Abstract
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint disease characterized by joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited mobility. Current treatments primarily offer partial and short-term relief, with concerns about the potential side effects. This underscores the need for safer and more effective therapeutic strategies. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of cellular energy metabolism, plays an essential role in maintaining the homeostasis of articular cartilage, synovium, and subchondral bone. AMPK signaling has been shown to protect joint tissues from damage caused by mechanical stress and inflammatory responses. Studies suggest that modulating AMPK signaling can influence processes such as autophagy, inflammation, and oxidative stress through downstream targets, including the SIRT family and FoxO family. These mechanisms may help reduce cartilage degradation, osteophyte formation, and synovial inflammation. This review provides a systematic overview of the role of AMPK signaling in joint tissues and explores its potential as a therapeutic target for OA, with the aim of informing the development of targeted therapies that may contribute to more effective and safer management of OA symptoms.
1 Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common arthritis, characterized by cartilage degeneration, bone remodeling, osteophyte formation, and synovial inflammation, resulting in joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and a loss of normal joint function (Kolasinski et al., 2020). An epidemiology study found that approximately 300 million people worldwide suffer from osteoarthritis, which results in huge medical expenses and indirect costs due to reduced mobility and motor function (GBD, 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators, 2018). The contemporary management of OA primarily emphasizes a multifaceted approach that includes structured exercise regimens, analgesics for pain relief, the application of non-steroidal and anti-inflammatory drugs, and, in cases of advanced degeneration, joint replacement surgery (Bijlsma et al., 2011; Katz et al., 2021). However, there are many concerns regarding the adverse reactions of analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as well as the prognosis following surgical interventions, which necessitate novel therapies to improve symptoms and ensure patient safety (Guermazi et al., 2020; Price et al., 2018; Volkow and McLellan, 2016). The understanding of the pathological mechanisms underlying OA continues to evolve. Growing evidence now emphasizes the critical role of the cellular signaling pathways, particularly those involving inflammatory mediators, metabolic intermediates that are considered key drivers in the pathophysiology of OA (Hunter and Bierma-Zeinstra, 2019). In this case, the therapies aimed at modulating OA-associated pathways to maintain joint homeostasis may be a pivotal measure to reduce the symptoms and prevent the progression of OA (Yao et al., 2023). As a primary sensor of cellular energy, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays an important role in maintaining cell and tissue homeostasis by regulating metabolism in response to fluctuations in the ratio of ADP/ATP or AMP/ATP (Lin and Hardie, 2018). Interestingly, recent research indicates that AMPK not only indirectly affects OA through metabolic disorders, which contribute to obesity and subsequent biomechanical stress on joints, but also directly participates in OA-related pathways to protect cells and tissues of the joint from stress-induced damage while mitigating inflammation (Liu-Bryan, 2015). Herein, we explore the recent advances in understanding the role of AMPK in regulating joint tissue homeostasis, as well as its potential as a therapeutic target in the treatment of OA.
2 AMPK signaling
AMPK is a heterotrimeric complex composed of α-subunits with a catalytic domain and regulatory β- and γ-subunits (Calabrese et al., 2014). The α-subunit contains a kinase domain and an activation loop, Thr172, which is phosphorylated by an upstream kinase to achieve full activation of AMPK (Oakhill et al., 2012). The γ-subunit enables AMPK to sense cellular energy levels and responses to fluctuations in the ATP-to-AMP or ATP-to-ADP ratio, facilitating AMPK phosphorylation by upstream kinases (Garcia and Shaw, 2017). Three subunits of AMPK have different isoforms that can form various αβγ complexes and are found in different types of cells. In chondrocytes, the α1, α2, β1, and β2 subunits, as well as the γ1 subunit, are present (Terkeltaub et al., 2011). In subchondral bone, mice lacking AMPKα1 or AMPKα2 presented reduced bone mass. Specifically, AMPKα1 inhibits the receptor activator of nuclear factor κB (RANK) signaling in osteoclast precursors, leading to the downregulation of osteoclast differentiation (Kang H. et al., 2013), whereas AMPKα2 exhibits increased osteogenesis (Wang Y. G. et al., 2016a). The β-subunits are also associated with bone mass and microstructure; however, the deficiency of β-subunits has no effect on the number of osteoclasts or osteoblasts. The underlying mechanism needs to be further explored (Quinn et al., 2010). It is worth noting that the β2 isoform is highly expressed in skeletal muscle and is associated with glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation, which is important for the regulation of AMPK in the metabolism of glucose and lipid (Steinberg et al., 2010). The structure and precise function of each subunit have not yet been fully confirmed, and the mechanisms explaining the activation of AMPK are still being investigated. It is now believed that AMP promotes Thr172 phosphorylation by upstream kinases, with liver kinase B1 (LKB1) being the main kinase responsible (Woods et al., 2003). Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinases (CAMKKs), including CAMKKα and CAMKKβ, have also been shown to phosphorylate AMPK in response to decreased ATP levels caused by ATP-driven Ca2+ pumps facilitating Ca2+ entry into cells (Hurley et al., 2005).
As a conserved energy sensor, AMPK can respond swiftly to the ratio of ATP to AMP in cells and restore ATP levels during metabolic stress by inhibiting ATP-consuming biosynthesis pathways and activating ATP-generating catabolic pathways (Kahn et al., 2005). Moreover, AMPK activates a variety of downstream proteins and participates in multiple functional pathways, including autophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis, and inflammation signaling pathways. Also, activation of AMPK is influenced by these metabolic activities, so as to maintain metabolic homeostasis and improve cellular resistance to stress (Trefts and Shaw, 2021). Notably, these findings highlight the significant role of AMPK signaling in maintaining joint homeostasis (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1
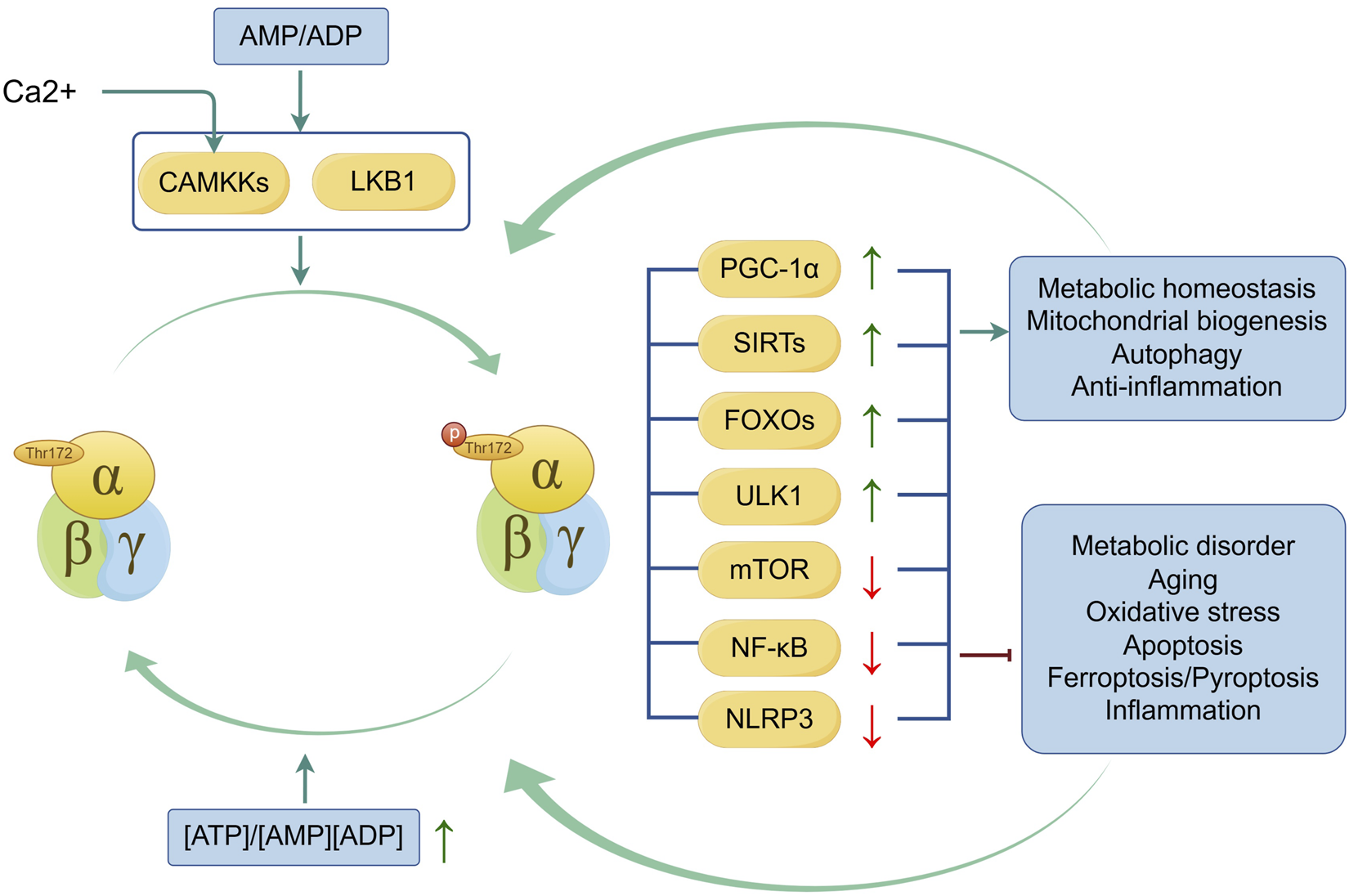
Mechanism and regulation of AMPK activation. LKB1 and CAMKKs (when facilitating Ca2+ entry into cells) are involved in the phosphorylation of AMPK, a process induced by the ATP-to-AMP or ATP-to-ADP ratio. Activation of AMPK and its downstream proteins of AMPK, including Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), Sirtuins(SIRTs), Forkhead box Os (FOXOs), Unc-51-like autophagy activating kinase 1(ULK1), mammalian target of rapamycin(mTOR), nuclear factor-kappa B(NF-κB) and Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) improve metabolic homeostasis, mitochondrial biogenesis, autophagy and anti-inflammation and inhibit metabolic disorder, aging, oxidative stress, apoptosis, ferroptosis, pyroptosis and inflammation. Conversely, the activities improved by AMPK signaling help the phosphorylation of AMPK, and the inhibited activities suppress the activation of AMPK. The green line indicates promotion, and the red line indicates suppression. ↑ signifies an increase, while ↓ signifies a decrease.
3 AMPK signaling is involved in the homeostasis of the joint
Under physiological conditions, articular cartilage, which is composed of chondrocytes and an extracellular matrix (ECM), creates a smooth surface and absorbs external shock, assisting in the transmission of loads with low friction. In response to mechanical loading, chondrocytes promote their own proliferation and enhance ECM synthesis to maintain cartilage integrity (Salinas et al., 2019). The synovium produces synovial fluid to reduce friction and absorb shock, as well as to transport nutrients and waste in the joint (Levick and McDonald, 1995). Subchondral bone dynamically adapts to the mechanical forces exerted on the joint through a coordinated process of bone remodeling, thereby re-establishing normal physiological conditions (Stegen and Carmeliet, 2024). In OA, articular cartilage and the microstructure alteration of subchondral bone suffer from progressive thinning and fragmentation, resulting in increased friction between the two articular surfaces, along with inflammation (Neogi et al., 2009). Synovium, when it develops into synovitis, undergoes changes in the composition and volume of synovial fluid, leading to increased inflammation and pain sensitization (Benito et al., 2005). Researchers have realized that metabolic disorders, such as obesity, contribute not only to the mechanical load causing joint wear and tear but also to elevated metabolic factors, particularly altered levels of adipokines (Zhuo et al., 2012). This disruption affects the function of joint cells, resulting in the non-load-bearing joints in patients with metabolic syndrome suffering OA (Thijssen et al., 2015). In recent years, increasing studies have proved that AMPK, as a crucial regulator of energy metabolism, participates in joint dynamical adaptation (Liu-Bryan and Terkeltaub, 2015) (Figure 2). Typically, activation of AMPK promotes osteogenic differentiation and mineralization as well as suppresses osteoclasts and bone resorption by downregulating receptor activator of nuclear kappa B ligand (RANKL), which is an essential transcription factor for osteoclast differentiation (Lee et al., 2010; Kim J. Y. et al., 2015; Park S. H. et al., 2020; Kanazawa et al., 2008). AMPK has also been found to promote osteogenesis and inhibit adipogenesis in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs), which identifies the significance of AMPK signaling in fatty metabolism (Wang Y. G. et al., 2016b). Other important cellular activities involved in AMPK-mediated homeostasis in joints are listed below.
