- 1Department of Respiratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang, China
- 2Division of Spinal Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang, China
Objective: The clinical role of Tislelizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer (LC) remains controversial. This study aims to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of Tislelizumab in treating these patients through a meta-analysis.
Methods: Databases including PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, and Web of Science were searched up to 19 May 2025. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and single-arm studies assessing the efficacy and safety of Tislelizumab for locally advanced or metastatic LC were included. Literature screening and data extraction were performed according to the PRISMA guidelines, and pooled odds ratios (OR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using STATA 15.0 software.
Results: A total of 8 studies were included, of which 5 were RCTs and 3 were single-arm studies. In the RCT subgroup, the Tislelizumab group demonstrated a higher objective response rate (ORR) [OR = 2.29, 95%CI(1.43,3.64), P = 0.001] and disease control rate (DCR) [OR = 1.64, 95%CI(1.30,2.07), P < 0.001] compared to the control group, but no significant differences were found in overall survival (OS) [OR = 0.81, 95%CI(0.60,1.10), P = 0.179] or progression-free survival (PFS) [OR = 0.74, 95%CI(0.39,1.41), P = 0.364]. Single-arm study data indicated that Tislelizumab treatment achieved a high ORR [OR = 0.54, 95%CI (0.34,0.74), P < 0.001] and DCR [OR = 0.86, 95%CI (0.78,0.92), P < 0.001]. Subgroup analysis revealed that Tislelizumab had similar effects on ORR and DCR in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Conclusion: The meta-analysis results suggest that Tislelizumab demonstrates significant short-term efficacy (ORR and DCR) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC. However, the existing evidence is inadequate to confirm its long-term survival benefits (OS and PFS), and more high-quality studies are needed for validation.
1 Introduction
LC is one of the most prevalent malignant tumors globally, characterized by the highest incidence and mortality rates. Among these, NSCLC and SCLC are the most common pathological types (Abu Rous et al., 2023; Allemani et al., 2018; Frödin, 1996; Sullivan, 2018). For patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC, despite continuous advancements in treatment modalities, the prognosis remains poor, highlighting the urgent need for more effective therapeutic strategies. Currently, clinical management primarily relies on comprehensive approaches, including chemotherapy (Li et al., 2023; Legha et al., 1977; Nagasaka and Gadgeel, 2018), radiotherapy (Vinod and Hau, 2020; Schild, 2020), brachytherapy (International BR, 2023; Lin et al., 2023), and targeted therapy (Herrera-Juárez et al., 2023; Wu and Lin, 2022; Meyer et al., 2024). In standard treatment protocols, chemotherapy remains a cornerstone, particularly for patients without driver gene mutations or those with SCLC. However, traditional chemotherapeutic agents often cause significant systemic toxicities, such as myelosuppression, nausea, vomiting, and alopecia, with limited efficacy leading to drug resistance and disease progression (Sha et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2019a). Radiotherapy plays a pivotal role in the radical or palliative treatment of locally advanced NSCLC, but it also carries the risk of local recurrence and may cause complications like radiation pneumonitis and esophagitis (Liu et al., 2023; Mutsaers et al., 2023). With advancements in molecular biology research, targeted therapy drugs against specific driver genes (e.g., EGFR, ALK) have significantly improved survival in corresponding subtypes of patients (Garassino et al., 2023; de Castro et al., 2023). However, these drugs often face acquired resistance and are only applicable to a small proportion of patients carrying specific gene mutations (Fu et al., 2022; Xiang et al., 2024).
In recent years, the advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has revolutionized LC treatment (Tang et al., 2022; Passaro et al., 2022; Konen et al., 2024), particularly antibodies targeting programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) or its ligand (PD-L1), which have significantly improved survival outcomes in some patients (Yin et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2024; Cho et al., 2020). PD-1 is an immunosuppressive receptor expressed on activated T lymphocytes. In the tumor microenvironment, tumor cells or immunosuppressive cells highly express PD-L1, which, upon binding to PD-1 on T cells, transmits inhibitory signals, leading to T-cell exhaustion and impaired proliferation, thereby facilitating tumor evasion from immune recognition and clearance (Cheng W. et al., 2024; Cheng et al., 2022; Figure 1). Tislelizumab is a humanized IgG4 anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, uniquely designed to block the binding of PD-1 to PD-L1/PD-L2 with high specificity, thereby alleviating the suppression of T cells by the PD-1 pathway. More specifically, Tislelizumab has low affinity for Fc receptors (FcRs) on macrophages via its Fc segment, which reduces the potential interference of antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) on pharmacodynamic effects, theoretically aiding in more effectively maintaining T-cell function. By restoring T-lymphocyte-mediated immune responses, Tislelizumab aims to reactivate anti-tumor immune responses (Zhao et al., 2024; Daei Sorkhabi et al., 2023; Cheng Y. et al., 2024).
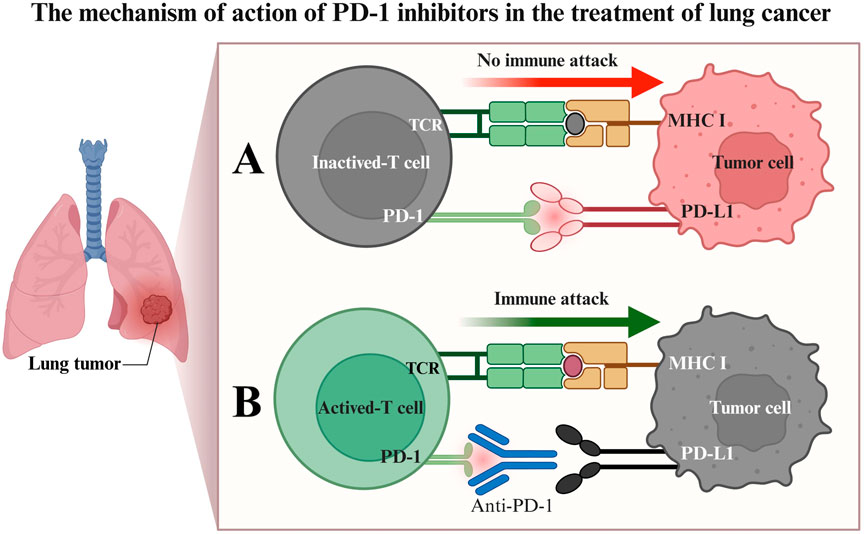
Figure 1. Mechanism of PD-1 inhibitor therapy for lung cancer. (A) Binding of the PD-1 receptor to the PD-L1 ligand results in T-cell inactivation, impairing the ability of T cells to attack tumor cells immunologically; (B) PD-1 inhibitors competitively bind to the PD-1 receptor, blocking its interaction with PD-L1. This preserves T-cell activity, enabling T cells to initiate an immune attack against tumor cells, leading to tumor cell apoptosis.
Based on this mechanism of action, multiple clinical trials have preliminarily explored the potential of Tislelizumab in LC treatment, demonstrating certain ORR and DCR in monotherapy or combination therapy for locally advanced or metastatic LC (Zhao et al., 2024; Daei Sorkhabi et al., 2023; Lu et al., 2024). However, variations among studies in patient populations, treatment lines, combination regimens, and control group selection have led to inconsistencies in the exact efficacy and safety data, leaving the clinical positioning of Tislelizumab in such patients still controversial.
In the absence of direct head-to-head RCTs comparing tislelizumab with other established immunotherapies, indirect treatment comparisons (ITCs) have emerged as a crucial methodological approach to inform clinical decision-making. ITCs, including network meta-analyses and adjusted indirect comparisons, allow for the estimation of relative treatment effects by leveraging common comparator arms across different trials (e.g., chemotherapy alone). Recent ITCs have specifically evaluated tislelizumab versus pembrolizumab, both combined with chemotherapy, as first-line treatment for advanced NSCLC. For instance, a systematic review and indirect comparison by Guo et al. (2023) found no significant differences in PFS (HR = 1.04, 95% CI: 0.82–1.31), ORR (RR = 0.79, 95% CI: 0.59–1.07), or incidence of grade ≥3 Adverse event (AE) (RR = 0.99, 95% CI: 0.87–1.12) between tislelizumab and pembrolizumab combinations, suggesting comparable efficacy and safety profiles. Similarly, Messori et al. (2023) applied the IPDfromKM-Shiny method to reconstruct individual patient data from Kaplan-Meier curves of five RCTs and reported substantial equivalence in PFS between the two regimens (HR = 0.952, 95% CI: 0.775–1.168). These findings were further supported by a real-world retrospective cohort study in the neoadjuvant setting, which demonstrated no significant differences in pathological response rates, survival outcomes, or toxicity profiles between pembrolizumab and tislelizumab when combined with chemotherapy (Hu et al., 2025). Given the consistent results across these methodological approaches, ITCs provide robust supplementary evidence for positioning tislelizumab relative to other immunotherapies, highlighting its non-inferior efficacy and safety in advanced LC contexts.
To comprehensively and objectively evaluate the therapeutic effects and safety of Tislelizumab in locally advanced or metastatic LC, we systematically searched for relevant RCTs and single-arm studies up to 19 May 2025, and conducted a meta-analysis based on the PRISMA guidelines. This study aims to integrate existing evidence, focusing on comparing the differences between Tislelizumab and standard treatment or placebo in terms of ORR, DCR, OS, and PFS, and to explore its performance in different subtypes of LC, thereby providing more reliable evidence-based medical support for clinical decision-making.
2 Materials and methods
This protocol has been registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO: CRD420251069321).
