Abstract
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is clinically complex. Management approaches have focused on addressing the traits of metabolic syndrome and promoting weight loss. However, current treatment options are inadequate, leaving key disease-driving factors unaddressed. Evidence suggests that immune dysregulation determines disease trajectory. Metabolic pathways shape the immune landscape, and the immune system influences metabolic homeostasis. Developing therapies that integrate metabolic correction with immune restoration is essential. We review current available strategies and discuss areas where further research is needed to design drugs and therapeutic combinations that mitigate the complex metabolic and inflammatory interactions driving obesity-associated chronic liver disease. The immunomodulatory effects of obesity-focused interventions remain poorly understood. Bariatric surgery and incretin-based therapies can reduce body fat while reprogramming the hepatic immune environment. Metabolic modulators can reduce lipotoxicity, suppress harmful cytokine networks, and promote reparative immune responses. Other strategies include blocking danger-signaling pathways, modulating chemokine axes, and using cellular therapies. The goal is to interrupt pro-inflammatory amplification cascades and preserve reparative immune cell populations, redefining therapeutic possibilities for liver diseases. Despite advancements in the field, uncertainties still exist regarding the immunometabolic integration. Ongoing clinical trials and the recent approval of two drugs for treating this condition will provide valuable real-world insights in the future about the long-term safety and effectiveness of potentially more accurate treatment approaches. Moreover, causal and clinical biomarkers are being investigated to enhance the diagnosis and management of the significant challenges associated with MASLD-related cirrhosis. Prioritizing and initiating treatment earlier are key factors for achieving successful outcomes.
Introduction
In 1980, specific histologic features identified a then-new and rare chronic liver condition associated with obesity and diabetes mellitus, termed nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, as patients consistently reported no history of chronic alcohol abuse (Ludwig et al., 1980). This condition represented the progressive form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Concurrent with rising obesity prevalence over subsequent decades, metabolic dysfunction emerged as a central driver of progression from hepatic fat accumulation to inflammation and fibrosis. Contemporary nomenclature reflects this mechanistic understanding: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its inflammatory stage, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), have replaced earlier terms (Kanwal et al., 2024). MASLD has evolved from a rare entity to a multisystem disease affecting one-quarter of the global population and constituting a substantial global health burden, with implications extending to extrahepatic complications (Estes et al., 2018; Younossi et al., 2021; Tacke et al., 2024).
MASLD represents a major obesity-related complication characterized by genetic predisposition, disrupted gut-liver and adipose-liver axis signaling, and persistent immune dysfunction (Anstee et al., 2019; Loomba et al., 2021). While promising metabolism-based drugs targeting MASLD are emerging, immune mechanisms linking metabolic injury to inflammation and fibrosis require further investigation (Peiseler et al., 2022). The liver functions as an immunological sentinel. The immune dysregulation caused by obesity primarily affects the adipose tissue and extends to the liver and other metabolic organs (Hotamisligil, 2006). Current models suggest that transition to a pro-inflammatory hepatic environment begins with stress sensing by resident immune cells, followed by recruitment of pro-inflammatory myeloid populations and subsequent lymphocyte engagement (Mladenić et al., 2024). However, conceptualizing the immune system as a unidirectional driver of tissue injury oversimplifies the pathophysiology. Immune cells can orchestrate tissue repair and restore hepatic homeostasis (Zhao et al., 2022). This dual function necessitates a comprehensive characterization of immune profile changes and nuanced risk stratification across clinical contexts. The emerging immunometabolic paradigm challenges the traditional perception of MASLD as a purely metabolic disease with secondary immune dysregulation. Instead, it supports an integrated framework that recognizes metabolic pathways shape immune functions, while immune responses determine metabolic homeostasis. This complexity provides the foundation for therapeutic approaches that synchronize metabolic correction with immune restoration in current and future drugs.
Weight loss-related strategies
The association between obesity and MASLD suggests that effective anti-obesity treatments can contribute substantially to disease remission (Brunner et al., 2019; Polyzos et al., 2019). However, these approaches achieve therapeutic benefits not merely through weight reduction, but by simultaneously remodeling the hepatic immune microenvironment. Weight loss through lifestyle modifications remains the cornerstone of MASLD management. Sustained reduction of 7%–10% body weight improves steatosis and lobular inflammation, whereas losses exceeding 10% are required to reverse fibrosis (Vilar-Gomez et al., 2015). Bariatric surgery extends these effects through greater and sustained weight loss, improving insulin sensitivity and glycemic control, downregulating de novo lipogenesis (DNL), and upregulating lipid-oxidation genes (Lee et al., 2019; Lassailly et al., 2020; Verrastro et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2025). However, some patients may not experience halted MASLD progression or reversal of advanced fibrosis despite substantial weight loss (Pais et al., 2022).
The efficacy of bariatric surgery on MASLD transcends energy balance through direct immunomodulatory mechanisms. This procedure reduces systemic inflammatory markers (CRP, LBP, HGF, IL-6, and TNFα) while promoting gut microbiome shifts that increase hepatic natural killer T cells and reduce pro-inflammatory macrophages (Shera et al., 2024). Evidence from murine sleeve-gastrectomy models indicates that TREM2+ macrophages emerge as key mediators of post-surgical hepatic improvements (Fredrickson et al., 2024). These cells contribute to the clearance of cellular debris, the attenuation of local inflammation, and the remission of fibrosis. In the liver, TREM2+ macrophages localize to hepatic crown-like structures that encircle lipid-laden apoptotic hepatocytes, promoting their efferocytosis. Conversely, prolonged hypernutrition activates ADAM17 metalloproteinase through TNFα and IL-1β signaling, leading to TREM2 cleavage and impaired macrophage efferocytosis, thereby promoting disease progression (Daemen et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023; Ganguly et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024). Although preliminary clinical observations align with these findings, validation in larger cohorts remains necessary.
Incretin-based therapies represent a paradigm shift from weight loss-dependent to dual metabolic-immune targeting strategies. In obesity, gut barrier dysfunction and dysbiosis enable microbial products to reach the liver via the portal vein, activating resident immune cells and sustaining inflammation and progression of MASLD (Tilg et al., 2021). In contrast, incretins secreted in the gut, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), represent beneficial signals that can be therapeutically harnessed. GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists are the most effective incretin-based therapies (Newsome and Ambery, 2023). These agents facilitate weight loss and glycemic control by enhancing satiety and stimulating glucose-dependent insulin secretion (Drucker, 2022; Newsome and Ambery, 2023). Beyond metabolic effects, their capacity to suppress inflammation across multiple tissues positions them as immunomodulatory agents relevant to MASLD (He et al., 2025). Clinically, liraglutide and semaglutide increase rates of histological resolution versus placebo (Armstrong et al., 2016; Sanyal et al., 2025). In phase III clinical trials (ESSENCE), semaglutide also promoted fibrosis remission and improved noninvasive fibrosis markers. Interim analysis of histological results resulted in approval by the FDA in 2025 as wegovy (US Food and Drug Administration, 2025). Multi-receptor incretin agonists, currently in phase II or early phase III trials, aim to enhance therapeutic efficacy by incorporating GIP or glucagon receptor activation. Examples include dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonists (tirzepatide), dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor agonists (survodutide, pemvidutide, cotadutide), and triple GLP-1/GIP/glucagon receptor agonists (retatrutide). However, their specific immunomodulatory mechanisms remain to be fully characterized (Loomba et al., 2024b; Sanyal et al., 2024; Shankar et al., 2024; Harrison et al., 2025) (Figure 1A).
