- 1Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 2The First Clinical Medical College, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 3Jiangxi Clinical Medical Research Center for Cancer, Ganzhou, China
- 4Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China
Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, has emerged as a multifaceted therapeutic agent in oncology due to its dual anti-inflammatory and antitumor properties. This review synthesizes recent advances in understanding the molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of celecoxib in cancer treatment. Celecoxib not only hinders the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells by inhibiting COX-2 synthesis, but also inhibits the intratumoral infiltration of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and activates cytotoxic T cells, thereby reshaping the inhibitory immune microenvironment. Preclinical and clinical studies demonstrate its synergistic effects with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy, particularly in augmenting immune checkpoint blockade efficacy. Despite the breakthrough of celecoxib in the field of oncology treatment, large-scale trials are warranted to validate its long-term safety and biomarker-driven accuracy. This work underscores the potential of celecoxib as a cornerstone in multimodal cancer therapy and provides a roadmap for its integration into personalized treatment paradigms.
1 Introduction
Malignant neoplasms are a major global public health challenge, with nearly 20 million new cancer cases as well as 9.7 million cancer deaths in 2022 according to global cancer statistics (Bray et al., 2024), and a complex challenge for clinical oncology, characterized by heterogeneity and the ability to evade immune surveillance. The pathogenesis of cancer involves a variety of factors, including genetic mutations, epigenetic modifications, and the tumor microenvironment, which work together to contribute to tumor growth, progression, and metastasis (Swanton et al., 2024). Among them, the chronic inflammatory state in the tumor microenvironment is a key factor in the occurrence and progression of malignant tumors (Balkwill and Mantovani, 2001; Greten and Grivennikov, 2019). Inflammatory mediators can not only induce angiogenesis and epithelial interstitial and accelerate tumor invasion and metastasis, but also lead to chemoresistance and immunotherapy resistance by reshaping the tumor immune microenvironment. The activation of tumor-associated inflammation is closely related to the activation of the COX-2 pathway, which is highly expressed in a variety of solid tumors. It can drive tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and immune evasion, and is resistant to anti-tumor therapy (Bell et al., 2022; Bell and Zelenay, 2022; Cheki et al., 2018). The selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib has attracted much attention due to its precise regulation of inflammatory pathways.
COX-2 is an enzyme that plays a key role in the inflammatory process and is also implicated in various stages of tumorigenesis. COX-2 is elevated in many types of malignancies (Tołoczko-Iwaniuk et al., 2019), and it has long been found to promote tumor development by modulating malignant transformation, aberrant proliferation, inhibition of programmed apoptosis, tumor angiogenesis, aggressiveness and metastasis, and immune responses (Hashemi Goradel et al., 2019; Trifan and Hla, 2003). Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), a type of eicosanoid, is a pro-inflammatory agent that activates various pro-cancer signaling pathways, including cAMP/PKA, ERK, and NF-κB, by binding to EP4 receptors. This binding drives tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and immune evasion. Additionally, PGE2can foster immunosuppression and treatment resistance within the tumor microenvironment by suppressing NK cell function and inducing the expression of MDSCs and cancer stem cell (CSC) phenotypes (Wang and Dubois, 2010; Holt et al., 2012; Ching et al., 2020; Mao et al., 2014); COX-2 can facilitate the progression of tumor cells by promoting the transformation of arachidonic acid into PGE2, while suppressing anti-cancer immunity (Zelenay et al., 2015; Lira et al., 2024; Li et al., 2020). In summary, COX-2 expression is associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target for cancer. Celecoxib exerts its antitumor effects by inhibiting COX-2, not only reducing the production of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins, but also influencing various signaling pathways related to tumor growth through its influence. Figure 1 illustrates the multiple mechanisms of action of the COX-2/PGE2 2 signaling axis in tumorigenesis and progression.
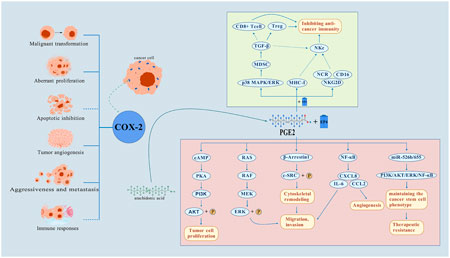
Figure 1. Multiple mechanisms of action of COX-2/PGE2 2 signaling axis in tumorigenesis and development. This figure summarizes the core pathway of COX-2 to drive tumor malignancy by catalyzing PGE2 synthesis: 1. Activation of pro-cancer signaling: PGE2 binds to EP4 receptor and activates multiple pathways such as cAMP/PKA, RAS/MAPK, PI3K/AKT and NF-κB, which synergistically promote tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis inhibition, invasion and metastasis, and angiogenesis. 2. Immune microenvironment remodeling: PGE2 binds to EP2 and EP4 receptors to induce the expression of Treg and MDSC inhibitory immune cells and inhibit NK cytotoxicity, weakening the anti-tumor immune response. 3. Stem cell phenotypic maintenance: PGE2 maintains cancer stem cell (CSC) properties by stimulating the expression of miR-526 b and miR-655 and mediates treatment resistance. (


Celecoxib, which is known as a COX-2 inhibitor selectively, is becoming important in the field of pharmacology due to its unique mechanism that is different from traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (Davies et al., 2000). The typical non-selective NSAIDs, they block both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, while celecoxib selectively targets COX-2, which is general upregulated in inflammatory conditions and various malignant tumors (Tołoczko-Iwaniuk et al., 2019). This selectivity reduces the gastrointestinal side effects typically associated with non-selective NSAIDs, making celecoxib a promising candidate for cancer treatment (Rao and Reddy, 2004) (Quiñones and Pierre, 2019). The pharmacological characteristics of celecoxib has been extensively studied, revealing its potential to inhibit proliferation and promote apoptosis of various cancers, including colorectal cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, and so on (Wen et al., 2020).
The dual effects of anti-inflammatory and potentially anti-cancer properties are important manifestations of celecoxib in cancer research. Numerous studies have shown that it is effective in inhibiting COX-2 expression in tumor cells, thereby mitigating tumor growth and increasing the effectiveness of conventional cancer therapy (Tai et al., 2019). More and more studies have shown that there is a complex interaction network between tumor inflammatory state and tumor progression, so the in-depth analysis of the regulatory mechanism of celecoxib on tumor inflammation by anti-inflammatory drugs will provide a key theoretical basis for realizing tumor immune microenvironment reprogramming and breaking through the treatment bottleneck (Negi et al., 2019).
2 Clinical applications: from symptom control to multimodal therapy
2.1 Pain relief
The analgesic efficacy of celecoxib in patients with malignancies has been extensively studied for its ability to reduce inflammation and pain response by selectively inhibiting COX-2 and decreasing prostaglandin synthesis, and is commonly used for mild to moderate pain caused by cancer, and in a study by Hou et al., the addition of celecoxib was effective in improving pain in patients with carcinomatous neuralgia (Hou et al., 2021). Furthermore, clinical trials have shown that celecoxib can relieve pain caused by radiotherapy (Ghasemi et al., 2018). In addition, the use of celecoxib can reduce the need for opioids in postoperative patients, thereby reducing opioid side effects such as respiratory depression, nausea, constipation, and high dependence rates (Carpenter et al., 2018). In the treatment of metastatic bone cancer, celecoxib can be used in combination with opioids or other analgesics to significantly enhance the analgesic effect, and the combination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can also reduce morphine use (Liu et al., 2017). However, a meta-analysis suggests that while celecoxib is effective in the treatment of chronic pain and inflammatory diseases, the associated risks associated with long-term use, such as cardiovascular disease, need to be carefully considered (Ye et al., 2022). Therefore, celecoxib has shown good analgesic effect in pain management of patients with malignancy, especially in relieving chronic pain caused by cancer, reducing opioid demand, and being used in combination with other drugs, but its potential risks should be carefully considered in the long term.
2.2 Combination of celecoxib with other treatments
In addition to analgesic effects, the use of celecoxib in combination with other treatments in malignant tumors is also gradually recognized. An important area of focus is its potential role in enhancing the efficacy of cancer treatment. For example, the combination of celecoxib with chemotherapy can significantly prolong the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of patients (Bąk and Krupa, 2023). In terms of radiation therapy, celecoxib also exhibited synergistic anti-cancer effects (Mitryayeva et al., 2024). In addition, celecoxib has been shown to enhance anti-tumor by enhancing the effects of PD-1 inhibitors immunity (Hu et al., 2022). Although celecoxib has demonstrated potential synergies in combination with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy, this does not mean that simply adding celecoxib necessarily improves treatment outcomes (Li et al., 2023; Meyerhardt et al., 2021). The actual effect still depends on the combination of multiple factors, so more clinical studies are needed to verify its long-term safety and efficacy.
2.2.1 Chemotherapy
Celecoxib as a selective COX-2 inhibitor has shown promising prospects in combination with chemotherapy. This strategy is supported by evidence that drugs such as cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil have been shown to enhance COX-2 expression in preclinical models such as lung and colorectal cancer, which not only enhances tumor cell survival, invasion, and angiogenesis, but also drives the production of prostaglandin E2 to increase inflammation and recruit immunosuppressive cells such as myeloid-derived suppressor cells and regulatory T cells, thereby limiting the efficacy of chemotherapy and immunotherapy (Bell et al., 2022; Bell and Zelenay, 2022). By targeting this resistance axis, celecoxib can enhance the cytotoxicity of conventional chemotherapeutic agents. or example, In an in vitro study and tumor bering mouse model using the SGC-7901/DDP cell lines for gastric cancer, cisplatin combined with celecoxib enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity in a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent manner (Xu et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2016). Similarly, in an in vitro study using human skin cancer, celecoxib combined with doxorubicin was found to significantly reduce cell viability by inhibiting the AKT and COX-2 pathways, thereby promoting cell death (Singh, 2018). And in a MATE analysis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer, celecoxib combined with chemotherapy significantly improved overall response and survival (Zhang et al., 2020). In addition, celecoxib during chemotherapy can also reduce side effects caused by chemotherapy, such hand-foot syndrome (HFS), thereby improving patient tolerance (Shayeganmehr et al., 2023). However, although the combination of celecoxib has been shown to improve survival in some cases, it has also been suggested that it may increase the risk of certain adverse effects, such as hematologic toxicity and cardiovascular events (Zhang et al., 2020). Therefore, in clinical application, the potential benefits and risks of celecoxib need to be weighed against the specific situation of the patient.
2.2.2 Radiotherapy
Celecoxib is often used as a sensitizer for radiation therapy. It may reduce adaptive resistance to radiotherapy by inhibiting COX-2-dependent angiogenesis and tumor aggressiveness (Cheki et al., 2018). Studies have found that celecoxib can enhance the sensitivity of radiotherapy to non-small cell lung cancer cells and promote radiotherapy-induced apoptosis, which may be related to celecoxib’s downregulation of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway (Zhang et al., 2019). Sun et al. also found that celecoxib could enhance radiotherapy-induced apoptosis (Sun et al., 2017). In a study of radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, celecoxib was found to improve the effectiveness of radiotherapy, especially against the effects of angiogenesis (Mitryayeva et al., 2024). In addition, the use of celecoxib may reduce the adverse effects associated with radiotherapy and help relieve the discomfort associated with radiotherapy (Bi et al., 2019). There are also many clinical trials that have confirmed the therapeutic efficacy of celecoxib in radiotherapy (Liao et al., 2005; Xue et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2014). Therefore, the combination of celecoxib with radiotherapy may provide a new strategy for improving radiotherapy efficacy.