2.1 Search strategy
We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science for articles published up to 19 May 2025, on the efficacy and safety of Tislelizumab in treating locally advanced or metastatic LC. The search terms were (Lung Cancer, Nasopharyngeal, nasopharyngeal cancer, NPC) AND (tislelizumab, BGB-A317). The specific search strategies for PubMed and Embase are provided in Supplementary Tables S1, S2.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
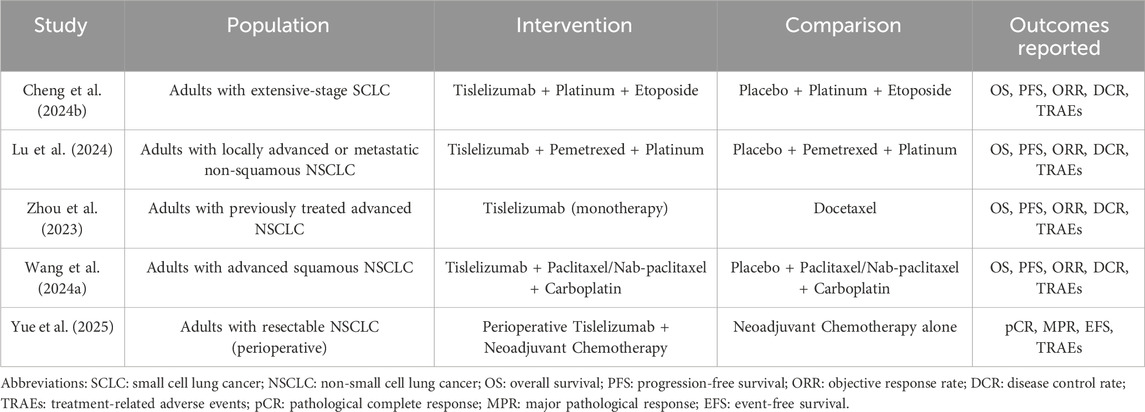
Inclusion criteria (Abu Rous et al., 2023): Study design: RCTs or single-arm studies (Allemani et al., 2018); Study population: patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC (including NSCLC and SCLC) diagnosed by histology or cytology (Frödin, 1996); Intervention: the study group received Tislelizumab (either as monotherapy or in combination with other therapies) as a treatment regimen (Sullivan, 2018); Comparator: For RCTs, the control group received one of the following standard-of-care comparators: a. Placebo plus chemotherapy. b. alone (e.g., platinum-based doublets such as carboplatin/paclitaxel, cisplatin/pemetrexed). c. Active drugs (e.g., docetaxel as second-line therapy) (Li et al., 2023). For single-arm studies, the efficacy of Tislelizumab was evaluated against historical benchmarks or within the study cohort without a direct concurrent control group (Legha et al., 1977). Outcome measures: studies reporting at least one of the following outcomes: OS, PFS, ORR [defined as the sum of complete response (CR) and partial response (PR)], or DCR [defined as the sum of CR, PR, and stable disease (SD)], or treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs).
Exclusion criteria (Abu Rous et al., 2023): Document type: duplicate publications, conference abstracts, literature reviews, meta-analyses, or case reports (Allemani et al., 2018); Study relevance: studies unrelated to the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic LC with Tislelizumab (Frödin, 1996); Data integrity: studies from which complete data or required outcome measures (such as OS, PFS, ORR, DCR, TRAEs) could not be obtained.
2.3 Data extraction
Extracted data included author names, publication year, drug type, number of included cases, drug dosage, follow-up duration, median OS, median PFS, median ORR, median DCR, TRAEs, and basic study information. Data extraction was independently performed by two researchers.
2.4 Risk of bias assessment
For RCTs: the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool for randomized trials 2.0 (RoB2) was used to assess the risk of bias (Sterne et al., 2019). RoB2 was applied by two independent researchers, and a third researcher resolved any disagreements in bias risk assessment. Evaluators examined the randomization process, deviations from intended interventions, missing outcome data, selection of outcome measures, and reported outcomes. Thus, studies were categorized as having low, moderate, or high risk of bias. For single-arm studies: the Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies (MINORS) (Slim et al., 2003) was used to assess quality, with the following grading: 0–12 points: low quality; 13–18 points: moderate quality; 19–24 points: high quality. Any disagreements were resolved through consultation (Supplementary Table S3).
2.5 Data analysis
For randomized controlled trials, we analyzed binary variables such as ORR, DCR, PFS, and OS using OR and 95% CI. For single-arm studies, we used effect sizes (ES) and 95% CI. Due to substantial heterogeneity in treatment types, frequencies, and durations across studies, a random-effects model was employed for the meta-analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using Stata software (version 15.0; Stata Corp, College Station, TX, United States). Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 values or Q statistics. I2 values of 0%, 25%, 50%, and 75% indicated no, low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively. When I2 ≥ 50%, a sensitivity analysis was conducted to investigate potential sources of heterogeneity; otherwise, a fixed-effects model was applied. Additionally, publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s test or Begg’s test with a random-effects model. A two-sided p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Literature screening and characteristics
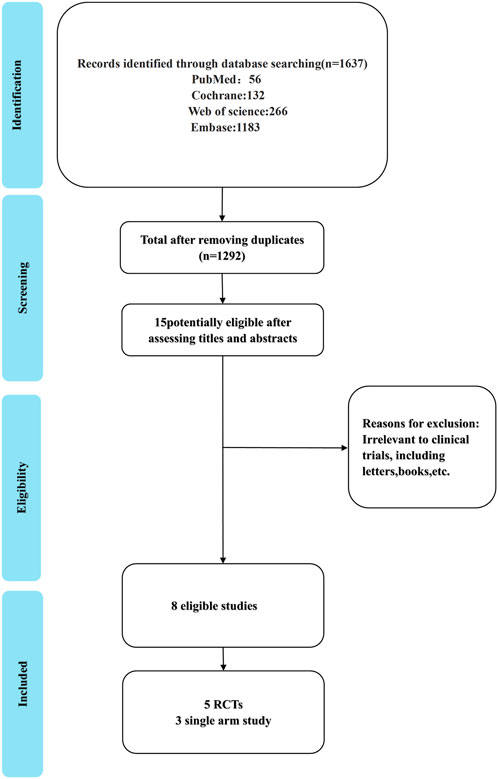
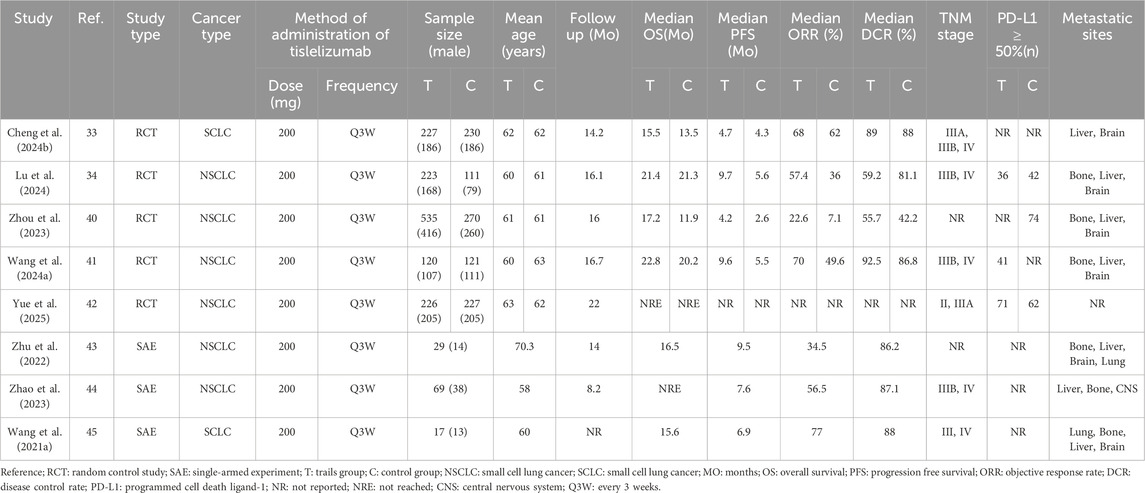
Our search yielded 1,637 articles, of which 1,292 remained after duplicate removal. A detailed review of titles and abstracts narrowed down the selection to 15 articles, and upon thorough full-text evaluation, we included 8 high-quality studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Yue et al., 2025; Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021; Figure 2). Five of these were RCTs (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Yue et al., 2025), encompassing 2,290 participants with 1,331 in the Tislelizumab group and 959 in the control group, the PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) characteristics of these RCTs are summarized in Table 1. The remaining three were single-arm studies (Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021) with 115 participants. Notably, one RCT (Yue et al., 2025) did not provide data on median ORR, median OS, median PFS, or median DCR, but it did report TRAES, and thus it was included in our analysis (Figure 3; Table 2).
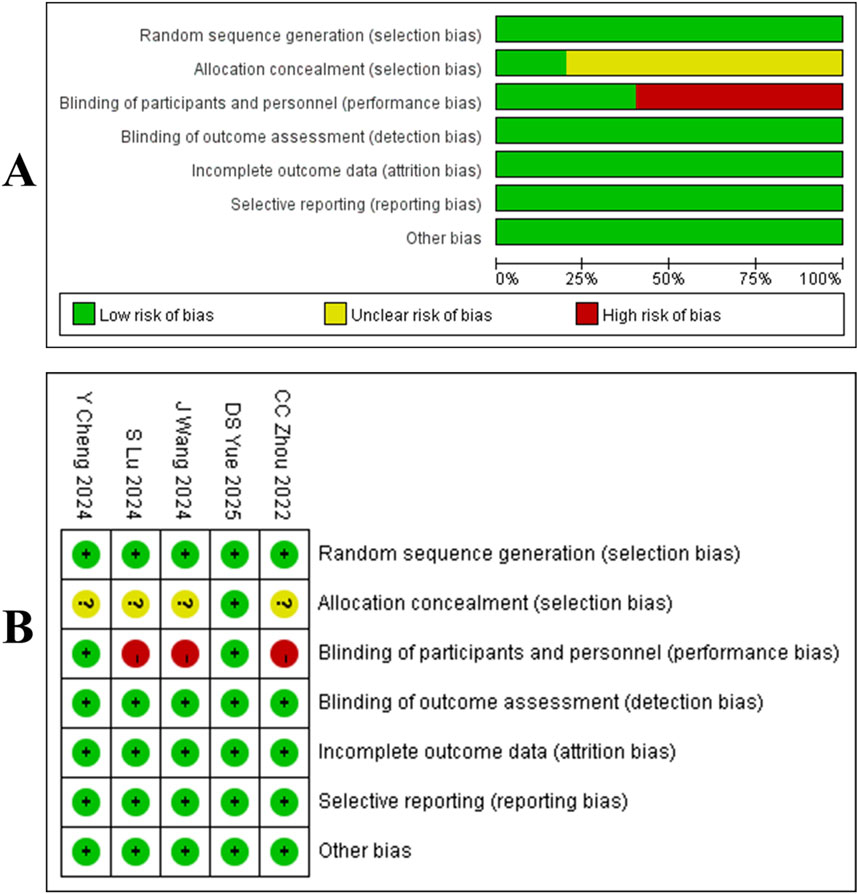
Figure 2. (A) Quality assessment results of included literature. (B) three risk levels are intuitively represented using a combination of colors and symbols: Low risk: Indicated by a green circle containing a plus sign (+). Some concerns: Indicated by a yellow circle containing a question mark (?). High risk: Indicated by a red circle containing a question mark (?).
