- 1Department of Pharmacy, The Affiliated Changsha Hospital of Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, The First Hospital of Changsha, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China
Purpose: This retrospective, single-center study aimed to evaluate the genetic and non-genetic factors influencing voriconazole (VRC) trough concentration (Ctrough), efficacy and safety in hematological patients.
Methods: Medical records of inpatients were reviewed retrospectively. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify factors contributing to the variability of VRC Ctrough.
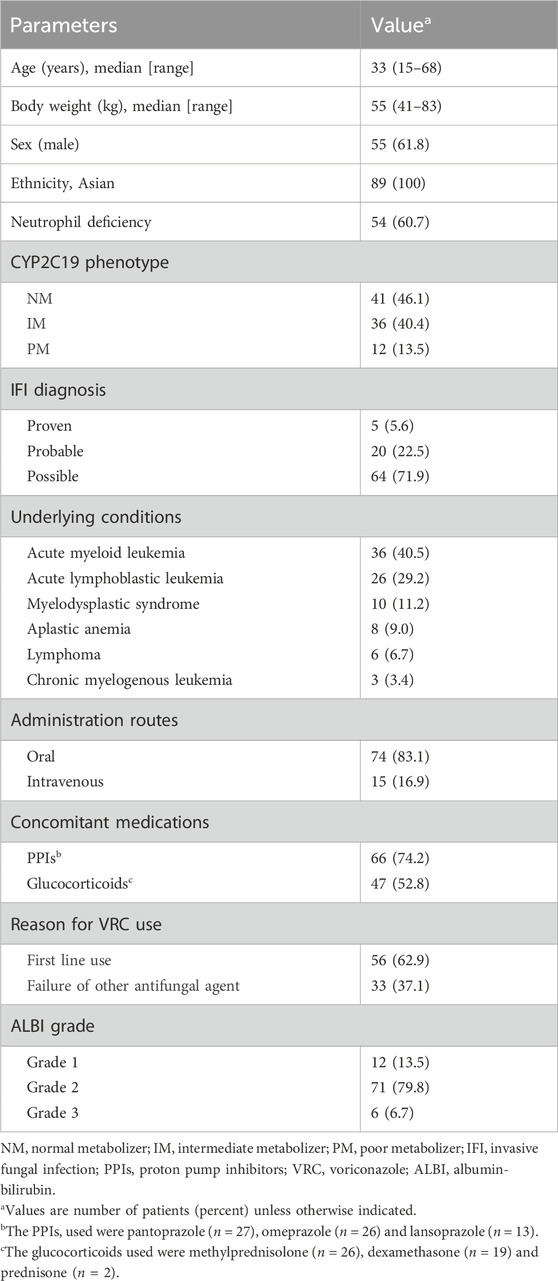
Results: A total of 375 VRC Ctrough measurements from 89 patients were analyzed. At the time of the initial Ctrough assessment, 74 patients (83.1%) received oral VRC, while 15 patients (16.9%) received intravenous VRC. Among these first Ctrough measurements, 68.5% of patients achieved the target therapeutic range (1.0–5.5 mg/L), whereas 28.1% had subtherapeutic concentrations and 3.4% had supratherapeutic concentrations. The dose-normalized VRC Ctrough (Ctrough/D) were significantly higher in poor metabolizers (PMs) compared to normal metabolizers (NMs) (P = 0.001) and intermediate metabolizers (IMs) (P = 0.021). The albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade, a novel liver function assessment tool, was significantly associated with VRC Ctrough/D. Patients with ALBI grade 3 had significantly higher Ctrough/D values compared to those with grade 2 (P = 0.001) and grade 1 (P < 0.001). The linear mixed model revealed that sex, concomitant glucocorticoid use, creatinine clearance rate (Ccr), CYP2C19 genotype, and ALBI grade were statistically significant predictors of VRC Ctrough/D. A total of 10 patients (11.2%) had their VRC dosage adjusted based on therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). The overall treatment success rate was 75.3% (67/89). Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were observed in 12 patients (13.5%) during VRC therapy.
Conclusion: CYP2C19 phenotype, ALBI grade, sex, Ccr and concomitant use of glucocorticoids contribute to the variability of VRC Ctrough and should be comprehensively considered when determining VRC dosage in Chinese hematological patients.
Introduction
Invasive fungal infections (IFIs) are opportunistic infections with high mortality rates that occur primarily in immunocompromised patients, especially in those with hematological diseases (Wang et al., 2019). Voriconazole (VRC), a broad-spectrum triazole antifungal agent, is the first-line treatment for the prevention and management of IFIs (Patterson et al., 2016). Given its nonlinear pharmacokinetics and high inter- and intra-individual variability, therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is essential. Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) associated with VRC, including hepatotoxicity, visual disturbances, and hallucinations, have been correlated with elevated trough concentrations (Ctrough) (Hanai et al., 2021; Jin et al., 2016). Therefore, individualized VRC dosing is critical to optimizing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing the risk of toxicity.
VRC is primarily metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) enzyme (Weiss et al., 2009). CYP2C19 exhibits genetic polymorphisms, with allelic variants such as *2, *3, and *17 contributing to interindividual differences in metabolic capacity. According to the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines (CPIC, 2018), the distribution of CYP2C19 phenotypes varies between Asian and Caucasian populations, potentially affecting optimal VRC dosing. The 2022 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and the Japanese Society of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (JSC/JSTDM) consensus (Takesue et al., 2022) recommends population-specific VRC dosing strategies for Asians and non-Asians to minimize the risk of overdose. Beyond genetic variation, our previous research has also identified non-genetic factors—including age, concomitant medications, and liver function, as significant contributors to variability in VRC Ctrough (Hu et al., 2024a).
