Abstract
Background:
Staphylea arguta (Lindl.) Byng & Christenh. [Staphyleaceae] (Staphylea arguta), a tree or shrub species belonging to the Staphyleaceae family, is widely distributed in subtropical regions of China, particularly in Jiangxi Province, where it is recognized as a geo-authentic botanical drug. It thrives in humid, shaded mountainous areas at elevations of 400–700 m. Traditionally, it has been used for treating breast abscesses, paralysis, sore throat, ulcers, and contusions. Despite its widespread use, systematic reviews on its phytochemistry and pharmacology are limited, and quality control remains challenging due to the lack of standardized markers. This review aims to summarize its metabolites and pharmacological activities, and predict potential quality markers (Q-markers) based on the “five principles” of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) quality control to address these research gaps.
Methods:
The metabolites and pharmacological activities of Staphylea arguta were reviewed using data retrieved from scientific databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). The “five principles” of TCM Q-markers, which include kinship and chemical specificity, traditional medicinal properties, traditional efficacy, metabolites measurability, and different origins, were applied to identify potential candidates for Staphylea arguta.
Results:
This review summarizes 451 metabolites from Staphylea arguta, including flavonoids, terpenoids, volatile oils and other metabolites, which exhibit anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and immunomodulatory effects. In addition, it is predicted that ligustroflavone (no.23), rhoifolin (no.24), corosolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (no.56), 23-hydroxyoleanolic acid (no.77), squalene (no.253), α-copaene (no.225), and additional identified metabolites can serve as Q-markers for Staphylea arguta.
Conclusion:
This comprehensive review not only consolidates the existing knowledge on Staphylea arguta but also proposes a foundation for its quality standardization. The identified Q-markers will facilitate the development of a robust quality control system, ensuring the safety and efficacy of Staphylea arguta-based products for clinical use. This work is significant for promoting the rational utilization and further development of this medicinal resource.

1 Introduction
Staphylea arguta (Lindl.) Byng & Christenh. [Staphyleaceae] (Staphylea arguta), locally known as Shanxiangyuan with aliases including Qiandachui (Thousand-Hammer), Qicunding (Seven-Inch Nail), and Eziyao (Moth Medicine), is a tree or shrub species of the genus Staphylea in the Staphyleaceae family (Institute of Botany, 1972; Commission, 2010). It is naturally distributed across East Asia, including China, Japan, and India, with a predominant presence in the subtropical regions of southern China. In China, it grows mainly in Jiangxi, Hunan, Hubei, Guangxi, and Guizhou provinces, typically in humid, shaded mountainous areas at elevations of 400–700 m. It is recognized as a geo-authentic botanical drug in Jiangxi Province (Wang et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2022). Staphylea arguta possesses medicinal value, with its main active metabolites including flavonoids, terpenoids, and volatile oils (Li et al., 2015). It is included in the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2010 edition) (Commission, 2010) and holds a significant position in both traditional and modern medicine. In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), the dried leaves are used to clear heat and detoxify (Qingre Jiedu), soothe the throat and reduce swelling (Liyan Xiaozhong), and activate blood circulation to alleviate pain (Huoxue Zhitong). It is clinically applied in the treatment of tonsillitis/pharyngitis, sore throat, skin abscesses, and traumatic injuries. Preparations derived from Staphylea arguta leaves include Staphylea arguta granules and Staphylea arguta baccal tablets. In folk practice, fresh leaves are decocted for oral administration to treat pharyngitis, acute and chronic tonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess, and upper respiratory tract infections, or crushed for topical application on boils and sores, demonstrating rapid efficacy (Li, 2007; Sun, 2008; Zhao et al., 2018; Liu, 2022). As documented in Flora of China, the leaves are applied externally to stop bleeding and heal wounds, or taken orally to treat traumatic injuries (Fang, 1981). Modern studies have confirmed its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory properties. Further research on its clinical therapeutic potential and value will enhance its added value and promote its utilization and development (Zhao et al., 2012; Duan and Gao, 2019; Zhang H. W. et al., 2025).
Academician Liu Changxiao proposed the Quality Markers (Q-markers) theory, which was developed by integrating traditional principles of medicinal properties, preparation methods for Chinese patent medicines, and clinical applications of botanical drugs. The Q-markers theory emphasizes the identification of multi-metabolite biomarkers that collectively reflect the quality, efficacy, and consistency of TCM materials and formulations. The theory is centered on the “The effectiveness of TCMs-the material basis for the quality control of the signature metabolites”. Furthermore, it offers research insights aimed at enhancing the efficacy and safety of TCM, as well as improving the quality standards of its products for clinical application (Liu et al., 2016; Zhang T. et al., 2025). To date, limited systematic reviews have been published on Staphylea arguta, with most focusing narrowly on specific metabolites or activities. No comprehensive review integrating phytochemical, pharmacological, and quality marker perspectives is available. This review aims to fill this gap by providing a holistic overview and proposing Q-markers to support quality standardization and further research.
2 Methods of data acquisition
A comprehensive literature search was conducted using the PubMed, Web of Science, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases. The search terms included: “Staphylea arguta (Lindl.) Byng & Christenh.“, “Staphylea arguta”, “Turpinia arguta Seem”, “Turpiniae Folium”, “Shanxiangyuan”, “T. arguta”, “Qiandachui”, “Qicunding”, “Eziyao”, “Turpinia”, and “Turpinia ternata”. The search was concluded on 1 February 2025. The criteria for admission and disqualification were as follows: (1) Traditional application and pharmacological research of Staphylea arguta; (2) The pharmacological mechanisms by which Staphylea arguta or its extracts exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, antibacterial, or analgesic effects; (3) Identification and structural elucidation of the metabolites of Staphylea arguta; (4) Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of chemical markers for the quality control of Staphylea arguta. Reviews, meta-analyses, case reports, and patents were excluded from the study. Based on the literature collected from the above-mentioned databases, including classic Chinese medicine books, all eligible studies were analyzed and summarized to predict the potential Q-markers of Staphylea arguta according to the “Five Principles” of TCM quality control.
3 Botanical characteristics
Staphylea arguta is an evergreen shrub (Figure 1A). Its fruit contains 2 to 26 seeds, with a thousand-seed weight of 20 g. The leaves are opposite and pinnately compound. The leaf axis is about 15 cm long, slender and green (Figure 1B). There are five leaflets, opposite, papery, oblong to oblong-elliptic, measuring (4-)5–6 cm in length and 2–4 cm in width. The leaf tip is caudate-acuminate with a slender tail measuring 5–7 mm, and the base is broadly cuneate. The margins bear sparse rounded teeth or serrations. Both surfaces are glabrous; the upper surface is green, while the lower surface is lighter in color (Figure 1B). There are numerous lateral veins, slightly visible on the upper side and distinct on the lower side. The reticulate veins are barely visible on both surfaces. The lateral leaflets have petiolules 2–3 mm long, while the central leaflet can have a petiolule up to 15 mm long, which is slender and green. The inflorescence is a terminal panicle, with a rachis up to 17 cm long. The flowers are numerous, loosely arranged, and small, about 3 mm in diameter (Figure 1C). The floral buds begin differentiation from late October to early March of the following year, with flowering occurring in mid-to-late March of the following year and the peak flowering period in early to mid-April. The entire differentiation process lasts for 5 months, proceeding centripetally from the outside inward, with the apical flower in the center of the inflorescence differentiating first. There are 5 sepals, glabrous, broadly elliptic, about 1.3 mm long. The petals are 5, elliptic to circular, pubescent or glabrous, about 2 mm long. The filaments are glabrous. The fruit is spherical, 4–7 mm in diameter, with a thin exocarp about 0.2 mm thick (Figure 1D). It has two to three locules, each containing one seed. The general propagation method is seed propagation (Figure 1E) (Li and Li, 2012).
FIGURE 1

Morphological characteristics of Staphylea arguta. (A) Shrub. (B) Leaves. (C) Flowers. (D) Fruits. (E) Seeds.
4 Phytochemistry
A total of 451 metabolites have been identified in Staphylea arguta, including 55 flavonoids (NO.1–55), 76 terpenoids (no.56–131), 46 phenolics (no.132–177), 17 megastigmanes (no.178–194), 9 tannins (no.195–203), 14 alkaloids (no.204–217), 7 phenylpropanoids (no.218–224), 67 volatile oils (no.225–291) and 160 additional identified metabolites (no.292–451). The names of specific metabolites are shown in Supplementary Table 1 of the Appendix.