3.2 Meta-analysis of RCTs
3.2.1 ORR
Four studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024) enrolled a total of 1,837 patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC, including 1,105 in the tislelizumab group and 732 in the control group (I2 = 74.6%, p = 0.008), indicating high heterogeneity. The forest plot showed [OR = 2.29, 95%CI (1.43, 3.64), p = 0.001],suggesting that tislelizumab significantly improved the ORR in these patients (Figure 4A; Table 2). Sensitivity analysis, conducted by sequentially excluding studies, indicated that potential heterogeneity may stem from Cheng Y. et al. (2024) (Supplementary Figure S1A). Publication bias was assessed using Egger’s test (p = 0.122) and Begg’s test (p = 0.497), both p-values >0.05, suggesting a low likelihood of publication bias (Supplementary Table S4).
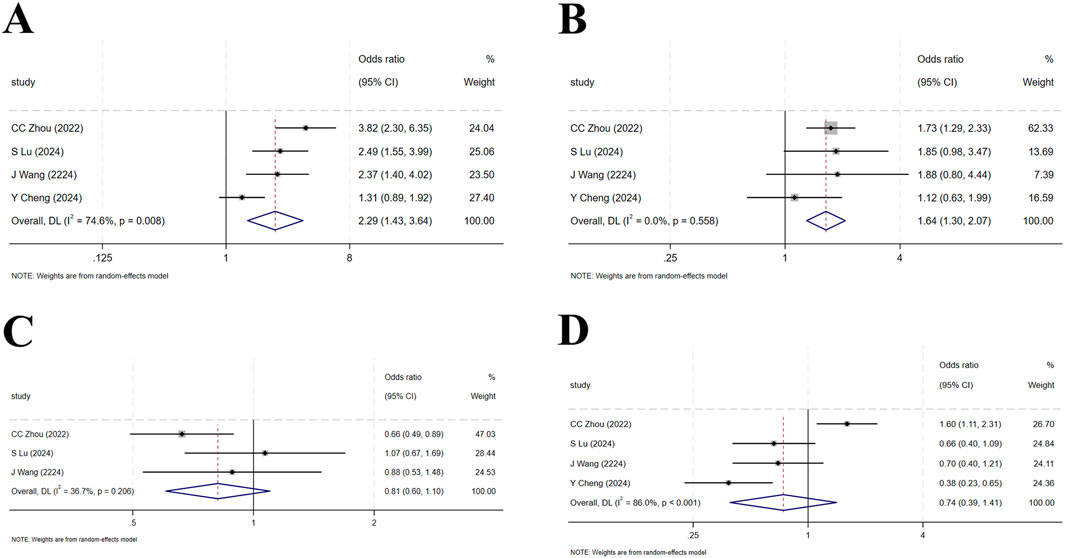
Figure 4. (A) Forest plot of overall response rate (ORR) in RCTs; (B) Forest plot of disease control rate (DCR) in RCTs; (C) Forest plot of overall survival (OS) in RCTs; (D) Forest plot of progression-free survival (PFS) in RCTs.
3.2.2 DCR
Four studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024) included 1,837 patients, with 1,105 in the tislelizumab group and 732 in the control group (I2 = 0, p = 0.558), indicating low heterogeneity. The forest plot showed [OR = 1.64, 95%CI (1.30, 2.07), p < 0.001], demonstrating that tislelizumab significantly improved the DCR in patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC (Figure 4B; Table 2). Publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s test (p = 0.806) and Begg’s test (p = 0.497), both p-values >0.05, indicating a low likelihood of publication bias (Supplementary Table S4).
3.2.3 OS
Four studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024) involved 1,837 patients, with 1,105 in the tislelizumab group and 732 in the control group (I2 = 36.7%, p = 0.206), suggesting moderate heterogeneity. The forest plot showed [OR = 0.81, 95%CI (0.60, 1.10), p = 0.179], suggesting that tislelizumab did not improve the OS in patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC (Figure 4C; Table 2). Publication bias was assessed using Egger’s test (p = 0.309) and Begg’s test (p = 0.602), both p-values >0.05, indicating a low likelihood of publication bias (Supplementary Table S4).
3.2.4 PFS
Four studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024) included 1,380 patients, with 878 in the tislelizumab group and 502 in the control group (I2 = 86.0%, p < 0.001), indicating high heterogeneity. The forest plot showed [OR = 0.74, 95%CI (0.39, 1.41), p = 0.364], indicating that tislelizumab did not improve the OS in patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC (Figure 4D; Table 2). Sensitivity analysis by sequentially removing studies revealed that potential heterogeneity may originate from C Zhou (2023) (Zhou et al., 2023; Supplementary Figure S1B). The p-values of Egger’s test (p = 0.079) and Begg’s test (p = 0.497) were both >0.05, indicating a low likelihood of publication bias (Supplementary Table S4).
3.3 Meta-analysis of single-arm studies
3.3.1 ORR
Three studies (Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021) involved a total of 115 patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC. High heterogeneity was observed among the studies (I2 = 74.43%, p = 0.02). The forest plot showed [OR = 0.54, 95%CI (0.34, 0.74), p < 0.001], indicating that tislelizumab improved the ORR in these patients (Figure 5A; Table 2). Sensitivity analysis suggested that potential heterogeneity may stem from the study by Zhu et al. (2022) (Supplementary Figure S2). Assessment of publication bias using Egger’s test (p = 0.873) and Begg’s test (p = 0.602) yielded p-values >0.05, indicating a low likelihood of publication bias (Supplementary Table S4).
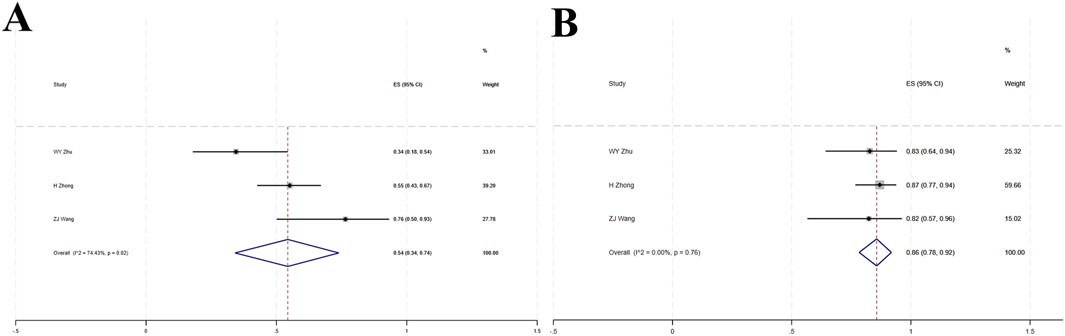
Figure 5. (A) Forest plot of overall response rate (ORR) in single-arm studies; (B) Forest plot of disease control rate (DCR) in single-arm studies.
3.3.2 DCR
Three studies (Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021) included a total of 115 patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC. Low heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 0, p = 0.76). The forest plot showed [OR = 0.86, 95%CI (0.78, 0.92), p < 0.001], indicating that tislelizumab improved the DCR in these patients (Figure 5B; Table 2). Assessment of publication bias using Egger’s test (p = 0.209) and Begg’s test (p = 0.602) yielded p-values >0.05, indicating a low likelihood of publication bias (Supplementary Table S4).
3.4 Subgroup analysis
Subgroup analyses were conducted based on the histological subtypes of LC.
3.4.1 ORR
Seven studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021) involving a total of 547 patients were included. This population comprised 380 patients with NSCLC from five studies (Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023) and 167 patients with SCLC from two studies. In the NSCLC subgroup, high heterogeneity was observed among the studies (I2 = 97.42%, p < 0.001), and the forest plot showed [OR = 0.48, 95%CI (0.26, 0.74), p < 0.001], suggesting that tislelizumab improved the ORR in patients with NSCLC. For the SCLC subgroup, [OR = 0.69, 95%CI (0.63, 0.75), p < 0.001] indicated that tislelizumab improved the ORR in patients in the SCLC subgroup. The heterogeneity between the two groups for tislelizumab was not significant (p = 0.076), indicating that the effect of tislelizumab was similar in the two subgroups (Figure 6A; Table 2).
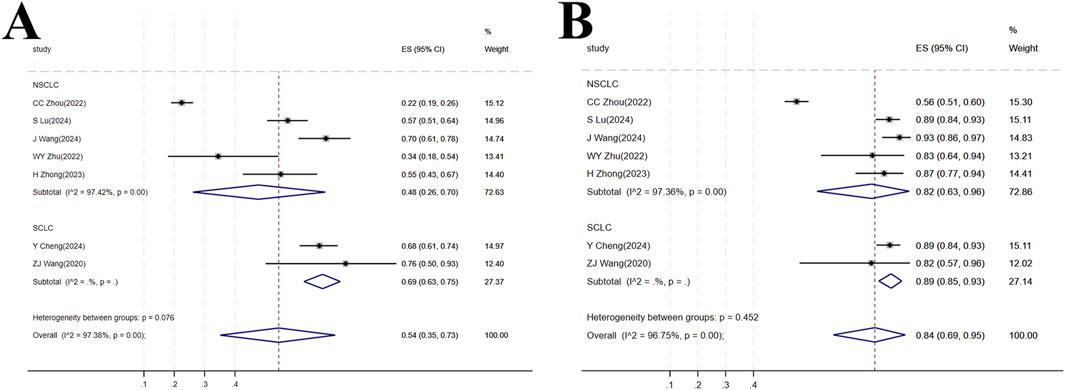
Figure 6. (A) Forest plot of overall response rate (ORR) in subgroup analyses; (B) Forest plot of disease control rate (DCR) in subgroup analyses.