Our recent research demonstrated a significant correlation between VRC Ctrough and Child-Pugh (CP) classification in patients with hepatic dysfunction (Hu et al., 2024b). Similarly, a population pharmacokinetic (PPK) study by Tang et al. identified a significant association between VRC clearance (CL) and total bilirubin (TBIL) levels (Tang et al., 2021). In clinical practice, VRC dosing is frequently adjusted based on the patient’s liver function. While the CP classification remains the most commonly used tool for liver function assessment, recent studies (Nashimoto et al., 2023; Asai et al., 2025) have suggested that the albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade may also correlate with VRC Ctrough and could aid in optimizing initial dosing and predicting hepatotoxicity. The ALBI grade is calculated using two readily accessible biomarkers—serum albumin (ALB) and TBIL, both of which are obtained through routine blood tests.
Therefore, this study retrospectively collected clinical data from patients who had simultaneous measurements of steady-state VRC Ctrough and CYP2C19 genotypes. Liver function was assessed using the ALBI grade. The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the influence of both genetic and non-genetic factors on VRC Ctrough. In addition, the study assessed the efficacy and safety of VRC in Chinese hematological patients, providing a scientific basis for the individualized use of VRC in this population.
Methods
Study design
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of inpatients who had received VRC and undergone measurement of steady-state VRC Ctrough and CYP2C19 genotyping through the department of hematology at Xiangya Hospital of the Central South University between 01 May 2015 and 01 May 2021. Inclusion criteria: (i) patients aged ≥15 years. (ii) patients who underwent measurement of steady-state VRC plasma Ctrough and CYP2C19 genotyping during hospitalization. Exclusion criteria: patients who received concomitant antifungal agents in addition to VRC. Steady-state was considered to be reached at 24 h following oral or intravenous loading dose and regarding the evidence and variability among patients, obtaining the first blood sample on day 3. Without oral or intravenous loading dose, it was reported that steady-state was considered to be reached on day 4–7 of twice daily dosing (Chen et al., 2018).
Ethics
This retrospective study strictly followed the Helsinki Declaration and the protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Xiangya Hospital (Approval number 2018091069). The identity information of all patients in this study has been coded to ensure that identity information is not leaked. The data are anonymous, and the requirement for informed consent was therefore waived.
Measurement of VRC plasma Ctrough and CYP2C19 phenotype
All Ctrough were collected 30 min before the next dose. The measurement of VRC Ctrough was performed by the methods described in our previous publication (Hu et al., 2018). In brief, analysis of VRC concentrations was performed using high-performance liquid chromatography (analytical range, 0.02–19.60 mg/L). According to our previous experience, the target range of VRC Ctrough is still 1.0–5.5 mg/L in this study (Hu et al., 2018). Each patient could have multiple steady-state Ctrough measurements during hospitalization. Detection of CYP2C19 *2, *3, and *17 alleles, associated with reduced CYP2C19 enzymatic activity, was performed using a DNA microarray chip method (BaiO®, Shanghai, China). Based on genotyping results, patients were categorized as follows: ultra-rapid metabolizers (UM, *17/*17), rapid metabolizers (RM, *1/*17), normal metabolizers (NM, *1/*1), intermediate metabolizers (IM, *1/*2, *1/*3, *2/*17, or *3/*17), and poor metabolizers (PM, *2/*2, *2/*3, or *3/*3).
Data collection
Medical records were retrieved from the electronic medical record system. The following patient data were extracted: ethnicity, diagnosis of IFI, treatment indication, dosage and duration of VRC therapy, route of administration, concomitant medications, VRC TDM results, CYP2C19 phenotype, ALB, TBIL, and serum creatinine (Scr). The ALBI grade was calculated using the formula:
ALBI grades were categorized as follows: grade 1 (≤−2.60), grade 2 (−2.59 to −1.39), and grade 3 (>−1.39) (Asai et al., 2025), with higher scores indicating poorer liver function. Renal function was assessed using the creatinine clearance rate (Ccr).
Evaluation of efficacy and safety
Treatment response was evaluated based on the updated guidelines of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) (Donnelly et al., 2020). IFIs were categorized as possible, probable, or proven according to the EORTC/MSG criteria. ADRs were assessed using the National Cancer Institute’s Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 5.0 (CTCAE). A VRC-related ADR was defined as one with possible or stronger relationship.
