proliferation and differentiation of immune cells by activating the TLR4 receptor and its downstream MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway, augmenting immune responsiveness and enhancing tumor cell recognition and cytotoxic activity (Long et al., 2018). PSP was further shown to efficiently prevent the depletion of HSPCs and lymphoid progenitor cells induced by TNBC, while modulating immunosuppressive conditions within the tumor microenvironment (Xie et al., 2021). It also regulated the spatial distribution of immunosuppressive myeloid cells in the tumor microenvironment and exert protective effects by maintaining splenic immune cell homeostasis. In addition, steroidal saponin can exert antitumor effects by modulating immune responses and enhancing host resistance to tumor development (Zhai, 2024).
4.7 Other antitumor mechanisms
In addition to the above pathways, the antitumor active metabolitess of Polygonatum spp. can also influence tumor cell energy metabolism through modulation of associated signaling cascades. In the context of prostate cancer treatment, through multiple synergistic mechanisms, PSP effectively suppressed the activation of the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways, downregulating the phosphorylation of PI3K, AKT, and p65, thereby promoting tumor cell apoptosis and inhibiting growth. Concurrently, Caspase-3 expression was upregulated, and the concentrations of immunomodulatory cytokines in the blood—such as TNF-α, IL-2, and IL-6—were regulated synergistically (Yang et al., 2025). Polygonatum spp. was found to modulate tumor progression and interfere with tumor cell energy metabolism (Yang et al., 2025). Furthermore, PCL also exerted anti-metastatic effects by inhibiting tumor cell aggregation and suppressing glycolysis in PC3 prostate cancer cells with bone metastasis, primarily through downregulation of hexokinase 2 (HK2), a key enzyme in the Warburg effect (Zhang et al., 2017). In addition, the Ras–Raf and PI3K–AKT signaling pathways also serve as critical negative regulators in the anti-tumor mechanism of Polygonatum spp. (Liu et al., 2010).
5 Combination medication
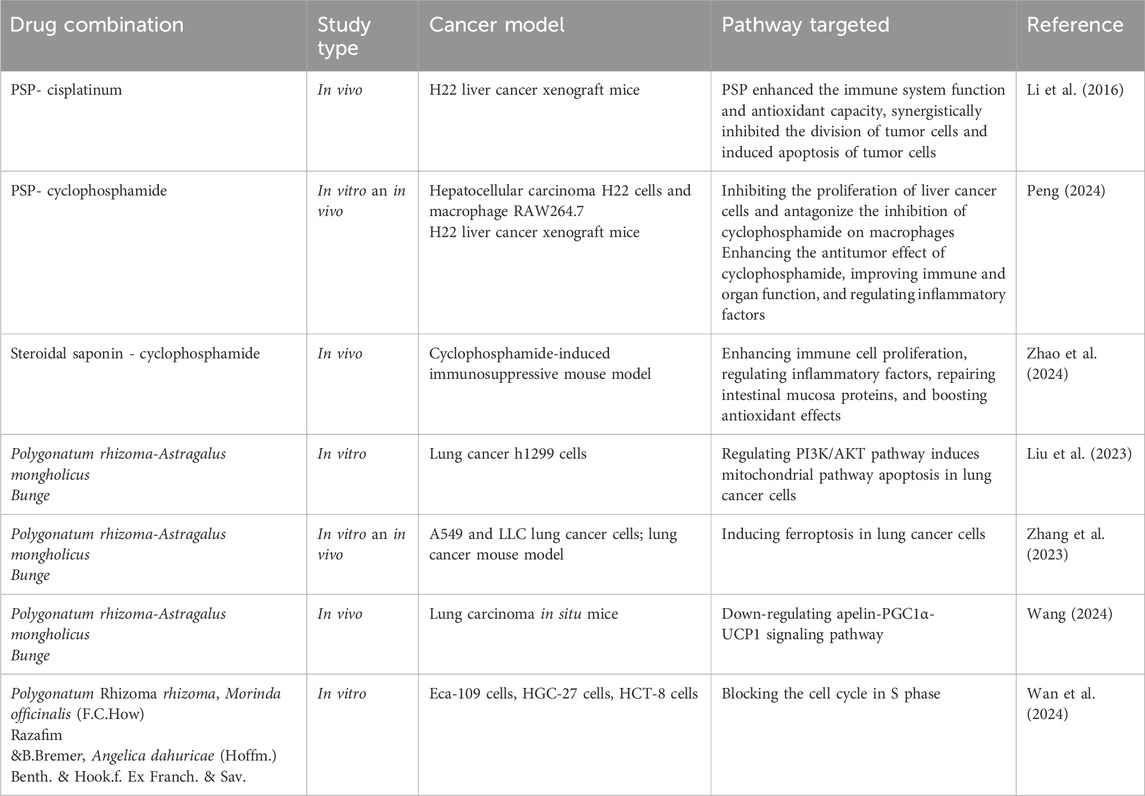
Multi-drug combination strategy is a crucial approach for improving cancer treatment, and it represents a mainstream modality in clinical oncology. TCM is characterized by its moderate efficacy, holistic treatment philosophy, and relatively low toxicity, which addresses the limitations of conventional therapies and is increasingly recognized as a valuable adjunct in tumor management. Recent studies have indicated that active metabolites of Polygonatum spp. can significantly enhance therapeutic outcomes when used in combination with conventional chemotherapeutic agents. For instance, co-administration of PSP with cyclophosphamide has been shown to reduce toxicity and reverse cisplatin resistance, whereas combination with Astragalus polysaccharides resulted in a synergistic enhancement of antitumor activity (Table 2).
5.1 Combinations with chemotherapeutic agents
