Abstract
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been used in the treatment of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) in patients for hundreds of years. Ethnopharmacological researches have been conducted in recent years to elucidate their therapeutic effects on cognitive deficits and potential mechanisms in animal models. This manuscript critically reviewed recent 5-year experimental researches from PubMed on the topic, including 11 TCM formulae, 8 herb extracts, and 21 pure compounds extracted from TCM, including polyphenols, flavonoids, alkaloids, terpenoids, saponins, iridoid glycosides, glucosides, and others in rodent CCH models, using bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO, 2VO), bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS), and unilateral common carotid artery occlusion (UCCAO). The underlying mechanisms are multiple, including the maintenance of blood brain barrier and endothelium integrity, the increase in cerebral blood flow, the amelioration of white matter lesions, the modulation of microglia M1/M2 phenotype, the scavenge of reactive oxidative oxygen species and reduction of proinflammatory factors, the maintenance of mitochondrial function, the inhibition of apoptosis, ferroptosis and pyroptosis, and the promotion of neuronal regeneration and angiogenesis through the regulation of gene/protein expressions, including the Toll, NF-κB, MAPK, PPARγ, and/or Nrf2 pathways. These mechanisms are not mutually exclusive, rather they play an integrated role to fortify the multi-components, multi-targets feature of TCM in the treatment of CCH and human vascular cognitive impairments.
1 Introduction
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) refers to a long-term reduction of cerebral blood flow (CBF), typically below 24–45 mL/100 g/min (normal 50–60 mL/100 g/min), and is the major cause of vascular cognitive impairments in a step-wise progression manner from mild to moderate cognitive impairment to vascular dementia (VaD) (Rajeev et al., 2023). Blood brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction occurs early in CCH, contributing to white matter damage and cognitive deficits (Xu et al., 2022). Pathologically, CCH triggers oxidative stress, neuroinflammation (Poh et al., 2022), mitochondrial dysfunction (Li et al., 2025), synaptic damage and Aβ accumulation (Wang et al., 2010), contributing to cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), VaD, and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Cerebral ischemic stroke occurs not only after acute CBF reduction and focal cell death but also under CCH (Zhang et al., 2020; Zheng et al., 2023; Fadoul et al., 2024). The commonly used preclinical model for acute cerebral ischemic stroke is middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mainly characterized by cerebral infarction (Tuo et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2023; Fadoul et al., 2024), which is different from CCH rodent models characterized mainly by cognitive impairments (Tuo et al., 2021; Kimura et al., 2025). Traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) have been shown to be effective against both acute and chronic ischemic stroke through different mechanisms at different stages (Zhang et al., 2020; Li et al., 2022). This review focused mainly on CCH.
Figure 1 illustrates major pathophysiology of CCH: Cerebral blood flow (CBF) reduction during CCH leads to blood brain barrier dysfunction (Rajeev et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2022). The BBB tightly regulates the movements between blood and brain, BBB breakdown could cause energy imbalance, glial activation and neuroinflammation, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction (Rajeev et al., 2023), which initiates a vicious cycle contributing to microglia over-activation (Zhang et al., 2024), mitochondrial dysfunction (Wang Y. et al., 2023), mitophagy dysregulation (Chen et al., 2024), oxidative damage (Rajeev et al., 2023), leading to neuronal apoptosis, ferroptosis (Zhao et al., 2022), pyroptosis (He et al., 2023), and white matter injury (Kimura et al., 2025). These pathologies ultimately result in cognitive impairments and progress to CSVD, AD, and VaD.
FIGURE 1
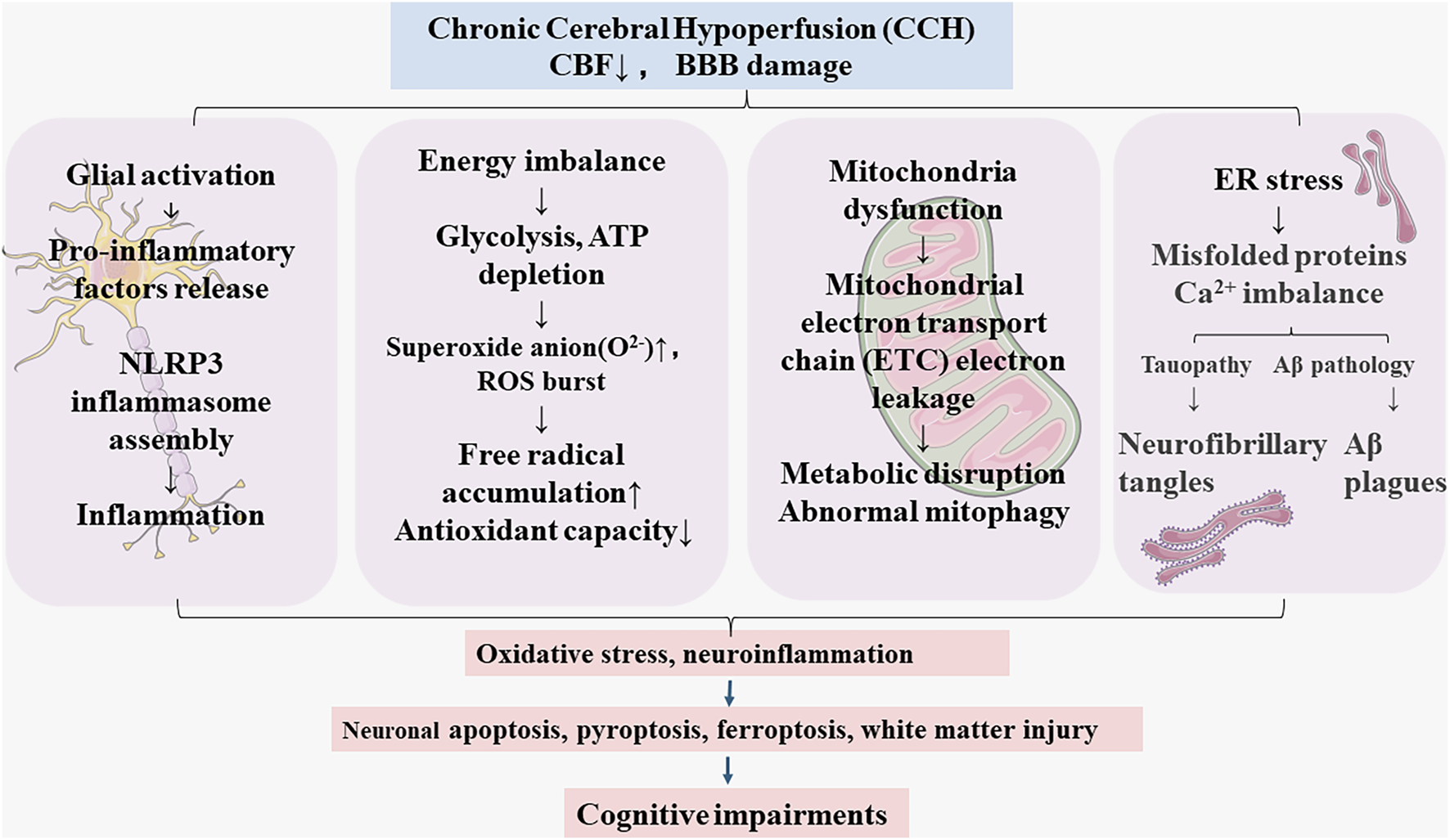
The pathological features of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH).
Traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) have been used in the treatment of cognitive impairments, AD, VaD and various neurodegenerative diseases for thousands of years (Pei et al., 2020), and are still used today, especially for patients with mild cognitive impairment (Liang et al., 2022). The unique feature of TCM is the compound formulation, in which poly-herbs and other ingredients are composed in defined ratios to play integrated roles as “Sovereign, Minister, Assistant, and Courier” (君臣佐使 in Chinese). In 2025 Edition of Pharmacopeia of China, over 1,600 formulae are listed for treatment of various diseases and are available in Chinese drug stores (Pharmacopoeia, 2025). Front Pharmacol has published a nice review on TCM formulae against CCH (Wang Y. et al., 2023), and TCM formulae and extracts against ischemia-reperfusion induced cerebrovascular diseases (Cheng et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2024) to provide evidence of TCM as the potential research direction. The pure compounds (monomers) extracted from single herbs from TCMs, however, emerge as the novel research trend (Xie et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024).
The present manuscript aimed to review recent 5-year publications in PubMed on the protective effects of TCMs against preclinical CCH models, not to duplicate the existing reviews (Wang Y. et al., 2023). We started with 11 formulae, followed by 8 herb extracts, and finally focused on 21 pure compounds extracted from herbs against various CCH animal models, focusing on efficacy and underlying mechanisms. The bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO, 2VO), including gradual 2VO (right artery was ligated first and the left ligation 1 week later), Unilateral common carotid artery occlusion (UCCAO), and bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS) (Tuo et al., 2021; Kimura et al., 2025) were selected, while the MCAO model was excluded as MCAO produced acute cerebral ischemic stroke compared to CCH of 2VO, UCCAO and BCAS, and had been reviewed recently (Zheng et al., 2023).
2 The protective effects of TCM formulae against CCH animal models
Compound formulations are the core form of clinical applications of TCM. By combining multiple medicinal herbs, formulae could achieve synergistic efficacy in the treatment of complex diseases through multi-component and multi-target mechanisms, which aligns with modern medicine’s combination therapy. The formulae strategy is also consistent with paradigm of modern systems biology and network pharmacology, offering the best therapeutic efficacy. Nine formulae against CCH models have been reviewed in Front Pharmacol (Wang Y. et al., 2023), the researches on additional 11 formulae in recent 4 years are concisely listed in Table 1, and detailed descriptions in the following text. The Chinese names of the formulae were included in the text to facilitate reader’s understanding as exampled by previous reviews on TCM formulae in Front Pharmacol (Wang Y. et al., 2022; Wang Y. et al., 2023).
TABLE 1
| TCM formulae | Model | Effects | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buqi Huoxue Tong nao | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficit and pathology; anti-inflammation; anti-apotosis. | ↓TNFα, IL-1β, iNOS, Caspase-3; ↑AKT/PI3K; ↑LXRα/CYP7A1. | Gao et al. (2024) |
| Chuanzhitongluo) | BCAS/mice | Improved cognitive deficit; anti-inflammation via cholinergic pathway. | ↑ChAT, α7nAchR; ↓NF-κB, TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6; RNA-Seq profiled targets. | Wang et al. (2024c) |
| Bushen-Yizhi formula | 2VO/Rats (gradual) | Improved cognitive deficit and pathology; anti-oxidative stress; anti-apotosis. | ↓ Mito PINK1, Parkin; ↓ LC3II/I; Cyto PINK1, Parkin; ↑ LAMP1. | (Xiao et al., 2023) |
| Fo-Shou-San | UCCAO/Mice | Improved cognitive deficit and pathology; anti-oxidative stress; anti-apotosis. | ↓ Ferroptosis marker SLC7A11, GPX4, ROX, 4HNE; ↓ NRF2, HO-1. | Wang et al. (2023a) |
| Shunaoxin dropping pill | 2VO/Rats (gradual) | improved cognitive deficit and hippocampal damage; anti-inflammation; improved fecal microbiota dysbiosis. | ↑SOD; ↓ TNFα, IL-6, IL-10 and MDA; ↑Bacteroidetes, ↓ proteobacteria; modulated metabolomics. | Bo et al. (2023) |
| Modified Dioscorea pills | 2VO/Rats (gradual) | Improved cognitive deficit and hippocampal damage. | ↑ Expression of Ang-1, Ang-2, Tie-2, VEGF and CD43 staining. | Kuang et al. (2023) |
| Xinshubao tablet | BCAS/mice | Improved cognitive deficit; improve CBF; reduced WML and mitochondrial damage; anti-inflammation. | ↓ NF-κB; ↓ activations of microglia and astrocyte; ↑ neurogenesis; ↑ Sox2. | Xiao et al. (2024) |
| Codonopsis decoction | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficit; improved CBF; reduced neuron damage; anti-inflammation. | ↓ CKLF1 and HIF-1α; ↓ CD16/32, TNF-α, IL-1β. | Wang et al. (2024b) |
| Jiawei Kongsheng Zhenzhong Pill | 2VO/Rats (gradual) | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced hippocampal damage; improved synaptic plasticity of hippocampal neurons. | ↑SYN, GAP43, PSD95; ↓ proBDNF/mBDNF. | Wu et al. (2025) |
| Taohong Siwu decoction | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced hippocampal neuron apoptosis; reduced ER stress. | ↓ GRP78 (Bip), p-IRE1α, ATF6, p-eIF2α, ATF4; ↑ Bcl-2, Bax. | Fan et al. (2024) |
| Xi-Xian-Tong_Shuan | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive dysfunction; reduced white matter lesions; anti-inflammation. | ↑ intensity of MBP/NF200 in brain; ↓ IL-6, TNFα, MCP-1 in CSF; ↑ NeuN, MAP2 stain in the brain. | Yan et al. (2022) |
Protective effects of TCM formulae on CCH rodent models.
