- 1The Third School of Clinical Medicine, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3Department of Neurology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 4Department of Neurology, Tiantai People’s Hospital of Zhejiang Province (Tiantai Branch of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital), Hangzhou Medical College, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
Background: Stroke is a leading cause of global death and disability. Post-stroke cerebral edema significantly worsens neurological outcomes. While conventional therapies face safety limitations, selected traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) interventions offer a potential alternative.
Aim of the study: This narrative review aims to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy and safety of TCM interventions for post-stroke cerebral edema and elucidate their potential mechanisms based on experimental evidence.
Materials and methods: A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, and other databases using keywords related to stroke, cerebral edema, and TCM interventions. Studies were screened according to predefined inclusion criteria to ensure methodological rigor.
Results: Clinical and preclinical studies indicate that TCM interventions can reduce cerebral edema volume, improve neurological outcomes, and exhibit good safety. These effects may be associated with modulation of ion homeostasis and aquaporins, neuroinflammatory inhibition, blood-brain barrier protection, oxidative stress reduction, and apoptosis suppression.
Conclusion: Selected TCM interventions show promise for post-stroke cerebral edema. Their clinical experience and mechanistic insights provide a valuable foundation for future research and drug development.
1 Introduction
Stroke, a primary global cause of death and severe long-term disability, is frequently complicated by cerebral edema—a potentially fatal condition affecting 10%–78% of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke patients (Jiang et al., 2022). Each 1 mL increase in edema volume elevates the risk of adverse outcomes by 8.0%, exacerbating neurological deficits and mortality (Nawabi et al., 2019). BBB disruption is the most common etiology. Mannitol remains the first-line osmotic diuretic clinically, but carries significant limitations: high doses risk osmotic nephropathy, and rapid renal excretion can cause rebound intracranial hypertension (Cook et al., 2020; Papagianni et al., 2018). Decompressive craniectomy effectively reduces mortality but often leaves severe disability (Cooper et al., 2011). Consequently, clinical management of post-stroke cerebral edema remains challenging, driving increasing patient interest in TCM as an alternative or adjunctive therapy seeking improved efficacy and reduced adverse effects.
In China, TCM has been used to treat stroke for over 2000 years, demonstrating notable efficacy and safety (Zhao et al., 2024). Recent research increasingly reveals its potential for post-stroke edema management. Numerous botanical drugs, formulas, and metabolites have been shown to reduce brain swelling, lower intracranial pressure, and improve neurological function in preclinical models and early clinical trials (Li X. et al., 2020; Widmann et al., 2018). Compared to mannitol or surgery, TCM therapies generally present lower risks of adverse reactions, making them particularly attractive for patients with comorbidities such as cardiac or renal insufficiency or diabetes (Lin et al., 2022). However, the clinical evidence and mechanisms underlying TCM require further elucidation. This article is presented as a narrative review that synthesizes current advances in the clinical efficacy and pharmacological mechanisms of TCM for post-stroke cerebral edema, aiming to guide clinical application and accelerate drug development.
2 Methods
In this review, we conducted a comprehensive literature search across six databases—Web of Science, PubMed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), VIP, Wanfang, and SinoMed—from inception to 23 July 2025 to evaluate the efficacy and safety of TCM for post-stroke cerebral edema. Key search terms included: “stroke,” “cerebral ischemia,” “intracerebral hemorrhage,” “edema,” “traditional Chinese medicine,” “herbal,” “TCM,” “formula,” “Clinical” and “patient.” Detailed search strategies for each database are listed in Supplementary.
For clinical studies, the exclusion criteria were as follows: (a) case reports, reviews, commentaries, and animal studies; (b) studies involving non-ischemic or non-hemorrhagic stroke patients; (c) complementary and alternative therapies other than TCM, including acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, massage, qigong, tai chi, yoga, and music therapy; and (d) studies without reported clinical outcomes.
For preclinical studies, the exclusion criteria were as follows: (a) case reports, reviews, commentaries, and clinical studies; (b) studies using cell or animal models unrelated to stroke; (c) studies involving complementary and alternative therapies other than TCM, such as acupuncture, cupping, massage, and music therapy; and (d) studies lacking experimental outcome measures related to cerebral edema.
3 Clinical evidence for selected TCM interventions in post-stroke cerebral edema
3.1 Chinese botanical drug injections
Chinese herbal injections are modern TCM preparations made from effective substances extracted from Chinese medicines (single botanical drugs or compound formulas), formulated as sterile solutions for intravenous or intramuscular injection to directly enter the systemic circulation.
Xueshuantong Injection is a standardized TCM product extracted from Panax notoginseng (Burkill) F.H.Chen, with total saponins of P. notoginseng as its main metabolites. Panax notoginseng is widely used for promoting blood circulation and resolving stasis in the treatment of post-stroke cerebral edema. Pharmacological studies have shown that P. notoginseng can improve cerebral blood flow, protect vascular endothelial function, and scavenge free radicals (Pan et al., 2022). In clinical cases, Xueshuantong Injection has been shown to reduce the volume of cerebral edema and hematoma, improve hemodynamics, and decrease infarct volume (He et al., 2002). A systematic review of 21 clinical studies involving 1759 patients demonstrated that Xueshuantong exerts a protective effect on brain tissue during acute intracerebral hemorrhage and is more effective than the control group in reducing cerebral edema (Yu et al., 2011). A 160-patient clinical trial showed that compared with conventional treatment alone, Xueshuantong Injection combined with conventional treatment reduced edema volume and infarct size, enhanced anti-inflammatory responses, promoted neurological recovery, lowered disability rates, and improved quality of life and prognosis in patients with post-hemorrhagic stroke edema (Wang, 2018). Another clinical trial involving 115 patients reported that Xueshuantong Injection had a relatively safe, with an adverse reaction rate of 5.26% in the observation group and 3.45% in the control group. The main adverse reactions include gastrointestinal discomfort, skin rashes, fatigue, and other allergic reactions (Shang et al., 2022). The molecular biological mechanism of Xueshuantong Injection involves regulating the HIF1-α/VEGFA/VEGFR2 signaling pathway to promote vascular remodeling in the ischemic area after stroke, thereby reducing BBB leakage (Fang et al., 2023; Hatakeyama et al., 2020). Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses further revealed that Xueshuantong Injection significantly regulates the expression of related proteins and genes (VEGFA, VEGFR2, AKT, p-AKT, HIF-1α, GAPDH, EGFR, IL-6, HSP90AA1, NFKB1, PTEN) in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model rats, suggesting that the HIF1-α/VEGFA/VEGFR2 signaling pathway is a potential key pathway for alleviating post-ischemic cerebral edema (Xiao et al., 2024).
Shuxuetong Injection is a sterile aqueous solution extracted from animal-derived medicinal materials Hirudo nipponia Whitman (leech) and Pheretima aspergillum (E. Perrier) using modern biotechnology. Its main metabolites include hirudin-like polypeptides, earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes, and collagen hydrolysates (Sun et al., 2022). An 85-patient trial in intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) patients showed that Shuxuetong Injection improved cerebral edema severity, reduced hematoma volume, enhanced NIHSS scores, and promoted neurological recovery in post-hemorrhagic cerebral edema, with no significant adverse effects reported (Yao, 2012). In addition, another clinical trial involving 120 patients with intracerebral hemorrhage showed that compared with conventional treatment, Shuxuetong Injection combined with conventional treatment was more effective in reducing the volume of cerebral edema and hematoma (Liang and Yang, 2012). Mechanistic insights from preclinical models propose that Shuxuetong may alleviate cerebral edema by inhibiting pyroptosis, a pro-inflammatory form of cell death, potentially via the CD44/NLRP3/GSDMD signaling pathway (Shang et al., 2025).
3.2 Commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation (CCPP)
Commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation are standardized TCM preparations produced in batches with fixed formulas and processes, using Chinese medicinal materials as raw materials, and having specific dosage forms and efficacy.
Naoxueshu Oral Liquid, a clinically utilized Chinese CCPP for qi-supplementing, blood-activating, stasis-resolving, and fluid-promoting effects, contains components including Astragalus mongholicus Bunge, H. nipponia Whitman, Acorus tatarinowii Schott, Achyranthes bidentata Blume, Paeonia suffruticosa Andr., Rheum officinale Baill., and Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort (Li P. et al., 2024). Modern studies on its active substances have identified over 100 distinct metabolites in the formula, which exert synergistic multi-target effects to facilitate edema absorption and neurological recovery after stroke (Li R. et al., 2024). A network meta-analysis of 19 studies (n = 2,335 patients) demonstrated that Naoxueshu combined with Western medicines (nimodipine, nifedipine, edaravone) significantly reduced cerebral edema volume and hematoma size, improved NIHSS scores, and exerted anti-inflammatory effects compared to Western medicines alone (Mei et al., 2022). A 220-patient trial showed that Naoxueshu plus conventional treatment Moderately decreased edema and hematoma volume while improving neurological function scores versus conventional treatment alone (Song et al., 2022). In addition, A 120-patient study in post-stroke rehabilitation reported that 7-day Naoxueshu treatment reduced cerebral hematoma and edema volume without affecting fibrinogen levels or causing adverse effects (Song et al., 2021). Experimental research suggests potential mechanisms for these benefits. Studies in rat models of intracerebral hemorrhage indicate that Naoxueshu may reduce BBB permeability and alleviate edema, potentially through modulating astrocyte function, promoting the expression of the tight junction protein ZO-1, and inhibiting AQP4 protein (Wang et al., 2019).
Angong Niuhuang Pill is a commercially available Chinese CCPP. This pill is composed of 11 medicinal components: Bos taurus domesticus Gmelin, Moschus moschiferus Linnaeus, Bubalus bubalis Linnaeus (horn, concentrated powder), Pinctada martensii (Dunker), Cinnabaris, Realgar, Coptis chinensis Franch., Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, Curcuma aromatica Salisb., and Dryobalanops aromatica Gaertn. f (Bai et al., 2024). An 80-patient trial in acute cerebral infarction (ACI) demonstrated that Angong Niuhuang Pill combined with conventional treatment significantly reduced edema volume and improved NIHSS and GCS scores compared to conventional treatment alone (Feng and Yang, 2015). In addition, A larger 122-patient trial in ACI reported that the pill restored midline shift, Significantly decreased edema volume, modulated vascular tone, and enhanced neurological function and quality of life (Zhang and Chen, 2016). Notably, realgar and cinnabar—key components—contributed to neuroprotective effects without inducing hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity in transient ischemic brain injury models (Tsoi et al., 2019a).