Cyclophosphamide and cisplatin are widely utilized as chemotherapeutic agents for treating a variety of cancers. Nevertheless, their clinical use is frequently restricted due to the significant adverse effects, including immunosuppression, gastrointestinal injury, and hematological abnormalities, which collectively impair immune function and increase susceptibility to infection (Spears et al., 2019). Studies have shown that the co-administration of Polygonatum spp. with these agents not only enhances the chemosensitivity and mitigates toxicity to healthy tissues, but also reinforces the inhibitory influences on tumor cells. The combination of PSP with low-dose cisplatin effectively suppressed the growth of H22 hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts in mice, with the synergistic anti-tumor effect attributed to the reduction of oxidative stress (Li et al., 2016). Furthermore, PSP combined with cyclophosphamide enhanced the inhibitory effect on H22 solid tumors while simultaneously reducing the toxicity typically associated with chemotherapy (Peng, 2024). Steroidal saponins were found to alleviate cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression and enhance its antitumor activity through multiple mechanisms, including improvement of immune organ indices, stimulation of lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation, regulation of inflammatory cytokines, and alleviation of oxidative stress (Zhao et al., 2024).
5.2 Co-administration with other botanical drugs
Considering the complexity of cancer pathogenesis, monotherapy often falls short in achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes. The theory of TCM combination therapy emphasizes t synergistic effect between the botanical metabolites. This approach can effectively improve the efficacy, reduce the toxicity, and broaden the therapeutic window through multi-metabolite, multi-target, and multi-pathway mechanisms (Zhou et al., 2017). As a multi-metabolite, multi-target traditional Chinese medicine, Polygonatum spp. is well-suited for such strategies. Its co-administration with other Chinese botanical drugs can produce significant synergistic effects, offering novel strategies and methods for cancer treatment.
Recent pharmacological investigations have further elucidated the therapeutic potential of Polygonatum spp. when incorporated into combination therapies, especially in the intervention of lung cancer. Steroidal saponins were found to alleviate cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression and enhance its antitumor activity through multiple mechanisms, including improvement of immune organ indices, stimulation of lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation, regulation of inflammatory cytokines, and alleviation of oxidative stress (Liu et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023). The Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté–Astragalus mongholicus Bunge [Fabaceae; Astragalus] metabolites have been shown to inhibit mitochondrial uncoupling, restore oxidative phosphorylation, suppress aerobic glycolysis, and reverse the Warburg effect by downregulating the apelin–PGC1α–UCP1 signaling pathway, effectively suppressing lung cancer progression (Wang, 2024).