2.1 Buqi Huoxue Tongnao prescription (BQHXTN, 补气活血通脑方)
Buqi Huoxue Tongnao prescription (BQHXTN, 补气活血通脑方) is a hospital TCM preparation derived from Erchen decoction (Pinellia temata, Citrus maxima Burm.) and Buyang Huanwu decoction (dried root of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge, Angelica sinensis, Paeonia lactiflora Pall, Ligusticum sinense, Prunus persica, Carthamus tinctorius L.), used for treating sequelae of stroke of “Qi-deficiency” and “Blood-stasis,” and improved cerebral blood circulation and neurological functions in patients. In 2VO rats, BOHXTN (2.5–10 g/kg, 30 days) alleviated cognitive impairment, neuron loss, decreased inflammation by inhibiting IL-1β, TNF-α, cleaved caspase-3, and iNOS by activating the PI3K/AKT and LXRα/CYP7A1 signaling pathways. These findings were also observed in BV2 cells subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) (Gao et al., 2024).
2.2 Chuanzhitongluo capsule (CZTL, 川蛭通络胶囊)
Chuanzhitongluo capsule (CZTL, 川蛭通络胶囊) is composed of four ingredients: Leech (Shuizhi), Sichuan lovase Rhizome, dried root of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge, and dried root of Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizona and is reputed for its effective protection against cerebral ischemia. In CCH mice induced by BCAS, CZTL (0.15, 0.3, 0.6, 1.2 g/kg, 30 days) improved the spatial learning and memory abilities by upregulating the choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and α7 subunit-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR); CZTL also inhibited the NF-κB signaling pathway and inflammatory mediators (Wang Z. et al., 2024). CZTL was also effective in improving microcirculation (Sun et al., 2022).
2.3 Bushen-Yizhi formula (BSYZ, 补肾益智方)
Bushen-Yizhi formula (BSYZ, 补肾益智方) consists of 6 herbs (Cnidium monnieri, (L.) Guss, Panax ginseng C.A.Mey, Reynoutria multiflorum Thunb, Paeonia suffruticosa Andr, Ligustrum lucidum Ait, and Lycium barbarum L.) and is used in treating cognitive impairment and neurodegenerative disorders associated with “Kidney deficiency.” In gradual 2VO rats (the left side was ligated 1 week later), BSYZ (3–6 g/kg, 4 weeks) was effective in mitigating cognitive impairments, decreasing pathological amyloid plaque formation, and alleviating oxidative stress in hippocampal regions. Furthermore, the use of OGD/R-injured PC12 cells confirmed these findings. BSYZ drug serum also increased cell survival rates while decreasing intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels (Xiao et al., 2023).
2.4 Fo-Shou-San (FSS, 佛手散)
Fo-Shou-San (FSS, 佛手散) comprises Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels and Ligusticum wallichii Franch. and is used in the treatment of VaD patients. In UCCAO mice, FSS (0.5, 1, 2 g/kg, 32 days) alleviated cognitive impairments and mitigated oxidative stress by regulating the NRF2/HO-1 pathway and decreased the expression of ferroptosis markers, including SLC7A11, GPX4, ROX, and 4-hydroxynonenal (4HNE) (Wang J. et al., 2023).
2.5 Shunaoxin dropping pill (SNX, 舒脑心滴丸)
Shunaoxin dropping pill (SNX, 舒脑心滴丸) has been clinically used to treat cerebrovascular diseases. The recipe of SNX is composed of two herbs, namely, Chuanxiong (Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort) and Danggui (Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels). SNX (60 and 200 mg/kg, 28 days) alleviated cognitive deficits and restored imbalances in fecal microbiota and serum metabolites in rats with CCH. SNX failed to prevent cognitive impairment in CCH rats treated with antibiotics, indicating the importance of the microbiota-gut-brain axis as a potential therapeutic target for treating cognitive impairment induced by CCH (Bo et al., 2023).
2.6 Modified Dioscorea pills (MDP, 改良薯蓣丸)
Modified Dioscorea pills (MDP, 改良薯蓣丸) are composed of 14 herbal ingredients: Dioscorea rhizome, Rehmannia glutinosa, Polygonum multiflorum, Angelica sinensis, Eucommia ulmoides, L. chuanxiong, Codonopsis pilosula, Poria cocos, Atractylodes macrocephala, Paeonia lactiflora, L. barbarum, Acorus tatarinowii, Polygala tenuifolia, and Schisandra chinensis. MDP (1 mL/100 g, 45 days) mitigated neuronal loss and facilitated the repair of impaired hippocampal structures in CCH rats. MDP also enhanced angiogenesis and remodeled microcirculation in CCH rats through the Ang/Tie signaling pathway (Kuang et al., 2023).
2.7 Xinshubao tablet (XSB, 心舒宝片)
Xinshubao tablet (XSB, 心舒宝片) is a patented TCM formula that comprises five Chinese herbal medicines, including air-dried root of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen), P. lactiflora Pall (Baishao), Acanthopanax senticosus (Ciwujia), air-dried root of Curcuma longal L. (Yujin), and air-dried mature fructus of Crataegus pinnatifida (Shanzha). XSB is used for cardiovascular diseases and dementia in patients. In BCAS mice, XSB (3.75–15 g/kg, 8 weeks) improved cognitive deficits and brain pathology through multiple mechanisms: improving cerebral blood flow (CBF), reducing white matter lesions, inhibiting glial cell activation, attenuating neuroinflammation and promoting neurogenesis. Importantly, the NF-κB signaling pathway was identified as a central component in mediating these protective effects (Xiao et al., 2024).
2.8 Codonopsis decoction (党参汤)
Codonopsis decoction(党参汤) is mainly composed of C. pilosula (Franch.) Nannf. and dried fruits of Ginkgo Biloba L. extract and is known for “invigorating the spleen,” “nourishing the lungs,” “promoting blood circulation,” and “generating fluid” properties. Codonopsis decoction (2.7–10.8 g/kg, 4 weeks) demonstrated protective effects against CCH rats by effectively reducing brain damage, improving CBF in ischemic regions, and enhancing learning and memory capabilities, possibly through the reduction of chemokines, hypoxia-inducible factors, and neuroinflammatory mediators (Wang J. et al., 2024).
2.9 Jiawei Kongsheng Zhenzhong Pill (JKZP, 加味孔圣枕中丹)
Jiawei Kongsheng Zhenzhong Pill (JKZP, 加味孔圣枕中丹) is derived from the “Kongsheng Zhenzhong Pill” in “Thousand-Golden-Prescriptions,” and S. miltiorrhiza Bunge, Conioselinum anthriscoides (H.Boissieu), Cornus officinalis Sieb et Zucc., and Cistanche deserticola Ma. were added to strengthen the efficacy in “Tonifying the kidneys,” benefiting the “Vital essence,” activating blood circulation, and removing blood stasis. In gradual 2VO rats, JKZP (11.3 g/kg, 60 days) treatment for 60 days improved learning and memory ability, alleviated neuronal and synaptic structural damage in the hippocampal CA1 region. It reversed the reduction in dendritic spine density and increased the expression of synaptic-related proteins, such as synaptophysin (SYN), growth-associated protein 43 (GAP43), and postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD95). Additionally, JKZP significantly reduced the ratio of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (pro-BDNF) to mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor (mBDNF) by activating S100A10/tPA, thereby improving synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Using primary hippocampal neuron cultures under OGD/R, the efficacy of JKZP drug serum and the importance of the S100A10/tPA/BDNF signaling via sh-S100A10 were verified (Wu et al., 2025).
2.10 Taohong Siwu decoction (TSD, 桃红四物汤)
Taohong Siwu decoction (TSD, 桃红四物汤) is a classic TCM formula composed of R. glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC., Juglans regia L., Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels), Carthamus tinctorius L., P. lactiflora Pall, C. anthriscoides (H. Boissieu), and is used for the treatment of vascular diseases, including VaD in clinics. After 2VO surgery in rats, TSD (4.5–13.5 g/kg, 4 weeks) improved cognitive deficits and ameliorated neuron damage in the CA1 region of hippocampus. Mechanistically, TSD attenuated endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERs) and the unfolded protein response (UPR) responses, and reduced apoptosis (Fan et al., 2024).
2.11 Xi-Xian-Tong-Shuan (豨莶通栓胶囊)
Xi-Xian-Tong-Shuan (豨莶通栓胶囊) is composed of Herba Siegesbeckiae (broiled in honey wine) and 13 other ingredients that could remove “Wind-phlegm,” produce “Tendon relaxation,” cause “Meridian activation,” activate blood circulation by removal of stasis, and produce “consciousness-restoring” effects, and is mainly used for hemiplegia, hemianesthesia, skewed mouth, deviated tongue, and slurred speech. In 2VO rats, this formula (500 mg/kg, 42 days) improved cognitive impairment in Morris water maze, ameliorated white matter lesions and reduced neuron loss in the cortex and hippocampus, decreased the release of IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, and IL-33 in the cerebrospinal fluid and in plasma (Yan et al., 2022).
Front Pharmacol has already published reviews on TCM formulae against 2VO CCH rodent models include Phlegm-purging decoction (涤痰汤), Shenmayizhi decoction (参麻益智汤), Zuogui Pill (左归丸), Kai Xin San (开心散), Qufeng Tongqiao decoction (祛风通窍汤), Fuzhi capsule (复智胶囊), Modified decoction of Rehmanniae (地黄饮子加减方), Naomaitai capsule (脑脉泰胶囊) and Shenzhi Jiannao Formula (参知健脑方) (Wang Y. et al., 2023). In addition, Danggui Shaoyao San (当归勺药散) (Cheng et al., 2022) and Taohong Siwu decoction (桃红四物汤) have been reported to be effective against MCAO model (Chen et al., 2024). In general, TCM formulae are more effective than single herb, extracts, or pure compounds, as multi-components function in an integrated manner to enhance pharmacological efficacy and reduce toxicity.
3 The protective effects of TCM extracts against CCH animal models
In addition to TCM formulae, a lot of studies are conducted on total extracts from herbs including water extracts, ethanol extracts, total flavonoids, total alkaloids, etc., Table 2 summarized 8 TCM extracts against CCH in animal models.
