Abstract
Bacterial persisters are growth-arrested cells with low metabolic activities, but have no genetic mutations compared to their parental cells. The dormant nature of persister cells enables them to tolerate high doses of conventional antibiotics and restart growth after the antibiotic is withdrawn, posing an important challenge to infection control. To promote more research in this important area, we present a concise review of current persister control strategies and discuss future opportunities.
What are persister cells and why are they important?
Persister cells are growth-arrested phenotypic variants found in essentially all bacterial populations (Balaban et al., 2004; Lewis, 2010). Persisters can form both spontaneously (Balaban et al., 2019) and triggered by stressors such as pH change (Leimer et al., 2016), nutrient limitation (Nguyen et al., 2011), and antibiotic attack (Dewachter et al., 2019).
Conventional antibiotics were discovered based on bacterial growth inhibition. These molecules target and corrupt growth associated cellular processes, such as cell wall synthesis, DNA replication, and protein synthesis (Halawa et al., 2024). These processes require energy and are rather inactive in dormant persister cells (Germain et al., 2013; Amarh and Arthur, 2019); thus, conventional antibiotics commonly fail to eradicate persisters (Salcedo-Sora and Kell, 2020). Persister cells play an important role in recalcitrant diseases such as chronic lung infections of cystic fibrosis patients (Mulcahy et al., 2010), medical device-associated infections (Mishra et al., 2024), and Lyme disease (Sharma et al., 2015). Persisters also provide a reservoir of cells for the development of antibiotic-resistant strains over time (Santi et al., 2021). Thus, finding effective treatment for persister cells is a necessity for disease control.
In this mini-review, we briefly summarize the current strategies for persister control and discuss our view for future development. As a mini review, it is not a comprehensive overview with in-depth coverage of all related topics, but rather focuses on the principles and future perspectives. We are in debt to the scholars whose work is not cited here due to the limit of its scope.
What strategies have been developed for killing persister cells?
Although persister cells are dormant and tolerant to most conventional antibiotics, persister cells still need to retain cell integrity and a capability to return to normal cells upon favorable changes in the environment. Thus, some targets of antimicrobials are retained in persister cells and new strategies can be developed leveraging unique characteristics of these metabolically dormant cells (Figure 1). The major strategies of persister control are summarized in Table 1 and discussed in the sections below.
FIGURE 1
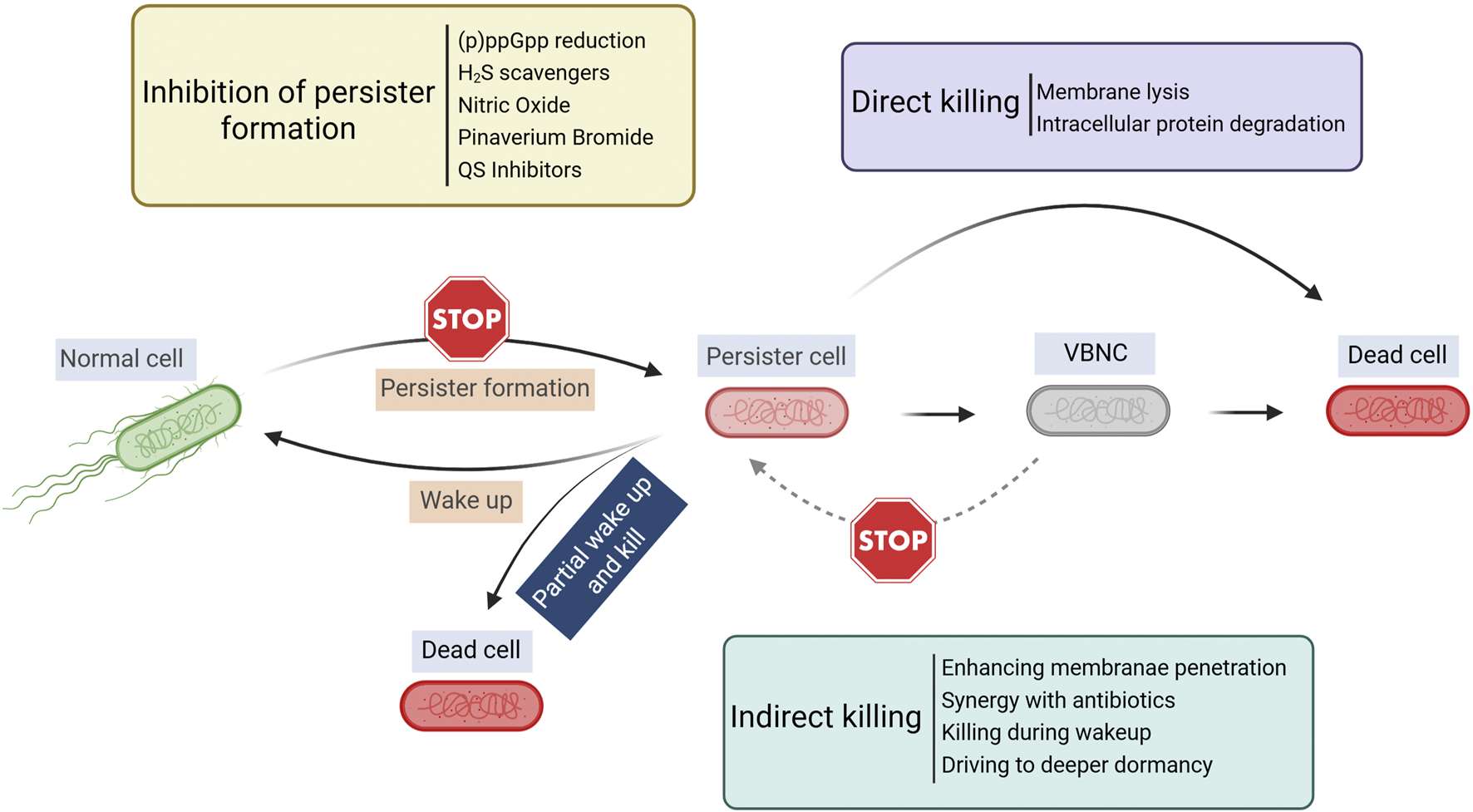
Overview of persister control strategies. Created in BioRender. Lab R. (2025) https://BioRender.com/krlwzbz.