Systems biology approaches have shown that Angong Niuhuang Pill can effectively improve cerebrovascular edema in mice, which may be associated with the inhibition of VE-cadherin expression and the upregulation of CAV-1 phosphorylation and AQP4 expression in mouse brain tissue (Liu et al., 2024). Another study suggested a potential mechanism involving the prevention of MMP-9 activation via scavenging peroxynitrite, thereby protecting microvascular integrity (Chen H. et al., 2022).
3.3 Chinese medicinal formulae
Chinese Medicinal Formulae represent systematic combinations of multiple herbs—often guided by principles such as “monarch, minister, assistant, and guide”—with the goal of producing synergistic therapeutic effects.
Buyang Huanwu Decoction, derived from Yilin Gaicuo by Wang Qingren in the Qing Dynasty, is a classic formula for treating post-stroke sequelae, composed of seven medicinal components: Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge, Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, Paeonia lactiflora Pall., L. chuanxiong Hort., P. aspergillum (E. Perrier), Prunus persica (L.) Batsch, and Carthamus tinctorius L. Its standardized extract contains core metabolites such as astragaloside IV, ferulic acid, paeoniflorin, and hydroxysafflor yellow A (Pan et al., 2025). A 104-patient trial post-intracerebral hemorrhage surgery showed that Buyang Huanwu Decoction combined with ultra-early urokinase significantly reduced cerebral edema probability, increased overall response rates, and demonstrated a favorable safety profile compared to urokinase alone (Hou et al., 2022). Another 52-patient study in ACI reported that Buyang Huanwu Decoction can reduce the content of β2-MG in CSF of patients with acute cerebral infarction, alleviate cerebral edema, and has reliable clinical efficacy (Jia and Liu, 2007; Xiao et al., 2021). Separately, research suggests it may prevent cerebral edema after ischemia by inhibiting the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway and stabilizing β-ENaC ion channels in the brain.
Preclinical studies have proposed multiple potential mechanisms. In rat models, its effects have been associated with the inhibition of the NIK-mediated non-canonical NF-κB pathway to reduce inflammatory responses after intracerebral hemorrhage (Xiao et al., 2021). Separately, research suggests it may prevent cerebral edema after ischemia by inhibiting the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway and stabilizing β-ENaC ion channels in the brain (Chen et al., 2019).
Clinical reports on Chinese Botanical Drug Injections, commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation and TCM Formulas are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1. Clinical reports related to the treatment of post-stroke cerebral edema with selected TCM interventions.
3.4 Adverse reactions
In recent years, With the expanding clinical application of TCM, reports of adverse reactions have correspondingly increased. The most common reactions involve the skin, digestive, and respiratory systems, manifesting as pruritus, rashes, flatulence, fatigue, vomiting, headache, and dizziness. Primary management strategies include drug discontinuation and symptomatic treatment (Lai et al., 2013). A meta-analysis of 40 RCTs (n = 3,868) showed no significant difference in adverse reaction rates between Xueshuantong plus conventional therapy (12.5%) and conventional therapy alone (11.4%) (Lyu et al., 2020). Another systematic review of Naoxueshu Injection for ICH (n = 1,602) reported significantly reduced cerebral edema in the treatment group versus controls, with no abnormalities in safety parameters (blood/coagulation profiles, liver/kidney function) and no mortality difference (Wang et al., 2025). Animal toxicology studies demonstrated that rats administered Angong Niuhuang Pill at human-equivalent doses exhibited no mercury accumulation in blood, liver, or kidneys within 7–14 days; although arsenic levels increased in the liver and blood (not kidneys), short-term use (≤7 days) remained safe (Tsoi et al., 2019b). However, most of the included clinical studies did not use standardized reporting protocols for adverse events, and some studies did not report adverse reactions at all, which may limit the comparability and interpretation of safety data across studies. In summary, Selected TCM interventions exhibits an acceptable safety profile in clinical practice. Future efforts should prioritize standardized adverse event reporting, rigorous safety evaluations, and long-term follow-up in large-scale trials to further strengthen the reliability of safety data.
4 Pharmacological mechanisms of selected TCM interventions in post-stroke cerebral edema
The pathological mechanisms of cerebral edema after stroke differ essentially between intracerebral hemorrhage and cerebral ischemia. Intracerebral hemorrhage drives progressive vasogenic edema through thrombin-mediated endothelial injury combined with iron-catalyzed Fenton reactions from hemoglobin degradation, which disrupt BBB integrity. Cerebral ischemia initially induces cytotoxic edema due to sodium-potassium pump dysfunction caused by energy failure, and then transforms into vasogenic edema during reperfusion as reactive oxygen species (ROS) bursts activate matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) to degrade tight junction proteins. The treatment of cytotoxic edema primarily involves regulating fluid metabolism and ion homeostasis, while the key to treating vasogenic edema lies in protecting and repairing the BBB (Wang et al., 2024a). The treatment of both types of edema requires inhibiting the neuroinflammatory cascade to block the transformation of cytotoxic edema to vasogenic edema, ultimately achieving edema resolution (Zheng et al., 2023).
Preclinical evidence suggests that selected TCM interventions may ameliorate cerebral edema by targeting interconnected pathological processes. Evidence for their potential mechanisms of action comes primarily from animal and cell-based models, and points to several key processes: the regulation of ion homeostasis and aquaporins, inhibition of neuroinflammatory cascades, protection and repair of the BBB, and the mitigation of oxidative stress and apoptosis. These potential mechanisms are illustrated in Figure 1. Basic research on TCM monomers and Chinese Herbal Formulas are presented in Tables 2, 3, respectively. It is important to note that this evidence currently constitutes a framework of hypotheses that must be rigorously tested. The critical next steps for the field will involve establishing causal validation of these mechanisms in humans and identifying the principal active constituents within the complex formulas. Building on this foundation, the following sections will elaborate on each of these mechanisms.

Figure 1. Pharmacological mechanisms of selected traditional Chinese medicine interventions for post-stroke cerebral edema.
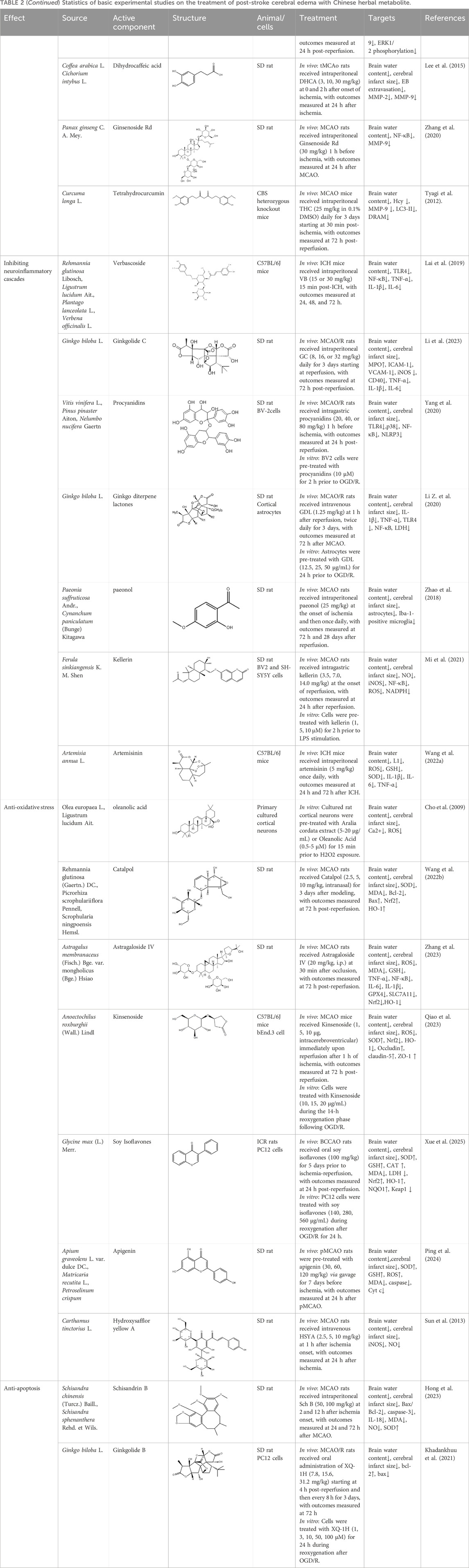
Table 2. Statistics of basic experimental studies on the treatment of post-stroke cerebral edema with Chinese herbal metabolite.
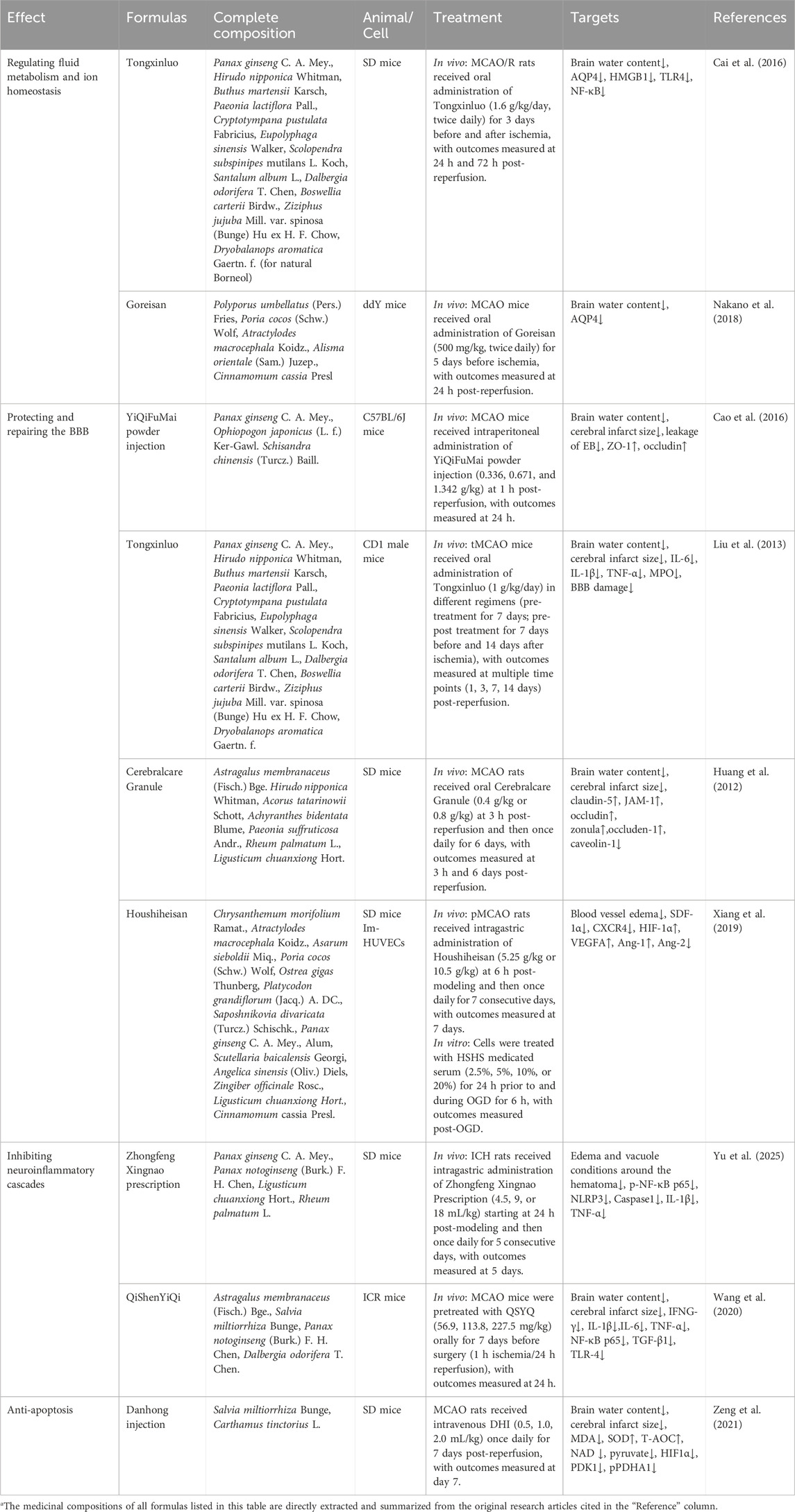
Table 3. Statistics of basic experimental studies on the treatment of post-stroke cerebral edema with Chinese herbal formulae.