TABLE 2
| TCM extracts | Model | Effects | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epimedium flavonoids | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; preserved myelin and synapse ultrastructure; reduced neuron loss. | ↑BDNF, NRG1, PI3K; ↓Lingo-1, Fyn, ROCK2; ↑PSD95, Synaptic plasticity-related proteins. | Niu et al. (2020a), Niu et al. (2020b) |
| Scutellaria baicalensis extracts | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; anti-inflammation. | ↓p-ERK, p-JNK, p-P38; ↓Activation of macroglia. | Hwang et al. (2011) |
| Fructus mume extracts | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; anti-neuronal apoptosis; anti-inflammation. | ↓Death of neurons; ↓p38 MAPK phosphorylation; ↓COX-2, IL-1β, IL-6. | Lee et al. (2015) |
| Aster ageratoides extract | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; improves the deterioration of the hippocampal structure. | ↓ Neuronal loss; ↓ Microglial activation. | Jeong et al. (2020) |
| Radix Polygoni Multiflori (Raw and Processed) | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced neuron loss in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. | Both RPM and PPM ameliorated 2VO-related metabolomic abnormalities. | Wu et al. (2022) |
| Nigella sativa extract and active ingredient thymoquinone | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits. | ↑SOD; ↓MDA, AChE activity. | Fanoudi et al. (2019) |
| Ginkgo biloba extracts (GBE) | 2VO/Rats | Suppressed activation of microglia and astrocytes. | ↓TLR4, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6; ↓MyD88, RACE, Ang-II; ↓ERK, p38, JNK; ↑ChAT+ neurons. | Kim et al. (2016) |
| Polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum | 2VO/Mice | Improved cognitive deficits, regulated Treg cells. | ↑Foxp3 (+) Treg cell; ↑IL-10, TGF-β1. | Zhang et al. (2022) |
Protective effects of TCM herb extracts on chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
3.1 Epimedium flavonoids (EF)
Epimedium flavonoids (EF) were mainly extracted from Epimedium brevicornum Maxim., EF 50–200 mg/kg, 12 weeks improved cognitive impairment, reduced white matter lesions and maintained ultrastructure of myelin sheaths and neurons in 2VO rats. The loss of oligodendrocytes was prevented. Mechanistically, EF inhibited the Lingo-1/Fyn/ROCK pathways and activated the BDNF/NRG1/PI3K pathways (Niu et al., 2020b). EF also reduced 2VO-induced apoptosis and neuron loss and ameliorated synapse ultrastructure damage. EF protected synaptic plasticity by increasing the expression of synaptophysin, synaptotagmin-I, synapsin I, PSD-95, p-NNMDAR2B and p-CaMKIIα; and protected neuronal dendrites via increasing MAP2 and NF200 protein expression in the hippocampus of 2VO rats. The NRG1/ErbB4 and BDNF/Fyn signaling pathways were involved in EF protection (Niu et al., 2020a).
3.2 Scutellaria baicalensis (Lamiaceae)
Scutellaria baicalensis (Lamiaceae) water extracts contain several flavonoids, such as wogonin, baicalin, and oroxylin and were orally administered (100 and 200 mg/kg/d) to 2VO rats (starting 20 days after 2VO for 40 days) and in LPS-infused rats via minipump (staring 7 days after minipump implant for 32 days). Scutellaria baicalensis extracts improved cognitive deficit in CCH rats and in chronic LPS-infusion rats. The mechanism is probably mediated through hippocampal mitogen-activated protein kinases (pERK, pJNK, and p-p38) signaling and reduced microglial activation (OX-6 stain) (Hwang et al., 2011).
3.3 Fructus mume (Sieb.)
Fructus mume (Sieb.) ethanol extracts (200 mg/kg/d, po, initiated 21 days after 2VO surgery and continued for 42 days) demonstrated neuroprotective effects in CCH rats by preserving myelin basic protein expression in hippocampal and white matter regions and by decreasing neuroinflammatory markers including COX-2, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the hippocampus, while concurrently inhibiting the activation of TLR4/MyD88 and modulating the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways (Lee et al., 2015).
3.4 Aster ageratoides Turcz
Aster ageratoides Turcz water extracts (AAE, 10, 50 mg/kg, ip, for 14 days) improved cognitive deficits in 2VO rats and in Scopolamine-treated rats. 2VO-induced neuron loss and macroglia activation in the CA1 region of hippocampus were ameliorated following AAE treatments (Jeong et al., 2020).
3.5 Dried-root of Polygonum multiflorum
Dried-root of Polygonum multiflorum is usually processed for the use in TCM. Raw Polygoni Multiflori (RPM) was compared to Processed Polygoni Multiflori (PPM) for their efficacy in the treatment of 2VO rats. Four days after 2VO, the surviving rats were given RPM or PPM (2.0 g/kg, po for 28 days). Both RPM and PPM were effective in improving cognitive deficits, ameliorated neuron loss in the CA1 region of hippocampus. In metabolomic studies, both RPM and PPM ameliorated 2VO-induced abnormal vitamin B6 metabolism, pentose phosphate pathways, taurine and hypotaurine metabolism. The metabolism of cysteine and methionine was regulated only by RPM, and riboflavin metabolism was modulated only by PPM. The results suggested that raw and processed PM had comparable efficacy in the treatment of dementia with some mechanistic differences (Wu et al., 2022).
3.6 Nigella sativa seed hydroalcoholic extracts
Nigella sativa seed hydroalcoholic extracts (NSE, 100, 200, 400 mg/kg, ip for 10 days) improved cognitive deficits in 2VO rats. NSE ameliorated 2VO-elevated lipid peroxidation (MDA) levels, while increased SOD activity in the hippocampus. The 2VO-increased AChE activity was also reduced by NSE. Its active ingredient thymoquinone (TQ 10, 20, 40 mg/kg, ip) also produced similar effects in a dose-dependent manner (Fanoudi et al., 2019).
3.7 Ginkgo biloba L. extracts
Ginkgo biloba L. extracts (GBE 5, 10, 20, 40 mg/kg, po) administration to 2VO rats staring 21 days after 2VO surgery for 42 days suppressed the activation of microglia and astrocytes in the brain, reduced proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6), TLR4, MyD88, RAGE, Ang-II, and phosphorylated MAPKs (ERK, p38, and JNK). GBE treatment restored the ChAT-positive cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain (Kim et al., 2016).
3.8 Polysaccharide
Polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum (Lingzhi) (30 mg/kg, po, 30 days) alleviated cognitive impairment in gradual 2VO mice. Flow cytometry found the treatment of Polysaccharide from G. lucidum increased CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells, and subsequently increased levels of IL-10 and TGF-β1, to ameliorate abnormal metabolism (Zhang et al., 2022).
4 The protective effects of TCM pure compounds against CCH animal models
Further research utilized purified monomeric component from TCM that have clearer structural definitions and controllable purity levels, producing reproducible results compared to TCM formulae and extracts (Xie et al., 2021). It should be mentioned that these pure compounds existed in many medicinal herbs although only the initial isolated herbs were mentioned, and the pure compounds helped to elucidate the mechanisms of protection. Table 3 summarized 21 of TCM monomers against CCH in animal models. The structures of these 21 TCM monomers are presented in Figure 2.
TABLE 3
| Classification | Monomer | Model | Effects | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyphenol | Resveratrol | BCAS/Mice | Improved cognitive deficits without affecting CBF; reduced cholinergic cell loss. | ↑ChAT neurons. | Fagerli et al. (2024) |
| Salvianolic acid A | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits and pathology; suppressed neuronal apoptosis; anti-inflammation. | ↓Caspase-3; ↓TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6; ↓NF-κB; ↑Cryab, Drd2. | Yang et al. (2022) | |
| Salvianolic acid B | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; suppressed neuronal apoptosis. | ↑IGF-1; ↑p-Akt. | Ma et al. (2017) | |
| Honokiol | BCAS/Mice | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced myelin injury; promoted oligodendrocyte regeneration. | ↑Akt/p-Akt, mTOR/p-mTOR; ↑MBP, Sox10, MAG; ↓NG2. | Zhang et al. (2023) | |
| Flavonoids | Icariin | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced hippocampal damage and Aβ deposition. | ↑ADAM10, IDE; ↓Aβ, APP, BACE1, TGF-β1, Smad2/3. | Li et al. (2015) |
| Icarrin | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; ameliorated oxidative stress. | ↑SOD; ↓MDA; ↑ACh, AChE. | Xu et al. (2009) | |
| Icariside II | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced hippocampal neuron loss; reduced Aβ accumulation. | ↓Aβ, APP, BACE1; ↑ADAM10, IDE; ↑BDNF, TrkB, p-Akt, p-CREB; PPARγ. | Yin et al. (2018) | |
| Icariside II | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits and hippocampal damage; promoted neuronal axon regeneration. | ↑GAP43, MAP2; ↓Nogo-A. | Liu et al. (2019) | |
| Alkaloids | Vitexin | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; suppressed neuronal apoptosis; anti-inflammation. | ↑Epac1, Epac2, Rap1, p-ERK; ↓NLRP3, caspase-1, IL-1β, IL-6, caspase-3. | Zhang et al. (2021) |
| Berberine | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced hippocampal damage and apoptosis. | ↓Apoptotic cell death, Caspase 3, MDA; ↑ SOD, CAT. | Aski et al. (2018), Pirmoradi et al. (2019) | |
| Berberine | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits and pathology; reduced neuron loss. | ↑ Hippocampal p-ERK, Nrf2; ↓VEGF-A, MMP-9. | Wang et al. (2022a) | |
| Betaine | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; anti-oxidative stress. | ↑PSD93, PSD95, MAP2; ↑SOD, GSH; ↓ROS, MDA. | Nie et al. (2016) | |
| Anisodine Hydrobromide | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced neuron loss; modulated cholinergic system. | ↑ Brain 5-HT; ↓AchE; ↑ Bcl2, p-Akt, GSK-3β; ↓Bax. | Chen et al. (2017) | |
| Glucosides | Salidroside | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced neuron loss and apoptosis; ameliorated LTP inhibition | ↓ Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activation. | Yan et al. (2015) |
| Salidroside | BCAS/Mice | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced neuroinflammation. | ↓ Cleaved casoase 3; ↓ iNOS, TNF-α, and IL-1β by shifting microglia M1 to M2. | Ji et al. (2025) | |
| Salidroside | BCAS/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; protected the BBB; promoted angiogenesis. | ↑Notch1, Hes1, Hes5, and ITGB1. | Zhilan et al. (2025) | |