In recent years, advances in network pharmacology and molecular docking techniques have significantly advanced research into the combination of flavonoids with other traditional Chinese medicines in the field of cancer therapy. The Polygonati rhizoma–Lilium brownii var. viridulum Baker [Liliaceae; Lilium] pair was predicted to exert anticancer effects by arresting the tumor cell cycle, inducing apoptosis and autophagy, enhancing immune function, and modulating relevant signaling pathways (Yu et al., 2020). The Panax ginseng C. A. Mey [Araliaceae; Panax]–Polygonati rhizoma pair was shown to alleviate cancer-related fatigue by modulating multiple targets and pathways associated with apoptosis, metastasis, and inflammation in cancer cells (Jiang et al., 2022). Various concentrations of Polygonatum rhizoma, Morinda officinalis, and Angelicae dahuricae (Hoffm.) Benth. & Hook.f. Ex Franch. & Sav. [Apiaceae; Angelicae dahuricae Radix], whether used in pairwise combinations or as a formulation of three botanical drugs, effectively induced S-phase arrest and promoted apoptosis in tumor cells (Sun, 2012). Additionally, the combination of Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté and Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce has been suggested to enhance immune responses, offering new therapeutic insights for cancer treatment (Zhuang and Wang, 2019).
6 Discussion
Despite continuous breakthroughs in cancer therapy, a definitive solution for completely eradicating cancer has yet to be achieved. Chemotherapy remains one of the primary treatment modalities, making substantial contributions to tumor control. However, its inherent limitations—such as poor targeting and pronounced toxicity—have significantly hindered its broader clinical application. In this context, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has emerged as a promising field in oncology, owing to its multi-metabolite nature, multi-target mechanisms of action, immunomodulatory effects, and relatively low toxicity.
Among TCM botanical drugs, Polygonatum spp. has attracted increasing attention in recent years due to its significant progress in antitumor research. Extensive phytochemical investigations have isolated a diverse range of bioactive metabolites in Polygonatum, including polysaccharides (PSP), steroidal saponins, flavonoids, volatile metabolites, and PCL, all of which exhibit strong antitumor activity. These metabolites exert synergistic effects through multiple mechanisms, including cell cycle arrest, apoptosis promotion, autophagy induction, tumor proliferation suppression, and immune modulation, demonstrating substantial therapeutic potential.
However, despite these promising findings, Polygonatum spp. research faces several critical limitations that warrant further investigation.
Firstly, although the antitumor properties of key metabolites such as PSP, steroidal saponins, and flavonoids have been established, most studies to date have focused on isolated targets or signaling pathways, lacking a comprehensive understanding of their multi-target interactions. Future studies should adopt integrative approaches, including network pharmacology and omics technologies, to elucidate the complex molecular mechanisms underlying the actions of Polygonatum spp., especially its flavonoid metabolites.
Secondly, there is an urgent need to strengthen in vivo and clinical investigations. Most existing studies have been limited to in vitro experiments, and in vivo efficacy and clinical outcomes remain underexplored. Animal studies and rigorously designed clinical trials are essential to confirm the safety and efficacy of Polygonatum spp., thereby facilitating its transition into clinical application.
Thirdly, the quality control system for Polygonatum spp. requires substantial refinement. The l metabolite of Polygonatum spp. is influenced by multiple factors, including geographical origin, cultivation conditions, harvesting season, and processing methods. These variables can affect the content, stability, and bioactivity of its metabolites, thereby influencing its pharmacological properties. It is imperative to establish standardized cultivation techniques, processing protocols, and quality control methods to ensure the reproducibility and consistency of its bioactive metabolites.
Lastly, more research should be dedicated to optimizing drug combination strategies. While current studies have demonstrated promising synergistic effects of Polygonatum spp. in combination with chemotherapeutic agents, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data remain scarce. Future research should address these aspects to ensure the safety and efficacy of combination therapies.
With the increasing global recognition of TCM, Polygonatum spp. holds significant promise, not only as a valuable therapeutic agent but also as part of integrative oncology treatments. Its application could bridge the gap between traditional and modern cancer therapies, making it a promising candidate in the global fight against cancer. Priority areas for future research include: (1) clarifying multi-target interactions via systems biology and omics-based approaches; (2) expanding in vivo and clinical studies with a focus on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety; (3) establishing standardized cultivation, processing, and quality control methods; and (4) developing mechanism-based and clinically validated combination strategies with chemotherapeutics and other TCM botanical drugs.
