- 1Institute of Medicinal Plant Development, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
- 2Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory of Resources Conservation and Development of Southern Medicine, Hainan Branch of the Institute of Medicinal Plant Development, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Haikou, China
Boswellic acids (BAs), a group of pentacyclic triterpenoids derived from the gum resin of Boswellia species, exhibit promising anti-inflammatory potential through diverse mechanisms. This review provides a comprehensive and structured summary of BAs’ anti-inflammatory actions, spanning key signaling pathways including NF-κB, MAPK, 5-LOX, COX-2, and NLRP3 inflammasome, as well as their modulation of cytokines, immune cell activity, and oxidative stress. We further highlight recent progress in molecular docking and dynamic simulations that elucidate BA–protein interactions at the structural level. The review integrates evidence from preclinical and clinical studies, with detailed pharmacological parameters such as model types, dose ranges, and control settings. Challenges related to BAs’ poor solubility and limited bioavailability are critically addressed. Recent advances in delivery systems, including nanoparticles, micelles, phytosomes, and ligand-targeted carriers—are summarized with mechanistic insight. Safety, toxicity, and formulation limitations are also discussed to provide a balanced perspective on their clinical translation. Overall, this review aims to clarify how BAs exert multi-target immunomodulatory effects and proposes directions for future research and therapeutic development.
1 Introduction
1.1 Inflammation and its pathophysiological significance
Inflammation is a complex biological response of body tissues to infection, injury, or other harmful stimuli, aimed at eliminating pathogens and damaged cells, and promoting tissue repair. It encompasses a broad spectrum of responses that vary depending on the triggering stimulus and subsequent signaling events, involving a diverse array of pathogenic cells, stromal cells, and components of both the innate and adaptive immune systems (Paus et al., 2018). However, if uncontrolled or persistent, inflammation can contribute to the development of autoimmune or autoinflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and even cancer (Mantovani et al., 2008; Dinarello, 2010). Inflammation is generally classified into two types:
Acute inflammation: This is typically induced by infections, tissue injury, or exposure to toxins, and is characterized by local vasodilation, leukocyte infiltration, and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines derived from macrophages, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (Paus et al., 2018).
Chronic inflammation: This form persists over time and is often associated with autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, and cancer. It is marked by continuous infiltration of immune cells—primarily macrophages and T lymphocytes—and sustained tissue damage (Medzhitov, 2008).
1.2 Mechanisms of inflammatory response
Inflammation is a highly dynamic and multifaceted process that involves both innate and adaptive immune mechanisms. It is initiated when host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), leading to activation of transcription factors such as NF-κB and induction of pro-inflammatory mediators (Newton and Dixit, 2012; Zindel and Kubes, 2020).
Innate immunity: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a central role by sensing microbial ligands and triggering downstream NF-κB and MAPK pathways, thereby promoting cytokine release (O'Neill et al., 2013). In addition, activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome results in caspase-1–mediated maturation of IL-1β and IL-18, which amplify local and systemic inflammation (Guo et al., 2015).
Adaptive immune cells also play critical roles in sustaining and shaping inflammation. Distinct CD4+ T helper (Th) cell subsets mediate different inflammatory programs: Th1 responses are typically associated with IFN-γ–driven cellular immunity, Th17 responses with IL-17–mediated recruitment of neutrophils and chronic tissue inflammation, while regulatory T cells (Tregs) limit excessive immune activation through suppressive cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β (Paul and Zhu, 2010). B cells further contribute to chronic inflammation by producing antibodies and immune complexes that perpetuate tissue injury and amplify inflammatory cascades (Coussens and Werb, 2002).
Cytokine and chemokine networks. Key mediators such as IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ are pivotal in driving both acute and chronic inflammatory responses (Dinarello, 2010). Chemokines further guide neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes to inflamed tissues, ensuring amplification and persistence of the immune response (Mantovani et al., 2008).
Oxidative and stress pathways. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by NADPH oxidases and mitochondria function as signaling messengers that activate MAPKs (ERK, JNK, p38) and JAK-STAT cascades, further regulating inflammatory gene expression (Morgan and Liu, 2011). Dysregulation of these signaling networks is closely associated with the transition from acute to chronic inflammation and contributes to disease pathogenesis (Nathan and Ding, 2010).
Inflammation plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Consequently, anti-inflammatory therapies have become a central focus of medical research. The most used clinical anti-inflammatory agents include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), glucocorticoids (GCs), biological agents, and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. These drugs effectively control inflammatory responses (Staa et al., 2002; Beaulieu and Morand, 2011; Schjerning et al., 2020); however, their long-term use is often limited by a range of adverse effects, development of drug resistance, and safety concerns. These limitations have restricted their widespread clinical use. For instance, the inhibition of COX-1 by NSAIDs can damage gastric mucosa, increasing the risk of gastric ulcers and bleeding. Additionally, some COX-2 inhibitors, such as celecoxib, have been associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular events (Bindu et al., 2020). Although glucocorticoids are potent anti-inflammatory agents, prolonged administration can cause osteoporosis, hypertension, diabetes, and immunosuppression (Staa et al., 2002). Biologics, while targeting specific inflammatory mediators and thereby reducing broad immunosuppression, are costly and may induce drug resistance or immune dysregulation in some patients after long-term use (Dinarello, 2010). Moreover, JAK inhibitors, a relatively recent class of anti-inflammatory drugs, may increase the risk of infections due to their extensive effects on the immune system.
In recent years, natural products have emerged as a significant focus in anti-inflammatory research due to their broad-spectrum multi-target effects and relatively low side effects. Among these, boswellic acids (BAs) are a class of pentacyclic triterpenoids extracted from plants of the Boswellia genus (Efferth and Oesch, 2022).
1.3 Overview of boswellic acids
Frankincense refers to the oleo-gum resins obtained from trees of the genus Boswellia Roxb. ex Colebr. (family Burseraceae), (Howes, 1949). The genus Boswellia Roxb. ex Colebr. (family Burseraceae) comprises 23 Accepted species distributed across India, the Arabian Peninsula, and Africa (Plants of the World Online, 2025).
Among them, Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr., Boswellia. frereana Birdw., Boswellia. sacra Flueck., and Boswellia. papyrifera (Caill.) Hochst. are the principal sources of medicinal frankincense. All species names have been validated following Plants of the World Online (Boswellia serrata Roxb, 2025; Boswellia sacra Flück, 2025; Boswellia papyrifera (Caill.) Hochst (2025); Boswellia frereana Birdw, 2025).
However, only a small subset of these metabolites exhibits significant medicinal value. Indian frankincense is the gum resin collected from the Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae), while African frankincense contains gum resins from Boswellia carteri Birdw. (Burseraceae) and Boswellia. frereana Birdw. (Burseraceae) (Büchele et al., 2003). The use of frankincense in traditional medical systems, such as Ayurveda and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is particularly important. In Ayurveda, frankincense, known as “Shallaki” [Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae)], has been used for centuries to treat inflammatory conditions, joint disorders, and respiratory ailments (Gupta et al., 2011). Ayurvedic formulations often combine frankincense with other botanicals to enhance its therapeutic efficacy, particularly in managing rheumatoid arthritis (Amavata) and osteoarthritis (Siddiqui, 2011).
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), frankincense (“Ru Xiang”) is highly valued for its ability to promote blood circulation, reduce swelling, and alleviate pain (Efferth and Oesch, 2022). It is frequently used in combination with myrrh (“Mo Yao”), which is the gum resins obtained from trees of Commiphora myrrha (T.Nees) Engl. (Burseraceae) (Commiphor amyrrha Engl, 2025), to treat traumatic injuries, inflammation, and chronic pain conditions. TCM practitioners believe that frankincense can clear stagnant blood (“blood stasis”), making it a key metabolite in formulations for wound healing, menstrual disorders, and inflammatory diseases (Liao et al., 2021).
In African and Arabian traditional medicine, frankincense has played a crucial role in managing infections, wounds, and inflammatory conditions (Miran et al., 2022). In Oman and Somalia, for example, it is commonly used as a chewing resin for improving digestion and oral health, while its smoke is believed to have antiseptic and mood-enhancing properties (Khan and Rashan, 2025). Additionally, in Ethiopian traditional medicine, frankincense has been used in remedies for neurological disorders, including epilepsy and depression, highlighting its potential neuroprotective effects (Khalifa et al., 2023).
In the past few decades, more than 200 natural products have been identified or isolated from frankincense, including terpenoids, polyphenols, essential oils, tannins, alkaloids, saponins and other metabolites (Efferth and Oesch, 2022; Hussain et al., 2022). Among these metabolites, terpenoids are the most abundant and predominant metabolites, with pentacyclic triterpenes receiving particular attention due to their notable biological activities. The primary active metabolites of frankincense are BAs with a pentacyclic triterpenoid structure (Huang et al., 2022), especially α-boswellic acid (α-BA), β-boswellic acid (β-BA), 11-keto-β-boswellic acid (KBA), 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA), 9,11-dehydro-β-boswellic acid, 9,11-dehydro-α-boswellic acid,3-O-acetyl-11-hydroxy-β-boswellic acid, 3-acetyl-9,11-dehydro-α-boswellic acid, 3-acetyl-α-boswellic acid, 3α-O-acetyl-9,11-dedro-β-boswellic acid. The specific information is shown on the table (Figure 1).
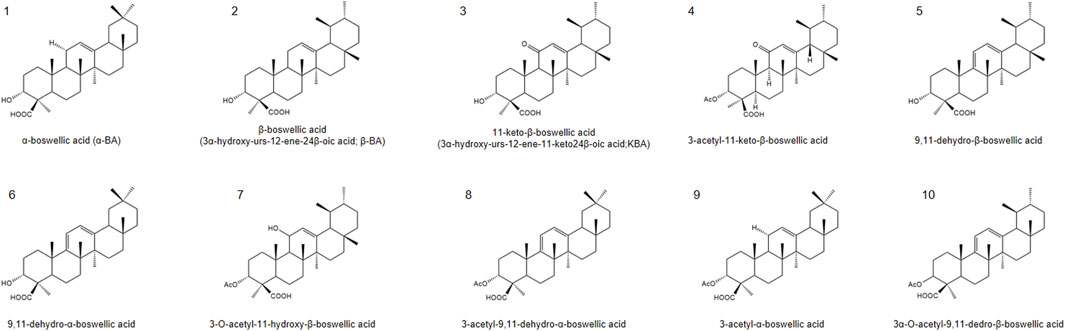
Figure 1. Chemical structures of representative boswellic acids: (1) α-boswellic acid, (2) β-boswellic acid, (3) 11-keto-β-boswellic acid (KBA), (4) 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA), (5) 9,11-dehydro-β-boswellic acid, (6) 9,11-dehydro-α-boswellic acid, (7) 3-O-acetyl-11-hydroxy-β-boswellic acid, (8) 3-acetyl-9,11-dehydro-α-boswellic acid, (9) 3-acetyl-α-boswellic acid, (10) 3α-O-acetyl-9,11-dedro-β-boswellic acid.
Boswellic acids as a popular research subject, there are abundant related research reports on it, it also has been reviewed quite often. However, previous reviews on boswellic acids have primarily focused on their anti-inflammatory and pharmacological activities (Ammon, 2010; Börner et al., 2021). While these studies have provided valuable insights, they often lack systematic comparisons of pharmacokinetics across species, detailed evaluations of experimental design (e.g., dose ranges, active concentrations, control settings), and an in-depth analysis of translational limitations. In addition, the discussion of formulation strategies has mostly remained descriptive, with limited attention to advanced targeted delivery approaches.
In contrast, this review provides a comprehensive and updated synthesis by (1) highlighting species-specific metabolic and pharmacokinetic challenges, (2) critically appraising both in vitro and in vivo pharmacological studies with detailed methodological parameters, (3) integrating the latest nano formulation and ligand-targeted strategies for improving bioavailability, and (4) illustrating the diverse anti-inflammatory mechanisms of BAs through refined mechanistic diagrams and comparative tables. These features distinguish our work from previous reports and aim to bridge the gap between mechanistic studies and clinical translation.
2 Methods
This review adopted a systematic literature search strategy to ensure the inclusion of the most recent studies on boswellic acids and their delivery systems in anti-inflammatory therapy. The primary databases searched included PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Embase. Additionally, Google Scholar was used as a supplementary source to identify potentially missed studies. To maintain the scientific rigor and reliability of the review, only peer-reviewed articles were included, while conference abstracts and unpublished theses or dissertations were excluded.
A combination of keywords and Boolean operators was employed during the search process to enhance both the precision and comprehensiveness of the retrieval. The primary search terms included but were not limited to “Boswellic acids,” “Boswellia extract,” and “Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA),” in conjunction with inflammation-related terms such as “Anti-inflammatory,” “Inflammation,” “NF-κB,” and “5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX).” For studies focusing on delivery systems, additional keywords such as “Nanoformulation,” “Nanoparticles,” “Drug delivery,” and “Bioavailability enhancement” were incorporated to capture the latest applications of boswellic acids in drug delivery technologies. To improve the standardization of the search, controlled vocabulary terms were applied where appropriate, particularly in PubMed. For example, queries such as [“Boswellic Acids” (Title)] AND [“Anti-Inflammatory Agents” (Title)] were used to ensure the relevance of the retrieved literature. To ensure taxonomic accuracy, the nomenclature of all Boswellia species included in this review was verified using curated botanical databases, namely Plants of the World Online (POWO), and World Flora Online (WFO). Accepted names, author citations, this verification process ensured consistency in species identification across pharmacological and clinical literature.
The literature selection process followed strict inclusion and exclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) the study must be an in vitro, in vivo, or clinical trial, excluding purely computational models; (2) the research must focus on the anti-inflammatory properties of boswellic acids and their nano-delivery strategies rather than other pharmacological effects; (3) only English-language articles were considered to maintain consistency in academic communication. The exclusion criteria included review articles, conference abstracts, non-peer-reviewed studies, and those that were irrelevant to the primary topic.
3 Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of boswellic acid
Boswellic acids exhibit potent anti-inflammatory effects through multiple interconnected mechanisms, making it effective in managing inflammatory conditions. Here’s a structured breakdown of its key mechanisms (Figure 2).
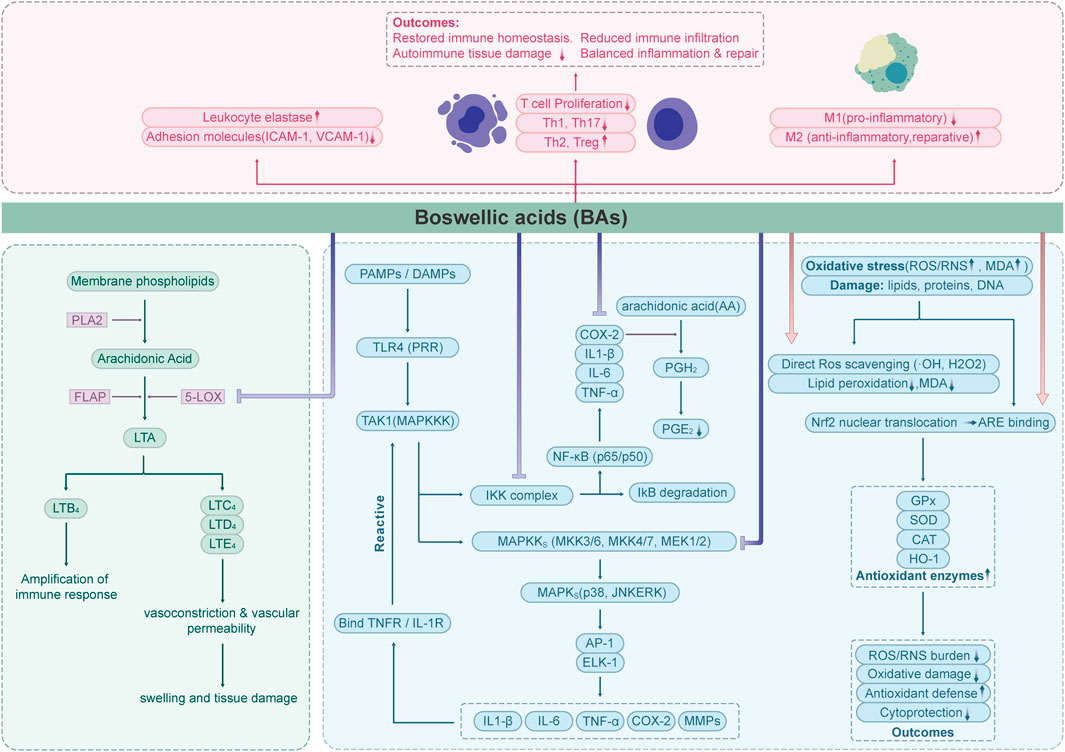
Figure 2. Flow chart depicting the effects of Boswellic acids (BAs) on immune and oxidative stress pathways.
