- Shandong Key Laboratory of Digital Traditional Chinese Medicine, Institute of Pharmacy (Institute of TCM Health Industrial Technology), Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
The clinical safety and therapeutic performance of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) are closely tied to its quality. However, with the rapid expansion of the TCM industry, conventional quality control approaches based on empirical observations and single-metabolite quantification have become increasingly inadequate for addressing the complex and variable requirements of quality assessment. In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI)—with strong capabilities in data processing and pattern recognition—has emerged as a promising tool for establishing predictive models to efficiently handle heterogeneous, multi-source datasets (such as spectra, chromatograms, images, and textual information). This enables intelligent prediction of quality indicators and anomaly detection, and offering novel strategies for modernizing TCM quality control. This review provides a comprehensive synthesis of commonly applied machine learning and deep learning algorithms, systematically outlining recent advances in AI-enabled sensing applications such as image recognition, odor analysis, authenticity verification, origin tracing, quality grading, and storage-age determination. It further emphasizes the integration of AI with multi-omics and bioinformatics approaches for efficacy-oriented evaluation and safety assessment, including identification of Q-markers, elucidation of pharmacodynamic mechanisms, and predictive modeling of both endogenous and exogenous toxic metabolites. It also identifies key challenges and technical bottlenecks, and outlines priorities for building scalable, regulation-aware, data-driven quality-control systems that support the sustainable, high-quality development of the TCM industry.
1 Introduction
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) receives growing international attention for its integrative treatment principles, clinically validated efficacy, favorable safety profile, and emphasis on personalized care (Monakhova et al., 2018). TCM has long emphasized the integration of medicinal materials with clinical practice. In this context, identifying, selecting, and applying TCM are closely tied to clinical decisions. Among these factors, the consistency of TCM quality is essential for maintaining the clinical reliability of TCM interventions (Zhao J. et al., 2018; Liu C.-L. et al., 2024; Soltani et al., 2025).
However, the heterogeneous sources of medicinal materials, chemical complexity of TCM, absence of unified quality control standards, and incomplete understanding of pharmacological mechanisms collectively lead to substantial inconsistencies in the quality and therapeutic performance of TCM (Wang and Li, 2022; Busia, 2024). Conventional quality control in TCM primarily relies on sensory-based techniques and basic physicochemical assessments. These include traditional diagnostic methods such as wang, wen, wen, and qie (inspection, olfaction and auscultation, inquiry, and palpation), as well as organoleptic evaluation to determine the Four Qi (cold, hot, warm, cool) and Five Flavors (pungent, sweet, sour, bitter, salty). Despite their convenience, such methods are inherently subjective and lack reproducibility, rendering them inadequate for modern quality evaluation standards (Li et al., 2020; Luo et al., 2024). Modern analytical technologies, including chromatography and spectroscopy, have enabled metabolite profiling systems. However, these platforms predominantly quantify selected marker metabolites. Such approaches often fail to capture the intrinsic complexity of TCM, which involves multiple bioactive metabolites acting synergistically through diverse targets and pathways. Furthermore, the correlation between such analytical data and actual pharmacological efficacy or safety remains weak (Li and Zhang, 2013). The widespread application of modern quality control approaches is also limited by their reliance on elaborate sample preparation, costly instrumentation, and the need for specialized personnel (Liu Y. et al., 2025).
The modernization and globalization of TCM demand the development of a standardized, data-driven, and intelligent quality control system to support accurate assessment and effective regulation of product quality. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have opened new avenues for innovation in TCM quality control. Machine learning (ML) algorithms have been effectively deployed in phenotypic tasks such as origin traceability, species authentication, and quality grade classification, thereby improving the objectivity and consistency of TCM characterization. Meanwhile, the integration of AI with analytical platforms such as chromatography, mass spectrometry, and multi-omics technologies has advanced the automation and standardization of TCM quality evaluation (Caratti et al., 2024; Chi et al., 2024).
TCM-derived metabolites exhibit pronounced structural heterogeneity, while their pharmacological actions are often complex and synergistic. As a result, phenotypic-level intelligent recognition alone is insufficient to capture the multi-metabolite, multi-target and multi-pathway characteristics of TCM. In contrast, bioinformatics and multi-omics platforms—including transcriptomics, metabolomics, and proteomics—offer a multidimensional perspective on the underlying therapeutic mechanisms. When combined with AI-driven computational modeling, these approaches make it possible to trace the pathway from bioactive metabolites to defined molecular targets, and further to the modulation of signaling networks that mediate therapeutic efficacy (Soon et al., 2013; Liu and Guo, 2020; Wang et al., 2021; Li D. et al., 2022).
Within the intelligent quality control framework, AI-assisted phenotypic recognition—covering morphological features and spectral fingerprints—functions as the primary entry point for assessment. At a deeper analytical tier, the integration of AI with bioinformatics enables the elucidation of intricate target–pathway–outcome relationships, thereby linking chemical composition and pharmacodynamic mechanisms to the holistic efficacy of TCM. Notably, such a dual-level strategy strengthens the scientific rigor and reproducibility of quality evaluation. Collectively, these advances pave the way for the establishment of an efficacy-driven, mechanism-informed quality control system.
2 Artificial intelligence technologies
Among various AI approaches, ML—particularly its subset deep learning (DL)—has found the broadest application in the medical field (Russell and Norvig, 2022) (Figure 1A). Since its inception, AI has maintained a close connection with healthcare and has gradually expanded to encompass diverse domains of human activity (Figure 1B) (Aydın Temel et al., 2023). In the context of TCM research, AI facilitates the recognition, modeling, and prediction of complex and heterogeneous data. It enables automated extraction of sensory features and chemical fingerprints—parameters that have traditionally been challenging to quantify—and can be integrated with mechanistic models to inform efficacy and safety assessment in TCM.
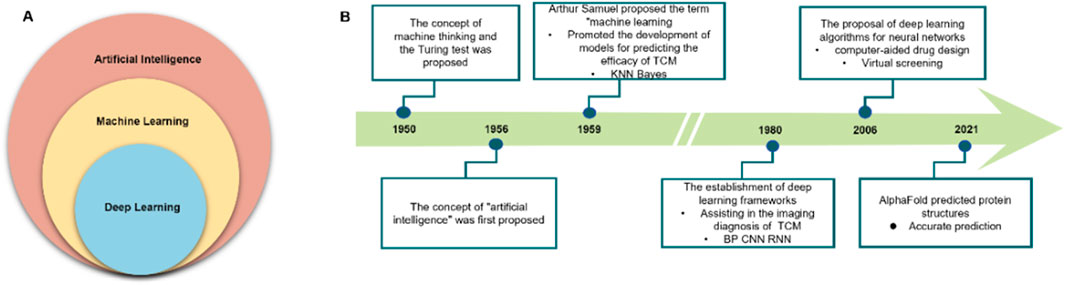
Figure 1. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL): advances in healthcare. (A) Relationship among AI, ML, and DL. (B) Evolution of AI in daily life and healthcare.
2.1 Machine learning techniques
ML is typically categorized into three main types: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. This review primarily focuses on supervised learning and unsupervised learning relevant to TCM quality assessment (Figure 2).
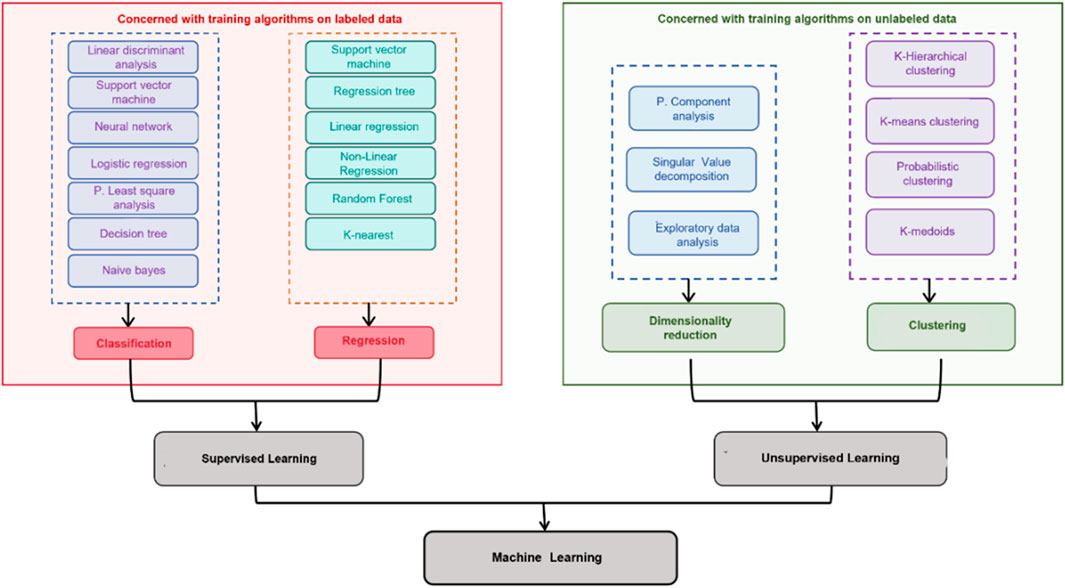
Figure 2. Classification of ML techniques: distinction between supervised learning and unsupervised learning.
2.1.1 Supervised learning
Supervised learning constitutes a fundamental framework within ML, wherein models are trained on labeled datasets to establish explicit mappings between inputs and outputs (Suriyaamporn et al., 2024). By capturing such relationships, supervised algorithms can perform both classification tasks and regression tasks with high predictive accuracy, where classification assigns inputs to discrete categories, while regression predicts continuous outcomes (Maione et al., 2019). A broad spectrum of algorithms is routinely employed, including Naïve Bayes (NB), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), decision trees (DT), random forests (RF), support vector machines (SVM), logistic regression (LR), k-nearest neighbors (KNN), and regression approaches such as simple linear, multiple linear, and polynomial regression. These models support both classification and regression pipelines commonly encountered in TCM quality evaluation, spectrum–structure correlation, and pharmacokinetic modeling.
NB: NB is a probabilistic classifier grounded in Bayes’ theorem and the conditional-independence assumption among features (Ou et al., 2025). By combining prior distributions with class-conditional likelihoods, it estimates posterior probabilities and assigns each sample to the most probable class. Despite its austerity, NB is computationally frugal, robust on small or high-dimensional spaces, and comparatively tolerant of irrelevant variables. Notably, NB has been used across TCM-related tasks—including classical medical text categorization, adulteration screening of decoction pieces, and time-series analyses of pharmacodynamic readouts—where rapid, baseline performance is desirable.
LDA: LDA is a supervised method for classification and dimensionality reduction that seeks projections maximizing interclass separation while minimizing intraclass variance (Lam et al., 2024). Assuming multivariate normality with a common covariance structure, LDA yields linear decision boundaries, which in turn facilitate interpretability and efficient computation. In contrast to previous reports focusing solely on visualization, recent TCM studies deploy LDA for spectral feature extraction (e.g., NIR, HSI), geographic-origin authentication, and prediction of chemical-composition profiles aligned with Q-markers frameworks and multi-omics fingerprints.
DT: DT is supervised learners applicable to both classification and regression, representing decision rules in a hierarchical, tree-like structure. Through recursive partitioning on feature thresholds, DTs generate models that are straightforward to visualize and implement (Sarker, 2021). In TCM research, they have been widely adopted for efficacy prediction, quantification of active metabolites, and routine quality control of medicinal materials (Ren et al., 2022; Zhang W. et al., 2025).
RF: RF is an ensemble learning approach that builds multiple decision trees and aggregates their outputs to generate the final prediction. In classification tasks, the predicted class is determined by majority voting, whereas in regression tasks, the results are obtained by averaging the outputs of individual tree (Figure 3A). Due to its strong robustness to noise and ability to capture complex feature interactions, RF has shown high accuracy for botanical drug origin traceability and in recognizing multi-metabolite feature patterns characteristic of TCM formulations (Gong et al., 2023).
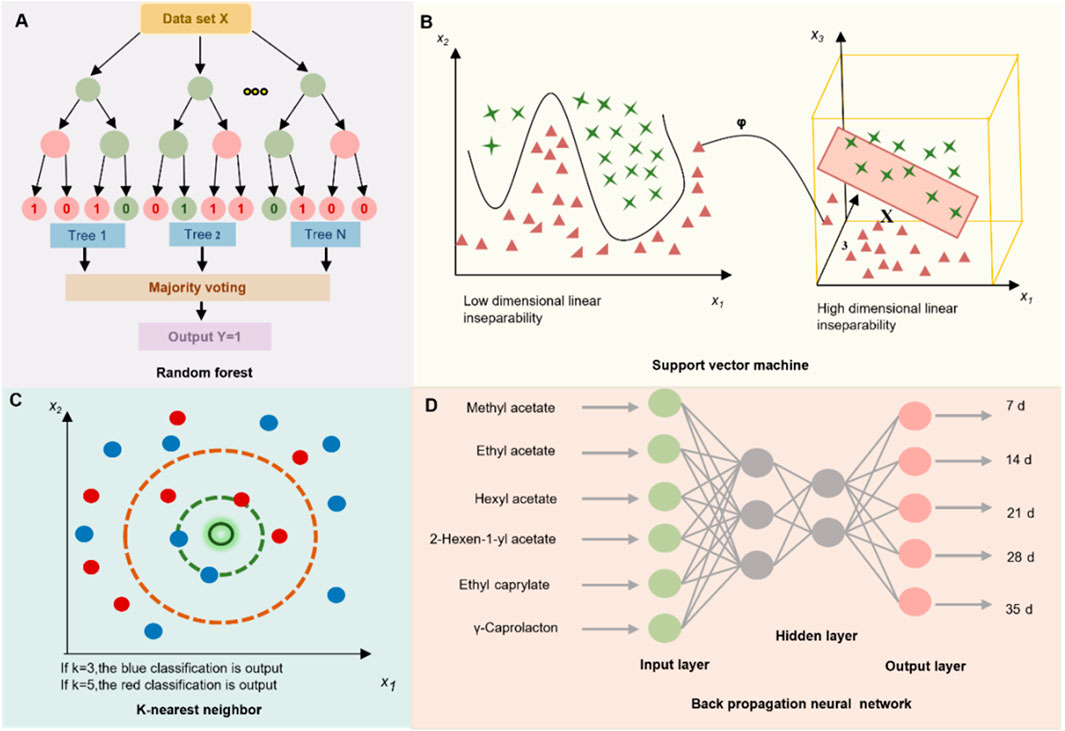
Figure 3. Schematic representation of 4 ML models employed in TCM research: Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN).
