- 1Graduate School, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Oncology, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Objective: To serve as a clinical reference, we conducted a meta-analysis to assess and compare the efficacy and safety of combining Chinese herbal injections (CHIs) with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) for treating advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Predetermined databases contained randomized controlled studies comparing CHIs + EGFR-TKIs to EGFR-TKIs alone. The Cochrane Reviewer’s Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions was used to evaluate study methodology. To assess the effects of CHIs on patients with NSCLC receiving EGFR-TKIs, R (version 4.4.0) and RevMan (version 5.4) were used to conduct a meta-analysis using the Mantel–Haenszel or Inverse Variance method. The quality of results was evaluated using the Grade of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) method.
Results: The 13 qualifying trials included 899 subjects. The objective response rate (ORR) was significantly increased by Kanglaite injection (RR = 1.52, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.07–2.15, p = 0.02). The disease control rate (DCR) was influenced by Kanglaite injection (RR = 1.14, 95% CI: 1.01–1.29, p = 0.04) and Aidi injection (RR = 1.23, 95% CI: 1.02–1.48, p = 0.03). Shenmai injection + EGFR-TKIs reduced dermatologic toxicities (RR = 0.35, 95% CI: 0.18–0.69, p = 0.002). The combination of CHIs with EGFR-TKIs improved the expression of CD3+ (standardized mean difference [SMD] = 1.38, 95% CI: 0.46–2.30, p = 0.003), CD4+ (SMD = 1.08, 95% CI: 0.51–1.65, p = 0.0002), and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (SMD = 0.96, 95% CI: 0.54–1.38, p < 0.00001) compared to EGFR-TKIs alone. The GRADE method revealed that most outcomes exhibited low certainty evidence.
Conclusion: The combination of CHIs and EGFR-TKIs improved ORR, DCR, adverse effects, and immune function in patients with NSCLC. Due to limitations in the assessed research, high-quality clinical studies with rigorous designs are required to confirm the findings.
Systematic Review: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024561845, Identifier CRD42024561845.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounting for approximately 85% of all documented cases (Sung et al., 2021). Comprehensive surgical therapy is used for early-stage NSCLC, whereas intermediate- and late-stage NSCLC are frequently managed with a combination of radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene were detected in 15%–20% of patients with NSCLC, primarily in adenocarcinoma patients without smoking history and Asian patients (Jänne et al., 2005). Extensive phase III clinical studies (Tan et al., 2016; Rosell et al., 2012; Sequist et al., 2013; Wu et al., 2015) have validated EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) as the preferred first-line treatment for EGFR mutant NSCLC, outperforming chemotherapy in terms of progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and quality of life (QOL). Currently, erlotinib, gefitinib, and icotinib are categorized as first-generation EGFR-TKIs, afatinib and dacomitinib as second-generation, and osimertinib and almonertinib as third-generation EGFR-TKIs (Koulouris et al., 2022). It is important to acknowledge that targeted therapy may induce adverse effects, leading to multi-organ toxicity or malfunction, as well as the unavoidable issue of drug resistance, complicating subsequent treatment options.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) posits that cancer is primarily caused by an imbalance of Yin and Yang, a deficiency of Zhengqi, and an excess of Xieqi. Therefore, the therapeutic principles reside in Fuzheng (harmonization) and Quxie (removal of pathogenic elements), as well as supplementation and promotion of Yin-Yang rebalancing (Li et al., 2025). TCM inhibits tumor cell proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis, and lymphangiogenesis, and promotes tumor cell death (Wang et al., 2021). Early studies have demonstrated that Chinese herbal injections (CHIs), a preparation of botanical extracts, are widely used in the treatment of cancer. For instance, Xiaoaiping injection alters the cell cycle, mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, and regulatory proteins to inhibit the proliferation of human esophageal cancer cells. Kangai injection incorporates Astragalus, ginseng, and kurorinone as primary extracts and is extensively used in treating lung, gastric, and liver cancers. CHIs and targeted therapies demonstrate synergistic effects. For example, Complex Ku Shen injection was administered alongside sorafenib, a TKI, to treat hepatocellular carcinoma (Li et al., 2025).
TCM has gained significant popularity as an alternative and supplementary treatment for advanced NSCLC (Jiao et al., 2019), potentially mitigating the adverse effects of EGFR-TKIs (Hu et al., 2021) and improving QOL. Numerous network meta-analyses of CHIs in conjunction with chemotherapy have been performed (Wen et al., 2023; Li et al., 2022). Integrating several types of CHIs with chemotherapy is useful for increasing response rates, improving QOL, and strengthening immune function. Given the increasing use of targeted therapy in lung cancer treatment, we specifically investigated the role of CHIs in integrating targeted therapy. In recent years, advances in clinical research on CHIs in conjunction with EGFR-TKIs have yielded new evidence-based medical findings. A comprehensive assessment of the efficacy and safety of combining CHIs with EGFR-TKIs is necessary to establish a foundation for their clinical use in NSCLC treatment.
2 Methods
This network meta-analysis was performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (Supplementary Table S1) (Hutton et al., 2015). The protocol is registered in the Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) (CRD42024561845). Detailed documents are provided in Supplementary Materials.
2.1 Standard evaluation of the composition of CHIs
Phytochemical characterization was conducted according to the ConPhyMP consensus recommendations for medicinal plant extract analysis to maintain methodological rigor. We standardized botanical nomenclature for all medical plant using the Medical Plant Name Service (http://mpns.kew.org/mpns-portal/) and Plants of the World Online (http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org). Composition summaries were organized according to the Four Pillars of Best Practice in Ethnopharmacology (Table 1). Additional information regarding the CHIs is listed in Supplementary Table S2.
2.2 Data sources and searches
We searched Chinese databases, including the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Chinese Biological Medicine Database (CBM), Wanfang Database, and VIP Database for Chinese Technical Periodicals, as well as English databases, including MEDLINE (via PubMed), Embase (via Ovid), and Cochrane Library, to find related articles up to 10 October 2024. Two investigators independently searched for articles using a mix of primary search terms “NSCLC,” “EGFR-TKIs,” and “Chinese herbal injections” within the context of “randomized controlled trial.” The search approach is listed in Supplementary Table S3.
2.3 Study selection
Randomized controlled trials that were published and met the following requirements were included: Trials including participants with advanced (stage III/IV) histology or cytological confirmation with EGFR-activating mutations in NSCLC; the baseline circumstances of the experimental and control groups did not differ significantly (p > 0.05); the experimental group was administered CHIs + EGFR-TKIs, while the control group received only EGFR-TKIs, including the first-generation (Gefitinib) to third-generation (Osimertinib); both groups received the same supportive care, without other anti-tumor therapies; ORR and disease control rate (DCR) were reported as primary outcomes, while secondary outcomes included QOL, adverse effects, and immune function.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: Studies involving patients with additional primary malignancies; studies in which treatments were coupled with surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or other TCM therapies; studies in which the name, dosage, and treatment regimen of CHIs and EGFR-TKIs were not specified; duplicate studies, non-randomized controlled trials, or studies using flawed randomization procedures; studies lacking credible effectiveness and safety evidence or a clear delineation of the efficacy evaluation criteria.
2.4 Outcome indicators and evaluation criteria
ORR and DCR were assessed according to the World Health Organization evaluation criteria or the response evaluation criteria in solid tumors. The responses were classified as complete relief (CR), partial remission (PR), stable disease (SD), or progressive disease (PD). ORR was calculated as (CR + PR)/total number of cases × 100%, and DCR was calculated as (CR + PR + SD)/total number of cases × 100%.
The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Group (EORTC QLG Core Questionnaire [EORTC QLQ-C30]) or Karnofsky Performance Scale (KPS) was used to assess the patient’s QOL. EORTC QLQ-C30 can be divided into three aspects: Functional areas, symptom fields, and overall health status. The average score of each aspect was compared between the experimental and control groups to validate the improvement in QOL.
Common adverse reactions associated with targeted therapy were evaluated, including gastrointestinal toxicities (nausea and vomiting), dermatologic toxicities (erythema and pruritus), and hepatic insufficiency.
Furthermore, the efficacy of CHIs + EGFR-TKIs was estimated using the incidence of changes in the cellular immune index (CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+/CD8+ ratio). Immunocytochemistry or flow cytometry was used to analyze immunological changes in the included studies.
2.5 Data obtaining and quality evaluation
The general features of qualifying studies were independently retrieved and cross-checked by two researchers. A third researcher was consulted to resolve any disagreements. The first author’s name, year of publication, number of patients in each group, patients’ gender, age, and tumor stage, specifics of the intervention (targeted therapy regimens or treatment course), and the outcome indicators were obtained from each paper. Two reviewers assessed the methodological quality of each included RCT according to the Cochrane Collaboration’s risk of bias criteria (Higgins et al., 2019), based on the following factors: Random sequence generation (selection bias), allocation concealment (selection bias), blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias), blinding of outcome data (detection bias), incomplete outcome data (attrition bias), selective reporting (reporting bias), and other biases.