FIGURE 2
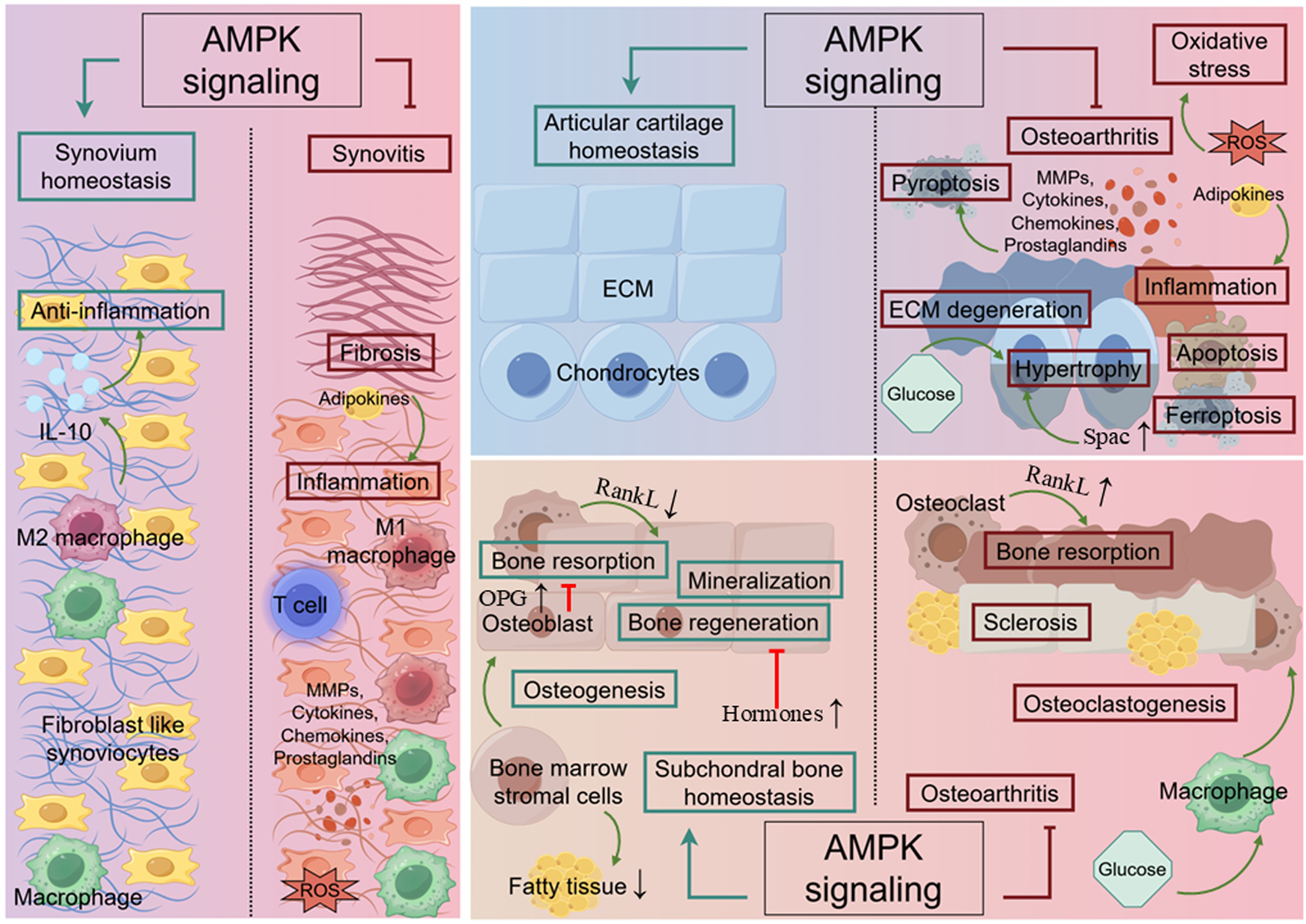
The role of AMPK in joint. In cartilage, AMPK signaling promotes chondrocyte proliferation and enhances ECM synthesis in response to mechanical loading. Simultaneously, it inhibits ECM degeneration, chondrocyte hypertrophy, apoptosis, ferroptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation triggered by MMPs, cytokines, chemokines, and prostaglandins. In synovium, AMPK signaling involves in preventing synovitis by suppressing the activation of inflammatory cells, pyroptosis and fibrosis. In subchondral bone, AMPK signaling facilitates bone regeneration by activating autophagy while preventing excessive bone resorption and sclerosis. The green line indicates promotion, and the red line indicates suppression. ↑ signifies an increase, while ↓ signifies a decrease.
3.1 Metabolic homeostasis and disorder
Due to its heightened sensitivity to alterations in intracellular AMP levels, AMPK plays an important role in the metabolism of glucose and lipid to regulate homeostasis of joints (Figure 3). On the one hand, AMPK improves metabolic disorders and inhibits the development of obesity, which is one of the risk factors for OA. It is noted that AMPK activity is lower in multiple tissues of individuals with obesity and insulin resistance (Bandyopadhyay et al., 2006). Moreover, a great number of studies show that AMPK activation reduces lipid storage by promoting fatty acid oxidation while suppressing fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis, regulates carbohydrate metabolism by increasing glucose uptake or promoting glycolysis, thus avoiding obese diseases that cause wear and tear of joints (Steinberg and Carling, 2019). The excellent effect of AMPK in improving metabolic disorders attracts researchers to develop AMPK activators for application in metabolic diseases, as detailed in part 5.2. On the other hand, researchers have also realized that metabolic disorders contribute to elevated metabolic factors; this disruption results in the non-load-bearing joints in patients with metabolic syndrome suffering OA. In lipid metabolism, adipokines deserve attention (Zhuo et al., 2012). Studies have shown that adipokine is significantly increased in synovial cells from OA patients, alongside the raised expression of inflammatory factors and monocyte adhesion via activation of AMPK in human synovial fibroblasts (Tang et al., 2007; Law et al., 2020). These studies considered the pro-inflammatory effect of AMPK regulated by adipokines. However, most studies revealed the anti-inflammatory effect of AMPK, which are discussed in part 3.4. In glucose metabolism, hyperglycemia inhibits the AMPK signaling pathway, leading to the suppression of osteoclast differentiation and function, abnormal osteogenesis and the accelerated ageing of chondrocytes by increasing ROS and inhibiting autophagy (Zhen et al., 2010; Wang B. et al., 2021; Cai et al., 2018). Besides, AMPK activity decreases with age, resulting in suppressed insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and ultimately leading to bone metabolism disorders and OA. The exact mechanisms by which AMPK activity is diminished in ageing tissues are not fully understood; however, one study showed that increased DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), which is related to increased DNA double-strand breaks, was responsible for decreased AMPK activity in skeletal muscle (Park et al., 2017).
FIGURE 3
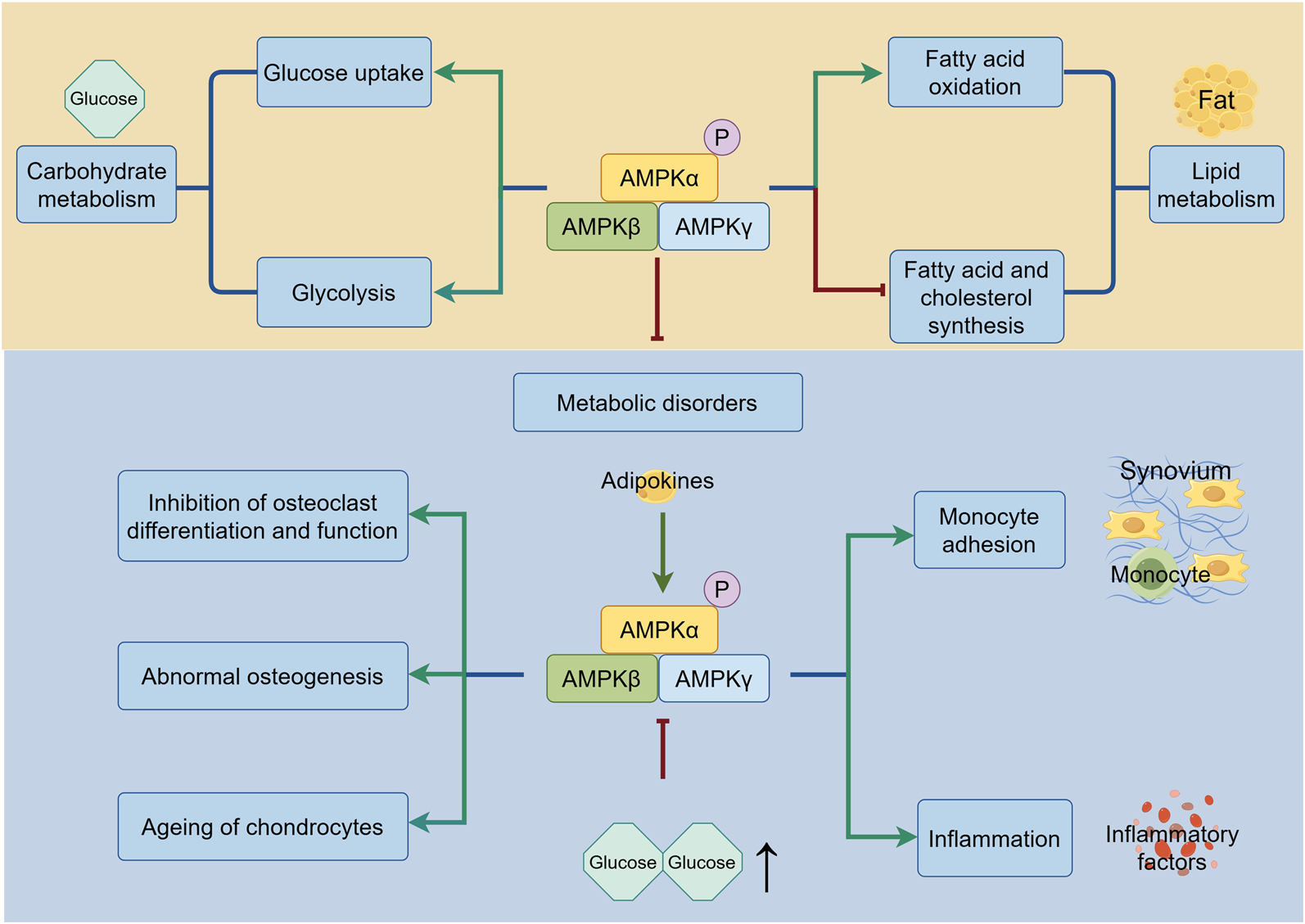
The regulation of AMPK in metabolism. Under the metabolism homeostasis, AMPK regulates carbohydrate metabolism by improving glucose uptake and glycolysis, and lipid metabolism by increasing fatty acid oxidation and lowering fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis. During the metabolic disorders, AMPK promotes monocyte adhesion and inflammation induced by adipokines. Suppression of AMPK caused by hyperglycemia leads to inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and function, abnormal osteogenesis and ageing of chondrocytes. The green line indicates promotion, and the red line indicates suppression.↑ signifies an increase.
The relationship between metabolic disorders and OA is not only related to abnormal glucose and lipid levels, but is also characterized by oxidative stress, autophagy, and inflammation. The following discussion covers these topics.