3.4.2 DCR
The same seven studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021) including 547 patients were analyzed for DCR. The NSCLC subgroup consisted of 380 patients from five studies (Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023) while the SCLC subgroup comprised 167 patients from two studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Wang Z. et al., 2021). High heterogeneity was present within the NSCLC subgroup (I2 = 97.36%, p < 0.001). The forest plot showed [OR = 0.82, 95%CI (0.63, 0.96), p < 0.001], indicating that tislelizumab improved the DCR in this patient group. In the SCLC subgroup, [OR = 0.89, 95%CI (0.85, 0.93), p < 0.001], suggesting an improvement in DCR with tislelizumab. The non-significant heterogeneity between the subgroups (p = 0.452) implied a comparable effect of tislelizumab on DCR in both NSCLC and SCLC patients (Figure 6B; Table 2).
3.5 TRAES
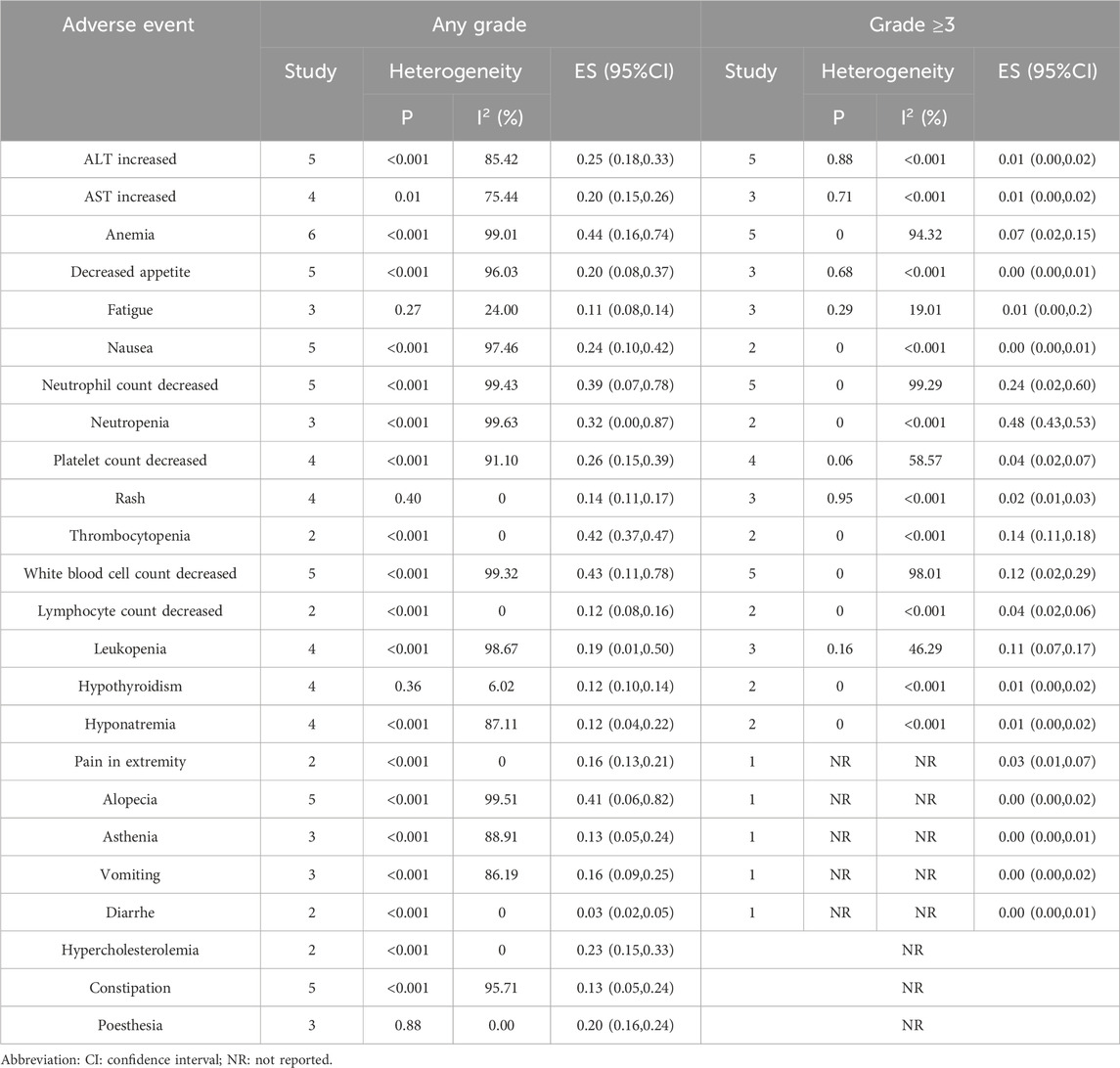
A meta-analysis was conducted on TRAES reported in the 8 included studies (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Yue et al., 2025; Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021). The analysis focused on events reported in at least two studies. Common AEs included increased Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), increased Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), anemia, decreased appetite, nausea, decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, rash, decreased white blood cell count, leukopenia, hypothyroidism, and hyponatremia. The incidence rates for these events were as follows: increased ALT (18.87%), increased AST (13.62%), anemia (32.15%), decreased appetite (10.92%), nausea (16.18%), decreased neutrophil count (23.78%), decreased platelet count (10.16%), rash (5.4%), decreased white blood cell count (26.55%), leukopenia (10.23%), hypothyroidism (8.36%), and hyponatremia (4.19%). Regarding events of Grade 3 or higher, the rates were: increased ALT (0.89%), increased AST (0.62%), anemia (4.70%), decreased appetite (0.20%), nausea (0.13%), decreased neutrophil count (17.15%), decreased platelet count (1.79%), rash (0.69%), decreased white blood cell count (8.71%), leukopenia (3.18%), hypothyroidism (0.20%), and hyponatremia (0.34%). Constipation was also observed as a common AE, with an overall incidence of 8.50%, although no Grade 3 or higher events related to constipation were reported (Table 3).
4 Discussion
4.1 Summary of main efficacy findings
Compared with chemotherapy, PD-L1 inhibitors have been reported to prolong PFS and OS, particularly in patients with high tumor PD-L1 expression (Mok et al., 2019; Jassem et al., 2021; Sezer et al., 2021; Herbst et al., 2020). Several global trials have demonstrated that anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 therapy provides significant efficacy and safety advantages for advanced LC (Borghaei et al., 2015; Barlesi et al., 2018; Herbst et al., 2016; Brahmer et al., 2015; Rittmeyer et al., 2017). This study, through a systematic review and meta-analysis, aims to integrate existing evidence and evaluate the efficacy and safety of Tislelizumab in the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic LC. The comprehensive analysis results indicate that Tislelizumab shows positive potential in improving short-term efficacy indicators in patients, especially in ORR and DCR, but its impact on long-term survival benefits still requires more high-quality data for confirmation.
4.2 Mechanistic rationale for short-term efficacy and Fc engineering advantage
First, regarding efficacy, we observed that in the RCT subgroup, Tislelizumab significantly increased the ORR [OR = 2.29, 95%CI (1.43,3.64), P = 0.001] and DCR [OR = 1.64, 95%CI (1.30,2.07), P < 0.001] of patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC compared with the control group (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Yue et al., 2025). This finding is consistent with Tislelizumab’s mechanism as a PD-1 inhibitor, which aims to relieve T-cell inhibition and restore anti-tumor immune responses, suggesting that it can effectively induce tumor regression or stabilization (Lin et al., 2025; Dammeijer et al., 2020; Kumagai et al., 2020). Furthermore, the distinct structural design of Tislelizumab is hypothesized to contribute to its efficacy profile. Unlike some conventional anti-PD-1 antibodies, Tislelizumab is engineered with a specific Fc domain modification that minimizes binding to Fcγ receptors (FcγR) on macrophages and other myeloid cells (Zhao et al., 2024; Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Dahan et al., 2015). This design is crucial because binding of an anti-PD-1 antibody’s Fc domain to activating FcγRs (e.g., FcγRIIIa) can trigger ADCP of T cells expressing PD-1, paradoxically depleting the very immune effector cells intended to be activated (Dahan et al., 2015; Arlauckas et al., 2017). By mitigating this Fc-mediated effector function, Tislelizumab may potentially preserve the tumor-infiltrating T-cell pool, leading to a more robust and sustained anti-tumor immune response compared to antibodies capable of inducing significant ADCP (Zhang et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2017). This theoretical advantage in the tumor microenvironment could provide a mechanistic rationale for the significant improvements in short-term efficacy endpoints (ORR and DCR) observed in our pooled analysis. However, it is important to note that direct comparative clinical data confirming this mechanistic superiority over other PD-1 inhibitors remain limited, and the impact of this design on long-term survival outcomes requires further validation in well-controlled studies.
4.3 Interpretation of long-term survival outcomes and potential explanations
However, for the more critical long-term survival indicators, namely, OS and PFS, the RCT subgroup analysis did not show a statistically significant increase OS [OR = 0.81, 95%CI (0.60,1.10), P = 0.179]; PFS [OR = 0.74, 95%CI (0.39,1.41), P = 0.364]. Although the OR value of OS is less than 1, indicating a potential survival benefit trend, which is basically consistent with the report by Zhang et al. (2022) the confidence interval includes the null value, and PFS also did not reach significance, suggesting that the current evidence based on RCTs is insufficient to confirm that Tislelizumab can provide definite long-term survival advantages. A doubt worth further exploration is why Tislelizumab performs well in short-term indicators (ORR/DCR) but fails to show statistical advantages in OS/PFS, which reflect long-term benefits. This may not mean that Tislelizumab is ineffective, but rather reflects potential limitations in study design or execution. For example, the included RCTs may have relatively limited sample sizes, resulting in insufficient statistical power to detect true differences in OS/PFS; or, the follow-up time may not be long enough to fully capture the long-term survival improvement effect of the treatment. Additionally, factors such as the choice of the control group (e.g., placebo or active drug), heterogeneity in baseline patient characteristics, and tumor type (e.g., NSCLC or SCLC, although the abstract did not clearly distinguish, but different subtypes exhibit significant differences in response patterns to immunotherapy) may also affect the between-group comparison results of OS/PFS. Heterogeneity analysis suggests that differences between some studies may have affected the stability of the pooled effect size, such as the contribution of Cheng Y. et al. (2024) to the heterogeneity of ORR and the influence of Zhou et al. (2023) on the heterogeneity of PFS, which also reflects potential differences in baseline patient characteristics, treatment lines, or combination regimens among different studies to some extent. Therefore, we are cautious about the conclusion that Tislelizumab did not significantly improve OS/PFS, believing that this reflects more the strength of current evidence rather than a final negation of its long-term value.