2.2.3 Immunotherapy
In immunotherapy, celecoxib also exhibits a synergistic effect. Tumor cells can induce tumor immune escape via the COX-2-PGE2 pathway (Jin et al., 2023), and the combination of celecoxib with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies is faster than anti-PD-1 alone to induce tumor eradication (Zelenay et al., 2015). Celecoxib in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors significantly increases tumor-infiltrating T cell activity and improves anti-tumor immune responses (Cao et al., 2023; Pelly et al., 2021). Zhang et al. found that celecoxib in combination with roscovitine significantly enhanced the anti-tumor immune response by eliminating inflammation-related immunosuppression and reversing IFN-γ-mediated immune resistance (Zhang et al., 2022). In breast cancer models, celecoxib has been demonstrated to reprogram the CAF-like cell-mediated immunosuppressive microenvironment, promote the infiltration of cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and inhibit regulatory T cell (Treg) activity, thereby enhancing the efficacy of immunotherapy (Samoudi et al., 2024). In addition, Pan et al. also found that celecoxib derivatives (2,5-dimethylcelecoxib) can inhibit the expression of programmed cell death protein-1 by regulating the tumor microenvironment and upregulate the expression of NK and T cells, providing a reference for combined immunotherapy,but this derivative is independent of the COX-2 signaling pathway (Pan et al., 2023). The mechanism of COX-2-PGE2 pathway promoting progression in malignant tumors through immunosuppression has been continuously explored (Pu et al., 2021), providing a new strategy for COX-2 inhibitor combination immunotherapy (Kosaka et al., 2023; Veltman et al., 2010), and the development of some celecoxib derivatives has also provided some mechanism exploration for non-COX-2 dependence (Tan et al., 2021; Sigler et al., 2025), which may be a new path, but the efficacy of celecoxib combined with immunotherapy needs to be verified by more clinical trials.
2.2.4 Other applications
In addition to the above-mentioned applications, there are some other applications of celecoxib that are still being explored. For example, it is also effective in combination with targeted drugs (Lin et al., 2018; Valverde et al., 2017; Tudor et al., 2021; Xiao et al., 2019), and it can also be used in combination with some novel therapies [such as oncolytic virus therapy (Tang et al., 2020), nano delivery system (Bai et al., 2024), immunophotodynamic therapy (An et al., 2024; Ding et al., 2024)] for anti-tumor, which can help improve the research of celecoxib in cancer and provide more personalized treatment strategies.
3 Celecoxib’s antitumor mechanism
3.1 The apoptotic induction mechanism of celecoxib
Celecoxib induces apoptosis through a multi-target mechanism, ranging from upstream signaling regulation to terminal effector activation (Figure 2). The core mechanism initiates with a significant accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which serve as a pro-apoptotic signaling hub. These ROS not only directly activate downstream death pathways (Sung et al., 2017; Pritchard et al., 2018), but also enhances the sensitivity of cancer cells to death ligands such as FasL/RAIL, demonstrating synergistic pro-apoptotic effects (Zhu et al., 2021). At the regulatory level of key signaling pathways, the drug effectively blocks the anti-apoptotic function of Bcl-2 protein and Akt kinase downstream of NF-kB by inhibiting the activation of NF-kB in the NF-kB pathway and the phosphorylation of Akt kinase in the PI3K/Akt pathway, respectively, and alleviates the inhibitory effect on the cell death program (Li et al., 2020; Hsu et al., 2000). Celecoxib can also inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by promoting TCF7L2 protein degradation, thereby decreasing the expression of downstream cyclin D1 and survivin and promoting apoptosis, which is a COX-2-independent pathway (Egashira et al., 2017). The molecular regulatory network exhibits a two-way dynamic balance: the upregulation of the expression of pro-apoptotic protein (Puma/Bad) and the downregulation of anti-apoptotic factors (survivin/XIAP/cFLIP/Mcl-1/Bcl-w) create a cascade amplification effect, which significantly promotes the process of apoptosis (Zhu et al., 2021). Additionally, celecoxib upregulates GRP78, C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP), death receptor 5 (DR5), and activates the endoplasmic reticulum stress response through the unfolded protein response (UPR), opening up another independent apoptosis signaling pathway (Thi Thanh Nguyen and Yoon, 2024). This multi-layered network of action, initiated by oxidative stress, transduced through key pathway nodes (ROS/Akt), and converging on apoptosis executive proteins, explains the unique advantages of celecoxib in combination therapy. This has been confirmed to produce a synergistic sensitization effect when combined with conventional therapy, providing a new direction for optimizing anti-cancer strategies (Qadir et al., 2023).
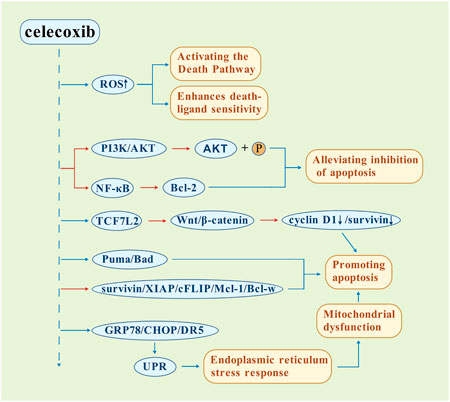
Figure 2. Mechanistic framework of celecoxib-induced apoptosis. The driving role of ROS was revealed, and the inhibition of multiple key survival pathways, the regulation of apoptosis regulatory proteins, and the activation of independent endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways to mitochondrial dysfunction were demonstrated. The Wnt/β-catenin and UPR/ERS pathways are COX-2-independent pathways. (


Notably, substantial evidence underscores the importance of the COX-2-independent pathway in celecoxib-induced apoptosis. For example, celecoxib directly inhibits 3-phosphoinositol-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK-1), an upstream activator of the survival-promoting Akt pathway. This inhibition attenuates Akt signaling and helps induce apoptosis in cancer cells independent of COX-2 inhibition (Li et al., 2006; Tseng et al., 2006; Kulp et al., 2004). In addition, celecoxib has been shown to inhibit p38 and p55 MAPKs in the JNK pathway and activate pro-apoptotic pathways (Gallicchio et al., 2008). The apoptosis mechanisms of these COX-2-independent pathways offer different ideas for exploration.
3.2 The impact of celecoxib on the tumor microenvironment
Celecoxib is a highly selective COX-2 inhibitor with numerous mechanisms of action within the tumor microenvironment (TME). Its core mechanism is reflected in the bidirectional regulation of the immunosuppressive network and the activation of immune responses (Figure 3) (Jahani et al., 2023; Xun et al., 2021; Cecil et al., 2022; Rao, 2022; Kobayashi et al., 2020; Ouyang et al., 2024; Raaijmakers et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2013; Qin et al., 2022). First, celecoxib directly inhibits the recruitment and function of immunosuppressive cells by reducing the PGE2 level in TME: (1) it decreases the expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and their IL-10 secretion, and downregulates their FOXP3 expression to break immune tolerance (Jahani et al., 2023; Cecil et al., 2022; Kobayashi et al., 2020); (2) it blocks the ARG1/ROS-dependent T cell inhibitory function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), inhibiting the number and function of MDSCs while inhibiting their migration to tumor tissue (Veltman et al., 2010; Jahani et al., 2023; Ouyang et al., 2024); and (3) it reverses macrophage to M2 phenotypic polarization and reduces TGF-β-mediated CD8+ T cell exhaustion (Xun et al., 2021). Additionally, the drug alleviates the inhibition of T cell activity by interfering with the COX-2/PGE2/IDO1 axis and inhibiting abnormal tryptophan metabolism in tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) (Ouyang et al., 2024). Collectively, hese effects weaken the immunosuppressive barrier within the TME.
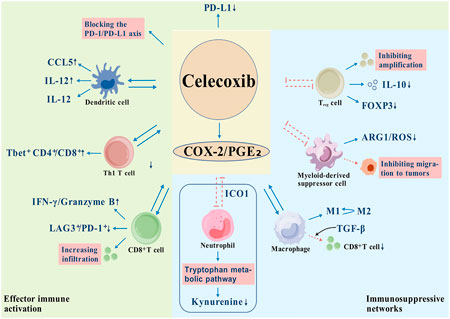
Figure 3. Celecoxib remodels the tumor immune microenvironment by targeting the COX-2/PGE2 axis. 1. Immunosuppression is relieved (blue area): ↓Tregs amplification: Immune tolerance is broken by reducing IL-10 secretion and down-regulating FOXP3 expression; ↓MDSCs function: block ARG1/ROS-dependent T cell inhibition and inhibit its migration to tumors; ↓M2 macrophage polarization: reversal of TGF-β-mediated CD8+T cell exhaustion; ↓Abnormal tryptophan metabolism: inhibits IDO1-mediated kynurenine accumulation in TANs. 2. Effector immune activation (green area): ↑DC: promotes the production of CCL5 by NK cells, regulates the increase of Th1 cytokine IL-12 and decreases the Th2 cytokine IL-10; ↓Immune checkpoints: block the PD-1/PD-L1 axis and relieve T cell inhibition; ↑CD8+T cell function: promotes tumor infiltration, upregulates IFN-γ/granzyme B, and reduces depletion markers (LAG3+/PD-1+); ↑Th1 immune response: regulates the balance of T cell subsets and forms anti-tumor cell communities. Metabolic-signaling synergistic regulation (box area): Key metabolic interventions: inhibition of IDO1 activity→blocking of tryptophan-kynurenine aberrant metabolism → reduction of immunosuppressive metabolite accumulation. (


At the effector immune cell level, celecoxib enhances the anti-tumor immune response through dual regulation of metabolism and signaling. On one hand, the reduction of PGE2 significantly downregulates the PD-L1 expression of tumor cells and myeloid cells, thereby blocking the inhibitory effect of PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoints on T cells (Cecil et al., 2022; Rao, 2022). On the other hand, the drug promotes CD8+ T cell infiltration and enhances its function: it improves cytotoxicity by upregulating IFN-γ and granzyme B secretion, while decreasing LAG3+/PD-1+ depletion marker expression (Rao, 2022; Kobayashi et al., 2020; Raaijmakers et al., 2022). Notably, celecoxib increases the proportion of Th1 T cells (Tbet+ CD4+/CD8+) with antitumor activity by regulating T cell subset homeostasis and forming a cell community conducive to immune attack (Cecil et al., 2022; Rao, 2022). Additionally, dendritic cells (DCs) are essential for the activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and the drug can increase the recruitment of DCs and enhance the ability of DCs: celecoxib can support the recruitment of DCs by promoting the chemokine CCL5 produced by NK cells, and can enhance the DC effect by increasing the Th1 cytokine IL-12 and decreasing the Th2 cytokine IL-10 (Raaijmakers et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2013; Qin et al., 2022). This dynamic regulation from inhibition release to effect activation reflects its multi-level intervention on the immune microenvironment.