In summary, Polygonatum spp., as a medicinal and edible plant with significant antitumor potential, represents a valuable candidate for future cancer therapy. However, its successful clinical application will depend on continued exploration in key areas, including mechanistic elucidation, clinical validation, standardization, and combination therapy optimization. Through sustained and rigorous scientific inquiry, the full therapeutic potential of Polygonatum spp. can be realized, ultimately offering cancer patients safer, more effective, and integrative treatment options.
Author contributions
MZ: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. GC: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. JL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. CY: Visualization, Writing – original draft. YY: Visualization, Writing – original draft. WL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. XZ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (81874344) and Hunan Natural Science Foundation (2023JJ60474), and the Major Scientific Research Projects for High Level Health Talents in Hunan Province (R2023139), and Changsha Natural Science Foundation (kq2208191), and Hunan innovative province construction project (2024RC8110).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Chan, K. (1995). Progress in traditional Chinese medicine. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 16, 182–187. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(00)89019-7
Chen, J., Xia, J., Yin, F., Yu, J., Huo, J., Shi, Y., et al. (2023). UPLC-Q-Exactive-MS combined with network pharmacology to explore the antitumor effect of Polygonatum sibiricum leaf tea. J. Food Biochem. 2023, 1–12. doi:10.1155/2023/4174625
Chhikara, B. S., and Parang, K. (2023). Global cancer statistics 2022: the trends projection analysis. Chem. Biol. Lett. 10, 451. Available online at: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=urn:nbn:sciencein.cbl.2023.v10.451.
Debnath, J., Gammoh, N., and Ryan, K. M. (2023). Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol. 24, 560–575. doi:10.1038/s41580-023-00585-z
Duan, H., Wang, B., and Zhang, Y. (2014). Anti-tumor effects and mechanism of Rhizoma Polygonati polysaccharide on H22 tumor bearing mice. Traditional Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 25, 5–7. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-9783.2014.01.002
Geindreau, M., Ghiringhelli, F., and Bruchard, M. (2021). Vascular endothelial growth factor, a key modulator of the anti-tumor immune response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4871. doi:10.3390/ijms22094871
Han, S. Y., Hu, M. H., Qi, G. Y., Ma, C. X., Wang, Y. Y., Ma, F. L., et al. (2016). Polysaccharide from Polygonatum inhibits the proliferation of prostate cancer-associated fibroblasts cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 17, 3829–3833. doi:10.14456/apjcp.2016.177/APJCP.2016.17.8.3829
Hou, Y. (2023). Polygonatum sibiricum regulates M2 macrophage polarization by AMPK/PDH axis and inhibits lung cancer cell migration. Anhui Medical University. doi:10.26921/d.cnki.ganyu.2022.000985
Hu, Y., Tang, Y., Zhang, Z., Guo, X., Wu, Z., Li, Z., et al. (2023). Recent advances in polysaccharides from the genus Polygonatum: isolation, structures, bioactivities, and application. Food Hydrocoll. 140, 108634. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108634
Jiang, J., Niu, Z., Jiang, Q., Zhou, Y., Zhou, X., and Chi, W. (2022). Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking, the mechanism of Ginseng-polygonati Rhizoma herb pair in the treatment of cancer-related fatigue was studied. Mod. J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med. 31, 2301–2309.
Keibler, M. A., Wasylenko, T. M., Kelleher, J. K., Iliopoulos, O., Vander Heiden, M. G., and Stephanopoulos, G. (2016). Metabolic requirements for cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Metab. 4, 16. doi:10.1186/s40170-016-0156-6
Lai, W., Ning, Q., Wang, G., Gao, Y., Liao, S., and Tang, S. (2024). Antitumor activity of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides. Arch. Pharm. Res. 47, 696–708. doi:10.1007/s12272-024-01511-3
Łaniewski, P., Ilhan, Z. E., and Herbst-Kralovetz, M. M. (2020). The microbiome and gynaecological cancer development, prevention and therapy. Nat. Rev. Urol. 17, 232–250. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0286-z
Lei, X., Lei, Y., Li, J.-K., Du, W.-X., Li, R.-G., Yang, J., et al. (2020). Immune cells within the tumor microenvironment: biological functions and roles in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 470, 126–133. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.009
Li, L. (2019). Study on the physicochemical properties and activities of polysaccharides seguentially extracted from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Hefei, China: Hefei University of Technology. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CDFD&dbname=CDFDLAST2019&filename=1018273477.nh (Accessed September 12, 2025).