2.6 Statistical analysis
R (version 4.4.0) was used for meta-analysis to evaluate the overall impact of CHIs on NSCLC. The analysis was conducted using the R package “meta.” Standardized mean differences (SMDs) and risk ratios (RRs) were used to investigate the effect size for continuous and dichotomous outcomes, respectively. The effect size and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to calculate RRs and SMDs. P < 0.05 indicated statistical significance. The Mantel–Haenszel method was used for dichotomous outcomes with low event incidence, while the inverse variance method was deemed more appropriate due to its broader applicability and capacity to evaluate heterogeneity. A fixed or random-effects model was selected based on the heterogeneity among trials and evaluated using the I2 statistic and conceptual heterogeneity. The extent of heterogeneity among studies within the overall variation was quantitatively delineated using I2. I2 > 50% indicated a significant level of variability. However, I2 exhibits certain limitations. It fails to identify the source of heterogeneity and exhibits minimal test power when the number of included studies is limited. The consistency of the included studies on population, intervention, comparison, and outcome (PICO) is crucial when discussing heterogeneity. If the studies exhibit consistency in PICO, a fixed-effect model is preferred. Conversely, a random-effect model is more suitable when there is an anticipated and justifiable variation in PICO among studies. RevMan (version 5.4) was used to validate the results and generate forest plots. Funnel plots were generated, Egger’s tests were conducted for continuous data, and Peter’s tests were conducted for dichotomous data to assess potential publication bias. A sensitivity analysis, conducted by sequentially omitting individual studies, was used to confirm the stability of the aggregated results.
Furthermore, based on results of the meta-analysis, we used the Grade of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) method to assess the quality of evidence for each outcome. Evidence certainty was classified into four grades: High, Moderate, Low, and Very Low. Evidence from randomized controlled trials is generally of high quality; however, its validity may be compromised by five factors: (1) Risk of bias, (2) inconsistency, (3) imprecision, (4) indirectness, and (5) publication bias. Conversely, three factors may improve its validity: (1) Large effect sizes, (2) dose-response relationships, and (3) plausible confounding. Each outcome was rated by two independent reviewers, and any disagreements were resolved through discussion or adjudication by a third researcher. The Summary of Findings Table was created using GRADEpro GDT software.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search and quality assessment
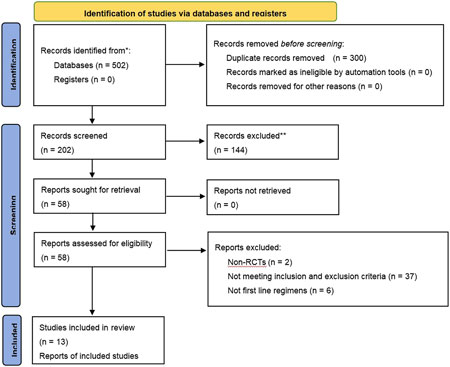
Of the 502 studies identified in the literature search, 300 duplicates were removed. After screening and full-text review, 13 studies (Dai, 2021; Huang et al., 2024; Jiang et al., 2019; Shi and Chen, 2013; Wang and LI, 2020; Wang et al., 2022; Yang, 2016; Yang et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2018; Zhang, 2016; Zheng et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2017) involving 899 patients were included, encompassing six CHIs treatments: Kanglaite, Aidi, Shenfu, Shenmai, Xiaoaiping, and Elemene injection. Five types of EGFR-TKIs were investigated in 13 studies, which were categorized as first-generation (erlotinib, gefitinib, and icotinib) and third-generation (osimertinib and almonertinib). A flowchart illustrating the study selection process is depicted in Figure 1, while Table 2 enumerates the characteristics of the included studies.
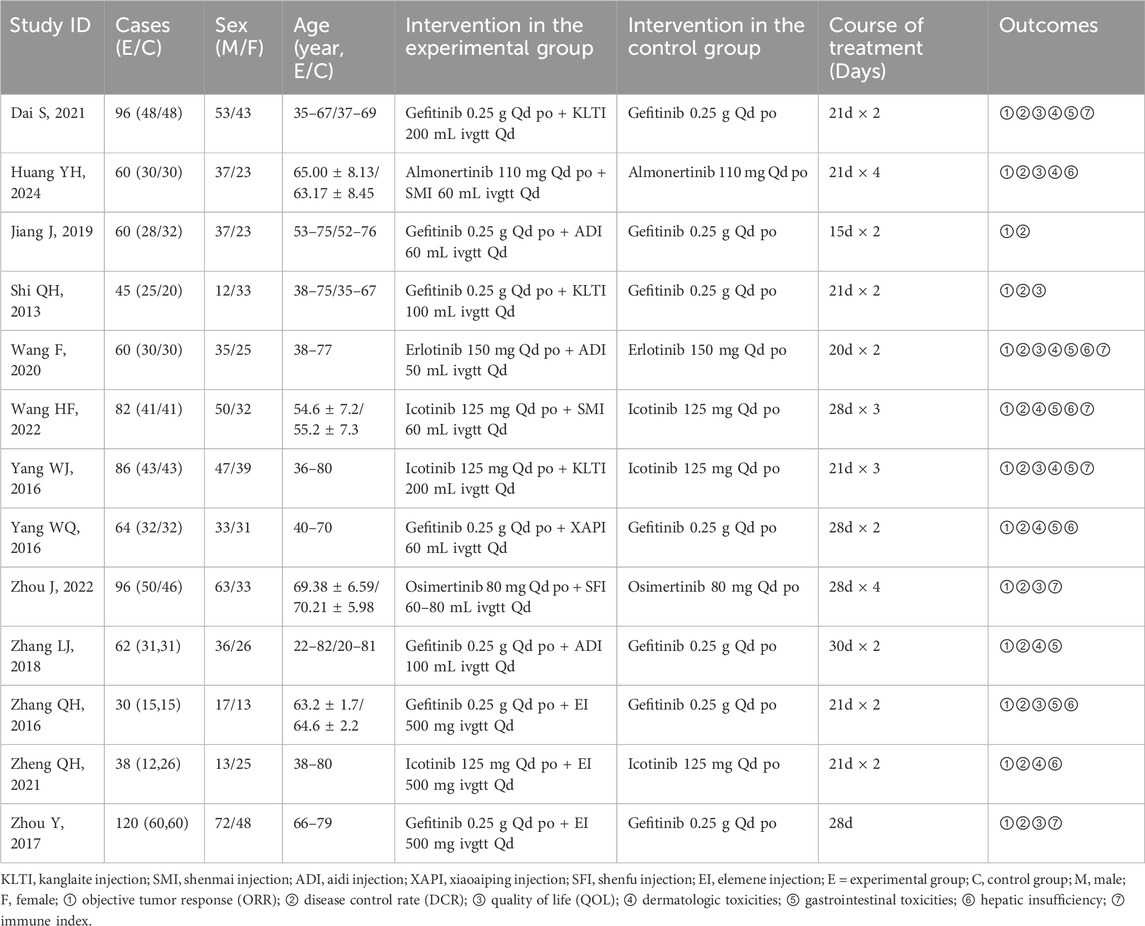
Table 2. Initial features of studies included in the network meta-analysis of patients with NSCLC having advanced EGFR mutations.
3.2 Evaluation of methodological quality
The results of the methodological assessment are depicted in Figure 2. The case number of each study was used as a weight in the analysis. While all 13 publications referenced randomization, only eight specified the precise mechanism of random allocation (Dai, 2021; Jiang et al., 2019; Wang and LI, 2020; Wang et al., 2022; Yang, 2016; Yang et al., 2016; Zheng et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2017) and demonstrated a low risk of random sequence generation. None of the studies specified techniques for allocation concealment, leaving the risk ambiguous. The selected studies did not reference double-blinding or blinding of outcome assessments. The outcomes, including ORR, DCR, adverse effects, and immune indexes, were considered objective and thus unaffected by double-blinding. However, EORTC QLQ-C30 was implemented as an outcome measure in four studies (Dai, 2021; Wang and LI, 2020; Zhou et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2017), which is somewhat subjective. Consequently, these studies were classified as high risk for participant and personnel blinding. Regarding reporting bias, four studies (Dai, 2021; Wang and LI, 2020; Zhou et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2017) using EORTC QLQ-C30 did not present complete findings of the questionnaire and were categorized as “high risk.”
