Abstract
Introduction:
Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction (HLJDD), a botanical drug used in traditional medicine, has been used in the management of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the mechanisms underlying its preventive effects remain inadequately understood, particularly due to the absence of metabolomic studies examining alterations in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) metabolites. Moreover, the potential toxicities and side effects of HLJDD necessitate further pharmacological investigation. This study aims to explore the differential effects of HLJDD on AD model rats and healthy controls through a metabolomics approach and uncover the underlying mechanisms based on changes in serum and CSF metabolites. The findings are expected to provide a scientific foundation for enhancing the clinical safety and rational use of HLJDD.
Methods:
The composition of HLJDD was characterized by UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap HRMS. Aβ1-42-induced SD rats served as the AD animal model. Rats in the sham + HLJDD and Aβ1-42 + HLJDD groups (0.604 g/kg freeze-dried powder) were treated with HLJDD via gavage for 28 days. Nissl staining was performed to assess hippocampal neuronal changes, while H&E staining was used to evaluate histopathological alterations in the brain, liver, kidneys, stomach, large intestine, and small intestine. Aβ expression was determined using IHC and ELISA, and inflammatory levels in both peripheral and central systems were quantified by ELISA. MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression were analyzed through IHC. LC-MS was employed to investigate metabolic variations in serum and CSF.
Results:
HLJDD reduced Aβ deposition in Alzheimer’s disease rats, enhanced neuronal survival, reduced inflammation, preserved blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity, and alleviated damage to the brain, kidneys, and stomach. These therapeutic effects were associated with the arginine biosynthesis pathway and ferroptosis. In contrast, HLJDD induced peripheral and central inflammation, impaired neuronal function, compromised BBB integrity, and caused damage to the liver, kidneys, and large intestine in normal rats. These adverse effects were linked to disruptions in aminobenzoate degradation and nucleotide metabolism.
Conclusion:
HLJDD may alleviate Aβ-induced damage repair in Alzheimer’s disease rats, but it also induces varying degrees of toxicity in normal rats.
1 Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by memory loss and cognitive impairments (Blanchard et al., 2022). Recent research has focused on the pathogenesis of AD, with Amyloid-beta (Aβ)-mediated neuroinflammation identified as a central mechanism in its development (Alam et al., 2016; Finneran and Nash, 2019; Huang and Mucke, 2012; Leng and Edison, 2021). Soluble Aβ oligomers (AβOs) correlate more strongly with the severity of cognitive decline than other Aβ species. The neurotoxic effects of Aβ aggregates, particularly AβOs, within the brain have been widely acknowledged (Haass and Selkoe, 2007). Inflammatory cytokine overexpression promotes Aβ deposition, leading to neuronal damage and synaptic loss (Gehrmann et al., 1995). This inflammatory environment significantly compromises the blood-brain barrier (BBB), exacerbating the inflammatory response and influencing AD progression (Halliday et al., 2016; Poole et al., 2014). Despite the approval of Aβ-targeted drugs by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), their high cost, adverse effects, and contraindications hinder their clinical application and widespread use (Hollmann, 2022).
Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction (HLJDD), a traditional herbal formulation consisting of Rhizoma Coptidis, Radix Scutellariae, Cortex Phellodendri, and Fructus Gardeniae, originated in the Zhou-Hou-Bei-Ji-Fang (Emergency Prescriptions Handbook, circa 4th century CE), as outlined in classical pharmacopeia (Jy et al., 2023). Its long-standing clinical relevance is reflected in its inclusion in both Qi-Xiao-Liang-Fang (1470 CE) and Wai-Tai-Mi-Yao (752 CE), continuing to be used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for over eighteen centuries, primarily for heat-clearing and detoxifying purposes (X. Yang et al., 2024). Modern research has expanded its pharmacological scope, demonstrating potential therapeutic benefits in metabolic disorders, including tumors, type 2 diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases like AD (Durairajan et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2015; X.-J. Zhang et al., 2014). In recent years, HLJDD has been employed in the treatment of AD in China and other Asian countries (Fang et al., 2013; Okamoto et al., 2013). HLJDD can modulate gut microbiota dysbiosis, reduce Aβ accumulation, and alleviate cognitive dysfunction (X et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2023). Furthermore, clinical trials have shown that HLJDD, when combined with donepezil, enhances cognitive function in patients with AD and potentiates the anti-inflammatory effects of donepezil (Xu et al., 2023). However, the precise mechanisms underlying HLJDD’s effects on AD remain unclear. Currently, most research has predominantly focused on specific mechanistic pathways, lacking a global profile of metabolic changes in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). To capture the holistic and systemic mechanisms of this multi-component herbal medicine, we adopted a metabolomics approach, which provides insights beyond targeted analysis and may elucidate novel mechanisms of action. With the increasing clinical use of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), reports of adverse reactions have also risen. Yamano et al. suggested that metabolites of Gardenia components could be linked to hepatotoxicity (Yamano et al., 1988; Yamano et al., 1990), while other studies propose that Gardenia may reduce hepatotoxicity in rats (L et al., 2017) and exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (Shin et al., 2021). This raises questions regarding its hepatoprotective versus hepatotoxic effects. Coptis chinensis, a bitter, cold-natured botanical drug containing berberine, is known to bind to bitter taste receptors (TAS2Rs). In individuals sensitive to these receptors, this interaction may induce vomiting and diarrhea (Avau et al., 2015; Meyerhof et al., 2010; Yue et al., 2018). The Medical Classic of the Yellow Emperor asserts that when therapeutic interventions are precisely tailored to a patient’s pathophysiological profile and accurately implemented, even pharmacologically toxic substances can be utilized safely (Peng et al., 2015). Therefore, the toxicological evaluation of Chinese materia medica requires a comprehensive approach that integrates the recipient’s constitutional traits and current homeostatic conditions. Presently, most toxicological studies of TCM focus on organ damage induced by single botanical drugs, which does not align with the clinical application of botanical drug formulations (Lu et al., 2020). This approach neglects the differential effects of multiple components in botanical drug formulations under pathological and physiological conditions, limiting a full understanding of HLJDD’s scientific basis and its clinical relevance. This gap underscores the rationale for including a healthy control group in our study. Comparing the effects of HLJDD on AD rats versus normal rats is essential to determine whether its therapeutic and adverse effects are disease-state specific. This design enables the distinction between genuine disease-modifying effects and general physiological impacts, thereby critically informing its safety profile and appropriate clinical application for AD patients.
In this study, the differential effects of HLJDD in AD and normal rats were examined. HLJDD was administered orally at a dose of 3 g/kg (equivalent to the crude drug), which was determined to be the optimal concentration based on our previous research. Since the primary aim was to compare the effects of HLJDD between the two groups, only this single dose was used in the experiments. In this study, we investigated the differential effects of HLJDD in AD and normal rats were examined. A single oral dose of 3 g/kg (crude drug) HLJDD was used. The selection of this dose was based on a systematic dose-response investigation in our previous work (Dong et al., 2021), which tested 1.5, 3, and 6 g/kg (crude drug). The 3 g/kg dose was determined to be optimal as it consistently produced significant improvements in learning and memory behaviors and effectively downregulated key molecules of the hippocampal NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β pathway. Its efficacy was comparable to the 6 g/kg dose across most key indicators, making it the most cost-effective choice. As the primary aim of the present study was to compare the effects of HLJDD between groups rather than to re-establish dose dependency, this single, efficacious dose was deemed appropriate.
Pathological changes in AD were assessed through H&E staining and Nissl staining of brain tissue, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for Aβ detection. Peripheral and central inflammatory cytokine levels, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-4 (IL-4), were measured via ELISA in serum and CSF. BBB integrity was evaluated through IHC detection of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Pathological changes in the liver, kidneys, stomach, large intestine, and small intestine were observed via H&E staining. Additionally, metabolic profiles in serum and CSF were analyzed. By characterizing the distinct impacts of HLJDD on rats in different physiological states, this study offers valuable insights into its potential rational clinical application for AD treatment and strategies to enhance its clinical safety.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Chemical regents
Rhizoma Coptidis, Radix Scutellariae, Cortex Phellodendri, and Fructus Gardeniae were sourced from Sichuan Neautus Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd. (China, production batch numbers: 2207067, 2205041, 2208121, 2208046). β-Amyloid 1-42 (Aβ1-42 oligomer) was obtained from Med Chem Express (United States, production batch number: HY-P1388). Huperzine A was purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (China, production batch number: 102518-79-6). The IHC antibodies for MMP-2 and MMP-9 were sourced from ZEN-BIOSCIENCE (China, production batch number: R380817, 1:50) and Servicobio (China, production batch number: GB11132, 1:100), respectively. The Aβ antibody was obtained from Proteintech (China, production batch number: 25524-1-AP, 1:200). The ELISA kits for TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-4 were purchased from JINGMEI (China, TNF-α: production batch number: JM-01587R1; IL-1β: production batch number: JM-01454R1; IL-4: production batch number: JM-01598R1). The Aβ42 ELISA kit was obtained from Fine (China, production batch number: ER0755).
2.2 Preparation and quality control of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction
The HLJDD formulation was prepared using a specific ratio of its components: Rhizoma Coptidis, Radix Scutellariae, Cortex Phellodendri, and Fructus Gardeniae in a dry weight ratio of 9:6:6:9 (Table 1). All botanical drugs were purchased from Sichuan Neautus Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd., and authenticated as genuine by Professor Yuntong Ma from the College of Pharmacy, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The botanical drugs were thoroughly mixed, and water was added in successive volumes of 10, 8, and 8 times the dry botanical drug weight, respectively. The mixture was soaked for 30 min and then extracted three times at 120 °C. The extracts were stored at 4 °C for preservation. After two rounds of extraction, the combined liquids were concentrated using a rotary evaporator under reduced pressure and then freeze-dried. Regarding the dosage, the human clinical dose was set at 30 g of crude drug per day for a 60-kg adult. Based on established allometric scaling principles, the equivalent dosage for rats was calculated to be 6 times that of humans, resulting in 3 g/kg/day of crude drug. Considering the yield of the lyophilized powder was 20.13%, the final administered dose was determined as 0.604 g/kg, prepared at a concentration of 0.06 g/mL.
TABLE 1
| Chinese name | Pharmaceutical name | Plant name | Weight(g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huanglian | Coptidis rhizoma | Coptis chinensis Franch | 9 |
| Huangqin | Scutellariae radix | Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | 6 |
| Huangbai | Phellodendri chinensis cortex | Phellodendron Chinense Schneid | 6 |
| Zhizi | Gardenia fructus | Gardenia jasminoides Ellis | 9 |
Composition of HLJDD.
The HLJDD powder was dissolved in 80% methanol, sonicated, and mixed for 40 min, then passed through a 0.22 μm microporous filter membrane for detection. The final analysis was conducted using UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap HRMS. The experiments were performed on a Thermo Scientific UPLC system (Waltham, MA, United States) coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS, Q Exactive Orbitrap). Chromatographic separation was carried out on an Ultimate UHPLC XB-C18 column (2.1 mm × 100 mm, 1.8 µm). Data were collected in full-scan mode (Full-MS), with a scanning range of m/z 100–1,500 Da (resolution: 35,000). A secondary scan (dd-MS2, m/z 100–1,500 Da, resolution: 17,500) was also employed.
2.3 Experimental animals
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (specific pathogen-free [SPF] grade, 8 weeks old, weighing 200 ± 20 g) were obtained from Chengdu DOSSY Experimental Animal Co., Ltd. The animals were housed in the laboratory of the School of Pharmacy at Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, under license number SYXK (Sichuan) 2020-030. Rats were acclimatized for 1 week at a temperature of 22 °C ± 1 °C and relative humidity of 55% ± 5%. Each rat was provided with 30 g of standard feed daily and had ad libitum access to water.
In this study, a total of 30 rats were randomly allocated into five groups (n = 6 per group) as follows: the Sham group, the Aβ1-42 group, the Huperzine A (Hup A) + Aβ1-42 group, the Sham + HLJDD group, and the HLJDD + Aβ1-42 group. The randomization was performed using a random number table generated by Microsoft Excel, where each animal was assigned a number and then allocated to one of the groups based on the numerical order to ensure an unbiased grouping procedure. Regarding the interventions, the Sham and Sham + HLJDD groups received bilateral injections of 5 μL of control solvent into the hippocampal CA1 region, while the other three groups were administered 5 μL of Aβ1-42 bilaterally into the same region to establish the model. Aβ1-42 oligomer (5 mg) was dissolved in 1,130 μL of Hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) to create a uniform solution, which was incubated. Then, DMSO and PBS were added to reach a final concentration of 4 μg/μL. The solution was incubated at 4 °C for 24 h. For the control solvent, Aβ1-42 oligomers were omitted, with all other conditions remaining identical. After a 7-day recovery period, all groups received continuous gavage for 28 days.
