- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Women and Children’s Hospital, Peking University People’s Hospital, Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong, China
- 2Qingdao Medical College, Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong, China
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong, China
Morphine remains a first-line analgesic for both acute and chronic pain. However, its prolonged use often results in the development of tolerance, diminishing its analgesic efficacy and limiting its long-term clinical utility. Emerging evidence highlights the pivotal role of microglial activation in the central nervous system as a key contributor to morphine tolerance. Phytochemicals, natural metabolites derived from plants, have garnered attention for their multi-target mechanisms, low toxicity, and broad biological activities, positioning them as promising candidates for mitigating morphine tolerance. This review systematically explores the key receptors and signaling pathways involved in microglial activation during morphine tolerance, and elucidates how various phytochemicals modulate these pathways to attenuate tolerance. Furthermore, it discusses the translational challenges associated with phytochemical-based interventions and outlines future directions for their clinical application. The aim is to provide a theoretical framework to support translational research and the development of novel adjunct therapies for opioid analgesia.
1 Introduction
Morphine, a classic opioid analgesic, remains the cornerstone drug for treating moderate to severe pain. However, its prolonged use is associated with a major and challenging side effect—morphine tolerance (Bekhit, 2010). Morphine tolerance refers to the phenomenon in which patients must gradually increase the drug dosage to maintain the initial level of analgesia. This not only diminishes the analgesic efficacy but also increases the risk of adverse effects, including nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression, and addiction (Ing Lorenzini et al., 2022). Consequently, a deeper understanding of morphine tolerance mechanisms and the discovery of effective countermeasures are urgently needed in pain pharmacology.
Traditionally, research on the mechanisms of morphine tolerance has primarily focused on neurons, particularly involving μ-opioid receptor (MOR) desensitization, internalization dysfunction, and compensatory upregulation of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling and other adaptive neuronal changes (Williams et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2023; Lim et al., 2005). However, accumulating evidence suggests that innate immune cells in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically microglia, play a crucial role in the development of morphine tolerance (Du et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2024). As the first line of immune defense in the CNS, microglia mediate neuroinflammatory responses by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), disrupting neuronal homeostasis and accelerating the development of morphine tolerance (Shen et al., 2012).
Currently, no drugs have been approved for clinical use specifically to prevent or reverse morphine tolerance. Conventional strategies, such as increasing opioid doses or rotating opioids, have limited efficacy and are associated with significant risks. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop new adjunctive therapies. In this context, phytochemicals, with their wide availability, structural diversity, favorable safety profiles, and capacity to regulate multiple biological targets, have emerged as valuable resources for novel drug development (Patridge et al., 2016). Preclinical evidence indicates that various phytochemicals, including flavonoids, alkaloids, and phenolics, can effectively inhibit the abnormal activation of microglia, thereby alleviating morphine tolerance in rodent models, demonstrating their great potential for further development.
Here we summarize the critical role of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in morphine tolerance, with a particular focus on summarizing recent research on phytochemicals that modulate microglial function to alleviate morphine tolerance. Additionally, the review discusses the limitations of current research and the challenges for clinical translation, aiming to provide new perspectives on the application of phytochemicals in the treatment of morphine tolerance.
2 Literature search methodology
A systematic search was conducted using PubMed and Web of Science, with a cutoff date of June 2025. The search strategy included keyword combinations such as “morphine tolerance,” “microglia,” “inflammation,” “natural compounds,” and “phytochemicals” to ensure the relevance and accuracy of the results. Studies included in this review were required to investigate the role of microglia in the mechanisms of morphine tolerance or to explore how phytochemicals alleviate morphine tolerance by targeting microglia. All included studies were published in peer-reviewed journals.
3 Microglia and morphine tolerance
Microglia, the resident immune cells of the CNS, are critical for maintaining neuroenvironmental homeostasis (Azam et al., 2021). In both humans and rodents, microglia originate from erythro-myeloid progenitors (EMPs) in the yolk sac, although the timing and processes of their development differ between species. In humans, EMPs emerge between gestational weeks 4 and 5, migrate from the meninges and the ventricular zone to the developing brain, and mature during later pregnancy stages. In rodents (e.g., mice), EMPs appear between embryonic days 7.5 and 9, colonize the brain via trans-tissue and transvascular routes, and rapidly differentiate into mature microglia (Chen et al., 2025). These developmental differences may contribute to variations in microglial function and their response mechanisms across species, thereby influencing their roles in disease.
Under normal physiological conditions, microglia are in a resting state, primarily conducting immune surveillance and providing neuroprotection through their elongated processes. Upon damage, infection, or inflammation in the nervous system, microglia rapidly become activated, with increased cell body size and shortened processes, adopting an ameboid morphology. Based on their activation states, microglia are typically classified into two types: classical pro-inflammatory activation (M1) and alternative anti-inflammatory activation (M2) (Depp et al., 2025). Although advanced techniques such as single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) have revealed the complexity and heterogeneity of microglial phenotypes, far beyond the traditional M1/M2 dichotomy, this classification remains widely used to describe their functional states. M1 microglia, through the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6), activate neuroinflammatory responses, which generally have a detrimental role in morphine tolerance. In contrast, M2 microglia promote tissue repair and neuroprotection through the secretion of anti-inflammatory factors (e.g., IL-10, TGF-β), which help alleviate morphine tolerance (Tu et al., 2021). Therefore, modulating the balance between M1 and M2 microglia is considered a potential therapeutic strategy for reducing morphine tolerance.
Moreover, microglia exhibit significant sex dimorphism in their functions, which may contribute to the sex differences observed in morphine tolerance. In rodent models, female mice are more susceptible to developing morphine tolerance than male mice (Gabel et al., 2023). Clinical studies also show that female patients typically require approximately 30% higher doses of morphine than male patients to achieve comparable analgesic effects (Averitt et al., 2019; Cepeda and Carr, 2003). However, existing studies on morphine tolerance have predominantly focused on male animal models. Future research on therapeutic strategies for morphine tolerance should incorporate sex as a variable to comprehensively assess drug efficacy and further elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
4 Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in morphine tolerance
4.1 Microglial receptors in morphine tolerance
Microglia are the primary immune cells mediating the brain’s inflammatory response. They express various receptors on both their surface and intracellular compartments, which are implicated in activation, migration, and phagocytosis. Morphine directly or indirectly activates these receptors, triggering multiple intracellular signaling pathways that result in the release of numerous cytokines, thereby promoting the development of morphine tolerance.
4.1.1 μ-opioid receptor (MOR)
The expression of MOR encoded by the Oprm1 gene in microglia remains controversial. Several studies provide strong evidence for the presence and function of MOR in microglia. Maduna et al. detected Oprm1 mRNA and MOR protein in microglia isolated from both rodents and humans (Maduna et al., 2018), directly confirming its existence. Further experiments by Reiss et al. demonstrated that specific knockout of MOR in microglia significantly delayed the development of morphine tolerance, with this effect consistently observed in both male and female mice, suggesting that microglial MOR plays a crucial role in regulating morphine tolerance (Reiss et al., 2022). Additionally, other studies have shown that morphine can activate a series of signaling pathways through MOR in microglia, particularly the MOR-protein kinase C epsilon (PKCε)-protein kinase B (Akt)-Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling axis, leading to upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and enhanced nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activity, which in turn promotes the release of nitric oxide (NO) and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α (Merighi et al., 2013; Gessi et al., 2016). These studies collectively support the expression of MOR in microglia and its involvement in morphine tolerance.
However, other studies have reached opposing conclusions. Kao et al. found that morphine still induced microglial activation in global MOR knockout mice (Kao et al., 2012). Corder et al. used high-sensitivity RNA sequencing and in situ hybridization techniques but detected no significant MOR expression in microglia, raising concerns regarding the accuracy and sensitivity of previous detection methods (Corder et al., 2017).
Despite the contradictory results in the existing literature, the majority of evidence supports the expression of MOR in microglia and its role in regulating morphine tolerance. However, to fully resolve this controversy and clarify the exact role of microglial MOR in morphine tolerance, future studies should employ more advanced and precise techniques. For example, scRNA-seq can reveal gene expression profiles of different microglial subpopulations, which will aid in accurately detecting MOR expression and addressing the confounding effects of microglial heterogeneity.
4.1.2 Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
TLRs are a class of glycoproteins located on the cell membrane, and studies have shown that microglia express all known TLRs (from TLR1 to TLR9) (Olson and Miller, 2004). Among these, TLR4 has been the most extensively studied in the context of morphine tolerance. Morphine can activate inflammatory signaling pathways by directly binding to the TLR4/MD-2 complex on microglial membranes (Hutchinson et al., 2010; Lewis et al., 2010). In addition, morphine indirectly activate the TLR4 signaling pathway in microglia by inducing neurons to release damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), such as high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) (Qian et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2023) and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) (Qu et al., 2017). Chronic morphine administration increases the expression of TCF7L2 in microglia, which further upregulates TLR4 expression through transcriptional regulation (Chen et al., 2021). Upon activation, TLR4 induces the expression of myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) in spinal cord tissue (Xu et al., 2014), which recruits the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) complex and activates the transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) signaling pathway, leading to the phosphorylation of IκB and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Phosphorylation of IκB promotes the nuclear translocation of NF-κB, while MAPK activation triggers the transcription factor AP-1 (Bai et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2021). Moreover, PKCε is a critical downstream target of TLR4. High doses of morphine activate the PKCε-Akt-ERK1/2 signaling cascade through a TLR4-dependent mechanism, enhancing the transcriptional activity of NF-κB (Merighi et al., 2013). These signaling pathways collectively promote the generation and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby exacerbating the inflammatory response. However, some studies have suggested that microglial activation in morphine tolerance may not be dependent on the TLR4 signaling pathway (Mattioli et al., 2014; Fukagawa et al., 2013), which may be attributed to differences in the mouse strains and animal models used.
