- 1School of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu, China
- 2Shenzhen Prevention and Treatment Center for Occupational Diseases, Shenzhen, China
- 3School of Life Science, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Osteoporosis (OP) is characterized by decreased bone mass and deterioration of bone microstructure, significantly increasing fracture risk. Icariin (ICA), a natural compound, has demonstrated efficacy in improving bone microstructure and bone mineral density (BMD) across multiple OP models, with its targeting efficacy enhanced through innovative drug delivery systems. This review systematically summarizes recent advances in ICA research, focusing on its application dosage forms, therapeutic performance in various animal models, and underlying molecular mechanisms. In order to ensure a comprehensive and reliable report, we conducted a systematic search in the core collection of web of science according to PRISMA guidelines, and finally included 182 publications for in-depth analysis. ICA’s therapeutic efficacy is enhanced through innovative delivery systems, including traditional Chinese medicine formulations and advanced biomaterials. Studies across postmenopausal, glucocorticoid-induced, aging, and diabetic OP models consistently demonstrate ICA’s ability to improve bone microarchitecture and BMD. Mechanistically, ICA exerts dual-regulation effects by promoting osteogenesis while inhibiting osteoclastogenesis, coupled with multi-target actions involving autophagy regulation, anti-inflammatory effects, iron overload mitigation, and oxidative stress reduction. In conclusion, ICA’s comprehensive and multi-mechanistic intervention strategy, augmented by advanced delivery systems, presents a natural, safe, and efficacious candidate for OP treatment. This review synthesizes critical advances from molecular mechanisms to biomedical applications, supporting further clinical translation of ICA-based therapies.
1 Introduction
Osteoporosis (OP), characterized by reduced bone mass and microstructural deterioration, is a systemic bone metabolic disease. Prevalent among postmenopausal women and the elderly, it significantly increases fracture risk and poses a global public health challenge (Ilyas et al., 2024; Tan et al., 2024; Chaichit et al., 2022; Lin et al., 2020; García-Espinosa et al., 2024). At present, there are mainly three kinds of drugs for the prevention or treatment of OP in clinic: inhibitors of bone resorption (such as bisphosphonates, RANKL inhibitors, estrogen and related drugs, etc.), which can slow down bone loss by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts; Osteogenic drugs (such as parathyroid hormone analogue teriparatide) can increase bone mass and strength by stimulating osteoblasts (Su et al., 2024; Khoury, 2024); Drugs with dual effects (such as sclerostin inhibitor Romozozumab and strontium ranelate) can simultaneously inhibit bone resorption and promote bone formation (Bonnelye et al., 2008). However, the long-term safety and potential adverse reactions of existing drugs are important considerations in their clinical application. For example, bisphosphonates can effectively inhibit bone resorption, but there is a risk of jaw necrosis after long-term use (Park et al., 2025). Strontium ranelate has been proved to effectively reduce the risk of vertebral and hip fractures in postmenopausal osteoporosis patients, but it also increases the risk of venous thromboembolism, myocardial infarction and severe skin allergic reactions (Cacoub et al., 2013). Romosozumab demonstrates significant efficacy in increasing bone mineral density; however, its clinical application is limited by the high cost and potential cardiovascular risk (Takeuchi, 2025). These limitations highlight the continuing demand for safer, more effective, and more economical treatments in the field of osteoporosis treatment.
In contrast, icariin (ICA), as a natural anti osteoporosis drug candidate, has shown unique appeal. ICA, the primary active flavonoid glycoside in Epimedium spp., has been used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for thousands of years, which provides strong support for its good safety characteristics (Wang et al., 2024; Quan et al., 2024). First of all, in terms of therapeutic mechanism, ICA has a significant dual regulatory effect: it can not only promote bone formation by activating Hippo Yap/TAZ (Lin et al., 2024), IGF-1/ER α (Zhou et al., 2021) and other signaling pathways, but also inhibit bone resorption by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast differentiation (Ji et al., 2022; Cheng et al., 2022). Its core advantage is that it can effectively regulate the imbalance of bone homeostasis through multi-target and multi-channel synergy (e.g., targeting PPARγ, ERα/AKT/β-Catenin) (Long et al., 2022; Cheng et al., 2024). This “network” treatment strategy may be more suitable for the treatment of complex chronic diseases such as osteoporosis than single target powerful drugs. Secondly, at the clinical and economic levels, numerous clinical trials support the efficacy of its compound preparations against primary/secondary osteoporosis (Wu L. et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2016). In addition, as a small molecule natural product, ICA has lower potential production cost, especially when compared with expensive biological agents such as Romozozumab, this advantage is more prominent, and is expected to become an economic and universal treatment option. Therefore, in-depth study of ICA has important strategic significance for the development of safe, effective and economical new anti osteoporosis drugs.
Building upon these advantages of ICA, substantial research efforts have been dedicated to addressing its pharmacokinetic limitations to facilitate clinical translation. At the application level, innovative delivery systems have significantly enhanced ICA’s efficacy and targeting to address bioavailability challenges (Teo et al., 2019; Xin et al., 2015). Compound traditional Chinese patent medicines and simple preparations (Wang et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2024) can improve efficacy through multi-component synergism (Wang et al., 2025; Ren L. et al., 2023). Innovative biomaterial delivery systems [e.g., exosomes (Han et al., 2025), composite hydrogels (Zhang et al., 2025; Li et al., 2024a; Wu Y. et al., 2025), bioglass scaffolds (Kong et al., 2025)] substantially increase ICA’s targeting and efficacy. Numerous studies in various animal models—including postmenopausal (Chen C. et al., 2023), glucocorticoid-induced (Zhang L. et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2015), and aging (Xu et al., 2018) rodent models, as well as chicken (Huang J. et al., 2020) and fish models (Jiang J. et al., 2022)—have reported ICA’s treatment of osteoporosis. These studies demonstrate ICA’s therapeutic efficacy from multiple perspectives and provide important references for developing drug treatments for different osteoporosis types. At the molecular level, ICA exerts central effects by synergistically activating osteogenic pathways [e.g., SPI1/SMAD5 (Zhang J. et al., 2024), Wnt/β-catenin (Gao et al., 2021)] and inhibiting osteoclastogenesis [e.g., Cullin 3/Nrf2 (Si et al., 2024), RANKL-p38/ERK-NFAT (Cheng et al., 2022)]. Key mechanisms include: upregulating osteogenic gene expression in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs); suppressing adipogenic differentiation markers [e.g., PPARγ (Chen X. et al., 2025)] and oxidative stress factors [NOX1/NOX4 (Ji et al., 2022)]; restoring OPG/RANKL balance to inhibit osteoclastogenesis (Sun et al., 2021); and optimizing the bone microenvironment via lipid metabolism reprogramming (Sharifi et al., 2020). ICA also activates autophagy flux to inhibit pro-apoptotic factors (Li et al., 2024b), suppresses the NF-κB inflammatory pathway (Zhang et al., 2014), chelates free iron ions to alleviate iron overload-induced oxidative damage (Tian et al., 2016), and enhances bone cell antioxidant capacity through Nrf2 pathway activation (Zhang C. et al., 2023), collectively protecting bone cell function. Its active metabolites, as shown in Figure 1, target mesenchymal stem cell bone morphogenesis pathways, underscoring multi-target advantages (Indran et al., 2016).
This review systematically integrates ICA’s anti-OP research progress (Figure 2), summarizes its dosage forms—from traditional/simple preparations to novel biomaterial delivery systems—and collates therapeutic efficacy across osteoporosis animal models. Finally, it comprehensively examines ICA’s multi-target mechanisms, spanning bidirectional regulation of osteogenesis/osteoclast inhibition, autophagy/apoptosis balance, anti-inflammation, iron overload mitigation, antioxidant stress, and metabolic homeostasis. The review aims to provide theoretical support for translating ICA from basic research to clinical practice.

Figure 2. Photograph abstract: Application dosage form, animal model and molecular mechanism of icariin for the treatment of osteoporosis.
2 Review methodology
The literature search for this review was conducted exclusively in the Web of Science Core Collection. This database was selected to ensure the inclusion of a consistent and high-quality dataset comprised of peer-reviewed articles from rigorously indexed journals, thereby enhancing the reliability and scholarly rigor of our analysis. The search, which encompassed literature published up to May 2025, was structured using a combination of topic-specific keywords. The search strategy was as follows: #1 (Osteoporosis Concept): TS=[(osteoporosis) OR (Osteoporoses) OR (Bone Loss, Age-Related)]. #2 (Icariin Concept): TS=((icariin) OR (3-((6-deoxymannopyranosyl)oxy)-7-(glucopyranosyloxy)-5-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one)). Final Search: #1 AND #2 (Initial Results: 272). The screening process involved a two-tiered approach. First, the titles and abstracts of the 272 identified records were reviewed. This led to the exclusion of 90 publications that were deemed irrelevant. Primary reasons for exclusion were studies not focusing on icariin’s anti-osteoporotic effects, or those lacking investigations into dosage forms, mechanisms of action, or animal models. Subsequently, a full-text assessment of the remaining 182 articles was performed to confirm their eligibility, resulting in the final inclusion of n = 182 publications for in-depth analysis in this systematic review. This review strictly followed the systematic evaluation specifications of the PRISMA guidelines, and the specific literature screening process is detailed in the visualisation flowchart shown in Figure 3.
3 Progress in the application of icariin dosage forms
3.1 Traditional Chinese medicine formulations
Icariin (ICA), the core component of Epimedium in TCM (Shen et al., 2007; Sze et al., 2010), faces clinical translation challenges due to its low bioavailability and complex mechanism. Current research focuses on two primary approaches: 1) Enhancing bone density and regulating bone metabolism through herbal formulation; 2) Developing novel dosage forms combined with omics technology to elucidate mechanisms regulating lipid metabolism, calcium balance, and signaling pathways, paving the way for precise treatment (as shown in Table 1).
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formulas offer a safe and effective alternative for osteoporosis treatment, leveraging innovative dosage forms and synergistic effects of active ingredients. Qin et al. (2008) demonstrated that icariin in Erxian Decoction (EXD) exerts bidirectional regulation on bone metabolism in Ovariectomized (OVX) rats, promoting bone formation while inhibiting resorption. Additionally, Ren M. et al. (2023) confirmed that serum-derived icariin from EXD enhances Collagen Type I and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (BMP-2) expression in osteoblasts by suppressing BK channels.
Regarding traditional Chinese patent medicines and simple preparations, Wang et al. (2025) demonstrated that the novel Kunxinning formulation alleviates bone loss by targeting perimenopausal estrogen deficiency via ICA-mediated CYP19A1 activation, with confirmed clinical safety. Zhu et al. (2012) established that Xianling Gubao Capsules safely increase lumbar spine bone mineral density (BMD) in postmenopausal women. Using network pharmacology and molecular docking, Wang et al. (2024) verified Gushukang’s inhibition of RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation, downregulation of PTGS2 expression, and reduction of TRAP activity. Feng et al. (2022) utilizing 1H-NMR metabolomics, revealed that Gu-Gu-Dan ameliorates kidney yang deficiency syndrome through arginine metabolism, supporting the “kidney governs bone” theory. Li et al. (2022) further showed that Gushukang activates the IGF-1 pathway, reversing dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy and bone loss in mice through bone-muscle crosstalk protection.
In summary, current research on traditional Chinese patent medicines and simple preparations has enhanced the bioavailability of icariin and other active constituents. These formulations demonstrate efficacy against osteoporosis through bone metabolism pathway regulation. Future studies should focus on: elucidating multi-component synergistic mechanisms, optimizing sustained-release delivery systems, and advancing large-scale clinical trials to overcome limitations of current dosage forms—notably transient efficacy, long-term instability, and dose-dependent effects.
3.2 Biomaterial design
As a natural anti-inflammatory flavonoid (Singh and Singh, 2025; Seyedi et al., 2023), ICA’s application in osteoporosis therapy is limited by the low bioavailability and poor targeting of conventional formulations (Zhao and Zhang, 2025). In biomaterials research, innovative delivery systems enable spatio-temporal controlled release, bone microenvironment modulation, and multi-mechanism synergy of ICA. These approaches address three critical aspects: local drug enrichment, inflammation-osteogenesis imbalance correction, and bone metabolic microenvironment remodeling—effectively overcoming the off-target effects and inefficiency of systemic administration.
