Abstract
Objective:
To investigate the efficacy of anlotinib, an antiangiogenic multikinase inhibitor, as an add-on therapy to first-line epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine-kinase inhibitor (TKI) for patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who were previously untreated before first-line EGFR TKI but subsequently developed oligoprogression.
Methods:
This multicenter, retrospective cohort study (ALTER-L058) analyzed data from the electronic health records-derived de-identified systems at 16 cancer centers in China. Adult patients between 18 and 75 years of age with histologically or cytologically confirmed locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who received first-line third-generation EGFR TKI monotherapy and had an oligoprogressive disease were included. Eligible patients received anlotinib (8, 10 or 12 mg) on days 1–14 of each 3-week cycle for ≥6 cycles. Tumor response was assessed radiologically by investigators per RECIST, version 1.1. The primary outcome was investigators-assessed progression-free survival, calculated from the date of medication initiation for the oligoprogressive disease to the first documented progressive disease or death.
Results:
Between January 2020 and December 2023, 100 patients received EGFR TKI plus anlotinib and 50 received EGFR TKI. At the data cutoff (20 November 2024), the median progression-free survival was 9.23 months (95% CI, 8.94–10.87) with EGFR TKI plus anlotinib versus 5.42 months (95% CI, 4.83–6.80) with EGFR TKI (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.38, 95% CI, 0.26–0.56; log rank test, P < 0.0001), meeting the primary endpoint. Anlotinib was generally well tolerated, with manageable adverse events.
Conclusion:
Anlotinib, when added onto EGFR TKI therapy following gradual progression or oligo-progression, conferred significant PFS benefits upon EGFR mutant NSCLC patients, supporting adding anlotinib to ongoing first-line EGFR TKI therapy for oligoprogressive disease.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer is the most prevalent cancer, accounting for one in eight cancer cases worldwide, and remains a principal cause of cancer death in both sexes globally (Bray et al., 2024). China is experiencing an increasing burden of lung cancer cases, with approximately 1,060,600 new cases and 733,300 deaths in 2022, accounting for 21.98% of new cancer cases and 28.49% of cancer deaths in China (Han et al., 2024). Activating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations exon 19 deletions (ex19del) and exon 21 L858R mutations make up 85%–90% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cases (Gazdar, 2009). Targeting actionable oncogenic driver alterations, which occur in approximately 60% of lung cancer cases, remains a cornerstone in targeted therapy for NSCLC (Hanna et al., 2020).
The advent of EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs) is paradigm changing for the treatment of EGFR mutant NSCLC patients. Currently, third-generation EGFR TKIs, which are marked for their potent central nervous system (CNS) penetrance, are the standard-of-care (SOC) first-line treatment for advanced-stage EGFR-mutant NSCLC (Cheng et al., 2024; Soria et al., 2018; Ramalingam et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2022). In China, apart from osimertinib, furmonertinib, a pan-EGFR TKI with CNS antitumor activity, and aumolertinib, formerly almonertinib, an oral EGFR-TKI that is selective for mutant EGFR over wild-type EGFR, have demonstrated efficacy for EGFR mutated NSCLC and were approved in China for the treatment of locally advanced, metastatic NSCLC with confirmed EGFR T790M mutation whose disease has progressed during or after EGFR TKI therapy (Shi et al., 2022; Bao et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2020). However, in untreated EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients, third-generation EGFR TKIs only lead to a modest gain in overall survival (OS) compared to first-generation EGFR TKIs. In addition, the median progression-free survival (PFS) of EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients is less than 2 years (Ramalingam et al., 2020) with first-line third-generation EGFR TKIs and disease progression eventually ensues. Two major patterns of progression after initial response to systemic therapy have been reported (systemic progression and oligoprogression): in contrast to widespread metastases involving multiple sites (polymetastatic disease), patients may exhibit different kinetics of disease progression and have a controlled primary tumor and 1 to 5 metachronous metastases (Hellman and Weichselbaum, 1995; Niibe and Hayakawa, 2010; Niibe and Chang, 2012; Xu et al., 2021). A retrospective analysis of 148 EGFR mutant advanced NSCLC patients across 13 Swiss centers showed that 77% experienced oligoprogressive disease following treatment with first line osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR TKI, and they had a longer OS than patients who had systemic progressive disease (Schuler et al., 2024). In the multicenter, real-world FLOWER Study in Italy, 44 of 126 EGFR mutant advanced NSCLC patients had disease progression and 20.1% of them had oligoprogression and 54.5% had systemic progression (Lorenzi et al., 2022). In the multicenter, real-world Reiwa Study in Japan, 344 (59.0%) of 583 EGFR mutant advanced NSCLC patients had disease progression and 20.1% of them had oligoprogression and 54.5% patients who received first-line osimertinib developed progressive disease and 156 (45.4%) of them had oligoprogressive disease (Watanabe et al., 2024).
As oligoprogressive disease is characterized by localized progression of a maximum of three to five metastatic lesions while the primary disease and lesions in other areas remain under control or stable (Patel et al., 2019), its treatment goals and treatment strategies are different from systemic progressive disease. Local ablative radiotherapy with or without systemic therapy, continuation of systemic therapy or combination therapy may be pursued depending on the oligometastatic disease state and the treatment goals (Guckenberger et al., 2020; Iyengar et al., 2023; Lim, 2021). In the Reiwa Study, approximately half (49.5% [77/156]) of the patients with oligoprogressive disease continued osimertinib therapy. Emergence of resistance to third-generation EGFR TKI is one of the major causes of treatment failure and resistance mechanisms involve EGFR-dependent and independent pathways (Cooper et al., 2022). The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-VEGF receptor (VEGFR) signaling pathway plays a key role in driving oncoangiogenesis in lung cancer. Dual blockade of EGFR and VEGF-VEGFR signaling represents a promising therapeutic strategy in the treatment of EGFR mutant NSCLC patients with oligoprogressive disease given extensive crosstalk between these pathways in oncoangiogenesis and drug resistance (Zhou et al., 2025; Choi et al., 2022). Several retrospective studies have explored bevacizumab for EGFR mutant NSCLC patients who had oligoprogressive disease after first-line EGFR TKI therapy, but with rather limited data on third-generation EGFR TKI(Long et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2022).