In addition to TLR4, TLR2 is also involved in morphine-induced microglial activation (Zhang et al., 2011). During the development of morphine tolerance, TLR2 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome through the MyD88-dependent pathway, thereby mediating neuroinflammatory responses (Peng et al., 2023). TLR3 is an endosomal receptor that recognizes double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and plays a unique role in chronic morphine tolerance. Morphine downregulates adenosine deaminase RNA-specific 1 (ADAR1) in neurons, leading to the accumulation of dsRNA. Subsequently, this accumulated dsRNA is taken up by microglia via exosomes, activating the TLR3-TRIF pathway and promoting the release of inflammatory mediators and exacerbating morphine tolerance (Wang B. et al., 2024).
Thus, multiple members of the TLR family may play a critical role in the development of morphine tolerance. Future studies should further explore the mechanisms underlying the involvement of these receptors in morphine tolerance to provide new insights for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
4.1.3 P2X purinergic receptors (P2XRs)
P2XRs are ligand-gated ion channels that primarily respond to ATP. Among these receptors, P2X4R and P2X7R are involved in the development of morphine tolerance by modulating microglial activation. These two receptors exhibit significant differences in their sensitivity to ATP: P2X4R is activated at lower ATP concentrations (≤0.1 mM), whereas P2X7R typically requires higher ATP concentrations (≥1.0 mM) for activation (Asatryan et al., 2018). This concentration-dependent difference has been confirmed in human and mouse microglia.
Under physiological conditions, P2X7R typically remains in an inactive state. Chronic morphine exposure increases glutamate levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (Wen et al., 2004), triggering ATP release from spinal cord glial cells through an α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR)-mediated, Ca2+-dependent route (Liu G. J. et al., 2006). This creates a local microenvironment with elevated ATP concentrations, which activates P2X7R. Activation of P2X7R further promotes the release of ATP and glutamate (Suadicani et al., 2006), establishing a positive feedback loop. Furthermore, morphine can specifically phosphorylate the Y382-384 site in the C-terminal domain of P2X7R via the MOR-Src kinase signaling pathway, significantly enhancing P2X7R channel activity in microglia (Leduc-Pessah et al., 2017). Therefore, developing small molecule inhibitors targeting this phosphorylation site could offer a potential therapeutic strategy for morphine tolerance. Notably, gene knockout and pharmacological inhibition studies have shown that P2X7R primarily participates in the induction phase of morphine tolerance, rather than its maintenance phase (Wang H. et al., 2020).
P2X4R also plays a critical role in morphine tolerance. Intrathecal injection of P2X4R antisense oligonucleotides significantly delays the onset of morphine tolerance (Horvath et al., 2010). Moreover, TLR4 signaling may contribute to the upregulation of P2X4R in microglia. Specifically, morphine enhances the membrane trafficking of P2X4R by promoting TLR4-mediated endocytosis, thereby increasing the release of inflammatory factors such as IL-1β (Liang et al., 2016).
In summary, P2XRs interact with signaling pathways such as AMPAR and TLR4, establishing a feedback network that leads to an imbalance between neuronal excitation and inhibition. Targeted interventions on P2XRs can effectively disrupt the positive feedback loop between microglia and neurons, providing a novel therapeutic strategy for alleviating morphine tolerance in clinical settings.
4.1.4 Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
RTKs are transmembrane receptors that regulate essential physiological and pathological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, metabolism, and immune responses.
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is involved in the development of morphine tolerance in various rodent models, including the cancer-induced bone pain rat model (Yang et al., 2021) and the spinal nerve ligation rat model (Puig et al., 2020). Studies have shown that gefitinib, a clinically approved EGFR inhibitor, effectively prevents and reverses morphine tolerance in rats (Puig et al., 2020). EGFR may play a role in the development of morphine tolerance by binding to its ligands, such as TNF-α, and activating ERK and other downstream signaling pathways.
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor β (PDGFRβ) is another important member of the RTK family. Studies have shown that inhibiting the PDGFRβ signaling pathway can reverse morphine-induced analgesic tolerance (Wang et al., 2012). Additionally, RTKs interact with members of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, including MOR. Morphine acts on MOR to activate the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling cascade, thereby promoting the phosphorylation of PDGFRβ (Li et al., 2020). The activated PDGFRβ then induces autophagy in GABAergic inhibitory interneurons in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord via its downstream p38 MAPK signaling pathway (Jia et al., 2021), which may facilitate central sensitization by reducing the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters.
In summary, RTKs such as EGFR and PDGFRβ play key roles in the development of morphine tolerance. The clinically approved EGFR inhibitor gefitinib could be translated into clinical strategies, offering a precise and efficient intervention for blocking tolerance.
4.2 Signaling pathways regulating microglial activation in morphine tolerance
4.2.1 Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway
The MAPK family includes ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK (Chen and Sommer, 2009), with p38 MAPK playing a pivotal role in the mechanism of morphine tolerance. After repeated intrathecal morphine administration in rats, the number of phosphorylated p38-immunoreactive cells in laminae I-IV of the spinal dorsal horn increases significantly by day 3 and remains elevated until at least day 7. Double-labelling immunohistochemistry revealed that the majority of these cells were microglia (Cui et al., 2006). Consistently, the microglial inhibitor minocycline significantly attenuates morphine tolerance by inhibiting p38 activity. In addition to TLR4, both P2X7R (Zhou et al., 2010) and PDGFRβ (Jia et al., 2021) can trigger downstream cascades, ultimately leading to p38 phosphorylation in microglia. In parallel, sustained morphine exposure potentiates microglial p38 signaling through several convergent mechanisms, including upregulation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Pellino one in microglia (Wang L. et al., 2020), lysosomal release of cathepsin S (CTSS) (Xiao et al., 2019), and neuronal production of NO (Liu W. et al., 2006), along with the release of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) (Wang et al., 2010a; Wang et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2010b). Activated p38 subsequently enhances NF-κB transcriptional activity through phosphorylation of the p65 subunit, promoting the expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6. This ultimately exacerbates neuroinflammation and accelerates morphine tolerance. Therefore, selective inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway may represent a potential therapeutic target for mitigating morphine tolerance.
4.2.2 NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) signaling pathway
The NLRP3 inflammasome, composed of the receptor NLRP3, the adaptor protein ASC, and the inactive pro-caspase-1, serves as a core platform for amplifying inflammatory signals in the innate immune system. Morphine triggers its assembly through two primary pathways: first, morphine directly activates TLR4/TLR2, inducing a conformational change in NLRP3, leading to its oligomerization (Wang et al., 2021; Peng et al., 2023); second, morphine activates the P2X7R channel, causing K+ efflux, and the resulting low intracellular K+ concentration further stabilizes the NLRP3 oligomer (Wang H. et al., 2020). Additionally, morphine-induced mitochondrial dysfunction generates large amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and promotes lysosomal rupture, releasing cathepsin B (CTSB) (Liu et al., 2020; Hayashi et al., 2014). These danger signals collectively function as a second stimulus, recruiting ASC and activating pro-caspase-1, ultimately leading to its cleavage. The activated caspase-1 processes pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into their mature forms and rapidly releases them, further amplifying neuroinflammation, enhancing synaptic plasticity abnormalities, and thereby accelerating the development of morphine tolerance. Therefore, targeting the activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome may be a key strategy for mitigating morphine tolerance.
4.2.3 AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway
AMPK is a cellular energy sensor that is activated when the AMP/ATP or ADP/ATP ratio increases. Recent studies have revealed that this “energy switch” also regulates neuroinflammation: its agonist, metformin, significantly delays morphine tolerance by inhibiting the excessive activation of microglia (Pan et al., 2016). In addition, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) serves as a negative regulator of microglial activation. Lidocaine enhances AMPK phosphorylation via a calcium-dependent protein kinase kinase β (CaMKKβ)-dependent pathway, upregulating SOCS3 expression, which in turn suppresses the release of IL-1β and TNF-α, alleviating morphine tolerance (Zhang et al., 2017). On the other hand, AMPK-mediated autophagy activation degrades DICER and AGO2, thereby blocking the maturation of miR-30a-5p, which upregulates SOCS3 and further suppresses inflammatory signaling (Wan et al., 2022). Therefore, the cross-regulatory role of AMPK in energy metabolism and inflammation may provide new perspectives for alleviating neuroinflammation and mitigating morphine tolerance.
In conclusion, the receptors and signaling pathways discussed above play a crucial role in the progression of morphine tolerance by driving microglial activation and amplifying inflammatory responses. An overview of the microglial signaling pathways associated with morphine tolerance is shown in Figure 1.