To overcome ICA delivery bottlenecks, researchers have systematically investigated material structures and release mechanisms. Hydrogel systems have emerged as a primary focus: Zhang et al. (2025) find a composite hydrogel mimicking bone matrix properties for bone defect repair, though its mechanical strength/sustained-release efficiency balance requires optimization. 3D printing technology enables complex bone reconstruction: Kong et al. (2025) confirm strontium-substituted mesoporous bioactive glass/polycaprolactone scaffolds with uniform pores (achieved via electrospray printing), co-releasing Sr2+ and ICA to simultaneously activate osteogenic differentiation and suppress osteoclast activity; Wang W. et al., 2022) find layered titanium alloy scaffolds for controlled ICA/Mg2+ release, inducing macrophage M2 polarization and enhancing osseointegration. Photoresponsive innovations enable precise modulation: Li et al. (2024a) constructed selenium-gold multishell nanocomposites that trigger Se/ICA release under NIR irradiation, dually suppressing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory factors; Yan et al. (2022) integrated upconversion nanoparticles with MMP13-sensitive peptides to link real-time osteogenesis monitoring with therapeutic feedback. Coating technology advances are significant: Zhu et al. (2021) co-loaded Sr/ICA onto TiO2 nanotube coatings, demonstrating enhanced alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and new bone formation in osteoporotic rats, accelerating clinical translation of titanium implants.
As research advances, scholars recognize that single delivery systems inadequately address OP’s multi-pathological mechanisms, driving exploration of multi-component synergy. Targeted delivery systems represent a key direction: Luo et al. (2024) confirm hydroxyapatite-responsive macrocyclic amphiphiles to enhance bone density via localized drug enrichment. Li et al., 2024c) find self-assembled ICA/Ca2+/zoledronic acid nanocomposites that release drugs under in vitro shock waves, reversing osteogenic-adipogenic differentiation imbalance. Immune microenvironment regulation proves critical: Chai et al. (2022) induced macrophage M2 polarization and bone resorption inhibition using sulfonated polyetheretherketone; Mosqueira et al. (2020) demonstrated strontium/ICA co-loaded bioactive glass microspheres reverse diminished osteogenic potential in osteoporotic stem cells; Lu et al. (2021) confirm PLGA-co-encapsulated quercetin/curcumin nanoparticles inhibiting trabecular bone loss by enhancing flavonoid bioavailability. Han et al. (2025) revealed Epimedium-derived extracellular vesicles promote osteodifferentiation via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, with composite bone repair materials functioning as dual-action “phytoestrogen carriers.”
Current studies demonstrate that novel ICA biomaterials substantially enhance therapeutic precision and efficacy for osteoporosis through intelligent responsive release, ionic synergy, and immune modulation. However, key challenges requiring resolution include: biocompatibility and metabolic safety verification, and optimization of mechanical properties versus drug release kinetics.
4 Advances in the application of animal models in the anti-osteoporotic effects of icariin
4.1 Model of postmenopausal osteoporosis
Ovariectomized (OVX) rats, serving as a classic model for mimicking postmenopausal osteoporosis (Wang et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2021), offer a pivotal platform for investigating the bone-protective mechanisms of ICA. Recent research has confirmed that, in this model, ICA not only mimics the osteogenic effects of estrogen but also exhibits non-estrogen-dependent mechanisms, such as modulating neuropeptide signaling and stabilizing bone mineral phase structures, thereby providing a crucial theoretical foundation for the development of novel anti-osteoporosis drugs (as shown in Table 2).
In recent years, significant advancements have been achieved in elucidating the bone-protective mechanisms of ICA in OVX rat models. Li et al. (2014) demonstrated that ICA exerts a dual role in OVX rats: promoting new bone formation, inhibiting bone resorption, and suppressing bone marrow adipogenesis. Yang et al. (2014), through comparative studies on OVX rats, confirmed that although icariin exhibits a slightly lesser bone-protective effect compared to genistein, both can mimic estrogenic actions, significantly enhance BMD, and hold potential for osteoporosis treatment. Liu Y. et al., 2017) conducted a meta-analysis that synthesized evidence to show that ICA notably increases BMD and improves bone microstructure in OVX rats. Zhang et al. (2007) reported that ICA-derived phytoestrogens significantly delayed lumbar spine BMD loss in postmenopausal women at an advanced stage randomized controlled trial, without causing endometrial hyperplasia or estradiol fluctuations. Building upon these findings, Liu et al. (2012) discovered that the combination of ICA and exercise therapy enhances the bone biomechanical properties of OVX rats and upregulates the expression of Osterix, a key osteoblast gene. Further mechanistic investigations by Ouyang et al. (2014) revealed that a compound extract containing ICA (Bushen Huayu extract) may inhibit IL-6 expression, increase osteoblast counts, and decrease osteoclast numbers by modulating estradiol levels. Zhao et al. (2016) significantly improved the trabecular bone microstructure in OVX rats by upregulating osteoprotegerin and inhibiting the expression of receptor activator of RANKL.
It is noteworthy that the mechanism of action of icariin extends beyond direct regulation of bone metabolism. Liu et al. (2018) innovatively demonstrated its role in regulating the “brain-spinal cord-bone axis” by upregulating NPY1R/CRLR and other factors in bone tissue. In addressing the clinical challenge of OP fractures, Zhang et al. (2020) verified that ICA facilitates fracture healing by activating the OPG/RANKL pathway,and there are no uterine stimulation side effects.
In summary, ICA exerts anti-osteoporotic effects in OVX rats through a triple mechanism: direct regulation of bone metabolism; intervention in lipid-bone balance; and modulation of the neuropeptide axis. Its therapeutic efficacy remains effective and safe in complex scenarios including fracture repair and microgravity-induced bone loss. However, current research exhibits significant limitations: mechanisms are primarily validated at the tissue level with unclear cellular specificity, and the clinical translation evidence chain requires completion through standardized studies.
4.2 Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis model
The underlying pathology of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIOP) is intricate (Chen M. et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2019), with ICA demonstrating distinctive advantages in regulating bone metabolism through multiple targets. Animal studies have validated its efficacy in enhancing trabecular bone structure, preserving bone cell viability, and maintaining calcium homeostasis.
During GIOP pathogenesis, icariin regulates bone metabolic balance via multi-target signaling pathways. Hu et al. (2017) demonstrated using in vitro and in vivomodels that ICA activates the ERK pathway to inhibit osteocyte apoptosis and attenuate bone loss. Further studies reveal icariin’s regulatory effects on osteoblast differentiation: Lin et al. (2017) identified ICA-mediated targeted suppression of the GILZ pathway, reversing dexamethasone-induced osteogenesis inhibition and restoring mineralization capacity. Notably, ICA’s anti-resorptive effects involve microRNA regulation—Ma et al. (2018) confirmed ICA activates microRNA-186 to suppress cathepsin K expression, thereby reversing hyperactive bone resorption and structural deterioration. In GIOP mouse models, Zhang et al. (2015) observed ICA-enhanced bone formation markers, suppressed resorption markers, improved calcium homeostasis, and restored bone microarchitecture. Beyond classical pathways, icariin’s bidirectional modulation of the EphB4/Ephrin-B2 axis provides new evidence for its polypharmacology: Huang M. et al. (2020) and Qiu et al. (2023) demonstrated ICA and its analog Epimedin C reverse trabecular loss and rebalance bone formation-resorption through this axis. Morphologically, Yang et al. (2023) utilized synchrotron radiation imaging to confirm ICA significantly repairs early GIOP-associated femoral head necrosis lesions and reconstructs trabecular networks.
In summary, ICA enhances GIOP through a synergistic effect involving multidimensional mechanisms. Its homolog, Epimedin C, exhibits the ability to bolster bone metabolism homeostasis by modulating Runx2/LGR4 expression, hinting at the potential existence of shared targets among icariin-like compounds. Nevertheless, current research is confined to preclinical models, and the interplay among various icariin pathways remains unelucidated. Moving forward, it is imperative to develop animal models that more accurately mirror the pathological features of human GIOP to validate its therapeutic efficacy.
4.3 Elderly osteoporosis model
The elderly osteoporosis model is characterized by aging-induced reductions in bone formation and disrupted bone turnover, culminating in low bone mass (Johnston and Dagar, 2020; Qadir et al., 2020). As a core anti-osteoporotic agent, ICA demonstrates potential for improving bone density quality in aged models including caged laying hens (CLO), SAMP6 mice, and senile osteoporosis (SOP) rats. Its mechanisms involve regulating osteogenesis-related genes, modulating signaling pathways, and restoring calcium homeostasis.
Research on ICA’s anti-osteoporotic mechanisms in aged models has progressively revealed its metabolic and molecular regulatory networks through multispecies studies. Huang J. et al. (2020) demonstrated via metabolomics that ICA improves bone microarchitecture and homeostasis in CLO by modulating pyrimidine/taurine/lipid metabolism. Building on this, Xu et al. (2018) focused on osteoblast differentiation in senescence-accelerated SAMP6 mice, revealing ICA enhances BMP-2-driven osteogenesis through connective tissue growth factor downregulation. As mechanistic understanding deepens, research has expanded to ICA-containing compound preparations: Li et al. (2020) developed Gushukang (ICA-containing traditional herbal formula) that synergistically activates vitamin D metabolism, bidirectionally regulates calcium transporters, and improves bone structure/mechanical properties plus calcium homeostasis in high-calcium-diet aged mice. Separately, Li et al. (2024b) established that an Epimedium-Ligustrum lucidum compound containing ICA ameliorates bone microstructure and oxidative damage in SOP rats by balancing autophagy-apoptosis equilibrium via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis.
In summary, the multi-target mechanisms of ICA and its compounds have been elucidated through metabolic, differentiation-regulatory, and compound optimization perspectives. Limitations include: heterogeneity in mechanisms explaining pathological variations across animal models; and unclear multi-component synergistic mechanisms.
4.4 Diabetes osteoporosis model
Diabetic osteoporosis (DOP) is characterized by hyperglycemia-induced bone turnover imbalance, ROS accumulation, and bone marrow adiposity, coupled with OPG/RANKL signaling dysregulation and primary cilia/Gli2 pathway inhibition (Kupai et al., 2024; Romero-Díaz et al., 2021). When investigating ICA’s intervention mechanisms in DOP, studies reveal its multi-target regulatory properties across diverse models.
Qi et al. (2019) demonstrated in STZ-induced rats that ICA lowers blood glucose, inhibits marrow steatosis, increases bone density, and reduces bone turnover markers. Zhang et al. (2020) confirmed via proteomics that Zishen Jiangtang Pill, a compound containing ICA, improves bone microstructure in DOP rats by modulating ribosome pathways and vitamin/fat metabolism. Notably, Liu et al. (2022) revealed that ICA promotes osteogenic differentiation by clearing ROS to maintain mitochondrial primary cilium homeostasis, thereby activating the primary cilium/Gli2/osteocalcin (OCN) pathway.
In summary, ICA effectively reverses bone loss through dual regulation of bone metabolism and ROS clearance. Future efforts should focus on advancing its clinical translation and further elucidating its multi-target mechanisms, aiming to develop a natural, multi-target anti-osteoporosis agent that integrates blood glucose reduction, bone protection, and antioxidant functions.
4.5 Other animal species models
The expansion of osteoporosis research into non-mammalian models offers new perspectives for studying ICA’s anti-osteoporotic mechanisms. Aquatic models, such as zebrafish and bluefish, leverage their genetic and high-throughput advantages to provide insights into ICA’s action and help analyze the impact of glycosylation modifications on its activity (Carnovali et al., 2020; Priya et al., 2023). Similarly, chicken models have demonstrated therapeutic efficacy in studies of avian bone diseases (Sarnella et al., 2024; Dodgson, 2007).
Recent studies highlight the unique advantages of non-rodent models in elucidating ICA’s anti-osteoporotic mechanisms. Pham Pham et al. (2021) innovatively applied the I-M quantification method in a bluefish RANKL model, demonstrating that ICA provides bone protection equivalent to alendronate sodium. In zebrafish models, multi-pathway mechanisms of ICA have been revealed: Jiang J. et al. (2022) verified through molecular docking and zebrafish assays that ICA and icaritin (IT) effectively reverses bone injury. Notably, Jiang et al. (2023) further confirmed using zebrafish and rat models that IT promotes bone formation by chelating iron ions to reverse overload. This mechanistic diversity extends to inflammation-related osteoporosis, where Liu L. et al., 2024) found that icariin B (EB) inhibits neuroinflammation and ROS accumulation in zebrafish by regulating the MAPK/NF-κB/NOD-like receptor pathway.
Huang J. et al. (2020) demonstrated that dietary ICA supplementation in aged caged chickens effectively increases BMD and alleviates osteoporosis symptoms. These beneficial effects are attributed to ICA’s precise modulation of endogenous pyrimidine, taurine, and lipid metabolism. Notably, ICA’s osteoreparative capacity extends beyond aged bone: Iqbal et al. (2018) successfully repaired tibial dyschondroplasia in fast-growing chickens by activating the BMP-2 signaling pathway.