FIGURE 1
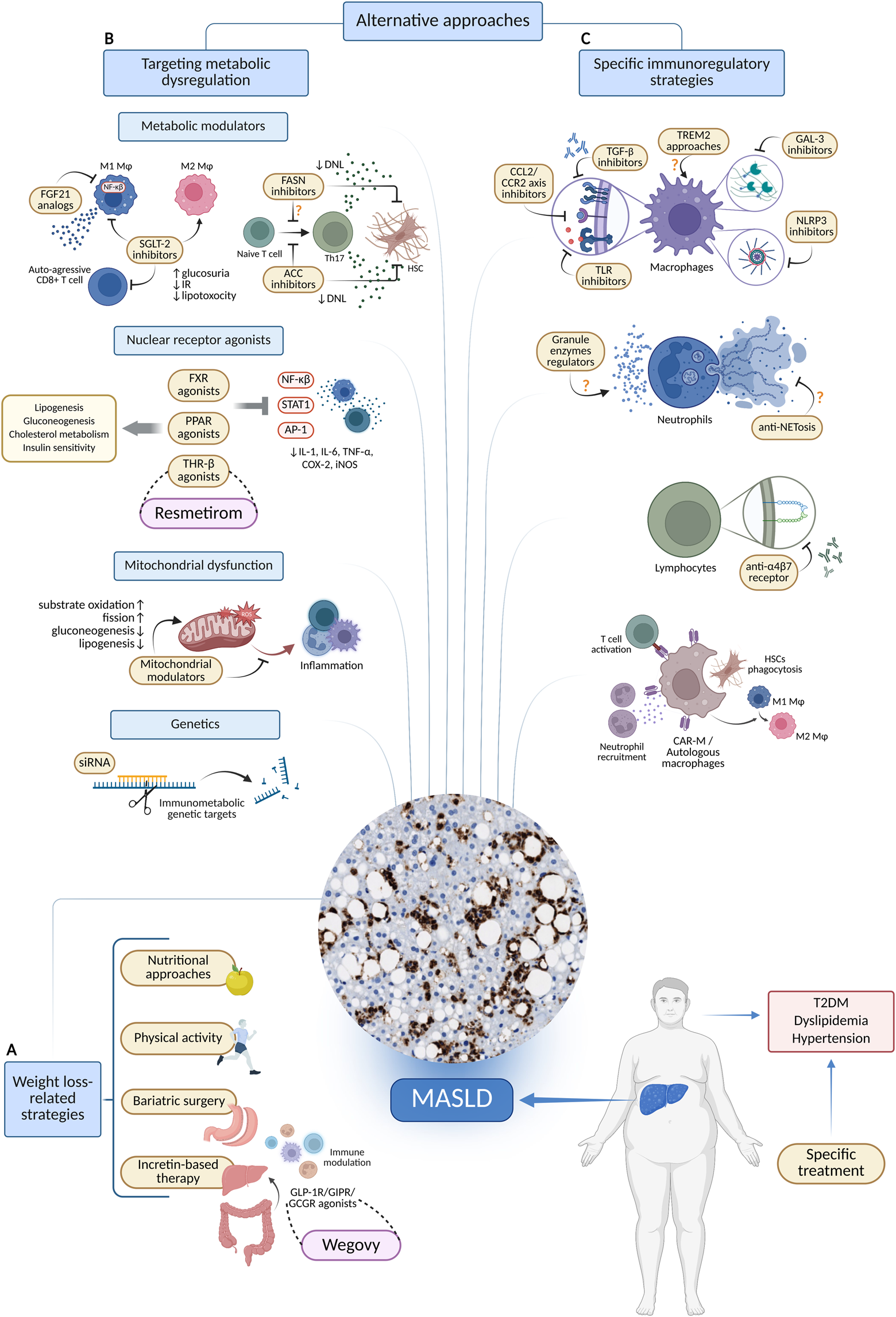
Therapeutic approaches targeting metabolic and immune alterations in MASLD. (A) Strategies associated with obesity. (B) Therapies focused on metabolism. (C) Specific strategies for immune modulation. Created in BioRender. Joven, J. (2025) https://BioRender.com/d9mzal6. Abbreviations: ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AP-1, activator protein 1; CAR-M, chimeric antigen receptor modified macrophage; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; CCR2, C-C chemokine receptor 2; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; DNL, de novo lipogenesis; FASN, fatty acid synthase; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; GAL3, galectin 3; GCGR, glucagon receptor; GIPR, glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor; GLP-1, glucagon like peptide 1; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; IL-1, interleukin 1; IL-6, interleukin six; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; NET, neutrophil extracellular trap; NF-κB, nuclear factor of the κ chain in B cells; NLRP3, nucleotide binding domain, leucine-rich repeat protein 3; SGLT-2, sodium glucose cotransporter 2; siRNA, small interfering RNA; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; Th17, T helper 17 cells; THR-β, thyroid hormone receptor β; TLR, toll like receptor; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TREM2, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
Metabolic dysregulation and immunomodulation
In MASLD, macrophages, T cells, and other immune populations undergo metabolic reprogramming (Ma et al., 2025). This immunometabolic dimension could inform therapeutic strategies that target core metabolic pathways independent of weight loss while simultaneously modulating immune functions (Figure 1B). Nuclear receptor agonists represent promising therapeutic targets, as they activate transcription factors that regulate both metabolism and immunity. Among them, resmetirom, an oral liver-directed thyroid hormone receptor-β (THR-β) selective agonist, exemplifies this approach. Following the demonstration of increased rates of MASH resolution and improvement in fibrosis in the MAESTRO-NASH phase 3 trial, resmetirom received accelerated FDA approval as the first pharmacological therapy for MASH (Harrison et al., 2024; Keam, 2024). Mechanistically, resmetirom acts on the expression of key enzymes and modulates hepatic lipid metabolism by enhancing triglyceride breakdown and reducing DNL. Several data suggest a significant role in mitochondrial biogenesis, improving hepatic fatty acid oxidation and attenuating lipotoxicity-driven inflammation (Petta et al., 2024). The farnesoid X receptor (FXR) illustrates the complexity of nuclear receptor targeting. FXR functions as a bile acid sensor regulating cholesterol and bile acid homeostasis, gluconeogenesis, and lipogenesis (Fiorucci et al., 2022). It is expressed in monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and natural killer T cells, where its activation exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting NF-κB (Fiorucci et al., 2022). However, obeticholic acid, the most prominent FXR agonist, has shown limited success in MASH resolution and raised safety concerns (Sanyal et al., 2023). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) represent archetypal nodes of immunometabolism. PPARs function as fatty acid sensors regulating lipid metabolism, insulin sensitivity, inflammation, and fibrogenesis (Francque et al., 2021). All PPAR isotypes (PPARα, PPARγ and PPARβ/δ) are expressed in immune cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells, and T cells, where they modulate anti-inflammatory responses (Christofides et al., 2021). They attenuate macrophage and neutrophil activation by limiting leukotriene B4 signaling, suppressing NF-κβ, AP-1 and STAT1 pathways, and downregulating pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, and iNOS (Qiu et al., 2023; Staels et al., 2023). PPARγ also favors anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage polarization via glutamine metabolism. These effects provide a robust mechanistic rationale for indicating PPARs in MASLD. Lanifibranor, a pan-PPAR agonist, has demonstrated significant reductions in hepatic steatosis and improvements in tissue insulin resistance in a phase 2 trial (Barb et al., 2025). This agent reduces hepatic macrophage accumulation, downregulates their pro-inflammatory gene programs, and upregulates lipid-handling gene expression (Lefere et al., 2020).