TABLE 1
| Strategy | Function | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct killing of persister cells | Causes cell lysis by disrupting bacterial membranes or degrading proteins | Independent of bacterial growth state or metabolic activity | Off-target toxicity needs to be considered |
| Inhibiting persister formation | Alters bacterial metabolism, or inhibits QS | Bacteria-specific targets; reduces persister formation and antibiotic tolerance | May not be effective against already-formed persisters |
| Synergistic killing with antibiotics | Disrupts membrane integrity, enhances antibiotic uptake, alters metabolic state of persisters, or leverages other controls, e.g., electrochemical factors | Can eradicate both persister and actively growing bacterial cells | Needs to be effective across different bacterial species |
| Exploiting persister dormancy | Binds to intracellular targets to kill during wake-up or drives to deeper dormancy | Specifically target dormant cells | Limited research; mechanisms not fully understood |
Major persister control strategies, advantages, and limitations (see specific sections above for references).
Direct killing
Targeting cell membrane
Direct killing strategies attack growth-independent targets such as the cell membrane to cause cell lysis. Membrane damage can also generate lethal level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), contributing to persister killing (Gray et al., 2024). Multiple agents have shown activities against persister cells or dormant cells in general by directly damaging cell membranes. Some examples include 2D-24 (Bahar et al., 2015), AM-0016 (Mukherjee et al., 2016), XF-70 and XF-73 (Ooi et al., 2010; Board-Davies et al., 2023), SA-558 (Iu et al., 2023), thymol triphenylphosphine conjugates (TPP-Thy3) (Tang et al., 2024), and tea tree essential components (Nguyen et al., 2023). For example, SA-558 is a synthetic cation transporter. It disrupts bacterial homeostasis, leading to autolysis (Iu et al., 2023). Both XF-70 and XF-73 (Ooi et al., 2010; Board-Davies et al., 2023) are effective in killing non-dividing and slow-growing cells of Staphylococcus aureus by disrupting cell membranes. In addition, XF-73 generates ROS upon light activation, which oxidizes essential cellular components as a mechanism of its cidal effects (Maisch et al., 2005).
Additionally, synthesized cephalosporin derivatives (Chen et al., 2025) and red blood cell membrane-coated nanoparticles (Hb-Naf@RBCM NPs), which incorporate naftifine and oxygenated hemoglobin, effectively kill S. aureus persisters including those in biofilms (Zhu J. et al., 2024). Organo-soluble antimicrobial polymer nanocomposite (Patra et al., 2024) and semapimod (an anti-inflammatory drug) (Zheng et al., 2024) also exhibit anti-persister effects. Furthermore, cationic silver nanoparticle shelled nanodroplets (C-AgND) interact with the negatively charged components of the extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) layer, enabling effective killing of S. aureus persisters within biofilms (Bose and Das, 2025).
Other targets for direct killing
Pyrazinamide is a prodrug against Mycobacterium tuberculosis persisters. Its active form pyrazinoic acid disrupts membrane energetics, and binds to PanD (essential for coenzyme A biosynthesis) to trigger degradation of PanD by ClpC1-ClpP (Gopal et al., 2020; Conlon et al., 2013; Niu et al., 2024)Another example is ADEP4, a semi-synthetic acyldepsipeptide that binds to the ClpP protease and causes conformational changes, enabling ATP-independent protein degradation. This results in breakdown of over 400 intracellular proteins, including metabolic enzymes essential for persister wake-up. Their destruction renders the cells unable to recover and resume growth (Conlon et al., 2013; Niu et al., 2024).
Direct lysis of persisters is an effective approach as it does not require metabolic activities of the target cell. However, if an agent also affects mammalian membranes, it will limit its therapeutic potential due to off-target toxicity (Kaldalu et al., 2020). The field will benefit from more research on persister physiology and discovery of new persister-specific targets.
Indirect killing
Most challenges posed by persister cells stem from their dormant nature. Conceptually, persisters can be eradicated either by preventing cells from entering dormancy or by inducing them to exit the persister state. Once reactivated, these cells become more susceptible to conventional antimicrobials. Alternatively, if a cell enters a deeper dormancy from which it cannot resuscitate, it effectively results in cell death. Exploiting shifts in dormancy depth may also create synergies with other treatments such as antibiotics.