In summary, non-mammalian models effectively elucidate the complex multi-target/pathway mechanisms through which ICA and its derivatives exert bone-protective effects. Future research should prioritize cross-species mechanism validation, methodological standardization, and optimization of active structural components to accelerate ICA’s translational pipeline for osteoporosis therapy.
5 Molecular mechanism of icariin against osteoporosis
5.1 Osteogenesis and osteoclast regulation
The homeostatic imbalance between osteoblast-mediated bone formation and osteoclast-driven bone resorption constitutes a fundamental pathological mechanism in osteoporosis. Therapeutic strategies therefore focus on restoring bone metabolic equilibrium by modulating these cellular activities (Hou and Tian, 2022; Zhang X. et al., 2023). As a natural anti-osteoporotic agent, ICA exhibits systematically validated multi-target effects (Xue et al., 2016): it inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption (Cao et al., 2012; Fang et al., 2017; Liang et al., 2012) while promoting osteogenesis through activation of bone-forming pathways (Meng et al., 2005; Tang et al., 2018). This bidirectional regulatory capacity provides a mechanistic basis for its clinical translation (as shown in Table 3).
Significant advances have been made in understanding ICA’s molecular regulation of osteogenic differentiation. Notably, Li et al. (2016) demonstrated in OVX mice that the ICA-ferulic acid combination synergistically activates BMP/Wnt signaling, enhances bone matrix protein expression, and increases bone density/mineralization. Ye et al. (2017) established that ICA promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in rat adipose-derived stem cells through RhoA-TAZ signaling, with this effect being abolished by RhoA inhibitor C3. Jin Y. et al. (2024) revealed ICA upregulates METTL14-mediated P4HB m6A modification to enhance stability and bone formation in BMSCs. Chen et al. (2007) identified cell-type specificity: ICA enhances osteogenic differentiation in rat BMSCs but shows no significant effect on rat calvarial osteoblasts. Clinical translation studies further validate ICA’s therapeutic potential. Saud et al. (2019) systematically reviewed ICA’s regulation of mesenchymal stem cell fate via BMP-2/Runx2 and other pathways, supporting bone regeneration material development. Yang et al. (2019) emphasized that ICA’s multidimensional control of BMSC proliferation/differentiation constitutes a key anti-osteoporotic mechanism. Corroborating this, Wang Z. et al. (2018) demonstrated ICA’s dual regulatory function: activating BMSC osteogenesis while inhibiting osteoclast activity.
The mechanisms underlying ICA’s inhibition of osteoclasts have been progressively elucidated. Yang et al. (2024) demonstrated that ICA suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation via the ERα/c-Src/RANK pathway. Notably, Ma et al. (2022) confirmed that its metabolite Baohuoside I (BS) inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by blocking the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Further mechanistic insight was provided by Xu Q. et al. (2019) who showed ICA synergistically inhibits RANKL-triggered NF-κB/MAPK signaling and disrupts F-actin ring formation, thereby impairing bone resorption. Through in vitro studies, Kim et al. (2018) revealed that ICA downregulates TRAF6 expression and ERK phosphorylation while reducing osteoclast-specific markers, offering novel therapeutic strategies for bone-related diseases. In vivo evidence confirms ICA’s osteoclast-inhibitory effects are linked to systemic bone homeostasis regulation: Cheng et al. (2022) reported in a thioacetamide-induced rat model that ICA reduces osteoclastogenesis through downregulation of RANKL-p38/ERK-NFATc1 signaling. Corroborating this, Wang Q. et al. (2018) demonstrated in OVX mice that ICA combined with mechanical loading increases the OPG/RANKL ratio while upregulating osteogenic genes and downregulating osteoclast-related genes.
In summary, ICA primarily inhibits osteoclast differentiation by modulating the RANKL signaling network, exerting anti-osteoporotic effects through: OPG/RANKL regulation, metabolic improvement, and enhanced bone coupling (Figure 4). Current research faces three key limitations: mechanisms predominantly validated in cellular/small-animal models lack clinical evidence; unclear bioactivity and synergy of ICA metabolites; insufficient understanding of osteoclast-BMSC crosstalk mechanisms.

Figure 4. Research progress on ICA treats osteoporosis by regulating osteogenic and osteoclast activity.
5.2 Regulation of adipogenic differentiation
Excessive adipogenic differentiation and suppressed osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) constitute key cellular mechanisms underlying bone marrow adiposity, bone mass reduction, and osteoporosis (An et al., 2023; Du et al., 2021). Recently, ICA has emerged as a natural active compound for osteoporosis treatment, regulating stem cell differentiation balance and bone metabolic microenvironment via multi-target therapy. Through stem cell transplantation and epigenetic strategies, ICA bidirectionally modulates osteogenic-adipogenic differentiation, reshapes bone-lipid homeostasis, and provides a theoretical basis for ICA-based biomaterials.
Key breakthroughs in ICA’s regulation of stem cell differentiation include: Lin et al. (2024) demonstrated ICA inhibits Hippo-YAP/TAZ phosphorylation, promoting osteogenesis while suppressing adipogenesis in Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs). Notably, Chen X. et al. (2025) revealed in postmenopausal OP models that ICA enhances SOST promoter methylation to inhibit ERα binding, thereby upregulating Wnt signaling and driving BMSC osteogenic differentiation. This epigenetic mechanism was further confirmed by Li et al. (2024d) showing ICA blocks BMSC adipogenesis via S100A16 inhibition.
At the hormone signaling level, multiple studies highlight the pivotal role of estrogen receptor (ER) pathways. Li et al. (2018) confirmed ICA upregulates osteogenic markers while suppressing adipogenic factors in rat BMSCs via ER. Zhang et al. (2016) further elucidated ICA’s dual ER-mediated regulation: inhibiting osteoclast activation through OPG/RANKL upregulation and blocking osteoblast-to-adipocyte transdifferentiation. Notably, Liu H. et al. (2017) demonstrated ICA inhibits Notch signaling and downregulates PPARγ/C/EBPα/FABP4, suppressing BMSC adipogenesis in OVX rats. This discovery is similar to the clinical approach of Zhao et al. (2024) - ICA improves bone microstructure by inhibiting FABP4 expression and increasing OCN levels, confirming its ability to inhibit key factors in fat metabolism. Significantly, Zhang et al. (2017) established ICA’s bidirectional effects in tri-cell coculture systems: promoting MC3T3-E1 osteogenesis, inhibiting RAW264.7 osteoclastogenesis, and reducing BMSC adipogenesis.
In summary, ICA demonstrates advantages in stem cell transplantation, epigenetic modulation, and bone-lipid microenvironment remodeling by regulating osteogenic-adipogenic differentiation balance through multi-target synergistic pathways (Figure 5). Future research should focus on elucidating ICA’s polypharmacology—particularly osteogenic/adipogenic equilibrium—and exploring cross-pathway interactions to advance precision-targeted therapies.
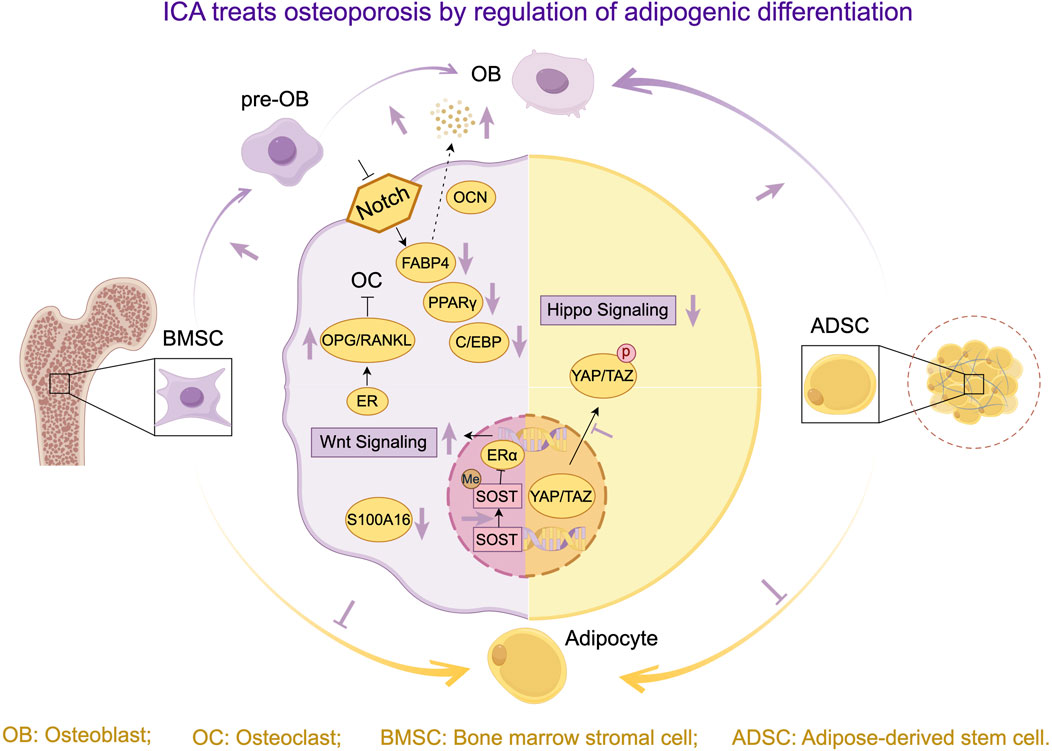
Figure 5. Research progress on ICA treats osteoporosis by regulating osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation.
5.3 Regulation of autophagy and apoptosis balance
Autophagy dysfunction compromises bone cell stress resistance, accelerates apoptosis, and disrupts bone remodeling balance, promoting osteoporosis development (Tang et al., 2019; Jin Z. et al., 2024). Osteoporosis therapeutic strategies are evolving toward multi-target synergistic regulation, with ICA emerging as a research focus due to its dual autophagy-apoptosis regulatory capacity (Liang et al., 2019; Verma et al., 2022; Shao et al., 2022).
The mechanisms underlying ICA’s regulation of autophagy and apoptosis are increasingly elucidated: Li et al. (2024b) demonstrated that an Epimedium-Ligustrum lucidum compound upregulates Bcl-2/Beclin-1/LC3-II while downregulating p53 in aged OP rats, ameliorating osteoblast apoptosis-autophagy imbalance. Zou et al. (2024) revealed ICA bidirectionally modulates autophagic flux via the AMPK/ULK1 and Akt/mTOR axes in OVX rats, reversing osteocyte autophagic dysfunction. This mechanism was confirmed by Liu W. et al. (2024) in ketogenic-diet OP models, where ICA inhibits mTOR phosphorylation, enhances autophagy, and reverses BMSC adipogenic-osteogenic imbalance. Notably, ICA’s polypharmacology extends beyond single pathways: Bai et al. (2023) established that ICA activates autophagy to inhibit TNF-α signaling and SASP secretion in senescent macrophages, rescuing osteogenic dysfunction in aged BMSCs. Chen et al. (2022) further corroborated in IL-1β-induced cartilage degeneration models that ICA alleviates degeneration by suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR phosphorylation and activating ULK1-mediated autophagy.
In summary, Epimedium and its active constituents induce osteoblast autophagy, suppress apoptosis, improve bone microarchitecture, and promote bone formation through key signaling pathway modulation (Figure 6). Future research should prioritize exploring targeted therapeutics that balance autophagy-apoptosis equilibrium for clinical osteoporosis treatment, with emphasis on optimizing multi-pathway synergistic regulation to enhance bone-targeting capacity and treatment efficacy.

Figure 6. Research progress on the molecular mechanism of ICA in the treatment of osteoporosis by coordinating anti-inflammatory and antioxidant stress, regulating autophagy and apoptosis, and intervening in iron overload.
5.4 Anti inflammatory mechanism
Inflammation activates osteoclasts and suppresses osteoblasts via pro-inflammatory cytokine release, disrupting bone remodeling equilibrium and accelerating osteoporosis progression (Lu et al., 2022; Xiang et al., 2025). Recently, the anti-inflammatory properties of ICA and its derivatives in OP treatment have garnered significant attention (Ma et al., 2020). Studies demonstrate that ICA exerts central therapeutic effects by synergistically reshaping the inflammatory microenvironment through key multi-pathway mechanisms.