The gavage doses for rats were calculated based on human equivalent doses adjusted for body surface area: HLJDD 0.604 g/kg freeze-dried powder (equivalent to 3 g/kg crude drug; yield 20.13%) and Hup A 2 × 10−5 g/kg. Control rats were given equivalent ultrapure water, with each group receiving 1 mL/100 g by gavage. The body weight of the rats was recorded (in grams) every 7 days. On the 28th day of the experiment, the rats were euthanized via intraperitoneal injection of 2% pentobarbital sodium 1 h after gavage. Blood samples were collected via abdominal aorta puncture, and CSF, brain, liver, kidney, large intestine, small intestine, and stomach tissues were harvested for subsequent analysis. All animal experiments were conducted in strict accordance with relevant laws and ethical guidelines and were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Approval No.: 2024DL-018; Date of approval: 3 June 2024).
2.4 Histopathological analysis
Tissues from the brain, liver, kidney, large intestine, small intestine, and stomach were fixed, embedded, and sectioned. Dewaxing and hydration were performed, followed by H&E staining. Brain tissue underwent both H&E and Nissl staining, and neutral resin adhesive was used for transparent sealing. Morphological and structural changes in the tissues were observed under a light microscope.
2.5 Measurement of cytokines
Blood and CSF (cisterna magna) were collected from each rat, centrifuged at 4 °C, 3,000 rpm for 10 min. All procedures were carried out according to the kit instructions. The control was diluted to the specified multiplicity as instructed. Seven concentration series were established for each inflammatory factor (IL-4, TNF-α, IL-1β) and Aβ42 to prepare the standard curves, with the corresponding concentrations determined based on the optical density (OD) values of the samples.
2.6 Immunohistochemical analysis
Brain tissues were fixed in paraformaldehyde solution, dehydrated with alcohol, subjected to xylene transparency, and embedded using a three-step dip-waxing method, followed by sectioning. The slices were baked in an oven for routine dewaxing, rinsed with PBS three times, treated with 3% H2O2 for 10 min, and rinsed again with PBS three times. Antigen retrieval was performed using a microwave method, followed by additional PBS rinsing. The PBS was blotted dry, and the tissue sections were circled with an IHC pen. Bovine serum blocking solution was added for 20 min at room temperature. Primary antibodies against MMP-2 (1:50), MMP-9 (1:100), and Aβ42 (1:200) were applied and incubated in a wet box at 4 °C overnight. The sections were rinsed with PBS, and DAB was used for color development at room temperature. Hematoxylin was used for nuclear counterstaining, followed by rinsing with running water. The sections were then dehydrated, mounted, and images were captured using a microcamera for analysis and counting.
2.7 Detection of serum and CSF metabolites using liquid chromatography mass spectrometer (LC-MS)
For LC-MS analysis, 100 μL of serum and 100 μL of CSF were mixed with 400 μL of extraction solution, vortexed for 30 s, and extracted using low-temperature ultrasonic extraction. The supernatant was transferred to an injection vial for online analysis after re-solution. Additionally, 20 μL of each sample was mixed separately as quality control (QC) samples. LC-MS was performed using a UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X system. Chromatographic conditions included an ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm i.d., 1.8 µm; Waters, Milford, United States of America), with mobile phase A consisting of 95% water and 5% acetonitrile (containing 0.1% formic acid) and mobile phase B consisting of 47.5% acetonitrile, 47.5% isopropanol, and 5% water (containing 0.1% formic acid). The injection volume was 3 μL, and the column temperature was set to 40 °C.
2.8 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0, and data were graphed using GraphPad Prism 7 software. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by LSD post hoc tests was applied to all dependent variables between groups. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), with P-values <0.05 considered significant. The value of n refers to the number of rats. Raw data generated by UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap HRMS were processed using Xcalibur software (version 3.1) for relative quantification. Metabolomics analysis was conducted using ProgenesisQI software (Waters Corporation, Milford, United States of America).
3 Results
3.1 UPLC-Q-exactive orbitrap HRMS analysis identified the primary chemical metabolites of HLJDD
The primary chemical metabolites of HLJDD were identified using UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap HRMS. The total ion flow diagram of HLJDD in both negative and positive ion modes is shown in Figure 1. A total of 23 metabolites, including Neochlorogenic acid, Geniposide, Berberine, Scutellarin, and Baicalin, were identified. Detailed information about these metabolites is provided in Table 2.
FIGURE 1
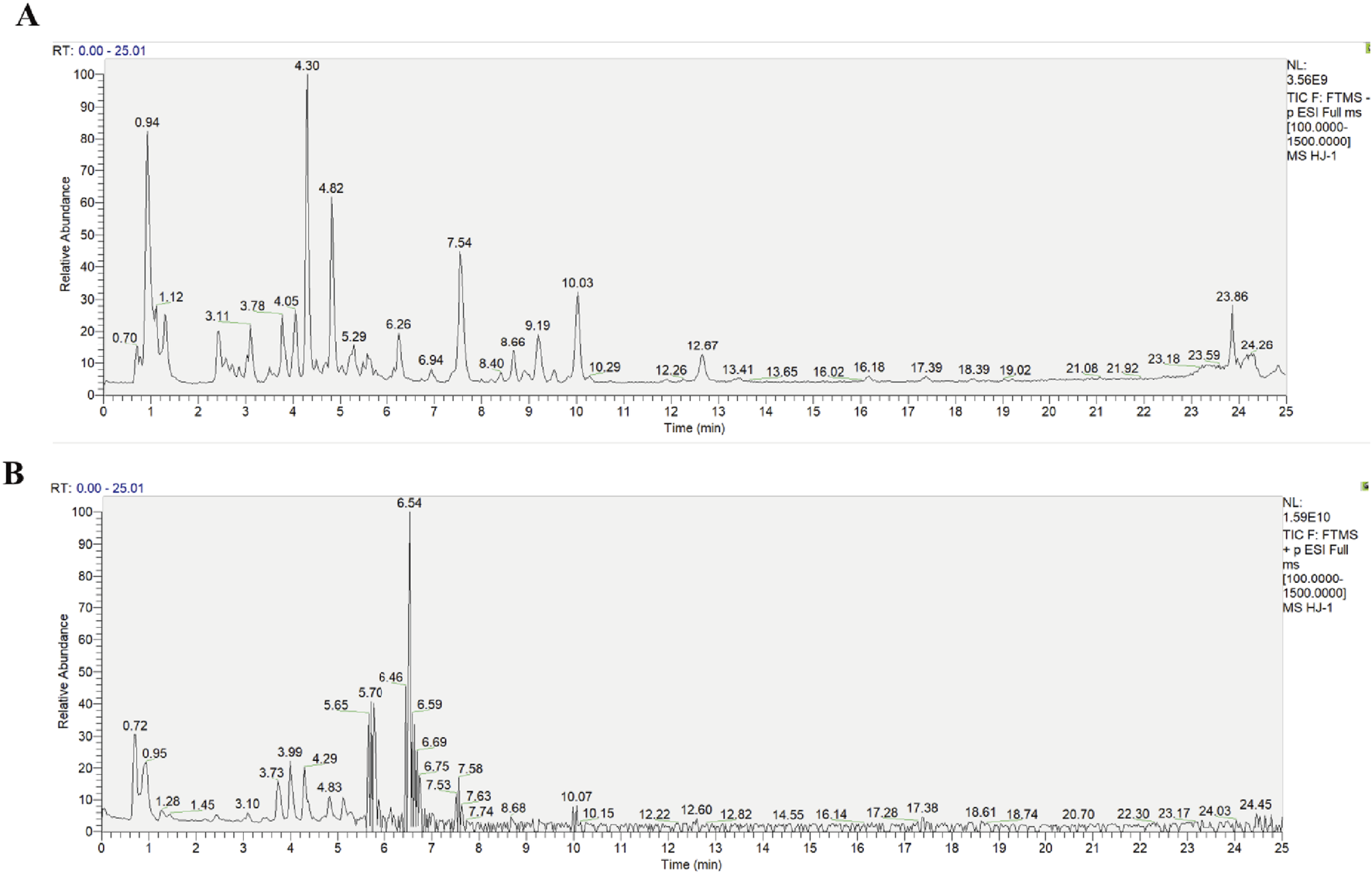
Diagram of the total ion flow of the traditional Chinese medicine metabolite Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction in ion modes. (A) Negative ion mode, (B) Positive ion mode.
TABLE 2
| No. | Formula | tR/min | Theoretical (Da) | Calculated mass (Da) | Error (ppm) | Adducts | MS fragmentation | Component name | mzCloud best match | mzVault best match |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C16H18O9 | 3.19 | 355.09528 | 355.10288 | 0.56 | [M+H]+1 | 191.05556, 179.03435, 135.04431 | Neochlorogenic acid | 95.9 | 94.3 |
| 2 | C16H18O9 | 3.84 | 353.09515 | 353.08781 | 0.23 | [M-H]−1 | 191.05573 | Chlorogenic acid | 99.9 | 95.1 |
| 3 | C20H23NO4 | 3.99 | 342.16324 | 342.17055 | 1.57 | [M+H]+1 | 326.10208, 299.13851 | Phellodendrine | 98.7 | 92.3 |
| 4 | C17H24O10 | 4.29 | 433.13667 | 433.13481 | −0.72 | [M-H]−1 | 225.07531, 175.03895, 147.04342 | Geniposide | 98.8 | 92.6 |
| 5 | C9H8O4 | 4.34 | 179.04162 | 179.03435 | −3.52 | [M-H]−1 | 135.04437, 113.11392 | Caffeic acid | 99.8 | 97.4 |
| 6 | C7H12O6 | 4.82 | 191.06269 | 191.05542 | −3.63 | [M-H]−1 | 173.00813, 85.02856 | Quinic acid | 94.2 | 86 |
| 7 | C10H10O4 | 4.84 | 195.05806 | 195.06534 | 0.81 | [M+H]+1 | 178.90244, 134.59469 | Ferulic acid | 98.6 | 93.4 |
| 8 | C19H15NO4 | 5.11 | 322.10665 | 322.10794 | 1.73 | [M+H]+1 | 307.08389, 279.08911 | Berberrubine | 93.9 | 85.9 |
| 9 | C27H30O16 | 5.24 | 609.15372 | 609.14632 | 0.56 | [M-H]−1 | 365.69574, 300.02716, 243.78491 | Rutin | 99.7 | 95.9 |
| 10 | C26H34O11 | 5.35 | 521.20019 | 521.20302 | 0.14 | [M-H]−1 | 359.14886, 329.13980 | Lariciresinol 4-O-glucoside | 94.8 | 86.1 |
| 11 | C19H13NO4 | 5.79 | 320.08461 | 320.09189 | 0.37 | [M+H]+1 | 292.09695, 262.08643 | Coptisine | 92.2 | 86.5 |
| 12 | C20H20NO4 | 5.80 | 338.13125 | 338.13853 | 18.89 | [M+H]+1 | 322.10773, 308.09183, 294.11264 | Jatrorrhizine | 93.8 | 92.3 |
| 13 | C44H64O24 | 6.26 | 975.37895 | 975.37116 | 0.21 | [M-H]−1 | 327.15983, 283.17015, 239.18008 | Crocin | 87.7 | 85.8 |
| 14 | C20H17NO4 | 6.57 | 336.1163 | 336.12357 | 1.61 | [M+H]+1 | 320.09198, 292.09706, 306.07642 | Berberine | 97.1 | 94.7 |
| 15 | C21H22NO4 | 6.95 | 352.14715 | 352.15443 | 0.43 | [M+H]+1 | 336.12326, 308.12823, 322.10767 | Palmatine | - | 92.2 |
| 16 | C21H18O12 | 7.55 | 461.06975 | 461.07278 | −0.16 | [M-H]−1 | 461.07261, 285.04053 | Scutellarin | 97.4 | 89.2 |
| 17 | C21H18O11 | 7.56 | 447.09494 | 447.0924 | 0.07 | [M+H]+1 | 269.04667 | Baicalin | 99.8 | 94.9 |
| 18 | C16H12O5 | 8.39 | 283.06168 | 283.06116 | 0.73 | [M-H]−1 | 285.07599, 270.05310 | Glycitein | 95.6 | 82.9 |
| 19 | C22H20O11 | 8.46 | 461.10804 | 461.10853 | 1.04 | [M+H]+1 | 269.04565 | Baicalin methyl ester | - | 85.9 |
| 20 | C21H18O11 | 8.99 | 445.07519 | 445.07774 | 0.63 | [M-H]−1 | 445.07115, 269.04641 | Apigenin 7-O-glucuronide | 99.5 | 83.5 |
| 21 | C22H20O11 | 10.02 | 459.10051 | 459.09317 | −0.12 | [M-H]−1 | 283.06312, 268.03921 | Wogonoside | - | 92.5 |
| 22 | C15H10O5 | 12.69 | 269.04297 | 269.04558 | 0.55 | [M-H]-1 | 269.04535, 241.04561, 223.02674 | Baicalein | 99.6 | 92.4 |
| 23 | C16H12O5 | 17.38 | 285.07869 | 285.07598 | 0.77 | [M+H]+1 | 270.05065 | Wogonin | 99.8 | 93.4 |
Chemical composition of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction identified using UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap HRMS.