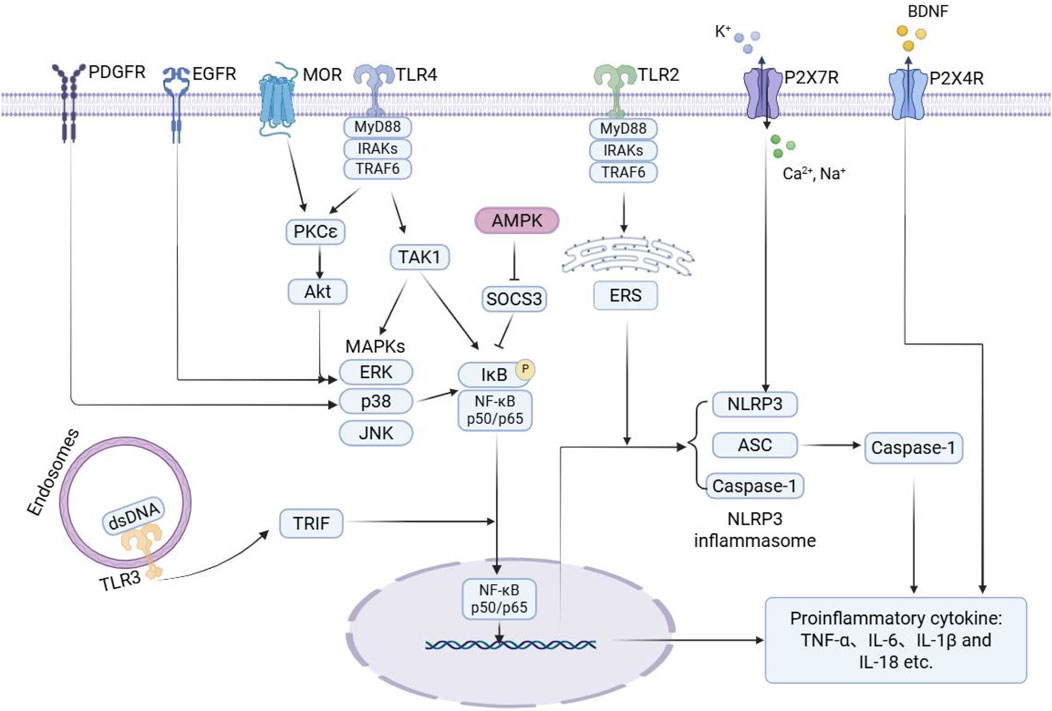
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of microglial signaling pathways associated with morphine tolerance. During the development of morphine tolerance, morphine activates key receptors on microglia, directly or indirectly, such as MOR, TLRs, P2XRs, and RTKs. This activation then triggers downstream signaling pathways, including MAPK, NF-κB, NLRP3, and AMPK. The activation of these pathways promotes the release of various pro-inflammatory mediators from microglia, thereby exacerbating neuroinflammation and contributing to the onset of morphine tolerance. Arrows indicate activation, and blunt-ended lines represent inhibition. PDGFR: platelet-derived growth factor receptor; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; MOR: μ-opioid receptor; TLR: toll-like receptor; P2X7R: purinergic P2X7 receptor; P2X4R: purinergic P2X4 receptor; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary response 88; IRAKs: interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases; TRAF6: TNF receptor-associated factor 6; PKCε: protein kinase C epsilon; Akt: protein kinase B; TAK1: transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; SOCS3: suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; ERS: endoplasmic reticulum stress; MAPKs: mitogen-activated protein kinases; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; IκB: inhibitor of kappa B; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor protein 3; ASC: apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; TRIF: TIR-domain containing adaptor inducing interferon-β; dsDNA: double-stranded DNA; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α.
4.3 Cytokines mediating interactions between microglia, astrocytes, and neurons
Upon activation of signaling pathways in microglia, a variety of cytokines are released, transmitting inflammatory signals to astrocytes and neurons in the microenvironment. This cytokine-mediated intercellular interaction plays a pivotal role in the development of morphine tolerance.
On one hand, prolonged morphine use activates microglia, prompting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-18, and complement C1q subcomponent subunit A (C1qA). These inflammatory mediators drive astrocytes to transition to a neurotoxic A1 phenotype. Complement C3 (C3) secreted by A1 astrocytes further activates microglia by binding to C3a receptors (C3aR), creating a positive feedback loop that exacerbates neuroinflammation (Peng et al., 2025). Meanwhile, D-serine released by activated astrocytes promotes morphine tolerance by activating N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) on neurons and triggering the PKCγ signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2012).
On the other hand, cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 secreted by microglia not only upregulate the expression and activity of neuronal MOR, forming a “neuroinflammation-MOR overactivation” positive feedback loop (Cuitavi et al., 2024), but also significantly interfere with glutamatergic neurotransmission. Studies have shown that the TNF-α inhibitor etanercept restores the functional expression of glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST and downregulates the overactivated AMPA and NMDA receptor subunits (Shen et al., 2011). Additionally, microglia can release brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which binds to the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), activating downstream pathways such as MAPK/ERK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt. This upregulates the transcription and expression of vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGluT2), promoting glutamate release and increasing spinal cord neuronal excitability (He et al., 2022).
In summary, microglia play a vital role in the development of morphine tolerance by mediating complex interactions among neuroimmune cells. The signaling network established between microglia, astrocytes, and neurons through cytokines is a key mechanism driving synaptic dysfunction, central sensitization, and the progression of morphine tolerance (Figure 2).
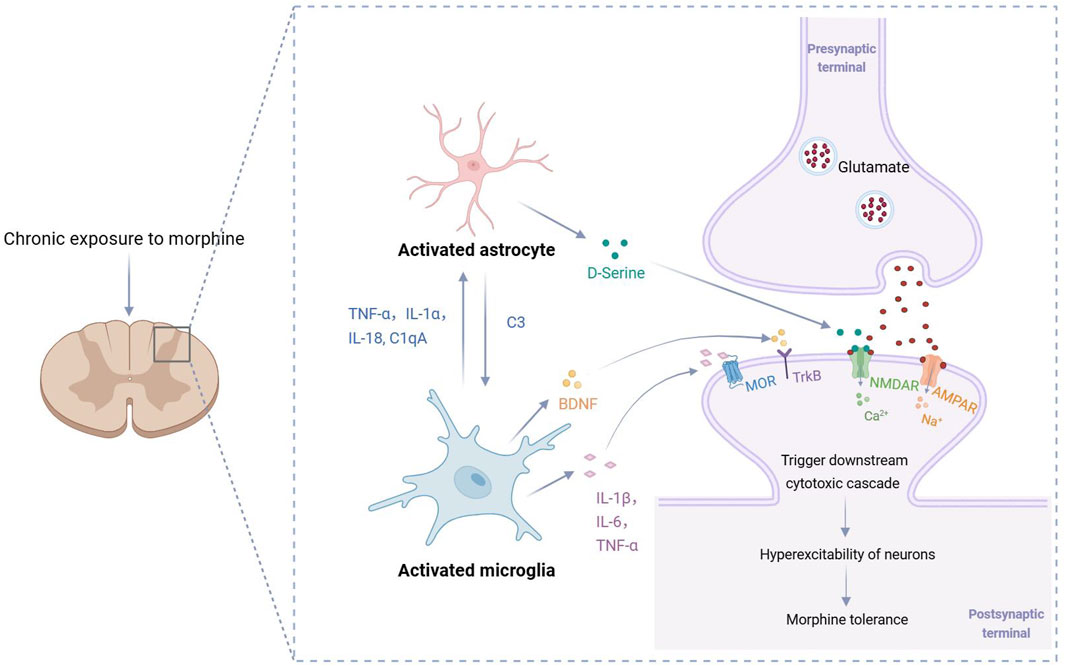
Figure 2. Cytokine-mediated mechanisms of morphine tolerance. Excessive activation of microglia releases cytokines that activate astrocytes, which in turn further activate microglia and amplify the inflammatory cascade. Additionally, the cytokines released by activated microglia and astrocytes (such as IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, D-serine and BDNF) collectively contribute to the excessive excitation of dorsal horn neurons in the spinal cord, thereby promoting the onset and progression of morphine tolerance. C1qA: complement C1q subcomponent subunit A; C3: complement C3; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; MOR: μ-opioid receptor; TrkB: tropomyosin receptor kinase B; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; AMPAR: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor.
5 Phytochemicals alleviate morphine tolerance by modulating microglial activity
In recent years, phytochemicals have demonstrated significant potential in alleviating morphine tolerance due to their multi-target effects, high safety profile, and effective neuroimmune modulation. Several phytochemicals have been shown to delay the onset and progression of morphine tolerance by regulating microglial function (Table 1; Figure 3). Here we systematically overview these findings.
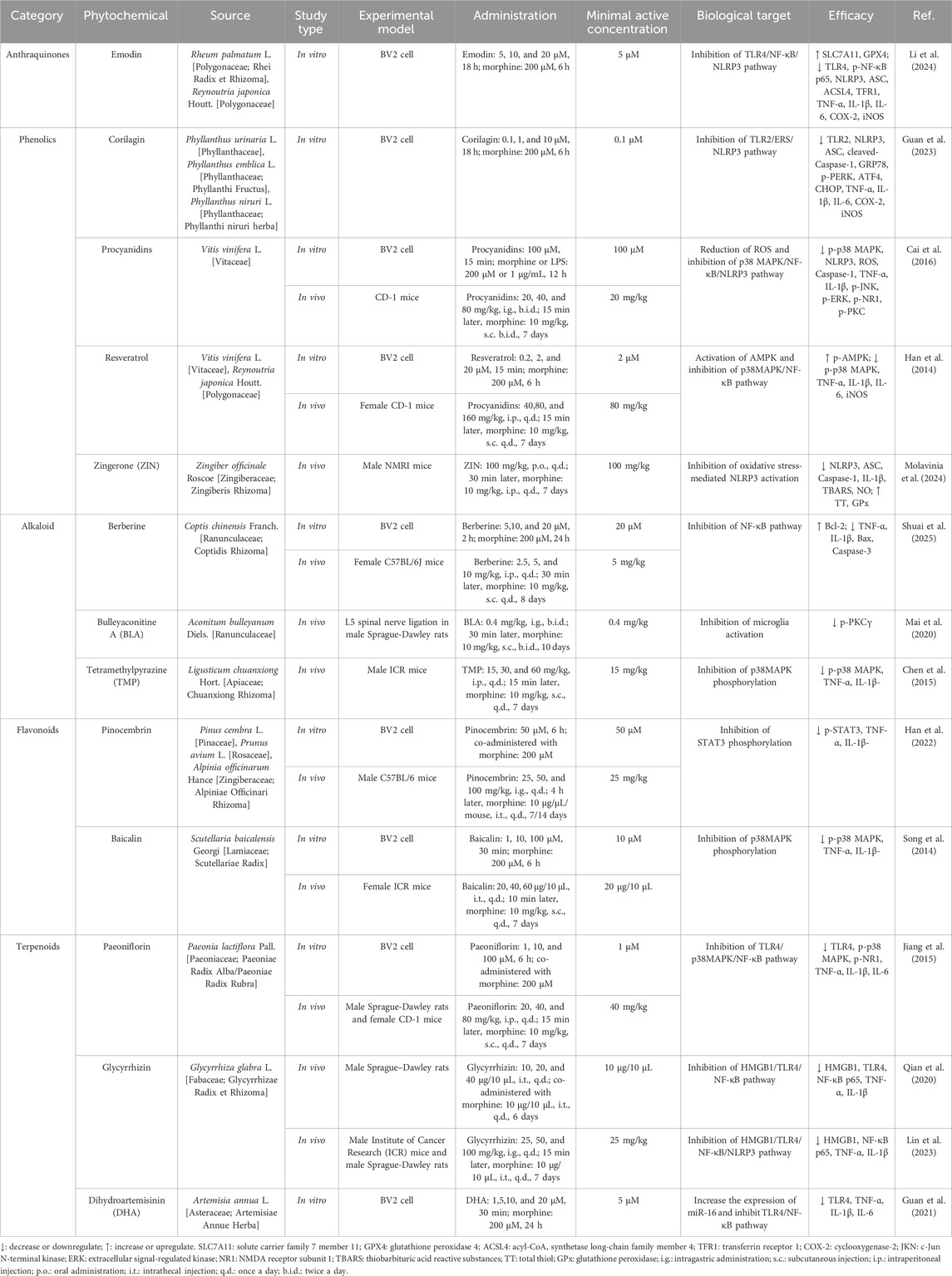
Table 1. Phytochemicals alleviate morphine tolerance by regulating microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in preclinical studies.