4.1 Regulating fluid metabolism and ion homeostasis
Disorders of fluid metabolism and ion homeostasis are the core pathological hubs of post-stroke cerebral edema, presenting distinct processes in cerebral ischemia and intracerebral hemorrhage. Cerebral ischemia initially causes sodium and water retention in neurons due to Na+/K+-ATPase dysfunction from energy failure (Sylvain et al., 2021), forming cytotoxic edema, accompanied by abnormal polarity distribution of astrocyte AQP4 aquaporins, which exacerbates swelling (Kitchen et al., 2020; Markou et al., 2022). Intracerebral hemorrhage directly impairs microcirculation due to mechanical compression by hematoma, combined with thrombin activation and free iron from hemoglobin degradation, which damage endothelial ion transport function, triggering vasogenic edema (Wan et al., 2023). Therefore, regulating fluid metabolism and ion homeostasis may reduce the severity of post-stroke cerebral edema: for post-ischemic cerebral edema, the focus is on repairing the sodium-potassium pump and regulating the expression and distribution of aquaporin AQP4; for post-hemorrhagic cerebral edema, the emphasis is on clearing toxic substances and restoring endothelial channel function.
Regulating the expression and distribution of AQP4 is a hypothesized key mechanism for reducing astrocyte swelling and stabilizing BBB integrity. Preclinical studies suggest that several TCM interventions may act through this pathway. For instance, experimental models indicate that Tongxinluo Capsule can downregulate AQP4 expression, reduce T2WI relative signal intensity, and decrease brain water content (Cai et al., 2016). Similarly, the classic formula Wuling Powder has been shown in mice to reduce brain water content after ischemic stroke by suppressing AQP4, a mechanism that involves Mn2+ and Zn2+ ions and is consistent with its observed inhibition of AQP4-dependent permeability in MLE-12 cells (Nakano et al., 2018). In addition, emodin, a botanical metabolite exerts a protective effect on post-ischemic cerebral edema both in vivo and in vitro, inhibiting astrocyte swelling and BBB disruption mediated by AQP4 (Chen et al., 2024). Other botanical metabolites, such as cornel glycosides, which significantly reduced cerebral edema (p = 0.0018) (Wang et al., 2024b), and total steroid saponins, which also significantly reduced cerebral edema (p < 0.01) (Zhang et al., 2014), function through this pathway.
Restoring ion pump function (enhancing Na+/K+-ATPase activity) and regulating ion channels (promoting intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ efflux) are core strategies for intervening in cytotoxic edema, aiming to maintain ion homeostasis in neurons and glial cells. The botanical metabolite gastrodin, for example, has been demonstrated in rat models to reduce excitotoxicity and oxidative damage by inhibiting glutamate release, blocking calcium overload, and reducing nitric oxide production, thereby decreasing infarct and edema volumes and improving neurological function (Zeng et al., 2006).
4.2 Protecting and repairing the BBB
Vasogenic edema is the main type of edema in intracerebral hemorrhage and the main form of edema transformation after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion, fundamentally resulting from disrupted BBB integrity, leading to extravasation of plasma components, especially protein-rich fluids, into the brain parenchyma. In the early stage of injury, activated endothelial cells and microglia/infiltrating inflammatory cells release matrix metalloproteinases MMP-9/MMP-2, which disrupt the BBB through a continuous three-level cascade (Lu and Wen, 2024): first, degrading key components of the basement membrane, such as laminin and type IV collagen; then, exposing adhesion receptors on the endothelial cell surface, promoting further adhesion and infiltration of inflammatory cells; finally, directly hydrolyzing tight junction proteins occludin, claudin-5, and ZO-1, leading to complete disintegration of anchoring structures between endothelial cells (Wang P. et al., 2022). Extravasated plasma components accumulate in the brain tissue interstitium to form vasogenic edema, and mechanically compress the local microcirculation system, exacerbating ischemic injury, thus forming a vicious cycle where edema aggravates ischemia and ischemia further exacerbates edema (Ng et al., 2022). Therefore, targeted inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase activity and promotion of tight junction protein network reconstruction are important intervention strategies to reduce cerebral edema and improve neurological prognosis.
The key to repairing BBB tight junction structures lies in enhancing the expression, proper assembly, and localization of junction proteins (such as ZO-1, occludin, claudin-5). This is usually achieved by activating protective signaling pathways (such as HO-1, GSK-3β/β-catenin) or inhibiting destructive factors (such as caveolin-1) to reduce plasma leakage. For instance, Yiqi Fumai Powder Injection has been shown in mouse models to attenuate BBB leakage, upregulate the tight junction proteins ZO-1 and occludin (Cao et al., 2016). Similarly, Tongxinluo Capsule shares the same anti-edema mechanism in treating post-stroke cerebral edema (Liu et al., 2013). Naomao Granule alleviates BBB disruption and ischemic post-stroke cerebral edema by protecting tight junction proteins between cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, such as claudin-5, JAM-1, occludin, ZO-1, and inhibiting the expression of caveolin-1 (Huang et al., 2012). At the metabolite level, naringenin is proposed to upregulate tight junction proteins via the GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway (Yang et al., 2024), while curcumin (Wang et al., 2013) and baicalin (Zhu et al., 2012) have been reported to enhance junctional integrity, potentially through activating the HO-1 pathway.
Inhibiting the expression and enzymatic activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs, especially MMP-9 and MMP-2) is an effective mechanism to reduce vasogenic edema. This can be achieved by blocking their upstream activation signaling pathways (such as NF-κB, ERK1/2) or directly interfering with their synthesis and activation processes, effectively protecting the basement membrane and tight junction proteins from degradation. Preclinical studies indicate that crocin protects cortical microvascular endothelial cells from ultrastructural damage after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. These protective effects are associated with the inhibition of ERK1/2 phosphorylation, blockade of GRK2 membrane translocation, and downregulation of MMP-9 expression, which collectively contribute to the reduction of oxidative stress and vasogenic edema, conferring multi-faceted protection (Zheng et al., 2007). Dihydrocaffeic acid, a metabolite of coffee components, has been reported to inhibit the expression and activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9, exerting a protective effect on ischemia-induced neuronal injury and cerebral edema (Lee et al., 2015). Ginsenoside Rd is proposed to reduce BBB injury and edema severity by inhibiting proteasome activity, reducing IκBα degradation, blocking NF-κB activation pathway, and downregulating MMP-9 expression (Zhang et al., 2020). Tetrahydro curcumin reduces MMP-9 activity and oxidative damage by inhibiting homocysteinylation of cytochrome c (Hcy-cyto-c), thereby alleviating BBB disruption and cerebral edema (Tyagi et al., 2012).
Promoting angiogenesis and improving cerebral blood perfusion help alleviate ischemic injury and secondary edema. Houshi Heisan can promote angiogenesis through the HIF-1α/VEGF and SDF-1/CXCR4 pathways, relieve vascular edema, and reduce injury to blood vessels and neurons in the ischemic area (Xiang et al., 2019). Separately, studies suggest that the hexane extract of Uncaria rhynchophylla enhances endothelium-dependent vasodilation by activating the Akt/eNOS signaling pathway, improves perfusion in the ischemic penumbra, and may thereby contribute to the reduction of cerebral edema (Park et al., 2011).
4.3 Inhibiting neuroinflammatory cascades
Neuroinflammation is a key bridge connecting cytotoxic and vasogenic edema, amplifying both processes. In the acute phase of stroke, activated microglia, infiltrating neutrophils, and reactive astrocytes release various pro-edema mediators, including IL-1β, HMGB1, and MMPs (Chen et al., 2021; Wang X. et al., 2022). These factors exacerbate edema formation through multiple pathways: IL-1β and HMGB1 activate the endothelial cell NF-κB pathway, induce matrix metalloproteinase expression, and indirectly disrupt the integrity of BBB tight junction proteins; simultaneously activated complement cascades produce C3a/C5a, synergistically promoting leukocyte adhesion and inflammatory infiltration. Sustained inflammatory stimulation also disrupts the polar distribution of aquaporin AQP4, promoting the transformation of cytotoxic edema to vasogenic edema (Zheng et al., 2025). It should be noted that pro-inflammatory mediators released by reactive astrocytes in the early stage exacerbate injury, but they also participate in protection in the later stage by secreting neurotrophic factors and barrier repair proteins. Therefore, early targeted intervention in the neuroinflammatory cascade can effectively reduce cerebral edema and improve neurological prognosis.