SVM: SVM is a versatile ML technique used for various purposes, including classification and regression. It projects input data into a high-dimensional feature space using kernel functions, enabling the linear separation of inherently nonlinear patterns (Figure 3B) (Kremer et al., 2014). In the TCM domain, SVM has been widely employed for spectral data analysis—such as near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) and hyperspectral imaging (HSI)—as well as for classifying pharmacological effects across different decoction pieces and TCM prescriptions (Kumari et al., 2021; Ouyang et al., 2023).
LR: LR is a supervised statistical learning method used chiefly for binary classification and, via standard extensions, multiclass tasks. It maps a linear combination of predictors through the logistic (sigmoid) link to obtain class-membership probabilities, with coefficients directly interpretable as odds ratios. In TCM research, LR has been applied to classify TCM species from chromatographic or spectral fingerprints, to predict the therapeutic efficacy of metabolites, and to assess toxicity risks in complex multi-metabolite formulations, consistent with the field’s focus on holistic efficacy and rigorous quality evaluation.
KNN: K-NN is an ML algorithm for classification and regression. It assigns a label to a sample based on the majority class among its k nearest neighbors, identified using distance metrics such as Euclidean or Mahalanobis distance (Figure 3C). Owing to its ease of implementation and dependable performance, this approach has proven to be a practical choice for a range of applications in TCM, including species authentication of TCM materials, tracing geographic origin, and assigning quality grades (Boniecki et al., 2014; Li et al., 2022b).
BPNN: A feed-forward artificial neural network trained using the backpropagation learning algorithm, the BPNN is particularly effective in modeling complex and nonlinear relationships between chemical composition and pharmacological efficacy (Figure 3D). In the field of TCM research, BPNN has been extensively applied to optimize processing parameters, enhance extraction protocols, and predict multi-index quality attributes (Yi, 2019).
Regression analysis—an essential supervised approach for continuous outcomes—has been increasingly applied in TCM to quantify links between chemical composition and quality attributes. By integrating spectral or metabolomic data with regression models such as partial least squares (PLS), these workflows enable rapid estimation of active metabolite levels, discrimination of authentic metabolites from adulterants, and the construction of robust quality-control frameworks (Moreno-Torres et al., 2024; Zhang X. et al., 2024).
2.1.2 Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning refers to algorithms that discover hidden structures and patterns in unlabeled data without predefined outputs. Typical methods include clustering and dimensionality reduction (Castiglioni et al., 2021).The following introduces several common unsupervised algorithms, including K-means clustering (K-means), Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN), Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) and Principal Metabolite Analysis (PCA).
K-means: K-means is an unsupervised learning algorithm that partitions data into k clusters by minimizing the within-cluster variance. It iteratively assigns samples to the nearest cluster centroid and updates centroids until convergence.
DBSCAN:DBSCAN is an unsupervised clustering algorithm that groups data points based on density, identifying high-density regions as clusters and treating sparse points as noise or outliers. Unlike K-means, it does not require specifying the number of clusters in advance and can discover clusters of arbitrary shape.
GMMs: GMMs are probabilistic unsupervised learning algorithms that assume data are generated from a mixture of multiple Gaussian distributions, each representing a cluster. Unlike K-means, GMMs provide soft clustering by assigning probabilities for each data point belonging to different clusters. In TCM research, GMMs have been used to classify TCM samples based on spectral or metabolomic data and to distinguish authentic materials from adulterants with overlapping chemical features (Bai and Zhang, 2024).
PCA: A linear dimensionality reduction method that transforms correlated variables into a smaller set of uncorrelated principal metabolites while retaining most of the variance. In TCM, PCA is widely used to simplify spectral or chromatographic data for quality evaluation (Thapa et al., 2025).
In parallel, unsupervised techniques—such as hierarchical clustering, t-SNE, and autoencoders—have been applied to data visualization, authenticity verification of decoction pieces, adulteration detection, and quality evaluation (Paolanti and Frontoni, 2020; Bansal et al., 2024). Taken together, supervised and unsupervised workflows constitute an integrated ML toolkit that supports classification, regression, clustering, and dimensionality reduction across complex TCM systems.
2.2 Deep learning techniques
DL, a prominent branch of supervised learning within ML, is known for its remarkable capacity to extract high-level, discriminative features from complex datasets. Leveraging neural network (NN) architectures, DL enables data-driven decision-making in intricate systems by uncovering latent patterns from both large-scale structured data—such as images, spectral profiles, and textual corpora—and diverse unstructured datasets (Chen et al., 2022). Its superior representational and predictive capacity has positioned DL as a pivotal methodological tool in data-intensive TCM research.
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): CNNs typically comprise convolutional layers, pooling layers, and fully connected layers. Through convolutional operations, they automatically learn hierarchical feature representations, which makes them particularly effective for high-dimensional image and signal processing in big data environments (Zeng et al., 2023a). Within TCM, CNNs have been applied to analyze surface morphology and microstructural features of medicinal materials, facilitating image-based authentication, geographic origin tracing, and the detection of pest (Kabir et al., 2022a).
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN): RNNs are designed to capture temporal dependencies and sequential patterns, rendering them well suited for time series and textual data. They have achieved wide application in natural language processing and biomedical literature mining. In the TCM context, RNNs support structured knowledge extraction from classical medical texts, the modeling of prescription sequences, and the analysis of biological time-series data, thereby contributing to knowledge standardization and semantic modeling (Tian et al., 2024).
Deep Neural Network (DNN): DNNs, characterized by multiple hidden layers, can model complex, high-dimensional relationships between input features and target outputs. In TCM research, they have been used to develop predictive models of pharmacological efficacy based on chemical composition profiles. Such end-to-end learning frameworks allow direct inference of pharmacological mechanisms from raw, multi-modal data (He et al., 2015).
Beyond CNN, RNN, and DNN, DL encompasses other influential architectures. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can generate realistic synthetic data to augment limited datasets; Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) enable efficient feature compression and latent space modeling; and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) optimizes decision-making policies through interaction with complex environments. These methods are widely adopted in fields such as natural language processing, robotics, and autonomous systems.
3 Mechanism-oriented transformation of TCM quality control: from sensing to mechanistic evaluation
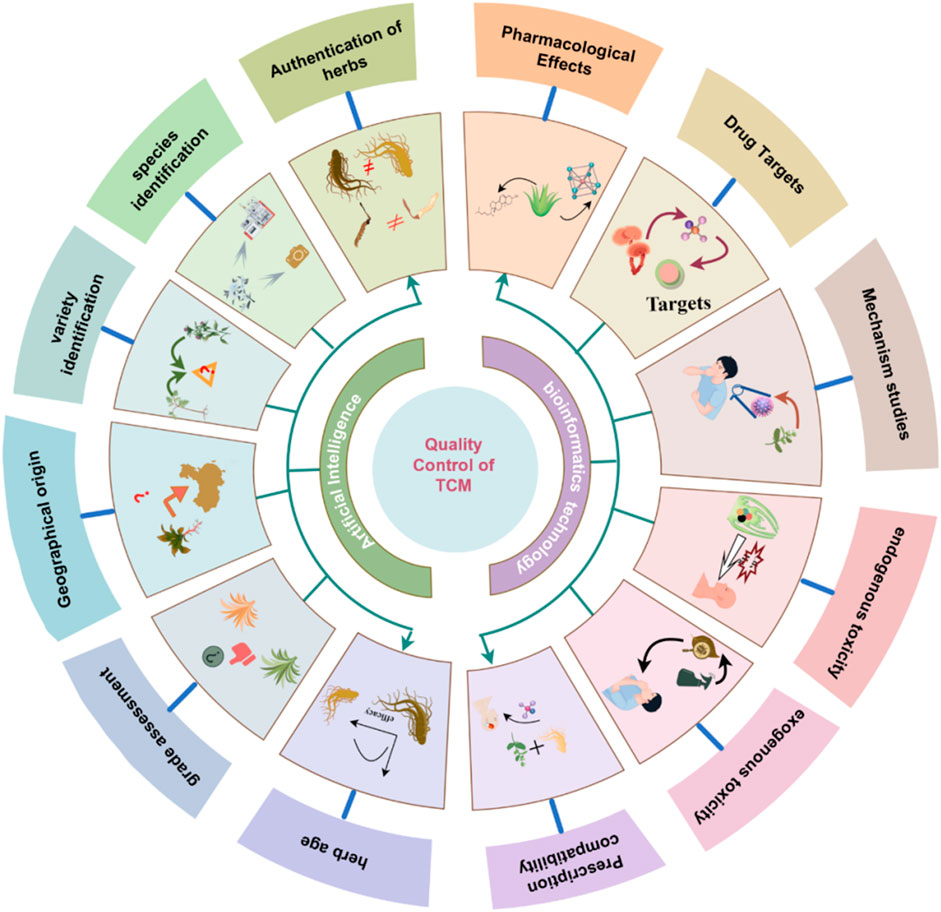
In recent years, the TCM industry have been undergoing a transition toward the integration of intelligent technologies. This shift reflects a broader transformation from experience- and perception-based evaluation to data-driven, mechanistically informed quality control model. AI has shown particular strengths in sensing. When integrated with bioinformatics, it supports the systematic construction of mechanistic frameworks for assessing efficacy and safety of TCM (Figure 4). This chapter focuses on the two major stages of this intelligent transformation and illustrates representative applications and recent advancements in TCM quality control.
3.1 AI-enabled sensing for the quality assessment of botanical drugs
AI leverages a range of ML techniques to strengthen TCM quality control and address the inherent limitations of conventional multivariate statistical approaches. These technologies are increasingly utilized in key domains—including origin traceability, species authentication, and quality grading—reflecting the multi-dimensional nature of TCM quality evaluation (Figure 5). Table 1 summarizes representative case of AI applications in TCM quality control, highlighting algorithm types, data modalities, and specific application scenarios.
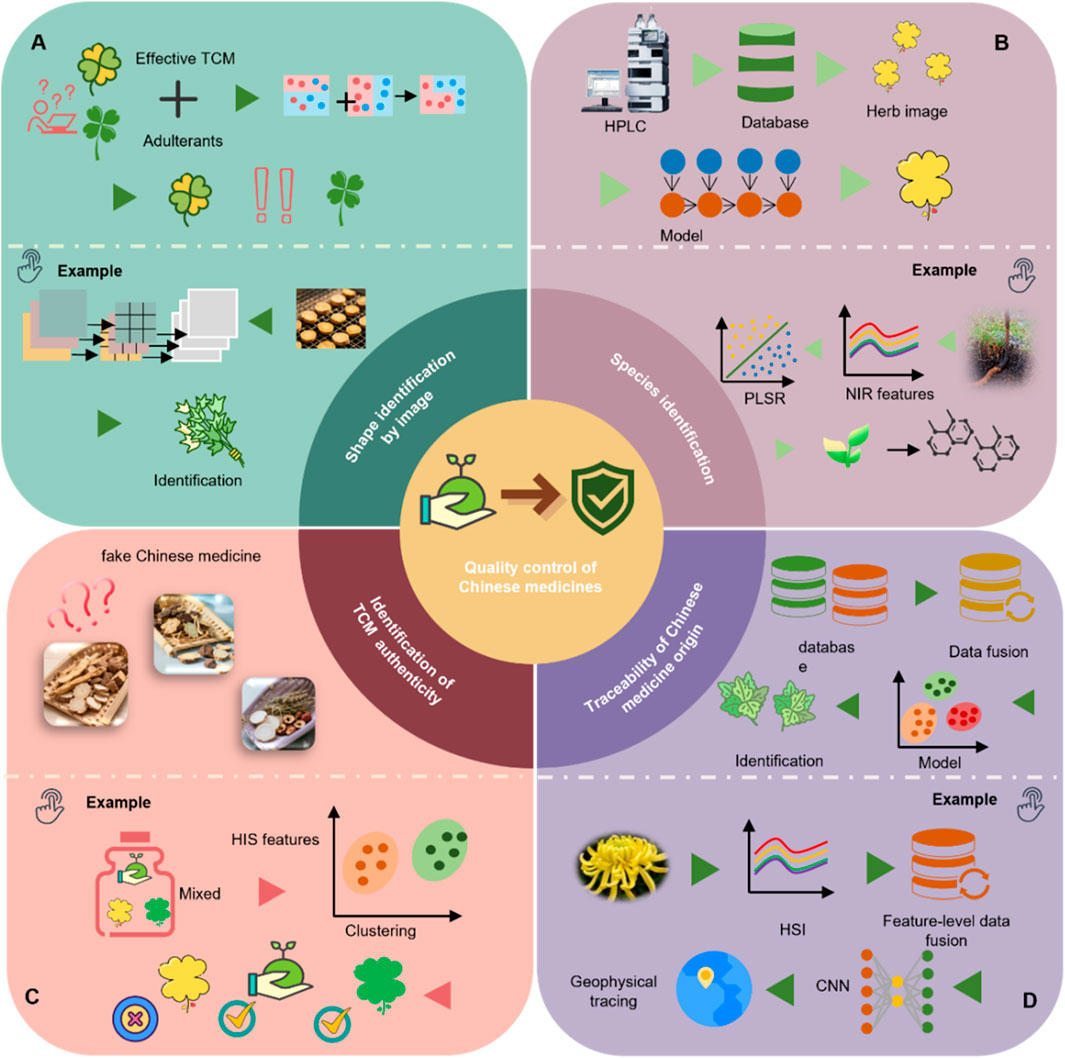
Figure 5. Representative applications of ML in TCM quality control. (A) Morphological identification based on image analysis: for instance, an improved ConvNeXt model is used for feature extraction and image classification to accurately identify TCM. (B) Species identification: for example, ATR-FTIR spectroscopy combined with partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) is used to distinguish different varieties of Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Berk.) G.H. Sung, J.M. Sung, Hywel-Jones and Spatafora. (C) Authenticity verification: for example, hyperspectral imaging (HSI) combined with ML algorithms is used to differentiate naturally sun-dried from sulfur-fumigated TCM materials. (D) Origin tracing: for example, HSI combined with CNNs is applied to determine the production region of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat.
