- 1School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 2Hunan Province Key Laboratory of Cerebrovascular Disease Prevention and Treatment of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 3Pulmonary Medicine-Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Ningxiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Changsha, China
- 4School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 5The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), characterized by abnormal lipid accumulation in hepatocytes, is prevalent in conditions such as type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity, which are associated with dysregulated glucose and lipid metabolism. Bile acids (BAs) are critical regulators of lipid and glucose homeostasis. Emerging research suggests that disturbances in BA metabolism not only exacerbate metabolic imbalance but also promote ferroptosis via lipid peroxidation. This review differs by systematically linking BA regulation, ferroptosis, and TCM, highlighting the multi-component and multi-target advantages of TCM in preventing and treating NAFLD. We summarize the mechanisms by which BAs regulate hepatic lipid synthesis and oxidation, and how lipid peroxidation connects to ferroptosis through glutathione/glutathione disulfide (GSH/GSSG) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Finally, we review studies on TCM modulation of BA metabolism and ferroptosis to improve lipid peroxidation and metabolic disorders, providing timely insights into innovative therapeutic strategies for NAFLD.
Highlights
Insulin resistance boosts lipogenesis, reduces fatty acid oxidation, and triggers NAFLD.
Bile acids participate in hepatic steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and hepatic fibrosis.
Bile acids regulate lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis via FXR activation and signaling.
TCM prevents fat accumulation, fibrosis, stress, and inflammation, and regulates bile acid and microbiota levels.
1 Introduction
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a group of diseases caused by excessive lipid accumulation in the liver, often associated with metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension (Chalasani et al., 2018). Its pathological progression is closely related to abnormalities in lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and cell death. The occurrence of NAFLD is often associated with insulin resistance and lipid metabolism disorders, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), hyperlipidemia, obesity, and other endocrine diseases. Insulin resistance not only aggravates lipid deposition but also significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and other metabolic complications (Yang et al., 2016a; Kim et al., 2024). Epidemiological studies show that about 70% of T2DM patients also have NAFLD, and the risk of insulin resistance and T2DM is two to three times higher in NAFLD patients compared to healthy individuals (Younossi et al., 2024). Therefore, studying the interaction mechanism between dyslipidemia and NAFLD is of great significance for improving patient prognosis, reducing complications, and enhancing clinical treatment outcomes.
In recent years, ferroptosis—a form of programmed cell death dependent on iron ions and lipid peroxidation—has garnered significant attention in the pathogenesis of NAFLD (Li et al., 2020c). Studies have shown that bile acid metabolism disorders disrupt lipid metabolic balance and promote ferroptosis by inducing lipid peroxidation, thereby participating in the pathological mechanisms of NAFLD (Quintero et al., 2014). Although numerous studies have explored the relationships between bile acid metabolism, lipid peroxidation, and ferroptosis, many questions remain unresolved. Despite numerous studies on the relationship between bile acid metabolism, lipid peroxidation, and ferroptosis, many questions remain. Existing reviews often treat these processes separately or focus on just one or two aspects. Additionally, while Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is increasingly recognized for its multi-target therapeutic potential, few studies have focused on how TCM interventions modulate bile acid metabolism, improve lipid peroxidation, and regulate ferroptosis in the treatment of NAFLD.
This review first outlines how bile acids regulate lipid synthesis and oxidation, and how these processes intersect with lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in NAFLD. We then examine key signaling pathways, particularly those involving glutathione/glutathione disulfide (GSH/GSSG), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and ferroptosis-related lipid metabolism. Next, we summarize evidence on Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) interventions and their potential to modulate bile acid metabolism, attenuate lipid peroxidation, and regulate ferroptosis. Finally, we discuss translational implications and future research directions (Figure 1).
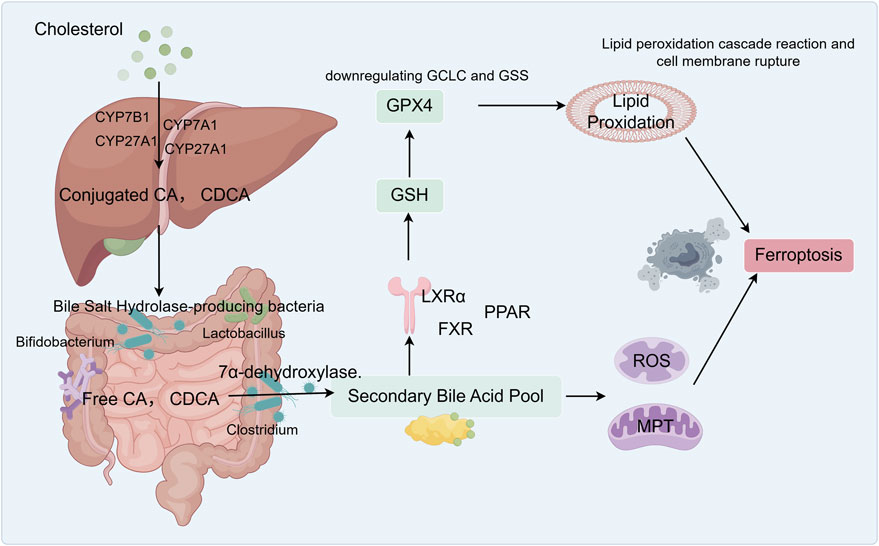
Figure 1. Graphical abstract: Bile acids participate in ferroptosis and influence lipid metabolism in NAFLD. The liver synthesizes primary bile acids, such as cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), from cholesterol. These primary bile acids conjugate with glycine or taurine to form conjugated bile acids. In the small and large intestines, anaerobic bacteria produce bile salt hydrolase (BSH), which deconjugates these primary bile acids, generating free CA and CDCA. Free CA enters the colon, where specific Clostridium species convert it via 7 α-dehydroxylase into the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (DCA). Free CDCA is similarly converted into lithocholic acid (LCA) by these bacteria. Hydrophobic bile acids (DCA, CDCA, and LCA) activate FXR, which inhibits genes responsible for glutathione synthesis (GCLC and GSS), thereby reducing GSH production. DCA directly damages mitochondria, triggering the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that attack membrane phospholipids, leading to the accumulation of lipid peroxides. Together with ROS, the GPX4 pathway ultimately induces ferroptosis.
2 Glucose and lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
2.1 Epidemiology
NAFLD is a group of diseases characterized by excessive lipid accumulation in the liver, with its pathological progression closely linked to abnormalities in lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and cell death (Chalasani et al., 2018). NAFLD has become the leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, with a global adult prevalence of 29.9%–34.9%. The prevalence in men (39.7%) is significantly higher than in women (25.6%). Notably, the prevalence in overweight/obese individuals reaches 51.6%, while 14.4% in individuals with normal weight (Riazi et al., 2022). Multiple factors drive the pathogenesis of NAFLD, including abnormalities in lipid metabolism and insulin resistance. These factors contribute to fat accumulation, chronic inflammation, and gut microbiota dysbiosis, further aggravating hepatic cell damage and metabolic abnormalities (Buzzetti et al., 2016; Marra and Svegliati-Baroni, 2018; Byrne and Targher, 2020). In NAFLD patients, hepatic lipid accumulation is closely associated with metabolic disorders such as obesity, T2DM, hypertriglyceridemia, and hypertension, as well as cardiovascular diseases (Quek et al., 2023; Younossi et al., 2024). Among these, insulin resistance is a key factor contributing to lipid metabolism disorders. Therefore, NAFLD and T2DM often coexist and influence each other.
Diabetes has become a global public health issue and is the eighth leading cause of death and disability worldwide (GBD, 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators, 2020). According to the latest GBD 2021 study published in The Lancet, 529 million people were living with diabetes worldwide in 2021, and 96.0% of these cases were T2DM (GBD, 2021 Diabetes Collaborators, 2023). Both diabetes and NAFLD are chronic metabolic diseases, and if left uncontrolled for an extended period, they can lead to dysfunction, disability, and various severe complications. It is estimated that 60%–70% of T2DM patients have NAFLD, and 20%–30% of these patients may progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Additionally, the risk of NAFLD progressing to cirrhosis in T2DM patients is 2–3 times higher than in non-diabetic individuals (Younossi et al., 2024). In conclusion, NAFLD and T2DM are closely linked global public health challenges that influence each other. Studying their pathogenesis and new therapeutic approaches is essential for reducing incidence, delaying progression, and improving patient prognosis.
2.2 Physiopathological mechanism
The liver is the body’s primary metabolic organ, responsible for various functions, including synthesizing, breaking down, and transporting lipids. It maintains the balance of lipids in the body by synthesizing and breaking down fatty acids, cholesterol, and triglycerides (Nguyen et al., 2008). The physiological functions of lipid metabolism include providing energy, synthesizing cell membranes, and producing hormones and vitamins. Normal lipid metabolism supplies energy to cells and participates in critical physiological processes such as cell signal transduction and immune responses (Prentki and Madiraju, 2008; Dukewich et al., 2025). Dietary lipids are primarily absorbed in the intestines and transported through the blood to adipose tissue and the liver. In NAFLD, triglycerides are hydrolyzed into diglycerides, monoglycerides, and glycerol, releasing fatty acids in the process. On the one hand, the increased fatty acid load is delivered to the liver, where it is cleared by enzymes such as fatty acid translocase, fatty acid transport proteins, and caveolin, and then incorporated into lipid droplets (Wilson et al., 2016; Enooku et al., 2020; Geng et al., 2021). On the other hand, fatty acids are oxidized in the mitochondria, peroxisomes, and microsomes, accompanied by an increase in the production of ROS (Geng et al., 2021; Moreno-Fernandez et al., n.d.). Lipid metabolism disorders are primarily characterized by abnormal fat accumulation in the liver, resulting in hepatocyte injury and dysfunction. The pathological mechanisms include insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammatory responses (Bugianesi et al., 2005; Hirsova et al., 2016). The pathological features of fatty liver mainly include abnormal accumulation of fat in hepatocytes, liver inflammation, and fibrosis, which may eventually lead to severe consequences such as cirrhosis and liver cancer (Lee et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2022). In NAFLD, the liver’s role in lipid metabolism disorders—particularly the contributions of insulin resistance and oxidative stress—is central to the disease’s pathology. These factors lead to abnormal fat accumulation and exacerbate liver damage through multiple pathways.
Insulin resistance is a key factor contributing to lipid metabolism disorders. Under conditions of insulin resistance, liver cells exhibit reduced responsiveness to insulin, resulting in an inability to effectively inhibit fatty acid synthesis and the regular promotion of fatty acid oxidation. This metabolic abnormality leads to the accumulation of fatty acids in the liver, ultimately causing fatty liver disease. Chronic insulin resistance and fat accumulation further exacerbate the liver’s burden, laying the groundwork for the development of other metabolic disorders [25,26]. Oxidative stress is another key factor in lipid metabolism disorders. The liver is an organ with active oxidative metabolism in the body. Oxidative stress arises from the excessive production of ROS and free radicals, leading to lipid peroxidation and liver cell damage (Sumida et al., 2013). Oxidative stress exacerbates hepatocyte damage, increases the infiltration of F4/80-positive macrophages, reduces their activation, and promotes the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and genes, thereby further exacerbating hepatic inflammatory responses (Ji et al., 2019). As the disease progresses, the persistent presence of oxidative stress can lead to endothelial autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ultimately hepatic fibrosis, potentially resulting in liver failure (Ruart et al., 2019; Abulikemu et al., 2023). Therefore, understanding the role of lipid metabolism in liver diseases provides new perspectives and potential therapeutic targets for the prevention and treatment of related diseases.
