- 1Shemyakin-Ovchinnicov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry (Branch), Russian Academy of Sciences, Pushchino, Russia
- 2Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia named after Patrice Lumumba, Moscow, Russia
- 3Valenta Pharm JSC, Moscow, Russia
Background: Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a life-threatening lung disease. PF develops under the influence of various damaging agents. To study new therapeutic strategies, a PF model with intratracheal administration of bleomycin (BLM) is used.
Methods: We studied the effect of different doses of BLM. The study was performed on male SD rats. BLM was administrated at doses of 0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 3, and 5 mg/kg. Animals were observed for 21 days for the following parameters: the overall health status, body weight gain, and external respiratory function. On the 22nd day, the lung weight, cellular composition of the bronchoalveolar fluid (BALF), and hydroxyproline content were determined, and the degree of lung fibrosis was histologically assessed.
Results: With an increase in the BLM dose, the overall health status deteriorates, the function of external respiration worsens, BALF neutrophilic infiltration increases, and PF severity increases. The least marked PF manifestations were observed after the administration of BLM at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg, and the most marked manifestations were observed after the administration of BLM at a dose of 5 mg/kg.
Conclusion: Results obtained in the study demonstrate a dose-dependent effect of BLM on the PF severity, which provides information that will help select BLM dose suitable for obtaining desired degree of PF in animal models.
1 Introduction
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a severe, life-threatening lung disease characterized by sudden onset and rapid, inexorable progression (Li et al., 2024; Richeldi et al., 2020) that often develops as a consequence of pneumonia, interstitial lung pneumonia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (Travis et al., 2013; Ware and Matthay, 2000). Globally, PF affects approximately 5 million individuals (Kreuter et al., 2022). The 5-year survival rate is only 20%–25% after PF diagnosis (Lederer and Martinez). Overall, the etiology of PF development remains unclear, and PF is most often characterized by the term “idiopathic” (IPF) (Taskar and Coultas, 2006; Chen et al., 2023). Numerous epidemiological studies have shown the contribution of environmental factors to the risk of developing PF, such as exposure to metal dust (Gandhi et al., 2023). Thus, in Japan, over a 12-year period of studying postmortem changes in the lungs, PF phenomena were identified in workers at metallurgical plants, agricultural workers, poultry workers, miners, and people working with wood, organic solvents (Iwai et al., 1994; Baumgartner et al., 2000; Miyake et al., 2005), and metal dust (Harris et al., 2001). In postmortem studies conducted in Japan, patients with PF were found to have higher levels of inorganic particles such as silicon and aluminum in the pulmonary hilum lymph nodes (Kitamura et al., 2007). A multicenter study conducted in Korea in 2017 found that exposure to metal dust or any harmful environmental impact for more than 1 year was consistently associated with IPF (Koo et al., 2017). European studies have shown that air pollution, including excess levels of gases such as NO3, NO2, and O3—mainly from vehicle exhaust gases—increases the incidence and exacerbation of PF (Conti et al., 2018). Smoking significantly increases the incidence of PF (Kärkkäinen et al., 2017). Drugs are among the most common causes of PF. The greatest contribution to the development of PF, based on data from the top 10 countries that submitted spontaneous case reports (SRs) from 2019 to 2024 from the National Pharmacovigilance database (Canada, United States, Japan, Germany, Russia, France, Brazil, Argentina, United Kingdom, and China), is made by drugs from the antineoplastic and immunomodulating agent group—particularly rituximab (51.9% of all SRs)—followed by systemic hormonal preparations excluding sex hormones and insulins (7.4%) and agents for the respiratory system (7.1%) (Butranova et al., 2024). As PF is a serious lung disease that leads to decreased quality of life, disability, and rapid death, the search for new drugs for the treatment of PF is a major task in pharmaceutical and medical sciences. Animal models of PF are used to study the effectiveness of new therapeutic agents for the treatment of PF, particularly modeling using intratracheal administration of the antitumor glycopeptide antibiotic, bleomycin (BLM). The mechanism of BLM action is based on DNA fragmentation and the destruction of its spiral structure, which leads to the inhibition of cell fission (Cheson et al., 2001). One of the side effects of BLM is pulmonary toxicity, particularly the development of PF (De Lena et al., 1972; Blum et al., 1973; Azambuja et al., 2005). It was previously established that the incidence of pulmonary complications in people receiving BLM antitumor therapy depends on the dose of BLM received, the route of administration, the scheme and frequency of administration (Haas et al., 1976; Krakoff et al., 1977; Cooper and Hong, 1981), and the accumulation of BLM (Willson, 1978; Collis, 1980; Hay et al., 1991). In preclinical practice, pulmonary toxicity of BLM is used to model PF in rats and mice with intravenous and intratracheal administration. However, with intravenous administration, PF develops over a long period of time and is not as reproducible as with intratracheal administration (Della Latta et al., 2015). The BLM-induced PF model is the gold standard in preclinical studies of therapeutic agents’ efficacy. For example, the efficacy of drugs approved by the FDA as effective in PF treatment, namely, nintedanib and pirfenidone, which were approved by the FDA on 15 October 2014 (a; b), was initially studied using this model (Wollin et al., 2014; Inomata et al., 2014; Kehrer and Margolin, 1997; Schelegle et al., 1997). To model PF in mice and rats, different investigators use intratracheal administration of BLM in different doses: 0.3 (Principi et al., 2023), 0.8 (Hung et al., 2022), 1 (Prêle et al., 2022), 1.5 (Chen et al., 2024), 2 (Bonatti et al., 2023), 2.5 (Kadam and Schnitzer, 2024a), 3 (Xie et al., 2023), 5 (Liang et al., 2024), 7.5 (Santos-Ribeiro et al., 2023), 8 (Chu et al., 2019), and 10 mg/kg (Ge et al., 2024). Studies using multiple doses of BLM are very limited. There are very few studies where research workers use multiple doses of BLM; for example, Kim et al. (2010) performed studies in mice, which showed that different doses of BLM can have different effects. In addition, Kadam et al. (Kadam and Schnitzer, 2024a; Kadam and Schnitzer, 2024b) administered several doses of BLM to mice and rats, and an extremely high sensitivity of mice to a dose of BLM of 3 mg/kg was observed. The animals were studied for the expression of various inflammation inhibitors, signaling peptides, and proteins, and the signaling pathways that contribute to the development of the fibrotic phenotype at different stages of PF development were studied. Because there are so many rodent PF modeling studies using only a single dose of BLM, with the doses varying across studies, it is difficult for research workers to select the optimal dose of BLM, so we chose to conduct a study using multiple doses of BLM simultaneously to determine whether the severity of PF is dependent on the dose of BLM noxious agent administered directly into the trachea. Our ultimate goal is to enable research workers modeling PF to select the desired degree of lung injury that suits their specific research goals using a widely available and inexpensive arsenal of methods.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animals
The study used 60 mature male SD rats that were 8–10 weeks old. Animals were obtained from the Pushchino Nursery of Laboratory animals (Pushchino, Russia). All animal procedures and manipulations were approved by the Committee for Control over Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of BIBCh RAS (IACUC) (protocol number 936/23 from 24.04.2023) and were carried out in accordance with the EU Directive 2010/63/EU. After receiving from the nursery, the animals were adapted within 7 days. During the adaptation period, the health status of the animals was monitored through clinical examination. Animals with no signs of health problems were selected for the experiment. Animals were randomly divided into groups using body weight as a criterion so that the average weight of animals did not differ between the groups. Each animal was assigned an individual number, according to which the animal was marked with a puncture of the auricle. During the study, the animals were kept under controlled environmental conditions in a barrier zone with a “clean” and “dirty” corridor system with controlled environmental conditions (temperature 20 °C–24 °C, relative humidity 30%–55%, 12 h light cycle; 08:00–20:00—“day,” 20:00–08:00—“night”; 10-fold change in air volume in the room per hour). The animals received ad libitum Velaz FORTI 1324 Maintenance Diet as food (Altromin Spezialfutter GmbH & Co KG, Im Seelenkamp 20, D-32791 Lage, Germany).
2.2 Design description
The animals were divided into groups of 10. The animals were modeled for PF by intratracheal administration of BLM solution in different doses. Animals of the first group were administered saline (VEH). Animals of the second, third, fourth, fifth, and sixth groups were administered BLM at doses of 0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 3, and 5 mg/kg, respectively. The injection volume was 0.5 mL/kg (Table 1). Before administration (day 0) and on days 3, 7, 14, and 21 after PF modeling, the following parameters were determined in animals: clinical signs of health abnormalities, body weight, feed consumption, and respiratory parameters. In the presence of significant clinical abnormalities, the clinical signs of health abnormalities were recorded daily. If animals developed abnormalities incompatible with life, the animals were subjected to unplanned euthanasia and necropsy with lung sampling. At the end of the in-life phase, on the 22nd day after BLM administration, the animals were euthanized under anesthesia with a mixture of Telazol® (tiletamine + zolazepam) + xylazine, followed by exsanguination, and the lungs were collected, cleaned, and weighed. The left lung was subjected to bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), and the right lung was fixed for subsequent histological analysis. After BAL, the left lung of six animals from each group was frozen at −70 °C for subsequent hydroxyproline ELISA. For the remaining four animals, the left lung was fixed for further histological evaluation along with the right lung.
2.3 PF modeling
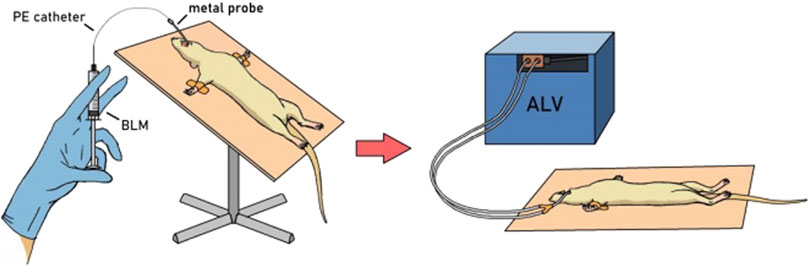
PF was modeled as described previously (Tukhovskaya et al., 2024) by a single intratracheal administration of BLM solution in different doses (Table 1) in a volume of 0.5 mL/kg followed by hyperventilation. The procedure was performed on animals anesthetized with an intramuscular injection of a mixture of Telazol® + Xyla® at a dose of 40 mg/kg + 10 mg/kg. The animals were fixed on a raised operating table in a supine position by the hind legs and upper incisors. The oral cavity was opened, and a metal probe with a ball on the end was inserted along the surface of the tongue. On exhalation, overcoming the resistance of the vocal cords, the probe was inserted into the trachea. A polyethylene catheter (PE-10, outer diameter 0.60 mm) was inserted into the probe opening and introduced to a premeasured depth (from the incisors to the middle of the sternum). A syringe with the BLM solution (or saline in the control group) was attached to the catheter and, holding the animal in a vertical position, the BLM solution was slowly injected. Immediately after intratracheal administration of BLM or saline, hyperventilation of the lungs was performed. A Ugo Basile 7025 artificial lung ventilation apparatus was connected to the probe located in the trachea (Figure 1). The following hyperventilation parameters were set: tidal volume 30 mL/kg, respiratory rate 60 times/min, and exposure time 10 min. After completion of the procedure, the animals were returned to the holding cage under constant observation until recovery from anesthesia.