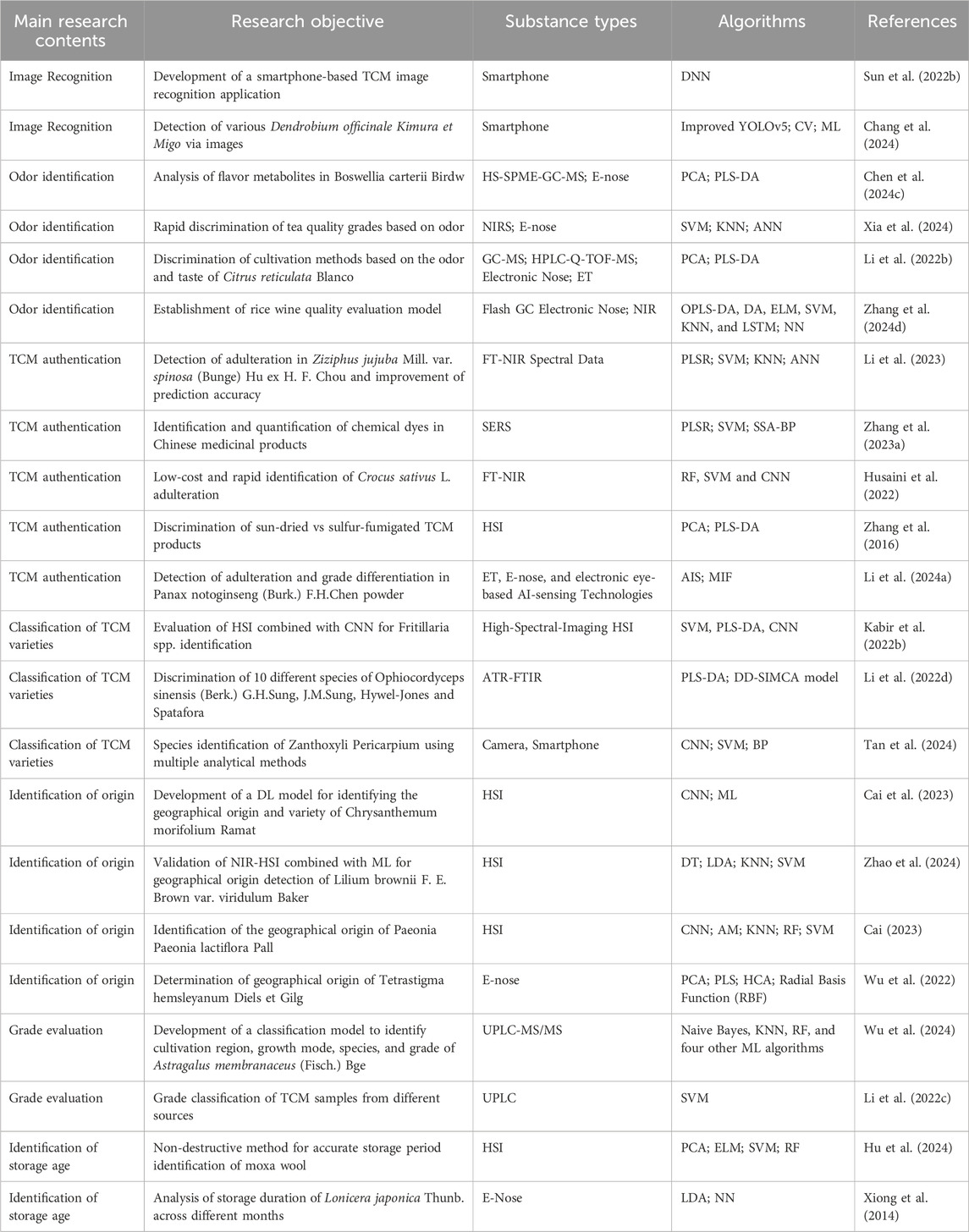
Table 1. Representative studies on the application of artificial intelligence in the quality control of TCM.
3.1.1 Image recognition
Morphological identification is a fundamental step in ensuring the quality consistency of TCM. It requires systematic recognition of key features such as color, shape, leaf structure, and texture. However, inter-species similarity and intra-species morphological variation often compromise the reliability of manual identification, introducing subjectivity and reducing reproducibility.
AI-powered image recognition has emerged as a highly effective strategy for enhancing both the accuracy and efficiency of morphological identification in medicinal botanical drugs (Sun et al., 2022c). To overcome performance constraints, researchers have optimized ML architectures to improve classification precision and generalizability in botanical drug image recognition tasks (Xu et al., 2016). For example, transfer learning strategies have been applied using five pre-trained deep neural network architectures—ResNet34, DenseNet121, VGG11, ConvNeXt, and Swin Transformer—to improve classification accuracy. Among these, ConvNeXt achieved accuracies of 92.8% for Vietnamese samples and 92.5% for Indonesian samples, highlighting its strong adaptability to geographically diverse TCM datasets. In a related development, Xu et al. (2021) proposed an Attention Pyramid Network (APN) designed to dynamically capture multi-scale features from medicinal botanical drug images. Comparative evaluations revealed that APN consistently outperformed conventional Feature Pyramid Networks (FPN) within attention-based frameworks, confirming its superior accuracy and practical applicability.
The morphological authentication of certain medicinal species—Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo, for instance—has traditionally depended on expert judgment. Although highly effective when performed by trained professionals, such reliance poses practical challenges for non-specialist users, especially in cases involving subtle interspecific variations or closely related adulterants. To overcome the barrier and facilitate field deployment, researchers have developed an image-based recognition system optimized through an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm. This system can be deployed on smartphones, enabling real-time identification of D. officinale Kimura et Migo and supporting on-site market regulation (Chang et al., 2024). Additionally, Sun et al. (2022b) design a DL–driven mobile application that maintains reliable performance on smartphones, thereby extending the accessibility of botanical drug recognition technologies to resource-limited settings.
3.1.2 Odor identification
The identification and quality evaluation of TCM have historically relied on sensory assessment, focusing primarily on visual appearance, odor, and taste (Li et al., 2013). The therapeutic efficacy of TCM is often attributed to the synergistic interplay among multiple bioactive metabolites, some of which possess distinctive volatile profiles that contribute both to sensory recognition and to potential pharmacological effects (Ye et al., 2011). Consequently, reliable odor detection constitutes a critical foundation for the standardization and quality control of TCM. Conventional odor analysis—whether based on manual assessment, instrumental detection, or a combination of both—remains susceptible to variability introduced by individual factors (e.g., physical condition, mood) and environmental influences (e.g., temperature, humidity).
In recent years, ML models have gained notable traction in odor profiling and predictive analytics within TCM research, offering greater efficiency, reproducibility, and resistance to subjective bias than conventional sensory evaluation methods (Zeng et al., 2023b). One particularly effective strategy integrates headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS) with electronic nose (E-nose) systems, enabling comprehensive characterization of volatile organic metabolites (VOCs) and decoding complex aromatic signatures (Xia et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2024). For example, the aroma profile of Boswellia carterii Birdw. has long been regarded as a critical determinant of both product quality and consumer acceptance (Di Stefano et al., 2020). Using the dual analytical approach, researchers determined that alcohols constituted the dominant VOC class (22.15%), with p-cymenol identified as a principal contributor to the characteristic fragrance, thereby providing a chemical basis for quality differentiation (Chen X. et al., 2024). In a related application, Xia et al. (2024) employed the same methodology to differentiate tea grades according to olfactory profiles, highlighting its potential for sensory-driven quality assessment in TCM contexts.
Li et al. (2022b) combined E-nose and electronic tongue (ET) technologies with chemometric analysis to discriminate Citrus reticulata Blanco samples derived from different cultivation practices. Key volatile metabolites—including β-myrcene, limonene, β-trans-ocimene, γ-terpinene, and terpinolene—were identified as flavor-dominant metabolites and proposed as potential chemical markers for quality stratification. Huangjiu, a traditional fermented product frequently used as an excipient in TCM, can influence both physicochemical attributes and sensory characteristics of formulations, thereby modulating therapeutic outcomes (Wu et al., 2018). Taking Jimo rice wine (JRW) as a case study, researchers combined Flash gas chromatography–based electronic nose (Flash GC E-nose) and NIR with ML algorithms to develop a rapid quality evaluation model. This integrative strategy provides a reference framework for the intelligent quality control of other TCM and auxiliary materials (Zhang Z.-T. et al., 2024).
3.1.3 TCM authentication
The presence of counterfeit and adulterated TCM constitutes a serious threat to clinical safety and public health (Lord et al., 2001). Adulteration in the TCM market can be broadly classified into three categories (Lau et al., 2003): 1) substitution with morphologically similar species; (2) cost-driven adulteration by incorporating foreign substances; and (3) post-harvest treatments, including sulfur fumigation and artificial coloring to improve visual appeal. The high morphological similarity between adulterants and authentic specimens complicates visual authentication, particularly in the absence of standardized evaluation criteria. The incorporation of AI techniques into authenticity assessment has enhanced objectivity, analytical throughput, and reproducibility in TCM authentication practices.
Ziziphus jujuba Mill. var. spinosa (Bunge) Hu ex H. F. Chou (ZZS), which features a chemically diverse profile with multiple metabolites reported to have sedative or hypnotic potential, has experienced growing demand and price inflation, which has economically incentivized its adulteration using Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. (ZMS) and Hovenia acerba Lindl. (HAS) (Ren et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023). To address this issue, Li et al. (2023) established an authentication model integrating Fourier Transform Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-NIR) with multivariate statistical analysis. By incorporating pattern recognition algorithms—namely SVM, KNN, and ANN—the model achieved a significant improvement in identification accuracy, increasing from 77.06% to 97.58%.
In response to complex adulteration forms such as synthetic dyeing and sulfur fumigation, integrated spectroscopic and algorithmic approaches have demonstrated superior precision and analytical robustness. In a representative study, Zhang L. et al. (2023) addressed the challenge of counterfeit Crocus sativus L., which had been fraudulently dyed to mimic the distinctive red hue of authentic material. Using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) in combination with ML algorithms—including Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR), SVM, and Sparrow Search Algorithm based BP Neural Network (SSA-BP)—the authors developed a quantitative detection model capable of identifying both the type and concentration of added dyes. Husaini et al. (2022) combined CNNs with a Foldscope—a portable optical microscope—to create a mobile platform for saffron authentication. This lightweight yet robust system delivered markedly higher classification accuracy than conventional ML approaches such as SF and SVM. Similarly, Zhang et al. (2016) utilized hyperspectral imaging (HSI) in conjunction with chemometric analysis to identify C. sativus L. subjected to illicit sulfur fumigation. PCA was applied to extract key spectral features, while partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) enabled precise classification, achieving a sensitivity of 96.4% and a specificity of 98.3%. Together, these studies provide compelling technical support for the establishment of standardized detection protocols in TCM processing and quality assurance.
To address complex adulteration scenarios, Li H. et al. (2024) developed a multimodal detection framework that integrates Artificial Intelligence Sensory (AIS) technology with Multisource Information Fusion (MIF), enabling simultaneous analysis across multiple sensory modalities. By combining data from ET, E-nose, and computer vision system, the authors constructed a comprehensive quality assessment model for Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H.Chen powder (PNP). Under controlled laboratory conditions, this model achieved a classification accuracy of 100%, underscoring its potential as a precise and reliable authentication tool for TCM quality control.
3.1.4 Classification of TCM varieties
Accurate species identification of Chinese medicinal materials is critical for safeguarding clinical efficacy and advancing the standardization and modernization of TCM research (Malik et al., 2022). Conventional morphological identification methods, which rely heavily on empirical observation, are inherently subjective and low-throughput, rendering them insufficient for distinguishing morphologically similar species or processed medicinal products (Li et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2021). Fritillaria thunbergia Miq., for instance, exhibits substantial germplasm diversity, which in turn leads to pronounced interspecific variation in its bioactive metabolites (Nile et al., 2021). To address this challenge, Kong et al. (Kabir et al., 2022b) developed a classification model that integrates HSI with CNN to discriminate among 12 Fritillaria species, achieving higher cross-validation accuracy than conventional approaches.
In parallel, infrared spectroscopy coupled with chemometric analysis has emerged as a robust, non-destructive analytical approach for quality evaluation in spectroscopic studies (Cheng, 2003; Cheng et al., 2004). Li et al. (2022d) utilized attenuated total reflectance–Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) in conjunction with PLS-DA to distinguish 10 species of Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Berk.) G.H. Sung, J.M. Sung, Hywel-Jones and Spatafora with high accuracy. This method has also demonstrated effectiveness in the classification of other medicinal TCM, including Houttuynia cordata Thunb., Mentha haplocalyx Briq., Andrographis paniculate (Burm. f.) Nees, and D. officinale Kimura et Migo (Wang et al., 2018; Song et al., 2025). DL techniques have been increasingly applied to image-based recognition tasks in TCM, particularly for the analysis of macrostructural characteristics of medicinal materials. In response to the frequent confusion in species identification of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim., Tan et al. (2024) established a CNN–based recognition model capable of differentiating multiple species with a classification accuracy of 99.35%.
3.1.5 Identification of origin
Geo-authentic medicinal materials refer to TCM cultivated in defined ecological zones, where unique environmental conditions contribute to consistent quality and validated therapeutic efficacy (Zhao et al., 2012). Clinical evidence indicates that variations in geographical origin and seasonal factors markedly influence the secondary metabolite composition of a given species, potentially altering its pharmacodynamic properties (Yang et al., 2018; Miao et al., 2023). Consequently, the establishment of scientifically validated origin traceability technologies is critical for ensuring batch-to-batch consistency in the quality of Chinese medicinal materials.
HSI enables the simultaneous acquisition of spatial and spectral data, allowing non-destructive analysis of both morphological traits and chemical signatures. It has become a widely adopted tool for rapid origin identification of TCM. Recent advances have shown that combining HSI with DL algorithms can substantially enhance the accuracy of geographic origin classification for medicinal TCM. For instance, HSI integrated with CNN has been used to differentiate Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. samples from 14 distinct production regions, yielding markedly higher classification performance than conventional methods (Cai et al., 2023). Similarly, NIR-HSI coupled with ML classifiers—such as SVM and RF—has demonstrated strong robustness in distinguishing Lilium species from different origins, with notable generalizability across geographically diverse datasets (Zhao et al., 2024). In another study, He et al. (2024) combined HSI, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and ResNet-34 DL framework to classify the origin of Lilium brownii F. E. Brown var. viridulum Baker, with the optimized model achieving an accuracy of 95.63%. Likewise, Cai (2023) extracted spectral features from both the visible–near-infrared (VNIR) and NIR bands to develop an attention-enhanced CNN model for the origin authentication of Paeonia lactiflora Pall., which significantly outperformed traditional classifiers—including KNN, RF, and SVM—in both accuracy and robustness.
Beyond HSI-based methods, infrared spectroscopy coupled with ML algorithms has also been successfully applied to origin identification of diverse medicinal TCM, such as Bos taurus domesticus Gmelin, demonstrating high classification performance and reliable inter-regional generalization (Wei et al., 2024). Although still in an early stage of development, E-nose technology has shown promising potential for geographic origin determination based on volatile metabolite profiles. For example, E-nose data combined with ML algorithms have been used to differentiate the origin of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg.,illustrating the feasibility of volatile-based traceability for TCM species (Wu et al., 2022).