Li, C., Zhou, Y., and Wang, F. (2016). Inhibition of Polygonati Rhizoma polysaccharide combined with low-dose cisplatin on the growth of H22 liver cancer xenografts in mice and its anti-oxidative damage effect. Chin. J. Gerontology 36, 1038–1040. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.05.006
Li, L., Thakur, K., Cao, Y.-Y., Liao, B.-Y., Zhang, J.-G., and Wei, Z.-J. (2020). Anticancerous potential of polysaccharides sequentially extracted from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua in human cervical cancer Hela cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 148, 843–850. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.223
Li, M., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Wang, W., You, S., et al. (2022). Anti-cancer potential of polysaccharide extracted from Polygonatum sibiricum on HepG2 cells via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Front. Nutr. 9, 938290. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.938290
Li, X., Ma, R., Ni, Z., Wang, W., Thakur, K., Zhang, J., et al. (2024). Dioscin from Polygonatum sibiricum induces apoptosis and autophagy in Ishikawa human endometrial cancer cell and in vivo. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 13, 2601–2616. doi:10.26599/fshw.2022.9250209
Liu, B., Cheng, Y., Bian, H., and Bao, J. (2009a). Molecular mechanisms of Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells. Autophagy 5, 253–255. doi:10.4161/auto.5.2.7561
Liu, B., Cheng, Y., Zhang, B., Bian, H., and Bao, J. (2009b). Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human melanoma A375 cells through a mitochondria-mediated ROS–p38–p53 pathway. Cancer Lett. 275, 54–60. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.042
Liu, B., Wu, J., Li, J., Liu, J., Li, W., Li, C., et al. (2010). Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces murine fibrosarcoma L929 cell apoptosis and autophagy via blocking Ras–Raf and PI3K–Akt signaling pathways. Biochimie 92, 1934–1938. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2010.08.009
Liu, T., Wu, L., Wang, D., Wang, H., Chen, J., Yang, C., et al. (2016). Role of reactive oxygen species-mediated MAPK and NF-κB activation in polygonatum cyrtonema lectin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. J. Biochem. 160, 315–324. doi:10.1093/jb/mvw040
Liu, J., Peng, Y., and Wei, W. (2022). Cell cycle on the crossroad of tumorigenesis and cancer therapy. Trends cell Biol. 32, 30–44. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2021.07.001
Liu, H., Yue, L., Li, Y., Zheng, T., Zhang, W., Li, C., et al. (2023). Combination of Polygonatum and Scutellaria baicalensis triggers apoptosis through down-regulation of PON3-induced mitochondrial damage and endoplasmic reticulum stress in lung cancer cells. Available online at: https://assets-eu.researchsquare.com/files/rs-3045676/v1/f6b0849c-b32f-46b1-9f7d-76805cd894e6.pdf (Accessed September 12, 2025).
Liu, B., Zhou, H., Tan, L., Siu, K. T. H., and Guan, X.-Y. (2024a). Exploring treatment options in cancer: tumor treatment strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9, 175. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01856-7
Liu, R., Zhang, X., Cai, Y., Xu, S., Xu, Q., Ling, C., et al. (2024b). Research progress on medicinal components and pharmacological activities of Polygonatum sibiricum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 328, 118024. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118024
Long, T. (2018). The study to explore Rhizoma Polygonati polysaccharide on cancer by immune regulation based on TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Chongqing, China: Chongqing Medical University. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201802&filename=1018864819.nh (Accessed September 12, 2025).