2.4 Drugs
To model PF, we used the pharmaceutical drug (bleomycin hydrochloride) manufactured by JSC Omutninskaya Scientific Experimental Industrial Base, Russia. The drug was a lyophilizate in a glass vial. The BLM solution for administration was prepared immediately before use by adding a calculated amount of water for injection to the vial to obtain a stock solution with a concentration of 10 mg/mL. This stock solution was used to administer BLM at a dose of 5 mg/kg. To prepare BLM solutions for doses of 3, 2.5, 1.5, and 0.5 mg/kg, the stock solution was diluted with water for injection by 1.7, 2, 3.3, and 10 times, respectively. The prepared BLM doses were administered to the animals immediately after preparation; any remaining solution was discarded.
To anesthetize animals during PF modeling and before necropsy, we used Telazol, Zoetis Manufacturing & Research Spain, S.L., Spain, mixed with Xyla, Interchemie werken “De Adelaar” BV, Estonia. The Telazol solution was prepared according to the instructions by adding 5 mL of the solvent (water for injection) to the vial containing the lyophilizate. The resulting solution was stored in the refrigerator (at 2 °C–8 °C) for no longer than 30 days. Xyla is available as a ready-to-use solution. After opening for the first time, the solution was stored in the refrigerator (at 2 °C–8 °C) for no longer than 30 days.
2.5 Registration of clinical signs of deviations in the health status of animals
The health status of the animals was assessed before group formation and on days 3, 7, 14, and 21 after PF modeling. In the presence of significant deviations in health, the health status of the animals was recorded daily. If deviations incompatible with life appeared in the animals, they were euthanized, and an autopsy was performed with the collection of lung samples.
2.6 Body weight and weight gain
Animals were weighed when forming groups and then on the third, seventh, 14th, and 21st days after modeling PF, but in the presence of pronounced health deviations, animals were weighed daily. Body weight gain was calculated relative to the body weight on day 1 of the study.
2.7 Food consumption
Food consumption was assessed by weighing the feed rack at the start of the 24-h food consumption recording before PF modeling and then on days 2–3, 6–7, 13–14, and 20–21.
2.8 External respiration parameters (spirometry)
The external respiration parameters of the animals (respiratory rate, tidal volume, and the maximum expiratory volume) were recorded before BLM administration on day 0 and then on days 2, 7, 14, and 21 after BLM administration using an FE141 Spirometer with PowerLab 8/35 computer system (ADInstruments Pty Ltd., Australia).
2.9 Euthanasia and necropsy
On the 22nd day after modeling, the animals were subjected to planned euthanasia under anesthesia with a mixture of Telazol® (tiletamine + zolazepam) + Xyla at doses of 40 mg/kg + 10 mg/kg, followed by total blood sampling from the inferior vena cava. During necropsy, the animal lungs and trachea were removed, clearing them of connective tissue.
2.10 Visual assessment of lung damage
The removed lungs were visually assessed for external signs of damage.
2.11 Lung weight
During necropsy, the lungs with trachea were weighed and the relative weight of the lungs relative to the body weight was calculated.
2.12 BAL procedure
The right bronchus was ligated, and BAL was performed to obtain the bronchoalveolar fluid (BALF). BAL was made by the infusion of 2 mL of PBS solution into the lung through the trachea and draining the resulting wash by gravity into a 15-mL test tube. The procedure was performed three times, and the total volume of PBS for BAL was 6 mL. The BALF was divided into two parts: one was used to count the total number of nucleated cells in a Goryaev’s chamber and the second was centrifuged to prepare a smear.
2.13 Counting of BALF cells in Goryaev’s chamber
The concentration of nucleated cells was calculated. For this purpose, a tenfold dilution of BALF in 4% acetic acid was performed to lyse the erythrocytes, the resulting sample was used to fill the Goryaev’s chamber, and the nucleated cells were counted per 100 cells.
2.14 Preparation of a BALF smear and cell counting
The BALF was centrifuged in an Eppendorf 5804 R centrifuge at 3,000 rpm at 4 °C for 15 min. The supernatant was collected, and a smear was prepared from the sediment after pipetting with 3 μL of fetal calf serum. The smear was stained according to Pappenheim. The cellular composition of the stained smears was analyzed: the percentage of alveolar macrophages, segmented neutrophils, band neutrophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes was calculated per 100 cells.
2.15 Lung tissue sampling and preparation for hydroxyproline ELISA analysis
During necropsy, lungs from six animals in each group were taken from the animals along with the trachea. After performing BAL for the left lung, the left bronchus was ligated and the left lung was cut off. The left lung was divided into two parts, which were placed in weighed 2-mL Eppendorf tubes. Lung samples were frozen at −70 °C until the homogenate was prepared. To prepare the homogenate, the lung sample was grinded with a manual homogenizer MT 30K directly in the Eppendorf tube after defrosting. The tube with the homogenate was weighed, and the mass of the resulting homogenate was calculated by subtracting the mass of the empty tube from the mass of the tube with the homogenate. The homogenate was frozen at 70 °C, defrosted again, and PBS was added at 1:12 ratio of weight: volume. For the homogenate + PBS mixture, two cycles of freezing at −70 °C and thawing were performed to more effectively grind the tissue. After the last thawing, the sample was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm at 4 °C for 15 min and then at 5,000 rpm at 15 °C for 15 min. The obtained supernatant was concentrated in special JetSpinTM Centrifugal Filter tubes, 5 mL, 100,000 MWCO, PES, non-sterile, BIOFIL, China. The tubes for concentration were prewashed with PBS solution according to the instructions. The supernatant from the sample + PBS was poured into the washed tube and centrifuged at 3,500 rpm. The centrifugation time for all the samples was different (from 35 to 135 min). The samples were centrifuged to a double volume relative to the homogenate mass (e.g., homogenate weight 0.3 g; centrifugation-concentration to a volume of 0.6 mL).
2.16 Lung hydroxyproline enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
The hydroxyproline content in the sample was determined by ELISA using the Rat Hyp (hydroxyproline) ELISA Kit, ELK Biotechnology, using an immunological plate spectrophotometer Multiskan™GO 1.01.12, Thermo Scientific, and measurement was carried out at 450 nm.
2.17 Preparation and analysis of the histological specimens
The right lung for all the animals and additionally the left lung for four animals from each group were pre-filled with 10% neutral formalin solution, fixed in the above solution, washed in running tap water, dehydrated in alcohols of increasing concentration, and embedded in paraffin. Paraffin sections of 4 μm–5 μm thickness were stained using the Masson method (Masson Trichrome dye, Bio-Optica, Italy). Histological preparations were examined using conventional light microscopy on an AxioScope.A1 microscope (Carl Zeiss, Germany). Micrographs of the histological preparations were obtained using a high-resolution Axiocam 305 color camera (Carl Zeiss, Germany) using ZEN 2.6 lite software (Carl Zeiss, Germany). The severity of PF was assessed in paraffin sections stained with a specific Masson trichrome dye using a modified semi-quantitative eight-point Ashcroft scale (Wollin et al., 2014). The final PF severity was assessed as the average score of fibrotic changes in the lungs in all the assessed fields of vision and in all sections of the organ (for all lobes). To increase the reliability of semi-quantitative assessment and prevent biased assessment, the histologist was blinded and histological slides were coded, making it impossible to know which group the animals belonged to.
2.18 Statistics
Microsoft Excel and Statistica for Windows, version 7, were used for statistical processing of the experimental data. The normality of distribution of all measurement data was tested using the Shapiro–Wilk W test. The mean values (MEAN) and standard deviations (SD) were calculated for all numerical data. Between-group differences for repeated measurement data (body weight, weight gain, and spirometry) were assessed using repeated measures ANOVA with power testing using Duncan’s multi-stage post hoc test. Between-group differences for outcome-based data (BALF cytology, lung tissue hydroxyproline concentration, lung weight, and histological semi-quantitative assessment data) were assessed using one-way ANOVA with power testing using Duncan’s multi-stage post hoc test.
The chi-square test was used to analyze the intergroup differences in the frequency of manifestation of a sign (frequency of manifestation of clinical signs in health status deviations).
2.19 Ethical considerations
All procedures and manipulations with animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of BIBCh RAS (IACUC) (protocol number 936/23 from 24.04.2023) and were carried out in accordance with the EU Directive 2010/63/EU.