Unlike bevacizumab that only targets the VEGFR signaling pathway, anlotinib is an oral multikinase inhibitor (MKI) that simultaneously suppresses VEGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and c-Kit (Shen et al., 2018; Lin et al., 2018). Currently, it is approved in China as third and later-line treatment for advanced NSCLC based on the results of the ALTER 0303 trial (Han et al., 2018). An exploratory subgroup analysis of this trial showed that anlotinib significantly improved PFS and OS of patients with both sensitive EGFR mutations and wild-type EGFR (Zhao et al., 2022). The clinical activities of anlotinib in EGFR mutant NSCLC patients with oligoprogressive disease following first or second-line EGFR TKI therapy were explored in the single arm phase 2 ALTER-L001 trial showing that the addition of anlotinib to EGFR TKI therapy led to a median PFS of 9.1 months and an overall response rate (ORR) of 6.7% (Chen et al., 2025). Meta-analytic evidence indicates that combining anlotinib with docetaxel improves response and PFS in advanced NSCLC, supporting the feasibility of multi-agent anlotinib-based regimens (Hetta et al., 2025c). Numerous trials also showed effective anlotinib-containing combination regimens, such as anlotinib combined with PD-1 blockades (Chu et al., 2025; Shi et al., 2025), anlotinib plus third generation EGFR TKI (Wang et al., 2025) have shown promising efficacy in terms of improved survival outcomes. Recent pharmacological reviews further elucidate the multitarget and microenvironment-modulating actions of anlotinib that can potentiate EGFR-TKI efficacy (Hetta et al., 2025b). In a retrospective study of 121 EGFR mutant NSCLC patients with gradual progression following first-line EGFR TKI, the addition of anlotinib extended the median PFS by 3 months over EGFR TKI alone (6.7 vs. 3.6 months, P < 0.001) (Xiang et al., 2024).
Oligo-progression is seldomly evaluated as a study endpoint in clinical trials. To augment insight from the ALTER-L001 trial and to increase evidence on the choice of anlotinib as an add-on therapy to ongoing systemic therapy in the context of primary treatment, we carried out this real-world study to investigate the efficacy and safety of anlotinib for the treatment of EGFR mutant NSCLC patients who developed gradual or oligo-progression while on first-line third-generation EGFR TKI therapy. This is the first real-world, multicenter Chinese cohort specifically evaluating anlotinib with third-generation EGFR-TKIs in oligoprogressive NSCLC.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Ethics
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Shanghai East Hospital, the lead institution (2024YS-252). No patient consent was required given the nature of the retrospective study. Patient data were anonymized in this report.
2.2 Cohort selection
This retrospective, real-world cohort study utilized data from the electronic health records-derived de-identified systems at 16 cancer centers in China. De-identified patient-level structured data such as demographics and unstructured data including disease characteristics, treatment, treatment response and survival outcomes were curated via technology-enabled chart abstraction. Adult patients between 18 and 75 years of age with histologically or cytologically confirmed locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who received first-line third-generation EGFR TKI monotherapy between January 2020 and December 2023 (≤2 cycles of intercalating chemotherapy were allowed) and had a gradual progression or oligoprogressive disease were included. Gradual progression was defined as a controlled primary tumor for ≥6 months with EGFR TKI monotherapy, no target lesion progression (non-target lesion progression and/or newly developed metastases), and no deterioration of clinical symptoms (Chen et al., 2025). Oligo-progression was defined as a controlled primary tumor for ≥3 months with EGFR TKI monotherapy, progression limited to ≤5 sites (solitary extracranial lesion or intracranial lesion confined within the radiation field), and no deterioration of clinical symptoms. For the convenience of this report, gradual progression and oligoprogression are referred to as oligoprogressive disease. Other eligibility criteria were evidence of an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status score of 0–1, at least one measurable lesion per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1 within the preceding 3 months, EGFR mutations, including EGFR 19del and exon 21 L858R (exon 20ins excluded), based on local testing or reports from a non-participating hospital.
Patients were ineligible if they had primary resistance to third-generation EGFR TKIs (<3 months of treatment) or if they had dramatic progression, defined as a controlled primary tumor for ≥3 months with EGFR TKI monotherapy, rapid deterioration in clinical symptoms, and marked target lesion progression in comparison with the preceding assessment (Chen et al., 2025), during first-line third-generation EGFR TKI monotherapy. Other exclusion criteria were the presence of druggable targets such as MET amplification and EGFR C797X mutation, and small cell lung cancer (including mixed small cell lung cancer and NSCLC).
Patients with a controlled primary tumor for ≥3 months with a third-generation EGFR TKI who had a gradual progression or oligoprogressive disease continued to receive the EGFR TKI at the same dose and schedule at the discretion of the investigators. In addition, eligible patients should have received oral anlotinib (8, 10 or 12 mg; Chia-tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) on days 1–14 of each 3-week cycle for ≥6 cycles and have radiological data. Patients who received concurrent or sequential systemic therapy including chemotherapy or antiangiogenic therapy with bevacizumab were excluded.
2.3 Assessments and outcomes
Tumor response was assessed radiologically by investigators per RECIST, version 1.1; PFS was calculated from the date of medication initiation for the primary disease (PFS2) or the oligoprogressive disease (PFS) to the first documented progressive disease or death, whichever occurred earlier. The primary outcome of the study was investigators-assessed PFS. The secondary outcomes included ORR, defined as the proportion of patients who had a complete or partial response as their best overall response to anlotinib, disease control rate, defined as the proportion of patients who had a complete or partial response or a stable disease, and OS, defined as the time from the date of medication initiation for gradual or oligo-progression to the date of death of any cause.
Adverse events (AEs) were monitored using the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 5.0 (NCI CTCAE 5). The occurrences, frequencies, and severities of treatment-related (TRAEs) were tabulated, and all AEs were described using the latest version of MedDRA preferred terms and CTCAE grade.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Based on literature, the median PFS was 3.1(Park et al., 2016), 5.4 (Soria et al., 2015) and 5.4 months (Soria et al., 2015), respectively, for patients who were treated with single agent erlotinib, an EGFR TKI plus platinum-containing doublet regimen, or standard platinum-containing doublet regimen after emergence of resistance to EGFR TKIs. In the ALTER-L001 trial, the median PFS was 9.2 months for patients with gradual, local or oligo-progression who were treated with anlotinib with continued EGFR TKI therapy (Chen et al., 2025). Based on previous studies and the ALTER-L001 trial (Soria et al., 2015; Park et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2025), a target sample size of 150 was anticipated that would provide 82% power with a one-sided α of 0.05, corresponding to a median PFS of 9.2 months and 5.4 months for the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group (100 patients) and the EGFR TKI group (50 patients), respectively.