Beyond nuclear receptors, other metabolic modulators demonstrate how targeting specific metabolic pathways can directly reprogram immune cell function. A notable example is the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2), a membrane protein that reabsorbs most of the filtered glucose in the early proximal tubules of the kidney. Pharmacologic SGLT-2 inhibitors promote glycosuria, reduce insulin resistance and lipotoxicity, and create sustained caloric deficits, leading to decreased body weight and concomitant hepatic improvements in MASLD (Ong Lopez and Pajimna, 2024). These metabolic shifts are coupled to direct immunoregulatory actions. In murine models, empagliflozin ameliorates MASH by directly suppressing auto-aggressive CXCR6+ CD8+ T cell activation and infiltration through ketogenesis-dependent mechanisms (Liu et al., 2024). It also enhances autophagy in hepatic macrophages via AMPK/mTOR signaling, suppressing the IL-17/IL-23 axis (Meng et al., 2021). Similarly, dapagliflozin and canagliflozin inhibit M1 macrophage glycolysis and promote reprogramming toward oxidative metabolism consistent with M2 polarization in the murine liver (Lin et al., 2024). However, clinical evidence supporting these immunomodulatory mechanisms remains limited. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a liver-derived endogenous hormone whose pharmacologic analogs exhibit therapeutic promise in obesity, type 2 diabetes, and MASLD by regulating lipid metabolism and enhancing insulin sensitivity (Jin et al., 2023). Beyond metabolic effects, FGF21 suppresses macrophage expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNFα, IL-6, IL-1β, and IFN-γ, by promoting NRF2 nuclear translocation and inhibiting NF-κB signaling (Yu et al., 2016). Consistently, FGF21 analog administration in obese nonhuman primates with MASLD reduced hepatic neutrophil and macrophage infiltration (Cui et al., 2020). In phase IIb studies, pegozafermin improved fibrosis, whereas efruxifermin achieved both fibrosis and MASH resolution (Harrison et al., 2023; Loomba et al., 2023).
Targeting de novo lipogenesis also provides evidence for immunometabolic integration. While fibrosis is the principal predictor of MASLD-related mortality, hepatic steatosis initiates the inflammatory cascade leading to disease progression. Targeting rate-limiting enzymes in hepatic DNL pathways represents a rational therapeutic approach with additional benefits stemming from immune cell modulation (Castro Cabezas and de Jong, 2025). Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) enables T cell membrane phospholipid synthesis and Th17 differentiation, with pharmacological inhibition reducing IL-17 production and alleviating MASH (Ross et al., 2020). Downstream of ACC, fatty acid synthase (FASN) is a critical immunometabolic node for Th17 differentiation, but this function remains to be determined in humans (Young et al., 2017). The oral FASN inhibitor denifanstat achieved clinically significant MASH and fibrosis resolution in a phase IIb trial (Loomba et al., 2024a). Certain metabolic interventions target hepatic stellate cell (HSC) transdifferentiation into myofibroblasts, a process dependent on metabolic reprogramming involving enhanced glycolysis, glutaminolysis, and DNL (Martínez García de la Torre et al., 2025). Preclinical models demonstrate that ACC and FASN inhibitors reduce HSC-driven matrix deposition and fibrosis (Ross et al., 2020; O’Farrell et al., 2022). Enhancing PPAR-γ activation also induces HSC quiescence and reduces fibrogenic capacity (Lefere et al., 2020).
Cutting-edge mitochondrial and genetic approaches
Mitochondrial dysfunction represents a fundamental immunometabolic target in MASLD. The resulting oxidative stress triggers and perpetuates inflammatory responses, establishing mitochondria as promising immunoregulatory targets (Hernández-Aguilera et al., 2013). HU6, metabolized in the liver to the mitochondrial uncoupler 2,4-dinitrophenol, acts as a metabolic accelerator promoting lipid and substrate oxidation. In MASLD patients with elevated BMI, it demonstrated dose-dependent reductions in hepatic fat content relative to placebo (Noureddin et al., 2023). MSDC-0602K, a mitochondrial pyruvate carrier inhibitor, failed to meet histological endpoints in phase II clinical trials in patients with MASH (Harrison et al., 2020). However, the highest doses demonstrated reductions in fasting glucose, insulin, ALT, and AST levels. This approach, as a therapeutic strategy, remains experimental. Metformin represents another plausible MASLD therapy targeting mitochondrial alterations. It activates AMPK, facilitating mitochondrial fission and mitophagy, suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis, and enhancing fatty acid oxidation (Perazza et al., 2024). In experimental models, the combination of metformin and genistein exerts immunoregulatory effects by polarizing macrophages toward the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype (Zamani-Garmsiri et al., 2021).
Emerging evidence demonstrates that specific genetic variants orchestrate the complex interplay between metabolic dysfunction and immune cell dynamics in MASLD (Sookoian et al., 2020). Metabolism-related genes proposed as MASLD progression biomarkers, including HPRT1, GPD1, and GCK, correlate with hepatic immune cell infiltration (Xie et al., 2025). Additionally, a Mendelian randomization study demonstrated the association of eight genetically determined immunophenotypes with MASLD risk (Ye et al., 2024). These insights are guiding the development of targeted genetic therapies that address the fundamental genetic determinants of immunometabolic dysfunction. Current investigational approaches for MASLD use small-interfering RNAs to mimic the protective loss-of-function of HSD17B13 variant with agents such as GSK4532990 and ALN-HSD, with early signs of reduction of liver fat and stiffness in clinical trials (Noureddin, 2024).
Challenges in specific immunoregulatory strategies
MASLD evolves within a highly interactive immune niche. Therefore, conventional agents providing broad immunosuppression are unsuitable (Tacke et al., 2023). Precision immunomodulation specifically targets immune cell signaling, trafficking, and effector functions. Currently, clinical trial failures are learning opportunities rather than dead ends (Figure 1C; Table 1).