3.2 Mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative stress
During the development of OA, mitochondrial dysfunction causes a relative overload of reactive oxygen species (ROS), including nitric oxide, superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide, leading to oxidative stress and resultant metabolic disorder (Lepetsos and Papavassiliou, 2016). During these processes, AMPK and its downstream signaling attempt to maintain the homeostasis of mitochondrial biogenesis and reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions (Figure 4). Mitochondrial biogenesis regulator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) is the key participant and is essential for AMPK-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis (O’Neill et al., 2013). The deletion of either AMPK or PGC-1α leads to a decrease in mitochondrial proteins with impaired mitochondria and increased ROS, resulting in metabolic disorder. However, the mechanism by which the two interact with each other is not fully understood (Leick et al., 2010; O’Neill et al., 2011). Sirtuin (SIRT), an energy sensor that shares similar effects on diverse processes with AMPK, is also important in AMPK-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis (Wang Y. et al., 2015). On one hand, AMPK phosphorylation increases cellular NAD+ level, which boosts SIRT activity and helps protect mitochondrial homeostasis of chondrocytes from oxidative stress by clearing ROS that damages mitochondrial DNA (Cantó et al., 2009; Chen L. Y. et al., 2018). On the other hand, SIRT deacetylates LKB1 and thereby increases the activation of AMPK, accomplishing positive feedback regulation (Chen Y. et al., 2021; Ruderman et al., 2010). They work together to maintain joint homeostasis. In the cartilage, abnormal biomechanical loading or other environmental stress causes an excessive unfolded protein response (UPR) within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen. This is highly associated with inflammation and induces apoptosis by activating C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), while the activation of AMPK and SIRT reduces excessive CHOP expression when chondrocytes are subjected to biomechanical injury (Zhang and Kaufman, 2008; Kang X. et al., 2018). Furthermore, SIRT is involved in the regulation of the AMPK-PGC-1α axis, which protects chondrocytes from impairments caused by abnormal catabolic responses by enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis (Wang Y. et al., 2015). Regulations of this axis in the spinal cord have been reported to alleviate OA pain caused by neuroinflammation (Sun J. et al., 2022). It should be noted that the activity of AMPK, SIRTs and PGC-1α is reduced by metabolic disturbances. For instance, an elevated homocysteine level induces mitochondrial dysfunction and stimulates oxidative stress, thereby disturbing chondrocyte metabolism and decreasing the levels of AMPK, SIRTs and PGC-1α proteins in OA chondrocytes (Ma et al., 2018). Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of non-apoptotic cell death, is one of the outcomes of ROS overload and is involved in the development of OA (Dixon et al., 2012; Stockwell et al., 2017; An et al., 2023). Studies have shown that AMPK signaling is necessary for the inhibition of ferroptosis through the inhibitory phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1) and other probable substrates required for lipid biosynthesis. This protects cells from the accumulation of lipid hydroperoxides and ferroptosis in chondrocytes, thereby alleviating OA (Li C. et al., 2020; Zou et al., 2025; Xie et al., 2023). Forkhead box O3A (FoxO3A) is another factor involved in AMPK-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis that has the same ability as PGC-1α in limiting oxidative stress (Zhao et al., 2014). Damage to the activity and sensitivity of AMPK, SIRTs, PGC-1α and FoxOs is also evident in cartilage with age. Researchers considered that dysregulation of AMPK signaling weakens the ability of ageing chondrocytes to resist mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, thereby accelerating the development of osteoarthritis (Petursson et al., 2013; Matsuzaki et al., 2014; Zhao X. et al., 2014). In subchondral bone, SIRT inhibits the interaction between FoxOs and β-catenin, thereby supporting the wingless-related integration site (Wnt)/β-catenin and T-cell factor (TCF)/lymphoid-enhancing factor (Lef) family-mediated transcription and promoting osteogenesis (Iyer et al., 2014). Furthermore, SIRT suppresses transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) expression and decreases sclerostin (SOST) levels, thereby stopping the abnormal activation of Wnt signaling and improving dysregulated bone mineralization and sclerosis in chondrocytes (Abed et al., 2014).
FIGURE 4
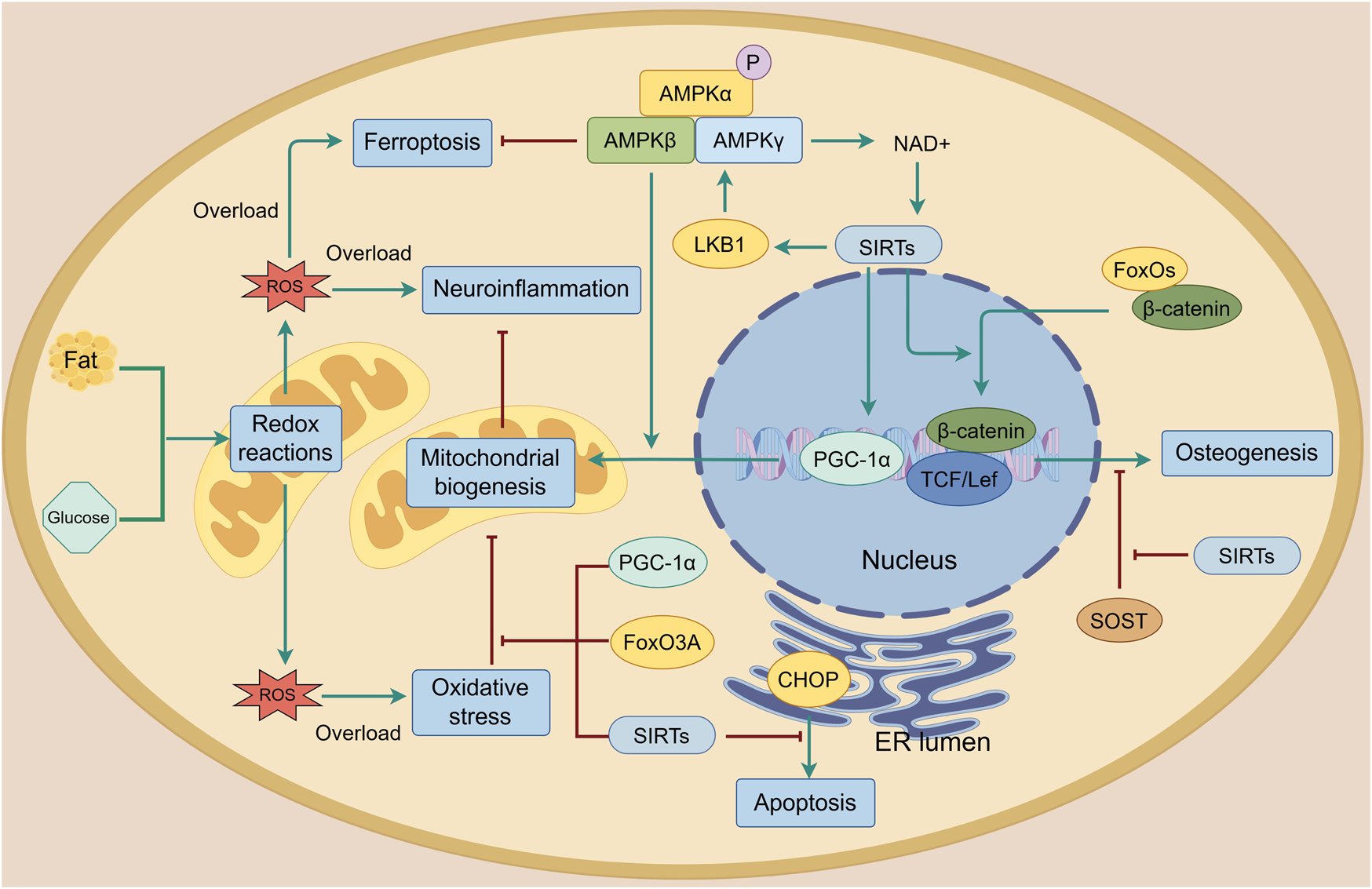
Mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative stress in the joint. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced during lipid and glucose metabolism. When there is an overload, mitochondrial biogenesis is damaged, resulting in oxidative stress, ferroptosis, neuroinflammation and apoptosis. AMPK and its downstream targets including PGC-1α, SIRTs and FoxO3A protect mitochondrial biogenesis from oxidative stress and enhance it. AMPK activates SIRTs by increasing cellular NAD+ levels. SIRTs can also phosphorylate AMPK through LKB1 to form a positive feedback loop that improves mitochondrial biogenesis. Additionally, the AMPK-SIRT signaling pathway inhibits apoptosis by reducing CHOP levels and improves osteogenesis by protecting β-catenin from sclerostin (SOST) and FoxOs. The green line indicates promotion, and the red line indicates suppression.
3.3 Autophagy
Autophagy, a cell turnover of cytosolic components, long-lived proteins, or damaged organelles, is able to relieve cell damage and maintain cells with a normal phenotype (Almonte-Becerril et al., 2010). Autophagy also participates in bone homeostasis. For osteoblasts, autophagy is involved in their mineralization to maintain bone mass and protects them from evaluated stress, during which autophagy-related proteins such as autophagy-related 7 (Atg7), Atg5, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3-I and LC3-Ⅱ) exert their effect (Nollet et al., 2014). For osteoclasts, Beclin-1(also known as Atg6), Atg5, Atg7, Atg4B, LC3-I and LC3-Ⅱ are indispensable in their differentiation, maturation and osteoclast-mediated bone resorption (DeSelm et al., 2011). Some studies have indicated that AMPK signaling directly or indirectly regulates autophagy, thus helping the balance between catabolic and anabolic factors in joints (Figure 5). For example, activation of AMPK inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a protein that directly inhibits autophagy when activated, thereby initiating a protective autophagic program during biomechanical load and preventing articular cartilage degradation and synovial fibrosis (Zhang Y. et al., 2015). This inhibition is also found in T cell-mediated inflammatory responses, which prevents the progression of synovitis (Wen et al., 2019). Further studies have demonstrated that mTOR signaling was crucial in osteoclast maturation, while AMPK activation significantly suppressed osteoclast genesis and promoted osteogenic differentiation by inhibiting mTOR signaling (Indo et al., 2013; She et al., 2014). Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is another important factor in stopping osteoclast activation and promoting osteoclast apoptosis to maintain bone metabolic balance via competitive inhibition of RANK/RANKL connection. AMPK/mTOR signaling is involved in this process (Udagawa et al., 2000; Tong et al., 2020). Furthermore, AMPK phosphorylation directly activates the autophagy-initiating kinase, unc-51-like autophagy activating kinase 1(ULK1) (Kim J. et al., 2011). Under mechanical stress, AMPK activation promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone regeneration via ULK1-mediated autophagy, resulting in increased expression levels of Atg7, LC3B-I and LC3B-II (Zhang S. et al., 2022). FOXOs also synergize with AMPK to activate autophagy by binding to the genes and maintain cellular homeostasis in response to environmental stress (Eijkelenboom and Burgering, 2013). This axis exerts its effects through Ca2+ signal transduction in response to mechanical stimulation (Dai et al., 2017). Hormones are another factor influencing AMPK signaling-mediated autophagy. Specifically, 17β-estradiol can upregulate SIRT1 to promote autophagy and inhibit apoptosis in osteoblasts via AMPK/FoxO3A signaling. However, during estrogen withdrawal, osteoblasts secrete osteonectin (Sparc), which downregulates the expression of AMPK/FoxO3A in chondrocytes and promotes their hypertrophy and degeneration, ultimately leading to osteoarthritis (Jiang et al., 2023). It should be noted that AMPK-mediated autophagy plays a role in metabolic processes (Steinberg and Carling, 2019). Dysregulation of autophagy can lead to metabolic diseases such as obesity, which can exacerbate joint damage (see part 3.1) and directly impair the normal function of joints (Wang B. et al., 2021; Cai et al., 2018). Furthermore, autophagy declines in ageing organs, including joints, as AMPK activity decreases with age. The relationship between this decline in autophagy and AMPK remains to be explored (Kim Y. A. et al., 2013).