Data were collected in full-scan mode (Full-MS) with a scanning range of m/z 100–1,500 Da (resolution: 35,000); the data were further analyzed with a secondary scan (dd-MS2, m/z 100–1,500 Da, resolution 17,500).
3.2 Effect of HLJDD on pathological damage in the brain of the Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats
The experimental timeline is presented in Figure 1A. Throughout the study, qualitative observations were recorded. Sham-operated rats displayed a sleek coat, normal posture and gait, and formed, solid feces. In contrast, rats in the Aβ1-42 model group presented with a ruffled and unkempt coat, a hunched posture, decreased spontaneous activity, and loose stools. HLJDD treatment ameliorated the appearance of the coat and improved activity levels and general condition in the model groups. Notably, sham-operated rats administered HLJDD exhibited piloerection, signs of agitation in response to handling, perianal soiling, and hard, dry feces. Body weight, as a direct indicator of growth, gradually increased across all groups, with no significant differences observed at the end of the experiment (Figure 2B).
FIGURE 2
![Flowchart of an Alzheimer's disease (AD) rat model study shows experimental groups and treatments, including control and treated with Aβ[1-42], Hup A, and HLJDD. Graph B shows weight changes over 28 days with little variance among groups. Graph C displays Nissl body counts, with treatment groups showing improvements. Panels D and E provide histological brain images, stained differently, comparing tissue structure across groups.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1710919/xml-images/fphar-16-1710919-g002.webp)
Effect of HLJDD on pathological damage in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats. (A) Experimental design, (B) Body weight of rats (n = 6), (C) Number of Nissl bodies (n = 3), (D) H&E staining (Magnification ×400, scale bars: 50 μm) (n = 3), (E) Nissl staining (Magnification ×400, scale bars: 20 μm) (n = 3). Data are presented as means ± SD. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. Sham group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. Aβ1-42 group.
H&E staining revealed that HLJDD administration to the sham group did not significantly affect pyramidal cell pathology in the hippocampus CA1 region. In comparison to the sham group, the Aβ1-42 group exhibited degenerative necrosis of pyramidal cells, glial cell proliferation, reduced cell volume, intensified staining, and blurred intracellular structures in the hippocampal CA1 region. The Hup A-treated Aβ1-42 group showed less pronounced alterations, including an increase in the number of darkly stained neurons and reduced cell volume with intensified staining. However, HLJDD significantly ameliorated the pathological changes in the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group (Figure 2D). Nissl staining was conducted to assess neuronal changes. In the Aβ1-42 group, there was a significant reduction in the number of healthy and surviving neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region, resulting in typical neuropathological features such as loss of Nissl bodies and nuclear disappearance, compared to the sham group (P = 0.000). In contrast, the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group showed improved survival of hippocampal neurons and prevented the loss of neurons in the CA1 area as well as the preservation of Nissl bodies (P = 0.019). Interestingly, the HLJDD-treated sham group exhibited a decrease in Nissl bodies (P = 0.028) (Figures 2C,E). These results suggest that HLJDD can prevent hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in AD rats but may cause functional impairment to neurons in normal rats, with this damage not being exclusively linked to Aβ.
3.3 Effect of HLJDD on Aβ accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats
Excessive Aβ deposition disrupts the structural integrity of neural synapses (Clinton et al., 2010) and activates pro-inflammatory cytokines leading to neuronal dysfunction (Carrano et al., 2012; LaFerla and Oddo, 2005). To determine whether HLJDD could suppress Aβ accumulation, Aβ expression was assessed through IHC and ELISA. Consistent with the pathological findings, both IHC and ELISA results showed increased Aβ1-42 expression in the hippocampal CA1 region, CSF, and serum of the Aβ1-42 group (both P = 0.000), confirming successful model establishment. Moreover, the expression of Aβ in these regions was significantly reduced in both the Hup A-treated Aβ1-42 group (IHC: P = 0.001, CSF: P = 0.000, serum: P = 0.000) and the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group (IHC: P = 0.006, CSF: P = 0.000, serum: P = 0.000) (Figure 3). These results indicate that HLJDD exerts neuroprotective effects by reducing Aβ deposition in the brains of AD rats, with no significant impact on Aβ levels in normal rats.
FIGURE 3
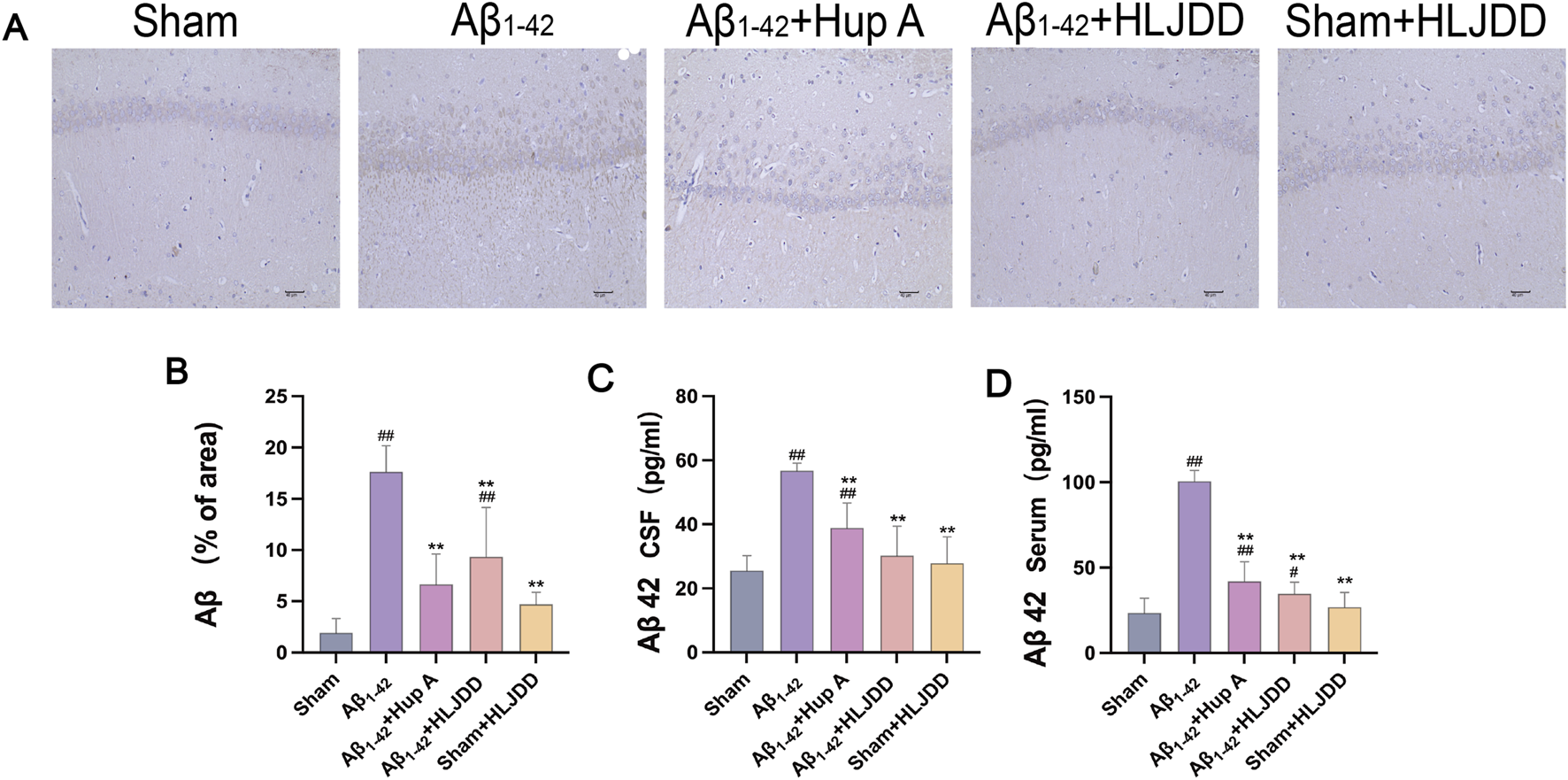
Effect of HLJDD on Aβ accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats. (A) Immunohistochemical detection of Aβ (Magnification ×200, scale bars: 40 μm) (n = 3), (B) Immunohistochemical detection of Aβ (% of area) in the CA1 region of the hippocampus (n = 3), (C) ELISA detection of Aβ levels in CSF (n = 6), (D) ELISA detection of Aβ levels in serum (n = 6). Data are presented as means ± SD. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. Sham group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. Aβ1-42 group.
3.4 Effect of HLJDD on the inflammation of Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats
This examined the effect of HLJDD on peripheral and central inflammation in both AD and normal rats by measuring IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-4 in serum and CSF using ELISA kits. The levels of IL-1β and TNF-α were significantly elevated in both the CSF and serum of the Aβ1-42 group compared to the sham group, while IL-4 levels were significantly reduced (IL-1β CSF: P = 0.015, IL-1β serum: P = 0.000, IL-4 CSF: P = 0.000, IL-4 serum: P = 0.007, TNF-α CSF: P = 0.000, TNF-α serum: P = 0.000). HLJDD treatment significantly decreased the concentrations of IL-1β and TNF-α in both serum and CSF, while increasing the level of IL-4 (IL-1β CSF: P = 0.003, IL-1β serum: P = 0.000, IL-4 CSF: P = 0.001, IL-4 serum: P = 0.003, TNF-α CSF: P = 0.000, TNF-α serum: P = 0.001). In contrast, compared to the sham group, the HLJDD-treated sham group exhibited significantly higher levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in both serum and CSF, along with a decrease in CSF IL-4 levels, reflecting an inflammatory profile similar to that of the Aβ1-42 group (IL-1β serum: P = 0.000, IL-4 CSF: P = 0.004, TNF-α CSF: P = 0.000, TNF-α serum: P = 0.000) (Figure 4). These results suggest that while HLJDD alleviates peripheral and central inflammation and offers neuroprotection in AD rats, it may induce peripheral and central inflammation in normal rats.
FIGURE 4
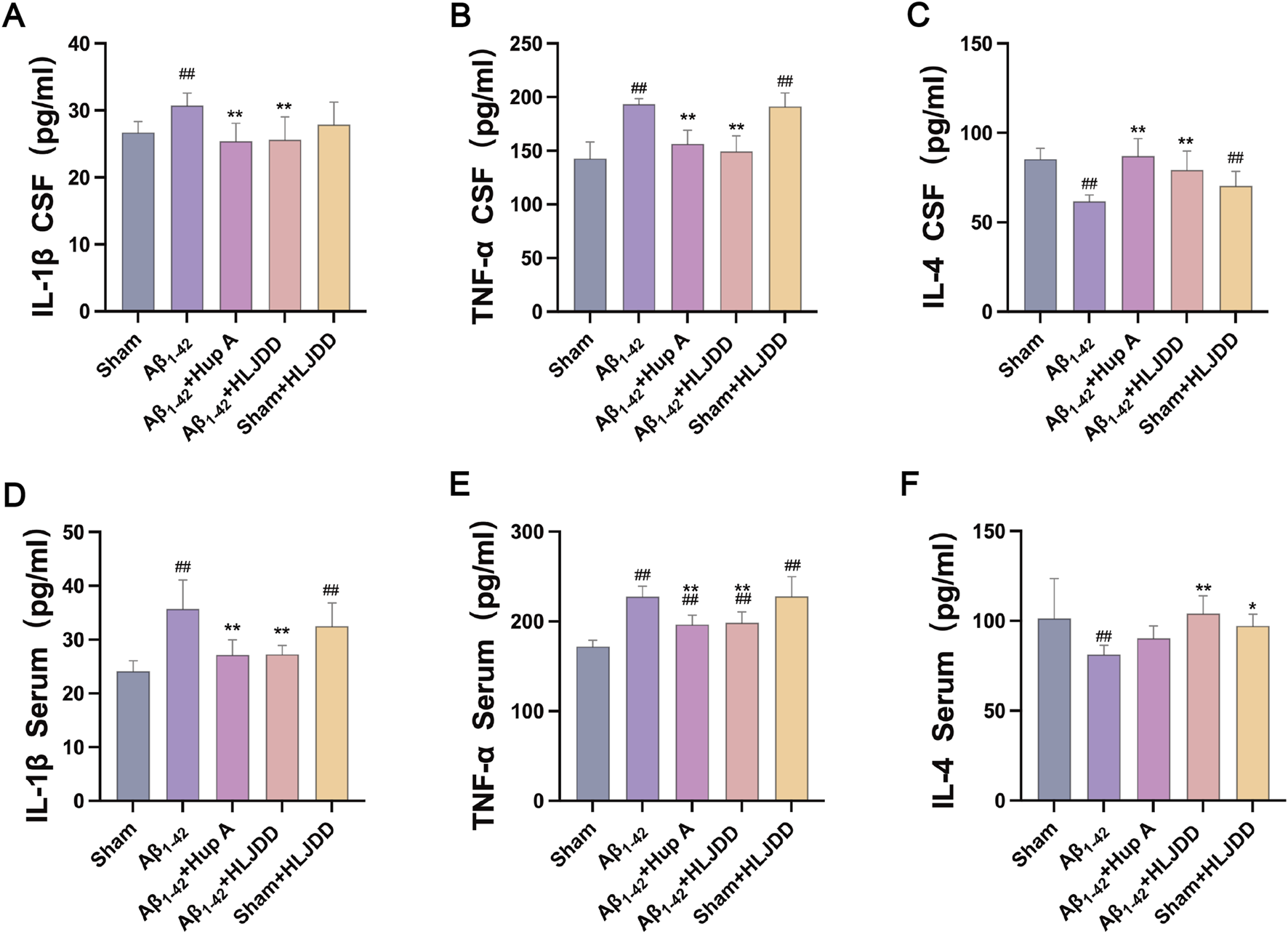
ELISA detection of cytokines (Serum and CSF). (A) IL-1β in CSF, (B) TNF-α in CSF, (C) IL-4 in CSF, (D) IL-1β in serum, (E) TNF-α in serum, (F) IL-4 in serum. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 6). #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. Sham group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. Aβ1-42 group.