Statistical analysis
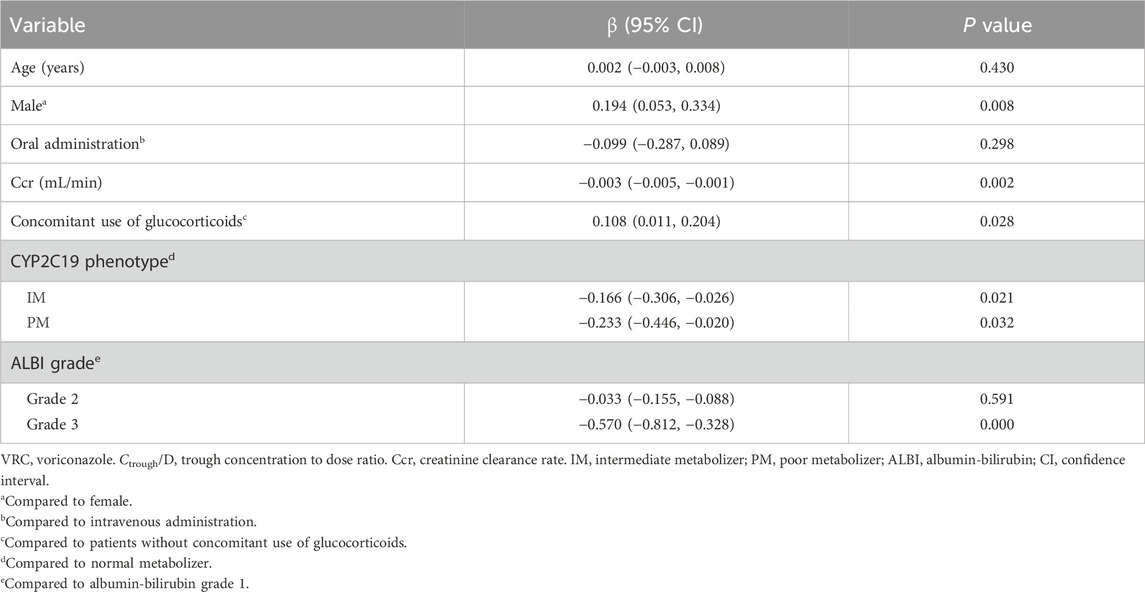
All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 25.0. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify factors associated with VRC Ctrough. To account for variability in dosage and body weight, the standardized dose normalized to body weight - Ctrough (mg/L)/D (mg/kg) was utilized. Variables included in the univariate analysis were age, sex, route of administration, concomitant use of glucocorticoids and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), Ccr, CYP2C19 genotype, and ALBI grade. The χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test was used to compare categorical variables, while the Mann–Whitney U test and Kruskal–Wallis test were applied for continuous variables. Spearman’s correlation coefficient was employed to assess the associations between continuous variables. A linear mixed model was applied for the multivariate analysis of factors influencing VRC Ctrough. The dependent variable was defined as log(Ctrough/D). To address the non-independence of repeated measurements within the same patient, patient ID was included as a random intercept. Fixed effects were selected based on variables identified in the univariate analysis. Each CYP2C19 polymorphism was evaluated for compliance with Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. A two-sided P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient characteristics
A total of 168 patients were initially screened. After excluding those < 15 years (n = 50), those lacking CYP2C19 genotype data (n = 19), and those without steady-state VRC Ctrough (n = 10), 89 patients remained for the final analysis. Fifth-five (61.8%) were male, 34 (38.2%) were female. The median age and weight were 33 years old (range, 15–68 years old) and 55 kg (range, 41–83 kg), respectively. All patients had malignant hematological diseases. Thirty-six (40.5%) of patients had acute myeloid leukemia. Proven, probable, and possible IFIs were reported for 5 (5.6%), 20 (22.5%), and 64 (71.9%) patients, respectively. Sixty-six (74.2%) patients received a coadministration of VRC and PPIs, and 47 (52.8%) patients received a coadministration of VRC and glucocorticoids. Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
VRC dosing and Ctrough
A total of 375 VRC Ctrough were measured from 89 patients in this study. The median number of measurements per patient was 3 (range, 1–20). The median VRC initial Ctrough was 1.76 mg/L (range, 0.06–10.67 mg/L). At the measurement of the first Ctrough, the target range was achieved in 68.5% of patients, while subtherapeutic and supratherapeutic concentrations were obtained in 28.1% and 3.4% of patients, respectively. The median duration of VRC treatment was 24 days (range, 7–163 days). At the time of the initial Ctrough measurement, 74 patients (83.1%) received oral VRC, while 15 patients (16.9%) received intravenous VRC. The median intravenous and oral maintenance daily dose to reach a therapeutic range was 7.3 mg/kg (range, 4.8–8.3 mg/kg) and 7.1 mg/kg (range, 4.6–9.8 mg/kg), both significantly lower than the recommended dose of 8 mg/kg (P = 0.009 and P < 0.001, respectively). The distribution of initial VRC Ctrough values across different weight-adjusted dose groups is shown in Figure 1.
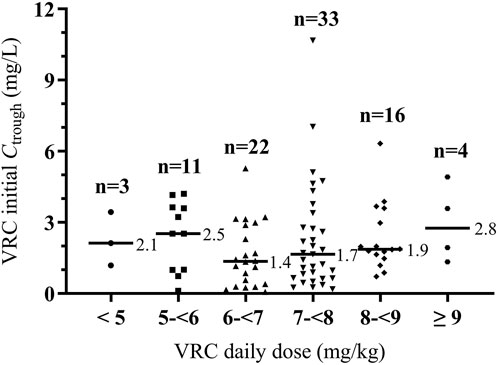
Figure 1. Distribution of initial VRC Ctrough across different weight-adjusted dosing groups. Horizontal bars represent median initial trough value for each dose group. VRC, voriconazole. Ctrough, trough concentration.
Univariate analysis to explore factors affecting VRC Ctrough
The wild-type CYP2C19 phenotype (NM) was the most commonly identified phenotype (41/89 patients [46.1%]), followed by the mutant types IM (36/89 patients [40.4%]) and PM (12/89 patients [13.5%]). No UMs or RMs were identified in this study. The allele frequencies of the CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*3 alleles were 30.3% and 3.4%, respectively. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was respected for each allele (CYP2C19*2, χ2 = 0.009, P = 0.92; CYP2C19*3, χ2 = 0.11, P = 0.74). A significant difference in Ctrough/D was observed among the three CYP2C19 phenotypes. PMs exhibited significantly higher Ctrough/D values compared to NMs and IMs (P = 0.001 and P = 0.021, respectively). Additionally, IMs had significantly higher Ctrough/D values than NMs (P = 0.002). At the time of the first Ctrough measurement, subtherapeutic concentrations were observed in 46.3% (19/41) of NMs and 16.7% (6/36) of IMs. The comparison of VRC Ctrough/D across CYP2C19 phenotypes is presented in Figure 2A.