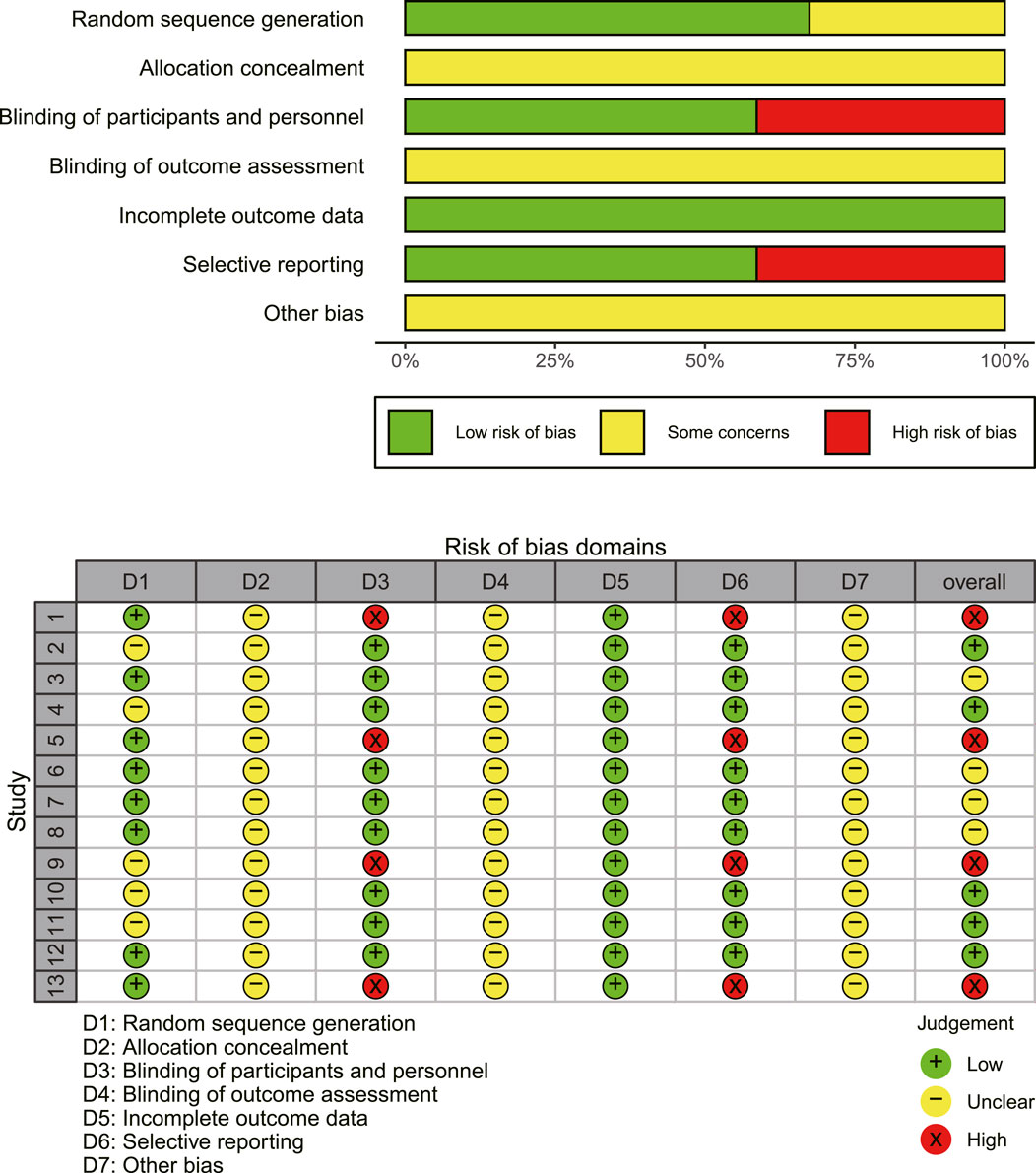
Figure 2. An overview of the findings from studies evaluated using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Study numbers in the traffic plot: 1. Dai (2021), 2. Huang et al. (2024), 3. Jiang et al. (2019), 4. Shi and Chen (2013), 5. Wang and Li (2020), 6. Wang et al. (2022), 7. Yang et al. (2016), 8. Yang et al. (2016), 9. Zhou et al. (2022), 10. Zhang et al. (2018), 11. Zhang (2016), 12. Zheng et al. (2021), 13. Zhou et al. (2017).
3.3 Primary outcomes
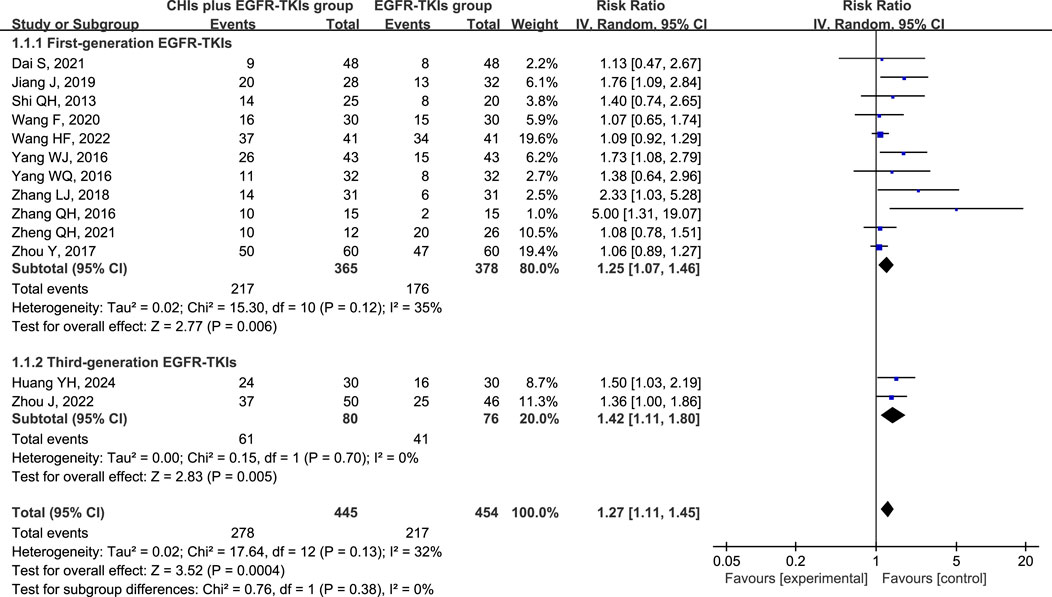
All 13 studies reported ORR and DCR as primary outcomes, with 899 patients (445 in the experimental group and 454 in the control group). A subgroup analysis was conducted based on the use of first- or third-generation EGFR-TKIs in the control group due to the significant difference in efficacy between them (Zhao et al., 2019). Simultaneously, another subgroup was created based on the various CHIs used in the experimental group to investigate their individual effects. However, the findings from Xiaoaiping and Shenfu injection subgroups cannot be deemed credible because each CHI was represented by only one study in the subgroups.
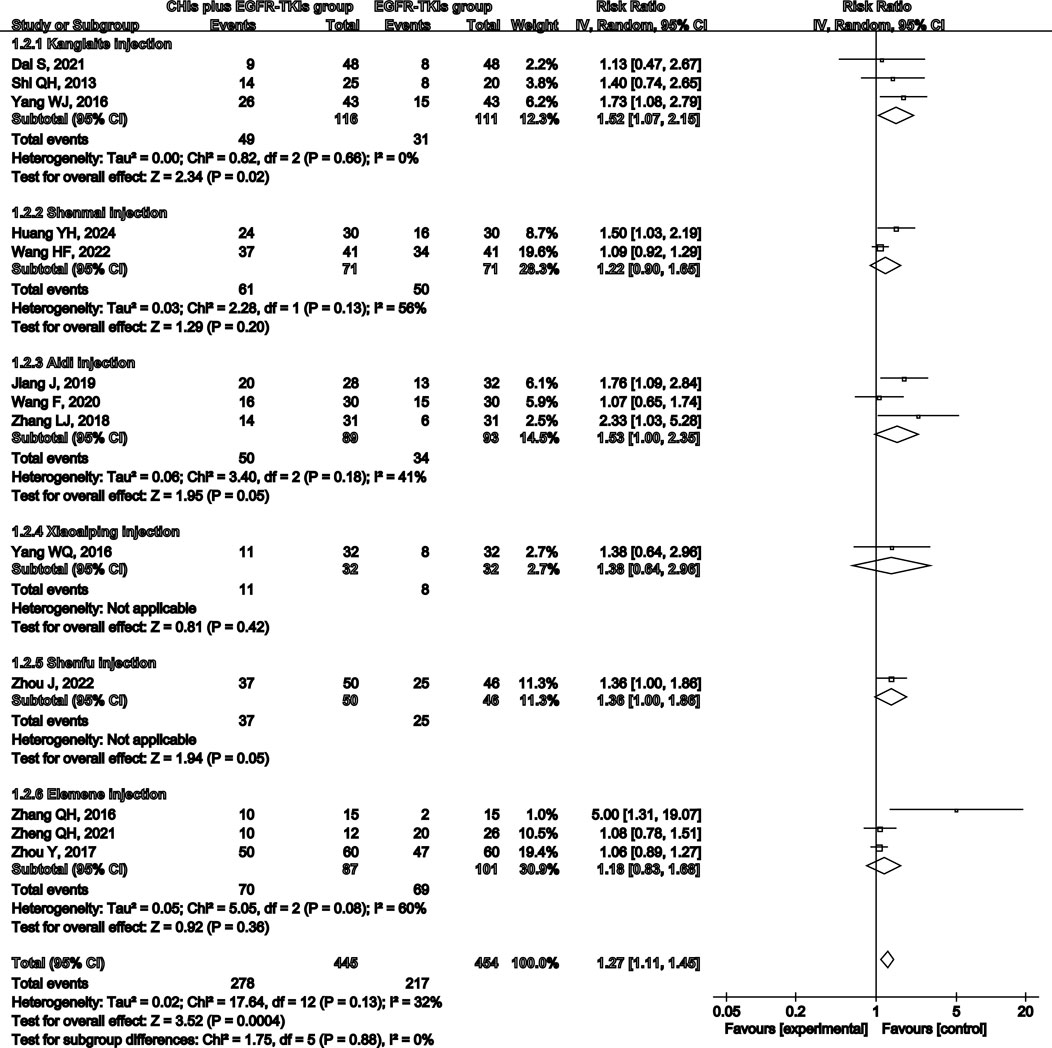
Total analysis of the included papers on ORR demonstrated low heterogeneity (p = 0.13, I2 = 32%); however, there were differences in the types of CHIs and EGFR-TKIs included in the studies. The random-effects model was a safer and more conservative choice because it accounted for potential differences across studies, yielding generalizable results. Our data indicated that patients receiving CHIs + EGFR-TKIs demonstrated significantly higher ORRs than those receiving EGFR-TKIs alone (RR = 1.27, 95% CI: 1.11–1.45, p = 0.0004). Subgroup analysis of first- and third-generation EGFR-TKIs yielded comparable outcomes (RR = 1.25, 95% CI: 1.07–1.46, p = 0.006 versus RR = 1.42, 95% CI: 1.11–1.80, p = 0.005) (Figure 3). Additionally, Kanglaite injection significantly improved ORR in combination with EGFR-TKIs (RR = 1.52, 95% CI: 1.07–2.15, p = 0.02). Conversely, Shenmai injection (RR = 1.22, 95% CI: 0.90–1.65, p = 0.20), Aidi injection (RR = 1.53, 95% CI: 1.00–2.35, p = 0.05), and Elemene injection (RR = 1.18, 95% CI: 0.83–1.68, p = 0.36) demonstrated no significant influence (Figure 4).