Targeting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway represents a promising strategy to reduce neuroinflammation and cerebral edema, as this pathway is activated by DAMPs to drive pro-inflammatory factor expression. Similarly, inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome and its upstream signals (e.g., CaMKII/NF-κB) may effectively block inflammatory cascade amplification, thereby reducing BBB injury (Cai et al., 2016). Zhongfeng Xingnao Decoction was shown to reduce inflammatory responses and the volume of perihematomal edema by regulating the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome after intracerebral hemorrhage, which is related to the CaMKII/NF-κB p65/NLRP3/GSDMD signaling axis (Yu et al., 2025). Pretreatment with Qishen Yiqi Formula in mouse models inhibited neuroinflammatory responses, protected the BBB, and reduced cerebral edema, which significantly attenuated midline shift caused by brain swelling (p < 0.001), concomitant with downregulation of IFNG-γ, IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB p65, and TLR-4 mRNA (Wang et al., 2020). Network pharmacological analysis shows that Miaoyao Xuemaitong Capsule can alleviate intracerebral hemorrhage-induced inflammation and edema by regulating the TNFR1/NF-κB and TNFR1/MAPK signaling pathways (Zhang et al., 2021). In addition, the botanical metabolite verbenalin reduces acute inflammatory injury and cerebral edema in intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting TLR4 (Lai et al., 2019). Both jolkinolide B (Ma et al., 2024) and ginkgolide B (Chen et al., 2018) improve hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in newborn male rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation, alleviating cerebral edema. Ginkgolide C (Li et al., 2023) reduces inflammation-induced injury caused by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion by inhibiting the CD40/NF-κB pathway, improves microvascular ultrastructural characteristics, and ameliorates BBB disruption, thereby reducing cerebral edema.
Regulating the MAPK signaling pathway (such as JNK, p38) is an important approach to intervene in inflammatory mediator release and BBB disruption. Experimental studies suggest that leonurine can reduce BBB disruption in vivo by inhibiting hemoglobin degradation and inflammatory mediator release, a process associated with the JNK signaling pathway and the inhibition of oxyhemoglobin-induced inflammatory protein expression in BV-2 cells (Lin et al., 2016). Similarly, proanthocyanidins have been shown in rat models to exert neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia, which are correlated with the inhibition of the TLR4-p38-NF-κB-NLRP3 signaling pathway and a reduction in cerebral edema (Yang et al., 2020).
Modulating the activity of microglia and astrocytes offers a broader anti-inflammatory approach. The combination of jolkinolide B and ginsenoside Rg1 has been reported to reduce neuroinflammation and cerebral edema in experimental models, potentially by inhibiting miR-155-5p expression in microglia (Wang et al., 2018). Ginkgo diterpene lactones can alleviate OGD/R injury in primary astrocytes and LPS-induced inflammatory responses, reducing infarct volume and cerebral edema (Li X. et al., 2020). Methanol extracts of Glycyrrhiza uralensis and its roots regulate inflammation-related neuronal cells such as microglia and astrocytes, thereby reducing edema volume and exerting neuroprotective effects on ischemic stroke (Choi et al., 2022). Other botanical metabolite such as tetramethylpyrazine (Liao et al., 2004), paeonol (Zhao et al., 2018), and furanocoumarin dimers (Mi et al., 2021) also function through this mechanism. Other pathways, such as artemisinin, can upregulate the expression of neural cell adhesion molecule L1, inhibit inflammation and oxidative stress, and alleviate cerebral edema (Wang X. et al., 2022).
4.4 Anti-oxidative stress
After ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, excessive production of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species triggers cascading oxidative damage, leading to lipid peroxidation of vascular endothelial cell membranes (Kim et al., 2021), and inducing nitration or carbonylation of key structural proteins such as tight junction proteins, thereby disrupting BBB integrity, increasing microvascular permeability, and ultimately promoting the formation of vasogenic edema (Chen S. et al., 2022). In addition, mitochondrial oxidative stress can further exacerbate neuronal apoptosis and cytotoxic edema (Panickar and Anderson, 2011). Therefore, anti-oxidative stress can indirectly exert anti-edema effects on post-stroke cerebral edema by repairing the BBB.
Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway is a core cellular anti-oxidative defense mechanism. Preclinical studies indicate that several TCM interventions may confer protection by enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes and decreasing levels of lipid peroxides. For instance, Multiple studies have demonstrated that Dracocephalum moldavica (Jia et al., 2017), lavender oil (Vakili et al., 2014), Houttuynia cordata, and the botanical metabolite oleanolic acid (Cho et al., 2009) can enhance endogenous antioxidant defense, inhibit oxidative stress, and thus reduce cerebral edema by decreasing malondialdehyde content and increasing the activities of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase. Among them, lavender oil also exerts synergistic effects by increasing VEGF expression. Intranasal administration of catalpol upregulates the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 to reduce oxidative stress injury, increase SOD activity, decrease MDA activity, and reduce infarct volume, neurological dysfunction, and cerebral edema (Wang P. et al., 2022) The botanical metabolite astragaloside IV (Zhang et al., 2023), dendrobium nobile glycoside (Qiao et al., 2023), and soy isoflavones (Xue et al., 2025) also function through this signaling pathway. In addition, apigenin can promote DNA repair by inhibiting the PARP1/AIF pathway, reduce ROS and malondialdehyde, increase glutathione and superoxide dismutase, improve antioxidant capacity, thereby reducing infarct volume and neurological deficits, decreasing edema volume, and reducing blebbing and cell death (Ping et al., 2024).
Direct scavenging of harmful reactive nitrogen species or inhibiting their key generating enzymes can specifically reduce oxidative damage such as protein nitration, thereby alleviating cerebral edema. Hydroxysafflor yellow A reduces protein tyrosine nitration by directly scavenging peroxynitrite and inhibiting the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), thereby reducing post-ischemic cerebral edema (Sun et al., 2013).
4.5 Anti-apoptosis
In cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, activation of the neuronal apoptotic pathway exacerbates cerebral edema through dual mechanisms: caspase activation driven by the mitochondrial pathway leads to caspase-3-mediated cleavage of the Na+/K+-ATPase α subunit, directly di (Cheng et al., 2020; Panickar and Anderson, 2011)srupting ion homeostasis and worsening cytotoxic edema. Meanwhile, damage-associated molecular patterns released by apoptotic neurons activate microglia, triggering cascading release of pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-1β, which further degrade tight junction proteins and induce vasogenic edema (Sadeghian et al., 2019).
Targeting upstream apoptotic signal hubs (PI3K/AKT, MAPK) can inhibit apoptosis. Experimental evidence suggests that Shilong Qingxue Granule (SQG) alleviates glutamate-induced neuronal calcium overload, ROS accumulation, and mitochondrial damage by inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and regulating the MAPK signaling pathway, thereby relieving cytotoxic edema (Hu et al., 2025). Schisandrin reduces apoptosis, inflammatory responses, and oxidative stress in MCAO rats by regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway, preventing ischemic brain injury and reducing brain water content (Hong et al., 2023). Ginkgolide B has been shown in vivo and in vitro to inhibit apoptosis by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway, suggesting a neuroprotective effect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury that includes a reduction in cerebral edema (Khadankhuu et al., 2021).
Inhibiting apoptosis can be achieved by intervening in related processes such as autophagy and energy metabolism. Excessive autophagy can induce apoptotic death, and energy failure directly activates apoptosis, both of which are closely coupled with apoptosis. Danhong Injection has been demonstrated in rat models to alleviate cerebral edema and rescue neuronal injury in the ischemic penumbra. This effect is proposed to involve the regulation of intracellular energy metabolism—namely, restoring cytoplasmic glycolytic activity and relieving mitochondrial metabolic inhibition—potentially through inhibiting the activation of the PARP1/AIF and HIF1α/PDK1 signaling pathways (Zeng et al., 2021). Arctigenin improves cerebral ischemia by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy, reducing cerebral edema and improving neurological function scores (Yang et al., 2021).
4.6 Other potential mechanisms
Focusing on metabolic homeostasis repair, regulating key metabolic pathways such as membrane components and energy metabolism can reduce glial cell edema. A study using metabolomics demonstrated that Longxue Tongluo Capsule can normalize metabolic disorders and reduce neuroglial interstitial edema by regulating metabolic pathways involving glycerophospholipid metabolism, glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis, nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism, and sphingolipid metabolism (Sun et al., 2023). Improving cerebral microcirculation, anti-platelet aggregation, and anti-thrombosis can reduce neuronal necrosis and glial cell edema caused by ischemia. Supercritical CO2 extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza (SCED) improves microcirculation by inhibiting platelet PLC/PKC signaling pathway activation, blocking thromboxane A2 release, and inhibiting platelet aggregation, thereby improving cerebral blood perfusion and reducing cerebral ischemic injury and edema (Fei et al., 2017).
5 Current limitations and future perspectives
5.1 Defects in clinical trial design
Although multiple clinical studies have demonstrated the improvement effect of Chinese botanical drug preparations, Chinese botanical drug, and their metabolites on post-stroke cerebral edema, there remains a problem of insufficient sample size. Moreover, the included clinical studies exhibited certain heterogeneity in experimental design, with some lacking detailed double-blind procedures, which may increase the risk of bias. Some studies did not perform formal sample size calculations or power analyses, potentially limiting the statistical reliability of their findings.
Furthermore, most available publications tend to report positive or favorable outcomes, while studies with negative or inconclusive findings are rarely accessible, particularly within Chinese-language databases. This publication and selection bias may lead to an overestimation of the therapeutic efficacy of Chinese botanical drugs. Another critical issue identified in the reviewed clinical trials is the lack of standardized safety reporting. Adverse event reporting is often inconsistent or inadequately detailed, which hinders the comprehensive assessment of the safety profile of Chinese botanical drugs in clinical settings. This gap in safety reporting, combined with the aforementioned methodological issues, further diminishes the overall reliability of the evidence.
Future investigations should prioritize well-designed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with adequate sample sizes and standardized outcome measures to enhance the robustness and reproducibility of clinical evidence. In particular, studies should adhere to rigorous adverse event reporting standards to ensure comprehensive safety evaluation. In addition, the differential effects of TCM in different stages of cerebral edema, i.e., the acute phase (0–72 h) and the recovery phase (7–14 days), need further exploration.
5.2 Insufficient translation from basic research to clinical practice
Basic studies have revealed multiple mechanisms through which TCM may alleviate post-stroke cerebral edema. However, despite these mechanistic advances, effective clinical translation remains limited. Many preclinical findings have not been systematically verified in humans, leading to uncertainties in dose–response relationships, pharmacodynamic stability, and safety under complex clinical conditions (Li et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2019).