TABLE 1
| Pharmacological agent | Mechanism of action | Immunological outcomes | Evidence type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liraglutide (Armstrong et al., 2016; Li et al., 2019) | GLP-1 receptor agonist | Evidence of Kupffer cell M2 polarization | Preclinical |
| Cotadutide (Boland et al., 2020; Shankar et al., 2024) | Dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor agonist | Reduction of hepatic ALT and AST in humans. Reduced hepatic immune cell infiltration and inflammatory markers in murine models. Discontinued after phase II trials for strategic portfolio considerations | Clinical/Preclinical |
| Resmetirom (Harrison et al., 2024) | THR-β agonist | Attenuated lipotoxicity-driven inflammation by modulating lipid metabolism | Clinical |
| Lanifibranor (Lefere et al., 2020) | pan-PPAR agonist | Reduced hepatic monocyte-derived macrophage infiltration and activation | Preclinical |
| Empagliflozin (Meng et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2024) | SGLT-2 inhibitors | Suppressed auto-aggressive CD8+ T cell subsets activation by modulating ketogenesis. Enhanced hepatic macrophage autophagy via AMPK activation and mTOR inhibition, suppressing IL-17/IL-23 axis | Preclinical |
| Dapagliflozin (Lin et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2024) | Reduced CD8+ T cell infiltration in human livers. Induced metabolic reprogramming of hepatic murine macrophages and M2 polarization | Clinical/Preclinical | |
| PF-05221304 (Ross et al., 2020) | ACC inhibitor | Inhibition of CD4+ T cells polarization into Th17 cells | Preclinical |
| Metformin and genistein (Zamani-Garmsiri et al., 2021) | AMPK activators | Reduced hepatic macrophage infiltration and induced M2 polarization | Preclinical |
| Belapectin (Chalasani et al., 2020) | Galectin-3 inhibitor | Despite promising preclinical data, no clinical efficacy has been proven for fibrosis or inflammation | Clinical |
| Cenicriviroc (Anstee et al., 2024) | Dual CCR2/CCR5 antagonist | Diminished monocyte recruitment. Discontinued after phase III trials showed no antifibrotic efficacy | Clinical |
| CAR-Ms (Dai et al., 2024) | Macrophages expressing an anti-uPAR CAR | Phagocytose uPAR+ HSCs and stimulate T-cell antifibrotic responses, neutrophil recruitment, NK cell activation, and macrophage anti-inflammatory functions | Preclinical |
| Autologous macrophages (Brennan et al., 2025) | Macrophage therapy targeting fibrosis | No statistically significant differences in phase II trial, but a proven safety profile | Clinical |
Ongoing strategies for MASLD considering immunoregulatory effects.
Macrophage-targeted interventions
Hepatic macrophages represent primary targets for cell subset-specific approaches, functioning as early sentinels of metabolic stress that rapidly polarize toward pro-inflammatory states. Investigational interventions at this stage focus on upstream pattern-recognition and danger-sensing pathways, specifically inhibiting TLR signaling or blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activation (Yu et al., 2022; 2024). Macrophages represent a significant source of the pro-fibrotic mediator galectin-3. Galectin-3-deficient mice demonstrated protection against fibrosis through inhibition of TGF-β-mediated myofibroblast activation (Subramanian et al., 2022; Sotoudeheian, 2024). However, the clinical evaluation of the galectin-3 inhibitor belapectin in patients with MASH, cirrhosis, and portal hypertension failed to demonstrate significant fibrosis reduction (Chalasani et al., 2020). Moreover, TGF-β neutralization with antibodies such as fresolimumab and metelimumab has been investigated in other diseases but discontinued due to unacceptable risks, including immunosuppression and tumorigenesis (Györfi et al., 2018).
Therapeutic efforts targeting the CCL2-CCR2 chemokine axis, including the dual CCR2/CCR5 antagonist cenicriviroc, aimed to inhibit monocyte recruitment to the liver. Despite initial promise, cenicriviroc did not demonstrate sustained antifibrotic efficacy in phase III trials and was discontinued as a monotherapy for MASH (Anstee et al., 2024). Given the role of chemokines in orchestrating hepatic immune cell trafficking, modulation of these axes remains of therapeutic interest. However, broad suppression of monocyte infiltration risks collateral effects on reparative subsets, including TREM2+ macrophages (Hendrikx et al., 2022). To harness the beneficial effects of TREM2+ macrophages, several strategies have been proposed. These include direct TREM2 agonism, gene therapy to enhance TREM2 expression, and modulation of gut permeability and dysbiosis to improve TREM2 activation in hepatic macrophages (Shi et al., 2025).
Neutrophil and T cell modulation
Neutrophils exemplify the complexity of immune targeting in MASLD. They contribute to hepatic injury through granule enzyme secretion and neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation (Chen et al., 2021). Although pharmacological modulation of neutrophil-derived factors and tissue infiltration control is being explored in various conditions, MASLD-specific efficacy remains undetermined (Hwang et al., 2021). Anti-NETosis strategies may hold promise for curbing inflammation, fibrosis, and HCC progression (van der Windt et al., 2018). In contrast, neutrophils perform reparative functions in MASLD. They promote macrophage polarization toward pro-resolving states via ROS and deliver miRNA-223 to suppress inflammatory programs in hepatocytes while restraining fibrogenic signaling in HSCs (Calvente et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2019; He et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). However, therapeutic strategies designed to enhance neutrophil-mediated repair remain undeveloped.
T cell-targeted approaches have been evaluated in preclinical models. For example, monoclonal antibodies targeting the integrin α4β7 receptor have demonstrated efficacy in preventing CD4+ T cells migration to both the intestinal tract and the liver, resulting in a reduction of hepatic inflammation and fibrotic progression (Rai et al., 2020). Clinical efficacy and safety of these strategies remain to be established in human cohorts.
Immune-mediated fibrosis remission
Hepatic fibrosis demonstrates unique potential for reversibility compared to fibrosis in other organs (Sun and Kisseleva, 2015; Pei et al., 2023). Accumulating evidence indicates that fibrosis remission is, to a significant extent, an immune-mediated process involving macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells, and T cells (Tacke et al., 2023). Therefore, immune cells have been targeted for this purpose. In preclinical models, chimeric antigen receptor-modified macrophages (CAR-Ms) targeting the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) have shown significant efficacy in reducing liver fibrosis (Dai et al., 2024). CAR-Ms exert antifibrotic effects by phagocytosing activated HSCs, presenting antigens to CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and promoting neutrophil recruitment and macrophage polarization toward anti-inflammatory phenotypes. However, CAR-Ms therapy remains experimental, with clinical applicability yet to be established. Furthermore, clinical studies of autologous macrophage infusion have demonstrated improvements in fibrosis (Moroni et al., 2019). Although a subsequent phase II randomized trial in compensated cirrhosis did not replicate those results, the treated cohort experienced few liver-related events and no deaths, underscoring the need for further evaluation in larger trials (Brennan et al., 2025).