FIGURE 5
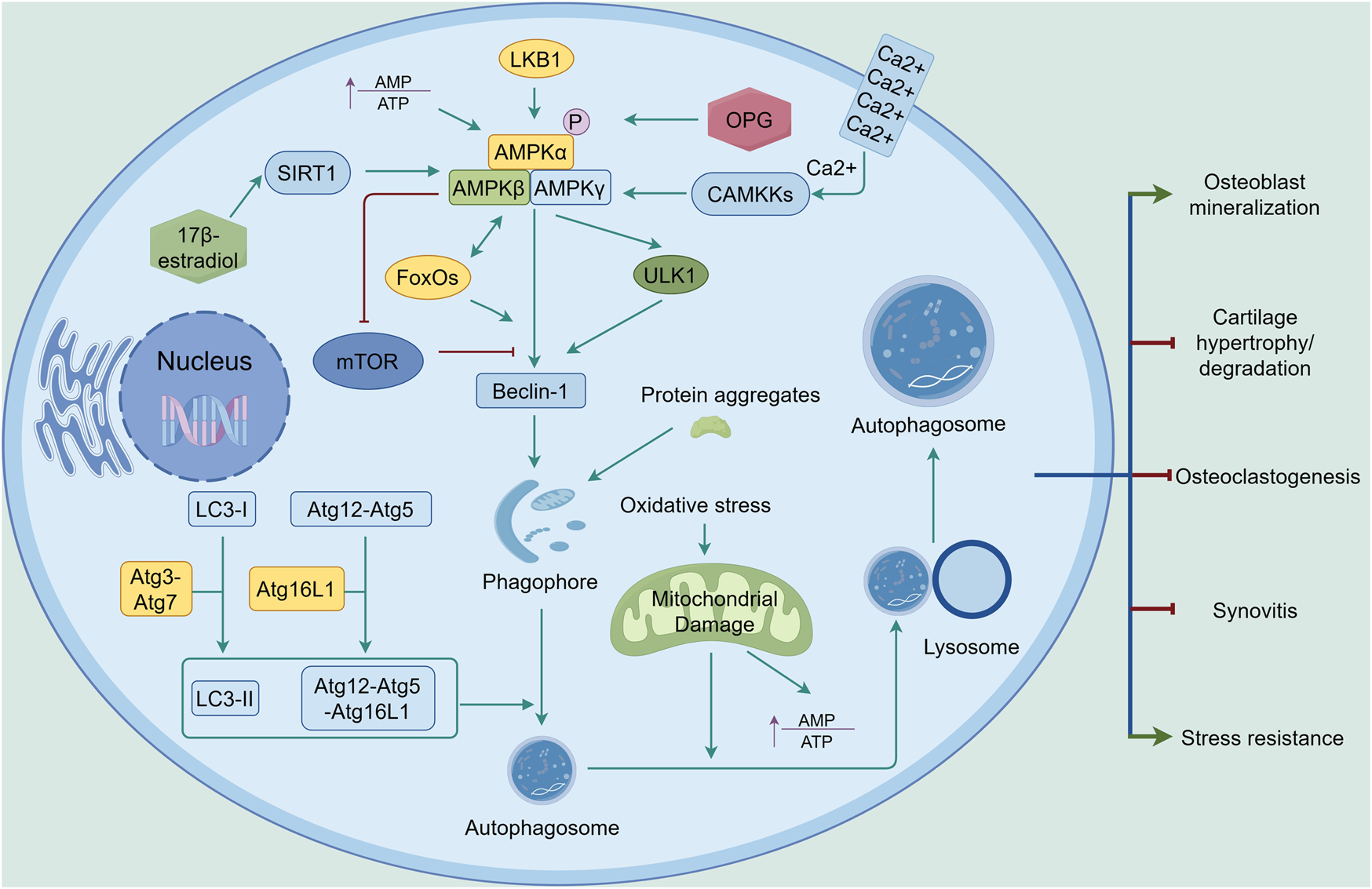
AMPK-mediated autophagy in the joint. Upon activation by increased AMP-to-ATP ratio, LKB1, CAMKKs, or OPG, AMPK signaling promotes autophagy through upregulation of Beclin-1, with ULK1, SIRT1, FoxOs, and mTOR playing key roles in the process. With the assistance of Atg3 and Atg7, LC3-I is converted to LC3-II. The Atg12-Atg5 complex binds to Atg16L1 to form the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L1 complex. Through the involvement of LC3-II and the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L1 complex, the phagophore matures into an autophagosome. Damaged mitochondria resulting from oxidative stress are engulfed by the autophagosome and subsequently degraded by lysosomes. Autophagy exerts its effects in joints by inhibiting cartilage degradation, synovitis, and osteoclastogenesis, while enhancing stress resistance and osteoblast mineralization. The green line indicates promotion, and the red line indicates suppression. ↑ signifies an increase.
3.4 Anti-inflammation and inflammation
OA is associated with ageing joint tissue, which often has low-grade inflammation. This inflammation may be related to the decrease in AMPK activity that occurs with ageing (Petursson et al., 2013; Lotz and Loeser, 2012). Inflammation resolution is essential for the return to tissue homeostasis after an inflammation, however, the failure of inflammation resolution leading to chronic inflammation, impaired repair, and eventually tissue injury is common in OA. Normally, AMPK alleviates inflammation and inhibits abnormal cell death after activation, while macrophages are the key in inflammation resolution regulated by AMPK (Newman et al., 2021; Salminen et al., 2011) (Figure 6). AMPKα1 is the predominant AMPKα isoform expressed in macrophages and deletion of the AMPK β1 subunit and AMPK α1 reduces the function of macrophages, resulting in disorders of fatty and glucose metabolism and inflammation (Caratti et al., 2023; Galic et al., 2011; Sag et al., 2008). By regulating energy metabolism such as glycolysis/oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid synthesis (FAS)/ fatty acid oxidation (FAO) in macrophage, AMPK exerts its protective effect in inflammation resolution by inducing M2 polarization, which is an anti-inflammatory type of macrophages with the ability to secrete anti-inflammation factors such as Interleukin-10 (IL-10) (Ko et al., 2023; Park et al., 2017; Sag et al., 2008). This regulation is important for maintaining metabolic homeostasis such as inhibiting insulin resistance caused by inflammation, avoiding the metabolic disorder-inflammation cycle and alleviating inflammatory pain (Yang Z. et al., 2010; Russe et al., 2013). In addition, AMPK signaling is able to downregulate the inflammatory signaling directly. In articular cartilage, activation of AMPK attenuates inflammation in chondrocytes stimulated by interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) to maintain the synthesis of ECM components such as proteoglycan (PG), inhibit nuclear factor-kappa B(NF-κB) signaling pathway, and decrease matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) levels (Terkeltaub et al., 2011). Conversely, in chondrocytes knocked down AMPKα or LKB1, after being induced by IL-1β and TNF-α, release of MMPs and catabolic responses are unregulated, accelerating OA progression (Petursson et al., 2013; Zhou S. et al., 2017). Accumulated inflammation induces pyroptosis, a form of programmed cell death that differs from apoptosis, leading to injury. Inflammasome NF-κB signaling and nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) take crucial participate in inflammation and pyroptosis, while the AMPK signaling pathway suppresses the production of NLRP3 inflammasome (ASC, Caspase-1, IL-1β, NLRP3, and cleaved Caspase-1) in OA chondrocytes, thus inhibiting pyroptosis and protecting chondrocytes from damage (Chen Y. et al., 2022). In synovium, activated by AMPK phosphorylation, SIRT1 deacetylates RelA/p65 component of the NF-κB complex, and finally inactivates NF-κB signaling. Conversely, NF-κB downregulates SIRT1 activity and accelerates the inflammation (Kauppinen et al., 2013). Activated by extracellular Ca2+ influx mediating CaMKKβ, AMPK signaling is also involved in joint mobilization, which suppresses the inflammatory response in synovium induced by TNF-α under mechanical force (Kunanusornchai et al., 2016a). Different from the pro-inflammatory effect shown in part 3.1, most studies have demonstrated the excellent anti-inflammatory properties of AMPK. There are several possible reasons for the conflicting research conclusions: Firstly, since AMPK is the center of energy metabolism and inflammation requires a large amount of energy, the production and activation of AMPK increase accordingly. Secondly, AMPK may exhibit anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory effects in different cells. For example, pro-inflammatory effects regulated by AMPK activation are more prevalent in synovial fibroblasts and chondrocytes, whereas in macrophages and other cells, AMPK activation exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. Thirdly, as most literature discusses the anti-inflammatory functions of AMPK, we suspect that enhanced AMPK expression is due to its anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory processes. Of course, the underlying mechanisms need to be further explained.
FIGURE 6
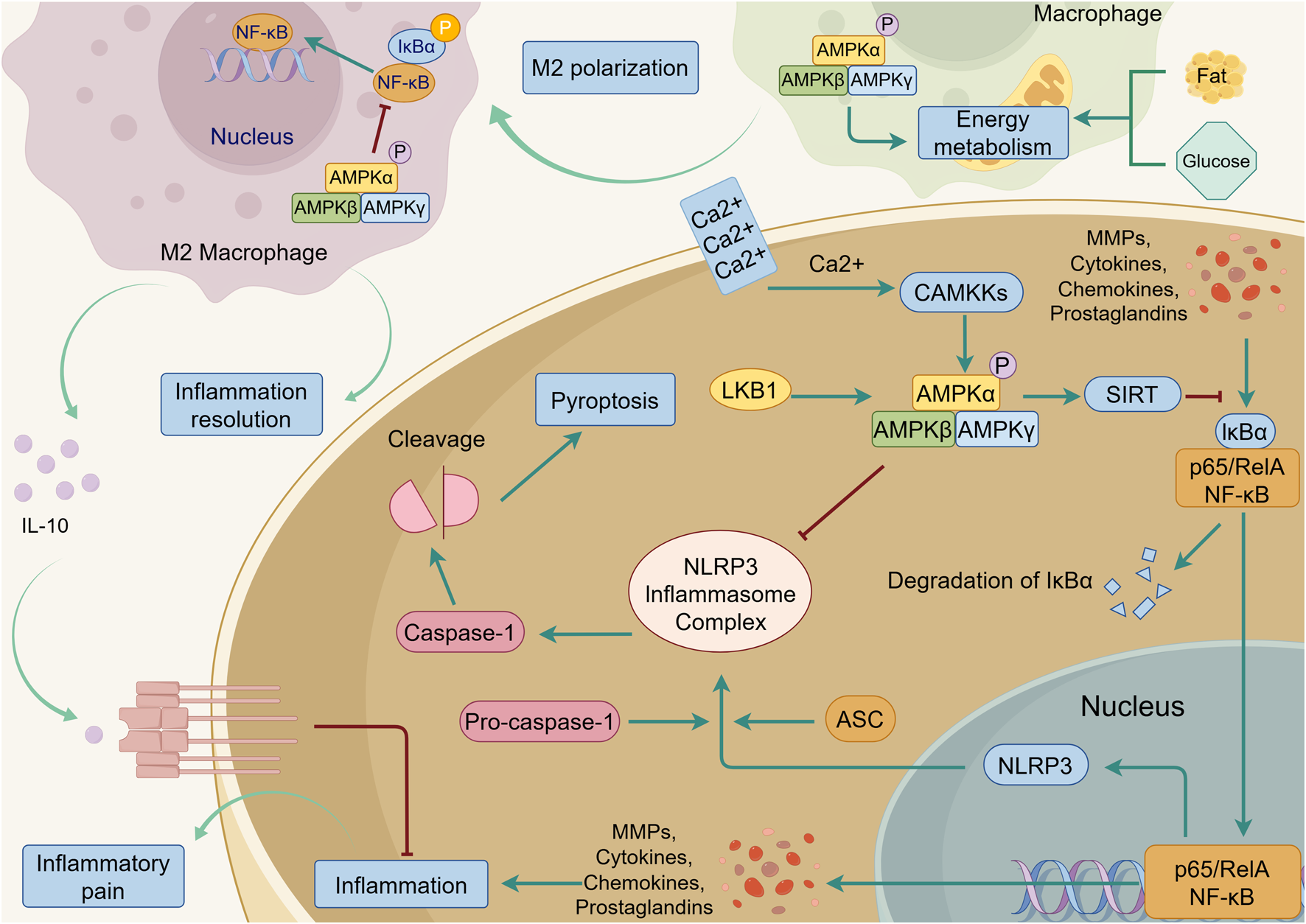
AMPK-mediated anti-inflammation in the joint. Upon activation by LKB1 and CAMKKs, AMPK inhibits NF-κB signaling triggered by MMPs, cytokines, chemokines, and prostaglandins, and suppresses the secretion of these inflammatory factors. NF-κB signaling promotes the assembly of nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), ASC, and pro-caspase-1 into the NLRP3 inflammasome complex. This complex activates caspase-1, which subsequently induces pyroptosis. AMPK signaling can effectively inhibit this process. In macrophage, AMPK promotes M2 polarization by regulating energy metabolism of fat and glucose. The M2 macrophage can secrete anti-inflammatory factors such as Interleukin-10 (IL-10), which suppresses inflammation and alleviates Inflammatory pain. The green line indicates promotion, and the red line indicates suppression.
