Abstract
Introduction:
Lilium spp., perennial bulbous plants native to the Northern Hemisphere, have long been valued in traditional medicine, particularly across Asia. The bulbs of Lilium brownii (“Bai He” in traditional Chinese medicine) have been documented since the Han dynasty as both food and medicine to nourish yin, moisten the lungs, clear heart fire, and calm the spirit—traditionally used for conditions such as depression and diabetes. Contemporary research has increasingly validated these traditional claims, revealing diverse pharmacological activities including antidepressant and antitumor effects.
Methods:
A comprehensive literature review was conducted using databases including Web of Science, PubMed, ACS Publications, Google Scholar, Baidu Scholar, and CNKI, as well as the Encyclopedia of Life, Flora of China, and Plants of the World Online. Taxa recorded in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2025) were included: Lilium lancifolium Thunb., Lilium brownii F. E. Brown var. viridulum Baker, and Lilium pumilum DC, and related species. All relevant multilingual publications were critically evaluated and accurately cited. Chemical structures of isolated metabolites were visualized using ChemDraw v19.0.
Results:
Lilium spp. are consumed in various culinary and processed forms, including steamed bulbs, flour, wine, and functional beverages. Nutritionally, they are rich in polysaccharides, saponins, dietary fibers, vitamins, amino acids, starch, pectin, phospholipids, and essential minerals such as calcium and iron. To date, 123 chemical metabolites have been isolated and characterized, with saponins, flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, and polysaccharides recognized as the principal bioactive metabolites. Pharmacological studies have demonstrated a wide range of biological activities-anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor, antidepressant, sedative, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic, joint-protective, and immunomodulatory-observed in both in vitro and in vivo models.
Discussion:
Lilium spp. represent a valuable traditional medicinal and nutritional resource with promising potential for modern therapeutic and functional applications. Their integration into health products and cosmetics continues to expand; however, clinical validation remains limited. Further well-designed clinical trials are required to confirm the efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of Lilium-derived preparations. This review highlights recent advances to support the continued scientific and industrial development of Lilium as a multifaceted natural resource.
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
As a genus of perennial herbaceouds bulbous plants, Lilium spp. is widely distributed across Asia, North America, and Europe.
This review summarizes the traditional uses, botanical descriptions, nutritional properties, pharmacological studies, and patent associated with the genus Lilium spp.
The primary metabolites and characteristic compounds of Lilium spp. were well highlighted.
The main biological activities and related material basis as well as underlying mechanisms of Lilium spp. were outlined.
Future perspectives and challenges of Lilium spp. were proposed.
1 Introduction
Lilium spp., members of the family Liliaceae, are perennial herbaceous bulbous plants primarily native to China and widely distributed across the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. They are extensively cultivated in East Asia, Europe, and North America, and are regarded as one of the most economically, horticulturally, and medicinally important plant genera worldwide (Chen et al., 2024). China is fully considered an important distribution center for Lilium spp., with 55 species having been reported to date (Chen X. et al., 2025). According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2025 Edition), the bulbs of Lilium lancifolium Thunb. (LL), L. brownii F. E. Brown var. viridulum Baker (LB) and L. pumilum DC. (LP) are official sources of Lilii Bulbus, a traditional Chinese medicine used to treat palpitations, insomnia, and hemoptysis (Wei et al., 2024). Highly valued for its diverse biological activities, Lilium spp. is also increasingly regarded as a functional food. In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), it is characterized as a cold-natured botanical drug with a sweet taste, and is used to moisten the lungs, clear heat, and calm the mind. Its applications include the treatment of cough, blood-tinged sputum, anxiety, insomnia, and disturbed sleep. The medicinal use of Lilium spp. in China dates back to the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (circa 25-220 AD), which documented the therapeutic properties of L. brownii viridulum (Tang et al., 2021).
Phytochemical investigations have revealed a diverse array of bioactive metabolites in Lilium spp., comprising polysaccharides, saponins, sterols, alkaloids, glycerolglycolipids, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, and phenolic acids (Li C. H. et al., 2024). Lilium spp. are extensively cultivated worldwide owing to their remarkable ornamental, edible, and medicinal properties. According to the Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine (1985), lily bulbs contain various bioactive constituents, including colchicine, alkaloids, starch, proteins, and lipids. The anthers of Lilium longiflorum are particularly rich in carotenoids, with flavonoids accounting for approximately 91.7%–94.0% of the total pigments. Similarly, the anthers of Lilium lancifolium contain 2.68% moisture, 4.17% ash, 21.29% protein, 12.43% lipids, 3.61% starch, and 11.47% reducing sugars, along with vitamins B1, B2, B6, vitamin C, and β-carotene (Liu X. Y. et al., 2025). As a member of the Liliaceae family, Lilium spp. is one of the primary botanical families used in skincare cosmetic formulations. Antioxidant and ultraviolet (UV) absorption capacities are important evaluation indices of cosmetic quality. Polyphenols (including phenolic acids, flavonoids, lignins, etc.) exhibit good UV absorption capacity due to their aromatic rings (Hutskalova and Sparr, 2025; Tang et al., 2022). Bulbs of Lilium spp. possess not only nutritional value but also medicinal properties (Wang M. et al., 2024). This potent traditional remedy is frequently employed in folk medicine for the effective treatment of various ailments, including, but not limited to, coughs, asthma, insomnia, and anxiety (Bao et al., 2024). In Japan, Lilium species are incorporated into culinary traditions and gourmet food production. Their petals are often used to garnish sushi and served during tea ceremonies. In Korea, lilies are also commonly utilized in food and beverage processing (Lupşor et al., 2025). Lily-derived polysaccharides have been increasingly applied in the development of functional foods and nutritional supplements. Owing to their abundance of essential amino acids and trace elements, these polysaccharides can be incorporated into various food products to enhance nutritional value and improve overall dietary profiles. For instance, lily polysaccharides have been utilized in the formulation of composite protein beverages (Chen X. et al., 2025). In the pharmaceutical field, lily polysaccharides can serve as immunomodulators, offering adjuvant therapy to patients with immunodeficiency or immune abnormalities (Wang M. et al., 2024).
In recent years, extensive phytochemical investigations have demonstrated that Lilium spp. are characterized by high levels of saponins, phenols, and phenylpropanoids. Saponins, which are widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom, have attracted increasing attention in the food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries due to their distinctive physicochemical properties and diverse biological activities, including anticancer and cholesterol-lowering effects (Wang M. et al., 2024). Moreover, pharmacological studies have revealed that crude extracts and purified metabolites from different organs of Lilium spp. possess a broad spectrum of bioactivities, such as antidiabetic, sedative, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, anti-obesity, gut-protective, and antidepressant effects. These pharmacological findings are consistent with the traditional medicinal and nutritional applications of the genus. Consequently, Lilium species have recently expanded their utilization beyond traditional medicine and food into the cosmetic and functional product industries (An et al., 2025).
In previous reviews, Zhou et al. systematically summarized the traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of Lilium spp. species, providing a foundation for their potential applications in medicinal, food, and industrial fields (Zhou et al., 2021). More recently, Wang et al. focused on the nutraceutical aspects of Lilium brownii (Baihe), highlighting its bioactive metabolites and therapeutic effects (Wang Y. F. et al., 2024). Despite these efforts, several limitations persist, including insufficient coverage of nutritional profiles, emerging pharmacological mechanisms, and practical applications such as patents. Specifically, Zhou et al. lack recent discoveries post-2021, such as newly isolated metabolites and activities like anti-insomnia and hepatoprotection. Although timely, Wang et al. offer a brief account of phytochemistry and pharmacology with limited mechanistic insight and no discussion of patents or commercial uses. To address these research gaps, this review provides a comprehensive and up-to-date synthesis of the botanical characteristics, ethnopharmacological uses, nutritional composition, phytochemical diversity, pharmacological progress, patent landscape, and practical applications of Lilium species documented in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Particular emphasis is placed on newly characterized bioactive metabolites and recent mechanistic insights into their anti-insomnia and hepatoprotective activities. Furthermore, a systematic analysis of relevant patents is conducted to bridge the gap between academic research and industrial application. Collectively, this review refines the existing research framework and proposes prospective directions for future development.