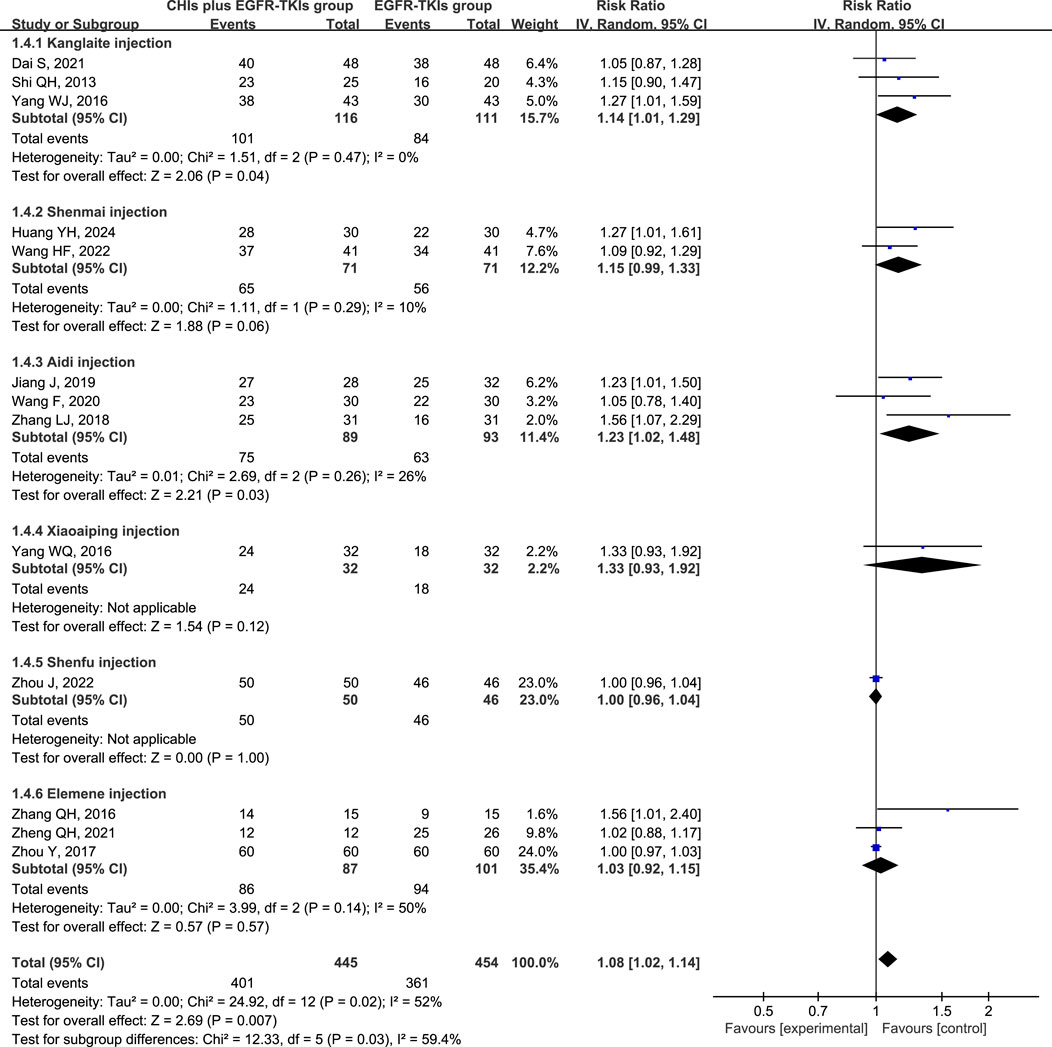
Heterogeneity analysis of DCR revealed significant heterogeneity (p = 0.02, I2 = 52%), implying the appropriateness of a random-effect model. DCR was significantly improved in patients using CHIs (RR = 1.08, 95% CI: 1.02–1.14, p = 0.007) and in the subgroup of first-generation EGFR-TKIs (RR = 1.12, 95% CI: 1.03–1.22, p = 0.007). However, no significant change was observed in the third-generation EGFR-TKIs subgroup (RR = 1.10, 95% CI: 0.87–1.38, p = 0.43) (Figure 5). In several subgroups of different CHIs, administration of Kanglaite injection (RR = 1.14, 95% CI: 1.01–1.29, p = 0.04) and Aidi Injection (RR = 1.23, 95% CI: 1.02–1.48, p = 0.03) in conjunction with EGFR-TKIs significantly improved DCR. Shenmai (RR = 1.15, 95% CI: 0.99–1.33, p = 0.06) and elemene (RR = 1.03, 95% CI: 0.92–1.15, p = 0.57) injections demonstrated no significant influence (Figure 6).
3.4 Secondary outcomes
3.4.1 Quality of life (QOL)
In 8 out of 13 studies, QOL was assessed using various instruments: Four used the EORTC QLG Core Questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30) (Dai, 2021; Wang and Li, 2020; Zhou et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2017), three used KPS (Huang et al., 2024; Shi and Chen, 2013; Yang, 2016), and one used the Zubrod scale (ZPS) (Zhang QH, 2016). Except for Zhang QH, 2016, all studies reported a significant enhancement in QOL. However, different assessment methodologies were identified within these groups. For instance, only two of the four studies using the EORTC QLQ-C30 provided average scores for three dimensions (functional, symptom, and overall health), whereas the others only reported scores for functional areas. Two studies used changes in KPS scores to calculate QOL improvement rate using different definition methods. The significant variability in the reporting of QOL outcomes across studies indicates that both meta- and subgroup analyses were inapplicable.