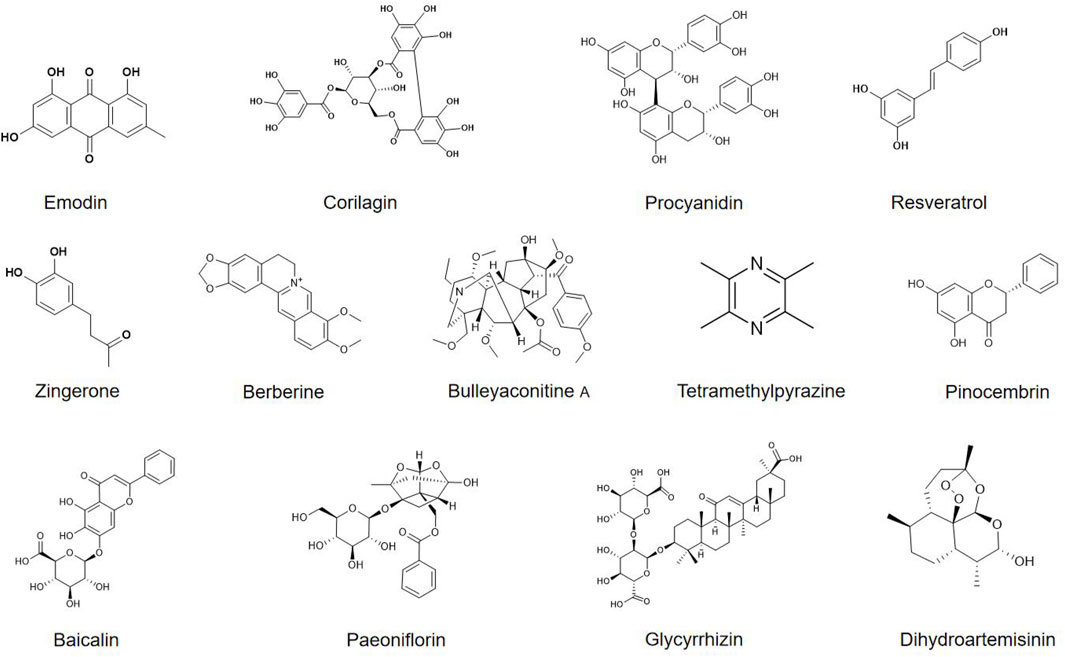
Figure 3. Chemical structures of phytochemicals that target microglia for alleviating morphine tolerance.
5.1 Anthraquinones
Emodin (C15H10O5) is a natural anthraquinone primarily found in medicinal plants such as Rheum palmatum L. and Reynoutria japonica Houtt. It’s medicinal application history is over 2,000 years (Mitra et al., 2022). Modern pharmacological studies have shown that emodin possesses various bioactivities, including cardioprotective, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory effects (Zheng et al., 2021). Li et al. predicted a potential interaction between emodin and TLR4 through molecular docking and confirmed in BV2 microglial cells that emodin can block the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway, inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation, thereby reducing morphine-induced neuroinflammation (Li et al., 2024). However, these findings at the cellular level still need further validation in animal models.
5.2 Phenolics
Corilagin (C27H22O18) is a water-soluble natural tannin predominantly found in plants of the Phyllanthus genus, such as Phyllanthus urinaria L., Phyllanthus emblica L., and Phyllanthus niruri L. Modern pharmacological studies have confirmed its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor activities (Wang et al., 2023). Guan et al. used molecular docking to predict that corilagin binds to TLR2 with an affinity of −5.4 kcal/mol (moderate binding). In BV2 cells, corilagin downregulates TLR2, thereby blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation, ultimately attenuating morphine-induced microglial overactivation (Guan et al., 2023). However, these cellular-level findings require further validation in animal models to confirm their translational relevance.
Procyanidin (C30H26O13) is a natural polyphenol widely distributed in plants. It is a condensed tannin formed by polymerization of flavan-3-ol monomers, with Vitis vinifera L. being the most abundant source (Wang Y. et al., 2024). Procyanidin possesses potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities and a high safety profile, with a maximum tolerated dose of 2,500 mg/day for adults (Sano, 2017), making it widely used as a dietary supplement. In mouse studies, Cai and colleagues demonstrated that procyanidin can alleviate the development of chronic morphine tolerance. The underlying mechanism involves the inhibition of p38 MAPK phosphorylation, blockade of p65 NF-κB nuclear translocation, and subsequent suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome activation, thereby reducing neuroinflammation. Additionally, procyanidin significantly decreases morphine-induced ROS levels (Cai et al., 2016). These findings suggest that procyanidin holds strong therapeutic potential for mitigating morphine tolerance through modulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling pathways.
Resveratrol (C14H12O3) is a natural polyphenol found abundantly in Vitis vinifera L. and Reynoutria japonica Houtt. It exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and neuroprotective effects (Radeva and Yoncheva, 2025). Animal studies have shown that resveratrol significantly attenuates chronic morphine tolerance (Tsai et al., 2016; Tsai et al., 2012). Mechanistically, resveratrol activates AMPK, suppresses the downstream p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway, and thereby reduces microglia-mediated neuroinflammation, delaying the development of morphine tolerance (Han et al., 2014).
Zingerone (ZIN, C11H14O3) is a natural phenolic primarily extracted from Zingiber officinale Roscoe. It exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory activities (Rashpa et al., 2025). ZIN has a favorable safety profile, with an oral LD50 of 657.55 mg/kg in mice. In animal studies, co-administration of ZIN with morphine significantly prolongs the thermal nociceptive latency, enhancing and sustaining the analgesic effect of morphine. The underlying mechanism may involve the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation, which is induced by oxidative stress (Molavinia et al., 2024).
5.3 Alkaloids
Berberine (C20H18NO4+) is a typical isoquinoline alkaloid primarily extracted from Coptis chinensis Franch. It exhibits a variety of pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, immunomodulatory, and antimicrobial activities. In recent years, several in vivo studies have demonstrated that berberine effectively inhibits the development of analgesic tolerance induced by prolonged morphine administration (Shuai et al., 2023; Yoo et al., 2006). Han et al. further elucidated the underlying mechanism through in vitro experiments, showing that berberine inhibits morphine-induced activation of BV2 cells, suppresses NF-κB signaling to reduce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and mitigates morphine-induced apoptosis by regulating apoptosis-related proteins, including upregulating Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax and Caspase-3 (Shuai et al., 2025). These findings provide important insights into the pharmacological mechanisms of berberine in attenuating morphine tolerance.
Bulleyaconitine A (BLA, C35H49NO9) is a C19-diterpenoid alkaloid isolated from Aconitum bulleyanum Diels., known for its potent analgesic activity (Zhao et al., 2021). Since 1985, BLA has been widely used in China for the treatment of chronic pain. Multiple studies have demonstrated that oral administration of BLA effectively alleviates various types of chronic pain, with favorable safety and tolerability profiles (Xie et al., 2018). In a rat model of neuropathic pain induced by L5 spinal nerve ligation (L5-SNL), BLA delayed the development of morphine tolerance. The underlying mechanism may involve the inhibition of PKCγ phosphorylation in spinal dorsal horn neurons, as well as the attenuation of abnormal activation of microglia and astrocytes (Mai et al., 2020). However, the precise mechanisms by which BLA inhibits microglia-mediated inflammatory responses remain to be fully elucidated.
Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP, C8H12N2) is the principal alkaloid isolated from the rhizome of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort., and has been documented in the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing for its ability to activate blood circulation and relieve pain (Lin et al., 2022). Modern studies have shown that TMP not only exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects but also crosses the blood-brain barrier, exerting pharmacological actions within the central nervous system. Chen et al. have suggested that TMP may delay the onset of morphine tolerance by inhibiting the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in microglial cells, thereby reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β (Chen et al., 2015).