3.1 5-LOX inhibition
The synthesis of leukotriene was inhibited by Inhibition of 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LOX) (Rådmark et al., 2007). 5-Lipoxygenase (EC 1.13.11.34) is the key enzyme catalyzing the initial steps of leukotriene biosynthesis and represents an important therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Inhibitors of 5-LOX are being actively investigated as potential anti-inflammatory agents (Lin et al., 2014; Gilbert et al., 2021).
Previous studies have confirmed that boswellic acids (BAs) act as specific non-redox inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) product formation. They exert their effects either by directly interacting with the 5-LOX enzyme or by blocking its translocation. Among the BAs, acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) demonstrates the most potent inhibitory activity against 5-LOX products, with a reported IC50 value of 1.5 μM (in human neutrophils; non-redox, non-competitive; in vitro) (Safayhi et al., 1995). It directly inhibits 5-LOX by a selective, enzyme-directed, non-redox and non-competitive mechanism. β-Boswellic acid (β-BA) lacking the 11-keto function, only partially and incompletely inhibited 5-LOX (Sailer et al., 1996). Early studies on the pharmacological activity of boswellic acids (BAs) were primarily conducted in vitro, and the inhibitory effects observed varied across different experimental settings. According to the research and review by Werz, the efficacy of 5-LOX inhibitors in both intact cell and cell-free assays depends on assay conditions, such as substrate concentration, the presence of 5-LOX activating cofactors (e.g., phosphatidylcholine, lipid hydroperoxides, Ca2+), and the type of stimulus used to activate intact cells (Werz and Steinhilber, 2005; Werz and Steinhilber, 2006; Werz, 2007). In the study by Ulf Siemoneit et al., the inhibitory effects of different boswellic acids on 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) were evaluated across various in vitro test systems, including (1) purified 5-LOX enzyme, (2) supernatants of E. coli lysates, and (3) neutrophils. Both acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) and 11-keto-β-boswellic acid (KBA) demonstrated strong inhibition of 5-LOX across all systems, while α-boswellic acid (α-BA) exhibited greater inhibitory activity than β-boswellic acid (β-BA). Notably, the study found that in the presence of albumin (10 mg/mL), the inhibitory effect of 11-keto boswellic acid (up to 30 μM) on neutrophil 5-LOX was abolished (Siemoneit et al., 2009). This finding explains why 11-keto boswellic acid (KBA) failed to inhibit 5-LOX product formation in human whole blood during in vitro assays, and why single oral administration of Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae) resin extract in a Phase I clinical trial did not suppress plasma leukotriene B4 levels in subjects. This may be attributed to the strong binding affinity of 11-keto boswellic acid to albumin (>95%) and its relatively low bioavailability in vivo, among other factors (as will be discussed in the “Pharmacokinetic and Metabolic Challenges of Boswellic Acids” section below).
3.2 Suppression of NF-κB pathway
The NF-κB signaling pathway regulates the expression of genes involved in immune responses, cell survival, and chronic inflammation. In its inactive state, NF-κB is sequestered in the cytoplasm through interaction with inhibitory proteins (IκBs). Upon stimulation—such as exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α—signaling cascades are triggered that lead to the phosphorylation and subsequent degradation of IκBs. This allows NF-κB to translocate into the nucleus, where it initiates the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes (Hinz and Scheidereit, 2014).
This activation can be suppressed by blocking IκB kinase (IKK), thereby preventing IκB degradation. Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) has been shown to inhibit the NF-κB pathway, preventing IκBα phosphorylation and degradation, and reducing the nuclear translocation of NF-κB subunits (Syrovets et al., 2005a; Takada et al., 2006).
Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) has been shown to inhibit the NF-κB pathway, thereby reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g.: TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), chemokines, and inflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (shown in LPS-stimulated Mice model) (Cuaz-Pérolin et al., 2008). Experimental evidence from animal models of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriasis, osteoarthritis, and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) has confirmed that AKBA-mediated suppression of the NF-κB pathway contributes to its anti-inflammatory effects (Wang et al., 2009; Nadeem et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022; Zhang and Jiang, 2023).
3.3 Antioxidant activity
Oxidative stress refers to a pathological condition in which the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) exceeds the capacity of the endogenous antioxidant defense system, leading to oxidative damage of cellular components such as lipids, proteins, and DNA (Jomova et al., 2023). Recent studies have demonstrated that boswellic acid exerts antioxidant effects through multiple mechanisms. One key mechanism is the direct scavenging of ROS—such as hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)—via active functional groups like phenolic hydroxyls. This activity helps inhibit lipid peroxidation chain reactions and reduces the formation of oxidative end-products, such as malondialdehyde (MDA) (Liu and Ng, 2000; Barakat et al., 2018; Elgazar et al., 2023). In addition, boswellic acid can enhance the endogenous antioxidant defense system by promoting the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2) (Upadhayay et al., 2022). Once translocated into the nucleus, Nrf2 binds to antioxidant response elements (AREs), leading to the transcriptional activation of various antioxidant enzymes, including glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). This pathway significantly strengthens the cellular antioxidant capacity and protects against oxidative damage (Eltahir et al., 2020).
3.4 Immune cell modulation
Immune cell modulation refers to the process of regulating the function, activity, or population of immune cells—such as T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells—through chemical, biological, or physical means, with the aim of either enhancing or suppressing immune responses (Strzelec et al., 2023). Boswellic acid has been shown to inhibit the activation of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages while promoting the polarization toward the anti-inflammatory and tissue-reparative M2 phenotype. This shift contributes to the restoration of immune homeostasis by balancing inflammatory and reparative processes (Nischang et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024). Moreover, studies have shown that boswellic acid can modulate T cell-mediated immune responses by inhibiting T cell proliferation and suppressing the differentiation of pro-inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cells, while promoting a shift toward anti-inflammatory Th2 responses. This immunomodulatory effect contributes to the attenuation of pathological damage in autoimmune diseases (Stürner et al., 2014; Meyiah et al., 2023). Additionally, it inhibits leukocyte elastase and adhesion molecule (ICAM-1, VCAM-1) expression, limiting immune cell infiltration into inflamed tissues (Safayhi et al., 1997; Roy et al., 2005).
3.5 Selective COX-2 inhibition
Unlike conventional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), boswellic acids have been proposed to preferentially inhibit COX-2 over COX-1 under certain conditions; however, several studies indicate that they may still exert inhibitory effects on COX-1 (e.g. 11-keto-β-boswellic acids inhibited COX-1 in stimulated human platelets, IC50 = 6–17 μM, with comparatively weaker inhibition of COX-2) (Siemoneit et al., 2008).
Boswellic acids (BAs) modulate prostaglandin biosynthesis mainly by downregulating COX-2 expression through suppression of NF-κB and AP-1 signaling, rather than by directly blocking the COX-2 catalytic site (Siemoneit et al., 2011; Verhoff et al., 2014). Compared to COX-1, BAs exhibit greater inhibitory potency against COX-2, as evidenced by lower IC50 values (Abdel-Tawab, 2021). This selective inhibition leads to a reduction in inflammation-associated prostaglandins such as PGE2, while preserving COX-1–mediated physiological functions like gastric mucosal protection, thereby minimizing the risk of gastrointestinal ulceration commonly associated with NSAID therapy.
3.6 Apoptosis induction in inflammatory cells
Resolution of Inflammation: AKBA induces apoptosis in hyperactive immune cells (e.g., macrophages, synoviocytes), curtailing prolonged inflammatory responses.
Boswellic acids can induce apoptosis by directly activating apoptosis-related caspase proteases, thereby initiating the intrinsic apoptotic program within cells (Takada et al., 2006; Kunnumakkara et al., 2018).
3.7 Decreased the expression of matrix metallopeptidase (MMPs)
Boswellic acids are reported to downregulate matrix metallopeptidases (MMPs), a family of zinc-dependent endopeptidases that play crucial roles in the degradation and remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Functionally, MMPs are involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including wound healing, inflammatory responses, and tumor metastasis. By modulating MMP activity, boswellic acids may contribute to the regulation of tissue remodeling and inflammatory progression (Cui et al., 2017; de Almeida et al., 2022). In the context of inflammation, the overexpression of MMPs is closely associated with cartilage degradation, particularly in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA). MMPs are considered potential biomarkers and key mediators of disease progression in these conditions (Visse and Nagase, 2003). To date, numerous phytochemicals have been investigated for their potential as matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitors (Alamgeer et al., 2020). Among these, boswellic acids—natural metabolites with potent anti-inflammatory properties—have attracted considerable attention for their ability to modulate MMP activity. Firstly, boswellic acids, especially acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA), are believed to directly interfere with the promoter activity of MMP genes. It has been demonstrated that AKBA downregulates the mRNA expression levels of MMP-2, MMP-3, and MMP-9 by suppressing their promoter activity, thereby reducing the synthesis of these matrix metalloproteinases (Ranzato et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2020).
Moreover, current studies suggest that NF-κB is a key transcription factor responsible for the induction of MMP expression and is highly activated under inflammatory conditions. As discussed above, boswellic acids—particularly AKBA—suppress NF-κB activation by inhibiting the phosphorylation of IκBα, thereby preventing NF-κB nuclear translocation. This results in reduced transcriptional activation of MMP promoters, including those of MMP-2, MMP-3, and MMP-9 (Park et al., 2011). Moreover, experimental studies have demonstrated that inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway—particularly in human fibroblasts, glioma cells, and macrophages under inflammatory stimulation—leads to a significant reduction in MMP-9 expression (Liang et al., 2012). AKBA has been shown to markedly inhibit the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2, thereby suppressing MAPK-mediated transcriptional activation of MMPs(Syrovets et al., 2005b). These findings suggest that boswellic acids can reduce MMP expression not only through inhibition of NF-κB signaling but also via suppression of the MAPK cascade.
3.8 TLR and IFN pathways
In addition to classical anti-inflammatory mechanisms, boswellic acids (BAs) have been reported to modulate innate immune recognition pathways. AKBA markedly attenuated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)–induced cardiac dysfunction in mice, reducing NF-κB activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine release, thereby implicating suppression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)–mediated signaling (Taherzadeh et al., 2022). Such findings suggest that BAs may interfere with TLR-dependent activation cascades that drive inflammatory injury. Evidence also indicates that BAs affect interferon pathways. Several studies have documented reduced IFN-γ production in T-cell and macrophage models upon BA treatment, shifting immune responses away from Th1-dominated profiles (Gomaa et al., 2021; Moudgil and Venkatesha, 2022). Complementary in silico analyses predicted frankincense diterpenoids and triterpenoids to target IFN-γ and associated JAK/STAT components, further supporting the plausibility of BA–IFN pathway interactions (Halim et al., 2020). Nevertheless, not all reports are consistent: in certain macrophage models, BA failed to suppress IFN-γ–induced iNOS expression (Henkel et al., 2012), suggesting that modulation of interferon signaling may be context-dependent.
3.9 Structure-informed and computational insights into BA–target interactions
While extensive experimental studies have delineated the multiple signaling pathways regulated by boswellic acids, the question remains as to how these metabolites can engage such a wide array of molecular targets. Recent structural and computational investigations provide additional insights into this issue by examining their binding modes and dynamic interactions with inflammation-related proteins.
Recent computational and structural studies have started to rationalize how boswellic acids (BAs) engage multiple nodes in inflammatory pathways. For 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX), Gaussian-accelerated MD (GaMD) combined with Markov state models (MSMs) captured stable AKBA-bound conformers and inhibitor transit routes, indicating a non-substrate pocket consistent with historical pharmacology (Liu et al., 2024). In parallel, MD simulations on AKBA derivatives reported persistent hydrogen-bond/hydrophobic networks and low RMSD/Rg fluctuations that align with their experimental inhibition trends, supporting a structure–activity rationale at 5-LOX (Bolbolian et al., 2020). At the enzyme level, natural-product structural work on 5-LOX highlights an exploitable allosteric region that can underlie isoform-selective inhibition—a logic that coheres with AKBA’s non-redox, non-competitive behavior (Gilbert et al., 2020). Classic biochemical evidence further anchors this model: AKBA directly targets 5-LOX at a pentacyclic-triterpene-selective site distinct from the arachidonate pocket, and photoaffinity labeling maps a regulatory site whose occupancy is modulated by triterpenes rather than competitive 5-LOX blockers (Safayhi et al., 1995; Sailer et al., 1998).
At the signaling level, an in silico focused analysis in psoriasis indicates frankincense diterpenoids/triterpenoids can engage cytokine hubs (TNF-α, IL-17/-13/-23/-36γ) and kinases (JAK1/2/3, MAPK2), offering a systems-level view that complements target-centric docking/MD (Halim et al., 2020). Meanwhile, matrix-facing evidence shows BAs dock to collagenase and elastase with supportive in-vitro inhibition, connecting BA chemistry to extracellular-matrix remodeling relevant to inflammatory skin biology (Hourfane et al., 2022). Finally, in osteoarthritic joint cells, β-BA integrates in silico predictions with proteomic/transcriptomic validation to suppress TLR4/IL-1R–driven innate responses and downstream NF-κB/MAPK axes, exemplifying a disease-context pipeline from computational prioritization to wet-lab confirmation (Franco-Trepat et al., 2023). In summary, structural and computational studies provide a mechanistic basis for the diverse anti-inflammatory actions of boswellic acids, while also highlighting open questions that warrant further biochemical validation.
Collectively, pharmacological evidence for boswellic acids has been derived from both in vitro systems (e.g., RAW264.7 macrophages, human PBMCs, microglia; 1–50 μM) and in vivo rodent models (25–200 mg/kg oral extracts for 1–4 weeks), typically with indomethacin or dexamethasone as positive controls. While these studies consistently demonstrate inhibition of NF-κB, NLRP3, and TLR signaling, variability in assay design, extract type, and duration underscores the importance of careful interpretation and the need for standardized clinical studies.
4 Anti-inflammatory effects of boswellic acids: evidence from experimental and clinical studies
In recent decades, both preclinical and clinical research on boswellic acids (BAs) has expanded substantially, driven by their potent anti-inflammatory potential. Numerous studies have explored the effects of BAs using a wide range of experimental systems—from cell-based assays to rodent disease models—alongside a growing number of clinical trials in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions. These studies have collectively advanced our understanding of pharmacological actions, mechanisms, and translational promise of BAs. The following sections provide a structured overview of the evidence base, beginning with mechanistic insights from pharmacological experiments.
4.1 Pharmacological study evidence
Due to the long-standing historical use of Boswellia extracts and the well-characterized bioactivity of their major metabolites—boswellic acids (BAs)—extensive pharmacological studies have been conducted to investigate their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. A large body of literature provides mechanistic insights into the effects of boswellic acids through both in vitro and in vivo models.