Inhibit persister formation
Although the mechanism of persister formation is still not fully understood, multiple strategies have been shown to reduce persister formation (Balaban et al., 2019). For example, the pheromone cCf10 inhibits Enterococcus faecalis persister formation by reducing (p)ppGpp alarmone accumulation and maintaining its metabolically active state (Zhu L. et al., 2024). Another example is potentiation of persister killing using inhibitors of H2S biogenesis. protects bacteria under stress conditions by scavenging free radicals and increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes (Pal et al., 2018). Bacterial cystathionine g-lyase (bCSE) is the primary generator of H2S in S. aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. CSE inhibitors were found to reduce biofilm formation and the number of persister cells, and potentiate antibiotics against both bacteria (Shatalin et al., 2021). Additionally, synthetic scavengers were found to sensitize S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, E. coli, and MRSA persisters to gentamicin (Sun et al., 2024).
Also effective in preventing persister formation are nitric oxide (NO) that act as a metabolic disruptor (Orman and Brynildsen, 2016), and pinaverium bromide (PB) that disrupts PMF and generates ROS (Mao et al., 2023). In addition, some medium-chain saturated fatty acids have been shown to reduce persister formation, e.g., undecanoic acid, lauric acid, and N-tridecanoic acid (Jin et al., 2021).
While persister formation is controlled at the individual cell level, signaling between bacterial cells via quorum sensing (QS) has also been shown to affect persistence. QS is a bacterial cell-cell communication system that regulates multicellular behaviors in response to increase in cell density (Papenfort and Bassler, 2016). Möker et al. (2010) showed that the QS signals phenazine pyocyanin and the N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone increase persister formation in P. aeruginosa by inducing oxidative stress and metabolic changes. Compounds that share a benzamide-benzimidazole backbone were found to bind to the QS regulator MvfR and inhibit MvfR regulon in P. aeruginosa, reducing its persister formation without affecting growth (Starkey et al., 2014; Maura and Rahme, 2017). Similarly, brominated furanones that are QS inhibitors reduce persister formation in P. aeruginosa (Pan et al., 2012).
Synergy between antibiotics and other factors
Increasing membrane permeability has been shown to sensitize persister cells to antibiotics. For example, MB6-a potent methylazanediyl bisacetamide derivative-and two synthetic retinoids, CD437 and CD1530, bind to and embed in the MRSA lipid bilayer, thereby disrupting membrane integrity and increasing antibiotic uptake. Combined treatment of these compounds with gentamicin showed strong anti-persister activities (Kim et al., 2018; Heo et al., 2024). Similarly, Kim et al. (2019) reported MRSA persister cell killing by cotreatment with gentamicin and membrane active compounds bithionol and nTZDpa. Also functioning through membrane disruption are IMT-P8, a cell-penetrating peptide (Singh and Nandanwar, 2024), polymyxin B nonapeptide (PMBN) (Kim et al., 2024), and the polymyxin B derivative SPR741 (She et al., 2022). Moreover, Schmidt et al. (2014) engineered the aminoglycoside antibiotic tobramycin by adding 12 amino acids to convert it to the transporter sequence. The resultant molecule (Pentobra) exhibits strong activities in persister penetration and killing. In addition, gold nanocluster adjuvant, when combined with ofloxacin, could effectively kill persister cells (Cao et al., 2022). This was attributed to the ability of AuNC@CPP to hyperpolarize the cell membrane and disrupt the proton gradient (Cao et al., 2022). Dihydropyrrolidone-thiadiazole disrupts biofilm integrity and cell wall homeostasis by binding to cardiolipin, leading to cell wall disruption. Consistently, it showed synergistic effects with daptomycin in persister killing (Xiong et al., 2024).
Another strategy is to combine multiple antibiotics to eradicate persisters. Colistin paired with either aminoglycosides or ciprofloxacin is effective against persisters of E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and A. baumannii. Colistin is able to disrupt the outer membrane and then facilitate penetration of other antibiotics and increase their lethality (Bialvaei and Samadi Kafil, 2015; Chung and Ko, 2019).
Besides membrane disruption, antimicrobials can gain more penetration by manipulating membrane channels. An example is felodipine, an FDA approved dihydropyridine class of calcium channel blocker, which has low cytotoxicity to mammalian cells. When combined with gentamicin, the treatment dissipates MRSA membrane potential and increases cell membrane permeability. Additionally, felodipine reduces the TCA cycle and expression of aminoglycoside resistance proteins such as AacA-AphD. These led to killing MRSA persisters and biofilm cells in a mouse model (Zhang et al., 2022).
Disruption of proton motive force (PMF) also hinders efflux pump activities and increases the accumulation of certain antibiotics (Dewachter et al., 2019). One example is econazole, an FDA approved drug that dissipates the PMF and kills persister cells when used in combination with ampicillin, gentamycin, or ciprofloxacin. Cotreatment with econazole and ceftazidime was also found to kill tolerant bacterial populations in vivo (Wang et al., 2022). Additionally, exogenous adenosine and/or guanosine were found to increase accumulation of tetracycline in Vibrio splendidus persister cells, and cause cell death during the wake-up phase (Li et al., 2023).