3 Results
3.1 Assessing animals’ general state of health
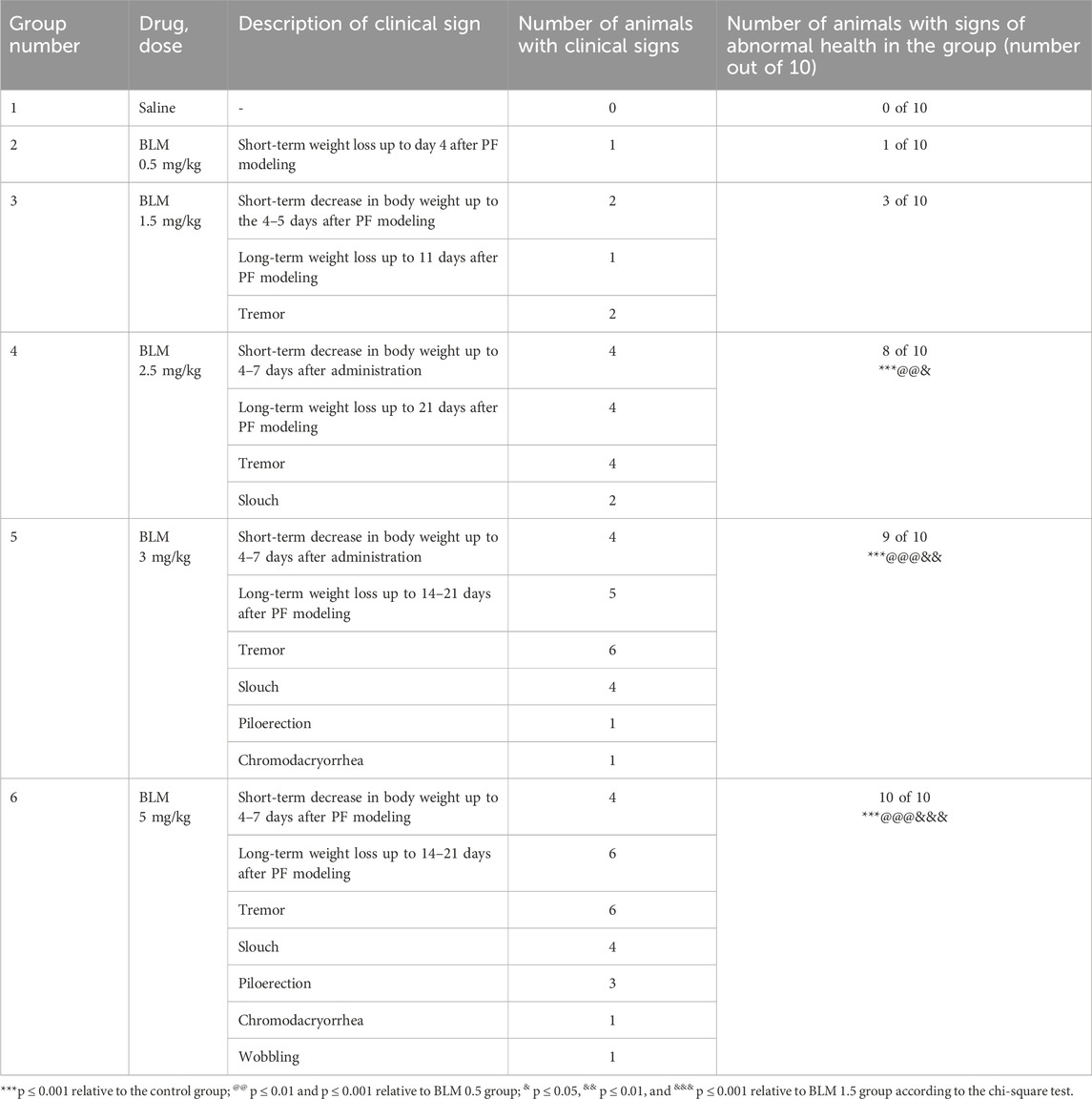
No mortality was observed in the study; however, two animals, one receiving BLM at a dose of 3 mg/kg and the other receiving BLM at a dose of 5 mg/kg, developed severe cachexia (weight loss of approximately 50% of the initial weight) by the 14th day after the PF modeling and were, therefore, euthanized. Table 2 presents the daily clinical observations for animals with health abnormalities. It is evident that as the BLM dose increases, the frequency, number, severity, and duration of health problems also increase, indicating that the worsening of the animals’ condition is dose-dependent.
3.2 Body weight and weight gain
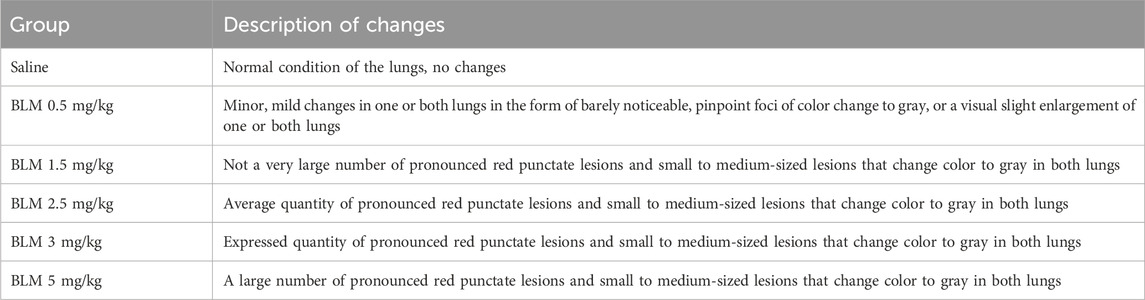
The body weight of animals with BLM administration starting from the third day after PF modeling was significantly lower than that of the group receiving the vehicle saline. The dynamics of body weight reduction over the 21 days of observations indicates a dose-dependence of the BLM effect; that is, with an increase in the BLM dose, the body weight reduction was more pronounced (Figure 2).
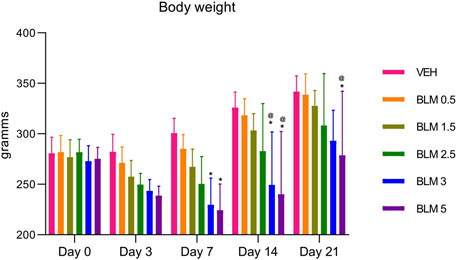
Figure 2. Dynamics of changes in the body weight of animals after administration of BLM in different doses.*p ≤ 0.05 relative to the control group and @ p ≤ 0.05 relative to the BLM 0.5 group according to the repeated measures test ANOVA with post hoc Duncan’s test. N for all groups = 10; for BLM 3 and BLM 5 groups on the 21st day of the study, N = 9. Data are presented as the MEAN ± SD.
In all animals that were administered BLM, the body weight gain parameter decreased on the third day. The decrease in the body weight gain parameter was maintained on the seventh day in animals that received BLM at doses of 1.5, 2.5, 3, and 5 mg/kg and on the 14th day in animals that received BLM at doses of 2.5, 3, and 5 mg/kg. Starting from the 14th day, the animals showed a recovery increase in the body weight gain parameter; on the 21st day, the body weight gain parameter increased in all groups of animals. The dynamics of the body weight gain parameter indicates the dose-dependence of the BLM effect—with an increase in the BLM dose, the decrease in the body weight gain parameter is more pronounced and longer (Figure 3).
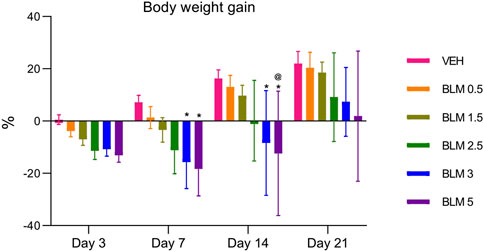
Figure 3. Dynamics of the body weight gain index of animals after PF modeling by the administration of BLM in different doses. *p ≤ 0.05 relative to the control group and @ p ≤ 0.05 relative to the BLM 0.5 group according to repeated measures test ANOVA with post hoc Duncan’s test. N for all groups = 10; for BLM 3 and BLM 5 groups on the 21st day of the study, N = 9. Data are presented as the MEAN ± SD.
3.3 Food consumption
Food consumption is an indicator of the general health of animals. All animals showed a decrease in food consumption after PF modeling, and it was dose-dependent—an aggravation of the decrease in the indicator was observed with an increase in the BLM dose. A decrease in food consumption was observed until the seventh day after PF modeling, and from the 14th day, food consumption did not differ between the groups (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Dynamics of food consumption by animals after PF modeling by the administration of BLM in different doses. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, and ***p ≤ 0.001 relative to the control group; @ p ≤ 0.05, @@ p ≤ 0.01, and @@@ p ≤ 0.001 relative to the BLM 0.5 group; & p ≤ 0.05 relative to the BLM 1.5 group according to repeated measures test ANOVA with post hoc Duncan’s test. N for all groups = 10; for BLM 3 and BLM 5 groups on the 21st day of the study, N = 9. Data are presented as the MEAN ± SD.
3.4 Evaluation of the external respiratory function—spirometry
After PF modeling, the respiratory rate in all the animals increased significantly, and on the third day after modeling, the parameter did not differ between the groups with PF. Starting from the seventh day, the dose-dependence of the BLM effect was observed—with an increase in the BLM dose, the recovery of the respiratory rate over time was longer and less pronounced; however, recovery of the parameter was not complete in any of the groups (Figure 5a).
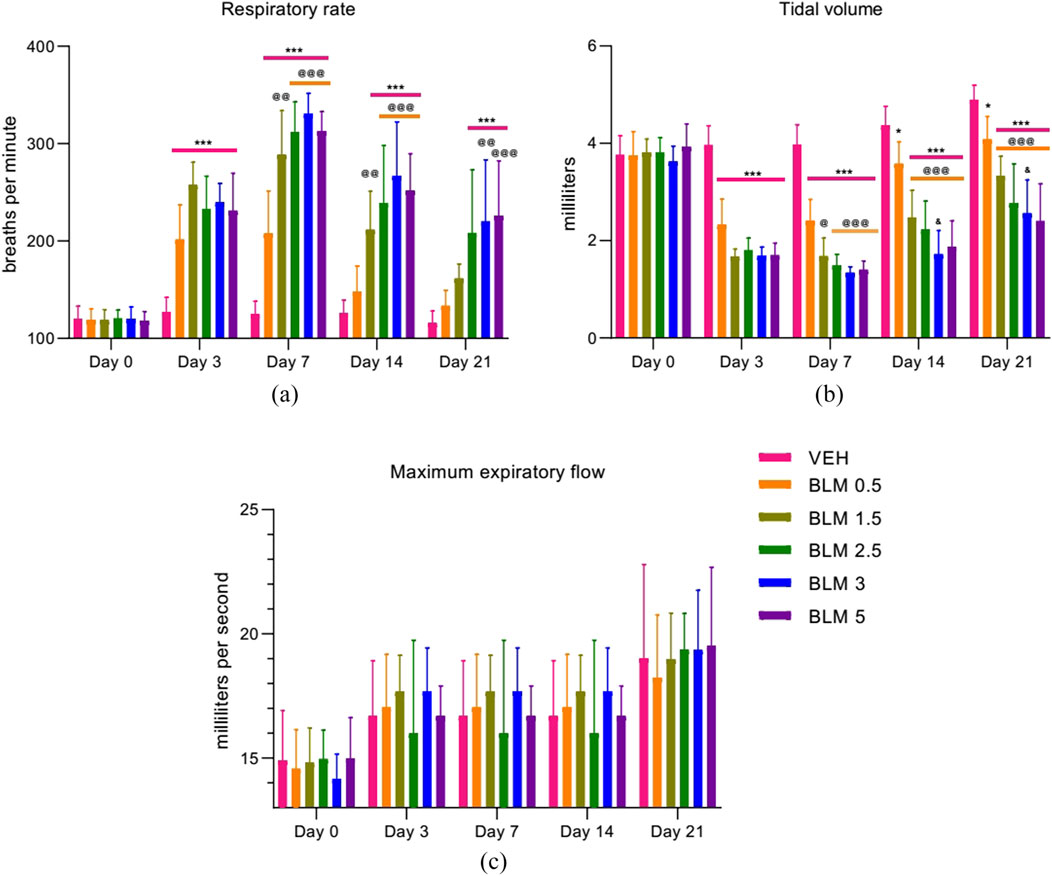
Figure 5. Dynamics of the external respiratory function parameters after PF modeling by the administration of BLM in different doses: (a) respiratory rate, (b) tidal volume, and (c) maximum expiratory flow. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, and ***p ≤ 0.001 relative to the control group; @ p ≤ 0.05, @@ p ≤ 0.01, and @@@ p ≤ 0.001 relative to the BLM 0.5 group; & p ≤ 0.05 relative to the BLM 1.5 group according to repeated measures test ANOVA with post hoc Duncan’s test. N for all groups = 10; for BLM 3 and BLM 5 groups on the 21st day of the study, N = 9. Data are presented as the MEAN ± SD.