3.4.2 Adverse effects
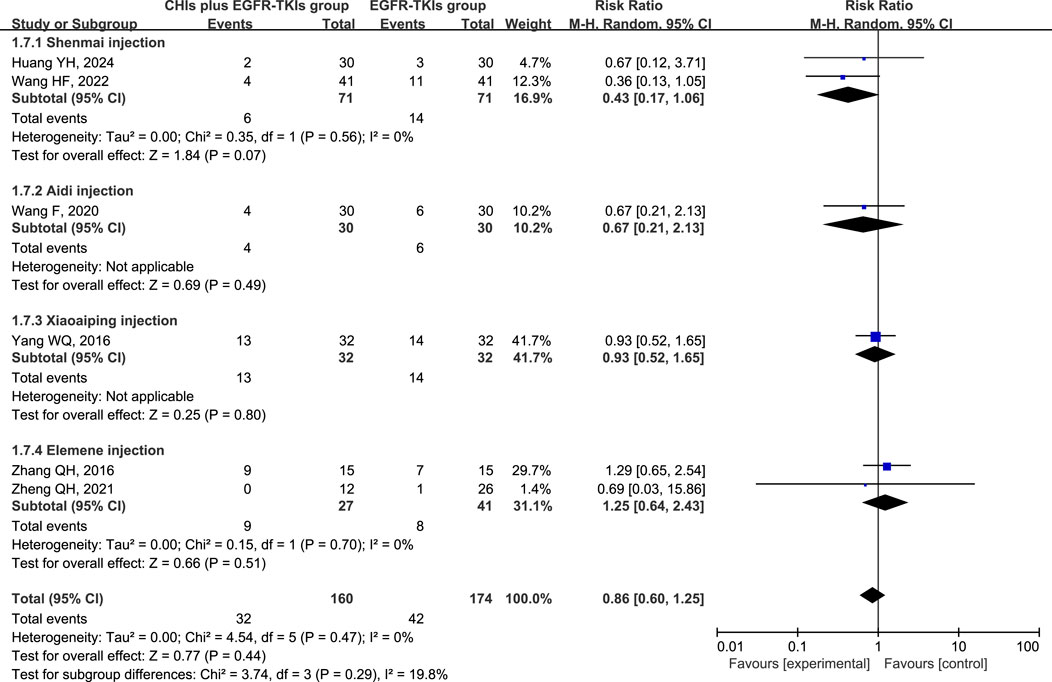
The three most frequently reported adverse effects in the included studies were dermatologic toxicity, gastrointestinal toxicity, and hepatic insufficiency. A random-effects model was used to assess adverse effects arising from differences in the types of CHIs and EGFR-TKIs included in the studies. The effects of each CHI were determined using a subgroup analysis. The most commonly reported adverse effect, dermatologic toxicities, was included in eight trials with 548 individuals (267 in the experimental group and 281 in the control group). The relative risks revealed that EGFR-TKIs alone were less effective than combination therapies of CHIs and EGFR-TKIs in reducing the occurrence of dermatologic toxicities (RR = 0.61, 95% CI: 0.45–0.84, p = 0.002). Subsequent analysis revealed that only the combination of Shenmai injection and EGFR-TKIs (RR = 0.35, 95% CI: 0.18–0.69, p = 0.002) significantly affected the incidence of dermatologic toxicities, whereas other subgroups demonstrated no notable impact (Figure 7). In a review of seven trials including 480 participants (240 in the experimental group and 240 in the control group), no significant reduction in the incidence of gastrointestinal toxicities was observed in the experimental group (RR = 0.75, 95% CI: 0.54–1.03, p = 0.08) compared to the control group. Despite a reduction in gastrointestinal toxicities among the subgroup receiving Shenmai injection (RR = 0.53, 95% CI: 0.28–0.99, p = 0.05), the findings were deemed inconclusive due to the inclusion of only one study (Figure 8). The meta-analysis of hepatic insufficiency (six studies) reported no significant difference between the experimental and control groups (RR = 0.86, 95% CI: 0.60–1.25, p = 0.47), with a total of 334 participants (160 in the experimental and 174 in the control group). Comparable results were observed across all analyzed subgroups (Figure 9).
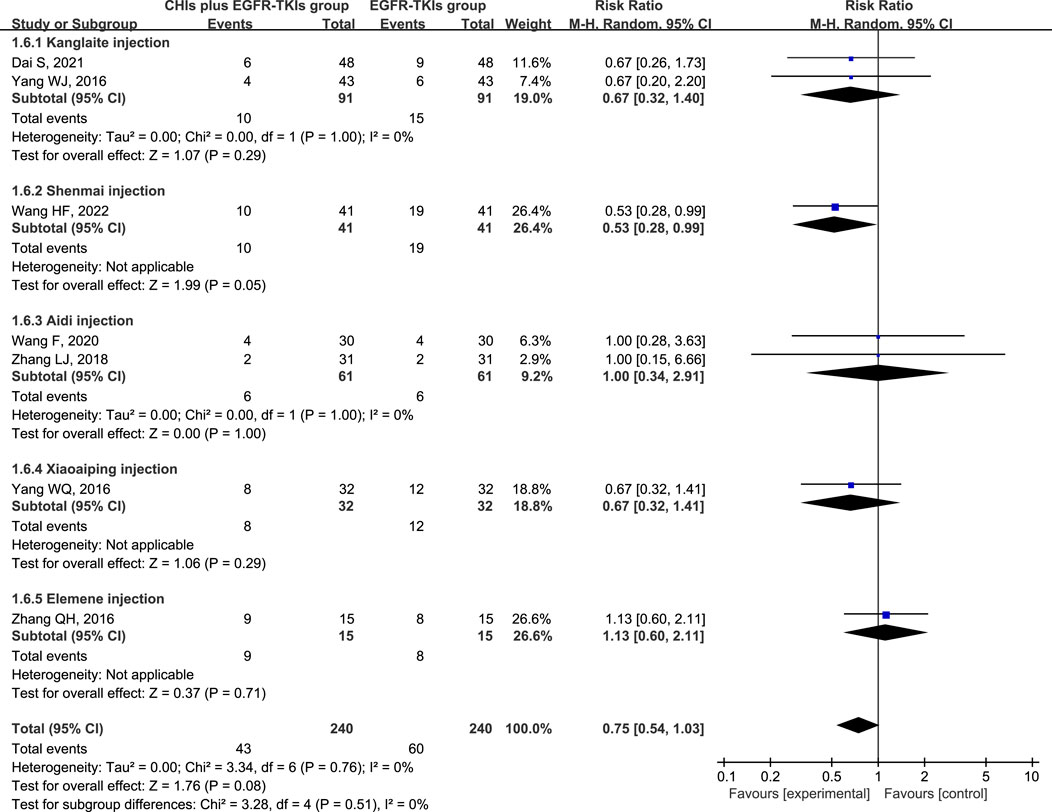
Figure 8. Forest plot illustrating the incidence of gastrointestinal toxicity in the included studies.
3.4.3 Immune index
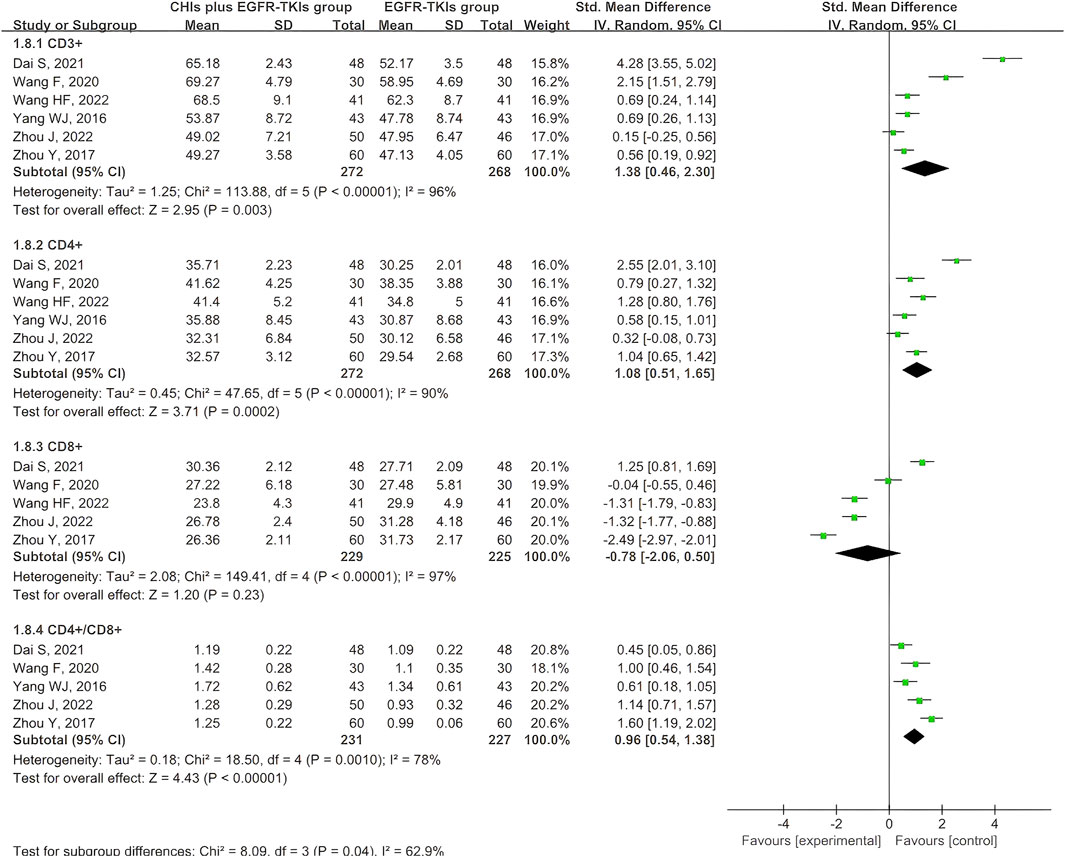
Six articles documented the immune index, specifically the expression of T cell subtypes. All six studies reported CD3+ and CD4+ expression, whereas five reported CD8+ expression and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio. Given the variability of the four outcomes, the data were obtained using a random-effects model. The aggregated SMD analysis revealed that CHIs and EGFR-TKIs significantly enhanced the expression of CD3+ (SMD = 1.38, 95% CI: 0.46–2.30, p = 0.003), CD4+ (SMD = 1.08, 95% CI: 0.51–1.65, p = 0.0002), and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (SMD = 0.96, 95% CI: 0.54–1.38, p < 0.00001) compared to EGFR-TKIs alone. However, no significant difference was observed in CD8+ expression between the two groups (SMD = −0.78, 95% CI: –2.06 to 0.50, p = 0.23) (Figure 10).