Contrary to the approaches to reduce membrane integrity and PMF, increase in PMF and ATP could also reduce bacterial tolerance to antibiotics by increasing membrane energetics. Higher PMF, in addition to promoting the production of ROS, powers the uptake of antibiotics, especially the aminoglycosides, increasing their lethality (Lee et al., 2023). Compounds such as fumarate (Allison et al., 2011; Koeva et al., 2017), n-Butanol (Lv et al., 2022a), small molecule SA-558 (Iu et al., 2023), L-lysine (Deng et al., 2020) have anti-persister effects through increased antibiotic uptake. It is important to note that for the approaches that increase bacterial energetics, caution should be taken so that bacteria do not resume full growth and overpower the antimicrobials and the host immune system.
Other mechanisms of synergy in persister killing
Besides chemical agents, hypoionic shock physically disrupts the cytoplasmic membrane, leading to activation of mechanosensitive channels. If effective antibiotics are applied during this process, it can result in substantial killing of persister cells (Lv et al., 2022b). In addition, low level electric currents have been found to increase persister killing by antibiotics. Electric currents can depolarize the cell membrane and facilitate passive diffusion of ions and antibiotics to persister cells (Niepa et al., 2012; 2016; 2017; Wang et al., 2020); Non-transducing phages have also been found to work in synergy with ciprofloxacin and ampicillin against cultures of uropathogenic E. coli (Vera-Mansilla et al., 2023).
Leveraging the dormant nature of persister cells
Persisters are metabolically dormant and thus have reduced efflux activities. We reported recently that the agents capable of penetrating persister cells by passive diffusion can kill persister during wake up if the intracellular targets are available and if target binding is strong (Roy et al., 2021). These criteria can help guide the rational search for persister control agents. One example that fits these criteria is eravacycline, which is an amphiphilic antibiotic from the tetracycline family. It can enter persister cells through passive diffusion. Interestingly, it is more effective against persister cells than normal cells. This was attributed to the reduction of efflux in persister cells (Roy et al., 2021). Using eravacycline as a lead, we recently searched a small antimicrobial compound library with a chemoinformatic model. It is encouraging that 5 out of 11 candidate compounds identified through clustering are effective against persister cells (Roy et al., 2025). These findings provide helpful insights for finding new agents.
Drive persister to deeper dormancy states
Previous research suggested that persisters and the viable but non-culturable (VBNC) state are not distinct, but rather stages along a dormancy spectrum (Ayrapetyan et al., 2018). A key driver of the transition from dormant persistence to difficult-to-resuscitate VBNC is protein aggregation during nutrient starvation (Dewachter et al., 2021). Thus, persister control may be achieved by driving cells to a deeper dormancy state like VBNC (Zhou et al., 2023). With more in-depth studies carried out in future, this could have major implications for antibiotic treatment strategies, chronic infection management and resuscitation protocols in the field. For example, it was found that lactate dehydrogenase (involved in pyruvate metabolism) promotes resuscitation of E. coli VBNCs, and cells with enhanced oxidative stress defense were more likely to resuscitate (Wagley et al., 2021). Finding new strategies/control agents that can stop VBNCs from resuscitation and/or going to deeper dormancy will also kill persisters. This is still a largely unexplored area.
How to find better persister control agents?
Since persister cells are growth arrested, the search for persister killing agents should be focused on targets independent of metabolic activities. This requires new knowledge and strategies to identify these targets and new leads.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are quickly transforming drug discovery and have been used in searching for better persister control agents (Wan et al., 2024; Zheng et al., 2024). AI, particularly deep learning models, enables researchers to efficiently screen millions of chemical compounds for antibacterial activities in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods. For example, large chemical libraries with more than 107 million molecules have been screened, leading to the discovery of new antibiotics including halicin (Stokes et al., 2020). In addition, deep learning-powered virtual screens were successfully applied to search for new agents against metabolically dormant bacteria, e.g., semapimod (Zheng et al., 2024). There is no doubt that the field will see more applications of AI models to accelerate both drug screening and the development of new models.
To better combat persistent infections, there are also needs for changes in drug discovery strategies. For persister control, this requires a shift from conventional MIC based screening to more specific targets in dormant cells. It is important to identify predictors for persister penetration, target binding, and killing activities based on new mechanisms. One method to gaining significant knowledge is the utilization of microfluidic platforms to isolate and manipulate individual bacterial cells in controlled environments (Luo et al., 2022). Integrating AI can automate imaging and predict cell fate, streamlining key steps in drug discovery.
To identify new targets in persister cells, we must obtain an in-depth understanding of persister formation mechanism and the true physiological stage of persister cells. There have been significant debates about the molecular mechanism of persister formation, which is partially attributed to the lack of robust methods to obtain persister cells in large quantities and the capability to separate the effects of persister formation itself from the effects of inducers applied to trigger persister formation. Heterogeneity in persister populations and the stochastic nature of formation is another challenge, which can possibly be solved by new persister isolation protocols and new technologies such as single cell RNAseq (Yan et al., 2024). To better eradicate persister cells, the drug of choice needs to bind the target strongly to overcome dormancy related slow killing kinetics. This can be achieved by modifying the drug molecule for stronger targeting including covalent binding. However, because these molecules are more active, the activity of the lead and possibility of undesired side effects must be carefully considered.