2 Botanical description, geographic distribution, and taxonomy
2.1 Botanical description
Botanically, Lilium spp., as showed in Figure 1B, is a genus of perennial herbaceous bulbous plants, characterized by ovoid or nearly spherical bulbs (Figure 1D). The bulbs possess numerous fleshy scales, which are ovate or lanceolate in shape, jointless or jointed, and typically white, though rarely yellow (Figure 1C). The stem is cylindrical, exhibiting small papillae either present or absent, with some varieties displaying purple stripes. Leaves are usually scattered, less often whorled, and come in various forms such as lanceolate, oblong-lanceolate, oblong-oblanceolate, elliptic, or linear. They are sessile or have short petioles, with entire margins or small papillae. The flower can be solitary or arranged in a raceme, and are rarely subumbellate or corymbose. Bracts are leaf-like but smaller in size (Figure 1A). Flowers are often brightly colored and sometimes fragrant (Figure 1E). There are six tepals arranged in two whorls, free and often somewhat connivent, forming a trumpet-shaped or campanulate structure, and rarely strongly recurved, usually lanceolate or spatulate. A nectary is present at the base, which may bear papillae on both sides, and some also possess a cristate or fimbriate appendage. The six stamens have subulate filaments that are pubescent or glabrous. Anthers are elliptic, dorsifixed, and T-shaped. The ovary is cylindrical, and the style is generally slender. The stigma is enlarged and three-lobed. Capsules are oblong and loculicidal. Seeds are numerous, flattened, and winged around (Flora of China Editorial Committee, 2015).
FIGURE 1

The growing habit (A) the morphology of plants (B) the plant specimen (C) the bulb of plants (D) the flowers (E) the distribution diagram worldwide (F) of the Lilium spp. (https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/4062681685; https://ppbc.iplant.cn/sp/41183; https://cn.bing.com/images/search?q=%E7%99%BE%E5%90%88&form=HDRSC2&first=1).
2.2 Geographic distribution
Globally, it is estimated that there are approximately 100–175 species of wild Lilium spp., primarily distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, including Asia (approximately 70 species), North America (approximately 24 species), and Europe (approximately 10–22 species). The eastern coast of Asia, the western coast of North America, and the Mediterranean region are particularly abundant in Lilium spp. resources (Figure 1F). As the center of natural distribution for Lilium spp. species, China boasts 36 original species and 15 varieties that are endemic to the country. Within China, Lilium spp. species are predominantly found in western Sichuan Province, northwestern Yunnan Province, southeastern Tibet Autonomous Region, and the northeastern regions (https://cn.vibaike.com/1260/).
2.3 Taxonomy
According to the 2025 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the crude drug “Bulbus Lilii” is exclusively sourced from Lilium spp. taxonomically anchored in the kingdom Plantae, phylum Streptophyta, class Equisetopsida, subclass Magnoliidae, order Liliales, and family Liliaceae. The monograph unequivocally recognizes three botanical origins: (i) Lilium lancifolium Thunb., synonym Lilium tigrinum; (ii) Lilium brownii F. E. Brown var. viridulum Baker, synonyms L. brownii var. viridulum Baker, Lilium brownii var. Ferum, and Lilium aduncum; and (iii) Lilium pumilum DC., synonyms Lilium pumilum Redouté and Lilium tenuifolium (http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org).
3 Traditional uses and nutritional properties
3.1 Traditional uses
Lily Bulbus was originally recorded in the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing, and was listed as a medium grade Chinese medicine. It has the effects of nourishing yin, moistening the lung, clearing the heart, and calming the nerves. As a Chinese medicine for both medicine and food, Lily Bulbus has a long history of processing, dating back to the Han dynasty. Lilium spp. plants also have long been integral to traditional medicine systems across the globe, exhibiting extensive medicinal and culinary applications that reflect rich cross-cultural ethnopharmacological diversity. In China, Lilium spp. has been in use since the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing of the Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220 AD), which documented the bulb of L. brownii viridulum as capable of “alleviating abdominal pain, promoting bowel movement, nourishing viscera, and clearing the heart to calm the mind” (Wang C. H. et al., 2018). Historical records reveal that in ancient times, different Lilium spp. species were often used interchangeably. Notably, L. brownii var. viridulum Baker, L. lancifolium Thunb., L. pumilum DC., and L. concolor Salisb. were all utilized for medicinal purposes (Wang C. H. et al., 2018). From the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing to the Ben Cao Meng Quan of the Ming Dynasty (1,368–1,644), L. brownii F.E.Br. ex Miellez and its variant (var. viridulum) became established as the orthodox botanical origin. These were primarily sourced from authentic producing areas such as Jingzhou (Hubei), Cheng County (Gansu), Chuzhou (Anhui), and Heze (Shandong). Subsequent classic texts enriched the understanding of its efficacy. The Ri Hua Zi Ben Cao (circa 1,100) first recorded the medicinal use of L. pumilum. The Ming Yi Bie Lu (Han Dynasty, 220–450) and Kai Bao Ben Cao (circa 1,000) highlighted the non-toxicity of its bulb and its ability to reduce swelling and relieve pain. The Ben Cao Jing Shu (Ming Dynasty, 1,368–1,644) added the treatment of abdominal pain, heat-clearing, and bowel-movement-promoting functions to its portfolio. Li Shizhen’s Ben Cao Gang Mu (1,368–1,644) systematically distinguished L. brownii var. viridulum Baker, L. lancifolium, and L. pumilum. It established the legal status of all three as botanical origins, clarified that L. brownii var. viridulum was the authentic medicinal product, and refined the system of authentic producing areas (Zhang et al., 2019).
Building on this foundation, the modern Chinese Pharmacopoeia standardizes the use of bulbs from the aforementioned species, with a recommended daily dose of 6–12 g, for the treatment of palpitation, insomnia, and hemoptysis. It also includes the classical formula Baihe Dihuang Decoction (BDD), originally recorded in Zhang Zhongjing’s Synopsis of the Golden Chamber from the Eastern Han Dynasty. This decoction combines bulbs of Lilium brownii var. viridulum with roots of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. ex Fisch. et Mey. Contemporary studies have verified the efficacy of BDD in managing perimenopausal syndrome, insomnia, and pulmonary disorders (Jiang et al., 2019). Baihe Zhimu Decoction, a combination of bulbs from the same species with roots of Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge, is used clinically to address depression (Chen and Ding, 2012). The 2015 edition of the Pharmacopoeia further includes preparations such as Baihe Gujin Oral Liquid, thereby facilitating the transformation of traditional knowledge into standardized medications. The Chinese “medicine-food homology” system expands the scope of application. The Compendium of Materia Medica records that fresh bulbs can be steamed, cooked, consumed directly, or processed into powder. In summer, lily soup or porridge (sweetened with sugar) is consumed to relieve summer heat and moisten the lungs, leading to the creation of medicinal dishes such as stir-fried lily with celery. The core therapeutic principle of “nourishing Yin and moistening the lungs, clearing the heart and calming the mind” targets symptoms such as Yin-deficiency cough, hemoptysis, and insomnia associated with asthenia and vexation. This principle underlies the development of syndrome differentiation formulas such as Baihe Gujin Tang (BGD), indicated for lung and kidney Yin-deficiency syndromes, and Baihe Zhinue Tang (BZD), formulated for deficiency-heat with body fluid impairment syndromes (Chen and Ding, 2012). Furthermore, modern honey-processed Lilium spp. and Baihe Gujin Wan (2015 edition of the Pharmacopoeia) continue to enhance the development of clinical solutions for lung diseases.
Traditional medicine practices worldwide showcase regional specificity. For instance, North American indigenous tribes (Yurok/Karuk/Yana) utilize L. pardalinum Kellogg bulbs as a food source. They directly consume Lilium plants, prepared by steaming, baking, and other methods, as a source of carbohydrates and dietary fiber. (Munafo and Gianfagna, 2015). In Europe, L. candidum L. is used to treat trauma and mastitis. Folk practitioners often pound it and apply it to skin wounds and ulcers to promote wound healing; it is also used to address mastitis, particularly in lactating women. L. martagon L. is employed for liver diseases and can also alleviate symptoms such as dyspepsia and abdominal distension caused by mild hepatic damage. (Bruni et al., 1997; Pieroni, 2000). Japan uses L. candidum in burn treatment, and traditionally, it has also been employed there as a sedative, anti-inflammatory, antitussive, and general tonic botanical drug (Mimaki et al., 1999). And Korea employs L. lancifolium roots to address respiratory diseases (Lee et al., 2013). In India, L. polyphyllum D.Don bulbs are regarded as having galactagogue, expectorant, and tonic properties (Wang Y. F. et al., 2024). In summary, the “dual-use as medicine and food” tradition of Lilium spp. plants not only underscores the unique value of ethno-pharmacology but also offers a vital traditional knowledge base for modern active metabolite research and clinical translation.