The antitumor mechanism of celecoxib is also involved in key processes of immunometabolic reprogramming. It reverses T cell functional exhaustion by inhibiting indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) activity, blocking the aberrant metabolism of tryptophan to kynurenine and reducing the accumulation of immunosuppressive metabolites (Ouyang et al., 2024). The synergistic effect of these metabolic interventions with immune signaling pathways further strengthens the position of the COX-2/PGE2 axis as a core hub for the regulation of the tumor immune microenvironment.
4 Research progress and therapeutic application of celecoxib in a variety of malignant tumors
A growing number of preclinical trials and clinical trials have shown that celecoxib has an important role in the treatment of different malignancies, and it exerts anti-cancer effects through different mechanisms. The following is a summary of the research progress and therapeutic application of celecoxib in different malignant tumors, which is summarized in Table 1. Table 2 shows some clinical trials of celecoxib in different malignancies.
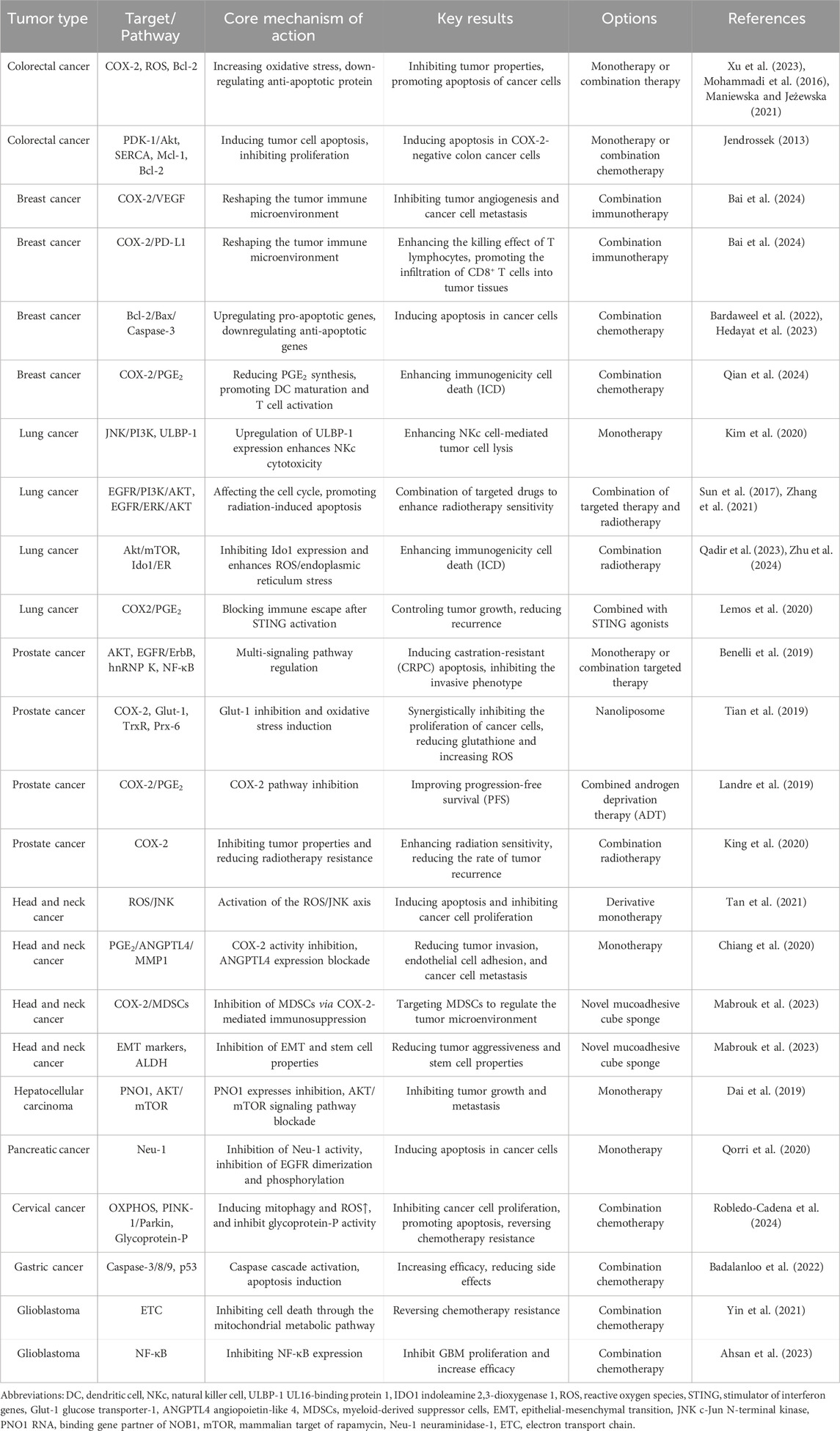
Table 1. Research progress and therapeutic application of celecoxib in a variety of malignant tumors.
4.1 Colorectal cancer
Celecoxib has proven to be an effective selective COX-2 inhibitor in the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Research indicates that the drug augments the anti-tumor effects of various medications, including neoadjuvant therapies, by influencing mechanisms such as cell cycle regulation and apoptosis pathways. Studies by Xu and Mohammadi et al. using human colorectal cancer cell lines HCT116, HT-29, and nude mouse models have shown that celecoxib can inhibit the biological behavior of colorectal cancer cells, change the cell cycle, induce apoptosis, and enhance the anti-tumor efficacy of the drug when combined with other drugs [5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione (ADT-OH), heat shock protein 90 (HSP90)] (Xu et al., 2023; Mohammadi et al., 2016). Additionally, the results of randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical studies of several NSAIDs found that celecoxib helps chemoprevention of colorectal cancer and may help reduce the incidence of CRC in high-risk populations (Maniewska and Jeżewska, 2021). Furthermore, the drug’s capacity to target inflammatory pathways that are linked to tumor progression makes it a valuable addition to CRC treatment strategies (Jendrossek, 2013), potentially resulting in increased disease-free survival rates for patients (Hu et al., 2023).
4.2 Breast cancer
In the context of breast cancer, celecoxib has been investigated for its potential impact on the efficacy of standard treatments (Bardaweel et al., 2022), particularly in the latest research concerning triple-negative breast cance (Bai et al., 2024). Hedayat et al. demonstrated that paclitaxel in combination of paclitaxel with celecoxib can significantly reduce the viability of breast cancer cells (Hedayat et al., 2023), and it can enhance the efficacy of paclitaxel in inducing immunogenic cell death in tumor cells (Qian et al., 2024). However, the effects of celecoxib in breast cancer may vary, depending on COX-2 expression and estrogen receptor (ER) status, highlighting the necessity for an individualized approach to therapy (Hamy et al., 2019). In an experimental study, celecoxib was found to exhibit different pro-apoptotic effects across different breast cancer subtypes (Wang et al., 2017). These findings emphasize the importance of further exploring the role of celecoxib in the management of breast cancer, particularly in optimizing treatment options for specific patient populations.
4.3 Lung cancer
Lung cancer, with the highest incidence and mortality rates worldwide, is the subject of ongoing research into celecoxib, particularly for its potential to modulate the tumor microenvironment and improve the effectiveness of synergistic treatments. Its ability to downregulate COX-2 expression contributes to increased susceptibility to natural killer cell cytotoxicity (Kim et al., 2020), and it can also serve as a radiosensitizer for lung cancer (Zhang et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2021), underscoring its potential as a therapeutic adjunct. There is evidence that targeted drugs in combination with celecoxib can enhance efficacy by modulating apoptosis (Zhang et al., 2021; Qadir et al., 2023). Zhu et al. discovered that celecoxib can influence the immune response in lung cancer patients and may improve prognosis when combined with ICD inducer (Zhu et al., 2024). Furthermore, the combination of celecoxib can boost antitumor response and overcome resistance to lung cancer STING agonist treatment (Lemos et al., 2020). Nonetheless, due to variations in patient responses, further exploration is necessary to ascertain the benefits of celecoxib in treating lung cancer.
4.4 Prostate cancer
Celecoxib has emerged as a significant contender in the realm of prostate cancer therapy, particularly in managing castration-resistant disease. It modulates pathways associated with castration resistance (CRPC) progression, curbing cell growth and prompting apoptosis via AKT inhibition, PARP-1 cleavage, and the proteasomal degradation of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1 (Benelli et al., 2019). A study by Tian et al. revealed that celecoxib suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting pathways integral to androgen receptor signaling and inflammation (Tian et al., 2019). Clinical trials have also demonstrated that combining celecoxib with other drugs, such as docetaxel, leads to enhanced treatment efficacy and improved quality of life (Landre et al., 2019). In a retrospective study, the drug’s capacity to modulate PSA levels in radiotherapy patients underscored its potential in controlling the progression of prostate cancer (King et al., 2020). As ongoing research continues to unravel the intricate interactions of celecoxib within prostate cancer biology, integrating it into standard treatment protocols may offer new strategies to enhance outcomes for patients afflicted with this complex malignancy.
4.5 Head and neck cancer
The role of celecoxib in head and neck cancer (HNC) has been extensively studied, and it has demonstrated significant anti-cancer potential due to its anti-inflammatory properties and its ability to modulate the tumor microenvironment. Celecoxib inhibits the COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway, reduces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, and suppresses the proliferation, growth, and metastasis of head and neck cancer cells, while also decreasing PGE2-mediated immune escape (Chiang et al., 2020). Mabrouk et al. also observed that the growth and spread of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) can be retarded by inhibiting tumor-associated inflammatory factors (e.g., COX-2, IL-6, TGF-β), and by modulating the function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which helps to attenuate the immune escape mechanism of tumors. Their cube sponge system for celecoxib administration is a promising approach (Mabrouk et al., 2023). And in a recent in vitro study using human HNC cell lines, celecoxib was found to exert anti-cancer effects on PIK3CA-mutated head and neck cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress, reactive oxygen species, and mitochondrial dysfunction (Thi Thanh Nguyen and Yoon, 2024). While celecoxib exerts its anticancer effects in this cancer type through multiple mechanisms, large-scale clinical data are still required to substantiate the efficacy and safety of its clinical application.
4.6 Other types of tumors
In addition to colorectal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, and head and neck cancer, the application of celecoxib in other types of malignant tumors has gradually attracted attention. For instance, some in vitro studies have shown that celecoxib may inhibit the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PNO1 (Dai et al., 2019), and it can induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells by targeting mammalian neuraminidase-1 (Qorri et al., 2020). Regarding cervical cancer, the combination of celecoxib with conventional chemotherapy exhibits synergistic effects, hindering tumor progression via multiple mechanisms (Robledo-Cadena et al., 2024). In the context of gastric cancer, celecoxib itself exerts cytotoxic effects on cancer cells; notably, its combination with topotecan significantly enhances therapeutic efficacy (Badalanloo et al., 2022). Moreover, extensive in vitro and in vivo studies reveal that it not only effectively inhibits glioblastoma (GBM) cell proliferation but also potentiates the efficacy of temozolomide against chemotherapy resistance (Yin et al., 2021; Ahsan et al., 2023; Pak et al., 2025), while concurrently acting as a radiosensitizer for radiation-resistant CD133 (+) GBM cells (Ma et al., 2011). Notably, a novel celecoxib derivative can cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to inhibit recurrence of brain malignancies in animal models (Shen et al., 2025). As research into the effects of celecoxib on malignant tumors continues to expand, it offers new perspectives and avenues for cancer treatment.