4 Potential therapies targeting AMPK signaling in OA
The important role of AMPK in maintaining tissue homeostasis within joints highlights its potential as a therapeutic target for OA. Experimental studies have demonstrated that enhancing AMPK signaling can alleviate OA progression, and therapies targeting AMPK signaling are under development.
4.1 Metformin
Some researchers have shown that Metformin exerts its effect on glucose and lipid metabolism by promoting AMPK activation (Zhou G. et al., 2001). In a series of experiments, metformin is able to protect cartilage, relieve synovial inflammatory reactions, and thus alleviate the development and OA progression (He et al., 2022). For example, Jun Li et al. find that metformin delays OA progression and attenuates OA pain in wild-type mice; however, this protective effect is completely absent in mice with knockdown of AMPK α1. Furthermore, they confirm that metformin alleviates OA progression in non-human primates, which identifies the effectiveness of metformin on OA pathogenesis (Li J. et al., 2020). Following the activation of AMPK signaling by metformin, its downstream SIRT1 signaling and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) signaling are enhanced while β-catenin signaling is suppressed, which contributes to autophagy in chondrocytes, preventing the synthesis, accumulation and deposition of cholesterol, and inhibiting ferroptosis (Zhu et al., 2022; Wang C. Z. et al., 2020; Xing et al., 2022; Zou et al., 2025). Metformin also attenuates the inflammatory response of synovitis and increases the levels of hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1 (HAPLN1) through the activation of AMPK signaling, which helps to improve synovium (Chen Y. et al., 2020).
4.2 Direct AMPK activator under development
Given the important role of AMPK in metabolic processes, many studies have attempted to develop its direct activators to treat metabolic diseases. Several small molecules developed as allosteric activators of AMPK appear to bind to the ‘allosteric drug and metabolite’ (ADaM) site, which connects the regulatory β subunit and the catalytic α subunit (Steinberg and Carling, 2019). Furthermore, some activators can suppress the dephosphorylation of pAMPK, thereby maintaining AMPK activity. These AMPK activators have been shown to be highly effective in both animal and human studies.
4.2.1 PXL770
PXL770 is an orally bioavailable thienopyridone small molecule that increases AMPK activity by both allosteric activation and protection from dephosphorylation. Study shows that it has the ability to reverse hyperglycemia, enhances insulin sensitivity, and ameliorates other metabolic disorders in rats with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (Gluais-Dagorn et al., 2022). In a randomized, double-blind four-week trial, PXL770 is shown to improve metabolic disorders in overweight/obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and insulin resistance (Fouqueray et al., 2021).
4.2.2 O304
With the ability to suppress dephosphorylation of pAMPK, O304 is found to increase glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, reduce β cell stress, and promote β cell rest in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice. A subsequent clinical trial demonstrated that O304 improves glucose homeostasis in patients with type 2 diabetes (Steneberg et al., 2018).
4.2.3 PF-739
PF-739 is a benzimidazole derivative that binds to and activates all AMPK heterotrimers with similar potency via the ADaM site. PF-739 has been shown to decrease plasma glucose levels in DIO mice and cynomolgus monkeys by activating AMPK signaling in skeletal muscle (Cokorinos et al., 2017).
4.2.4 PF-06409577
PF-06409577-mediated activation of AMPK can inhibit the pathways involved in de novo lipid and cholesterol synthesis, thereby reducing hepatic lipids and the expression of markers of hepatic fibrosis. This lowers hepatic and systemic lipid and cholesterol levels in mice and cynomolgus monkeys with NAFLD (Esquejo et al., 2018).
4.2.5 MK-8722
As an effective activator of β complexes, MK-8722 is developed to improve glucose homeostasis in dysmetabolic and diabetic rodents and rhesus monkeys by inducing glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscle (Myers et al., 2017).
Although different AMPK activators are emerging, their appropriate targeted disease and potential adverse effects need to be further confirmed. It deserves more exploration into this area.
4.3 Natural medicine
A series of studies have explored the protective effects of traditional medicine in relieving osteoarthritis from anti-inflammation to anti-oxidative stress. Many of these studies have revealed AMPK activation as a key underlying mechanism (Table 1).
TABLE 1
| Therapy | Research subjects | Model | Year | References | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geniposide | Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. C28/I2 human chondrocyte cell line | Intra-articular injection of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA). IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury | 2023 | Huang et al. (2023) | Promotion of chondrocyte autophagy in OA chondrocyte through activation of GLP-1R/AMPK/mTOR pathway |
| Sinensetin | 10-week-old male C57BL/6 mice. Primary chondrocytes isolated from mice | Destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM). Tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP)-induced injury | 2021 | Zhou W. et al. (2021) | Promotion of chondrocyte autophagy in OA chondrocyte through activation of AMPK/mTOR pathway |
| Resveratrol | 10-week-old male C57BL/6 mice | DMM. | 2017 | Qin et al. (2017) | Promotion of chondrocyte autophagy in OA chondrocyte through activation of AMPK/mTOR pathway |
| Osthole | SD rats. Primary chondrocytes isolated from rats | Huth method. IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury | 2022 | Ma T. et al. (2022) | Promotion of chondrocyte autophagy in OA chondrocyte through activation of AMPK/ULK1 pathway |
| Harpagide | SD rats. Primary chondrocytes isolated from rats | Anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT). TNF-α-induced chondrocyte injury | 2024 | Xu et al. (2024) | Inhibition of cartilage degeneration and inflammation through activation of AMPK signaling |
| Hesperetin | SD rats. Primary chondrocytes isolated from rats | ACLT. TNF-α-induced chondrocyte injury | 2021 | Wu et al. (2021) | Inhibition of cartilage degeneration and inflammation through activation of AMPK signaling |
| Chitosan oligosaccharide | Three-month-old New Zealand White rabbits. Human synoviocytes from OA patients. Primary chondrocytes isolated from New Zealand White rabbits | ACLT. TNF-α-induced synovitis | 2016 | Kunanusornchai et al. (2016b) | Inhibition of synovitis through activation of AMPK signaling |
| Berberine | 12-week-old male C57bl/6 mice. Primary chondrocytes isolated from mice. Human knee chondrocytes | DMM. IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury | 2022 | Li J. et al. (2022) | Inhibition of cartilage degeneration and inflammation through activation of AMPK/SIRT1 signaling |
| Bilobalide | 7-week-old male C57bl/6 mice. Human knee chondrocytes | DMM. IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury | 2022 | Zhao Z. et al. (2022) | Inhibition of cartilage degeneration and inflammation through activation of AMPK/SIRT1 signaling |
| SD rats. ATDC5 cells | ACLT. IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury | 2022 | Ma et al. (2022) | Inhibition of cartilage degeneration and inflammation through activation of AMPK/SIRT1/mTOR signaling | |
| Safflower yellow | SD rats. Primary rat chondrocytes | ACLT. TNF-α-induced chondrocyte injury | 2020 | Wang C. L. et al. (2020) | Inhibition of cartilage degeneration and inflammation through NF-κB/SIRT1/AMPK signaling |
| Total flavonoids from Rhizoma Drynariae | SD rats. Primary chondrocytes isolated from OA patients | Huth method. IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury | 2023 | Chen G. Y. et al. (2023) | Prevention of cartilage degeneration and inflammation through activation of AMPK signaling and inhibition of NF-κB |
| Xanthohumol | SD rats. Human chondrocytes from OA patients | DMM. Palmitate (PA)-induced chondrocyte injury | 2023 | Sun W. et al. (2023) | Inhibition of cartilage degeneration, NLRP3 inflammasome, mitochondria dysfunction through activation of AMPK/NF-κB signaling |
| Quercetin | Male SD rats. Primary chondrocytes isolated from rats | Medial meniscotibial ligament transection. TBHP-induced injury | 2019 | Feng et al. (2019) | Inhibition of ER stress through AMPK/SIRT1 signaling |
| Male SD rats. Primary chondrocytes isolated from rats | DMM. | 2018 | Qiu et al. (2018) | Inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction through AMPK/SIRT1 signaling | |
| Baicalein | 8-week-old C57BL/6J wild-type mice. Human knee chondrocytes. Primary chondrocytes isolated from mice | DMM. IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury | 2023 | Wan et al. (2023) | Inhibition of ferroptosis through AMPK/Nrf2 signaling |
| Asiatic acid | Male SD rats. Human knee chondrocytes | ACLT. | 2020 | Liu et al. (2020) | Inhibition of chondrocyte hypertrophy and fibrosis through AMPK/PI3K/AKT signaling |
Natural medicines that target AMPK signaling in the treatment of OA.
4.3.1 Increased autophagy
Geniposide (GEN, an iridoid glycoside extracted from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv), Sinensetin (Sin, a polymethoxylated flavonoid found in citrus fruits), Resveratrol (a polyphenolic phytoalexin presents in many plants) and Osthole (an ingredient from the root of Freziera biserrate) have been confirmed their abilities to mediate autophagy for maintaining cartilage homeostasis, protecting chondrocytes and ECM from damage, deformation and degeneration, and attenuating OA pain via AMPK/mTOR or AMPK/ULK1 signaling (Huang et al., 2023; Zhou W. et al., 2021; Qin et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2022).
4.3.2 Anti-inflammation
The anti-inflammatory effects of natural medicines have been used to alleviate OA progression. Harpagide (an iridoid glycoside natural molecule from the root of Harpagophytum procumbens var. sublobatum (Engl.)), Hesperetin (a natural flavonoid from the Citrus L.) and Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS, an oligomer of d-glucosamine) have been found to suppress the expression of inflammatory cytokines and MMP, thereby protecting cartilage from damage and abnormal proliferation, improving synovitis, inhibiting osteophyte formation and attenuating pain through AMPK signaling (Xu et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2021; Kunanusornchai et al., 2016b). Further investigation revealed that these effects are regulated by the activation of AMPK and its downstream signaling pathways. For example, SIRT1 signaling could be regulated by Berberine (an isoquinoline alkaloid extracted from plants) and Bilobalide (a lactone extracted from Ginkgo biloba) (Li J. et al., 2022; Zhao Z. et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2022). NF-κB signaling was inhibited by Safflower yellow (an active ingredient of Carthamus tinctorius L.), total flavonoids from Rhizoma Drynariae (the main active ingredients from the dried rhizome of Davallia mariesii T. Moore ex Baker) (Wang C. L. et al., 2020; Chen G. Y. et al., 2023). And NLRP3 inflammasome pathway was suppressed by Xanthohumol (Sun W. et al., 2023).
4.3.3 Oxidative stress
Some medicines have been found to decrease oxidative stress and attenuate OA progression by modulating AMPK signaling and its downstream pathways. For instance, quercetin inhibited ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction via AMPK/SIRT1 signaling (Feng et al., 2019; Qiu et al., 2018). Baicalein activated AMPK signaling and then induced nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a key regulator of antioxidant responses, to block ferroptosis (Wan et al., 2023). Asiatic acid (a pentacyclic triterpene isolated from Centella asiatica) had the ability to reduce hypertrophic and fibrotic differentiation by targeting the AMPK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (Liu et al., 2020).
Natural medicines offer promising prospects for the treatment of OA, with some of them showing positive effects in the activation of AMPK signaling. Nonetheless, several issues need to be addressed: First, the composition and interaction of these ingredients of TCM are under exploration. Second, it is hard to make a conclusion that these natural medicines exert their effect by directly activating AMPK since they did not explore the structure of AMPK or the combination of compounds and AMPK after the application. Third, the appropriate dosage range and potential therapeutic relevance are not fully defined and explained. High doses are not beneficial in humans and lack translational value due to concerns about toxicity and bioavailability.