Modern research on the genus Lilium centers on its core traditional uses, such as “nourishing Yin and moistening the lungs, clearing the heart, and calming the spirit.” Through pharmacological experiments and clinical studies, researchers have gradually elucidated the active metabolites and their mechanisms of action. Alkaloids, polysaccharides, steroidal saponins, and other metabolites (Sharifi-Rad et al., 2022) isolated from Lilium species have demonstrated clear anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, sedative-hypnotic, and lung-protective effects, aligning well with traditional Chinese medicine records for treating Yin-deficiency cough, insomnia, and palpitations. Significant progress has been made in modern research on the traditional applications of Lilium plants. Classic formulas such as Baihe Dihuang Tang and Baihe Zhimu Tang, recorded in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, have been clinically validated to effectively alleviate perimenopausal syndrome, depression, and lung diseases (Fiorito et al., 2020).
3.2 Nutritional properties
In the natural world, there’s a plant with a bulb made up of dozens of white scales arranged like a lotus. Ancient people named it “Lily,” which means “a hundred pieces joined together.” Not only does the lily beautify nature with its elegant looks, but it also benefits human health thanks to its rich nutrients and medicinal properties. As early as 2002, the former Ministry of Health listed lily as one of the first “items that are both food and medicine,” showing the state’s long-term acknowledgment of its health benefits (Li and Liu, 2025). The lily, with its edible and medicinal dual attributes, holds a pivotal position in China’s food industry. Its dual-purpose utility was first recorded in the ancient Shen Nong’s Herbal Classic, making it a quintessential symbol of China’s traditional food and medicine heritage. Lily can be enjoyed in various culinary forms, from steaming and boiling as a fresh metabolite to being processed into products like lily powder, wine, and functional beverages. In traditional Chinese medicine, lily is esteemed for its abilities to alleviate phlegm and cough, nourish Yin and moisten the lungs, combat oxidative stress, modulate the immune system, and help regulate blood sugar.
Nutritionally, lily is a powerhouse, containing active bio-metabolites such as polysaccharides, saponins, and dietary fiber, along with essential nutrients like vitamins, amino acids, starch, pectin, and phospholipids, complemented by minerals including calcium and iron (Yu et al., 2024). Lily bulbs are a versatile metabolite that can be easily added to daily meals for their health benefits. For example, Lily Bulb and Lotus Seed Congee nourishes Yin and moistens the lungs, while Lily Bulb and White Fungus Soup enhances the complexion. According to traditional Chinese medicine, lily bulbs are also known for their skin-beautifying effects, thanks to their rich mucilage and various vitamins (Liu and Kang, 2025). In 1990, the Gansu Academy of Agricultural Sciences analyzed three key Chinese lily species (Lilium davidii, Lilium brownii var. viridulum, Lilium pumilum), finding protein (3.12%–3.36%), sucrose (3.67%–10.39%), reducing sugar (1.54%–3.00%), pectin (3.80%–5.61%), starch (11.10%–19.54%), fat (0.08%–0.18%), potassium (0.38%–0.64%), phosphorus (0.05%–0.07%), crude fiber (0.86%–1.11%), and ash (1.05%–1.35%). Lily bulbs are rich in nutrients, containing not only active metabolites such as polysaccharides (fresh weight 2.0–5.0g/100 g), steroidal saponins (fresh weight 0.1–0.3g/100 g), and dietary fiber (fresh weight 1.0–2.5g/100 g), but also abundant in vitamins, amino acids, starch (dry weight 11.10%–19.54%), and pectin (dry weight 3.80%–5.61%) (Ding et al., 2004). Modern medicine’s progress has spurred robust pharmacological research on lilies. Extracted active metabolites from lilies are driving the development of drugs and health products, especially for immune modulation and anti-tumor applications. Lily polysaccharide-based immunomodulators show promise in boosting immunity and treating diseases linked to low immune function, offering new treatment options for such patients. Meanwhile, research into lily-derived anti-tumor metabolites is ongoing, with the aim of creating innovative anti-cancer drugs that could significantly advance tumor treatment (Yuan, 2025). Lily is an economically efficient natural resource abundant in bioactive metabolites and nutrients, making it an ideal candidate for the development of functional foods with significant market potential. Meanwhile, as pharmacological research into lilies advances, active metabolites extracted from them are contributing to the development of drugs and health products (Zengin et al., 2022). Their efficacy has been particularly notable in immune regulation and anti-cancer fields, promising the development of new drugs that boost immunity and combat cancer (Sharifi Rad et al., 2014).
4 Phytochemical composition
Currently, approximately 123 phytochemicals have been isolated and identified from various tissues of Lilium spp. (Table 1; Table 2). These mainly include saponins, phenols and phenylpropanoids, and other metabolites. Saponins, phenols, and phenylpropanoids are considered bioactive metabolites and are known to possess various pharmacological activities. The chemical metabolites that have been isolated and identified from the Lilium spp. are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2, while the structures of the major bioactive metabolites are illustrated in Figure 2.
TABLE 1
| NO | Chemical metabolites | Molecular formula | Extracts | Parts | Source | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saponins | ||||||
| 1 | (16S,17R,20S)-3β,16,17,20-tetrahydroxy-pregnane-5-ene-3-O-{β-Dglucopyranosyl-(1→4)-6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C35H56O15 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 2 | (16S,17R,20S)-3β,16,17,20-tetrahydroxy-5α-pregnane-3-O-{β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-6-Oacetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C35H58O15 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 3 | (24S,25S)-3β,17α,24-trihydroxy-spirostan-5-ene-3-O-{O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C47H74O20 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 4 | (25R)-3β,12α-dihydroxy-spirostan-5-ene-3-O-{O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranosid-e} | C47H74O19 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 5 | (25S)-3β,17α,27-trihydroxy-5α-spirostan-3-O-{O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C45H74O19 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 6 | (25S)-3β,17α,27-trihydroxy-5α-spirostan-3-O-{O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosy-l-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C47H76O20 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 7 | (25R)-3β,12α-dihydroxy-5α-spirostan-3-O-{O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O [6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C47H76O19 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 8 | (25S)-3β,17α,27-trihydroxy-5αspirostan-3-O-{β-D-glucopyranoside-(1→4)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C47H76O21 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 9 | (25S)-3β,17α,27-trihydroxy-spirostan-5-ene-3-O-{O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C47H74O20 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 10 | (25S)-5α-spirostane-3β,17α,27-triol 3-O-{O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→2)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C45H74O20 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Liu et al. (2025b) |
| 11 | Lililancifoloside B | C46H74O19 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 12 | Lililancifoloside C | C48H76O20 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 13 | Lililancifoloside D | C33H52O11 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 14 | Lililancifoloside E | C46H74O19 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 15 | Spongipregnoloside A | C34H52O10 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 16 | (25R,26R)-26-methoxyspirost-5-en-3β-ol3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-Dglucopyranoside | C48H78O16 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 17 | Ophiogenin3-O-α-L- rhanopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C40H64O13 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 18 | (25R)-3β,17α-dihydroxy-5α- spirostan-6-one 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(l→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C40H64O13 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 19 | (25R) -3β-5α-spirostan-6-one 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)- β-D-glucopyranoside | C40H64O12 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhou N. et al. (2024) |
| 20 | (25S)-spirost-5-ene-3β,27-diol3-0-{0-x-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-0-[x-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→3)]-B-β-glucopy- ranoside} | C44H70O17 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. longiflorum | Mimaki et al. (1994) |
| 21 | (25R)-27-0-[(S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl]-spirost-5-ene-3β,27-diol3-0-{0-a-L-rhamnopyranosy-(1→2)-0-[a-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1–3)]-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C50H73O19 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. longiflorum | Mimaki et al. (1994) |