3.1.6 Grade evaluation
Grading evaluation of TCM is essential for ensuring clinical efficacy and maintaining batch-to-batch consistency, and is traditionally performed by quantifying selected active metabolites (Zhang and Wang, 2023; Lin et al., 2024). In recent years, the integration of histological analysis, metabolomics, and ML has introduced a novel, data-driven paradigm for TCM quality grading. For instance, the Chinese Pharmacopoeia designates astragaloside IV and calycosin-7-O-glucoside as quality control markers for Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. (AR). While sufficient for meeting Pharmacopoeia standards, these markers alone are inadequate for distinguishing between different quality grades. Wu et al. (2024) integrated metabolomic profiling with 7 ML algorithms to identify discriminatory metabolites and construct a robust classification framework for quality grading. Among the identified metabolites, amino acids—such as alanine and phenylalanine—emerged as key markers for grade differentiation, while long-chain fatty acids, including behenic acid and lignoceric acid, were critical for distinguishing wild from cultivated sources. This integrative analytical strategy has also been applied to rare and economically valuable medicinal materials. Li et al. (2022c) developed a classification model for B. taurus domesticus Gmelin by combining transcriptomic and metabolomic datasets, enabling reliable discrimination between natural B. taurus domesticus Gmelin and synthetic substitutes.
For rapid quality assessment, attenuated total reflectance–Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy combined with ML was applied to classify Gastrodia elata powder into four distinct quality levels. Compared with HPLC-based protocols, this approach offered higher efficiency, reduced labor requirements, and allowed for non-destructive testing (Zhan et al., 2022).
Furthermore, for the detection of internal defects, the integration of X-ray imaging with a YOLOv5 deep learning architecture substantially improved sensitivity and accuracy in identifying internal cavities and pest-induced damage in Panax ginseng, significantly outperforming conventional manual inspection methods (Boniecki et al., 2014; Xue et al., 2023).
3.1.7 Identification of storage age
The traditional adage, “For a 7-year illness, seek three-year-old moxa wool (MW),” reflects the critical role of storage duration in shaping the therapeutic efficacy of TCM (Xue et al., 2020). Extended storage can markedly alter the VOCs of MW, with potential consequences for its pharmacological activity. Therefore, precise determination of the storage period for TCM materials is essential to ensure product quality, preserve chemical stability, and promote standardization in both clinical practice and industrial production.
Recent studies have shown that combining HSI with ML provides a powerful non-destructive approach for determining the storage age of TCM. For instance, Hu et al. (Hu et al., 2024) developed a rapid classification model for MW with varying storage durations by integrating HSI data with ML algorithms. The optimized model achieved classification accuracies of 99.78% in the VNIR range and 99.47% in the short-wave infrared (SWIR) range, offering a practical, non-invasive solution for rapid quality assessment based on storage-dependent spectral signatures. Similarly, for C. reticulata Blanco (CRP), HSI data acquired in the 874–1734 nm range were combined with an extreme learning machine (ELM) classifier to differentiate samples stored for 1, 5, 10, and 15 years. The resulting model achieved an accuracy exceeding 85%, confirming the feasibility of the HSI–ELM approach for storage-age classification of CRP (Li et al., 2024c). In parallel, E-nose systems have demonstrated considerable potential for distinguishing Lonicera japonica Thunb. samples by capturing storage-dependent odor fingerprints, thereby offering a complementary, sensory-based modality for non-destructive quality evaluation (Xiong et al., 2014).
3.1.8 Analysis of TCM metabolites
Advances in AI provide sophisticated tools for identifying chemical metabolites of TCM, thereby improving the precision and efficiency of metabolite analysis and deepening mechanistic understanding. In particular, AI-assisted interpretation of chromatographic fingerprints and spectroscopic data (e.g., mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance) enables rapid, accurate identification of metabolites within TCM and complex formulations. For example, Guo et al. (2021) integrated DL with UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS to enhance the chemical profiling of Qianghuoshengshi decoction; the model achieved TCM-specific classification of coumarins and chromones, guided identification via characteristic ions and neutral-loss patterns, and produced fingerprints that supported sensitive, multi-target quantification by UHPLC-sMRM. Building on this theme, Zuo et al. (2021) orthogonally optimized LC–QTOF/MS conditions to maximize metabolite coverage in Gelsemium elegans (Gardn.&Champ.) Benth., and then implemented an AI-assisted data-mining pipeline—database-guided annotation combined with diagnostic-ion and neutral-loss filters—to automate high-intensity chemical profiling. Collectively, these studies illustrate how rule-based AI embedded in MS data mining accelerates metabolite discovery while enabling validated quantitation in complex TCM matrices.
Beyond organic-metabolite profiling, AI also facilitates the identification, classification, and prediction of elemental fingerprints in TCM (Zhang and Wang, 2023; Ding et al., 2024a). For instance, Zhao Y. et al. (2018) compared 13 trace elements and caffeoylquinic-acid–based actives in Lonicera confusa (Sweet) DC. and L. japonica Thunb. by using PCA and DA and achieved clear interspecies classification. Wei et al. (2024) combined NIR with SVM regression to non-destructively quantify seven active metabolites and elements in Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc., while ICP-AES multi-element profiling plus correlation analysis demonstrated stronger associations between in-sample inorganic elements and active metabolites than with rhizosphere soil elements and revealed notable K/Ca enrichment patterns.
3.1.9 Process optimization
Variability in TCM processing remains common due to unstandardized operations, imprecise temperature control, and metabolite loss, leading to inconsistent quality (Kouadio et al., 2024; Zhang J. et al., 2024). Batch-to-batch uniformity and efficiency are also difficult to maintain under manual workflows (Ni et al., 2020). AI coupled with big-data analytics and model training has been applied to processing and quality control. Procedures can be optimized, quality monitored, metabolite consistency supported, and production automated, thereby improving overall quality and efficacy (Zhang et al., 2020).
At raw-material procurement, big-data analyses have been used to evaluate origin, season, and climate effects on TCM quality (Xu et al., 2023). Predictive models trained on historical sources and standards can rank high-quality suppliers and flag noncompliant lots, informing purchasing decisions (Ameer et al., 2020).
During concoction, AI-assisted optimization of technique selection and parameters has been reported to enhance efficacy and reduce adverse reactions (Chen H. et al., 2024). ML has been used to analyze the effects of frying, roasting, and calcining on active metabolites (Kang et al., 2016). Processing conditions—temperature, humidity, and time—can be automatically optimized. For example, E-nose and NIR combined with AI have been used to detect internal and surface changes during Curcuma longa L. processing. Liu Q. et al. (2025) employed HSI for nondestructive monitoring of jujube quality during hot-air drying and built deep-learning models that accurately predict dried-product attributes. Historical and experimental data have also been used to predict and adjust parameters in real time, reducing thermal degradation of active metabolites at high temperatures (Liu et al., 2023).
3.2 AI-driven mechanistic evaluation using bioinformatics
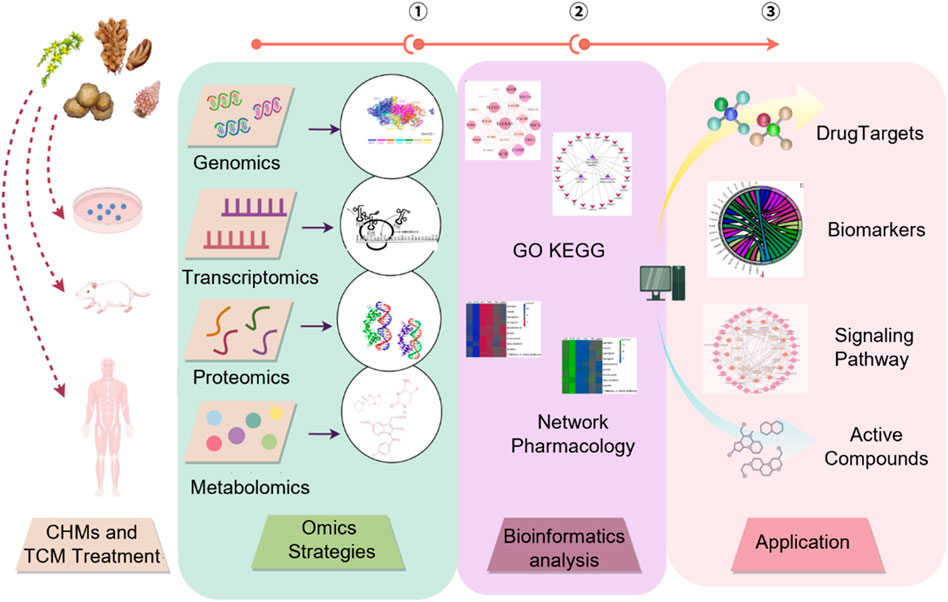
The therapeutic efficacy of TCM often derives from synergistic interactions that cannot be fully explained by quantifying a limited subset of chemical metabolites. The integration of bioinformatics with AI has notably facilitated the development of a mechanism-oriented quality control framework, offering a forward-looking pathway toward the scientific modernization of TCM.
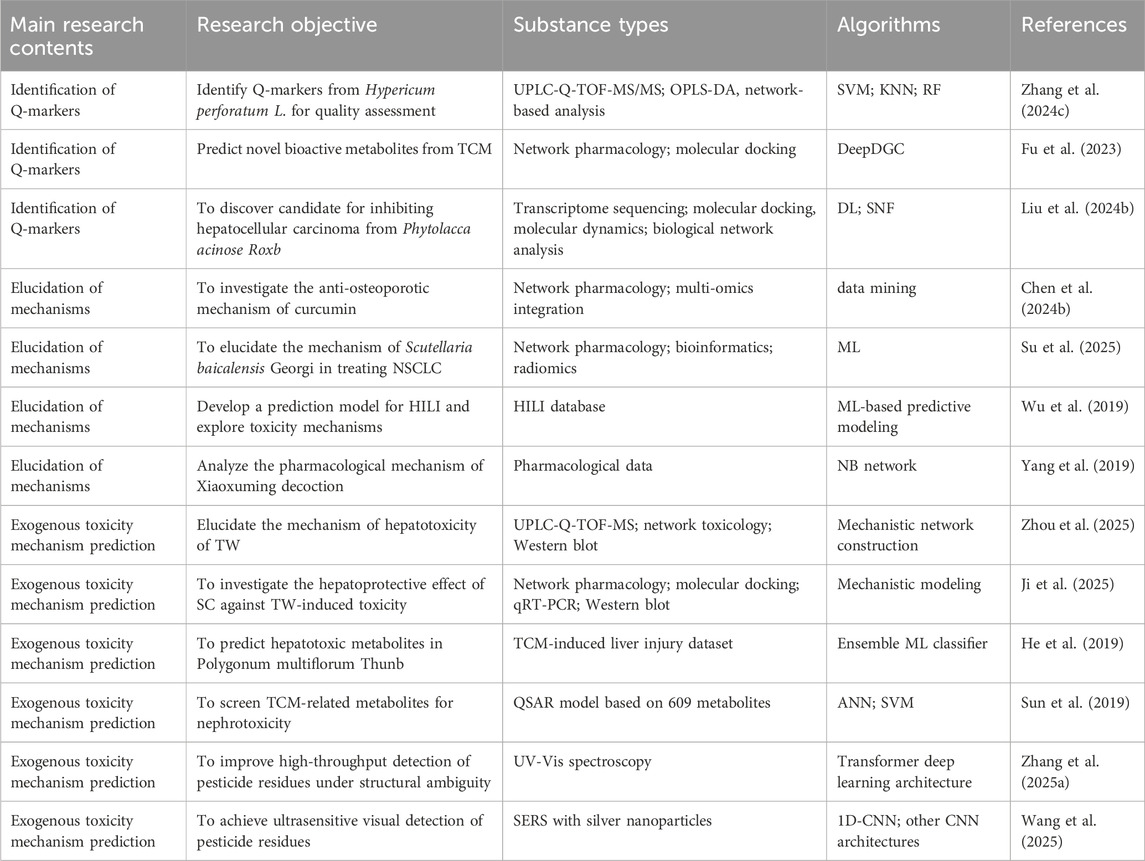
This emerging paradigm emphasizes the creation of a causality-driven system that seamlessly links the identification of Q-markers, the elucidation of therapeutic targets and detailed mechanistic analysis. By integrating transcriptomic, metabolomic, and network-level datasets with advanced intelligent algorithms, the framework enables automated prediction of pharmacological mechanisms, target profiles, and potential toxicity risks (Figure 6). Table 2 summarizes typical cases of the application of AI combined with various technologies in the mechanism evaluation of TCM.
3.2.1 Efficacy-oriented evaluation based on pharmacological mechanisms
The modernization of TCM efficacy evaluation calls for a decisive transition from the conventional model—rooted in metabolite quantification and empirical judgment—to a precision-oriented framework anchored in pharmacologically relevant mechanisms. This shift depends on the identification of biomarkers that are closely linked to therapeutic efficacy and on the elucidation of pharmacodynamic mechanisms.
3.2.1.1 Identification of Q-markers
Reliable biomarkers that accurately capture the pharmacological effects of TCM are essential for precision quality control. Unlike conventional indicators—typically derived from quantitative chemical assays or empirical selection—modern evaluation frameworks place greater emphasis on Q-markers that are directly linked to therapeutic efficacy and possess clearly defined pharmacological functions (Zhou et al., 2023).
For example, Hypericum perforatum L., which exhibits pronounced chemical variation across its medicinal parts, has been studied using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS), orthogonal projections to latent structures discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), and network-based analytical approaches. Through these methods, bioactive differential metabolites were identified as candidate Q-markers and subsequently validated using ML models—including SVM, KNN, and RF—confirming their utility in quality assessment (Zhang Z. et al., 2024). Fu et al. (2023) developed DeepDGC, a DL–based framework that integrates network pharmacology with molecular docking to predict novel bioactive metabolites. Among the predicted candidates, glabrone and vestitol showed binding affinity for SARS-CoV-2–associated proteins and modulated inflammation-related targets such as PTEN and MAP3K8, highlighting their potential as Q-markers.
Moreover, integrating DL with similarity network fusion (SNF) has shown substantial promise in elucidating the mechanisms underlying complex diseases. For instance, in assessing the hepatocellular carcinoma–inhibitory potential of Phytolacca acinose Roxb., Liu et al. (Liu J. et al., 2024) combined biological network analysis, transcriptome sequencing, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations to identify xanthomicrol as a promising therapeutic candidate. Subsequent in vivo experiments not only validated its antitumor efficacy but also clarified its molecular mechanism of action. Collectively, this integrative research framework exemplifies a representative paradigm for Q-markers studies in TCM, seamlessly bridging predictive modeling, mechanistic elucidation, and experimental validation.