ICA and its derivatives exhibit multidimensional anti-inflammatory effects: Liu L. et al. (2024) demonstrated in zebrafish models that EB attenuates inflammation by reducing ROS accumulation, modulating MAPK/NF-κB/NOD-like receptor pathways, and downregulating pro-inflammatory factors. Zhang et al. (2014) highlighted ICA’s synergistic regulation of bone cell inflammation and activation of osteoinductive pathways. As research progresses, ICA-regulated molecular networks are being clarified. Song et al. (2024) combined network pharmacology with experimental validation to show Epimedium components inhibit osteoclast markers/activity and bidirectionally regulate bone metabolism via FoxO/MAPK/TNF signaling. Zhang et al. (2022) established ICA’s ERK/MAPK-mediated estrogen-like effects suppress inflammation while promoting osteogenesis. In LPS models, Hsieh et al. (2011) confirmed ICA blocks osteoclast maturation and pro-inflammatory factors by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB/HIF-1α/PGE2 cascade. Hwang et al. (2018) extended findings to skin models, where ICA/ICT activates Nrf2/ARE while suppressing MAPK/AP-1/NF-κB, reducing MMP-1 and inflammatory cytokine release.
Collectively, ICA alleviates OP by targeting classical inflammatory pathways and cross-network systems to suppress inflammation, demonstrating pleiotropic effects in zebrafish and cellular models. Nevertheless, current evidence predominantly derives from in vitro/animal studies, and pathway crosstalk mechanisms within distinct inflammatory microenvironments require elucidation. Future research should focus on: identifying targets in aging-related chronic inflammation, and optimizing bone-targeted delivery strategies to accelerate clinical translation.
5.5 Iron overload intervention mechanism
Iron overload triggers excessive ROS generation via the Fenton reaction, inhibiting osteogenesis, promoting osteoclast differentiation, and disrupting bone homeostasis—a significant pathogenic factor in osteoporosis (Tian et al., 2016; Xia et al., 2019; Jiang Z. et al., 2022). ICA and its derivatives exhibit multifaceted intervention potential in both zebrafish and mammalian models.
The zebrafish model offers unique advantages for analyzing ICA components: Yan et al. (2025) demonstrated that ICA and its glycosides inhibit lipid peroxidation while enhancing osteogenic differentiation markers. Notably, Jing et al. (2019) elucidated mechanisms in iron-overloaded mice, showing ICA: inhibits mitochondrial membrane potential depolarization and ROS accumulation; restores Runx2/ALP/OPN expression in osteoblasts; suppresses osteoclast differentiation. In vivo analyses further revealed reduced bone marrow iron deposition and systemic iron metabolism regulation. Mechanistically, ICA’s cytoprotective effects involve mitochondrial homeostasis and signaling pathways: Yao et al. (2019) revealed ICA protects BMSCs against iron overload-induced mitochondrial damage by modulating ERK1/2/JNK-MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR cascades.
In summary, ICA effectively mitigates iron overload-induced bone loss across diverse models (Figure 6). However, further exploration is warranted: pharmacological differences and structure-activity relationships between ICA and its glycosidic derivatives; crosstalk mechanisms between mitochondrial homeostasis and signaling pathways in iron-overloaded bone metabolism; clinical translational potential and long-term safety profiles.
5.6 Anti oxidative stress mechanism
Oxidative stress contributes to osteoporosis pathogenesis by damaging osteoblasts, promoting osteoclast activation, and accelerating bone metabolic imbalance (Zhang C. et al., 2023; Kimball et al., 2021; Iantomasi et al., 2023). Recent studies demonstrate ICA’s therapeutic potential for OP through multi-targeted regulation of oxidative stress equilibrium. It provides comprehensive intervention strategies via antioxidant effects, anti-inflammatory properties, and modulation of stem cell fate.
Recent studies have elucidated the pivotal role of ICA’s antioxidant mechanisms in osteoporosis treatment. Ji et al. (2022) demonstrated that ICA downregulates NOX1/NOX4, blocks RANKL-induced ROS production, and inhibits osteoclast differentiation—indicating its suppression of osteoclastogenesis via oxidative stress targeting. Xi et al. (2019) reported that Baohuoside I reduces serum pro-inflammatory cytokines, enhances SOD activity, and decreases Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in OVX rats, promoting BMSC osteogenic differentiation through synergistic antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Ma et al. (2014) further established that ICA inhibits ROS/MDA generation in osteoblasts while reducing inflammation and apoptosis, thereby maintaining RUNX-2/BMP-2 expression and protecting bone formation via phytoestrogen-like activity and anti-hypoxic effects.
Collectively, this evidence elucidates ICA’s molecular mechanisms for ameliorating osteoporosis through antioxidant pathways. Specifically, ICA targets the Cullin-3/Nrf2 axis to inhibit osteoclast differentiationand counter iron overload-induced lipid peroxidation (Figure 6). Nevertheless, current findings predominantly derive from animal/cellular models, necessitating validation of clinical translation potential via randomized controlled trials to advance precision osteoporosis therapeutics.
5.7 Regulation of bone metabolism homeostasis
ICA reshapes bone tissue energy metabolism homeostasis through precise modulation of estrogen signaling (Yao et al., 2025), gut microbiota (Zhang Y. et al., 2021), OCN (Mohammadi et al., 2024), and ALP (Omidvar et al., 2022), providing a targeted therapeutic strategy for metabolic disorder-associated osteoporosis (Xie et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2008).
5.7.1 Regulation of estrogen signaling pathway
Estrogen deficiency, a primary etiology of osteoporosis, activates osteoclasts and disrupts bone resorption regulation, accelerating bone mass loss and microstructural deterioration (Yao et al., 2025; Kverka and Stepan, 2024; Wu W. et al., 2025; Zhu et al., 2024). Recent studies have progressively unveiled molecular mechanisms by which ICA modulates bone metabolism via ER stimulation (Wu Z. et al., 2017). Sun et al. (2021) demonstrated ICA upregulates the OPG/RANKL ratio and ALP/OPN activity through ER, enhancing osteoblast proliferation and mineralization. Luo et al. (2015) confirmed ICA restores osteogenic differentiation capacity of BMSCs in OVX rats via ER, progesterone receptor, and pS2 pathways. Song et al. (2013) revealed ICA activates ERK/JNK phosphorylation through ER, promoting proliferation and mineralization in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Notably, Yang et al. (2013) established that ICA activates aromatase to stimulate estrogen synthesis, augmenting osteoblast ALP activity and OPG expression. This dual-regulatory mode shows clinical promise: Xue et al. (2012) found both ICA and estrogen improved bone density in OVX rats, but ICA uniquely inhibited osteoclastic resorption with significantly reduced uterine side effects. Complementarily, Zhang et al. (2012) delineated ICA and baohuoside-I suppress RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation via ER-dependent pathways, decreasing TRAP and MMP-9 biomarkers. Mok et al. (2010) integrated mechanisms in OVX mice, showing ICA induces ligand-independent ERα Ser118 phosphorylation, upregulates OPG/RANKL mRNA ratio, and prevents bone loss without uterine hyperplasia.
5.7.2 Gut microbiota bone axis regulation
Recent studies implicate gut-bone axis dysbiosis in osteoporosis pathogenesis via pro-inflammatory responses, immune dysregulation, and intestinal barrier impairment (Zhang Y. et al., 2021; Awuti et al., 2022; Zhang Y. et al., 2024). Integrating TCM with probiotics synergistically improves microbiota balance and enhances bioavailability. Intestinal microbiota-mediated metabolic mechanisms of ICA and its OP regulatory effects have emerged as research priorities (Fan et al., 2025). Wu et al. (2016) revealed key bacterial strains hydrolyze ICA into IT and desmethylicaritin, significantly increasing bioavailability and mediating estrogen-like anti-osteoporotic effects. However, pathological conditions may impair ICA’s metabolic efficiency. Zhou et al. (2015) observed reduced hydrolysis/absorption of 7-glucosylated flavonoids in OVX rats due to microbiota alterations, indicating diminished metabolic capacity under pathological states. Significantly, Wang S. et al., 2022) demonstrated ICA upregulates beneficial bacteria in OVX models, improving bone microarchitecture via microbial metabolite-mediated RANKL/OPG pathway regulation.
5.7.3 Expression and functional regulation of osteocalcin
Elevated serum OCN levels significantly correlate with accelerated bone turnover in osteoporosis, serving as key biomarkers for diagnosing and monitoring postmenopausal osteoporosis (Mohammadi et al., 2024; Alam et al., 2019; Raymond et al., 1999). The mechanism by which ICA ameliorates osteoporosis through OCN pathway modulation has been systematically validated across multiple models (Chen et al., 2016). In postmenopausal osteoporosis models: Zhao et al. (2024) demonstrated ICA inhibits adipogenic marker FABP4, elevates serum OCN, and enhances trabecular bone structure Nian et al. (2009) found ICA reverses decreased serum OCN, restores BMD and biomechanical properties, with efficacy comparable to estrogen replacement therapy. Furthermore, He et al. (2018) extended this mechanism in simulated microgravity-induced bone loss models, showing ICA maintains OCN expression and enhances mineralization via stabilization of bone apatite crystals.
5.7.4 Regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity
Elevated ALP levels serve as auxiliary indicators of accelerated bone turnover and active remodeling in osteoporosis (Omidvar et al., 2022; Chen R. et al., 2025; Che et al., 2023). Recent advances elucidate molecular mechanisms by which ICA regulates osteoblast differentiation and ALP activity: Xu et al. (2020) demonstrated ICA activates STAT3 phosphorylation, enhancing ALP activity and mineralization nodule formation in rat mandibular BMSCs; Xu Y. et al. (2019) further established that while ICA inhibits Notch signaling in MC3T3-E1/C3H10T1/2 cells, activation of this pathway abrogates ICA’s ALP-elevating effects.
The regulatory effects of ICA on ALP activity may vary across different cell models and experimental designs. Owen et al. (2020) observed in human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal progenitors that although lithium chloride transiently increases ALP, it reduces ultimate mineralization—suggesting transient ALP elevation does not necessarily promote bone formation and requires evaluation alongside long-term mineralization outcomes. Complementary studies on natural products offer mechanistic insights for ICA: Oh et al. (2019) reported that brown algae PFF-A enhances ALP and mineralization of human BMSCs synchronously by activating BMP-2/β - catenin. Shi et al. (2022) in a systematic review, showing significantly lower serum ALP levels in patients receiving Epimedium monotherapy versus conventional drugs. This indicates Epimedium regulates bone metabolism by suppressing bone resorption markers with superior therapeutic efficacy.
In summary, ICA multi-targetedly regulates estrogen signaling, gut microbiota metabolism, OCN activity, and ALP function to reshape bone tissue energy metabolism homeostasis, offering novel targeted intervention strategies for metabolic disorder-associated osteoporosis. Future research should focus on: optimizing ICA metabolic efficiency under pathological conditions; elucidating multi-component synergistic mechanisms; and advancing clinical translation to achieve precise metabolic modulation of osteoporosis.
6 Summary, current challenges and future prospects
In summary, ICA-based formulations have significantly enhanced bioavailability and bone targeting through multi-component synergism in traditional preparations and biomaterial innovations, enabling precise local bone repair. Across diverse osteoporosis models (postmenopausal, glucocorticoid-induced, senile, and diabetic), ICA consistently improves bone microarchitecture and increases BMD. Its mechanisms encompass multidimensional regulation of bone-lipid homeostasis, neuropeptide axis modulation, and ROS scavenging. Mechanistic studies further reveal ICA promotes osteogenesis while suppressing osteoclastogenesis via multiple pathways, bidirectionally modulating BMSC osteogenic-adipogenic differentiation. Additional synergistic effects include restoring autophagy-apoptosis equilibrium, mitigating iron overload, exerting anti-inflammatory/antioxidant actions, and maintaining osseous microenvironment homeostasis.
Although icariin (ICA) shows unique advantages in the treatment of osteoporosis due to its multi-target mechanism, its research and clinical transformation still face several challenges. 1) Poor pharmacokinetic characteristics and delivery bottleneck: the oral bioavailability of ICA is low (about 12%), the plasma half-life is short (usually 1.2–3.5 h) (Hu et al., 2025), and the traditional dosage form is difficult to reach and maintain the effective therapeutic concentration in the bone tissue, which largely limits its curative effect. 2) The complex mechanism of action is not fully clarified: ICA plays a role through Wnt/β - Catenin, BMP, OPG/RANKL, MAPK and other signaling pathways, but the interaction network between the pathways and its core molecular targets are still unclear. In addition, many studies have found that the metabolites of ICA in vivo (such as IT, icaritin) also have biological activities, but the specific contribution of these metabolites and the synergistic mechanism with the mother drug are not enough. 3) Weak clinical evidence chain and transformation risk: at present, the vast majority of evidence supporting the efficacy of ICA comes from animal experiments (such as OVX rats, SAMP6 mice, etc.). Although some small-scale clinical studies (for example, Xianlinggubao capsule can safely increase the BMD of lumbar vertebra in postmenopausal women, and ICA derived phytoestrogen significantly delays the loss of lumbar BMD in postmenopausal women, without causing endometrial hyperplasia or estradiol fluctuations.) have shown positive effects, there is a lack of large-scale, multi center randomized controlled trials to systematically verify its long-term efficacy and safety in the population. In addition, the low bioavailability of ICA in human body may lead to its clinical efficacy less than expected.