The field also need to address challenges in clinical translation of persister-targeting strategies. A central hurdle revolves around drug delivery of candidate compounds to niches where persisters reside, typically within biofilms (Wood et al., 2013), host tissues, or intracellularly within immune cells (Niu et al., 2024). Off-target toxicity is also a concern if the target is not bacteria specific and/or a high dosage of treatment agent is needed. Regulatory considerations may introduce further complexities such as fitting persister therapies within existing approved frameworks or introducing new regulations to fit the relapse and chronic nature of persistent infections (Defraine et al., 2018). Addressing these barriers is essential to moving persister therapies from the bench into clinical practice.
By exploiting the predictive power and speed of artificial intelligence and new biotech tools, scientists are now able to discover anti-persister drugs more efficiently. This marks a significant step forward in the global effort to develop the next-generation therapeutics for persistent infections.
Statements
Author contributions
MH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YDK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. DR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The research in Ren lab is supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (1R01EB030621, 1R21AI185651).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Allison K. R. Brynildsen M. P. Collins J. J. (2011). Metabolite-enabled eradication of bacterial persisters by aminoglycosides. Nature473, 216–220. 10.1038/nature10069
2
Amarh V. Arthur P. K. (2019). DNA double-strand break formation and repair as targets for novel antibiotic combination chemotherapy. Future Sci. OA5. 10.2144/fsoa-2019-0034
3
Ayrapetyan M. Williams T. Oliver J. D. (2018). Relationship between the viable but nonculturable state and antibiotic persister cells. J. Bacteriol.200, e00249-18. 10.1128/jb.00249-18
4
Bahar A. A. Liu Z. Totsingan F. Buitrago C. Kallenbach N. Ren D. (2015). Synthetic dendrimeric peptide active against biofilm and persister cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.99, 8125–8135. 10.1007/s00253-015-6645-7
5
Balaban N. Q. Merrin J. Chait R. Kowalik L. Leibler S. (2004). Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science305, 1622–1625. 10.1126/science.1099390
6
Balaban N. Q. Helaine S. Lewis K. Ackermann M. Aldridge B. Andersson D. I. et al (2019). Definitions and guidelines for research on antibiotic persistence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.17, 441–448. 10.1038/s41579-019-0196-3
7
Bialvaei A. Z. Samadi Kafil H. (2015). Colistin, mechanisms and prevalence of resistance. Curr. Med. Res. Opin.31, 707–721. 10.1185/03007995.2015.1018989
8
Board-Davies E. L. Rhys-Williams W. Hynes D. Love W. G. Williams D. W. (2023). Antimicrobial effects of XF drugs against Candida albicans and its biofilms. Front. Fungal Biol.4, 1225647. 10.3389/ffunb.2023.1225647
9
Bose S. Das S. K. (2025). Biofilm microenvironment-sensitive anti-virulent and immunomodulatory nano-on-nanodroplets to combat refractory biofilm infection through toxin neutralization and phagocytosis. Adv. Healthc. Mater.14, 2403528. 10.1002/adhm.202403528
10
Cao Z. Chen X. Chen J. Xia A. Bacacao B. Tran J. et al (2022). Gold nanocluster adjuvant enables the eradication of persister cells by antibiotics and abolishes the emergence of resistance. Nanoscale14, 10016–10032. 10.1039/D2NR01003H
11
Chen S. Qu Y. Li R. Ampomah-Wireko M. Kong H. Li D. et al (2025). Exploration of membrane-active cephalosporin derivatives as potent antibacterial agents against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms and persisters. Eur. J. Med. Chem.289, 117484. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117484
12
Chung E. S. Ko K. S. (2019). Eradication of persister cells of Acinetobacter baumannii through combination of colistin and amikacin antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.74, 1277–1283. 10.1093/jac/dkz034
13
Conlon B. Nakayasu E. Fleck L. LaFleur M. Isabella V. Coleman K. et al (2013). Activated ClpP kills persisters and eradicates a chronic biofilm infection. Nature503, 365–370. 10.1038/nature12790
14
Defraine V. Fauvart M. Michiels J. (2018). Fighting bacterial persistence: current and emerging anti-persister strategies and therapeutics. Drug Resist Updat38, 12–26. 10.1016/j.drup.2018.03.002
15
Deng W. Fu T. Zhang Z. Jiang X. Xie J. Sun H. et al (2020). L-lysine potentiates aminoglycosides against Acinetobacter baumannii via regulation of proton motive force and antibiotics uptake. Emerg. Microbes Infect.9, 639–650. 10.1080/22221751.2020.1740611
16
Dewachter L. Fauvart M. Michiels J. (2019). Bacterial heterogeneity and antibiotic survival: understanding and combatting persistence and heteroresistance. Mol. Cell76, 255–267. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.028
17
Dewachter L. Bollen C. Wilmaerts D. Louwagie E. Herpels P. Matthay P. et al (2021). The dynamic transition of persistence toward the viable but nonculturable state during stationary phase is driven by protein aggregation. mBio12, e0070321. 10.1128/mbio.00703-21
18