3.2.1.2 Elucidation of pharmacodynamic mechanisms
TCM is characterized by its inherently multi-target and multi-pathway therapeutic strategies. While such characteristic have yielded substantial clinical benefits, they also present considerable challenges in elucidating the underlying mechanisms (Zhai et al., 2019). The long-standing issues of “unclear mechanisms” and “undefined targets” remain central points of critique toward TCM (Guo et al., 2019). In this context, integrating AI with multi-omics technologies and network pharmacology provides a robust and systematic approach to dissect the complex pharmacodynamic networks underlying TCM interventions. This, in turn, enables a more precise and evidence-based interpretation of their therapeutic mechanisms. A representative example is the mechanistic investigation of curcumin in the treatment of osteoporosis (OP). Chen S. et al. (2024) employed bioinformatics and data mining techniques to examine the involvement of ferroptosis in OP, with the aim of identifying key regulatory factors. Their analysis revealed MAPK3, TGFB1, CYBB, EGFR, and PTGS2 as hub genes closely linked to ferroptosis, offering novel insights into the molecular basis of curcumin’s anti-osteoporotic effects. Subsequent analysis revealed that curcumin modulates iron homeostasis via EGFR and PTGS2, supporting its potential therapeutic role in OP management.
In cancer therapy, Su et al. (2025) conducted a comprehensive analysis of the therapeutic potential of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi in treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) through the integration of network pharmacology, bioinformatics, ML, and radiomics. They constructed an “active metabolite–target–disease” (ATD) network and, through computational analysis, identified five core targets—FABP4, XDH, GPBAR1, CA4, and CDH1—as pivotal nodes within this network. This study elucidated the multi-target pharmacological mechanisms of S. baicalensis and offered theoretical insights into personalized therapeutic strategies through a data-driven analytical framework.
In TCM toxicology, Wu et al. (2019) created a prediction model using the TCM-induced liver injury (HILI) database to support large-scale screening and explore toxicity mechanisms. Yang et al. (2019) used Bayesian network to analyze the pharmacological mechanism of Xiaoxuming decoction. The model demonstrated robust performance in characterizing the pharmacological profiles of multi-metabolite formulations, highlighting the utility of probabilistic inference methods in elucidating complex TCM mechanisms.
With advances in AI and bioinformatics, TCM research is undergoing a transformation from empirical knowledge to data-driven analysis. This shift includes analysis of both single TCMs and complex prescriptions, and expands from single-target prediction to network-level mechanism reconstruction.
3.2.2 Safety assessment driven by toxicological mechanisms
The safety of TCM is fundamental to its clinical application and global acceptance. Nevertheless, TCM safety evaluation still faces several critical challenges, such as the complex and variable nature of toxic metabolites, the absence of clearly defined toxic thresholds, the limited understanding of detoxification mechanisms, and the lack of precise and standardized detection technologies. Conventional safety assessments primarily depend on animal experimentation and empirical judgment, which fail to elucidate the causal links between endogenous and exogenous toxicants in TCM and their corresponding target organs or toxicological pathways. To meet the urgent needs and technical challenges in TCM safety evaluation, it is crucial to enhance fundamental research both internally and externally, with particular emphasis on in-depth exploration and comprehensive understanding of the biological mechanisms underlying toxic effects. In this context, the integration of bioinformatics, multi-omics technologies, and AI has facilitated the establishment of a multi-dimensional safety evaluation framework encompassing mechanistic toxicology, predictive modeling, and risk screening.
3.2.2.1 Mechanistic prediction of endogenous toxic metabolites
Numerous natural bioactive metabolites in TCM possess intrinsic toxicity, among which hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity are the most frequently observed, raising considerable safety concerns. The integration of modern multi-omics approaches with network toxicology offers a robust strategy for identifying key toxic metabolites, their molecular targets, and associated signaling pathways. Zhou et al. (2025) used untargeted metabolomics based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) combined with network toxicology and Western blotting, to reveal that the hepatotoxicity of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. (TW) involves multiple signaling pathways and abnormal protein expression. They also constructed a mechanistic network linking metabolites to their target proteins. In clinical practice, Spatholobus suberectus Dunn (SC) has been reported to alleviate the adverse effects induced by TW. Ji et al. (2025) explored the hepatoprotective mechanisms of SC through network pharmacology and molecular docking, followed by experimental validation using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot analysis. The results demonstrated that SC mitigates TW-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting the HIF-1α/VEGFA signaling axis and lowering triptolide levels, while preserving its anti-inflammatory efficacy (He et al., 2020; Sun S. et al., 2022).
AI has emerged as a crucial tool in advancing TCM quality and safety evaluation, particularly in the prediction of hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. He et al. (2019) developed a large-scale dataset on TCM-induced liver injury and applied multiple ML algorithms to construct an ensemble classifier, which identified 25 potentially hepatotoxic metabolites in Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. Sun et al. (2019) established a quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) model based on 609 metabolites, including natural products, modern drugs, and hybrid datasets. ANN and SVM algorithms were applied for nephrotoxicity prediction, and validation demonstrated the highest accuracy in the natural product subset, with ANN and SVM achieving 96.7% and 93.3%, respectively. These modeling approaches provide practical tools and valuable references for screening TCM-related metabolites for nephrotoxicity and for evaluating the toxicological profiles of natural products.
AI has emerged as a crucial tool in advancing TCM quality and safety evaluation, particularly in the prediction of hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. He et al. [106] developed a large-scale dataset on TCM-induced liver injury and applied multiple ML algorithms to construct an ensemble classifier, which identified 25 potentially hepatotoxic metabolites in Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. Sun et al. [107] established a quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) model based on 609 metabolites, including natural products, modern drugs, and hybrid datasets. ANN and SVM algorithms were applied for nephrotoxicity prediction, and validation demonstrated the highest accuracy in the natural product subset, with ANN and SVM achieving 96.7% and 93.3%, respectively. These modeling approaches provide practical tools and valuable references for screening TCM-related metabolites for nephrotoxicity and for evaluating the toxicological profiles of natural products.
3.2.2.2 Mechanistic studies of exogenous toxic metabolites
Exogenous hazardous substances—such as heavy metals and pesticide residues—are commonly present during the cultivation, harvesting, processing, and storage of medicinal TCMs, posing substantial risks to the safety and quality control of TCM. These substances can interact complexly with the bioactive or toxic metabolites of TCM, potentially interfering with therapeutic efficacy or exacerbating toxicity. Therefore, elucidating the toxicological mechanisms of exogenous substances in the context of TCM is essential for ensuring medicinal safety and advancing TCM modernization.
Heavy metal contaminants—such as As, Cd, Pb, and Hg—commonly detected in medicinal materials primarily arise from plant bioaccumulation, cross-contamination during processing, and the application of heavy metal–containing therapeutic agents or metalloids (Nagarajan et al., 2014b; 2014a). Integrating ionomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics, researchers have shown that Cd induces neurotoxicity and multi-organ dysfunction through disruption of metabolic pathways and alteration of gene expression. Meanwhile, Se has shown significant protective and detoxifying effects, alleviating Cd-induced toxicity (Zhang X. et al., 2023). Xie et al. (2023) further employed spatially resolved metallomics to systematically map the Se distribution in seeds of the hyperaccumulator plant Cardamine violifolia O.E. Schulz, revealing selenium-associated tolerance mechanisms. This study offers theoretical insights into metalloid accumulation and detoxification mechanisms in medicinal TCMs.
For pesticide residue detection, conventional methods—such as spectrophotometry, GC, thin layer chromatography (TLC), and HPLC—generally provide sufficient sensitivity and specificity. However, their application to metabolites with undefined or poorly characterized structures remains limited, primarily due to restricted analytical throughput and heavy reliance on predefined molecular targets (Xiong et al., 2018; Pan et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023). To address these challenges, AI-enhanced spectroscopic strategies have emerged as promising alternatives. For example, Zhang H. et al. (2025) integrated UV-Vis spectroscopy with a Transformer deep learning architecture, where the self-attention mechanism captured complex spectral dependencies and resolved overlap, offering a feasible approach for high-throughput pesticide residue detection in cases of structural ambiguity. Moreover, to overcome these limitations, researchers have established a multifunctional SERS–based detection system for the simultaneous visualization and quantification of pesticide residues. The system employs silver nanoparticles as the SERS substrate and combines vertex metabolite analysis with the Euclidean distance algorithm to achieve ultrasensitive visual detection of pesticide residues (Wang et al., 2025). Building on this, SERS has the potential to be integrated with AI algorithms—such as one-dimensional convolutional neural networks (1D-CNN) and other CNN architectures—to enable precise identification, classification, and quantification of multiple pesticide residues (Li et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2024). The emergence of these “SERS + AI” hybrid models has enhanced the efficiency and sensitivity of pesticide residue detection in medicinal TCMs, while providing advanced tools and theoretical foundations for developing intelligent quality control systems in accordance with modern TCM quality standards.
4 Advantages and challenges
4.1 Advantages
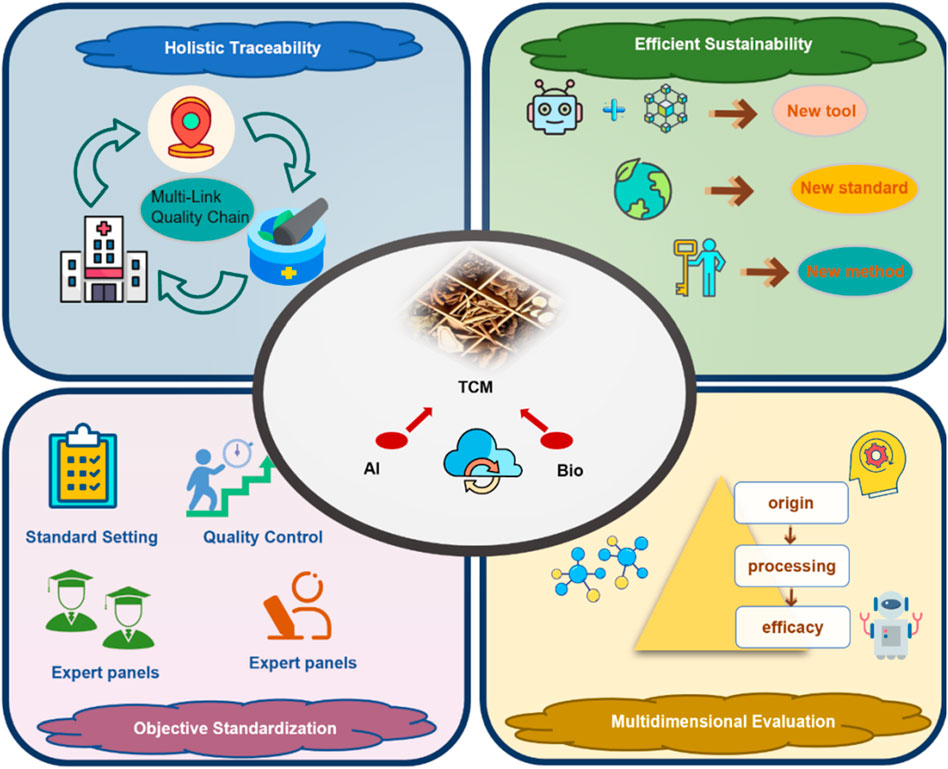
The integration of AI and bioinformatics into TCM quality control provides systematic, data-driven solutions to overcome the limitations of conventional methods. As shown in Figure 7, these advantages are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Enhancing holistic understanding of TCM and supporting multi-link quality traceability
AI can be applied across the full TCM lifecycle, from cultivation to storage, and concurrently support mechanistic analyses to safeguard clinical safety and efficacy. By modeling multidimensional data—such as environmental factors, growth traits, and phytochemical profiles—these tools help identify pharmacologically active metabolites and intrinsic Q-markers. This supports the development of evaluation systems with features specific to TCM (Yang et al., 2022; Kousar et al., 2023). Crucially, along the time axis, AI consolidates what conventional non-AI workflows treat as sequential, manual steps—literature triage, feature curation, and repeated chromatographic re-runs—into a front-loaded model training phase followed by millisecond-to-second per-sample inference, thereby shortening batch turnaround and reducing reviewer time in routine quality control.
2. Enhancing research efficiency, reducing costs, and supporting environmentally sustainable development
AI algorithms can rapidly identify pharmacologically active and potentially toxic metabolites from large-scale datasets, thereby streamlining and accelerating fundamental TCM research. In the investigation of rare medicinal TCMs or complex formulations, AI reduces iterative experimental cycles, shortens research timelines, and minimizes reliance on animal testing, in accordance with ethical and sustainability principles (Liu T. et al., 2025). Relative to conventional trial-and-error or rule-based screening, once trained, AI yields lower per-sample operating cost and markedly faster inference throughput, shifting costs from repeated assays to one-time model development.
3. Enhancing objectivity in quality control and promoting standardization
Traditional identification hinges on inspector expertise, introducing subjectivity and variability. Incorporating ML enables advanced analysis of high-throughput imaging and spectroscopic profiles, improving the objectivity and reproducibility of assessments (Ding et al., 2024b). Under external validation, AI models generally show higher accuracy and better cross-batch robustness than non-AI chemometric baselines, providing firmer ground for standardization and inter-lab transfer. In addition, aligning mechanisms with quality models establishes a robust scientific basis for standardized quality control.
4. Supporting multidimensional quality evaluation aligned with the holistic nature of TCM formulas
AI and bioinformatics enable multidimensional evaluation of TCM quality—spanning metabolites, targets, and pathways—addressing the limitations of single-parameter models. This better reflects TCM’s intrinsic characteristics (multiple metabolites, diverse targets, interconnected pathways). In practice, AI supports scalable fusion of origin, growth duration, and mechanistic readouts, yielding more comprehensive and clinically applicable quality attributes than conventional one-factor approaches (Li et al., 2022e; 2024b).
4.2 Challenges
Despite their promising applications in TCM quality control, AI and bioinformatics face several practical challenges, summarized as follows:
1. Data standardization and model reliability require further improvement
The effectiveness of AI and bioinformatics models relies heavily on high-quality, standardized, and representative datasets. However, in the context of TCM, heterogeneous data types, outdated omics databases, and inconsistent metadata annotations significantly reduce model performance, reproducibility, and cross-context generalizability. In addition, AI-based predictions often lack mechanistic interpretability, highlighting the need for biological validation to enhance reliability and reduce the risks posed by opaque “black-box” models that may mislead scientific conclusions (Messeri and Crockett, 2024).