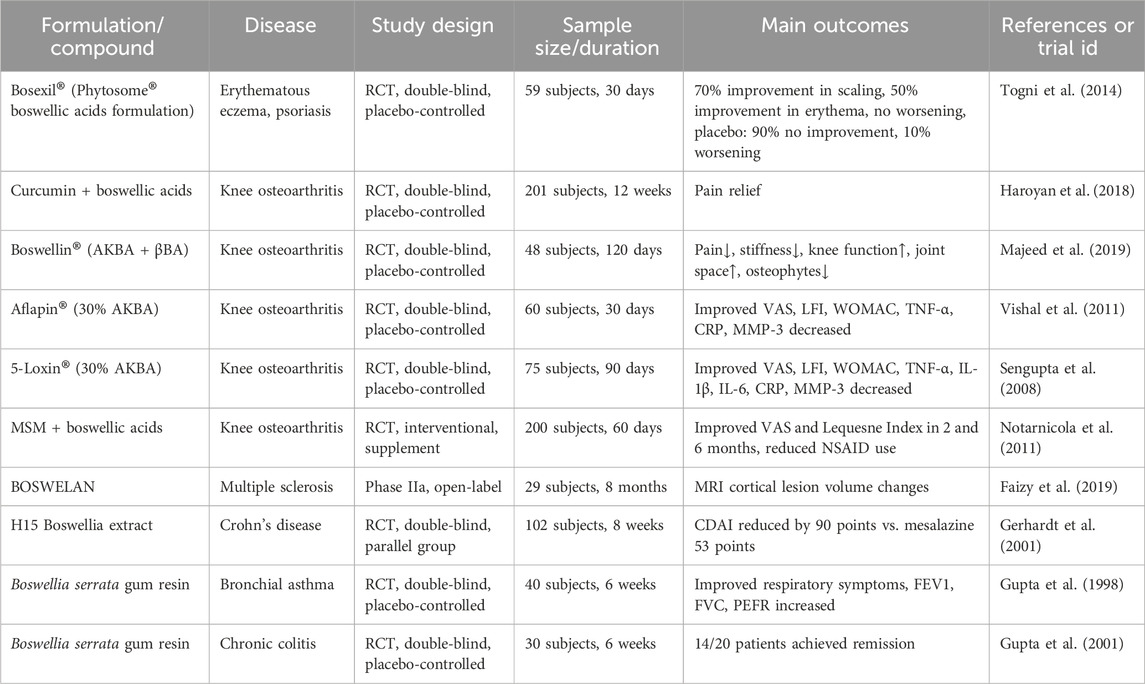
Table 1 summarizes key findings from past research that illustrate the pharmacological activities of BAs and their underlying molecular mechanisms (Table 1).
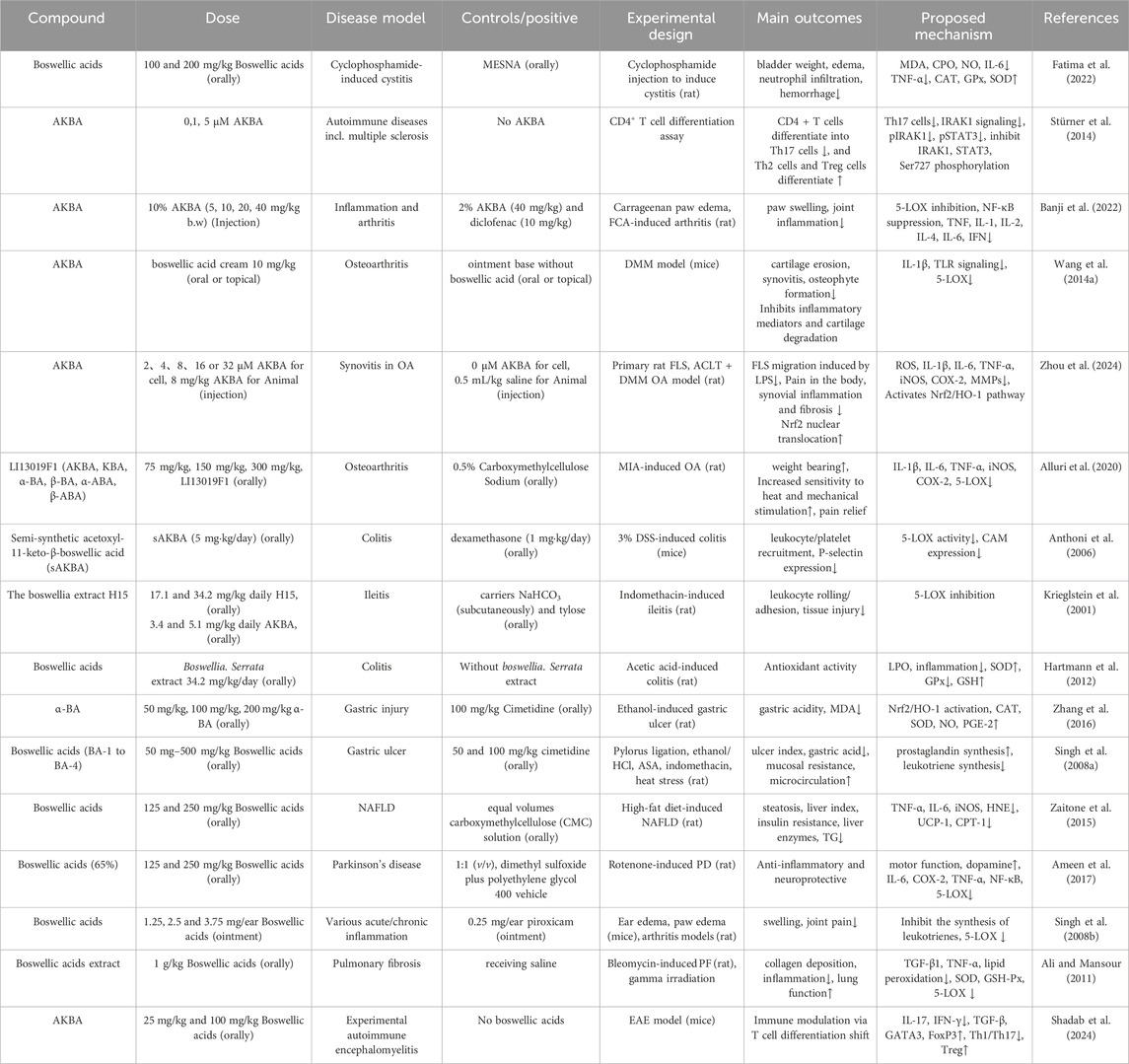
Table 1. Preclinical pharmacological studies of boswellic acids in inflammatory and immune-related diseases.
Upon treatment with either purified boswellic acids or Boswellia-derived mixtures containing BAs, several phenotypic changes have been consistently observed. In the immune system, these include reduced differentiation of inflammatory T effector cells, increased regulatory T cell differentiation, reduced leukocyte infiltration and systemic inflammatory markers, and diminished immune cell infiltration into inflamed tissues (Meyiah et al., 2023; Salama et al., 2023; Ragab et al., 2024). Concurrently, reduction of oxidative stress has also been reported, including decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and lipid peroxidation products such as malondialdehyde (MDA) (Zaitone et al., 2015; Fatima et al., 2022). In vivo studies, notable attenuation of inflammation has been widely observed, including decreases in inflamed tissue weight, reduction of edema, and alleviation of inflammatory manifestations such as cartilage degradation, ulceration, attenuation of inflammation-associated manifestations such as tissue edema, cartilage degradation, and fibrosis. In diet-induced NASH models, BA treatment also mitigated organ degeneration, hepatic inflammation, and metabolic disturbances (Zaitone et al., 2015; Salama et al., 2023).
Based on these findings, we can conceptualize the primary mode of action of boswellic acids in anti-inflammatory effects: phenotypic changes—such as reduced inflammatory tissue edema, decreased oxidative stress, alleviated pain, and reduced inflammatory cell infiltration—are underpinned by molecular mechanisms including activation of antioxidant enzymes, inhibition of pro-inflammatory and hepatic enzymes, modulation of intracellular signaling pathways, and activation/inhibition of gene-regulating transcription factors. Pro-inflammatory cytokines are downregulated, and anti-inflammatory cytokines are upregulated. But most mechanistic data derive from in vitro systems, with activities strongly influenced by material type (purified AKBA/KBA vs. standardized extracts), controls (e.g., indomethacin, dexamethasone), and assay duration, which should be considered when extrapolating to disease relevance. Collectively, the preclinical pharmacological literature strongly supports the anti-inflammatory activity of boswellic acids in vitro and in vivo.
4.2 Clinical evidence and translational prospects
Although boswellic acids have demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities in both in vitro and in vivo studies, their real-world efficacy in humans requires further validation through clinical research. Given the complexity of disease microenvironments and individual variability, it remains uncertain whether boswellic acids possess strong translational potential in clinical settings. Therefore, it is necessary to systematically review and analyze the current clinical research to evaluate the therapeutic prospects and limitations of boswellic acids in the treatment of inflammatory and immune-related diseases. This section primarily focuses on randomized controlled trials (RCTs), which are considered the gold standard for assessing clinical efficacy due to their higher representativeness and methodological rigor.
Boswellic acids and their derivative formulations have shown promising therapeutic effects in various chronic inflammatory conditions. In multiple randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials involving osteoarthritis (OA) patients, several Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae)–derived formulations enriched in boswellic acids—such as Boswel®, Aflapin®, and 5-Loxin®—were found to significantly improve pain scores, joint stiffness, and functional impairment. Some formulations also demonstrated the ability to reduce inflammatory markers (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6, CRP) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) (Sengupta et al., 2008; Vishal et al., 2011; Kizhakkedath, 2013). In dermatological conditions such as eczema and psoriasis, boswellic acid-based treatments were reported to alleviate erythema, scaling, and pruritus with good tolerability (Togni et al., 2014). In patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and chronic colitis, Boswellia extracts significantly improved clinical scores and remission rates, suggesting modulatory effects on intestinal mucosal inflammation (Gerhardt et al., 2001; Gupta et al., 2001). However, some RCTs have shown no statistically significant differences between treatment and placebo groups in patients with Crohn’s disease or collagenous colitis (Madisch et al., 2007; Holtmeier et al., 2011) (Table 2).
Beyond the conditions mentioned above, boswellic acids have also demonstrated neuroprotective potential in central nervous system disorders such as multiple sclerosis (MS), where MRI findings indicated a reduction in cortical lesion progression (Stürner et al., 2018). In respiratory diseases such as bronchial asthma, Boswellia extracts were associated with improvements in pulmonary function and a reduction in acute exacerbations (Gupta et al., 1997). Notably, even in non-typical indications such as kidney stones, a reduction in stone volume was observed following intervention (Al-Marhoon et al., 2023). Some studies have also suggested that combining boswellic acids with other botanicals, such as curcumin, may result in synergistic anti-inflammatory effects (Sethi et al., 2022). Collectively, preclinical and early-phase clinical trials support the therapeutic potential and favorable safety profile of boswellic acids in various inflammatory disorders, though their long-term efficacy and mechanisms of action require further systematic investigation.
At present, clinical research specifically targeting boswellic acids remains limited and relatively underdeveloped. While the focus of this review is on boswellic acids (BAs), most published RCTs have investigated Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae) extracts—such as H15 extract, Boswelan®, or native resin capsules—as the intervention. These extracts often contain a complex mixture of multiple boswellic acids along with various resinous and volatile metabolites. However, the precise content of boswellic acids is frequently not standardized, nor is it specified which particular BA (e.g., AKBA, KBA) is responsible for the observed activity. Many RCTs only refer to “standardized Boswellia extract” without indicating the identity or percentage of active metabolites such as AKBA (typically expected to range from 3% to 10%) (Börner et al., 2021; Majeed et al., 2021). This lack of specificity makes it difficult to attribute observed therapeutic effects to boswellic acids alone, as synergistic contributions from other metabolites cannot be excluded. Only a few studies have employed purified boswellic acid monomers (e.g., AKBA) as the sole active metabolite. Therefore, existing clinical evidence is insufficient to directly validate the standalone clinical efficacy of boswellic acids, leading to a clear disconnect between mechanistic pharmacological studies and clinical applications.
5 Toxicological and safety profile of boswellic acids
In addition to their pharmacological efficacy, the toxicological and safety characteristics of boswellic acids (BAs) must be carefully considered to provide a balanced overview. Both preclinical toxicology data and clinical adverse drug reaction (ADR) profiles are summarized below.
5.1 Preclinical toxicology
Animal studies indicate that Boswellia extracts and isolated boswellic acids have relatively low acute toxicity. Reported oral LD50 values in rodents exceed 2,000 mg/kg, suggesting low acute lethality (Efferth and Oesch, 2022). Subacute and subchronic toxicity studies showed that repeated administration of standardized Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae) extracts (up to 1,000 mg/kg/day) in rats produced no major organ toxicity, although mild hepatic enzyme elevations and gastrointestinal irritation were occasionally observed (Ammon, 2010). Limited animal data, including small-scale supplementation studies in dogs, suggest overall good tolerability, though comprehensive long-term controlled toxicity studies in canines are lacking (Siddiqui, 2011).
5.2 Clinical safety and adverse events
In randomized controlled trials of osteoarthritis patients, standardized Boswellia extracts such as 5-Loxin® and Aflapin® were generally safe, with most adverse events being mild gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain) and occurring at rates comparable to placebo (Sengupta et al., 2008; Vishal et al., 2011; Kizhakkedath, 2013). Dermatological applications in eczema and psoriasis reported good tolerability, with occasional mild erythema or pruritus, and no serious events (Togni et al., 2014). Trials in inflammatory bowel disease indicated that Boswellia extracts were not associated with severe ADRs, although mild gastrointestinal complaints were again the most common side effects (Gerhardt et al., 2001; Holtmeier et al., 2011). In patients with multiple sclerosis, Boswellia supplementation was well tolerated with no serious adverse events or clinical evidence of hepatic or renal toxicity (Stürner et al., 2018).
Overall, boswellic acids exhibit a favorable toxicological and safety profile across preclinical and clinical studies. Acute and sub chronic toxicity appear low, and adverse reactions are typically limited to mild gastrointestinal or transient dermatologic effects. Serious toxicity has not been reported to date, though comprehensive long-term and reproductive or genotoxicity studies remain limited.
6 Pharmacokinetic and metabolic challenges of boswellic acids
Among the various types of boswellic acids (BAs), 11-keto-β-boswellic acid (KBA) and 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA) are considered the most pharmacologically active (Du et al., 2015). However, their absorption in the human body is influenced by multiple molecular and physiological factors. One of the key elements affecting the absorption of BAs is their solubility, which is closely related to their chemical nature (Cui et al., 2024). In the digestive system, substances that are soluble in aqueous environments have a higher likelihood of being absorbed because they can dissolve in gastrointestinal fluids. However, boswellic acids are inherently steroid-like molecules with lipophilic properties, resulting in low aqueous solubility and poor dissolution in intestinal fluids (Du et al., 2015). According to a study by Phillip Krüger, the Caco-2 apparent permeability coefficient (P_app) of KBA at 37 °C was determined to be 1.69 × 10−6 cm/s. Under the same experimental conditions, AKBA exhibited a permeability of less than 0.05%, and it was not possible to determine a precise P_app value for AKBA (Krüger et al., 2008). These findings suggest that KBA possesses moderate permeability, whereas AKBA exhibits poor permeability.
In addition to solubility and permeability, the oral bioavailability of these metabolites also depends significantly on their distribution and metabolic characteristics (Hill et al., 2017).