Key barriers include inconsistent dose conversion between animal and human studies, variability in pharmacokinetics among multi-component botanical formulations, and the absence of unified regulatory and quality-assessment frameworks. Furthermore, poor bioavailability and limited blood–brain barrier permeability of metabolites often compromise therapeutic efficacy (Sanchez-Martinez et al., 2022).
Future research should prioritize dose optimization, formulation improvement to enhance bioavailability, and pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modeling (Dewi et al., 2022; Xie et al., 2025). Integrating TCM-based evidence into standardized and evidence-based evaluation systems will be essential to improve credibility and facilitate clinical adoption (Li R. et al., 2024).
5.3 Difficulties in analyzing components of Chinese medicines
In basic research, TCM, especially botanical formulas, has extremely complex compositions: a single Chinese medicinal material may contain dozens to hundreds of active metabolites, while formulas are combinations of multiple medicinal materials, leading to superimposed metabolites. This complexity enables them to exert therapeutic effects through multiple mechanisms, but precise analysis of specific molecular targets is challenging. The optimal effective doses and proportions of different active components in compound formulas, as well as the pathways through which different components synergistically function, require in-depth research.
5.4 Challenges in quality control of botanical drug
Contamination and adulteration of TCM raw materials can cause severe adverse reactions. A systematic review including 26 cases of botanical drug contamination and adulteration pointed out that the most common herbal contaminants include dust, pollen, insects, rodents, parasites, microorganisms, fungi, molds, toxins, pesticides, and toxic heavy metals. Adulteration and contamination can cause severe adverse reactions such as arsenic, lead, or mercury poisoning, hepatorenal syndrome, nephrotoxicity, metabolic acidosis, renal or liver failure, cerebral edema, and coma (Posadzki et al., 2013). Contamination and adulteration of TCM are core issues threatening medication safety, which need to be addressed through multiple dimensions such as technological innovation, strengthened supervision, and international cooperation to unify standards.
In recent years, several pharmacopeial and international standards have been established to improve quality assurance in botanical drug production. The Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 Edition) and WHO Monographs on Selected Medicinal Plants specify detailed requirements for botanical identification, permissible levels of heavy metals, pesticide residues, and microbial contamination (Leong et al., 2020). In parallel, modern analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography, liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, and emerging molecular tools like DNA barcoding and metabarcoding have greatly improved the accuracy of species authentication and detection of adulterants (Bogusz et al., 2006; Techen et al., 2014). Integration of these pharmacopeial standards and analytical methods provides a practical and effective framework for ensuring the safety, consistency, and authenticity of TCM products (Wang et al., 2023).
Future research should focus on the toxic mechanisms and risk thresholds of contaminants to provide a basis for formulating scientific limit standards.
6 Conclusion
This review has synthesized evidence on the efficacy, safety, and potential mechanisms of selected TCM interventions for post-stroke cerebral edema. Clinical evidence, primarily from preliminary studies, suggests that specific TCM formulations can reduce cerebral edema volume and improve neurological function with a generally acceptable safety profile. The preclinical findings summarized herein indicate that these benefits may be mediated by multi-target effects, including the regulation of ion homeostasis and aquaporins, inhibition of neuroinflammatory cascades, protection of the blood-brain barrier, and mitigation of oxidative stress and apoptosis.
While osmotic agents and surgery remain the standard of care, the profiled TCM interventions hold promise as adjunctive therapies due to their potential to simultaneously target multiple interconnected pathways in the edema pathological network. However, this very complexity necessitates future research that prioritizes rigorous, large-scale clinical trials to confirm efficacy, standardized safety monitoring, and mechanistic studies to establish causal relationships in humans and identify the key active constituents. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial to translate these promising preclinical findings into validated therapeutic strategies.
Author contributions
JH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YJ: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision. YC: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – review and editing. MW: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review and editing. JW: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang University (XY2024028 to YJ).
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our appreciation to all authors of eligible studies which were included in the review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1709821/full#supplementary-material
References
Bai, X., Zheng, E., Tong, L., Liu, Y., Li, X., Yang, H., et al. (2024). Angong Niuhuang Wan inhibit ferroptosis on ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke by activating PPARγ/AKT/GPX4 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 321, 117438. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117438
Bogusz, M. J., Hassan, H., Al-Enazi, E., Ibrahim, Z., and Al-Tufail, M. (2006). Application of LC-ESI-MS-MS for detection of synthetic adulterants in herbal remedies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 41 (2), 554–564. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2005.12.015
Cai, M., Yu, Z., Wang, L., Song, X., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., et al. (2016). Tongxinluo reduces brain edema and inhibits post-ischemic inflammation after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 181, 136–145. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.01.026
Cao, G., Ye, X., Xu, Y., Yin, M., Chen, H., Kou, J., et al. (2016). YiQiFuMai powder injection ameliorates blood-brain barrier dysfunction and brain edema after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 10, 315–325. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S96818
Chen, A., Xu, Y., and Yuan, J. (2018). Ginkgolide b ameliorates NLRP3 inflammasome activation after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the neonatal male rat. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 69, 106–111. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2018.07.004
Chen, Z. Z., Gong, X., Guo, Q., Zhao, H., and Wang, L. (2019). Bu yang huan wu decoction prevents reperfusion injury following ischemic stroke in rats via inhibition of HIF-1 alpha, VEGF and promotion beta-ENaC expression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 228, 70–81. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2018.09.017
Chen, Y., Chen, S., Chang, J., Wei, J., Feng, M., and Wang, R. (2021). Perihematomal edema after intracerebral hemorrhage: an update on pathogenesis, risk factors, and therapeutic advances. Front. Immunol. 12, 740632. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.740632
Chen, Y. Y., Gong, Z. C., Zhang, M. M., and Huang, Z. H. (2024). Brain-targeting emodin mitigates ischemic stroke via inhibiting AQP4-mediated swelling and neuroinflammation. Transl. Stroke Res. 15 (4), 818–830. doi:10.1007/s12975-023-01170-4
Chen, H., Luo, Y., Tsoi, B., Gu, B., Qi, S., and Shen, J. (2022). Angong niuhuang wan reduces hemorrhagic transformation and mortality in ischemic stroke rats with delayed thrombolysis: involvement of peroxynitrite-mediated MMP-9 activation. Chin. Med. 17 (1), 51. doi:10.1186/s13020-022-00595-7
Chen, S., Li, L., Peng, C., Bian, C., Ocak, P. E., Zhang, J. H., et al. (2022). Targeting oxidative stress and inflammatory response for blood-brain barrier protection in intracerebral hemorrhage. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 37 (1-3), 115–134. doi:10.1089/ars.2021.0072
Cheng, Y., Li, S., Liu, Y., Li, J., Chen, Y., and Zhao, H. (2020). Treatment of brain edema by wogonoside is associated with inhibition of neuronal apoptosis and SIRT1 activation in rats. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, e921250. doi:10.12659/MSM.921250
Cho, S. O., Ban, J. Y., Kim, J. Y., Ju, H. S., Lee, I. S., Song, K. S., et al. (2009). Anti-ischemic activities of aralia cordata and its active component, oleanolic acid. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32 (6), 923–932. doi:10.1007/s12272-009-1615-1
Choi, M., Lim, C., Lee, B. K., and Cho, S. (2022). Amelioration of brain damage after treatment with the methanolic extract of glycyrrhizae radix et rhizoma in mice. Pharmaceutics 14 (12), 2776. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14122776
Cook, A. M., Morgan, J. G., Hawryluk, G., Mailloux, P., Mclaughlin, D., Papangelou, A., et al. (2020). Guidelines for the acute treatment of cerebral edema in neurocritical care patients. Neurocrit. Care 32 (3), 647–666. doi:10.1007/s12028-020-00959-7
Cooper, D. J., Rosenfeld, J. V., Murray, L., Arabi, Y. M., Davies, A. R., D’Urso, P., et al. (2011). Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 364 (16), 1493–1502. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102077
Dewi, M. K., Chaerunisaa, A. Y., Muhaimin, M., and Joni, I. M. (2022). Improved activity of herbal medicines through nanotechnology. Nanomaterials 12 (22), 4073. doi:10.3390/nano12224073
Fan, J. H. (2019). Efficacy observation of “tongfu method” (purging fu-organs method) in the treatment of cerebral edema after cerebral hemorrhage of phlegm-heat and fu-organ excess type. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 12 (13), 83–84. doi:10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2019.13.046
Fang, J., Wang, Z., and Miao, C. Y. (2023). Angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 44 (7), 1305–1321. doi:10.1038/s41401-023-01061-2
Fei, Y. X., Wang, S. Q., Yang, L. J., Qiu, Y. Y., Li, Y. Z., Liu, W. Y., et al. (2017). Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge (danshen) extract attenuates permanent cerebral ischemia through inhibiting platelet activation in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 207, 57–66. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.06.023
Feng, Y. M., and Yang, H. (2015). Observation on the awakening effect of angong niuhuang wan in the treatment of comatose patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 21 (06), 179–182. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2015060179
Fu, Q. H., Yang, H. J., Xie, J., and Zhou, B. (2019). Efficacy observation of changpu yujin decoction on cerebral edema after craniotomy for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Med. J. Natl. Defending Forces Southwest China 29 (05), 611–613. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2019.05.037
Gao, J. Y., Shi, D. L., Gao, X. L., Liu, T. F., Wang, L. W., Cao, B., et al. (2020). Effect of huoxue ditan decoction combined with hyperbaric oxygen on neurological function recovery speed and hemodynamic level in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Chin. Archives Traditional Chin. Med. 38 (09), 213–216. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2020.09.054
Hatakeyama, M., Ninomiya, I., and Kanazawa, M. (2020). Angiogenesis and neuronal remodeling after ischemic stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 15 (1), 16–19. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.264442
He, D., Liu, Q. R., Zhao, J. X., Dong, Q., and Zhang, R. L. (2002). Efficacy observation of xueshuantong in the treatment of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Chin. J. Integr. Traditional West. Med. Crit. Care (01), 27–29. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1008-9691.2002.01.007
Hong, Q. L., Ding, Y. H., Chen, J. Y., Shi, S. S., Liang, R. S., and Tu, X. K. (2023). Schisandrin b protects against ischemic brain damage by regulating PI3k/AKT signaling in rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 29 (10), 885–894. doi:10.1007/s11655-023-3596-1