Considering the high heterogeneity in expression of CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+/CD8+ ratio, we investigated potential covariates, including continuous variables such as publication year, sample size, and treatment course, as well as categorical variables such as methodological quality, EGFR-TKI types, and CHI types. Meta-regression analysis was used for continuous variables, while for categorical variables, subgroup analysis was used. Meta-regression analysis revealed no statistical association between the continuous variables and significant heterogeneity (Supplementary Table S4). Subgroup analysis of categorical variables revealed that studies with high methodological quality risk were the primary source of heterogeneity in CD3+ expression (Supplementary Figure S1A), as well as high heterogeneity in CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+/CD8+ ratio (Supplementary Figures S12-S4). Given the small number of studies in each subgroup, reliable subgroup analyses were not possible to assess statistical significance for different types of EGFR-TKIs and CHIs (Supplementary Figures S1-S4). Therefore, we only provided a descriptive report. The significant differences observed in outcomes across subgroups demonstrated that variations among these types of EGFR-TKIs and CHIs may be a potential source of heterogeneity.
3.5 Publication bias
The potential publication bias in the primary outcomes, ORR and DCR, was investigated using funnel plots (Figure 11). Furthermore, Peter’s tests were used for quantitative analysis. Funnel plots of ORR revealed a possible asymmetry due to clearly deviating spots (Figure 11A), confirmed by Peter’s tests (p = 0.04). This phenomenon implied that smaller-scale studies may have been published because their results achieved higher benefit estimates, whereas a few studies with smaller benefits or negative outcomes may have remained unpublished or excluded. Such publication bias may have resulted in a potential overestimation of the overall benefit. To identify the source of publication bias, the study with the most obvious heterogeneity (Zhang QH, 2016) was removed, and the analysis was repeated. The funnel plot results revealed better symmetry (Figure 11B), whereas Peter’s tests revealed no evidence of publication bias (p = 0.59). The eliminated studies may introduce publication bias due to their smaller sample sizes and larger effect sizes. Furthermore, Peter’s tests demonstrated no discernible bias for the DCR (p = 0.19), consistent with the funnel plot analysis (Figure 11C).
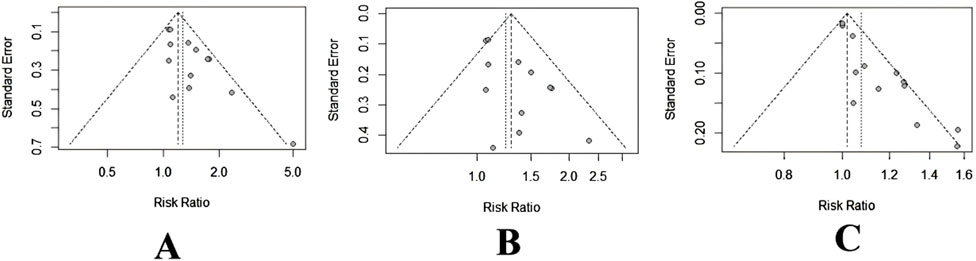
Figure 11. Funnel plot of ORR and DCR. (A) ORR. (B) ORR after removing Zhang (2016). (C) DCR.
3.6 Sensitivity analysis
We performed a sensitivity analysis for outcomes by excluding studies one by one (Supplementary Figure S5). The results revealed that the combined effect size estimates were robust, thereby improving the reliability of our conclusions.
3.7 Certainty of evidence analysis through the GRADE method
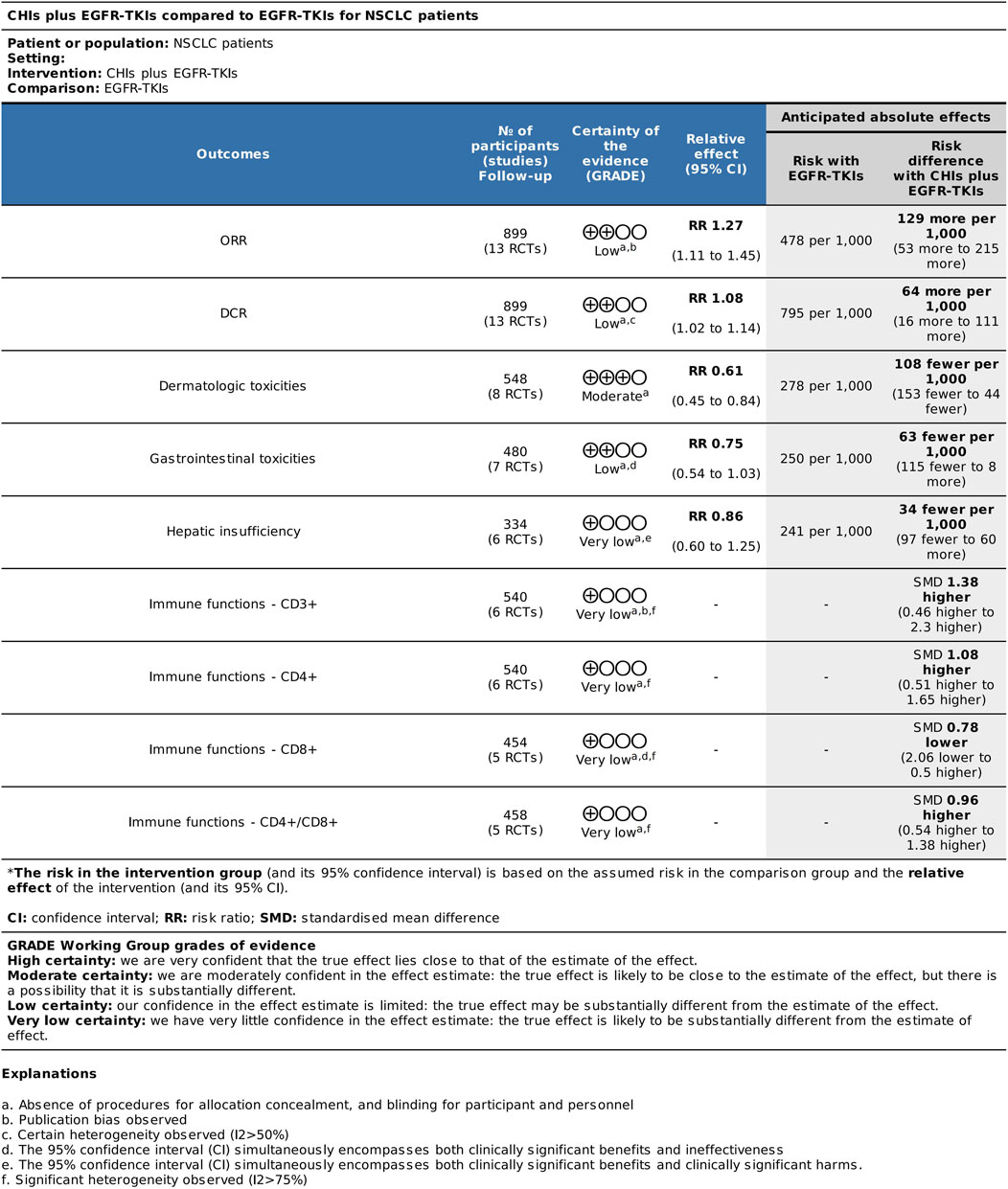
Based on the results of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, we conducted certainty of evidence analysis for major efficacy, adverse reaction, and immune index outcomes (Figure 12). All outcome grades were downgraded by one level due to the absence of allocation concealment and blinding procedures for participants and personnel in the inclusion study. The certainty of evidence for ORR was rated as low for major efficacy outcomes. Publication bias resulted in further downgrade. The certainty of evidence for DCR was downgraded by another level to low due to heterogeneity (I2 = 52%). The certainty of evidence for dermatologic toxicities was moderate. The results for gastrointestinal toxicities and hepatic insufficiency were low and very low due to imprecision. The 95% CI for gastrointestinal toxicity outcomes included both clinically significant benefits and ineffectiveness, whereas the 95% CI for hepatic insufficiency included both clinically significant benefits and harm. Moreover, the certainty of evidence for the immune index was very low due to significant heterogeneity (I2 > 75%), which downgraded the quality of evidence by two levels.
4 Discussion
4.1 Efficacy and safety analysis
Our systematic review included 13 studies with 899 patients. Overall, meta-analysis of ORR and DCR revealed that the combination of CHIs and EGFR-TKIs was significantly more efficacious than EGFR-TKIs alone. The funnel plot asymmetry and Peter’s test of ORR indicated a small-sample effect, potentially leading to an overestimation of ORR benefits. Therefore, we should be cautiously optimistic about the current ORR results. In terms of certainty of evidence, the combination of CHIs and EGFR-TKIs potentially improved anti-tumor efficacy with uncertain results, compared to EGFR-TKIs alone (low certainty evidence).
Subgroup analysis for first-generation EGFR-TKIs revealed that CHIs were associated with improved ORR and DCR, while in subgroup analysis for third-generation EGFR-TKIs, CHIs were associated with improved ORR without any significant influence on DCR. The subgroup analysis for third-generation EGFR-TKIs included only two studies, probably due to the delayed clinical application and research progress of third-generation EGFR-TKIs compared to first-generation EGFR-TKIs. Additionally, the differences in efficacy and adverse reactions between the two generations have expanded the opportunities for TCM interventions in combination with first-generation EGFR-TKIs. Due to the limited number of studies on third-generation EGFR-TKIs and the small sample sizes, the statistical efficacy was insufficient to reliably elucidate the real effect differences. Given their widespread use, high-quality clinical studies are required to focus on the combination of CHIs with third-generation EGFR-TKIs, which are currently scarce.