4.1 Flavonoids
Flavonoids are the characteristic and primary active metabolites of Staphylea arguta, not only due to their high quantity and diversity but also because of their well-documented biological activities (Li et al., 2015). This class of metabolites includes flavonols, flavanones, isoflavones, and flavonoid glycosides which are classified according to their chemical structure. Argutosides A-E (no.7–11), hyperoside (no.22),ligustroflavone (no.23), rhoifolin (no.24), quercetin-3-O-robinobioside (no.25), and the new flavonoid apigenin-7-(2′-rhamnosyl) rotinoside (no.36) were identified from Staphylea arguta (Zhang et al., 2009a; Sun et al., 2012; Ma et al., 2018). The structures of some metabolites are shown in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2
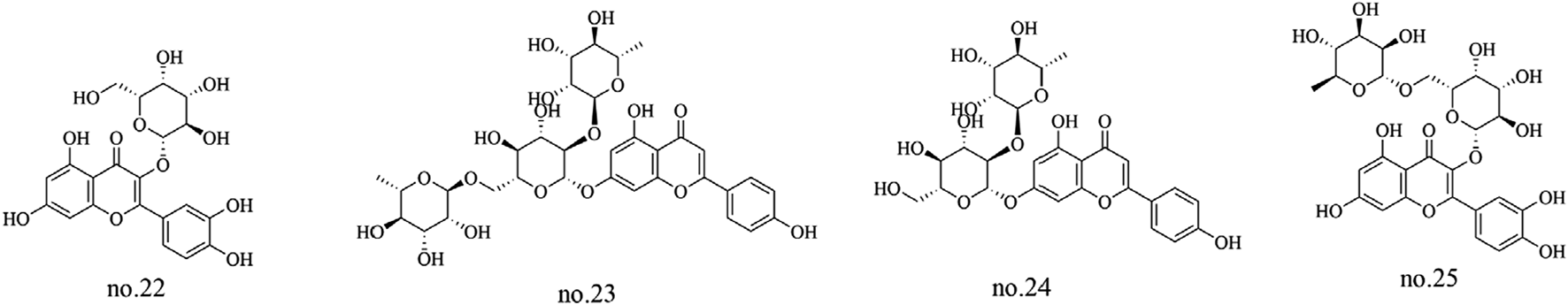
Chemical structure of some flavonoids in Staphylea arguta.
4.2 Terpenoids
Terpenoids represent a major class of natural products in Staphylea arguta, with structural diversity primarily encompassing triterpenes and their derivatives. Among the identified terpenoids, several triterpenic metabolites have been isolated and characterized, including corosolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside ester (no.56), 2α-peroxyhydroxy ursolic acid (no.60), pomolic acid (no.76), 23-hydroxyoleanolic acid (no.77), 2α,3α,23-trihydroxy ursolic acid (no.78), ursolic acid (no.79), and asiaticoside A (no.80) (Ma et al., 2013; Wu et al., 2012; Kuang et al., 2019). Additionally, 2α,3β,19β-23-tetrahydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid (no.75) were identified from Staphylea arguta (Huang et al., 2012). The structures of some metabolites are shown in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3

Chemical structures of some terpenoids in Staphylea arguta.
4.3 Phenolics
Based on their structural characteristics, phenolic metabolites can be categorized into phenols, phenylpropanoids, and others. Gallic acid ethyl ester (no.137), caffeic acid (no.138), syringin (no.140), chlorogenic acid methyl ester (no.141), chlorogenic acid butyl ester (no.142), methyl gallate (no.143) and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (no.144) were identified from Staphylea arguta (Wu, 2010; Li et al., 2013; Li et al., 2015). The structures of some metabolites are shown in Figure 4.
FIGURE 4

Chemical structure of some phenolics in Staphylea arguta.
4.4 Megastigmanes
Megastigmanes constitute a class of organic metabolites characterized by distinctive cage-like frameworks. 3S,5R,6R,9S-stetrahydroxy megastigmane (no.179), corchoionoside C (no.180), icariside B4 (no.181), turpinionosides A to E (no.182–186), megastigman-7-ene-3,5,6,9-tetrol-9-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (no.191), byzantionoside B6′-O-β-D-apiofuranoside (no.192), byzantionoside B (no.193) and megastigmene-3,6,9-triol (no.194) were identified from Staphylea arguta (Yu et al., 2002; Wu et al., 2014). The structures of some metabolites are shown in Figure 5.
FIGURE 5

Chemical structure of some megastigmanes in Staphylea arguta.
4.5 Tannins
Tannins are a class of polyphenolic metabolites, among which tannin glycosides are the predominant type isolated from Staphylea arguta. Specific metabolites identified include 4′-O-methyl ellagic acid-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (no.195), ellagic acid-3-O-β-D-glucoside (no.196) and ellagic acid-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (no.197) (Huang et al., 2012; Li et al., 2015). 3′-O-methyl ellagic acid 4-O-β-D-xylopyranoside (no.198), 3′-O-methylellagic acid 4-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (no.199),3,4′-di-O-methylellagic acid-4-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside (no.200), 3,3′-di-O-methylellagic acid-4′-O-α-D-glucopyranoside (no.201), ellagic acid (no.202) and 3-O-methylellagic acid (no.203) were identified from Staphylea arguta (Matthew et al., 2007; Huang et al., 2012). The structures of some metabolites are shown in Figure 6.
FIGURE 6
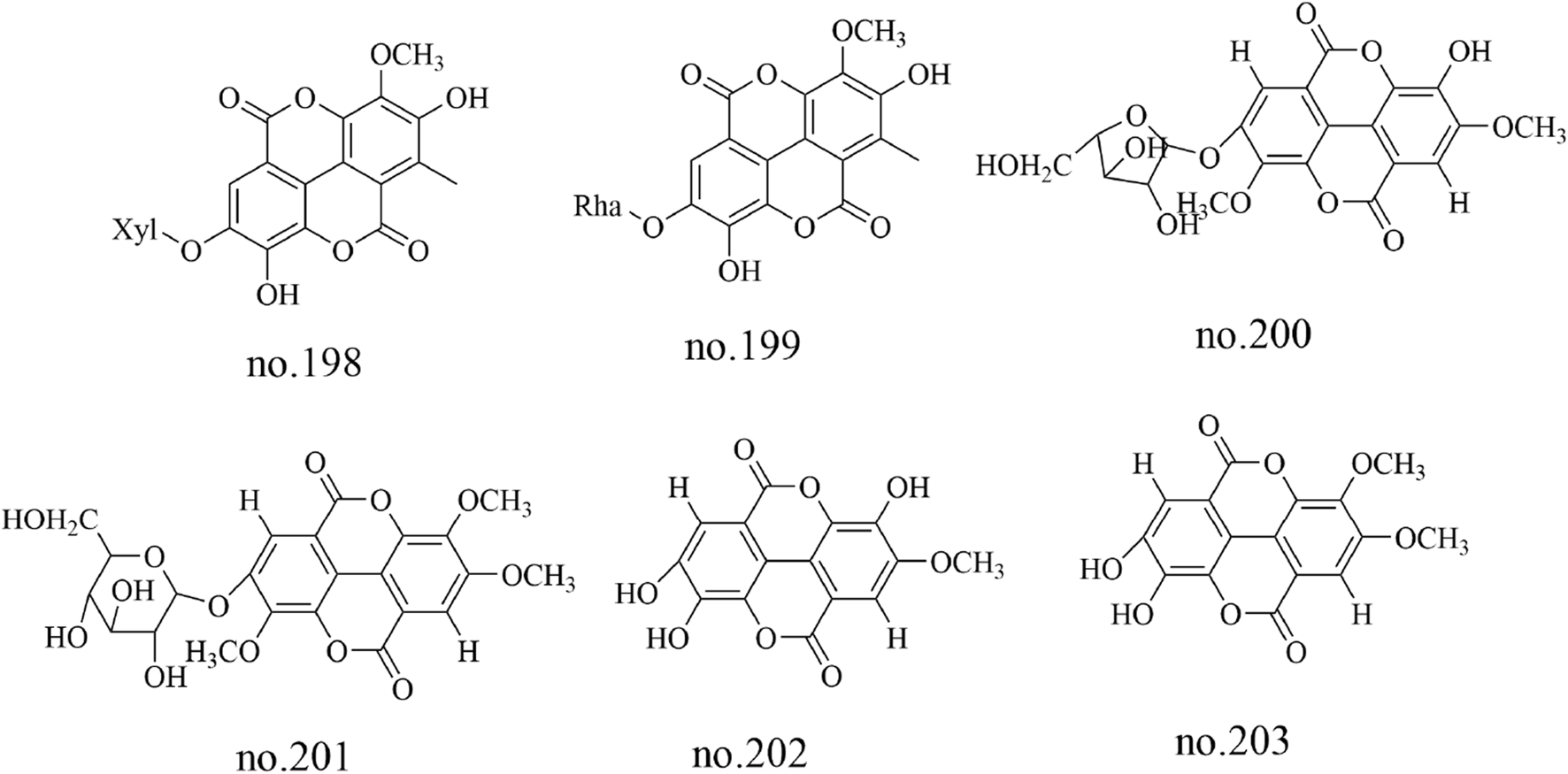
Chemical structure of some tannins in Staphylea arguta.
4.6 Alkaloids
Five alkaloids, including 11-methoxyjavaniside (204), vincosamide (205), (3R)-pumiloside (206), turpiniside (207), and paratunamide C (208), were isolated from Staphylea arguta (Wu et al., 2011). Liu et al. employed LC-MS to analyze the moderately polar metabolites in its volatile oil, identifying nine alkaloid metabolites including coniine (210), caffeine (211), and trigonelline HCl (212) (Liu et al., 2022). The structures of some metabolites are shown in Figure 7.