Hou, D. W., Zhu, Y. J., and Zhang, D. (2022). Effect observation of buyang huanwu decoction combined with ultra-early urokinase administration in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage after minimally invasive surgery. Sichuan J. Traditional Chin. Med. 40 (09), 124–127. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3649.2022.9.sczy202209037
Hu, N., Cheng, Z., Cao, Y., Li, X., Bai, F., Wang, J., et al. (2025). Therapeutic potential of shilong qingxue granule and its extract against glutamate induced neural injury: insights from in vivo and in vitro models. J. Ethnopharmacol. 342, 119396. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2025.119396
Huang, P., Zhou, C. M., Liu, Y. Y., Hu, B. H., Chang, X., Zhao, X. R., et al. (2012). Cerebralcare granule(r) attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Exp. Neurol. 237 (2), 453–463. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.07.017
Jia, X. Q., and Liu, J. C. (2007). Effect of buyang huanwu decoction on β2-microglobulin (β2-mg) and cerebral edema in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chin. J. Basic Med. Traditional Chin. Med. 7, 534–535. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-3250.2007.07.022
Jia, J. X., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z. L., Yan, X. S., Jin, M., Huo, D. S., et al. (2017). The inhibitory effects of dracocephalum moldavica l. (DML) on rat cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J. Toxicol. Env. Health Part A 80 (22), 1206–1211. doi:10.1080/15287394.2017.1367139
Jiang, Q. M., Yu, S., Dong, X. F., Wang, H. S., Hou, J., Huang, Z. C., et al. (2022). Predictors and dynamic nomogram to determine the individual risk of malignant brain edema after endovascular thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. J. Clin. Neurol. 18 (3), 298–307. doi:10.3988/jcn.2022.18.3.298
Jiao, J., and Xu, S. N. (2015). Clinical study on lingyang gouteng decoction (modified according to syndrome differentiation) in the treatment of elderly patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Chin. J. Pract. Nerv. Dis. 18 (07), 21–23. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5110.2015.07.011
Khadankhuu, B., Fei, Y., Li, X., Fang, W., and Li, Y. (2021). 10-o-(n n-dimethylaminoethyl)-ginkgolide b methane-sulfonate (XQ-1h) ameliorates cerebral ischemia via suppressing neuronal apoptosis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 30 (9), 105987. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105987
Kim, M., Byun, J., Chung, Y., Lee, S. U., Park, J. E., Park, W., et al. (2021). Reactive oxygen species scavenger in acute intracerebral hemorrhage patients: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Stroke 52 (4), 1172–1181. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032266
Kitchen, P., Salman, M. M., Halsey, A. M., Clarke-Bland, C., Macdonald, J. A., Ishida, H., et al. (2020). Targeting aquaporin-4 subcellular localization to treat central nervous system edema. Cell 181 (4), 784–799. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.037
Lai, J. N., Tang, J. L., and Wang, J. D. (2013). Observational studies on evaluating the safety and adverse effects of traditional Chinese medicine. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 697893. doi:10.1155/2013/697893
Lai, X., Xiong, Y., Zhou, J., Yang, F., Peng, J., Chen, L., et al. (2019). Verbascoside attenuates acute inflammatory injury in experimental cerebral hemorrhage by suppressing TLR4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 519 (4), 721–726. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.057
Lee, K., Lee, B. J., and Bu, Y. (2015). Protective effects of dihydrocaffeic acid, a coffee component metabolite, on a focal cerebral ischemia rat model. Molecules 20 (7), 11930–11940. doi:10.3390/molecules200711930
Leong, F., Hua, X., Wang, M., Chen, T., Song, Y., Tu, P., et al. (2020). Quality standard of traditional Chinese medicines: comparison between European pharmacopoeia and Chinese pharmacopoeia and recent advances. Chin. Med. 15, 76. doi:10.1186/s13020-020-00357-3
Li, C., Jia, W. W., Yang, J. L., Cheng, C., and Olaleye, O. E. (2022). Multi-compound and drug-combination pharmacokinetic research on Chinese herbal medicines. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 43 (12), 3080–3095. doi:10.1038/s41401-022-00983-7
Li, B., Zhang, B., Li, Z., Li, S., Li, J., Wang, A., et al. (2023). Ginkgolide C attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory impairments by suppressing CD40/NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 312, 116537. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116537
Li, P., Wang, S., and Chen, Y. (2024). Use of real-world evidence in regulatory decisions for traditional Chinese medicine: current status and future directions. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 58 (1), 34–41. doi:10.1007/s43441-023-00588-0
Li, R., Song, M., Zheng, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, S., and Fan, X. (2024). Naoxueshu oral liquid promotes hematoma absorption by targeting CD36 in M2 microglia via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 1), 117116. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117116
Li, X., Huang, L., Liu, G., Fan, W., Li, B., Liu, R., et al. (2020). Ginkgo diterpene lactones inhibit cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induced inflammatory response in astrocytes via TLR4/NF-κB pathway in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 249, 112365. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.112365
Li, Z., Xiao, G., Lyu, M., Wang, Y., He, S., Du, H., et al. (2020). Shuxuening injection facilitates neurofunctional recovery via down-regulation of g-CSF-mediated granulocyte adhesion and diapedesis pathway in a subacute stroke mouse model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 127, 110213. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110213
Liang, Z. K., and Yang, Y. L. (2012). Clinical observation of shuxuetong injection in the treatment of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Clin. Med. 32 (01), 57–59. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3548.2012.01.033
Liao, S. L., Kao, T. K., Chen, W. Y., Lin, Y. S., Chen, S. Y., Raung, S. L., et al. (2004). Tetramethylpyrazine reduces ischemic brain injury in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 372 (1-2), 40–45. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.09.013
Lin, S., Wu, J., Guo, W., and Zhu, Y. (2016). Effects of leonurine on intracerebral haemorrhage by attenuation of perihematomal edema and neuroinflammation via the JNK pathway. Pharmazie 71 (11), 644–650. doi:10.1691/ph.2016.6692
Lin, W., Hou, J., Han, T., Zheng, L., Liang, H., and Zhou, X. (2022). Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine for intracranial hemorrhage by promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 942657. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.942657
Liu, Y., Tang, G. H., Sun, Y. H., Lin, X. J., Wei, C., Yang, G. Y., et al. (2013). The protective role of tongxinluo on blood-brain barrier after ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 148 (2), 632–639. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.018
Liu, B. T., Li, Q., Sun, K., Pan, C. S., Huo, X. M., Huang, P., et al. (2024). Angong niuhuang wan ameliorates LPS-induced cerebrovascular edema by inhibiting blood‒brain barrier leakage and promoting the membrane expression of AQP4. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1421635. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1421635
Lu, W., and Wen, J. (2024). Crosstalk among glial cells in the blood-brain barrier injury after ischemic stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 61 (9), 6161–6174. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-03939-6
Lyu, J., Xie, Y., Sun, M., and Zhang, L. (2020). Efficacy and safety of xueshuantong injection on acute cerebral infarction: clinical evidence and GRADE assessment. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 822. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00822
Ma, Y., Hu, X., Shen, S., and Pan, D. (2024). Geniposide ameliorates brain injury in mice with intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. Neurol. Res. 46 (4), 346–355. doi:10.1080/01616412.2024.2321014
Markou, A., Unger, L., Abir-Awan, M., Saadallah, A., Halsey, A., Balklava, Z., et al. (2022). Molecular mechanisms governing aquaporin relocalisation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1864 (4), 183853. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183853
Mei, L., Fengqun, M., Xiaozhuo, L., Qing, W., Mingming, F., Zhengyao, Z., et al. (2022). Effect western medicines combined with nao-xue-shu in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage: a network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 892904. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.892904
Mi, Y., Jiao, K., Xu, J. K., Wei, K., Liu, J. Y., Meng, Q. Q., et al. (2021). Kellerin from ferula sinkiangensis exerts neuroprotective effects after focal cerebral ischemia in rats by inhibiting microglia-mediated inflammatory responses. J. Ethnopharmacol. 269, 113718. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113718
Nakano, T., Nishigami, C., Irie, K., Shigemori, Y., Sano, K., Yamashita, Y., et al. (2018). Goreisan prevents brain edema after cerebral ischemic stroke by inhibiting aquaporin 4 upregulation in mice. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 27 (3), 758–763. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.10.010
Nawabi, J., Flottmann, F., Hanning, U., Bechstein, M., Schon, G., Kemmling, A., et al. (2019). Futile recanalization with poor clinical outcome is associated with increased edema volume after ischemic stroke. Invest. Radiol. 54 (5), 282–287. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000539
Ng, F. C., Churilov, L., Yassi, N., Kleinig, T. J., Thijs, V., Wu, T. Y., et al. (2022). Microvascular dysfunction in blood-brain barrier disruption and hypoperfusion within the infarct posttreatment are associated with cerebral edema. Stroke 53 (5), 1597–1605. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.036104
Pan, Y. W., Wu, D. P., Liang, H. F., Tang, G. Y., Fan, C. L., Shi, L., et al. (2022). Total saponins of panax notoginseng activate akt/mTOR pathway and exhibit neuroprotection in vitro and in vivo against ischemic damage. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 28 (5), 410–418. doi:10.1007/s11655-021-3454-y
Pan, Y., Nie, L., Chen, W., Guan, D., Li, Y., Yang, C., et al. (2025). Buyang Huanwu Decoction prevents hemorrhagic transformation after delayed t-PA infusion via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis associated with microglial PGC-1α. J. Ethnopharmacol. 340, 119275. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.119275
Panickar, K. S., and Anderson, R. A. (2011). Effect of polyphenols on oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in neuronal death and brain edema in cerebral ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12 (11), 8181–8207. doi:10.3390/ijms12118181
Papagianni, M., Tziomalos, K., Kostaki, S., Angelopoulou, S. M., Christou, K., Bouziana, S. D., et al. (2018). Treatment with mannitol is associated with increased risk for in-hospital mortality in patients with acute ischemic stroke and cerebral edema. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 18 (5), 397–403. doi:10.1007/s40256-018-0285-0
Park, S. H., Kim, J. H., Park, S. J., Bae, S. S., Choi, Y. W., Hong, J. W., et al. (2011). Protective effect of hexane extracts of Uncaria sinensis against photothrombotic ischemic injury in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 138 (3), 774–779. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.10.026
Ping, N., Zuo, K., Cai, J., Rong, C., Yu, Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). Apigenin protects against ischemic stroke by increasing DNA repair. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1362301. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1362301
Posadzki, P., Watson, L., and Ernst, E. (2013). Contamination and adulteration of herbal medicinal products (HMPs): an overview of systematic reviews. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 69 (3), 295–307. doi:10.1007/s00228-012-1353-z
Qiao, N., An, Z., Fu, Z., Chen, X., Tong, Q., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Kinsenoside alleviates oxidative stress-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction via promoting nrf2/HO-1 pathway in ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 949, 175717. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175717