5 Side effects and safety of celecoxib and other drugs that inhibit the COX-2/PGE2 axis
Celecoxib is widely used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, with a well-defined safety profile. The most significant concerns involve potential gastrointestinal (GI), cardiovascular (CV), and renal adverse effects. Compared to non-selective NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen), which inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, celecoxib’s selectivity for COX-2 significantly reduces the risk of GI mucosal injury, with GI event rates as low as 0.34% (Yeomans et al., 2018). However, high doses (>400 mg/day) or long-term use may increase the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke (Obeid et al., 2022). The PRECISION trial further indicated that CV risk correlates with treatment duration and dose (Pepine and Gurbel, 2017). Notably, some cancer-specific studies have not observed a significant increase in CV events (Hu et al., 2023; Coombes et al., 2021). Renal side effects, such as edema and hypertension, are less common but require monitoring (Biase et al., 2024). Despite these potential risks, the incidence of adverse effects associated with celecoxib use in oncology settings, particularly at therapeutic doses and durations relevant to cancer treatment, is generally manageable.
While celecoxib is the most extensively studied selective COX-2 inhibitor in oncology, other pharmacological agents targeting this axis exist. Rofecoxib is also a selective COX-2 inhibitor and has been withdrawn from the market due to cardiovascular safety concerns, which limits its long-term use in cancer prevention (Bresalier et al., 2005). Etoricoxib, another selective COX-2 inhibitor, has shown significant anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in preclinical studies in lung and hepatocellular carcinoma, highlighting the co-antitumor potential of this drug class in addition to celecoxib (Md et al., 2021; Ali et al., 2022). Moreover, diclofenac is a non-selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug but has a strong affinity for COX-2, and its anticancer efficacy observed in studies in colorectal cancer and melanoma is related not only to COX-2 inhibition, but also to the induction of oxidative stress and the regulation of oncogenic signaling pathways (Yilmaz et al., 2021; Qin et al., 2025). These comparisons put celecoxib’s position in context: its risk is a category consideration, but its extensive oncological evidence base and unique pharmacokinetic profile support its sustained action. The presence of multiple drugs targeting this axis highlights its therapeutic effectiveness and offers alternatives for future research and potential combination strategies.
6 Discussion and future perspectives
Celecoxib has firmly established itself not only as an adjunctive analgesic or anti-inflammatory agent in oncology, but also as an effective immunomodulator capable of reshaping the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). This review synthesizes compelling evidence for its anti-tumor efficacy, both as monotherapy and in a multimodal regimen, fundamentally stemming from its ability to disrupt the immunosuppressive COX-2/PGE2 axis. By inhibiting Tregs, MDSCs, and M2 macrophage polarization while enhancing CD8+ T cell infiltration, cytotoxicity, and dendritic cell function, celecoxib effectively eliminates key barriers to anti-tumor immunity. Synergy with chemotherapy (e.g., enhancing drug toxicity and reducing cancer cell viability), radiotherapy (e.g., enhancing radiosensitivity by inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway), and especially immunotherapy (e.g., inhibiting the immunosuppressive environment) (Section 2.2), underscores its versatility as a cornerstone of contemporary cancer treatment strategies.
As noted above, this preclinical research evidence consistently demonstrates a clear mechanistic principle across different cancer types, revealing the anti-cancer ability of celecoxib, sensitizing tumors to conventional therapies, and effectively reprogramming the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. In the clinical field (Table 2), pivotal trials have successfully translated this commitment into tangible benefits, with multiple studies showing significant improvements in outcomes. However, existing limitations must also be acknowledged. Preclinical models often employ celecoxib concentrations that may not be clinically achievable while elucidating key mechanisms, raising questions about translational relevance (Tołoczko-Iwaniuk et al., 2019). In addition, the heterogeneity of clinical trial outcomes [e.g., the significant efficacy of celecoxib in combination with toripalimab in the phase II PICC trial contrasted with the negative results of the phase III CALGB 30801 trial in patients with unselected NSCLC and the lack of a disease-free survival benefit in the CALGB/SWOG 80702 trial (Hu et al., 2022; Meyerhardt et al., 2021; Edelman et al., 2017)] highlights the limited efficacy of celecoxib and is highly dependent on the context, specifically tumor type, combination agent, and vital patient selection biomarkers. Therefore, while the available data firmly establish celecoxib as a compelling therapeutic-beneficial drug, there is an urgent need for more and more rigorously designed, biomarker-selected clinical trials to definitively determine its role in multimodal oncology.
More notably, the true transformative potential of celecoxib extends beyond its established mechanisms, pointing to new areas of cancer treatment that require attention:
Deepening the Understanding of Immunometabolic Reprogramming: While celecoxib’s immunomodulatory effects are well described, its impact on immunometabolism within TIME represents a critical and underexplored aspect. The ability of celecoxib to inhibit IDO1 activity and correct abnormal tryptophan metabolism in tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) and other cells directly links COX-2 inhibition to metabolic pathways that control T cell depletion (Ouyang et al., 2024). This makes celecoxib unique at the intersection of inflammation, metabolism, and immunity. Future research should dissect how celecoxib-induced metabolic shifts (e.g., reduced kynurenine accumulation) interact synergistically with immune signaling pathways to create a relaxed environment for effector cells, potentially revealing novel combinatorial targets beyond IDO1 and deepening our understanding of its role in overcoming metabolic immunosuppression.
Patient heterogeneity and towards personalized treatment: The efficacy of celecoxib is heterogeneous among different patient populations, and future clinical translation may depend on identifying patient subgroups most likely to benefit. For example, tumor biology, where COX-2 overexpression may predict benefit, as shown by the trend of improved survival in this subgroup in a negative phase III NSCLC trial, underscores the importance of biomarkers driving patient selection (Edelman et al., 2017). Second, pharmacogenomics, genetic polymorphisms in CYP2C9 (the main metabolizing enzyme of celecoxib) can significantly alter drug clearance, meaning that individuals with adverse metabolizer genotypes may experience higher drug exposure, affecting efficacy and the risk of dose-dependent adverse effects (Dean et al., 2016; Kim et al., 2017). Finally, in terms of gender differences, sex-specific differences in the use of NSAIDs were observed in an epidemiological study of bladder cancer risk, suggesting that sex hormones or other physiological differences may modulate the COX-2/PGE2 axis (Daugherty et al., 2011). Therefore, it is crucial to integrate robust biomarkers that include tumor COX-2 status, germline genetic variants, and potentially sex-specific factors into the design of future clinical trials. These parameters precisely define the role of celecoxib in personalized treatment modalities.
Precision Delivery and Biomarker-Driven Integration: The limitations of systemic celecoxib, particularly the cardiovascular risks associated with long-term/high-dose use (Obeid et al., 2022; Pepine and Gurbel, 2017), necessitate more informed dosing strategies and refined patient selection. Innovations in nanodelivery systems offer a very promising solution (Bai et al., 2024). By encapsulating celecoxib or combining it with other drugs (e.g., gemcitabine, immunomodulators) in nanoparticles, these systems enhance tumor-specific targeting, minimize off-target effects (potentially mitigating CV risk), and can achieve localized high-dose effects critical for effective TIME remodeling (Zhang et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2024). In addition, the efficacy of these advanced delivery methods can be evaluated in combination with robust biomarker-guided strategies. In addition to static COX-2 expression assessments, dynamic monitoring utilizing circulating factors (e.g., VEGF reflecting angiogenesis/inflammatory regulation, IL-8) (Passaro et al., 2024; Dovizio et al., 2012; Perroud et al., 2016), single-cell sequencing to analyze dynamic changes in immune cell subsets within the TME (Pan et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2021), and functional testing using patient-derived 3D organoid models capable of predicting real-time treatment response are key to identifying subgroups of patients most likely to benefit (Xie et al., 2021; Ban et al., 2024). This comprehensive approach shifts the paradigm from a single modality to a truly personalized combination therapy, defining the optimal timing, sequence, and dosage of celecoxib in a complex multimodal protocol.
Expanding the Portfolio Arsenal with Emerging Immunotherapies: Celecoxib could significantly enhance next-generation immunotherapies, an exciting and underexplored avenue. Its potential to enhance the invasion, activation state, and antitumor function of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) through metabolic regulation provides a strong case for its combination with TIL therapy (Kosaka et al., 2023; Cecil et al., 2022; Ferrandina et al., 2006). In immunophotodynamic therapy (IPDT), celecoxib significantly broadens the therapeutic window by stabilizing mitochondrial membrane potentials, thereby reducing phototoxicity in normal tissues and simultaneously enhancing ROS-induced immunogenic cell death (An et al., 2024; Agostinis et al., 2011). Similarly, in oncolytic virutherapy, celecoxib can enhance immune efficacy against glioma by inhibiting the immunosuppressive environment (Tang et al., 2020). In addition, experimental studies have established a link between next-generation immune checkpoints (such as LAG3) and celecoxib (Cecil et al., 2022; Hashemi et al., 2025), and more combination regimens are expected to be used in tumor treatment in the future, although these still require a large amount of research to promote clinical translation.
Harnessing the Potential of Novel Derivatives: The discovery of COX-2-independent antitumor effects of certain celecoxib derivatives opens up a critical avenue. Derivatives such as 2,5-dimethylcelecoxib can induce apoptosis through ROS/JNK activation or modulate PD-1 expression through mechanisms involving the gut microbiota-AMPK-mTOR axis (Pan et al., 2023; Tan et al., 2021), thereby preserving therapeutic benefits while potentially circumventing the cardiovascular risks associated with conventional COX-2 inhibition. More translationally meaningful novel structure-modifying derivatives (designed to cross the BBB) have demonstrated efficacy in inhibiting tumor recurrence in animal models of GBM (Shen et al., 2025). This breakthrough addresses a key challenge in targeting CNS tumors and provides a powerful new tool for modulating the local immunosuppressive microenvironment of GBM. Prioritizing the development and clinical evaluation of these innovative derivatives is a strategic avenue to accelerate the translation of safer and more effective celecoxib therapies.
In conclusion, celecoxib transcends its origins as a mere COX-2 inhibitor. It is a multifaceted immunomodulator capable of reprogramming the immunosuppressive TIME, thereby enhancing the efficacy of multiple anti-cancer modalities. By focusing research on the aforementioned frontier areas–deepening our understanding of immunometabolic crosstalk, advancing the precise delivery of dynamic biomarker guidance, exploring synergies with cutting-edge immunotherapies like TIL and IPDT, and actively developing novel derivatives–celecoxib has the potential to evolve from a valuable adjuvant to a central pillar of the next-generation of immune-focused medicines for multimodal cancer treatment.