FIGURE 7
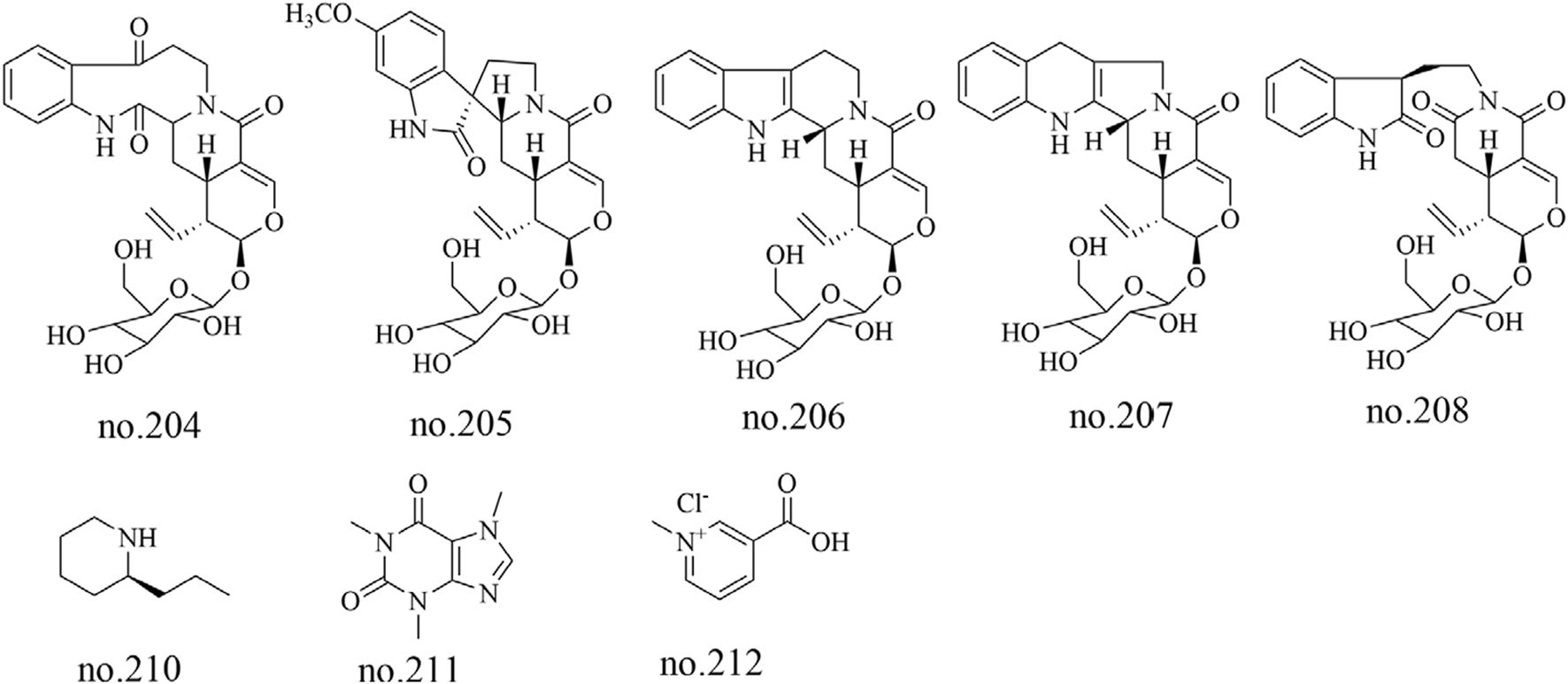
Chemical structure of some alkaloids in Staphylea arguta.
4.7 Phenylpropanoids
Phenylpropanoids, a diverse group of secondary metabolites, have been relatively sparsely documented in Staphylea arguta, with only seven such metabolites isolated and identified from the species to date: aesculetin (no.218), epiphyllocoumarin (no.219), cinchonain Ic (no.220), cinchonain Ia (no.221), categuanin B (no.222), turformosin A (no.223) and (−)-(7′S,8′S)-threo-carolignan X (no.224) (Wu, 2010; Huang et al., 2012). The structures of some metabolites are shown in Figure 8.
FIGURE 8
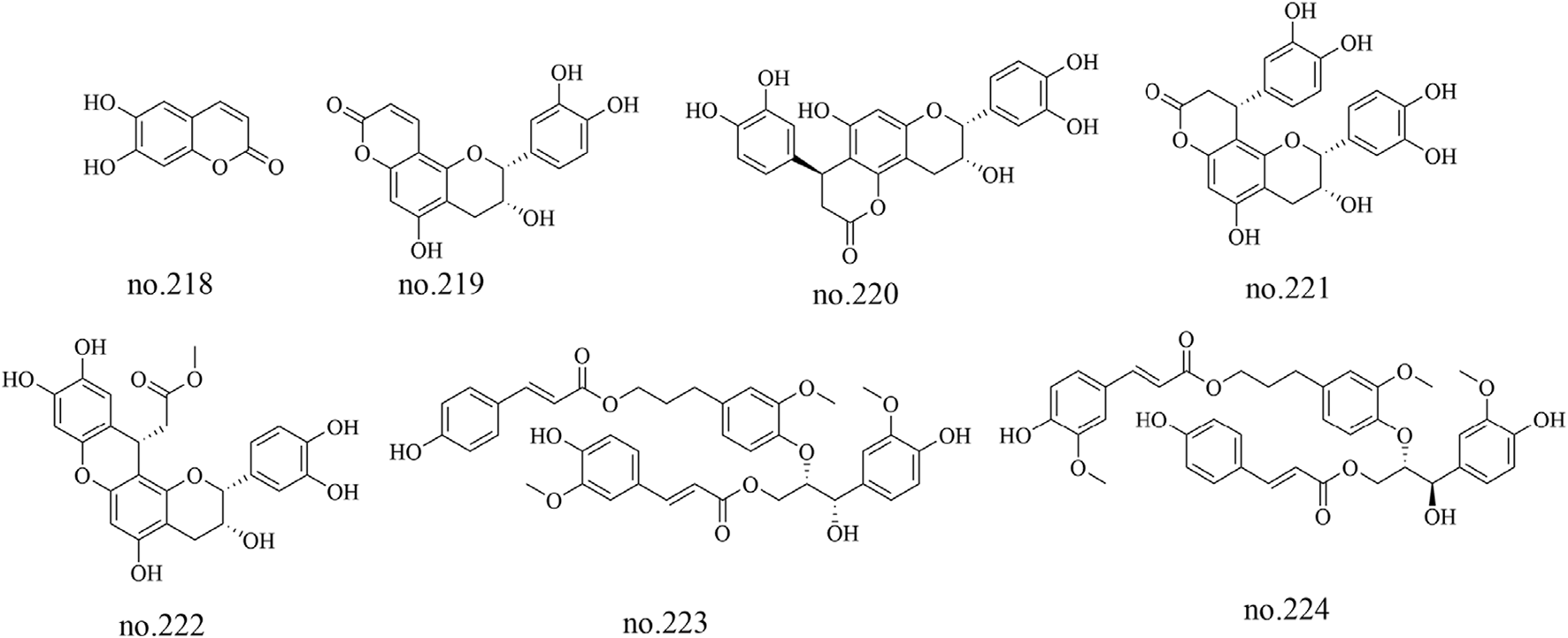
Chemical structure of some phenylpropenoids in Staphylea arguta.
4.8 Volatile oils
Volatile oils, commonly referred to as essential oils, are aromatic plant-derived liquids obtained mainly through distillation. Liu et al. extracted the volatile oil from Staphylea arguta, and identified 67 metabolites through GC-MS analysis of low polarity substances, as detailed in Supplementary Table 1 (no.225–291) (Liu et al., 2022).
4.9 Additional identified metabolites
In addition to the aforementioned metabolites, Staphylea arguta also contains fatty acids, coumarins, lactones, vitamins, and other metabolites. Liu et al. utilized LC-MS to analyze the moderately polar metabolites in the volatile oil extracted from Staphylea arguta. They identified fatty acid metabolites, including isopalmitic acid (no.292), oleic acid (no.293) and myristic acid (no.294), as well as coumarin metabolites such as phellopterin (no.335) and isoimperatorin (no.337) (Liu et al., 2022). The structures of some metabolites are shown in Figures 9, 10.
FIGURE 9

Chemical structure of some fatty acids in Staphylea arguta.
FIGURE 10
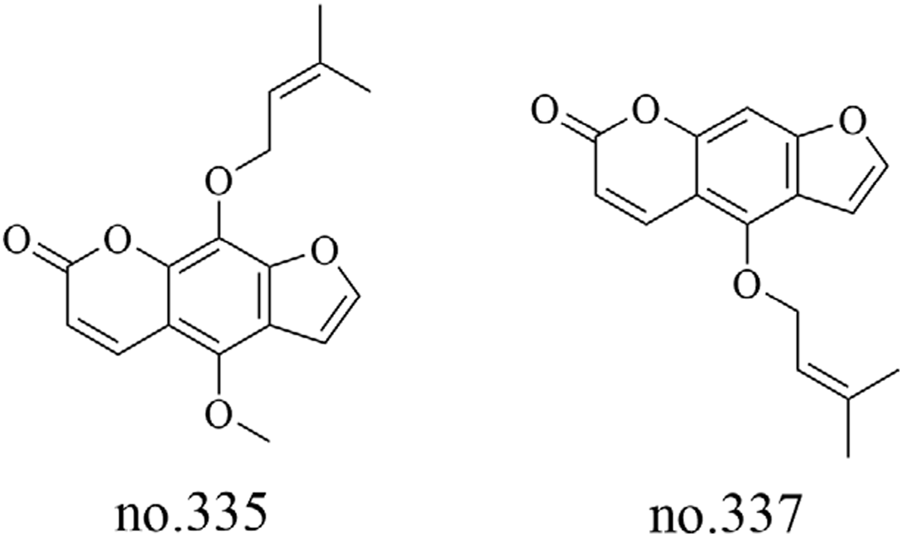
Chemical structure of some coumarins in Staphylea arguta.