2.3 Interactions between glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism
Globally, 60%–70% of patients with T2DM also have NAFLD, and 20%–30% of these patients may progress to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) (Younossi et al., 2024). The underlying mechanisms of this progression primarily include insulin resistance, disrupted hepatic fatty acid metabolism, oxidative stress, and enhanced inflammatory responses. Insulin resistance is a key pathogenic feature of metabolic syndrome, and NAFLD is closely associated with reduced systemic insulin sensitivity and increased insulin resistance in the liver and adipose tissue. On one hand, insulin promotes glycolysis, improves glucose utilization, inhibits hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, and suppresses hepatic glucose output (Saltiel and Kahn, 2001; Titchenell et al., 2017). On the other hand, insulin promotes cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver and enhances the re-esterification of fatty acids into triglycerides in adipocytes and the liver (Uehara et al., 2023). Under physiological conditions, insulin regulates hepatic glucose production by modulating lipolysis in adipose tissue, thereby reducing the influx of fatty acids into the liver (Rebrin et al., 1996). In NAFLD patients with insulin resistance, glucose undergoes glycolysis in the liver, ultimately being converted into fatty acids, which are then esterified into triglycerides. Triglycerides are the primary lipid form in the livers of patients with NAFLD (Donnelly et al., 2005; Heeren and Scheja, 2021). Insulin resistance leads to increased hepatic gluconeogenesis, enhanced glucose and fat production, and disrupted glucose and lipid metabolism, resulting in excessive production of free fatty acids (FFAs). FFAs enter hepatocytes and are converted into triglycerides, promoting hepatic lipid deposition and increasing the risk of NAFLD (Biddinger et al., 2008; Vatner et al., 2015)。
The primary transcription factors involved in insulin-mediated fat synthesis are Upstream Stimulator Factor (USF) (Wang and Sul, 1997), sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) (Raghow et al., 2008), carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) (Postic et al., 2007), and liver X receptor alpha (LXRα). SREBP family genes are believed to regulate genes involved in controlling cholesterol homeostasis and de novo fatty acid synthesis (Raghow et al., 2008). SREBP-1a transactivates genes involved in lipogenesis and cholesteryl ester synthesis (Foretz et al., 1999). In contrast, SREBP-2 regulates genes involved in cholesterol biosynthesis and metabolism. ChREBP is a key glucose-activated transcription factor that regulates approximately 50% of lipogenesis in the liver (Iizuka et al., 2004; Herman and Samuel, 2016). The primary function of ChREBP is to regulate fructose metabolism and participate in the expression of genes involved in carbohydrate transport, glycolysis, and de novo lipogenesis (Iizuka et al., 2004; Jeong et al., 2011). The interaction between ChREBP and SREBP-1c coordinates postprandial glycolysis and lipogenesis in the liver (Linden et al., 2018). These results indicate that SREBP-1c is involved in insulin-induced activation of lipid synthesis genes, while ChREBP mediates glucose-induced activation of glycolysis and lipid synthesis genes. LXR is a ligand-activated nuclear receptor, and the expression of SREBP-1c and ChREBP is regulated by LXR, which controls the expression of genes involved in glycolysis and lipid synthesis, thereby playing a crucial role in the transcriptional control of lipid metabolism (Cha and Repa, 2007; Wang and Tontonoz, 2018). In summary, insulin resistance can lead to hepatic lipid accumulation by increasing FFA transport to the liver, enhancing de novo lipogenesis, and reducing hepatic fatty acid oxidation, thereby driving disease progression.
3 Biological functions of bile acids
3.1 Synthesis and secretion of bile acids
Bile acids (BAs) primarily consist of primary and secondary bile acids. Primary bile acids, such as cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), are synthesized from cholesterol in the liver. In contrast, secondary bile acids, such as lithocholic acid (LCA) and deoxycholic acid (DCA), are produced through the metabolism of intestinal microbiota. They participate in metabolic processes such as fat digestion and absorption, cholesterol metabolism, and immune regulation (Wahlström et al., 2016; Guzior and Quinn, 2021). 95% of bile acids are reabsorbed in the ileum and transported back to the liver to recycle and regulate de novo synthesis. The remaining 5% reaches the colon, where it is metabolized by the gut microbiota and excreted in feces (Fiorucci et al., 2021). In the classical pathway, the hydroxylation of cholesterol at the C-7 position is catalyzed by cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1), which is exclusively distributed in the liver and serves as the rate-limiting enzyme for bile acid synthesis. Then, 7α-hydroxy cholesterol is further modified by sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1), ultimately forming CA and CDCA (Russell and Setchell, 1992). CYP27A1 effectively catalyzes the first rate-limiting step in the alternative pathway, while 7α-hydroxysteroid 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7B1) participates in subsequent 7α-hydroxylation, responsible for the majority of CDCA synthesis (Mihalik et al., 2002). Approximately 95% of bile acid reabsorption depends on the apical sodium-dependent bile salt transporter (ASBT) in the terminal ileum (Dawson et al., 2003; Li et al., 2020b). Bile acids bind to intrahepatic bile acid-binding protein (I-BABP) within cells. They are secreted into the portal venous circulation via the OSTα/β heterodimer on the basolateral membrane (Rao et al., 2008). After entering the portal vein, bile acids are taken up by hepatocytes via the organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) and the sodium-taurate cotransporter polypeptide (NTCP) on the basolateral membrane (Meier and Stieger, 2002; Suga et al., 2017).
BAs are a class of cholesterol metabolites, and their synthesis and excretion constitute the primary pathways for cholesterol catabolism. The metabolic regulatory roles of BAs in lipid and glucose metabolism, as well as insulin sensitivity, are associated with the expression of the FXR and TGR5 receptors (Zhang et al., 2006). Bile acids participate in the pathophysiological processes of NAFL and NASH through multiple mechanisms. FXR and TGR5 are widely expressed in tissues and organs, including the liver, intestines, white adipose tissue, and heart. Several distinct mechanisms in the liver and intestine regulate bile acid homeostasis by activating the FXR and TGR5 receptors. FXR inhibits the transcription of the CYP7A1 gene by suppressing the expression of hepatic nuclear factor 1α and hepatic nuclear factor 4α, which in turn inhibits SREBP1c and reduces lipid synthesis in the liver (Goodwin et al., 2000; Lu et al., 2000). In the intestine, FXR stimulates the expression of fibroblast growth factor 15 (FGF15) or FGF19, which in turn inhibits hepatic CYP7A1 gene transcription, thereby directly or indirectly suppressing SREBP1c and aiding in the inhibition of hepatic lipid synthesis (Inagaki et al., 2005; Di Ciaula et al., 2022). Hepatic gluconeogenesis can be suppressed by activating FXR, which inhibits the expression of several key transcription factors mediated by SHP (Yamagata et al., 2004). Activated FXR in the intestine induces FGF15/19, which dephosphorylates and inactivates the cAMP response element-binding protein, further inhibiting the expression of gluconeogenesis-related genes (Potthoff et al., 2011). In summary, FXR induces SHP expression in the liver, thereby inhibiting CYP7A1 expression. In the intestine, FXR increases the circulating levels of FGF19/FGF15, thereby reducing the expression of CYP7A1 and CYP8B1 and inhibiting bile acid synthesis (Shapiro et al., 2018).
3.2 Bile acids and NAFLD
The liver-gut axis is the bidirectional communication system between the liver and the gut. Nutrients, microbial antigens, metabolites, and bile acids regulate the metabolism and immune responses of the gut and liver, thereby mutually shaping the structure and function of the microbiota (Bruneau et al., 2021; Tilg et al., 2022). The function of the gut-liver axis depends on the interaction between the liver, gut, and microbiota. Gut microbiota influence liver metabolism and immune function, and the disruption of gut barrier integrity and host-microbiota interactions are essential factors in the development of NAFLD (Li et al., 2022b; Forlano et al., 2024). In the hepaticointestinal axis, bile acids act as crucial signaling molecules, regulating bile secretion, lipid metabolism, and glucose metabolism in the liver. Studies have found that circulating bile acid levels are associated with histopathological and genetic determinants of the progression from NAFLD to NASH (Nimer et al., 2021). Therefore, bile acids have become an essential target for preventing and treating NAFLD. Specifically, NASH livers exhibit elevated levels of TCA and TDCA in bile acid metabolomics, while CA and glycocholic acid (GDCA) levels are reduced (Lake et al., 2013). In NAFLD subjects, glycocholate, taurocholate, and glycochenodeoxycholate levels are significantly elevated (Kalhan et al., 2011). The ratio of bile acids to taurocholate and secondary bile acids to primary bile acids is negatively correlated with NAFLD activity scores. When the secondary bile acid ratio is high, an increased level of conjugated bile acids may be associated with a higher risk of significant fibrosis (Puri et al., 2018). Bile acid accumulation in the liver may exacerbate liver disease, with CDCA and glycine-conjugated bile acids related to higher macrovesicular steatosis scores, elevated serum ALT levels, and a larger quantified fibrosis area (Jia et al., 2014). Administration of CA or ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is associated with reduced hepatic triglyceride levels and complete reversal of histological steatosis (Quintero et al., 2014). Changes in bile acids are closely related to hepatic steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and liver fibrosis.
Bile acids not only directly act on the liver to regulate hepatic steatosis but may also prevent the progression of NAFLD by activating the FXR receptor. FXR plays a crucial role in mediating communication between the host and the gut microbiota, particularly through regulating the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids (Zhang et al., 2016). The potency of bile acids in activating FXR is ranked as follows: CDCA > DCA > LCA > CA (Wang et al., 1999). Compared to NAFLD patients, NASH patients exhibit reduced levels of FXR, SHP, and NTCP proteins, and FXR plays a protective role in the progression from NAFLD to NASH (Aguilar-Olivos et al., 2015). Alterations in the gut microbiota result in increased levels of tauroconjugated bile acids (TCBAs) in both the gut and the liver. TCBA activates thermogenic adipose tissue and regulates blood glucose through FXR and TGR5 receptor-mediated signaling (Münzker et al., 2022). TUDCA inhibits the expression of FXR and fatty acid transport protein 5 (FATP5), thereby reducing fatty acid absorption and hepatic lipid accumulation, enhancing intestinal barrier function, and promoting the growth of Allobaculum and Bifidobacterium (Wang et al., 2024b). FXR-deficient mice are resistant to obesity induced by a high-fat diet, and transferring their microbiota to germ-free wild-type mice reduces obesity and improves glucose tolerance, indicating that the gut microbiota promotes weight gain and hepatic steatosis in an FXR-dependent manner (Parséus et al., 2017). The mechanism by which intestinal FXR activation shapes the gut microbiota to activate TGR5/GLP-1 signaling to improve hepatic glucose and insulin sensitivity and increase adipose tissue browning (Pathak et al., 2018). In summary, bile acids play a crucial role in the early prevention of NAFLD through pathways such as FXR regulation and the gut-liver axis. They may also serve as potential therapeutic targets for NAFLD and its complications.
4 Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis
4.1 The relationship between lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis
Lipid peroxidation is the most significant type of oxidative free radical damage in biological systems, comprising a free radical chain reaction with three distinct stages: initiation, propagation, and termination (Valgimigli, 2023). The process of lipid peroxidation typically begins with the generation of free radicals. Cellular organelles, such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum, produce ROS during metabolic processes, which stimulate the generation of free radicals through various pathways. When free radicals come into contact with lipids, they can cause the unsaturated bonds in lipids to break, generating a lipid free radical (Lai and Piette, 1978; Greene et al., 2017). The generated lipid free radicals can react with oxygen to form lipid peroxy radicals, which attack surrounding lipid molecules and expand the lipid peroxidation chain reaction (Porter, 2013). Antioxidants can react with lipid free radicals, stabilize them, and prevent further oxidative reactions (Jones and Saso, 2007). Alternatively, lipid peroxides (LOOH) can react with other free radicals to form inactive products, halting the oxidative process (Saraev and Pratt, 2024). Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are generally considered the primary substrates for lipid peroxidation. The abundance of PUFAs determines the extent of available lipid peroxidation sites, thereby influencing susceptibility to ferroptosis (Yang et al., 2016b). The final products of lipid peroxidation, including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), peroxides, and malondialdehyde (MDA), can disrupt cellular membrane structure and contribute to pathological processes such as inflammatory responses and cell death (Spitz et al., 1990; Ayala et al., 2014). Lipid peroxides generated by lipid peroxidation cause damage to the structure and function of cellular membranes, thereby triggering cell death, particularly playing a key role in iron-dependent death processes.
Ferroptosis is a non-apoptotic form of regulated cell death driven by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, primarily occurring within cells. It is characterized by reduced mitochondrial volume, increased double membrane density, and reduced or absent mitochondrial cristae, while the cell membrane remains intact and the nucleus maintains normal size (Dixon et al., 2012). Intracellular glutathione (GSH) depletion, decreased activity of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), and the inability of lipid peroxides to be metabolized through the reductive reaction catalyzed by GPX4 lead to Fe2+ oxidizing lipids and generating a large amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby promoting ferroptosis (Chen et al., 2022). At the molecular mechanism level, the initiation of ferroptosis is closely related to three principal regulatory axes: regulation of the GSH/GPX4 pathway, regulation of iron metabolism, and regulation of pathways related to lipid metabolism (Li et al., 2020a). GPX4 converts GSH into oxidized glutathione (GSSG) and reduces cytotoxic LOOH to their corresponding alcohols (L-OH) (Liu et al., 2023). GSH, as a substrate for GPX4, also plays a key role in anti-ferroptosis. Changes in GSH metabolism ultimately lead to alterations in cellular sensitivity to ferroptosis (Friedmann Angeli et al., 2014). Therefore, inhibition of GPX4 activity can lead to the accumulation of lipid peroxides, which are markers of ferroptosis. The dynamic balance of the intracellular free iron pool plays a decisive role in ferroptosis sensitivity. Excess iron promotes lipid and ROS production through iron-dependent Fenton reactions and catalytic lipid peroxidation chain reactions, while also acting as a cofactor for lipoxygenases in the peroxidation modification of polyunsaturated fatty acids (Henning et al., 2022). Abnormal activation of lipid metabolic enzyme systems (such as ACSL4 and LOXs) promotes the synthesis of phospholipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are more susceptible to oxidative damage (Shah et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2022).