3.5 Effect of HLJDD on the structural integrity of Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats
Excessive Aβ deposition has been implicated in the disruption of the BBB integrity (Storck and Pietrzik, 2018; van de Haar et al., 2017). MMP-2 and MMP-9 play a role in BBB disruption by degrading basement membrane proteins of cerebral capillaries. To investigate the effect of HLJDD on BBB permeability, IHC analyses were performed to assess MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats (Zhu et al., 2018). Compared to the sham group, the Aβ1-42 group exhibited a significant increase in MMP-2 and MMP-9 positive cells (MMP-2: P = 0.002, MMP-9: P = 0.001). In the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group, the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 was significantly downregulated (MMP-2: P = 0.003, MMP-9: P = 0.001). Interestingly, the HLJDD-treated sham group showed an upregulation of MMP-9 (MMP-9: P = 0.017) (Figure 5). These preliminary results suggest that while HLJDD can effectively preserve the structural integrity of the BBB in AD rats, it may negatively impact it in normal rats. However, these findings are preliminary and should be interpreted with caution, necessitating further research to validate and elaborate on the observed dual effects.
FIGURE 5
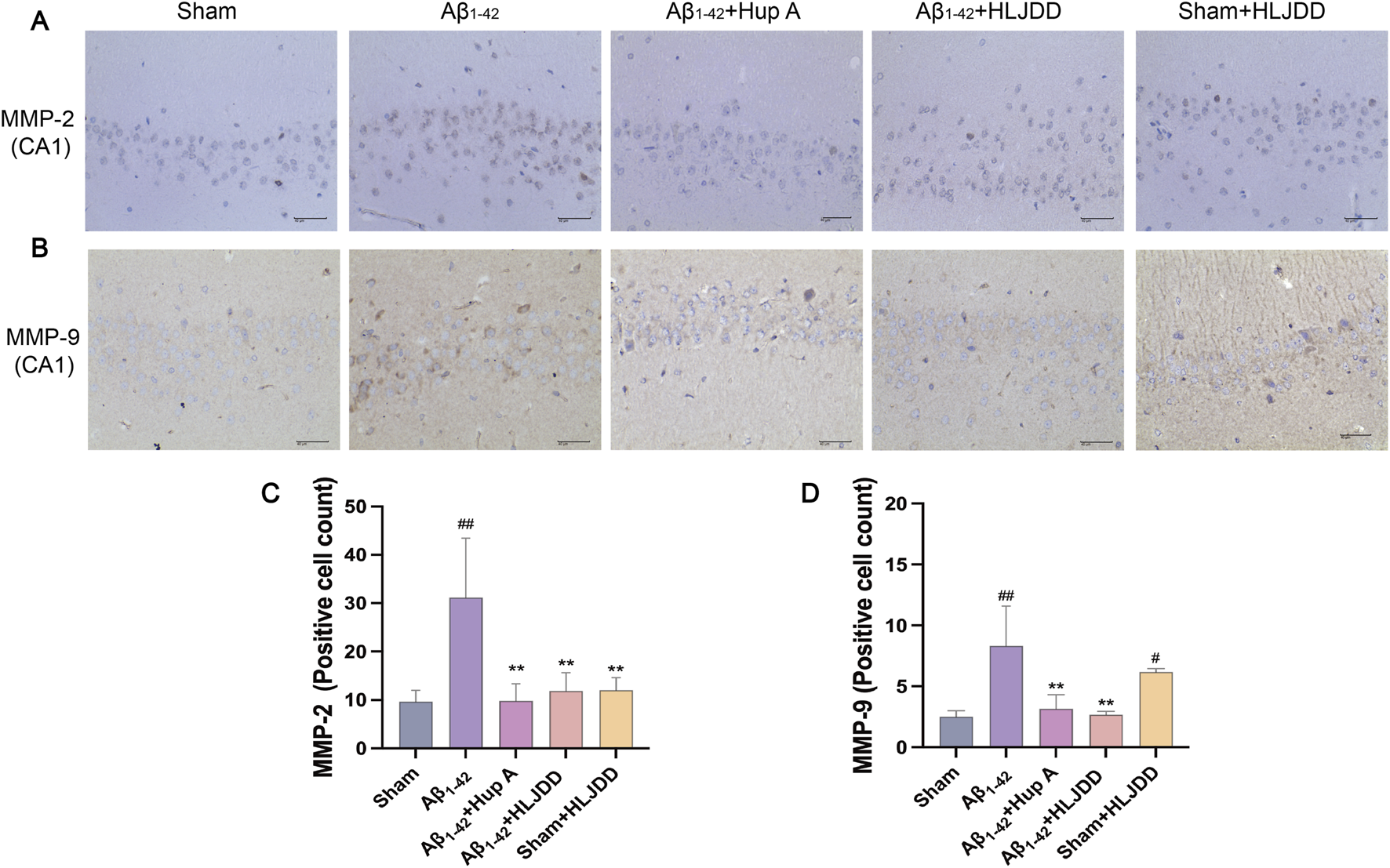
Effect of HLJDD on structural integrity in Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats. (A,C) Representative images of MMP-2 staining in the hippocampal CA1 region of brain tissue, and quantification of MMP-2 expression. (B,D) Representative images of MMP-9 staining in the hippocampal CA1 region of brain tissue, and quantification of MMP-9 expression. (Magnification ×400, scale bars: 40 μm). Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 3). #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. Sham group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. Aβ1-42 group.
3.6 Effect of HLJDD on the metabolic organs of Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats
TCM and its components may pose direct organ-damaging toxicity. To evaluate the potential toxicity of HLJDD, H&E staining was conducted on tissues from the liver, kidneys, stomach, large intestine, and small intestine to assess its effects on the digestive system. In liver tissues, the HLJDD-treated sham group exhibited hepatocellular necrosis, inflammatory cell infiltration, and fibrotic tissue proliferation, while the Aβ1-42 and Hup A-treated Aβ1-42 groups showed sporadic minor hepatocyte steatosis and vacuolar degeneration. Importantly, HLJDD treatment in the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group alleviated these liver pathologies (Figure 6A). In renal tissues, the Aβ1-42 group displayed moderate tubular dilatation with flattened tubular epithelial cells, whereas the Hup A-treated Aβ1-42 group showed mild interstitial inflammatory infiltration and subtle fibrotic proliferation. While HLJDD treatment attenuated renal lesions in the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group, the HLJDD-treated sham group exhibited tubular epithelial swelling, luminal dilatation, proteinaceous casts, inflammatory infiltration, and fibroplasia (Figure 6B). Gastric analysis revealed mild glandular dilatation with epithelial flattening in the Aβ1-42 and Hup A-treated Aβ1-42 groups, which was mitigated in the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group. No gastric abnormalities were observed in the HLJDD-treated sham group (Figure 6C). In colonic tissues, mucosal epithelial detachment, lamina propria necrosis, inflammatory infiltration, and villous dissolution were found exclusively in the HLJDD-treated sham group, with no significant lesions in other groups (Figure 6D). The small intestines in all experimental groups remained structurally intact with no significant histopathological changes (Figure 6E). These results suggest that HLJDD can mitigate pathological damage in the renal and gastric tissues of AD rats. Although serum samples were unavailable for biochemical analysis of indicators such as ALT and AST, histopathological examination clearly revealed tissue injury. Overall, histopathological findings indicated that HLJDD’s toxic effects in normal rats are associated with damage to the liver, kidneys, and large intestine.
FIGURE 6
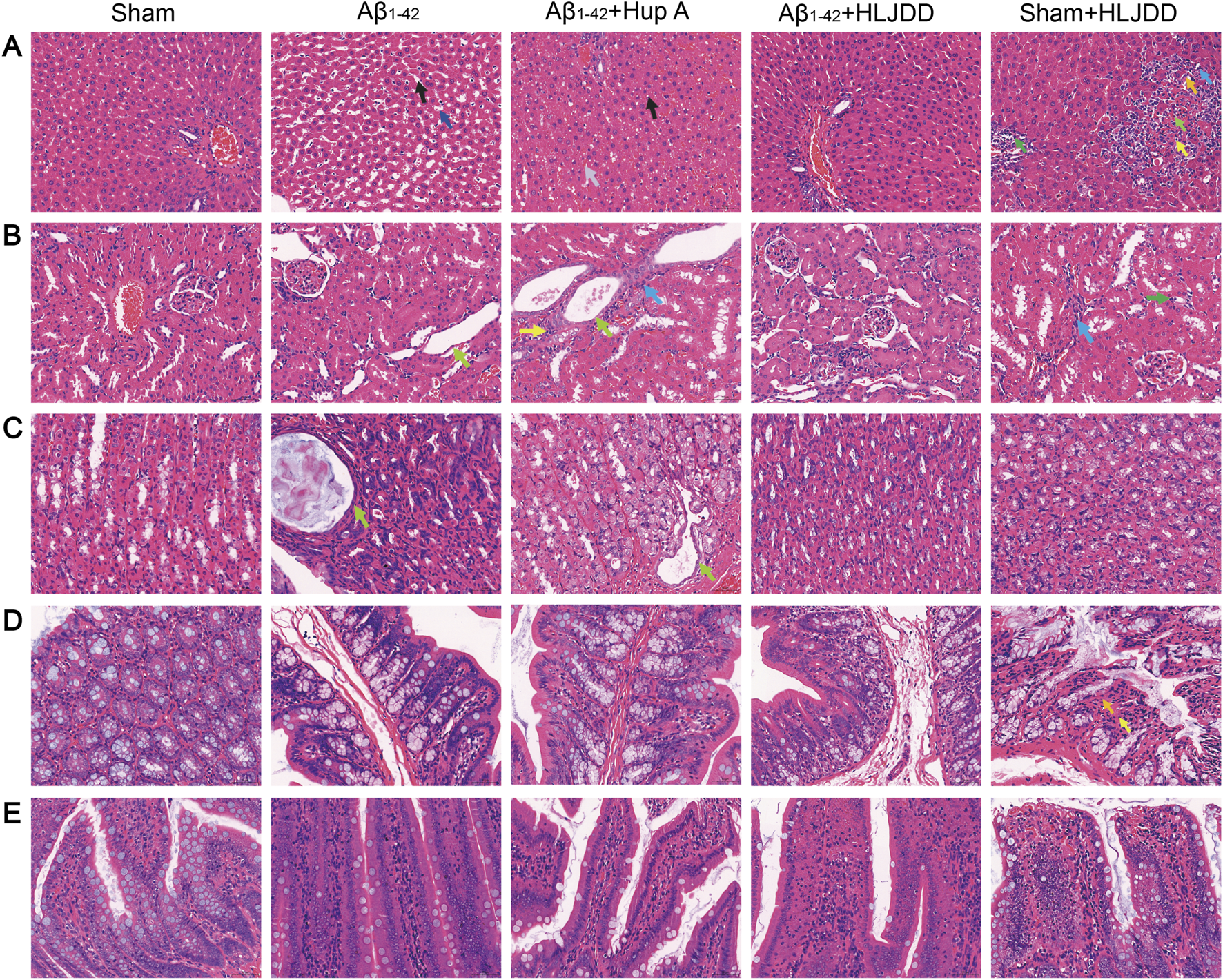
The bidirectional effect of HLJDD on drug-metabolizing organs in Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats. (A) Histopathological changes in liver tissues. Hepatocellular necrosis (↑), LymphocyteNeutrophils (↑), Fibroblast (↑), Fibrocyte (↑), Fatty degeneration of liver (↑), Hepatic sinusoidal dilatation (↑), Hepatic sinusoidal congestion (↑). (B) Histopathological changes in renal tissues. Renal tubular epithelial cells are flattened (↑), Lymphocyte (↑), Fibrocytes (↑), Neutrophils (↑). (C) Histopathological changes in gastric tissues. Gastric glandular epithelial cells are flattened (↑). (D) Histopathological changes in large intestine tissues. Lamina propria necrosis (↑), neutrophils (↑). (E) Histopathological changes in small intestine tissues. H&E staining of histological sections. (Magnification ×400, scale bars: 50 μm) (n = 3).