| 22 | 22-0-methy1-26-0-β-D-glucopyranosy-(25R)-furost-5-ene-3β,22ξ,26-triol3-0-{0-x-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-0-[α-L-arabinopyranosy-(1→3)]-B-D-glucopyranoside} | C52H77O22 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. longiflorum | Mimaki et al. (1994) |
| 23 | 22-0-methy-26-0-β-D-glucopvranosyl-(25R)-furost-5-ene-3β,225,26-triol3-0-{0-a-L-rhamnopyranosy-(1-2)-0-[β-D-xylopyranosy-(1→3)-B-D-glucopyranoside} | C52H77O22 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. longiflorum | Mimaki et al. (1994) |
| 24 | (25S)-spirost-5-ene-3β,17d,27-triol 3-O-{O-β-D-glu-(1→2)-O-β-D-glu-(1→4)-β-D-glu} | C45H72O20 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. martagon | Satou et al. (1996) |
| 25 | (25S)-5α-spirostane-3β,17d,27-triol 3-O-{O-β-D-glu-(1→2)-O-β-D-glu-(1→4)-β-D-glu} | C45H74O20 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. martagon | Satou et al. (1996) |
| 26 | (25S)-3β-{β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy}spirost-5-en-27-ol | C47H76O18 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum L | Haladová et al. (1998) |
| 27 | (25R,26R)-3β-{β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β- d -glucopyranosyloxy}-26-methoxyspirost-5-ene | C48H78O18 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum L | Haladová et al. (1998) |
| 28 | (25R,26R)-26-methoxyspirost-5-ene-3β,17α-diol 3-0-{0-α-L-rhamnopyranos}l-(1→2)-0-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]β-D-glucopyranoside} | C46H74O19 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1998) |
| 29 | (25R,26R)-26-methoxyspirost-5-ene-3β,17α-diol 3-0-{0-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-0-[6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C48H76O20 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1998) |
| 30 | (25R,26R)-26-methoxyspirost-5-ene-3β,17α-diol 3-0-{0-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C40H64O14 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1998) |
| 31 | (25S)-spirost-5-ene-3β,27-diol 3-0-{O-β-D-glucopy-ranosyl-(1→3)-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside} | C51H82O23 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1998) |
| 32 | (25R)-spirost-5-ene-3β-yl O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C45H72O17 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1999) |
| 33 | (25S)-27-hydroxyspirost-5-ene-3β-yl O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-Dglucopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C45H72O18 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1999) |
| 34 | (23S,25R)-23-hydroxyspirost-5-ene-3β-yl O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C45H72O18 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1999) |
| 35 | (25R,26R)-26-methoxyspirost-5-ene-3β-yl O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C46H74O18 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1999) |
| 36 | (25R,26R)-17α-hydroxy-26-methoxyspirost-5-ene-3β-yl O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C46H74O19 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1999) |
| 37 | (25R)-26-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-22-methoxyfurost-5-en-3β-yl O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C52H86O23 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Mimaki et al. (1999) |
| 38 | (25R)-spirost-5-en-3β,27-ol 3-O-α-L- rhamnopyranosyl -(1→2)-β-D- glucopyranoside | C39H63O13 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Haladova et al. (2011) |
| 39 | (25S)-spirost-5-en-3β,27-ol 3-O-α-L- rhamnopyranosyl -(1→2)-β-D- glucopyranoside | C39H63O13 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Haladova et al. (2011) |
| 40 | (25R)-27-O-[(S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylylutaryl]-spirost-5-ene-3β,27-diol 3-O-α-L-rha-(1→2)-β-D- glucopyranoside | C45H71O17 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Haladova et al. (2011) |
| 41 | (25R)-27-O-[(S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylylutaryl]-spirost-5-ene-3β,27-diol3-O-{α-L-rha-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glu-(1→4)]-β-D- glucopyranoside } | C51H81O22 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. candidum | Haladova et al. (2011) |
| 42 | 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosylnuatigenin3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C47H74O20 | MeOH | Bulbs | L.brownii | Mimaki and Sashida (1990) |
| 43 | 27-O-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroyl)spirost-5-ene-3β,27-diol (isonarthogenin)-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranoside-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C49H77018 | MeOH | Bulbs | L.brownii | Mimaki and Sashida (1990) |
| 44 | 27-O-[(3S)-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl 3-methylglutaroyl]isonarthogenin 3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C51H80O22 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Yang et al. (2012) |
| 45 | (24S,25S)-3β,17α,24-trihydroxy-5α-spirostan-6-one 3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C39H62O15 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Yang et al. (2012) |
| 46 | Tenuifoliol 3-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C39H66O15 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Yang et al. (2012) |
| 47 | 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosylnuatigenin | C33H52O9 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Yang et al. (2012) |
| 48 | 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosylnuatigenin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C39H62O14 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Yang et al. (2012) |
| 49 | 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosylnuatigenin 3-O-{α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)]}-β-D-glucopyranoside | C51H82O23 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Yang et al. (2012) |
| 50 | 26-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranosylnuatigenin 3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C51H82O23 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Yang et al. (2012) |
| 51 | (25R)-27-O-[(S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroyl]-spirost-5-ene-3 β,27-diol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]- β-D-glucopyranoside | C51H80O22 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. regale | Mimaki et al. (1993) |
| 52 | (25S)-spirost-5-ene-3 β,17 α,27-triol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O- β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C52H86O23 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. regale | Mimaki et al. (1993) |
| 53 | (25R,26R)-26-methoxyspirost-5-en-3 β-ol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→3)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C45H72O17 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. dauricum | Mimaki et al. (1992) |
| 54 | (25R,26R)-26-methoxyspirost-5-en-3 β-ol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]- β-D-glucopyranoside | C46H74O18 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. dauricum | Mimaki et al. (1992) |
| 55 | (25R)-spirost-5-en-3 β-ol (diosgenin) 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→3)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C45H72O17 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. dauricum | Mimaki et al. (1992) |
| 56 | (25R)-3 β,17 α-dihydroxy-5 α-spirostan-6-one 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C39H62O14 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. dauricum | Mimaki et al. (1992) |
| 57 | (25R)-3 β, 17 α-dihydroxy-5 α-spirostan-6-one 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-[α-L- arabinopyranosyl-(1→3)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C39H71O19 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. dauricum | Mimaki et al. (1992) |
| 58 | (20R,22R)-3 β,20,22-trihydroxy-5 α-cholestan-6-one (tenuifoliol) 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C39H66O14 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. dauricum | Mimaki et al. (1992) |
| 59 | Lililancifoloside A | C44H69H11 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Yang et al. (2012) |
| 60 | Diosgenin | C27H42O3 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. Brownii | Ji and Ding (2003) |
| 61 | Tigogenin | C27H44O3 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. Brownii | Ji and Ding (2003) |
| 62 | (22R,25R)-spirosol-5-en-3β-yl O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)-[6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C47H76O17 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. longiflorum | Munafo et al. (2010) |
| 63 | (25R)-26-O-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-furost-5-en-3β,22α,26-triol 3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)-α-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1->3)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C50H82O22 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. longiflorum | Munafo et al. (2010) |
| 64 | (25R)-26-O-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-furost-5-en-3β,22α,26-triol 3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)-α-l-xylopyranosyl-(1->3)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C51H85O22 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. longiflorum | Munafo et al. (2010) |
| 65 | (25R)-26-[(β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-22α-hydroxyfurost-5-en-3β-yl O-α-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1→3)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C56H92O27 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. pumilum | Matsuo et al. (2015) |
| 66 | (25R)-26-[(β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-22α-hydroxyfurost-5-en-3β-yl O-α-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C56H92O27 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. pumilum | Matsuo et al. (2015) |