5.4 Flavonoids
Pinocembrin (C15H12O4) is a naturally occurring flavonoid found in plants such as Pinus cembra L., Prunus avium L., and Alpinia officinarum Hance. It readily crosses the blood–brain barrier and exhibits broad pharmacological activities, including antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer activities (Gong et al., 2020). In mouse models of chronic morphine exposure, Han et al. demonstrated that pinocembrin not only prevents the development of morphine tolerance but also reverses established tolerance. The underlying mechanism appears to involve the inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) phosphorylation in microglia, leading to the downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β, attenuation of neuroinflammation, and restoration of morphine analgesic efficacy (Han et al., 2022).
Baicalin (C21H18O11) is a flavonoid isolated from the dried roots of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. It exhibits a wide range of pharmacological activities, including antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, sedative, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective effects (Wen et al., 2025). Song et al. found that baicalin significantly alleviates morphine tolerance. The underlying mechanism may involve the inhibition of aberrant p38 MAPK signaling pathway activation, thereby reducing morphine-induced microglial overactivation (Song et al., 2014).
5.5 Terpenoids
Paeoniflorin (C23H28O11) is a water-soluble monoterpene glycoside extracted from the roots of Paeonia lactiflora Pall., known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and neuroprotective effects (Hong et al., 2022). In a mouse model of morphine tolerance, Jiang et al. demonstrated that paeoniflorin significantly attenuates the development of morphine tolerance. The underlying mechanisms include downregulation of TLR4 expression, inhibition of p38 MAPK phosphorylation, and blockade of NF-κB nuclear translocation, collectively reducing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (Jiang et al., 2015).
Glycyrrhiza glabra L. is a cornerstone medicinal plant in traditional Chinese medicine with a long clinical history. The Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing documented its ability to tonify the heart and spleen and to harmonize the flow of Qi (vital energy), and it has been traditionally used for pain relief, expectoration, and cough suppression (Wahab et al., 2021). Glycyrrhizin (C42H62O16), the principal active metabolite of its root, has been shown to attenuate morphine tolerance in animal models. Chronic morphine administration induces spinal neurons to release HMGB1, which activates the microglial TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling axis, thereby fostering tolerance. Glycyrrhizin inhibits HMGB1, blocking this pathway, reducing neuroinflammation, and restoring the analgesic efficacy of morphine (Qian et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2023).
Dihydroartemisinin (DHA, C15H24O5) is a reduced derivative of artemisinin isolated from Artemisia annua L. and belongs to the sesquiterpene lactone family. Although widely used as a first-line antimalarial, DHA also exhibits immunomodulatory, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory activities (Yu et al., 2021). Guan et al. demonstrated in vitro that DHA upregulates miRNA-16, thereby suppressing overactivation of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway and attenuating morphine-induced BV2 microglial inflammation, which in turn attenuates the development of morphine tolerance (Guan et al., 2021). However, these cellular findings still need further validation in animal models.
6 Clinical translational challenges and strategies of phytochemicals in treating morphine tolerance
Although phytochemicals demonstrate significant therapeutic potential in alleviating morphine tolerance, several challenges remain in translating them into clinical practice.
6.1 Optimization of pharmacokinetics and nanocarrier delivery
Phytochemicals often face significant pharmacokinetic challenges, such as poor solubility, rapid metabolism, and low bioavailability, which severely limit their clinical application. For example, emodin is rapidly metabolized into its glucoside form in the body, losing its bioactivity and significantly reducing its bioavailability, thereby restricting its clinical use (Sharifi-Rad et al., 2022). Similarly, DHA, due to its unique structure, exhibits poor water solubility and low bioavailability, often requiring multiple injections to achieve the desired therapeutic effect (Dai et al., 2021). The advent of nanoparticle delivery systems provides a practical solution to these issues. Technologies such as liposomes, nanoparticles, polymeric micelles, and nanogels can effectively improve the in vivo distribution properties of drugs and enhance targeted delivery efficiency. For instance, recent preclinical studies have shown that nanoformulated berberine not only retained its antitumor activity comparable to conventional therapies but also reduced the required dose to one-tenth of the traditional dosage, significantly reducing gastrointestinal side effects (Sun et al., 2024). Additionally, several studies have demonstrated that nanocarrier technologies can effectively reduce the toxicity of phytochemicals (Ai et al., 2025; Zhao et al., 2020). Therefore, the continued development and refinement of nanoparticle-based delivery systems are crucial for enhancing the clinical utility of phytochemicals in the treatment of morphine tolerance.
6.2 Advancement of clinical evidence and translational research
Clinical research on phytochemicals for the treatment of morphine tolerance remains scarce, lacking large-scale, high-quality clinical trial data. This has become a major bottleneck for their clinical translation, as their efficacy and safety have not been fully validated. Fortunately, some phytochemicals have gradually entered clinical trial phases. For example, a Phase I clinical trial involving 58 healthy participants demonstrated that intravenous administration of glucosides (maximum daily dose of 120 mg) have acceptable safety and tolerability (Cao et al., 2015). Glycyrrhizin, the main active metabolite of Glycyrrhiza glabra L., has been recognized for its safety by the Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives of the World Health Organization (Huan et al., 2021). In addition, some phytochemicals have entered the market in the form of dietary supplements. For example, resveratrol has long been considered to have potential health benefits, with approximately 6,000 participants from different age groups (including children and the elderly) involved in related trials. Although resveratrol has demonstrated good tolerability at doses up to 1 g/day, standardized dosing regimens for specific diseases or therapeutic targets have yet to be established (Brown et al., 2024). Therefore, to promote the clinical application of phytochemicals in alleviating morphine tolerance, large-scale, multi-center, randomized controlled clinical trials are warranted. Through rigorous study designs and sound statistical analysis methods, their efficacy and safety should be evaluated systematically, reliable clinical evidence could provid a solid foundation for their eventual clinical application.
6.3 Enhancement of safety and risk mitigation
Although phytochemicals are widely studied and appreciated for their natural origin and relatively mild side effects, their potential toxicity risks cannot be ignored. For instance, BLA, a potent analgesic, is widely used in the treatment of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and lumbosacral pain. However, its application is often accompanied by adverse reactions such as nausea, palpitations, and rashes (Li et al., 2022). Similarly, although emodin has a wide range of pharmacological activities and is considered a promising phytochemical, studies have shown that it may induce hepatocyte apoptosis, cause renal damage, and lead to reproductive dysfunction (Chen et al., 2024). Therefore, before clinical advancement of phytochemicals, comprehensive and systematic toxicological studies must be conducted. These should include assessments of acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, genotoxicity, and reproductive toxicity, to determine safe dosage ranges and provide reliable scientific evidence for their safe clinical use.
6.4 Improvement of standardization and quality assurance
Standardization and stringent quality control are the cornerstones for the sustainable clinical application of phytochemicals. Given the diverse sources and complex compositions of phytochemicals, it is crucial to establish systematic quality standards and standardized dosing regimens. Modern analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry should be employed to comprehensively characterize candidate compounds and accurately identify active constituents, thereby facilitating the optimization of their bioavailability and dosing strategies. Additionally, it is essential to develop regulatory frameworks that comply with international standards, clearly defining the requirements for the production, quality assessment, and clinical use of phytochemicals to ensure their safety and efficacy.
7 Conclusions and prospects
Currently, there is still no fully effective treatment for morphine tolerance in clinical practice, prompting researchers to investigate phytochemicals as potential therapeutic strategies. Morphine tolerance involves is driven by a complex interplay of mechanisms, including neuroinflammation, aberrant microglial activation, and alterations in neural plasticity. Due to their multi-target and multi-pathway regulatory properties, phytochemicals align well with the “single drug-multiple targets” therapeutic concept, and thus demonstrate unique therapeutic potential.
This review highlights that phytochemicals can effectively alleviate morphine tolerance by inhibiting microglial activation and the subsequent neuroinflammatory response. Notably, different types of phytochemicals may target similar signaling pathways, with TLRs and their downstream NF-κB and MAPK pathways being the most commonly regulated targets. Nevertheless, further research is required to comprehensively elucidate the multi-target mechanisms of phytochemicals, which will provide a more robust theoretical foundation for their clinical application in the treatment of morphine tolerance.
Through a systematic analysis of the current literature, we identified key limitations in the existing research: (1) Most studies use male animal models, without adequately accounting for sex differences in drug efficacy. Future studies should incorporate gender factors to assess the therapeutic potential of phytochemicals more comprehensively. (2) Pain models not mimicking clinical conditions well enough. It is necessary to establish pain models that more closely resemble clinical conditions in order to enhance the clinical translation value of the findings. (3) Phytochemicals commonly face challenges such as low bioavailability, poor pharmacokinetic properties, potential toxicity, and unclear drug interactions. Addressing these challenges is crucial for advancing their clinical application.
Encouragingly, the rapid development of artificial intelligence technologies has led to significant progress in, receptor-ligand interaction prediction, particularly through molecular docking approaches. These developments offer new avenues for investigating the structure-activity relationships of phytochemicals and for designing efficient, low-toxicity derivatives. Moving forward, research should not only deepen our understanding of the mechanisms underlying phytochemical actions but also address key technological bottlenecks in clinical translation, thereby promoting more precise, standardized, and practical applications in the treatment of morphine tolerance.
Author contributions
RS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Visualization. TJ: Writing – review and editing, Investigation. WX: Writing – review and editing, Investigation. YL: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Project No. ZR2023MH270 supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation.