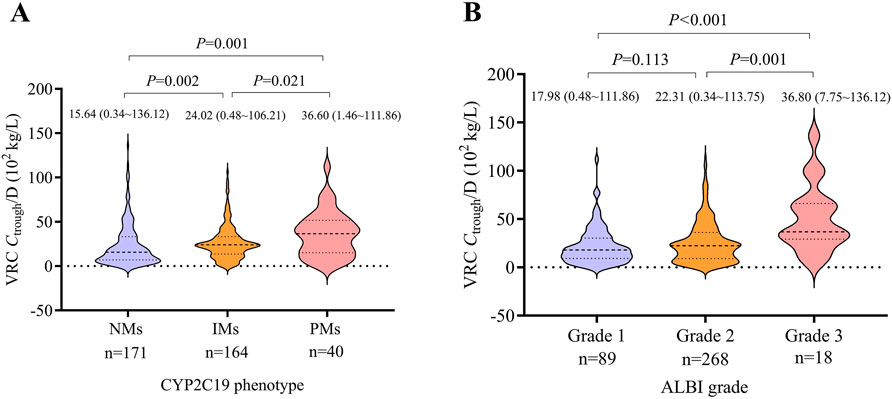
Figure 2. Violin plots illustrating the distribution of Ctrough/D across different CYP2C19 phenotypes and ALBI grades. (A) Comparison of VRC Ctrough/D among CYP2C19 phenotypes. (B) Comparison of VRC Ctrough/D across ALBI grades. Median values (with ranges) and corresponding P-values are indicated above each plot. The number of VRC Ctrough measurements in each group is displayed below the X-axis. VRC, voriconazole. Ctrough/D, trough concentration to dose ratio. NM, normal metabolizer. IM, intermediate metabolizer. PM, poor metabolizer. ALBI, albumin-bilirubin.
There were 12, 71, and 6 patients with ALBI grades 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Patients with ALBI grade 3 showed significantly higher Ctrough/D values compared to those with grade 2 and grade 1 (P = 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively). No significant difference was observed between ALBI grades 1 and 2. The comparison of VRC Ctrough/D across different ALBI grades is shown in Figure 2B.
The median Ctrough/D in male patients was 27.04 (range, 0.34–136.12), which was significantly higher than in female patients, whose median Ctrough/D was 15.21 (range, 0.38–96.66) (P < 0.001). Patients receiving concomitant glucocorticoids had a significantly lower median Ctrough/D of 18.82 (range, 0.34–113.75) compared to 24.75 (range, 0.48–136.12) in those not receiving glucocorticoids (P < 0.001). Additionally, patients receiving intravenous VRC had a significantly higher median Ctrough/D of 26.33 (range, 0.93–106.21) than those receiving oral administration, whose median was 20.73 (range, 0.34–136.12) (P = 0.026). Spearman’s correlation analysis indicated that Ctrough/D was positively associated with age (r = 0.103, P = 0.047) and negatively associated with Ccr (r = −0.127, P = 0.014). The median VRC Ctrough/D was 19.30 (range, 0.60–113.75) in patients ≤18 years and 21.46 (range, 0.34–136.12) in patients >18 years, with no significant difference between the two groups (P = 0.896). No significant difference in Ctrough/D was observed between patients with and without concomitant use of PPIs (P = 0.098).
Multivariate analysis by linear mixed model
Significant variables identified in the univariate analysis were included in the linear mixed model, comprising seven factors: age, sex, route of administration, concomitant use of glucocorticoids, Ccr, CYP2C19 genotype, and ALBI grade. The results indicated that sex, concomitant use of glucocorticoids, Ccr, CYP2C19 genotype, and ALBI grade had a statistically significant impact on VRC Ctrough/D. No significant associations were observed for the remaining covariates, as presented in Table 2.
Dose adjustments based on TDM
A total of 10 patients (11.2%) adjusted dose according to TDM during VRC treatment. Six patients with low concentration of VRC or lack of response increased the VRC dose (25% dose increase in one patient, 33.3% dose increase in three patients, and 50% dose increase in two patients). Finally, VRC concentrations were elevated in all six patients after dose adjustments and five patients reached the target range. Four patients with high Ctrough (>5.0 mg/L) or documented toxicity decreased the VRC dose (25% dose decrease in one patient, 33.3% dose decrease in one patient, 50% dose decrease in one patient, and discontinuance of VRC in one patient) and Ctrough were decreased in all four patients.
Efficacy and safety of VRC treatment
According to the criteria for therapeutic efficacy, the overall rate of the treatment success was 75.3% (67/89). The lack of response to VRC therapy was more frequent in patients with a VRC initial Ctrough of < 1.0 mg/L (40.0%) than in patients with a VRC initial Ctrough of ≥ 1.0 mg/L (18.8%) (P = 0.037). ADRs were observed in 12 patients (13.5%) during VRC treatment, including hepatotoxicity in six cases, hallucinations in two cases, diarrhea in two cases, unconscious in two cases and tremor in one case. Only one patient with both unconscious and hepatotoxicity had an average VRC Ctrough of 6.16 mg/L (>5.5 mg/L), and the remaining 11 patients had an average VRC Ctrough of 0.73–3.29 mg/L. The average VRC Ctrough in patients with documented toxicity was higher than patients without ADR (mean Ctrough, 2.40 mg/L vs. 1.91 mg/L, respectively, P = 0.195), however, it trended higher but was not significant. The effective rates for proven, probable, and possible IFIs were 60.0% (3/5), 65.0% (13/20), and 79.7% (51/64), respectively. No significant differences in efficacy were observed among the three groups (P = 0.297). The rates of ADRs were 40.0% (2/5), 20.0% (4/20), and 9.4% (6/64), respectively, with no statistically significant differences observed among the groups (P = 0.097).
Discussion
This study evaluated the impact of both CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms and non-genetic factors, including ALBI grade, on VRC Ctrough in Chinese patients. It also investigated the VRC dosing required to achieve the target therapeutic range and described dose adjustments, efficacy, and safety within the study population.