| 67 | (25R)-26-[(β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-furosta-5,20 (22)-dien-3β-yl O-α-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1→3)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C56H90O26 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. pumilum | Matsuo et al. (2015) |
| 68 | (25R)-26-[(β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-furosta-5,20 (22)-dien-3β-yl O-α-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | C56H90O26 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. pumilum | Matsuo et al. (2015) |
| Phenolics | ||||||
| 69 | 1-O-feruloylglycerol | C13H16O6 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Luo et al. (2012) |
| 70 | 1-O-p-coumaroyl-glycerol | C12H14O5 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Luo et al. (2012) |
| 71 | 1-O-caffeoyl-3-O-p-coumaroylglycerol | C21H20O8 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Luo et al. (2012) |
| 72 | 1,2-O-diferuloylglycerol | C23H24O9 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Luo et al. (2012) |
| 73 | 1,3-O-diferuloylglyc-erol | C23H24O9 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Luo et al. (2012) |
| 74 | 1-O-feruloyl-3-O-p-coumaroylglycerol | C22H22O8 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Luo et al. (2012) |
| 75 | 1,3-O-di-p-coumaroylglycerol | C21H20O7 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Luo et al. (2012) |
| 76 | Carvacrol-2-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H32O10 | EtOH | Root | L. dauricum | Xia et al. (2022) |
| 77 | 1-methyl-3-isopropylphenol-4-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H32O10 | EtOH | Root | L. dauricum | Xia et al. (2022) |
| 78 | P-methoxythymol-5-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C22H34O11 | EtOH | Root | L. dauricum | Xia et al. (2022) |
| 79 | 8-O-4′ neolignan enantiomers (5a/5b) | C21H26O7 | EtOH | Root | L. dauricum | Xia et al. (2022) |
| 80 | 1-O-feruloyl-2-O-p-coumaroylglycerol | C22H22O8 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Ma et al. (2017) |
| 81 | 1,3-O-diferuloylglycerol | C23H24O9 | MeOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Ma et al. (2017) |
| 82 | P-coumaric acid | C6H4O4 | MeOH | Bulbs | Lilium spp. | Wang et al. (2015) |
| 83 | Ferulic acid | C10H10O4 | MeOH | Bulbs | Lilium spp. | Wang et al. (2015) |
| 84 | Chlorogenic acid | C16H18O9 | MeOH | Bulbs | Lilium spp. | Wang et al. (2015) |
| 85 | 1-O-p-coumaroyl glycerol | C13H14O4 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhao et al. (2019) |
| 86 | 1-O-caffeoyl-3-O-p-coumaroyl glycerol | C21H20O8 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhao et al. (2019) |
| 87 | 1-O-p-coumaroyl-3-O-caffeoyl-3-hydroxy glycerol | C21H20O9 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhao et al. (2019) |
| 88 | 1-O-caffeoyl-3-O-feruloyl glycerol | C22H21O9 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhao et al. (2019) |
| 89 | 1-O-caffeoyl-3-O-sinapoyl glycerol | C23H22O10 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhao et al. (2019) |
| 90 | P-coumaroyl | C9H8O3 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhao et al. (2019) |
| 91 | 1,3-O-p-coumaroylacetyl glycerol | C23H22O9 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. lancifolium | Zhao et al. (2019) |
| Phenylpropanoids | ||||||
| s92 | 3-O-acetyl-1-O-caffeoylglycer-ol | C14O7H16 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Hui, C. et al. (2024a) |
| 93 | 3-O-acetyl-1-O-p-coumaroylglycerol | C14O6H16 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Hui, C. et al. (2024a) |
| 94 | Regaloside A | C18H24O10 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Seo et al. (2024) |
| 95 | Regaloside B | C20H26O11 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Seo et al. (2024) |
| 96 | Regaloside C | C18H24O11 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Seo et al. (2024) |
| 97 | Regaloside E | C20H26O12 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Seo et al. (2024) |
| 98 | Regaloside F | C19H26O11 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Seo et al. (2024) |
| 99 | Regaloside H | C18H24O10 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Seo et al. (2024) |
| 100 | Regaloside I | C20H26O11 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Seo et al. (2024) |
| 101 | Regaloside K | C18H24O11 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. brownii | Seo et al. (2024) |
| 102 | (2,4,6-trichloro-3-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)methyl β-D-glucopyranoside | C14H17Cl3O8 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. regale | Yan et al. (2021) |
| 103 | (2,4-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl 6-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside | C21H30Cl2O13 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. regale | Yan et al. (2021) |
| 104 | 4-chloro-3-methoxy-5-methylphenyl 6-O-(6-deoxy-β-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside | C20H29ClO11 | EtOH | Bulbs | L. regale | Yan et al. (2021) |
| Others | ||||||
| 105 | Liliumtide A | C21H29N3O6 | MeCO | Bulbs | L. davidii var. unicolor | Zhang H. et al. (2022) |
| 106 | Liliumtide B | C27H39N3O11 | MeCO | Bulbs | L. davidii var. unicolor | Zhang H. et al. (2022) |
Chemical metabolites isolated and structurally identified from different medicinal parts of Lilium spp.
EtOH, ethanol; MeOH, methanol; MeCO, acetone.
TABLE 2
| No. | Polysaccharides | Monosaccharide composition | M.W. (Da) | Structures | Bioactivities | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LDP | D-mannose, D-glucose, D-galactose, with molar ratios of 10 : 19: 1 | 5.17 × 104 | The main chain of the LDP is primarily made up of a 1,4-linked form for -Glc and a 1,3-linked form for -Man, with approximate molecule ratios 2 : 1. On average, there is one 1,6-linked form for -Gal or one 1,3-linked form for -Man residues which can be substituted at 6-O from among 30 sugar residues | ND | Zhang et al. (2010) |
| 2 | LLPS-1 | Glucose: mannose = 2:1; with a trace amount of arabinose and galactose | 3.505 × 105 | ND | Immune enhancement activity | Chen et al. (2014) |
| 3 | LLPS-2 | Glucose: mannose = 1:1; with a minuscule amount of arabinose | 4.033 × 105 | ND | Immune enhancement activity | Chen et al. (2014) |
| 4 | LLPS-3 | Arabinose: galactose: glucose: mannose = 2:2:2:1 | 1.462 × 105 | ND | Immune enhancement activity | Chen et al. (2014) |
| 5 | LP2-1 | L-rhamnopyranose, D-arabinofuranose, D-glucopyranose and D-galactopyranose in the molar ratio of 1.88:2.13:1.00:2.50 | 8.52 × 106 | Major functional groups of LP2-1 were ACOOA and AOH | Antioxidant activity | Gao et al. (2015) |
| 6 | LLP-1 | Mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galacturonic acid, glucose, galactose, arabinose glucose and galactose | 2.25 × 106 | ND | Antioxidant activity | Xu et al. (2016) |
| 7 | LLP-2 | Mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galacturonic acid, glucose, galactose, arabinose glucose and galactose | 2.02 × 106 | ND | Antioxidant activity | Xu et al. (2016) |
| 8 | LLP-3 | Mannose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galacturonic acid, glucose, galactose, arabinose glucose and galactose | 2.08 × 106 | ND | Antioxidant activity | Xu et al. (2016) |
| 9 | LLP-1A | Mannose and glucose at a molar ratio of 1.77:1 | 7.861 × 104 | The presence of uronic acid, pyranose rings and β-glycosidic bonds | Immune enhancement activity | Pan et al. (2017) |
| 10 | LDP-2 | four kinds of monosaccharides (Lyxose, Mannose, Glucose, and Galactose in an approximate weight ratio of 6.74: 6.28: 76.50: 10.48) | 6.2 × 104 | ND | Hypoglycemic activity | Wang F. et al. (2018) |
| 11 | BHP-1 | Glucose and mannose in a relative molar ratio of 5.9:2.0 | 1.93 × 105 | Mainly contained α-(1→4)-linked D-glucopyranosyl | Antioxidant activity | Hui et al. (2019b) |
| 12 | BHP-2 | Glucose, galactose, mannose and arabinose with approximate molar ratios of 8.3:1.5:1.0:1.1 | 3.52 × 104 | Mainly contained α-(1→4)-linked D-glucopyranosyl | Antioxidant activity | Hui et al. (2019b) |
| 13 | LPR | Glucose and mannose with a molar ratio of2.9:3.3 | 5.12 × 104 | The backbonemainly contained β-(1→4)-linked D-glucopyranosyl and β-(1→4)-linkedDmannopyanosyl, and the branches probably linked at O-2 and/or O-3 ofthe mannosyl and glucosyl residues | Antioxidant activity | Hui et al. (2019a) |
| 14 | L01-B1 | Rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galacturonic acid, galactose, and arabinose in a molar ratio of 13.4: 1.8: 11.1: 37.2: 36.5 | 4.39 × 104 | The backbone was composed of 1, 6-β-Galp, 1, 4-α-GalpA, and 1, 2-α-Rhap, whereas the branches included 1, 5-α-Araf, 1, 4-β-Galp, and T-β-GlcpA attached to C-4 of rhamnose, and 1, 3-β-Galp and T-β-Galp linked to C-3 of galactose | ND | Li M. et al. (2025) |
| 15 | WLBP-A3-c | Homogalacturonan, rhamnogalacturonan I, and rhamnogalacturonan domains, with mass ratios of 76.0: 17.2:6.8 | 5.9 × 104 | Composed of repeating units of [→2)-α-L-Rhap-(1→4)-α-D-GalpA-(1→] with highly branched neutral sugar side chains at the O-4 position of Rhap | Antioxidant activity | Zhao et al. (2024) |
| 16 | LBP | Mannose and glucose of the corresponding molar ratios are 0.582 and 0.418 | 3.12 × 105 | ND | Immune enhancement activity | Li X. J. et al. (2024) |
| 17 | LLP11 | Mannoglucan | 1.2 × 104 | A backbone of→4)-α-D-Glcp-(1→and→4)-β-D-Manp-(1→with a branch of T-α-D-Glcp-(1→substituted at C-6 of→4,6)-α-D-Glcp-(1→ | ND | Bai et al. (2024) |
Monosaccharides composition, molecular weight, structures, and bioactivities of polysaccharides purified from Lilium spp.