| Gastrodin | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits and neuron loss; improved energy metabolism disorders. | ↓ Aβ and Tau Protein Expression; ↓ Mitochondrial dysfunction in HT-22 cells. | Wu et al. (2023) | |
| Iridoid glycoside | Harpagoside | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced hippocampal neuron loss. | ↑ p-PTEN, p-Akt; ↓ GSK-3β. | Chen et al. (2018) |
| Geniposide | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits and pathology; anti-inflammation. | ↓ GFAP, iNOS, NF-κB; ↓ TNF-α and IL-6. | Li et al. (2020) | |
| GJ-4,a Geniposide derivative | BCAS/Mice | Improved cognitive deficits and CBF; reduced WMI; improved lipid metabolism; anti-oxidative stress | ↑ Bcl-2/Bax ratio; ↓ Caspase-3; ↓ ROS; ↑SOD, GSH, Nrf2/HO-1. | Pang et al. (2024) | |
| Diterpeniod | Andrographolide | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits and pathology; anti-apotosis. | ↓TNF-α, IL-1β, caspase-3; ↓GFAP; ↑BDNF, TrkB; ↓ p-PETN and ↑ p-Akt. | Wang et al. (2019), Wang et al. (2020) |
| Trierpenoid saponins | Gypenoside | 2VO/rats | Improved cognitive deficits; attenuated white matter lesions; anti-oxidative stress; anti-inflammation. | ↓ Kluver-Barrera staining; ↓ 4-HNE, 8-OHdG, and GAFP positive cells; ↑SOD; ↓MDA. | Zhang et al. (2011) |
| Ginsenoside Rd | BCAS/Mice | Improved cognitive deficits; promoted neuronal survival; decreased apoptosis. | ↑ BDNF; ↑ p300/CBP; ↓ HDAC2; ↓ Casp-3, Ac-H3, HDAC2 in OGD/R neurons. | Wan et al. (2017) | |
| Pseudoginsenoside-F11 | 2VO/Rats (Gradual) | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced white matter injury; modulated mTOR-mediated autophagy. | ↓ Axon demyelination and loss; ↓ p-mTOR, p-ULK1; modulated autophagy proteins. | Wang et al. (2024a) | |
| Dihydrophthalide | Ligustilide | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficit; prevented neuron loss and apoptosis; reduced dendritic damage. | ↑ Nissl+, NeuN+ neurons; ↓ Caspase-3, GFAP; MAP2. | Feng et al. (2012) |
| Ligustilide | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; reduced ER stress and oxidative stress. | ↑ Nissl+ neurons; ↑ SOD, CAT, GSH-Px; ↓ MDA, Bip, p-IRE1α, XBP1, CHOP, ↑ SIRT1. | Peng et al. (2022) | |
| Furanocoumarin | Imperatorin | 2VO/Rats | Improved cognitive deficits; attenuated neuronal damage; improved synaptic ultrastructure. | ↑ Bcl-2; Bax, Caspase-3; ↑ PSD-95. | Huang et al. (2021) |
Protective effects of TCM pure compounds on chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
FIGURE 2
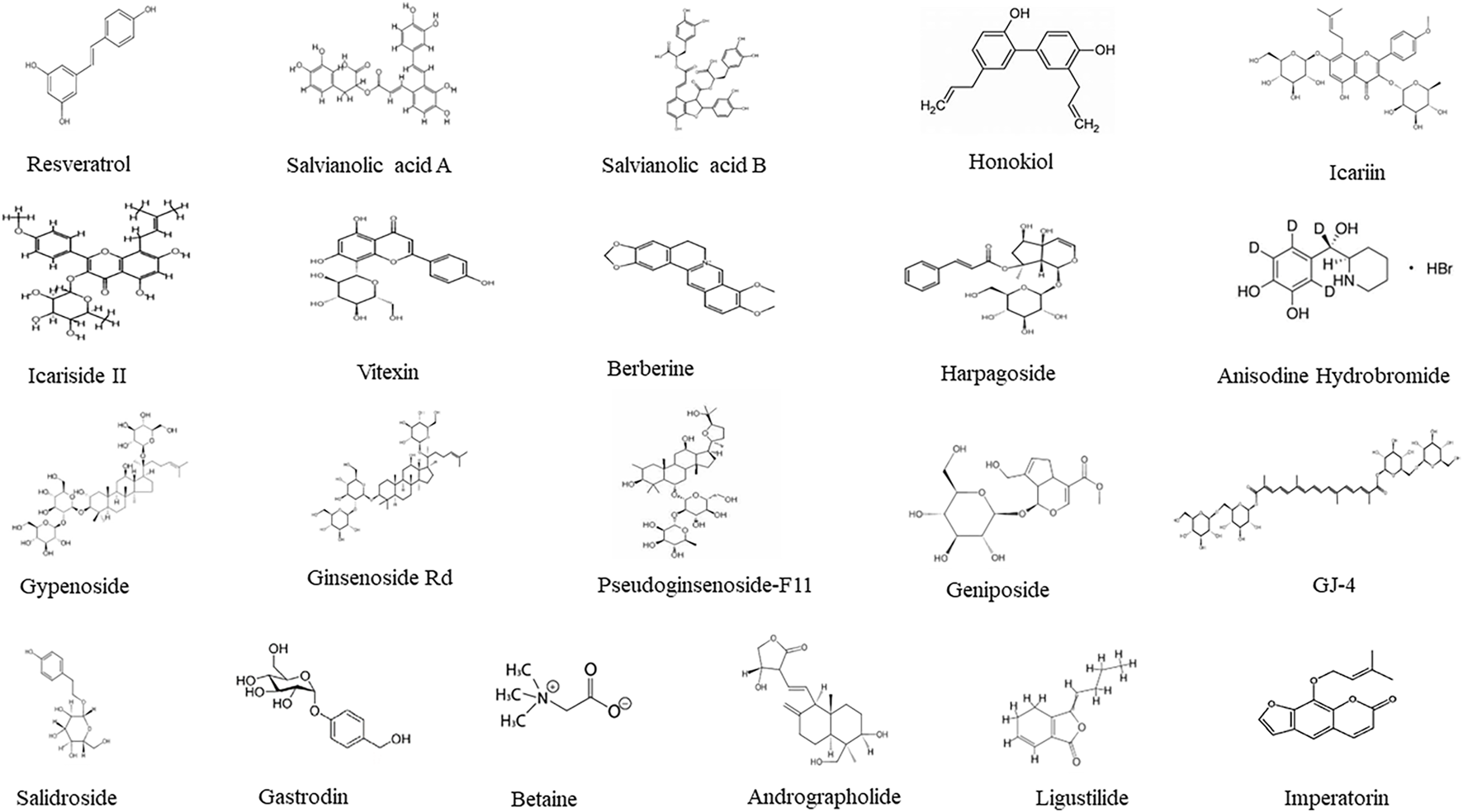
Structures of 21 TCM pure compounds effective against CCH.
4.1 The neuroprotective effects of polyphenol compounds
4.1.1 Resveratrol (RSV)
Resveratrol (RSV) is a natural polyphenol found in grape and many herbs RSV (10 mg/kg, ip, twice/week for 10 injections) alleviated cognitive deficits in a gradual BCAS mouse model, evidenced by novel object recognition test. This protection was not due to increases in CBF as determined by Laser Speckle Contrast Image, but was associated with the preservation of cholinergic neurons in the septal nucleus, offering potential therapeutic insights for neurodegenerative diseases beyond AD, including vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID) (Fagerli et al., 2024).
4.1.2 Salvianolic acid A (SalA) and Salvianolic acid B (SalB)
Salvianolic acid A (SalA) and Salvianolic acid B (SalB) are from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, a traditional Chinese medicinal herb widely used for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. SalA (5, 10, 20 mg/kg, po for 28 days) could improve the cognitive function of 2VO rats, reduce pathological damage of cortex and hippocampus, inhibit neuroinflammation and apoptosis, and suppress the activation of NF-κB by regulating the Drd2/Cryab pathway. These findings were further verified in SH-SY5Y cells injured by hypoglycemia and hypoxia (Yang et al., 2022). SalB (20 mg/kg, po for 6 weeks) ameliorated cognitive deficits in 2VO rats, and reduced neuron damage and apoptosis in the CA1 region of hippocampus. The protection is probably mediated through recover of hippocampal IGF-1/Akt pathway. Although CCH did not alter hippocampal Akt levels, the p-Akt was decreased along with decreased IGF-1, which was returned to normal after SalB treatment at both mRNA and protein levels (Ma et al., 2017).
4.1.3 Honokiol and magnolol
Honokiol and magnolol are two major compounds derived from Magnolia officinalis L., both are shown to facilitate the differentiation of primary oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) into mature oligodendrocytes. Honokiol (10 mg/kg, ip for 30 days) improved cognitive deficits in BACS mice, ameliorated myelin injury in several brain regions via Black-Gold staining and electron microscopy. Although Honokiol did not affect CBF, it did inhibit activation of astrocytes (GFAP) but not microglia (Iba1). Honokiol could increase p-Akt and p-mTOR in BACS mice and in OPC cell cultures, suggesting its beneficial effects could be associated with OPC differentiation (Zhang et al., 2023).
4.2 The neuroprotective effects of flavonoid compounds
4.2.1 Icariin (ICA)
Icariin (ICA) is a flavonoid compound and the primary active ingredient of plants of Epimedium brevicornu Maxim. ICA (10–120 mg/kg, po for 1–3 months) positively modulated multiple targets associated with Aβ pathways and thus, may be beneficial in attenuating the level of Aβ in the VaD or AD brain by decreasing the production of Aβ (via downregulation of beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) and upregulation of ADAM10) and by increasing the degradation of Aβ (upregulation of IDE). Furthermore, suppression of TGF-β1 signaling pathway may also be involved in the ICA-induced reduction of Aβ (Li et al., 2015). ICA could also alleviate oxidative stress in the brain caused by 2VO, as evidenced by a reduction in MDA levels and the preservation of superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Furthermore, ICA prevented the decline in hippocampal levels of acetylcholine, acetylcholinesterase, and choline acetyltransferase associated with CCH (Xu et al., 2009).
4.2.2 Icariside II (ICS II)
Icariside II (ICS II) is the main metabolites of ICA. ICS II (4–16 mg/kg, po for 28 days) improved spatial learning and memory in 2VO rats in MWM tests, and ameliorated hippocampal damage (HE staining) and neuron loss (Nissl staining). Aβ accumulation was reduced dose-dependently, probably by downregulating amyloid precursor protein (APP) and β-secretase 1 (BACE1), as well as by upregulating ADAM10 and IDE. The CCH-suppressed BDNF/TrkB, p-Akt/Akt, and p-CREB pathways were recovered by ICS II, and CCH-inhibited PPAR-α and PPAR-γ were returned to Sham levels (Yin et al., 2018). ICS II (4 and 8 mg/kg/day, po for 4, 8 and 12 weeks) reduced the escape latency and increased the time in target quadrant in MWM, with the high dose more effective. Hippocampal lesions were ameliorated. Notably, ICS II promoted neuron axon regeneration and repair by increasing GAP-43 and MAP-2 expression and reducing Nogo-A expression in the CA1 of the hippocampus via immunohistochemical staining (Liu et al., 2019).
4.2.3 Vitexin
Vitexin is a naturally occurring flavonoid glycoside extracted from Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge, Vigna radiata, Passiflora incarnata and other herbs, and is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Vitexin (2.5, 5, 10 mg/kg, ip for 4 weeks) improved cognitive decline in 2VO rats, reduced pathological damage in the cortex and hippocampus. Vitexin mitigated inflammation-induced damage in CCH by downregulating the expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, IL-1β, IL-6, and cleaved caspase-3. The CCH-decreased levels of exchange protein directly activated by cAMP 1 (Epac1), Epac2, Ras-associated protein 1 (Rap1), and p-ERK1/2 were reversed by Vitexin. These in vivo findings were further confirmed in hippocampal HT22 cells under OGD/R (Zhang et al., 2021).
4.3 The neuroprotective effects of alkaloids
4.3.1 Berberine (BBR)
Berberine (BBR) is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid extracted from many herbs such as Berberis, Coptis chinensis, B. integerrima or B. vulgaris with a long history of medicinal applications in traditional medicines with many pharmacological effects. BBR (50–100 mg/kg, po for up to 2 months) ameliorated 2VO-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal damages in the CA1 hippocampal subregion and in frontal cortex. 2VO-induced hippocampal neuronal loss and apoptosis were alleviated by BBR, probably mediated by reducing MDA, increasing antioxidant SOD and CAT activities, as well as by decreasing caspase-3 to exert anti-apoptotic effects (Aski et al., 2018; Pirmoradi et al., 2019). In 2VO-induced CCH rats, BBR (90 mg/kg, po for 42 days) reduced escape latency and increased time crossing platform in MWM test. The fluorescence intensity of NeuN in the cortex, hippocampus CA1 and CA3 was increased compared to CCH rats. Notably, the expression of Nrf2 and p-ERK proteins in the brain was increased as evidenced by immunofluorescences stain and WB. BBR could also reduce BBB injury by inhibiting CCH-elevated VEGFA and MMP9, while increasing SMA and Collogen IV with immunofluorescence stain (Wang N. et al., 2022).
4.3.2 Betaine
Betaine is a kind of water-soluble quaternary amine-type alkaloid widely existing in food, such as wheat germ, beet, spinach, shrimp and wolfberry. Betaine (12.5 mg/kg/d via drinking water for 14 days) decreased the escape latency and increased the time spent in the target quadrant of 2VO rats, indicating the improvement of memory function. Betaine also improved synaptic function by upregulating postsynaptic proteins (PSD93, PSD95, and MAP2). At the same time, Betaine could also upregulate SOD and GSH, and downregulate ROS and MDA to normal levels, thus playing an antioxidative stress role (Nie et al., 2016).
4.3.3 Anisodine Hydrobromide (AH)
Anisodine Hydrobromide (AH) is a tropane alkaloid drug derived from the plant Anisodus tanguticus Maxim. It is used in the treatment of various vascular and neurological conditions. In CCH rats, low dose of AH (0.3–1.2 mg/kg) improved cognitive impairments in MWM test. TUNEL and Nissl staining showed amelioration of CCH-induced apoptosis and neuron loss. The cholinergic system was modulated with AChE activity reduction, while increasing 5-HT. Protein expression of Bcl2, p-Akt and p-GSK-3β increased, while Bax decreased, consistent with reduced apoptosis (Chen et al., 2017).