Efficacy was based on the full analysis set (FAS) that included all patients who met the study eligibility criteria. PFS and other time-to-event end points were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method and the corresponding 95% CIs were calculated and compared using log-rank test. The ORR and disease control rate, along with their two-sided 95% CIs, were estimated for each group using the Clopper-Pearson method and compared by Chi-square test or Fisher exact test.
The safety set included all patients who met the study eligibility criteria and had postbaseline safety data. AEs were summarized using descriptive statistics.
Statistical analysis was done using SAS 9.4 (The SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
3 Results
3.1 Patient characteristics
Between January 2020 and December 2023, 712 patients were screened for eligibility and 150 patients were eligible for the study, including 100 in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and 50 in the EGFR TKI group (Figure 1). The patients had a median age of 59 years and 38.0% were male. Most patients (95.3%) had clinical stage IV disease. Forty-four (29.3%) patients had brain metastasis. Ninety-five (63.3%) patients in the overall population had EGFR ex19del mutation and 55 (36.7%) harbored EGFR ex21L858R mutation. Prior third generation EGFR TKI therapy included osimertinib (76.0% [114/150]), aumolertinib (14.7% [22/150]) and furmonertinib (9.3% [14/150]). The demographic and baseline characteristics were well balanced between the two groups (Table 1).
FIGURE 1
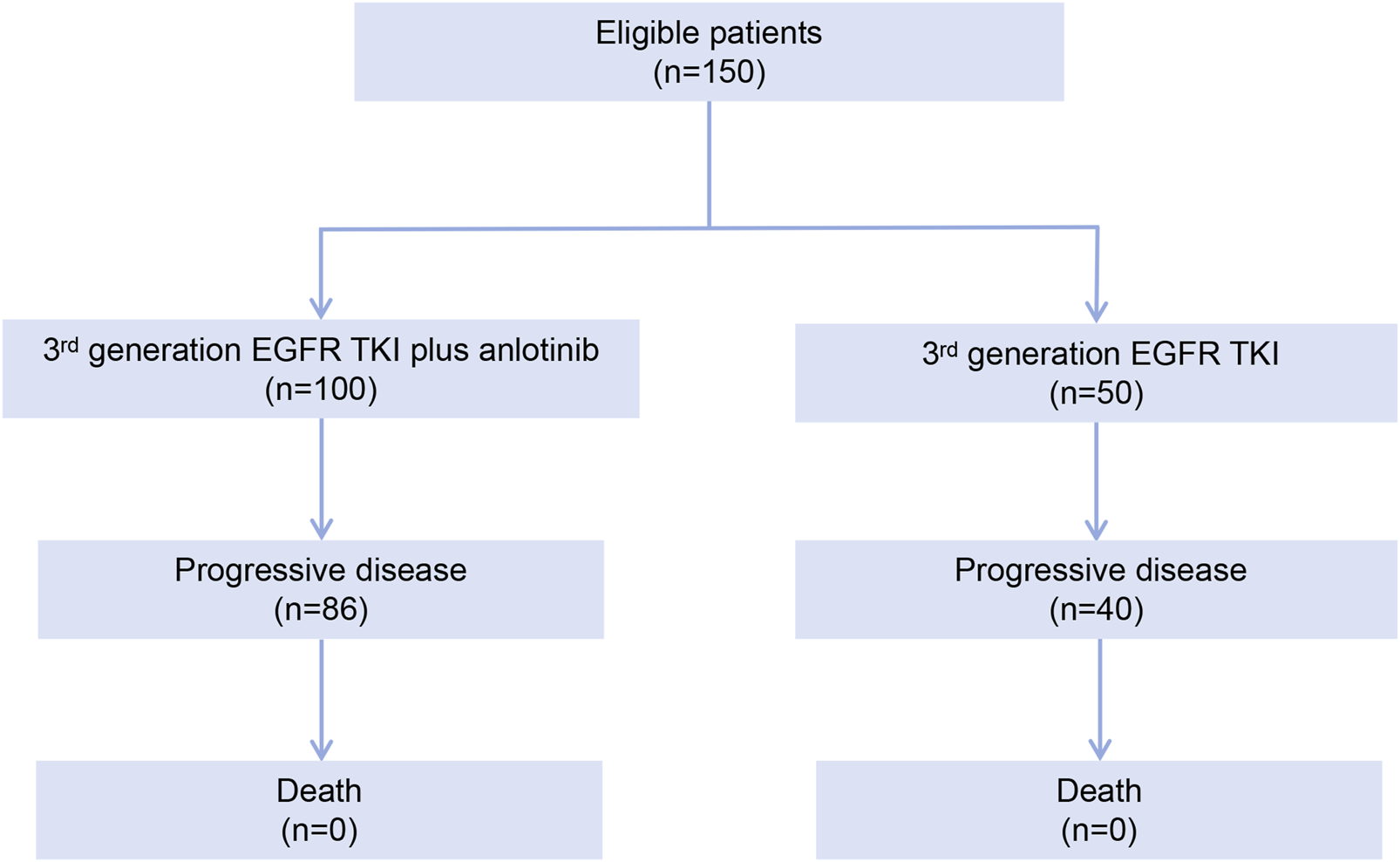
Patient disposition flowchart.