4.2 The impact of ferroptosis on the NAFLD
Iron overload and lipid peroxidation are the primary characteristics of ferroptosis. Previous studies have reported that ferroptosis is associated with the pathogenesis of various diseases, such as tumors (Bai et al., 2019), kidney injury (Friedmann Angeli et al., 2014), encephalopathy (Hambright et al., 2017), and NAFLD (Li et al., 2020c). The liver is the primary regulatory organ for iron homeostasis, including iron absorption, utilization, storage, and secretion (Protchenko et al., 2021), promoting systemic regulation of iron homeostasis and storing excess iron in cases of iron overload (Gao et al., 2022). Iron overload is a crucial factor in NAFLD, and ferroptosis plays a role in its pathogenesis. A close relationship exists between the grading of hepatic steatosis and the expression of several genes involved in ferroptosis, including GSS, ACSL4, and ACSL3 (Dai et al., 2022). The ferroptosis inducer RSL3 reduces hepatic expression of GPX4, exacerbating hepatic steatosis and inflammation in NASH mouse models (J et al., 2020). In contrast, the ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1 (Fer1) significantly reduces lipid accumulation and markedly lowers hepatic triglyceride levels, alleviating inflammation, fibrosis, and liver damage in NASH mice (Li et al., 2020c). Iron-induced lipid peroxidation is a primary trigger of NAFLD, with GPX4 serving as a key regulator that mediates lipid peroxidation-induced ferroptosis. Hepatocyte lipid accumulation leads to endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction and increases sensitivity to lipid peroxidation by altering membrane phospholipid composition. Under the synergistic effects of iron overload and lipotoxicity, GPX4 activity in hepatocytes is doubly inhibited: on one hand, iron ions weaken GPX4 substrate supply by consuming GSH (Kose et al., 2019). On the other hand, accumulated lipid peroxides directly deplete GPX4’s enzymatic activity reserves (Luo et al., 2023). This vicious cycle leads to the collapse of the hepatocyte antioxidant defense system, ultimately triggering irreversible ferroptosis.
Macrophages in the liver recycle large amounts of free iron released by the iron-induced death of hepatocytes. Iron accumulation promotes their polarization toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype. At the same time, free iron also regulates the tricarboxylic acid cycle in macrophages, thereby further regulating the production of inflammatory cytokines (M et al., 2019). Iron overload promotes the production of ROS in T cells, leading to DNA damage and impairing T cell responsiveness, thereby accelerating the inflammatory pathological process (Wang et al., 2018). Therefore, the release of free iron from hepatic iron death significantly promotes the initiation of the inflammatory cascade. Clinical studies have reported hepatic iron overload in NAFLD and NASH patients, which is associated with increased severity and progression of NAFLD (Corradini et al., 2021). Serum ferritin levels help identify patients with NAFLD who are at risk for NASH and advanced fibrosis (Kowdley et al., 2012; Jung et al., 2019). In summary, hepatic steatosis, chronic inflammation, and hepatic fibrosis are the primary characteristics of NAFLD. Ferroptosis significantly promotes the progression of NASH/NAFLD by facilitating the development of hepatic steatosis, chronic inflammation, and hepatic fibrosis. Current iron death regulatory strategies targeting GPX4 demonstrate potential therapeutic value. Liproxstatin-1 inhibits GPX4-induced iron death (Fan et al., 2021, p. 4), while N-acetylcysteine alleviates mitochondrial oxidative damage and iron death by enhancing mitochondrial GSH activity and mitochondrial redox homeostasis (Li et al., 2022a). The harmful role of non-classical GPX4 subtypes in ferroptosis has been demonstrated, and selective targeting of non-classical GPX4 transcription variants (iGPX4) may represent a promising therapeutic strategy for MAFLD (Tong et al., 2022). FXR acts as a guardian against ferroptosis by upregulating the expression of anti-ferroptotic genes, thereby reducing lipid peroxidation (Tschuck et al., 2023). These findings provide a theoretical basis for developing NAFLD therapeutic drugs targeting the ferroptosis pathway (Figure 2).
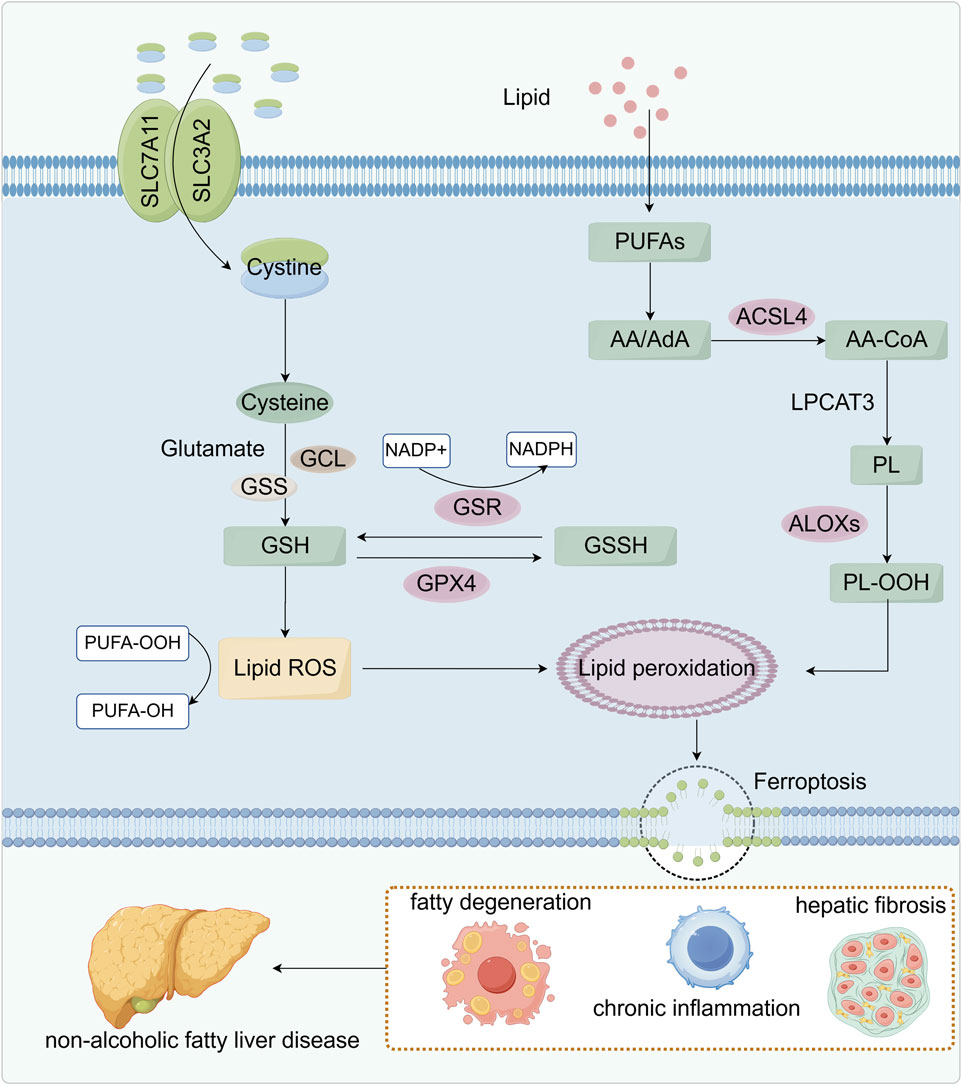
Figure 2. Relationship between lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. SLC7A11 and SLC3A2 on the cell membrane co-transport cystine, which is reduced to cysteine and used with glutamate to synthesize glutathione (GSH). Glutathione reductase (GSR) uses NADPH to regenerate GSH from its oxidized form (GSSG), sustaining the antioxidant cycle. GSH also works through glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) to eliminate lipid ROS and inhibit lipid peroxidation. Meanwhile, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are esterified by ACSL4 and LPCAT3 into phospholipids, which ALOX enzymes then oxidize to peroxidized phospholipids (PL-OOH), thereby fueling lipid peroxidation. When GSH is depleted or GPX4 is inhibited, lipid ROS accumulate, driving ferroptosis. These metabolic disturbances lead to steatosis, chronic inflammation, and hepatic fibrosis, ultimately promoting the development of NAFLD.
5 Bile acid-mediated lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis
5.1 Bile acids and lipid peroxidation
5.1.1 Bile acids and regulation of lipid metabolism
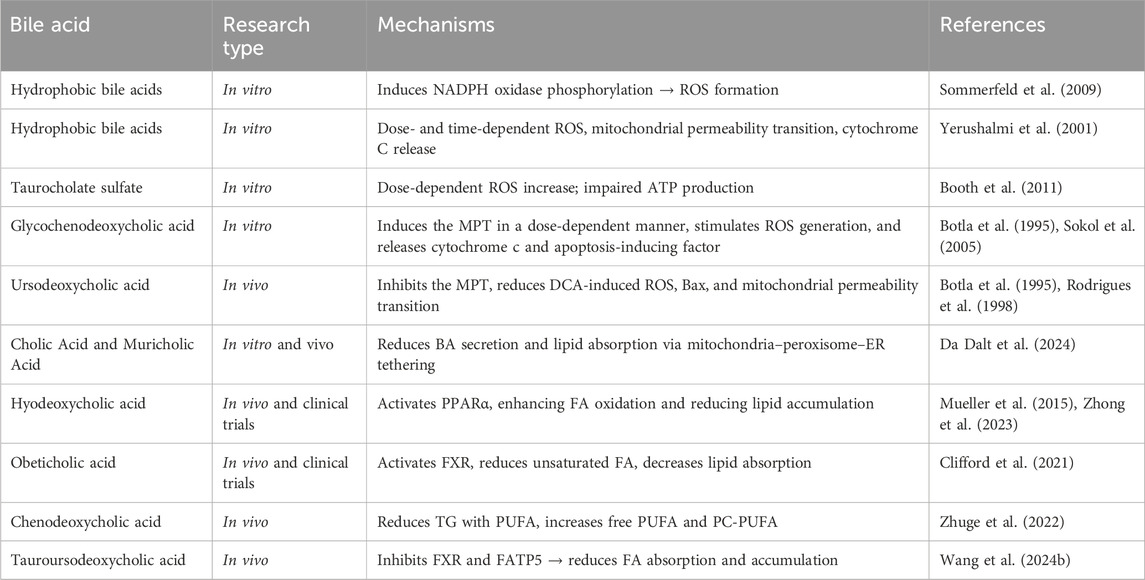
Bile acids, as end products of cholesterol metabolism, play a central role in lipid homeostasis. Through activation of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR), bile acids suppress sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c), thereby reducing fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis (Cha and Repa, 2007; Wang and Tontonoz, 2018). They also enhance fatty acid oxidation, particularly through the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα). Hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA) improves NAFLD via PPARα activation, inhibits abnormal nuclear–cytoplasmic shuttling, and reduces lipid accumulation and oxidative stress (Zhong et al., 2023). Clinical studies have revealed that HDCA levels are significantly reduced in individuals with obesity, diabetes, and NAFLD (Zheng et al., 2021). Obeticholic acid (OCA), a synthetic bile acid, activates the FXR to regulate bile acid and lipid metabolism (Clifford et al., 2021). However, microbiota-induced lipid peroxidation can impair its antifibrotic effects (Zhuge et al., 2022). Usodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) exerts protective effects against liver damage by antagonizing FXR, thereby regulating lipid absorption, reducing lipid accumulation, and mitigating oxidative stress (Mueller et al., 2015). Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), a taurine-conjugated form of UDCA, helps alleviate NAFLD by modulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism, while preventing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction (Wang et al., 2024b). Thus, bile acids influence both fatty acid synthesis and oxidation through multiple pathways, impacting lipid homeostasis and contributing to the development of metabolic disorders when dysregulated.