Subsequent investigation revealed that the combination of Kanglaite injection with EGFR-TKIs was more effective in improving ORR, while the combination of Kanglaite or Aidi injection with EGFR-TKIs effectively improved DCR. Kanglaite injection demonstrated numerous activities, including apoptosis induction in cancer cells, impeding cancer cell mitosis, killing malignant cells, and improving immune function in advanced NSCLC (Wen et al., 2020). A study demonstrated that Kanglaite injection decreased serum miRNA-21 expression in individuals with advanced lung cancer (Wu et al., 2018). Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated that Aidi injection affects tumor cells by slowing their proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and modulating immune function (Guo et al., 2021). The studies included in the meta-analysis used ORR and DCR as primary outcomes, with a limited follow-up period of 3–4 months. However, to validate the impact of CHIs in conjunction with EGFR-TKIs, the anti-tumor efficacy requires additional assessment over an extended observation period using PFS or overall survival.
Regarding QOL, only qualitative analysis was conducted due to the significant variability of different outcome measures. Numerous studies have validated improvements in QOL; however, the presence of fragmentary data necessitates caution in interpreting these findings. Future research must establish standardized reporting criteria for QOL and provide comprehensive data to assess the impact of CHIs on QOL.
Overall, the combination of CHIs with EGFR-TKIs was associated with reduced dermatologic toxicity (moderate certainty evidence). However, the risks of gastrointestinal toxicity and hepatic insufficiency remain uncertain (low or very low certainty evidence). The combination of Shenmai injection with EGFR-TKIs significantly reduced the incidence of dermatological toxicity compared to EGFR-TKIs alone. EGFR is often expressed in hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and keratinocytes. EGFR-TKIs may influence cellular proliferation and differentiation, induce the release of chemokines and cytokines, and facilitate the development of skin inflammation (Curry et al., 2014). Ginsenosides have been recognized as the principal active component in SMI (Liu et al., 2012). Excessive generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is associated with severe inflammation and cellular apoptosis in several cell types. Targeting ROS is considered a vital mechanism by which ginsenosides regulate pathological inflammation (Paik et al., 2023). Future experimental studies are needed to elucidate the involvement of CHIs in this process.
Fatigue, a common adverse effect of EGFR-TKIs, has not been reported in any of the trials reviewed thus far. The FLAURA trial data revealed that the incidence of fatigue with osimertinib therapy was 58.1% (Leighl et al., 2020). Fatigue significantly affects QOL and adversely affects patients’ adherence to therapy when severe. There is a demand for clear and effective intervention strategies. Consequently, studies on TCM interventions, including commercial Chinese polyherbal preparations, should be conducted in this regard.
This meta-analysis is the first to assess the impact of CHIs on the immune index following EGFR-TKI therapy. CHIs combined with EGFR-TKIs improved the expression of CD3+ and CD4+ T cells, as well as the CD4+/CD8+ ratio, implying that CHIs exert their anti-tumor activity by augmenting human immune function. Due to the risk of bias and significant heterogeneity, the evidence was highly uncertain. Our results should be interpreted cautiously. Future clinical trials should investigate these issues further to obtain more compelling data.
4.2 Limitations
This study has some limitations. First, there were several biases in the included studies. We identified publication bias based on the funnel plots about ORR, which was confirmed by Peter’s tests. Despite all studies reporting random allocation, only eight specified the exact random allocation method used. The lack of reporting on randomization methods made it impossible to confirm that all studies achieved true randomization, potentially leading to selection bias. Although the impact of such bias on the direction of combined effect sizes was difficult to quantify precisely, it undermined the reliability of our findings. This was because the observed effects might partially stem from baseline imbalances rather than the intervention. None of the studies disclosed procedures for allocation concealment, participant and personnel blinding, or rates of follow-up and withdrawal. The absence of allocation concealment indicated that researchers involved in patient enrollment might have anticipated the grouping arrangements. This could have resulted in systematic differences between the intervention and control groups at baseline, even if randomization was appropriate. Such scenarios often artificially inflate the efficacy of interventions. The absence of participant and personnel blinding may have introduced significant performance bias. Patients aware of their group assignments may have given more positive evaluations due to psychological expectations, while researchers familiar with the groups may have unconsciously favored intervention outcomes when assessing subjective indicators. Consequently, some observed inter-group differences may originate from such expectation effects rather than the biological efficacy of the interventions, potentially leading to overestimation of actual therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, four of these studies exhibited selective reporting, indicating a degree of reporting bias. Researchers reported only indicators with statistically significant differences and ignored negative outcome indicators, especially in QOL scales that contain many items, potentially leading to an overestimation of the results. Second, linguistic bias may have influenced our results because all the relevant research was conducted in Chinese. Our findings warrant careful interpretation due to these concerns and should be validated through more comprehensive investigations with enhanced methodological rigor. Third, the lack of patient categorization by gender, smoking status, or EGFR mutation type (exon 19 deletion and Leu858Arg mutations) may influence therapy efficacy. Furthermore, because numerous studies lacked specific outcomes, they were excluded from all analyses. For instance, only eight treatments were evaluated for dermatologic toxicities, while seven studies addressed gastrointestinal toxicities and six focused on hepatic insufficiency, potentially compromising the precision of the analytical outcomes. Fourth, subgroup analysis revealed that the current clinical data for the combination of TCM injections and EGFR-TKIs are insufficient. In several subgroup analyses, only one study was included, yielding unreliable analytical outcomes.
5 Conclusion
Our meta-analysis revealed that combining CHIs with EGFR-TKIs improved ORR and DCR, reduced side effects, and modulated immune function in patients with NSCLC. Therefore, in conjunction with targeted therapy, CHIs may serve as a supplemental therapy for NSCLC. However, our results must be interpreted cautiously due to the generally low certainty evidence. Obtaining additional clinical data from randomized controlled trials with more stringent designs is necessary to comprehensively examine overall and individual effectiveness and safety, yielding more reliable findings for clinical applications.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
ZY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. MY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. TW: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. GZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review and editing. GY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from Chinese Society of Traditional Chinese Medicine [Grant No. CACMLHJJ-20220102].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1670501/full#supplementary-material
References
Curry, J. L., Torres-Cabala, C. A., Kim, K. B., Tetzlaff, M. T., Duvic, M., Tsai, K. Y., et al. (2014). Dermatologic toxicities to targeted cancer therapy: shared clinical and histologic adverse skin reactions. Int. J. Dermatol 53 (3), 376–384. doi:10.1111/ijd.12205
Dai, S. (2021). Efficacy of gefitinib and Kanglaite injection in advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its impact on immune function and quality of life. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use. 14 (26), 68–70. doi:10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2021.26.025
Guo, S., Li, Y., Su, H., Meng, M., Xi, J., Mo, G., et al. (2021). Aidi injection as adjunctive treatment to gemcitabine-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharm. Biol. 59 (1), 1260–1275. doi:10.1080/13880209.2021.1973038
Higgins, J. P., Savović, J., Page, M. J., Elbers, R. G., and Sterne, J. A. (2019). Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. Cochrane Handb. Syst. Rev. Interventions2019, 205–228. doi:10.1002/9781119536604.ch8
Hu, S., Dan, W., Liu, J., Ha, P., Zhou, T., Guo, X., et al. (2021). The use of traditional Chinese medicine in relieving EGFR-TKI-Associated diarrhea based on network pharmacology and data mining. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 5530898. doi:10.1155/2021/5530898
Huang, Y., Xia, Z., Dai, Y., Zheng, L., Wang, Y., Ruan, Z., et al. (2024). Recent efficacy observation and safety analysis of shenmai injection combined with amitinib in EGFR mutation advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Zhejiang Clin. Med. J. 26 (4), 523–524. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-7664.2024.4.zjlcyx202404015
Hutton, B., Salanti, G., Caldwell, D. M., Chaimani, A., Schmid, C. H., Cameron, C., et al. (2015). The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern Med. 162 (11), 777–784. doi:10.7326/M14-2385
Jänne, P. A., Engelman, J. A., and Johnson, B. E. (2005). Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer: implications for treatment and tumor biology. J. Clin. Oncol. 23 (14), 3227–3234. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.09.985
Jiang, J., Liang, X., Yu, S., Qian, X., Yin, W., and Li, L. (2019). Clinical efficacy of aidi injection combined with gefitinib in the treatment of patients with advanced EGFR gene mutation lung cancer. Contemp. Med. 25 (15), 97–99. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2019.15.037