6.1 Tissue distribution and target organ accumulation of boswellic acids
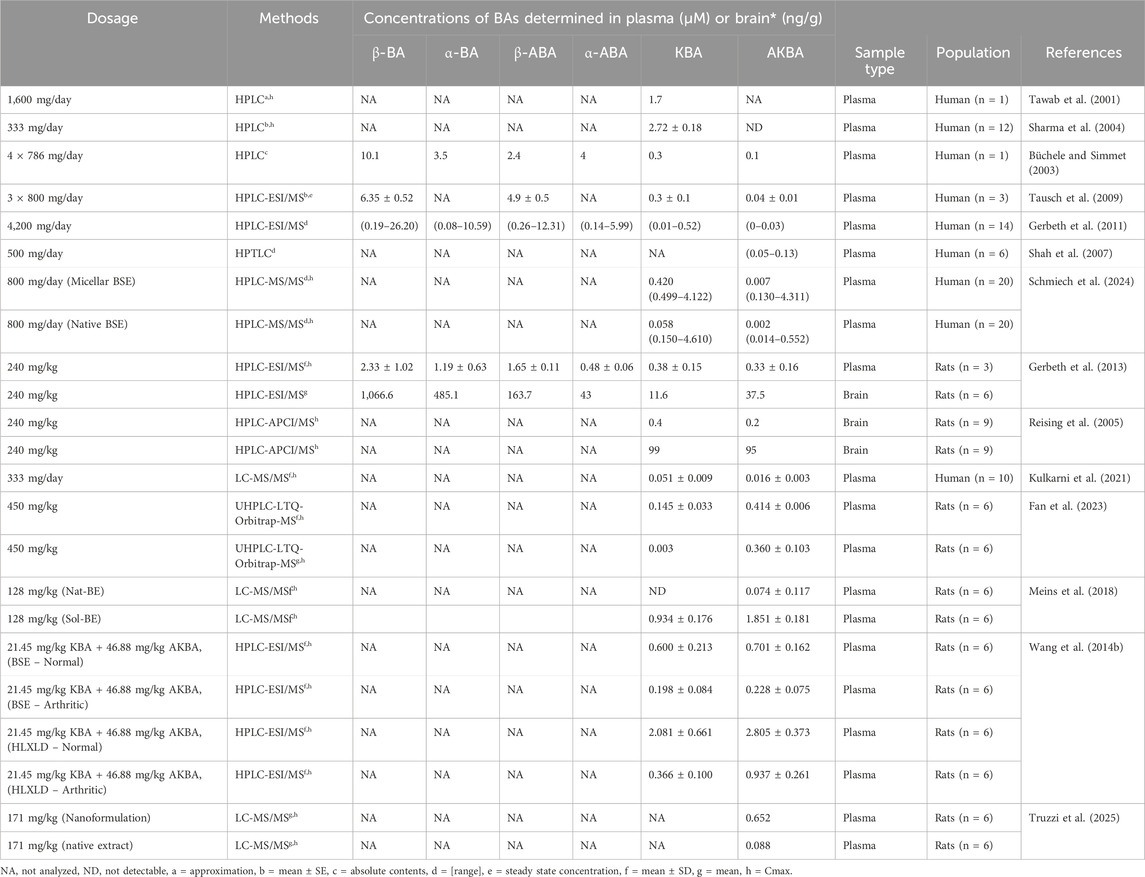
Boswellic acids (BAs)—primarily 11-keto-β-boswellic acid (KBA) and 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA)—exhibit a distinct in vivo distribution profile that is influenced by their lipophilic nature and inherent challenges with oral bioavailability (Table 3).
In animal studies, following a single oral dose of Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae) extract, both KBA and AKBA have been detected in plasma as well as in brain tissue. For example, in a rat model reported by Reising et al. (2005), KBA reached concentrations of approximately 99 ng/g in brain tissue (which corresponds to roughly 9.9 ng/mL when expressed in brain homogenate), while AKBA was found at about 95 ng/g. In these animals, plasma levels were considerably higher, with KBA generally ranging between 150 and 200 ng/mL and AKBA present at somewhat lower levels (Reising et al., 2005).
Human studies using solid lipid formulation designed to enhance the bioavailability of Bas. In the study of Kulkarni et al. (2021), peak plasma concentrations were reached at about 1.5 h for AKBA and 2.3 h for KBA, with C_max values of approximately 8.04 ng/mL for AKBA and 23.83 ng/mL for KBA. The elimination half-life was notably longer for AKBA (around 6.8 h) compared to KBA (approximately 2.45 h). These relatively low plasma levels reflect both species differences and formulation strategies aimed at improving bioavailability (Kulkarni et al., 2021).
Furthermore, a study by Fan et al. (2023) in rats demonstrated that when Boswellia extract is administered in combination with myrrh (a compatibility that is often used in traditional formulations), the plasma C_max values of both metabolites are modulated. In that setting, AKBA reached a plasma C_max of around 212 ng/mL before compatibility, with both AKBA and KBA levels declining upon co-administration with myrrh (Fan et al., 2023).
Together, these findings highlight that although BAs have inherently low oral bioavailability, they do distribute into key compartments, including the central nervous system, as evidenced by their measurable concentrations in brain tissue at the nanogram-per-gram level—and circulate systemically at concentrations that may be pharmacologically relevant for anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anticancer effects. Notably, the lipophilic nature of boswellic acids enables their accumulation in tissues such as the liver and brain, despite their overall low plasma concentrations. Reising et al. (2005) detected KBA and AKBA in rat brain tissue at levels up to ∼100 ng/g, following oral administration of Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae) extract (Reising et al., 2005). These tissue distributions are critical for the therapeutic potential of boswellic acids in conditions such as neuroinflammation and arthritis.
6.2 Metabolic pathways and biotransformation of boswellic acids
According to the study conducted by Philipp Krüger et al., KBA (11-keto-β-boswellic acid) undergoes extensive phase I metabolism in both rat liver microsomes, hepatocytes, and human liver microsomes. The predominant metabolic pathway involves oxidation to hydroxylated metabolites, which appears to be the main route of KBA biotransformation in vivo. In parallel, the study reported a similar metabolic profile of KBA in in vitro experiments using rat plasma and liver tissue, indicating good correlation between in vitro and in vivo metabolic behavior (Krüger et al., 2008).
Importantly, the study did not detect any metabolites of AKBA (3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid) in vivo and thus refuted the previously assumed hypothesis that AKBA is deacetylated to form KBA in vivo. This finding suggests that AKBA may exhibit poor bioavailability and metabolic stability under physiological conditions, highlighting the necessity for further investigation into its pharmacokinetics and delivery strategies (Krüger et al., 2008). In contrast to the findings of Philipp Krüger et al., a study published by Cui et al. (2016) provided more detailed insight into the phase I and phase II metabolism of both AKBA (3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid) and KBA (11-keto-β-boswellic acid) in human liver microsomes (HLM) and human intestinal microsomes (HIM). This study demonstrated that deacetylation is the initial metabolic step for AKBA, primarily catalyzed by carboxylesterase 2 (CE2). Subsequently, KBA becomes the predominant form found in human plasma (Cui et al., 2016).
According to Cui et al. (2016), KBA is metabolized via CYP-mediated oxidation in human microsomes, with CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7 all capable of catalyzing hydroxylation of KBA; among these, CYP3A4 plays a predominant role in forming mono-hydroxylated KBA metabolites (e.g. 21- and 20-mono-hydroxylated KBA) in human liver preparations (Cui et al., 2016). To reconcile the discrepancies with Krüger’s findings, Cui et al. proposed that AKBA deacetylation may be a human-specific reaction, and not observable in rodents or other species. This hypothesis is supported by their cross-species comparative analysis, which revealed significant interspecies differences in both the presence of deacetylation activity and the distribution of hydroxylated KBA metabolites. Specifically, the deacetylation of AKBA was only observed in human tissues, while it was absent in six other animal species studied. This suggests that AKBA metabolism exhibits pronounced species selectivity and highlights the limitations of extrapolating metabolic profiles from animal models to humans (Cui et al., 2016).
To date, the metabolic studies on boswellic acids have primarily focused on Phase I biotransformation. According to Krüger et al. (2008), KBA (m/z 469.4 [M−H] -, t = 11.3 min) undergoes extensive oxidation, resulting in at least three monohydroxylated metabolites (m/z +16), six dihydroxylated metabolites (m/z +32), and two monohydroxylated-dehydrogenated metabolites (m/z +14). Similarly, AKBA (m/z 511.4 [M−H] -, t = 12.2 min) was shown to produce at least three monohydroxylated metabolites (Krüger et al., 2008). Further structural elucidation by Cui et al. (2016) using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) confirmed the identity of four major KBA metabolites: (1) 21-β-hydroxy-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (2) 20-β-hydroxy-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (3) 16-β-hydroxy-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (4) 30-hydroxy-11-keto-β-boswellic acid These findings suggest that hydroxylation at multiple positions is the dominant metabolic pathway for KBA, reflecting a diverse pattern of CYP-mediated oxidation (Cui et al., 2016).
In terms of metabolic stability, data from Sharma and Jana (2020) demonstrated that boswellic acids exhibit limited stability in simulated gastric and intestinal fluids, as well as in intestinal S9 fractions, raising concerns about their oral bioavailability (Sharma and Jana, 2020). Importantly, recent pharmacokinetic profiling indicates that neither AKBA nor KBA undergo Phase II conjugation reactions, such as glucuronidation or sulfation, as evidenced by the study of Rajabian et al. (2023). This absence of Phase II metabolism further emphasizes the predominant role of oxidative Phase I pathways in boswellic acid clearance (Rajabian et al., 2023).
7 Strategies to enhance the bioavailability of boswellic acids
Numerous pre-clinical pharmacological and clinical studies have demonstrated that boswellic acids (BAs) possess significant anti-inflammatory activity. However, the strong hydrophobicity and poor water solubility of BAs result in extremely low oral absorption (Sharma et al., 2010). Pharmacokinetic studies have shown that the systemic absorption of BAs—particularly KBA and AKBA—is very limited in both animals and humans (Hüsch et al., 2013).
Several Boswellia-derived formulations are already available on the market or have been tested in clinical settings. These include Casperome™ (Phytosome® technology), which improves BA solubility and systemic absorption (Hüsch et al., 2013), an AKBA-enriched extract evaluated in osteoarthritis trials and shown to be safe and effective in reducing joint pain (Sengupta et al., 2008), a next-generation extract with enhanced bioavailability and anti-inflammatory efficacy (Vishal et al., 2011) and a topical formulation used in dermatological conditions such as eczema and psoriasis (Togni et al., 2014).
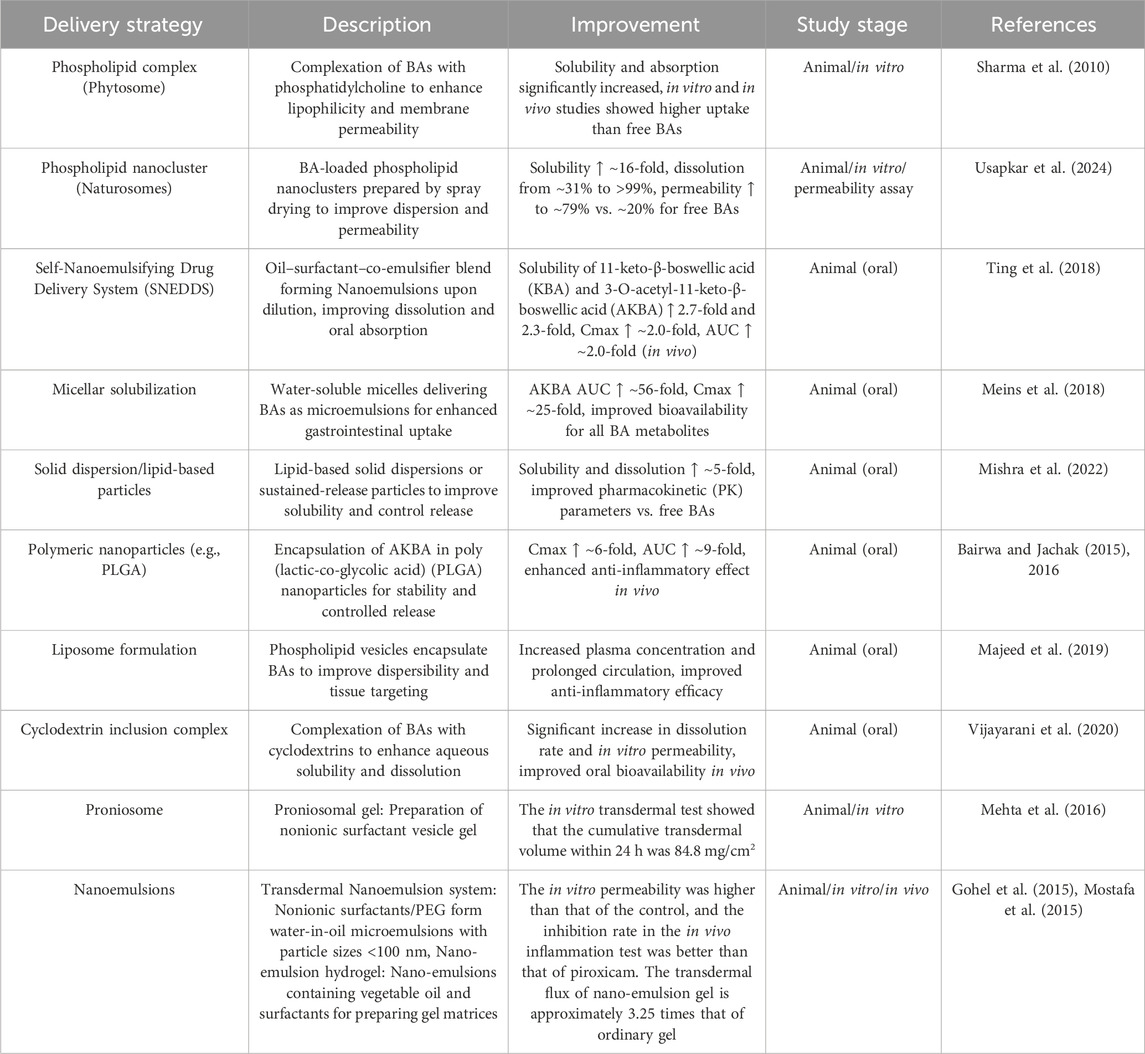
Despite these advances, important limitations remain. Most current formulations rely on oral or topical routes, and although they improve absorption compared to raw extracts, the overall bioavailability of boswellic acids is still relatively low. In addition, most clinical studies have been of short duration and modest sample size, and long-term safety or pharmacokinetic consistency data are lacking. These constraints highlight that while current formulations provide proof-of-concept for clinical use, further optimization is required. Given the limited oral bioavailability of BAs observed in clinical studies, optimization strategies have gained increasing attention. To address these challenges, various drug delivery strategies and formulation technologies have been developed to enhance the solubility, permeability, and bioavailability of BAs. This section summarizes the major improvement approaches and the supporting experimental evidence (Table 4).
7.1 Anoparticle carriers (polymeric nanoparticles)
Polymeric nanoparticles such as PLGA significantly improve the oral absorption of BAs. In a study by Bairwa et al., PLGA nanoparticles loaded with KBA increased its oral bioavailability by approximately 7-fold (Bairwa and Jachak, 2016); In a subsequent study, AKBA-loaded PLGA nanoparticles enhanced its C_max by about 6-fold and AUC by 9-fold. These nanoparticles also showed enhanced anti-inflammatory activity in a rat model of CAR-induced inflammation (Bairwa and Jachak, 2015). Similarly, natural polymer-based nanoparticles such as chit osan have also been used to deliver BAs, improving their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in the nervous system (Bairwa and Jachak, 2015; Ding et al., 2016). Overall, polymeric nanoparticles markedly increase drug concentrations and efficacy, although studies remain at the animal experimental stage.
7.2 Solid dispersions
Solid dispersions improve BA solubility and dissolution rate by co-melting or co-dissolving BAs with hydrophilic polymers. A study showed that solid dispersions of BAs prepared with polyethylene glycol PXM 188 and 407 at ratios of 1:2 (PXM188) and 1:1 (PXM407) demonstrated optimal performance in saturation solubility and in vitro release studies (Tambe et al., 2018). This system significantly enhances the water solubility and dissolution of BAs and offers a simple and practical oral delivery route. However, it currently lacks vivo absorption data.
7.3 Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS/SNES)
SNEDDS enhances BA solubilization by spontaneously forming nanoemulsions from oil and surfactants. According to Ting et al., the SNES formulation increased the aqueous solubility of KBA and AKBA by approximately 2.7-fold and 2.3-fold, respectively. In rabbit pharmacokinetic studies, the formulation improved the bioavailability of KBA and AKBA by about 2.2-fold and 2.0-fold compared to standard oil suspensions (Ting et al., 2018).These findings indicate that SNEDDS can stabilize BA particles and enhance GI absorption, demonstrating promising results for future clinical application.