3.7 Effect of HLJDD on metabolism of Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats analyzed by LC-MS analyses of metabolic profiles
Differences in the metabolic microenvironment influence the body’s response to drug treatments. This study examined the variations in HLJDD metabolism in the peripheral and central regions of AD and normal rats using LC-MS analysis on CSF and serum samples. Multivariate analysis, including PCA and PLS-DA, revealed distinct metabolomic profiles among the Sham, Sham + HLJDD, Aβ1-42, and Aβ1-42 + HLJDD groups. The presence of clusters in the QC samples confirmed the stability of the analytical system, demonstrating good reproducibility and instrument reliability during the analysis (Figures 7A–D). The results indicated the presence of both conserved and differential metabolic constituents under normal and pathological conditions. Using a t-test (P < 0.05) and VIP >1, with a fold change threshold of 1.5, differential metabolites between the groups were identified. Comparative metabolomic analysis revealed significant alterations in metabolite profiles across experimental groups. In serum, 70 differentially expressed metabolites (DEMs) were identified between the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group and the Aβ1-42 group, with 15 upregulated and 55 downregulated metabolites. Similarly, 89 DEMs were detected in CSF, including 24 upregulated and 65 downregulated metabolites. For the sham-operated groups, 79 DEMs were observed in serum between the HLJDD-treated sham group and the sham group (21 upregulated, 58 downregulated), while 91 DEMs were identified in CSF (22 upregulated, 69 downregulated) (Figures 7E–I).
FIGURE 7
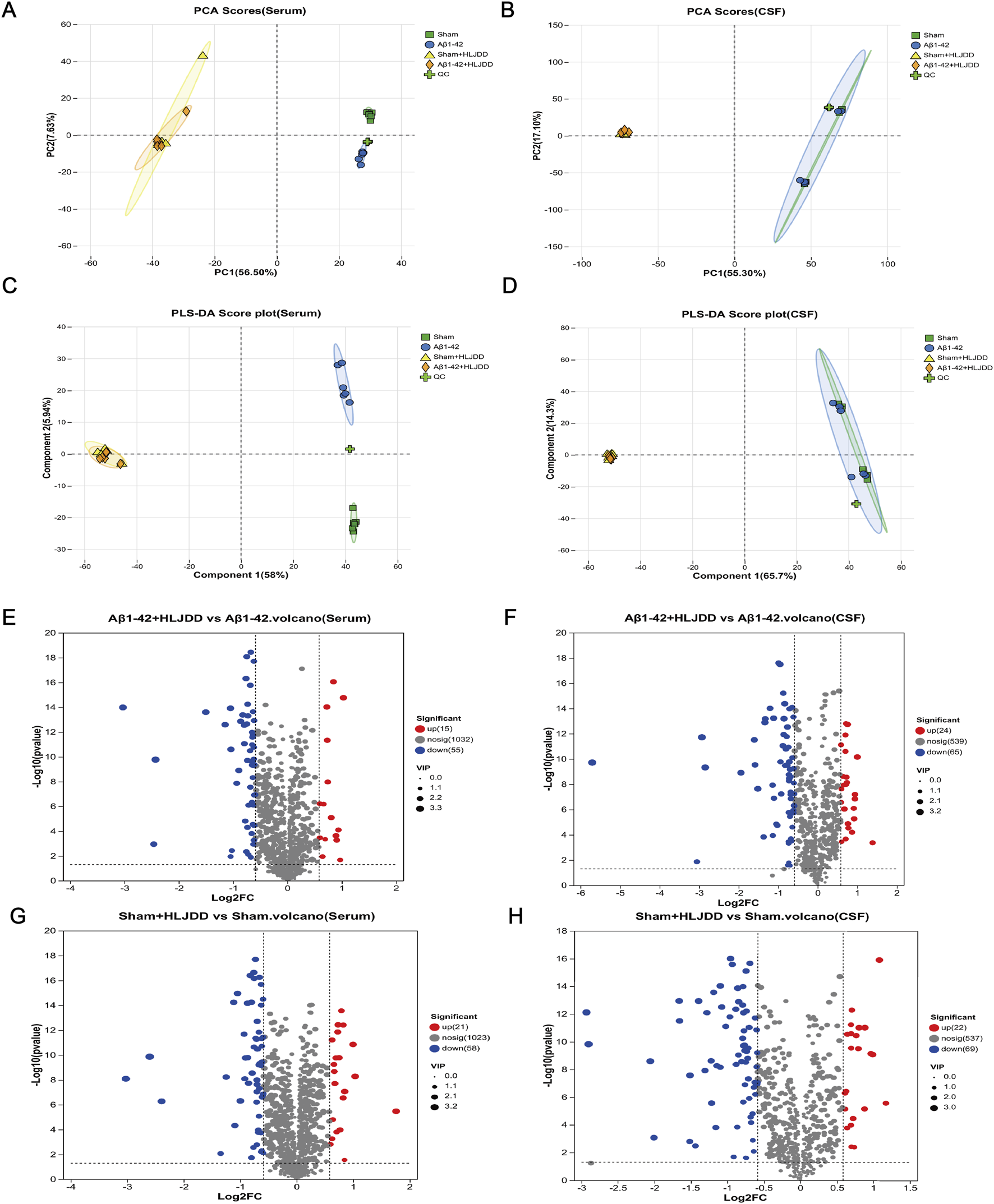
Metabolite analysis of HLJDD in the HLJDD-treated sham group and HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group rats via untargeted metabolic profiling. (A) PCA score (serum), (B) PCA score (CSF), (C) PLS-DA score (serum), (D) PLS-DA score (CSF), (E) QC represents a quality control sample. Volcano plot for Aβ1-42 + HLJDD vs. Aβ1-42 (serum) (F) and Aβ1-42 + HLJDD vs. Aβ1-42 (CSF), (G) Sham + HLJDD vs. Sham (serum), (H) Sham + HLJDD vs. Sham (CSF). Red: upregulated differential metabolites, blue: downregulated differential metabolites, gray: insignificant differential metabolites. VIP: Variable importance value from the PLS-DA model. The larger the VIP, the greater the contribution of the variable to the grouping (n = 6).
3.8 Metabolic pathway analysis
To further elucidate the metabolic discrepancies underlying the differential effects of HLJDD between AD and normal rats, KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was performed on CSF and serum samples from the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group and the Aβ1-42 group. The analysis revealed significant enrichment of various differentially expressed pathways in both serum and CSF, including long-term depression, retrograde endocannabinoid signaling, arginine biosynthesis, and ferroptosis. In CSF, notable alterations were observed in the biosynthesis of alkaloids derived from the shikimate pathway and the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids. Arginine biosynthesis was identified as a commonly enriched pathway in both CSF and serum, suggesting its critical role in mediating the context-dependent therapeutic efficacy of HLJDD in AD and normal rats. Additionally, an analogous analysis between the HLJDD-treated sham group and the sham group identified co-enriched metabolic perturbations in pathways such as aminobenzoate degradation, nucleotide metabolism, caprolactam degradation, and glycerophospholipid metabolism across serum and CSF (Figure 8). These results suggest that HLJDD may disrupt these pathways in normal rats, potentially contributing to its organotoxic effects in non-pathological conditions.
FIGURE 8
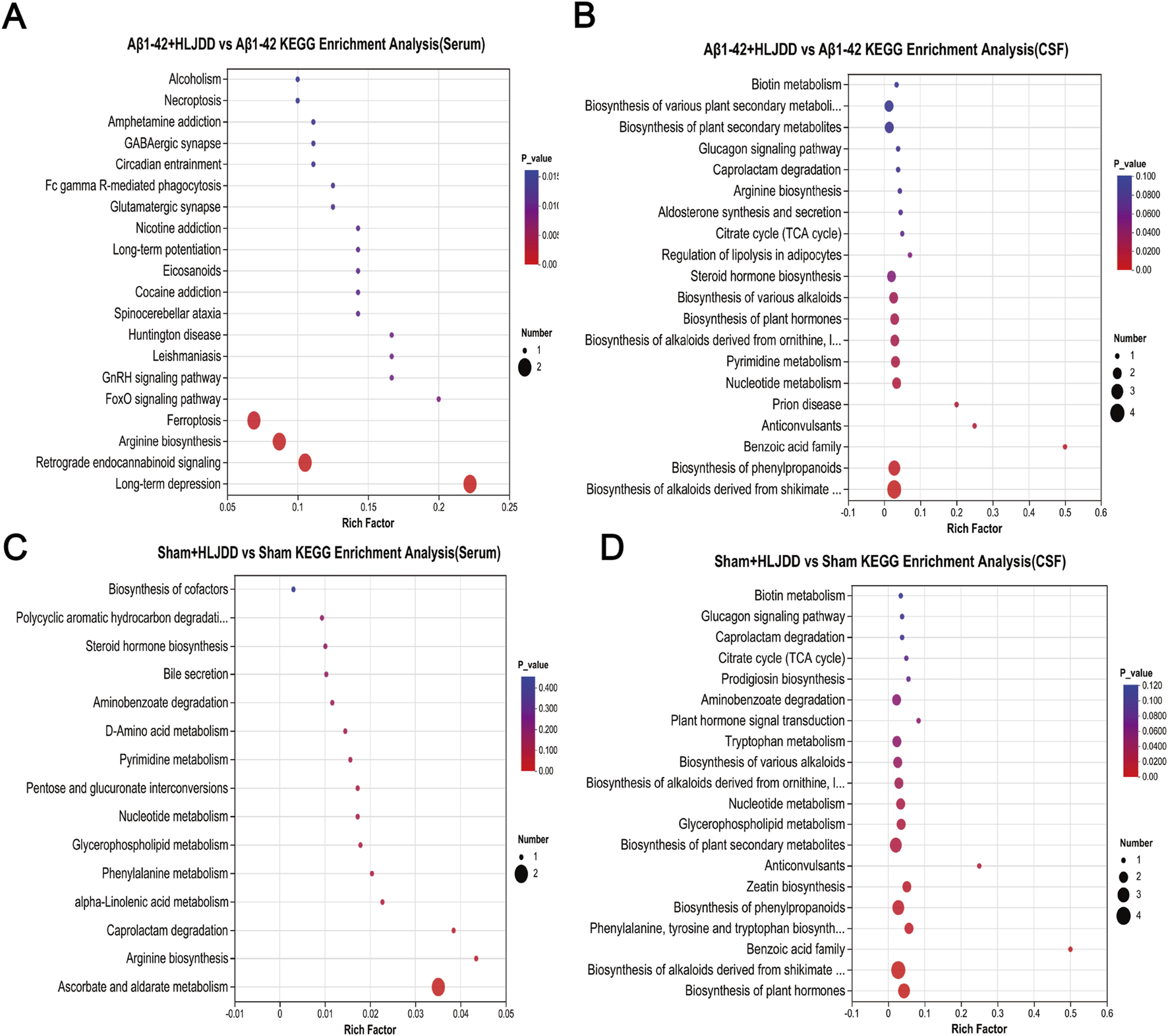
KEGG enrichment analysis of differential metabolites. (A) Aβ1-42 + HLJDD vs. Aβ1-42 KEGG enrichment analysis (serum), (B) Aβ1-42 + HLJDD vs. Aβ1-42 KEGG enrichment analysis (CSF), (C) Sham + HLJDD vs. Sham KEGG enrichment analysis (serum), (D) Sham + HLJDD vs. Sham KEGG enrichment analysis (CSF). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). P-value: t-test results to evaluate significant differences between two groups, with P < 0.05 considered significant.
3.9 Cluster analysis of differential metabolites
Cluster heatmap analysis of DEMs revealed distinct metabolic shifts between the experimental groups. In serum, N-acetylornithine and 3-methyl-2,5-furandione were significantly upregulated in the HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 group compared to the Aβ1-42 group, while arachidonic acid, L-glutamic acid, and phytosphingosine were markedly downregulated. In CSF, N2-acetyl-L-ornithine and chlorphenacil levels were elevated, while triethanolamine and isocitric acid were reduced. For the sham-operated groups, serum analysis revealed upregulation of cyclohexanone and N-lauroylglycine in the HLJDD-treated sham group compared to the sham group, alongside downregulation of ascorbic acid, terephthalic acid, and cytosine. In CSF, benzamide and 1-anilino-9,10-dioxo-2-anthroic acid were upregulated, while adenine, thymidine, and aminocaproic acid were suppressed (Figure 9).