In view of the above challenges and limitations, making full use of the advantages of ICA in the treatment of OP, future research should focus on: 1) optimizing targeted delivery systems: actively developing and optimizing new targeted delivery systems (such as smart hydrogels, 3D printing stents, nanoparticles), increasing the effective concentration and action time of ICA in vivo, in order to overcome the bottleneck of ICA bioavailability. 2) Deepen mechanism research: using multiomics technology and artificial intelligence, systematically analyze the multi-target action network of ICA, and clarify the contribution of its active metabolites, so as to explore and promote the combined treatment of ICA and standard drugs. 3) Promote clinical transformation and application: carry out more high-quality and standardized preclinical studies, promote well-designed clinical trials, determine the optimal dose scheme of ICA in human body, and monitor the long-term safety. At the same time, we should further explore the role of ICA in specific populations (such as diabetic osteoporosis) and its unclear molecular mechanism, and evaluate its synergistic effect with standard treatment (e.g., bisphosphonates), to expand its scope of indications.
Author contributions
BF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. SY: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. SC: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. BH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by General Project of Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2024A515010616), Project of Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission (JCYJ2023080815805012), Special Project for Traditional Chinese Medicine Research of Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 2023 (2023MS529).
Acknowledgements
We thank Figdraw (www.figdraw.com) for expert assistance in the pattern drawing. We would like to express our gratitude to DeepSeek (www.deeepsek.com) for their assistance in language polishing during manuscript preparation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. We would like to express our gratitude to DeepSeek (d3d3LmRlZWVwc2VrLiBjb20=) for their assistance in language polishing during manuscript preparation.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
OP, Osteoporosis; ICA, Icariin; BMSCs, bone marrow stromal cells; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; TCM, Traditional Chinese medicine; EXD, Erxian decoction; BMD, Bone mineral density; OVX, Ovariectomized; GIOP, Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis; CLO, Caged laying hens; SOP, Senile osteoporosis; DOP, Diabetic osteoporosis; IT, Icaritin; EB, Icariin B; BMSCs, Bone marrow stromal cells and Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; RANKL, nuclear factor-κB ligand; BMP-2, Bone morphogenetic protein-2; BS, Baohuoside I; MDA, Malondialdehyde; ER, Estrogen receptor; OOCN, steocalcin; ALP, Alkaline phosphatase; ADSCs, Adipose-derived stem cells.
References
Alam, M. F., Rana, M. A., and Alam, M. S. (2019). Osteocalcin, a promising marker of osteoporosis: evaluation in post-menopausal females with osteoporosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 6, 1746–1749. doi:10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20194639
An, F., Wang, X., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Sun, B., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). Research progress on the role of lncRNA-miRNA networks in regulating adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1210627. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1210627
Awuti, K., Wang, X., Sha, L., and Leng, X. (2022). Exploring the regulatory mechanism of osteoporosis based on intestinal flora: a review. Medicine 101, e32499. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000032499
Bai, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, P., Hang, R., Xiao, Y., et al. (2023). Osteoporosis remission via an anti-inflammaging effect by icariin activated autophagy. Biomaterials 297, 122125. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122125
Bonnelye, E., Chabadel, A., Saltel, F., and Jurdic, P. (2008). Dual effect of strontium ranelate: stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of osteoclast formation and resorption in vitro. Bone 42, 129–138. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2007.08.043
Cacoub, P., Descamps, V., Meyer, O., Speirs, C., Belissa-Mathiot, P., and Musette, P. (2013). Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) in patients receiving strontium ranelate. Osteoporos. Int. 24, 1751–1757. doi:10.1007/s00198-013-2265-1
Cao, H., Ke, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Qian, W., and Zhang, G. (2012). Icariin stimulates MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation and differentiation through up-regulation of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 29, 435–439. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2011.845
Carnovali, M., Banfi, G., and Mariotti, M. (2020). Liquiritigenin reduces osteoclast activity in zebrafish model of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 143, 300–306. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2020.06.001
Chai, H., Sang, S., Luo, Y., He, R., Yuan, X., and Zhang, X. (2022). Icariin-loaded sulfonated polyetheretherketone with osteogenesis promotion and osteoclastogenesis inhibition properties via immunomodulation for advanced osseointegration. J. Mater. Chem. B 10, 3531–3540. doi:10.1039/d1tb02802b
Chaichit, S., Wongrattanakamon, P., Sirithunyalug, B., Nimmanpipug, P., and Jiranusornkul, S. (2022). Multitarget-based virtual screening for identification of herbal substances toward potential osteoclastic targets. Appl. Sci. 12, 2621. doi:10.3390/app12052621
Cheng, X., and Zhao, C. (2023). The correlation between serum levels of alkaline phosphatase and bone mineral density in adults aged 20 to 59 years. Medicine 102, e34755. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000034755
Chen, K., Ma, H., Ge, B., Liu, X., Ma, L., Bai, M., et al. (2007). Icariin enhances the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells but has no effects on the differentiation of newborn calvarial osteoblasts of rats. Die Pharm. 62, 785–789. doi:10.3892/etm.2016.3333
Chen, G., Wang, C., Wang, J., Yin, S., Gao, H., Xiang, L. U., et al. (2016). Antiosteoporotic effect of icariin in ovariectomized rats is mediated via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 12, 279–287. doi:10.3892/etm.2016.3333
Chen, R., Yang, Y., Sun, K., Liu, S., Guo, W., Zhang, J., et al. (2021). Potential mechanism of Ziyin Tongluo Formula in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: based on network pharmacology and ovariectomized rat model. Chin. Med. 16, 88. doi:10.1186/s13020-021-00503-5
Chen, Y., Pan, X., Zhao, J., Li, C., Lin, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis through PI3K/Akt/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway. Eur. J. Med. Res. 27, 204. doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00820-x
Chen, C., Lei, H., Zhao, Y., Hou, Y., Zheng, H., Zhang, C., et al. (2023). A novel small molecule effectively ameliorates estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis by targeting the gut-bone signaling axis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 954, 175868. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175868
Chen, M., Fu, W., Xu, H., and Liu, C. J. (2023). Pathogenic mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 70, 54–66. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2023.03.002
Chen, X., Liu, X., Wan, J., Hu, Y., and Wei, F. (2025). Icariin facilitates osteogenic differentiation and suppresses adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing SOST methylation in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J. Gene Med. 27, e70010. doi:10.1002/jgm.70010
Chen, R., Gong, K., Chen, W., Chen, Z., Hua, X., Tan, J., et al. (2025). Association of serum alkaline phosphatase levels with bone mineral density, osteoporosis prevalence, and mortality in US adults with osteoporosis: evidence from NHANES 2005–2018. Osteoporos. Int. 36, 283–297. doi:10.1007/s00198-024-07324-w
Cheng, L., Jin, X., Shen, H., Chen, X., Chen, J., Xu, B., et al. (2022). Icariin attenuates thioacetamide-induced bone loss via the RANKL-p38/ERK-NFAT signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 25, 126. doi:10.3892/mmr.2022.12642
Cheng, X., Jin, S., Feng, M., Miao, Y., Dong, Q., and He, B. (2024). The role of herbal medicine in modulating bone homeostasis. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 24, 634–643. doi:10.2174/0115680266286931240201131724
Dodgson, J. B. (2007). The chicken genome: some good news and some bad news. Poult. Sci. 86, 1453–1459. doi:10.1093/ps/86.7.1453
Du, G., Cheng, X., Zhang, Z., Han, L., Wu, K., Li, Y., et al. (2021). TGF-beta induced key genes of osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells and MiRNA–mRNA regulatory networks. Front. Genet. 12, 759596. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.759596
Fan, K., Hua, X., Wang, S., Efferth, T., Tan, S., and Wang, Z. (2025). A promising fusion: traditional Chinese medicine and probiotics in the quest to overcome osteoporosis. FASEB J. 39, e70428. doi:10.1096/fj.202403209R
Fang, H., Zhou, L., Shen, L., Zhou, H., Fang, Y., and Fan, H. (2017). Effects of icariin on the proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 10, 14876–14882.
Feng, Q., Tong, L., Lu, Q., Liu, S., Zhao, L., and Xiong, Z. (2022). 1H NMR serum metabolomics and its endogenous network pharmacological analysis of Gushudan on kidney-yang-deficiency-syndrome rats. Anal. Biochem. 643, 114580. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2022.114580
Gao, J., Xiang, S., Wei, X., Yadav, R. I., Han, M., Zheng, W., et al. (2021). Icariin promotes the osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through regulating Sclerostin and activating the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 6666836. doi:10.1155/2021/6666836
García-Espinosa, M. E., Limias-Quezada, P., Ortega-Meléndez, A. I., Ballinas-Verdugo, M. A., López-Gómez, R. E., López-Espinosa, E., et al. (2024). Acupuncture-induced gene co-expression networks in postmenopausal women with osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: in-silico analysis. Acupunct. Herb. Med. 4, 538–551. doi:10.1097/hm9.0000000000000132
Han, R., Gao, C., Tang, R., Gui, X., Chen, W., Fu, J., et al. (2025). A comprehensive study on Herba Epimedium-derived extracellular nanovesicles as a prospective therapy for alveolar bone regeneration in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nanoscale 17, 12270–12289. doi:10.1039/d5nr00508f
He, J., Feng, X., Wang, J., Shi, W., Li, H., Danilchenko, S., et al. (2018). Icariin prevents bone loss by inhibiting bone resorption and stabilizing bone biological apatite in a hindlimb suspension rodent model. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 39, 1760–1767. doi:10.1038/s41401-018-0040-8
Hou, X., and Tian, F. (2022). STAT3-mediated osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis in osteoporosis. Cell Commun. Signal. 20, 112. doi:10.1186/s12964-022-00924-1
Hsieh, T., Sheu, S., Sun, J., and Chen, M. (2011). Icariin inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by suppression of MAPKs/NF-κB regulated HIF-1α and PGE2 synthesis. Phytomedicine 18, 176–185. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2010.04.003
Hu, J., Mao, Z., He, S., Zhan, Y., Ning, R., Liu, W., et al. (2017). Icariin protects against glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis, increases the expression of the bone enhancer DEC1 and modulates the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin integrated signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 136, 109–121. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.010
Hu, W. J., Si, Y. M., Xie, X., and Xu, J. B. (2025). Research progress on icariin promoting bone injury repair and regeneration. Pharmaceuticals-Base 18, 1174. doi:10.3390/ph18081174
Huang, J., Hu, Y., Tong, X., Zhang, L., Yu, Z., and Zhou, Z. (2020). Untargeted metabolomics revealed therapeutic mechanisms of icariin on low bone mineral density in older caged laying hens. Food Funct. 11, 3201–3212. doi:10.1039/c9fo02882j
Huang, M., Wang, Y., and Peng, R. (2020). Icariin alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through EphB4/Ephrin-B2 axis. eCAM 2020, 2982480. doi:10.1155/2020/2982480
Hwang, E., Lin, P., Ngo, H. T. T., Gao, W., Wang, Y., Yu, H., et al. (2018). Icariin and icaritin recover UVB-induced photoaging by stimulating Nrf2/ARE and reducing AP-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways: a comparative study on UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes. Photochem. Photobiological Sci. 17, 1396–1408. doi:10.1039/c8pp00174j
Iantomasi, T., Romagnoli, C., Palmini, G., Donati, S., Falsetti, I., Miglietta, F., et al. (2023). Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoporosis: molecular mechanisms involved and the relationship with microRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 3772. doi:10.3390/ijms24043772
Ilyas, S., Lee, J., and Lee, D. (2024). Emerging roles of natural compounds in osteoporosis: regulation, molecular mechanisms and bone regeneration. Pharm. (Basel, Switz.) 17, 984. doi:10.3390/ph17080984
Indran, I. R., Liang, R. L. Z., Min, T. E., and Yong, E.-L. (2016). Preclinical studies and clinical evaluation of compounds from the genus Epimedium for osteoporosis and bone health. Pharmacol. and Ther. 162, 188–205. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.01.015