5 Discussion
The activation of AMPK signaling offers protection against environmental stress by promoting autophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. By contrast, disturbances in AMPK signaling resulting from metabolic disorder lead to cellular injury or even death due to oxidative stress, inflammation. The impact of AMPK signaling dysregulation during OA progression highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting AMPK signaling as a promising strategy for OA (Figures 2–6). It should be noted that these mechanisms do not exist in isolation but affect each other. Metabolic disorders are caused by oxidative stress, the inhibition of autophagy, and inflammation. Inflammation aggravates oxidative stress. Oxidative stress leads to the production of inflammatory factors, thereby promoting inflammation. All of these factors inhibit autophagy, which further causes metabolic disorders. AMPK, at the center of energy metabolism, participates in almost every energy-requiring biological process, reflecting its important role in maintaining homeostasis.
However, there are several limitations of targeting AMPK signaling in the treatment of OA. First, although numerous animal studies have confirmed the role of AMPK signaling in maintaining joint homeostasis, there is a lack of clinical trials demonstrating the effectiveness of AMPK-targeted therapy for OA patients. Some human clinical studies have reported the beneficial effect of metformin in OA (Wang Y. et al., 2019). However, a record cohort study enrolling 3217 patients with type 2 diabetes in the United Kingdom found that metformin treatment had no significant effect on the progression of OA (Barnett et al., 2017).
Overall, due to the current limitations in OA management, exploring novel therapies is crucial. In the future, more effort will be put into clarifying the role of AMPK signaling in OA progression and clinical application to protect patients from OA damage.
Statements
Author contributions
LC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. X-HH: Writing – original draft. X-YW: Data curation, Writing – original draft. XZ: Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. Y-XH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – original draft. G-YC: Conceptualization, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. Q-WT: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by the National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (No. 2023-NHLHCRF-YXHZ-ZRMS-07).
Acknowledgments
The images were generated using Figdraw (www.figdraw.com).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abed É. Couchourel D. Delalandre A. Duval N. Pelletier J. P. Martel-Pelletier J. et al (2014). Low sirtuin 1 levels in human osteoarthritis subchondral osteoblasts lead to abnormal sclerostin expression which decreases Wnt/β-catenin activity. Bone59, 28–36. 10.1016/j.bone.2013.10.020
2
Almonte-Becerril M. Navarro-Garcia F. Gonzalez-Robles A. Vega-Lopez M. A. Lavalle C. Kouri J. B. (2010). Cell death of chondrocytes is a combination between apoptosis and autophagy during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis within an experimental model. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. cell death15 (5), 631–638. 10.1007/s10495-010-0458-z
3
An F. Zhang J. Gao P. Xiao Z. Chang W. Song J. et al (2023). New insight of the pathogenesis in osteoarthritis: the intricate interplay of ferroptosis and autophagy mediated by mitophagy/chaperone-mediated autophagy. Front. cell Dev. Biol.11, 1297024. 10.3389/fcell.2023.1297024
4
Bandyopadhyay G. K. Yu J. G. Ofrecio J. Olefsky J. M. (2006). Increased malonyl-CoA levels in muscle from Obese and type 2 diabetic subjects lead to decreased fatty acid oxidation and increased lipogenesis; thiazolidinedione treatment reverses these defects. Diabetes55 (8), 2277–2285. 10.2337/db06-0062
5
Barnett L. A. Jordan K. P. Edwards J. J. van der Windt D. A. (2017). Does metformin protect against osteoarthritis? An electronic health record cohort study. Prim. health care Res. Dev.18 (6), 623–628. 10.1017/S1463423617000287
6
Benito M. J. Veale D. J. FitzGerald O. van den Berg W. B. Bresnihan B. (2005). Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann. rheumatic Dis.64 (9), 1263–1267. 10.1136/ard.2004.025270
7
Bijlsma J. W. Berenbaum F. Lafeber F. P. (2011). Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet London, Engl.377 (9783), 2115–2126. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60243-2
8
Cai Z. Y. Yang B. Shi Y. X. Zhang W. L. Liu F. Zhao W. et al (2018). High glucose downregulates the effects of autophagy on osteoclastogenesis via the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathway. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun.503 (2), 428–435. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.052
9
Calabrese M. F. Rajamohan F. Harris M. S. Caspers N. L. Magyar R. Withka J. M. et al (2014). Structural basis for AMPK activation: natural and synthetic ligands regulate kinase activity from opposite poles by different molecular mechanisms. Struct. Lond. Engl. 199322 (8), 1161–1172. 10.1016/j.str.2014.06.009
10
Cantó C. Gerhart-Hines Z. Feige J. N. Lagouge M. Noriega L. Milne J. C. et al (2009). AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD+ metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature458 (7241), 1056–1060. 10.1038/nature07813
11
Caratti G. Desgeorges T. Juban G. Stifel U. Fessard A. Koenen M. et al (2023). Macrophagic AMPKα1 orchestrates regenerative inflammation induced by glucocorticoids. EMBO Rep.24 (2), e55363. 10.15252/embr.202255363
12
Chen L. Y. Wang Y. Terkeltaub R. Liu-Bryan R. (2018). Activation of AMPK-SIRT3 signaling is chondroprotective by preserving mitochondrial DNA integrity and function. Osteoarthr. Cartil.26 (11), 1539–1550. 10.1016/j.joca.2018.07.004
13
Chen Y. Qiu F. Yu B. Chen Y. Zuo F. Zhu X. et al (2020). Metformin, an AMPK activator, inhibits activation of FLSs but promotes HAPLN1 secretion. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev.17, 1202–1214. 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.05.008
14
Chen Y. Wu Y. Y. Si H. B. Lu Y. R. Shen B. (2021). Mechanistic insights into AMPK-SIRT3 positive feedback loop-mediated chondrocyte mitochondrial quality control in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Pharmacol. Res.166, 105497. 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105497
15
Chen Y. Liu Y. Jiang K. Wen Z. Cao X. Wu S. (2022). Linear ubiquitination of LKB1 activates AMPK pathway to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome response and reduce chondrocyte pyroptosis in osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Transl.39, 1–11. 10.1016/j.jot.2022.11.002
16
Chen G. Y. Liu X. Y. Yan X. E. Yu X. Liu Y. Luo J. et al (2023). Total flavonoids of rhizoma drynariae treat osteoarthritis by inhibiting arachidonic acid metabolites through AMPK/NFκB pathway. J. Inflamm. Res.16, 4123–4140. 10.2147/JIR.S418345
17
Cokorinos E. C. Delmore J. Reyes A. R. Albuquerque B. Kjøbsted R. Jørgensen N. O. et al (2017). Activation of skeletal muscle AMPK promotes glucose disposal and glucose lowering in non-human Primates and mice. Cell metab.25 (5), 1147–1159.e10. 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.010
18
Dai B. Zhu F. Chen Y. Zhou R. Wang Z. Xie Y. et al (2017). ASIC1a promotes acid-induced autophagy in rat articular chondrocytes through the AMPK/FoxO3a pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci.18 (10), 2125. 10.3390/ijms18102125
19
DeSelm C. J. Miller B. C. Zou W. Beatty W. L. van Meel E. Takahata Y. et al (2011). Autophagy proteins regulate the secretory component of osteoclastic bone resorption. Dev. cell21 (5), 966–974. 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.016
20
Dixon S. J. Lemberg K. M. Lamprecht M. R. Skouta R. Zaitsev E. M. Gleason C. E. et al (2012). Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell149 (5), 1060–1072. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
21
Eijkelenboom A. Burgering B. M. (2013). FOXOs: signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol.14 (2), 83–97. 10.1038/nrm3507
22
Esquejo R. M. Salatto C. T. Delmore J. Albuquerque B. Reyes A. Shi Y. et al (2018). Activation of liver AMPK with PF-06409577 corrects NAFLD and lowers cholesterol in rodent and primate preclinical models. EBioMedicine31, 122–132. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.04.009
23
Feng K. Chen Z. Pengcheng L. Zhang S. Wang X. (2019). Quercetin attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via SIRT1/AMPK-mediated inhibition of ER stress in rat chondrocytes and prevents the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. J. Cell. physiology234 (10), 18192–18205. 10.1002/jcp.28452
24
Fouqueray P. Bolze S. Dubourg J. Hallakou-Bozec S. Theurey P. Grouin J. M. et al (2021). Pharmacodynamic effects of direct AMP kinase activation in humans with insulin resistance and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a phase 1b study. Cell Rep. Med.2 (12), 100474. 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100474
25
Galic S. Fullerton M. D. Schertzer J. D. Sikkema S. Marcinko K. Walkley C. R. et al (2011). Hematopoietic AMPK β1 reduces mouse adipose tissue macrophage inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. J. Clin. investigation121 (12), 4903–4915. 10.1172/JCI58577
26
Garcia D. Shaw R. J. (2017). AMPK: mechanisms of cellular energy sensing and restoration of metabolic balance. Mol. cell66 (6), 789–800. 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.032
27
GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators (2018). Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet London, Engl.392 (10159), 1789–1858. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7
28
Gluais-Dagorn P. Foretz M. Steinberg G. R. Batchuluun B. Zawistowska-Deniziak A. Lambooij J. M. et al (2022). Direct AMPK activation corrects NASH in rodents through metabolic effects and direct action on inflammation and fibrogenesis. Hepatol. Commun.6 (1), 101–119. 10.1002/hep4.1799
29
Guermazi A. Neogi T. Katz J. N. Kwoh C. K. Conaghan P. G. Felson D. T. et al (2020). Intra-articular corticosteroid injections for the treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis-related pain: considerations and controversies with a focus on imaging-radiology scientific expert panel. Radiology297 (3), 503–512. 10.1148/radiol.2020200771
30
He M. Lu B. Opoku M. Zhang L. Xie W. Jin H. et al (2022). Metformin prevents or delays the development and progression of osteoarthritis: new insight and mechanism of action. Cells11 (19), 3012. 10.3390/cells11193012
31
Huang J. Chen Z. Wu Z. Xie X. Liu S. Kong W. et al (2023). Geniposide stimulates autophagy by activating the GLP-1R/AMPK/mTOR signaling in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomedecine Pharmacother.167, 115595. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115595
32
Hunter D. J. Bierma-Zeinstra S. (2019). Osteoarthr. Lancet London, Engl.393 (10182), 1745–1759. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30417-9
33
Hurley R. L. Anderson K. A. Franzone J. M. Kemp B. E. Means A. R. Witters L. A. (2005). The Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinases are AMP-Activated protein kinase kinases. J. Biol. Chem.280 (32), 29060–29066. 10.1074/jbc.M503824200
34
Indo Y. Takeshita S. Ishii K. A. Hoshii T. Aburatani H. Hirao A. et al (2013). Metabolic regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function. J. bone mineral Res. official J. Am. Soc. Bone Mineral Res.28 (11), 2392–2399. 10.1002/jbmr.1976
35
Iyer S. Han L. Bartell S. M. Kim H. N. Gubrij I. de Cabo R. et al (2014). Sirtuin1 (Sirt1) promotes cortical bone formation by preventing β-catenin sequestration by FoxO transcription factors in osteoblast progenitors. J. Biol. Chem.289 (35), 24069–24078. 10.1074/jbc.M114.561803
36
Jiang A. Xu P. Yang Z. Zhao Z. Tan Q. Li W. et al (2023). Increased sparc release from subchondral osteoblasts promotes articular chondrocyte degeneration under estrogen withdrawal. Osteoarthr. Cartil.31 (1), 26–38. 10.1016/j.joca.2022.08.020
37