Sadeghian, N., Shadman, J., Moradi, A., Ghasem, G. M., and Panahpour, H. (2019). Calcitriol protects the blood-brain barrier integrity against ischemic stroke and reduces vasogenic brain edema via antioxidant and antiapoptotic actions in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 150, 281–289. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.06.010
Sanchez-Martinez, J. D., Valdes, A., Gallego, R., Suarez-Montenegro, Z. J., Alarcon, M., Ibanez, E., et al. (2022). Blood-brain barrier permeability study of potential neuroprotective compounds recovered from plants and agri-food by-products. Front. Nutr. 9, 924596. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.924596
Shang, L., Wang, X., Sun, H., Wei, W., Sun, Y., Cai, G., et al. (2022). Effects of the triple therapy of carnosine glycoside, edaravone, and xueshuantong in hemorrhagic cerebral infarction. Am. J. Transl. Res. 14 (2), 1024–1033. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35273704/
Shang, J., Huang, G., Wang, B., Wang, J., Wei, W., Cui, Y., et al. (2025). Shuxuetong injection inhibits pyroptosis in acute ischemic stroke via CD44/NLRP3/GSDMD signal. J. Ethnopharmacol. 345, 119618. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2025.119618
Song, J., Nie, Y., Wang, P., Lu, H., and Gao, L. (2021). Naoxueshu relieves hematoma after clot removal in acute spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Behav. 11 (1), e01957. doi:10.1002/brb3.1957
Song, J., Nie, Y., Qin, X., Wang, P., Lu, H., and Gao, L. (2022). Efficacy of naoxueshu in acute spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a multicenter observational study. Neurol. Sci. 43 (3), 1885–1891. doi:10.1007/s10072-021-05582-8
Sun, L., Yang, L., Fu, Y., Han, J., Xu, Y., Liang, H., et al. (2013). Capacity of HSYA to inhibit nitrotyrosine formation induced by focal ischemic brain injury. Nitric Oxide-Biol. Chem. 35, 144–151. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2013.10.002
Sun, S., Wang, Y., Wu, A., Ding, Z., and Liu, X. (2019). Influence factors of the pharmacokinetics of herbal resourced compounds in clinical practice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 1983780. doi:10.1155/2019/1983780
Sun, W., Zhang, L., Fang, Z., Han, L., Wang, Q., Leng, Y., et al. (2022). Shuxuetong injection and its peptides enhance angiogenesis after hindlimb ischemia by activating the MYPT1/LIMK1/cofilin pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 292, 115166. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115166
Sun, J., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Song, Y., Pan, B., Fan, B., et al. (2023). Neuroprotective effects of longxue tongluo capsule on ischemic stroke rats revealed by LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics approach. Chin. Herb. Med. 15 (3), 430–438. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2022.12.010
Sylvain, N. J., Salman, M. M., Pushie, M. J., Hou, H., Meher, V., Herlo, R., et al. (2021). The effects of trifluoperazine on brain edema, aquaporin-4 expression and metabolic markers during the acute phase of stroke using photothrombotic mouse model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1863 (5), 183573. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183573
Tan, L. L., Huang, R. S., Zhou, G., Chen, X. H., and Liu, Y. H. (2021). Clinical study on Jianshen lishui granule combined with furosemide in the treatment of secondary cerebral edema after intracerebral hemorrhage. China Med. Her. 18 (14), 72–75. doi:10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2021.14.018
Techen, N., Parveen, I., Pan, Z., and Khan, I. A. (2014). DNA barcoding of medicinal plant material for identification. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 25, 103–110. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2013.09.010
Tsoi, B., Chen, X., Gao, C., Wang, S., Yuen, S. C., Yang, D., et al. (2019a). Neuroprotective effects and hepatorenal toxicity of Angong Niuhuang Wan against ischemia-reperfusion brain injury in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 593. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00593
Tsoi, B., Wang, S., Gao, C., Luo, Y., Li, W., Yang, D., et al. (2019b). Realgar and cinnabar are essential components contributing to neuroprotection of Angong Niuhuang Wan with no hepatorenal toxicity in transient ischemic brain injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 377, 114613. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2019.114613
Tyagi, N., Qipshidze, N., Munjal, C., Vacek, J. C., Metreveli, N., Givvimani, S., et al. (2012). Tetrahydrocurcumin ameliorates homocysteinylated cytochrome-c mediated autophagy in hyperhomocysteinemia mice after cerebral ischemia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 47 (1), 128–138. doi:10.1007/s12031-011-9695-z
Vakili, A., Sharifat, S., Akhavan, M. M., and Bandegi, A. R. (2014). Effect of lavender oil (Lavandula angustifolia) on cerebral edema and its possible mechanisms in an experimental model of stroke. Brain Res. 1548, 56–62. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2013.12.019
Wan, Y., Holste, K. G., Hua, Y., Keep, R. F., and Xi, G. (2023). Brain edema formation and therapy after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurobiol. Dis. 176, 105948. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105948
Wang, J. (2018). Effect of Xueshuantong injection on neurological function, high-sensitivity c-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Chin. J. Ration. Drug Explor. 15 (07), 24–27. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2096-3327.2018.07.008
Wang, Y. F., Gu, Y. T., Qin, G. H., Zhong, L., and Meng, Y. N. (2013). Curcumin ameliorates the permeability of the blood-brain barrier during hypoxia by upregulating heme oxygenase-1 expression in brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 51 (2), 344–351. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-9989-4
Wang, J., Li, D., Hou, J., and Lei, H. (2018). Protective effects of geniposide and ginsenoside rg1 combination treatment on rats following cerebral ischemia are mediated via microglial microRNA-155-5p inhibition. Mol. Med. Rep. 17 (2), 3186–3193. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.8221
Wang, X. F., Tian, C., Zhang, Y., Yuan, M. C., Zhang, H. L., Wang, L. Q., et al. (2019). Effect of naoxueshu oral liquid on the expression of zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and aquaporin 4 (AQP4) in brain tissue of rats with intracerebral hemorrhage model. China Med. Her. 16 (16), 8–12.
Wang, Y., Xiao, G., He, S., Liu, X., Zhu, L., Yang, X., et al. (2020). Protection against acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by QiShenYiQi via neuroinflammatory network mobilization. Biomed. Pharmacother. 125, 109945. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109945
Wang, J., Yin, J., and Zheng, X. (2022a). Artemisinin upregulates neural cell adhesion molecule l1 to attenuate neurological deficits after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Brain Behav. 12 (5), e2558. doi:10.1002/brb3.2558
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, M., Sun, S., Zhong, Y., Han, L., et al. (2022b). Feasibility of catalpol intranasal administration and its protective effect on acute cerebral ischemia in rats via anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic mechanisms. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 16, 279–296. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S343928
Wang, P., Ren, Q., Shi, M., Liu, Y., Bai, H., and Chang, Y. Z. (2022c). Overexpression of mitochondrial ferritin enhances blood-brain barrier integrity following ischemic stroke in mice by maintaining iron homeostasis in endothelial cells. Antioxidants 11 (7), 1257. doi:10.3390/antiox11071257
Wang, X., Chen, G., Wan, B., Dong, Z., Xue, Y., Luo, Q., et al. (2022d). NRF1-mediated microglial activation triggers high-altitude cerebral edema. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 14 (5), mjac036. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjac036
Wang, H., Chen, Y., Wang, L., Liu, Q., Yang, S., and Wang, C. (2023). Advancing herbal medicine: enhancing product quality and safety through robust quality control practices. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1265178. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1265178
Wang, Z., Xue, F., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Hu, E., Zheng, Y., et al. (2024a). The cornel iridoid glycoside attenuated brain edema of the cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats by modulating the polarized aquaporin 4. Fitoterapia 177, 106098. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106098
Wang, Z., Zhang, X., Zhang, G., Zheng, Y. J., Zhao, A., Jiang, X., et al. (2024b). Astrocyte modulation in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: a promising therapeutic strategy. Exp. Neurol. 378, 114814. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114814
Wang, X., Shang, Z., Zhao, J., Hou, H., Li, Y., and Song, J. (2025). Efficacy and safety of early use of naoxueshu within 72 hours in the treatment of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a real-world retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 18, 2057–2065. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S511802
Wei, D. Z., Liu, H. Y., Wang, Z. H., Chu, J., Zhang, M., Han, H. Y., et al. (2024). Clinical study on erigeron breviscapus injection combined with edaravone in the treatment of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Mod. Drugs Clin. 39 (12), 3099–3103. doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2024.12.013
Widmann, C., Gandin, C., Petit-Paitel, A., Lazdunski, M., and Heurteaux, C. (2018). The traditional Chinese medicine MLC901 inhibits inflammation processes after focal cerebral ischemia. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 18062. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-36138-0
Xiang, Y., Yao, X., Wang, X., Zhao, H., Zou, H., Wang, L., et al. (2019). Houshiheisan promotes angiogenesis via HIF-1α/VEGF and SDF-1/CXCR4 pathways: in vivo and in vitro. Biosci. Rep. 39 (10), BSR20191006. doi:10.1042/BSR20191006
Xiao, W., He, Z., Luo, W., Feng, D., Wang, Y., Tang, T., et al. (2021). BYHWD alleviates inflammatory response by NIK-mediated repression of the noncanonical NF-κB pathway during ICH recovery. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 632407. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.632407
Xiao, H., Liu, S., Fang, B., Zhang, W., Wang, M., Ye, J., et al. (2024). Panax notoginseng saponins promotes angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Ginseng Res. 48 (6), 592–602. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2024.08.004
Xie, Y., Zhang, W., Wang, H., Hu, H., Zhang, S., Wang, S., et al. (2025). Application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling in the research of anti-HIV drugs. Curr. Drug Metab. 26, 472–488. doi:10.2174/0113892002392579250902053006
Xue, H., Feng, Z., Jin, C., Zhang, Y., Ai, Y., Wang, J., et al. (2025). Soy isoflavones protects against stroke by inhibiting keap1/NQO1/nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway: network pharmacology analysis combined with the experimental validation. Pharmaceuticals 18 (4), 548. doi:10.3390/ph18040548
Yang, B., Sun, Y., Lv, C., Zhang, W., and Chen, Y. (2020). Procyanidins exhibits neuroprotective activities against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting TLR4-NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway. Psychopharmacologia 237 (11), 3283–3293. doi:10.1007/s00213-020-05610-z
Yang, Y., Gao, H., Liu, W., Liu, X., Jiang, X., Li, X., et al. (2021). Arctium lappa l. roots ameliorates cerebral ischemia through inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and suppressing AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy. Phytomedicine 85, 153526. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153526
Yang, Y., Li, L., Yu, L., Xia, Y., Fang, Z., and Wang, S. (2024). Naringenin protected against blood brain barrier breakdown after ischemic stroke through GSK-3β/β-Catenin pathway. Neurochem. Res. 50 (1), 17. doi:10.1007/s11064-024-04259-w
Yao, Y. H. (2012). Clinical study on early application of shuxuetong injection in the treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage. Chin. J. Clin. Res. 25 (01), 38–39.