ND, not detected; M.W., molecular weight.
FIGURE 2

Chemical structures of metabolites isolated from the Lilium spp.
4.1 Saponins
Saponins are ubiquitous in the plant kingdom, featuring a structure with a triterpene or steroid aglycone linked to one or more sugar chains. Owing to their physicochemical (surfactant) properties and diverse biological activities, including anticancer and anticholesterol effects, their applications in the food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries are continuously expanding (Guclu-Ustundag and Mazza, 2007). Numerous studies have reported that lilies are rich in diverse saponin metabolites. So far, researchers have successfully isolated and chemically characterized a total of 68 saponin metabolites (1–68) from various medicinal parts of Lilium spp., such as bulbs and roots. It is widely reported that L. lancifolium is rich in various steroidal saponins. Researchers isolated nine previously undescribed metabolites (1–9) and one known metabolite (10) from the bulbs of L. lancifoliumL Thunb. Among these, metabolites 1 and 2 possess unique structures based on the known polyoxygenated pregnane skeleton. These metabolites were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) (Liu, S. et al., 2025b).
Four steroidal glycosides (11–14) and five known ones (15–19) were isolated from the bulbs of L. lancifolium. All isolated metabolites were evaluated for cytotoxicity against MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, HepG2, and A549 tumor cell lines. Among them, metabolite 6 emerged as the most potent, exhibiting IC50 values of 3.31, 5.23, 1.78, and 1.49 μM, respectively. Notably, metabolites 3, 5, and 9 also displayed selective cytotoxic effects. Subsequent mechanistic studies revealed that metabolite 6 arrests HepG2 cells at the G2/M phase and induces apoptosis (Zhou J. et al., 2024). Two previously undescribed spirostanol saponins (20–21) and two new furostanol saponins (22–23) were isolated from the fresh bulbs of Lilium longiflorum together with several known saponins (Mimaki et al., 1994). Two previously undescribed steroidal saponins (24–25) were isolated from the fresh bulbs of Lilium martagon (Satou et al., 1996). Two steroidal saponins (26–27) from Lilium candidumL. and their structures were derived mainly from NMR and mass spectra (Haladová et al., 1998). Four new metabolites were isolated from the fresh bulbs of Lilium candidum (Mimaki et al., 1998). Five new spirostanol saponins and a previously undescribed furostanol saponin (32–37) were isolated from the fresh bulbs of Lilium candidum (Mimaki et al., 1999). metabolites 38 and 39 are isomeric structures of 3-L-rhamnopyranosyl-12D-glucopyranosyloxyspirost-5-en-27-ol, which were isolated from Lilium candidum (Haladova et al., 2011). metabolites 42 and 43 are novel steroidal saponins isolated from the fresh bulbs of L. brownii (Mimaki and Sashida, 1990). The bulbs of L. brownii led to the isolation of seven steroidal saponins (44–50) (Yang et al., 2012). Two new steroidal saponins (51–52) were isolated from the fresh bulbs of Lilium regale (Mimaki et al., 1993). The bulbs of Lilium dauricum yielded six isolated steroidal glycosides (Mimaki et al., 1992). Lililancifoloside A (59) is a previously undescribed steroidal saponin (Yang et al., 2012). Diosgenin (60) and tigogenin (61) is a steroidal saponin that has been isolated from L. brownii (Ji and Ding, 2003).A steroidal glycoalkaloid (62) and two furostanol saponins (63–64) were isolated from the bulbs of L. longiflorum (Munafo et al., 2010). Four novel steroidal glycosides (65–68), containing a 2,3,4-trisubstituted β-D-glucopyranosyl group, have been successfully isolated from the bulbs of Lilium pumilum (Matsuo et al., 2015).
4.2 Phenolics
Studies indicate that dietary phenolic acids, monophenols, and polyphenols can inhibit the invasive and metastatic behaviors of various cancer cells (such as adhesion, migration, and angiogenesis) both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, daily consumption of natural foods rich in phenolics may help prevent cancer metastasis (Djafarou et al., 2025). To date, researchers have isolated 23 phenolic metabolites from lily bulbs (69–91). Phenolic metabolites are very important active metabolites in L. lancifolium, which play a significant role in antioxidation, antitumor (Sharifi-Rad et al., 2023), and treatment of cardiovascular diseases (Sharifi-Rad et al., 2021), while phenylpropanoid glycerol esters are common phenolic metabolites in the plant kingdom. In this study, preparative separation of seven phenylpropenoid glycerides (69–75) from the bulbs of L. lancifolium, was conducted by high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) with a two-phase solvent system composed of n-hexane-ethyl acetate-methanol-0.05% aqueous trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) (3:5:3:5, v/v/v/v). Their structures were identified by ESI-MS, 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra (Luo et al., 2012).
Three phenolic glycosides and a pair of 8-O-4′ neolignan enantiomers (5A:/5B) (76–79), were isolated from the roots of Lilium dauricum (Xia et al., 2022). In the study, Ma et al. (2017)using bioassay-guided isolation method, two phenylpropenoid acylglycerols, 1-O-feruloyl-2-O-p-coumaroylglycerol (80) and 1,3-O-diferuloylglycerol (81), were obtained and identified from the chloroform fraction of the bulbs of L. brownii var. viridulum (Ma et al., 2017). metabolite 82, 83, and 84 is a phenolic metabolite that occurs in Lilium spp. (Wang et al., 2015). metabolite 85–91 is a phenolic metabolite that was isolated from L. lancifoliumL (Zhao et al., 2019).
4.3 Phenylpropanoids
A variety of fruits, vegetables, cereals, beverages, spices, and botanical drugs contain phenylpropanoids and their derivatives, which are plant secondary metabolites. They have diverse roles, such as antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, and anti-cancer activities, along with nephroprotective, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, and hepatoprotective effects (Neelam et al., 2019). So far, 13 phenylpropanoid metabolites (92–104) have been successfully isolated and chemically identified from lily bulbs and roots. Based on their substructure types, these metabolites can be classified into simple phenylpropanoids, lignans, and coumarins. In the study, two phenylpropanoid metabolites including 3-O-acetyl-1-O-caffeoylglycerol (92) and 3-O-acetyl-1-O-p-coumaroylglycerol (93) were isolated from the bulbs of L. brownii. Their structures were identified by spectroscopic method and the effect on monoamine oxidase activity was determined using an enzyme labeling method. The results show 92 and 93 have anti-monoamine oxidase activity with 20.96% and 22.31% inhibition rates at 50 μg/mL, respectively (Hui, C. et al., 2024a). A simultaneous quantitative method was developed for the quality control of Bulbs of L. lancifoliumL Thunb. (BLL) using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a photodiode array detector (HPLC-PDA), and their antioxidant effects were evaluated. Eight regalosides (i.e., regaloside A, B, C, E, F, H, I, and K) (94–101) were selected as marker substances. The method was validated with respect to linearity, sensitivities (limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ)), accuracy, and precision (Seo et al., 2024).
Three previously undescribed chlorophenyl glycosides, (2,4,6-trichloro-3-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)methyl β-D-glucopyranoside (102), (2,4-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl 6-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (103) and 4-chloro-3-methoxy-5-methylphenyl 6-O- (6-deoxy-β-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside (104) were obtained from L. regale. The absolute configurations of these new finds were elucidated by comprehensive analyses of spectroscopic data combined with acid hydrolysis derivatization. (2,4-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl) methyl 6-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (103) can inhibit the proliferation of lung carcinoma A549 cells with an IC50 value of 29 μΜ (Yan et al., 2021).
4.4 Other metabolites
Up to date, apart from the chemical metabolites listed above, only few metabolites have been also investigated. Briefly, twenty-five water-soluble metabolites were isolated from the bulbs of L. davidii var. unicolor, including two metabolites termed Liliumtides A and B (105–106) by Zhang H. et al. (2022). To confirm further the absolute configuration of Liliumtide A (105), and accumulate enough sample to study the anti-insomnia effect, a total synthesis was achieved by four steps (Zhang H. et al., 2022).