FIGURE 9
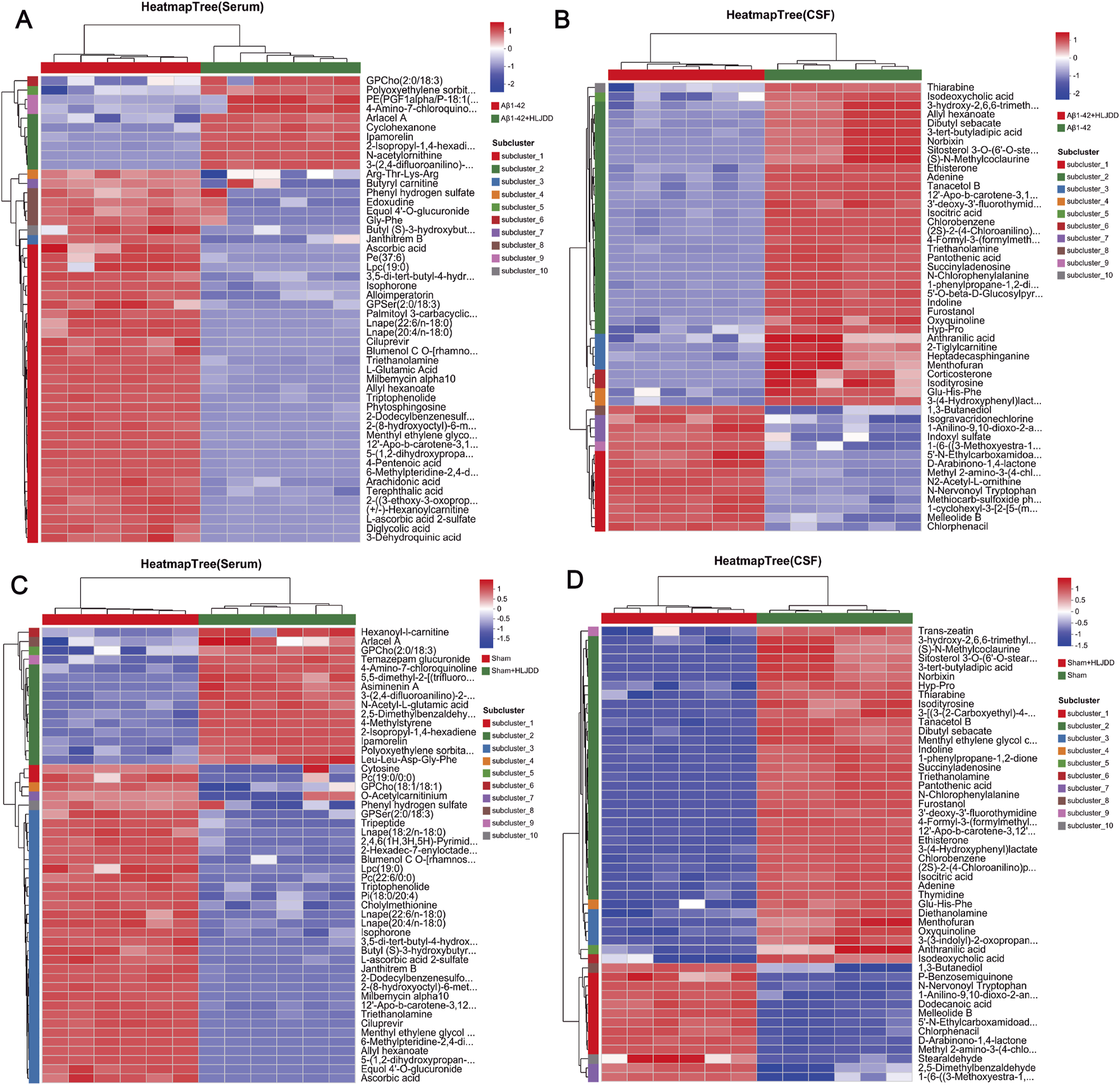
Hierarchical clustering diagram of differential metabolites. (A) Aβ1-42 vs. Aβ1-42 + HLJDD Heatmap (serum), (B) Aβ1-42 + HLJDD vs. Aβ1-42 Heatmap (CSF), (C) Sham vs. Sham + HLJDD Heatmap (serum), (D) Sham + HLJDD vs. Sham Heatmap (CSF). The color of each section represents the abundance value of each metabolite, calculated using the relative quantitation normalization method. The vertical axis represents significantly different metabolites, while the horizontal axis represents functional group information. Red and blue indicate upregulated and downregulated metabolites, respectively, in each sample (n = 6).
4 Discussion
To elucidate the mechanism of HLJDD in AD, an Aβ1-42-induced AD rat model was employed, a widely used approach for AD modeling due to its simplicity and reproducibility. It is important to note that this study utilized only male rats. This approach was chosen to eliminate potential confounds associated with the estrous cycle in females, thereby reducing biological variability and allowing for a more focused investigation into the core mechanisms of Aβ-induced toxicity and the effects of HLJDD. Histopathological evaluation (H&E and Nissl staining), IHC detection of Aβ deposition, and ELISA analysis of Aβ levels in CSF and serum revealed that HLJDD significantly alleviated brain injury, neuronal apoptosis, and Aβ deposition in AD rats. These findings align with the core pathological features of AD, in which Aβ neurotoxicity and subsequent neuronal apoptosis drive disease progression (Roda et al., 2022). IHC did not detect classic Aβ amyloid plaques, likely due to the transient nature of oligomers, which fail to reach the fibrillization threshold concentration necessary for plaque formation (Kramer et al., 2024). It is possible that the Aβ1-42 hippocampal CA1 injection model, being an acute and focal injury model, fails to replicate the characteristic progressive deposition of Aβ plaques seen in the AD process. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), multifunctional endopeptidases, modulate AD pathogenesis by regulating Aβ metabolism, inflammatory cytokine secretion, and BBB integrity (Beroun et al., 2019; Hillmer et al., 2023; Rivera et al., 2019; Spampinato et al., 2017; Woo et al., 2008). The BBB also serves as a conduit for systemic inflammatory signals to the brain, creating an interplay between BBB dysfunction, Aβ accumulation, and neuroinflammation (Laurent et al., 2018; Milo et al., 2020; T. Zhang et al., 2015). HLJDD primarily restores BBB function by enhancing its structural integrity and suppressing local inflammation and adhesion molecule expression, rather than directly penetrating the brain (C. Chen et al., 2025). Our data further revealed that HLJDD administration significantly reduced MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in the hippocampal CA1 region of AD rats, suggesting that its neuroprotective effects may involve BBB stabilization and anti-inflammatory regulation. In AD pathology, disrupted cerebral homeostasis and imbalanced inflammatory responses contribute to progressive neuronal loss and neuroinflammation (Kawahara et al., 2012; Minghetti et al., 2005; Sheng et al., 1996; Shepherd et al., 2000; Webers et al., 2020; Wynn et al., 2011). Notably, HLJDD treatment significantly reduced inflammatory cytokine levels in both CSF and serum of AD rats, supporting its dual anti-inflammatory actions in both peripheral and central compartments. Collectively, HLJDD demonstrates potential neuroprotective effects against AD through mechanisms involving Aβ deposition reduction, neuronal apoptosis inhibition, BBB integrity improvement, and suppression of peripheral and central inflammatory cascades. These findings provide critical insights into the pharmacological mechanisms of HLJDD and its therapeutic potential for AD. Our study identified 23 metabolites in HLJDD, primarily comprising flavonoids, alkaloids, and iridoids. It was demonstrated that the formula exerts neuroprotective effects primarily through the core representative component berberine (Y. Yang et al., 2013; Durairajan et al., 2012), in conjunction with alkaloids including jatrorrhizine and palmatine. These effects are mediated mainly by the alleviation of oxidative stress and suppression of neuroinflammation, with synergistic contributions from other active constituents such as wogonoside, baicalin, and geniposide (Cao et al., 2023).
Although HLJDD demonstrates significant neuroprotective effects in AD rats, its potential toxicity and underlying mechanisms in normal rats warrant critical evaluation. Under physiological conditions, the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines maintains systemic homeostasis (Anisman, 2004). However, HLJDD administration in normal rats paradoxically increased inflammatory cytokine levels in both CSF and serum, accompanied by heightened neuronal apoptosis, indicating that HLJDD may disrupt this balance, triggering peripheral and central inflammation along with partial neuronal damage. Furthermore, MMP-9 expression was significantly upregulated in this group. Given the established correlation between MMP-9 overexpression and exacerbated neuroinflammation, this change is hypothesized to further compromise BBB integrity in normal rats. However, this interpretation remains speculative due to the lack of key functional evidence, such as measurements of BBB permeability using Evans Blue dye or IgG immunohistochemistry. Therefore, future studies incorporating these assays are essential to validate this hypothesis. Previous studies have identified the liver as a primary target organ for HLJDD components (Yamano et al., 1988; Ma et al., 2010), with Coptidis Rhizoma (a key HLJDD metabolites) specifically linked to hepatotoxicity (Ma et al., 2010). Additionally, the kidneys, with their high vascularity and energy demands, are susceptible to drug-induced injury via systemic circulation (Griffin et al., 2019). Histopathological analysis using H&E staining revealed varying degrees of damage in the liver, kidneys, and large intestine of normal rats treated with HLJDD. Notably, oral administration of bitter metabolites is known to activate gastrointestinal protective mechanisms (e.g., diarrhea) (Meyerhof et al., 2010), while prolonged use of Coptidis Rhizoma has been shown to suppress intestinal motility and impair colonic barrier function in mice (Wu et al., 2025). As a bitter botanical drugs, long-term HLJDD use may induce adverse gastrointestinal effects. Consistent with these findings, HLJDD-treated sham-operated rats exhibited perianal soiling, loose stools, and large intestinal lesions. While histopathological observations revealed tissue alterations in the liver, kidneys, and large intestine of normal rats following HLJDD administration, the absence of supporting serum biochemical parameters (specifically ALT, AST, BUN, and creatinine) precludes a definitive conclusion on organ toxicity. Therefore, the present findings cannot establish but may hint at potential toxicological implications. These preliminary outcomes nonetheless provide crucial initial evidence, underscoring a need for more comprehensive safety evaluations that integrate both histopathological and serological data in future studies.
Drug toxicity and pharmacokinetics vary significantly depending on an individual’s physiological condition. For example, the toxicity of digoxin differs markedly between healthy individuals and those with heart failure. Metabolomic analysis revealed that the therapeutic effects of HLJDD in AD are linked to multiple metabolic pathways, including ferroptosis, the biosynthesis of alkaloids derived from the shikimate pathway, and arginine biosynthesis. Notably, the arginine biosynthesis pathway was co-enriched in both serum and CSF, highlighting its critical role in AD pathogenesis (Horgusluoglu et al., 2022). The ferroptosis pathway is particularly noteworthy, showing significant correlations with key metabolites such as arachidonic acid and L-glutamic acid. Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of regulated cell death, may exacerbate neuronal damage in AD through glutamic acid excitotoxicity. L-glutamic acid, the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, is pathologically elevated in AD. This elevation not only promotes cerebral tissue injury and neuronal apoptosis (Belousov et al., 2012) but also disrupts BBB integrity (Gruenbaum et al., 2022), accelerating AD progression through impaired clearance mechanisms (Bell et al., 2003; Tatara et al., 2023). Additionally, arachidonic acid, a polyunsaturated fatty acid critical for microglial activation, exacerbates neuroinflammation and BBB dysfunction under pathological conditions (Xu et al., 2024; Yagami et al., 2018; Ziegler et al., 2016). Baicalin, a bioactive component of HLJDD, modulates arachidonic acid metabolism (S. Chen et al., 2019), thereby reducing inflammatory infiltration and brain injury (Hwang et al., 2002). Consistent with this, HLJDD-treated Aβ1-42 -induced AD rats exhibited reduced serum levels of L-glutamic acid and arachidonic acid, alleviated CSF and serum inflammation, and restored BBB integrity. Moreover, abnormal elevations of isocitrate and citrate in patients with AD reflect dysregulated energy metabolism and cell cycle control (Bubber et al., 2005; van der Velpen et al., 2019). These metabolic disturbances aggravate neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis, ultimately impairing cognitive function (Hotamisligil, 2006). HLJDD intervention downregulated the levels of arachidonic acid, L-glutamic acid, and isocitric acid while upregulating N-acetylornithine and N2-acetyl-L-ornithine in AD rats. These findings suggest that HLJDD may ameliorate AD pathology by modulating arginine biosynthesis, which is associated with reduced apoptosis, diminished peripheral and central inflammation, and restored BBB integrity. Significant alterations in multiple metabolic pathways, including nucleotide metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism, and caprolactam degradation, were also observed in the CSF and serum of normal rats treated with HLJDD.