The tidal volume, a parameter related to the vital capacity of the lungs, significantly decreased in all animals with PF, with a subsequent tendency to recovery. At the same time, the dose-dependence of the effect of BLM on the parameter was observed starting from the third day after modeling—with increasing BLM dose, the recovery of the tidal volume over time was slower and less pronounced (Figure 5b).
The maximum expiratory flow rate significantly decreased on the third day after PF modeling. In the following days of the study, this parameter did not differ between the groups (Figure 5c).
3.5 Cellular composition of the BALF
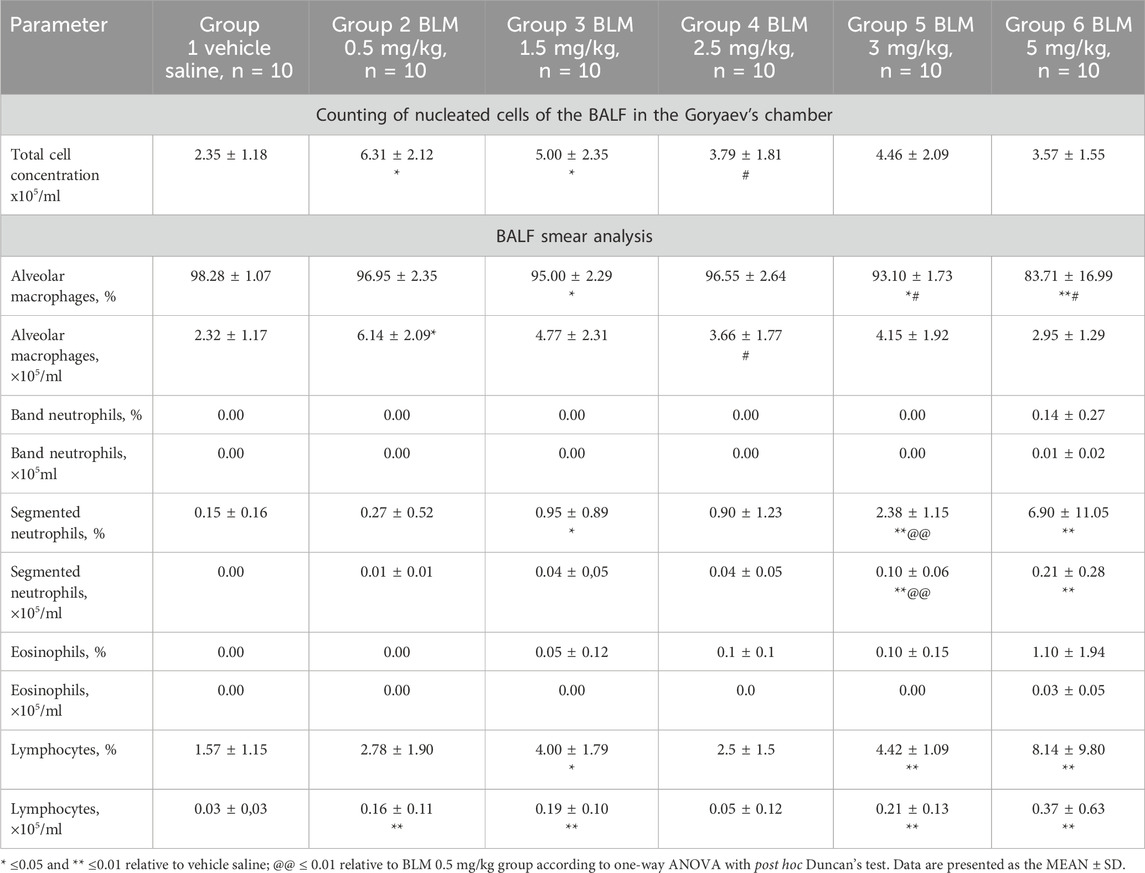
After PF modeling, an increase in the total number of nucleated cells in the BALF was observed along with changes in the cellular composition of the BALF, and these changes varied depending on the BLM dose. The maximum contribution to the increase in the total number of cells in the groups receiving BLM at the lowest doses, namely, 0.5 and 1.5 mg/kg, was made by alveolar macrophages. Starting with a BLM dose of 2.5 mg/kg, the increase in the total number of cells in the BALF was due to both an increase in the number of alveolar macrophages and an increase in segmented neutrophils and lymphocytes (Table 3).
3.6 Hydroxyproline content in the lungs determined by ELISA
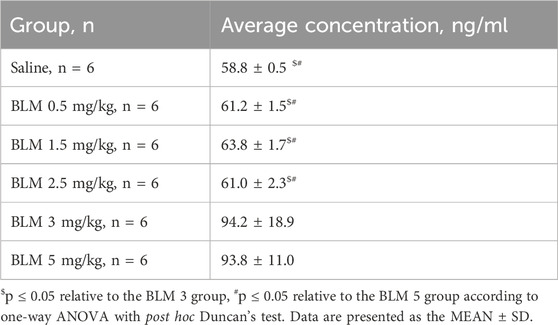
The hydroxyproline content was significantly increased in the groups receiving BLM at doses of 3 and 5 mg/kg compared with the control animals (Table 4).
3.7 Lung weight
After PF modeling, all animals showed an increase in the absolute and relative lung weight, which was least pronounced in the group receiving BLM at a minimum dose of 0.5 mg/kg (Figure 6).
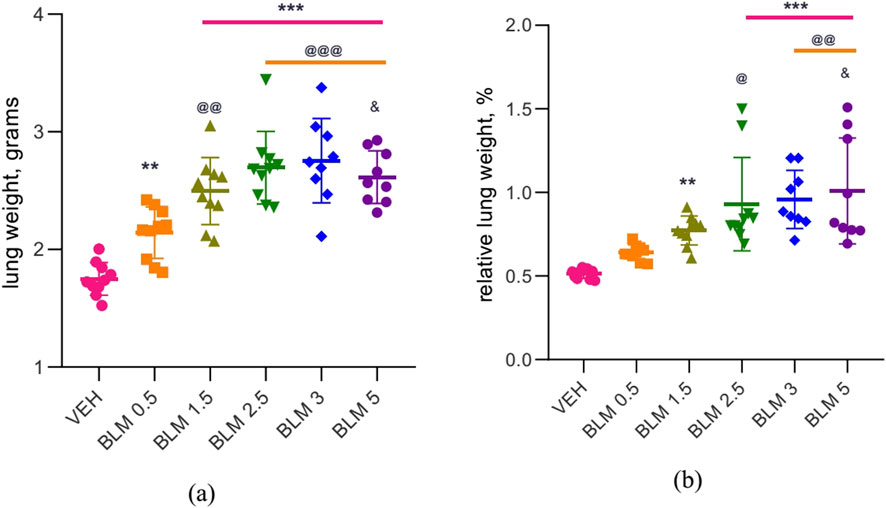
Figure 6. Lung weight in male SD rats on day 22 after PF modeling: (a) absolute lung weight, (b) relative lung weight relative to body weight at necropsy. ** р ≤ 0.01 and *** р ≤ 0.001 relative to saline; @ р ≤ 0.05, @@ р≤ 0.01, and @@@ р≤ 0.001 relative to BLM 0.5 mg/kg group; & р≤ 0.05 relative to BLM 1.5 mg/kg group according to one-way ANOVA with post hoc Duncan’s test. For groups VEH, BLM 0.5, BLM 1.5, and BLM 2.5, N = 10; for groups BLM 3 and BLM 5, N = 9. Data are presented as the MEAN ± SD.
3.8 Visual assessment of the lung condition
Animals receiving BLM had visually evident lung lesions, as shown in Table 5; Figure 7. The severity of these lesions increased with increasing BLM doses and was the lowest for animals receiving 0.5 mg/kg BLM and the highest for animals receiving 5 mg/kg BLM. In addition, two animals in the 3 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg BLM groups that developed cachexia and underwent unplanned euthanasia had significantly more severe lung lesions than all other animals, as visually assessed.
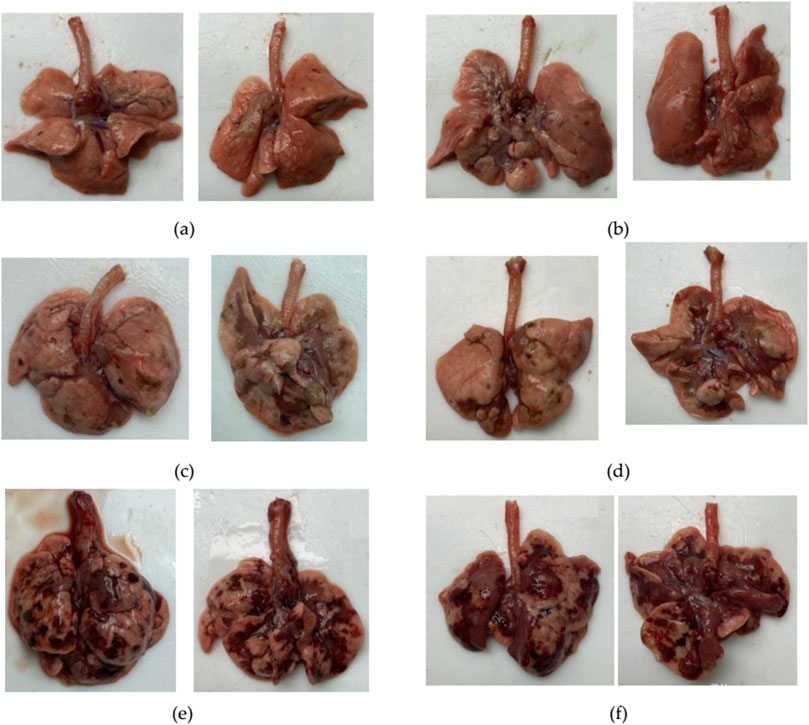
Figure 7. Photographs of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the lungs of animals after modeling PF. (a) Lungs on the 22nd day after BLM administration at a dose of 1.5 mg/kg. (b) Lungs on the 22nd day after BLM administration at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg. (c) Lungs on the 22nd day after BLM administration at a dose of 3 mg/kg. (d) Lungs on the 22nd day after BLM administration at a dose of 5 mg/kg. (e) Lungs of an animal subjected to unscheduled euthanasia due to cachexia on the 14th day after BLM administration at a dose of 3 mg/kg. (f) Lungs of an animal subjected to unscheduled euthanasia due to cachexia on the 14th day after BLM administration at a dose of 5 mg/kg. For animals receiving BLM at a dose of 1.5 mg/kg, visual abnormalities in the lungs could not be recorded in photographs as the changes were visually poorly distinguishable.