4.4 The neuroprotective effects of glucosides
4.4.1 Salidroside
Salidroside is primarily derived from plants of the Rhodiola genus (such as Rhodiola rosea and Rhodiola crenulata). Salidroside (20 mg/kg, po, 35 days) improved cognitive deficits in 2VO rats and attenuated apoptosis in the CA1 region of rat hippocampus. CCH-impaired long-term potentiation (LTP) was ameliorated by Salidroside, and CCH-activated caspase-3 and elevated Bax/Bcl2 ratio were also inhibited by Salidroside (Yan et al., 2015). In BCAS-induced CCH mouse models, BCAS produced a significant decrease in CBF, leading to cognitive impairment and neuronal apoptosis. Salidroside (10 mg/kg, ip, for 35 days) improved cognitive deficit in MWM test, despite its effects on CBF and Nissl staining were not mentioned, it shifted microglial polarization from the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, thus suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine release, and improving neuronal survival (Ji et al., 2025). Salidroside was also found to alleviate blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption induced by cerebral hypoperfusion and enhance angiogenesis by promoting endothelial cell budding. Further studies revealed that Salidroside upregulated Notch1, Hes1, Hes5, and ITGB1 to activate the Notch signaling pathway, which in turn promotes angiogenesis and protects the BBB integrity (Zhilan et al., 2025).
4.4.2 Gastrodin
Gastrodin is a glucoside of Gastrodigenin, both are derived from Gastrodia elata Bl, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine used for centuries to treat cognitive impairment, ischemic stroke, epilepsy, and dizziness. Gastrodin and Gastrodigenin (25 and 50 mg/kg, po for 4 weeks) improved the cognitive impairment of 2VO rats by reducing the expression of Aβ and inhibiting the phosphorylation of Tau protein. Brain metabolomics revealed that CCH-disrupted energy metabolism such as glycolysis, TCA cycle and pentose phosphate pathways were improved by Gastrodin and Gastrodigenin. Both compounds also protected HT-22 hippocampal cells from hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage by improving the mitochondrial function (Wu et al., 2023).
4.5 The neuroprotective effects of iridoid glycoside
4.5.1 Harpagoside
Harpagoside is a bioactive iridoid glycoside primarily extracted from the root of Devil’s Claw (Harpagophytum procumbens (Burch.) DC), a medicinal plant native to Southern Africa and traditionally used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Harpagoside (15 mg/kg, po for 2 months) improved cognitive deficit in MWM and avoidance tests and reduced neuron loss as evidenced in Nissl staining. Harpagoside increased p-PTEN and p-Akt expression, enhanced Akt activity and suppress GSK-3β activity, both of which are downstream effectors of PTEN (Chen et al., 2018).
4.5.2 Geniposide
Geniposide is a bioactive iridoid glycoside primarily extracted from the fruit of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis (Cape jasmine or Zhi zi), a traditional Chinese medicinal plant known for its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Geniposide (50, 100 mg/kg, po, 4 weeks) effectively mitigated cognitive decline caused by CCH in rats. It likely alleviated neuroinflammation during chronic cerebral ischemia by downregulating iNOS and NF-κB expression and inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6 (Li et al., 2020).
4.5.3 GJ-4, a geniposide derivative
GJ-4, a geniposide derivative, also alleviated cognitive impairments in BCAS mice at the dose of 50 mg/kg, po, for 28 days. GJ-4 improved CBF and reduced the white matter lesions. GJ-4 reduced oxidative stress and neuron apoptosis by decreasing ROS levels and caspase-3, and increasing the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway. The Bcl-2/Bax ratio and antioxidant SOD and GSH were also increased (Pang et al., 2024).
4.6 The neuroprotective effects of terpenoids and triterpenoid saponins
4.6.1 Andrographolide
Andrographolide is a bioactive diterpenoid lactone primarily extracted from the leaves and stems of Andrographis paniculata Burm.f. (commonly known as “green chiretta” or “king of bitters”), a medicinal plant widely used in traditional Asian medicine. Andrographolide (10 mg/kg, ip, 4 weeks) improved CCH-induced cognitive deficits and hippocampal apoptosis, inhibited astrocyte activation and decreased the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β caspase-3 in the hippocampus, while alleviated 2VO-induced decreases in the expression of BDNF and TrkB (Wang et al., 2019). Andrographolide could reverse 2VO-induced activation of p-PTEN, while attenuated 2VO-decreased p-Akt. Thus, both BDNF/TrkB and PTEN/AKT signaling pathways were likely involved in neuroprotective effects of Andrographolide (Wang et al., 2020).
4.6.2 Gypenoside (GP)
Gypenoside (GP) is a triterpenoid saponin extracted from Gyrostemma pentaphyllum (Thunnb.) Makino and exhibited multiple pharmacological effects. GP (400 mg/kg, po for 33 days) improved cognitive deficits in 2VO rats. Klüver–Barrera staining showed GP protection against CCH-induced axonal damage, and immunochemical stain for 4-HNE, 8-OHdG, and GAFP showed GP decreased oxidative stress and astroglia activation. WB showed that GP increased SOD and decreased MDA, demonstrating the therapeutic potential for GP to treat CCH (Zhang et al., 2011).
4.6.3 Ginsenoside Rd
Ginsenoside Rd is a bioactive saponin compound primarily extracted from the roots of Panax ginseng (Asian ginseng) and is widely used in traditional medicine for their neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties. Ginsenoside Rd (10 and 30 mg/kg, ip for 21 days) alleviated CCH-induced learning and memory impairments in BCAS mice, and this improvement was linked to enhanced neuronal survival and increased BDNF expression in the hippocampus and front cortex, with increased p300/CBP and decreased expression of HDAC2. The implicated epigenetic regulation was further investigated in primary neuronal cell culture subjected to ODG/R, suggesting the epigenetics could account for BDNF increase to achieve neuroprotection (Wan et al., 2017).
4.6.4 Pseudoginsenoside-F11 (PF11)
Pseudoginsenoside-F11 (PF11) is a triterpenoid saponin unique from Panax quinquefolium L., and has been shown to produce many neuroprotective effects. PF11 (6, 12, 24 mg/kg, po for 4 weeks) ameliorated gradual 2VO-induced cognitive impairment. PF11 alleviated white matter injury by improving the condition of the myelin sheath and axons and reducing their swelling. PF11 also prevented mature oligodendrocyte death and inhibited the activation of microglia and astrocytes. 2VO-increased p-mTOR, p-ULK1 and p-P70S6K were attenuated by PF11, thereby reducing the aberrant accumulation of autophagy substrates and increasing the level of autophagosomes in the white matter (Wang H. et al., 2024).
4.7 The neuroprotective effects of other compounds
4.7.1 Ligustilide
Ligustilide is a dihydrophthalide compound primarily extracted from the roots of Angelica sinensis and Ligusticum sinense ‘chuanxiong’, both of which are widely used in TCM for their cardiovascular and neuroprotective properties. Ligustilide (80 mg/kg, po, 7 days) demonstrated cognitive deficit improvements in 2VO rats. Neuron loss was ameliorated as evidenced by Nissl staining and NeuN staining; Dendritic integrity was maintained as evidenced by MAP2 staining; while the staining for caspase-3, and GFAP was attenuated, indicating its anti-apoptosis and astroglia inhibition properties (Feng et al., 2012). In a recent study, Ligustilide (20, 40 mg/kg, po, 28 days) improved cognitive deficit in 2VO rats, increased Nissl positive cells. Ligustilide showed effects against ER stress and oxidative stress, The antioxidant SOD, CAT and GSH-Px were increased, while apoptosis protein Bax decreased. Ligustilide reversed 2VO-decreased SIRT1 and PDI, while suppressed 2VO-increased CHOP, XBP1, p-IRE1α. The downregulation of the IRE1α/XBP1 pathway by activating SIRT1 were further verified in PC12 cells under OGD, and these effects were partially blocked by SIRT1 inhibitor EX-527, indicating the critical role of SIRT1 in the protection (Peng et al., 2022).
4.7.2 Imperatorin
Imperatorin is an active ingredient extracted from Aangelica dahurica (Baizhi) and other TCM herbs, and has many beneficial effects including neuroprotection. Imperatorin (2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg, ip for 12 weeks) improved 2VO-induced cognitive impairments in MWM, alleviated hippocampal CA1 neuron loss. Mechanistically, Imperatorin inhibited apoptosis by upregulating the expression of Bcl-2, and downregulating Bax and caspase-3. Imperatorin improved synaptic ultrastructure, increased synaptic active zone length, PSD thickness, and the expression of PSD-95, suggesting the maintenance of synapse function could contribute to CCH treatment (Huang et al., 2021).
The TCM pure compounds against 2VO/BCAS CCH models were categorized similarly as TCM monomers against acute MCAO ischemia models (Xie et al., 2021). Some pure compounds have more publications against 2VO CCH models, but only representative ones were selected (i.e., resveratrol), some had already included in citated reference, and duplication is avoided, such as Curcumin against 2VO rat model (He et al., 2023). TCM pure compounds research greatly advance the pharmacological basis of TCM in alleviating CCH.
5 Discussion
5.1 The CCH model is different from acute MCAO model
This manuscript reviewed 50 publications on the protective effects of 11 TCM formulae, 8 herb extracts, and 21 pure compounds on CCH using 2VO, BCAS, and UCCAO rodent models. In general, 2VO could produce 10% mortality, which could be as high as 28% (Feng et al., 2012). Thus, gradual 2VO (ligation of the other side 1 weeks later, 6 publications) and UCCAO (1 publication) were used to avoid acute CBF reduction and acute neuroinflammation to more closely mimic cognitive deficits after white matter damage (Tuo et al., 2021; Kimura et al., 2025). BCAS is primarily applied to mice (7 publications) but also applied to rats (Zhilan et al., 2025). In BCAS/Mice model, the 0.18 mm diameter is frequently chosen to reduce the mortality with 0.16 mm and increase the severity with 0.22 mm microcoils to better mimic stenosis patients (Tuo et al., 2021). In these CCH models, compensatory blood supply occurs via the vertebrobasilar system over weeks to months, together with vascular remodeling, that helped to restore cerebral blood flow to pre-occlusion levels, preventing sustained long-term cerebral ischemia in sharp comparison to acute MCAO model that produced focal cerebral infarction within hours with high mortality rate (30%–60%) (Tuo et al., 2021; Kimura et al., 2025). Therefore, the mechanism of TCM protection using CCH and MCAO models shared some common but had some different mechanisms (Zhang et al., 2020; Fadoul et al., 2024). As a results, CCH treatment usually lasted for 4 weeks and even months after CCH modeling, compared to a few days of pretreatment and a few hours after MCAO modeling. Thus, acute ischemic stroke induced by MCAO over a short period does not fully align with the pathological progression of clinical patients (Kimura et al., 2025; Zhilan et al., 2025).
5.2 Cognitive improvement is the main parameter in CCH models
The improvement of cognitive impairments was the first line of evidence of protection in CCH models. Among 50 publications, Morris water maze (MWM) is the mostly performed test (88%), approximate 15% studies also used Novel object recognition, Open field and Y-maze tests, and 8% used passive avoidance and step-down tests to evaluate cognitive functions. In comparison, neurological scores is mainly used to evaluate the behavior abnormalities in MCAO model of acute cerebral ischemic stroke, and the outcomes of MWM in MCAO vary considerably and the conclusions are not always consistent (DeVries et al., 2001).
5.3 Histopathology of CCH vs. MCAO
HE and Nissl staining were most widely used to evaluate neuron damage and loss (88%) and TUNEL for apoptosis (18%). Transmission electron microscope was used to assess mitochondria, synapse, and white matter lesions from CCH (Niu et al., 2020b; Huang et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2023; Wang H. et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2025). White matter includes nerve fibers (axons) covered by a fatty tissue called myelin. Reduced blood flow to the white matter can cause white matter injury responsible for cognitive deficits. Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry (65%) were widely used to locate selected cell-death molecules together with WB and qRT-PCR (Niu et al., 2020a; Yan et al., 2022; Pang et al., 2024; Wang H. et al., 2024; Xiao et al., 2024). Although these lesions were also observed in the MCAO brain, the TTC staining of infarction size is the golden histopathology for acute cerebral ischemic stroke.