2. Insufficient privacy protection mechanisms
TCM-related clinical and multi-omics datasets often contain sensitive personal information (Jin and Qin, 2021). However, a comprehensive, TCM-specific data governance framework for privacy protection remains underdeveloped. AI model training poses significant risks of patient data leakage and unauthorized use. Moreover, data-sharing mechanisms on bioinformatics platforms require further refinement under strict regulatory and ethical standards (Khalid et al., 2023).
3. Limited adaptability of current models
The inherent complexity of TCM, characterized by multi-metabolite formulations and nonlinear multi-target interactions, poses substantial challenges to the design and optimization of intelligent predictive models. At present, dedicated algorithms and predictive frameworks capable of systematically capturing multi-metabolite synergy in TCM remain underdeveloped. This deficiency impedes the advancement of intelligent research architectures that are consistent with the holistic and integrative therapeutic principles of TCM (Jiang et al., 2025).
4. Practical barriers to AI implementation in TCM production and regulatory
In TCM quality control, AI faces practical obstacles on production and regulatory contexts. The lack of demonstrated method equivalence and commutability under real raw-material variability (origin, season, processing) prevents AI outputs from replacing pharmacopeial release tests. Workflow integration remains fragile, with predictions not consistently mapped to SOP decision points or written to LIMS/MES and electronic batch records, limiting timely batch disposition. Transferability and model drift across instruments and sites necessitate frequent recalibration and external-batch re-validation, raising operational burden. Regulatory acceptance is further constrained by incomplete evidence packages—predefined statistical criteria, multicenter comparability, and audit-ready data lineage—together with insufficiently actionable explainability that links model attributions to pharmacopeial peaks or Q-markers. Finally, change control and potential re-approval for model updates, coupled with uncertain return on investment and limited analyst training, slow sustained adoption.
5. Key advantages and obstacles for explainable AI in TCM clinical and production
Explainable artificial intelligence can improve trust in TCM clinical and production settings. It links model rationales to pharmacopeial thresholds and SOP decision points. It also communicates calibrated reasoning and uncertainty and records traceable outputs in LIMS, MES, and electronic batch records. However, implementation remains constrained. Heterogeneous fingerprints and spectral collinearity can distort post hoc explanations such as partial dependence and Shapley attribution. Many explanations lack monotonic or shape constraints that match process windows. Communication of uncertainty and distribution shift is often inadequate. Standardized external validation remains limited, including fidelity, stability, calibration, and violation rates. Links to laboratory and manufacturing records are not consistently traceable. Human-in-the-loop triggers and change control with revalidation are immature. These issues temper adoption despite clear potential benefits.
5 Conclusion and prospect
In recent years, various AI-driven strategies have shown promising results in addressing core challenges in TCM quality control. As summarized in the preceding sections, representative ML and DL systems have been evaluated across three key dimensions: First, statistical validation employed cross-validation protocols—often nested—and bootstrap confidence intervals, with head-to-head comparisons against conventional chemometric baselines to quantify incremental benefit. Second, external and transfer validation was performed using geographically and temporally independent datasets (e.g., cross-region and cross-batch acquisitions, cross-instrument splits), demonstrating generalization under realistic shifts in fingerprint heterogeneity and spectral collinearity; representative tasks reported high discriminative performance in external settings. Third, clinical and regulatory alignment was addressed by anchoring model thresholds to pharmacopeial quality indices and predefined Q-markers ranges, and—where available—linking predictions to operational or clinical endpoints such as batch-release pass rate, rework rate, and turnaround time.
Collectively, these layers provide adoption-relevant evidence—rigorous statistics, external testing, and outcome linkage—that bridge algorithmic feasibility and real-world implementation, and they frame the strategic directions that follow.
Nonetheless, TCM’s unique holistic framework—centered on multi-TCM prescriptions, syndrome differentiation, and synergistic pharmacology—continues to pose system-level complexity that conventional methods cannot fully capture. Future efforts should therefore focus on the following strategic directions:
1. Building multidimensional databases to enable AI–domain knowledge co-modeling
Priority should be given to constructing a standardized, multidimensional TCM database that encompasses chemical composition profiles, target networks, toxicological pathways, multi-omics data, and clinical efficacy information. By incorporating ontologies, knowledge graphs, and domain-specific knowledge to enhance learning, AI models can be endowed with semantic understanding and reasoning capabilities in the TCM domain. This promotes the deep integration of theory and AI and facilitates the reconstruction of a closed-loop “data–knowledge–mechanism” system in TCM research.
2. Developing explainable AI and causal inference approaches to improve model transparency and trust
AI models with attention mechanisms can help dissect internal decision pathways, improving traceability and interpretability for scientific reproducibility. Incorporating causal directed acyclic graphs (causal DAGs) into bioinformatics analyses allows the identification of mechanistic targets and intervention pathways, reducing spurious predictions and enhancing biological relevance.
3. Strengthening privacy protection and ethical guidelines to build a compliant intelligent system
The application of privacy-preserving machine learning (PPML) is essential for secure and ethical TCM data sharing and model development. A multi-level, regulation-compliant ethical framework should be established to cover the entire data lifecycle—from acquisition and storage to sharing and analysis (Khalid et al., 2023).
4. Promoting visualization and low-code tools to support cross-disciplinary applications
Since most TCM researchers lack computational training, developing low-code or no-code AI platforms for biomedical applications is essential to facilitate adoption. Such tools can reduce the threshold for AI adoption and promote interdisciplinary innovation and translational research and clinical application (Sundberg and Holmström, 2023).
Author contributions
M-YL: Visualization, Methodology, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. J-QZ: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Conceptualization. X-NL: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Conceptualization. M-YW: Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. KD: Data curation, Writing – original draft. X-YL: Methodology, Writing – original draft. PG: Validation, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. Z-HJ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Co-construction Project of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine’s Science and Technology Department (GZY-KJS-SD-2024-055).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1687681/full#supplementary-material
References
Ameer, K., Jo, Y., Amir, R. M., Shahbaz, H. M., and Kwon, J.-H. (2020). Screening and identification of electron-beam irradiated dried spice-mixture products by electronic sensing and standard analytical methods through dose estimation. LWT 125, 108957. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108957
Aydın Temel, F., Cagcag Yolcu, O., and Turan, N. G. (2023). Artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches in composting process: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 370, 128539. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128539
Bai, Y., and Zhang, H. (2024). The cluster analysis of traditional Chinese medicine authenticity identification technique assisted by chemometrics. Heliyon 10, e37479. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37479
Bansal, C., Deepa, P. R., Agarwal, V., and Chandra, R. (2024). A clustering and graph deep learning-based framework for COVID-19 drug repurposing. Expert Syst. Appl. 249, 123560. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2024.123560
Boniecki, P., Piekarska-Boniecka, H., Świerczyński, K., Koszela, K., Zaborowicz, M., and Przybył, J. (2014). Detection of the granary weevil based on X-ray images of damaged wheat kernels. J. Stored Prod. Res. 56, 38–42. doi:10.1016/j.jspr.2013.11.001
Busia, K. (2024). Herbal medicine dosage standardisation. J. Herb. Med. 46, 100889. doi:10.1016/j.hermed.2024.100889
Cai, Z., Huang, Z., Li, C., Qi, H., Peng, J., et al. (2023). Identification of geographical origins of Radix paeoniae Alba using hyperspectral imaging with deep learning-based fusion approaches. Food Chem. 422, 136169. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136169
Cai, Z., He, M., Li, C., Qi, H., Bai, R., Yang, J., et al. (2023). Identification of chrysanthemum using hyperspectral imaging based on few-shot class incremental learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 215, 108371. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2023.108371
Caratti, A., Squara, S., Bicchi, C., Liberto, E., Vincenti, M., Reichenbach, S. E., et al. (2024). Boosting comprehensive two-dimensional chromatography with artificial intelligence: application to food-omics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 174, 117669. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2024.117669
Castiglioni, I., Rundo, L., Codari, M., Di Leo, G., Salvatore, C., Interlenghi, M., et al. (2021). AI applications to medical images: from machine learning to deep learning. Phys. Medica 83, 9–24. doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.02.006
Chang, Y., Zhou, D., Tang, Y., Ou, S., and Wang, S. (2024). An improved deep learning network for image detection and its application in dendrobii caulis decoction piece. Sci. Rep. 14, 13505. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-63398-w
Chen, S., Li, X., Wu, J., Li, J., Xiao, M., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). Plumula nelumbinis: a review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and safety. J. Ethnopharmacol. 266, 113429. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113429
Chen, X., Leung, Y.-L. A., and Shen, J. (2022). Artificial intelligence and its application for cardiovascular diseases in Chinese medicine. Digit. Chin. Med. 5, 367–376. doi:10.1016/j.dcmed.2022.12.003
Chen, H., Li, J., Chen, X., Mei, L., Feng, S., Duan, P., et al. (2024a). Development and characterization of Artemisia argyi essential oil-loaded nanoemulsion for sustainable weed control: enhanced stability, amplified activity, protected non-target. J. Clean. Prod. 457, 142487. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142487
Chen, S., Pan, Y., Guo, Y., Sun, X., Bai, X., Liu, M., et al. (2024b). Integrative bioinformatics and experimental analysis of curcumin’s role in regulating ferroptosis to combat osteoporosis. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 739, 150949. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150949
Chen, X., Yang, D., Huang, L., Li, M., Gao, J., Liu, C., et al. (2024c). Comparison and identification of aroma components in 21 kinds of frankincense with variety and region based on the odor intensity characteristic spectrum constructed by HS–SPME–GC–MS combined with E-nose. Food Res. Int. 195, 114942. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114942
Cheng, C. (2003). Direct identification of Perilla frutescens seeds from its confusable varieties by FTIR. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi 23, 282–284. Available online at: https://pm.yuntsg.com/details.html?pmid=12961871 (Accessed March 19, 2025).
Cheng, C., Ruan, Y., and Li, B. (2004). Studied on the identification of fructus amomi from its confusable varieties by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi 24, 1355–1358. Available online at: https://pm.yuntsg.com/details.html?pmid=15762475 (Accessed March 19, 2025).
Chi, J., Shu, J., Li, M., Mudappathi, R., Jin, Y., Lewis, F., et al. (2024). Artificial intelligence in metabolomics: a current review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 178, 117852. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2024.117852
Di Stefano, V., Schillaci, D., Cusimano, M. G., Rishan, M., and Rashan, L. (2020). In vitro antimicrobial activity of frankincense oils from boswellia sacra grown in different locations of the dhofar region (oman). Antibiot. (Basel) 9, 195. doi:10.3390/antibiotics9040195
Ding, R., Yu, L., Wang, C., Zhong, S., and Gu, R. (2024a). Quality assessment of traditional Chinese medicine based on data fusion combined with machine learning: a review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 54, 2618–2635. doi:10.1080/10408347.202.2189477
Ding, R., Yu, L., Wang, C., Zhong, S., and Gu, R. (2024b). Quality assessment of traditional Chinese medicine based on data fusion combined with machine learning: a review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 54, 2618–2635. doi:10.1080/10408347.2023.2189477
Fu, Y., Fang, Y., Gong, S., Xue, T., Wang, P., She, L., et al. (2023). Deep learning-based network pharmacology for exploring the mechanism of licorice for the treatment of COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 13, 5844. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31380-7
Gong, S., Liu, J., Liu, Y., Zhu, Y., Zeng, C., Peng, C., et al. (2023). A mid-infrared spectroscopy-random forest system for the origin tracing of Chinese geographical indication aconiti lateralis radix praeparata. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 292, 122394. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2023.122394
Guo, S., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Bi, K., Zhang, Z., et al. (2019). Study on the multitarget synergistic effects of kai-xin-san against alzheimer’s disease based on systems biology. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 1707218. doi:10.1155/2019/1707218
Guo, J., Zhang, L., Shang, Y., Yang, X., Li, J., He, J., et al. (2021). A strategy for intelligent chemical profiling-guided precise quantitation of multi-components in traditional Chinese medicine formulae-QiangHuoShengShi decoction. J. Chromatogr. A 1649, 462178. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462178
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2015). Deep residual learning for image recognition. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1512.03385
He, S., Zhang, X., Lu, S., Zhu, T., Sun, G., and Sun, X. (2019). A computational toxicology approach to screen the hepatotoxic ingredients in traditional Chinese medicines: polygonum multiflorum thunb as a case Study. Biomolecules 9, 577. doi:10.3390/biom9100577
He, T., Liu, J., Wang, X., Duan, C., Li, X., and Zhang, J. (2020). Analysis of cantharidin-induced nephrotoxicity in HK-2 cells using untargeted metabolomics and an integrative network pharmacology analysis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 146, 111845. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111845