7 Conclusion
Celecoxib effectively reprograms the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by targeting the COX-2/PGE2 axis, inhibiting immunosuppressive cells (Tregs, MDSCs, M2 macrophages) while enhancing CD8+ T cell infiltration and activity. Its synergistic enhancement of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy, especially immune checkpoint blockade, stems primarily from disrupting this critical axis, thereby overcoming key mechanisms of treatment resistance and immune evasion. Nanodelivery strategies offer promising avenues for improving tumor targeting and mitigating systemic risks, particularly cardiovascular problems associated with long-term use. Future integration into cancer treatment requires biomarker-driven patient selection and clinical validation. Prioritizing the development of novel derivatives and exploring synergies with next-generation immunotherapies (e.g., TILs, IPDTs) will further unlock their potential as a cornerstone of multimodal precision oncology.
Author contributions
BK: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Conceptualization. KY: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Visualization. XZ: Visualization, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. YT: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. YZ: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. JY: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The work was supported by the Science and Technology Plan Project Funded by Jiangxi Province Health Commission (grant no.: 202410340).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Agostinis, P., Berg, K., Cengel, K. A., Foster, T. H., Girotti, A. W., Gollnick, S. O., et al. (2011). Photodynamic therapy of cancer: an update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 61 (4), 250–281. doi:10.3322/caac.20114
Ahsan, H., Malik, S. I., Shah, F. A., El-Serehy, H. A., Ullah, A., and Shah, Z. A. (2023). Celecoxib suppresses NF-κB p65 (RelA) and TNFα expression signaling in glioblastoma. J. Clin. Med. 12 (20), 6683. doi:10.3390/jcm12206683
Ali, G., Omar, H., Hersi, F., Abo-Youssef, A., Ahmed, O., and Mohamed, W. (2022). The protective role of etoricoxib against diethylnitrosamine/2-acetylaminofluorene- induced hepatocarcinogenesis in Wistar rats: the impact of NF-κB/COX-2/PGE2 signaling. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 15 (1), 252–262. doi:10.2174/1874467214666210708103752
Allegrini, G., Di Desidero, T., Barletta, M. T., Fioravanti, A., Orlandi, P., Canu, B., et al. (2012). Clinical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluations of metronomic UFT and cyclophosphamide plus celecoxib in patients with advanced refractory gastrointestinal cancers. Angiogenesis 15 (2), 275–286. doi:10.1007/s10456-012-9260-6
An, J., Lv, K. P., Chau, C. V., Lim, J. H., Parida, R., Huang, X., et al. (2024). Lutetium texaphyrin-Celecoxib conjugate as a potential immuno-photodynamic therapy agent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146 (28), 19434–19448. doi:10.1021/jacs.4c05978
Badalanloo, K., Naji, T., and Ahmadi, R. (2022). Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of celecoxib and topotecan on AGS and HEK 293 cell lines. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 53 (1), 99–104. doi:10.1007/s12029-020-00434-8
Bai, L., Liu, H., You, R., Jiang, X., Zhang, T., Li, Y., et al. (2024). Combination nano-delivery systems remodel the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Mol. Pharm. 21 (5), 2148–2162. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00242
Bąk, U., and Krupa, A. (2023). Challenges and opportunities for celecoxib repurposing. Pharm. Res. 40 (10), 2329–2345. doi:10.1007/s11095-023-03571-4
Balkwill, F., and Mantovani, A. (2001). Inflammation and cancer: back to virchow? Lancet 357 (9255), 539–545. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04046-0
Ban, Q. Y., Li, H. S., Jiang, X. X., Liu, M., Ge, X. Y., Lu, M. J., et al. (2024). Current applications of colorectal cancer organoids: a review. J. Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 33 (2), 269–277. doi:10.15403/jgld-5388
Bardaweel, S. K., Dahabiyeh, L. A., Akileh, B. M., Shalabi, D. D., AlHiary, A. K., Pawling, J., et al. (2022). Molecular and metabolomic investigation of celecoxib antiproliferative activity in mono-and combination therapy against breast cancer cell models. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 22 (8), 1611–1621. doi:10.2174/1871520621666210910101349
Bayraktar, S., Baghaki, S., Wu, J., Liu, D. D., Gutierrez-Barrera, A. M., Bevers, T. B., et al. (2020). Biomarker modulation study of celecoxib for chemoprevention in women at increased risk for breast cancer: a phase II pilot study. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 13 (9), 795–802. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-20-0095
Bell, C. R., and Zelenay, S. (2022). COX-2 upregulation by tumour cells post-chemotherapy fuels the immune evasive dark side of cancer inflammation. Cell Stress 6 (9), 76–78. doi:10.15698/cst2022.09.271
Bell, C. R., Pelly, V. S., Moeini, A., Chiang, S. C., Flanagan, E., Bromley, C. P., et al. (2022). Chemotherapy-induced COX-2 upregulation by cancer cells defines their inflammatory properties and limits the efficacy of chemoimmunotherapy combinations. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 2063. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29606-9
Benelli, R., Barboro, P., Costa, D., Astigiano, S., Barbieri, O., Capaia, M., et al. (2019). Multifocal signal modulation therapy by celecoxib: a strategy for managing castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (23), 6091. doi:10.3390/ijms20236091
Bi, N., Liang, J., Zhou, Z., Chen, D., Fu, Z., Yang, X., et al. (2019). Effect of concurrent chemoradiation with celecoxib vs concurrent chemoradiation alone on survival among patients with non-small cell lung cancer with and without cyclooxygenase 2 genetic variants: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2 (12), e1918070. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.18070
Biase, T.M.M.A., Rocha, J. G. M., Silva, M. T., Ribeiro-Vaz, I., and Galvão, T. F. (2024). Renal effects of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor anti-inflammatory drugs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Explor Res. Clin. Soc. Pharm. 15, 100475. doi:10.1016/j.rcsop.2024.100475
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74 (3), 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Bresalier, R. S., Sandler, R. S., Quan, H., Bolognese, J. A., Oxenius, B., Horgan, K., et al. Adenomatous Polyp Prevention on Vioxx (APPROVe) Trial Investigators (2005). Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 352 (11), 1092–1102. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050493
Cao, Y., Li, J., Liang, Q., Yang, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). Tumor microenvironment sequential drug/gene delivery nanosystem for realizing multistage boosting of cancer-immunity cycle on cancer immunotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 15 (47), 54898–54914. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c11394
Carpenter, P. S., Shepherd, H. M., McCrary, H., Torrecillas, V., Kull, A., Hunt, J. P., et al. (2018). Association of celecoxib use with decreased opioid requirements after head and neck cancer surgery with free tissue reconstruction. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 144 (11), 988–994. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2018.0284
Cecil, D. L., Gad, E. A., Corulli, L. R., Drovetto, N., Lubet, R. A., and Disis, M. L. (2022). COX-2 inhibitors decrease expression of PD-L1 in Colon tumors and increase the influx of type I tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 15 (4), 225–231. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-21-0227
Cheki, M., Yahyapour, R., Farhood, B., Rezaeyan, A., Shabeeb, D., Amini, P., et al. (2018). COX-2 in radiotherapy: a potential target for radioprotection and radiosensitization. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 11 (3), 173–183. doi:10.2174/1874467211666180219102520
Chiang, K. H., Shieh, J. M., Shen, C. J., Chang, T. W., Wu, P. T., Hsu, J. Y., et al. (2020). Epidermal growth factor-induced COX-2 regulates metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through upregulation of angiopoietin-like 4. Cancer Sci. 111 (6), 2004–2015. doi:10.1111/cas.14400
Ching, M. M., Reader, J., and Fulton, A. M. (2020). Eicosanoids in cancer: Prostaglandin E2 receptor 4 in cancer therapeutics and immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 819. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00819
Coombes, R. C., Tovey, H., Kilburn, L., Mansi, J., Palmieri, C., Bartlett, J., et al. Randomized European Celecoxib Trial (REACT) Trial Management Group and Investigators (2021). Effect of celecoxib vs placebo as adjuvant therapy on disease-free survival among patients with breast cancer: the REACT randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 7 (9), 1291–1301. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.2193
Dai, H., Zhang, S., Ma, R., and Pan, L. (2019). Celecoxib inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and migration by targeting PNO1. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 7351–7360. doi:10.12659/MSM.919218
Daugherty, S. E., Pfeiffer, R. M., Sigurdson, A. J., Hayes, R. B., Leitzmann, M., Schatzkin, A., et al. (2011). Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and bladder cancer: a pooled analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 173 (7), 721–730. doi:10.1093/aje/kwq437
Davies, N. M., McLachlan, A. J., Day, R. O., and Williams, K. M. (2000). Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of celecoxib: a selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 38 (3), 225–242. doi:10.2165/00003088-200038030-00003
Dean, L., and Kane, M. (2016). “Celecoxib therapy and CYP2C9 genotype,” in Medical genetics summaries. Editors V. M. Pratt, S. A. Scott, M. Pirmohamed, B. Esquivel, B. L. Kattman, and A. J. Malheiro (Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information US).