Germain E. Castro-Roa D. Zenkin N. Gerdes K. (2013). Molecular mechanism of bacterial persistence by HipA. Mol. Cell52, 248–254. 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.045
19
Gopal P. Sarathy J. P. Yee M. Ragunathan P. Shin J. Bhushan S. et al (2020). Pyrazinamide triggers degradation of its target aspartate decarboxylase. Nat. Commun.11, 1661. 10.1038/s41467-020-15516-1
20
Gray D. A. Wang B. Sidarta M. Cornejo F. A. Wijnheijmer J. Rani R. et al (2024). Membrane depolarization kills dormant Bacillus subtilis cells by generating a lethal dose of ROS. Nat. Commun.15, 6877. 10.1038/s41467-024-51347-0
21
Halawa E. M. Fadel M. Al-Rabia M. W. Behairy A. Nouh N. A. Abdo M. et al (2024). Antibiotic action and resistance: updated review of mechanisms, spread, influencing factors, and alternative approaches for combating resistance. Front. Pharmacol.14, 1305294. 10.3389/fphar.2023.1305294
22
Heo H. Y. Zou G. Baek S. Kim J.-S. Mylonakis E. Ausubel F. M. et al (2024). A methylazanediyl bisacetamide derivative sensitizes Staphylococcus aureus persisters to a combination of gentamicin and daptomycin. Adv. Sci.11, 2306112. 10.1002/advs.202306112
23
Iu H.-T.-V. Fong P.-M. Yam H.-C.-B. Gao P. Yan B. Lai P.-M. et al (2023). Identification of a small molecule compound active against antibiotic-tolerant Staphylococcus aureus by boosting ATP synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 6242. 10.3390/ijms24076242
24
Jin X. Zhou J. Richey G. Wang M. Hong S. M. C. Hong S. H. (2021). Undecanoic acid, lauric acid, and N-Tridecanoic acid inhibit Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation, J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.31, 130–136. 10.4014/jmb.2008.08027
25
Kaldalu N. Hauryliuk V. Turnbull K. J. La Mensa A. Putrinš M. Tenson T. (2020). In vitro studies of persister cells. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev.84, e00070-20. 10.1128/mmbr.00070-20
26
Kim W. Zhu W. Hendricks G. L. Van Tyne D. Steele A. D. Keohane C. E. et al (2018). A new class of synthetic retinoid antibiotics effective against bacterial persisters. Nature556, 103–107. 10.1038/nature26157
27
Kim W. Zou G. Hari T. P. A. Wilt I. K. Zhu W. Galle N. et al (2019). A selective membrane-targeting repurposed antibiotic with activity against persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.116, 16529–16534. 10.1073/pnas.1904700116
28
Kim S. J. Jo J. Kim J. Ko K. S. Lee W. (2024). Polymyxin B nonapeptide potentiates the eradication of Gram-negative bacterial persisters. Microbiol. Spectr.12, e0368723–e0368723. 10.1128/spectrum.03687-23
29
Koeva M. Gutu A. D. Hebert W. Wager J. D. Yonker L. M. O’Toole G. A. et al (2017). An antipersister strategy for treatment of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.61, e00987-17. 10.1128/aac.00987-17
30
Lee A. H. Gupta R. Nguyen H. N. Schmitz I. R. Siegele D. A. Lele P. P. (2023). Heterogeneous distribution of proton motive force in nonheritable antibiotic resistance. mBio14, e02384-22. 10.1128/mbio.02384-22
31
Leimer N. Rachmühl C. Palheiros Marques M. Bahlmann A. S. Furrer A. Eichenseher F. et al (2016). Nonstable Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants are induced by low pH and sensitized to antimicrobial therapy by phagolysosomal alkalinization. J. Infect. Dis.213, 305–313. 10.1093/infdis/jiv388
32
Lewis K. (2010). Persister cells. Annu. Rev. Microbiol.64, 357–372. 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134306
33
Li Y. Liang W. Li C. (2023). Exogenous adenosine and/or guanosine enhances tetracycline sensitivity of persister cells. Microbiol. Res.270, 127321. 10.1016/j.micres.2023.127321
34
Luo X. Chen J.-Y. Ataei M. Lee A. (2022). Microfluidic compartmentalization platforms for single cell analysis. Biosensors12, 58. 10.3390/bios12020058
35
Lv B. Bian M. Huang X. Sun F. Gao Y. Wang Y. et al (2022a). n-Butanol potentiates subinhibitory aminoglycosides against bacterial persisters and multidrug-resistant MRSA by rapidly enhancing antibiotic uptake. ACS Infect. Dis.8, 373–386. 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00559
36
Lv B. Zeng Y. Zhang H. Li Z. Xu Z. Wang Y. et al (2022b). Mechanosensitive channels mediate hypoionic shock-induced aminoglycoside potentiation against bacterial persisters by enhancing antibiotic uptake. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.66, e01125-21. 10.1128/aac.01125-21
37
Maisch T. Bosl C. Szeimies R.-M. Lehn N. Abels C. (2005). Photodynamic effects of novel XF porphyrin derivatives on prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.49, 1542–1552. 10.1128/aac.49.4.1542-1552.2005
38
Mao T. Chai B. Xiong Y. Wang H. Nie L. Peng R. et al (2023). In vitro inhibition of growth, biofilm Formation, and persisters of Staphylococcus aureus by pinaverium bromide. ACS Omega8, 9652–9661. 10.1021/acsomega.3c00340
39
Maura D. Rahme L. G. (2017). Pharmacological inhibition of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa MvfR quorum-sensing system interferes with biofilm formation and potentiates antibiotic-mediated biofilm disruption. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.61, e01362-17. 10.1128/aac.01362-17
40
Mishra A. Aggarwal A. Khan F. (2024). Medical device-associated infections caused by biofilm-forming microbial pathogens and controlling strategies. Antibiotics13, 623. 10.3390/antibiotics13070623
41