He, C., Shi, X., Lin, H., Li, Q., Xia, F., Shen, G., et al. (2024). The combination of HSI and NMR techniques with deep learning for identification of geographical origin and GI markers of Lycium barbarum L. Food Chem. 461, 140903. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.140903
Hu, H., Mei, Y., Wei, Y., Liu, C., Xu, H., Mao, X., et al. (2024). Rapid identification of moxa wool storage period based on hyperspectral imaging technology and machine learning. Heliyon 10, e37650. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37650
Husaini, A. M., Haq, S. A. U., Shabir, A., Wani, A. B., and Dedmari, M. A. (2022). The menace of saffron adulteration: Low-cost rapid identification of fake look-alike saffron using foldscope and machine learning technology. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 945291. doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.945291
Ji, L., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Song, L., Zhang, T., Du, C., et al. (2025). Concoctive principles of detoxification and retention of the main toxicity of Tripterygium wilfordii and its anti-inflammatory efficacy by concocting with the medicinal excipient Spatholobi caulis juice. Fitoterapia 181, 106400. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2025.106400
Jiang, Q., Yang, S., He, S., and Li, F. (2025). AI drug discovery tools and analysis technology: new methods aid in studying the compatibility of traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharmacol. Res. - Mod. Chin. Med. 14, 100566. doi:10.1016/j.prmcm.2024.100566
Jin, Y., and Qin, X. (2021). Significance of TP53 mutation in treatment and prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biomark. Med. 15, 15–28. doi:10.2217/bmm-2020-0400
Kabir, M. H., Guindo, M. L., Chen, R., Liu, F., Luo, X., and Kong, W. (2022a). Deep learning combined with hyperspectral imaging technology for variety discrimination of Fritillaria thunbergii. Molecules 27, 6042. doi:10.3390/molecules2786042
Kabir, M. H., Guindo, M. L., Chen, R., Liu, F., Luo, X., and Kong, W. (2022b). Deep learning combined with hyperspectral imaging technology for variety discrimination of fritillaria thunbergii. Molecules 27, 6042. doi:10.3390/molecules27186042
Kang, Q., Ru, Q., Liu, Y., Xu, L., Liu, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2016). On-line monitoring the extract process of fu-fang shuanghua oral solution using near infrared spectroscopy and different PLS algorithms. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 152, 431–437. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2015.07.098
Khalid, N., Qayyum, A., Bilal, M., Al-Fuqaha, A., and Qadir, J. (2023). Privacy-preserving artificial intelligence in healthcare: techniques and applications. Comput. Biol. Med. 158, 106848. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106848
Kouadio, Y. H., Kouassi, K. N., Kouassi, K. B., Konan, G. A. J., Kouakou, K. A., Dappah, K. D., et al. (2024). Effect of warehouse storage on the alteration, cooking and organoleptic characteristics of kponan yam (dioscorea cayenensis-rotundata) of Côte d’ivoire. Heliyon 10, e40014. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40014
Kousar, M., Kim, Y. R., Kim, J. Y., and Park, J. (2023). Enhancement of growth and secondary metabolites by the combined treatment of trace elements and hydrogen water in wheat sprouts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 16742. doi:10.3390/ijms242316742
Kremer, J., Steenstrup Pedersen, K., and Igel, C. (2014). Active learning with support vector machines. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 4, 313–326. doi:10.1002/widm.1132
Kumari, L., Jaiswal, P., and Tripathy, S. S. (2021). Various techniques useful for determination of adulterants in valuable saffron: a review. Trends Food Sci. and Technol. 111, 301–321. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.061
Lam, B. S. Y., Choy, S. K., and Yu, C. K. W. (2024). Linear discriminant analysis with trimmed and difference distribution modeling. Knowledge-Based Syst. 299, 112093. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2024.112093
Lau, A.-J., Holmes, M. J., Woo, S.-O., and Koh, H.-L. (2003). Analysis of adulterants in a traditional herbal medicinal product using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 31, 401–406. doi:10.1016/s0731-7085(02)00637-4
Li, S., and Zhang, B. (2013). Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 11, 110–120. doi:10.1016/S1875-5364(13)60037-0
Li, C., Xu, F., Cao, C., Shang, M.-Y., Zhang, C.-Y., Yu, J., et al. (2013). Comparative analysis of two species of asari radix et rhizoma by electronic nose, headspace GC–MS and chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 85, 231–238. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.034
Li, G., Nikolic, D., and van Breemen, R. B. (2016). Identification and chemical standardization of licorice raw materials and dietary supplements using UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64, 8062–8070. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02954
Li, Y., Shen, Y., Yao, C.-L., and Guo, D.-A. (2020). Quality assessment of herbal medicines based on chemical fingerprints combined with chemometrics approach: a review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 185, 113215. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113215
Li, H., Mehedi Hassan, M., Wang, J., Wei, W., Zou, M., Ouyang, Q., et al. (2021). Investigation of nonlinear relationship of surface enhanced raman scattering signal for robust prediction of thiabendazole in apple. Food Chem. 339, 127843. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127843
Li, D., Hu, J., Zhang, L., Li, L., Yin, Q., Shi, J., et al. (2022a). Deep learning and machine intelligence: new computational modeling techniques for discovery of the combination rules and pharmacodynamic characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 933, 175260. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175260
Li, X., Yang, Y., Zhu, Y., Ben, A., and Qi, J. (2022b). A novel strategy for discriminating different cultivation and screening odor and taste flavor compounds in xinhui tangerine peel using E-nose, E-tongue, and chemometrics. Food Chem. 384, 132519. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132519
Li, X., Yao, Y., Chen, M., Ding, H., Liang, C., Lv, L., et al. (2022c). Comprehensive evaluation integrating omics strategy and machine learning algorithms for consistency of Calculus bovis from different sources. Talanta 237, 122873. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122873
Li, Y., Bi, Q., Wei, W., Yao, C., Zhang, J., and Guo, D. (2022d). Sequential decision fusion pipeline for the high-throughput species recognition of medicinal caterpillar fungus by using ATR-FTIR. Microchem. J. 179, 107437. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2022.107437
Li, Y., Ju, S., Lin, Z., Wu, H., Wang, Y., Jin, H., et al. (2022e). Bioactive-chemical quality markers revealed: an integrated strategy for quality control of chicory. Front. Nutr. 9, 934176. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.934176
Li, M., Shi, Y., Zhang, J., Wan, X., Fang, J., Wu, Y., et al. (2023). Rapid evaluation of Ziziphi spinosae semen and its adulterants based on the combination of FT-NIR and multivariate algorithms. Food Chem. X 20, 101022. doi:10.1016/j.fochx.2023.101022
Li, H., Gui, X., Wang, P., Yue, Y., Li, H., Fan, X., et al. (2024a). Research on rapid quality identification method of Panax notoginseng powder based on artificial intelligence sensory technology and multi-source information fusion technology. Food Chem. 440, 138210. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.138210
Li, Y., Wang, L., Yang, W., Xie, Q., Xu, H., Wen, R., et al. (2024b). Promotion of a quality standard for Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis based on the efficacy-oriented effect-constituent index. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 238, 115843. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115843
Li, Y., Zhao, W., Qian, M., Wen, Z., Bai, W., Zeng, X., et al. (2024c). Recent advances in the authentication (geographical origins, varieties and aging time) of tangerine peel (Citri reticulatae pericarpium): a review. Food Chem. 442, 138531. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138531
Lin, L., Liu, G., Zhang, D., Yu, F., Tan, L., Mu, X., et al. (2024). Quality grade evaluation of nvjin pills based on traditional Chinese medicine reference drug and network pharmacology of target-focused compounds. J. Sep. Sci. 47, e2300134. doi:10.1002/jssc.202300134
Liu, C., and Guo, D. (2020). Inheriting essence, keeping integrity and innovation. Chin. Herb. Med. 12, 1–2. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2020.01.001
Liu, J., Shi, X., Lin, H., He, C., Li, Q., Shen, G., et al. (2023). Geographical origin identification and quality comparison of ningxia goji berries (lycium barbarum L.) by NMR-based techniques. J. Food Compos. Analysis 119, 105258. doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2023.105258
Liu, C.-L., Jiang, Y., and Li, H.-J. (2024a). Quality consistency evaluation of traditional Chinese medicines: current status and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 55, 684–701. doi:10.1080/10408347.2024.2305267
Liu, J., Zhou, Y., Zhou, P., He, T., Liu, P., Wang, J., et al. (2024b). Mechanistic insights into xanthomicrol as the active anti-HCC ingredient of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb.: a network pharmacology analysis and transcriptomics integrated experimental verification. J. Ethnopharmacol. 333, 118467. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118467
Liu, Q., Jiang, X., Wang, F., Fan, S., Zhu, B., Yan, L., et al. (2025a). Evaluation and process monitoring of jujube hot air drying using hyperspectral imaging technology and deep learning for quality parameters. Food Chem. 467, 141999. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141999
Liu, T., Zhuang, X. X., Zheng, W. J., and Gao, J. R. (2025b). Integrative multi-omics and network pharmacology reveal the mechanisms of fangji huangqi decoction in treating IgA nephropathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 337, 118996. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118996
Liu, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, X., Bian, X., and Tian, W. (2025c). Modern spectroscopic techniques combined with chemometrics for process quality control of traditional Chinese medicine: a review. Microchem. J. 213, 113605. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2025.113605
Lord, G. M., Cook, T., Arlt, V. M., Schmeiser, H. H., Williams, G., and Pusey, C. D. (2001). Urothelial malignant disease and Chinese herbal nephropathy. Lancet 358, 1515–1516. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(01)06576-x
Luo, Y., Yang, H., and Tao, G. (2024). Systematic review on fingerprinting development to determine adulteration of Chinese herbal medicines. Phytomedicine 129, 155667. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155667
Maione, C., Barbosa, F., and Barbosa, R. M. (2019). Predicting the botanical and geographical origin of honey with multivariate data analysis and machine learning techniques: a review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 157, 436–446. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2019.01.020
Malik, O. A., Ismail, N., Hussein, B. R., and Yahya, U. (2022). Automated real-time identification of medicinal plants species in natural environment using deep learning models-a case study from borneo region. Plants (Basel) 11, 1952. doi:10.3390/plants11151952
Messeri, L., and Crockett, M. J. (2024). Artificial intelligence and illusions of understanding in scientific research. Nature 627, 49–58. doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07146-0
Miao, J., Huang, Y., Wang, Z., Wu, Z., and Lv, J. (2023). Image recognition of traditional Chinese medicine based on deep learning. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1199803. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1199803
Monakhova, Y. B., Holzgrabe, U., and Diehl, B. W. K. (2018). Current role and future perspectives of multivariate (chemometric) methods in NMR spectroscopic analysis of pharmaceutical products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 147, 580–589. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2017.05.034
Moreno-Torres, M., López-Pascual, E., Rapisarda, A., Quintás, G., Drees, A., Steffensen, I.-L., et al. (2024). Novel clinical phenotypes, drug categorization, and outcome prediction in drug-induced cholestasis: analysis of a database of 432 patients developed by literature review and machine learning support. Biomed. Pharmacother. 174, 116530. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116530
Nagarajan, S., Krishnaswamy, S., Pemiah, B., Rajan, K. S., Krishnan, U., and Sethuraman, S. (2014a). Scientific insights in the preparation and characterisation of a lead-based naga bhasma. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 76, 38–45. Available online at: https://pm.yuntsg.com/details.html?pmid=24799737 (Accessed April 7, 2025).
Nagarajan, S., Sivaji, K., Krishnaswamy, S., Pemiah, B., Rajan, K. S., Krishnan, U. M., et al. (2014b). Safety and toxicity issues associated with lead-based traditional herbo-metallic preparations. J. Ethnopharmacol. 151, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.037
Ni, J., Ding, C., Zhang, Y., and Song, Z. (2020). Impact of different pretreatment methods on drying characteristics and microstructure of goji berry under electrohydrodynamic (EHD) drying process. Innovative Food Sci. and Emerg. Technol. 61, 102318. doi:10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102318
Nile, S. H., Su, J., Wu, D., Wang, L., Hu, J., Sieniawska, E., et al. (2021). Fritillaria thunbergii miq. (zhe beimu): a review on its traditional uses, phytochemical profile and pharmacological properties. Food Chem. Toxicol. 153, 112289. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112289
Ou, G.-L., He, Y.-L., Fournier-Viger, P., and Huang, J. Z. (2025). A novel multi-source weighted naive bayes classifier. Inf. Sci. 721, 122568. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2025.122568
Ouyang, X.-J., Li, J.-Q., Zhong, Y.-Q., Tang, M., Meng, J., Ge, Y.-W., et al. (2023). Identifying the active ingredients of carbonized typhae pollen by spectrum-effect relationship combined with MBPLS, PLS, and SVM algorithms. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 235, 115619. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115619
Pan, H., Ahmad, W., Jiao, T., Zhu, A., Ouyang, Q., and Chen, Q. (2022). Label-free au NRs-based SERS coupled with chemometrics for rapid quantitative detection of thiabendazole residues in citrus. Food Chem. 375, 131681. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131681
Paolanti, M., and Frontoni, E. (2020). Multidisciplinary pattern recognition applications: a review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 37, 100276. doi:10.1016/j.cosrev.2020.100276
Ren, Y., Gao, F., Li, B., Yuan, A., Zheng, L., and Zhang, Y. (2022). A precise efficacy determination strategy of traditional Chinese herbs based on Q-markers: anticancer efficacy of astragali radix as a case. Phytomedicine 102, 154155. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154155
Ren, A., Wu, T., Wang, Y., Fan, Q., Yang, Z., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Integrating animal experiments, mass spectrometry and network-based approach to reveal the sleep-improving effects of ziziphi spinosae semen and γ-aminobutyric acid mixture. Chin. Med. 18, 99. doi:10.1186/s13020-023-00814-9
Russell, S. J., and Norvig, P. (2022). Artificial intelligence: a modern approach. Fourth edition, global edition. Boston: Pearson.