Perspectives
The complex nature of MASLD necessitates therapeutic strategies that acknowledge it as an immunometabolic disorder. Ongoing data are transforming drug development, shifting the focus from treatments that rely solely on weight loss to approaches that target the interaction between metabolism and the immune system. Therapies that concentrate exclusively on metabolic pathways often provide anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic benefits by reducing metabolic damage. However, the lasting reversal of fibrosis may be limited. Strategies targeting immune cell functions must strike a balance between suppressing inflammation and preserving protective mechanisms. Over-suppression can compromise the immune response and liver clearance functions, while unchecked immune activation can lead to tissue damage and progressive fibrosis. Some cellular therapies, such as CAR-macrophage treatments and autologous macrophage infusions, illustrate the use of intentional immune modulation to address liver diseases. These methods can reprogram immune cells to reverse disease progression rather than exacerbating it. It is also important to consider the combination of synergistic mechanisms, which improves tolerability and reduces the likelihood of developing therapeutic resistance. The heterogeneity of MASLD necessitates tailored therapeutic strategies instead of generic solutions. Precision medicine approaches, informed by new insights into genetic variants related to metabolism and immune interactions, have the potential to enhance patient stratification and tailor treatments to individual disease mechanisms. The clinical implementation of these approaches relies on the development of biomarkers that can simultaneously capture both metabolic dysfunction and immune activation states. These biomarkers are essential for optimizing trial design and monitoring therapeutic responses.
The future of treating MASLD lies not in choosing between metabolic and immune interventions, but in integrating both systems to halt disease progression and restore liver balance. A comprehensive understanding of immune dynamics in liver disease is essential for developing next-generation therapies that effectively combine metabolic and immunological targets. This potential integration represents a promising pathway to transform MASLD from a progressively worsening condition into one that is treatable and reversible.
Statements
Author contributions
SG-S: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. A-IO: Writing – review and editing. JC: Writing – review and editing. JJ: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Research in our laboratory is funded by LA CAIXA FOUNDATION (Barcelona, Spain), grant number HR21-00430 and the INSTITUTO DE SALUD CARLOS III (Madrid Spain) co-funded by the European Union, grant number PI24/01146.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
- ACC
acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- ADAM17
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- AMPK
adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- AP-1
activator protein 1
- AST
aspartate aminotransferase
- BMI
body mass index
- CAR-M
chimeric antigen receptor macrophage
- CCL2
C-C motif chemokine ligand 2
- CCR2
C-C chemokine receptor type 2
- CCR5
C-C chemokine receptor type 5
- CD4
cluster of differentiation 4
- CD8
cluster of differentiation 8
- COX-2
cyclooxygenase-2
- CRP
C-reactive protein
- CXCR6
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 6
- DNL
de novo lipogenesis
- FASN
fatty acid synthase
- FDA
food and drug administration
- FGF21
fibroblast growth factor 21
- FXR
farnesoid X receptor
- GCK
glucokinase
- GIP
glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide
- GLP-1
glucagon like peptide 1
- GLP-1R
glucagon like peptide 3 receptor
- GPD1
glycerol 3 phosphate dehydrogenase 1
- HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HGF
hepatocyte growth factor
- HPRT1
hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1
- HSC
hepatic stellate cells
- HSD17B13
hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 13
- IFN-γ
interferon gamma
- IL-1
interleukin 1
- IL-1β
interleukin 1 beta
- IL-6
interleukin 6
- IL-17
interleukin 17
- IL-23
interleukin 23
- iNOS
inducible nitric oxide synthase
- LBP
lipopolysaccharide binding protein
- MASH
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
- MASLD
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease miRNA-223, microRNA-223
- mTOR
mechanistic target of rapamycin
- NET
neutrophil extracellular traps
- NF-κB
nuclear factor of the κ chain in B cells
- NLRP3
nucleotide binding domain, leucine-rich repeat protein 3
- NRF2
nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2
- PPARα
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha
- PPARβ/δ
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor beta/delta
- PPARγ
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma
- RNA
ribonucleic acid
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- SGLT-2
sodium glucose cotransporter 2
- STAT1
signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
- TGF-β
transforming growth factor beta
- Th17
T helper 17 cells
- THR-β
thyroid hormone receptor beta
- TLR
toll like receptor
- TNFα
tumor necrosis factor alpha
- TREM2
triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2
- uPAR
urokinase type plasminogen activator receptor.
References
1
Anstee Q. M. Reeves H. L. Kotsiliti E. Govaere O. Heikenwalder M. (2019). From NASH to HCC: current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.16, 411–428. 10.1038/s41575-019-0145-7
2
Anstee Q. M. Neuschwander-Tetri B. A. Wai-Sun Wong V. Abdelmalek M. F. Rodriguez-Araujo G. Landgren H. et al (2024). Cenicriviroc lacked efficacy to treat liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: AURORA phase III randomized study. Clin. Gastroenterology Hepatology22, 124–134.e1. 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.003
3
Armstrong M. J. Gaunt P. Aithal G. P. Barton D. Hull D. Parker R. et al (2016). Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet387, 679–690. 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X
4
Barb D. Kalavalapalli S. Godinez Leiva E. Bril F. Huot-Marchand P. Dzen L. et al (2025). Pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in patients with T2D and MASLD. J. Hepatol.82, 979–991. 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.12.045
5
Boland M. L. Laker R. C. Mather K. Nawrocki A. Oldham S. Boland B. B. et al (2020). Resolution of NASH and hepatic fibrosis by the GLP-1R/GcgR dual-agonist Cotadutide via modulating mitochondrial function and lipogenesis. Nat. Metab.2, 413–431. 10.1038/S42255-020-0209-6
6
Brennan P. N. MacMillan M. Manship T. Moroni F. Glover A. Troland D. et al (2025). Autologous macrophage therapy for liver cirrhosis: a phase 2 open-label randomized controlled trial. Nat. Med.31, 979–987. 10.1038/S41591-024-03406-8
7
Brunner K. T. Henneberg C. J. Wilechansky R. M. Long M. T. (2019). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity treatment. Curr. Obes. Rep.8, 220–228. 10.1007/S13679-019-00345-1
8
Calvente C. J. Tameda M. Johnson C. D. Del Pilar H. Lin Y. C. Adronikou N. et al (2019). Neutrophils contribute to spontaneous resolution of liver inflammation and fibrosis via microRNA-223. J. Clin. Invest129, 4091–4109. 10.1172/JCI122258
9
Castro Cabezas M. de Jong V. D. (2025). Can targeting de novo lipogenesis improve liver health?Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.10, 873–874. 10.1016/S2468-1253(25)00161-X
10
Chalasani N. Abdelmalek M. F. Garcia-Tsao G. Vuppalanchi R. Alkhouri N. Rinella M. et al (2020). Effects of belapectin, an inhibitor of Galectin-3, in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Gastroenterology158, 1334–1345.e5. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.296
11
Chen S. Guo H. Xie M. Zhou C. Zheng M. (2021). Neutrophil: an emerging player in the occurrence and progression of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Int. Immunopharmacol.97, 107609. 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107609
12
Christofides A. Konstantinidou E. Jani C. Boussiotis V. A. (2021). The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in immune responses. Metabolism114, 154338. 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154338