Iqbal, M., Zhang, H., Mehmood, K., Li, A., Jiang, X., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Icariin: a potential compound for the recovery of tibial dyschondroplasia affected chicken via up-regulating BMP-2 expression. Biol. Proced. 20, 15. doi:10.1186/s12575-018-0080-y
Ji, R., Wu, D., and Liu, Q. (2022). Icariin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells via inhibition of reactive oxygen species production by reducing the expression of NOX1 and NOX4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 600, 6–13. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.02.023
Jiang, J., Xiao, J., He, J., Cai, Z., Chen, J., and Yin, J. (2022). Prediction and verification of Epimedium flavonoids with different glycosylation numbers in reversing glucocorticoid-induced bone formation inhibition by molecular docking and zebrafish. Front. Environ. Sci. 9, 793527. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2021.793527
Jiang, Z., Wang, H., Qi, G., Jiang, C., Chen, K., and Yan, Z. (2022). Iron overload-induced ferroptosis of osteoblasts inhibits osteogenesis and promotes osteoporosis: an in vitro and in vivo study. IUBMB life 74, 1052–1069. doi:10.1002/iub.2656
Jiang, J., He, J., Xiao, S., Shenyuan, J., Chen, T., and Pei, D. (2023). Screening of superior anti-osteoporotic flavonoids from Epimedii folium with dual effects of reversing iron overload and promoting osteogenesis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 37, e5686. doi:10.1002/bmc.5686
Jin, Y., Wu, A., Bian, S., and Teng, J. (2024). Icariin upregulates methyltransferase-like 14-mediated prolyl 4-hydroxylase beta subunit m6A modification to promote osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cells. Exp. Cell Res. 440, 114138. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114138
Jin, Z., Xu, H., Sun, X., Yan, B., and Wang, L. (2024). Targeting SAT1 prevents osteoporosis through promoting osteoclast apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 175, 116732. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116732
Jing, X., Du, T., Chen, K., Guo, J., Xiang, W., Yao, X., et al. (2019). Icariin protects against iron overload-induced bone loss via suppressing oxidative stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 10123–10137. doi:10.1002/jcp.27678
Johnston, C. B., and Dagar, M. (2020). Osteoporosis in older adults. Med. Clin. N. Am. 104, 873–884. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2020.06.004
Khoury, M. I. (2024). Osteoporosis and inflammation: cause to effect or comorbidity? Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 27 (10), 8. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.15357
Kim, B., Lee, K. Y., and Park, B. (2018). Icariin abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the RANKL-mediated TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway in Raw264.7 cells. Phytomedicine 51, 181–190. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.06.020
Kimball, J. S., Johnson, J. P., and Carlson, D. A. (2021). Oxidative stress and osteoporosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 103, 1451–1461. doi:10.2106/JBJS.20.00989
Kong, C. H., Steffi, C., Cai, Y., and Wang, W. (2025). E-jet printed polycaprolactone with strontium-substituted mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Biomater. Adv. 169, 214173. doi:10.1016/j.bioadv.2024.214173
Kupai, K., Kang, H., Pósa, A., Csonka, Á., Várkonyi, T., and Valkusz, Z. (2024). Bone loss in diabetes mellitus: diaporosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 7269. doi:10.3390/ijms25137269
Kverka, M., and Stepan, J. J. (2024). Associations among estrogens, the gut microbiome and osteoporosis. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 23, 2. doi:10.1007/s11914-024-00896-w
Li, G., Xu, Z., Chang, S., Nian, H., Wang, X., and Qin, L. (2014). Icariin prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss and lowers marrow adipogenesis. Menopause (New York, N.Y.) 21, 1007–1016. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000201
Li, M., Zhang, N., Wang, Y., Han, T., Jiang, Y., Rahman, K., et al. (2016). Coordinate regulatory osteogenesis effects of icariin, timosaponin B II and ferulic acid from traditional Chinese medicine formulas on UMR-106 osteoblastic cells and osteoblasts in neonatal rat calvaria cultures. J. Ethnopharmacol. 185, 120–131. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.023
Li, X., Peng, B., Pan, Y., Wang, P., Sun, K., Lei, X., et al. (2018). Icariin stimulates osteogenic differentiation and suppresses adipogenic differentiation of rBMSCs via estrogen receptor signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 18, 3483–3489. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.9325
Li, X., Xu, F., Lin, F., Ai, L., Zhao, Y., Bi, X., et al. (2020). A naringin-and icariin-contained herbal formula, Gushukang, ameliorated aged osteoporosis of aged mice with high calcium intake. Am. J. Chin. Med. 48, 1671–1691. doi:10.1142/S0192415X20500834
Li, X., Wang, L., He, M., Li, W., Zhang, J., Fu, Y., et al. (2022). A clinical herbal prescription gu-shu-kang capsule exerted beneficial effects on the musculoskeletal system of dexamethasone-treated mice by acting on tissue IGF-1 signalling pathway. Pharm. Biol. 60, 2098–2109. doi:10.1080/13880209.2022.2132029
Li, Y., Feng, X., Li, Y., Song, Q., Long, N., Fu, X., et al. (2024a). Icariin-loaded selenium-gold multi-shell nanocomposites with NIR-II response release to relieve post-damaged bone microenvironment for osteoporosis synergy therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 499, 156421. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.156421
Li, Y., Yu, P., Gao, Y., Ma, Z., Wang, H., Long, Y., et al. (2024b). Effects of the combination of Epimedii Folium and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus on apoptosis and autophagy in SOP rats and osteoblasts via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 173, 116346. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116346
Li, H., Hu, F., Liu, Q., Lv, L., Liang, H., Yuan, M., et al. (2024c). Enhanced osteogenic differentiation for osteoporosis treatment through controlled icariin release in the bone cavity via extracorporeal shock wave. Nano Today 58, 102408. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102408
Li, D., Cao, C., Li, Z., Chang, Z., Cai, P., Zhou, C., et al. (2024d). Icariside II protects from marrow adipose tissue (MAT) expansion in estrogen-deficient mice by targeting S100A16. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 73, e240020. doi:10.1530/JME-24-0020
Liang, W., Lin, M., Li, X., Li, C., Gao, B., Gan, H., et al. (2012). Icariin promotes bone formation via the BMP-2/Smad4 signal transduction pathway in the hFOB 1.19 human osteoblastic cell line. Int. J. Mol. Med. 30, 889–895. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2012.1079
Liang, X., Hou, Z., Xie, Y., Yan, F., Li, S., Zhu, X., et al. (2019). Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells and prevents bone loss in OVX mice via activating autophagy. J. Cell. Biochem. 120, 13121–13132. doi:10.1002/jcb.28585
Lin, Z., Jiang, Z. L., Chen, L. H., Sun, Y., Chen, S. Z., Zhou, P., et al. (2017). Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper may play an important role in icariin by suppressing osteogenesis inhibition induced by glucocorticoids in osteoblasts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 90, 237–243. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.042
Lin, W., Lin, P., Hung, Y., and Hsueh, T. (2020). Benefits of herbal medicine on bone mineral density in osteoporosis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Chin. Med. 48, 1749–1768.
Lin, S., Meng, Z., Wang, M., Ye, Z., Long, M., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). Icariin modulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation in ADSCs via the Hippo-YAP/TAZ pathway: a novel therapeutic strategy for osteoporosis. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1510561. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1510561
Liu, M., Zhong, C., He, R., and Chen, L. (2012). Icariin associated with exercise therapy is an effective treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Chin. Med. J. 125, 1784–1789. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.2012.10.018
Liu, Y., Zuo, H., Liu, X., Xiong, J., and Pei, X. (2017). The antiosteoporosis effect of icariin in ovariectomized rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-Grand, France) 63, 124–131. doi:10.14715/cmb/2017.63.11.22
Liu, H., Xiong, Y., Zhu, X., Gao, H., Yin, S., Wang, J., et al. (2017). Icariin improves osteoporosis, inhibits the expression of PPARγ, C/EBPα, FABP4 mRNA, N1ICD and jagged1 proteins, and increases Notch2 mRNA in ovariectomized rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 13, 1360–1368. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4128
Liu, H., Xiong, Y., Wang, H., Yang, L., Wang, C., Liu, X., et al. (2018). Effects of water extract from epimedium on neuropeptide signaling in an ovariectomized osteoporosis rat model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 221, 126–136. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.035
Liu, J., Cheng, Q., Wu, X., Zhu, H., Deng, X., Wang, M., et al. (2022). Icariin treatment rescues diabetes induced bone loss via scavenging ROS and activating primary Cilia/Gli2/Osteocalcin signaling pathway. Cells 11, 4091. doi:10.3390/cells11244091
Liu, L., Zhong, Y., Zheng, T., Zhao, J., Ding, S., Lv, J., et al. (2024). Epimedin B exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by regulating the MAPK/NF-κB/NOD-like receptor signalling pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 150, 109657. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109657
Liu, W., Xiang, S., Wu, Y., Zhang, D., Xie, C., Hu, H., et al. (2024). Icariin promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via the mTOR/autophagy pathway to improve ketogenic diet-associated osteoporosis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 19, 127. doi:10.1186/s13018-024-04529-x
Long, L., Wang, X., Lei, Y., Guo, S., Wang, C., Dai, W., et al. (2022). Icariin: a potential alternative against osteoporosis. Nat. Product. Commun. 17, 1934578X221134881. doi:10.1177/1934578x221134881
Lu, Z., Li, P., Chen, Z., and Zhang, L. (2021). Co-encapsulation of combinatorial flavonoids in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles for improved anti-osteoporotic activity in ovariectomized rats. Environ. Technol. Innovation 24, 102079. doi:10.1016/j.eti.2021.102079
Lu, F., Wu, X., Hu, H., Zhang, J., Song, X., Jin, X., et al. (2022). Yangonin treats inflammatory osteoporosis by inhibiting the secretion of inflammatory factors and RANKL expression. Inflammopharmacology 30, 1445–1458. doi:10.1007/s10787-022-00985-1
Luo, Z., Liu, M., Sun, L., and Rui, F. (2015). Icariin recovers the osteogenic differentiation and bone formation of bone marrow stromal cells from a rat model of estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 12, 382–388. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.3369
Luo, G., Wang, Z.-H., Yang, H.-Z., Fan, Y., Jiang, Z.-T., Li, Y.-Q., et al. (2024). Enhancing osteoporosis treatment using a targeted, sustained-release drug delivery system based on macrocyclic amphiphile. Int. J. Pharm. 661, 124457. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124457
Ma, H., Ma, X., Ge, B., Zhen, P., Zhou, J., Gao, Y., et al. (2014). Icariin attenuates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in osteoblasts and preserves their osteogenic differentiation potential in vitro. Cell Prolif. 47, 527–539. doi:10.1111/cpr.12147
Ma, Y., Yang, H., and Huang, J. (2018). Icariin ameliorates dexamethasone-induced bone deterioration in an experimental mouse model via activation of microRNA-186 inhibition of cathepsin K. Mol. Med. Rep. 17, 1633–1641. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.8065
Ma, D., Zhan, L., and Li, L. (2020). Anti-inflammatory effects and underlying mechanisms of Epimedium extracts. Prog. Biochem. Biophysics 47, 685–699. doi:10.16476/j.pibb.2020.0147
Ma, M., Fan, A.-Y., Liu, Z., Yang, L.-Q., Huang, J.-M., Pang, Z.-Y., et al. (2022). Baohuoside I inhibits osteoclastogenesis and protects against ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 874952. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.874952
Meng, F., Li, Y., Xiong, Z., Jiang, Z., and Li, F. (2005). Osteoblastic proliferative activity of Epimedium brevicornum Maxim. Phytomedicine 12, 189–193. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2004.03.007
Mohammadi, S. M., Saniee, N., Mousaviasl, S., Radmanesh, E., and Doustimotlagh, A. H. (2024). The role of osteocalcin in patients with osteoporosis: a systematic review. Iran. J. Public Health 53, 2432–2439. doi:10.18502/ijph.v53i11.16945
Mok, S., Chen, W., Lai, W., Leung, P., Wang, X., Yao, X., et al. (2010). Icariin protects against bone loss induced by oestrogen deficiency and activates oestrogen receptor-dependent osteoblastic functions in UMR 106 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 159, 939–949. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00593.x
Mosqueira, L., Barrioni, B. R., Martins, T., Ocarino, N. M., Serakides, R., and Pereira, M. M. (2020). In vitro effects of the co-release of icariin and strontium from bioactive glass submicron spheres on the reduced osteogenic potential of rat osteoporotic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed. Mater 15, 055023. doi:10.1088/1748-605X/ab9095