5.4 Reduced CBF is more evident in MCAO than in CCH models
Reduced cerebral blood flow (CBF) is more evident in acute MCAO model than in chronic CCH models. However, CCH could activate a molecular and cellular cascade leading to breakdown of the blood-brain-barrier (BBB), that could initiate and contribute to a vicious cycle, causing neurodegeneration (Rajeev et al., 2022). Among 8 studies with CBF, three were used to verify the CCH model only (Jeong et al., 2020; Wang H. et al., 2024; Ji et al., 2025), Buqi Huoxue Tongnao (Gao et al., 2024) Xinshubao tablet (Xiao et al., 2024), and GJ-4 (Pang et al., 2024) could improve CBF in CCH models. However, Resveratrol (Fagerli et al., 2024) and Honokiol (Zhang et al., 2023) did not improve CBF. Thus, the improvement of CBF is ideal, but other mechanisms might also be responsible for the protective effects of TCM on CCH, and the maintenance of BBB is an important mechanism of TCM protection (Zhilan et al., 2025).
5.5 Anti-oxidative stress as one of the major protection mechanisms
Oxidative stress from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondrial dysfunction is one important pathological features of CCH and MCAO (Rajeev et al., 2023; Kimura et al., 2025). Taohong Siwu decoction reduced GRP78 (Bip), p-eIF2α, p-IRE1α and ATF6 in 2VO rats (Fan et al., 2024), Ligustilide reduced Bip, p-IRE1α, XBP1, and CHOP in 2VO rats, probably mediated through upregulating SIRT1, as the SIRT1 inhibitor attenuated such effects (Peng et al., 2022).
One of the mechanisms of TCM against CCH is to improve mitochondrial dysfunction (Wang Y. et al., 2023). Approximate 10% manuscripts focused on mitochondria as a mechanism of protection, including ultrastructure, mitochondrial membrane potential, and mitochondrial proteins for ROS production, mitophagy, and cell death. TCM formulae appeared to be more effective in improving CCH-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. In addition to a review on 9 TCM formulae against CCH (Wang Y. et al., 2023), recent publications showed that Bushen-Yizhi regulated mitophagy with the improvement of mitochondrial membrane activity and lysosomal proteins (Xiao et al., 2023), Xinshubao tablet improved BCAS-induced ultrastructural alterations on mitochondria and synapses and reduced white matter injury (Xiao et al., 2024), and ShenmaYizhi Decoction improved mitochondrial ultrastructure and cognitive deficits through the AMPK/UCP2 signaling (Sun et al., 2021), indicating the better therapeutic efficacy of TCM formulae over monomers.
5.6 Anti-inflammation as one of the major protection mechanisms
Neuroinflammation contributes to main pathologies in both MCAO and CCH models and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is the key receptor responsible for immune and inflammatory reactions (Rajeev et al., 2023; Yawoot et al., 2025), and inhibition of neuroinflammation has been considered the one of major mechanisms of TCM protection in every studies.
Microglia activation is a normal physiological response to stimuli, however, microglia over-activation could produce excess ROS, which in turn triggers neuroinflammation for many neurodegenerative diseases including ischemia stroke and is a major mechanism of TCM protection against CCH (Zhang et al., 2024). The inhibition of microglia (including astroglia), reduction of ROS and inflammatory mediators account for 64% (32/50) of the manuscript reviewed, and applies for TCM formulae, extracts and pure compounds.
With anti-neuroinflammation via TCM, CCH-induced injury to synapses and myelin could be attenuated by maintaining the ultrastructure (Niu et al., 2020a; Huang et al., 2021; Xiao et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2025), and by modulating the related proteins such as PSD93, PSD95, MAP2, etc. (Nie et al., 2016; Huang et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2025). Thus, anti-neuroinflammation by TCM could help to maintain synaptic plasticity and myelin integrity in CCH models.
With anti-neuroinflammation by TCM, the abnormal accumulation of Aβ and phosphorylated Tau were reduced following treatment with Icariin (Li et al., 2015), Icariside II (Yin et al., 2018), and Gastrodin (Wu et al., 2023). Reduced Aβ and phosphorylated Tau accumulation could further play roles in improving cognitive deficits in CCH but also in AD.
5.7 Promote neuro-regeneration as one of the major protection mechanisms
TCM formulae and extracts have been demonstrated to promote tissue repair as exampled in myocardial ischemic infarction (Wang Y. et al., 2022), which emerges as the new direction to explore the mechanism of TCM protection against CCH. Indeed, Xinshubao tablet could rescue hippocampal neurogenesis dysfunction in BCAS mice (Xiao et al., 2024), Icariside II could improve neuron axon regeneration in CCH rats (Liu et al., 2019), Salidroside could promote angiogenesis through the Notch signaling pathway (Zhilan et al., 2025), while Modified Dioscorea pills promoted angiogenesis and microcirculation remodeling through the Ang/Tie signaling (Kuang et al., 2023). Pseudoginsenoside-F11 could increase mature oligodendrocytes in the corpus callosum (Wang H. et al., 2024). Thus, the promotion of neuro-regeneration could be a novel mechanism of TCM protection against CCH.
5.8 Advanced technologies to elucidate TCM protection mechanism
The advanced biotechnology provides opportunity of using Omics to profile/screen the potential targets of TCM protection against CCH. RNA-Seq was applied to study the protective effects of Chuanzhitongluo capsule (Wang Z. et al., 2024) and Xinshubao tablet (Xiao et al., 2024) in BCAS mice to reveal novel molecular events. Metabolomics were performed to profile CCH-induced abnormal brain energy metabolism (Wu et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2023) and lipid metabolism impairment (Pang et al., 2024) and the protective effects of TCM. 16S rRNA-Seq was performed to assess whether the protective effects of Shunaoxin dropping pill against gradual 2VO rats was mediated through the microbiota-gut-brain axis (Bo et al., 2023). In addition, network pharmacology of Buqi Huoxue Tong nao against 2VO rats was performed to seek the potential signaling pathways of protection (Gao et al., 2024). Omics approaches could add our understanding of multi-target feature of TCM in the treatment of CCH.
To confirm and verify in vivo findings, a number of in vitro models were utilized together with CCH animal models. The most used in vitro model was OGD/R in primary neuron cultures (Wan et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2025), in microglial BV2 cells (Gao et al., 2024) and in PC12 cells (Peng et al., 2022; Xiao et al., 2023). The H2O2-treated hippocampal HT-22 cells (Wu et al., 2023) and OLN-93 cells (Pang et al., 2024) were also used. These in vitro studies affirmed in vivo findings and greatly advanced our understanding of molecular events responsible for TCM protection against CCH.
Neurotransmitter modulation could be another mechanism of TCM protection. For example, there are several manuscripts targeting cholinergic pathway as a protective mechanism against cognitive impairment, the increase in ChAT+ cells (Xu et al., 2009; Kim et al., 2016; Fagerli et al., 2024; Wang Z. et al., 2024) could improve cognitive deficits and modulate neuroinflammation. Anisodine hydrobromide, a brain cholinergic receptor modulator, could affect cholinergic system and neurotransmitter imbalance to exert protective effects in 2VO rats (Chen et al., 2017).
5.9 Signaling pathways
Under conditions of CCH, the protective effects of TCM could be derived from the synergistic modulation of core signaling pathways such as Nrf2/ARE, NF-κB, and BDNF/CREB by its multiple bioactive components. These pathways engage in extensive crosstalk: activation of Nrf2 not only enhances antioxidant defenses but also indirectly suppresses NF-κB-mediated inflammatory signaling, thereby disrupting the vicious cycle between oxidative stress and neuroinflammation (Fadoul et al., 2024). Meanwhile, the improved microenvironment facilitates the release of BDNF, which activates CREB-dependent neuroplasticity and regenerative processes. Enhanced neurotrophic signaling, in turn, further suppresses neuroinflammation and augments antioxidant capacity. Ultimately, through multi-pathway interactions, TCMs construct a coordinated regulatory network that collectively mitigate neuronal injury and promotes functional recovery.
The MAPK signaling pathways were frequently involved in TCM protection against CCH, such as Ginkgo biloba extracts (Kim et al., 2016), Fructus mume extracts (Lee et al., 2015), and Scutellaria baicalensis extracts (Hwang et al., 2011). The modulation of BDNF/TrkB pathways was implicated in the protective effects of Icariside II (Yin et al., 2018), Andrographolide (Wang et al., 2019), Ginsenoside Rd (Wan et al., 2017) and Epimedium flavonoids (Niu et al., 2020b). The modulation of the SIRT1/IRE1α/XBP1/CHOP pathway was implicated in Ligustilide protection in 2VO rats (Peng et al., 2022). The regulation of Nrf2/ARE antioxidant pathway was implicated in GJ-4 protection in BCAS mice (Pang et al., 2024). Other pathways such as PTEN and mTOR/Akt pathways as well as the epigenetic regulations were also investigated as the mechanism of protection.
6 Limitations and future perspectives
Upon a thorough search, we found that the clinical efficacy and safety reports using TCM in the treatment of CCH is limited in the literature despite the availability of these formulae in TCM drug stores/in hospital preparations and in clinical practices. Nonetheless, the preclinical findings could provide strong pharmacological basis and rationale for future clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy and safety of TCM formulae in patients with CCH or vascular cognitive impairment.
This article has reviewed 21 pure compounds extracted from TCM. However, these pure compounds are widely existed in the plant-kingdom, not unique to a certain herb originally extracted. These pure compounds belong to polyphenols, flavonoids, alkaloids, terpenoids, saponins, iridoid glycosides, glucosides, and other categories (Xie et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2023; Shu et al., 2025). These components act together in designed recipes to play integrated roles, rather than exclude each other, to target multiple pathways. The strategy of “combination drug therapy” to enhance efficacy and reduce toxicity could be future perspectives.