13
Cui A. Li J. Ji S. Ma F. Wang G. Xue Y. et al (2020). The effects of b1344, a novel fibroblast growth factor 21 analog, on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in nonhuman primates. Diabetes69, 1611–1623. 10.2337/db20-0209
14
Daemen S. Gainullina A. Kalugotla G. He L. Chan M. M. Beals J. W. et al (2021). Dynamic shifts in the composition of resident and recruited macrophages influence tissue remodeling in NASH. Cell Rep.34, 108626. 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108626
15
Dai H. Zhu C. Huai Q. Xu W. Zhu J. Zhang X. et al (2024). Chimeric antigen receptor-modified macrophages ameliorate liver fibrosis in preclinical models. J. Hepatol.80, 913–927. 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.01.034
16
Drucker D. J. (2022). GLP-1 physiology informs the pharmacotherapy of obesity. Mol. Metab.57, 101351. 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101351
17
Estes C. Anstee Q. M. Arias-Loste M. T. Bantel H. Bellentani S. Caballeria J. et al (2018). Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol.69, 896–904. 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036
18
Fiorucci S. Zampella A. Ricci P. Distrutti E. Biagioli M. (2022). Immunomodulatory functions of FXR. Mol. Cell Endocrinol.551, 111650. 10.1016/j.mce.2022.111650
19
Francque S. Szabo G. Abdelmalek M. F. Byrne C. D. Cusi K. Dufour J. F. et al (2021). Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: the role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.18, 24–39. 10.1038/S41575-020-00366-5
20
Fredrickson G. Florczak K. Barrow F. Mahmud S. Dietsche K. Wang H. et al (2024). TREM2 macrophages mediate the beneficial effects of bariatric surgery against MASH. Hepatology81, 1776–1791. 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001098
21
Ganguly S. Rosenthal S. B. Ishizuka K. Troutman T. D. Rohm T. V. Khader N. et al (2024). Lipid-associated macrophages’ promotion of fibrosis resolution during MASH regression requires TREM2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.121, e2405746121. 10.1073/pnas.2405746121
22
Györfi A. H. Matei A. E. Distler J. H. W. (2018). Targeting TGF-β signaling for the treatment of fibrosis. Matrix Biol.68 (69), 8–27. 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.12.016
23
Harrison S. A. Alkhouri N. Davison B. A. Sanyal A. Edwards C. Colca J. R. et al (2020). Insulin sensitizer MSDC-0602K in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIb study. J. Hepatol.72, 613–626. 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.023
24
Harrison S. A. Frias J. P. Neff G. Abrams G. A. Lucas K. J. Sanchez W. et al (2023). Safety and efficacy of once-weekly efruxifermin versus placebo in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (HARMONY): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.8, 1080–1093. 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00272-8
25
Harrison S. A. Bedossa P. Guy C. D. Schattenberg J. M. Loomba R. Taub R. et al (2024). A phase 3, randomized, controlled trial of resmetirom in NASH with liver fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med.390, 497–509. 10.1056/NEJMoa2309000
26
Harrison S. A. Browne S. K. Suschak J. J. Tomah S. Gutierrez J. A. Yang J. et al (2025). Effect of pemvidutide, a GLP-1/glucagon dual receptor agonist, on MASLD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Hepatol.82, 7–17. 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.07.006
27
He Y. Rodrigues R. M. Wang X. Seo W. Ma J. Hwang S. et al (2021). Neutrophil-to-hepatocyte communication via LDLR-dependent miR-223–enriched extracellular vesicle transfer ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Investigation131, e141513. 10.1172/JCI141513
28
He Y. Chen Y. Qian S. van Der Merwe S. Dhar D. Brenner D. A. et al (2025). Immunopathogenic mechanisms and immunoregulatory therapies in MASLD. Cell. and Mol. Immunol.2025, 1159–1177. 10.1038/s41423-025-01307-5
29
Hendrikx T. Porsch F. Kiss M. G. Rajcic D. Papac-Miličević N. Hoebinger C. et al (2022). Soluble TREM2 levels reflect the recruitment and expansion of TREM2+ macrophages that localize to fibrotic areas and limit NASH. J. Hepatol.77, 1373–1385. 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.004
30
Hernández-Aguilera A. Rull A. Rodríguez-Gallego E. Riera-Borrull M. Luciano-Mateo F. Camps J. et al (2013). Mitochondrial dysfunction: a basic mechanism in inflammation-related non-communicable diseases and therapeutic opportunities. Mediat. Inflamm.2013, 1–13. 10.1155/2013/135698
31
Hotamisligil G. S. (2006). Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature444, 860–867. 10.1038/nature05485
32
Hwang S. Yun H. Moon S. Cho Y. E. Gao B. (2021). Role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne)12, 751802. 10.3389/fendo.2021.751802
33
Jin L. Yang R. Geng L. Xu A. (2023). Fibroblast growth factor–based pharmacotherapies for the treatment of obesity-related metabolic complications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.63, 359–382. 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-032322-093904
34
Kanwal F. Neuschwander-Tetri B. A. Loomba R. Rinella M. E. (2024). Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: update and impact of new nomenclature on the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases practice guidance on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology79, 1212–1219. 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000670
35
Keam S. J. (2024). Resmetirom: first approval. Drugs84, 729–735. 10.1007/s40265-024-02045-0
36
Lassailly G. Caiazzo R. Ntandja-Wandji L. C. Gnemmi V. Baud G. Verkindt H. et al (2020). Bariatric surgery provides long-term resolution of Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and regression of fibrosis. Gastroenterology159, 1290–1301.e5. 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.006
37
Lee Y. Doumouras A. G. Yu J. Brar K. Banfield L. Gmora S. et al (2019). Complete resolution of nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterology Hepatology17, 1040–1060.e11. 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.10.017
38
Lefere S. Puengel T. Hundertmark J. Penners C. Frank A. K. Guillot A. et al (2020). Differential effects of selective- and pan-PPAR agonists on experimental steatohepatitis and hepatic macrophages. J. Hepatol.73, 757–770. 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.025
39
Li Z. Feng P.-P. Zhao Z.-B. Zhu W. Gong J.-P. Du H.-M. (2019). Liraglutide protects against inflammatory stress in non-alcoholic fatty liver by modulating Kupffer cells M2 polarization via cAMP-PKA-STAT3 signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.510, 20–26. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.149
40
Lin X. F. Cui X. N. Yang J. Jiang Y. F. Wei T. J. Xia L. et al (2024). SGLT2 inhibitors ameliorate NAFLD in mice via downregulating PFKFB3, suppressing glycolysis and modulating macrophage polarization. Acta Pharmacol. Sin.45, 2579–2597. 10.1038/S41401-024-01389-3
41
Liu W. You D. Lin J. Zou H. Zhang L. Luo S. et al (2024). SGLT2 inhibitor promotes ketogenesis to improve MASH by suppressing CD8+ T cell activation. Cell Metab.36, 2245–2261.e6. 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.08.005
42
Liu H. Lefere S. Guillot A. Zheng M. H. Tacke F. (2025). Bariatric surgery for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): current knowledge of mechanisms. Hepatology. 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001417
43
Loomba R. Friedman S. L. Shulman G. I. (2021). Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell184, 2537–2564. 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.015
44
Loomba R. Sanyal A. J. Kowdley K. V. Bhatt D. L. Alkhouri N. Frias J. P. et al (2023). Randomized, controlled trial of the FGF21 analogue pegozafermin in NASH. N. Engl. J. Med.389, 998–1008. 10.1056/NEJMoa2304286
45
Loomba R. Bedossa P. Grimmer K. Kemble G. Bruno Martins E. McCulloch W. et al (2024a). Denifanstat for the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.9, 1090–1100. 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00246-2
46
Loomba R. Hartman M. L. Lawitz E. J. Vuppalanchi R. Boursier J. Bugianesi E. et al (2024b). Tirzepatide for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis with liver fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med.391, 299–310. 10.1056/NEJMoa2401943