Jiao, L., Xu, J., Sun, J., Chen, Z., Gong, Y., Bi, L., et al. (2019). Chinese herbal medicine combined with EGFR-TKI in EGFR mutation-positive advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma (CATLA): a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 732. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00732
Koulouris, A., Tsagkaris, C., Corriero, A. C., Metro, G., and Mountzios, G. (2022). Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: from mechanisms to new therapeutic strategies. Cancers (Basel) 14 (14), 3337. doi:10.3390/cancers14143337
Leighl, N. B., Karaseva, N., Nakagawa, K., Cho, B. C., Gray, J. E., Hovey, T., et al. (2020). Patient-reported outcomes from FLAURA: osimertinib versus erlotinib or gefitinib in patients with EGFR-Mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 125, 49–57. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.11.006
Li, J., Zhu, G. H., Liu, T. T., Xu, B. W., and Li, J. (2022). Comparative efficacy of 10 Chinese herbal injections combined with GP regimen chemotherapy for patients with advanced NSCLC a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Cancer 13 (2), 465–480. doi:10.7150/jca.66410
Li, S., Chen, X., Shi, H., Yi, M., Xiong, B., and Li, T. (2025). Tailoring traditional Chinese medicine in cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 24 (1), 27. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-02213-6
Liu, R., Nie, L. X., Li, X. F., Cheng, X. L., Zhang, Y. Y., Wang, G. L., et al. (2012). Simultaneous determination of ginsenosides and lignans in Sheng-mai injection by ultra-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Pharmazie 67 (1), 14–19. doi:10.1691/ph.2012.1069
Paik, S., Song, G. Y., and Jo, E. K. (2023). Ginsenosides for therapeutically targeting inflammation through modulation of oxidative stress. Int. Immunopharmacol. 121, 110461. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110461
Rosell, R., Carcereny, E., Gervais, R., Vergnenegre, A., Massuti, B., Felip, E., et al. (2012). Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 13 (3), 239–246. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X
Sequist, L. V., Yang, J. C., Yamamoto, N., O'Byrne, K., Hirsh, V., Mok, T., et al. (2013). Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 31 (27), 3327–3334. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.44.2806
Shi, Q., and Chen, G. (2013). Clinical observation of kanglaite injection combined with gefitinib in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR positive in medium or late stage. Chin. Manip. & Rehabilitation Med. 4 (04), 76–78. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-1879.2013.04.040
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71 (3), 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
Tan, D. S., Yom, S. S., Tsao, M. S., Pass, H. I., Kelly, K., Peled, N., et al. (2016). The international association for the study of lung cancer consensus statement on optimizing management of EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer: status in 2016. J. Thorac. Oncol. 11 (7), 946–963. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2016.05.008
Wang, F., and Li, S. (2020). Effects of aidi injection combined with erlotinib on T lymphocytes, vascular endothelial growth factor and quality of life in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. World Clin. Drugs 41 (04), 301–306. doi:10.13683/j.wph.2020.04.012
Wang, K., Chen, Q., Shao, Y., Yin, S., Liu, C., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Anticancer activities of TCM and their active components against tumor metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 133, 111044. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111044
Wang, H., Zhang, X., Liu, Z., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Effect of shenmai injection combined with icotinib in treating advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. J. Rural Med. Pharm. 29 (08), 29–30. doi:10.19542/j.cnki.1006-5180.006186
Wen, J., Yang, T., Wang, J., Ma, X., Tong, Y., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Kanglaite injection combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for the improvement of clinical efficacy and immune function in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 8586596. doi:10.1155/2020/8586596
Wen, L., Xie, L., Gong, F., Zhang, S., and Xi, T. (2023). Efficacy and safety of Chinese medicine injections in combination with docetaxel and cisplatin for non-small cell lung cancer: a network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1277284. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1277284
Wu, Y. L., Zhou, C., Liam, C. K., Wu, G., Liu, X., Zhong, Z., et al. (2015). First-line erlotinib versus gemcitabine/cisplatin in patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: analyses from the phase III, randomized, open-label, ENSURE study. Ann. Oncol. 26 (9), 1883–1889. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv270
Wu, Y., Zhang, J., Hong, Y., and Wang, X. (2018). Effects of kanglaite injection on serum miRNA-21 in patients with advanced lung cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 24, 2901–2906. doi:10.12659/MSM.909719
Yang, W. (2016). Clinical study on kanglaite injection combined with icotinib in treatment of nonsmall cell lung cancer. Drugs & Clin. 31 (12), 1984–1987. doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2016.12.027
Yang, W., Wang, K., Wang, H., Jiao, Q., and Li, J. (2016). Efficacy of combined xiaoaiping injection with gefitinib on advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Med. J. Wuhan Univercity 37 (05), 786–789. doi:10.14188/j.1671-8852.2016.05.021
Zhang, Q. (2016). Clinical study of gefitinib combined with elemene injection for advanced pulmonary adenocarci-noma with EGFR mutation. Chin. J. Front. Med. Sci. 8 (10), 113–116. doi:10.12037/YXQY.2016.10-28
Zhang, L., Han, N., Ding, Y., Zhang, J., and Feng, G. (2018). Clinical observation of gefitinib tablets combined with aidi injection in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR positive. Prog. Mod. Biomed. 18 (14), 2696–2700. doi:10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2018.14.020
Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Cai, X., Pan, Z., Liu, J., Yin, W., et al. (2019). Efficacy and safety of first line treatments for patients with advanced epidermal growth factor receptor mutated, non-small cell lung cancer: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Bmj 367, l5460. doi:10.1136/bmj.l5460
Zheng, Q., Yu, J., Miao, Q., and Wang, S. (2021). Prospective randomized controlled study of icotinib with β-elemene injection for advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Zhejiang J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med. 31 (5), 428–431. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4561.2021.05.008
Zhou, Y., Wan, D., Qian, X., Jiang, H., and Feng, J. (2017). Effect of elemene injection combined with gefitinib on immune function and life quality of advanced elder lung cancer patients with EGFR mutant Chinese. J. Cinical Healthc. 20 (05), 502–505. doi:10.3969/J.issn.1672-6790.2017.05.006
Zhou, J., Peng, C., Fan, Z., Ni, H., and Fan, Y. (2022). Efficacy of shenfu injection combined with osimertinib in the treatment of patients with advanced EGFR-Positive NSCLC and its effect on the immune function of patients. Prog. Mod. Biomed. 22 (10). doi:10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2022.10.025
Glossary
ADI Aidi Injection
CBM Chinese Biological Medicine Database
CHIs Chinese herbal injections
CNKI China National Knowledge Infrastructure
CR complete relief
DCR disease control rate
EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor
EGFR-TKIs epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors
EI Elemene injection
EORTC QLQ-C30 EORTC QLG Core Questionnaire
GRADE Grade of Recommendations AssessmentDevelopment and Evaluation
KLTI Kanglaite injection
KPS Karnofsky scale
MDR multiple-drug resistance
NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer
ORR objective response rate
OS overall survival
PD progressive disease
PFS progression free survival
PR partial remission
PRISMA preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
QOL quality of life
RCTs Randomized controlled trials
RECIST Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors
RRs risk ratios
SD stable disease
SFI Shenfu injection
SMD Standardized mean differences
SMI Shenmai injection
TCM Traditional Chinese medicine
XAPI Xiaoaiping injection
Keywords: Chinese herbal injections, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, non-small cell lung cancer, meta-analysis, systematic review
Citation: Yuan Z, Yan M, Wu T, Zhang G, Yang G and Wang X (2025) Chinese herbal injections combined with EGFR-TKIs for intervention of non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1670501. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1670501
Received: 21 July 2025; Accepted: 22 October 2025;
Published: 19 November 2025.
Edited by:
Ebenezer Idowu Olatunbosun Ajayi, Osun State University, NigeriaReviewed by:
Tianye Li, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, ChinaBin Luo, Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Yuan, Yan, Wu, Zhang, Yang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guowang Yang, Z3Vvd2FuZ195YW5nQDE2My5jb20=; Xiaomin Wang, d2FuZ3hpYW9taW5fYmh0Y21AMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Zichun Yuan
Zichun Yuan Mei Yan
Mei Yan Tongtong Wu
Tongtong Wu Ganlin Zhang
Ganlin Zhang Guowang Yang
Guowang Yang Xiaomin Wang
Xiaomin Wang
![Forest plot illustrating the risk ratios of various studies comparing CHIs plus EGFR-TKIs group to EGFR-TKIs group alone. Subgroups are categorized into first-generation and third-generation EGFR-TKIs. Risk ratios for individual studies are represented by blue squares with horizontal lines indicating confidence intervals. Diamonds represent pooled estimates. Heterogeneity statistics and total event numbers are shown for each subgroup and overall. The plot suggests an overall risk ratio of 1.08 [1.02, 1.14] favoring the experimental group.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1670501/fphar-16-1670501-HTML/image_m/fphar-16-1670501-g005.jpg)
![Forest plot showing a meta-analysis of CHIs plus EGFR-TKIs versus EGFR-TKIs alone. Five subgroups include Kanglaite, Shenmai, Aidi, Xiaoaiping, and Elemene injections. Risk ratios and confidence intervals are presented with diamonds indicating overall effects. Shenmai and Elemene show significant favoring of the experimental group, while others show mixed results. Overall, the total effect favors CHIs plus EGFR-TKIs with a risk ratio of 0.61 [0.45, 0.84].](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1670501/fphar-16-1670501-HTML/image_m/fphar-16-1670501-g007.jpg)