Ding, Q., Wang, Y., Zhang, P., and Mei, L. (2024). Breakthrough in cancer therapy: lutetium texaphyrin-celecoxib conjugate for immune and photodynamic treatment. J. Mater Chem. B 12 (47), 12136–12138. doi:10.1039/d4tb02019g
Dovizio, M., Tacconelli, S., Ricciotti, E., Bruno, A., Maier, T. J., Anzellotti, P., et al. (2012). Effects of celecoxib on prostanoid biosynthesis and circulating angiogenesis proteins in familial adenomatous polyposis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 341 (1), 242–250. doi:10.1124/jpet.111.190785
Edelman, M. J., Wang, X., Hodgson, L., Cheney, R. T., Baggstrom, M. Q., Thomas, S. P., et al. (2017). Phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of celecoxib in addition to standard chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression: CALGB 30801 (Alliance). J. Clin. Oncol. 35 (19), 2184–2192. doi:10.1200/JCO.2016.71.3743
Egashira, I., Takahashi-Yanaga, F., Nishida, R., Arioka, M., Igawa, K., Tomooka, K., et al. (2017). Celecoxib and 2,5-dimethylcelecoxib inhibit intestinal cancer growth by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 108 (1), 108–115. doi:10.1111/cas.13106
Ferrandina, G., Ranelletti, F. O., Legge, F., Salutari, V., Martinelli, E., Fattorossi, A., et al. (2006). Celecoxib up-regulates the expression of the zeta chain of T cell receptor complex in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in human cervical cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 12 (7 Pt 1), 2055–2060. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2530
Fontana, A., Galli, L., Fioravanti, A., Orlandi, P., Galli, C., Landi, L., et al. (2009). Clinical and pharmacodynamic evaluation of metronomic cyclophosphamide, celecoxib, and dexamethasone in advanced hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 15 (15), 4954–4962. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3317
Gallicchio, M., Rosa, A. C., Dianzani, C., Brucato, L., Benetti, E., Collino, M., et al. (2008). Celecoxib decreases expression of the adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in a colon cancer cell line (HT29). Br. J. Pharmacol. 153 (5), 870–878. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0707634
Gandhi, S., Slomba, R. T., Janes, C., Fitzpatrick, V., Miller, J., Attwood, K., et al. (2024). Systemic chemokine-modulatory regimen combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 12 (11), e010058. doi:10.1136/jitc-2024-010058
Ghasemi, A., Danesh, B., Yazdani-Charati, J., and Hosseinimehr, S. J. (2018). Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of celecoxib for the prevention of skin toxicity in patients receiving radiation therapy for breast cancer. Antiinflamm. Antiallergy Agents Med. Chem. 17 (1), 57–67. doi:10.2174/1871523017666180411162114
Greten, F. R., and Grivennikov, S. I. (2019). Inflammation and cancer: triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity 51 (1), 27–41. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.025
Hamy, A. S., Tury, S., Wang, X., Gao, J., Pierga, J. Y., Giacchetti, S., et al. (2019). Celecoxib with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer might worsen outcomes differentially by COX-2 expression and ER status: exploratory analysis of the REMAGUS02 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 37 (8), 624–635. doi:10.1200/JCO.18.00636
Hashemi, V., Baradaran, B., Naseri, B., Masoumi, J., Baghbani, E., Alizadeh, N., et al. (2025). The effect of immunomodulatory celecoxsib on the gene expression of inhibitory receptors in dendritic cells generated from monocyte cells. BMC Res. Notes 18 (1), 164. doi:10.1186/s13104-025-07226-y
Hashemi Goradel, N., Najafi, M., Salehi, E., Farhood, B., and Mortezaee, K. (2019). Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: a review. J. Cell Physiol. 234 (5), 5683–5699. doi:10.1002/jcp.27411
Hedayat, M., Khezri, M. R., Jafari, R., Malekinejad, H., and Majidi Zolbanin, N. (2023). Concomitant effects of paclitaxel and celecoxib on genes involved in apoptosis of triple-negative metastatic breast cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 40 (9), 263. doi:10.1007/s12032-023-02119-1
Holt, D. M., Ma, X., Kundu, N., Collin, P. D., and Fulton, A. M. (2012). Modulation of host natural killer cell functions in breast cancer via prostaglandin E2 receptors EP2 and EP4. J. Immunother. 35 (2), 179–188. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e318247a5e9
Hou, J., Lin, Y., Fang, Y., Li, X., Li, X. N., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). Clinical efficacy evaluation and prevention of adverse reactions in a randomized trial of a combination of three drugs in the treatment of cancerous pudendal neuralgia. Ann. Palliat. Med. 10 (5), 5754–5762. doi:10.21037/apm-21-590
Hsu, A. L., Ching, T. T., Wang, D. S., Song, X., Rangnekar, V. M., and Chen, C. S. (2000). The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib induces apoptosis by blocking Akt activation in human prostate cancer cells independently of Bcl-2. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (15), 11397–11403. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.15.11397
Hu, H., Kang, L., Zhang, J., Wu, Z., Wang, H., Huang, M., et al. (2022). Neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade with toripalimab, with or without celecoxib, in mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high, locally advanced, colorectal cancer (PICC): a single-centre, parallel-group, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7 (1), 38–48. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00348-4
Hu, T., Liu, C. J., Yin, X., Tang, W., Yin, L., Bai, H., et al. (2023). Selective COX-2 inhibitors do not increase gastrointestinal reactions after colorectal cancer surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 23 (1), 281. doi:10.1186/s12876-023-02918-w
Jahani, V., Yazdani, M., Badiee, A., Jaafari, M. R., and Arabi, L. (2023). Liposomal celecoxib combined with dendritic cell therapy enhances antitumor efficacy in melanoma. J. Control Release 354, 453–464. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.01.034
Jendrossek, V. (2013). Targeting apoptosis pathways by celecoxib in cancer. Cancer Lett. 332 (2), 313–324. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.01.012
Jin, K., Qian, C., Lin, J., and Liu, B. (2023). Cyclooxygenase-2-Prostaglandin E2 pathway: a key player in tumor-associated immune cells. Front. Oncol. 13, 1099811. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1099811
Kamali, K., Nikbakht, J., Ayubi, E., Nabizadeh, M., and Sarhadi, S. (2020). Comparison of the efficacy of oxybutynin, phenazopyridine, celecoxib, and placebo in the treatment of urinary tract symptoms after BCG therapy in patients with bladder tumors. Urol. J. 18 (4), 439–444. doi:10.22037/uj.v16i7.5947
Kapoor, A., Gupta, A., Sansar, B., Mishra, B. K., Gupta, P., Singh, A., et al. (2025). Triple oral metronomic chemotherapy versus chemotherapy of physician discretion after failure of platinum-based therapy in advanced head and neck cancer: a phase III randomized study (METRO-CHASE study). JCO Glob. Oncol. 11, e2500032. doi:10.1200/GO-25-00032
Kim, S. H., Kim, D. H., Byeon, J. Y., Kim, Y. H., Kim, D. H., Lim, H. J., et al. (2017). Effects of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of celecoxib and its carboxylic acid metabolite. Arch. Pharm. Res. 40 (3), 382–390. doi:10.1007/s12272-016-0861-2
Kim, J., Noh, M. H., Hur, D. Y., Kim, B., Kim, Y. S., and Lee, H. K. (2020). Celecoxib upregulates ULBP-1 expression in lung cancer cells via the JNK/PI3K signaling pathway and increases susceptibility to natural killer cell cytotoxicity. Oncol. Lett. 20 (6), 279. doi:10.3892/ol.2020.12142
Kim, P., Saba, N. F., McCook-Veal, A., Liu, Y., Klein, A. M., Beitler, J. J., et al. (2025). Prospective pilot study of second primary tumor prevention with erlotinib and celecoxib in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: long-term follow-up. Head. Neck 47 (9), 2594–2602. doi:10.1002/hed.28178
King, L., Christie, D., Arora, D., and Anoopkumar-Dukie, S. (2020). Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors delay relapse and reduce prostate specific antigen (PSA) velocity in patients treated with radiotherapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer: a pilot study. Prostate Int. 8 (1), 34–40. doi:10.1016/j.prnil.2019.10.004
Kobayashi, K., Kaira, K., and Kagamu, H. (2020). Recovery of the sensitivity to Anti-PD-1 antibody by celecoxib in lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 40 (9), 5309–5311. doi:10.21873/anticanres.14537
Kosaka, A., Yajima, Y., Yasuda, S., Komatsuda, H., Nagato, T., Oikawa, K., et al. (2023). Celecoxib promotes the efficacy of STING-targeted therapy by increasing antitumor CD8+ T-cell functions via modulating glucose metabolism of CD11b+ Ly6G+ cells. Int. J. Cancer 152 (8), 1685–1697. doi:10.1002/ijc.34394
Kulp, S. K., Yang, Y. T., Hung, C. C., Chen, K. F., Lai, J. P., Tseng, P. H., et al. (2004). 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1/Akt signaling represents a major cyclooxygenase-2-independent target for celecoxib in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 64 (4), 1444–1451. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-2396
Landre, T., Guetz, G. D., Chouahnia, K., Fossey-Diaz, V., Taleb, C., and Culine, S. (2019). Is there a benefit of addition docetaxel, abiraterone, celecoxib, or zoledronic acid in initial treatments for patients older than 70 years with hormone-sensitive advanced prostate cancer? A meta-analysis. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer. 17 (4), e806–e813. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2019.05.001
Lemos, H., Ou, R., McCardle, C., Lin, Y., Calver, J., Minett, J., et al. (2020). Overcoming resistance to STING agonist therapy to incite durable protective antitumor immunity. J. Immunother. Cancer 8 (2), e001182. doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-001182
Li, J., Zhu, J., MelvinMuscarella, W. S. P., and Chen, C. S. (2006). A structurally optimized celecoxib derivative inhibits human pancreatic cancer cell growth. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 10 (2), 207–214. doi:10.1016/j.gassur.2005.07.025
Li, D., Ma, Y., Liu, W., Ren, X., Chen, M., Xu, X., et al. (2020). Celecoxib combined with salirasib strongly inhibits pancreatic cancer cells in 2D and 3D cultures. Int. J. Med. Sci. 17 (12), 1795–1802. doi:10.7150/ijms.47546
Li, L., Zhang, Y., and Qin, L. (2023). Effect of celecoxib plus standard chemotherapy on cancer prognosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Invest 53 (6), e13973. doi:10.1111/eci.13973
Liao, Z., Komaki, R., Milas, L., Yuan, C., Kies, M., Chang, J. Y., et al. (2005). A phase I clinical trial of thoracic radiotherapy and concurrent celecoxib for patients with unfavorable performance status inoperable/unresectable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 11 (9), 3342–3348. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1741
Lin, J. Z., Hameed, I., Xu, Z., Yu, Y., Ren, Z. Y., and Zhu, J. G. (2018). Efficacy of gefitinib-celecoxib combination therapy in docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer. Oncol. Rep. 40 (4), 2242–2250. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6595
Lipton, A., Campbell-Baird, C., Witters, L., Harvey, H., and Ali, S. (2010). Phase II trial of gemcitabine, irinotecan, and celecoxib in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 44 (4), 286–288. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181cda097
Lira, M. C., Galluzzi, L., and Vanpouille-Box, C. (2024). COX2-dependent suppression of anticancer immunity. Trends Cancer 10 (7), 573–575. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2024.05.006
Liu, Z., Xu, Y., Liu, Z. L., Tian, Y. Z., and Shen, X. H. (2017). Combined application of diclofenac and celecoxib with an opioid yields superior efficacy in metastatic bone cancer pain: a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 22 (5), 980–985. doi:10.1007/s10147-017-1133-y