5 Pharmacological effects
Modern pharmacological studies have demonstrated that Staphylea arguta exhibits a range of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, antibacterial, and analgesic effects (Figure 11). Metabolites with pharmacological activities include flavonoids, volatile oils, among others (Table 1).
FIGURE 11

Pharmacological effects of Staphylea arguta.
TABLE 1
| Activity | Sample | Model/Assay | Dosage | Effect/mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | Total flavonoids | Adjuvant arthritis rat model | 80, 160, 320 mg/kg | The flavonoids from Staphylea arguta can inhibit secondary swelling, polyarthritis, and pathological changes of ankle arthritis in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats | Zhang et al. (2008) |
| Total flavonoids | Chronic pharyngitis rat model | 0.208 g kg-1, 0.416 g kg-1, 0.832 g kg-1 | The total flavonoids from Staphylea arguta ameliorate pharyngeal histopathology in the model rats, downregulate the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and NF-κB p65, and upregulate the expression of IκBα | Chen et al., 2020; Wang (2020) | |
| Total flavonoids | Mouse monocyte-macrophage leukemic cells RAW 264.7 | 100, 200, 400 mg L-1 | The total flavonoids of Staphylea arguta inhibit the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK, and p38, and reduce the secretion of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 | Huang et al. (2019) | |
| Total flavonoids | Mouse monocyte-macrophage leukemic cells RAW 264.7 | 100, 200, 300 μg mL-1 | The anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids are mediated through the inhibition of NF-κB activity and suppression of iNOS and COX-2 expression | Chen et al. (2016) | |
| Antioxidant | Volatile oil | DPPH; ABTS | 0.25,0.5,1,2,4,6 mg mL-1 | The essential oil from the Staphylea arguta exhibits significant free radical scavenging activity against both DPPH and ABTS radicals | Liu et al. (2022) |
| Total flavonoids, total polysaccharides, polyphenols | GSH-Px | N/A | The extract from Staphylea arguta significantly enhanced the activity of GSH-Px | Song et al. (2022) | |
| Polysaccharides | Hydroxyl radical scavenging, DPPH radical scavenging | N/A | Staphylea arguta polysaccharides exhibited their potential as natural antioxidants | Yan et al. (2022) | |
| Immunomodulatory | Total flavonoids | Adjuvant arthritis rat model | 10−4, 10−5, 10−6, 10−7, 10−8 mg L-1 | The total flavonoids from Staphylea arguta regulate the abnormal immune function in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats | Zhang et al. (2007) |
| Total flavonoids | Adjuvant arthritis rat model | 80, 160, 320 mg kg-1 | The immunomodulatory effect on the body was related to balancing the T cell subsets | Zhang et al. (2008) | |
| Antibacterial | Staphylea arguta baccal tablets | Staphylococcus aureus intraperitoneal infection mouse model | 5, 10 g kg-1 | Staphylea arguta baccal tablets lowered the death rate in mice with Staphylococcus aureus infection | Zhan et al. (2005b) |
| Staphylea arguta baccal tablets | N/A | N/A | Staphylea arguta baccal tablets inhibit Streptococcus B | Luo et al. (2003) | |
| The extract of Staphylea arguta | In vitro experiment | N/A | The extract of Staphylea arguta exhibits an inhibitory effect on Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus aureus | Xiong et al. (2025) | |
| Analgesic | Staphylea arguta baccal tablets | Mouse acetic acid-induced writhing model | N/A | The analgesic rate of Staphylea arguta baccal tablets for pain induced by acetic acid injection into the abdominal cavity was 60.3% | Zhan et al. (2005a) |
Pharmacological effects of Staphylea arguta.
5.1 Anti-inflammatory effects
The anti-inflammatory effects of Staphylea arguta may be achieved through the inhibition of inflammatory cell activation and the reduction of inflammatory mediator release (Xu, 2011). Zhang et al. investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of total flavonoids extracted from Staphylea arguta through animal experiments, and the results demonstrated that these flavonoids could significantly suppress inflammatory responses (Zhang et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2008). Chen et al. and Wang et al. investigated the mechanism of action of total flavonoids from Staphylea arguta in the treatment of chronic pharyngitis. The results demonstrated that the anti-inflammatory mechanism was associated with the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) expression and reduction in nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor alpha (IκBα) dissociation, and downregulation of inflammatory factors such as Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), Interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) (Chen et al., 2020; Wang, 2020). Huang et al. investigated the effect of total flavonoids from Staphylea arguta on Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. The results demonstrated that the anti-inflammatory mechanism was associated with the inhibition of extracellular signal regulated protein kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38) phosphorylation levels as well as the reduction in TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 secretion (Huang et al., 2019). Chen et al. reported that total flavonoids from Staphylea arguta inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and NF-кB expression in RAW264.7 cells. The results demonstrated that the mechanism of its anti-inflammatory effect was associated with the downregulation of NF-кB activity and the suppression of iNOS and COX-2 expression (Chen et al., 2016).
5.2 Antioxidant effects
Staphylea arguta possess antioxidant properties. Liu et al. assessed the antioxidant effect of volatile oil of Staphylea arguta utilizing both 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydra-zyl radical (DPPH) and 2,2′-Azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthiazo-line-6-sulfonic acid), diammonium salt (ABTS) methods. The results indicate that the volatile oil of Staphylea arguta exhibits significant antioxidant properties. However, its scavenging ability towards ABTS radicals is comparatively weaker than that towards DPPH radicals (Liu et al., 2022). Song et al. investigated the effects of incorporating Staphylea arguta extract to diets on the antioxidant function of Wenchang chickens. The results demonstrated that the extract from Staphylea arguta significantly enhanced the activity of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and markedly reduced the serum IL-1β levels in Wenchang chickens (Song et al., 2022). Staphylea arguta polysaccharides exhibited significant hydroxyl radical scavenging, DPPH radical scavenging activities, suggesting their potential as natural antioxidants (Yan et al., 2022).
5.3 Immunomodulatory effects
Staphylea arguta possess immunomodulatory effects. Zhang et al. investigated the impact of total flavonoids from Staphylea arguta on immune function in rats with adjuvant arthritis. The results demonstrated that total flavonoids extracted from Staphylea arguta could enhance the compromised immune function of this model rats (Zhang et al., 2007). Zhang et al. studied the mechanism of action of total flavonoids from Staphylea arguta in the treatment of adjuvant arthritis. The results showed that the immunomodulatory effect on the body was related to balancing the T cell subsets (Zhang et al., 2008).
5.4 Antibacterial effects
Zhan et al. conducted antibacterial experiments on Staphylea arguta baccal tablets and found that they significantly reduced the mortality rate of mice infected with Staphylococcus aureus (Zhan et al., 2005b; Zhang H. W. et al., 2025). Luo et al. investigated the antibacterial effects of Staphylea arguta and demonstrated their ability to significantly inhibit Streptococcus B (Luo et al., 2003). Xiong et al. discovered in an in vitro study that the extract of Staphylea arguta exhibits an inhibitory effect on Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and S. aureus (Xiong et al., 2025).
5.5 Analgesic effects
Staphylea arguta possesses anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Zhan et al. investigated the effects of Staphylea arguta baccal tablets on pain responses induced by acetic acid injection into the abdominal cavity, hot plate tests, ear swelling and toe swelling caused by xylene, and increased abdominal capillary permeability due to H+. The results indicated that the analgesic rate of Staphylea arguta baccal tablets for pain induced by acetic acid injection into the abdominal cavity was 60.3% (Zhan et al., 2005a).
6 Research status of Q-markers
Current research in the quality control of TCM comprehensively considers multiple factors, including the growing environment, geographical origin, metabolites, and pharmacological effects of botanical drugs. The complex nature of TCM constitutes the core challenge in quality control studies, as it contains numerous metabolites, each potentially critical to its therapeutic efficacy. Therefore, rapid profiling of crude botanical drug extracts using liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry enables metabolite identification; gas chromatography-mass spectrometry facilitates the analysis of volatile metabolites such as essential oils and fatty acids; isolation and purification of individual metabolites are achieved through techniques like column chromatography and preparative liquid chromatography, followed by precise structural elucidation using nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry. Academician Liu Changxiao proposed the innovative concept of “Q-marker”, which is based on five principles - kinship and chemical specificity, traditional medicinal properties, traditional efficacy, metabolites measurability, and different origins - providing a novel framework for quality control TCM (Liu et al., 2016). Building on this, Gao et al. integrated the clinical applications and pharmacological effects of Shenling Baizhu San, utilizing the five core principles of Q-markers to predict potential Q-markers for this botanical drug in the treatment of respiratory diseases (Gao et al., 2025). Similarly, Luo et al. combined phytochemical and pharmacological studies of the Miao medicine Tiekuaizi, applying the same principles to identify its potential Q-markers (Luo et al., 2024). This comprehensive approach has significantly enhanced the scientific rigor and applicability of quality assessment in TCM.
7 Q-markers prediction analysis
TCM contains a complex and diverse array of metabolites, with clinical efficacy often resulting from synergistic interactions among them. Consequently, quality control based on single-metabolite indicators is insufficient for botanical drugs. The 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia currently designates only ligustroflavone (no.23) and rhoifolin (no.24) as quality control markers for Staphylea arguta, which inadequately reflects its comprehensive quality profile (Commission, 2020). To address the limitations of existing quality standards, this study aims to identify potential Q-markers for Staphylea arguta based on the Q-marker concept proposed by Academician Liu Changxiao (Liu et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2024), which encompasses five core principles: kinship and chemical specificity, traditional medicinal properties, traditional efficacy, metabolites measurability, and different origins. The objective is to establish a scientifically robust quality evaluation system for this botanical drug (Figure 12).