Acknowledgements
The figures were created using www.biorender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ai, Z., Liu, B., Chen, J., Zeng, X., Wang, K., Tao, C., et al. (2025). Advances in nano drug delivery systems for enhanced efficacy of emodin in cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. X 9, 100314. doi:10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100314
Asatryan, L., Ostrovskaya, O., Lieu, D., and Davies, D. L. (2018). Ethanol differentially modulates P2X4 and P2X7 receptor activity and function in BV2 microglial cells. Neuropharmacology 128, 11–21. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.09.030
Averitt, D. L., Eidson, L. N., Doyle, H. H., and Murphy, A. Z. (2019). Neuronal and glial factors contributing to sex differences in opioid modulation of pain. Neuropsychopharmacology 44, 155–165. doi:10.1038/s41386-018-0127-4
Azam, S., Haque, M. E., Kim, I. S., and Choi, D. K. (2021). Microglial turnover in ageing-related neurodegeneration: therapeutic avenue to intervene in disease progression. Cells 10, 150. doi:10.3390/cells10010150
Bai, L., Zhai, C., Han, K., Li, Z., Qian, J., Jing, Y., et al. (2014). Toll-like receptor 4-mediated nuclear factor-κB activation in spinal cord contributes to chronic morphine-induced analgesic tolerance and hyperalgesia in rats. Neurosci. Bull. 30, 936–948. doi:10.1007/s12264-014-1483-7
Bekhit, M. H. (2010). Opioid-induced hyperalgesia and tolerance. Am. J. Ther. 17, 498–510. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ed83a0
Brown, K., Theofanous, D., Britton, R. G., Aburido, G., Pepper, C., Sri Undru, S., et al. (2024). Resveratrol for the management of human health: how far have we come? A systematic review of resveratrol clinical trials to highlight gaps and opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 747. doi:10.3390/ijms25020747
Cai, Y., Kong, H., Pan, Y. B., Jiang, L., Pan, X. X., Hu, L., et al. (2016). Procyanidins alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. J. Neuroinflammation 13, 53. doi:10.1186/s12974-016-0520-z
Cao, G., Ying, P., Yan, B., Xue, W., Li, K., Shi, A., et al. (2015). Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of single and multiple-doses of pinocembrin injection administered intravenously in healthy subjects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 168, 31–36. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.041
Cepeda, M. S., and Carr, D. B. (2003). Women experience more pain and require more morphine than men to achieve a similar degree of analgesia. Anesth. Analg. 97, 1464–1468. doi:10.1213/01.Ane.0000080153.36643.83
Chen, Y., and Sommer, C. (2009). The role of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in morphine tolerance and dependence. Mol. Neurobiol. 40, 101–107. doi:10.1007/s12035-009-8074-z
Chen, M. L., Cao, H., Chu, Y. X., Cheng, L. Z., Liang, L. L., Zhang, Y. Q., et al. (2012). Role of P2X7 receptor-mediated IL-18/IL-18R signaling in morphine tolerance: multiple glial-neuronal dialogues in the rat spinal cord. J. Pain 13, 945–958. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2012.06.007
Chen, L., Li, J., Pan, C., Zhou, D., Liu, W., and Zhang, G. (2015). Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates morphine tolerance through suppressing spinal microglia activation in mice. J. China Pharm. Univ. 46, 230–234. Available online at: https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/wpr-811939.
Chen, J., Wang, G., Sun, T., Ma, C., Huo, X., and Kong, Y. (2021). Involvement of TCF7L2 in generation of morphine-induced antinociceptive tolerance and hyperalgesia by modulating TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 in microglia. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 416, 115458. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2021.115458
Chen, R., Zhang, H., Zhao, X., Zhu, L., Zhang, X., Ma, Y., et al. (2024). Progress on the mechanism of action of emodin against breast cancer cells. Heliyon 10, e38628. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38628
Chen, C., Qiao, G., Tang, D., Xu, F., Dong, J., Zhang, J., et al. (2025). Repopulation of microglia and its implications for CNS disorders: insights from the single-cell era. Neurobiol. Dis. 215, 107066. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2025.107066
Corder, G., Tawfik, V. L., Wang, D., Sypek, E. I., Low, S. A., Dickinson, J. R., et al. (2017). Loss of μ opioid receptor signaling in nociceptors, but not microglia, abrogates morphine tolerance without disrupting analgesia. Nat. Med. 23, 164–173. doi:10.1038/nm.4262
Cui, Y., Chen, Y., Zhi, J. L., Guo, R. X., Feng, J. Q., and Chen, P. X. (2006). Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in spinal microglia mediates morphine antinociceptive tolerance. Brain Res. 1069, 235–243. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.11.066
Cuitavi, J., Duart-Abadia, P., Sanchez, J., Sánchez-López, C. M., Lorente, J. D., Marcilla, A., et al. (2024). Activated microglia secretome and proinflammatory cytokines increase neuronal mu-opioid receptor signalling and expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 230, 116608. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116608
Dai, X., Zhang, X., Chen, W., Chen, Y., Zhang, Q., Mo, S., et al. (2021). Dihydroartemisinin: a potential natural anticancer drug. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17, 603–622. doi:10.7150/ijbs.50364
Depp, C., Doman, J. L., Hingerl, M., Xia, J., and Stevens, B. (2025). Microglia transcriptional states and their functional significance: context drives diversity. Immunity 58, 1052–1067. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2025.04.009
Du, E. R., Fan, R. P., Rong, L. L., Xie, Z., and Xu, C. S. (2020). Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of microglial inhibitors in neuropathic pain and morphine tolerance. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 21, 204–217. doi:10.1631/jzus.B1900425
Fukagawa, H., Koyama, T., Kakuyama, M., and Fukuda, K. (2013). Microglial activation involved in morphine tolerance is not mediated by toll-like receptor 4. J. Anesth. 27, 93–97. doi:10.1007/s00540-012-1469-4
Gabel, F., Hovhannisyan, V., Andry, V., and Goumon, Y. (2023). Central metabolism as a potential origin of sex differences in morphine antinociception but not induction of antinociceptive tolerance in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 180, 843–861. doi:10.1111/bph.15792
Gessi, S., Borea, P. A., Bencivenni, S., Fazzi, D., Varani, K., and Merighi, S. (2016). The activation of μ-opioid receptor potentiates LPS-induced NF-kB promoting an inflammatory phenotype in microglia. FEBS Lett. 590, 2813–2826. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.12313
Gong, L. J., Wang, X. Y., Gu, W. Y., and Wu, X. (2020). Pinocembrin ameliorates intermittent hypoxia-induced neuroinflammation through BNIP3-dependent mitophagy in a murine model of sleep apnea. J. Neuroinflammation 17, 337. doi:10.1186/s12974-020-02014-w
Guan, S., Jin, T., Han, S., Fan, W., Chu, H., and Liang, Y. (2021). Dihydroartemisinin alleviates morphine-induced neuroinflammation in BV-2 cells. Bioengineered 12, 9401–9410. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1982311
Guan, S., Miao, F., Wang, D., Hu, J., and Wang, H. (2023). Corilagin attenuates morphine-induced BV2 microglial activation and inflammation via regulating TLR2-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Toxicol. Sci. 48, 387–398. doi:10.2131/jts.48.387
Han, Y., Jiang, C., Tang, J., Wang, C., Wu, P., Zhang, G., et al. (2014). Resveratrol reduces morphine tolerance by inhibiting microglial activation via AMPK signalling. Eur. J. Pain 18, 1458–1470. doi:10.1002/ejp.511
Han, D., Dong, W., and Jiang, W. (2022). Pinocembrin alleviates chronic morphine-induced analgesic tolerance and hyperalgesia by inhibiting microglial activation. Neurol. Res. 44, 946–955. doi:10.1080/01616412.2022.2075656
Hayashi, Y., Koga, Y., Zhang, X., Peters, C., Yanagawa, Y., Wu, Z., et al. (2014). Autophagy in superficial spinal dorsal horn accelerates the cathepsin B-dependent morphine antinociceptive tolerance. Neuroscience 275, 384–394. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.06.037
He, L., Xu, W., Zhang, C., Ding, Z., Guo, Q., Zou, W., et al. (2022). Dysregulation of vesicular glutamate transporter VGluT2 via BDNF/TrkB pathway contributes to morphine tolerance in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 861786. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.861786
Hong, H., Lu, X., Wu, C., Chen, J., Chen, C., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). A review for the pharmacological effects of paeoniflorin in the nervous system. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 898955. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.898955
Horvath, R. J., Romero-Sandoval, A. E., and De Leo, J. A. (2010). Inhibition of microglial P2X4 receptors attenuates morphine tolerance, Iba1, GFAP and mu opioid receptor protein expression while enhancing perivascular microglial ED2. Pain 150, 401–413. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.02.042
Huan, C., Xu, Y., Zhang, W., Guo, T., Pan, H., and Gao, S. (2021). Research progress on the antiviral activity of glycyrrhizin and its derivatives in liquorice. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 680674. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.680674
Hutchinson, M. R., Zhang, Y., Shridhar, M., Evans, J. H., Buchanan, M. M., Zhao, T. X., et al. (2010). Evidence that opioids may have toll-like receptor 4 and MD-2 effects. Brain Behav. Immun. 24, 83–95. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2009.08.004
Ing Lorenzini, K., Wainstein, L., Spechbach, H., Sarasin, F., Ramlawi, M., Desmeules, J., et al. (2022). Opioid-related adverse drug reactions in patients visiting the emergency division of a tertiary hospital. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 10, e01033. doi:10.1002/prp2.1033
Jia, X., Zhang, A., Li, Z., Peng, X., Tian, X., and Gao, F. (2021). Activation of spinal PDGFRβ in microglia promotes neuronal autophagy via p38 MAPK pathway in morphine-tolerant rats. J. Neurochem. 158, 373–390. doi:10.1111/jnc.15383
Jiang, C., Xu, L., Chen, L., Han, Y., Tang, J., Yang, Y., et al. (2015). Selective suppression of microglial activation by paeoniflorin attenuates morphine tolerance. Eur. J. Pain 19, 908–919. doi:10.1002/ejp.617