7.4 Mplexes/phytosomes (phytosome)
Complexing BAs with phospholipids markedly improves hydrophilicity and membrane permeability. Hüsch et al. showed that formulating standardized Boswellia extract with soybean phospholipids into Casperome™ increased the AUC of KBA by approximately 7-fold and β-BA by 3-fold in mice. Notably, Casperome™ elevated KBA and AKBA concentrations in brain tissue by nearly 35-fold (Hüsch et al., 2013). Similarly, the novel “naturosome” formulation increased BA water solubility by 16-fold, in vitro cumulative release from ∼31% to >99%, and permeability from ∼20% to ∼79% (Usapkar et al., 2024). Early in vitro models have also confirmed that BA–phosphatidylcholine complexes achieve better intestinal absorption compared to free BA (Sharma et al., 2010). These results suggest that phospholipid complexes significantly improve BA absorption and distribution, with some formulations already moving toward clinical development (Hüsch et al., 2013).
7.5 Liposomes and elastic vesicles (spanlastics, proniosomes)
For topical delivery, lipid vesicles can enhance skin permeation. Badria et al. reported that a Spanlastic nanovesicle formulation of AKBA (based on Span60/Tween80) significantly increased transdermal delivery in vitro compared to free drug (Badria and Mazyed, 2020). Similarly, Mehta et al. developed a proniosomal gel (≈708 nm, 98.5% encapsulation efficiency) with 24-h cumulative skin penetration reaching 84.8 mg/cm2. It’s in vivo anti-inflammatory effect was superior to that of commercial formulations (Mehta et al., 2016). These lipid-based systems improve BA solubilization and surface properties, thus enhancing local absorption and sustained release. Most current studies are limited to in vitro and animal models, and further preclinical data are needed.
7.6 Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes
Cyclodextrins (CDs) form inclusion complexes with hydrophobic drugs to improve water solubility. Complexes of BA with β-CD or HP-β-CD at molar ratios of 1:1 and 1:2 showed significantly higher release rates in simulated gastric (pH 1.2) and intestinal fluids (pH 6.8) at a 1:2 ratio (Tambe et al., 2018). These results suggest that CD-based carriers can enhance BA dissolution in aqueous media, though in vivo pharmacokinetic data are currently lacking.
7.7 PEGylation and polymeric carriers
PEGylation of BAs or their covalent linkage to polymers improves solubility and allows for controlled release. A recent report described BA-PEG nanoparticles (∼253 nm) with high stability and spherical morphology. Drug release studies confirmed a sustained-release profile (Thakur and Kiranmai, 2024). In addition, various polymeric carriers (e.g., chitosan, acrylate copolymers, hydrogels) have been explored for BA delivery, offering prolonged release and targeting capabilities. These studies remain preliminary, focusing mainly on physicochemical evaluation and in vitro release; further investigation is needed to confirm enhanced bioavailability and efficacy.
7.7.1 Emerging nanotechnologies
Beyond the aforementioned systems, cutting-edge nanotechnology strategies—such as polymeric micelles, metal nanoparticles, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), and nanogels—have also been applied to BA delivery, reportedly improving oral bioavailability and pharmacodynamic outcomes (Nakhaei et al., 2023). For instance, BAs have been formulated into zinc oxide nanoparticles or incorporated into BA–MOF complexes, both enhancing release and absorption. Collectively, these advanced techniques show great promise at the preclinical level and offer diverse pathways for future application.
7.8 Impact of optimization strategies on absorption and anti-inflammatory efficacy
The above strategies have demonstrated significant improvements in both in vitro and in vivo models. Multiple studies report that optimized formulations significantly enhance water solubility, dissolution rate, membrane permeability, and plasma concentrations of BAs.For instance, solid dispersions and phospholipid complexes have increased BA solubility and in vitro release rates by several folds (Tambe et al., 2018; Usapkar et al., 2024). PLGA nanoparticles increased the C_max of AKBA by about 6-fold and AUC by 9-fold (Bairwa and Jachak, 2015). SNEDDS formulations increased KBA/AKBA AUC by approximately 2-fold (Ting et al., 2018); Casperome™ increased KBA AUC by 7-fold (Hüsch et al., 2013). In terms of pharmacodynamics, Nanoformulation generally exhibited stronger therapeutic effects in animal models of inflammation. For example, AKBA-loaded nanoparticles showed significantly greater inhibition in the rat paw edema test compared to free AKBA (Bairwa and Jachak, 2015). BA-Phytosome formulations significantly alleviated joint edema and inflammation in murine arthritis models (Usapkar et al., 2024). These findings demonstrate that enhanced absorption and systemic drug exposure are usually associated with increased anti-inflammatory efficacy (Figure 3).
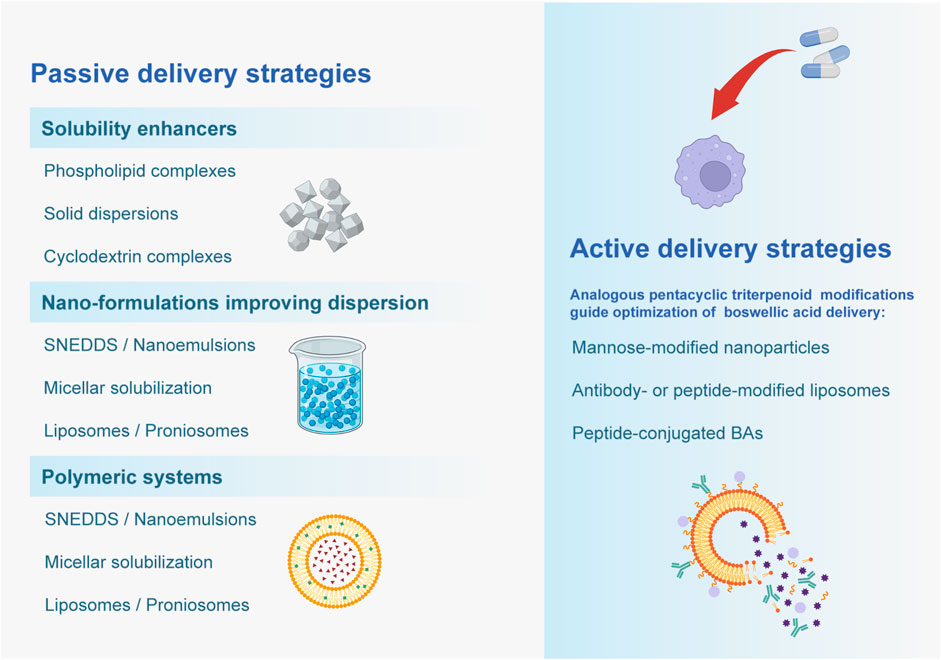
Figure 3. Passive and active delivery strategies for improving Boswellic acid delivery are depicted.
Although most current formulations of boswellic acids (BAs) focus on passive strategies that improve solubility, dissolution, or absorption, little attention has been paid to active targeting approaches. Active targeting typically involves surface modification of nanocarriers with ligands (e.g., mannose, antibodies, or peptides) to enhance selective uptake by immune cells such as macrophages or inflamed endothelial cells (Lee et al., 2021; Fei et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2023). Although direct evidence for ligand-targeted nanocarrier delivery of boswellic acids is lacking, analogous nanoparticle systems with other triterpenoids and phytochemicals—such as ursolic acid and asiatic acid loaded into SLNs or nanoparticles—have shown enhanced uptake and anti-inflammatory or neuroprotective effects (Ganesan et al., 2018; Miatmoko et al., 2021; Islamie et al., 2023). These findings support the possibility that ligand-based targeting of BAs may similarly improve their pharmacological performance.” Incorporating such ligand-targeted delivery strategies into BA nanocarrier design could therefore represent a promising future direction to maximize their pharmacological efficacy.
8 Discussion
Boswellic acids (BAs), the major active metabolites of frankincense resin, have shown promising therapeutic potential in inflammatory diseases, as demonstrated by numerous in vitro and animal studies (Poeckel and Werz, 2006; Ammon, 2010; Ragab et al., 2024). Current research has extensively reported that BAs exert anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects primarily through the inhibition of key signaling pathways and enzymes, such as NF-κB, 5-LOX, COX-2, and iNOS(Werz and Steinhilber, 2005; Abdel-Tawab, 2021; Efferth and Oesch, 2022). In addition, BAs downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and upregulate anti-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-10), exhibiting consistent biological effects across various inflammatory models (Gupta et al., 2001; Ragab et al., 2024).
Despite the substantial progress in preclinical studies, clinical research has not kept pace, particularly in the form of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) utilizing purified BAs such as AKBA and KBA. Most existing clinical studies have employed Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae) extract (BSE) as the intervention, which contains a complex mixture of metabolites with undefined BA content (Börner et al., 2021; Majeed et al., 2021). This complexity makes it difficult to attribute therapeutic effects specifically to BAs, thereby limiting the translation of mechanistic findings to human applications. While some RCTs have shown that BSE may provide clinical benefits for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and asthma, these studies are often limited by small sample sizes, variable control settings, short follow-up periods, and a lack of biomarker validation—rendering the evidence insufficient for firm conclusions (Gupta et al., 1997; Gerhardt et al., 2001; Holtmeier et al., 2011; Stürner et al., 2018).
One of the major barriers to the clinical efficacy of BAs is their poor water solubility and low intestinal absorption. Pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that both AKBA and KBA exhibit very low oral C_max and AUC values, with plasma levels sometimes undetectable in certain individuals (Hüsch et al., 2013; Kulkarni et al., 2021). Furthermore, their high plasma protein binding significantly reduces the concentration of free drug available for therapeutic action (Krüger et al., 2008). Additional factors such as intestinal efflux mechanisms (e.g., P-glycoprotein) and hepatic metabolism (e.g., CYP3A4) further contribute to their rapid clearance (Cui et al., 2016). These combined challenges make it difficult for orally administered BAs to reach effective systemic concentrations, thereby limiting their pharmacological impact in vivo.
To overcome these bioavailability and distribution challenges, a variety of delivery systems have been developed, including Phytosome, PLGA nanoparticles, solid dispersions, self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS), proniosomes, microemulsions/nanoemulsions, and spanlastics for topical use (Sharma et al., 2010; Hüsch et al., 2013; Bairwa and Jachak, 2015; Mehta et al., 2016; Tambe et al., 2018; Ting et al., 2018; Badria and Mazyed, 2020). While these systems have shown marked improvements in pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy in vitro and in animal models, most remain at the experimental stage. Issues such as large-scale production, formulation stability, and clinical safety evaluation have yet to be fully addressed. Additionally, there is a lack of comparative studies among these delivery platforms, and indications for specific diseases remain to be clarified (Usapkar et al., 2024).
At present, structural modifications of BAs have been primarily aimed at enhancing their pharmacological activity rather than improving their in vivo pharmacokinetic profile. Few studies have investigated chemical modifications designed specifically to optimize the distribution and metabolism of BAs in the human body. This represents a major gap that should be addressed in future research (Csuk et al., 2015; Li et al., 2017; Huang et al., 2018).
It is also important to consider the species-specific differences in BA metabolism. For example, AKBA undergoes deacetylation to KBA in humans, a pathway not observed in rats. In humans, KBA is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4-mediated hydroxylation, while rats possess a distinct enzymatic profile (Krüger et al., 2008; Cui et al., 2016). This discrepancy explains why rodent studies often fail to detect AKBA-derived metabolites, whereas human pharmacokinetic trials report measurable KBA levels following AKBA administration (Reising et al., 2005; Kulkarni et al., 2021).
Such differences indicate that animal models may underestimate the contribution of AKBA metabolism to systemic activity, leading to potential misinterpretation of translational relevance. More importantly, many pharmacological studies still provide insufficient methodological details—such as dose ranges, minimal active concentrations, or the nature of controls—making it difficult to evaluate the validity of reported effects.
Together, these challenges highlight the need for greater reliance on human-relevant models and more rigorous reporting standards to ensure reproducibility and to bridge the gap between preclinical findings and clinical translation.
The Future studies should emphasize the use of humanized liver microsomes, organoids, or integrated gut–liver models to better simulate human metabolic dynamics and improve translational relevance.
In recent years, the gut microbiota has emerged as a major research focus in inflammation and immunity, making it important to consider in the context of boswellic acids (BAs). Although direct evidence remains limited, one study demonstrated that dietary supplementation with Indian frankincense [Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr. (Burseraceae)] resin not only alleviated allergic pulmonary inflammation but also significantly altered gut microbial composition (Suther et al., 2022). These findings suggest that modulation of the gut microbiota could represent an indirect pathway by which BAs exert immunoregulatory effects. Further work integrating microbiome profiling and mechanistic immunology will be essential to clarify this connection.
Moreover, tissue distribution studies have observed accumulation of BAs in the brain and liver (Hüsch et al., 2013). Based on these findings, there has been a growing interest in the application of BAs, particularly AKBA, in central nervous system disorders (Ding et al., 2014; Gong et al., 2022). The ability of BAs to cross the blood–brain barrier and reach effective concentrations in brain tissue has been associated with neuroprotective effects in various neuroinflammation-related models. However, research exploring the hepatic effects of BAs remains limited. Their potential protective roles in liver injury, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and hepatic fibrosis warrant further pharmacological and clinical investigation.
Collectively, current evidence highlights the versatile pharmacological potential of boswellic acids but also underscores persistent challenges related to bioavailability, tissue distribution, and clinical translation. Future investigations should focus on long-term pharmacokinetic profiling, targeted delivery strategies, and large-scale clinical trials to fully elucidate the therapeutic value of these natural triterpenoids.