3.9 Histological assessment of the lungs
Figure 8 shows micrographs reflecting the gradation of the severity of PF, which was assessed in preparations stained with Masson’s trichrome dye, according to the modified Ashcroft scale (Hübner et al., 2008). From a histological analysis perspective, it was appropriate to consider the data from individual animals in groups 5 and 6 that underwent unscheduled euthanasia on the 14th day due to cachexia together with the data from other animals that underwent planned euthanasia on the 22nd day after BLM administration.
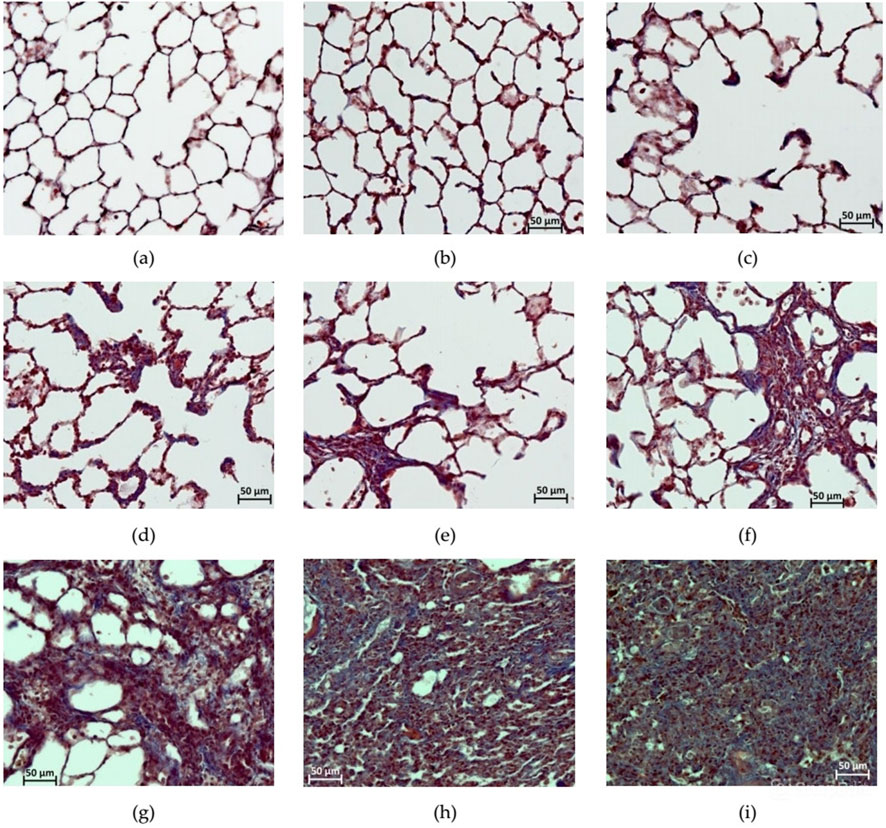
Figure 8. Photomicrographs of histological preparations of the lungs stained with Masson trichrome dye, at 200x magnification, corresponding to the score according to the modified Ashcroft scale. (a) Score 0: no deviations from the norm; (b) score 1: minor isolated fibrous changes in the inter-alveolar septa (less than three times thicker than normal) and the histoarchitecture of the lungs is not affected; (c) score 2: obvious fibrous changes in the inter-alveolar septa (>3 times thicker than normal) with a nodular formation, but not connected to each other, the alveoli are enlarged in size, and the histoarchitecture of the lungs is not affected; (d) score 3: adjacent fibrously altered walls of inter-alveolar septa (septum >3 times thicker than normal) mainly throughout the field of view, where alveoli are significantly enlarged in size and histoarchitecture of the lungs is not altered; (e) score 4: single fibrous formations (≤10% of the microscope field of view); (f) score 5: confluent fibrous changes occupying more than 10% but less than 50% of the microscope field of view, and the lung structure is significantly altered but still preserved; (g) score 6: large adjacent fields of fibrous tissue occupying more than 50% of the microscope field of view, and the histoarchitecture of the organ is mostly not preserved; (h) score 7: alveoli are erased by fibrous masses, but single air fragments still remain; (i) score 8: in the field of view of the microscope, there is complete obliteration of the lung parenchyma by fibrous masses.
After a single intratracheal administration of BLM with subsequent hyperventilation of the lungs, focal PF phenomena were observed in all animals; the foci of fibrous tissue were most often localized in the hilar peribronchial spaces, less often in the pulmonary acini, and only in isolated cases subpleurally. The severity of PF had a clear dose-dependent character (Table 6; Figures 8–10).
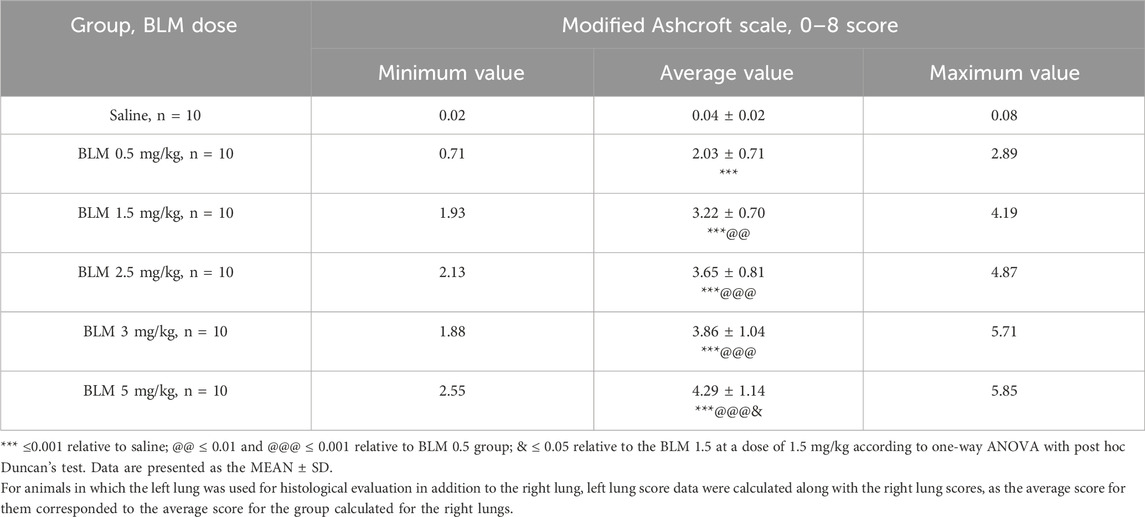
Table 6. Summary of the assessment of changes of degree in the lungs of SD males on the 22nd day after intratracheal administration of BLM at different doses.
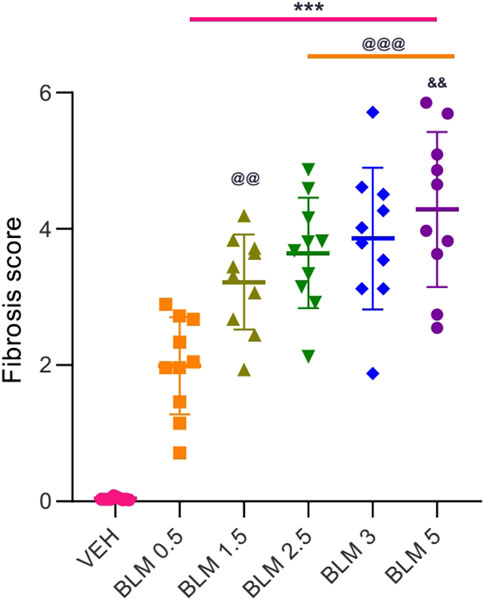
Figure 9. Score semi-quantitative assessment according to the 8-point Ashcroft scale of the severity of fibrosis in the lungs of SD males on the 22nd day after a single intratracheal administration of BLM at different doses. *** ≤0.001 relative to saline; @@ ≤ 0.01 and @@@ ≤ 0.001 relative to BLM 0.5 group at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg; & р≤ 0.05 relative to BLM 1.5 mg/kg according to one-way ANOVA with post hoc Duncan’s test. Data are presented as the MEAN ± SD. For all groups, N = 10.
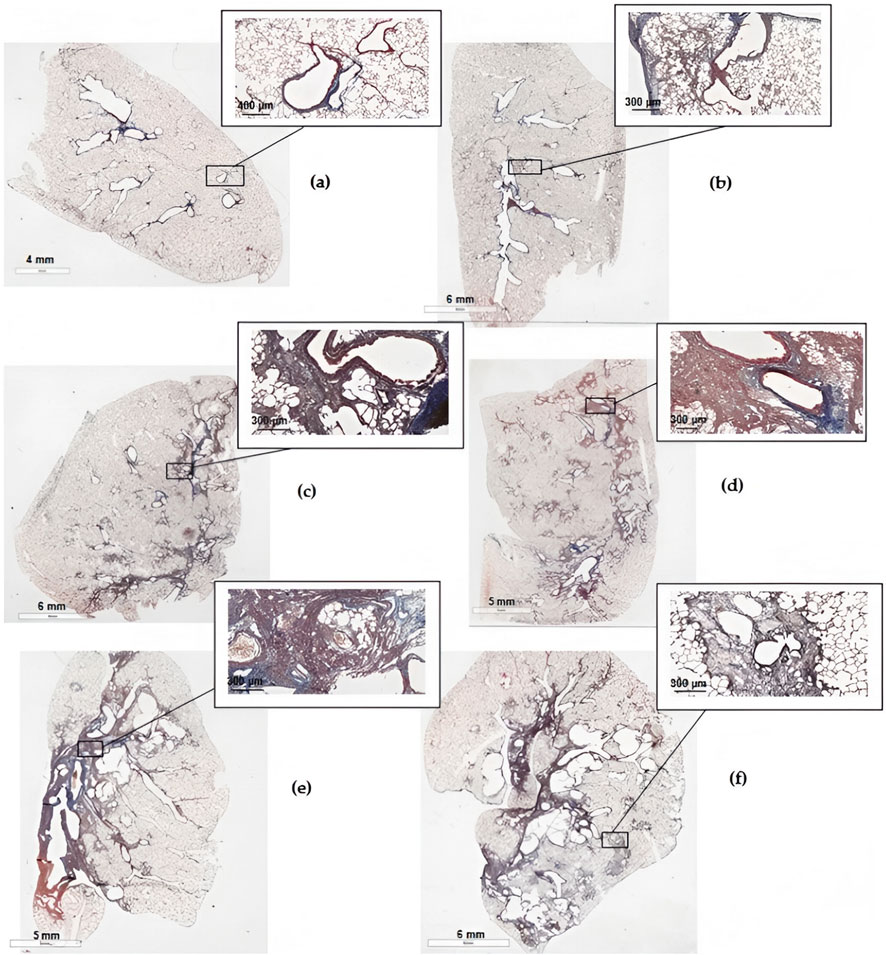
Figure 10. Scans of histological sections of the left lung of animals on the 22nd day after the introduction of BLM in different doses. (a) Control saline; (b) BLM 0.5 mg/kg; (c) BLM 1.5 mg/kg; (d) BLM 2.5 mg/kg; (e) BLM 3 mg/kg; (f) BLM 5 mg/kg (KF-PRO-020-HI, China, magnification is indicated on the scale bar).