TABLE 1
| Characteristic | EGFR TKI plus anlotinib (n = 100) | EGFR TKI (n = 50) | P a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR), years | 59 (53–64) | 62 (52–67) | P = 0.163 |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 38 (38.0) | 19 (38.0) | P = 1.000 |
| Female | 62 (62.0) | 31 (62.0) | |
| Pathologic types | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 99 (99.0) | 50 (100.0) | P > 0.999 |
| Adenosquamous carcinoma | 1 (1.0) | 0 (0) | |
| Smoking status | |||
| Never smokers | 70 (70.0) | 36 (72.0) | P = 0.895 |
| Former smokers | 27 (27.0) | 12 (24.0) | |
| Current smokers | 3 (3.0) | 2 (4.0) | |
| ECOG performance status score | |||
| 0 | 23 (23.0) | 11 (22.0) | P = 0.888 |
| 1 | 77 (77.0) | 39 (78.0) | |
| EGFR mutational status | |||
| Exon 19 deletion | 63 (63.0) | 32 (64.0) | P = 0.920 |
| L858R | 37 (37.0) | 18 (36.0) | |
| Tumor staging | |||
| IIIB | 5 (5.0) | 2 (4.0) | P > 0.999 |
| IV | 95 (95.0) | 48 (96.0) | |
| CNS metastases | |||
| Yes | 29 (29.0) | 15 (30.0) | P = 0.888 |
| No | 71 (71.0) | 35 (70.0) | |
| Third-generation EGFR TKI | |||
| Osimertinib | 77 (77.0) | 37 (74.0) | P = 0.956 |
| Aumolertinib | 14 (14.0) | 8 (16.0) | |
| Furmonertinib | 9 (9.0) | 5 (10.0) | |
Patient baseline characteristics.
Data are expressed as number (%) unless otherwise indicated.
Two independent sample t-test for continuous variables; Fisher exact test for categorical variables.
Definitions:
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance-status scores range from 0 to 5, with higher numbers indicating increasing impairment in activities of daily living.
Never smokers, defined as smoking <100 cigarettes/lifetime; former smokers, defined as abstinence from smoking for at least 15 years on the day before the start of therapy; current smokers, defined as smoking >100 cigarettes/lifetime, or smoking >100 cigarettes/lifetime but abstinence from smoking for less than 1 year on the day before the start of therapy for oligoprogressive disease.
3.2 Efficacy
A total of 86 and 40 investigators-confirmed PFS events occurred from the date of medication initiation for the oligoprogressive disease to the data cutoff date (20 November 2024) in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and the EGFR TKI group, respectively. The median PFS was 9.23 months (95% CI, 8.94–10.87 months) in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group versus 5.42 months (95% CI, 4.83–6.80 months) in the EGFR TKI group, meeting the primary study endpoint (Figure 2a). The addition of anlotinib to EGFR TKI led to a 62% reduction in the risk of progression (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.38, 95% CI 0.26–0.56; log rank test, P < 0.0001).
FIGURE 2
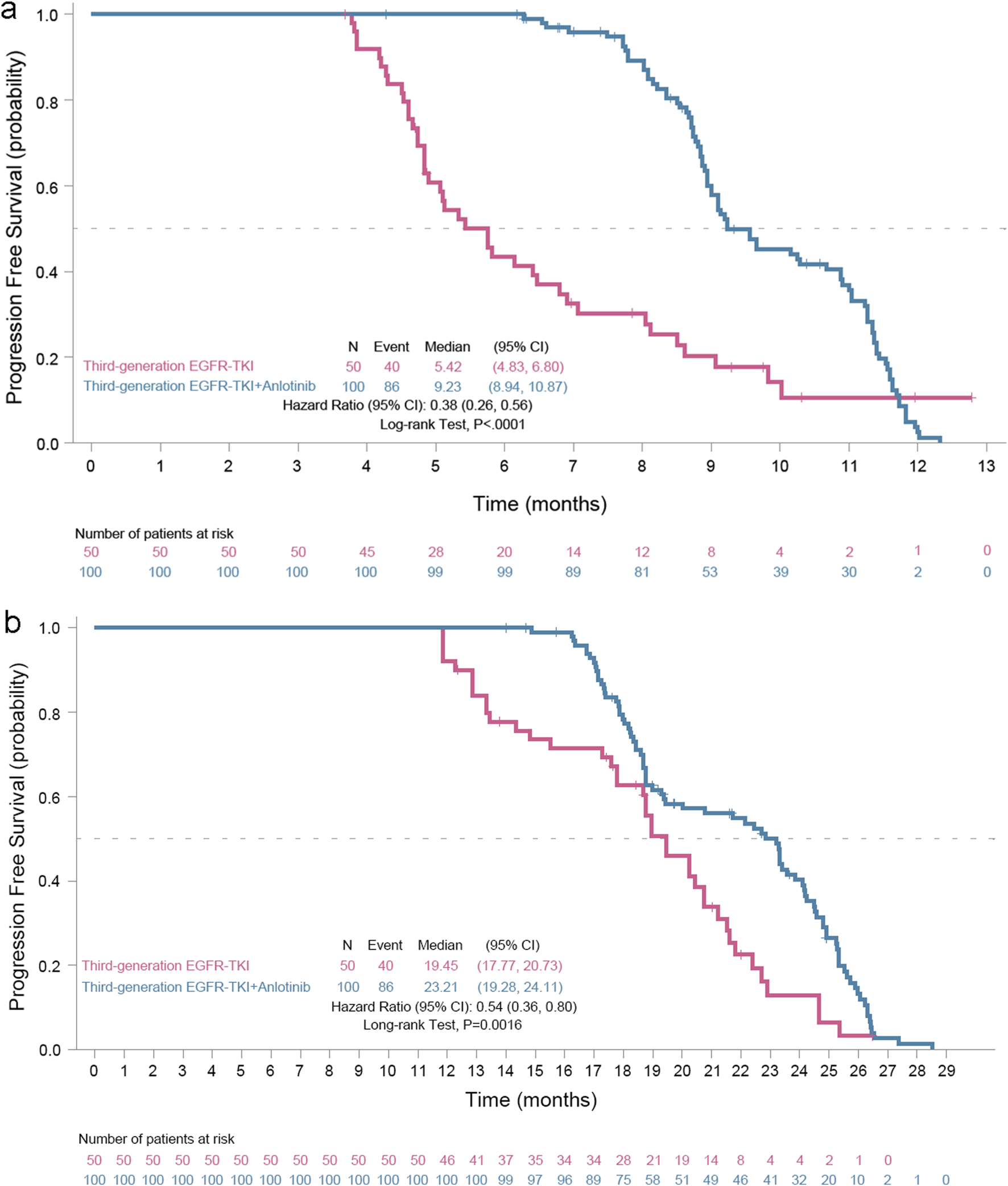
Kaplan-Meier progression-free survival (PFS) curves of EGFR mutant advanced nonsmall cell cancer patients with oligoprogressive disease. (a) PFS, the primary study outcome, was calculated from the date of medication initiation for the oligoprogressive disease and (b) PFS2, was calculated from the date of medication initiation for the primary disease to the first documented progressive disease or death, whichever occurred earlier.