47
Ludwig J. Viggiano T. R. McGill D. B. Ott B. J. (1980). Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Mayo Clinic experiences with a Hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin. Proc.55, 434–438. 10.1016/S0025-6196(24)00530-5
48
Ma C. H. Wang S. Dong B. Tian Y. (2025). Metabolic reprograming of immune cells in MASH. Hepatology. 10.1097/HEP.0000000000001371
49
Martínez García de la Torre R. A. Vallverdú J. Xu Z. Ariño S. Ferrer-Lorente R. Zanatto L. et al (2025). Trajectory analysis of hepatic stellate cell differentiation reveals metabolic regulation of cell commitment and fibrosis. Nat. Commun.16, 1489. 10.1038/S41467-025-56024-4
50
Meng Z. Liu X. Li T. Fang T. Cheng Y. Han L. et al (2021). The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin negatively regulates IL-17/IL-23 axis-mediated inflammatory responses in T2DM with NAFLD via the AMPK/mTOR/autophagy pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol.94, 107492. 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107492
51
Mladenić K. Lenartić M. Marinović S. Polić B. Wensveen F. M. (2024). The “Domino effect” in MASLD: the inflammatory cascade of steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Immunol.54, e2149641. 10.1002/eji.202149641
52
Moroni F. Dwyer B. J. Graham C. Pass C. Bailey L. Ritchie L. et al (2019). Safety profile of autologous macrophage therapy for liver cirrhosis. Nat. Med.25, 1560–1565. 10.1038/S41591-019-0599-8
53
Newsome P. N. Ambery P. (2023). Incretins (GLP-1 receptor agonists and dual/triple agonists) and the liver. J. Hepatol.79, 1557–1565. 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.07.033
54
Noureddin M. (2024). MASH clinical trials and drugs pipeline: an impending tsunami. Hepatology82, 1325–1340. 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000860
55
Noureddin M. Khan S. Portell F. Jorkasky D. Dennis J. Khan O. et al (2023). Safety and efficacy of once-daily HU6 versus placebo in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and high BMI: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.8, 1094–1105. 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00198-X
56
Ong Lopez A. M. C. Pajimna J. A. T. (2024). Efficacy of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on hepatic fibrosis and steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep.14, 2122. 10.1038/S41598-024-52603-5
57
O’Farrell M. Duke G. Crowley R. Buckley D. Martins E. B. Bhattacharya D. et al (2022). FASN inhibition targets multiple drivers of NASH by reducing steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis in preclinical models. Sci. Rep.12, 15661. 10.1038/s41598-022-19459-z
58
Pais R. Aron‐Wisnewsky J. Bedossa P. Ponnaiah M. Oppert J. Siksik J. et al (2022). Persistence of severe liver fibrosis despite substantial weight loss with bariatric surgery. Hepatology76, 456–468. 10.1002/hep.32358
59
Pei Q. Yi Q. Tang L. (2023). Liver fibrosis resolution: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 9671. 10.3390/ijms24119671
60
Peiseler M. Schwabe R. Hampe J. Kubes P. Heikenwälder M. Tacke F. (2022). Immune mechanisms linking metabolic injury to inflammation and fibrosis in fatty liver disease – novel insights into cellular communication circuits. J. Hepatol.77, 1136–1160. 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.012
61
Perazza F. Leoni L. Colosimo S. Musio A. Bocedi G. D’Avino M. et al (2024). Metformin and the liver: unlocking the full therapeutic potential. Metabolites14, 186. 10.3390/metabo14040186
62
Petta S. Targher G. Romeo S. Pajvani U. B. Zheng M. H. Aghemo A. et al (2024). The first MASH drug therapy on the horizon: current perspectives of resmetirom. Liver Int.44, 1526–1536. 10.1111/liv.15930
63
Polyzos S. A. Kountouras J. Mantzoros C. S. (2019). Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism92, 82–97. 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.014
64
Qiu Y.-Y. Zhang J. Zeng F.-Y. Zhu Y. Z. (2023). Roles of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Pharmacol. Res.192, 106786. 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106786
65
Rai R. P. Liu Y. Iyer S. S. Liu S. Gupta B. Desai C. et al (2020). Blocking integrin α4β7-mediated CD4 T cell recruitment to the intestine and liver protects mice from western diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol.73, 1013–1022. 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.047
66
Ross T. T. Crowley C. Kelly K. L. Rinaldi A. Beebe D. A. Lech M. P. et al (2020). Acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibition improves multiple dimensions of NASH pathogenesis in model systems. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.10, 829–851. 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2020.06.001
67
Sanyal A. J. Ratziu V. Loomba R. Anstee Q. M. Kowdley K. V. Rinella M. E. et al (2023). Results from a new efficacy and safety analysis of the REGENERATE trial of obeticholic acid for treatment of pre-cirrhotic fibrosis due to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol.79, 1110–1120. 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.07.014
68
Sanyal A. J. Bedossa P. Fraessdorf M. Neff G. W. Lawitz E. Bugianesi E. et al (2024). A phase 2 randomized trial of survodutide in MASH and fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med.391, 311–319. 10.1056/NEJMoa2401755
69
Sanyal A. J. Newsome P. N. Kliers I. Østergaard L. H. Long M. T. Kjær M. S. et al (2025). Phase 3 trial of semaglutide in Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med.392, 2089–2099. 10.1056/NEJMoa2413258
70
Shankar S. S. Daniels S. J. Robertson D. Sarv J. Sánchez J. Carter D. et al (2024). Safety and efficacy of novel incretin Co-agonist cotadutide in biopsy-proven noncirrhotic MASH with fibrosis. Clin. Gastroenterology Hepatology22, 1847–1857.e11. 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.04.017
71
Shera S. Katzka W. Yang J. C. Chang C. Arias-Jayo N. Lagishetty V. et al (2024). Bariatric-induced microbiome changes alter MASLD development in association with changes in the innate immune system. Front. Microbiol.15, 1407555. 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1407555
72
Shi S. Zhou Y. Zhang H. Zhang J. (2025). TREM2 in MASH: integrating lipid metabolism and immune response. Front. Immunol.16, 1604837. 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1604837
73
Sookoian S. Pirola C. J. Valenti L. Davidson N. O. (2020). Genetic pathways in nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease: insights from systems biology. Hepatology72, 330–346. 10.1002/hep.31229
74
Sotoudeheian M. (2024). Galectin-3 and severity of liver fibrosis in Metabolic dysfunction-associated Fatty liver disease. Protein Pept. Lett.31, 290–304. 10.2174/0109298665301698240404061300
75
Staels B. Butruille L. Francque S. (2023). Treating NASH by targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. J. Hepatol.79, 1302–1316. 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.07.004
76
Subramanian P. Hampe J. Tacke F. Chavakis T. (2022). Fibrogenic pathways in Metabolic dysfunction associated Fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci.23, 6996. 10.3390/ijms23136996
77
Sun M. Kisseleva T. (2015). Reversibility of liver fibrosis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol.39, S60–S63. 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.06.015
78
Tacke F. Puengel T. Loomba R. Friedman S. L. (2023). An integrated view of anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic targets for the treatment of NASH. J. Hepatol.79, 552–566. 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.038
79
Tacke F. Horn P. Wai-Sun Wong V. Ratziu V. Bugianesi E. Francque S. et al (2024). EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol.81, 492–542. 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.04.031
80
Tilg H. Adolph T. E. Dudek M. Knolle P. (2021). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the interplay between metabolism, microbes and immunity. Nat. Metab.3 (12 3), 1596–1607. 10.1038/s42255-021-00501-9
81
US Food and Drug Administration (2025). FDA approves treatment for serious liver disease known as “MASH”. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-treatment-serious-liver-disease-known-mash (Accessed August 25, 2025).