4 Discussion
In our study, after the intratracheal administration of BLM in all doses, PF developed, but the severity of its manifestations was dose-dependent, worsening with an increase in the BLM dose. In humans, body weight is an important parameter characterizing the severity of lung damage in interstitial pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), leading to the development of PF. Severe lung damage in humans leads to the development of pulmonary cachexia (Schols, 2002), which is characterized by a significant, progressive decrease in body weight and is a risk factor for mortality in patients with COPD (von Haehling and Anker, 2014). In our study, a decrease in body weight was observed in all animals after modeling PF, and the higher the BLM dose, the longer and more pronounced this decrease was. It has been shown that in patients suffering from IPF with a decrease in body weight, the risk of mortality increases (Comes et al., 2022). We also observed the same in our study, when after the introduction of BLM at doses of 3 and 5 mg/kg, cachexia incompatible with life developed in the animals. In healthy SD rats aged 2–3 months, a steady increase in body weight was observed, which we also observed in the control animals (Brower et al., 2015). In animals with PF in our study, the body weight gain rate significantly decreased. A similar decrease in body weight gain has been observed in other studies on animals with PF (Li et al., 2024; Xie et al., 2023; Chu et al., 2019; Gul et al., 2023). However, body weight is not always recorded in studies on animals with PF (Kadam and Schnitzer, 2024a; Zeng et al., 2023; Qu et al., 2020), which we consider a major omission, as body weight and body weight gain are the most important parameters illustrating the degree of progression of lung damage and predicting the outcome of the disease (Pugashetti and Oldham, 2022; Pugashetti et al., 2018; Kulkarni et al., 2019); for example, a two- to three-fold increase in 2-year mortality after the diagnosis of IPF in patients with weight loss has been observed (Nakatsuka et al., 2018). In our study, we showed that the decrease in body weight and the rate of body weight gain were dose-dependent, worsening with an increase in the dose of the damaging agent BLM, which can be used by research workers to make the most informed choice of the BLM dose depending on the objectives of the study. External respiratory function in PF worsens in patients with lung damage, particularly in case of PF (Kulkarni et al., 2019). Increased respiratory rate and decreased vital capacity of the lungs are observed in patients with PF (Flaherty et al., 2000; Weissman et al., 2003; Doherty et al., 1997), as in our study. The dynamics of changes in the respiratory parameters has a pronounced predictive power in relation to the outcome of the disease (Ley et al., 2011; Fujita et al., 2022). In our study, an increase in the respiratory rate and a decrease in the tidal volume of the lungs act as prognostic indicators in relation to the severity of lung damage with an increase in the dose of the damaging agent—BLM. The analysis of BALF in our study showed dose-dependent neutrophil infiltration, which indicates a pronounced inflammatory process. The effect of inflammation on the process of fibrosis development is actively studied. Currently, the leading paradigm for the development of fibrosis is considered to be the imbalance between the destruction of the alveolar endothelial matrix and the healing of this matrix, that is, persistent lung damage and ineffective epithelial healing. Thus, the inflammatory process persists and resolves through apoptosis and phagocytosis of inflammatory and mesenchymal cells. Normally, during recovery from injury, the normal pulmonary architecture is restored. However, in PF, persistent inflammation and impaired recovery lead to intensive development of fibrous tissue and disruption of the pulmonary architecture (Coward et al., 2010). Neutrophil infiltration has been shown to influence the development of PF through enzymes that promote matrix degradation, such as neutrophil elastase (NE), the level of which is increased in the lung parenchyma of patients with PF (Obayashi et al., 1997). NE is a destructive elastase that attacks the extracellular matrix and modulates inflammation and tissue remodeling (Pol et al., 2017). In animals with targeted deletion of the ne−/− gene or after specific inhibition of NE, the development of fibrosis is reduced in a mouse model of PF (Coward et al., 2010; Takemasa et al., 2012; Chua et al., 2007; Taooka et al., 1997; Gregory et al., 2015). In our study, the neutrophil content in the BALF increases with the BLM dose and is associated with worsening of PF, which is consistent with what was described above regarding neutrophil infiltration and the effect of NE on the severity of PF. The increase in lung mass in our study is a characteristic of PF and occurs due to diffuse or multifocal lesions associated with infiltration by inflammatory cells, destruction of the alveolar endothelial matrix, and thickening and fibrosis of the alveolar walls associated with increased collagen deposition (Ge et al., 2024; Cowley et al., 2019). A typical picture of fibrotic lung damage is the presence of fibrotic foci—clusters of active fibroblasts and myofibroblasts—hyperplastic alveolar epithelial cells type 2, whose interconnections with mesenchymal cells enhance the pro-fibrotic environment through the increased activity of growth factors such as TGF-β1, PDGF, and Wnt. Cellular interactions in fibrotic foci lead to excessive production of the intercellular matrix and an imbalance between the deposition and degradation of collagen in favor of the former (Sgalla et al., 2018). The severity of PF is related to the collagen content in fibrotic foci. To quantitatively determine collagen in lung tissue in laboratory animals, the content of hydroxyproline is measured—a degradation product of type-1 collagen, which is the main component of fibrous tissue that forms the basis of fibrous foci in PF (Von Haehling and Anker, 2014; Xu et al., 2019; Ju et al., 2022). According to the American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/Japanese Respiratory Society/Asociación Latinoamericana de Tórax (ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT) guideline published in 2022, the severity of PF lesions in humans is visualized using high-resolution computed tomography. There are differential signs that indicate the diagnosis of PF and assess its presence and severity, such as honeycombing and/or traction bronchiectasis (Raghu et al., 2022). The same guideline suggests performing the transbronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC) procedure to verify the diagnosis of PF. In this study, we allow to establish the histological picture of fibrosis in lung samples taken from different lobes and locations (Troy et al., 2020). However, as the procedure is performed during life and taking biopsy samples has physiological limitations, the level of evidence for the results of this diagnostic method is not high (Raghu et al., 2022). In addition, lung biopsy may not be suitable for patients with severe respiratory dysfunction, pulmonary hypertension, and uncorrectable risk of bleeding (Aburto et al., 2020; Hutchinson et al., 2016; Lentz et al., 2017). In any case, the diagnosis of IPF in humans is possible only with a combination of lung tissue damage visualization techniques, namely, HRCT and histological data obtained during lung biopsy (Rajan et al., 2023). In animal models of PF, visualization of lung tissue fibrosis is performed during postmortem lung histology, with the lungs being assessed as a whole, unlike human lungs during in-life biopsy. In histological preparations stained with Masson trichrome dye (a variant of three-color staining of micropreparations that allows differentiation of collagen fibers, fibrin, muscle tissue, and erythrocytes), the degree of PF expression is assessed using the Ashcroft scale (Hung et al., 2022; Kadam and Schnitzer, 2024a; Liang et al., 2024; Ge et al., 2024; Abd-Elmawla et al., 2023; Mansouri et al., 2019). Our study showed a gradient development of PF, expressed in the scoring of histological preparations; with an increase in the BLM dose, the average score on the Ashcroft scale also increases.
5 Conclusion
The presented study demonstrates a dose-dependent effect of BLM on the severity of PF. With an increase in the BLM dose, the general condition of the animals worsens dose-dependently, the function of external respiration worsens, neutrophilic infiltration in the BALF increases, and dose-dependent increase in the average histological score characterizing the degree of PF severity occurs. The least pronounced manifestations of PF were observed when using BLM at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg, and the most pronounced manifestations were observed when using BLM at a dose of 5 mg/kg. These results are addressed to research workers planning to use the BLM-induced PF model to orient themselves in the required degree of PF severity and, accordingly, in the required BLM dose. In addition, our results were obtained using widely used and inexpensive methods available to most laboratories working with preclinical studies on rodents.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The animal study and all procedures and manipulations with animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of BIBCh RAS (IACUC) (protocol number 936/23 from 24.04.2023) and were carried out in accordance with the EU Directive 2010/63/EU. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
ET: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YP: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MS: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. AI: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. VP: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. GS: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. NB: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. EM: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. IK: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. VK: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. EkK: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. ElK: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. ER: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. VR: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review and editing. OP: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. AG: Formal analysis, Writing – review and editing. EJ: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review and editing. AK: Formal analysis, Writing – review and editing. AM: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by funding from Valenta Pharm JSC, Ryabinovaya street 26, building 10, Moscow, 121471, Russia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abd-Elmawla, M. A., Ghaiad, H. R., Gad, E. S., Ahmed, K. A., and Abdelmonem, M. (2023). Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by ivermectin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 24 (8), 723–733. doi:10.1631/jzus.B2200385
Aburto, M., Pérez-Izquierdo, J., Agirre, U., Barredo, I., Echevarria-Uraga, J. J., Armendariz, K., et al. (2020). Complications and hospital admission in the following 90 days after lung cryobiopsy performed in interstitial lung disease. Respir. Med. 165, 105934. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105934
Azambuja, E., Fleck, J. F., Batista, R. G., and Menna Barreto, S. S. (2005). Bleomycin lung toxicity: who are the patients with increased risk? Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 18 (5), 363–366. doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2005.01.007
Baumgartner, K. B., Samet, J. M., Coultas, D., Stidley, C. A., Hunt, W. C., Colby, T. V., et al. (2000). Occupational and environmental risk factors for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a multicenter case-control study. Collaborating centers. Am. J. Epidemiol. 152 (4), 307–315. doi:10.1093/aje/152.4.307
Blum, R. H., Carter, S. K., and Agre, K. (1973). A clinical review of bleomycin--a new antineoplastic agent. Cancer 31 (4), 903–914. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(197304)31:4<903::aid-cncr2820310422>3.0.co;2-n
Bonatti, M., Pitozzi, V., Caruso, P., Pontis, S., Pittelli, M. G., Frati, C., et al. (2023). Time-course transcriptome analysis of a double challenge bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis rat model uncovers ECM homoeostasis-related translationally relevant genes. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 10 (1), e001476. doi:10.1136/bmjresp-2022-001476
Brower, M., Grace, M., Kotz, C. M., and Koya, V. (2015). Comparative analysis of growth characteristics of sprague dawley rats obtained from different sources. Lab. Anim. Res. 31 (4), 166–173. doi:10.5625/lar.2015.31.4.166
Butranova, O. I., Terekhina, E. N., Zyryanov, S. K., Gildeeva, G. N., Abramova, A. A., Kustov, Y. O., et al. (2024). Drug-induced pulmonary fibrosis: national database analysis. Biomedicines 12 (12), 2650. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12122650
Chen, G., Li, J., Liu, H., Zhou, H., Liu, M., Liang, D., et al. (2023). Cepharanthine ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway, fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition and inflammation. Molecules 28 (2), 753. doi:10.3390/molecules28020753
Chen, H., Liu, C., Zhan, Y., Wang, Y., Hu, Q., and Zeng, Z. (2024). Alpinetin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by repressing fibroblast differentiation and proliferation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 171, 116101. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116101
Cheson, B. D., and Vita, De (2001). “Pharmacology of cancer chemotherapy: miscellaneous chemotherapeutic agents,” in Cancer principles and practice of oncology. Editors S. Hellmann, and A. S. Rosenberg (Lippincott Willians&Wilkins;), 452–459.