Long, T., Liu, Z., Shang, J., Zhou, X., Yu, S., Tian, H., et al. (2018). Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides play anti-cancer effect through TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 111, 813–821. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.070
Luo, Y. (2024). Study on the extraction, separation, and antitumor activity of saponins from rhizoma of Polygonati and dioscin. Harbin University of Commerce. doi:10.27787/d.cnki.ghrbs.2023.000419
Lv, P. T., and Duan, X. B. (2020). The anti-tumor and immunomodulatory effects of Polygonati Rhizoma polysaccharide on MFC gastriccancer tumor-bearing mice. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 42, 2169–2172. doi:10.3969/j.Issn.1001-1528.2020.08.041
Ma, Y. L., Zhang, Y. S., Zhang, F., Zhang, Y. Y., Thakur, K., Zhang, J. G., et al. (2019). Methyl protodioscin from Polygonatum sibiricum inhibits cervical cancer through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 132, 110655. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2019.110655
Matthews, H. K., Bertoli, C., and de Bruin, R. A. M. (2022). Cell cycle control in cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 23, 74–88. doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00404-3
Nagata, S. (2018). Apoptosis and clearance of apoptotic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 36, 489–517. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053010
Ning, D., Jin, M., Xv, T., Sun, J., and Li, M. (2018). Homoisoflavanone-1 isolated from Polygonatum odoratum arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis in A549 cells. Oncol. Lett. 16, 3545–3554. doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9085
Peng, X. (2024). “Research on attenuated and synergistic effects of polysaccharide from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua on cyclophosphamide,” in H22 tumor-bearing mice (Chongqing, China: Southwest University). doi:10.27684/d.cnki.gxndx.2021.004805
Petroni, G., Buqué, A., Zitvogel, L., Kroemer, G., and Galluzzi, L. (2021). Immunomodulation by targeted anticancer agents. Cancer cell 39, 310–345. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.11.009
Qian, S., Wei, Z., Yang, W., Huang, J., Yang, Y., and Wang, J. (2022). The role of BCL-2 family proteins in regulating apoptosis and cancer therapy. Front. Oncol. 12, 985363. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.985363
Rafi, M. M., and Vastano, B. C. (2007). Identification of a structure specific Bcl-2 phosphorylating homoisoflavone molecule from Vietnamese coriander (Polygonatum odoratum) that induces apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cell lines. Food Chem. 104, 332–340. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.11.045
Ren, H., Deng, Y., Zhang, J., Ye, X., Xia, L., Liu, M., et al. (2020). Research progress on processing history evolution, chemical components and pharmacological effects of Polygonati Rhizoma. China J. Chin. Materia Medica 45, 4163–4182. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200522.601
Sahoo, G., Samal, D., Khandayataray, P., and Murthy, M. K. (2023). A review on caspases: key regulators of biological activities and apoptosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 60, 5805–5837. doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03433-5
Sharma, S., Chhimwal, J., Kumar, S., Padwad, Y., and Kumar, D. (2021). Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from Polygonatum verticillatum Linn. Phytochem. Lett. 45, 30–36. doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2021.07.010
Singh, S. K., and Patra, A. (2018). Evaluation of phenolic composition, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of Polygonatum verticillatum (L.). J. Integr. Med. 16, 273–282. doi:10.1016/j.joim.2018.04.005
Song, L., Geng, C., Xing, C., Wang, Q., Guo, Y., Chen, Y., et al. (2024). Compositional analysis and antitumor activity of aqueous extracts of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Traditional Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 35, 952–962. doi:10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2024.07.003
Spears, N., Lopes, F., Stefansdottir, A., Rossi, V., De Felici, M., Anderson, R. A., et al. (2019). Ovarian damage from chemotherapy and current approaches to its protection. Hum. Reprod. update 25, 673–693. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmz027
Su, L., Li, X., Guo, Z., Xiao, X., Chen, P., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). Effects of different steaming times on the composition, structure and immune activity of Polygonatum polysaccharide. J. Ethnopharmacol. 310, 116351. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116351
Sun, X. (2012). Study on anti-tumor effect of effective components of Polygonati Rhizoma Morindae Officinalis Radix and Angelicae Dahuricae Radix in vitro. Henan, China: Zhengzhou University. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD2012&filename=1012352007.nh (Accessed September 12, 2025).