Möker N. Dean C. R. Tao J. (2010). Pseudomonas aeruginosa increases formation of multidrug-tolerant persister cells in response to quorum-sensing signaling molecules. J. Bacteriol.192, 1946–1955. 10.1128/jb.01231-09
42
Mukherjee D. Zou H. Liu S. Beuerman R. Dick T. (2016). Membrane-targeting AM-0016 kills mycobacterial persisters and shows low propensity for resistance development. Future Microbiol.11, 643–650. 10.2217/fmb-2015-0015
43
Mulcahy L. R. Burns J. L. Lory S. Lewis K. (2010). Emergence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains producing high levels of persister cells in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Bacteriol.192, 6191–6199. 10.1128/JB.01651-09
44
Nguyen D. Joshi-Datar A. Lepine F. Bauerle E. Olakanmi O. Beer K. et al (2011). Active starvation responses mediate antibiotic tolerance in biofilms and nutrient-limited bacteria. Science334, 982–986. 10.1126/science.1211037
45
Nguyen L. DeVico B. Mannan M. Chang M. Rada Santacruz C. Siragusa C. et al (2023). Tea tree essential oil kills Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis persisters. Biomolecules13, 1404. 10.3390/biom13091404
46
Niepa T. H. R. Gilbert J. L. Ren D. (2012). Controlling Pseudomonas aeruginosa persister cells by weak electrochemical currents and synergistic effects with tobramycin. Biomaterials33, 7356–7365. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.06.092
47
Niepa T. H. R. Snepenger L. M. Wang H. Sivan S. Gilbert J. L. Jones M. B. et al (2016). Sensitizing Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics by electrochemical disruption of membrane functions. Biomaterials74, 267–279. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.10.007
48
Niepa T. H. R. Wang H. Gilbert J. L. Ren D. (2017). Eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells by cathodic electrochemical currents delivered with graphite electrodes. Acta Biomater.50, 344–352. 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.12.053
49
Niu H. Gu J. Zhang Y. (2024). Bacterial persisters: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic development. Sig Transduct. Target Ther.9, 174–32. 10.1038/s41392-024-01866-5
50
Ooi N. Miller K. Randall C. Rhys-Williams W. Love W. Chopra I. (2010). XF-70 and XF-73, novel antibacterial agents active against slow-growing and non-dividing cultures of Staphylococcus aureus including biofilms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.65, 72–78. 10.1093/jac/dkp409
51
Orman M. A. Brynildsen M. P. (2016). Persister formation in Escherichia coli can be inhibited by treatment with nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med.93, 145–154. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.02.003
52
Pal V. K. Bandyopadhyay P. Singh A. (2018). Hydrogen sulfide in physiology and pathogenesis of bacteria and viruses. IUBMB Life70, 393–410. 10.1002/iub.1740
53
Pan J. Bahar A. A. Syed H. Ren D. (2012). Reverting antibiotic tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 persister cells by (Z)-4-bromo-5-(bromomethylene)-3-methylfuran-2(5H)-one. PLoS One7, e45778. 10.1371/journal.pone.0045778
54
Papenfort K. Bassler B. L. (2016). Quorum sensing signal–response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.14, 576–588. 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.89
55
Patra D. Ghosh S. Mukherjee S. Acharya Y. Mukherjee R. Haldar J. (2024). Antimicrobial nanocomposite coatings for rapid intervention against catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Nanoscale16, 11109–11125. 10.1039/D4NR00653D
56
Roy S. Bahar A. A. Gu H. Nangia S. Sauer K. Ren D. (2021). Persister control by leveraging dormancy associated reduction of antibiotic efflux. PLOS Pathog.17, e1010144. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010144
57
Roy S. Cakmak Z. S. Kyeremeh S. P. Nangia S. Luo J. Ren D. (2025). A rational approach to discovering new persister control agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.69, e01814-24. 10.1128/aac.01814-24
58
Salcedo-Sora J. E. Kell D. B. (2020). A quantitative survey of bacterial persistence in the presence of antibiotics: towards antipersister antimicrobial discovery. Antibiotics9, 508. 10.3390/antibiotics9080508
59
Santi I. Manfredi P. Maffei E. Egli A. Jenal U. (2021). Evolution of antibiotic tolerance shapes resistance development in chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. mBio12, e03482-20. 10.1128/mbio.03482-20
60
Schmidt N. W. Deshayes S. Hawker S. Blacker A. Kasko A. M. Wong G. C. L. (2014). Engineering persister-specific antibiotics with synergistic antimicrobial functions. ACS Nano8, 8786–8793. 10.1021/nn502201a
61
Sharma B. Brown A. V. Matluck N. E. Hu L. T. Lewis K. (2015). Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of lyme disease, forms drug-tolerant persister cells. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy59, 4616–4624. 10.1128/aac.00864-15
62
Shatalin K. Nuthanakanti A. Kaushik A. Shishov D. Peselis A. Shamovsky I. et al (2021). Inhibitors of bacterial H2S biogenesis targeting antibiotic resistance and tolerance. Science372, 1169–1175. 10.1126/science.abd8377
63
She P. Liu Y. Xu L. Li Y. Li Z. Liu S. et al (2022). SPR741, Double- or triple-combined with erythromycin and clarithromycin, combats drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, its biofilms, and persister cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.12, 858606. 10.3389/fcimb.2022.858606