Chu, K. A., Wang, S. Y., Yeh, C. C., Fu, T. W., Fu, Y. Y., Ko, T. L., et al. (2019). Reversal of bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis by a xenograft of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly. Theranostics 9 (22), 6646–6664. doi:10.7150/thno.33741
Chua, F., Dunsmore, S. E., Clingen, P. H., Mutsaers, S. E., Shapiro, S. D., Segal, A. W., et al. (2007). Mice lacking neutrophil elastase are resistant to bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 170 (1), 65–74. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.060352
Collis, C. H. (1980). Lung damage from cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 4 (1), 17–27. doi:10.1007/BF00255453
Comes, A., Wong, A. W., Fisher, J. H., Morisset, J., Johannson, K. A., Farrand, E., et al. (2022). Association of BMI and change in weight with mortality in patients with fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Chest 161 (5), 1320–1329. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.11.008
Conti, S., Harari, S., Caminati, A., Zanobetti, A., Schwartz, J. D., Bertazzi, P. A., et al. (2018). The association between air pollution and the incidence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in northern Italy. Eur. Respir. J. 51, 1700397. doi:10.1183/13993003.00397-2017
Cooper, K. R., and Hong, W. K. (1981). Prospective study of the pulmonary toxicity of continuously infused bleomycin. Cancer Treat. Rep. 65 (5-6), 419–425.
Coward, W. R., Saini, G., and Jenkins, G. (2010). The pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 4 (6), 367–388. doi:10.1177/1753465810379801
Cowley, P. M., Roberts, C. R., and Baker, A. J. (2019). Monitoring the health status of mice with bleomycin-induced lung injury by using body condition scoring. Comp. Med. 69 (2), 95–102. doi:10.30802/AALAS-CM-18-000060
De Lena, M., Guzzon, A., Monfardini, S., and Bonadonna, G. (1972). Clinical, radiologic, and histopathologic studies on pulmonary toxicity induced by treatment with bleomycin (NSC-125066). Cancer Chemother. Rep. 56 (3), 343–356.
Della Latta, V., Cecchettini, A., Del Ry, S., and Morales, M. A. (2015). Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction: from biological mechanisms to counteractions. Pharmacol. Res. 97, 122–130. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2015.04.012
Doherty, M. J., Pearson, M. G., O'Grady, E. A., Pellegrini, V., and Calverley, P. M. (1997). Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis with preserved lung volumes. Thorax 52 (11), 998–1002. doi:10.1136/thx.52.11.998
Flaherty, K. R., and Martinez, F. J. (2000). The role of pulmonary function testing in pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 6 (5), 404–410. doi:10.1097/00063198-200009000-00003
Fujita, K., Ohkubo, H., Nakano, A., Takeda, N., Fukumitsu, K., Fukuda, S., et al. (2022). Decreased peak expiratory flow rate associated with mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a preliminary report. Chron. Respir. Dis. 19, 14799731221114153. doi:10.1177/14799731221114153
Gandhi, S., Tonelli, R., Murray, M., Samarelli, A. V., and Spagnolo, P. (2023). Environmental causes of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (22), 16481. doi:10.3390/ijms242216481
Ge, S., Guo, Z., Xiao, T., Sun, P., Yang, B., and Ying, Y. (2024). Qingfei tongluo mixture attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis through mTOR-Dependent autophagy in rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 8, 5573353. doi:10.1155/2024/5573353
Gregory, A. D., Kliment, C. R., Metz, H. E., Kim, K. H., Kargl, J., Agostini, B. A., et al. (2015). Neutrophil elastase promotes myofibroblast differentiation in lung fibrosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 98 (2), 143–152. doi:10.1189/jlb.3HI1014-493R
Gul, A., Yang, F., Xie, C., Du, W., Mohammadtursun, N., Wang, B., et al. (2023). Pulmonary fibrosis model of mice induced by different administration methods of bleomycin. BMC Pulm. Med. 23 (1), 91. doi:10.1186/s12890-023-02349-z
Haas, C. D., Coltman, C. A., Gottlieb, J. A., Haut, A., Luce, J. K., Talley, R. W., et al. (1976). Phase II evaluation of bleomycin. A southwest oncology group study. Cancer 38 (1), 8–12. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(197607)38:1<8::aid-cncr2820380103>3.0.co;2-4
Hanson, D., Winterbauer, R. H., Kirtland, S. H., and Wu, R. (1995). Changes in pulmonary function test results after 1 year of therapy as predictors of survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 108 (2), 305–310. doi:10.1378/chest.108.2.305
Harris, J. M., Cullinan, P., and McDonald, J. C. (2001). Occupational distribution and geographic clustering of deaths certified to be cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis in England and Wales. Chest 119, 428–433. doi:10.1378/chest.119.2.428
Hay, J., Shahzeidi, S., and Laurent, G. (1991). Mechanisms of bleomycin-induced lung damage. Arch. Toxicol. 65 (2), 81–94. doi:10.1007/BF02034932
Hübner, R. H., Gitter, W., El Mokhtari, N. E., Mathiak, M., Both, M., Bolte, H., et al. (2008). Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples. Biotechniques 44 (4), 507–517. doi:10.2144/000112729
Hung, C. F., Wilson, C. L., Chow, Y. H., Liles, W. C., Gharib, S. A., Altemeier, W. A., et al. (2022). Effect of lung pericyte-like cell ablation on the bleomycin model of injury and repair. Am. J. physiology. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiology 322 (4), L607–L616. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00392.2021
Hutchinson, J. P., Fogarty, A. W., McKeever, T. M., and Hubbard, R. B. (2016). In-Hospital mortality after surgical lung biopsy for interstitial lung disease in the United States. 2000 to 2011. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 193 (10), 1161–1167. doi:10.1164/rccm.201508-1632OC
Inomata, M., Kamio, K., Azuma, A., Matsuda, K., Kokuho, N., Miura, Y., et al. (2014). Pirfenidone inhibits fibrocyte accumulation in the lungs in bleomycin-induced murine pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 15 (1), 16. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-15-16
Iwai, K., Mori, T., Yamada, N., Yamaguchi, M., and Hosoda, Y. (1994). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Epidemiologic approaches to occupational exposure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 150, 670–675. doi:10.1164/AJRCCM.150.3.8087336
Johannson, K. A., Vittinghoff, E., Lee, K., Balmes, J. R., Ji, W., Kaplan, G. G., et al. (2014). Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis associated with air pollution exposure. Eur. Respir. J. 43, 1124–1131. doi:10.1183/09031936.00122213
Ju, N., Hayashi, H., Shimamura, M., Baba, S., Yoshida, S., Morishita, R., et al. (2022). Prevention of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by a RANKL peptide in mice. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 12474. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-16843-7
Kadam, A. H., and Schnitzer, J. E. (2024a2024a). Insights into disease progression of translational preclinical rat model of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis through endpoint analysis. Cells 13 (6), 515. doi:10.3390/cells13060515
Kadam, A. H., and Schnitzer, J. E. (2024b2024b). Highly calibrated relationship between bleomycin concentrations and facets of the active phase fibrosis in classical mouse bleomycin model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (22), 12300. doi:10.3390/ijms252212300
Kärkkäinen, M., Kettunen, H. P., Nurmi, H., Selander, T., Purokivi, M., and Kaarteenaho, R. (2017). Effect of smoking and comorbidities on survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 18, 160–10. doi:10.1186/s12931-017-0642-6
Kehrer, J. P., and Margolin, S. B. (1997). Pirfenidone diminishes cyclophosphamide-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 90 (2-3), 125–132. doi:10.1016/s0378-4274(96)03845-3
Kim, S. N., Lee, J., Yang, H. S., Cho, J. W., Kwon, S., Kim, Y. B., et al. (2010). Dose-response effects of bleomycin on inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Toxicol. Res. 26 (3), 217–222. doi:10.5487/TR.2010.26.3.217
Kitamura, H., Ichinose, S., Hosoya, T., Ando, T., Ikushima, S., Oritsu, M., et al. (2007). Inhalation of inorganic particles as a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-elemental microanalysis of pulmonary lymph nodes obtained at autopsy cases. Pathol. Res. Pract. 203, 575–585. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2007.04.008
Koo, J.-W., Myong, J.-P., Yoon, H.-K., Rhee, C. K., Kim, Y., Kim, J. S., et al. (2017). Occupational exposure and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a multicentre case-control study in Korea. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 21, 107–112. doi:10.5588/ijtld.16.0167
Krakoff, I. H., Cvitkovic, E., Currie, V., Yeh, S., and LaMonte, C. (1977). Clinical pharmacologic and therapeutic studies of bleomycin given by continuous infusion. Cancer 40 (5), 2027–2037. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(197711)40:5<2027::aid-cncr2820400506>3.0.co;2-a
Kreuter, M., Picker, N., Schwarzkopf, L., Baumann, S., Cerani, A., Postema, R., et al. (2022). Epidemiology, healthcare utilization, and related costs among patients with IPF: results from a German claims database analysis. Respir. Res. 23, 62. doi:10.1186/s12931-022-01976-0
Kulkarni, T., Yuan, K., Tran-Nguyen, T. K., Kim, Y. I., de Andrade, J. A., Luckhardt, T., et al. (2019). Decrements of body mass index are associated with poor outcomes of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. PLoS One 14 (10), e0221905. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0221905
Lederer, D. J., and Martinez, F. J. (2018). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 378 (19), 1811–1823. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1705751
Lentz, R. J., Argento, A. C., Colby, T. V., Rickman, O. B., and Maldonado, F. (2017). Transbronchial cryobiopsy for diffuse parenchymal lung disease: a state-of-the-art review of procedural techniques, current evidence, and future challenges. J. Thorac. Dis. 9 (7), 2186–2203. doi:10.21037/jtd.2017.06.96