7 Conclusion
TCM demonstrated the clear therapeutic efficacy against CCH models, either from TCM formulae, herb extracts, or from pure compounds extracted from TCM. Many advanced techniques were used in ethnopharmacology investigations. It is clear that the protective effects of TCM against CCH are mediated through multi-component and multi-target mechanisms as summarized in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3
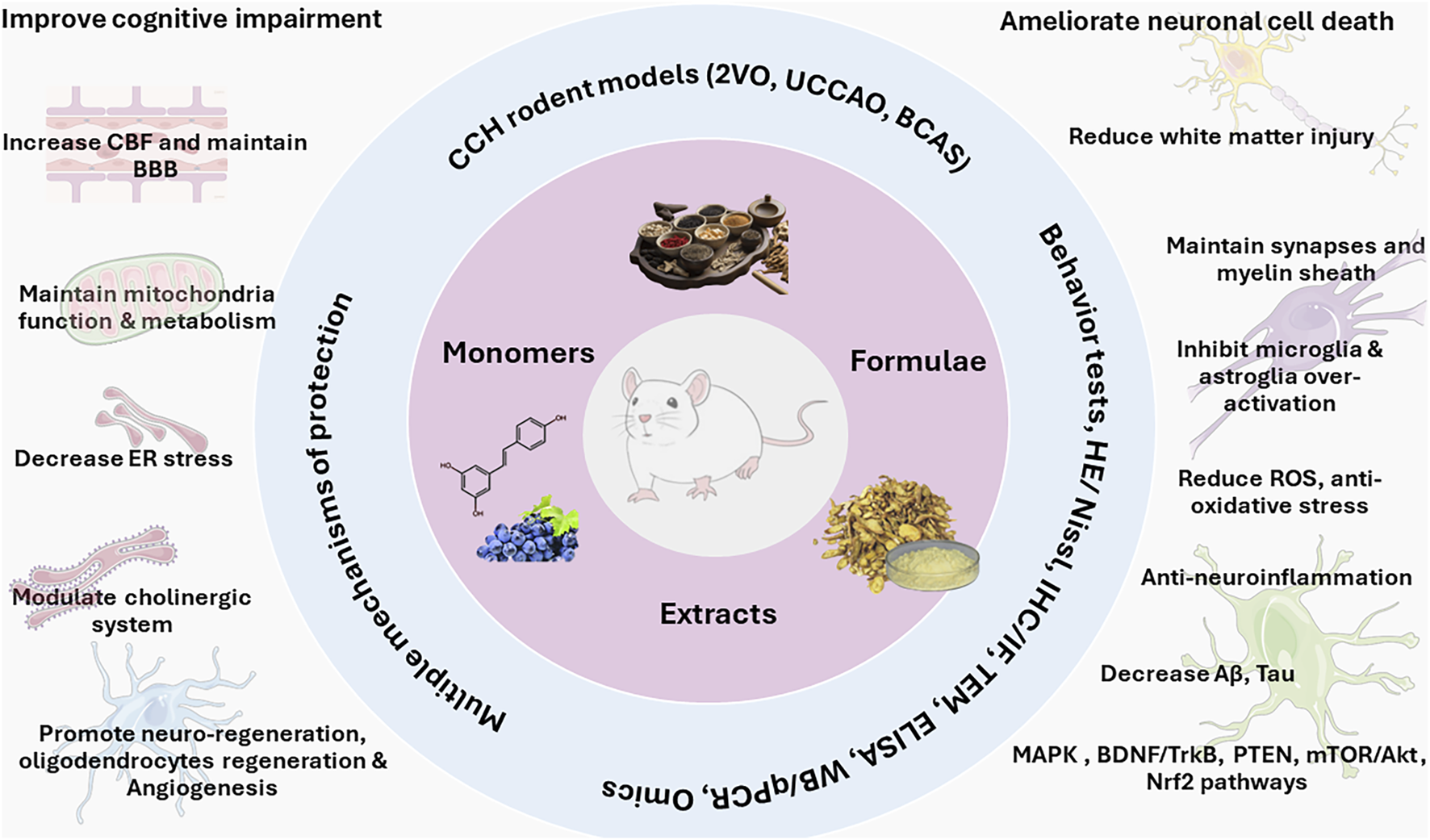
Multi-component and multi-target feature for TCM formulae, extracts, and pure compounds in the protection against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. It should be noted that these protection mechanisms and signaling pathways are not mutually exclusive, rather, they function together in an integrated manner to protect CCH.
Statements
Author contributions
X-TM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Investigation. B-YL: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation. JL: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – review and editing, Validation, Data curation. BL: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Investigation, Resources, Conceptualization, Validation, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82560832), Zunyi Science and Technology Plan Project [Zunshi Kehe HZ Word (2021) No. 26 and (2022) No. 226]. Zunyi Medical University 2020 Academic New Talent Cultivation and Innovation Exploration Special Project (Qianke Platform Talent [2020]-040).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Aski M. L. Rezvani M. E. Khaksari M. Hafizi Z. Pirmoradi Z. Niknazar S. et al (2018). Neuroprotective effect of berberine chloride on cognitive impairment and hippocampal damage in experimental model of vascular dementia. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci.21, 53–58. 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.23195.5865
2
Bo T. Cai W. Sun P. Zhang T. Gao P. Han J. et al (2023). Shunaoxin dropping pill improves cognitive functions of rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Brain Res.1798, 148158. 10.1016/j.brainres.2022.148158
3
Chen D. Peng C. Xie X. Chen Q. Liu H. Zhang S. et al (2017). Low dose of anisodine hydrobromide induced neuroprotective effects in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets16, 1111–1119. 10.2174/1871527316666171026114043
4
Chen C. Zhang H. Xu H. Xue R. Zheng Y. Wu T. et al (2018). Harpagoside rescues the memory impairments in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by inhibiting PTEN activity. J. Alzheimers Dis.63, 445–455. 10.3233/JAD-171170
5
Chen Y. Zhang Y. Wu Q. Chen J. Deng Y. (2024). The neuroprotective effect of Chinese herbal medicine for cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through regulating mitophagy. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1378358. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1378358
6
Cheng X. Hu J. Liu X. Tibenda J. J. Wang X. Zhao Q. (2022). Therapeutic targets by traditional Chinese medicine for ischemia-reperfusion injury induced apoptosis on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Front. Pharmacol.13, 934256. 10.3389/fphar.2022.934256
7
Devries A. C. Nelson R. J. Traystman R. J. Hurn P. D. (2001). Cognitive and behavioral assessment in experimental stroke research: will it prove useful?Neurosci. Biobehav Rev.25, 325–342. 10.1016/s0149-7634(01)00017-3
8
Fadoul G. Ikonomovic M. Zhang F. Yang T. (2024). The cell-specific roles of Nrf2 in acute and chronic phases of ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther.30, e14462. 10.1111/cns.14462
9
Fagerli E. Jackson C. W. Escobar I. Ferrier F. J. Perez Lao E. J. Saul I. et al (2024). Resveratrol mitigates cognitive impairments and cholinergic cell loss in the medial septum in a mouse model of gradual cerebral hypoperfusion. Antioxidants (Basel)13, 984. 10.3390/antiox13080984
10
Fan L. L. Fang H. Zheng J. Y. Qiu Y. H. Wu G. L. Cai Y. F. et al (2024). Taohong Siwu decoction alleviates cognitive impairment by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis signaling pathway in vascular dementia rats. J. Ethnopharmacol.333, 118407. 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118407
11
Fanoudi S. Alavi M. S. Hosseini M. Sadeghnia H. R. (2019). Nigella sativa and thymoquinone attenuate oxidative stress and cognitive impairment following cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Metab. Brain Dis.34, 1001–1010. 10.1007/s11011-019-00394-4
12
Feng Z. Lu Y. Wu X. Zhao P. Li J. Peng B. et al (2012). Ligustilide alleviates brain damage and improves cognitive function in rats of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Ethnopharmacol.144, 313–321. 10.1016/j.jep.2012.09.014
13
Gao Y. Zhao P. Wang C. Fang K. Pan Y. Zhang Y. et al (2024). Buqi Huoxue Tongnao prescription protects against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via regulating PI3K/AKT and LXRα/CYP7A1 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine132, 155844. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155844
14
He Y. Chen X. Wu M. Hou X. Zhou Z. (2023). What type of cell death occurs in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion? A review focusing on pyroptosis and its potential therapeutic implications. Front. Cell Neurosci.17, 1073511. 10.3389/fncel.2023.1073511
15
Huang Y. Liao X. Wang H. Luo J. Zhong S. Zhang Z. et al (2021). Effects of imperatorin on apoptosis and synaptic plasticity in vascular dementia rats. Sci. Rep.11, 8590. 10.1038/s41598-021-88206-7
16
Hwang Y. K. Jinhua M. Choi B. R. Cui C. A. Jeon W. K. Kim H. et al (2011). Effects of Scutellaria baicalensis on chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced memory impairments and chronic lipopolysaccharide infusion-induced memory impairments. J. Ethnopharmacol.137, 681–689. 10.1016/j.jep.2011.06.025
17
Jeong J. H. Lee S. E. Lee J. H. Kim H. D. Seo K. H. Kim D. H. et al (2020). Aster ageratoides Turcz. extract attenuates Alzheimer’s disease-associated cognitive deficits and vascular dementia-associated neuronal death. Anat. Cell Biol.53, 216–227. 10.5115/acb.20.011
18
Ji W. Zhang Z. Jin T. Meng D. Zhou X. Hu J. et al (2025). Salidroside attenuates cognitive deficits induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via modulating microglial phenotypic transformation in mice. J. Neuroimmunol.400, 578544. 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2025.578544
19
Kim M. S. Bang J. H. Lee J. Han J. S. Baik T. G. Jeon W. K. (2016). Ginkgo biloba L. extract protects against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by modulating neuroinflammation and the cholinergic system. Phytomedicine23, 1356–1364. 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.07.013
20
Kimura S. Iwata M. Takase H. Lo E. H. Arai K. (2025). Oxidative stress and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: an overview from preclinical rodent models. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab.45, 381–395. 10.1177/0271678X241305899
21
Kuang G. Shu Z. Zhu C. Li H. Zhang C. (2023). The promoting effect of modified Dioscorea pills on vascular remodeling in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via the Ang/Tie signaling pathway. Transl. Neurosci.14, 20220302. 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0302
22
Lee K. M. Bang J. Kim B. Y. Lee I. S. Han J. S. Hwang B. Y. et al (2015). Fructus mume alleviates chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced white matter and hippocampal damage via inhibition of inflammation and downregulation of TLR4 and p38 MAPK signaling. BMC Complement. Altern. Med.15, 125. 10.1186/s12906-015-0652-1
23
Li W. X. Deng Y. Y. Li F. Liu B. Liu H. Y. Shi J. S. et al (2015). Icariin, a major constituent of flavonoids from Epimedium brevicornum, protects against cognitive deficits induced by chronic brain hypoperfusion via its anti-amyloidogenic effect in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav.138, 40–48. 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.09.001
24
Li L. J. Han Z. F. Li L. X. Yan B. (2020). Effects of geniposide on the neuroinflammation in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.51, 480–487. 10.12182/20200760104
25
Li X. H. Yin F. T. Zhou X. H. Zhang A. H. Sun H. Yan G. L. et al (2022). The signaling pathways and targets of natural compounds from traditional Chinese medicine in treating ischemic stroke. Molecules27, 3099. 10.3390/molecules27103099
26
Li L. Yuan R. Wu M. Yin X. Zhang M. Chen Z. (2025). Progress in the regulatory mechanism of mitophagy in chronic cerebral ischemic neuronal injury. Exp. Neurol.383, 115003. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.115003
27
Liang N. Chen Y. Yang S. Liang C. Gao L. Wang S. et al (2022). Chinese herbal medicine for mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Front. Neurol.13, 903224. 10.3389/fneur.2022.903224
28
Liu T. He F. Yan J. Kuang W. Yu C. (2019). Icariside II affects hippocampal neuron axon regeneration and improves learning and memory in a chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol.12, 826–834.
29
Ma X. Xu W. Zhang Z. Liu N. Yang J. Wang M. et al (2017). Salvianolic acid B ameliorates cognitive deficits through IGF-1/Akt pathway in rats with vascular dementia. Cell Physiol. Biochem.43, 1381–1391. 10.1159/000481849
30
Nie C. Nie H. Zhao Y. Wu J. Zhang X. (2016). Betaine reverses the memory impairments in a chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model. Neurosci. Lett.615, 9–14. 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.11.019
31
Niu H. M. Ma D. L. Wang M. Y. Chen X. P. Zhang L. Li Y. L. et al (2020a). Epimedium flavonoids protect neurons and synapses in the brain via activating NRG1/ErbB4 and BDNF/Fyn signaling pathways in a chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model. Brain Res. Bull.162, 132–140. 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.06.012
32
Niu H. M. Wang M. Y. Ma D. L. Chen X. P. Zhang L. Li Y. L. et al (2020b). Epimedium flavonoids improve cognitive impairment and white matter lesions induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion through inhibiting the Lingo-1/Fyn/ROCK pathway and activating the BDNF/NRG1/PI3K pathway in rats. Brain Res.1743, 146902. 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146902
33
Pang Q. Q. Zang C. X. Li T. Zeng X. C. Liu L. X. Zhang D. et al (2024). Neuroprotective effect of GJ-4 against cognitive impairments in vascular dementia by improving white matter damage. Phytomedicine132, 155877. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155877
34
Pei H. Ma L. Cao Y. Wang F. Li Z. Liu N. et al (2020). Traditional Chinese medicine for Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive impairment: a review. Am. J. Chin. Med.48, 487–511. 10.1142/S0192415X20500251
35
Peng D. Wang Y. X. Huang T. H. Luo D. Qiao L. J. Wang Q. et al (2022). Ligustilide improves cognitive impairment via regulating the SIRT1/IRE1α/XBP1s/CHOP pathway in vascular dementia rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2022, 6664990. 10.1155/2022/6664990
36
Pharmacopoeia (2025). Pharmacopoeia of the people’s Republic of China, 1. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press.