Kahn B. B. Alquier T. Carling D. Hardie D. G. (2005). AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell metab.1 (1), 15–25. 10.1016/j.cmet.2004.12.003
38
Kanazawa I. Yamaguchi T. Yano S. Yamauchi M. Sugimoto T. (2008). Metformin enhances the differentiation and mineralization of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells via AMP kinase activation as well as eNOS and BMP-2 expression. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun.375 (3), 414–419. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.034
39
Kang H. Viollet B. Wu D. (2013). Genetic deletion of catalytic subunits of AMP-activated protein kinase increases osteoclasts and reduces bone mass in young adult mice. J. Biol. Chem.288 (17), 12187–12196. 10.1074/jbc.M112.430389
40
Kang X. Yang W. Wang R. Xie T. Li H. Feng D. et al (2018). Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) stimulates growth-plate chondrogenesis by attenuating the PERK-eIF-2α-CHOP pathway in the unfolded protein response. J. Biol. Chem.293 (22), 8614–8625. 10.1074/jbc.M117.809822
41
Katz J. N. Arant K. R. Loeser R. F. (2021). Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. JAMA325 (6), 568–578. 10.1001/jama.2020.22171
42
Kauppinen A. Suuronen T. Ojala J. Kaarniranta K. Salminen A. (2013). Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders. Cell. Signal.25 (10), 1939–1948. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007
43
Kim J. Kundu M. Viollet B. Guan K. L. (2011). AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. cell Biol.13 (2), 132–141. 10.1038/ncb2152
44
Kim Y. A. Kim Y. S. Oh S. L. Kim H. J. Song W. (2013). Autophagic response to exercise training in skeletal muscle with age. J. physiology Biochem.69 (4), 697–705. 10.1007/s13105-013-0246-7
45
Kim J. Y. Min J. Y. Baek J. M. Ahn S. J. Jun H. Y. Yoon K. H. et al (2015). CTRP3 acts as a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis through AMPK-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling in vitro and RANKL-induced calvarial bone destruction in vivo. Bone79, 242–251. 10.1016/j.bone.2015.06.011
46
Ko C. Y. Lin Y. Y. Achudhan D. Chang J. W. Liu S. C. Lai C. Y. et al (2023). Omentin-1 ameliorates the progress of osteoarthritis by promoting IL-4-dependent anti-inflammatory responses and M2 macrophage polarization. Int. J. Biol. Sci.19 (16), 5275–5289. 10.7150/ijbs.86701
47
Kolasinski S. L. Neogi T. Hochberg M. C. Oatis C. Guyatt G. Block J. et al (2020). 2019 American college of rheumatology/arthritis foundation guideline for the management of osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis care Res.72 (2), 149–162. 10.1002/acr.24131
48
Kunanusornchai W. Muanprasat C. Chatsudthipong V. (2016a). Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activation and suppression of inflammatory response by cell stretching in rabbit synovial fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biochem.423 (1-2), 175–185. 10.1007/s11010-016-2835-6
49
Kunanusornchai W. Witoonpanich B. Tawonsawatruk T. Pichyangkura R. Chatsudthipong V. Muanprasat C. (2016b). Chitosan oligosaccharide suppresses synovial inflammation via AMPK activation: an in vitro and in vivo study. Pharmacol. Res.113 (Pt A), 458–467. 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.09.016
50
Law Y. Y. Lin Y. M. Liu S. C. Wu M. H. Chung W. H. Tsai C. H. et al (2020). Visfatin increases ICAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion in human osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts by reducing miR-320a expression. Aging12 (18), 18635–18648. 10.18632/aging.103889
51
Lee Y. S. Kim Y. S. Lee S. Y. Kim G. H. Kim B. J. Lee S. H. et al (2010). AMP kinase acts as a negative regulator of RANKL in the differentiation of osteoclasts. Bone47 (5), 926–937. 10.1016/j.bone.2010.08.001
52
Leick L. Fentz J. Biensø R. S. Knudsen J. G. Jeppesen J. Kiens B. et al (2010). PGC-1{alpha} is required for AICAR-induced expression of GLUT4 and mitochondrial proteins in mouse skeletal muscle. Am. J. physiology. Endocrinol. metabolism299 (3), E456–E465. 10.1152/ajpendo.00648.2009
53
Lepetsos P. Papavassiliou A. G. (2016). ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochimica biophysica acta1862 (4), 576–591. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.01.003
54
Levick J. R. McDonald J. N. (1995). Fluid movement across synovium in healthy joints: role of synovial fluid macromolecules. Ann. rheumatic Dis.54 (5), 417–423. 10.1136/ard.54.5.417
55
Li C. Dong X. Du W. Shi X. Chen K. Zhang W. et al (2020). LKB1-AMPK axis negatively regulates ferroptosis by inhibiting fatty acid synthesis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.5 (1), 187. 10.1038/s41392-020-00297-2
56
Li J. Wang Y. Chen D. Liu-Bryan R. (2022). Oral administration of berberine limits post-traumatic osteoarthritis development and associated pain via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in mice. Osteoarthr. Cartil.30 (1), 160–171. 10.1016/j.joca.2021.10.004
57
Li J. Zhang B. Liu W. X. Lu K. Pan H. Wang T. et al (2020). Metformin limits osteoarthritis development and progression through activation of AMPK signalling. Ann. rheumatic Dis.79 (5), 635–645. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216713
58
Lin S. C. Hardie D. G. (2018). AMPK: sensing Glucose as well as cellular energy status. Cell metab.27 (2), 299–313. 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.10.009
59
Liu N. Fu D. Yang J. Liu P. Song X. Wang X. et al (2020). Asiatic acid attenuates hypertrophic and fibrotic differentiation of articular chondrocytes via AMPK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Arthritis Res. Ther.22 (1), 112. 10.1186/s13075-020-02193-0
60
Liu-Bryan R. (2015). Inflammation and intracellular metabolism: new targets in OA. Osteoarthr. Cartil.23 (11), 1835–1842. 10.1016/j.joca.2014.12.016
61
Liu-Bryan R. Terkeltaub R. (2015). Emerging regulators of the inflammatory process in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.11 (1), 35–44. 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.162
62
Lotz M. Loeser R. F. (2012). Effects of aging on articular cartilage homeostasis. Bone51 (2), 241–248. 10.1016/j.bone.2012.03.023
63
Ma C. H. Chiua Y. C. Wu C. H. Jou I. M. Tu Y. K. Hung C. H. et al (2018). Homocysteine causes dysfunction of chondrocytes and oxidative stress through repression of SIRT1/AMPK pathway: a possible link between hyperhomocysteinemia and osteoarthritis. Redox Biol.15, 504–512. 10.1016/j.redox.2018.01.010
64
Ma T. Lv L. Yu Y. Jia L. Song X. Xu X. et al (2022). Bilobalide exerts anti-inflammatory effects on chondrocytes through the AMPK/SIRT1/mTOR pathway to attenuate ACLT-induced post-traumatic osteoarthritis in rats. Front. Pharmacol.13, 783506. 10.3389/fphar.2022.783506
65
Ma T. Wang X. Qu W. Yang L. Jing C. Zhu B. et al (2022). Osthole suppresses knee osteoarthritis development by enhancing autophagy activated via the AMPK/ULK1 pathway. Mol. Basel, Switz.27 (23), 8624. 10.3390/molecules27238624
66
Matsuzaki T. Matsushita T. Takayama K. Matsumoto T. Nishida K. Kuroda R. et al (2014). Disruption of Sirt1 in chondrocytes causes accelerated progression of osteoarthritis under mechanical stress and during ageing in mice. Ann. rheumatic Dis.73 (7), 1397–1404. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202620
67
Myers R. W. Guan H. P. Ehrhart J. Petrov A. Prahalada S. Tozzo E. et al (2017). Systemic pan-AMPK activator MK-8722 improves glucose homeostasis but induces cardiac hypertrophy. Sci. (New York, N.Y.)357 (6350), 507–511. 10.1126/science.aah5582
68
Neogi T. Felson D. Niu J. Lynch J. Nevitt M. Guermazi A. et al (2009). Cartilage loss occurs in the same subregions as subchondral bone attrition: a within-knee subregion-matched approach from the multicenter osteoarthritis study. Arthritis rheumatism61 (11), 1539–1544. 10.1002/art.24824
69
Newman H. Shih Y. V. Varghese S. (2021). Resolution of inflammation in bone regeneration: from understandings to therapeutic applications. Biomaterials277, 121114. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121114
70
Nollet M. Santucci-Darmanin S. Breuil V. Al-Sahlanee R. Cros C. Topi M. et al (2014). Autophagy in osteoblasts is involved in mineralization and bone homeostasis. Autophagy10 (11), 1965–1977. 10.4161/auto.36182
71
O'Neill H. M. Maarbjerg S. J. Crane J. D. Jeppesen J. Jørgensen S. B. Schertzer J. D. et al (2011). AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) beta1beta2 muscle null mice reveal an essential role for AMPK in maintaining mitochondrial content and glucose uptake during exercise. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.108 (38), 16092–16097. 10.1073/pnas.1105062108
72
O'Neill H. M. Holloway G. P. Steinberg G. R. (2013). AMPK regulation of fatty acid metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis: implications for obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.366 (2), 135–151. 10.1016/j.mce.2012.06.019
73
Oakhill J. S. Scott J. W. Kemp B. E. (2012). AMPK functions as an adenylate charge-regulated protein kinase. Trends Endocrinol. metabolism TEM23 (3), 125–132. 10.1016/j.tem.2011.12.006
74
Park S. Y. Lee S. W. Lee S. Y. Hong K. W. Bae S. S. Kim K. et al (2017). SIRT1/Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase α signaling enhances macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory phenotype in rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol.8, 1135. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01135
75
Park S. J. Gavrilova O. Brown A. L. Soto J. E. Bremner S. Kim J. et al (2017). DNA-PK promotes the mitochondrial, metabolic, and physical decline that occurs during aging. Cell metab.25 (5), 1135–1146.e7. 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.008
76
Park S. H. Kang M. A. Moon Y. J. Jang K. Y. Kim J. R. (2020). Metformin coordinates osteoblast/osteoclast differentiation associated with ischemic osteonecrosis. Aging12 (6), 4727–4741. 10.18632/aging.102796
77
Petursson F. Husa M. June R. Lotz M. Terkeltaub R. Liu-Bryan R. (2013). Linked decreases in liver kinase B1 and AMP-activated protein kinase activity modulate matrix catabolic responses to biomechanical injury in chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther.15 (4), R77. 10.1186/ar4254
78
Price A. J. Alvand A. Troelsen A. Katz J. N. Hooper G. Gray A. et al (2018). Knee replacement. Lancet London, Engl.392 (10158), 1672–1682. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32344-4
79
Qin N. Wei L. Li W. Yang W. Cai L. Qian Z. et al (2017). Local intra-articular injection of resveratrol delays cartilage degeneration in C57BL/6 mice by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR pathway. J. Pharmacol. Sci.134 (3), 166–174. 10.1016/j.jphs.2017.06.002
80
Qiu L. Luo Y. Chen X. (2018). Quercetin attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction and biogenesis via upregulated AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway in OA rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomedecine Pharmacother.103, 1585–1591. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.003
81
Quinn J. M. Tam S. Sims N. A. Saleh H. McGregor N. E. Poulton I. J. et al (2010). Germline deletion of AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunits reduces bone mass without altering osteoclast differentiation or function. FASEB J. official Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol.24 (1), 275–285. 10.1096/fj.09-137158
82
Ruderman N. B. Xu X. J. Nelson L. Cacicedo J. M. Saha A. K. Lan F. et al (2010). AMPK and SIRT1: a long-standing partnership?Am. J. physiology. Endocrinol. metabolism298 (4), E751–E760. 10.1152/ajpendo.00745.2009
83
Russe O. Q. Möser C. V. Kynast K. L. King T. S. Stephan H. Geisslinger G. et al (2013). Activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase reduces inflammatory nociception. J. pain14 (11), 1330–1340. 10.1016/j.jpain.2013.05.012
84
Sag D. Carling D. Stout R. D. Suttles J. (2008). Adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase promotes macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory functional phenotype. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md181 (12), 8633–8641. 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8633