FIGURE 12
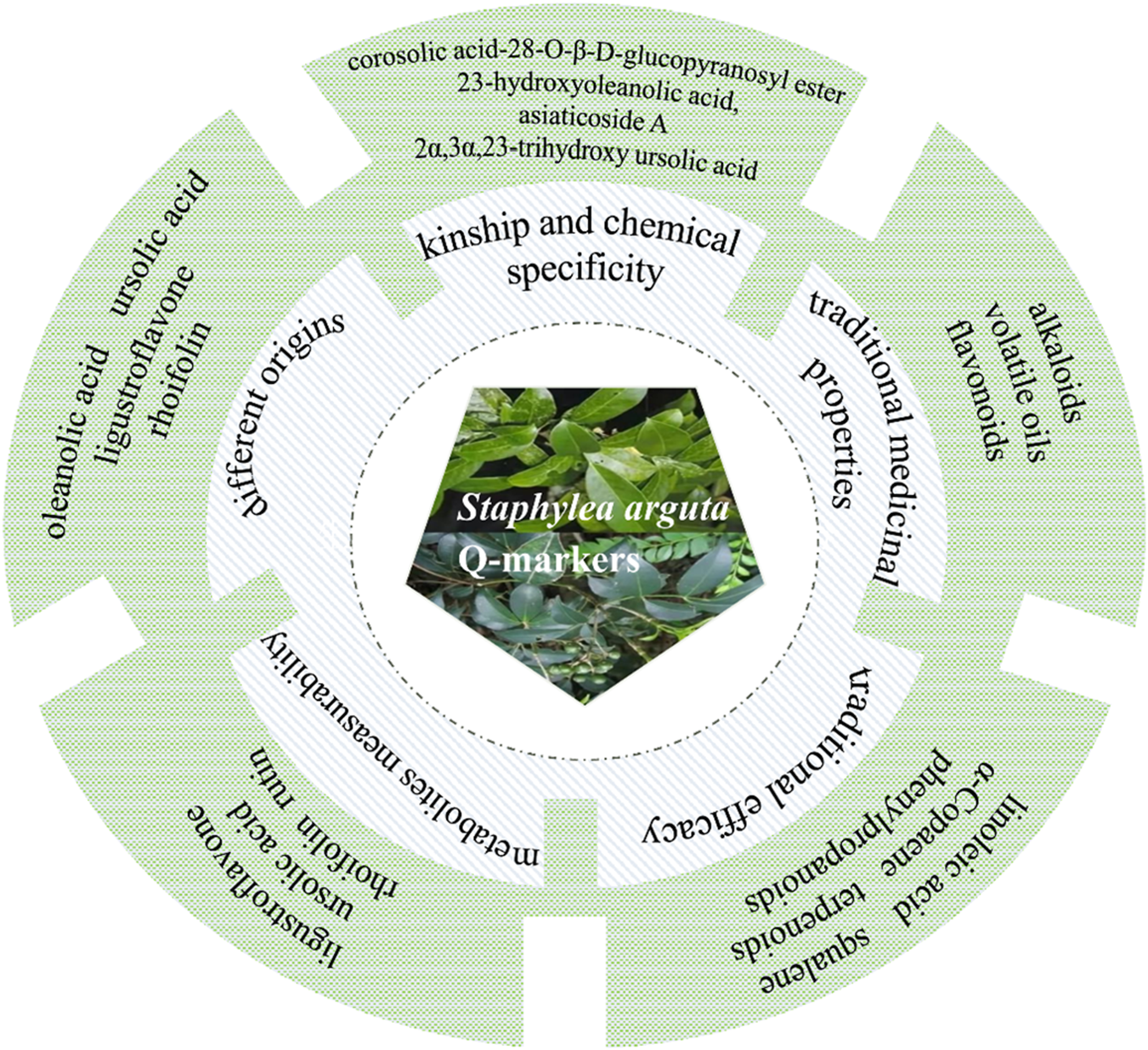
Q-markers prediction analysis of Staphylea arguta.
7.1 Q-markers prediction based on kinship and chemical specificity
Staphylea arguta belongs to the genus Staphylea within the Staphyleaceae family. The family Staphyleaceae includes the genera Tapiscia Oliv., Staphylea Linn., Euscaphis Sieb. et Zucc., and Turpinia Vent., among others, with approximately 60 species (Duan and Gao, 2019). In China, the Staphyleaceae family comprises four genera and 22 species. These species are found across the country, with a higher concentration in southwestern regions. The genus Staphylea comprises approximately 30–40 species, predominantly distributed across Japan, North America, India, Sri Lanka, and other regions, with 13 species identified in China. The plants within the genus Staphylea are abundant in a diverse array of metabolites, primarily comprising flavonoids, terpenoids, phenylpropanoids, volatile oils, and other metabolites. Staphylea arguta also contains flavonoids, terpenoids, and other metabolites, which exhibit pharmacological activities including anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, analgesic, and immunomodulatory effects (Xiao et al., 2019). It has been reported that several metabolites, including corosolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (no.56), 23-hydroxyoleanolic acid (no.77), asiaticoside A (no.80), 2α,3α,23-trihydroxy ursolic acid (no.78), caffeic acid (no.138), 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (no.144), 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (no.165), and chlorogenic acid (no.145) have been isolated from Staphylea arguta for the first time (Li et al., 2015; Kuang et al., 2019). Among these metabolites, corosolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (no.56), 23-hydroxyoleanolic acid (no.77), asiaticoside A (no.80), and 2α,3α,23-trihydroxy ursolic acid (no.78) are reported for the first time within the Staphyleaceae family. These metabolites can be considered distinctive markers that differentiate Staphylea arguta from other genera within the same family. In summary, based on the above Kinship and Chemical Specificity, the following metabolites of Staphylea arguta can be regarded as Q-markers: corosolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (no.56), 23-hydroxyoleanolic acid (no.77), asiaticoside A (no.80), and 2α,3α,23-trihydroxy ursolic acid (no.78).
7.2 Q-markers prediction based on the traditional medicinal properties
The four natures (cold, hot, warm and cool) and five flavors (spicy, sweet, sour, bitter, and salty) constitute the fundamental attributes of TCM. These findings are the outcomes of extensive clinical practice and in-depth investigation, systematically summarizing the properties and therapeutic effects of botanical drugs. Hence, the characteristics of TCM are pivotal in the identification and screening of Q-markers. According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 Edition), Staphylea arguta is considered to have a cold nature and a bitter taste, and it is classified as belonging to the lung and liver meridians (Commission, 2020). According to TCM, Staphylea arguta is used to clear heat, detoxify, relieve sore throat, and reduce swelling. TCM theory suggests that botanical drugs with a bitter taste, such as Staphylea arguta, possess properties that can drain, dry, and strengthen-effects consistent with heat-clearing and detoxifying functions. Bitter-tasting heat-clearing botanical drugs typically contain metabolites such as alkaloids, volatile oils, and flavonoids (Wu and Zhang, 2011; Lv et al., 2022). The flavonoid metabolite rhoifolin (no.24), as a representative metabolite of Staphylea arguta with bitter-cold property and lung meridian tropism, exerts anti-inflammatory effects through dual mechanisms. Fang et al. established a lipopolysaccharide-induced acute inflammation model in mice to investigate the effects of rhoifolin (no.24) on pathological damage in lung and liver tissues (Fang et al., 2020). Results demonstrated that rhoifolin (no.24) promoted the recovery of liver and lung injuries in acute inflammatory mice and significantly inhibited the secretion of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in serum of rat and mouse models. Cellular experiments revealed that 100 μmol/L rhoifolin (no.24) markedly enhanced cell viability, suppressed the production of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, downregulated mRNA expression of iNOS and C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), and inhibited phosphorylation of IκBα and IκB kinase beta (IκKβ). This mechanism is highly consistent with the traditional “heat-clearing and detoxifying” efficacy. In summary, based on the traditional medicinal properties of Staphylea arguta, its alkaloids, volatile oils, and flavonoids are potential candidates for its Q-markers.
7.3 Q-markers prediction based on the traditional efficacy
The established efficacy of traditional medicine serves as the fundamental premise for clinical pharmacotherapy and the cornerstone for ensuring safe drug utilization. “Medicinal properties” and “pharmacodynamic effects” collectively constitute the fundamental elements of the therapeutic efficacy of TCM. The Q-marker theory of TCM proposes a research model based on the ternary relationship of “property-efficacy- metabolite” and the holistic expression of efficacy (Figure 13) (Zhang T. et al., 2025). Staphylea arguta possesses the effects of clearing heat and detoxifying, alleviating sore throat and reducing swelling, as well as promoting blood circulation to relieve pain. It is extensively utilized in the treatment of sore throat, ulcerated sore throat, carbuncles and swellings due to toxic heat, as well as traumatic injuries (Zhao et al., 2012; Duan and Gao, 2019). Modern research indicates that linoleic acid (no.240) and squalene (no.253) in Staphylea arguta have protective effects on the cardiovascular system (Hildreth et al., 2020; Marangoni et al., 2020; Saini and Rai, 2020). Alpha-Copaene (no.225) demonstrates significant antibacterial and neuroprotective properties (Khoshnazar et al., 2020; Šimunović et al., 2020). Squalene (no.253) exhibits hepatoprotective, renocortical protective, and antitumor properties (Liu et al., 2022). Terpenoids exhibit neuroprotective properties (Suárez Montenegro et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021). While phenylpropanoids show promising therapeutic potential for neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, and associated neuroinflammation (Kolaj et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2019). In summary, linoleic acid (no.240), squalene (no.253), α-Copaene (no.225), terpenoids, and phenylpropanoids constitute the material foundation upon which Staphylea arguta exerts its clinical efficacy. These metabolites can be considered as potential Q-markers for Staphylea arguta.