Significant differences in VRC Ctrough were observed among the three CYP2C19 phenotypes. In this study, PMs exhibited significantly higher VRC Ctrough than NMs and IMs, were consistent with our previous studies (Hu et al., 2023a; Hu et al., 2023b). CYP2C19 phenotype has been shown to effectively guide initial VRC dosing and is often used to explain subtherapeutic concentrations (Zonios et al., 2014). NMs are less likely to present with subtherapeutic VRC levels. Our study demonstrated that patients with VRC concentrations < 1.0 mg/L exhibited poor treatment responses, aligning with findings by Pascual et al., who also reported that low VRC levels were associated with reduced therapeutic efficacy (Pascual et al., 2008). Treatment success significantly improves when the Ctrough is ≥ 1.0 mg/L (Hanai et al., 2021). Therefore, the VRC dose in NMs should be appropriately increased to enhance the likelihood of achieving therapeutic levels and improving treatment efficacy. The CPIC guidelines (CPIC, 2018) recommended using CYP2C19 genotyping to inform VRC dosing strategies. Standard dosing is advised for NMs and IMs. For PMs, alternative antifungal agents not primarily metabolized by CYP2C19 are preferred. However, if VRC remains the most appropriate option, a reduced dose in combination with TDM is recommended.
Numerous pharmacogenomic studies have demonstrated that the CYP2C19 PMs has the highest prevalence in East Asian populations (approximately 13%–23%), which is substantially higher than in Caucasian populations (approximately 1%–6%) (Desta et al., 2002; Zhou et al., 2019; Lamoureux et al., 2016; Zonios et al., 2014). In our study, CYP2C19 PMs accounted for 13.5% of the cohort, a frequency consistent with previous reports. Consequently, patients with hematologic diseases in Asian populations may have an inherently higher risk of VRC overexposure and related toxicity compared with populations where the PMs is less frequent. Given the higher prevalence of PMs in Asian populations, a reduced maintenance dose may be necessary to attain comparable Ctrough. Due to genetic differences, the manufacturer’s original dosing recommendations (Pfizer Limited, 2012) may not be optimal for Chinese patients. The 2022 JSC/JSTDM Consensus (Takesue et al., 2022) recommended a maintenance dose of 3 mg/kg for Asian patients, considering the tendency for elevated Ctrough levels and a higher incidence of ADRs.
Our findings underscore not only the universal importance of individualized VRC therapy but also its particular relevance in Asian populations. When extrapolating our results to other ethnic groups, the distribution of CYP2C19 genotypes in the target population must be carefully considered. For instance, in populations where the PMs is rare, other factors, such as drug–drug interactions and hepatic function, may play a comparatively greater role. Conversely, our data provide region-specific evidence supporting the implementation of CYP2C19 genotype-guided dosing strategies in Asian medical centers. Future multicenter, multiethnic studies are warranted to establish more generalizable models that can accurately quantify the combined effects of genotype, ethnicity, and clinical factors on VRC pharmacokinetics.
In this study, only CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms were analyzed, while other enzymes and transporters that may also affect VRC metabolism were not evaluated. He et al. provided novel insights into the role of CYP3A4 in VRC pharmacokinetics (He et al., 2015). Similarly, Gautier-Veyret et al. (2016) demonstrated that a combined genetic score incorporating CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 genotypes could predict VRC Ctrough. However, other studies have reported inconsistent findings. For instance, no significant associations were observed between CYP3A4, ABCB1, or FMO3 genotypes and plasma VRC Ctrough (Chuwongwattana et al., 2020). Furthermore, while several studies recommended CYP2C19 genotyping to optimize VRC dosing in patients, research in healthy Chinese adults suggested that polymorphisms in CYP2C9, CYP3A4, and FMO3 may have minimal impact on VRC pharmacokinetics (Liu et al., 2024).
Li et al. (2017) demonstrated that liver function and CYP2C19 polymorphisms are major determinants of VRC pharmacokinetic variability, a conclusion consistent with our findings. In our previous research, we also identified that ALB, alanine aminotransferase, and direct bilirubin levels significantly influence VRC Ctrough (Hu et al., 2024b; Hu et al., 2023b). Accordingly, in this study, we adopted the ALBI grade to assess liver function instead of the CP classification. Unlike the CP system, which incorporates subjective factors such as ascites and hepatic encephalopathy, the ALBI grade offers a more objective and precise evaluation of liver function and is applicable to patients with both cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic liver diseases. Therefore, using ALBI grading to assess liver function for guiding VRC dosing may offer a more broadly applicable alternative to the CP classification. The recent PPK study of VRC in patients with hepatic dysfunction evaluated optimal dosing based on ALBI grading. The recommended regimens were 100 mg twice daily, 75 mg twice daily, and 50 mg twice daily for ALBI scores of −3, −2, and −1, respectively (Nashimoto et al., 2025).
Our previously published studies (Hu et al., 2018) demonstrated that VRC Ctrough following intravenous administration were significantly higher than those observed after oral administration in pediatric patients. Similar findings were observed in the present cohort. A potential explanation is that VRC absorption differs between children and adults. The oral bioavailability of VRC in children is approximately 44% (Purkins et al., 2002), compared to over 90% in adults (Veringa et al., 2017) (the present study included patients as young as 15 years). Additionally, oral administration is more susceptible to first-pass metabolism and drug–drug interactions. Intestinal CYP3A4 also serves as a barrier to VRC absorption. Moreover, oral VRC absorption may be influenced by factors such as concurrent food intake, gastrointestinal complications, and diarrhea.
Allegra et al. (2018) reported that males had significantly higher median VRC Ctrough than females and that Ctrough was positively correlated with age. Similarly, Hashemizadeh et al. (2017) found that reduced VRC concentrations were associated with the concomitant use of glucocorticoids. These findings are consistent with the results of our study. In this study, 16.9% of patients received VRC via intravenous administration. The intravenous formulation contains sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin (SBECD), which is normally eliminated through the kidneys but may accumulate in patients with renal impairment, potentially leading to nephrotoxicity. At high cumulative doses (≥400 mg/kg), SBECD accumulation may further exacerbate renal dysfunction (Yasu et al., 2018). Dolton et al. (2014) proposed that glucocorticoids may induce cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP enzymes, thereby enhancing VRC metabolism and reducing its plasma concentration. Several studies have also examined the impact of PPIs on VRC Ctrough. For instance, Yan et al. (2018) reported that co-administration of omeprazole significantly increased VRC plasma levels. Hashemizadeh et al. (2017) similarly observed elevated VRC concentrations with the co-administration of omeprazole or pantoprazole. However, in our study, the concomitant use of PPIs did not have a statistically significant effect on VRC Ctrough. A possible explanation is that most patients in our cohort were co-administered pantoprazole or lansoprazole, which exert less inhibitory effect on CYP2C19 compared to omeprazole.