5.1.2 Hydrophobic and hydrophilic bile acids in oxidative stress
Hydrophobic bile acids (BAs) such as cholic acid (CA) and deoxycholic acid (DCA) are closely associated with lipid peroxidation and hepatocellular injury. Lipid peroxidation, characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxides, is a significant contributor to oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Hydrophobic BAs stimulate ROS production through multiple mechanisms. First, BAs enhance oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria, thereby increasing ROS output. In hepatic stellate cells, hydrophobic bile acids also induce epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) phosphorylation, leading to ROS production via NADPH oxidase activation (Sommerfeld et al., 2009). At the mitochondrial level, these BAs promote mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) and cytochrome c release, which subsequently trigger apoptosis (Yerushalmi et al., 2001). Experimental studies have demonstrated that taurocholate sulfate induces ROS accumulation in a dose-dependent manner, thereby impairing ATP production and leading to apoptosis and necrosis (Booth et al., 2011). Glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA) induces mitochondrial permeability transition in a dose-dependent manner, leading to excessive ROS generation and the release of cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), ultimately contributing to apoptosis (Botla et al., 1995; Sokol et al., 2005). In contrast, hydrophilic bile salts such as ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can mitigate BA-induced mitochondrial injury. UDCA decreases ROS production and Bax protein expression, stabilizes mitochondrial transmembrane potential, and inhibits cytochrome c release, thereby protecting hepatocytes from DCA-induced apoptosis (Botla et al., 1995; Rodrigues et al., 1998).
Bile acids influence lipid metabolism and oxidative stress via multiple pathways. Hydrophobic bile acids exacerbate oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction, while hydrophilic bile acids offer protective effects. These dual roles highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting bile acid metabolism and modulating lipid peroxidation in NAFLD (Table 1).
5.2 Bile acids and ferroptosis
Bile acid metabolism plays a key role in lipid metabolism and energy balance, while ferroptosis is a form of cell death triggered by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. Both processes involve the accumulation of peroxides of polyunsaturated fatty acids, leading to interactions in their pathological mechanisms. On the one hand, bile acid metabolism plays a direct role in regulating ferroptosis through lipid peroxidation. Studies have shown that DCA upregulates the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α) and divalent metal transporter-1 (DMT1), leading to the accumulation of ferrous ions, which enhances lipid peroxidation within cells and promotes the onset of ferroptosis (Wang et al., 2024a). UDCA is a naturally occurring, low-toxicity, hydrophilic bile acid in the human body, converted from primary bile acids by intestinal microbiota. UDCA binds to the cystine transporter SLC7A11, inhibiting cystine uptake and impairing de novo GSH, which leads to ROS accumulation and mitochondrial oxidative damage (Xie et al., 2025). TCA reduces ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1) and ferroptosis-related protein levels, upregulates intracellular iron, reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation levels, thereby exacerbating ferroptosis (Zeng et al., 2025). On the other hand, bile acids can regulate molecules associated with ferroptosis by activating the nuclear receptor FXR and its downstream signaling pathways. Bile acids activate FXR to inhibit ferroptosis, and FXR activation significantly reduces lipid peroxidation by upregulating ferroptosis gatekeepers GPX4, FSP1, PPARα, SCD1, and ACSL3, thereby acting as a guardian of ferroptosis (Tschuck et al., 2023). BAs can reverse Erastin-induced ferroptosis in gastric cancer, and BAs significantly increase the expression of glutathione synthase and GPX4 by activating FXR, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis sensitivity (Liu et al., 2024). FXR activation rescues lipid peroxidation, intracellular ROS, and Fe2+ accumulation, inhibits ferroptosis, and alleviates nephrotoxicity (Tang et al., 2023). Bile acids function as signaling molecules in regulating ferroptosis; however, current research on the regulation of hepatic ferroptosis by bile acids is limited, and further validation of their interaction mechanisms is needed in the future.
6 Traditional Chinese medicine intervention strategies
6.1 TCM regulation of bile acids in NAFLD
Currently, treatment options for NAFLD include lifestyle changes, fecal microbiota transplantation, surgery, and drug therapy. However, there are still no specific drugs for NAFLD, and no drugs have been approved for this condition. TCM, especially herbal medicine or herbal extracts, is receiving increasing attention due to its multi-component, multi-pathway, and multi-target characteristics, which give it unique advantages in preventing and treating NAFLD.
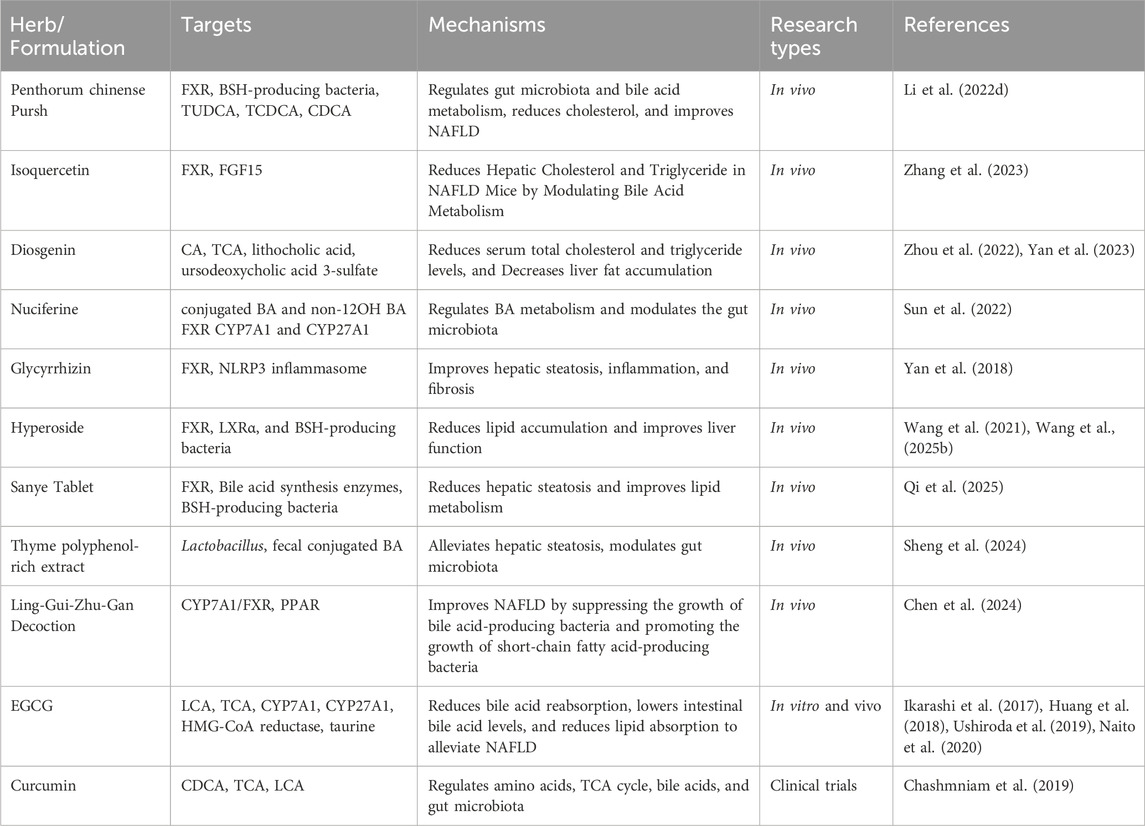
6.1.1 Enhancing bile acid synthesis and excretion
Penthorum chinense Pursh induces an alternative pathway of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) synthesis, activates FXR, promotes BA excretion, and reduces cholesterol levels, effectively ameliorating NAFLD in mouse models (Li et al., 2022d). Based on data mining, the bioactive components of Penthorum chinense Pursh bind to RXRA and FXR, significantly increasing the expression of RXRA, FXR, and bile salt export pump (BSEP) in L02 cells, while decreasing the expression of CYP7A1 (Li et al., 2022c). Isoquercetin activates alternative BA biosynthesis pathways and inhibits intestinal FXR-FGF15 signaling, which reduces cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the liver, improving NAFLD (Zhang et al., 2023). Nuciferine elevates conjugated BA and non-12OH BA levels, downregulates protein levels of FXR, FGF15, FGFR4, and ASBT, and upregulates protein levels of CYP7A1 and CYP27A1, decreases BSH-producing genus, 7α-dehydroxylation genus, and increases taurine metabolism-related genus (Sun et al., 2022). Diosgenin can regulate BAs metabolism through the liver FSR-shp and intestinal FSR-FGF15 pathways, especially in the CA, TCA, and treat NASH (Yan et al., 2023). Diosgenin can inhibit excessive weight gain in rats with NAFLD induced by a high-fat diet, reduce serum total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and decrease liver fat accumulation. It also regulates bile acid metabolism, particularly lithocholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid 3-sulfate (Zhou et al., 2022). Glycyrrhizin regulates BA metabolism, inhibits deoxycholic acid-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and improves hepatic inflammation, steatosis, and fibrosis in NAFLD (Yan et al., 2018).
6.1.2 Modulating gut microbiota and BSH-Producing bacteria
Sanye Tablet enhances taurine-conjugated bile acid levels in the liver and feces, upregulating enzymes involved in BA synthesis. It reduces lipid accumulation and suppresses BSH-producing bacteria, improving liver lipid metabolism and preventing hepatic steatosis in rodent models of NAFLD (Qi et al., 2025). Thyme polyphenol-rich extract reduces serum total BA levels and increases fecal BA levels, enhancing the relative abundance of Lactobacillus species, which positively influences bile acid metabolism and mitigates high-fat diet-induced NAFLD (Sheng et al., 2024). Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan Decoction influences BA biosynthesis and PPAR signaling, modulates gut microbiota composition, and reduces hepatic steatosis in NAFLD mice (Chen et al., 2024). Hyperoside, a flavonol glycoside found in various herbs, exhibits antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and anti-inflammatory properties. It has been shown to increase the expression of liver FXR and LXRα, promote fatty acid oxidation, and enhance BA efflux from the liver. Additionally, it regulates hepatic de novo lipogenesis and BA metabolism, inhibits gut microbes associated with bile salt hydrolase (BSH) activity, and reduces cholesterol and triglyceride levels in NAFLD rats (Wang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2025b). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) has been shown to exert beneficial effects on metabolic disorders and fatty liver disease. EGCG reduces BA reabsorption, decreases intestinal BA levels, and lowers lipid absorption, mitigating metabolic disorders and fatty liver disease induced by a high-fat diet (Huang et al., 2018; Ushiroda et al., 2019). Additionally, EGCG induces a hepatospecific decrease in CYP3A expression levels. This effect is attributed to alterations in the intestinal flora (Ikarashi et al., 2017). Further studies confirm that EGCG’s ability to lower intestinal BA levels and reduce lipid absorption plays a critical role in alleviating fatty liver and metabolic disorders (Naito et al., 2020).
In conclusion, these bioactive compounds and herbal formulations demonstrate promising therapeutic potential for managing NAFLD by regulating bile acid metabolism, enhancing liver function, and improving lipid homeostasis (Table 2).
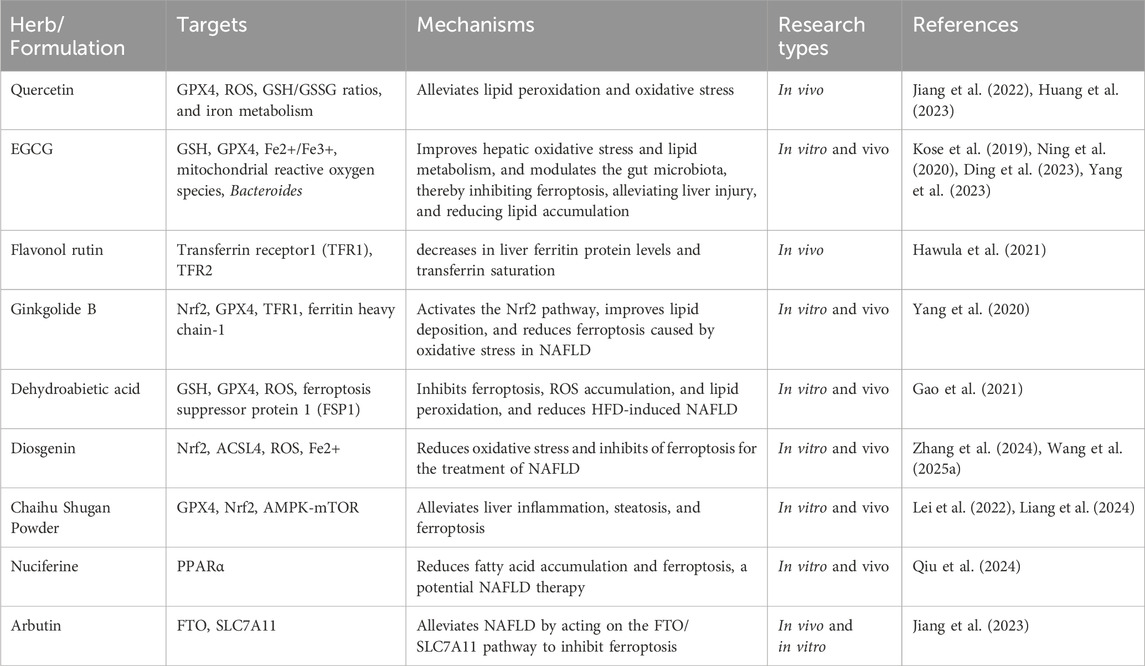
6.2 TCM regulation of lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in NAFLD
Ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death driven by lipid peroxidation, is increasingly recognized as a key mechanism in the progression of NAFLD. Several Chinese herbal medicines and their bioactive compounds have been shown to modulate lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis, offering new therapeutic strategies for NAFLD.