Liu, Y., He, J., Li, M., and Zhao, Z. (2024). Inflammation-driven nanohitchhiker enhances postoperative immunotherapy by alleviating prostaglandin E2-Mediated immunosuppression. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 16 (6), 6879–6893. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c17357
Ma, H. I., Chiou, S. H., Hueng, D. Y., Tai, L. K., Huang, P. I., Kao, C. L., et al. (2011). Celecoxib and radioresistant glioblastoma-derived CD133+ cells: improvement in radiotherapeutic effects. Laboratory investigation. J. Neurosurg. 114 (3), 651–662. doi:10.3171/2009.11.JNS091396
Mabrouk, A. A., El-Mezayen, N. S., Tadros, M. I., El-Gazayerly, O. N., and El-Refaie, W. M. (2023). Novel mucoadhesive celecoxib-loaded cubosomal sponges: anticancer potential and regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 182, 62–80. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2022.12.003
Maniewska, J., and Jeżewska, D. (2021). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in colorectal cancer chemoprevention. Cancers (Basel) 13 (4), 594. doi:10.3390/cancers13040594
Mao, Y., Sarhan, D., Steven, A., Seliger, B., Kiessling, R., and Lundqvist, A. (2014). Inhibition of tumor-derived prostaglandin-e2 blocks the induction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and recovers natural killer cell activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 20 (15), 4096–4106. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0635
Md, S., Alhakamy, N. A., Alharbi, W. S., Ahmad, J., Shaik, R. A., Ibrahim, I. M., et al. (2021). Development and evaluation of repurposed etoricoxib loaded nanoemulsion for improving anticancer activities against lung cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (24), 13284. doi:10.3390/ijms222413284
Meyerhardt, J. A., Shi, Q., Fuchs, C. S., Meyer, J., Niedzwiecki, D., Zemla, T., et al. (2021). Effect of celecoxib vs placebo added to standard adjuvant therapy on disease-free survival among patients with stage III Colon cancer: the CALGB/SWOG 80702 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA 325 (13), 1277–1286. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.2454
Mitryayeva, N., Grebinyk, L., Artiukh, S., Bilozor, N., and Starenkiy, V. (2024). Influence of conformal radiotherapy in combination with radiomodifiers on the content of VEGF, COX-2, and PGE-2 in blood serum of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Oncol. 46 (3), 253–259. doi:10.15407/exp-oncology.2024.03.253
Mohammadi, A., Yaghoobi, M. M., GholamhoseynianNajar, A., Kalantari-Khandani, B., Sharifi, H., and Saravani, M. (2016). HSP90 inhibitor enhances anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of celecoxib on HT-29 colorectal cancer cells via increasing BAX/BCL-2 ratio. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand). 62 (12), 62–67. doi:10.14715/cmb/2016.62.12.11
Mostafa, T. M., Alm El-Din, M. A., and Rashdan, A. R. (2022). Celecoxib as an adjuvant to chemotherapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized controlled clinical study. Saudi Med. J. 43 (1), 37–44. doi:10.15537/smj.2022.43.1.20210574
Nakai, Y., Tanaka, N., Asakawa, I., Anai, S., Miyake, M., Morizawa, Y., et al. (2020). Biochemical control of the combination of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor and 125 I-brachytherapy for prostate cancer: post hoc analysis of an open-label controlled randomized trial. Int. J. Urol. 27 (9), 755–759. doi:10.1111/iju.14294
Negi, R. R., Rana, S. V., Gupta, V., Gupta, R., Chadha, V. D., Prasad, K. K., et al. (2019). Over-expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 in colorectal cancer patients. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev. 20 (6), 1675–1681. doi:10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.6.1675
Noronha, V., Patil, V. M., Menon, N. S., Joshi, A., Goud, S., More, S., et al. (2022). Oral metronomic chemotherapy after definitive chemoradiation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a randomized clinical trial. Esophagus 19 (4), 670–682. doi:10.1007/s10388-022-00923-8
O’Rawe, M., Wickremesekera, A. C., Pandey, R., Young, D., Sim, D., FitzJohn, T., et al. (2022). Treatment of glioblastoma with re-purposed renin-angiotensin system modulators: results of a phase I clinical trial. J. Clin. Neurosci. 95, 48–54. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2021.11.023
Obeid, S., Libby, P., Husni, E., Wang, Q., Wisniewski, L. M., Davey, D. A., et al. (2022). Cardiorenal risk of celecoxib compared with naproxen or ibuprofen in arthritis patients: insights from the PRECISION trial. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 8 (6), 611–621. doi:10.1093/ehjcvp/pvac015
Ouyang, Y., Zhong, W., Xu, P., Wang, B., Zhang, L., Yang, M., et al. (2024). Tumor-associated neutrophils suppress CD8+ T cell immunity in urothelial bladder carcinoma through the COX-2/PGE2/IDO1 axis. Br. J. Cancer 130 (5), 880–891. doi:10.1038/s41416-023-02552-z
Pak, O., Kosianova, A., Zaitsev, S., Sharma, A., Sharma, H., and Bryukhovetskiy, I. (2025). Valproic acid and celecoxib enhance the effect of temozolomide on glioblastoma cells. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 24 (5), 375–381. doi:10.2174/0118715273330268241008220702
Pan, B., Chen, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Yao, Y., Wu, X., et al. (2023). 2,5-dimethylcelecoxib alleviated NK and T-cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma via the gastrointestinal microbiota-AMPK-mTOR axis. J. Immunother. Cancer 11 (6), e006817. doi:10.1136/jitc-2023-006817
Passaro, A., Al Bakir, M., Hamilton, E. G., Diehn, M., André, F., Roy-Chowdhuri, S., et al. (2024). Cancer biomarkers: emerging trends and clinical implications for personalized treatment. Cell 187 (7), 1617–1635. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.02.041
Patil, V., Noronha, V., Dhumal, S. B., Joshi, A., Menon, N., Bhattacharjee, A., et al. (2020). Low-cost oral metronomic chemotherapy versus intravenous cisplatin in patients with recurrent, metastatic, inoperable head and neck carcinoma: an open-label, parallel-group, non-inferiority, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Glob. Health 8 (9), e1213–e1222. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30275-8
Patil, V. M., Noronha, V., Menon, N., Rai, R., Bhattacharjee, A., Singh, A., et al. (2023). Low-dose immunotherapy in head and neck cancer: a randomized study. J. Clin. Oncol. 41 (2), 222–232. doi:10.1200/JCO.22.01015
Pelly, V. S., Moeini, A., Roelofsen, L. M., Bonavita, E., Bell, C. R., Hutton, C., et al. (2021). Anti-Inflammatory drugs remodel the tumor immune environment to enhance immune checkpoint blockade efficacy. Cancer Discov. 11 (10), 2602–2619. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1815
Pepine, C. J., and Gurbel, P. A. (2017). Cardiovascular safety of NSAIDs: additional insights after PRECISION and point of view. Clin. Cardiol. 40 (12), 1352–1356. doi:10.1002/clc.22814
Perroud, H. A., Alasino, C. M., Rico, M. J., Mainetti, L. E., Queralt, F., Pezzotto, S. M., et al. (2016). Metastatic breast cancer patients treated with low-dose metronomic chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and celecoxib: clinical outcomes and biomarkers of response. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 77 (2), 365–374. doi:10.1007/s00280-015-2947-9
Pritchard, R., Rodríguez-Enríquez, S., Pacheco-Velázquez, S. C., Bortnik, V., Moreno-Sánchez, R., and Ralph, S. (2018). Celecoxib inhibits mitochondrial O2 consumption, promoting ROS dependent death of murine and human metastatic cancer cells via the apoptotic signalling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 154, 318–334. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2018.05.013
Pu, D., Yin, L., Huang, L., Qin, C., Zhou, Y., Wu, Q., et al. (2021). Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor: a potential combination strategy with immunotherapy in cancer. Front. Oncol. 11, 637504. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.637504
Qadir, A., Khalid, Z., Kashan Theba, F., Mujtaba Ali, M., Asif, M., and Rizvi, F. (2023). Celecoxib and bevacizumab synergistically inhibit non-small cell lung cancer by inducing apoptosis and modulating VEGF and MMP-9 expression. Pak J. Pharm. Sci. 36 (2), 501–506. doi:10.36721/PJPS.2023.36.2.REG.501-506.1
Qian, X., Yang, H., Ye, Z., Gao, B., Qian, Z., Ding, Y., et al. (2024). Celecoxib augments paclitaxel-induced immunogenic cell death in triple-negative breast cancer. ACS Nano 18 (24), 15864–15877. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c02947
Qin, X., Zhang, M., Zhao, Z., Du, Q., Li, Q., Jiang, Y., et al. (2022). A carrier-free photodynamic nanodrug to enable regulation of dendritic cells for boosting cancer immunotherapy. Acta Biomater. 147, 366–376. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.05.022
Qin, H., Li, Z., Wu, J., Liu, X., Wang, R., Xu, J., et al. (2025). Diclofenac enhances the response of BRAF inhibitor to melanoma through ROS/p38/p53 signaling. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 52 (3), e70022. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.70022
Qorri, B., Harless, W., and Szewczuk, M. R. (2020). Novel molecular mechanism of aspirin and celecoxib targeting mammalian neuraminidase-1 impedes epidermal growth factor receptor signaling axis and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 4149–4167. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S264122
Quiñones, O. G., and Pierre, M. B. R. (2019). Cutaneous application of celecoxib for inflammatory and cancer diseases. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 19 (1), 5–16. doi:10.2174/1568009618666180430125201
Raaijmakers, T. K., van den Bijgaart, R. J. E., Scheffer, G. J., Ansems, M., and Adema, G. J. (2022). NSAIDs affect dendritic cell cytokine production. PLoS One 17 (10), e0275906. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0275906
Rao, C. V. (2022). Anti-inflammatory drugs decrease the PD-L1 expression and increase the CD8+ T-cell infiltration. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 15 (4), 209–211. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-22-0052
Rao, C. V., and Reddy, B. S. (2004). NSAIDs and chemoprevention. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 4 (1), 29–42. doi:10.2174/1568009043481632
Robledo-Cadena, D. X., Pacheco-Velázquez, S. C., Vargas-Navarro, J. L., Padilla-Flores, J. A., López-Marure, R., Pérez-Torres, I., et al. (2024). Synergistic celecoxib and dimethyl-celecoxib combinations block cervix cancer growth through multiple mechanisms. PLoS One 19 (9), e0308233. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0308233
Samoudi, A., Abolhasani-Zadeh, F., Afgar, A., Jalilian, E., Zeinalynezhad, H., and Langroudi, L. (2024). Treatment of cancer-associated fibroblast-like cells with celecoxib enhances the anti-cancer T helper 1/Treg responses in breast cancer. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 398, 6099–6112. doi:10.1007/s00210-024-03641-3
Shayeganmehr, D., Ramezannia, F., Gharib, B., Rezaeilaal, A., Shahi, F., Jafariazar, Z., et al. (2023). Pharmaceutical and clinical studies of celecoxib topical hydrogel for management of chemotherapy-induced hand-foot syndrome. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 396 (7), 1571–1581. doi:10.1007/s00210-022-02339-8
Shen, C. J., Chen, H. C., Lin, C. L., Thakur, A., Onuku, R., Chen, I. C., et al. (2025). Contribution of prostaglandin E2-Induced neuronal excitation to drug resistance in glioblastoma countered by a novel blood-brain barrier crossing celecoxib derivative. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 12, e06336. doi:10.1002/advs.202506336
Sigler, S., Abdel-Halim, M., Fathalla, R. K., Da Silva, L. M., Keeton, A. B., Maxuitenko, Y. Y., et al. (2025). Novel celecoxib derivative, RF26, blocks Colon cancer cell growth by inhibiting PDE5, activating cGMP/PKG signaling, and suppressing β-catenin-dependent transcription. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 25 (1), 52–62. doi:10.2174/0118715206318802240821114353