4.4 Critical appraisal of single-arm evidence and its limitations
On the other hand, data from single-arm studies offer additional insights into the use of Tislelizumab (Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021). Although single-arm designs limit the ability to make direct comparisons with control groups, their findings also indicate favorable outcomes associated with Tislelizumab treatment (Iaquinto et al., 2025; Wang M. et al., 2024). The pooled ORR [OR = 0.54, 95%CI (0.34–0.74), P < 0.001] and DCR [OR = 0.86, 95%CI (0.78–0.92), P < 0.001] from these single-arm studies were both substantial, suggesting that Tislelizumab monotherapy or specific regimens can achieve meaningful clinical responses and disease control even without a direct comparator. This further underscores the potential value of Tislelizumab as a treatment option, particularly for patient populations who are ineligible or unsuitable for randomized controlled trials (Wang J. et al., 2021; Wang L. et al., 2024).
However, the interpretation of efficacy results from single-arm studies requires considerable caution due to inherent methodological limitations. The primary constraint is the absence of a concurrent control group, which makes it impossible to attribute observed outcomes (e.g., high ORR and DCR) solely to the investigational intervention (Booth and Tannock, 2014; Bothwell and Podolsky, 2016). Without randomization, significant biases can influence the results. These include selection bias, as patients enrolled in single-arm trials may not be representative of the broader patient population due to strict eligibility criteria; performance bias and detection bias, as the open-label design can influence both the administration of care and the assessment of outcomes; and confounding by unknown prognostic factors (Sacks et al., 1982; Vetter and Mascha, 2017). The favorable outcomes reported in the single-arm studies of Tislelizumab (Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021) could potentially be influenced by these biases. Therefore, while these results are promising and suggest clinical activity, they cannot establish causal efficacy or provide a robust estimate of the magnitude of benefit relative to a standard of care or placebo. The data from single-arm studies are best interpreted as generating hypotheses and providing preliminary evidence of activity, which must then be confirmed in well-designed randomized controlled trials (Owzar, 2008; Fogel, 2018). Consequently, the pooled ORR and DCR from our single-arm analysis, though statistically significant, should be viewed as supportive rather than conclusive evidence of Tislelizumab’s efficacy.
4.5 Efficacy across histological subtypes: NSCLC versus SCLC
Subgroup analysis yielded interesting results, indicating that Tislelizumab may exhibit similar efficacy in improving ORR and DCR across the two major LC subtypes: NSCLC and SCLC (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Wang Z. et al., 2021). Both the NSCLC and SCLC subgroups demonstrated statistically significant benefits with Tislelizumab. Furthermore, heterogeneity tests for the differences in effect sizes between these subgroups did not reach statistical significance, findings that align with those reported by Ul et al. (2025). This suggests Tislelizumab may possess broadly applicable short-term efficacy across different pathological types of LC. This observation provides a rationale for extending the use of Tislelizumab to a wider spectrum of LC patients.
While our subgroup analysis demonstrated a comparable magnitude of benefit in short-term efficacy (ORR and DCR) for Tislelizumab across both NSCLC and SCLC, it is critical to acknowledge the fundamental differences in the biology and management of these two major LC subtypes. NSCLC, which arises from epithelial cells (e.g., alveolar cells, bronchial cells) and encompasses several subtypes, primarily adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma, is often characterized by a slower proliferation rate and the presence of targetable driver oncogenes (e.g., EGFR, ALK, ROS1) in a significant subset of patients, guiding first-line therapy with specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) (Herrera-Juárez et al., 2023; Meyer et al., 2024; Herbst et al., 2018; Sung et al., 2021). In contrast, SCLC is defined by a high-grade neuroendocrine phenotype, exceptionally rapid growth, and an almost universal association with a heavy smoking history. It lacks these actionable driver mutations and is initially highly sensitive to platinum-etoposide chemotherapy, but is notorious for rapid acquisition of chemoresistance and a high propensity for early metastasis, particularly to the brain (Gazdar et al., 2017; Rudin et al., 2021; George et al., 2015).
Therapeutically, the role of ICIs has evolved differently: in NSCLC, ICIs are used across lines of therapy, both as monotherapy in PD-L1 high expressors and, more commonly, in combination with chemotherapy in the first-line setting regardless of PD-L1 status (Herbst et al., 2020; Paz-Ares et al., 2018). In extensive-stage SCLC, the addition of ICIs (e.g., atezolizumab, durvalumab) to first-line platinum-etoposide chemotherapy has become a standard of care, demonstrating a modest but significant improvement in overall survival, albeit the absolute benefits are generally more constrained than those seen in subsets of NSCLC (Horn et al., 2018; Paz-Ares et al., 2019). Therefore, the similar pooled ORR and DCR observed in our analysis for Tislelizumab in both subtypes are particularly noteworthy. They suggest that its mechanism of action—potently blocking the PD-1 pathway to reinvigorate T-cell immunity—is effective against the disparate tumor microenvironments of both NSCLC and SCLC (Cheng Y. et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Kumagai et al., 2020). This provides a compelling rationale for the broader application of Tislelizumab-based strategies across the histological spectrum of LC, while underscoring the necessity to evaluate its long-term survival impact within the context of these established, subtype-specific treatment frameworks.
Our analysis, which pooled data from different lines of therapy, found that the point estimates for ORR were numerically higher in the SCLC subgroup [OR = 0.69, 95%CI (0.63, 0.75)] compared to the NSCLC subgroup [OR = 0.48, 95%CI (0.26, 0.74)], though the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.076). This trend could reflect the particularly high responsiveness of SCLC to first-line chemo-immunotherapy combinations (Cheng Y. et al., 2024), whereas the NSCLC data encompass both later-line monotherapy and first-line combination regimens (Lu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024). It is noteworthy that the high tumor mutational burden (TMB) and immunogenic features of SCLC may contribute to higher initial response rates to immunotherapy, particularly when combined with chemotherapy (Rudin et al., 2021; Hellmann et al., 2018). Therefore, while Tislelizumab demonstrates activity in both histological types, its specific clinical role—whether as first-line combination therapy in SCLC and squamous NSCLC, or as later-line monotherapy in non-squamous NSCLC—is necessarily defined by the distinct therapeutic algorithms for each disease. Future studies with larger sample sizes and stratified by line of therapy are needed to further explore potential efficacy differences within these biologically and epidemiologically distinct entities.
4.6 Contextualizing findings with existing evidence and indirect comparisons
When contextualizing our findings within the existing landscape of meta-analyses on PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, both similarities and important distinctions emerge. Our results, demonstrating significant improvements in ORR and DCR with Tislelizumab, are consistent with the established efficacy profile of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in LC, as evidenced by numerous meta-analyses for other agents. For instance, large-scale meta-analyses of pembrolizumab and nivolumab have consistently shown superior ORR and DCR compared to chemotherapy in both first-line and second-line settings for NSCLC, particularly in patients with high PD-L1 expression (Wang et al., 2019b; Reck et al., 2016). Similarly, the lack of a statistically significant improvement in OS and PFS in our RCT analysis, despite a positive trend, echoes the nuanced results seen in some earlier meta-analyses of immunotherapy, where benefits were sometimes confined to specific subgroups or required longer follow-up to become apparent (Chen et al., 2018; Peng and Wu, 2019).
However, a key distinction of our study lies in its specific focus on Tislelizumab. While the efficacy signals (ORR, DCR) appear congruent with the class effect of PD-1 inhibitors, the ITCs cited in our introduction (Guo et al., 2023; Messori et al., 2023) are particularly relevant for cross-sectional comparison. These ITCs, which form a crucial part of the existing evidence base, directly compared Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in the first-line advanced NSCLC setting. The findings from Guo et al. (2023) and Messori et al. (2023)—showing no significant differences in PFS, ORR, or grade ≥3 AEs—suggest that Tislelizumab’s efficacy and safety profile may be comparable to that of the established benchmark, pembrolizumab, within the limitations of indirect comparison methodology. Our meta-analysis, by providing pooled estimates specifically for Tislelizumab from both direct and single-arm evidence, complements these ITCs and adds depth to the understanding of this particular agent’s profile.
4.7 Safety profile and tolerability in the context of PD-1 inhibitor class effects
Regarding safety, while this meta-analysis did not directly pool AE incidence data due to methodological limitations, reports from the included studies collectively suggest Tislelizumab is generally well-tolerated, exhibiting a safety profile that aligns with the established class effects of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. The spectrum of common AEs predominantly consists of manageable immune-related adverse events (irAEs), such as rash, hypothyroidism, and increased transaminases, alongside chemotherapy-associated toxicities like hematological events (anemia, neutropenia) and gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, decreased appetite) in combination regimens (Zhou et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2022; Thompson et al., 2020; Martins et al., 2019).
Crucially, when compared indirectly with other PD-1 inhibitors used in LC, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, the safety profile of Tislelizumab appears largely consistent. For instance, the incidence of all-grade TRAEs with Tislelizumab-based regimens in our analysis (ranging from 70% to 95% across studies) is comparable to the 66%–96% range reported for pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in the KEYNOTE-189 and KEYNOTE-407 trials (Paz-Ares et al., 2018; Gandhi et al., 2018), and to nivolumab-based regimens (Borghaei et al., 2015). Similarly, the spectrum of common irAEs (e.g., thyroid dysfunction, rash, hepatitis) mirrors that well-documented for the drug class (Thompson et al., 2020; Haanen et al., 2017). This cross-trial comparison, while acknowledging inherent limitations, suggests no major, novel safety concerns specific to Tislelizumab.