Kao, S. C., Zhao, X., Lee, C. Y., Atianjoh, F. E., Gauda, E. B., Yaster, M., et al. (2012). Absence of μ opioid receptor mRNA expression in astrocytes and microglia of rat spinal cord. Neuroreport 23, 378–384. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e3283522e1b
Leduc-Pessah, H., Weilinger, N. L., Fan, C. Y., Burma, N. E., Thompson, R. J., and Trang, T. (2017). Site-Specific regulation of P2X7 receptor function in microglia Gates morphine analgesic tolerance. J. Neurosci. 37, 10154–10172. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0852-17.2017
Lewis, S. S., Hutchinson, M. R., Rezvani, N., Loram, L. C., Zhang, Y., Maier, S. F., et al. (2010). Evidence that intrathecal morphine-3-glucuronide may cause pain enhancement via toll-like receptor 4/MD-2 and interleukin-1beta. Neuroscience 165, 569–583. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.011
Li, Z., Jia, X., Peng, X., and Gao, F. (2020). The interaction between spinal PDGFRβ and μ opioid receptor in the activation of microglia in morphine-tolerant rats. J. Pain Res. 13, 1803–1810. doi:10.2147/jpr.S255221
Li, X., Ou, X., Ni, J., Xu, Y., Zuo, H., Fu, Y., et al. (2022). Bulleyaconitine A is a sensitive substrate and competitive inhibitor of CYP3A4: one of the possible explanations for clinical adverse reactions. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 445, 116024. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2022.116024
Li, S., Tang, S., Dai, L., Jian, Z., and Li, X. (2024). Emodin relieves morphine-stimulated BV2 microglial activation and inflammation through the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Neuroreport 35, 518–528. doi:10.1097/wnr.0000000000002034
Liang, Y., Chu, H., Jiang, Y., and Yuan, L. (2016). Morphine enhances IL-1β release through toll-like receptor 4-mediated endocytic pathway in microglia. Purinergic Signal 12, 637–645. doi:10.1007/s11302-016-9525-4
Lim, G., Wang, S., and Mao, J. (2005). cAMP and protein kinase A contribute to the downregulation of spinal glutamate transporters after chronic morphine. Neurosci. Lett. 376, 9–13. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.11.016
Lin, J., Wang, Q., Zhou, S., Xu, S., and Yao, K. (2022). Tetramethylpyrazine: a review on its mechanisms and functions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 150, 113005. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113005
Lin, T. T., Jiang, C. Y., Sheng, L., Wan, L., Fan, W., Li, J. C., et al. (2023). Suppressing high mobility group box-1 release alleviates morphine tolerance via the adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase/heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Neural Regen. Res. 18, 2067–2074. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.366490
Liu, G. J., Kalous, A., Werry, E. L., and Bennett, M. R. (2006). Purine release from spinal cord microglia after elevation of calcium by glutamate. Mol. Pharmacol. 70, 851–859. doi:10.1124/mol.105.021436
Liu, W., Wang, C. H., Cui, Y., Mo, L. Q., Zhi, J. L., Sun, S. N., et al. (2006). Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase antagonizes morphine antinociceptive tolerance by decreasing activation of p38 MAPK in the spinal microglia. Neurosci. Lett. 410, 174–177. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2006.08.091
Liu, Q., Su, L. Y., Sun, C., Jiao, L., Miao, Y., Xu, M., et al. (2020). Melatonin alleviates morphine analgesic tolerance in mice by decreasing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol. 34, 101560. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101560
Maduna, T., Audouard, E., Dembélé, D., Mouzaoui, N., Reiss, D., Massotte, D., et al. (2018). Microglia express Mu opioid receptor: insights from transcriptomics and fluorescent reporter mice. Front. Psychiatry 9, 726. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00726
Mai, J. Z., Liu, C., Huang, Z., Mai, C. L., Zhou, X., Zhang, J., et al. (2020). Oral application of bulleyaconitine A attenuates morphine tolerance in neuropathic rats by inhibiting long-term potentiation at C-fiber synapses and protein kinase C gamma in spinal dorsal horn. Mol. Pain 16, 1744806920917242. doi:10.1177/1744806920917242
Mattioli, T. A., Leduc-Pessah, H., Skelhorne-Gross, G., Nicol, C. J., Milne, B., Trang, T., et al. (2014). Toll-like receptor 4 mutant and null mice retain morphine-induced tolerance, hyperalgesia, and physical dependence. PLoS One 9, e97361. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097361
Merighi, S., Gessi, S., Varani, K., Fazzi, D., Stefanelli, A., and Borea, P. A. (2013). Morphine mediates a proinflammatory phenotype via μ-opioid receptor-PKCɛ-Akt-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in activated microglial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 86, 487–496. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2013.05.027
Mitra, S., Anjum, J., Muni, M., Das, R., Rauf, A., Islam, F., et al. (2022). Exploring the journey of emodin as a potential neuroprotective agent: novel therapeutic insights with molecular mechanism of action. Biomed. Pharmacother. 149, 112877. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112877
Molavinia, S., Nikravesh, M., Pashmforoosh, M., Vardanjani, H. R., and Khodayar, M. J. (2024). Zingerone alleviates morphine tolerance and dependence in mice by reducing oxidative stress-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Neurochem. Res. 49, 415–426. doi:10.1007/s11064-023-04043-2
Olson, J. K., and Miller, S. D. (2004). Microglia initiate central nervous system innate and adaptive immune responses through multiple TLRs. J. Immunol. 173, 3916–3924. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.173.6.3916
Pan, Y., Sun, X., Jiang, L., Hu, L., Kong, H., Han, Y., et al. (2016). Metformin reduces morphine tolerance by inhibiting microglial-mediated neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflammation 13, 294. doi:10.1186/s12974-016-0754-9
Patridge, E., Gareiss, P., Kinch, M. S., and Hoyer, D. (2016). An analysis of FDA-approved drugs: natural products and their derivatives. Drug Discov. Today 21, 204–207. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2015.01.009
Peng, X., Wang, J., Li, Z., Jia, X., Zhang, A., Ju, J., et al. (2023). Toll-like receptor 2-Melatonin feedback loop regulates the activation of spinal NLRP3 inflammasome in morphine-tolerant rats. Neurochem. Res. 48, 3597–3609. doi:10.1007/s11064-023-03998-6
Peng, X., Ju, J., Li, Z., Liu, J., Jia, X., Wang, J., et al. (2025). C3/C3aR bridges spinal astrocyte-microglia crosstalk and accelerates neuroinflammation in morphine-tolerant rats. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 31, e70216. doi:10.1111/cns.70216
Puig, S., Donica, C. L., and Gutstein, H. B. (2020). EGFR signaling causes morphine tolerance and mechanical sensitization in rats. eNeuro 7, 18.2020. doi:10.1523/eneuro.0460-18.2020
Qian, J., Zhu, Y., Bai, L., Gao, Y., Jiang, M., Xing, F., et al. (2020). Chronic morphine-mediated upregulation of high mobility group box 1 in the spinal cord contributes to analgesic tolerance and hyperalgesia in rats. Neurotherapeutics 17, 722–742. doi:10.1007/s13311-019-00800-w
Qu, J., Tao, X. Y., Teng, P., Zhang, Y., Guo, C. L., Hu, L., et al. (2017). Blocking ATP-Sensitive potassium channel alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting HSP70-TLR4-NLRP3-mediated neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflammation 14, 228. doi:10.1186/s12974-017-0997-0
Radeva, L., and Yoncheva, K. (2025). Resveratrol-A promising therapeutic agent with problematic properties. Pharmaceutics 17, 134. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics17010134
Rashpa, S., Chadha, J., Khullar, L., Sharma, B., and Harjai, K. (2025). Revisiting the multifaceted phytochemical: an updated review on therapeutic potential, pharmaceutical formulations, pre-clinical studies, and clinical trials of zingerone. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 297, 117971. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117971
Reiss, D., Maduna, T., Maurin, H., Audouard, E., and Gaveriaux-Ruff, C. (2022). Mu opioid receptor in microglia contributes to morphine analgesic tolerance, hyperalgesia, and withdrawal in mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 100, 203–219. doi:10.1002/jnr.24626
Sano, A. (2017). Safety assessment of 4-week oral intake of proanthocyanidin-rich grape seed extract in healthy subjects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 108, 519–523. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2016.11.021
Sharifi-Rad, J., Herrera-Bravo, J., Kamiloglu, S., Petroni, K., Mishra, A. P., Monserrat-Mesquida, M., et al. (2022). Recent advances in the therapeutic potential of emodin for human health. Biomed. Pharmacother. 154, 113555. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113555
Shen, C. H., Tsai, R. Y., Tai, Y. H., Lin, S. L., Chien, C. C., and Wong, C. S. (2011). Intrathecal etanercept partially restores morphine's antinociception in morphine-tolerant rats via attenuation of the glutamatergic transmission. Anesth. Analg. 113, 184–190. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e318217f7eb
Shen, C. H., Tsai, R. Y., and Wong, C. S. (2012). Role of neuroinflammation in morphine tolerance: effect of tumor necrosis factor-α. Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwan 50, 178–182. doi:10.1016/j.aat.2012.12.004
Shuai, H., Hua, M., Tingting, J., Rubing, Y., Ziyi, W., Jie, Z., et al. (2023). Inhibitory effect of berberine on morphine tolerance and hyperalgesia in mice. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 43, 915–924. doi:10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230802.006
Shuai, H., Zhikang, D., Zirui, W., Tianfeng, H., Yali, G. E., Jianwen, S., et al. (2025). Network pharmacology approach to unveiling the mechanism of berberine in the amelioration of morphine tolerance. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 45, 376–384. doi:10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.012
Song, H., Zhou, D., Han, Y., and Liu, W. (2014). Baicalin attenuates morphine tolerance through suppressing spinal microglia activation in mice. J. China Pharm. Univ. 45, 346–351. Available online at: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20143288715.