Meanwhile, 86 and 40 investigators-confirmed PFS events occurred from the date of medication initiation for the primary disease to the data cutoff date in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and the EGFR TKI group, respectively. The median PFS2 was 23.21 months (95% CI 19.28–24.11 months) for the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group vs. 19.45 months (95% CI 17.77–20.73 months) for the EGFR TKI group, with a 46% reduction in the risk of progression (HR 0.54, 95% CI 0.36–0.80, P = 0.0016) (Figure 2b).
In the FAS, no patients in either group had a complete response. Seven patients in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group showed a partial response while none in the EGFR TKI group had an objective response. The investigators-assessed ORR was 7.0% (95% CI 3.4%–13.8%) for the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and 0% for the EGFR TKI group. In addition, 84 patients in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group had a stable disease and the disease control rate was 91.0% (95% CI 83.8%–95.2%). Seventeen patients in the EGFR TKI group had a stable disease and the disease control rate was 34.0% (95% CI 54.2%–79.2%).
OS data was still immature. No deaths were reported in either group.
3.3 Safety
Treatment-related AEs (TRAEs) of any grade occurred in 92 patients (92.0%) in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and 46 patients (92.0%) in the EGFR TKI group, including grade ≥3 TRAEs in 37 patients (37.0%) in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and 16 patients (34.0%) in the EGFR TKI group (Table 2). The most frequently reported grade 3 or worse TRAEs included hypertension (12.0%), γ-glutamyl transferase increased (5.0%) and hyponatremia (5.0%) in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and dry skin, paronychia and appetite decreased, each occurring in 8.0% patients in the EGFR TKI group (Table 2).
TABLE 2
| EGFR TKI plus anlotinib (n = 100) | EGFR TKI (n = 50) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred terms | Any grade | Grade 3 or worse | Any grade | Grade 3 or worse |
| Hypertension | 68 (68.0) | 12 (12.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 50 (50.0) | 1 (1.0) | 24 (48.0) | 2 (4.0) |
| Rash | 50 (50.0) | 1 (1.0) | 25 (50.0) | 2 (4.0) |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 45 (45.0) | 2 (2.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone increased | 43 (43.0) | 1 (1.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Palmar–plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome | 43 (43.0) | 3 (3.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Hypercholesterinemia | 42 (42.0) | 1 (1.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Cough | 35 (35.0) | 1 (1.0) | 8 (16.0) | 2 (4.0) |
| Fatigue | 30 (30.0) | 1 (1.0) | 6 (12.0) | 2 (4.0) |
| Dry skin | 30 (30.0) | 0 | 16 (32.0) | 4 (8.0) |
| Paronychia | 30 (30.0) | 0 | 15 (30.0) | 4 (8.0) |
| Proteinuria | 28 (28.0) | 2 (2.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Oral mucositis | 25 (25.0) | 0 | 13 (26.0) | 1 (2.0) |
| Appetite decreased | 25 (25.0) | 0 | 10 (20.0) | 4 (8.0) |
| γ-glutamyl transferase increased | 29 (29.0) | 5 (5.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Hyperbilirubinemia | 24 (24.0) | 2 (2.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Hemoptysis | 20 (20.0) | 3 (3.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Low density lipoprotein increased | 19 (19.0) | 1 (1.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Hyponatremia | 19 (19.0) | 5 (5.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Oropharyngeal dysphagia | 18 (18.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 18 (18.0) | 0 | 9 (18.0) | 1 (2.0) |
| Constipation | 15 (15.0) | 0 | 7 (14.0) | 1 (2.0) |
| Vomiting | 15 (15.0) | 0 | 7 (14.0) | 1 (2.0) |
| Body weight decreased | 15 (15.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Headache | 13 (13.0) | 0 | 6 (12.0) | 1 (2.0) |
| Hematuria | 12 (12.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Respiratory difficulty | 12 (12.0) | 0 | 6 (12.0) | 0 |
| Anemia | 12 (12.0) | 0 | 6 (12.0) | 1 (2.0) |
| Vomiting | 11 (11.0) | 0 | 5 (10.0) | 0 |
| Fever | 11 (11.0) | 0 | 5 (10.0) | 0 |
| Urinary tract infection | 11 (11.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 11 (11.0) | 0 | 5 (10.0) | 0 |
Treatment-related adverse events occurring in at least 10% of the patients in either group in the safety analysis population.
Data are expressed as number (%).
Treatment-related adverse events are described using the latest version of MedDRA, preferred terms and National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 5.0 (NCI CTCAE, 5) grade.
Serious AEs occurred in 12 (12.0%) patients in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and 6 patients (12.0%) in the EGFR TKI group. TRAEs led to dose reductions in 23 patients (23.0%) in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and 4 (8.0%) in the EGFR TKI group. TRAEs led to treatment interruptions in 25 patients (25.0%) in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group and 10 (20.0%) in the EGFR TKI group.
4 Discussion
Oligoprogressive disease following EGFR TKI therapy in EGFR mutant NSCLC patients leads to different clinical outcomes from systemic progressive disease and also has different treatment goals. Less than 30% of the patients in the ALTER-L001 trial received third-generation EGFR TKI (Chen et al., 2025). In this real-world study, all patients received first-line third-generation EGFR TKI systemic therapy. The addition of antiangiogenic agent anlotinib led to a 3.76-month extension of median PFS from medication initiation in patients with oligoprogressive disease compared to continued EGFR TKI monotherapy. Anlotinib was well tolerated and did not lead to a notable increase in the incidences of grade 3 or worse TRAEs and serious AEs. We felt that gradual or oligo-progression could offer a narrow therapeutic window that allows physicians to intervene early to change the failure treatment patterns from oligoprogressive disease to systemic progressive disease. Identifying EGFR mutant NSCLC patients with oligoprogressive disease and providing maintenance therapy with anlotinib would lead to significant PFS gains.