37
Pirmoradi Z. Yadegari M. Moradi A. Khojasteh F. Zare Mehrjerdi F. (2019). Effect of berberine chloride on caspase-3 dependent apoptosis and antioxidant capacity in the hippocampus of the chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci.22, 154–159. 10.22038/ijbms.2018.31225.7534
38
Poh L. Sim W. L. Jo D. G. Dinh Q. N. Drummond G. R. Sobey C. G. et al (2022). The role of inflammasomes in vascular cognitive impairment. Mol. Neurodegener.17, 4. 10.1186/s13024-021-00506-8
39
Rajeev V. Fann D. Y. Dinh Q. N. Kim H. A. De Silva T. M. Lai M. K. P. et al (2022). Pathophysiology of blood brain barrier dysfunction during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in vascular cognitive impairment. Theranostics12, 1639–1658. 10.7150/thno.68304
40
Rajeev V. Chai Y. L. Poh L. Selvaraji S. Fann D. Y. Jo D. G. et al (2023). Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: a critical feature in unravelling the etiology of vascular cognitive impairment. Acta Neuropathol. Commun.11, 93. 10.1186/s40478-023-01590-1
41
Shu H. Liao Q. Chen Z. Liang M. Zhang S. Liu J. et al (2025). Flavonoids serve as a promising therapeutic agent for ischemic stroke. Brain Res.1853, 149528. 10.1016/j.brainres.2025.149528
42
Sun C. Liu M. Liu J. Zhang T. Zhang L. Li H. et al (2021). Shenma Yizhi decoction improves the mitochondrial structure in the brain and ameliorates cognitive impairment in VCI rats via the AMPK/UCP2 signaling pathway. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat.17, 1937–1951. 10.2147/NDT.S302355
43
Sun Y. Cheng G. Du L. Gan Y. Li B. Yan S. et al (2022). Chuanzhitongluo capsule ameliorates microcirculatory dysfunction in rats: efficacy evaluation and metabolic profiles. Front. Pharmacol.13, 1011333. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1011333
44
Tuo Q. Z. Zou J. J. Lei P. (2021). Rodent models of vascular cognitive impairment. J. Mol. Neurosci.71, 1–12. 10.1007/s12031-020-01733-2
45
Wan Q. Ma X. Zhang Z. J. Sun T. Xia F. Zhao G. et al (2017). Ginsenoside reduces cognitive impairment during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion through brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulated by epigenetic modulation. Mol. Neurobiol.54, 2889–2900. 10.1007/s12035-016-9868-4
46
Wang X. Xing A. Xu C. Cai Q. Liu H. Li L. (2010). Cerebrovascular hypoperfusion induces spatial memory impairment, synaptic changes, and amyloid-β oligomerization in rats. J. Alzheimers Dis.21, 813–822. 10.3233/JAD-2010-100216
47
Wang D. P. Yin H. Lin Q. Fang S. P. Shen J. H. Wu Y. F. et al (2019). Andrographolide enhances hippocampal BDNF signaling and suppresses neuronal apoptosis, astroglial activation, neuroinflammation, and spatial memory deficits in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol.392, 1277–1284. 10.1007/s00210-019-01672-9
48
Wang D. P. Chen S. H. Wang D. Kang K. Wu Y. F. Su S. H. et al (2020). Neuroprotective effects of andrographolide on chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced hippocampal neuronal damage in rats possibly via PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Acta Histochem.122, 151514. 10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151514
49
Wang N. Tian Y. Yan F. Zhao F. Wang R. Luo Y. et al (2022a). Berberine protects against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced cognitive impairment and hippocampal damage via regulation of the ERK/Nrf2 pathway. J. Chem. Neuroanat.123, 102119. 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2022.102119
50
Wang Y. Xue Y. Guo H. D. (2022b). Intervention effects of traditional Chinese medicine on stem cell therapy of myocardial infarction. Front. Pharmacol.13, 1013740. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1013740
51
Wang J. Shi J. Xiao Y. Chen G. Yang C. Duan L. et al (2023a). Fo-Shou-San ameliorates chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced cognitive impairment in mice by regulating NRF2/HO-1 pathway against ferroptosis. J. Integr. Neurosci.22, 41. 10.31083/j.jin2202041
52
Wang Y. Wang Y. Li S. Jin H. Duan J. Lu X. et al (2023b). Insights of Chinese herbal medicine for mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced cognitive impairment: existed evidences and potential directions. Front. Pharmacol.14, 1138566. 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138566
53
Wang H. Liu Y. Cui M. Guo Z. Zhao Y. Yang J. et al (2024a). Pseudoginsenoside-F11 reduces cognitive impairment and white matter injury in vascular dementia by alleviating autophagy-lysosomal pathway deficiency. Phytomedicine133, 155883. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155883
54
Wang J. Li Q. Chu S. Liu X. Zhang J. He W. (2024b). Impact of codonopsis decoction on cerebral blood flow and cognitive function in rats with chronic cerebral ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol.323, 117585. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117585
55
Wang Z. Han B. Qi J. Cao X. Gu H. Sun J. (2024c). Chuanzhitongluo capsule improves cognitive impairment in mice with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Exp. Gerontol.189, 112407. 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112407
56
Wu F. Li Y. Liu W. Xiao R. Yao B. Gao M. et al (2022). Comparative investigation of raw and processed Radix Polygoni multiflori on the treatment of vascular dementia by liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometry based metabolomic approach. Metabolites12, 1297. 10.3390/metabo12121297
57
Wu S. Huang R. Zhang R. Xiao C. Wang L. Luo M. et al (2023). Gastrodin and gastrodigenin improve energy metabolism disorders and mitochondrial dysfunction to antagonize vascular dementia. Molecules28, 2598. 10.3390/molecules28062598
58
Wu Q. Zhou Y. Ou C. Gao Z. Wu X. Zhao Y. et al (2025). Jiawei Kongsheng Zhenzhong Pill (JKZP) alleviates chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced hippocampal synaptic damage via S100A10/tPA/BDNF pathway. Brain Behav.15, e70328. 10.1002/brb3.70328
59
Xiao Q. Liu H. Yang C. Chen Y. Huang Y. Xiao X. et al (2023). Bushen-Yizhi formula exerts neuroprotective effect via inhibiting excessive mitophagy in rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Ethnopharmacol.310, 116326. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116326
60
Xiao H. H. Zhang F. R. Li S. Guo F. F. Hou J. L. Wang S. C. et al (2024). Xinshubao tablet rescues cognitive dysfunction in a mouse model of vascular dementia: involvement of neurogenesis and neuroinflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother.172, 116219. 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116219
61
Xie Q. Li H. Lu D. Yuan J. Ma R. Li J. et al (2021). Neuroprotective effect for cerebral ischemia by natural products: a review. Front. Pharmacol.12, 607412. 10.3389/fphar.2021.607412
62
Xu R. X. Wu Q. Luo Y. Gong Q. H. Yu L. M. Huang X. N. et al (2009). Protective effects of icariin on cognitive deficits induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol.36, 810–815. 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05149.x
63
Xu W. Bai Q. Dong Q. Guo M. Cui M. (2022). Blood-Brain barrier dysfunction and the potential mechanisms in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced cognitive impairment. Front. Cell Neurosci.16, 870674. 10.3389/fncel.2022.870674
64
Yan Z. Q. Chen J. Xing G. X. Huang J. G. Hou X. H. Zhang Y. (2015). Salidroside prevents cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. J. Int. Med. Res.43, 402–411. 10.1177/0300060514566648
65
Yan F. Tian Y. Huang Y. Wang Q. Liu P. Wang N. et al (2022). Xi-Xian-Tong-Shuan capsule alleviates vascular cognitive impairment in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by promoting white matter repair, reducing neuronal loss, and inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory factors. Biomed. Pharmacother.145, 112453. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112453
66
Yang Y. Song J. Liu N. Wei G. Liu S. Zhang S. et al (2022). Salvianolic acid A relieves cognitive disorder after chronic cerebral ischemia: involvement of Drd2/Cryab/NF-κB pathway. Pharmacol. Res.175,105989. 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105989
67
Yawoot N. Tocharus J. Tocharus C. (2025). Toll-Like receptor 4-mediated neuroinflammation: updates on pathological roles and therapeutic strategies in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Mol. Neurobiol.62, 7242–7267. 10.1007/s12035-025-04718-7
68
Yin C. Deng Y. Liu Y. Gao J. Yan L. Gong Q. (2018). Icariside II ameliorates cognitive impairments induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by inhibiting the amyloidogenic pathway: involvement of BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling and Up-Regulation of PPARα and PPARγ in rats. Front. Pharmacol.9, 1211. 10.3389/fphar.2018.01211
69
Zhang G. Zhao Z. Gao L. Deng J. Wang B. Xu D. et al (2011). Gypenoside attenuates white matter lesions induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav.99, 42–51. 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.03.019
70
Zhang B. Saatman K. E. Chen L. (2020). Therapeutic potential of natural compounds from Chinese medicine in acute and subacute phases of ischemic stroke. Neural Regen. Res.15, 416–424. 10.4103/1673-5374.265545
71
Zhang Q. Fan Z. Xue W. Sun F. Zhu H. Huang D. et al (2021). Vitexin regulates Epac and NLRP3 and ameliorates chronic cerebral hypoperfusion injury. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.99, 1079–1087. 10.1139/cjpp-2021-0034
72
Zhang Y. Song S. Li H. Wang X. Song L. Xue J. (2022). Polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum alleviates cognitive impairment in a mouse model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by regulating CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Food Funct.13, 1941–1952. 10.1039/d1fo03698j
73
Zhang Z. Shu X. Cao Q. Xu L. Wang Z. Li C. et al (2023). Compound from Magnolia officinalis ameliorates white matter injury by promoting oligodendrocyte maturation in chronic cerebral ischemia models. Neurosci. Bull.39, 1497–1511. 10.1007/s12264-023-01068-z
74
Zhang W. Xu H. Li C. Han B. Zhang Y. (2024). Exploring Chinese herbal medicine for ischemic stroke: insights into microglia and signaling pathways. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1333006. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1333006
75
Zhao F. Peng C. Sun Y. Li H. Du K. Liu F. (2022). Potential application of traditional Chinese medicine in cerebral ischemia-Focusing on ferroptosis. Front. Pharmacol.13, 963179. 10.3389/fphar.2022.963179
76
Zheng T. Jiang T. Huang Z. Ma H. Wang M. (2023). Role of traditional Chinese medicine monomers in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury:a review of the mechanism. Front. Pharmacol.14, 1220862. 10.3389/fphar.2023.1220862
77
Zhilan T. Zengyu Z. Pengpeng J. Hualan Y. Chao L. Yan X. et al (2025). Salidroside promotes pro-angiogenesis and repair of blood brain barrier via Notch/ITGB1 signal path in CSVD Model. J. Adv. Res.68, 429–444. 10.1016/j.jare.2024.02.019
78
Zhou J. Sun F. Zhang W. Feng Z. Yang Y. Mei Z. (2024). Novel insight into the therapeutical potential of flavonoids from traditional Chinese medicine against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1352760. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1352760
Summary
Keywords
chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, cognitive impairment, traditional Chinese medicine, multi-component, multi-target mechanisms
Citation
Ma X-T, Lou B-Y, Liu J and Liu B (2025) Traditional Chinese medicines alleviate experimental chronic cerebral hypoperfusion injury through multi-components and multi-target mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1698436. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1698436
Received
03 September 2025
Accepted
17 October 2025
Published
28 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Irina Ielciu, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iuliu Hatieganu, Romania
Reviewed by
Yingyi Zheng, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
YunKai Yang, Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, China
Narahari Rishitha, Self-Employed, Bangalore, India
Jiahao Feng, Jiangsu University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Ma, Lou, Liu and Liu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Liu, Jie@Liuonline.com; Bo Liu, 463848472@qq.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.