64
Singh V. Nandanwar H. (2024). IMT-P8 potentiates Gram-positive specific antibiotics in intrinsically resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.68, e0075324–e0075324. 10.1128/aac.00753-24
65
Starkey M. Lepine F. Maura D. Bandyopadhaya A. Lesic B. He J. et al (2014). Identification of anti-virulence compounds that disrupt quorum-sensing regulated acute and persistent pathogenicity. PLOS Pathog.10, e1004321. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004321
66
Stokes J. M. Yang K. Swanson K. Jin W. Cubillos-Ruiz A. Donghia N. M. et al (2020). A deep learning approach to antibiotic discovery. Cell180, 688–702.e13. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.01.021
67
Sun J. Wang X. Gao Y. Li S. Hu Z. Huang Y. et al (2024). H2S scavenger as a broad-spectrum strategy to deplete bacteria-derived H2S for antibacterial sensitization. Nat. Commun.15, 9422. 10.1038/s41467-024-53764-7
68
Tang Z. Feng J. Challa M. Rowthu S. R. Xiong S. Zou C. et al (2024). Discovery of novel Thymol-TPP antibiotics that eradicate MRSA persisters. Eur. J. Med. Chem.270, 116381. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116381
69
Vera-Mansilla J. Silva-Valenzuela C. A. Sánchez P. Molina-Quiroz R. C. (2023). Bacteriophages potentiate the effect of antibiotics by eradication of persister cells and killing of biofilm-forming cells. Res. Microbiol.174, 104083. 10.1016/j.resmic.2023.104083
70
Wagley S. Morcrette H. Kovacs-Simon A. Yang Z. R. Power A. Tennant R. K. et al (2021). Bacterial dormancy: a subpopulation of viable but non-culturable cells demonstrates better fitness for revival. PLoS Pathog.17, e1009194. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009194
71
Wan F. Wong F. Collins J. J. de la Fuente-Nunez C. (2024). Machine learning for antimicrobial peptide identification and design. Nat. Rev. Bioeng.2, 392–407. 10.1038/s44222-024-00152-x
72
Wang H. Tampio A. J. F. Xu Y. Nicholas B. D. Ren D. (2020). Noninvasive control of bacterial biofilms by wireless electrostimulation. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng.6, 727–738. 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01199
73
Wang M. Chan E. W. C. Xu C. Chen K. Yang C. Chen S. (2022). Econazole as adjuvant to conventional antibiotics is able to eradicate starvation-induced tolerant bacteria by causing proton motive force dissipation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.77, 425–432. 10.1093/jac/dkab384
74
Wood T. K. Knabel S. J. Kwan B. W. (2013). Bacterial persister cell formation and dormancy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.79, 7116–7121. 10.1128/AEM.02636-13
75
Xiong Y. Wang R. Zheng J. Fang D. He P. Liu S. et al (2024). Discovery of novel dihydropyrrolidone-thiadiazole compound crosstalk between the YycG/F two-component regulatory pathway and cell membrane homeostasis to combat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. J. Med. Chem.277, 116770. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116770
76
Yan X. Liao H. Wang C. Huang C. Zhang W. Guo C. et al (2024). The emergence of visual category representations in infants' brains. eLife13. 10.7554/eLife.100260
77
Zhang S. Qu X. Jiao J. Tang H. Wang M. Wang Y. et al (2022). Felodipine enhances aminoglycosides efficacy against implant infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, persisters and biofilms. Bioact. Mater.14, 272–289. 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.11.019
78
Zheng E. J. Valeri J. A. Andrews I. W. Krishnan A. Bandyopadhyay P. Anahtar M. N. et al (2024). Discovery of antibiotics that selectively kill metabolically dormant bacteria. Cell Chem. Biol.31, 712–728.e9. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.10.026
79
Zhou Y. Liao H. Pei L. Pu Y. (2023). Combatting persister cells: the daunting task in post-antibiotics era. Cell Insight2, 100104. 10.1016/j.cellin.2023.100104
80
Zhu J. Xie R. Gao R. Zhao Y. Yodsanit N. Zhu M. et al (2024a). Multimodal nanoimmunotherapy engages neutrophils to eliminate Staphylococcus aureus infections. Nat. Nanotechnol.19, 1032–1043. 10.1038/s41565-024-01648-8
81
Zhu L. Yang X. Fu X. Yang P. Lin X. Wang F. et al (2024b). Pheromone cCF10 inhibits the antibiotic persistence of Enterococcus faecalis by modulating energy metabolism. Front. Microbiol.15, 1408701. 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1408701
Summary
Keywords
persister bacteria, antibiotic, antibiotic persistence, combination therapy, AI-driven drug discovery
Citation
Hashemi MJ, Dhaouadi Khattab Y and Ren D (2025) Mini review: Persister cell control strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1706115. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1706115
Received
15 September 2025
Accepted
07 October 2025
Published
15 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Jessica Amber Jennings, University of Memphis, United States
Reviewed by
Butool Durrani, University of Minnesota Twin Cities, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Hashemi, Dhaouadi Khattab and Ren.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dacheng Ren, dren3@utk.edu
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.