Singh, S. (2018). Liposome encapsulation of doxorubicin and celecoxib in combination inhibits progression of human skin cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomedicine 13 (T-NANO 2014 Abstracts), 11–13. doi:10.2147/IJN.S124701
Sun, J., Liu, N. B., Zhuang, H. Q., Zhao, L. J., Yuan, Z. Y., and Wang, P. (2017). Celecoxib-erlotinib combination treatment enhances radiosensitivity in A549 human lung cancer cell. Cancer Biomark. 19 (1), 45–50. doi:10.3233/CBM-160323
Sung, M. W., Lee, D. Y., Park, S. W., Oh, S. M., Choi, J. J., Shin, E. S., et al. (2017). Celecoxib enhances the inhibitory effect of 5-FU on human squamous cell carcinoma proliferation by ROS production. Laryngoscope 127 (4), E117–E123. doi:10.1002/lary.26309
Swanton, C., Bernard, E., Abbosh, C., André, F., Auwerx, J., Balmain, A., et al. (2024). Embracing cancer complexity: hallmarks of systemic disease. Cell 187 (7), 1589–1616. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.02.009
Tai, Y., Zhang, L. H., Gao, J. H., Zhao, C., Tong, H., Ye, C., et al. (2019). Suppressing growth and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by celecoxib through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Manag. Res. 11, 2831–2848. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S183376
Tan, T., Fu, X., Qu, J., Zhang, M., Chen, H., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). 2,5-dimethyl celecoxib induces apoptosis and autophagy via activation of ROS/JNK axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Aging (Albany NY) 13 (17), 21483–21496. doi:10.18632/aging.203488
Tang, B., Guo, Z. S., Bartlett, D. L., Yan, D. Z., Schane, C. P., Thomas, D. L., et al. (2020). Synergistic combination of oncolytic virotherapy and immunotherapy for glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 26 (9), 2216–2230. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3626
Thi Thanh Nguyen, N., and Yoon, L. S. (2024). Celecoxib and sulindac sulfide elicit anticancer effects on PIK3CA-mutated head and neck cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress, reactive oxygen species, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 224, 116221. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116221
Tian, J., Guo, F., Chen, Y., Li, Y., Yu, B., and Li, Y. (2019). Nanoliposomal formulation encapsulating celecoxib and genistein inhibiting COX-2 pathway and Glut-1 receptors to prevent prostate cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Lett. 448, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.01.002
Tołoczko-Iwaniuk, N., Dziemiańczyk-Pakieła, D., Nowaszewska, B. K., Celińska-Janowicz, K., and Miltyk, W. (2019). Celecoxib in cancer therapy and prevention - review. Curr. Drug Targets 20 (3), 302–315. doi:10.2174/1389450119666180803121737
Trifan, O. C., and Hla, T. (2003). Cyclooxygenase-2 modulates cellular growth and promotes tumorigenesis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 7 (3), 207–222. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2003.tb00222.x
Tseng, P. H., Wang, Y. C., Weng, S. C., Weng, J. R., Chen, C. S., Brueggemeier, R. W., et al. (2006). Overcoming trastuzumab resistance in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells by using a novel celecoxib-derived phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 inhibitor. Mol. Pharmacol. 70 (5), 1534–1541. doi:10.1124/mol.106.023911
Tudor, D. V., Bâldea, I., Olteanu, D. E., Fischer-Fodor, E., Piroska, V., Lupu, M., et al. (2021). Celecoxib as a valuable adjuvant in cutaneous melanoma treated with trametinib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (9), 4387. doi:10.3390/ijms22094387
Valverde, A., Peñarando, J., Cañas, A., López-Sánchez, L. M., Conde, F., Guil-Luna, S., et al. (2017). The addition of celecoxib improves the antitumor effect of cetuximab in colorectal cancer: role of EGFR-RAS-FOXM1-β- catenin signaling axis. Oncotarget 8 (13), 21754–21769. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.15567
Veltman, J. D., Lambers, M. E., van Nimwegen, M., Hendriks, R. W., Hoogsteden, H. C., Aerts, J. G. J. V., et al. (2010). COX-2 inhibition improves immunotherapy and is associated with decreased numbers of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mesothelioma. Celecoxib influences MDSC function. BMC Cancer 10, 464. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-464
Wang, D., and Dubois, R. N. (2010). Eicosanoids and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10 (3), 181–193. doi:10.1038/nrc2809
Wang, L. W., Hsiao, C. F., Chen, W. T., Lee, H. H., Lin, T. C., Chen, H. C., et al. (2014). Celecoxib plus chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: a phase II TCOG study. J. Surg. Oncol. 109 (6), 580–585. doi:10.1002/jso.23538
Wang, G., Li, J., Zhang, L., Huang, S., Zhao, X., and Zhao, X. (2017). Celecoxib induced apoptosis against different breast cancer cell lines by down-regulated NF-κB pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 490 (3), 969–976. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.148
Wen, B., Wei, Y. T., Mu, L. L., Wen, G. R., and Zhao, K. (2020). The molecular mechanisms of celecoxib in tumor development. Med. Baltim. 99 (40), e22544. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000022544
Xiao, J., Wang, F., Lu, H., Xu, S., Zou, L., Tian, Q., et al. (2019). Targeting the COX2/MET/TOPK signaling axis induces apoptosis in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cells. Cell Death Dis. 10 (10), 777. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-2020-4
Xie, L., Li, R., Zheng, B., Xie, Z., Fang, X., Dai, T., et al. (2021). One-step transformation from rofecoxib to a COX-2 NIR probe for human cancer tissue/organoid targeted bioimaging. ACS Appl. Bio Mater 4 (3), 2723–2731. doi:10.1021/acsabm.0c01634
Xu, H. B., Shen, F. M., and Lv, Q. Z. (2015). Celecoxib enhanced the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin in drug-resistant human gastric cancer cells by inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 769, 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.09.025
Xu, H. B., Shen, F. M., and Lv, Q. Z. (2016). Celecoxib enhanced the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin in chemo-resistant gastric cancer xenograft mouse models through a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent manner. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 776, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.02.035
Xu, H., Li, P., Ma, H., Tan, Y., Wang, X., Cai, F., et al. (2023). ADT-OH synergistically enhanced the antitumor activity of celecoxib in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Med. 12 (16), 17193–17211. doi:10.1002/cam4.6342
Xue, W. P., Bai, S. M., Luo, M., Bi, Z. F., Liu, Y. M., and Wu, S. K. (2011). Phase I clinical trial of nasopharyngeal radiotherapy and concurrent celecoxib for patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 47 (8), 753–757. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.06.002
Xun, X., Zhang, C., Wang, S., Hu, S., Xiang, X., Cheng, Q., et al. (2021). Cyclooxygenase-2 expressed hepatocellular carcinoma induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes exhaustion through M2 macrophage polarization. Am. J. Transl. Res. 13 (5), 4360–4375.
Ye, S. Y., Li, J. Y., Li, T. H., Song, Y. X., Sun, J. X., Chen, X. W., et al. (2022). The efficacy and safety of celecoxib in addition to standard cancer therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Curr. Oncol. 29 (9), 6137–6153. doi:10.3390/curroncol29090482
Yeomans, N. D., Graham, D. Y., Husni, M. E., Solomon, D. H., Stevens, T., Vargo, J., et al. (2018). Randomised clinical trial: gastrointestinal events in arthritis patients treated with celecoxib, ibuprofen or naproxen in the PRECISION trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 47 (11), 1453–1463. doi:10.1111/apt.14610
Yilmaz, Ç., Köksoy, S., Çeker, T., and Aslan, M. (2021). Diclofenac down-regulates COX-2 induced expression of CD44 and ICAM-1 in human HT29 colorectal cancer cells. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 394 (11), 2259–2272. doi:10.1007/s00210-021-02139-6
Yin, D., Jin, G., He, H., Zhou, W., Fan, Z., Gong, C., et al. (2021). Celecoxib reverses the glioblastoma chemo-resistance to temozolomide through mitochondrial metabolism. Aging (Albany NY) 13 (17), 21268–21282. doi:10.18632/aging.203443
Zelenay, S., van der Veen, A. G., et, L., Snelgrove, K. J., Rogers, N., Acton, S. E., et al. (2015). Cyclooxygenase-dependent tumor growth through evasion of immunity. Cell 162 (6), 1257–1270. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.015
Zhang, H., Tian, M., Xiu, C., Wang, Y., and Tang, G. (2013). Enhancement of antitumor activity by combination of tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells and celecoxib in a rat glioma model. Oncol. Res. 20 (10), 447–455. doi:10.3727/096504013x13685487925176
Zhang, P., He, D., Song, E., Jiang, M., and Song, Y. (2019). Celecoxib enhances the sensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells to radiation-induced apoptosis through downregulation of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and COX-2 expression. PLoS One 14 (10), e0223760. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0223760
Zhang, W., Yi, L., Shen, J., Zhang, H., and Luo, P. (2020). Comparison of the benefits of celecoxib combined with anticancer therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. J. Cancer 11 (7), 1816–1827. doi:10.7150/jca.35003
Zhang, P., Song, E., Jiang, M., and Song, Y. (2021). Celecoxib and afatinib synergistic enhance radiotherapy sensitivity on human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 97 (2), 170–178. doi:10.1080/09553002.2021.1846817
Zhang, M., Qin, X., Zhao, Z., Du, Q., Li, Q., Jiang, Y., et al. (2022). A self-amplifying nanodrug to manipulate the Janus-faced nature of ferroptosis for tumor therapy. Nanoscale Horiz. 7 (2), 198–210. doi:10.1039/d1nh00506e
Zhang, X., Liang, Q., Cao, Y., Yang, T., An, M., Liu, Z., et al. (2024). Dual depletion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and tumor cells with self-assembled gemcitabine-celecoxib nano-twin drug for cancer chemoimmunotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 22 (1), 319. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02598-y
Zheng, L., Qin, S., Si, W., Wang, A., Xing, B., Gao, R., et al. (2021). Pan-cancer single-cell landscape of tumor-infiltrating T cells. Science 374 (6574), abe6474. doi:10.1126/science.abe6474
Zhu, J., May, S., Ulrich, C., Stockfleth, E., and Eberle, J. (2021). High ROS production by celecoxib and enhanced sensitivity for death ligand-induced apoptosis in cutaneous SCC cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (7), 3622. doi:10.3390/ijms22073622
Zhu, X., Zhang, W., Yu, Z., Yang, X., Li, L., Chen, C., et al. (2024). Synergistic action of gemcitabine and celecoxib in promoting the antitumor efficacy of anti-programmed death-1 monoclonal antibody by triggering immunogenic cell death. Transl. Cancer Res. 13 (6), 3031–3045. doi:10.21037/tcr-24-698
Keywords: celecoxib, COX-2 inhibition, tumor microenvironment, combination therapy, precision oncology
Citation: Kuang B, Yang K, Zhong X, Tan Y, Zhou Y and Ye J (2025) Celecoxib in oncology: targeting the COX-2/PGE2 axis to reprogram the tumor immune microenvironment and enhance multimodal therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1691392. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1691392
Received: 23 August 2025; Accepted: 05 November 2025;
Published: 26 November 2025.
Edited by:
Nur Akmarina Mohd Said, University of Malaya, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Balram Chowbay, National Cancer Centre Singapore, SingaporeSurya P Singh, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 Kuang, Yang, Zhong, Tan, Zhou and Ye. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianming Ye, eWVqaWFubWluZ0BnbXUuZWR1LmNu; Yi Zhou, emhvdXlpMzAzMEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Boyang Kuang
Boyang Kuang Kuan Yang1,2†
Kuan Yang1,2† Xiaoting Zhong
Xiaoting Zhong Jianming Ye
Jianming Ye