6.2.1 Antioxidant defense and GPX4/GSH enhancement
Quercetin is widely recognized as an essential flavonoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (Anand David et al., 2016). Quercetin increases GPX4 and GSH/GSSG ratios, inhibits ROS, lipid peroxides, and iron overload, and suppresses iron-induced cell death in hepatocytes and the liver, alleviating NAFLD (Jiang et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2023). It also inhibits inflammasome responses and the activation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway, thereby improving lipid metabolism and alleviating inflammatory conditions associated with NAFLD (Porras et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2018). EGCG can prevent GSH depletion, GPX4 inactivation, and lipid peroxidation by chelating iron ions, and is considered a novel inhibitor of ferroptosis (Kose et al., 2019). EGCG alleviates liver damage, lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, and hepatic steatosis, increases NRF2 and GPX4 expression in iron-overloaded mice, and enhances antioxidant capacity (Ding et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023). It also improves intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in non-alcoholic NASH mice, thereby alleviating lipid accumulation and ferroptosis (Ning et al., 2020), indicating that EGCG is a potential inhibitor of ferroptosis. Dehydroabietic acid promotes the expression of GSH and GPX4, reduces ROS accumulation, reduces hepatic lipid peroxidation, inhibits hepatic ferroptosis, and improves NAFLD (Gao et al., 2021).
6.2.2 Pathway-specific regulation of ferroptosis and lipid accumulation
Diosgenin significantly alleviates ferroptosis and ROS accumulation in HepG2 cells by regulating the ACSL4/LPCAT3/ALOX15 pathway, thereby mitigating NAFLD (Wang et al., 2025a). Diosgenin reduces lipid accumulation and steatosis, upregulates the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and its downstream ferroptosis-related genes, and inhibits ferroptosis in the livers of rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (Zhang et al., 2024). Through network pharmacology and in vivo validation, Chaihu Shugan Powder (CSP) has been shown to improve liver inflammation in a hepatic steatosis model. It inhibits hepatic fatty acid synthesis by inhibiting the TNFα/TNFR1 signaling pathway (Lei et al., 2022). CSP inhibits the AMPK-mTOR pathway, restores autophagy and ferroptosis markers such as GPX4 and Nrf-2, and alleviates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting autophagic ferroptosis (Liang et al., 2024). Ginkgolide B significantly improves oxidative damage and lipid peroxidation by blocking ferroptosis, with its mechanism of action related to Nrf2 activation (Yang et al., 2020). Flavonol rutin reduces hepatic ferritin expression and serum transferrin saturation, with its hepatoprotective effect associated with inhibiting hepatic ferroptosis (Hawula et al., 2021). Arbutin, a natural antioxidant, inhibits obesity-associated protein (FTO), which increases the m6A methylation level of SLC7A11, promotes the expression of SLC7A11, and ultimately inhibits iron death, slowing down the progression of NAFLD in vivo and in vitro (Jiang et al., 2023). Nuciferine Ameliorates Fatty Acid Accumulation and Iron Death via the PPARα Signalling Pathway, PPARα Inhibitors Block the Protective Effects of Nuc, Resulting in Excessive Accumulation of Iron Ions, Suggesting that Nuc May Be a Potential Drug for the Treatment of NAFLD (Qiu et al., 2024).
Their therapeutic effects primarily involve strengthening antioxidant defenses by enhancing GPX4 and GSH activity, reducing ROS accumulation, and limiting iron-induced lipid damage, thereby protecting hepatocytes. These mechanisms highlight TCM’s multifaceted potential for NAFLD therapy (Table 3).
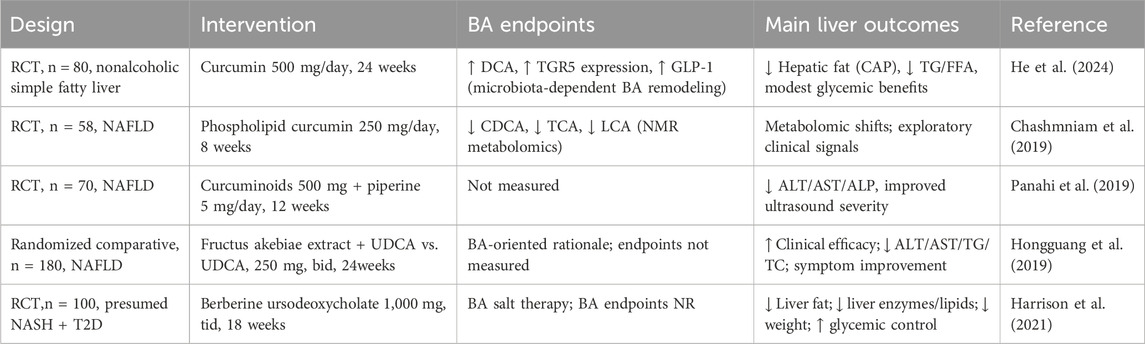
6.3 Clinical evidence of TCM targeting bile acid metabolism in NAFLD
Clinical data indicate that curcumin modulates BA metabolism in NAFLD and can improve hepatic and metabolic indices. In a 24-week randomized controlled trial, curcumin reduced hepatic fat and remodeled BA signaling, suggesting a gut microbiota-dependent BA mechanism (He et al., 2024). Earlier metabolomics work in NAFLD has shown that curcumin shifts multiple pathways, including decreases in chenodeoxycholic acid, taurocholic acid, and lithocholic acid, alongside changes in amino acids and TCA cycle intermediates (Chashmniam et al., 2019). Supplementation with curcumin, combined with piperine, has been reported to significantly improve liver function, lower cholesterol levels, and increase total iron-binding capacity, thereby exerting therapeutic benefits in patients with NAFLD (Panahi et al., 2019). However, another clinical trial found that an 8-week course of curcumin with piperine did not significantly reduce serum pro-oxidant–antioxidant balance (PAB) values, suggesting that the administered dose may have been insufficient to achieve a measurable reduction in oxidative stress (Mirhafez et al., 2019). In addition, clinical evidence suggests that Fructus akebiae, when combined with ursodeoxycholic acid, has been shown to significantly alleviate clinical symptoms and improve serum biochemical parameters, including ALT, AST, triglycerides, and total cholesterol, in patients with NAFLD (Hongguang et al., 2019). Berberine ursodeoxycholate significantly reduced liver fat, improved liver enzymes and lipid profiles, promoted weight loss, and enhanced glycemic control, supporting its potential as a dual metabolic and hepatoprotective therapy for NAFLD/NASH despite mild gastrointestinal adverse events (Harrison et al., 2021). These findings highlight the potential of traditional Chinese medicine to modulate bile acid metabolism in the treatment of NAFLD, and suggest that combining bile acid-based therapies with traditional Chinese medicine may offer additional therapeutic benefits (Table 4).
7 Future research directions
Recent studies suggest that bile acid metabolism plays a role in the development of NAFLD, particularly through its impact on lipid peroxidation. Lipid peroxidation, especially in its iron-dependent form, is a hallmark of ferroptosis and has been implicated as a key driver in NAFLD progression. Current research on bile acid–induced lipid peroxidation mainly emphasizes ROS generation, with ferroptosis and lipid peroxidation interconnected via the GSH/GSSG system and ROS balance. However, the precise mechanisms by which bile acids promote lipid peroxidation and trigger ferroptosis remain unclear. Future studies should focus on clarifying whether bile acids regulate the GSH/GPX4 pathway and thereby influence ferroptosis in NAFLD, as well as on understanding how ferroptosis mechanisms affect disease progression and prognosis.
8 Conclusion
In summary, bile acid metabolism plays a pivotal role in the onset and progression of NAFLD. It regulates hepatic lipogenesis, participates in lipid oxidation, and is closely linked to hepatic steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, and liver fibrosis. Bile acids modulate ROS, influencing lipid peroxidation, which is connected to ferroptosis via the GSH/GSSG system and ROS. By regulating bile acid metabolism, TCM improves hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis, offering a promising therapeutic strategy for NAFLD and underscoring the potential of TCM in treating metabolic diseases. These findings highlight the interplay between bile acid metabolism, lipid peroxidation, and ferroptosis, providing new insights into NAFLD pathophysiology and identifying potential therapeutic targets for clinical treatment, thus contributing to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for metabolic diseases.
Author contributions
JL: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. FL: Methodology, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. QZ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. WH: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. LY: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. SL: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. DL: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. YD: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is funded by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Innovation Team for the Prevention and Treatment of Diseases Related to Sugar and Lipid Metabolism (Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Team, No. 2020RC4050).