Polysaccharides, as important biomacromolecules, exhibit favorable biological properties, interact with various cell membrane structures, participate in diverse pharmacological activities, and are widely distributed throughout biological systems (Chen L. et al., 2025). Polysaccharides are among the most extensively studied classes of metabolites, exhibiting significant pharmacological effects in Lilium spp., from which 17 polysaccharide metabolites have been successfully isolated and purified. It is reported that they exhibit various pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and hypoglycemic effects.The polysaccharide LDP, derived from Lilium spp., is an amorphous powder composed of three monosaccharides: D-mannose (D-Man), D-glucose (D-Glc), and D-galactose (D-Gal), in approximate molar ratios of 10:19:1 (Zhang et al., 2010). In 2014, Chen et al. (2014) extracted water-soluble polysaccharides from tiger lily using an ultrasound-assisted method, subsequently separating and purifying LLPS-1, LLPS-2, and LLPS-3, with molecular weights of 350.5, 403.3, and 146.2 kDa, respectively. LLPS-1 and LLPS-2 primarily consisted of glucose and mannose in molar ratios of nearly 1:2 and 1:1, respectively. In contrast, LLPS-3 was primarily composed of arabinose, galactose, glucose, and mannose in a molar ratio of nearly 2:2:2:1 (Chen et al., 2014). A novel polysaccharide fraction (LP2-1) was isolated and purified from the edible bulbs of Lilium lancifolium Thunb. LP2-1 had an average molecular weight of approximately 8.52 × 103 kDa and was mainly composed of L-rhamnopyranose, D-arabinofuranose, D-glucopyranose and D-galactopyranose in the molar ratio of 1.88:2.13:1.00:2.50 (Gao et al., 2015). In other study, LLP-1, LLP-2, and LLP-3 three novel polysaccharide fractions were purified from the leaves of Lilium lancifolium (Xu et al., 2016).
In summary, the monosaccharide composition, molecular weight, structural characteristics, and biological activities of the aforementioned purified polysaccharides from Lilium spp. are presented in Table 2. The polysaccharides of Lilium spp., as detailed in Table 2, feature a composition of key monosaccharides including mannose, glucose, galactose, arabinose, rhamnose, glucuronic acid, galacturonic acid, and lyxose. Consequently, polysaccharides derived from Lilium spp. demonstrate diverse applications in the medical and healthcare fields, and their potential uses in scientific research and clinical settings are actively being explored.
In summary, 123 chemical metabolites have been isolated and identified from Lilium plants to date, with the core metabolites including saponins (68 species, such as metabolites 6, 9, 103, and total tigogenin saponins), phenolics (23 species, such as phenylpropanoid glycerol esters 69-75 and 1-O-Resina Ferulaen-2-O-p-coumaroyl glycerol), phenylpropanes (13 species, covering regalin A-K, metabolites 92-93, and chlorophenyl glycosides 102–104), and structural polysaccharides (17 species, including LDP, LLPS-1/2/3, LP2-1, and LP60-1, etc.). The mechanisms of action of some chemical metabolites have been elucidated, metabolite 6 exerts anti-neoplasms activity by arresting HepG2 Cell in the G2/M phase and inducing Apoptosis; regalin A achieves anti-Depression effect via regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway; structural polysaccharides achieve hypoglycemic and immunisation effects by inhibiting alglucosidase alfa/α-Diastase and interfering with the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, respectively; phenylpropanoid glycerol esters exhibit antioxidant effects by scavenging free radicals and chelating Metal ions. However, the structure-activity relationship of active metabolites in Lilium has not been systematically revealed and still needs further investigation.
5 Pharmacological properties
As previously mentioned, lilies have been widely used in traditional medicine in many countries for thousands of years to treat and prevent various diseases. Currently, numerous studies have reported on the pharmacological activities of Lilium spp. extracts from most of its effective chemical metabolites exhibit a wide range of pharmacological activities, including hypoglycemic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antidepressant, antitumor, neuroprotective, immune-enhancing, lung function maintenance, intestinal protection, and anti-insomnia effects. Consequently, Lilium spp. has recently garnered increasing attention. These pharmacological studies will be elaborated on in the following paragraphs. These biological activities are discussed individually in the following paragraphs, and a summary is presented in Table 3. Next, all these pharmacological findings will be summarized and discussed in the sections that follow. To this end, we listed the main pharmacological activities of the Lilium spp. using Sankey diagram in Figure 3, and graphically illustrated the pharmacological activities of the Lilium spp. in Figure 4.
TABLE 3
| No. | Metabolites/Extracts | Types | Testing subjects | Doses/Duration | Effects/Mechanisms | Positive controls/Negative control | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory activity | |||||||
| 1 | ELLB | In vitro | RAW 264.7 cells | 50–200 μg/mL for 24 h | IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels ↓; p-PI3K, p-Akt, and p-IKK protein expression ↓; MyD88 and TRAF6 expression levels ↓; IFN-β, secreted by activated IRF3 ↓ | Indomethacin/Lipopolysaccharide | Sim et al. (2020) |
| 2 | MLLR | In vitro | RAW 264.7 cells | 10, 20, 50, and 100 g/mL for 24 h | NO, PGE2, IL-6 and TNF-α production ↓; ERK1/2 and JNK and translocation of the NF-κB p65 subunit into nuclei ↓; interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 ↓ | NM/Lipopolysaccharide | Kwon et al. (2010) |
| 3 | ELLB | In vitro | RAW 264.7 cells | 0–300 μg/mL for 24 h | NO, iNOS, COX2, and TNF-α levels ↓; MyD88- and TRIF-induced NF-κB transcriptional activation and the nuclear translocation of NF-κB transcription factors, the NF-κB signaling pathway ↓ | Lipopolysaccharide/no Lipopolysaccharide | Han et al. (2018) |
| 4 | MLLB | In vitro | RAW 264.7 cells | 5–100 μg/mL for 24 h | IC50 were 9.12 µM and 12.01 µM; PGE2, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels ↓; NOS, COX-2 protein levels ↓; NF-κB p65 subunit, MAPKs pathway ↓ | Dexamethasone/Lipopolysaccharide | Ma et al. (2017) |
| 5 | ALLL | In vitro | LPS-induce HaCaT cells | 25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800 μg/ML for 24 h | IL-6, iNOS level ↓ | Aspirin/Lipopolysaccharide | Hu et al. (2025) |
| Antioxidant activity | |||||||
| 6 | ELLB | In vitro | CCK-8 assay (assess PC12 cells) | 50 μM for 24 h | Antioxidant activity ↓ | N-Acetylcysteine/RPMI-1640 Medium | Liu et al. (2025a) |
| 7 | ELLB | In vitro | DPPH assays | 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/mL | FRAP activity ↑ | Lipopolysaccharide + Indomethacin/Lipopolysaccharide | Sim et al. (2020) |
| 8 | ALLL | In vitro | DPPH, Hydroxyl, Superoxide, and Fe2+ chelating assays | 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 mg/mL | DPPH assays EC50 were 5.54, 2.34, and 1.43 mg/mL; Hydroxyl assays EC50 were 0.71, 0.52, 0.53, and 0.22 mg/mL; Superoxide assays EC50 were 0.09, 0.07, and 0.06 mg/mL; Fe2+ chelating assays EC50 were 0.71, 0.70, and 0.60 mg/mL | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid/Deionizedwater | Xu et al. (2016) |
| 9 | ELLB | In vitro | DPPH, Hydroxyl, reducing power, and Fe2+ chelating assays | 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 and 5.0 mg/mL | DPPH and hydroxyl radicals scavenging activities ↑; power and chelating activity on ferrous ion ↓ | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid/Deionizedwater | Gao et al. (2015) |
| 10 | MLLB | In vitro | DPPH, ABTS, cupric-reducing, and hydroxyl assays | NM | Antioxidant activity ↑ | Trolox/Deionizedwater | Jin et al. (2012) |
| 11 | ELLB | In vitro | DPPH, ABTS, FRAP assays | 100 μL | IC50 = 0.033 µM, Antioxidant capability; radical cation scav-enging capacities; Ferric reducing antioxidant power ↑ | Trolox/Deionizedwater | Luo et al. (2012) |