Sun, T., Liu, Y., Li, Z., Zong, S., Zhi, W., Di, Z., et al. (2022). Lectin PCL-2 of Polygonatum cyrtonema induces apoptosis of human prostate cancer LNCap cells and its mechanism. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 34, 255–262. doi:10.16333/j.1001-6880.2022.2.011
Taldaev, A., Terekhov, R., Nikitin, I., Zhevlakova, A., and Selivanova, I. (2022). Insights into the pharmacological effects of flavonoids: the systematic review of computer modeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 6023. doi:10.3390/ijms23116023
Tao, A., Zhang, X., Du, Z., Zhao, F., Xia, C., and Duan, B. (2018). Research progress on flavonoids in plants of Polygonatum Mill. and their pharmacological activities. Chin. Traditional Herb. Drugs 49, 2163–2171. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.09.029
Testa, U., Castelli, G., and Pelosi, E. (2018). Lung cancers: molecular characterization, clonal heterogeneity and evolution, and cancer stem cells. Cancers 10, 248. doi:10.3390/cancers10080248
Wan, X., Cui, L., and Xiao, Q. (2024). Metabolomics and network pharmacology-based identification of phenolic acids in Polygonatum kingianum var. grandifolium rhizomes as anti-cancer/tumor active ingredients. PloS One 19, e0315857. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0315857
Wang, Z. (2024). To explore the mechanism of Polygonatum and Astragalus compound in inhibiting lung adenocarcinoma based on APELIN-PGC1α -UCP1 signaling pathway. Jiangsu, China: Nanjing Medical University. doi:10.27249/d.cnki.gnjyu.2024.000498
Wang, S., Yu, Q., Bao, J., and Liu, B. (2011). Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin, a potential antineoplastic drug targeting programmed cell death pathways. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 406, 497–500. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.049
Wang, H., Hou, Y., Ma, X., Cui, L., Bao, Y., Xie, Y., et al. (2022). Multi-omics analysis reveals the mechanisms of action and therapeutic regimens of traditional Chinese medicine, Bufei Jianpi granules: implication for COPD drug discovery. Phytomedicine 98, 153963. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153963
Xia, Q., Hao, B., Liu, C., and Cao, Y. (2025). Inhibitory effect and mechanism of purified saponin from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua on human ovarian cancer cell A2780. Food Chem. Toxicol. 200, 115368. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115368
Xie, Y., and Chen, G. (2021). Dioscin induces ferroptosis and synergistic cytotoxicity with chemotherapeutics in melanoma cells. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun. 557, 213–220. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.024
Xie, Y., Jiang, Z., Yang, R., Ye, Y., Pei, L., Xiong, S., et al. (2021). Polysaccharide-rich extract from Polygonatum sibiricum protects hematopoiesis in bone marrow suppressed by triple negative breast cancer. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 137, 111338. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111338
Xu, Y. B., Wang, Y. Z., Zhang, M. Q., and Zhang, J. Y. (2021). Herbal textual research on Polygonati Rhizoma and ethnic usage. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 27, 237–250. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20211115
Xu, C., Xia, B., Zhang, Z., Lin, Y., Li, C., and Lin, L. (2023). Research progress in steroidal saponins from the genus Polygonatum: chemical components, biosynthetic pathways and pharmacological effects. Phytochemistry 213, 113731. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2023.113731
Xuan, Y., Xu, L., Zheng, J., Mo, W., Zou, X., and Ge, F. (2025). Chemical composition and activity of alkaloids and homoisoflavonoids from Polygonatum kingianum. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 37, 457–464. doi:10.16333/j.1001-6880.2025.3.008
Yang, Q. X. (1999). Steroidal saponins from five medicinal liliaceous plants. Diss, Kunming Kunming Inst. Bot. doi:10.1007/s11101-014-9381-1
Yang, S., Tang, Y., Zhou, Y., Dong, S., Zhao, X., Liu, X., et al. (2025). Study on the effect of polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides on nude mice model ofprostate cancer PC-3 cells based on PI3K/Akt and NF - κb signaling pathways. J. Hainan Med. Univ. 31, 824–832. doi:10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20241021.003
Ye, H., Zhang, X., Yu, H., Liu, H., and Jiang, J. (2008). Study on anti-tumor function of polysaccharidefrom Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae, 34–36. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2008.06.016
Ye, X. P., Hu, Y. Y., Chen, Y. X., Tang, Z. X., Jiang, Z. B., Fu, Y., et al. (2025). Flavonoids from the genus Polygonatum: biological activities and biosynthesis mechanism. Front. Nutr. 12, 1574182. doi:10.3389/fnut.2025.1574182
Yu, H., Zhang, X., Deng, M., Ye, H., and Jiang, J. (2008). Study on constituents and biological activity of volatile oil from tubers of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae, 4–6. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2008.05.014
Yu, T., Yang, Z., Long, F., Wu, W., Wang, J., Wu, J., et al. (2020). Anti-cancer mechanism of Polygonati Rhizoma-Lilii Bulbus based on network pharmacology. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 26, 168–177. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20192123
Zhai, Y. (2024). Study on extraction, isolation and biological activitives of saponins from Polygonatum sibiricum. Zhejiang, China: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University. doi:10.27786/d.cnki.gzjlg.2023.000621
Zhang, Y. (2020). Preparation, anti-cancer activity and molecule mechanism of saponins from Polygonatum sibiricum. Anhui, China: Hefei University of Technology. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD202001&filename=1019185858.nh (Accessed September 12, 2025).