Acknowledgments
We thank the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abulikemu, A., Zhao, X., Xu, H., Li, Y., Ma, R., Yao, Q., et al. (2023). Silica nanoparticles aggravated the metabolic associated fatty liver disease through disturbed amino acid and lipid metabolisms-mediated oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 59, 102569. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102569
Aguilar-Olivos, N. E., Carrillo-Córdova, D., Oria-Hernández, J., Sánchez-Valle, V., Ponciano-Rodríguez, G., Ramírez-Jaramillo, M., et al. (2015). The nuclear receptor FXR, but not LXR, up-regulates bile acid transporter expression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 14, 487–493. doi:10.1016/s1665-2681(19)31170-6
Anand David, A. V., Arulmoli, R., and Parasuraman, S. (2016). Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: a bioactive flavonoid. Pharmacogn. Rev. 10, 84–89. doi:10.4103/0973-7847.194044
Ayala, A., Muñoz, M. F., and Argüelles, S. (2014). Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 360438. doi:10.1155/2014/360438
Bai, T., Lei, P., Zhou, H., Liang, R., Zhu, R., Wang, W., et al. (2019). Sigma-1 receptor protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 23, 7349–7359. doi:10.1111/jcmm.14594
Biddinger, S. B., Hernandez-Ono, A., Rask-Madsen, C., Haas, J. T., Alemán, J. O., Suzuki, R., et al. (2008). Hepatic insulin resistance is sufficient to produce dyslipidemia and susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 7, 125–134. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2007.11.013
Booth, D. M., Murphy, J. A., Mukherjee, R., Awais, M., Neoptolemos, J. P., Gerasimenko, O. V., et al. (2011). Reactive oxygen species induced by bile acid induce apoptosis and protect against necrosis in pancreatic acinar cells. Gastroenterology 140, 2116–2125. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.054
Botla, R., Spivey, J. R., Aguilar, H., Bronk, S. F., and Gores, G. J. (1995). Ursodeoxycholate (UDCA) inhibits the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition induced by glycochenodeoxycholate: a mechanism of UDCA cytoprotection. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 272, 930–938. doi:10.1016/s0022-3565(25)24517-7
Bruneau, A., Hundertmark, J., Guillot, A., and Tacke, F. (2021). Molecular and cellular mediators of the gut-liver Axis in the progression of liver diseases. Front. Med. 8, 725390. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.725390
Bugianesi, E., Gastaldelli, A., Vanni, E., Gambino, R., Cassader, M., Baldi, S., et al. (2005). Insulin resistance in non-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: sites and mechanisms. Diabetologia 48, 634–642. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-1682-x
Buzzetti, E., Pinzani, M., and Tsochatzis, E. A. (2016). The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 65, 1038–1048. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012
Byrne, C. D., and Targher, G. (2020). What’s new in NAFLD pathogenesis, biomarkers and treatment? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 17, 70–71. doi:10.1038/s41575-019-0239-2
Cha, J.-Y., and Repa, J. J. (2007). The liver X receptor (LXR) and hepatic lipogenesis. The carbohydrate-response element-binding protein is a target gene of LXR. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 743–751. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605023200
Chalasani, N., Younossi, Z., Lavine, J. E., Charlton, M., Cusi, K., Rinella, M., et al. (2018). The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatol. Balt. Md 67, 328–357. doi:10.1002/hep.29367
Chashmniam, S., Mirhafez, S. R., Dehabeh, M., Hariri, M., Azimi Nezhad, M., and Nobakht M Gh, B. F. (2019). A pilot study of the effect of phospholipid curcumin on serum metabolomic profile in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 73, 1224–1235. doi:10.1038/s41430-018-0386-5
Chen, J., Ou, Z., Gao, T., Yang, Y., Shu, A., Xu, H., et al. (2022). Ginkgolide B alleviates oxidative stress and ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 ubiquitination to improve diabetic nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomedecine Pharmacother. 156, 113953. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113953
Chen, L.-P., Zhang, L.-F., Liu, S., Hua, H., Zhang, L., Liu, B.-C., et al. (2024). Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan decoction ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating the gut microbiota. Microbiol. Spectr. 12, e0197923. doi:10.1128/spectrum.01979-23
Clifford, B. L., Sedgeman, L. R., Williams, K. J., Morand, P., Cheng, A., Jarrett, K. E., et al. (2021). FXR activation protects against NAFLD via bile-acid-dependent reductions in lipid absorption. Cell Metab. 33, 1671–1684.e4. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2021.06.012
Corradini, E., Buzzetti, E., Dongiovanni, P., Scarlini, S., Caleffi, A., Pelusi, S., et al. (2021). Ceruloplasmin gene variants are associated with hyperferritinemia and increased liver iron in patients with NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 75, 506–513. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.014
Da Dalt, L., Moregola, A., Svecla, M., Pedretti, S., Fantini, F., Ronzio, M., et al. (2024). The inhibition of inner mitochondrial fusion in hepatocytes reduces non-alcoholic fatty liver and improves metabolic profile during obesity by modulating bile acid conjugation. Cardiovasc. Res. 119, 2917–2929. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvad169
Dai, X., Zhang, R., and Wang, B. (2022). Contribution of classification based on ferroptosis-related genes to the heterogeneity of MAFLD. BMC Gastroenterol. 22, 55. doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02137-9
Dawson, P. A., Haywood, J., Craddock, A. L., Wilson, M., Tietjen, M., Kluckman, K., et al. (2003). Targeted deletion of the ileal bile acid transporter eliminates enterohepatic cycling of bile acids in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 33920–33927. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306370200
Di Ciaula, A., Bonfrate, L., Baj, J., Khalil, M., Garruti, G., Stellaard, F., et al. (2022). Recent advances in the digestive, metabolic and therapeutic effects of farnesoid X receptor and fibroblast growth factor 19: from cholesterol to bile acid signaling. Nutrients 14, 4950. doi:10.3390/nu14234950
Ding, S.-B., Chu, X.-L., Jin, Y.-X., Jiang, J.-J., Zhao, X., and Yu, M. (2023). Epigallocatechin gallate alleviates high-fat diet-induced hepatic lipotoxicity by targeting mitochondrial ROS-mediated ferroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1148814. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1148814
Dixon, S. J., Lemberg, K. M., Lamprecht, M. R., Skouta, R., Zaitsev, E. M., Gleason, C. E., et al. (2012). Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of non-apoptotic cell death. Cell 149, 1060–1072. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Donnelly, K. L., Smith, C. I., Schwarzenberg, S. J., Jessurun, J., Boldt, M. D., and Parks, E. J. (2005). Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 1343–1351. doi:10.1172/JCI23621
Dukewich, M., Yuan, L., and Terrault, N. A. (2025). At the crossroads of health and disease: consequences of fat in the liver. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 87, 325–352. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-022724-105515
Enooku, K., Tsutsumi, T., Kondo, M., Fujiwara, N., Sasako, T., Shibahara, J., et al. (2020). Hepatic FATP5 expression is associated with histological progression and loss of hepatic fat in NAFLD patients. J. Gastroenterol. 55, 227–243. doi:10.1007/s00535-019-01633-2
Fan, B.-Y., Pang, Y.-L., Li, W.-X., Zhao, C.-X., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Liproxstatin-1 is an effective inhibitor of oligodendrocyte ferroptosis induced by inhibition of glutathione peroxidase 4. Neural Regen. Res. 16, 561–566. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.293157
Fiorucci, S., Carino, A., Baldoni, M., Santucci, L., Costanzi, E., Graziosi, L., et al. (2021). Bile acid signaling in inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 66, 674–693. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06715-3
Foretz, M., Guichard, C., Ferré, P., and Foufelle, F. (1999). Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c is a major mediator of insulin action on the hepatic expression of glucokinase and lipogenesis-related genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 12737–12742. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.22.12737
Forlano, R., Martinez-Gili, L., Takis, P., Miguens-Blanco, J., Liu, T., Triantafyllou, E., et al. (2024). Disruption of gut barrier integrity and host-microbiome interactions underlie MASLD severity in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Gut Microbes 16, 2304157. doi:10.1080/19490976.2024.2304157
Friedmann Angeli, J. P., Schneider, M., Proneth, B., Tyurina, Y. Y., Tyurin, V. A., Hammond, V. J., et al. (2014). Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 16, 1180–1191. doi:10.1038/ncb3064
Gao, G., Xie, Z., Li, E.-W., Yuan, Y., Fu, Y., Wang, P., et al. (2021). Dehydroabietic acid improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through activating the Keap1/Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway to reduce ferroptosis. J. Nat. Med. 75, 540–552. doi:10.1007/s11418-021-01491-4
Gao, H., Jin, Z., Bandyopadhyay, G., Wang, G., Zhang, D., Rocha, K. C. E., et al. (2022). Aberrant iron distribution via hepatocyte-stellate cell axis drives liver lipogenesis and fibrosis. Cell Metab. 34, 1201–1213.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2022.07.006
GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators (2020). Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet lond. Engl. 396, 1204–1222. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9
GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators (2023). Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet lond. Engl. 402, 203–234. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6
Geng, Y., Faber, K. N., de Meijer, V. E., Blokzijl, H., and Moshage, H. (2021). How does hepatic lipid accumulation lead to lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? Hepatol. Int. 15, 21–35. doi:10.1007/s12072-020-10121-2
Goodwin, B., Jones, S. A., Price, R. R., Watson, M. A., McKee, D. D., Moore, L. B., et al. (2000). A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol. Cell 6, 517–526. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00051-4
Greene, L. E., Lincoln, R., and Cosa, G. (2017). Rate of lipid peroxyl radical production during cellular homeostasis unraveled via fluorescence imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 15801–15811. doi:10.1021/jacs.7b08036
Guzior, D. V., and Quinn, R. A. (2021). Review: microbial transformations of human bile acids. Microbiome 9, 140. doi:10.1186/s40168-021-01101-1
Hambright, W. S., Fonseca, R. S., Chen, L., Na, R., and Ran, Q. (2017). Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox Biol. 12, 8–17. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.021
Harrison, S. A., Gunn, N., Neff, G. W., Kohli, A., Liu, L., Flyer, A., et al. (2021). A phase 2, proof of concept, randomised controlled trial of berberine ursodeoxycholate in patients with presumed non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 12, 5503. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25701-5
Hawula, Z. J., Secondes, E. S., Wallace, D. F., Rishi, G., and Subramaniam, V. N. (2021). The effect of the flavonol rutin on serum and liver iron content in a genetic mouse model of iron overload. Biosci. Rep. 41, BSR20210720. doi:10.1042/BSR20210720
He, Y., Chen, X., Li, Y., Liang, Y., Hong, T., Yang, J., et al. (2024). Curcumin supplementation alleviates hepatic fat content associated with modulation of gut microbiota-dependent bile acid metabolism in patients with nonalcoholic simple fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 120, 66–79. doi:10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.05.017
Heeren, J., and Scheja, L. (2021). Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol. Metab. 50, 101238. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101238
Henning, Y., Blind, U. S., Larafa, S., Matschke, J., and Fandrey, J. (2022). Hypoxia aggravates ferroptosis in RPE cells by promoting the Fenton reaction. Cell Death Dis. 13, 662. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05121-z
Herman, M. A., and Samuel, V. T. (2016). The sweet path to metabolic demise: fructose and lipid synthesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. Tem. 27, 719–730. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2016.06.005
Hirsova, P., Ibrahim, S. H., Krishnan, A., Verma, V. K., Bronk, S. F., Werneburg, N. W., et al. (2016). Lipid-induced signaling causes release of inflammatory extracellular vesicles from hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 150, 956–967. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.12.037
Hongguang, J., Xingjie, H., Mingliang, J., Yun, L., Tongjian, L., Jingmo, Y., et al. (2019). Clinical effect of the extract of TCM Fructus akebiae combined with ursodeoxycholic acid on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 32, 433–437. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331948985.
Huang, J., Feng, S., Liu, A., Dai, Z., Wang, H., Reuhl, K., et al. (2018). Green tea polyphenol EGCG alleviates metabolic abnormality and fatty liver by decreasing bile acid and lipid absorption in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 62, 1700696. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201700696
Huang, T., Zhang, K., Wang, J., He, K., Zhou, X., and Nie, S. (2023). Quercetin alleviates acrylamide-induced liver injury by inhibiting autophagy-dependent ferroptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 7427–7439. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01378
Iizuka, K., Bruick, R. K., Liang, G., Horton, J. D., and Uyeda, K. (2004). Deficiency of carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) reduces lipogenesis as well as glycolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 7281–7286. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401516101
Ikarashi, N., Ogawa, S., Hirobe, R., Kon, R., Kusunoki, Y., Yamashita, M., et al. (2017). Epigallocatechin gallate induces a hepatospecific decrease in the CYP3A expression level by altering intestinal flora. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 100, 211–218. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2017.01.022
Inagaki, T., Choi, M., Moschetta, A., Peng, L., Cummins, C. L., McDonald, J. G., et al. (2005). Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2, 217–225. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2005.09.001
Jeong, Y.-S., Kim, D., Lee, Y. S., Kim, H.-J., Han, J.-Y., Im, S.-S., et al. (2011). Integrated expression profiling and genome-wide analysis of ChREBP targets reveals the dual role for ChREBP in glucose-regulated gene expression. PloS One 6, e22544. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022544