Yu, Z. S., Xu, D. Y., Yang, Y. L., and Pang, Q. Q. (2011). Systematic review of total saponins of Panax notoginseng injection in the treatment of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Youjiang Med. Univ. Natl. 33 (01), 19–23. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5817.2011.01.008
Yu, W. Y., Yu, J. B., and Luo, G. (2018). Clinical study on longhu xingnao granule in preventing cerebral edema formation after acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Guid. J. Traditional Chin. Med. Pharm. 24 (06), 63–65. doi:10.13862/j.cnki.cn43-1446/r.2018.06.021
Yu, J., Lü, Y., Li, Z. M., and Yu, X. (2023). Clinical study on sanyu tongluo decoction in the treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio-Cerebrovascular Dis. 21 (21), 4006–4010. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.21.028
Yu, J., Zhou, H., Guo, J., Chen, T., Shao, C., Pan, Z., et al. (2025). Zhongfeng Xingnao prescription alleviates injury of intracerebral hemorrhage via regulating the CaMKII/NF-κB p65/NLRP3/GSDMD signaling axis. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 15 (1), 84–92. doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.03.005
Zeng, J. (2015). Clinical observation on salvia miltiorrhiza injection combined with nimodipine in the treatment of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Forum Prim. Med. 19 (04), 490–491.
Zeng, X., Zhang, S., Zhang, L., Zhang, K., and Zheng, X. (2006). A study of the neuroprotective effect of the phenolic glucoside gastrodin during cerebral ischemia in vivo and in vitro. Planta Med. 72 (15), 1359–1365. doi:10.1055/s-2006-951709
Zeng, M., Zhou, H., He, Y., Wang, Z., Shao, C., Yin, J., et al. (2021). Danhong injection alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by improving intracellular energy metabolism coupling in the ischemic penumbra. Biomed. Pharmacother. 140, 111771. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111771
Zhang, S. X., and Chen, J. Y. (2016). Effect of angong niuhuang wan on serum nitric oxide (NO) and asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in comatose patients with acute cerebral infarction and its clinical efficacy observation. Mod. J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med. 25 (17), 1873–1875. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.17.017
Zhang, X., Chen, L., Dang, X., Liu, J., Ito, Y., and Sun, W. (2014). Neuroprotective effects of total steroid saponins on cerebral ischemia injuries in an animal model of focal ischemia/reperfusion. Planta Med. 80 (8-9), 637–644. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1368584
Zhang, X., Liu, X., Hu, G., Zhang, G., Zhao, G., and Shi, M. (2020). Ginsenoside rd attenuates blood-brain barrier damage by suppressing proteasome-mediated signaling after transient forebrain ischemia. Neuroreport 31 (6), 466–472. doi:10.1097/WNR.0000000000001426
Zhang, B., Zeng, Z., and Wu, H. (2021). A network pharmacology-based analysis of the protective mechanism of miao medicine xuemaitong capsule against secondary brain damage in the ischemic area surrounding intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 377 (1), 86–99. doi:10.1124/jpet.120.000083
Zhang, C., Shi, Z., Xu, Q., He, J., Chen, L., Lu, Z., et al. (2023). Astragaloside IV alleviates stroke-triggered early brain injury by modulating neuroinflammation and ferroptosis via the nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Acta Cir. Bras. 38, e380723. doi:10.1590/acb380723
Zhao, Y. C., Wang, T., and Gao, Y. P. (2010). Clinical observation of huoxue tongli decoction in the treatment of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. China J. Traditional Chin. Med. Pharm. 25 (10), 1697–1699.
Zhao, B., Shi, Q. J., Zhang, Z. Z., Wang, S. Y., Wang, X., and Wang, H. (2018). Protective effects of paeonol on subacute/chronic brain injury during cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 15 (4), 3836–3846. doi:10.3892/etm.2018.5893
Zhao, G. F., Liu, D. L., Xu, Y. J., Wang, J. Y., and Wang, J. (2023). Clinical effect of xiaoxuming decoction in the treatment of cerebral edema after large-area cerebral infarction. Chin. Archives Traditional Chin. Med. 41 (01), 179–182. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2023.01.040
Zhao, Y., Cui, W., Xie, T., Zhao, K., Li, Y., Wan, Y., et al. (2024). Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage: protocol for a randomized placebo-controlled double-blinded multicenter trial. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 53 (4), 501–508. doi:10.1159/000534761
Zheng, Y. Q., Liu, J. X., Wang, J. N., and Xu, L. (2007). Effects of crocin on reperfusion-induced oxidative/nitrative injury to cerebral microvessels after global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1138, 86–94. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.12.064
Zheng, L., Meng, L., Liang, H., and Yang, J. (2023). Sanhua decoction: current understanding of a traditional herbal recipe for stroke. Front. Neurosci. 17, 1149833. doi:10.3389/fnins.2023.1149833
Zheng, F., Guo, X., Yan, Q., Zhou, Y., Hu, E., Zhu, H., et al. (2025). Hydroxysafflor yellow a attenuates the blood-brain barrier dysfunction and neuroinflammation through anti-inflammatory microglial polarization after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neuropharmacology 278, 110576. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2025.110576
Zhong, X. Y., Yang, W. Q., and Ye, R. H. (2019). Clinical study on liangxue sanyu decoction combined with nimodipine in the treatment of ischemic brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. China Med. Pharm. 9 (05), 57–59.
Zhu, H., Wang, Z., Xing, Y., Gao, Y., Ma, T., Lou, L., et al. (2012). Baicalin reduces the permeability of the blood-brain barrier during hypoxia in vitro by increasing the expression of tight junction proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 141 (2), 714–720. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.063
Glossary
ACI Acute Cerebral Infarction
ADL Activities of Daily Living
ADMA Asymmetric Dimethylarginine
AIF Apoptosis-Inducing Factor
AIS Acute Ischemic Stroke
Ang-1 Angiopoietin-1
AQP4 Aquaporin 4
BAI Barthel Index
BBB Blood-Brain Barrier
BCCAO Bilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion
BDNF Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
bid bis in die (twice daily)
BMVECs Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
CaMKII Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II
CAT Catalase
CBS Cystathionine Beta-Synthase
CD40 Cluster of Differentiation 40
CD44 Cluster of Differentiation 44
CD163 Cluster of Differentiation 163
CNKI China National Knowledge Infrastructure
CXCR4 C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 4
EB Evans Blue
EGFR Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
ERK Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase
ESS European Stroke Scale
ET Endothelin
FIB Fibrinogen
GAPDH Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
GCS Glasgow Coma Scale
GSDMD Gasdermin D
GSH Glutathione
GSH-px Glutathione Peroxidase
GPI Glycosylphosphatidylinositol
Hcy Homocysteine
HIF-1α Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-alpha
HMBG1 High-Mobility Group Box 1
HO-1 Heme Oxygenase-1
HSP Heat Shock Protein
hs-CRP High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein
ICH Intracerebral Hemorrhage
ICAM-1 Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1
IFN-γ Interferon Gamma
iNOS Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
IL Interleukin
ivgtt intravenous drip
JAM-1 Junctional Adhesion Molecule 1
JNK c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase
Keap1 Kelch-like ECH-Associated Protein 1
LC3-II Microtubule-Associated Protein 1A/1B-Light Chain 3-II
LDH Lactate Dehydrogenase
LPS Lipopolysaccharide
MABP Mean Arterial Blood Pressure
MCAO Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
MBP Myelin Basic Protein
MDA Malondialdehyde
miR-155-5p MicroRNA-155-5p
MMP Matrix Metalloproteinase
MPO Myeloperoxidase
NGF Nerve Growth Factor
NIHSS National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
NO Nitric Oxide
NQO1 NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1
Nrf2 Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2
NSE Neuron-Specific Enolase
OCD/R Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation
p-AKT Phosphorylated AKT
PDK1 Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 1
PI3K Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase
PKC Protein Kinase C
po per os (oral administration)
PRO Procalcitonin
q4h quaque 4 hora (every 4 hours)
qd quaque die (once daily)
RBMEC Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
RCT Randomized Controlled Trial
ROS Reactive Oxygen Species
S-100β S100 Calcium-Binding Protein Beta
SDF-1α Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1-alpha
SLC7A11 Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11
T-AOC Total Antioxidant Capacity
TCM Traditional Chinese Medicine
TGF-β1 Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1
TJK Tight Junction Protein
TLR4 Toll-Like Receptor 4
TNF-α Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha
tid ter in die (three times daily)
VEGFA Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
VEGFR2 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2
VCAM-1 Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1
ZO-1 Zonula Occludens-1
β2-MG Beta-2-Microglobulin
Keywords: stroke, cerebral edema, traditional Chinese medicine, safety, botanical drug
Citation: Huang J, Jin Y, Chen Y, Wang M and Wu J (2025) Selected traditional Chinese medicine interventions for post-stroke cerebral edema: a review integrating clinical evidence and mechanistic insights. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1709821. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1709821
Received: 23 September 2025; Accepted: 17 November 2025;
Published: 10 December 2025.
Edited by:
Sushil Kumar Chaudhary, Institute of Bio-Resources and Sustainable Development (IBSD), IndiaReviewed by:
Sharanbasappa Durg, Independent Researcher, Kalaburagi, IndiaNeeraj Kumar Patel, Bombay Hemp Company Private Limited, India
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Jin, Chen, Wang and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jian Wu, QXJjaG9uMDkwMkAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Junyue Huang1†
Junyue Huang1† Jian Wu
Jian Wu