Suadicani, S. O., Brosnan, C. F., and Scemes, E. (2006). P2X7 receptors mediate ATP release and amplification of astrocytic intercellular Ca2+ signaling. J. Neurosci. 26, 1378–1385. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3902-05.2006
Sun, L., Lan, J., Li, Z., Zeng, R., Shen, Y., Zhang, T., et al. (2024). Transforming cancer treatment with nanotechnology: the role of berberine as a star natural compound. Int. J. Nanomedicine 19, 8621–8640. doi:10.2147/ijn.S469350
Tsai, R. Y., Chou, K. Y., Shen, C. H., Chien, C. C., Tsai, W. Y., Huang, Y. N., et al. (2012). Resveratrol regulates N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor expression and suppresses neuroinflammation in morphine-tolerant rats. Anesth. Analg. 115, 944–952. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e31825da0fb
Tsai, R. Y., Wang, J. C., Chou, K. Y., Wong, C. S., and Cherng, C. H. (2016). Resveratrol reverses morphine-induced neuroinflammation in morphine-tolerant rats by reversal HDAC1 expression. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 115, 445–454. doi:10.1016/j.jfma.2015.05.010
Tu, H., Chu, H., Guan, S., Hao, F., Xu, N., Zhao, Z., et al. (2021). The role of the M1/M2 microglia in the process from cancer pain to morphine tolerance. Tissue Cell 68, 101438. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2020.101438
Wahab, S., Annadurai, S., Abullais, S. S., Das, G., Ahmad, W., Ahmad, M. F., et al. (2021). Glycyrrhiza glabra (Licorice): a comprehensive review on its phytochemistry, biological activities, clinical evidence and toxicology. Plants (Basel) 10, 2751. doi:10.3390/plants10122751
Wan, L., Jia, R. M., Ji, L. L., Qin, X. M., Hu, L., Hu, F., et al. (2022). AMPK-autophagy-mediated inhibition of microRNA-30a-5p alleviates morphine tolerance via SOCS3-dependent neuroinflammation suppression. J. Neuroinflammation 19, 25. doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02384-3
Wang, Z., Ma, W., Chabot, J. G., and Quirion, R. (2009). Cell-type specific activation of p38 and ERK mediates calcitonin gene-related peptide involvement in tolerance to morphine-induced analgesia. Faseb J. 23, 2576–2586. doi:10.1096/fj.08-128348
Wang, Z., Ma, W., Chabot, J. G., and Quirion, R. (2010a). Calcitonin gene-related peptide as a regulator of neuronal CaMKII-CREB, microglial p38-NFκB and astroglial ERK-Stat1/3 cascades mediating the development of tolerance to morphine-induced analgesia. Pain 151, 194–205. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.07.006
Wang, Z., Ma, W., Chabot, J. G., and Quirion, R. (2010b). Morphological evidence for the involvement of microglial p38 activation in CGRP-associated development of morphine antinociceptive tolerance. Peptides 31, 2179–2184. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2010.08.020
Wang, Y., Barker, K., Shi, S., Diaz, M., Mo, B., and Gutstein, H. B. (2012). Blockade of PDGFR-β activation eliminates morphine analgesic tolerance. Nat. Med. 18, 385–387. doi:10.1038/nm.2633
Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Ma, X., Wang, W., Xu, X., Huang, M., et al. (2020). Spinal TLR4/P2X7 receptor-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the development of tolerance to morphine-induced antinociception. J. Inflamm. Res. 13, 571–582. doi:10.2147/jir.S266995
Wang, L., Yin, C., Xu, X., Liu, T., Wang, B., Abdul, M., et al. (2020). Pellino1 contributes to morphine tolerance by microglia activation via MAPK signaling in the spinal cord of mice. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 40, 1117–1131. doi:10.1007/s10571-020-00797-3
Wang, H., Huang, M., Wang, W., Zhang, Y., Ma, X., Luo, L., et al. (2021). Microglial TLR4-induced TAK1 phosphorylation and NLRP3 activation mediates neuroinflammation and contributes to chronic morphine-induced antinociceptive tolerance. Pharmacol. Res. 165, 105482. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105482
Wang, X., Fisher, D., Pronyuk, K., Dang, Y., and Zhao, L. (2023). Agent in urgent need of clinical practice: corilagin. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 23, 1642–1652. doi:10.2174/1389557523666230112110317
Wang, B., Le, D. S., Liu, L., Zhang, X. X., Yang, F., Lai, G. R., et al. (2024). Targeting exosomal double-stranded RNA-TLR3 signaling pathway attenuates morphine tolerance and hyperalgesia. Cell Rep. Med. 5, 101782. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101782
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Xiao, H., Ye, X., Pan, H., and Chen, S. (2024). Revisiting dietary proanthocyanidins on blood glucose homeostasis from a multi-scale structural perspective. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 9, 100926. doi:10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100926
Wen, Z. H., Chang, Y. C., Cherng, C. H., Wang, J. J., Tao, P. L., and Wong, C. S. (2004). Increasing of intrathecal CSF excitatory amino acids concentration following morphine challenge in morphine-tolerant rats. Brain Res. 995, 253–259. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2003.10.008
Wen, Y. Q., Wang, Y. Z., Zhao, C. X., Zhao, B. Y., and Wang, J. G. (2025). Baicalin: an active natural product with potential medicinal values. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 27, 1087–1111. doi:10.1080/10286020.2025.2482054
Williams, J. T., Ingram, S. L., Henderson, G., Chavkin, C., von Zastrow, M., Schulz, S., et al. (2013). Regulation of μ-opioid receptors: desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance. Pharmacol. Rev. 65, 223–254. doi:10.1124/pr.112.005942
Xiao, L., Han, X., Wang, X. E., Li, Q., Chen, Y., Cui, Y., et al. (2019). Cathepsin S in the spinal microglia facilitates morphine-induced antinociceptive tolerance in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 690, 225–231. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2018.10.043
Xie, M. X., Zhu, H. Q., Pang, R. P., Wen, B. T., and Liu, X. G. (2018). Mechanisms for therapeutic effect of bulleyaconitine A on chronic pain. Mol. Pain 14, 1744806918797243. doi:10.1177/1744806918797243
Xu, H., Xu, T., Ma, X. Q., and Jiang, W. (2014). Chronic morphine treatment increased the expression of myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 in rat spinal cord. J. Integr. Neurosci. 13, 607–615. doi:10.1142/s0219635214500216
Yang, Y., Chen, Z., Hu, R., Sun, Y., Xiang, L., Yan, J., et al. (2021). Activation of the spinal EGFR signaling pathway in a rat model of cancer-induced bone pain with morphine tolerance. Neuropharmacology 196, 108703. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108703
Yoo, J. H., Yang, E. M., Cho, J. H., Lee, J. H., Jeong, S. M., Nah, S. Y., et al. (2006). Inhibitory effects of berberine against morphine-induced locomotor sensitization and analgesic tolerance in mice. Neuroscience 142, 953–961. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.07.008
Yu, R., Jin, G., and Fujimoto, M. (2021). Dihydroartemisinin: a potential drug for the treatment of malignancies and inflammatory diseases. Front. Oncol. 11, 722331. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.722331
Zhang, Y., Li, H., Li, Y., Sun, X., Zhu, M., Hanley, G., et al. (2011). Essential role of toll-like receptor 2 in morphine-induced microglia activation in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 489, 43–47. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.11.063
Zhang, Y., Tao, G. J., Hu, L., Qu, J., Han, Y., Zhang, G., et al. (2017). Lidocaine alleviates morphine tolerance via AMPK-SOCS3-dependent neuroinflammation suppression in the spinal cord. J. Neuroinflammation 14, 211. doi:10.1186/s12974-017-0983-6
Zhang, J. J., Song, C. G., Wang, M., Zhang, G. Q., Wang, B., Chen, X., et al. (2023). Monoclonal antibody targeting mu-opioid receptor attenuates morphine tolerance via enhancing morphine-induced receptor endocytosis. J. Pharm. Anal. 13, 1135–1152. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2023.06.008
Zhang, X., Jin, T., Wang, H., Han, S., and Liang, Y. (2024). Microglia in morphine tolerance: cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1499799. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1499799
Zhao, Y. N., Cao, Y. N., Sun, J., Liang, Z., Wu, Q., Cui, S. H., et al. (2020). Anti-breast cancer activity of resveratrol encapsulated in liposomes. J. Mater Chem. B 8, 27–37. doi:10.1039/c9tb02051a
Zhao, M. J., Wang, M. Y., Ma, L., Ahmad, K. A., and Wang, Y. X. (2021). Bulleyaconitine A inhibits morphine-induced withdrawal symptoms, conditioned place preference, and locomotor sensitization Via microglial dynorphin A expression. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 620926. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.620926
Zheng, Q., Li, S., Li, X., and Liu, R. (2021). Advances in the study of emodin: an update on pharmacological properties and mechanistic basis. Chin. Med. 16, 102. doi:10.1186/s13020-021-00509-z
Keywords: morphine tolerance, microglia, neuroinflammation, phytochemicals, therapeutic potential
Citation: Shi R, Jin T, Xu W and Liang Y (2025) The therapeutic potential of phytochemicals in morphine tolerance: targeting microglia-mediated neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1669257. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1669257
Received: 21 July 2025; Accepted: 20 October 2025;
Published: 06 November 2025.
Edited by:
Hiram Tendilla-Beltrán, Center for Research and Advanced Studies-IPN (Cinvestav), MexicoReviewed by:
Weidong Lai, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, ChinaArezou Mehrabi, Islamic Azad University Tonekabon, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Shi, Jin, Xu and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongxin Liang, bGlhbmd6aTY2QGhvdG1haWwuY29t
 Ruizhen Shi
Ruizhen Shi Tingting Jin
Tingting Jin Weilong Xu
Weilong Xu Yongxin Liang
Yongxin Liang