Sarker, I. H. (2021). Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2, 160. doi:10.1007/s42979-021-00592-x
Soltani, S., khodaie, L., and Surana, V. (2025). Artificial intelligence perspectives in advancing persian herbal medicine: a systematic review. Adv. Integr. Med. 12, 100471. doi:10.1016/j.aimed.2025.03.001
Song, C., An, Y., Zhao, W., Huang, Y., Zhang, L., Li, L., et al. (2025). A chemometric and machine learning scheme for classification of 37 kinds of aerial parts of medicinal herbs based on ATR-FTIR. Microchem. J. 209, 112671. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2025.112671
Soon, W. W., Hariharan, M., and Snyder, M. P. (2013). High-throughput sequencing for biology and medicine. Mol. Syst. Biol. 9, 640. doi:10.1038/msb.2012.61
Su, S., Luo, J., Wang, F., Li, S., Gao, Y., and Yan, L. (2025). The potential mechanism of antifluorescent lung cancer by Chinese medicine huang qin: based on bioinformatics molecular, network pharmacology and imaging histology analysis. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 18, 101381. doi:10.1016/j.jrras.2025.101381
Sun, Y., Shi, S., Li, Y., and Wang, Q. (2019). Development of quantitative structure-activity relationship models to predict potential nephrotoxic ingredients in traditional Chinese medicines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 128, 163–170. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2019.03.056
Sun, S., Wang, M., Yuan, Y., Wang, S., Ding, H., Liang, C., et al. (2022a). A new strategy for the rapid identification and validation of direct toxicity targets of psoralen-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 363, 11–26. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.05.002
Sun, X., Qian, H., Xiong, Y., Zhu, Y., Huang, Z., and Yang, F. (2022b). Deep learning-enabled mobile application for efficient and robust herb image recognition. Sci. Rep. 12, 6579. doi:10.1038/s4598-022-10449-9
Sun, X., Qian, H., Xiong, Y., Zhu, Y., Huang, Z., and Yang, F. (2022c). Deep learning-enabled mobile application for efficient and robust herb image recognition. Sci. Rep. 12, 6579. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-10449-9
Sundberg, L., and Holmström, J. (2023). Democratizing artificial intelligence: how no-code AI can leverage machine learning operations. Bus. Horizons 66, 777–788. doi:10.1016/j.bushor.2023.04.003
Suriyaamporn, P., Pamornpathomkul, B., Patrojanasophon, P., Ngawhirunpat, T., Rojanarata, T., and Opanasopit, P. (2024). The artificial intelligence-powered new era in pharmaceutical research and development: a review. AAPS PharmSciTech 25, 188. doi:10.1208/s12249-024-02901-y
Tan, C., Wu, C., Huang, Y., Wu, C., and Hu, C. (2024). Identification of different species of Zanthoxyli Pericarpium based on convolution neural network. PLOS ONE 15, e0230287. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0230287
Thapa, S., Maurya, S. N., Manjunath, K., Mahmood, A. A., Devi, K., Varghese, S. A., et al. (2025). LC-MS profiling and multi-target mechanistic insights of hibiscus rosa-sinensis in diabetes: network pharmacology, molecular docking, MD simulation, PCA, and in-vitro α-amylase inhibition. Pharmacol. Res. - Mod. Chin. Med. 16, 100636. doi:10.1016/j.prmcm.2025.100636
Tian, D., Chen, W., Xu, D., Xu, L., Xu, G., Guo, Y., et al. (2024). A review of traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis using machine learning: inspection, auscultation-olfaction, inquiry, and palpation. Comput. Biol. Med. 170, 108074. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108074
Wang, Z., and Li, S. (2022). Network pharmacology in quality control of traditional Chinese medicines. Chin. Herb. Med. 14, 477–478. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2022.09.001
Wang, Y., Huang, H.-Y., Zuo, Z.-T., and Wang, Y.-Z. (2018). Comprehensive quality assessment of Dendrubium officinale using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy combined with random forest and support vector machine regression. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 205, 637–648. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2018.07.086
Wang, T., Liu, J., Luo, X., Hu, L., and Lu, H. (2021). Functional metabolomics innovates therapeutic discovery of traditional Chinese medicine derived functional compounds. Pharmacol. and Ther. 224, 107824. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107824
Wang, K., Yue, Z., Fang, X., Lin, H., Wang, L., Cao, L., et al. (2023). SERS detection of thiram using polyacrylamide hydrogel-enclosed gold nanoparticle aggregates. Sci. Total Environ. 856, 159108. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159108
Wang, X., Jiang, S., Liu, Z., Sun, X., Zhang, Z., Quan, X., et al. (2024). Integrated surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy and convolutional neural network for quantitative and qualitative analysis of pesticide residues on pericarp. Food Chem. 440, 138214. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.138214
Wang, X., Sun, X., Huang, H., Huang, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, Z., et al. (2025). Multifunctional surface-enhanced raman scattering imaging for detection and visualization of pesticide residues in crops. J. Hazard. Mater. 491, 138020. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138020
Wei, J., Wang, Y., Tang, X., Du, Y., Bai, Y., Deng, Y., et al. (2024). Correlation analysis between active components of cornus officinalis and inorganic elements in rhizosphere soil and rapid analysis of origin quality by near-infrared spectroscopy combined with machine learning. Industrial Crops Prod. 210, 118101. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.118101
Wu, X., Wang, S., Lu, J., Jing, Y., Li, M., Cao, J., et al. (2018). Seeing the unseen of Chinese herbal medicine processing (paozhi): advances in new perspectives. Chin. Med. 13, 4. doi:10.1186/s13020-018-0163-3
Wu, Q., Cai, C., Guo, P., Chen, M., Wu, X., Zhou, J., et al. (2019). In silico identification and mechanism exploration of hepatotoxic ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 458. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00458
Wu, Z., Ye, X., Bian, F., Yu, G., Gao, G., Ou, J., et al. (2022). Determination of the geographical origin of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels and Gilg using an electronic nose technique with multiple algorithms. Heliyon 8, e10801. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10801
Wu, J., Deng, S., Yu, X., Wu, Y., Hua, X., Zhang, Z., et al. (2024). Identify production area, growth mode, species, and grade of astragali Radix using metabolomics “big data” and machine learning. Phytomedicine 123, 155201. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155201
Xia, H., Chen, W., Hu, D., Miao, A., Qiao, X., Qiu, G., et al. (2024). Rapid discrimination of quality grade of black tea based on near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), electronic nose (E-nose) and data fusion. Food Chem. 440, 138242. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.138242
Xie, H., Tian, X., He, L., Li, J., Cui, L., Cong, X., et al. (2023). Spatial metallomics reveals preferable accumulation of methylated selenium in a single seed of the hyperaccumulator cardamine violifolia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 2658–2665. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c08112
Xiong, Y., Xiao, X., Yang, X., Yan, D., Zhang, C., Zou, H., et al. (2014). Quality control of Lonicera japonica stored for different months by electronic nose. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 91, 68–72. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2013.12.016
Xiong, Z., Lin, M., Lin, H., and Huang, M. (2018). Facile synthesis of cellulose nanofiber nanocomposite as a SERS substrate for detection of thiram in juice. Carbohydr. Polym. 189, 79–86. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.02.014
Xu, L., Li, J., Lin, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., and Yan, Y. (2016). Pairwise comparison and rank learning for image quality assessment. Displays 44, 21–26. doi:10.1016/j.displa.2016.06.002
Xu, Y., Wen, G., Hu, Y., Luo, M., Dai, D., Zhuang, Y., et al. (2021). Multiple attentional pyramid networks for Chinese herbal recognition. Pattern Recognit. 110, 107558. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107558
Xu, Z., Hu, H., Wang, T., Zhao, Y., Zhou, C., Xu, H., et al. (2023). Identification of growth years of kudzu root by hyperspectral imaging combined with spectral–spatial feature tokenization transformer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 214, 108332. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2023.108332
Xu, J., Tu, Z., Wang, H., Hu, Y., Wen, P., Huang, X., et al. (2024). Discrimination and characterization of different ultrafine grinding times on the flavor characteristic of fish gelatin using E-nose, HS-SPME-GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS. Food Chem. 433, 137299. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137299
Xue, S., Wang, C., Li, T., Liu, S., and Shi, Y. (2020). Therapeutic efficacy observation on moxibustion with moxa of different storage years for moderate-to-severe primary knee osteoarthritis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 18, 345–351. doi:10.1007/s11726-020-1200-1
Xue, Q., Miao, P., Miao, K., Yu, Y., and Li, Z. (2023). An online automatic sorting system for defective Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma Rubra using deep learning. Chin. Herb. Med. 15, 447–456. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2023.01.001
Yang, X., Tian, X., Zhou, Y., Liu, Y., Li, X., Lu, T., et al. (2018). Evidence-based study to compare daodi traditional Chinese medicinal material and non-daodi traditional chinese medicinal material. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 6763130. doi:10.1155/2018/6763130
Yang, S., Shen, Y., Lu, W., Yang, Y., Wang, H., Li, L., et al. (2019). Evaluation and identification of the neuroprotective compounds of xiaoxuming decoction by machine learning: a novel mode to explore the combination rules in traditional Chinese medicine prescription. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 6847685. doi:10.1155/2019/6847685
Yang, L., Yan, Y., Zhao, B., Xu, H., Su, X., and Dong, C. (2022). Study on the regulation of exogenous hormones on the absorption of elements and the accumulation of secondary metabolites in the medicinal plant artemisia argyi leaves. Metabolites 12, 984. doi:10.3390/metabo12100984
Yang, M., Wang, H., Zhang, Y. L., Zhang, F., Li, X., Kim, S.-D., et al. (2023). The herbal medicine suanzaoren (Ziziphi spinosae Semen) for sleep quality improvements: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Integr. Cancer Ther. 22, 15347354231162080. doi:10.1177/15347354231162080
Ye, T., Jin, C., Zhou, J., Li, X., Wang, H., Deng, P., et al. (2011). Can odors of TCM be captured by electronic nose? The novel quality control method for musk by electronic nose coupled with chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 55, 1239–1244. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2011.03.018
Yi, L.-J. (2019). Optimization of water extraction technology of yiqi huoxue prescription based on orthogonal test design and BP neural network. Zhongcaoyao, 4305–4312. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.18.008
Zeng, X., Cao, R., Xi, Y., Li, X., Yu, M., Zhao, J., et al. (2023a). Food flavor analysis 4.0: a cross-domain application of machine learning. Trends Food Sci. and Technol. 138, 116–125. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.203.06.011
Zeng, X., Cao, R., Xi, Y., Li, X., Yu, M., Zhao, J., et al. (2023b). Food flavor analysis 4.0: a cross-domain application of machine learning. Trends Food Sci. and Technol. 138, 116–125. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2023.06.011
Zhai, B., Zhang, N., Han, X., Li, Q., Zhang, M., Chen, X., et al. (2019). Molecular targets of β-elemene, a herbal extract used in traditional Chinese medicine, and its potential role in cancer therapy: a review. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 114, 108812. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108812
Zhan, W., Yang, X., Lu, G., Deng, Y., and Yang, L. (2022). A rapid quality grade discrimination method for Gastrodia elata powderusing ATR-FTIR and chemometrics. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 264, 120189. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2021.120189
Zhang, Y., and Wang, Y. (2023). Recent trends of machine learning applied to multi-source data of medicinal plants. J. Pharm. Analysis 13, 1388–1407. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2023.07.012
Zhang, H., Wu, T., Zhang, L., and Zhang, P. (2016). Development of a portable field imaging spectrometer: application for the identification of sun-dried and sulfur-fumigated Chinese herbals. Appl. Spectrosc. 70, 879–887. doi:10.1177/0003702816638293
Zhang, C., Wu, W., Zhou, L., Cheng, H., Ye, X., and He, Y. (2020). Developing deep learning based regression approaches for determination of chemical compositions in dry black goji berries (lycium ruthenicum murr.) using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging. Food Chem. 319, 126536. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126536
Zhang, L., Zhang, C., Li, W., Li, L., Zhang, P., Zhu, C., et al. (2023a). Rapid indentification of auramine O dyeing adulteration in Dendrobium officinale, saffron and curcuma by SERS raman spectroscopy combined with SSA-BP neural networks model. Foods 12, 4124. doi:10.3390/foods12224124
Zhang, X., Li, F., Ji, C., and Wu, H. (2023b). Toxicological mechanism of cadmium in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum using combined ionomic, metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses. Environ. Pollut. 323, 121286. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121286
Zhang, J., Ding, C., Lu, J., Wang, H., Bao, Y., Han, B., et al. (2024a). Effects of electrohydrodynamics on drying characteristics and volatile profiles of goji berry (lycium barbarum L.). LWT 200, 116149. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116149
Zhang, X., Wang, L., Li, R., Wang, L., Fu, Z., He, F., et al. (2024b). Identification strategy of fructus gardeniae and its adulterant based on UHPLC/Q-orbitrap-MS and UHPLC-QTRAP-MS/MS combined with PLS regression model. Talanta 267, 125136. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2023.125136
Zhang, Z., Ying, Z., He, M., Zhang, Y., Nie, W., Tang, Z., et al. (2024c). UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS combined with machine learning methods for screening quality indicators of Hypericum perforatum L. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 248, 116313. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116313
Zhang, Z.-T., Li, Y., Bai, L., Chen, P., Jiang, Y., Qi, Y., et al. (2024d). Machine learning combined with multi-source data fusion for rapid quality assessment of yellow rice wine with different aging years. Microchem. J. 199, 110126. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2024.110126
Zhang, H., Duan, Q., Sun, L., Lee, J., Wu, W., Zhou, C., et al. (2025a). A multi-component heavy metal detection method using UV-vis superimposed spectrum and deep learning. J. Hazard. Mater. 496, 139187. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.139187
Zhang, W., Bai, X., and Zhao, D. (2025b). A study on the predictive model for ginsenoside content in wild ginseng based on decision tree and ensemble learning algorithms. Microchem. J. 212, 113318. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2025.113318
Zhao, Z., Guo, P., and Brand, E. (2012). The formation of daodi medicinal materials. J. Ethnopharmacol. 140, 476–481. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.01.048
Zhao, J., Ma, S., and Li, S. (2018a). Advanced strategies for quality control of Chinese medicines. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 147, 473–478. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2017.06.048
Zhao, Y., Dou, D., Guo, Y., Qi, Y., Li, J., and Jia, D. (2018b). Comparison of the trace elements and active components of lonicera japonica flos and lonicera flos using ICP-MS and HPLC-PDA. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 183, 379–388. doi:10.1007/s12011-017-1138-4
Zhao, Q., Miao, P., Liu, C., Yu, Y., and Li, Z. (2024). Accurate and non-destructive identification of origins for lily using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging combined with machine learning. J. Food Compos. Analysis 129, 106080. doi:10.1016/j.jfca.2024.106080
Zhou, Y., Jiang, H., Huang, X., Rao, K., Wang, D., Wu, Q., et al. (2023). Indistinct assessment of the quality of traditional Chinese medicine in precision medicine exampling as safflower. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 227, 115277. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115277
Zhou, G.-L., Su, S.-L., Yu, L., Shang, E.-X., Hua, Y.-Q., Yu, H., et al. (2025). Exploring the liver toxicity mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii extract based on metabolomics, network pharmacological analysis and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 337, 118888. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118888
Zhu, J., Sharma, A. S., Xu, J., Xu, Y., Jiao, T., Ouyang, Q., et al. (2021). Rapid on-site identification of pesticide residues in tea by one-dimensional convolutional neural network coupled with surface-enhanced raman scattering. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 246, 118994. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2020.118994
Zuo, M.-T., Liu, Y.-C., Sun, Z.-L., Lin, L., Tang, Q., Cheng, P., et al. (2021). An integrated strategy toward comprehensive characterization and quantification of multiple components from herbal medicine: an application study in gelsemium elegans. Chin. Herb. Med. 13, 17–32. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2020.06.002
Keywords: artificial intelligence, bioinformatics, quality control, traditional Chinese Medicine, mechanism, multi-omics technologies
Citation: Li M-Y, Zhu J-Q, Liu X-N, Wu M-Y, Dong K, Li X-Y, Gao P and Jiang Z-H (2025) Application and research progress on artificial intelligence in the quality of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1687681. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1687681
Received: 19 August 2025; Accepted: 09 October 2025;
Published: 17 October 2025.
Edited by:
Michael Heinrich, University College London, United KingdomReviewed by:
Xin Chen, Tongji University, ChinaPhuvamin Suriyaamporn, Silpakorn University, Thailand
Copyright © 2025 Li, Zhu, Liu, Wu, Dong, Li, Gao and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peng Gao, Z2FvcGVuZ0BzZHV0Y20uZWR1LmNu; Zhi-Hui Jiang, NjAyMzAxMDdAc2R1dGNtLmVkdS5jbg==
 Mei-Yu Li
Mei-Yu Li Jun-Qing Zhu
Jun-Qing Zhu Xiao-Nan Liu
Xiao-Nan Liu