Zhang, J. (2025). Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide inhibiting tumor growth and influencing serummetabolites in hepatocellular carcinoma tumor-bearing mice. Anhui, China: Hefei University of Technology. doi:10.27101/d.cnki.ghfgu.2023.000237
Zhang, F., Gao, Q., Kong, L., and Zhu, Y. (2007). Experimental study on anti-tumor effect of Polygonati Rhizoma polysaccharide. China Pract. Med., 95–96.
Zhang, Z., Peng, H., Li, C., Liu, J., Zhou, T.-T., Yan, Y., et al. (2010). Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces murine fibrosarcoma L929 cell apoptosis via a caspase-dependent pathway as compared to Ophiopogon japonicus lectin. Phytomedicine 18, 25–31. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2010.05.013
Zhang, H., Du, X., Sun, T.-T., Wang, C.-L., Li, Y., and Wu, S.-Z. (2017). Lectin PCL inhibits the warburg effect of PC3 cells by combining with EGFR and inhibiting HK2. Oncol. Rep. 37, 1765–1771. doi:10.3892/or.2017.5367
Zhang, W., Jin, J., Cao, C.-W., Wang, F., Zhai, H., Zheng, T.-S., et al. (2023). Combined treatment of polygonatum and Scutellaria baicalensis suppresses lung cancer cell proliferation through inducing ferroptosis. Phytomedicine Plus 3, 100482. doi:10.1016/j.phyplu.2023.100482
Zhang, S., Xiao, X., Yi, Y., Wang, X., Zhu, L., Shen, Y., et al. (2024). Tumor initiation and early tumorigenesis: molecular mechanisms and interventional targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9, 149. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01848-7
Zhao, P., Zhao, C., Li, X., Gao, Q., Huang, L., Xiao, P., et al. (2018). The genus Polygonatum: a review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 214, 274–291. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.12.006
Zhao, D., Liu, H., Yan, C., Teng, Y., Zou, Y., Ren, X., et al. (2024). Polygonatum sibiricum saponin prevents immune dysfunction and strengthens intestinal mucosal barrier function in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed BAlB/c mice. Foods 13, 934. doi:10.3390/foods13060934
Zhou, M., Hong, Y., Lin, X., Shen, L., and Feng, Y. (2017). Recent pharmaceutical evidence on the compatibility rationality of traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 206, 363–375. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.06.007
Zhou, D., Li, X., Chang, W., Han, Y., Liu, B., Chen, G., et al. (2019a). Antiproliferative steroidal glycosides from rhizomes of Polygonatum sibiricum. Phytochemistry 164, 172–183. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.05.013
Zhou, W., Hong, J., Zhu, J., and Wang, X. (2019b). Effects of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides (PSP) on human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) via NF- κ B signaling pathway. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2019/3852879
Keywords: Polygonatum spp., traditional uses, antitumor activity, bioactive metabolites, multi-targeted mechanisms, pharmacological properties
Citation: Zhu M, Chen G, Li J, Yi C, Yuan Y, Liu W and Zhang X (2025) The antitumor potential of Polygonatum spp.: a narrative review of traditional uses, bioactive metabolites, and multi-targeted mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1662839. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1662839
Received: 09 July 2025; Accepted: 22 October 2025;
Published: 10 November 2025.
Edited by:
Shashanka Prasad, JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research, IndiaReviewed by:
Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla, University of Zululand, South AfricaPatricia Quintero Rincón, University of Antioquia, Colombia
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Chen, Li, Yi, Yuan, Liu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenlong Liu, ZHJhZ29uNTI0MEAxMjYuY29t; Xili Zhang, eGlhb2xpNjEwQDEyNi5jb20=
 Mengqin Zhu
Mengqin Zhu Guang Chen
Guang Chen Jinyu Li
Jinyu Li Chang Yi1,2
Chang Yi1,2 Wenlong Liu
Wenlong Liu Xili Zhang
Xili Zhang