Ji, Y., Gao, Y., Chen, H., Yin, Y., and Zhang, W. (2019). Indole-3-Acetic acid alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice via attenuation of hepatic lipogenesis, and oxidative and inflammatory stress. Nutrients 11, 2062. doi:10.3390/nu11092062
Jia, X., Suzuki, Y., Naito, H., Yetti, H., Kitamori, K., Hayashi, Y., et al. (2014). A possible role of chenodeoxycholic acid and glycine-conjugated bile acids in fibrotic steatohepatitis in a dietary rat model. Dig. Dis. Sci. 59, 1490–1501. doi:10.1007/s10620-014-3028-3
Jiang, J.-J., Zhang, G.-F., Zheng, J.-Y., Sun, J.-H., and Ding, S.-B. (2022). Targeting mitochondrial ROS-mediated ferroptosis by quercetin alleviates high-fat diet-induced hepatic lipotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 876550. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.876550
Jiang, T., Xiao, Y., Zhou, J., Luo, Z., Yu, L., Liao, Q., et al. (2023). Arbutin alleviates fatty liver by inhibiting ferroptosis via FTO/SLC7A11 pathway. Redox Biol. 68, 102963. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102963
Jones, D. S., and Saso, L. (2007). Chemistry and biology of antioxidants. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 59, 1671. doi:10.1211/jpp.59.12.0009
Jung, J. Y., Shim, J.-J., Park, S. K., Ryoo, J.-H., Choi, J.-M., Oh, I.-H., et al. (2019). Serum ferritin level is associated with liver steatosis and fibrosis in Korean general population. Hepatol. Int. 13, 222–233. doi:10.1007/s12072-018-9892-8
Kalhan, S. C., Guo, L., Edmison, J., Dasarathy, S., McCullough, A. J., Hanson, R. W., et al. (2011). Plasma metabolomic profile in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 60, 404–413. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2010.03.006
Kim, K.-S., Hong, S., Han, K., and Park, C.-Y. (2024). Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study. BMJ 384, e076388. doi:10.1136/bmj-2023-076388
Kose, T., Vera-Aviles, M., Sharp, P. A., and Latunde-Dada, G. O. (2019). Curcumin and (-)- epigallocatechin-3-gallate protect murine MIN6 pancreatic beta-cells against iron toxicity and erastin-induced ferroptosis. Pharm. Basel Switz. 12, 26. doi:10.3390/ph12010026
Kowdley, K. V., Belt, P., Wilson, L. A., Yeh, M. M., Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A., Chalasani, N., et al. (2012). Serum ferritin is an independent predictor of histologic severity and advanced fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Balt. Md 55, 77–85. doi:10.1002/hep.24706
Lai, C. S., and Piette, L. H. (1978). Spin-trapping studies of hydroxyl radical production involved in lipid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 190, 27–38. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(78)90250-3
Lake, A. D., Novak, P., Shipkova, P., Aranibar, N., Robertson, D., Reily, M. D., et al. (2013). Decreased hepatotoxic bile acid composition and altered synthesis in progressive human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 268, 132–140. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2013.01.022
Lee, J. J., Lambert, J. E., Hovhannisyan, Y., Ramos-Roman, M. A., Trombold, J. R., Wagner, D. A., et al. (2015). Palmitoleic acid is elevated in fatty liver disease and reflects hepatic lipogenesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 101, 34–43. doi:10.3945/ajcn.114.092262
Lei, S., Zhao, S., Huang, X., Feng, Y., Li, Z., Chen, L., et al. (2022). Chaihu Shugan powder alleviates liver inflammation and hepatic steatosis in NAFLD mice: a network pharmacology study and in vivo experimental validation. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 967623. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.967623
Li, J., Cao, F., Yin, H., Huang, Z., Lin, Z., Mao, N., et al. (2020a). Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 11, 88. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
Li, M., Wang, Q., Li, Y., Cao, S., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2020b). Apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter, drug target for bile acid related diseases and delivery target for prodrugs: current and future challenges. Pharmacol. Ther. 212, 107539. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107539
Li, X., Wang, T.-X., Huang, X., Li, Y., Sun, T., Zang, S., et al. (2020c). Targeting ferroptosis alleviates methionine-choline deficient (MCD)-diet induced NASH by suppressing liver lipotoxicity. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 40, 1378–1394. doi:10.1111/liv.14428
Li, Q., Liao, J., Chen, W., Zhang, K., Li, H., Ma, F., et al. (2022a). NAC alleviative ferroptosis in diabetic nephropathy via maintaining mitochondrial redox homeostasis through activating SIRT3-SOD2/Gpx4 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 187, 158–170. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.05.024
Li, Q., Liu, W., Feng, Y., Hou, H., Zhang, Z., Yu, Q., et al. (2022b). Radix Puerariae thomsonii polysaccharide (RPP) improves inflammation and lipid peroxidation in alcohol and high-fat diet mice by regulating gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 209, 858–870. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.067
Li, X., Li, Y., Zhao, W., Yu, L., Hu, X., Zhao, Y., et al. (2022c). Dihydroflavonoids as bioactive components of Penthorum chinense, a miao ethnomedicine, against NAFLD through bile acid metabolism pathway. Chem. Biodivers. 19, e202200146. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202200146
Li, X., Zhao, W., Xiao, M., Yu, L., Chen, Q., Hu, X., et al. (2022d). Penthorum chinense Pursh. extract attenuates non-alcholic fatty liver disease by regulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 294, 115333. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115333
Liang, Z., Pi, D., Zhen, J., Yan, H., Zheng, C., Liang Chen, J., et al. (2024). The AMPK-mTOR pathway is inhibited by Chaihu shugan powder, which relieves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by suppressing autophagic ferroptosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2024, 4777789. doi:10.1155/2024/4777789
Linden, A. G., Li, S., Choi, H. Y., Fang, F., Fukasawa, M., Uyeda, K., et al. (2018). Interplay between ChREBP and SREBP-1c coordinates postprandial glycolysis and lipogenesis in livers of mice. J. Lipid Res. 59, 475–487. doi:10.1194/jlr.M081836
Liu, Y., Wan, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhang, L., and Cheng, W. (2023). GPX4: the hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1878, 188890. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188890
Liu, C.-X., Gao, Y., Xu, X.-F., Jin, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, Q., et al. (2024). Bile acids inhibit ferroptosis sensitivity through activating farnesoid X receptor in gastric cancer cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 30, 485–498. doi:10.3748/wjg.v30.i5.485
Lu, T. T., Makishima, M., Repa, J. J., Schoonjans, K., Kerr, T. A., Auwerx, J., et al. (2000). Molecular basis for feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol. Cell 6, 507–515. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00050-2
Luo, J., Song, G., Chen, N., Xie, M., Niu, X., Zhou, S., et al. (2023). Ferroptosis contributes to ethanol-induced hepatic cell death via labile iron accumulation and GPx4 inactivation. Cell Death Discov. 9, 311. doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01608-6
Marra, F., and Svegliati-Baroni, G. (2018). Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 68, 280–295. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.014
Meier, P. J., and Stieger, B. (2002). Bile salt transporters. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64, 635–661. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.64.082201.100300
Mihalik, S. J., Steinberg, S. J., Pei, Z., Park, J., Kim, D. G., Heinzer, A. K., et al. (2002). Participation of two members of the very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase family in bile acid synthesis and recycling. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 24771–24779. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203295200
Mirhafez, S. R., Farimani, A. R., Gholami, A., Hooshmand, E., Tavallaie, S., and Nobakht M Gh, B. F. (2019). The effect of curcumin with piperine supplementation on pro-oxidant and antioxidant balance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 34. doi:10.1515/dmpt-2018-0040
Moreno-Fernandez, M. E., Giles, D. A., Stankiewicz, T. E., Sheridan, R., Karns, R., Cappelletti, M., et al. (n.d.). Peroxisomal β-oxidation regulates whole body metabolism, inflammatory vigor, and pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. JCI Insight 3, e93626. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.93626
Mueller, M., Thorell, A., Claudel, T., Jha, P., Koefeler, H., Lackner, C., et al. (2015). Ursodeoxycholic acid exerts farnesoid X receptor-antagonistic effects on bile acid and lipid metabolism in morbid obesity. J. Hepatol. 62, 1398–1404. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.034
Münzker, J., Haase, N., Till, A., Sucher, R., Haange, S.-B., Nemetschke, L., et al. (2022). Functional changes of the gastric bypass microbiota reactivate thermogenic adipose tissue and systemic glucose control via intestinal FXR-TGR5 crosstalk in diet-induced obesity. Microbiome 10, 96. doi:10.1186/s40168-022-01264-5
Naito, Y., Ushiroda, C., Mizushima, K., Inoue, R., Yasukawa, Z., Abe, A., et al. (2020). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating the interaction between gut microbiota and bile acids. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 67, 2–9. doi:10.3164/jcbn.20-39
Nguyen, P., Leray, V., Diez, M., Serisier, S., Le Bloc’h, J., Siliart, B., et al. (2008). Liver lipid metabolism. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 92, 272–283. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0396.2007.00752.x
Nimer, N., Choucair, I., Wang, Z., Nemet, I., Li, L., Gukasyan, J., et al. (2021). Bile acids profile, histopathological indices and genetic variants for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression. Metabolism 116, 154457. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154457
Ning, K., Lu, K., Chen, Q., Guo, Z., Du, X., Riaz, F., et al. (2020). Epigallocatechin gallate protects mice against methionine-choline-deficient-diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by improving gut microbiota to attenuate hepatic injury and regulate metabolism. ACS Omega 5, 20800–20809. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c01689
Panahi, Y., Valizadegan, G., Ahamdi, N., Ganjali, S., Majeed, M., and Sahebkar, A. (2019). Curcuminoids plus piperine improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a clinical trial. J. Cell. Biochem. 120, 15989–15996. doi:10.1002/jcb.28877
Parséus, A., Sommer, N., Sommer, F., Caesar, R., Molinaro, A., Ståhlman, M., et al. (2017). Microbiota-induced obesity requires farnesoid X receptor. Gut 66, 429–437. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310283
Pathak, P., Xie, C., Nichols, R. G., Ferrell, J. M., Boehme, S., Krausz, K. W., et al. (2018). Intestine farnesoid X receptor agonist and the gut microbiota activate G-protein bile acid receptor-1 signaling to improve metabolism. Hepatol. Balt. Md 68, 1574–1588. doi:10.1002/hep.29857
Porras, D., Nistal, E., Martínez-Flórez, S., Pisonero-Vaquero, S., Olcoz, J. L., Jover, R., et al. (2017). Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 102, 188–202. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.037
Porter, N. A. (2013). A perspective on free radical autoxidation: the physical organic chemistry of polyunsaturated fatty acid and sterol peroxidation. J. Org. Chem. 78, 3511–3524. doi:10.1021/jo4001433
Postic, C., Dentin, R., Denechaud, P.-D., and Girard, J. (2007). ChREBP, a transcriptional regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 27, 179–192. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.27.061406.093618
Potthoff, M. J., Boney-Montoya, J., Choi, M., He, T., Sunny, N. E., Satapati, S., et al. (2011). FGF15/19 regulates hepatic glucose metabolism by inhibiting the CREB-PGC-1α pathway. Cell Metab. 13, 729–738. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.019
Prentki, M., and Madiraju, S. R. M. (2008). Glycerolipid metabolism and signaling in health and disease. Endocr. Rev. 29, 647–676. doi:10.1210/er.2008-0007
Protchenko, O., Baratz, E., Jadhav, S., Li, F., Shakoury-Elizeh, M., Gavrilova, O., et al. (2021). Iron chaperone poly rC binding protein 1 protects mouse liver from lipid peroxidation and steatosis. Hepatol. Balt. Md 73, 1176–1193. doi:10.1002/hep.31328
Puri, P., Daita, K., Joyce, A., Mirshahi, F., Santhekadur, P. K., Cazanave, S., et al. (2018). The presence and severity of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with specific changes in circulating bile acids. Hepatol. Balt. Md 67, 534–548. doi:10.1002/hep.29359
Qi, Y., Du, S., Li, W., Qiu, X., Zhou, F., Bai, L., et al. (2025). Sanye tablet regulates gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism to attenuate hepatic steatosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 345, 119514. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2025.119514
Qiu, J., Le, Y., Liu, N., Chen, L., Jiang, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2024). Nuciferine alleviates high-fat diet- and ApoE-/--induced hepatic steatosis and ferroptosis in NAFLD mice via the PPARα signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 24417–24431. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c04929
Quek, J., Chan, K. E., Wong, Z. Y., Tan, C., Tan, B., Lim, W. H., et al. (2023). Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 8, 20–30. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00317-X
Quintero, P., Pizarro, M., Solís, N., Arab, J. P., Padilla, O., Riquelme, A., et al. (2014). Bile acid supplementation improves established liver steatosis in obese mice independently of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. J. Physiol. Biochem. 70, 667–674. doi:10.1007/s13105-014-0336-1
Raghow, R., Yellaturu, C., Deng, X., Park, E. A., and Elam, M. B. (2008). SREBPs: the crossroads of physiological and pathological lipid homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. Tem. 19, 65–73. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2007.10.009
Rao, A., Haywood, J., Craddock, A. L., Belinsky, M. G., Kruh, G. D., and Dawson, P. A. (2008). The organic solute transporter alpha-beta, Ostalpha-Ostbeta, is essential for intestinal bile acid transport and homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 3891–3896. doi:10.1073/pnas.0712328105
Rebrin, K., Steil, G. M., Mittelman, S. D., and Bergman, R. N. (1996). Causal linkage between insulin suppression of lipolysis and suppression of liver glucose output in dogs. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 741–749. doi:10.1172/JCI118846
Riazi, K., Azhari, H., Charette, J. H., Underwood, F. E., King, J. A., Afshar, E. E., et al. (2022). The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 851–861. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0
Rodrigues, C. M., Fan, G., Wong, P. Y., Kren, B. T., and Steer, C. J. (1998). Ursodeoxycholic acid may inhibit deoxycholic acid-induced apoptosis by modulating mitochondrial transmembrane potential and reactive oxygen species production. Mol. Med. Camb. Mass 4, 165–178. doi:10.1007/bf03401914