In the randomised phase 3 FLAURA trial involving previously untreated patients with EGFR mutant NSCLC, osimertinib attained a median PFS of 18.9 months (Soria et al., 2018), which is comparable to the median PFS (19.5 months (95% CI 18.0–20.9 months)) of our patients who received EGFR TKI only. Seventy-six percent of our patients received first-line osimertinib. The 3.8-month extension in the median PFS EGFR TKI plus anlotinib overo EGFR TKI only occurred in EGFR mutant NSCLC patients who have already developed resistance while on first-line third-generation EGFR TKI, a class known for deep and durable responses. Extending PFS by 3.8 months in a post-resistance setting could be viewed in the context of NSCLC for which PFS gains of 2–4 months have historically supported regulatory approvals (e.g., osimertinib vs. erlotinib/gefitinib in FLAURA showed a 5.5-month PFS gain (Soria et al., 2018)). The 62% reduction in the risk of progression (HR = 0.38, 95% CI 0.26–0.56) is substantially greater than the 46% reduction following the start of treatment of the primary disease, suggesting that anlotinib may be particularly effective in targeting angiogenic escape mechanisms in oligoprogressive. By adding anlotinib rather than switching therapies, clinicians can maintain EGFR TKI exposure, which continues to suppress sensitive clones. This strategy delays clonal evolution and systemic progression, a key goal in precision oncology, while targeting clones that escape EGFR TKI through angiogenic escape mechanisms. The greater efficacy of EGFR TKI plus anlotinib post-oligoprogression suggests that angiogenesis may be a dominant resistance pathway in the subset of patients with gradual or oligo-progression, validating VEGFR/PDGFR inhibition with anlotinib as a rational combination strategy. However, real-world heterogeneity might influence the outcomes.
In the ALTER-L001 trial, patients who received third-generation EGFR TKI and anlotinib maintenance had a median PFS of 9.2 months (95% CI 6.7–12.6 months) (Chen et al., 2025). This is in line with the median PFS (9.23 months, 95% CI, 8.94–10.87 months) of patients in the EGFR TKI plus anlotinib group observed in the current real-world study. Most patients (90.8%) in the ALTER-L001 trial had gradual progression and 18.0% had brain metastasis. This real-world study has a similar prolife of patients. The favorable outcomes among patients with brain metastases in our cohort are consistent with recent meta-analyses demonstrating benefit of anlotinib–radiotherapy combinations in NSCLC with intracranial disease (Hetta et al., 2025a). In the retrospective study by Xiang et al., the median PFS of EGFR mutant NSCLC patients with gradual progression following first-line EGFR TKI who received anlotinib was 6.7 months compared to 3.6 months for those on continued EGFR TKI alone (Xiang et al., 2024). Their study only enrolled patients with gradual progression (disease control for ≥6 months) while our study included both patients with gradual progression and oligoprogression (disease control ≥3 months). Patients with disease control for ≥6 months are more likely to have metachronous oligometastatic disease, which is associated with a less aggressive disease phenotype and a better prognosis than synchronous oligometastatic disease (Ashworth et al., 2014). Currently, there is not a universally accepted definition for oligoprogressive disease. We limited progression to ≤5 sites, which is in line with most studies that use an arbitrary cutoff of 3–5 progressive lesions (Guckenberger et al., 2020).
Overall, the addition of anlotinib to EGFR TKI therapy did not notably increase the incidence of toxicities, with comparable rates of grade 3 or worse TRAEs and serious AEs between the two groups. The safety profile of anlotinib plus EGFR TKI is similar to previous report (Zhou et al., 2024). No new safety concerns emerged during the study.
The study has several limitations. This study was based on retrospective cohorts with potential bias in patient selection and non-randomized comparison, and the study findings need to be prospectively validated in randomized trials. There is also lack of molecular profiling (e.g., EGFR T790M mutation status, EGFR C797X) of the patients. Regarding OS, the number of events was immature; OS results will be reported upon data maturity. Osimertinib was shown to be superior to first-generation EGFR TKIs in OS (38.6 months vs. 31.8 months) (Ramalingam et al., 2020). Given accumulating trial evidence and our increased understanding of the multitarget and microenvironment-modulating actions of anlotinib (Chu et al., 2025; Shi et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2025; Hetta et al., 2025b) and the ever important role of biomarkers in guiding cancer therapy, we anticipate that future studies will address the important issues of the efficacy and safety of anlotinib combined with PD-1 blockades or other targeted therapy in the treatment of NSCLC patients with oligoprogressive disease, with elucidation of and guidance by predictive biomarkers. In conclusion, real-world evidence is important in identifying and addressing the gap between trials and real-world practice. The current real-world study shed insight into the effectiveness and safety of anlotinib as an add-on therapy to ongoing systemic therapy in the context of primary treatment in EGFR mutant NSCLC patients who developed gradual or oligo-progression while on first-line third-generation EGFR TKI therapy. The study demonstrated that anlotinib, when added onto EGFR TKI therapy following gradual progression or oligo-progression, conferred significant PFS benefits upon EGFR mutant NSCLC patients, adding to the growing evidence on the choice of anlotinib as an effective treatment after gradual progression or oligoprogression while patients are receiving first-line EGFR TKI therapy. The findings of this study will be very relevant and guide physicians for informed treatment of patients with EGFR mutant NSCLC, though prospective randomized validation of the study findings is required. Our findings support further exploration of combination regimens guided by molecular and imaging biomarkers.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The study was approved by the ethics committee of Shanghai East Hospital, the lead institution (2024YS-252). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
FZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. HW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. NY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. JL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. SJ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. ZH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. GZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. JL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. YS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. KW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. DH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. LL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. JC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. JB: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. FR: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. CZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AEs, Adverse events; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; TKI, tyrosine-kinase inhibitor; TRAEs, treatment-related adverse events; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; OS, overall survival; ORR, overall response rate; PFS, progression-free survival; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
References
1
Ashworth A. B. Senan S. Palma D. A. Riquet M. Ahn Y. C. Ricardi U. et al (2014). An individual patient data metaanalysis of outcomes and prognostic factors after treatment of oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer15 (5), 346–355. 10.1016/j.cllc.2014.04.003
2
Bao R. Gao P. Zhang F. Tong Z. Yu H. Xu Y. (2016). Abstract 3063: discovery of a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, which is highly selective and potent against both resistant and activating EGFR mutations for NSCLC therapy. Cancer Res.76 (14_Suppl. ment), 3063. 10.1158/1538-7445.Am2016-3063
3
Bray F. Laversanne M. Sung H. Ferlay J. Siegel R. L. Soerjomataram I. et al (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.74 (3), 229–263. 10.3322/caac.21834
4
Chen L. Zhou Y. Gan C. Wang X. Liu Y. Dong C. et al (2022). Three third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: similarities and differences. Cancer Invest40 (7), 590–603. 10.1080/07357907.2022.2069254
5
Chen H. J. Tu H. Y. Hu Y. Fan Y. Wu G. Cang S. et al (2025). A phase II trial of anlotinib plus EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with gradual, oligo, or potential progression after EGFR-TKIs treatment (CTONG-1803/ALTER-L001). J. Hematol. Oncol.18 (1), 3. 10.1186/s13045-024-01656-0
6
Cheng Z. Cui H. Wang Y. Yang J. Lin C. Shi X. et al (2024). The advance of the third generation EGFR TKI in the treatment of non small cell lung cancer (review). Oncol. Rep.51 (1), 16. 10.3892/or.2023.8675
7
Choi S. H. Yoo S. S. Lee S. Y. Park J. Y. (2022). Anti-angiogenesis revisited: reshaping the treatment landscape of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Arch. Pharm. Res.45 (4), 263–279. 10.1007/s12272-022-01382-6
8
Chu T. Zhong H. Yu Z. Wang J. Zhao Y. Mu X. et al (2025). Efficacy and safety of first-line sintilimab plus anlotinib versus chemotherapy for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a phase II, open-label, randomized controlled trial. Cancer Commun. (Lond)45 (4), 442–455. 10.1002/cac2.12654
9
Cooper A. J. Sequist L. V. Lin J. J. (2022). Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: mechanisms of resistance and management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.19 (8), 499–514. 10.1038/s41571-022-00639-9
10
Gazdar A. F. (2009). Activating and resistance mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: role in clinical response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene28 (Suppl. 1), S24–S31. 10.1038/onc.2009.198
11
Guckenberger M. Lievens Y. Bouma A. B. Collette L. Dekker A. deSouza N. M. et al (2020). Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: a european society for radiotherapy and oncology and european organisation for research and treatment of cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet Oncol.21 (1), e18–e28. 10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30718-1
12
Han B. Li K. Wang Q. Zhang L. Shi J. Wang Z. et al (2018). Effect of anlotinib as a third-line or further treatment on overall survival of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: the ALTER 0303 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol.4 (11), 1569–1575. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3039
13
Han B. Zheng R. Zeng H. Wang S. Sun K. Chen R. et al (2024). Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. J. Natl. Cancer Cent.4 (1), 47–53. 10.1016/j.jncc.2024.01.006
14
Hanna N. H. Temin S. Masters G. (2020). Therapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer without driver alterations: ASCO and OH (CCO) joint guideline update summary. JCO Oncol. Pract.16 (8), e844–e848. 10.1200/jop.19.00770
15
Hellman S. Weichselbaum R. R. (1995). Oligometastases. J. Clin. Oncol.13 (1), 8–10. 10.1200/jco.1995.13.1.8
16
Hetta H. F. Ali M. A. S. Alqifari S. F. Salem H. A. Qasem K. A. Alanazi F. E. et al (2025a). Is anlotinib and radiotherapy combination effective for non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases? A systematic scoping review and meta-analysis. Pharm. (Basel)18 (7), 974. 10.3390/ph18070974
17
Hetta H. F. Aljohani H. M. Sirag N. Elfadil H. Salama A. Al-Twalhy R. et al (2025b). Synergizing success: the role of anlotinib combinations in advanced non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Pharm. (Basel)18 (4), 585. 10.3390/ph18040585
18
Hetta H. F. Alqifari S. F. Alshehri K. Alhowiti A. Alharbi S. S. Mirghani H. et al (2025c). Efficacy of anlotinib plus docetaxel in advanced NSCLC previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharm. (Basel)18 (5), 652. 10.3390/ph18050652
19
Iyengar P. All S. Berry M. F. Boike T. P. Bradfield L. Dingemans A. M. C. et al (2023). Treatment of oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer: an ASTRO/ESTRO clinical practice guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol.13 (5), 393–412. 10.1016/j.prro.2023.04.004
20
Lim J. U. (2021). Management of oligometastasis and oligoprogression in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive NSCLC in the era of third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin. Lung Cancer22 (5), e786–e792. 10.1016/j.cllc.2021.03.004
21
Lin B. Song X. Yang D. Bai D. Yao Y. Lu N. (2018). Anlotinib inhibits angiogenesis via suppressing the activation of VEGFR2, PDGFRβ and FGFR1. Gene654, 77–86. 10.1016/j.gene.2018.02.026
22
Long J. Lei S. Wu Z. Xiong S. Wang C. Huang L. et al (2022). Efficacy and safety of original EGFR-TKI combined with bevacizumab in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients harboring EGFR-mutation experiencing gradual progression after EGFR-TKI treatment: a single-arm study. Ann. Transl. Med.10 (24), 1334. 10.21037/atm-22-6101
23
Lorenzi M. Ferro A. Cecere F. Scattolin D. Del Conte A. Follador A. et al (2022). First-line osimertinib in patients with EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: outcome and safety in the real world: FLOWER study. Oncologist27 (2), 87–e115. 10.1002/onco.13951
24
Lu S. Wang Q. Zhang G. Dong X. Yang C. T. Song Y. et al (2022). Efficacy of aumolertinib (HS-10296) in patients with advanced EGFR T790M+ NSCLC: updated post-national medical products administration approval results from the APOLLO registrational trial. J. Thorac. Oncol.17 (3), 411–422. 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.10.024