Author contributions
CP: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. BG: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision. XS: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. XY: Resources, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Key Research and Development Project of Hainan Province, China, Project No. ZDYF2024XDNY159, and the International Cooperation Project of Hainan Key Research and Development Program, Research on the Investigation, Collection, Preservation, Excavation and Utilization of Traditional Imported Southern Medicine Germplasm Resources, Project No. GHYF2024018, and Hainan Province Excellent Talent Team Project Name: The Second Batch of Hainan Province Excellent Talent Team Construction, Project No. HNYT20240003.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel-Tawab, M. (2021). Considerations to be taken when carrying out medicinal plant research-what we learn from an insight into the IC(50) values, bioavailability and clinical efficacy of exemplary anti-inflammatory herbal components. Pharm. (Basel) 14 (5), 437. doi:10.3390/ph14050437
Al-Marhoon, M. S., Al-Harrasi, A., Siddiqui, K., Ashique, M., Ali, H., and Ali, B. H. (2023). Effects of frankincense on experimentally induced renal stones in rats. BJUI Compass 4 (4), 437–445. doi:10.1002/bco2.227
Alamgeer, A., Hasan, U. H., Uttra, A. M., Qasim, S., Ikram, J., Saleem, M., et al. (2020). Phytochemicals targeting matrix metalloproteinases regulating tissue degradation in inflammation and rheumatoid arthritis. Phytomedicine 66, 153134. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153134
Ali, E. N., and Mansour, S. Z. (2011). Boswellic acids extract attenuates pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin and oxidative stress from gamma irradiation in rats. Chin. Med. 6, 36. doi:10.1186/1749-8546-6-36
Alluri, V. K., Kundimi, S., Sengupta, K., Golakoti, T., and Kilari, E. K. (2020). An anti-inflammatory composition of Boswellia serrata resin extracts alleviates pain and protects cartilage in monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 7381625. doi:10.1155/2020/7381625
Ameen, A. M., Elkazaz, A. Y., Mohammad, H. M. F., and Barakat, B. M. (2017). Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective activity of boswellic acids in rotenone parkinsonian rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 95 (7), 819–829. doi:10.1139/cjpp-2016-0158
Ammon, H. P. (2010). Modulation of the immune system by Boswellia serrata extracts and boswellic acids. Phytomedicine 17 (11), 862–867. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2010.03.003
Anthoni, C., Laukoetter, M. G., Rijcken, E., Vowinkel, T., Mennigen, R., Muller, S., et al. (2006). Mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory actions of boswellic acid derivatives in experimental colitis. Am. J. Physiology-Gastrointestinal Liver Physiology 290 (6), G1131–G1137. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00562.2005
Badria, F., and Mazyed, E. (2020). Formulation of nanospanlastics as a promising approach for Improiing the Topical Delivery of a Natural Leukotriene Inhibitor (3-Acetyl-11-Keto-β-Boswellic Acid): Statisticas Optimization, in vitroinavitrorization, and ex vivo Permeation Study. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 3697–3721. doi:10.2147/dddt.S265167
Bairwa, K., and Jachak, S. M. (2015). Development and optimisation of 3-Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid loaded poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid-nanoparticles with enhanced oral bioavailability and in-vivo anti-inflammatory activity in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67 (9), 1188–1197. doi:10.1111/jphp.12420
Bairwa, K., and Jachak, S. M. (2016). Nanoparticle formulation of 11-keto-β-boswellic acid (KBA): anti-inflammatory activity and in vivo pharmacokinetics. Pharm. Biol. 54 (12), 2909–2916. doi:10.1080/13880209.2016.1194437
Banji, D., Banji, O. J. F., Rashida, S., Alshahrani, S., and Alqahtani, S. S. (2022). Bioavailability, anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effect of acetyl keto boswellic acid and its combination with methotrexate in an arthritic animal model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 292, 115200. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115200
Barakat, B. M., Ahmed, H. I., Bahr, H. I., and Elbahaie, A. M. (2018). Protective effect of boswellic acids against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity: impact on Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 8296451. doi:10.1155/2018/8296451
Beaulieu, E., and Morand, E. F. (2011). Role of GILZ in immune regulation, glucocorticoid actions and rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 7 (6), 340–348. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2011.59
Bindu, S., Mazumder, S., and Bandyopadhyay, U. (2020). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: a current perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 180, 114147. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114147
Bolbolian, S., Bozorgmehr, M. R., and Morsali, A. (2020). Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid derivatives effects on 5-lipoxygenase: in silico viewpoint. J. Mol. Graph Model 94, 107464. doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2019.107464
Börner, F., Werner, M., Ertelt, J., Meins, J., Abdel-Tawab, M., and Werz, O. (2021). Analysis of boswellic acid contents and related pharmacological activities of frankincense-based remedies that modulate inflammation. Pharm. (Basel) 14 (7), 660. doi:10.3390/ph14070660
Boswellia frereana Birdw (2025). Plants of the world online. Kew Sci. Available online at: http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:127043-1 (Accessed September 9, 2025).
Boswellia papyrifera (Caill.) Hochst (2025). Plants of the world online. Kew Sci. Available online at: http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:127060-1 (Accessed September 9, 2025).
Boswellia sacra Flück (2025). Plants of the world online. Kew Sci. Available online at: http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:127065-1 (Accessed September 9, 2025).
Boswellia serrata Roxb (2025). Plants of the world online. Kew Sci. Available online at: http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:127067-1 (Accessed September 9, 2025).
Büchele, B., and Simmet, T. (2003). Analysis of 12 different pentacyclic triterpenic acids from frankincense in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 795 (2), 355–362. doi:10.1016/s1570-0232(03)00555-5
Büchele, B., Zugmaier, W., and Simmet, T. (2003). Analysis of pentacyclic triterpenic acids from frankincense gum resins and related phytopharmaceuticals by high-performance liquid chromatography. Identification of lupeolic acid, a novel pentacyclic triterpene. J. Chromatogr. B 791 (1-2), 21–30. doi:10.1016/s1570-0232(03)00160-0
Commiphora myrrha (T.Nees) Engl (2025). Plants of the world online. Kew science. Available online at: http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:127741-1 (Accessed September 9, 2025).
Coussens, L. M., and Werb, Z. (2002). Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420 (6917), 860–867. doi:10.1038/nature01322
Csuk, R., Niesen-Barthel, A., Schäfer, R., Barthel, A., and Al-Harrasi, A. (2015). Synthesis and antitumor activity of ring A modified 11-keto-β-boswellic acid derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 92, 700–711. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.01.039
Cuaz-Pérolin, C., Billiet, L., Baugé, E., Copin, C., Scott-Algara, D., Genze, F., et al. (2008). Antiinflammatory and antiatherogenic effects of the NF-kappaB inhibitor acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid in LPS-challenged ApoE-/- mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28 (2), 272–277. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.107.155606
Cui, Y., Tian, X., Ning, J., Wang, C., Yu, Z., Wang, Y., et al. (2016). Metabolic profile of 3-Acetyl-11-Keto-β-Boswellic acid and 11-Keto-β-Boswellic acid in human preparations in vitro, species differences, and bioactivity variation. Aaps J. 18 (5), 1273–1288. doi:10.1208/s12248-016-9945-7
Cui, N., Hu, M., and Khalil, R. A. (2017). Biochemical and biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 147, 1–73. doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.02.005
Cui, N., Li, M., Wang, Y., Meng, Q., Shi, Y., and Ding, Y. (2024). Boswellic acids: a review on its pharmacological properties, molecular mechanism and bioavailability. Tradit. Med. Res. 9 (10), 60. doi:10.53388/TMR20240128002
de Almeida, L. G. N., Thode, H., Eslambolchi, Y., Chopra, S., Young, D., Gill, S., et al. (2022). Matrix metalloproteinases: from molecular mechanisms to physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 74 (3), 712–768. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.121.000349
Dinarello, C. A. (2010). Anti-inflammatory agents: present and future. Cell 140 (6), 935–950. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.043
Ding, Y., Chen, M., Wang, M., Wang, M., Zhang, T., Park, J., et al. (2014). Neuroprotection by Acetyl-11-Keto-β-Boswellic acid, in ischemic brain injury involves the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway. Sci. Rep. 4 (1), 7002. doi:10.1038/srep07002
Ding, Y., Qiao, Y., Wang, M., Zhang, H., Li, L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2016). Enhanced neuroprotection of Acetyl-11-Keto-β-Boswellic acid (AKBA)-Loaded O-Carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Mol. Neurobiol. 53 (6), 3842–3853. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9333-9
Du, Z., Liu, Z., Ning, Z., Liu, Y., Song, Z., Wang, C., et al. (2015). Prospects of boswellic acids as potential pharmaceutics. Planta Med. 81 (4), 259–271. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1396313
Efferth, T., and Oesch, F. (2022). Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities of frankincense: targets, treatments and toxicities. Semin. Cancer Biol. 80, 39–57. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.01.015
Elgazar, A. A., El-Domany, R. A., Eldehna, W. M., and Badria, F. A. (2023). 3-Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid-based hybrids alleviate acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 by the regulation of inflammatory and oxidative stress pathways: an integrated approach. ACS Omega 8 (42), 39490–39510. doi:10.1021/acsomega.3c05247
Eltahir, H. M., Fawzy, M. A., Mohamed, E. M., Alrehany, M. A., Shehata, A. M., and Abouzied, M. M. (2020). Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of Boswellia serrate gum resin in CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity. Exp. Ther. Med. 19 (2), 1313–1321. doi:10.3892/etm.2019.8353
Faizy, T. D., Broocks, G., Thaler, C., Rauch, G., Gebert, P., Stürner, K. H., et al. (2019). Development of cortical lesion volumes on double inversion recovery MR I in patients with relapse-onset multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurology 10, 133. doi:10.3389/fneur.2019.00133
Fan, R. Y., Gao, R. M., Li, J. S., Su, S. L., Shang, E. X., Qian, D. W., et al. (2023). Comparative analysis of pharmacokinetics and metabolites of three main terpenoids before and after compatibility of frankincense and myrrh in rats by UHPLC-MS. Curr. Drug Metab. 24 (6), 434–447. doi:10.2174/1389200224666230808090614
Fatima, M., Anjum, I., Abdullah, A., Abid, S. Z., and Malik, M. N. H. (2022). Boswellic acids, pentacyclic triterpenes, attenuate oxidative stress, and bladder tissue damage in cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. ACS Omega 7 (16), 13697–13703. doi:10.1021/acsomega.1c07292
Fei, Q., Shalosky, E. M., Barnes, R., Shukla, V. C., Xu, S., Ballinger, M. N., et al. (2023). Macrophage-Targeted lipid nanoparticle delivery of microRNA-146a to mitigate hemorrhagic shock-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. ACS Nano 17 (17), 16539–16552. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c01814
Franco-Trepat, E., Alonso-Pérez, A., Guillán-Fresco, M., López-Fagúndez, M., Pazos-Pérez, A., Crespo-Golmar, A., et al. (2023). β boswellic acid blocks articular innate immune responses: an in silico and in vitro approach to traditional medicine. Antioxidants (Basel) 12 (2), 371. doi:10.3390/antiox12020371
Ganesan, P., Ramalingam, P., Karthivashan, G., Ko, Y. T., and Choi, D. K. (2018). Recent developments in solid lipid nanoparticle and surface-modified solid lipid nanoparticle delivery systems for oral delivery of phyto-bioactive compounds in various chronic diseases. Int. J. Nanomedicine 13, 1569–1583. doi:10.2147/ijn.S155593
Gerbeth, K., Meins, J., Kirste, S., Momm, F., Schubert-Zsilavecz, M., and Abdel-Tawab, M. (2011). Determination of major boswellic acids in plasma by high-pressure liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 56 (5), 998–1005. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2011.07.026
Gerbeth, K., Hüsch, J., Fricker, G., Werz, O., Schubert-Zsilavecz, M., and Abdel-Tawab, M. (2013). In vitro metabolism, permeation, and brain availability of six major boswellic acids from Boswellia serrata gum resins. Fitoterapia 84, 99–106. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2012.10.009
Gerhardt, H., Seifert, F., Buvari, P., Vogelsang, H., and Repges, R. (2001). Therapy of active crohn disease with Boswellia serrata extract H 15. Z Gastroenterol. 39 (1), 11–17. doi:10.1055/s-2001-10708
Gilbert, N. C., Gerstmeier, J., Schexnaydre, E. E., Börner, F., Garscha, U., Neau, D. B., et al. (2020). Structural and mechanistic insights into 5-lipoxygenase inhibition by natural products. Nat. Chem. Biol. 16 (7), 783–790. doi:10.1038/s41589-020-0544-7
Gilbert, N. C., Newcomer, M. E., and Werz, O. (2021). Untangling the web of 5-lipoxygenase-derived products from a molecular and structural perspective: the battle between pro- and anti-inflammatory lipid mediators. Biochem. Pharmacol. 193, 114759. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114759
Gohel, M., Soni, T., Hingorani, L., Patel, A., and Patel, N. (2015). Development and optimization of plant extract loaded nanoemulsion mixtures for the treatment of inflammatory disorder. Curr. Res. Drug Discov. 1, 29–38. doi:10.3844/crddsp.2014.29.38
Gomaa, A. A., Mohamed, H. S., Abd-Ellatief, R. B., and Gomaa, M. A. (2021). Boswellic Acids/Boswellia serrata extract as a potential COVID-19 therapeutic agent in the elderly. Inflammopharmacology 29 (4), 1033–1048. doi:10.1007/s10787-021-00841-8
Gong, Y., Jiang, X., Yang, S., Huang, Y., Hong, J., Ma, Y., et al. (2022). The biological activity of 3-O-Acetyl-11-keto-β-Boswellic acid in nervous System diseases. Neuromolecular Med. 24 (4), 374–384. doi:10.1007/s12017-022-08707-0
Guo, H., Callaway, J. B., and Ting, J. P. (2015). Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat. Med. 21 (7), 677–687. doi:10.1038/nm.3893
Gupta, I., Parihar, A., Malhotra, P., Singh, G. B., Lüdtke, R., Safayhi, H., et al. (1997). Effects of Boswellia serrata gum resin in patients with ulcerative colitis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2 (1), 37–43.
Gupta, I., Gupta, V., Parihar, A., Gupta, S., Lüdtke, R., Safayhi, H., et al. (1998). Effects of Boswellia serrata gum resin in patients with bronchial asthma: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, 6-week clinical study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 3 (11), 511–514.
Gupta, I., Parihar, A., Malhotra, P., Gupta, S., Lüdtke, R., Safayhi, H., et al. (2001). Effects of gum resin of Boswellia serrata in patients with chronic colitis. Planta Med. 67 (5), 391–395. doi:10.1055/s-2001-15802
Gupta, P. K., Samarakoon, S. M., Chandola, H. M., and Ravishankar, B. (2011). Clinical evaluation of Boswellia serrata (Shallaki) resin in the management of sandhivata (osteoarthritis). Ayu 32 (4), 478–482. doi:10.4103/0974-8520.96119
Halim, S. A., Khan, A., Csuk, R., Al-Rawahi, A., and Al-Harrasi, A. (2020). Diterpenoids and triterpenoids from frankincense are excellent anti-psoriatic agents: an in silico approach. Front. Chem. 8, 486. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00486
Haroyan, A., Mukuchyan, V., Mkrtchyan, N., Minasyan, N., Gasparyan, S., Sargsyan, A., et al. (2018). Efficacy and safety of curcumin and its combination with boswellic acid in osteoarthritis: a comparative, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 18 (1), 7. doi:10.1186/s12906-017-2062-z
Hartmann, R. M., Morgan Martins, M. I., Tieppo, J., Fillmann, H. S., and Marroni, N. P. (2012). Effect of Boswellia serrata on antioxidant status in an experimental model of colitis rats induced by acetic acid. Dig. Dis. Sci. 57 (8), 2038–2044. doi:10.1007/s10620-012-2134-3
Henkel, A., Kather, N., Mönch, B., Northoff, H., Jauch, J., and Werz, O. (2012). Boswellic acids from frankincense inhibit lipopolysaccharide functionality through direct molecular interference. Biochem. Pharmacol. 83 (1), 115–121. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.09.026
Hill, R., Kenakin, T., and Blackburn, T. (2017). Pharmacology for chemists: drug discovery in context. London: Royal Society of Chemistry. doi:10.1007/s10337-019-03700-5
Hinz, M., and Scheidereit, C. (2014). The IκB kinase complex in NF-κB regulation and beyond. EMBO Rep. 15 (1), 46–61. doi:10.1002/embr.201337983
Holtmeier, W., Zeuzem, S., Preiβ, J., Kruis, W., Böhm, S., Maaser, C., et al. (2011). Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of Boswellia serrata in maintaining remission of crohn's disease: good safety profile but lack of efficacy. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 17 (2), 573–582. doi:10.1002/ibd.21345
Hourfane, S., Mechqoq, H., Errajouani, F., Rocha, J. M., and El Aouad, N. (2022). In vitro and in silico evaluations of Boswellia carterii resin dermocosmetic activities. Cosmetics 9 (6), 131. doi:10.3390/cosmetics9060131
Huang, M., Li, A., Zhao, F., Xie, X., Li, K., Jing, Y., et al. (2018). Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of ring A modified 11-keto-boswellic acid derivatives as Pin1 inhibitors with remarkable anti-prostate cancer activity. Bioorg. and Med. Chem. Lett. 28 (19), 3187–3193. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.08.021
Huang, K., Chen, Y., Liang, K., Xu, X., Jiang, J., Liu, M., et al. (2022). Review of the chemical composition, pharmacological effects, pharmacokinetics, and quality control of Boswellia carterii. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 6627104. doi:10.1155/2022/6627104
Hüsch, J., Bohnet, J., Fricker, G., Skarke, C., Artaria, C., Appendino, G., et al. (2013). Enhanced absorption of boswellic acids by a lecithin delivery form (phytosome(®)) of boswellia extract. Fitoterapia 84, 89–98. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2012.10.002
Hussain, H., Rashan, L., Hassan, U., Abbas, M., Hakkim, F. L., and Green, I. R. (2022). Frankincense diterpenes as a bio-source for drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 17 (5), 513–529. doi:10.1080/17460441.2022.2044782
Islamie, R., Myint, S. L. L., Rojanaratha, T., Ritthidej, G., Wanakhachornkrai, O., Wattanathamsan, O., et al. (2023). Neuroprotective effect of nose-to-brain delivery of asiatic acid in solid lipid nanoparticles and its mechanisms against memory dysfunction induced by amyloid Beta(1-42) in mice. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23 (1), 294. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-04125-2
Jomova, K., Raptova, R., Alomar, S. Y., Alwasel, S. H., Nepovimova, E., Kuca, K., et al. (2023). Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging. Archives Toxicol. 97 (10), 2499–2574. doi:10.1007/s00204-023-03562-9
Khalifa, S. A. M., Kotb, S. M., El-Seedi, S. H., Nahar, L., Sarker, S. D., Guo, Z., et al. (2023). Frankincense of boswellia sacra: traditional and modern applied uses, pharmacological activities, and clinical trials. Industrial Crops Prod. 203, 117106. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.117106
Khan, F., and Rashan, L. (2025). Phytochemical analysis and pharmaceutical applications of monoterpenoids present in the essential oil of Boswellia sacra (omani Luban). Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 3536898. doi:10.1155/adpp/3536898
Kizhakkedath, R. (2013). Clinical evaluation of a formulation containing Curcuma longa and Boswellia serrata extracts in the management of knee osteoarthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 8 (5), 1542–1548. doi:10.3892/mmr.2013.1661
Krieglstein, C. F., Anthoni, C., Rijcken, E. J., Laukötter, M., Spiegel, H. U., Boden, S. E., et al. (2001). Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid, a constituent of a herbal medicine from Boswellia serrata resin, attenuates experimental ileitis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 16 (2), 88–95. doi:10.1007/s003840100292
Krüger, P., Daneshfar, R., Eckert, G. P., Klein, J., Volmer, D. A., Bahr, U., et al. (2008). Metabolism of boswellic acids in vitro and in vivo. Drug Metab. Dispos. 36 (6), 1135–1142. doi:10.1124/dmd.107.018424
Kulkarni, P. D., Damle, N. D., Hingorani, L., Bhaskar, V. H., Ghante, M. R., Patil, A., et al. (2021). Pharmacokinetics of solid lipid Boswellia serrata particles in healthy subjects. Drug Metab. Pers. Ther. 36 (3), 215–221. doi:10.1515/dmpt-2020-0176
Kunnumakkara, A. B., Banik, K., Bordoloi, D., Harsha, C., Sailo, B. L., Padmavathi, G., et al. (2018). Googling the guggul (commiphora and boswellia) for prevention of chronic diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 686–2018. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00686
Lee, N. K., Kim, S. N., and Park, C. G. (2021). Immune cell targeting nanoparticles: a review. Biomater. Res. 25 (1), 44. doi:10.1186/s40824-021-00246-2
Li, T., Fan, P., Ye, Y., Luo, Q., and Lou, H. (2017). Ring A-modified derivatives from the natural triterpene 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid and their cytotoxic activity. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. Former. Curr. Med. Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents 17 (8), 1153–1167. doi:10.2174/1871520616666161207144031
Liang, Y. H., Li, P., Zhao, J. X., Dai, M. K., and Huang, Q. F. (2012). Arsenic trioxide regulates the production and activities of matrix metalloproteinases-1, -2, and -9 in fibroblasts and THP-1. Chin. Med. J. Engl. 125 (24), 4481–4487.