FIGURE 13
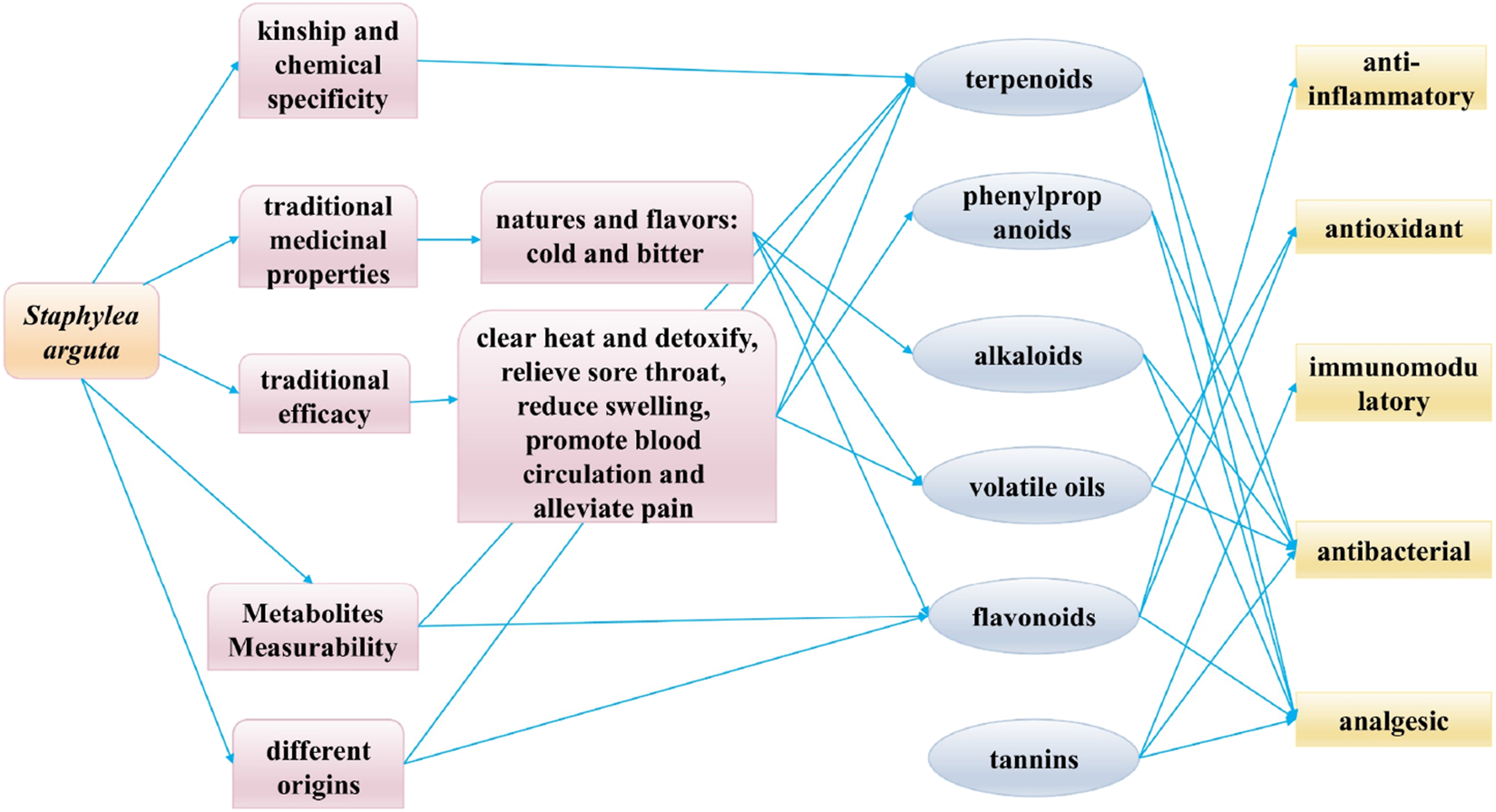
Connections between traditional properties, modern pharmacology, and Q-markers in Staphylea arguta.
7.4 Q-markers prediction based on the metabolites measurability
Staphylea arguta is rich in a diverse array of metabolites, and the measurability of these parameters serves as a critical foundation for identifying the Q-markers of TCM. Identifying the active metabolites provides a more comprehensive understanding of the material foundation underlying its pharmacological effects (Liu et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2019). The Chinese Pharmacopoeia specifies the analytical methods and limit requirements for ligustroflavone (no.23) and rhoifolin (no.24) in Staphylea arguta (Commission, 2020). To achieve more comprehensively control the quality of Staphylea arguta, numerous researchers have chosen methods such as high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis) for quantitative analysis of Staphylea arguta. Liang et al. employed HPLC to quantify the concentration of ligustroflavone (no.23) (Liang et al., 2023). Zhu et al. utilized HPLC to quantify the ursolic acid (no.79) content in Staphylea arguta (Zhu et al., 2009). Zhang et al. utilized HPLC to concurrently quantify the concentrations of ligustroflavone (no.23) and rhoifolin (no.24) in Staphylea arguta baccal tablets baccal tablets (Zhang et al., 2009b). Luo et al. employed UV-Vis spectroscopy to quantify the rutin (no.55) content in Staphylea arguta and Staphylea arguta oral liquid. The results demonstrated that the aforementioned methods are not only facile to implement but also exhibit superior reproducibility, thereby serving as a valuable reference for the quality control of this botanical drug (Luo et al., 2002a; Luo et al., 2002b). In summary, based on the distinct characteristics of ligustroflavone (no.23), ursolic acid (no.79), rhoifolin (no.24), and rutin (no.55) in Staphylea arguta, appropriate methods for determining these characteristic metabolites can be developed, and they can be considered as potential Q-markers for Staphylea arguta.
7.5 Prediction of Q-markers from different origins based on bioactive metabolites
The quality of botanical drugs varies among different growing regions due to factors such as temperature, humidity, soil composition, and other environmental conditions (Bao et al., 2025). Therefore, controlling the key factors that influence the quality of Staphylea arguta is of great significance for ensuring the quality of this botanical drugs. Li et al. utilized HPLC to analyze and compare the content differences of oleanolic acid (no.131) and ursolic acid (no.79) in crude leaf extracts of Staphylea arguta collected from 30 different producing areas in Jiangxi, Hunan, Hubei, Guangxi, and other regions. The results indicated that the leaves from Meijiang Town, Xiushan County, Chongqing; Anyuan, Jiangxi; Yudu, Jiangxi; and Taiping Town, Songtao, Guizhou exhibited the highest levels of these two terpenoid metabolites (Li et al., 2022). Xu et al. utilized HPLC to analyze the fingerprint of ligustroflavone (no.23) and rhoifolin (no.24) in crude extracts of Staphylea arguta from different sources and found that selecting the common peaks with stable retention time and peak area from each batch to calibrate the fingerprint resulted in a robust chromatographic system, and ligustroflavone (no. 23) could be used as an evaluation index for germplasm resources (Xu and Li, 2017). Liu et al. investigated the concentrations of ligustroflavone (no.23) and rhoifolin (no.24) in crude extracts of Staphylea arguta from 10 producing areas and found that the cultivation site with the highest content was the Anyuan base of Jiangxi Shanxiang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., which was far higher than the content standards in the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (Liu et al., 2012). Yang et al. utilized HPLC to determine the content of ellagic acid (no.202) in crude extracts of Staphylea arguta from 10 producing areas and found that the content in the medicinal material produced in Chongqing, Hunan, Hubei, and other regions was higher than that in Jiangxi and Fujian (Yang et al., 2014). Oleanolic acid (no.131), ursolic acid (no.79), ligustroflavone (no.23), rhoifolin (no.24), and ellagic acid (no.202) exhibit content variations correlated with different geographical origins, demonstrating their measurability. Furthermore, oleanolic acid (no.131), ursolic acid (no.79), ligustroflavone (no.23), and rhoifolin (no.24) have been confirmed to associate with traditional medicinal properties and efficacy, supporting their selection as Q-markers.
8 Conclusion and perspectives
Staphylea arguta represents a medicinally significant plant with considerable therapeutic potential. This review consolidates current knowledge on its phytochemical diversity, pharmacological activities, and Q-marker prediction. A total of 451 metabolites have been identified, encompassing flavonoids, terpenoids, phenolics, and volatile oils, which collectively underpin its broad pharmacological effects. Notably, the plant demonstrates anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, antibacterial, and analgesic properties, supporting its traditional uses. Guided by the Q-marker framework, several specific metabolites-including ligustroflavone (no.23), rhoifolin (no.24), corosolic acid-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (no.56), 23-hydroxyoleanolic acid (no.77), squalene (no.253), and α-copaene (no.225)-have been proposed as potential Q-markers based on their kinship and chemical specificity, traditional medicinal properties, traditional efficacy, metabolites measurability, and different origins. These Q-markers establish a scientific foundation for the quality control and standardization of Staphylea arguta. By identifying metabolites with strong specificity, well-defined efficacy, and measurability as potential Q-markers, this research enables precise quality assessment of TCM. Ultimately, this will contribute to the selection of optimal cultivation regions and ensure batch-to-batch consistency, which proves crucial for developing reliable botanical drugs and validating their traditional applications.