82
van der Windt D. J. Sud V. Zhang H. Varley P. R. Goswami J. Yazdani H. O. et al (2018). Neutrophil extracellular traps promote inflammation and development of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology68, 1347–1360. 10.1002/hep.29914
83
Verrastro O. Panunzi S. Castagneto-Gissey L. De Gaetano A. Lembo E. Capristo E. et al (2023). Bariatric–metabolic surgery versus lifestyle intervention plus best medical care in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (BRAVES): a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet401, 1786–1797. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00634-7
84
Vilar-Gomez E. Martinez-Perez Y. Calzadilla-Bertot L. Torres-Gonzalez A. Gra-Oramas B. Gonzalez-Fabian L. et al (2015). Weight loss through lifestyle modification significantly reduces features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology149, 367–e15. 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.005
85
Wang X. Seo W. Park S. H. Fu Y. Hwang S. Rodrigues R. M. et al (2021). MicroRNA-223 restricts liver fibrosis by inhibiting the TAZ-IHH-GLI2 and PDGF signaling pathways via the crosstalk of multiple liver cell types. Int. J. Biol. Sci.17, 1153–1167. 10.7150/ijbs.58365
86
Wang X. He Q. Zhou C. Xu Y. Liu D. Fujiwara N. et al (2023). Prolonged hypernutrition impairs TREM2-dependent efferocytosis to license chronic liver inflammation and NASH development. Immunity56, 58–77.e11. 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.11.013
87
Xie H. Wang J. Zhao Q. (2025). Identification of potential metabolic biomarkers and immune cell infiltration for metabolic associated steatohepatitis by bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. Sci. Rep.15, 16596–15. 10.1038/s41598-025-86397-x
88
Yang W. Tao Y. Wu Y. Zhao X. Ye W. Zhao D. et al (2019). Neutrophils promote the development of reparative macrophages mediated by ROS to orchestrate liver repair. Nat. Commun.10 (1 10), 1076–14. 10.1038/s41467-019-09046-8
89
Ye D. Wang J. Shi J. Ma Y. Chen J. Hu X. et al (2024). Genetically predicted metabolites mediate the association between immune cells and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: a mendelian randomization study. Lipids Health Dis.23, 249. 10.1186/S12944-024-02245-3
90
Young K. E. Flaherty S. Woodman K. M. Sharma-Walia N. Reynolds J. M. (2017). Fatty acid synthase regulates the pathogenicity of Th17 cells. J. Leukoc. Biol.102, 1229–1235. 10.1189/jlb.3AB0417-159RR
91
Younossi Z. M. Stepanova M. Ong J. Trimble G. AlQahtani S. Younossi I. et al (2021). Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the Most rapidly increasing indication for liver transplantation in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterology Hepatology19, 580–589.e5. 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.05.064
92
Yu Y. He J. Li S. Song L. Guo X. Yao W. et al (2016). Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation by activating Nrf2 and suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol.38, 144–152. 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.05.026
93
Yu L. Hong W. Lu S. Li Y. Guan Y. Weng X. et al (2022). The NLRP3 inflammasome in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis: therapeutic targets and treatment. Front. Pharmacol.13, 780496. 10.3389/fphar.2022.780496
94
Yu L. Gao F. Li Y. Su D. Han L. Li Y. et al (2024). Role of pattern recognition receptors in the development of MASLD and potential therapeutic applications. Biomed. Pharmacother.175, 116724. 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116724
95
Zamani-Garmsiri F. Hashemnia S. M. R. Shabani M. Bagherieh M. Emamgholipour S. Meshkani R. (2021). Combination of metformin and genistein alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Nutr. Biochem.87, 108505. 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108505
96
Zhao X. Chen J. Sun H. Zhang Y. Zou D. (2022). New insights into fibrosis from the ECM degradation perspective: the macrophage-MMP-ECM interaction. Cell Biosci.12, 117. 10.1186/s13578-022-00856-w
97
Zhou L. Qiu X. Meng Z. Liu T. Chen Z. Zhang P. et al (2024). Hepatic danger signaling triggers TREM2+ macrophage induction and drives steatohepatitis via MS4A7-dependent inflammasome activation. Sci. Transl. Med.16, eadk1866. 10.1126/scitranslmed.adk1866
Summary
Keywords
genetics, GLP-1, inflammation, lipid metabolism, MASH, mitochondrial dysfunction, obesity, pharmacotherapies
Citation
González-Serrano S, Onoiu A-I, Camps J and Joven J (2025) Immunometabolic integration in therapeutic strategies for managing MASLD. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1693753. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1693753
Received
27 August 2025
Revised
14 October 2025
Accepted
21 October 2025
Published
10 November 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Jose C. Fernandez-Checa, Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), Spain
Reviewed by
Ernest Saenz, Heidelberg University, Germany
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 González-Serrano, Onoiu, Camps and Joven.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sergio González-Serrano, sergio.gonzalez@estudiants.urv.cat; Jorge Joven, jorge.joven@salutsantjoan.cat
ORCID: Sergio González-Serrano, orcid.org/0009-0001-6380-7982; Alina-Iuliana Onoiu, orcid.org/0009-0006-9483-498X; Jordi Camps, orcid.org/0000-0002-3165-3640; Jorge Joven, orcid.org/0000-0003-2749-4541
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.