Liao, Y., Wang, J., Guo, C., Bai, M., Ju, B., Ran, Z., et al. (2021). Combination of systems pharmacology and experimental evaluation to explore the mechanism of synergistic action of frankincense-myrrh in the treatment of cerebrovascular diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 796224. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.796224
Lin, H. C., Lin, T. H., Wu, M. Y., Chiu, Y. C., Tang, C. H., Hour, M. J., et al. (2014). 5-Lipoxygenase inhibitors attenuate TNF-α-induced inflammation in human synovial fibroblasts. PLoS One 9 (9), e107890. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107890
Liu, F., and Ng, T. B. (2000). Antioxidative and free radical scavenging activities of selected medicinal herbs. Life Sci. 66 (8), 725–735. doi:10.1016/s0024-3205(99)00643-8
Liu, Y., Wang, K., Cao, F., Gao, N., and Li, W. (2024). Interactions between inhibitors and 5-Lipoxygenase: insights from gaussian accelerated molecular dynamics and markov State models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (15), 8295. doi:10.3390/ijms25158295
Madisch, A., Miehlke, S., Eichele, O., Mrwa, J., Bethke, B., Kuhlisch, E., et al. (2007). Boswellia serrata extract for the treatment of collagenous colitis. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 22, 1445–1451. doi:10.1007/s00384-007-0364-1
Majeed, M., Majeed, S., Narayanan, N. K., and Nagabhushanam, K. (2019). A pilot, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to assess the safety and efficacy of a novel Boswellia serrata extract in the management of osteoarthritis of the knee. Phytother. Res. 33 (5), 1457–1468. doi:10.1002/ptr.6338
Majeed, M., Nagabhushanam, K., Lawrence, L., Nallathambi, R., Thiyagarajan, V., and Mundkur, L. (2021). Boswellia serrata extract containing 30% 3-Acetyl-11-Keto-Boswellic acid attenuates inflammatory mediators and preserves extracellular matrix in collagen-induced arthritis. Front. Physiol. 12, 735247. doi:10.3389/fphys.2021.735247
Mantovani, A., Allavena, P., Sica, A., and Balkwill, F. (2008). Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454 (7203), 436–444. doi:10.1038/nature07205
Medzhitov, R. (2008). Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454 (7203), 428–435. doi:10.1038/nature07201
Mehta, M., Dureja, H., and Garg, M. (2016). Development and optimization of boswellic acid-loaded proniosomal gel. Drug Deliv. 23 (8), 3072–3081. doi:10.3109/10717544.2016.1149744
Meins, J., Behnam, D., and Abdel-Tawab, M. (2018). Enhanced absorption of boswellic acids by a micellar solubilized delivery form of boswellia extract. NFS J. 11, 12–16. doi:10.1016/j.nfs.2018.04.001
Meyiah, A., Shawkat, M. Y., Ur Rehman, N., Al-Harrasi, A., and Elkord, E. (2023). Effect of boswellic acids on T cell proliferation and activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 122, 110668. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110668
Miatmoko, A., Mianing, E. A., Sari, R., and Hendradi, E. (2021). Nanoparticles use for delivering ursolic acid in cancer therapy: a scoping review. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 787226. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.787226
Miran, M., Amirshahrokhi, K., Ajanii, Y., Zadali, R., Rutter, M. W., Enayati, A., et al. (2022). Taxonomical investigation, chemical composition, traditional use in medicine, and pharmacological activities of Boswellia sacra flueck. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 8779676. doi:10.1155/2022/8779676
Mishra, R., Paldewar, S., and Nandgude, T. (2022). Lipid based approach for bioavailability enhancement of Boswellia serrata. JMPACO111 11, 4129–4137. doi:10.55522/jmpas.V11I1.1693
Morgan, M. J., and Liu, Z. G. (2011). Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21 (1), 103–115. doi:10.1038/cr.2010.178
Mostafa, D. M., Ammar, N. M., Basha, M., Hussein, R. A., El Awdan, S., and Awad, G. (2015). Transdermal microemulsions of Boswellia carterii bird: formulation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity. Drug Deliv. 22 (6), 748–756. doi:10.3109/10717544.2014.898347
Moudgil, K. D., and Venkatesha, S. H. (2022). The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of natural products to control autoimmune inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (1), 95. doi:10.3390/ijms24010095
Nadeem, A., Ahmad, S. F., Al-Harbi, N. O., Sarawi, W., Attia, S. M., Alanazi, W. A., et al. (2022). Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid improves clinical symptoms through modulation of Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways in SJL/J mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 107, 108703. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108703
Nakhaei, K., Bagheri-Hosseini, S., Sabbaghzade, N., Behmadi, J., and Boozari, M. (2023). Boswellic acid nanoparticles: promising strategies for increasing therapeutic effects. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 33 (4), 713–723. doi:10.1007/s43450-023-00405-7
Nathan, C., and Ding, A. (2010). Nonresolving inflammation. Cell 140 (6), 871–882. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.029
Newton, K., and Dixit, V. M. (2012). Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4 (3), a006049. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a006049
Nischang, V., Witt, F. M., Börner, F., Gomez, M., Jordan, P. M., and Werz, O. (2023). Frankincense preparation promotes formation of inflammation-resolving lipid mediators by manipulating lipoxygenases in human innate immune cells. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1332628. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1332628
Notarnicola, A., Tafuri, S., Fusaro, L., Moretti, L., Pesce, V., and Moretti, B. (2011). The MESACA study: methylsulfonylmethane and boswellic acids in the treatment of gonarthrosis. Adv. Ther. 28 (10), 894–906. doi:10.1007/s12325-011-0068-3
O'Neill, L. A., Golenbock, D., and Bowie, A. G. (2013). The history of toll-like receptors - redefining innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13 (6), 453–460. doi:10.1038/nri3446
Park, B., Prasad, S., Yadav, V., Sung, B., and Aggarwal, B. B. (2011). Boswellic acid suppresses growth and metastasis of human pancreatic tumors in an orthotopic nude mouse model through modulation of multiple targets. PLOS ONE 6 (10), e26943. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026943
Paul, W. E., and Zhu, J. (2010). How are T(H)2-type immune responses initiated and amplified? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10 (4), 225–235. doi:10.1038/nri2735
Paus, C., Draper, D., Srinivas, M., and Aarntzen, E. H. J. G. (2018). “Inflammation and immune metabolism,” in Imaging and metabolism. Editors J. S. Lewis, and K. R. Keshari (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 155–173. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-61401-4_7
Plants of the World Online (POWO) (2025). Boswellia roxb. ex colebr. Royal botanic gardens, kew. Available online at: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:5117-1 (Accessed September 9, 2025).
Poeckel, D., and Werz, O. (2006). Boswellic acids: biological actions and molecular targets. Curr. Med. Chem. 13 (28), 3359–3369. doi:10.2174/092986706779010333
Rådmark, O., Werz, O., Steinhilber, D., and Samuelsson, B. (2007). 5-Lipoxygenase: regulation of expression and enzyme activity. Trends Biochem. Sci. 32 (7), 332–341. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2007.06.002
Ragab, E. A., Abd El-Wahab, M. F., Doghish, A. S., Salama, R. M., Eissa, N., and Darwish, S. F. (2024). The journey of boswellic acids from synthesis to pharmacological activities. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 397 (3), 1477–1504. doi:10.1007/s00210-023-02725-w
Rajabian, A., Farzanehfar, M., Hosseini, H., Arab, F. L., and Nikkhah, A. (2023). Boswellic acids as promising agents for the management of brain diseases. Life Sci. 312, 121196. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121196
Ranzato, E., Martinotti, S., Volante, A., Tava, A., Masini, M. A., and Burlando, B. (2017). The major Boswellia serrata active 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid strengthens interleukin-1α upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 via JNK MAP kinase activation. Phytomedicine 36, 176–182. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2017.09.010
Reising, K., Meins, J., Bastian, B., Eckert, G., Mueller, W. E., Schubert-Zsilavecz, M., et al. (2005). Determination of boswellic acids in brain and plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 77 (20), 6640–6645. doi:10.1021/ac0506478
Roy, S., Khanna, S., Shah, H., Rink, C., Phillips, C., Preuss, H., et al. (2005). Human genome screen to identify the genetic basis of the anti-inflammatory effects of boswellia in microvascular endothelial cells. DNA Cell Biol. 24 (4), 244–255. doi:10.1089/dna.2005.24.244
Safayhi, H., Sailer, E. R., and Ammon, H. P. (1995). Mechanism of 5-lipoxygenase inhibition by acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid. Mol. Pharmacol. 47 (6), 1212–1216. doi:10.1016/s0026-895x(25)08764-4
Safayhi, H., Rall, B., Sailer, E. R., and Ammon, H. P. (1997). Inhibition by boswellic acids of human leukocyte elastase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 281 (1), 460–463. doi:10.1016/s0022-3565(24)36628-5
Sailer, E. R., Subramanian, L. R., Rall, B., Hoernlein, R. F., Ammon, H. P., and Safayhi, H. (1996). Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid (AKBA): structure requirements for binding and 5-lipoxygenase inhibitory activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 117 (4), 615–618. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15235.x
Sailer, E. R., Schweizer, S., Boden, S. E., Ammon, H. P., and Safayhi, H. (1998). Characterization of an acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid and arachidonate-binding regulatory site of 5-lipoxygenase using photoaffinity labeling. Eur. J. Biochem. 256 (2), 364–368. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2560364.x
Salama, R. M., Abbas, S. S., Darwish, S. F., Sallam, A. A., Elmongy, N. F., and El Wakeel, S. A. (2023). Regulation of NOX/p38 MAPK/PPARα pathways and miR-155 expression by boswellic acids reduces hepatic injury in experimentally-induced alcoholic liver disease mouse model: novel mechanistic insight. Archives Pharmacal Res. 46 (4), 323–338. doi:10.1007/s12272-023-01441-6
Schjerning, A. M., McGettigan, P., and Gislason, G. (2020). Cardiovascular effects and safety of (non-aspirin) NSAIDs. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 17 (9), 574–584. doi:10.1038/s41569-020-0366-z
Schmiech, M., Abdel-Kahaar, E., Ulrich, J., Pfeiffer, M., Duweb, A., Zolk, O., et al. (2024). Single-dose comparative pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study of a micellar formulation versus a native Boswellia serrata dry extract in healthy volunteers. Phytomedicine 132, 155863. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155863
Sengupta, K., Alluri, K. V., Satish, A. R., Mishra, S., Golakoti, T., Sarma, K. V., et al. (2008). A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study of the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Res. Ther. 10 (4), R85. doi:10.1186/ar2461
Sethi, V., Garg, M., Herve, M., and Mobasheri, A. (2022). Potential complementary and/or synergistic effects of curcumin and boswellic acids for management of osteoarthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 14, 1759720X221124545. doi:10.1177/1759720x221124545
Shadab, A., Abbasi-Kolli, M., Yazdanpanah, E., Esmaeili, S. A., Baharlou, R., Yousefi, B., et al. (2024). Exploring the immune-modulating properties of boswellic acid in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Apmis 132 (6), 452–464. doi:10.1111/apm.13406
Shah, S. A., Rathod, I. S., Suhagia, B. N., Patel, D. A., Parmar, V. K., Shah, B. K., et al. (2007). Estimation of boswellic acids from market formulations of Boswellia serrata extract and 11-keto beta-boswellic acid in human plasma by high-performance thin-layer chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 848 (2), 232–238. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.10.026
Sharma, T., and Jana, S. (2020). Investigation of molecular properties that influence the permeability and oral bioavailability of major β-Boswellic acids. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 45 (2), 243–255. doi:10.1007/s13318-019-00599-z
Sharma, S., Thawani, V., Hingorani, L., Shrivastava, M., Bhate, V. R., and Khiyani, R. (2004). Pharmacokinetic study of 11-Keto beta-boswellic acid. Phytomedicine 11 (2-3), 255–260. doi:10.1078/0944-7113-00290
Sharma, A., Gupta, N. K., and Dixit, V. K. (2010). Complexation with phosphatidyl choline as a strategy for absorption enhancement of boswellic acid. Drug Deliv. 17 (8), 587–595. doi:10.3109/10717544.2010.501461
Siddiqui, M. Z. (2011). Boswellia serrata, a potential antiinflammatory agent: an overview. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 73 (3), 255–261. doi:10.4103/0250-474x.93507
Siemoneit, U., Dehm, F., Hofmann, B., Kather, N., Schneider, G., Jauch, J., et al. (2008). Boswellic acids from the anti-inflammatory remedy frankincense: identification and functional analysis of novel molecular targets within the arachidonic acid cascacde. Planta Med. 74 (09), SL111. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1083991
Siemoneit, U., Pergola, C., Jazzar, B., Northoff, H., Skarke, C., Jauch, J., et al. (2009). On the interference of boswellic acids with 5-lipoxygenase: mechanistic studies in vitro and pharmacological relevance. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 606 (1-3), 246–254. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.01.044
Siemoneit, U., Koeberle, A., Rossi, A., Dehm, F., Verhoff, M., Reckel, S., et al. (2011). Inhibition of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 as a molecular basis for the anti-inflammatory actions of boswellic acids from frankincense. Br. J. Pharmacol. 162 (1), 147–162. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01020.x
Singh, S., Khajuria, A., Taneja, S. C., Khajuria, R. K., Singh, J., Johri, R. K., et al. (2008a). The gastric ulcer protective effect of boswellic acids, a leukotriene inhibitor from Boswellia serrata, in rats. Phytomedicine 15 (6-7), 408–415. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2008.02.017
Singh, S., Khajuria, A., Taneja, S. C., Johri, R. K., Singh, J., and Qazi, G. N. (2008b). Boswellic acids: a leukotriene inhibitor also effective through topical application in inflammatory disorders. Phytomedicine 15 (6-7), 400–407. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2007.11.019
Staa, T. P. v., Staa, T. P. v., Staa, T. P. v., Leufkens, H. G. M., and Cooper, C. (2002). The epidemiology of corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 13 (10), 777–787. doi:10.1007/s001980200108
Strzelec, M., Detka, J., Mieszczak, P., Sobocińska, M. K., and Majka, M. (2023). Immunomodulation-a general review of the current state-of-the-art and new therapeutic strategies for targeting the immune system. Front. Immunol. 14, 1127704. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127704