Nian, H., Ma, M., Nian, S., and Xu, L. (2009). Antiosteoporotic activity of icariin in ovariectomized rats. Phytomedicine. 16, 320–326. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2008.12.006
Oh, J. H., Ahn, B. N., Karadeniz, F., Kim, J. A., Lee, J. I., Seo, Y., et al. (2019). Phlorofucofuroeckol A from edible brown alga Ecklonia cava enhances osteoblastogenesis in bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Mar. Drugs 17, 543. doi:10.3390/md17100543
Omidvar, M. H., Soltani-Zangbar, M. S., Zamani, M., Motavalli, R., Jafarpoor, M., Dolati, S., et al. (2022). The effect of osteoporotic and non-osteoporotic individuals’ T cell-derived exosomes on osteoblast cells' bone remodeling related genes expression and alkaline phosphatase activity. BMC Res. Notes 15, 272. doi:10.1186/s13104-022-06139-4
Ouyang, L., Zhang, Q., Ruan, X., Feng, Y., and Wang, X. (2014). Treatment effect of Bushen Huayu extract on postmenopausal osteoporosis in vivo. Exp. Ther. Med. 7, 1687–1690. doi:10.3892/etm.2014.1661
Owen, R., Bahmaee, H., Claeyssens, F., and Reilly, G. C. (2020). Comparison of the anabolic effects of reported osteogenic compounds on human mesenchymal progenitor-derived osteoblasts. Bioengineering 7, 12. doi:10.3390/bioengineering7010012
Park, J. H., Kong, S. H., Lee, J., Oh, J., Lee, J. R., Lee, H. J., et al. (2025). Time since last intravenous bisphosphonate and risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw in osteoporotic patients. Nat. Commun. 16, 4367. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-59718-x
Pham, C. V., Pham, T. T., Lai, T. T., Trinh, D. C., Nguyen, H. V. M., Ha, T. T. M., et al. (2021). Icariin reduces bone loss in a Rankl-induced transgenic medaka (Oryzias latipes) model for osteoporosis. J. Fish Biol. 98, 1039–1048. doi:10.1111/jfb.14241
Priya, P. S., Pavithra, V., Vaishnavi, S., Pachaiappan, R., Kumar, T. T. A., Rady, A., et al. (2023). Understanding the mechanisms and implications of acacetin in mitigating diabetic osteoporosis: insights from a zebrafish model. Process Biochem. 134, 63–74. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2023.09.019
Qadir, A., Liang, S., Wu, Z., Chen, Z., Hu, L., and Qian, A. (2020). Senile osteoporosis: the involvement of differentiation and senescence of bone marrow stromal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 349. doi:10.3390/ijms21010349
Qi, S., He, J., Zheng, H., Chen, C., and Lan, S. (2019). Icariin prevents diabetes-induced bone loss in rats by reducing blood glucose and suppressing bone turnover. Mol. (Basel, Switz.) 24, 1871. doi:10.3390/molecules24101871
Qin, L., Han, T., Zhang, Q., Cao, D., Nian, H., Rahman, K., et al. (2008). Antiosteoporotic chemical constituents from Er-Xian Decoction, a traditional Chinese herbal formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 118, 271–279. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2008.04.009
Qiu, L., Yang, Q.-w., Feng, J., Wang, Y., and Huang, M. (2023). Epimedin C prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis via balancing EphB4/EphrinB2 axis in a rodent model. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 22, 1197–1204. doi:10.4314/tjpr.v22i6.8
Quan, X., Chen, H., Wang, W., Gao, Y., Zhi, X., Li, X., et al. (2024). Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of endocrine therapy-related osteoporosis among patients with breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 11 (2), 148–164. doi:10.1016/j.jtcms.2024.03.004
Raymond, M. H., Schutte, B. C., Torner, J. C., Burns, T. L., and Willing, M. C. (1999). Osteocalcin: genetic and physical mapping of the human gene BGLAP and its potential role in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Genomics 60, 210–217. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5893
Ren, L., Li, Q., Zhang, L., Wang, R., Qin, F., Zhao, L., et al. (2023). Integrated serum pharmacochemistry, network pharmacology and pharmacokinetics to explore bioactive components of Gushudan in the treatment of osteoporosis. J. Chromatogr. B, Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 1225, 123762. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2023.123762
Ren, M., Xie, H., Ding, Y., Li, Z., and Liu, B. (2023). Er-xian decoction drug-containing serum promotes Mc3t3-e1 cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation via regulating BK channel. J. Ethnopharmacol. 302, 115887. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115887
Romero-Díaz, C., Duarte-Montero, D., Gutiérrez-Romero, S. A., and Mendivil, C. O. (2021). Diabetes and bone fragility. Diabetes Ther. 12, 71–86. doi:10.1007/s13300-020-00964-1
Sarnella, A., Ferrara, Y., Terlizzi, C., Albanese, S., Monti, S., Licenziato, L., et al. (2024). The chicken embryo: an old but promising model for in vivo preclinical research. Biomedicines 12, 2835. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12122835
Saud, B., Malla, R., and Shrestha, K. (2019). A review on the effect of plant extract on mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 7513404. doi:10.1155/2019/7513404
Seyedi, Z., Amiri, M. S., Mohammadzadeh, V., Hashemzadeh, A., Haddad-Mashadrizeh, A., Mashreghi, M., et al. (2023). Icariin: a promising natural product in biomedicine and tissue engineering. J. Funct. Biomaterials 14, 44. doi:10.3390/jfb14010044
Shao, Y., Sun, L., Yang, G., Wang, W., Liu, X., Du, T., et al. (2022). Icariin protects vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and degeneration via activating Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 937502. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.937502
Sharifi, S., Moghaddam, F. A., Abedi, A., Maleki Dizaj, S., Ahmadian, S., Abdolahinia, E. D., et al. (2020). Phytochemicals impact on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. BioFactors Oxf. Engl. 46, 874–893. doi:10.1002/biof.1682
Shen, P., Guo, B., Gong, Y., Hong, D., Hong, Y., and Yong, E. (2007). Taxonomic, genetic, chemical and estrogenic characteristics of Epimedium species. Phytochemistry 68, 1448–1458. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.03.001
Shi, S., Wang, F., Huang, Y., Chen, B., Pei, C., Huang, D., et al. (2022). Epimedium for osteoporosis based on Western and eastern medicine: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 782096. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.782096
Si, Y., Li, Y., Gu, K., Yin, H., and Ma, Y. (2024). Icariin ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by targeting Cullin 3/Nrf2/OH pathway for osteoclast inhibition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 173, 116422. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116422
Singh, D., and Singh, R. (2025). Pharmacological and therapeutic potential of a natural flavonoid icariside II in human complication. Curr. Drug Targets 26, 320–330. doi:10.2174/0113894501329810241117231839
Song, L., Zhao, J., Zhang, X., Li, H., and Zhou, Y. (2013). Icariin induces osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and mineralization through estrogen receptor-mediated ERK and JNK signal activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 714, 15–22. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.05.039
Song, L., Zhou, Y., Qu, L., Wang, D., Diao, X., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). Exploring effects and mechanism of ingredients of herba epimedii on osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 27, 2824–2837. doi:10.2174/0113862073243559231023065934
Su, Y. J., Lin, C. Y., and Hsu, C. Y. (2024). Analyzing the risk of osteoporosis and fracture in rheumatoid arthritis patients who have been treated with various biologics. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 27 (2), e15055. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.15055
Sun, L., Li, C., Wen, X., Guo, L., Guo, Z., Liao, L., et al. (2021). Icariin stimulates hFOB 1.19 osteoblast proliferation and differentiation via OPG/RANKL mediated by the estrogen receptor. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 22, 168–175. doi:10.2174/18734316mtazyoduex
Sze, S. C., Tong, Y., Ng, T. B., Cheng, C. L., and Cheung, H. P. (2010). Herba epimedii: anti-oxidative properties and its medical implications. Mol. (Basel, Switz.) 15, 7861–7870. doi:10.3390/molecules15117861
Takeuchi, Y. (2025). Cardiovascular safety of osteoanabolic agents. J. Bone Mineral Metabolism 43, 26–32. doi:10.1007/s00774-025-01580-4
Tan, M., Li, Q., Yang, B., Wang, S., and Chen, Z. (2024). Insight of Chinese herbal medicine in treating osteoporosis: achievements from 2013 to 2023. Am. J. Chin. Med. 52, 1303–1328. doi:10.1142/S0192415X24500526
Tang, D., Ju, C., Liu, Y., Xu, F., Wang, Z., and Wang, D. (2018). Therapeutic effect of icariin combined with stem cells on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats. J. Bone Mineral Metabolism 36, 180–188. doi:10.1007/s00774-017-0831-x
Tang, N., Zhao, H., Zhang, H., and Dong, Y. (2019). Effect of autophagy gene DRAM on proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy of osteoblast in osteoporosis rats. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 5023–5032. doi:10.1002/jcp.27304
Teo, Y. L., Cheong, W. F., Cazenave-Gassiot, A., Ji, S., Logan, S., Lee, Z. X. K., et al. (2019). Pharmacokinetics of prenylflavonoids following oral ingestion of standardized epimedium extract in humans. Planta Medica 85, 347–355. doi:10.1055/a-0806-7673
Tian, Q., Wu, S., Dai, Z., Yang, J., Zheng, J., Zheng, Q., et al. (2016). Iron overload induced death of osteoblasts in vitro: involvement of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. PeerJ 4, e2611. doi:10.7717/peerj.2611
Verma, A., Aggarwal, K., Agrawal, R., Pradhan, K., and Goyal, A. (2022). Molecular mechanisms regulating the pharmacological actions of icariin with special focus on PI3K-AKT and Nrf-2 signaling pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 49, 9023–9032. doi:10.1007/s11033-022-07778-3
Wang, L., Li, Y., Guo, Y., Ma, R., Fu, M., Niu, J., et al. (2016). Herba epimedii: an ancient Chinese herbal medicine in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 22, 328–349. doi:10.2174/1381612822666151112145907
Wang, Z., Wang, D., Yang, D., Zhen, W., Zhang, J., and Peng, S. (2018). The effect of icariin on bone metabolism and its potential clinical application. Osteoporos. Int.29, 535–544. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-4255-1
Wang, Q., Wang, G., Lu, Y., Cui, Y., Li, H., Li, R., et al. (2018). The combination of icariin and constrained dynamic loading stimulation attenuates bone loss in ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic mice. J. Orthop. Res. 36, 1415–1424. doi:10.1002/jor.23777
Wang, L., Heckmann, B. L., Yang, X., and Long, H. (2019). Osteoblast autophagy in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 3207–3215. doi:10.1002/jcp.27335
Wang, Y., Li, X., Deng, F., and Yin, R. (2021). Hydroxy-safflower yellow A alleviates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rat model by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase 2 activity. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 734539. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.734539
Wang, W., Xiong, Y., Zhao, R., Li, X., and Jia, W. (2022). A novel hierarchical biofunctionalized 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V scaffold with enhanced osteoporotic osseointegration through osteoimmunomodulation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 20, 68. doi:10.1186/s12951-022-01277-0
Wang, S., Wang, S., Wang, X., Xu, Y., Zhang, X., Han, Y., et al. (2022). Effects of icariin on modulating gut microbiota and regulating metabolite alterations to prevent bone loss in ovariectomized rat model. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 874849. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.874849
Wang, S., Zhu, S., Li, X., and Yang, Z. (2024). Study on the mechanism of action of the traditional Chinese medical prescription Gushukang in treating osteoporosis based on network Pharmacology and experimental verification. Curr. Computer-Aided Drug Des. 21, 752–765. doi:10.2174/0115734099282620240521102006
Wang, X., Cui, b., Xu, L., and Pei, X. (2024). Exploring the molecular mechanism of Epimedium brevicornu Maxim. in treating breast cancer via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 11 (2), 207–221. doi:10.1016/j.jtcms.2024.03.005
Wang, W., Yang, W., Wang, F., Gao, H., Liu, K., Zhang, J., et al. (2025). Kunxinning granules alleviate perimenopausal syndrome by supplementing estrogen deficiency. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1554479. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1554479
Wu, H., Kim, M., and Han, J. (2016). Icariin metabolism by human intestinal microflora. Mol. (Basel, Switz.) 21, 1158. doi:10.3390/molecules21091158
Wu, L., Ling, Z., Feng, X., Mao, C., and Xu, Z. (2017a). Herb medicines against osteoporosis: active compounds and relevant biological mechanisms. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 17, 1670–1691. doi:10.2174/1568026617666161116141033
Wu, Z., Ou, L., Wang, C., Yang, L., Wang, P., Liu, H., et al. (2017b). Icaritin induces MC3T3-E1 subclone14 cell differentiation through estrogen receptor-mediated ERK1/2 and p38 signaling activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 94, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.071
Wu, Y., Zhu, Y., Chen, J., Song, L., Wang, C., Wu, Y., et al. (2025a). Boosting mRNA-Engineered monocytes via prodrug-Like microspheres for bone microenvironment multi-phase remodeling. Adv. Healthc. Mater. Healthc. Mater. 14, 2403212. doi:10.1002/adhm.202403212
Wu, W., Qiao, A., and Du, T. (2025b). Tissue-specific mechanism of estrogen in osteoporosis and vascular calcification. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1002, 177783. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177783