Although CYP2C19 polymorphisms significantly influence VRC Ctrough, relying solely on CYP2C19 genotyping is insufficient for accurately guiding VRC dose optimization. Therefore, it is essential to integrate nonlinear pharmacokinetics, CYP2C19 genotyping, and other non-genetic factors when determining initial VRC dosing. Dose adjustments should subsequently be guided by TDM. Significant non-genetic factors identified in this study, such as ALBI grade and concomitant use of glucocorticoids, Ccr should be considered in future prospective PPK studies. Only 10 patients in our study underwent dose adjustments based on TDM, which limits the strength of conclusions regarding the effectiveness of TDM-guided interventions. However, evidence from previous studies suggested that earlier implementation of TDM may improve outcomes. For instance, Shen et al. (2022) reported that VRC-induced hepatotoxicity occurred in 66.7% of patients within 7 days of the first dose and in 94.4% within 15 days. Hu et al. (2024b) reported that the median time to onset of ADRs after initiating VRC therapy was 7.5 days. These findings underscore the potential of early TDM to substantially improve clinical outcomes. The Chinese Pharmacological Society (CPS) guidelines (Chen et al., 2018) recommended increasing the maintenance dose of VRC by 50% if Ctrough is < 1.0 mg/L or if treatment efficacy is inadequate. If the Ctrough is between 5 and 10 mg/L without CTCAE grade 2 or higher adverse events, a 20% dose reduction is advised. If the Ctrough > 10 mg/L or if CTCAE grade 2 or higher adverse events occur, VRC administration should be interrupted, followed by a 50% reduction in the maintenance dose upon resumption.
Recent researches have demonstrated that CRP, a biomarker of inflammation, is significantly correlated with VRC Ctrough (Hu et al., 2025; Encalada Ventura et al., 2016). Inflammatory status may reduce VRC metabolism, leading to elevated VRC Ctrough. Specifically, for every 1 mg/L increased in CRP, VRC Ctrough increased by approximately 0.015 mg/L (van Wanrooy et al., 2014). The risk of VRC overexposure and associated adverse reactions rised markedly in patients with CRP levels >102.23 mg/L (Lin et al., 2023). Furthermore, PPK studies have identified CRP as a significant covariate influencing the maximum enzymatic activity (Vmax) (van den Born et al., 2023). Consistently, Ling et al. (2024) reported that CRP is an important covariate affecting VRC clearance. However, our study did not include CRP concentration, preventing us from evaluating the impact of inflammatory factors on VRC Ctrough. Future large-scale prospective studies are warranted to investigate the optimal VRC dosing strategies based on CRP stratification.
The intrinsic characteristics of malignancy, such as disease type, stage, activity, and degree of inflammation, may indirectly affect VRC Ctrough by altering systemic physiological conditions, including inflammatory cytokine levels, serum protein concentrations, and liver function. These factors may therefore serve as potential unmeasured confounders. However, due to the retrospective nature of our study, specific biomarkers and detailed baseline disease status could not be obtained. Malignancy status represents an incompletely measured confounding factor, which should be addressed in the design of future studies.
Limitations
This study was conducted at a single institution using a retrospective design, which may introduce potential selection bias. Because all participants were recruited from one center, their demographic characteristics, underlying conditions, and prescribing practices may not fully represent a broader population, thereby limiting the generalizability of the findings. Moreover, retrospective studies often faced issues with incomplete data, such as genetic polymorphism of other metabolic enzymes (CYP3A4/5, FMO3). In addition, in our cohort, most patients did not have simultaneous measurements of VRC Ctrough and CRP levels, limiting our ability to assess this relationship and potentially resulting in incomplete findings.
Conclusion
CYP2C19 phenotype, ALBI grade, sex, Ccr and concomitant use of glucocorticoids were identified as significant contributors to the variability of VRC Ctrough/D and should be comprehensively considered when determining appropriate VRC dosing. Compared with the CP classification, ALBI grading may offer broader applicability for guiding individualized VRC therapy. Future PPK studies should incorporate these factors to establish more precise and personalized dosing strategies. Additionally, investigating VRC dose adjustment strategies in special populations, such as pediatric patients, individuals with hepatic impairment, or organ transplant recipients—is of particular importance due to limited existing data. Future research should prioritize these populations to enhance the efficacy and safety of VRC use.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Review Board of Xiangya Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
LH: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Writing – review and editing, Software, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Conceptualization, Visualization, Investigation, Validation, Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision. XT: Formal Analysis, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Investigation. YL: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Resources. JH: Visualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Software, Resources, Project administration, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2024JJ8227, 2024JJ8202), the Scientific Research Project of Hunan Provincial Health Commission (W20243243) and the Scientific Research Project of Changsha Municipal Health Commission (KJ-B2023042).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Allegra, S., Fatiguso, G., De Francia, S., Favata, F., Pirro, E., Carcieri, C., et al. (2018). Therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole for treatment and prophylaxis of invasive fungal infection in children. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 84 (1), 197–203. doi:10.1111/bcp.13401
Asai, Y., Kato, H., Tawara, I., Nakano, Y., and Iwamoto, T. (2025). Potential of albumin-bilirubin score for estimating the voriconazole-induced hepatotoxicity undergoing therapeutic drug monitoring: a single-center retrospective cohort study. Clin. Ther. 47 (4), 330–334. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2025.01.006
Chen, K., Zhang, X., Ke, X., Du, G., Yang, K., and Zhai, S. (2018). Individualized medication of voriconazole: a practice guideline of the division of therapeutic drug monitoring, Chinese pharmacological society. Ther. Drug Monit. 40 (6), 663–674. doi:10.1097/FTD.0000000000000561
Chuwongwattana, S., Jantararoungtong, T., Prommas, S., Medhasi, S., Puangpetch, A., and Sukasem, C. (2020). Impact of CYP2C19, CYP3A4, ABCB1, and FMO3 genotypes on plasma voriconazole in Thai patients with invasive fungal infections. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 8 (6), e00665. doi:10.1002/prp2.665
CPIC (2018). Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium (CPIC) guidelines for CYP2C19 and voriconazole therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 103 (2), 349. doi:10.1002/cpt.953
CTCAE. Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) version 5.0. US Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute.