Beyond incidence rates, the clinical management implications of these AEs are paramount. The irAEs associated with Tislelizumab, akin to other PD-1 inhibitors, are typically manageable with established protocols involving corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone), hormone replacement therapy (e.g., for hypothyroidism), or other immunosuppressants, alongside temporary dose interruption or permanent discontinuation in severe cases (Chen et al., 2018; Haanen et al., 2017; Brahmer et al., 2018). The low incidence of severe (Grade ≥3) specific irAEs in our pooled data (e.g., increased ALT: 0.89%; hypothyroidism: 0.20%; rash: 0.69%) is encouraging and sits within the expected range for this class. For example, the rate of Grade ≥3 pneumonitis with anti-PD-1 agents typically falls below 3% (Naidoo et al., 2016), and our analysis did not identify a significantly higher signal, suggesting a manageable risk profile consistent with its comparators.
However, this analysis represents a limitation requiring careful consideration: we could not directly access and analyze individual patient AE data, relying instead on fragmented descriptions within the published literature to infer safety. The limitations of this approach stem from potential variations across studies in how AEs are defined, graded, and reported, which hinders the derivation of a precise and comparable safety assessment. Although no significant deterioration in OS or PFS was observed in RCTs, and single-arm studies demonstrated favorable efficacy, this does not automatically confirm the treatment’s safety profile as “acceptable” in all contexts. For instance, the occurrence of rare but severe, potentially fatal AEs (e.g., pneumonitis, myocarditis, severe colitis) remains uncertain from our pooled data (Michot et al., 2016; Postow et al., 2018). Moreover, the safety profile in specific populations, such as the elderly or patients with comorbidities, requires further clarification. These aspects necessitate systematic evaluation using standardized, large-sample data.
Notably, the Fc-engineered design of Tislelizumab, which minimizes binding to FcγR on macrophages, is postulated to reduce ADCP (Dahan et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2018). This theoretical advantage might contribute to a differentiated safety profile by limiting Fc-mediated effector functions that could potentially contribute to certain inflammatory toxicities. While direct comparative safety data from head-to-head trials are lacking to confirm this hypothesis, the pooled safety data from this analysis does not raise any new or unexpected safety signals compared to the established PD-1 inhibitor class, and the incidence of severe irAEs appears numerically comparable to that reported for pembrolizumab and nivolumab (Wang et al., 2019b; Chen et al., 2018; Baxi et al., 2018).
Consequently, conclusions regarding the comprehensive safety of Tislelizumab remain preliminary but reassuring within the context of the known ICI class effects. Its potential risks, especially rare but severe events, should be vigilantly monitored during clinical application, adhering to the same rigorous monitoring, early detection, and prompt management strategies mandated for other ICIs (Chen et al., 2018; Haanen et al., 2017). Future research should prioritize standardized, systematic collection and analysis of safety data from large, real-world cohorts to fully characterize its risk-benefit profile across diverse patient populations and to enable more robust direct or indirect comparisons with other standard immune checkpoint inhibitors.
4.8 Conclusion and future directions
In summary, this meta-analysis indicates that Tislelizumab offers significant short-term therapeutic benefits for patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC. However, the current evidence from RCTs is not robust enough to draw definitive conclusions about its long-term survival advantages, potentially due to factors including study design, sample size, and follow-up duration. Regarding safety, preliminary data suggest a potentially manageable profile, although systematic and standardized evaluation data are lacking. Future research should prioritize (Abu Rous et al., 2023): Conducting well-designed, head-to-head RCTs with adequate follow-up to establish the actual differences in OS and PFS between Tislelizumab and standard treatments like chemotherapy (Allemani et al., 2018); Systematically collecting and analyzing Tislelizumab’s safety data to characterize its AE profile, incidence, and management approaches, which is essential for guiding safe clinical application (Frödin, 1996); Investigating the efficacy of Tislelizumab in combination therapies, for instance, alongside chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or other immunotherapies/targeted agents, with the goal of surpassing monotherapy limitations and enhancing patients’ long-term outcomes. Ultimately, only through more comprehensive and in-depth investigation can Tislelizumab’s definitive place in the treatment paradigm for locally advanced or metastatic LC be established.
5 Limitations
This study has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. First, the included RCTs and single-arm studies show heterogeneity in baseline patient characteristics, treatment lines, and control group settings, which may impact the estimation of the combined effect size and complicate result interpretation. Second, in the RCT subgroup analyses for OS and PFS, some studies had relatively small sample sizes or insufficient follow-up periods, which may have limited the statistical power of the analyses, especially when evaluating endpoints such as OS, potentially failing to fully capture the true efficacy difference of Tislelizumab. Additionally, the analysis of safety data primarily relies on descriptive information provided by the original studies, lacking standardized and systematic pooled assessments of TRAEs, making comprehensive and accurate depiction of Tislelizumab’s long-term safety profile and the spectrum of rare AEs challenging.
6 Conclusion
The results of this meta-analysis indicate that Tislelizumab demonstrates clinically meaningful short-term efficacy in treating patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC. Specifically, Tislelizumab significantly improves patients’ ORR and DCR, with similar treatment effects observed in NSCLC and SCLC subgroups. However, regarding whether it can provide patients with definite long-term survival benefits, i.e., improvements in OS and PFS, the evidence provided by the existing RCTs is insufficient to draw a definitive conclusion. Some studies did not observe statistically significant differences, which may be influenced by factors such as study design, sample size limitations, insufficient follow-up periods, or baseline heterogeneity among patients, but this does not represent a final negation of its long-term potential. Preliminary safety assessments indicate that Tislelizumab is generally well-tolerated, but a systematic safety analysis based on pooled data is lacking. In summary, Tislelizumab offers a promising short-term treatment strategy for patients with locally advanced or metastatic LC. However, its exact long-term clinical value and comprehensive safety profile still depend on future more rigorous, adequately followed-up high-quality randomized controlled trials and standardized safety studies to clarify, thereby providing a more solid evidence base for clinical practice and ultimately establishing Tislelizumab’s position in this treatment field.
Author contributions
YZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SZ: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JH: Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. HH: Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. JK: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the Key Research Program of Guangxi Science and Technology Department (grant number: AB21196010), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers: 82104499, and 82160783), Joint Project on Regional High-Incidence Diseases Research of Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (grant numbers: 2023GXNSFBA026146), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant number: 2023MD734158), First-class discipline innovation-driven talent program of Guangxi Medical University and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Health Commission self-funded scientific research section (grant numbers: Z-A20240492, and Z-A20240515).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all authors of the included studies for providing the data necessary for this meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1671018/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1 | (A) Sensitivity analysis of overall response rate (ORR) in RCTs; (B) Sensitivity analysis of progression-free survival (PFS) in RCTs.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S2 | Sensitivity analysis of overall response rate (ORR) in single-arm studies.
References
Abu Rous, F., Singhi, E. K., Sridhar, A., Faisal, M. S., and Desai, A. (2023). Lung cancer treatment advances in 2022. Cancer Invest 41 (1), 12–24. doi:10.1080/07357907.2022.2119479
Allemani, C., Matsuda, T., Di Carlo, V., Harewood, R., Matz, M., Nikšić, M., et al. (2018). Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 391 (10125), 1023–1075. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3
Arlauckas, S. P., Garris, C. S., Kohler, R. H., Kitaoka, M., Cuccarese, M. F., Yang, K. S., et al. (2017). In vivo imaging reveals a tumor-associated macrophage-mediated resistance pathway in anti-PD-1 therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 9 (389), eaal3604. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3604
Barlesi, F., Vansteenkiste, J., Spigel, D., Ishii, H., Garassino, M., de Marinis, F., et al. (2018). Avelumab versus docetaxel in patients with platinum-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (JAVELIN lung 200): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 19 (11), 1468–1479. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30673-9
Baxi, S., Yang, A., Gennarelli, R. L., Khan, N., Wang, Z., Boyce, L., et al. (2018). Immune-related adverse events for anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 360, k793. doi:10.1136/bmj.k793
Booth, C. M., and Tannock, I. F. (2014). Randomised controlled trials and population-based observational research: partners in the evolution of medical evidence. Br. J. Cancer 110 (3), 551–555. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.725
Borghaei, H., Paz-Ares, L., Horn, L., Spigel, D. R., Steins, M., Ready, N. E., et al. (2015). Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 373 (17), 1627–1639. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1507643
Bothwell, L. E., and Podolsky, S. H. (2016). The emergence of the randomized, controlled trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 375 (6), 501–504. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1604635
Brahmer, J., Reckamp, K. L., Baas, P., Crinò, L., Eberhardt, W. E. E., Poddubskaya, E., et al. (2015). Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 373 (2), 123–135. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504627
Brahmer, J. R., Lacchetti, C., Schneider, B. J., Atkins, M. B., Brassil, K. J., Caterino, J. M., et al. (2018). Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American society of clinical oncology Clinical Practice guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 36 (17), 1714–1768. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385
Chen, R., Tao, Y., Xu, X., Shan, L., Jiang, H., Yin, Q., et al. (2018). The efficacy and safety of nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and atezolizumab in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Discov. Med. 26 (143), 155–166. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30586539/.