Ley, B., Collard, H. R., and King, T. E. (2011). Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 183 (4), 431–440. doi:10.1164/rccm.201006-0894CI
Li, H., Wang, Y. G., Chen, T. F., Gao, Y. H., Song, L., Yang, Y. F., et al. (2024). Panax notoginseng saponin alleviates pulmonary fibrosis in rats by modulating the renin-angiotensin system. J. Ethnopharmacol. 318 (Pt B), 116979. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116979
Liang, Y., Yan, Y., Liu, N., Wang, J., and Fang, C. (2024). Shengxian decoction improves lung function in rats with bleomycin-induced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through the inhibition of PANoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 329, 118153. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118153
Mansouri, N., Willis, G. R., Fernandez-Gonzalez, A., Reis, M., Nassiri, S., Mitsialis, S. A., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes prevent and revert experimental pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of monocyte phenotypes. JCI Insight 4 (21), e128060. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.128060
Miyake, Y., Sasaki, S., Yokoyama, T., Chida, K., Azuma, A., Suda, T., et al. (2005). Occupational and environmental factors and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Japan. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 49, 259–265. doi:10.1093/annhyg/meh090
Nakatsuka, Y., Handa, T., Kokosi, M., Tanizawa, K., Puglisi, S., Jacob, J., et al. (2018). The clinical significance of body weight loss in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Respiration 96 (4), 338–347. doi:10.1159/000490355
Obayashi, Y., Yamadori, I., Fujita, J., Yoshinouchi, T., Ueda, N., and Takahara, J. (1997). The role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 112 (5), 1338–1343. doi:10.1378/chest.112.5.1338
Polverino, E., Rosales-Mayor, E., Dale, G. E., Dembowsky, K., and Torres, A. (2017). The role of neutrophil elastase inhibitors in lung diseases. Chest 152 (2), 249–262. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2017.03.056
Prêle, C. M., Miles, T., Pearce, D. R., O'Donoghue, R. J., Grainge, C., Barrett, L., et al. (2022). Plasma cell but not CD20-mediated B-cell depletion protects from bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 60 (5), 2101469. doi:10.1183/13993003.01469-2021
Principi, L., Ferrini, E., Ciccimarra, R., Pagani, L., Chinello, C., Previtali, P., et al. (2023). Proteomic fingerprint of lung fibrosis progression and response to therapy in bleomycin-induced mouse model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (5), 4410. doi:10.3390/ijms24054410
Pugashetti, J. V., and Oldham, J. M. (2022). Weighing on our minds: Baseline BMI and weight loss as predictors of interstitial lung disease outcome. Chest 161 (5), 1134–1135. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.11.013
Pugashetti, J., Graham, J., Boctor, N., Mendez, C., Foster, E., Juarez, M., et al. (2018). Weight loss as a predictor of mortality in patients with interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 52 (3), 1801289. doi:10.1183/13993003.01289-2018
Qu, S. J., Zhao, L., Song, Z. Z., Shen, W. P., Ju, P., and Li, Y. M. (2020). Expression and significance of miR-223 in rats with pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24 (7), 3951–3958. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202004_20864
Raghu, G., Remy-Jardin, M., Richeldi, L., Thomson, C. C., Inoue, Y., Johkoh, T., et al. (2022). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (an update) and progressive pulmonary fibrosis in adults: an official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 205 (9), e18–e47. doi:10.1164/rccm.202202-0399ST
Rajan, S. K., Cottin, V., Dhar, R., Danoff, S., Flaherty, K. R., Brown, K. K., et al. (2023). Progressive pulmonary fibrosis: an expert group consensus statement. Eur. Respir. J. 61 (3), 2103187. doi:10.1183/13993003.03187-2021
Richeldi, L., Kolb, M., Jouneau, S., Wuyts, W. A., Schinzel, B., Stowasser, S., et al. (2020). Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in patients with advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 20, 3. doi:10.1186/s12890-019-1030-4
Santos-Ribeiro, D., Lecocq, M., de Beukelaer, M., Verleden, S., Bouzin, C., Ambroise, J., et al. (2023). Disruption of GCN2 pathway aggravates vascular and parenchymal remodeling during pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 68 (3), 326–338. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2021-0541OC
Schelegle, E. S., Mansoor, J. K., and Giri, S. (1997). Pirfenidone attenuates bleomycin-induced changes in pulmonary functions in hamsters. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 216 (3), 392–397. doi:10.3181/00379727-216-44187
Schols, A. M. (2002). Pulmonary cachexia. Int. J. Cardiol. 85 (1), 101–110. doi:10.1016/s0167-5273(02)00238-3
Sgalla, G., Iovene, B., Calvello, M., Ori, M., Varone, F., and Richeldi, L. (2018). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis and management. Respir. Res. 19 (1), 32. doi:10.1186/s12931-018-0730-2
Takemasa, A., Ishii, Y., and Fukuda, T. (2012). A neutrophil elastase inhibitor prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Eur. Respir. J. 40 (6), 1475–1482. doi:10.1183/09031936.00127011
Taooka, Y., Maeda, A., Hiyama, K., Ishioka, S., and Yamakido, M. (1997). Effects of neutrophil elastase inhibitor on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 156 (1), 260–265. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.156.1.9612077
Taskar, V. S., and Coultas, D. B. (2006). Is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis an environmental disease? Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 3, 293–298. doi:10.1513/pats.200512-131TK
Travis, W. D., Costabel, U., Hansell, D. M., King, T. E., Lynch, D. A., Nicholson, A. G., et al. (2013). An official American thoracic society/european respiratory society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 188, 733–748. doi:10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST
Troy, L. K., Grainge, C., Corte, T. J., Williamson, J. P., Vallely, M. P., Cooper, W. A., et al. (2020). Diagnostic accuracy of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy for interstitial lung disease diagnosis (COLDICE): a prospective, comparative study. Lancet Respir. Med. 8, 171–181. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30342-X
Tukhovskaya, E. A., Palikova, Y. A., Severyukhina, M. S., Ismailova, A. M., Palikov, V. A., Slashcheva, G. A., et al. (2024). Comparison of the results of modeling pulmonary fibrosis in sprague dawley rats by intratracheal administration of bleomycin in the form of sulfate and chloride at a dose of 3 mg/kg. Pharm. (Basel) 17 (10), 1360. doi:10.3390/ph17101360
U.S. Food and Drug Administrasion (2014a). Drug Approval Package. Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2014/205832Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
U.S. Food and Drug Administrasion (2014b). Drug Approval Package. Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2014/022535Orig1s000TOC.cfm
von Haehling, S., and Anker, S. D. (2014). Prevalence, incidence and clinical impact of cachexia: facts and numbers-update 2014. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 5 (4), 261–263. doi:10.1007/s13539-014-0164-8
Ware, L. B., and Matthay, M. A. (2000). The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 342, 1334–1349. doi:10.1056/NEJM200005043421806
Weissman, I., Lynch, I. I. I. J., and Martinez, F. (2003). “Role of physiologic assessment in advanced lung disease,” in Management of non-neoplastic advanced lung disease. Editor J. Maurer (New York: Marcel Dekker).
Willson, J. K. (1978). Pulmonary toxicity of antineoplastic drugs. Cancer Treat. Rep. 62 (12), 2003–2008.
Wollin, L., Maillet, I., Quesniaux, V., Holweg, A., and Ryffel, B. (2014). Antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor nintedanib in experimental models of lung fibrosis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 349 (2), 209–220. doi:10.1124/jpet.113.208223
Xie, M., Yang, L., Cheng, J., Qu, H., Gu, Y., Ding, C., et al. (2023). Gracillin relieves pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the STAT3 axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 316, 116704. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116704
Xu, J., Li, W., Xu, S., Gao, W., and Yu, Z. (2019). Effect of dermatan sulphate on a C57-mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 47 (6), 2655–2665. doi:10.1177/0300060519842048
Keywords: pulmonary fibrosis, rats, bleomycin, general health status, dose-dependence, lung, respiratory function, histological assessment
Citation: Tukhovskaya EA, Palikova YA, Severyukhina MS, Ismailova AM, Palikov V, Slashcheva GA, Borozdina NA, Mikhaylov ES, Kravchenko IN, Kazakov V, Kazakova EN, Kalabina EA, Rasskazova EA, Rykov VA, Patsap O, Globenko AA, Jain EA, Kolosov A and Murashev AN (2025) Different degrees of expression of pulmonary fibrosis signs with intratracheal administration of bleomycin at different doses in male SD rats (a study aimed at helping to select the optimal bleomycin dose for modeling pulmonary fibrosis). Front. Pharmacol. 16:1702991. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1702991
Received: 10 September 2025; Accepted: 04 November 2025;
Published: 28 November 2025.
Edited by:
Somasundaram Arumugam, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, IndiaReviewed by:
Sidharth Mehan, Indo-Soviet Friendship College of Pharmacy, IndiaYuko Ishida, Wakayama Medical University, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Tukhovskaya, Palikova, Severyukhina, Ismailova, Palikov, Slashcheva, Borozdina, Mikhaylov, Kravchenko, Kazakov, Kazakova, Kalabina, Rasskazova, Rykov, Patsap, Globenko, Jain, Kolosov and Murashev. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Elena A. Tukhovskaya, dHVraG92c2theWFAYmliY2gucnU=
 Elena A. Tukhovskaya
Elena A. Tukhovskaya Yulia A. Palikova1
Yulia A. Palikova1 Victor Palikov
Victor Palikov Natalya A. Borozdina
Natalya A. Borozdina Vitaly Kazakov
Vitaly Kazakov Vladimir A. Rykov
Vladimir A. Rykov Olga Patsap
Olga Patsap Andrey Kolosov
Andrey Kolosov Arkady N. Murashev
Arkady N. Murashev