Ruart, M., Chavarria, L., Campreciós, G., Suárez-Herrera, N., Montironi, C., Guixé-Muntet, S., et al. (2019). Impaired endothelial autophagy promotes liver fibrosis by aggravating the oxidative stress response during acute liver injury. J. Hepatol. 70, 458–469. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.015
Russell, D. W., and Setchell, K. D. (1992). Bile acid biosynthesis. Biochemistry 31, 4737–4749. doi:10.1021/bi00135a001
Saltiel, A. R., and Kahn, C. R. (2001). Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414, 799–806. doi:10.1038/414799a
Saraev, D. D., and Pratt, D. A. (2024). Reactions of lipid hydroperoxides and how they may contribute to ferroptosis sensitivity. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 81, 102478. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2024.102478
Shah, R., Shchepinov, M. S., and Pratt, D. A. (2018). Resolving the role of lipoxygenases in the initiation and execution of ferroptosis. ACS Cent. Sci. 4, 387–396. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.7b00589
Shapiro, H., Kolodziejczyk, A. A., Halstuch, D., and Elinav, E. (2018). Bile acids in glucose metabolism in health and disease. J. Exp. Med. 215, 383–396. doi:10.1084/jem.20171965
Sheng, X., Zhan, P., Wang, P., He, W., and Tian, H. (2024). Mitigation of high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis by thyme (Thymus quinquecostatus Celak) polyphenol-rich extract (TPE): insights into gut microbiota modulation and bile acid metabolism. Food Funct. 15, 7333–7347. doi:10.1039/d3fo05235d
Sokol, R. J., Dahl, R., Devereaux, M. W., Yerushalmi, B., Kobak, G. E., and Gumpricht, E. (2005). Human hepatic mitochondria generate reactive oxygen species and undergo the permeability transition in response to hydrophobic bile acids. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 41, 235–243. doi:10.1097/01.mpg.0000170600.80640.88
Sommerfeld, A., Reinehr, R., and Häussinger, D. (2009). Bile acid-induced epidermal growth factor receptor activation in quiescent rat hepatic stellate cells can trigger both proliferation and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 22173–22183. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.005355
Spitz, D. R., Malcolm, R. R., and Roberts, R. J. (1990). Cytotoxicity and metabolism of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal and 2-nonenal in H2O2-resistant cell lines. Do aldehydic by-products of lipid peroxidation contribute to oxidative stress? Biochem. J. 267, 453–459. doi:10.1042/bj2670453
Suga, T., Yamaguchi, H., Sato, T., Maekawa, M., Goto, J., and Mano, N. (2017). Preference of conjugated bile acids over unconjugated bile acids as substrates for OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. PloS One 12, e0169719. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0169719
Sumida, Y., Niki, E., Naito, Y., and Yoshikawa, T. (2013). Involvement of free radicals and oxidative stress in NAFLD/NASH. Free Radic. Res. 47, 869–880. doi:10.3109/10715762.2013.837577
Sun, J., Fan, J., Li, T., Yan, X., and Jiang, Y. (2022). Nuciferine protects against high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70, 12014–12028. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c04817
Tang, J., Zeng, J., Chen, L., Wang, M., He, S., Muhmood, A., et al. (2023). Farnesoid X receptor plays a key role in ochratoxin A-induced nephrotoxicity by targeting ferroptosis in vivo and in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 14365–14378. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c04560
Tilg, H., Adolph, T. E., and Trauner, M. (2022). Gut-liver axis: pathophysiological concepts and clinical implications. Cell Metab. 34, 1700–1718. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.017
Titchenell, P. M., Lazar, M. A., and Birnbaum, M. J. (2017). Unraveling the regulation of hepatic metabolism by insulin. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. Tem. 28, 497–505. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2017.03.003
Tong, J., Li, D., Meng, H., Sun, D., Lan, X., Ni, M., et al. (2022). Targeting a novel inducible GPX4 alternative isoform to alleviate ferroptosis and treat metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 12, 3650–3666. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2022.02.003
Tschuck, J., Theilacker, L., Rothenaigner, I., Weiß, S. A. I., Akdogan, B., Lam, V. T., et al. (2023). Farnesoid X receptor activation by bile acids suppresses lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Nat. Commun. 14, 6908. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-42702-8
Uehara, K., Santoleri, D., Whitlock, A. E. G., and Titchenell, P. M. (2023). Insulin regulation of hepatic lipid homeostasis. Compr. Physiol. 13, 4785–4809. doi:10.1002/cphy.c220015
Ushiroda, C., Naito, Y., Takagi, T., Uchiyama, K., Mizushima, K., Higashimura, Y., et al. (2019). Green tea polyphenol (epigallocatechin-3-gallate) improves gut dysbiosis and serum bile acids dysregulation in high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 65, 34–46. doi:10.3164/jcbn.18-116
Valgimigli, L. (2023). Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant protection. Biomolecules 13, 1291. doi:10.3390/biom13091291
Vatner, D. F., Majumdar, S. K., Kumashiro, N., Petersen, M. C., Rahimi, Y., Gattu, A. K., et al. (2015). Insulin-independent regulation of hepatic triglyceride synthesis by fatty acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112, 1143–1148. doi:10.1073/pnas.1423952112
Wahlström, A., Sayin, S. I., Marschall, H.-U., and Bäckhed, F. (2016). Intestinal crosstalk between bile acids and microbiota and its impact on host metabolism. Cell Metab. 24, 41–50. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.005
Wang, D., and Sul, H. S. (1997). Upstream stimulatory factor binding to the E-box at -65 is required for insulin regulation of the fatty acid synthase promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26367–26374. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.42.26367
Wang, B., and Tontonoz, P. (2018). Liver X receptors in lipid signalling and membrane homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 14, 452–463. doi:10.1038/s41574-018-0037-x
Wang, H., Chen, J., Hollister, K., Sowers, L. C., and Forman, B. M. (1999). Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol. Cell 3, 543–553. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80348-2
Wang, Z., Yin, W., Zhu, L., Li, J., Yao, Y., Chen, F., et al. (2018). Iron drives T helper cell pathogenicity by promoting RNA-binding protein PCBP1-mediated proinflammatory cytokine production. Immunity 49, 80–92. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2018.05.008
Wang, S., Sheng, F., Zou, L., Xiao, J., and Li, P. (2021). Hyperoside attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via cholesterol metabolism and bile acid metabolism. J. Adv. Res. 34, 109–122. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.001
Wang, C., Chu, Q., Dong, W., Wang, X., Zhao, W., Dai, X., et al. (2024a). Microbial metabolite deoxycholic acid-mediated ferroptosis exacerbates high-fat diet-induced colonic inflammation. Mol. Metab. 84, 101944. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101944
Wang, H., Guo, Y., Han, W., Liang, M., Xiao, X., Jiang, X., et al. (2024b). Tauroursodeoxycholic acid improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 20194–20210. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c04630
Wang, L., Yu, H., Wang, D., Yin, G., Chen, S., Zhang, X., et al. (2025a). Diosgenin alleviates lipid accumulation in NAFLD through the pathways of ferroptosis defensive and executive system. J. Nutr. Biochem. 140, 109886. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2025.109886
Wang, S., Jia, Q., Liu, X., Ma, Y., Yang, Y., Rong, X., et al. (2025b). Hyperoside modulates bile acid and fatty acid metabolism, presenting a potentially promising treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Adv. Res. S2090-1232 (25), 00308–X. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2025.05.014
Wilson, C. G., Tran, J. L., Erion, D. M., Vera, N. B., Febbraio, M., and Weiss, E. J. (2016). Hepatocyte-specific disruption of CD36 attenuates fatty liver and improves insulin sensitivity in HFD-fed mice. Endocrinology 157, 570–585. doi:10.1210/en.2015-1866
Xie, F., Niu, Y., Chen, X., Kong, X., Yan, G., Zhuang, A., et al. (2025). Ursodeoxycholic acid inhibits the uptake of cystine through SLC7A11 and impairs de novo synthesis of glutathione. J. Pharm. Anal. 15, 101068. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101068
Yamagata, K., Daitoku, H., Shimamoto, Y., Matsuzaki, H., Hirota, K., Ishida, J., et al. (2004). Bile acids regulate gluconeogenic gene expression via small heterodimer partner-mediated repression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 and Foxo1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 23158–23165. doi:10.1074/jbc.M314322200
Yan, T., Wang, H., Cao, L., Wang, Q., Takahashi, S., Yagai, T., et al. (2018). Glycyrrhizin alleviates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via modulating bile acids and meta-inflammation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 46, 1310–1319. doi:10.1124/dmd.118.082008
Yan, M., Man, S., Liang, Y., Ma, L., Guo, L., Huang, L., et al. (2023). Diosgenin alleviates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through affecting liver-gut circulation. Pharmacol. Res. 187, 106621. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106621
Yang, K. C., Hung, H.-F., Lu, C.-W., Chang, H.-H., Lee, L.-T., and Huang, K.-C. (2016a). Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with metabolic syndrome independently of central obesity and insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 6, 27034. doi:10.1038/srep27034
Yang, W. S., Kim, K. J., Gaschler, M. M., Patel, M., Shchepinov, M. S., and Stockwell, B. R. (2016b). Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113, E4966–E4975. doi:10.1073/pnas.1603244113
Yang, Y., Chen, J., Gao, Q., Shan, X., Wang, J., and Lv, Z. (2020). Study on the attenuated effect of Ginkgolide B on ferroptosis in high fat diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Toxicology 445, 152599. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2020.152599
Yang, Y., Cai, J., Yang, X., Wang, K., Sun, K., Yang, Z., et al. (2022). Dysregulated m6A modification promotes lipogenesis and development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 30, 2342–2353. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.02.021
Yang, C., Wu, A., Tan, L., Tang, D., Chen, W., Lai, X., et al. (2023). Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate alleviates liver oxidative damage caused by iron overload in mice through inhibiting ferroptosis. Nutrients 15, 1993. doi:10.3390/nu15081993
Yerushalmi, B., Dahl, R., Devereaux, M. W., Gumpricht, E., and Sokol, R. J. (2001). Bile acid-induced rat hepatocyte apoptosis is inhibited by antioxidants and blockers of the mitochondrial permeability transition. Hepatol. Balt. Md 33, 616–626. doi:10.1053/jhep.2001.22702
Younossi, Z. M., Golabi, P., Price, J. K., Owrangi, S., Gundu-Rao, N., Satchi, R., et al. (2024). The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 22, 1999–2010.e8. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2024.03.006
Zeng, W.-J., Yang, H.-J., Gu, Y.-J., Yang, M.-N., Sun, M.-R., Cheng, S.-K., et al. (2025). High taurocholic acid concentration induces ferroptosis by downregulating FTH1 expression in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 25, 21. doi:10.1186/s12884-025-07143-9
Zhang, Y., Lee, F. Y., Barrera, G., Lee, H., Vales, C., Gonzalez, F. J., et al. (2006). Activation of the nuclear receptor FXR improves hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in diabetic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 1006–1011. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506982103
Zhang, L., Xie, C., Nichols, R. G., Chan, S. H. J., Jiang, C., Hao, R., et al. (2016). Farnesoid X receptor signaling shapes the gut microbiota and controls hepatic lipid metabolism. mSystems 1, e00070–e0007016. doi:10.1128/mSystems.00070-16
Zhang, H.-L., Hu, B.-X., Li, Z.-L., Du, T., Shan, J.-L., Ye, Z.-P., et al. (2022). PKCβII phosphorylates ACSL4 to amplify lipid peroxidation to induce ferroptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 24, 88–98. doi:10.1038/s41556-021-00818-3
Zhang, C., Shi, Z., Lei, H., Wu, F., Chen, C., Cao, Z., et al. (2023). Dietary isoquercetin reduces hepatic cholesterol and triglyceride in NAFLD mice by modulating bile acid metabolism via intestinal FXR-FGF15 signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 7723–7733. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c00952
Zhang, X., Yin, G., Chen, S., Meng, D., Yu, W., Liu, H., et al. (2024). Diosgenin ameliorating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via Nrf2-mediated regulation of oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 26, 5745–5756. doi:10.1111/dom.15945
Zheng, X., Chen, T., Zhao, A., Ning, Z., Kuang, J., Wang, S., et al. (2021). Hyocholic acid species as novel biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Nat. Commun. 12, 1487. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21744-w
Zhong, J., He, X., Gao, X., Liu, Q., Zhao, Y., Hong, Y., et al. (2023). Hyodeoxycholic acid ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting RAN-mediated PPARα nucleus-cytoplasm shuttling. Nat. Commun. 14, 5451. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-41061-8
Zhou, Y., Li, R., Zheng, Y., Song, M., Zhang, S., Sun, Y., et al. (2022). Diosgenin ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating the gut microbiota and related lipid/amino acid metabolism in high fat diet-fed rats. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 854790. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.854790
Zhu, X., Xiong, T., Liu, P., Guo, X., Xiao, L., Zhou, F., et al. (2018). Quercetin ameliorates HFD-induced NAFLD by promoting hepatic VLDL assembly and lipophagy via the IRE1a/XBP1s pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 114, 52–60. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2018.02.019
Keywords: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, bile acids, lipid peroxidation, ferroptosis, traditional Chinese medicine
Citation: Liu J, Li F, Zeng Q, Hu W, Yang L, Luo S, Li D and Deng Y (2025) Dysregulated bile acid metabolism drives lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in NAFLD: therapeutic potential for traditional Chinese medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1669805. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1669805
Received: 20 July 2025; Accepted: 21 August 2025;
Published: 18 September 2025.
Edited by:
Juei-Tang Cheng, Chang Jung Christian University, TaiwanReviewed by:
Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla, University of Zululand, South AfricaXue Xiaoyong, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Li, Zeng, Hu, Yang, Luo, Li and Deng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dingxiang Li, bGR4bHp5QGhvdG1haWwuY29t; Yihui Deng, ZGVuZ3lpaHVpQGhudWNtLmVkdS5jbg==
 Jing Liu
Jing Liu Fuxing Li3
Fuxing Li3 Le Yang
Le Yang Shengping Luo
Shengping Luo