Disruption of nucleotide metabolism can impair mitochondrial function in the kidneys, compromise cellular barrier integrity, and directly contribute to renal injury, promoting inflammation and fibrosis (Ralto et al., 2020). Among its key components, adenine and cytosine are closely linked to inflammatory regulation. Adenine is converted to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) via the salvage pathway (Dias et al., 2023). As an endogenous signaling molecule, adenosine exerts cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects under pathological conditions through upregulation of ectonucleotidase activity (Li et al., 2020). Cytosine, in contrast, modulates cytokine expression and contributes to inflammation (Meng et al., 2021). In this study, reduced levels of adenine and cytosine were observed in HLJDD-treated sham rats, suggesting metabolic suppression mythat may exacerbate inflammatory responses. Restoring mitochondrial membrane potential can reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine release and excessive MMP-9 expression (Sun et al., 2021). In this study, reduced levels of adenine and cytosine were observed in HLJDD-treated sham rats, suggesting metabolic suppression that may exacerbate inflammatory responses. Restoring mitochondrial membrane potential can reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine release and excessive MMP-9 expression (Brouns et al., 2010; Rochfort and Cummins, 2015). In line with this, HLJDD-treated sham rats exhibited peripheral and central inflammation, BBB dysfunction, and neuronal apoptosis, implying that their pathological changes may be related to metabolism imbalance. Notably, the most significantly altered pathway appeared to involve ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, characterized by reduced levels of ascorbic acid. Ascorbic acid enhances the activity of hepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, a critical enzyme for liver function, and its deficiency exacerbates liver injury (Arendt and Allard, 2011). Previous studies have reported the potential hepatotoxicity of geniposide, a metabolite of HLJDD (Yamano et al., 1990). Confirming this, UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap HRMS analysis in the current study identified geniposide within the HLJDD preparation. However, the hepatotoxic mechanism of HLJDD as a complex formula is likely multifactorial and cannot be solely attributed to geniposide. The results suggest that HLJDD-induced liver injury could be related to geniposide but might also involve disturbances in the ascorbate metabolic pathway. Non-targeted metabolomic analysis in this study revealed that HLJDD induces significant metabolic perturbations in both AD and normal rats, albeit with fundamental differences in the direction and magnitude of its effects. Notably, our KEGG pathway analysis highlighted several pathways exhibiting significant alterations in both animal groups. These included the Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis, Biosynthesis of alkaloids derived from shikimate pathway, and Protein digestion and absorption pathways in the CSF; as well as the Choline metabolism in cancer, Glycerophospholipid metabolism, Linoleic acid metabolism, and Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling pathways in the serum. These findings strongly suggest that the aforementioned pathways may represent critical targets for the bidirectional regulatory effects of HLJDD. It is important to note, however, that this conclusion remains preliminary and is derived primarily from metabolomic data. Further validation using molecular biology experiments is therefore warranted. We hope that these insights will provide valuable hypotheses and a solid foundation for subsequent research in the field.
5 Limitations
This study also has several aspects that could be further improved. First, although we assessed changes in MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels via immunohistochemistry, direct functional assays such as the Evans blue extravasation test were not performed to validate actual alterations in blood–brain barrier permeability. Second, while the observed metabolomic shifts suggest potential underlying mechanisms, the causal relationship between these changes and the observed effects remains unclear due to the lack of functional validation. Future studies should employ targeted metabolomics to identify key metabolites and further verify their functional roles. Third, the study did not include cognitive or behavioral assessments. As the primary focus was on pathological and biomarker differences between AD and normal rats, the absence of functional behavioral evaluation limits the interpretation of functional recovery, which should be addressed in future research. Lastly, although this single-dose study confirmed the toxic risk of HLJDD at the administered dose and revealed histopathological alterations in organs, the toxicological implications of these findings require more comprehensive evaluation incorporating serum biochemical parameters. Moreover, whether these toxic effects are reversible remains undetermined and should be clarified through subsequent continuous monitoring. Nevertheless, these findings collectively highlight the importance of closely monitoring organ functional safety in the clinical application of HLJDD.
6 Conclusion
In AD rats, HLJDD reduced Aβ deposition, enhanced neuronal survival, ameliorated systemic inflammation, improved BBB integrity, and attenuated cerebral, renal, and gastric injuries without causing organ damage, indicating its safety. These effects were mediated by modulation of the arginine biosynthesis pathway. In contrast, in healthy rats, HLJDD induced systemic inflammation, compromised neuronal and BBB integrity, and caused hepatic, renal, and colonic injuries. These differential effects suggest the possible involvement of metabolic pathways, including nucleotide metabolism, aminobenzoate degradation, glycerophospholipid metabolism, and caprolactam degradation. Collectively, these findings highlight that HLJDD exhibits context-dependent pharmacology, necessitating a precise mechanistic understanding for safe clinical application.
Statements
Data availability statement
Source data have been deposited to the EMBL-EBI MetaboLights database with the identifier MTBLS13256. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Animal Ethics Committee of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
MX: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. JC: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. FZ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. RW: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. JL: Project administration, Writing – review and editing. MQ: Project administration, Writing – review and editing. YF: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. PR: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. MC: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. JQ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. WW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82174358).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank to Key Laboratory for Visual Function and Ophthalmopathy, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Alam Q. Alam M. Z. Mushtaq G. Damanhouri G. A. Rasool M. Kamal M. A. et al (2016). Inflammatory process in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: central role of cytokines. Curr. Pharm. Des.22 (5), 541–548. 10.2174/1381612822666151125000300
2
Anisman H. (2004). Considering cytokine panels. Brain, Behav. Immun.18 (3), 221–222. 10.1016/j.bbi.2003.11.005
3
Arendt B. M. Allard J. P. (2011). Effect of atorvastatin, vitamin E and C on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: is the combination required?Am. J. Gastroenterology106 (1), 78–80. 10.1038/ajg.2010.310
4
Avau B. Rotondo A. Thijs T. Andrews C. N. Janssen P. Tack J. et al (2015). Targeting extra-oral bitter taste receptors modulates gastrointestinal motility with effects on satiation. Sci. Rep.5, 15985. 10.1038/srep15985
5
Bell K. F. S. de Kort G. J. L. Steggerda S. Shigemoto R. Ribeiro-da-Silva A. Cuello A. C. (2003). Structural involvement of the glutamatergic presynaptic boutons in a transgenic mouse model expressing early onset amyloid pathology. Neurosci. Lett.353 (2), 143–147. 10.1016/j.neulet.2003.09.027
6
Belousov A. B. Wang Y. Song J.-H. Denisova J. V. Berman N. E. Fontes J. D. (2012). Neuronal gap junctions play a role in the secondary neuronal death following controlled cortical impact. Neurosci. Lett.524 (1), 16–19. 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.06.065
7
Beroun A. Mitra S. Michaluk P. Pijet B. Stefaniuk M. Kaczmarek L. (2019). MMPs in learning and memory and neuropsychiatric disorders. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS76 (16), 3207–3228. 10.1007/s00018-019-03180-8
8
Blanchard J. W. Victor M. B. Tsai L.-H. (2022). Dissecting the complexities of Alzheimer disease with in vitro models of the human brain. Nat. Rev. Neurol.18 (1), 25–39. 10.1038/s41582-021-00578-6
9
Brouns R. Verkerk R. Aerts T. De Surgeloose D. Wauters A. Scharpé S. et al (2010). The role of tryptophan catabolism along the kynurenine pathway in acute ischemic stroke. Neurochem. Res.35 (9), 1315–1322. 10.1007/s11064-010-0187-2
10
Bubber P. Haroutunian V. Fisch G. Blass J. P. Gibson G. E. (2005). Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer brain: mechanistic implications. Ann. Neurology57 (5), 695–703. 10.1002/ana.20474
11
Cao D.-M. Liang Q.-F. Zhang Z.-T. He W.-J. Tang D. (2023). Combination of UHPLC-Q exactive-orbitrap MS, bioinformatics and molecular docking to reveal the mechanism of huan-lian-jie-du decoction in the treatment of diabetic encephalopathy. Chem. and Biodivers.20 (9), e202300434. 10.1002/cbdv.202300434
12
Carrano A. Hoozemans J. J. M. van der Vies S. M. van Horssen J. de Vries H. E. Rozemuller A. J. M. (2012). Neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier changes in capillary amyloid angiopathy. Neuro-Degenerative Dis.10 (1–4), 329–331. 10.1159/000334916
13
Chen S. Chen G. Shu S. Xu Y. Ma X. (2019). Metabolomics analysis of baicalin on ovalbumin-sensitized allergic rhinitis rats. R. Soc. Open Sci.6 (2), 181081. 10.1098/rsos.181081
14
Chen C. Li C. Lan X. Ren Z. Zheng Y. Chen D. et al (2025). Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction inhibits CD4+ T cell infiltration into CNS in MCAO rats by regulating BBB. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytotherapy Phytopharm.141, 156607. 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156607
15
Clinton L. K. Blurton-Jones M. Myczek K. Trojanowski J. Q. LaFerla F. M. (2010). Synergistic interactions between Abeta, tau, and alpha-synuclein: acceleration of neuropathology and cognitive decline. J. Neurosci. Official J. Soc. Neurosci.30 (21), 7281–7289. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0490-10.2010
16
Dias L. Pochmann D. Lemos C. Silva H. B. Real J. I. Gonçalves F. Q. et al (2023). Increased synaptic ATP release and CD73-Mediated formation of extracellular adenosine in the control of behavioral and electrophysiological modifications caused by chronic stress. ACS Chem. Neurosci.14 (7), 1299–1309. 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00810
17
Dong C. Cao L. Qu Y. Liang Y. Yang Y. Wu W. (2021). Effect of Huanglian jiedu decoction on NLRP3 inflammatory pathway in hippocampus of rats with Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater Med.37 (6), 7–13. 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2021.06.003
18
Durairajan S. S. K. Liu L.-F. Lu J.-H. Chen L.-L. Yuan Q. Chung S. K. et al (2012). Berberine ameliorates β-amyloid pathology, gliosis, and cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol. Aging33 (12), 2903–2919. 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.02.016
19
Durairajan S. S. K. Huang Y.-Y. Yuen P.-Y. Chen L.-L. Kwok K.-Y. Liu L.-F. et al (2014). Effects of Huanglian-Jie-Du-Tang and its modified formula on the modulation of amyloid-β precursor protein processing in Alzheimer’s disease models. PLoS ONE9 (3), e92954. 10.1371/journal.pone.0092954
20
Fang H. Wang Y. Yang T. Ga Y. Zhang Y. Liu R. et al (2013). Bioinformatics analysis for the antirheumatic effects of huang-lian-jie-du-tang from a network perspective. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med. eCAM2013, 245357. 10.1155/2013/245357
21
Finneran D. J. Nash K. R. (2019). Neuroinflammation and fractalkine signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation16 (1), 30. 10.1186/s12974-019-1412-9
22
Gehrmann J. Matsumoto Y. Kreutzberg G. W. (1995). Microglia: intrinsic immuneffector cell of the brain. Brain Res.20 (3), 269–287. 10.1016/0165-0173(94)00015-h
23
Griffin B. R. Faubel S. Edelstein C. L. (2019). Biomarkers of drug-induced kidney toxicity. Ther. Drug Monit.41 (2), 213–226. 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000589
24
Gruenbaum B. F. Zlotnik A. Fleidervish I. Frenkel A. Boyko M. (2022). Glutamate neurotoxicity and destruction of the blood-brain barrier: key pathways for the development of neuropsychiatric consequences of TBI and their potential treatment strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (17), 9628. 10.3390/ijms23179628
25
Haass C. Selkoe D. J. (2007). Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.8 (2), 101–112. 10.1038/nrm2101
26
Halliday M. R. Rege S. V. Ma Q. Zhao Z. Miller C. A. Winkler E. A. et al (2016). Accelerated pericyte degeneration and blood-brain barrier breakdown in apolipoprotein E4 carriers with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metabolism36 (1), 216–227. 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.44
27
Hillmer L. Erhardt E. B. Caprihan A. Adair J. C. Knoefel J. E. Prestopnik J. et al (2023). Blood-brain barrier disruption measured by albumin index correlates with inflammatory fluid biomarkers. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metabolism43 (5), 712–721. 10.1177/0271678X221146127
28
Hollmann P. (2022). Update: FDA approval of Biogen’s aducanumab. Geriatr. Nurs.43, 318–319. 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2021.12.018
29