Desta, Z., Zhao, X., Shin, J. G., and Flockhart, D. A. (2002). Clinical significance of the cytochrome P450 2C19 genetic polymorphism. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 41 (12), 913–958. doi:10.2165/00003088-200241120-00002
Dolton, M. J., Mikus, G., Weiss, J., Ray, J. E., and McLachlan, A. J. (2014). Understanding variability with voriconazole using a population pharmacokinetic approach: implications for optimal dosing. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69 (6), 1633–1641. doi:10.1093/jac/dku031
Donnelly, J. P., Chen, S. C., Kauffman, C. A., Steinbach, W. J., Baddley, J. W., Verweij, P. E., et al. (2020). Revision and update of the consensus definitions of invasive fungal disease from the european organization for research and treatment of cancer and the mycoses study group education and research consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 71 (6), 1367–1376. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz1008
Encalada Ventura, M. A., van Wanrooy, M. J., Span, L. F., Rodgers, M. G., van den Heuvel, E. R., Uges, D. R., et al. (2016). Longitudinal analysis of the effect of inflammation on voriconazole trough concentrations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60 (5), 2727–2731. doi:10.1128/AAC.02830-15
Gautier-Veyret, E., Fonrose, X., and Stanke-Labesque, F. (2016). A genetic score combining CYP450 2C19 and 3A4 genotypes to predict voriconazole plasma exposure? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 48 (2), 221–222. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.05.002
Hanai, Y., Hamada, Y., Kimura, T., Matsumoto, K., Takahashi, Y., Fujii, S., et al. (2021). Optimal trough concentration of voriconazole with therapeutic drug monitoring in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. Chemother. 27 (2), 151–160. doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2020.11.014
Hashemizadeh, Z., Badiee, P., Malekhoseini, S. A., Raeisi Shahraki, H., Geramizadeh, B., and Montaseri, H. (2017). Observational study of associations between voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring, toxicity, and outcome in liver transplant patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61 (12), e01211-17. doi:10.1128/AAC.01211-17
He, H. R., Sun, J. Y., Ren, X. D., Wang, T. T., Zhai, Y. J., Chen, S. Y., et al. (2015). Effects of CYP3A4 polymorphisms on the plasma concentration of voriconazole. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 34 (4), 811–819. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2294-5
Hu, L., Dai, T. T., Zou, L., Li, T. M., Ding, X. S., and Yin, T. (2018). Therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole in children from a tertiary care center in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62 (12), e00955–18. doi:10.1128/AAC.00955-18
Hu, L., Huang, S., Huang, Q., Huang, J., Feng, Z., and He, G. (2023a). Population pharmacokinetics of voriconazole and the role of CYP2C19 genotype on treatment optimization in pediatric patients. PLoS One 18 (9), e0288794. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0288794
Hu, L., Huang, Q., Huang, S., and Feng, Z. (2023b). Therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole and CYP2C19 phenotype for dose optimization in paediatric patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 79 (9), 1271–1278. doi:10.1007/s00228-023-03538-9
Hu, L., Huang, J., Li, Y., and He, G. (2024a). Clinical application of voriconazole in pediatric patients: a systematic review. Ital. J. Pediatr. 50 (1), 113. doi:10.1186/s13052-024-01684-z
Hu, L., Su, Y., Tang, X., Li, Y., Feng, J., and He, G. (2024b). Therapeutic drug monitoring and safety of voriconazole in patients with liver dysfunction. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 68 (11), e0112624. doi:10.1128/aac.01126-24
Hu, L., Wang, C., Tang, X., Huang, Q., Li, Y., and Huang, S. (2025). Therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole and the impact of inflammation on plasma trough concentrations in children. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1575233. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1575233
Jin, H., Wang, T., Falcione, B. A., Olsen, K. M., Chen, K., Tang, H., et al. (2016). Trough concentration of voriconazole and its relationship with efficacy and safety: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 71 (7), 1772–1785. doi:10.1093/jac/dkw045
Lamoureux, F., Duflot, T., Woillard, J. B., Metsu, D., Pereira, T., Compagnon, P., et al. (2016). Impact of CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on voriconazole dosing and exposure in adult patients with invasive fungal infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 47 (2), 124–131. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.12.003
Li, Z. W., Peng, F. H., Yan, M., Liang, W., Liu, X. L., Wu, Y. Q., et al. (2017). Impact of CYP2C19 genotype and liver function on voriconazole pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients. Ther. Drug Monit. 39 (4), 422–428. doi:10.1097/FTD.0000000000000425
Lin, L., Fu, X., and Hong, M. (2023). Lower prealbumin and higher CRP increase the risk of voriconazole overexposure and adverse reactions. Cureus 15 (9), e46107. doi:10.7759/cureus.46107
Ling, J., Yang, X., Dong, L., Jiang, Y., Zou, S., and Hu, N. (2024). Influence of C-reactive protein on the pharmacokinetics of voriconazole in relation to the CYP2C19 genotype: a population pharmacokinetics analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1455721. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1455721
Liu, S., Yao, X., Tao, J., Zhao, S., Sun, S., Wang, S., et al. (2024). Impact of CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP3A4, and FMO3 genetic polymorphisms and sex on the pharmacokinetics of voriconazole after single and multiple doses in healthy Chinese subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 64 (8), 1030–1043. doi:10.1002/jcph.2440