Despite these advances, several research gaps remain. Future studies should prioritize: expanding phytochemical characterization to less-explored metabolites such as alkaloids and phenylpropanoids using advanced UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS techniques; elucidating unresolved mechanisms, particularly the molecular targets for immunomodulatory and antibacterial effects; investigating multi-metabolite synergistic effects and conducting robust in vivo pharmacokinetic and dose-response studies to validate efficacy and safety; applying network pharmacology, molecular docking, and PBPK modeling to predict multi-target mechanisms and in vivo behavior of potential Q-markers. Addressing these aspects will be crucial for advancing the clinical and pharmaceutical application of Staphylea arguta, ultimately supporting its standardization and integration into evidence-based TCM.
Statements
Author contributions
HC: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. ZW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. CF: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XT: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. JY: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Basic Research and Talent Special Project of Jiangxi Academy of Forestry Sciences (2022511603); Major Science and Technology R&D Special Project of Jiangxi Province (20233AAE02017); National Natural Science Foundation of China (32360409); Science and Technology Innovation Project of Jiangxi Forestry Bureau (Innovation Special Project [2023] No. 1); Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Scientific and Technological Innovation Team Development Program (CXTD22007); Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Graduate Innovation Fund Project (XJ-B202501).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1684371/full#supplementary-material
References
1
BaoS. L.TaiB. D. L. H.ChunX.BaoL. M. (2025). Research progress on Gymnadenia conopsea and predictive analysis of its quality markers. West China J. Pharm. Sci.40 (1). 10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2025.01.018
2
ChenS. H.ZengX.LiangH.HuangP. B.CaoL. (2016). The effect of total flavonoids from Turpinia arguta seem on iNOS and COX-2 expression in LPS- stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Lishizhen Med. Materia Medica Res.27 (11), 2629–2631.
3
ChenS. H.DongD. G.WangS. J.LiM. Q.HuM. M.HuangP. B. (2020). The effect of total flavonoids from Turpinia arguta seem on NF-κB and IκBα expression in chronic pharyngitis model rats. J. Jiangxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 44 (3), 259–262. 10.16357/j.cnki.issn1000-5862.2020.03.08
4
CommissionC. P. (2010). Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing, China: China Medical Science and Technology Press.
5
CommissionC. P. (2020). Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing, China: China Medical Science and Technology Press.
6
DuanJ. L.GaoB. W. (2019). Advances in chemical constituent and pharmacology of medicinal plants of Staphyleaceae. Ginseng Res.31 (1), 52–60. 10.19403/j.cnki.1671-1521.2019.01.013
7
FangW. P. (1981). “Flora of China,”, 46. Beijing: Science Press, 27–37.
8
FangJ.CaoZ.SongX.ZhangX.MaiB.WenT.et al (2020). Rhoifolin alleviates inflammation of acute inflammation animal models and LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells via IKKβ/NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation43 (6), 2191–2201. 10.1007/s10753-020-01286-x
9
GaoZ.WangT.FuL.WuQ.WangY.WuZ.et al (2025). Clinical application, potential pharmacological targets and quality marker prediction of a TCM formulation used (shenling baizhu san) in the treatment of respiratory diseases. Front. Pharmacol.16, 1575903. 10.3389/fphar.2025.1575903
10
HildrethK.KodaniS. D.HammockB. D.ZhaoL. (2020). Cytochrome P450-derived linoleic acid metabolites EpOMEs and DiHOMEs: a review of recent studies. J. Nutr. Biochem.86, 108484. 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108484
11
HuangH. C.ChiouC. T.HsiaoP. C.LiawC. C.ZhangL. J.ChangC. L.et al (2012). Cytotoxic phenylpropanoids and a new triterpene, turformosinic acid, from Turpinia formosana nakai. Molecules17 (2), 1837–1851. 10.3390/molecules17021837
12
HuangP. B.WangS. J.LiangH.ShenS. H.CaoL. (2019). Effects of the total flavones from Turpinia arguta seem on MAPK signal pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Lishizhen Med. Materia Medica Res.30 (8), 1863–1865.
13
Institute of Botany (1972). “Iconographia Cormophytorum Sinicorum,”. Beijing: Science Press, Vol. 2, 691.
14
KhoshnazarM.ParvardehS.BigdeliM. R. (2020). Alpha-pinene exerts neuroprotective effects via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis.29 (8), 104977. 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104977
15
KolajI.Imindu LiyanageS.WeaverD. F. (2018). Phenylpropanoids and alzheimer's disease: a potential therapeutic platform. Neurochem. Int.120, 99–111. 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.08.001
16
KuangL.XiaoC. R.TuL. F.WuY. M.ZhangR. Z.LiuD. P.et al (2019). Chemical constituents from the leaves of Turpinia arguta. J. Chin. Med. Mater.42 (11), 2570–2573. 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2019.11.019
17
LiY. Q. (2007). Studies on the chemical constituents of Capparis himalayensis and Terpinia arguta. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College.
18
LiP. Q.LiY. C. (2012). Flora of Shenzhen. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, Vol. 3, 32.
19
LiL.ZhaoY.LiuW.FengF.XieN. (2013). HPLC with quadrupole TOF-MS and chemometrics analysis for the characterization of Folium Turpiniae from different regions. J. Sep. Sci.36 (15), 2552–2561. 10.1002/jssc.201300360
20
LiH. T.WuX. M.LinF. X.LuoY. M. (2015). Studies on the chemical constituents of Turpinia arguta Seem. Proceedings of 2015 5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 2015), 269–272. 10.2991/ICIMM-15.2015.46
21
LiY. F.LiuM. Y.DengS. B.WangZ. W.WangZ.HuangB. F.et al (2022). Determination of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in the turpiniae folium from different habitats by HPLC. J. Jiangxi Univ. Chin. Med.34 (3), 73–76.
22
LiangD. S.LuoH. T.HuangF.LiQ. (2023). Preparation of active ingredients in Shanxiangyuan and establishment of quality standards for HPLC determination. China Surfactant Deterg. and Cosmet.53 (1), 115–120.
23
LiuZ. B. (2022). Clinical observation on self-made Shanxiang Yuanye decoction in the treatment of chronic pharyngitis. Chin. Med. Mod. Distance Educ. China20 (20), 99–101.
24
LiuD. F.LiZ. Y.ChengF.WenH. L.LiaoG. H.YangX. L. (2012). Quality evaluation of Turpinia Arguta leaves from different habitats. Lishizhen Med. Materia Medica Res.23 (2), 476–477.
25
LiuC. X.ChenS. I.XiaoX. H.ZhangT. J.HouW. B.LiaoM. l. (2016). A new concept on quality marker of Chinese materia medica: quality control for Chinese medicinal products. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs47 (9), 1443–1457.
26
LiuC. X.ChengY. Y.GuoD. A.ZhangT. J.LiY. Z.HouW. B.et al (2017). A new concept on quality marker for quality assessment and process control of Chinese medicines. Chin. Herb. Med.9 (1), 3–13. 10.1016/s1674-6384(17)60070-4
27
LiuZ.LiL.TangY. Q. N.LinL. M.XiaB. H. (2022). Chemical composition, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of volatile oil from turpiniae folium. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev.34 (5), 723–738. 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2022.5.001
28
LiuS.ZhuX. L.SunG. Y.DongY. (2024). Screening of galangal quality markers based on taste information and ultra performance liquid chromatography. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm.39 (4).
29
LuY.LiuY.LiuX. Y.FengZ. K. (2022). Development status of genuine characteristic medicinal materials in Jiangxi province. J. Jiangxi Univ. Chin. Med.34 (6), 120–124.
30
LuoX. T.XiongY. X.YuS. P. (2002a). Determination of flavonoids content in Turpinia arguta leaves by UV spectrophotometry. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio-Cerebrovascular Dis. (5), 48–49.
31
LuoX. T.YuS. P.XiongY. X. (2002b). Study on the determination of flavonoids content in Turpinia arguta oral liquid. Strait Pharm. J. (4), 49–50.
32
LuoX. T.ChenL. H.LiC. (2003). Study on process for Shanxiangyuan baccal tablet. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. (4), 18–20.
33
LuoL. Y.ZhangX. D.MeiH. M.MaJ. H.PengX.DongM. H.et al (2024). Miao medicine tiekuaizi (radix Chimonanthi): a review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and predictive analysis on quality markers. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1491585. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1491585
34
LvJ. H.ZhuC.TangZ. X. (2022). Formation mechanism and biological significance of bitterness in traditional Chinese medicine. J. Guangxi Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 40 (5), 324–331. 10.16088/j.issn.1001-6600.2021100801
35
MaS. G.YuanS. P.HouQ.LiY.ChenX.YuS. S. (2013). Flavonoid glycosides from leaves of Turpinia arguta and their anti-inflammatory activity. China J. Chin. Materia Medica38 (11), 1747–1750.