Horgusluoglu E. Neff R. Song W.-M. Wang M. Wang Q. Arnold M. et al (2022). Integrative metabolomics-genomics approach reveals key metabolic pathways and regulators of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dementia J. Alzheimer’s Assoc.18 (6), 1260–1278. 10.1002/alz.12468
30
Hotamisligil G. S. (2006). Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature444 (7121), 860–867. 10.1038/nature05485
31
Huang Y. Mucke L. (2012). Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell148 (6), 1204–1222. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.040
32
Hwang Y. S. Shin C. Y. Huh Y. Ryu J. H. (2002). Hwangryun-Hae-Dok-tang (Huanglian-Jie-Du-Tang) extract and its constituents reduce ischemia-reperfusion brain injury and neutrophil infiltration in rats. Life Sci.71 (18), 2105–2117. 10.1016/s0024-3205(02)01920-3
33
Jy Z. Xx L. Wy L. S S. Hc W. Rd H. et al (2023). Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction alleviates depressive-like behaviors in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice via Trem2/Dap12 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol.315, 116658. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116658
34
Kawahara K. Suenobu M. Yoshida A. Koga K. Hyodo A. Ohtsuka H. et al (2012). Intracerebral microinjection of interleukin-4/interleukin-13 reduces β-amyloid accumulation in the ipsilateral side and improves cognitive deficits in young amyloid precursor protein 23 mice. Neuroscience207, 243–260. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.01.049
35
Kramer M. Hoang T.-H. Yang H. Shchyglo O. Böge J. Neubacher U. et al (2024). Intracerebral inoculation of healthy non-transgenic rats with a single aliquot of oligomeric amyloid-β (1-42) profoundly and progressively alters brain function throughout life. Front. Aging Neurosci.16, 1397901. 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1397901
36
L W. G W. F W. N J. Y L. (2017). Geniposide attenuates ANIT-induced cholestasis through regulation of transporters and enzymes involved in bile acids homeostasis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol.196, 178–185. 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.022
37
LaFerla F. M. Oddo S. (2005). Alzheimer’s disease: Abeta, tau and synaptic dysfunction. Trends Mol. Med.11 (4), 170–176. 10.1016/j.molmed.2005.02.009
38
Laurent C. Buée L. Blum D. (2018). Tau and neuroinflammation: what impact for Alzheimer’s disease and tauopathies?Biomed. J.41 (1), 21–33. 10.1016/j.bj.2018.01.003
39
Leng F. Edison P. (2021). Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: where do we go from here?Nat. Rev. Neurol.17 (3), 157–172. 10.1038/s41582-020-00435-y
40
Li X. Berg N. K. Mills T. Zhang K. Eltzschig H. K. Yuan X. (2020). Adenosine at the interphase of hypoxia and inflammation in lung injury. Front. Immunol.11, 604944. 10.3389/fimmu.2020.604944
41
Lu Z.-N. Luo Q. Zhao L.-N. Shi Y. Wang N. Wang L. et al (2020). The mutational features of aristolochic acid-induced mouse and human liver cancers. Hepatology71 (3), 929–942. 10.1002/hep.30863
42
Ma B.-L. Ma Y.-M. Shi R. Wang T.-M. Zhang N. Wang C.-H. et al (2010). Identification of the toxic constituents in Rhizoma coptidis. J. Ethnopharmacol.128 (2), 357–364. 10.1016/j.jep.2010.01.047
43
Meng C. Gu L. Li Y. Li R. Cao Y. Li Z. et al (2021). Ten-eleven translocation 2 modulates allergic inflammation by 5-hydroxymethylcytosine remodeling of immunologic pathways. Hum. Mol. Genet.30 (21), 1985–1995. 10.1093/hmg/ddab167
44
Meyerhof W. Batram C. Kuhn C. Brockhoff A. Chudoba E. Bufe B. et al (2010). The molecular receptive ranges of human TAS2R bitter taste receptors. Chem. Senses35 (2), 157–170. 10.1093/chemse/bjp092
45
Milo R. Korczyn A. D. Manouchehri N. Stüve O. (2020). The temporal and causal relationship between inflammation and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler.26 (8), 876–886. 10.1177/1352458519886943
46
Minghetti L. Ajmone-Cat M. A. De Berardinis M. A. De Simone R. (2005). Microglial activation in chronic neurodegenerative diseases: roles of apoptotic neurons and chronic stimulation. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev.48 (2), 251–256. 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.12.015
47
Okamoto H. Chino A. Hirasaki Y. Ueda K. Iyo M. Namiki T. (2013). Orengedoku-to augmentation in cases showing partial response to Yokukan-San treatment: a case report and literature review of the evidence for use of these Kampo herbal formulae. Neuropsychiatric Dis. Treat.9, 151–155. 10.2147/NDT.S38318
48
Peng W. Gao F. Jiang Y. Yang H. Gan Y. Lu J. et al (2015). Thinking of the safety application of TCM by You Gu Wu Yun, A Chinese Ancient medicine application principle. Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary Altern. Med.12 (5), 35. 10.4314/ajtcam.v12i5.6
49
Poole S. Singhrao S. K. Chukkapalli S. Rivera M. Velsko I. Kesavalu L. et al (2014). Active invasion of Porphyromonas gingivalis and infection-induced complement activation in ApoE-/- mice brains. J. Alzheimer’s Dis.43 (1), 67–80. 10.3233/JAD-140315
50
Ralto K. M. Rhee E. P. Parikh S. M. (2020). NAD+ homeostasis in renal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol.16 (2), 99–111. 10.1038/s41581-019-0216-6
51
Rivera S. García-González L. Khrestchatisky M. Baranger K. (2019). Metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS76 (16), 3167–3191. 10.1007/s00018-019-03178-2
52
Rochfort K. D. Cummins P. M. (2015). The blood-brain barrier endothelium: a target for pro-inflammatory cytokines. Biochem. Soc. Trans.43 (4), 702–706. 10.1042/BST20140319
53
Roda A. R. Serra-Mir G. Montoliu-Gaya L. Tiessler L. Villegas S. (2022). Amyloid-beta peptide and tau protein crosstalk in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res.17 (8), 1666–1674. 10.4103/1673-5374.332127
54
Sheng J. G. Ito K. Skinner R. D. Mrak R. E. Rovnaghi C. R. Van Eldik L. J. et al (1996). In vivo and in vitro evidence supporting a role for the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 as a driving force in Alzheimer pathogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging17 (5), 761–766. 10.1016/0197-4580(96)00104-2
55
Shepherd C. E. Thiel E. McCann H. Harding A. J. Halliday G. M. (2000). Cortical inflammation in Alzheimer disease but not dementia with lewy bodies. Archives Neurology57 (6), 817–822. 10.1001/archneur.57.6.817
56
Shin M.-R. Lee J. A. Kim M. Lee S. Oh M. Moon J. et al (2021). Gardeniae fructus attenuates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in mice via both AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway and Nrf2 signaling. Antioxidants10 (11), 1837. 10.3390/antiox10111837
57
Spampinato S. F. Merlo S. Sano Y. Kanda T. Sortino M. A. (2017). Astrocytes contribute to Aβ-induced blood-brain barrier damage through activation of endothelial MMP9. J. Neurochem.142 (3), 464–477. 10.1111/jnc.14068
58
Storck S. E. Pietrzik C. U. (2018). The blood brain-barrier and its role in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroforum24 (4), A197–A205. 10.1515/nf-2018-A014
59
Sun L. Gai J. Shi S. Zhao J. Bai X. Liu B. et al (2021). Protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR-2) antagonist AZ3451 mitigates oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL)-Induced damage and endothelial inflammation. Chem. Res. Toxicol.34 (10), 2202–2208. 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00154
60
Tatara Y. Yamazaki H. Katsuoka F. Chiba M. Saigusa D. Kasai S. et al (2023). Multiomics and artificial intelligence enabled peripheral blood-based prediction of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Curr. Res. Transl. Med.71 (1), 103367. 10.1016/j.retram.2022.103367
61
van de Haar H. J. Burgmans S. Jansen J. F. A. van Osch M. J. P. van Buchem M. A. Muller M. et al (2017). Blood-brain barrier leakage in patients with early alzheimer disease. Radiology282 (2), 615. 10.1148/radiol.2017164043
62
van der Velpen V. Teav T. Gallart-Ayala H. Mehl F. Konz I. Clark C. et al (2019). Systemic and central nervous system metabolic alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. and Ther.11 (1), 93. 10.1186/s13195-019-0551-7
63
Wang N. Feng Y. Tan H.-Y. Cheung F. Hong M. Lao L. et al (2015). Inhibition of eukaryotic elongation factor-2 confers to tumor suppression by a herbal formulation Huanglian-Jiedu decoction in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Ethnopharmacol.164, 309–318. 10.1016/j.jep.2015.02.025
64
Webers A. Heneka M. T. Gleeson P. A. (2020). The role of innate immune responses and neuroinflammation in amyloid accumulation and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Immunol. Cell Biol.98 (1), 28–41. 10.1111/imcb.12301
65
Woo M.-S. Park J.-S. Choi I.-Y. Kim W.-K. Kim H.-S. (2008). Inhibition of MMP-3 or -9 suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines and iNOS in microglia. J. Neurochem.106 (2), 770–780. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05430.x
66
Wu Z. Yang W. Wu T. Liu Y. Pu Y. Hu W. et al (2025). Long term Coptidis Rhizoma intake induce gastrointestinal emptying inhibition and colon barrier weaken via bitter taste receptors activation in mice. Phytomedicine136, 156292. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156292
67
Wynn T. A. Barron L. Thompson R. W. Madala S. K. Wilson M. S. Cheever A. W. et al (2011). Quantitative assessment of macrophage functions in repair and fibrosis. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. Chapter14, Unit14.22. 10.1002/0471142735.im1422s93
68
X G. J Z. Y Z. H W. N S. W R. et al (2021). Huanglian Jiedu decoction remodels the periphery microenvironment to inhibit Alzheimer’s disease progression based on the “brain-gut” axis through multiple integrated omics. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther.13 (1), 44. 10.1186/s13195-021-00779-7
69
Xu M. Yue Y. Huang J. (2023). Efficacy evaluation and metabolomics analysis of Huanglian Jiedu decoction in combination with donepezil for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis235, 115610. 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115610
70
Xu M. Liu D. Wang L. (2024). Role of oxylipins in ovarian function and disease: a comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomedecine Pharmacother.178, 117242. 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117242
71
Yagami T. Yamamoto Y. Koma H. (2018). Physiological and pathological roles of 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-Prostaglandin J2 in the central nervous system and neurological diseases. Mol. Neurobiol.55 (3), 2227–2248. 10.1007/s12035-017-0435-4
72
Yamano T. Tsujimoto Y. Noda T. Shimizu M. Ohmori M. Morita S. et al (1988). Hepatotoxicity of gardenia yellow color in rats. Toxicol. Lett.44 (1–2), 177–182. 10.1016/0378-4274(88)90144-0
73
Yamano T. Tsujimoto Y. Noda T. Shimizu M. Ohmori M. Morita S. et al (1990). Hepatotoxicity of geniposide in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol.28 (7), 515–519. 10.1016/0278-6915(90)90122-4
74
Yang Y. Wang H.-J. Yang J. Brantner A. H. Lower-Nedza A. D. Si N. et al (2013). Chemical profiling and quantification of Chinese medicinal formula Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction, a systematic quality control strategy using ultra high performance liquid chromatography combined with hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap and triple quadrupole mass spectrometers. J. Chromatogr. A1321, 88–99. 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.10.072
75
Yang X. Chi C. Li W. Zhang Y. Yang S. Xu R. et al (2024). Metabolomics and lipidomics combined with serum pharmacochemistry uncover the potential mechanism of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. J. Ethnopharmacol.324, 117748. 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117748
76
Yue X. Liang J. Gu F. Du D. Chen F. (2018). Berberine activates bitter taste responses of enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem.447 (1–2), 21–32. 10.1007/s11010-018-3290-3
77
Zhang X.-J. Deng Y.-X. Shi Q.-Z. He M.-Y. Chen B. Qiu X.-M. (2014). Hypolipidemic effect of the Chinese polyherbal Huanglian Jiedu decoction in type 2 diabetic rats and its possible mechanism. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytotherapy Phytopharm.21 (5), 615–623. 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.11.004
78
Zhang T. Fang S. Wan C. Kong Q. Wang G. Wang S. et al (2015). Excess salt exacerbates blood-brain barrier disruption via a p38/MAPK/SGK1-dependent pathway in permanent cerebral ischemia. Sci. Rep.5, 16548. 10.1038/srep16548
79
Zheng R. Shi S. Zhang Q. Yuan S. Guo T. Guo J. et al (2023). Molecular mechanisms of Huanglian Jiedu decoction in treating Alzheimer’s disease by regulating microbiome via network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.13, 1140945. 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1140945
80
Zhu H. Dai R. Zhou Y. Fu H. Meng Q. (2018). TLR2 ligand Pam3CSK4 regulates MMP-2/9 expression by MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in primary brain microvascular endothelial cells. Neurochem. Res.43 (10), 1897–1904. 10.1007/s11064-018-2607-7
81
Ziegler N. Awwad K. Fisslthaler B. Reis M. Devraj K. Corada M. et al (2016). β-Catenin is required for endothelial Cyp1b1 regulation influencing metabolic barrier function. J. Neurosci. Official J. Soc. Neurosci.36 (34), 8921–8935. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0148-16.2016
Summary
Keywords
HLJDD, AD, Chinese medicine compound complex, metabolomics, traditional Chinese medicine
Citation
Xu M, Zhu Y, Chen J, Zhong F, Wang R, Li J, Qiao M, Fan Y, Ren P, Chen M, Qin J and Wu W (2025) Differential effects of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction on Alzheimer’s disease and normal rats. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1710919. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1710919
Received
22 September 2025
Revised
22 October 2025
Accepted
23 October 2025
Published
11 November 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Chika Ifeanyi Chukwuma, Central University of Technology, South Africa
Reviewed by
Ramoji Kosuru, Versiti Blood Research Institute, United States
Hesham Refaat, The University of Iowa, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Xu, Zhu, Chen, Zhong, Wang, Li, Qiao, Fan, Ren, Chen, Qin and Wu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenbin Wu, wwb1201@vip.sina.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.