Xi, Y., Jiang, T., Yu, J., Xue, M., Xu, N., Wen, J., et al. (2019). Preliminary studies on the anti-osteoporosis activity of Baohuoside I. Biomed. Pharmacother. 115, 108850. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108850
Xia, D., Wu, J., Xing, M., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Xia, Y., et al. (2019). Iron overload threatens the growth of osteoblast cells via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a/DUSP14 signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 15668–15677. doi:10.1002/jcp.28217
Xiang, C., Cao, J., Hu, R., Li, K., Meng, T., Xia, Y., et al. (2025). Oleandrin inhibits osteoclast differentiation by targeting the LRP4/MAPK/NF-κB signalling pathway to treat osteoporosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 148, 114073. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114073
Xie, D., Xu, Y., Zhang, Y., Cai, W., Lan, X., and Yan, H. (2023). Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1–dependent metabolic reprogramming: a promising target for postmenopausal osteoporosis treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 160, 114411. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114411
Xin, X., Fan, G., Sun, Z., Zhang, N., Li, Y., Lan, R., et al. (2015). Biotransformation of major flavonoid glycosides in herb epimedii by the fungus Cunninghamella blakesleana. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 122, 141–146. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2015.05.021
Xu, B., Wang, X., Wu, C., Zhu, L., Chen, O., and Wang, X. (2018). Flavonoid compound icariin enhances BMP-2 induced differentiation and signalling by targeting to connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in SAMP6 osteoblasts. PLoS One 13, e0200367. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0200367
Xu, Q., Chen, G., Liu, X., Dai, M., and Zhang, B. (2019). Icariin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via modulation of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 508, 902–906. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.201
Xu, Y., Li, L., Tang, Y., Yang, J., Jin, Y., and Ma, C. (2019). Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation by suppressing Notch signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 865, 172794. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172794
Xu, H., Zhou, S., Qu, R., Yang, Y., Gong, X., Hong, Y., et al. (2020). Icariin prevents oestrogen deficiency-induced alveolar bone loss through promoting osteogenesis via STAT3. Cell Prolif. 53, e12743. doi:10.1111/cpr.12743
Xue, L., Wang, Y., Jiang, Y., Han, T., Nie, Y., Zhao, L., et al. (2012). Comparative effects of er-xian decoction, epimedium herbs, and icariin with estrogen on bone and reproductive tissue in ovariectomized rats. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2012, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2012/241416
Xue, L., Jiang, Y., Han, T., Zhang, N., Qin, L., Xin, H., et al. (2016). Comparative proteomic and metabolomic analysis reveal the antiosteoporotic molecular mechanism of icariin from Epimedium brevicornu maxim. J. Ethnopharmacol. 192, 370–381. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.037
Yan, R., Guo, Y., Wang, X., Liang, G., Yang, A., and Li, J. (2022). Near-infrared light-controlled and real-time detection of osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells by upconversion nanoparticles for osteoporosis therapy. ACS Nano 16, 8399–8418. doi:10.1021/acsnano.2c02900
Yan, C., Gu, X., Tan, S., Mei, A., Mao, J., Dai, Y., et al. (2025). Lipid peroxidation inhibition by icaritin and its glycosides as a strategy to combat iron overload-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish. Food Res. Int. 203, 115900. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2025.115900
Yang, L., Lu, D., Guo, J., Meng, X., Zhang, G., and Wang, F. (2013). Icariin from Epimedium brevicornum Maxim promotes the biosynthesis of estrogen by aromatase (CYP19). J. Ethnopharmacol. 145, 715–721. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.11.031
Yang, L., Yu, Z., Qu, H., and Li, M. (2014). Comparative effects of hispidulin, genistein, and icariin with estrogen on bone tissue in ovariectomized rats. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 70, 485–490. doi:10.1007/s12013-014-9945-0
Yang, A., Yu, C., Lu, Q., Li, H., Li, Z., and He, C. (2019). Mechanism of action of icariin in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 5747298. doi:10.1155/2019/5747298
Yang, X., Shi, L., Li, A., Gao, F., Sun, W., and Li, Z. (2023). Phase-contrast imaging with synchrotron hard X-ray reveals the effect of icariin on bone tissue morphology and microstructure in rabbits with early glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1155532. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1155532
Yang, S., Zhang, X., Liao, X., Ding, Y., and Gan, J. (2024). Icariin regulates RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation via the ERα/c-Src/RANK signaling. Biomed. Mater. (Bristol, Engl.) 19, 025049. doi:10.1088/1748-605x/ad2554
Yao, X., Jing, X., Guo, J., Sun, K., Deng, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Icariin protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against iron overload induced dysfunction through mitochondrial fusion and fission, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 163. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00163
Yao, Y., Cai, X., Chen, Y., Zhang, M., and Zheng, C. (2025). Estrogen deficiency-mediated osteoimmunity in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Med. Res. Rev. 45, 561–575. doi:10.1002/med.22081
Ye, Y., Jing, X., Li, N., Wu, Y., Li, B., and Xu, T. (2017). Icariin promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells by activating the RhoA-TAZ signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 88, 384–394. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.075
Zhang, G., Qin, L., and Shi, Y. (2007). Epimedium-derived phytoestrogen flavonoids exert beneficial effect on preventing bone loss in late postmenopausal women: a 24-month randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trial. J. Bone Mineral Res. 22, 1072–1079. doi:10.1359/jbmr.070405
Zhang, D., Cheng, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, X., Wang, N., Chen, Y., et al. (2008). Synergistic effect of trace elements and flavonoids from Epimedium koreanum Nakai on primary osteoblasts. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 347–356. doi:10.1007/s11434-007-0485-5
Zhang, J., Li, Y., Sun, J., Liu, C., and Zhang, D. (2011). Synergistic or antagonistic effect of MTE plus TF or icariin from Epimedium koreanum on the proliferation and differentiation of primary osteoblasts in vitro. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 143, 1746–1757. doi:10.1007/s12011-011-8987-z
Zhang, D., Zhang, J., Fong, C., Yao, X., and Yang, M. (2012). Herba epimedii flavonoids suppress osteoclastic differentiation and bone resorption by inducing G2/M arrest and apoptosis. Biochimie 94, 2514–2522. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2012.06.033
Zhang, X., Liu, T., Huang, Y., Wismeijer, D., and Liu, Y. (2014). Icariin: does it have an osteoinductive potential for bone tissue engineering? Phytotherapy Res. 28, 498–509. doi:10.1002/ptr.5027
Zhang, J., Song, J., and Shao, J. (2015). Icariin attenuates glucocorticoid-induced bone deteriorations, hypocalcemia and hypercalciuria in mice. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 8, 7306–7314.
Zhang, D., Fong, C., Jia, Z., Cui, L., Yao, X., and Yang, M. (2016). Icariin stimulates differentiation and suppresses adipocytic transdifferentiation of primary osteoblasts through estrogen receptor-mediated pathway. Calcif. Tissue Int. 99, 187–198. doi:10.1007/s00223-016-0138-2
Zhang, S., Feng, P., Mo, G., Li, D., Li, Y., Mo, L., et al. (2017). Icariin influences adipogenic differentiation of stem cells affected by osteoblast-osteoclast co-culture and clinical research adipogenic. Biomed. Pharmacother. 88, 436–442. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.050
Zhang, Y., Han, B., Wei, Y., Jing, J., and Li, J. (2020). Icariin promotes fracture healing in ovariectomized rats. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, e924554. doi:10.12659/MSM.924554
Zhang, L., Li, X., Ying, T., Wang, T., and Fu, F. (2021a). The use of herbal medicines for the prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Front. Endocrinol. 12, 744647. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.744647
Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Lu, P., Dai, G., Chen, X., and Rui, Y. (2021b). The modulatory effect and implication of gut microbiota on osteoporosis: from the perspective of “brain-gut-bone” axis. Food Funct. 12, 5703–5718. doi:10.1039/d0fo03468a
Zhang, D., Su, Y., He, Q., Zhang, Y., Gu, N., Zhang, X., et al. (2022). Icariin exerts estrogen-like actions on proliferation of osteoblasts in vitro via membrane estrogen receptors-mediated non-nuclear effects. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 21, e127000. doi:10.5812/ijpr-127000
Zhang, C., Li, H., Li, J., Hu, J., Yang, K., and Tao, L. (2023a). Oxidative stress: a common pathological state in a high-risk population for osteoporosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 163, 114834. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114834
Zhang, X., Sun, Z., Zhang, Y., Pan, L., Jiang, W., Dong, H., et al. (2023b). Periplocin targets low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 to attenuate osteoclastogenesis and protect against osteoporosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 211, 115516. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115516
Zhang, J., Mao, Y., and Rao, J. (2024a). The SPI1/SMAD5 cascade in the promoting effect of icariin on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells: a mechanism study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 19, 444. doi:10.1186/s13018-024-04933-3
Zhang, Y., Wu, Y., Liu, X., Chen, X., and Su, J. (2024b). Targeting the gut microbiota-related metabolites for osteoporosis: the inextricable connection of gut-bone axis. Ageing Res. Rev. 94, 102196. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2024.102196
Zhang, S., Hui, X., Pan, H., and Chen, G. (2025). Progress in composite hydrogels enriched with icariin for bone defect healing. Polym. Eng. Sci. 65, 2153–2163. doi:10.1002/pen.27152
Zhao, J., and Zhang, W. (2025). Icariin and related metabolites in fibrosis management: pharmacological properties and molecular mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1619581. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1619581
Zhao, B., Wang, J., Song, J., Wang, C., Gu, J., Yuan, J.-r., et al. (2016). Beneficial effects of a flavonoid fraction of herba epimedii on bone metabolism in ovariectomized rats. Planta Medica 82, 322–329. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1558294
Zhao, W., Li, X., Bi, H., and Li, F. (2024). Exploring the molecular mechanisms underlying icariin-mediated regulation of fatty acid-binding protein 4 gene expression in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 38, 3269–3279. doi:10.23812/j.biol.regul.homeost.agents.20243804.258
Zhou, J., Ma, Y. H., Zhou, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., and Gao, X. (2015). Intestinal absorption and metabolism of epimedium flavonoids in osteoporosis rats. Drug Metabolism Dispos. 43, 1590–1600. doi:10.1124/dmd.115.064386
Zhou, L., Poon, C.C.-W., Wong, K., Cao, S., Dong, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). Icariin ameliorates estrogen-deficiency induced bone loss by enhancing IGF-I signaling via its crosstalk with non-genomic ERα signaling. Phytomedicine 82, 153413. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153413
Zhu, H., Qin, L., Garnero, P., Genant, H., Zhang, G., Dai, K., et al. (2012). The first multicenter and randomized clinical trial of herbal Fufang for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 23, 1317–1327. doi:10.1007/s00198-011-1577-2
Zhu, Y., Zheng, T., Wen, L., Li, R., Zhang, Y., Bi, W., et al. (2021). Osteogenic capability of strontium and icariin-loaded TiO2 nanotube coatings in vitro and in osteoporotic rats. J. Biomaterials Appl. 35, 1119–1131. doi:10.1177/0885328221997998
Zhu, Y.-X., Tang, Z.-L., Lu, L., Qiu, Z.-C., Pan, D., Yu, Y., et al. (2024). Exploring a novel class tryptophan hydroxylase 1 inhibitor derived from Sambucus williamsii Hance for the osteoporosis treatment. Acupunct. Herb. Med. 4, 102–112. doi:10.1097/hm9.0000000000000095
Keywords: icariin, osteoporosis, bone metabolism, bone homeostasis, drug delivery, molecular mechanisms, animal models, therapeutic application
Citation: Fu B, Yu S, Chen S and Hu B (2025) Icariin against osteoporosis: a review of advances in molecular mechanisms to biomedical applications. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1688847. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1688847
Received: 19 August 2025; Accepted: 10 November 2025;
Published: 25 November 2025.
Edited by:
Yufeng Zhang, Tianjin Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Viney Kumar, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, United StatesYing Wang, Anhui Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Fu, Yu, Chen and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shengxiong Chen, ZHIuY2hlbnN4QGhvdG1haWwuY29t; Bo Hu, aHVib2hpbGxAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Boyi Fu
Boyi Fu Shasha Yu3†
Shasha Yu3† Shengxiong Chen
Shengxiong Chen