36
MaS. G.YuanS. P.LiuY. B.QuJ.LiY.WangX. J.et al (2018). 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl flavone glycosides from the leaves of Turpinia arguta. Fitoterapia124, 80–85. 10.1016/j.fitote.2017.10.017
37
MarangoniF.AgostoniC.BorghiC.CatapanoA. L.CenaH.GhiselliA.et al (2020). Dietary linoleic acid and human health: focus on cardiovascular and cardiometabolic effects. Atherosclerosis292, 90–98. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.11.018
38
MatthewS.KaoK. C.ChangY. S.AbreuP. (2007). Ellagic acid glycosides from Turpinia ternata. Nat. Prod. Res.21 (1), 83–88. 10.1080/14786410500441516
39
SainiS.RaiA. K. (2020). Linoleic acid inhibits the release of Leishmania donovani derived microvesicles and decreases its survival in macrophages. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol.10, 406. 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00406
40
ŠimunovićK.SahinO.KovačJ.ShenZ.KlančnikA.ZhangQ.et al (2020). (-)-α-Pinene reduces quorum sensing and Campylobacter jejuni colonization in broiler chickens. PLoS One15 (4), e0230423. 10.1371/journal.pone.0230423
41
SongW. J.SongQ. L.ZouZ. H.ChenX. L.LiuL. X.TanJ.et al (2022). Effects of turpiniae folium extract on growth Performance,Serum immune and antioxidant function and intestinal microflora of Wenchang chickens. Chin. J. Animal Nutr.34 (7), 4380–4393. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.5461.S.20220429.1150.004.
42
Suárez MontenegroZ. J.Álvarez-RiveraG.Sánchez-MartínezJ. D.GallegoR.ValdésA.BuenoM.et al (2021). Neuroprotective effect of terpenoids recovered from olive oil By-Products. Foods10 (7), 1507. 10.3390/foods10071507
43
SunJ. Y. (2008). Research on the chemical constituents and biological activities of Nauclea officinalis and Turpinia arguta. Shandong: Shandong University.
44
SunJ. Y.SunJ.WuH. Y.LiuK. (2012). Studies on the chemical constituents of turpiniae folium. Food Drug14 (5), 162–165.
45
WangS. J. (2020). Anti-chronic pharyngitis effect of total flavonoids from Turpinia arguta seem and its mechanism. Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine. 10.27180/d.cnki.gjxzc.2020.000242
46
WangY. L.CuiT.LiY. Z.LiaoM. l.ZhangH. B.HouW. B.et al (2019). Prediction of quality markers of traditional Chinese medicines based on network pharmacology. Chin. Herb. Med.11 (4), 349–356. 10.1016/j.chmed.2019.08.003
47
WangX. Y.ZhangL.CaoL.LiangF. (2020). ISSR analysis of genetic relationship and population structure of Turpinia arguta fresh leaves in Jiangxi province. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae26 (15), 150–155. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20201046
48
WuM. (2010). Study on the chemical constituents of Gentiana loureiroi and Turpinia arguta. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
49
WuA. Z.ZhangY. T. (2011). Discussion on the medicinal properties of bitter herbs and their compatibility effects. Inn. Mong. J. Tradit. Chin. Med.30 (7), 85–86. 10.16040/j.cnki.cn15-1101.2011.07.047
50
WuM.WuP.XieH.WuG.WeiX. (2011). Monoterpenoid indole alkaloids mediating DNA strand scission from Turpinia arguta. Planta Med.77 (3), 284–286. 10.1055/s-0030-1250239
51
WuM.ZhaoG. C.WeiX. Y. (2012). Triterpenoids from the leaves of Turpinia arguta. J. Trop. Subtropical Bot.20 (1), 78–83.
52
WuM.WuP.WeiX. Y. (2014). Megastigmans from Turpinia arguta. Chem. Nat. Compd.50 (4), 772–773. 10.1007/s10600-014-1081-y
53
XiaoC. R.TuL. F.ZhangR. Z.LiuD. P.LuoY. M. (2019). Research progress on chemical constituents and biological activities from turpinia species. China J. Chin. Materia Medica44 (7), 1295–1304. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190118.011
54
XiongP. W.SongW. J.ChenJ.SongQ. L.AiG. X.ZouZ. H.et al (2025). Study on optimization of extraction process of total flavonoids from turpiniae folium and in vitro antibacterial activity. Feed Res.48 (5), 107–114. 10.13557/j.cnki.issn1002-2813.2025.05.019
55
XuZ. H. (2011). Comparison effect on treating of upper respiratory infections with turpinia particles and yanning particles. Clin. J. Chin. Med.3 (5), 42–43.
56
XuL. F.LiP. (2017). Study on the fingerprint of Turpinia arguta seen medicinal materials with high performance liquid chromatography. Chin. Med. Mod. Distance Educ. China15 (22), 143–145.
57
YanJ.ZhaoL. J.LiY. M.ZhangZ. M.LinL. M.XiaB. H. (2022). Preparation and characterization of polysaccharides from turpiniae folium and its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory activities and antiproliferative effect on VSMCs. Chem. Biodivers.19 (11), e202200459. 10.1002/cbdv.202200459
58
YangX. L.LiuD. F.LiuW.XieN.ChengF.LiuP.et al (2014). Separaction and dertermination of ellagic acid from Turpinia arguta. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae20 (10), 54–57. 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2014100054
59
YangS. M.MeiJ. H.JiangR.YangX. L. (2021). Research progress of tetracyclic triterpenes in nervous disorders. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev.33 (12), 2157–2167. 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2021.12.020
60
YuQ.OtsukaH.HirataE.ShinzatoT.TakedaY. (2002). Turpinionosides A-E: megastigmane glucosides from leaves of Turpinia ternata nakai. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo)50 (5), 640–644. 10.1248/cpb.50.640
61
ZhanY. F.ZhangJ. J.ChenJ. T.MaoY. C.WangS. Z. (2005a). Studies on the analgesia effect of Shangxiangyuan baccal tablet. Lishizhen Med. Mat. Res.16 (5), 389–390.
62
ZhanY. F.ZhangJ. J.MaoY. C.MaoX. M. (2005b). Experimental study on the antibacterial effect of Turpinia arguta lozenge. J. Jiangxi Univ. Chin. Med. (2), 55.
63
ZhangL.LiJ.YuS. C.JinY.LvX. W.PengL. (2007). Effect of total flavonoids of turpinia arguta seen on immune function in adjuvant arthritis rats in vitro. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. (1), 106–110.
64
ZhangL.LiJ.YuS. C.JinY.LvX. W.ZouY. H.et al (2008). Therapeutic effects and mechanisms of total flavonoids of Turpinia Arguta seen on adjuvant arthritis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol.116 (1), 167–172. 10.1016/j.jep.2007.11.027
65
ZhangG. W.ZhouG. P.XieE. L.TangX. B.ZhangH. (2009a). Research on flavonoids in the leaves of Turpinia arguta. China J. Chin. Materia Medica34 (12), 1603–1604.
66
ZhangG. W.ZhouG. P.YangX. J.XieE. L. (2009b). HPLC simultaneous determination of ligustroflavone and rhoifolin in Shanxiangyuan tablets. Chin. J. Pharm. Analysis29 (6), 912–914.
67
ZhangS.HuangY.LiY.WangY.HeX. (2019). Anti-neuroinflammatory and antioxidant phenylpropanoids from Chinese olive. Food Chem.286, 421–427. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.031
68
ZhangH. W.LiuD. F.TaoX. H.ChenJ.XiaS. Q. (2025a). Study on extraction process optimization and composition of antifungal substances from Turpinia arguta. South China For. Sci.53 (2), 59–65. 10.16259/j.cnki.36-1342/s.2025.02.011
69
ZhangT.BaiG.LiuC. (2025b). Innovation theory, technical methods and industrial application of quality marker of traditional Chinese medicine. Chin. Herb. Med.17 (1), 84–86. 10.1016/j.chmed.2024.12.001
70
ZhaoJ.YaoM.LiuX. H.WuY. Z.LiX.LiW. J.et al (2012). Overview of pharmacological research on Turpinia vent. J.Anhui Agr Sci.40 (11), 6435–6436+6438. 10.13989/j.cnki.0517-6611.2012.11.074
71
ZhaoL. X.XiaB. H.LinL. M.XiongS. H.TangJ.LiaoD. F. (2018). Optimization of ultrasound-assisted enzymatic polysaccharide extraction from Turpiniae Folium based on response surface methodology. Digit. Chin. Med.1 (3), 239–246. 10.1016/S2589-3777(19)30031-X
72
ZhuJ. H.ZhangZ. B.YanR. M.ZengQ. G.ZhuD. (2009). Determination of ursolic acid content in Turpinia arguta by HPLC. Lishizhen Med. Materia Medica Res.20 (4), 827–828.
Summary
Keywords
Staphylea arguta (Lindl.) Byng & Christenh, traditional Chinese medicine, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality marker
Citation
Cui H, Wei Z, Feng C, Tao X and Yi J (2025) Research progress on phytochemistry and pharmacology of Staphylea arguta (Lindl.) Byng & Christenh. and prediction of quality markers: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1684371. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1684371
Received
12 August 2025
Accepted
29 September 2025
Published
15 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Irina Ielciu, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hatieganu, Romania
Reviewed by
Satyajit Mohanty, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, India
Namita Khantwal, Hemwati Nandan Bahuguna Garhwal University, India
Umer Younas, The University of Lahore, Pakistan
Fathi Abdellatif Belhouadjeb, Centre de recherche en agropastoralisme, Algeria
Olusesan Ojo, University of South Africa, South Africa
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Cui, Wei, Feng, Tao and Yi.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianfeng Yi, jianfeng_yi21@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.