Nashimoto, S., Imai, S., Sugawara, M., and Takekuma, Y. (2023). Usefulness of the albumin-bilirubin score in determining the initial dose of voriconazole for patients with liver cirrhosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 46 (2), 230–236. doi:10.1248/bpb.b22-00608
Nashimoto, S., Sugawara, M., and Takekuma, Y. (2025). Optimization of voriconazole dosage via population pharmacokinetic analysis based on the albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score of patients with liver dysfunction. J. Infect. Chemother. 31 (8), 102766. doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2025.102766
Pascual, A., Calandra, T., Bolay, S., Buclin, T., Bille, J., and Marchetti, O. (2008). Voriconazole therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with invasive mycoses improves efficacy and safety outcomes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 46 (2), 201–211. doi:10.1086/524669
Patterson, T. F., Thompson, G. R., Denning, D. W., Fishman, J. A., Hadley, S., Herbrecht, R., et al. (2016). Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis: 2016 update by the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 63 (4), e1–e60. doi:10.1093/cid/ciw326
Purkins, L., Wood, N., Ghahramani, P., Greenhalgh, K., Allen, M. J., and Kleinermans, D. (2002). Pharmacokinetics and safety of voriconazole following intravenous-to oral-dose escalation regimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46 (8), 2546–2553. doi:10.1128/AAC.46.8.2546-2553.2002
Shen, K., Gu, Y., Wang, Y., Lu, Y., Ni, Y., Zhong, H., et al. (2022). Therapeutic drug monitoring and safety evaluation of voriconazole in the treatment of pulmonary fungal diseases. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 13, 20420986221127503. doi:10.1177/20420986221127503
Takesue, Y., Hanai, Y., Oda, K., Hamada, Y., Ueda, T., Mayumi, T., et al. (2022). Clinical practice guideline for the therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole in non-Asian and Asian adult patients: consensus review by the Japanese society of chemotherapy and the Japanese society of therapeutic drug monitoring. Clin. Ther. 44 (12), 1604–1623. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2022.10.005
Tang, D., Yan, M., Song, B. L., Zhao, Y. C., Xiao, Y. W., Wang, F., et al. (2021). Population pharmacokinetics, safety and dosing optimization of voriconazole in patients with liver dysfunction: a prospective observational study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 87 (4), 1890–1902. doi:10.1111/bcp.14578
Trubiano, J. A., Crowe, A., Worth, L. J., Thursky, K. A., and Slavin, M. A. (2015). Putting CYP2C19 genotyping to the test: utility of pharmacogenomic evaluation in a voriconazole-treated haematology cohort. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 70 (4), 1161–1165. doi:10.1093/jac/dku529
van den Born, D. A., Märtson, A. G., Veringa, A., Punt, N. C., van der Werf, T. S., Alffenaar, J. C., et al. (2023). Voriconazole exposure is influenced by inflammation: a population pharmacokinetic model. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 61 (4), 106750. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106750
van Wanrooy, M. J., Span, L. F., Rodgers, M. G., van den Heuvel, E. R., Uges, D. R., van der Werf, T. S., et al. (2014). Inflammation is associated with voriconazole trough concentrations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58 (12), 7098–7101. doi:10.1128/AAC.03820-14
Veringa, A., Geling, S., Span, L. F., Vermeulen, K. M., Zijlstra, J. G., van der Werf, T. S., et al. (2017). Bioavailability of voriconazole in hospitalised patients. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 49 (2), 243–246. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.10.010
Wang, L., Wang, Y., Hu, J., Sun, Y., Huang, H., Chen, J., et al. (2019). Clinical risk score for invasive fungal diseases in patients with hematological malignancies undergoing chemotherapy: china assessment of antifungal therapy in hematological diseases (CAESAR) study. Front. Med. 13 (3), 365–377. doi:10.1007/s11684-018-0641-0
Weiss, J., Ten Hoevel, M. M., Burhenne, J., Walter-Sack, I., Hoffmann, M. M., Rengelshausen, J., et al. (2009). CYP2C19 genotype is a major factor contributing to the highly variable pharmacokinetics of voriconazole. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 49 (2), 196–204. doi:10.1177/0091270008327537
Yan, M., Wu, Z. F., Tang, D., Wang, F., Xiao, Y. W., Xu, P., et al. (2018). The impact of proton pump inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of voriconazole in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 108, 60–64. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.121
Yasu, T., Konuma, T., Kuroda, S., Takahashi, S., and Tojo, A. (2018). Effect of cumulative intravenous voriconazole dose on renal function in hematological patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62 (9), e00507–18. doi:10.1128/AAC.00507-18
Zhou, L., Sharma, P., Yeo, K. R., Higashimori, M., Xu, H., Al-Huniti, N., et al. (2019). Assessing pharmacokinetic differences in Caucasian and East Asian (Japanese, Chinese and Korean) populations driven by CYP2C19 polymorphism using physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modelling. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 139, 105061. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2019.105061
Keywords: voriconazole, CYP2C19 phenotype, albumin-bilirubin grade, hematological patients, therapeutic drug monitoring
Citation: Hu L, Tang X, Li Y and Huang J (2025) Personalizing voriconazole dosing in Chinese hematological patients: CYP2C19 phenotype and albumin-bilirubin grade as key predictors of trough concentrations. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1667461. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1667461
Received: 17 July 2025; Accepted: 08 October 2025;
Published: 16 October 2025.
Edited by:
Kunlu Shen, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Hu, Tang, Li and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lin Hu, MTE1MDcyMTA3MUBxcS5jb20=; Juanjuan Huang, ODU1Mjk3MjZAcXEuY29t
 Lin Hu
Lin Hu Xi Tang
Xi Tang Yanfei Li
Yanfei Li Juanjuan Huang
Juanjuan Huang