85
Salinas D. Mumey B. M. June R. K. (2019). Physiological dynamic compression regulates central energy metabolism in primary human chondrocytes. Biomechanics Model. Mechanobiol.18 (1), 69–77. 10.1007/s10237-018-1068-x
86
Salminen A. Hyttinen J. M. Kaarniranta K. (2011). AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-κB signaling and inflammation: impact on healthspan and lifespan. J. Mol. Med. Berlin, Ger.89 (7), 667–676. 10.1007/s00109-011-0748-0
87
She C. Zhu L. Q. Zhen Y. F. Wang X. D. Dong Q. R. (2014). Activation of AMPK protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced osteoblast apoptosis through autophagy induction and NADPH maintenance: new implications for osteonecrosis treatment?Cell. Signal.26 (1), 1–8. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.08.046
88
Stegen S. Carmeliet G. (2024). Metabolic regulation of skeletal cell fate and function. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.20 (7), 399–413. 10.1038/s41574-024-00969-x
89
Steinberg G. R. Carling D. (2019). AMP-activated protein kinase: the current landscape for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.18 (7), 527–551. 10.1038/s41573-019-0019-2
90
Steinberg G. R. O'Neill H. M. Dzamko N. L. Galic S. Naim T. Koopman R. et al (2010). Whole body deletion of AMP-activated protein kinase {beta}2 reduces muscle AMPK activity and exercise capacity. J. Biol. Chem.285 (48), 37198–37209. 10.1074/jbc.M110.102434
91
Steneberg P. Lindahl E. Dahl U. Lidh E. Straseviciene J. Backlund F. et al (2018). PAN-AMPK activator O304 improves glucose homeostasis and microvascular perfusion in mice and type 2 diabetes patients. JCI insight3 (12), e99114. 10.1172/jci.insight.99114
92
Stockwell B. R. Friedmann Angeli J. P. Bayir H. Bush A. I. Conrad M. Dixon S. J. et al (2017). Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell171 (2), 273–285. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021
93
Sun J. Song F. H. Wu J. Y. Zhang L. Q. Li D. Y. Gao S. J. et al (2022). Sestrin2 overexpression attenuates osteoarthritis pain via induction of AMPK/PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and suppression of neuroinflammation. Brain, Behav. Immun.102, 53–70. 10.1016/j.bbi.2022.02.015
94
Sun W. Yue J. Xu T. Cui Y. Huang D. Shi H. et al (2023). Xanthohumol alleviates palmitate-induced inflammation and prevents osteoarthritis progression by attenuating mitochondria dysfunction/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Heliyon9 (11), e21282. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21282
95
Tang C. H. Chiu Y. C. Tan T. W. Yang R. S. Fu W. M. (2007). Adiponectin enhances IL-6 production in human synovial fibroblast via an AdipoR1 receptor, AMPK, p38, and NF-kappa B pathway. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md179 (8), 5483–5492. 10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.5483
96
Terkeltaub R. Yang B. Lotz M. Liu-Bryan R. (2011). Chondrocyte AMP-activated protein kinase activity suppresses matrix degradation responses to proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor α. Arthritis rheumatism63 (7), 1928–1937. 10.1002/art.30333
97
Thijssen E. van Caam A. van der Kraan P. M. (2015). Obesity and osteoarthritis, more than just wear and tear: pivotal roles for inflamed adipose tissue and dyslipidaemia in obesity-induced osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl.54 (4), 588–600. 10.1093/rheumatology/keu464
98
Tong X. Zhang C. Wang D. Song R. Ma Y. Cao Y. et al (2020). Suppression of AMP-activated protein kinase reverses osteoprotegerin-induced inhibition of osteoclast differentiation by reducing autophagy. Cell Prolif.53 (1), e12714. 10.1111/cpr.12714
99
Trefts E. Shaw R. J. (2021). AMPK: restoring metabolic homeostasis over space and time. Mol. cell81 (18), 3677–3690. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.08.015
100
Udagawa N. Takahashi N. Yasuda H. Mizuno A. Itoh K. Ueno Y. et al (2000). Osteoprotegerin produced by osteoblasts is an important regulator in osteoclast development and function. Endocrinology141 (9), 3478–3484. 10.1210/endo.141.9.7634
101
Volkow N. D. McLellan A. T. (2016). Opioid abuse in chronic Pain--Misconceptions and mitigation strategies. N. Engl. J. Med.374 (13), 1253–1263. 10.1056/NEJMra1507771
102
Wan Y. Shen K. Yu H. Fan W. (2023). Baicalein limits osteoarthritis development by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med.196, 108–120. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.01.006
103
Wang Y. Zhao X. Lotz M. Terkeltaub R. Liu-Bryan R. (2015). Mitochondrial biogenesis is impaired in osteoarthritis chondrocytes but reversible via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α. Arthritis rheumatology (Hoboken, N.J.)67 (8), 2141–2153. 10.1002/art.39182
104
Wang Y. G. Han X. G. Yang Y. Qiao H. Dai K. R. Fan Q. M. et al (2016a). Functional differences between AMPK α1 and α2 subunits in osteogenesis, osteoblast-associated induction of osteoclastogenesis, and adipogenesis. Sci. Rep.6, 32771. 10.1038/srep32771
105
Wang Y. G. Qu X. H. Yang Y. Han X. G. Wang L. Qiao H. et al (2016b). AMPK promotes osteogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis through AMPK-Gfi1-OPN axis. Cell. Signal.28 (9), 1270–1282. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.06.004
106
Wang Y. Hussain S. M. Wluka A. E. Lim Y. Z. Abram F. Pelletier J. P. et al (2019). Association between metformin use and disease progression in obese people with knee osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis Initiative-a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther.21 (1), 127. 10.1186/s13075-019-1915-x
107
Wang C. L. Gao Y. Zhang Z. Chi Q. Liu Y. Yang L. et al (2020). Safflower yellow alleviates osteoarthritis and prevents inflammation by inhibiting PGE2 release and regulating NF-κB/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine Int. J. phytotherapy Phytopharm.78, 153305. 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153305
108
Wang C. Z. Yao Z. Zhang Y. Yang Y. Liu J. Shi Y. et al (2020). Metformin mitigates cartilage degradation by activating AMPK/SIRT1-Mediated autophagy in a mouse osteoarthritis model. Front. Pharmacol.11, 1114. 10.3389/fphar.2020.01114
109
Wang B. Shi Y. Chen J. Shao Z. Ni L. Lin Y. et al (2021). High glucose suppresses autophagy through the AMPK pathway while it induces autophagy via oxidative stress in chondrocytes. Cell death Dis.12 (6), 506. 10.1038/s41419-021-03791-9
110
Wen Z. Jin K. Shen Y. Yang Z. Li Y. Wu B. et al (2019). N-myristoyltransferase deficiency impairs activation of kinase AMPK and promotes synovial tissue inflammation. Nat. Immunol.20 (3), 313–325. 10.1038/s41590-018-0296-7
111
Woods A. Johnstone S. R. Dickerson K. Leiper F. C. Fryer L. G. Neumann D. et al (2003). LKB1 is the upstream kinase in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. Curr. Biol. CB13 (22), 2004–2008. 10.1016/j.cub.2003.10.031
112
Wu J. Qian Y. Chen C. Feng F. Pan L. Yang L. et al (2021). Hesperetin exhibits anti-inflammatory effects on chondrocytes via the AMPK pathway to attenuate anterior cruciate ligament transection-induced osteoarthritis. Front. Pharmacol.12, 735087. 10.3389/fphar.2021.735087
113
Xie Q. Sun Y. Xu H. Chen T. Xiang H. Liu H. et al (2023). Ferrostatin-1 improves BMSC survival by inhibiting ferroptosis. Archives Biochem. biophysics736, 109535. 10.1016/j.abb.2023.109535
114
Xing H. Liang C. Wang C. Xu X. Hu Y. Qiu B. (2022). Metformin mitigates cholesterol accumulation via the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway to protect osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun.632, 113–121. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.09.074
115
Xu C. Tang Y. Yang H. Jiang S. Peng W. Xie R. (2024). Harpagide inhibits the TNF-α-induced inflammatory response in rat articular chondrocytes by the glycolytic pathways for alleviating osteoarthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol.127, 111406. 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111406
116
Yang Z. Kahn B. B. Shi H. Xue B. Z. (2010). Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK) antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1. J. Biol. Chem.285 (25), 19051–19059. 10.1074/jbc.M110.123620
117
Yao Q. Wu X. Tao C. Gong W. Chen M. Qu M. et al (2023). Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.8 (1), 56. 10.1038/s41392-023-01330-w
118
Zhang K. Kaufman R. J. (2008). From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature454 (7203), 455–462. 10.1038/nature07203
119
Zhang Y. Vasheghani F. Li Y. H. Blati M. Simeone K. Fahmi H. et al (2015). Cartilage-specific deletion of mTOR upregulates autophagy and protects mice from osteoarthritis. Ann. rheumatic Dis.74 (7), 1432–1440. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204599
120
Zhang S. Xie Y. Yan F. Zhang Y. Yang Z. Chen Z. et al (2022). Negative pressure wound therapy improves bone regeneration by promoting osteogenic differentiation via the AMPK-ULK1-autophagy axis. Autophagy18 (9), 2229–2245. 10.1080/15548627.2021.2016231
121
Zhao X. Petursson F. Viollet B. Lotz M. Terkeltaub R. Liu-Bryan R. (2014). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α and FoxO3A mediate chondroprotection by AMP-Activated protein kinase. Arthritis and rheumatology (Hoboken, N.J.)66 (11), 3073–3082. 10.1002/art.38791
122
Zhao Z. Liu Y. Lu Y. Hou M. Shen X. Yang H. et al (2022). Gingko biloba-inspired lactone prevents osteoarthritis by activating the AMPK-SIRT1 signaling pathway. Arthritis Res. and Ther.24 (1), 197. 10.1186/s13075-022-02890-y
123
Zhen D. Chen Y. Tang X. (2010). Metformin reverses the deleterious effects of high glucose on osteoblast function. J. diabetes its Complicat.24 (5), 334–344. 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2009.05.002
124
Zhou G. Myers R. Li Y. Chen Y. Shen X. Fenyk-Melody J. et al (2001). Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J. Clin. investigation108 (8), 1167–1174. 10.1172/JCI13505
125
Zhou S. Lu W. Chen L. Ge Q. Chen D. Xu Z. et al (2017). AMPK deficiency in chondrocytes accelerated the progression of instability-induced and ageing-associated osteoarthritis in adult mice. Sci. Rep.7, 43245. 10.1038/srep43245
126
Zhou W. Shi Y. Wang H. Yu C. Zhu H. Wu A. (2021). Sinensetin reduces osteoarthritis pathology in the tert-butyl hydroperoxide-treated chondrocytes and the destabilization of the medial meniscus model mice via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol.12, 713491. 10.3389/fphar.2021.713491
127
Zhu Z. Huang Y. Li J. Yi D. Liao J. Xiao J. et al (2022). AMPK activator decelerates osteoarthritis development by inhibition of β-catenin signaling in chondrocytes. J. Orthop. Transl.38, 158–166. 10.1016/j.jot.2022.10.005
128
Zhuo Q. Yang W. Chen J. Wang Y. (2012). Metabolic syndrome meets osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.8 (12), 729–737. 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.135
129
Zou Z. Hu W. Kang F. Xu Z. Li Y. Zhang J. et al (2025). Interplay between lipid dysregulation and ferroptosis in chondrocytes and the targeted therapy effect of metformin on osteoarthritis. J. Adv. Res.69, 515–529. 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.012
Summary
Keywords
osteoarthritis, AMPK signaling, targeted-therapeutics, molecular mechanisms, metabolic disorder
Citation
Chen L, Hu X-H, Wu X-Y, Zhang X, Han Y-X, Liu Y, Chen G-Y and Tao Q-W (2025) AMPK signaling in osteoarthritis: from mechanisms to targeted therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1681610. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1681610
Received
28 August 2025
Revised
10 October 2025
Accepted
15 October 2025
Published
07 November 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Dezhao Lu, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, China
Reviewed by
Eduardo Dominguez, University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain
Yuan Xingyu, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Chen, Hu, Wu, Zhang, Han, Liu, Chen and Tao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qing-Wen Tao, taoqg1@sina.com; Guang-Yao Chen, chenguangyao1994@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.