Stürner, K. H., Verse, N., Yousef, S., Martin, R., and Sospedra, M. (2014). Boswellic acids reduce Th17 differentiation via blockade of IL-1β-mediated IRAK1 signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 44 (4), 1200–1212. doi:10.1002/eji.201343629
Stürner, K. H., Stellmann, J. P., Dörr, J., Paul, F., Friede, T., Schammler, S., et al. (2018). A standardised frankincense extract reduces disease activity in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (the SABA phase IIa trial). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 89 (4), 330–338. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2017-317101
Suther, C., Devon, L., Daddi, L., Matson, A., Panier, H., Yuan, H., et al. (2022). Dietary Indian frankincense (Boswellia serrata) ameliorates murine allergic asthma through modulation of the gut microbiome. J. Funct. Foods 97, 105249. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2022.105249
Syrovets, T., Gschwend, J. E., Büchele, B., Laumonnier, Y., Zugmaier, W., Genze, F., et al. (2005a). Inhibition of IkappaB kinase activity by acetyl-boswellic acids promotes apoptosis in androgen-independent PC-3 prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 280 (7), 6170–6180. doi:10.1074/jbc.m409477200
Syrovets, T., Büchele, B., Krauss, C., Laumonnier, Y., and Simmet, T. (2005b). Acetyl-boswellic acids inhibit lipopolysaccharide-mediated TNF-alpha induction in monocytes by direct interaction with IkappaB kinases. J. Immunol. 174 (1), 498–506. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.174.1.498
Taherzadeh, D., Baradaran Rahimi, V., Amiri, H., Ehtiati, S., Yahyazadeh, R., Hashemy, S. I., et al. (2022). Acetyl-11-Keto-β-Boswellic acid (AKBA) prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity on H9C2 cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2620710. doi:10.1155/2022/2620710
Takada, Y., Ichikawa, H., Badmaev, V., and Aggarwal, B. B. (2006). Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid potentiates apoptosis, inhibits invasion, and abolishes osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-kappa B and NF-kappa B-regulated gene expression. J. Immunol. 176 (5), 3127–3140. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.176.5.3127
Tambe, A., Pandita, N., Kharkar, P., and Sahu, N. (2018). Encapsulation of boswellic acid with β- and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: synthesis, characterization, in vitro drug release and molecular modelling studies. J. Mol. Struct. 1154, 504–510. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.10.061
Tausch, L., Henkel, A., Siemoneit, U., Poeckel, D., Kather, N., Franke, L., et al. (2009). Identification of human cathepsin G as a functional target of boswellic acids from the anti-inflammatory remedy frankincense. J. Immunol. 183 (5), 3433–3442. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0803574
Tawab, M. A., Kaunzinger, A., Bahr, U., Karas, M., Wurglics, M., and Schubert-Zsilavecz, M. (2001). Development of a high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of 11-keto-beta-boswellic acid in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 761 (2), 221–227. doi:10.1016/s0378-4347(01)00335-8
Thakur, S., and Kiranmai, M. (2024). Formulation of novel boswellic acid Loaded-PEGlyated nanoparticles and effect on SARS COVID 19 virus: in silico docking analysis and ADMET studies. Asian J. Chem. 36 (6), 1409–1416. doi:10.14233/ajchem.2024.31226
Ting, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhao, S., Li, C. C., Nibber, T., and Huang, Q. (2018). Self-nanoemulsifying system (SNES) enhanced oral bioavailability of boswellic acids. J. Funct. Foods 40, 520–526. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2017.11.043
Togni, S., Maramaldi, G., Di Pierro, F., and Biondi, M. (2014). A cosmeceutical formulation based on boswellic acids for the treatment of erythematous eczema and psoriasis. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol 7, 321–327. doi:10.2147/ccid.S69240
Truzzi, E., Vanti, G., Grifoni, L., Maretti, E., Leo, E., and Bilia, A. R. (2025). Plant resin delivery by nanovectors as an emerging approach to boost solubility, permeability and bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 17 (1), 53. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics17010053
Upadhayay, S., Mehan, S., Prajapati, A., Sethi, P., Suri, M., Zawawi, A., et al. (2022). Nrf2/HO-1 signaling stimulation through Acetyl-11-Keto-Beta-Boswellic acid (AKBA) provides neuroprotection in ethidium bromide-induced experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Genes (Basel) 13 (8), 1324. doi:10.3390/genes13081324
Usapkar, P., Saoji, S., Jagtap, P., Ayyanar, M., Kalaskar, M., Gurav, N., et al. (2024). QbD-guided phospholipid-tagged nanonized boswellic acid naturosomal delivery for effective rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Int. J. Pharm. X 7, 100257. doi:10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100257
Verhoff, M., Seitz, S., Paul, M., Noha, S. M., Jauch, J., Schuster, D., et al. (2014). Tetra- and pentacyclic triterpene acids from the ancient anti-inflammatory remedy frankincense as inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E(2) synthase-1. J. Nat. Prod. 77 (6), 1445–1451. doi:10.1021/np500198g
Vijayarani, K. R., Govindarajulu, M., Ramesh, S., Alturki, M., Majrashi, M., Fujihashi, A., et al. (2020). Enhanced bioavailability of boswellic acid by piper longum: a computational and pharmacokinetic Study. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 551911. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.551911
Vishal, A. A., Mishra, A., and Raychaudhuri, S. P. (2011). A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study evaluates the early efficacy of aflapin in subjects with osteoarthritis of knee. Int. J. Med. Sci. 8 (7), 615–622. doi:10.7150/ijms.8.615
Visse, R., and Nagase, H. (2003). Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ. Res. 92 (8), 827–839. doi:10.1161/01.Res.0000070112.80711.3d
Wang, H., Syrovets, T., Kess, D., Büchele, B., Hainzl, H., Lunov, O., et al. (2009). Targeting NF-kappa B with a natural triterpenoid alleviates skin inflammation in a mouse model of psoriasis. J. Immunol. 183 (7), 4755–4763. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900521
Wang, Q., Pan, X., Wong, H. H., Wagner, C. A., Lahey, L. J., Robinson, W. H., et al. (2014a). Oral and topical boswellic acid attenuates mouse osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 22 (1), 128–132. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.10.012
Wang, H., Zhang, C., Wu, Y., Ai, Y., Lee, D. Y., and Dai, R. (2014b). Comparative pharmacokinetic study of two boswellic acids in normal and arthritic rat plasma after oral administration of Boswellia serrata extract or Huo Luo Xiao Ling Dan by LC-MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 28 (10), 1402–1408. doi:10.1002/bmc.3182
Wang, Y., Xiong, Z., Qiao, Y., Zhang, Q., Zhou, G., Zhou, C., et al. (2024). Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid modulates macrophage polarization and schwann cell migration to accelerate spinal cord injury repair in rats. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (3), e14642. doi:10.1111/cns.14642
Werz, O. (2007). Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase product synthesis by natural compounds of plant origin. Planta Med. 73 (13), 1331–1357. doi:10.1055/s-2007-990242
Werz, O., and Steinhilber, D. (2005). Development of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors--lessons from cellular enzyme regulation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 70 (3), 327–333. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2005.04.018
Werz, O., and Steinhilber, D. (2006). Therapeutic options for 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. Pharmacol. and Ther. 112 (3), 701–718. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.05.009
Zaitone, S. A., Barakat, B. M., Bilasy, S. E., Fawzy, M. S., Abdelaziz, E. Z., and Farag, N. E. (2015). Protective effect of boswellic acids versus pioglitazone in a rat model of diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: influence on insulin resistance and energy expenditure. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives Pharmacol. 388 (6), 587–600. doi:10.1007/s00210-015-1102-9
Zhang, P., and Jiang, H. (2023). Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid confers protection in DSS-induced colitis via the JNK-p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Adv. Biol. (Weinh) 7 (6), e2200247. doi:10.1002/adbi.202200247
Zhang, Y., Jia, J., Ding, Y., Ma, Y., Shang, P., Liu, T., et al. (2016). Alpha-boswellic acid protects against ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats: involvement of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 pathway. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 68 (4), 514–522. doi:10.1111/jphp.12532
Zhang, R., Xu, H., Li, X., Liu, Z., Wang, Y., and Zhao, Z. (2020). 3-Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits cancer cell invasion and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells by abrogating the EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. Archives Med. Sci. doi:10.5114/aoms.2020.95421
Zheng, J., Jiang, J., Pu, Y., Xu, T., Sun, J., Zhang, Q., et al. (2023). Tumor-associated macrophages in nanomaterial-based anti-tumor therapy: as target spots or delivery platforms. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1248421. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1248421
Zhou, J., Han, Z., Li, X., Shao, Z., Qian, Y., Bai, L., et al. (2022). Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid restrains inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation of osteoarthritis via suppression of NF-κB pathway. Res. Square. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1234256/v2
Zhou, J., Li, X., Han, Z., Qian, Y., Bai, L., Han, Q., et al. (2024). Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid restrains the progression of synovitis in osteoarthritis via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 56 (11), 1644–1658. doi:10.3724/abbs.2024102
Zindel, J., and Kubes, P. (2020). DAMPs, PAMPs, and LAMPs in immunity and sterile inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 15, 493–518. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012419-032847
Glossary
5-LOX 5-Lipoxygenase
MAPK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase
IKK IκB Kinase
iNOS Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
COX-1/2 Cyclooxygenase-1/2
PGH2 Prostaglandin H2
Nrf2 Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2
ARE(s) Antioxidant Response Element(s)
GPx Glutathione Peroxidase
SOD Superoxide Dismutase
CAT Catalase
HO-1 Heme Oxygenase-1
ECM Extracellular Matrix
MMP(s) Matrix Metalloproteinase(s)
ROS Reactive Oxygen Species
RNS Reactive Nitrogen Species
MDA Malondialdehyde
PAMPs Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns
DAMPs Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns
PRRs Pattern-Recognition Receptors
Bas/BA Boswellic Acids
AKBA 3-O-Acetyl-11-keto-β-Boswellic Acid
KBA 11-keto-β-Boswellic Acid
α-BA/β-BA Alpha-/Beta-Boswellic Acid
sAKBA Semi-synthetic Acetoxyl-11-keto-β-Boswellic Acid
EAE Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
OA Osteoarthritis
IBD Inflammatory Bowel Disease(s)
RCT Randomized Controlled Trial
PD Parkinson’s Disease
PF Pulmonary Fibrosis
NAFLD Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NASH Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
MS Multiple Sclerosis
MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging
CRP C-Reactive Protein
VAS Visual Analogue Scale
WOMAC Western Ontario and McMaster Universities OA Index
LFI Lequesne Functional Index
CDAI Crohn’s Disease Activity Index
FEV1 Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 s
FVC Forced Vital Capacity
PEFR Peak Expiratory Flow Rate
HLM Human Liver Microsomes
HIM Human Intestinal Microsomes
CE2 Carboxylesterase 2
CYP3A4/5/7 Cytochrome P450 3A4/5/7
NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
MS/MS Tandem Mass Spectrometry
m/z Mass-to-Charge Ratio
LC-MS/MS Liquid Chromatography–Tandem MS
HPLC-ESI/MS High-Performance LC–Electrospray MS
UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS Ultra-HPLC–LTQ–Orbitrap MS
Cmax Maximum Plasma Concentration
AUC Area Under the Curve
NA Not Analyzed
ND Not Detectable
SE Standard Error
SD Standard Deviation
SNEDDS Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System/Self-Nanoemulsifying System
CDs Cyclodextrins
β-CD beta-Cyclodextrin
HP-β-CD Hydroxypropyl-beta-Cyclodextrin
PLGA Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)
NF-κB Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
AP-1 Activator Protein-1
JAK–STAT Janus Kinase–Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription
IκB Inhibitor of κB
ICAM-1 Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1
VCAM-1 Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1
PGE2 Prostaglandin E2
TNF-α Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
IL-1β Interleukin-1β
IL-6 Interleukin-6
IL-10 Interleukin-10
IL-17 Interleukin-17
IFN-γ Interferon-γ
ERK1/2 Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2
TLR Toll-Like Receptor
IRAK1 Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 1
pIRAK1 phosphorylated IRAK1
Th1/Th2/Th17 T helper 1/2/17
Treg Regulatory T cell
CD4+ Cluster of Differentiation 4 positive
GATA3 GATA-Binding Protein 3
FoxP3 Forkhead Box P3
GI Gastrointestinal
PXM188/407 Poloxamer 188/407
Nat-BE Native Boswellia Extract
Sol-BE Solubilized Boswellia Extract
HLXLD Huo Luo Xiao Ling Dan
DMM Destabilization of the Medial Meniscus
ACLT Anterior Cruciate Ligament Transection
FLS Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes
LPS Lipopolysaccharide
MIA Mon iodoacetate
DSS Dextran Sulfate Sodium
HK-2 Human Kidney-2 cell line
LDH Lactate Dehydrogenase
TGF-β1 Transforming Growth Factor-β1
SMAD2/3/4/7 SMAD family proteins
α-SMA Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin
UCP-1 Uncoupling Protein-1
CPT-1 Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase-1
HNE 4-Hydroxynonenal
LPO Lipid Peroxidation
NO Nitric Oxide
GSH Glutathione
ASA Acetylsalicylic Acid
HCl Hydrochloric acid
FCA Freund’s Complete Adjuvant
NSAIDs Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
GCs Glucocorticoids
MSM Methylsulfonylmethane
Keywords: boswellic acids, anti-inflammatory mechanisms, bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, clinical trials
Citation: Peng C, Yang Y, Wang Y, Gong B, Sun X and Yang X (2025) From bench to bedside, boswellic acids in anti-inflammatory therapy — mechanistic insights, bioavailability challenges, and optimization approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1692443. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1692443
Received: 26 August 2025; Accepted: 28 October 2025;
Published: 18 November 2025.
Edited by:
Javier Echeverria, University of Santiago, ChileReviewed by:
Veera Ganesh Yerra, Unity Health Toronto, CanadaS. K. Kanthlal, Sree Krishna College of Pharmacy and Research Centre, India
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Yang, Wang, Gong, Sun and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xinquan Yang, eHF5YW5nQGltcGxhZC5hYy5jbg==
 Chuhang Peng
Chuhang Peng Yujia Yang1,2
Yujia Yang1,2 Xiuting Sun
Xiuting Sun Xinquan Yang
Xinquan Yang