25
Niibe Y. Chang J. Y. (2012). Novel insights of oligometastases and oligo-recurrence and review of the literature. Pulm. Med.2012, 261096. 10.1155/2012/261096
26
Niibe Y. Hayakawa K. (2010). Oligometastases and oligo-recurrence: the new era of cancer therapy. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol.40 (2), 107–111. 10.1093/jjco/hyp167
27
Park K. Yu C. J. Kim S. W. Lin M. C. Sriuranpong V. Tsai C. M. et al (2016). First-line erlotinib therapy until and beyond response evaluation criteria in solid tumors progression in Asian patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: the ASPIRATION study. JAMA Oncol.2 (3), 305–312. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.4921
28
Patel P. H. Palma D. Mcdonald F. Tree A. C. (2019). The dandelion dilemma revisited for oligoprogression: treat the whole lawn or weed selectively?Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol.31 (12), 824–833. 10.1016/j.clon.2019.05.015
29
Ramalingam S. S. Vansteenkiste J. Planchard D. Cho B. C. Gray J. E. Ohe Y. et al (2020). Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med.382 (1), 41–50. 10.1056/NEJMoa1913662
30
Schuler A. Huser J. Schmid S. Schär S. Scherz A. Gautschi O. et al (2024). Patterns of progression on first line osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a Swiss cohort study. Lung Cancer187, 107427. 10.1016/j.lungcan.2023.107427
31
Shen G. Zheng F. Ren D. Du F. Dong Q. Wang Z. et al (2018). Anlotinib: a novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development. J. Hematol. Oncol.11 (1), 120. 10.1186/s13045-018-0664-7
32
Shi Y. Chen G. Wang X. Liu Y. Wu L. Hao Y. et al (2022). Furmonertinib (AST2818) versus gefitinib as first-line therapy for Chinese patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (FURLONG): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Respir. Med.10 (11), 1019–1028. 10.1016/s2213-2600(22)00168-0
33
Shi X. Lin C. Lou L. He Q. Lou G. Hong W. et al (2025). An open-label, single-arm, phase II trial of sintilimab plus anlotinib for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after first-line PD-(L)1 inhibitor. Cancer Med.14 (17), e71191. 10.1002/cam4.71191
34
Soria J. C. Wu Y. L. Nakagawa K. Kim S. W. Yang J. J. Ahn M. J. et al (2015). Gefitinib plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy in EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on first-line gefitinib (IMPRESS): a phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol.16 (8), 990–998. 10.1016/s1470-2045(15)00121-7
35
Soria J. C. Ohe Y. Vansteenkiste J. Reungwetwattana T. Chewaskulyong B. Lee K. H. et al (2018). Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med.378 (2), 113–125. 10.1056/NEJMoa1713137
36
Wang X. Li Z. Wang L. Liang Y. Huang C. Chen P. et al (2025). Osimertinib plus anlotinib for advanced NSCLC with acquired EGFR T790M mutation: results from a multicenter phase II study with ctDNA analysis. BMC Med.23 (1), 223. 10.1186/s12916-025-04044-8
37
Watanabe K. Hosomi Y. Naoki K. Nakahara Y. Tsukita Y. Matsumoto H. et al (2024). The whole picture of first-line osimertinib for EGFR mutation-positive advanced NSCLC: real-world efficacy, safety, progression pattern, and posttreatment therapy (reiwa study). JTO Clin. Res. Rep.5 (11), 100720. 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2024.100720
38
Xiang H. Danna D. Xuefei C. Zhao J. Jin G. (2024). The efficacy and safety of adding anlotinib in gradual progression on third-generation EGFR-TKIs for EGFR-mutant advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs35 (5), 433–439. 10.1097/cad.0000000000001575
39
Xu Y. Li H. Fan Y. (2021). Progression patterns, treatment, and prognosis beyond resistance of responders to immunotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol.11, 642883. 10.3389/fonc.2021.642883
40
Xu Z. Teng F. Hao X. Li J. Xing P. (2022). Bevacizumab combined with continuation of EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC beyond gradual progression. Cancer Manag. Res.14, 1891–1902. 10.2147/cmar.S363446
41
Yang J. C. Camidge D. R. Yang C. T. Zhou J. Guo R. Chiu C. H. et al (2020). Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of almonertinib (HS-10296) in pretreated patients with EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC: a multicenter, open-label, phase 1 trial. J. Thorac. Oncol.15 (12), 1907–1918. 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.09.001
42
Yu Y. Wang Y. Wu L. Xu X. Zhou H. Wang Q. et al (2021). Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) combined with bevacizumab for advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer patients with gradual progression on EGFR-TKI treatment: a cohort study. Med. Baltim.100 (5), e23712. 10.1097/md.0000000000023712
43
Zhao Y. Wang Q. Zhang L. Shi J. Wang Z. Cheng Y. et al (2022). The efficacy of anlotinib as third-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer by EGFR mutation status: a subgroup analysis of the ALTER0303 randomized phase 3 study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res.11 (5), 776–785. 10.21037/tlcr-22-320
44
Zhou H. Q. Zhang Y. X. Chen G. Yu Q. T. Zhang H. Wu G. W. et al (2024). Gefitinib (an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor) plus anlotinib (an multikinase inhibitor) for untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (FL-ALTER): a multicenter phase III trial. Signal Transduct. Target Ther.9 (1), 215. 10.1038/s41392-024-01927-9
45
Zhou F. Guo H. Xia Y. Le X. Tan D. S. W. Ramalingam S. S. et al (2025). The changing treatment landscape of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.22 (2), 95–116. 10.1038/s41571-024-00971-2
Summary
Keywords
non-small cell lung cancer, oligoprogression, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine-kinase inhibitor, antiangiogenic therapy, anlotinib
Citation
Zhou F, Zhuo M, Wang H, Yang N, Li J, Jin S, Han Z, Zeng G, Liu J, Song Y, Wang K, Huang D, Li L, Chen J, Bai J, Ran F and Zhou C (2025) Anlotinib added to third generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for advanced NSCLC patients with oligo-progression: a retrospective study (ALTER-L058). Front. Pharmacol. 16:1686364. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1686364
Received
15 August 2025
Revised
16 October 2025
Accepted
29 October 2025
Published
07 November 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Helal F Hetta, University of Tabuk, Saudi Arabia
Reviewed by
Shuhei Suzuki, Yamagata Prefectural Shinjo Hospital, Japan
Yasmine Ramadan, Assiut University, Egypt
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhou, Zhuo, Wang, Yang, Li, Jin, Han, Zeng, Liu, Song, Wang, Huang, Li, Chen, Bai, Ran and Zhou.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Caicun Zhou, caicunzhoudr@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.