Chen, Z., Ji, W., Feng, W., Cui, J., Wang, Y., Li, F., et al. (2024). PTPRT loss enhances anti-PD-1 therapy efficacy by regulation of STING pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 16 (763), eadl3598. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.adl3598
Cheng, B., Ding, K., Chen, P., Ji, J., Luo, T., Guo, X., et al. (2022). Anti-PD-L1/TGF-βR fusion protein (SHR-1701) overcomes disrupted lymphocyte recovery-induced resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Commun. (Lond) 42 (1), 17–36. doi:10.1002/cac2.12244
Cheng, W., Kang, K., Zhao, A., and Wu, Y. (2024a). Dual blockade immunotherapy targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 17 (1), 54. doi:10.1186/s13045-024-01581-2
Cheng, Y., Fan, Y., Zhao, Y., Huang, D., Li, X., Zhang, P., et al. (2024b). Tislelizumab plus platinum and etoposide versus placebo plus platinum and etoposide as first-line treatment for extensive-stage SCLC (RATIONALE-312): a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, phase 3 clinical trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 19 (7), 1073–1085. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2024.03.008
Cho, J.-W., Hong, M. H., Ha, S.-J., Kim, Y.-J., Cho, B. C., Lee, I., et al. (2020). Genome-wide identification of differentially methylated promoters and enhancers associated with response to anti-PD-1 therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 52 (9), 1550–1563. doi:10.1038/s12276-020-00493-8
Daei Sorkhabi, A., ZareDini, M., Fazlollahi, A., Sarkesh, A., Naseri, A., Mousavi, S. E., et al. (2023). The safety and efficacy of tislelizumab, alone or in combination with chemotherapy, for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review of clinical trials. BMC Pulm. Med. 23 (1), 495. doi:10.1186/s12890-023-02755-3
Dahan, R., Sega, E., Engelhardt, J., Selby, M., Korman, A. J., and Ravetch, J. V. (2015). FcγRs modulate the anti-tumor activity of antibodies targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis. Cancer Cell 28 (3), 285–295. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2015.08.004
Dammeijer, F., van Gulijk, M., Mulder, E. E., Lukkes, M., Klaase, L., van den Bosch, T., et al. (2020). The PD-1/PD-L1-Checkpoint restrains T cell immunity in tumor-draining lymph nodes. Cancer Cell 38 (5), 685–700. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.09.001
de Castro, G., Kudaba, I., Wu, Y.-L., Lopes, G., Kowalski, D. M., Turna, H. Z., et al. (2023). Five-year outcomes with pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy as first-line therapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and programmed death Ligand-1 tumor proportion score ≥ 1% in the KEYNOTE-042 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 41 (11), 1986–1991. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.02885
Fogel, D. B. (2018). Factors associated with clinical trials that fail and opportunities for improving the likelihood of success: a review. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 11, 156–164. doi:10.1016/j.conctc.2018.08.001
Fu, K., Xie, F., Wang, F., and Fu, L. (2022). Therapeutic strategies for EGFR-Mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with osimertinib resistance. J. Hematol. Oncol. 15 (1), 173. doi:10.1186/s13045-022-01391-4
Gandhi, L., Rodríguez-Abreu, D., Gadgeel, S., Esteban, E., Felip, E., De Angelis, F., et al. (2018). Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 378 (22), 2078–2092. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1801005
Garassino, M. C., Gadgeel, S., Speranza, G., Felip, E., Esteban, E., Dómine, M., et al. (2023). Pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed and platinum in nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: 5-year outcomes from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-189 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 41 (11), 1992–1998. doi:10.1200/JCO.22.01989
Gazdar, A. F., Bunn, P. A., and Minna, J. D. (2017). Small-cell lung cancer: what we know, what we need to know and the path forward. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17 (12), 765–37. doi:10.1038/nrc.2017.106
George, J., Lim, J. S., Jang, S. J., Cun, Y., Ozretić, L., Kong, G., et al. (2015). Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 524 (7563), 47–53. doi:10.1038/nature14664
Guo, Y., Jia, J., Hao, Z., and Yang, J. (2023). Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy versus pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: systematic review and indirect comparison of randomized trials. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1172969. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1172969
Haanen, JBAG, Carbonnel, F., Robert, C., Kerr, K. M., Peters, S., Larkin, J., et al. (2017). Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 28 (Suppl. l_4), iv119–iv142. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx225
Hellmann, M. D., Callahan, M. K., Awad, M. M., Calvo, E., Ascierto, P. A., Atmaca, A., et al. (2018). Tumor mutational burden and efficacy of nivolumab monotherapy and in combination with ipilimumab in small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 33 (5), 853–861.e4. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2018.04.001
Herbst, R. S., Baas, P., Kim, D.-W., Felip, E., Pérez-Gracia, J. L., Han, J.-Y., et al. (2016). Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387 (10027), 1540–1550. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7
Herbst, R. S., Morgensztern, D., and Boshoff, C. (2018). The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553 (7689), 446–454. doi:10.1038/nature25183
Herbst, R. S., Giaccone, G., de Marinis, F., Reinmuth, N., Vergnenegre, A., Barrios, C. H., et al. (2020). Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of PD-L1-Selected patients with NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 383 (14), 1328–1339. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1917346
Herrera-Juárez, M., Serrano-Gómez, C., Bote-de-Cabo, H., and Paz-Ares, L. (2023). Targeted therapy for lung cancer: beyond EGFR and ALK. Cancer 129 (12), 1803–1820. doi:10.1002/cncr.34757
Horn, L., Mansfield, A. S., Szczęsna, A., Havel, L., Krzakowski, M., Hochmair Maximilian, J., et al. (2018). First-line atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 379 (23), 2220–2229. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809064
Hu, Y., Ren, S., Feng, J., Zeng, C., Yang, L., Liu, J., et al. (2025). Real-world comparison of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus tislelizumab plus chemotherapy in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study of treatment outcomes. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 14 (2), 467–479. doi:10.21037/tlcr-24-721
Iaquinto, S., Bührer, L., Feldmann, M., Latal, B., and Held, U. (2025). How to quantify between-study heterogeneity in single-arm evidence synthesis? It depends. Syst. Rev. 14 (1), 138. doi:10.1186/s13643-025-02831-1
International BR (2023). Retracted: analysis on the efficacy of bronchial artery chemoembolization combined with 125I seed implantation in the therapy of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer based on the medical database. Biomed. Res. Int. 2023, 9765786. doi:10.1155/2023/9765786
Jassem, J., de Marinis, F., Giaccone, G., Vergnenegre, A., Barrios, C. H., Morise, M., et al. (2021). Updated overall survival analysis from IMpower110: atezolizumab versus platinum-based chemotherapy in treatment-naive programmed death-ligand 1-Selected NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 16 (11), 1872–1882. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2021.06.019
Konen, J. M., Wu, H., and Gibbons, D. L. (2024). Immune checkpoint blockade resistance in lung cancer: emerging mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 45 (6), 520–536. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2024.04.006
Kumagai, S., Togashi, Y., Kamada, T., Sugiyama, E., Nishinakamura, H., Takeuchi, Y., et al. (2020). The PD-1 expression balance between effector and regulatory T cells predicts the clinical efficacy of PD-1 blockade therapies. Nat. Immunol. 21 (11), 1346–1358. doi:10.1038/s41590-020-0769-3
Lee, C.-H., Romain, G., Yan, W., Watanabe, M., Charab, W., Todorova, B., et al. (2017). IgG Fc domains that bind C1q but not effector Fcγ receptors delineate the importance of complement-mediated effector functions. Nat. Immunol. 18 (8), 889–898. doi:10.1038/ni.3770
Legha, S. S., Muggia, F. M., and Carter, S. K. (1977). Adjuvant chemotherapy in lung cancer: review and prospects. Cancer 39 (4), 1415–1424. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(197704)39:4<1415::aid-cncr2820390410>3.0.co;2-o
Li, Y., Yan, B., and He, S. (2023). Advances and challenges in the treatment of lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 169, 115891. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115891
Lin, C., Yang, Z., and Liu, Q. (2023). Effect of I-125 seed implantation on lung cancer and its environmental impact. Health Phys. 125 (4), 273–280. doi:10.1097/HP.0000000000001714
Lin, S., Hong, M., Zhang, J., Zhao, W., Li, K., Wu, C., et al. (2025). Characterization and functional evaluation of JS207, a novel bispecific antibody against human PD-1 and VEGFA. Front. Immunol. 16, 1612547. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1612547
Liu, J., Yu, Q., Wang, X. S., Shi, Q., Wang, J., Wang, F., et al. (2023). Compound kushen injection reduces severe toxicity and symptom burden associated with curative radiotherapy in patients with lung cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 21 (8), 821–830.e3. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2023.7036
Lu, S., Wang, J., Yu, Y., Yu, X., Hu, Y., Ma, Z., et al. (2024). Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer (final analysis of RATIONALE-304: a randomized phase III trial). ESMO Open 9 (10), 103728. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103728
Martins, F., Sofiya, L., Sykiotis, G. P., Lamine, F., Maillard, M., Fraga, M., et al. (2019). Adverse effects of immune-checkpoint inhibitors: epidemiology, management and surveillance. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 16 (9), 563–580. doi:10.1038/s41571-019-0218-0
Messori, A., Rivano, M., Chiumente, M., and Mengato, D. (2023). Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy vs. pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: systematic review and indirect comparison of randomized trials. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 12 (5), 50. doi:10.21037/cco-23-26
Meyer, M.-L., Fitzgerald, B. G., Paz-Ares, L., Cappuzzo, F., Jänne, P. A., Peters, S., et al. (2024). New promises and challenges in the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 404 (10454), 803–822. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01029-8
Michot, J. M., Bigenwald, C., Champiat, S., Collins, M., Carbonnel, F., Postel-Vinay, S., et al. (2016). Immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint blockade: a comprehensive review. Eur. J. Cancer 54, 139–148. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2015.11.016
Mok, T. S. K., Wu, Y.-L., Kudaba, I., Kowalski, D. M., Cho, B. C., Turna, H. Z., et al. (2019). Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 393 (10183), 1819–1830. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32409-7
Mutsaers, A., Zhang, T. W., Louie, A., Rodrigues, G., Palma, D., and Qu, M. (2023). Stereotactic or conventional radiation for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 15 (4), e38198. doi:10.7759/cureus.38198
Nagasaka, M., and Gadgeel, S. M. (2018). Role of chemotherapy and targeted therapy in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 18 (1), 63–70. doi:10.1080/14737140.2018.1409624
Naidoo, J., Wang, X., Woo, K. M., Iyriboz, T., Halpenny, D., Cunningham, J., et al. (2016). Pneumonitis in patients treated with anti-programmed Death-1/Programmed death ligand 1 therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 35 (7), 709–717. doi:10.1200/JCO.2016.68.2005
Owzar, K. (2008). Alternate statistical tools and limitations in genetic marker association studies in single-arm drug cancer trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (9), 1400–1401. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.7306
Passaro, A., Brahmer, J., Antonia, S., Mok, T., and Peters, S. (2022). Managing resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in lung cancer: treatment and novel strategies. J. Clin. Oncol. 40 (6), 598–610. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01845
Paz-Ares, L., Luft, A., Vicente, D., Tafreshi, A., Gümüş, M., Mazières, J., et al. (2018). Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 379 (21), 2040–2051. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1810865
Paz-Ares, L., Dvorkin, M., Chen, Y., Reinmuth, N., Hotta, K., Trukhin, D., et al. (2019). Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 394 (10212), 1929–1939. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32222-6
Peng, T.-R., and Wu, T.-W. (2019). Efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Thorac. Cancer 10 (5), 1176–1181. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.13060
Postow, M. A., Sidlow, R., and Hellmann, M. D. (2018). Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 378 (2), 158–168. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1703481
Reck, M., Rodríguez-Abreu, D., Robinson, A. G., Hui, R., Csőszi, T., Fülöp, A., et al. (2016). Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 375 (19), 1823–1833. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1606774
Rittmeyer, A., Barlesi, F., Waterkamp, D., Park, K., Ciardiello, F., von Pawel, J., et al. (2017). Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 389 (10066), 255–265. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X
Rudin, C. M., Brambilla, E., Faivre-Finn, C., and Sage, J. (2021). Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 7 (1), 3. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-00235-0
Sacks, H., Chalmers, T. C., and Smith, H. (1982). Randomized versus historical controls for clinical trials. Am. J. Med. 72 (2), 233–240. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(82)90815-4
Schild, S. E. (2020). Optimizing the radiotherapy of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 15 (10), 1559–1560. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.07.004
Sezer, A., Kilickap, S., Gümüş, M., Bondarenko, I., Özgüroğlu, M., Gogishvili, M., et al. (2021). Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: a multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 397 (10274), 592–604. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00228-2
Sha, F., Zhuang, S., Zhou, L., Zhang, L., Yang, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2015). Biomarkers for cancer-related fatigue and adverse reactions to chemotherapy in lung cancer patients. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 3 (1), 163–166. doi:10.3892/mco.2014.439
Slim, K., Nini, E., Forestier, D., Kwiatkowski, F., Panis, Y., and Chipponi, J. (2003). Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J. Surg. 73 (9), 712–716. doi:10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
Sterne, J. A. C., Savović, J., Page, M. J., Elbers, R. G., Blencowe, N. S., Boutron, I., et al. (2019). RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366, l4898. doi:10.1136/bmj.l4898
Sullivan, R. (2018). Achieving better cancer intelligence for global cancer control. Lancet 391 (10125), 1003–1004. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30155-7
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71 (3), 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
Tang, S., Qin, C., Hu, H., Liu, T., He, Y., Guo, H., et al. (2022). Immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: progress, challenges, and prospects. Cells 11 (3), 320. doi:10.3390/cells11030320
Thompson, J. A., Schneider, B. J., Brahmer, J., Andrews, S., Armand, P., Bhatia, S., et al. (2020). NCCN guidelines insights: management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2020. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 18 (3), 230–241. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2020.0012
Ul, B. W., Ogedegbe, O. J., Qammar, A., Sumia, F., Ul Islam, M., Chaudhari, S. S., et al. (2025). Efficacy of tislelizumab in lung cancer treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cureus 17 (3), e80609. doi:10.7759/cureus.80609
Vetter, T. R., and Mascha, E. J. (2017). Bias, confounding, and interaction: lions and tigers, and bears, Oh My. Anesth. Analg. 125 (3), 1042–1048. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000002332
Vinod, S. K., and Hau, E. (2020). Radiotherapy treatment for lung cancer: current status and future directions. Respirology 25 (Suppl. 2), 61–71. doi:10.1111/resp.13870
Wang, Y., Zhang, R., Shen, Y., Su, L., Dong, B., and Hao, Q. (2019a). Prediction of chemotherapy adverse reactions and mortality in older patients with primary lung cancer through frailty index based on routine laboratory data. Clin. Interv. Aging 14, 1187–1197. doi:10.2147/CIA.S201873
Wang, Y., Zhou, S., Yang, F., Qi, X., Wang, X., Guan, X., et al. (2019b). Treatment-related adverse events of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in clinical trials: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 5 (7), 1008–1019. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0393
Wang, Z., Zhao, J., Ma, Z., Cui, J., Shu, Y., Liu, Z., et al. (2021a). Corrigendum to “A phase 2 study of tislelizumab in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced lung cancer in Chinese patients” [lung cancer 147 (2020) 259-268]. Lung Cancer 158, 166–167. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.06.007
Wang, J., Lu, S., Yu, X., Hu, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2021b). Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for advanced squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 7 (5), 709–717. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0366
Wang, J., Lu, S., Yu, X., Hu, Y., Zhao, J., Sun, M., et al. (2024a). Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for advanced squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: final analysis of the randomized, phase III RATIONALE-307 trial. ESMO Open 9 (10), 103727. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103727
Wang, M., Ma, H., Shi, Y., Ni, H., Qin, C., and Ji, C. (2024b). Single-arm clinical trials: design, ethics, principles. BMJ Support Palliat. Care 15 (1), 46–54. doi:10.1136/spcare-2024-004984
Wang, L., Liu, T., Lin, X., Zhang, Y., Shi, L., You, R., et al. (2024c). Economics of first-line treatment with tislelizumab in patients with nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. Immunotherapy 16 (20-22), 1217–1226. doi:10.1080/1750743X.2024.2433408
Wu, J., and Lin, Z. (2022). Non-small cell lung cancer targeted therapy: drugs and mechanisms of drug resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (23), 15056. doi:10.3390/ijms232315056
Xiang, Y., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Zheng, D., Meng, Q., Jiang, L., et al. (2024). Mechanisms of resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: promising strategies to overcoming challenges. Front. Immunol. 15, 1366260. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1366260
Yin, J., Wu, Y., Yang, X., Gan, L., and Xue, J. (2022). Checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis induced by Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: occurrence and mechanism. Front. Immunol. 13, 830631. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.830631
Yue, D., Wang, W., Liu, H., Chen, Q., Chen, C., Liu, L., et al. (2025). Perioperative tislelizumab plus neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with resectable non-small-cell lung cancer (RATIONALE-315): an interim analysis of a randomised clinical trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 13 (2), 119–129. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(24)00269-8
Zhang, T., Song, X., Xu, L., Ma, J., Zhang, Y., Gong, W., et al. (2018). The binding of an anti-PD-1 antibody to FcγRΙ has a profound impact on its biological functions. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 67 (7), 1079–1090. doi:10.1007/s00262-018-2160-x
Zhang, X., Zheng, J., Niu, Y., Xue, C., Yu, Y., Tan, K., et al. (2022). Long-term survival in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with different immune checkpoint inhibitors in multiple-line therapies: a case report and literature review. Front. Immunol. 13, 1059331. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1059331
Zhao, J., Yu, X., Huang, D., Ma, Z., Gao, B., Cui, J., et al. (2023). Assessing treatment outcomes of chemoimmunotherapy in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: an integrated clinical and radiomics approach. J. Immunother. Cancer 11 (2), e007492. doi:10.1136/jitc-2023-007492
Zhao, Z.-R., Liu, S.-L., Zhou, T., Chen, G., Long, H., Su, X.-D., et al. (2024). Stereotactic body radiotherapy with sequential tislelizumab and chemotherapy as neoadjuvant therapy in patients with resectable non-small-cell lung cancer in China (SACTION01): a single-arm, single-centre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 12 (12), 988–996. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(24)00215-7
Zhou, C., Huang, D., Fan, Y., Yu, X., Liu, Y., Shu, Y., et al. (2023). Tislelizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated advanced NSCLC (RATIONALE-303): a phase 3, open-label, randomized controlled trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 18 (1), 93–105. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2022.09.217
Zhu, W., Geng, Q., Peng, H., Jin, Z., Li, D., Pu, X., et al. (2022). Efficacy and safety of low-dose nab-paclitaxel plus tislelizumab in elderly patients with previously treated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 12, 802467. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.802467
Glossary
LC Lung cancer
RCTs Randomized controlled trials
OR Odds ratios
CI Confidence intervals
ORR Objective response rate
DCR Disease control rate
OS Overall survival
PFS Progression-free survival
NSCLC Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
SCLC Small Cell Lung Cancer
ICIs Immune checkpoint inhibitors
PD-1 Programmed death receptor 1
PD-L1/2 Programmed death ligand 1/2
FcRs Fc receptors
ADCP Antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis
ITCs Indirect treatment comparisons
HR Hazard Ratio
RR Risk Ratio
AE Adverse event
NPC Nasopharyngeal, nasopharyngeal cancer
CR Complete response
PR Partial response
SD Stable disease
TRAEs Treatment-related adverse events
RoB2 Randomized trials 2.0
MINORS Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies
ES Effect sizes
ALT Alanine Aminotransferase
AST Aspartate Aminotransferase
FcγR Fcγ receptors
EGFR Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
ALK Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
ROS1 ROS Proto-Oncogene 1, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
TKIs Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
TMB Tumor mutational burden
irAEs Immune-related adverse events
Keywords: tislelizumab, LC, efficacy, safety, meta-analysis
Citation: Zhou Y, Liu S, Zheng S, Han J, Huang H and Kong J (2025) The efficacy and safety of tislelizumab in the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1671018. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1671018
Received: 22 July 2025; Accepted: 08 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Zhaofeng Liang, Jiangsu University, ChinaReviewed by:
Daniele Mengato, University Hospital of Padua, ItalyJun Jiang, Qinghai University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Liu, Zheng, Han, Huang and Kong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinliang Kong, a2psMDcxQDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yue Zhou1†
Yue Zhou1† Shaochu Zheng
Shaochu Zheng Jiahui Han
Jiahui Han Jinliang Kong
Jinliang Kong