| 12 | ELLB | In vitro | DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays | NM | Antioxidant activity↑ | Trolox/Deionizedwater | Liang et al. (2022) |
| 13 | AELBB | In vitro | DPPH, ABTS, and Hydroxyl radical scavenging assays; HepG2 cells | 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0 and 10.0 mg/mL; 100 or 200 μg/mL for 24 h | IC50 values for DPPH, hydroxyl and ABTS radicals were 35.3, 7.1 and 36.4 mg/mL, respectively | GlcA/Deionizedwater | Zhao et al. (2024) |
| 14 | PELDB | In vitro | DPPH assays | 0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 mg/mL | IC50 values: 0.63, 0.32, and 0.30 mg/mL, respectively | Floralfragranceextract/DealcoholizedWine | Gao et al. (2022) |
| Antidepressant activity | |||||||
| 15 | ALLB | In vivo | Male C57BL/6 J mice with PTZ-induced seizures | 500 mg/kg; p.o., daily for 14 days | Hyperactivation and ectopic migration of DGCs ↓; PTZ kindling-induced MFS ↓; MFS by regulating hippocampal Netrin-1/Sema3A/Sema3F ↓ | Valproicacid/PTZ | Park and Cai (2024) |
| 16 | ELLB | In vitro | SH-SY5Y cell injury model induced by CORT | 5, 15, 25, 50, 75, and 100 μM for 24 or 48 h | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, tyrosine kinase receptor B phosphorylation levels ↑; phatidylinositol 3 kinase, protein kinase B, and mammalian target of rapamycin proteins expression ↑; Damage of corticosterone in SH-SY5Y cells ↓ | Corticosterone/DMEMmedium | Yuan et al. (2021) |
| 17 | ALLL | In vitro | CORT-induced in PC12 cells | 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 μM for 24 h | UPRs (GRP78 and CHOP), Ca2+ level ↓; Neuronal apoptosis-related proteins expression ↓; CORT-induced DNA fragmentation ↓; Intracellular ROS levels ↓ | Corticosterone/Dimethylsulfoxide | Lee et al. (2025) |
| 18 | ALLR | In vivo | OVX mice | 1.8 g/kg, i.g., daily for 3 weeks | Hippocampal NGF, prefrontal GDNF ↑; uterine and brain regional ERβ expression levels ↑ | Ovariectomized/vehicle | Zhou et al. (2019a) |
| 19 | ALLR | In vivo | OVX mice | 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg, i.g., daily for 6 days | The glutamate levels and NMDAR1 expression↓; the p-CaMKII/CaMKII ratio ↑ | Ovariectomized/vehicle | Zhou et al. (2019b) |
| 20 | EELBB | In vivo | Mice with PD induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine hydrochloride | Ethanol groups (1.25 g/kg, 2.5 g/kg) aqueous groups (0.78125 g/kg, 1.5625 g/kg), i. g., daily for 30 days | The number of neurons in the substantia nigra region ↑; MDA, Fe2+, SOD, and GSH-Px levels ↑ | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridinehydrochloride/Normalsaline | Hui, C. et al. (2024b) |
| 21 | LLS | In vivo | Mice exposure to the chronic unpredictable mild stress | 50 mg/kg, i.g., daily for 30 days | COX-2, PGE2, and IL-22 protein expression ↓ | Chronicunpredictablemildstress/NM | Ma et al. (2024) |
| 22 | LLLPS | In vitro | BV-2 cells | 1 mg/L for 24 h | BV-2 microglial cell activation, inflammation, and neuron apoptosis↓ | Chronicunpredictablemildstress/NM | Ma et al. (2024) |
| Antitumor activity | |||||||
| 23 | ELLB | In vitro | Cytotoxic potential against the MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, HepG2, and A549 cell | 100, 10, 1, 0.1 μM for 24 h | MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, HepG2, and A549 cell lines IC50 values: 3.31, 5.23, 1.78, and 1.49 μM, respectively | Paclitaxel/DimethylSulfoxide | Zhou J. et al. (2024) |
| 24 | ELLB | In vitro | SGC-7901 and HGC-27 cells | 0, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 μg/mL for 24 h | PCNA, anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 expression level ↓; p21 level, pro-apoptotic protein Bax expression ↑; Cell migration and invasion, MMP-2 expression ↓; TIMP-1 expression ↑ | Cisplatin/0.3%ethanol | Zhang et al. (2020) |
| 25 | ALLB | In vitro | MDA-MB-231, A549, HepG2, and MCF7 cell | 50–400 μg/mL | MDA-MB-231, A549, HepG2, MCF7. IC50 were 267.7, 131.8, 123.8, and 99.63 μg/mL, respectively | Paclitaxel/0.1% (v/v)DimethylSulfoxide | Zhang M. et al. (2022) |
| 26 | MELLB | In vitro | G292, A431 and KB cancer and HGF-1 normal cells | 50 μg/mL | BID/MAPK14 expression ↑; decreased MDM2/BCL2/MYC expression, p53 protein-induced apoptosis↓ | Doxorubicin/0.1% (w/v)DimethylSulfoxide | Partovi et al. (2023) |
| Hypoglycemic activity | |||||||
| 27 | ELLF | In vitro | The glucose uptake and consumption of metabolites on Caco-2 cells | 400, 200, 100, 50, 25, 12.5, and 6.25 μM for 48 h | Glucose by normal Caco-2 cells absorption ↑; SGLT1 and GLUT2 and mRNA transcription protein expression levels ↑; Glucose tracer 2-NBDG on Caco-2 cells uptake ↑ | NM/Phosphate-BufferedSaline | Xu et al. (2021) |
| 28 | ELLB | In vivo | STZ induced diabetic mice | 200 mg/kg, i.g., daily for 28 days | MDA in serum, liver and kidney levels ↓; SOD, CAT and GPx in the serum, liver and kidney levels ↑ | Glibenclamide/DistilledWater | Zhang et al. (2014) |
| 29 | MLLB | In vitro | HepG2 cells, 3T3L1 adipocytes, and 3T3-L1 preadipocyte | 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL | Glucose consumption in HepG2 cells and 3T3-L1 adipocytes; 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation ↑ | Metformin/DimethylSulfoxide | Zhu et al. (2014) |
| 30 | AELDB | In vitro | α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition assay | 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 mg/mL | IC50 values: 0.31 and 0.18 mg/mL, 0.27 and 0.12 mg/mL | Acarbose/Phosphate-BufferedSaline | Hui, H. et al. (2024a) |
| 31 | AELDB | In vitro | α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition assay | 4, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25 and 0.125 mg/mL | α-glucosidase and α-amylase ↓ | Acarbose/Phosphate-BufferedSaline | Hui, H. et al. (2024b) |
| Immune enhancement activity | |||||||
| 32 | ELLB | In vitro | RAW264.7 cells | 0, 75, 150, 300, and 600 μg/mL for 20 h | Cytokines interleukin-6, monocyte chemotactic protein 1, tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β expression ↑; Toll-like receptor 4 and phosphorylation of the inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase, inhibitor of NF-κB, and nuclear factor-kappa B protein expression ↑ | Lipopolysaccharide/Phosphate-BufferedSaline | Pan et al. (2017) |
| 33 | ALLB | In vitro | RAW264.7 cells | 5 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL for 24 h | TNF-α, iNOS, IL-6, IL-1β and TLRs mRNA expression ↑ | Lipopolysaccharide/Dulbecco’sModifiedEagleMedium | Li X. J. et al. (2024) |
| 34 | AELDB | In vitro | RAW 264.7 cells | 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25 and 3.125 μg/mL for 24 h | RAW 264.7 cells significantly phagocytosis, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-2, acid phosphatase, and CD86 and CD80 molecular expression ↑ | Lipopolysaccharide/Dulbecco’sModifiedEagleMedium | Li et al. (2021) |
| 35 | AELDB | In vivo | Immunosuppressive modeling mice | 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg, i.g., daily for 5 days | Immune organs index, interferon-γ, IL-6, immunoglobulin (Ig)G and IgM, lymphocyte proliferation ↑ | Cyclophosphamide/PhysiologicSaline | Li et al. (2021) |
| Maintain lung function activity | |||||||
| 36 | ALLR | In vivo | C57BL/6 mice prior CS exposure | 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, and 150 mg/kg, i.g., daily for 3 weeks | Inflammatory cells (macrophages and neutrophils), pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β), chemokine (MCP-1), and protease (MMP-12) level ↓; Airway enlargement in CS-exposed mice ↓ | Dexamethasone/DistilledWater | Lee et al. (2013) |
| 37 | ALLB | In vivo | COPD mouse models induced by cigarette smoke extract and porcine pancreas elastase | 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg, i.g., daily for 22 days | Production of inflammatory mediators and infiltration of immune cells involving neutrophils and macrophages ↓; IL-6 and MIP-2 production, NF-κB ↓ | Roflumilast/Phosphate-BufferedSaline | Eom et al. (2023) |
| 38 | ALLF | In vivo | C57BL/6J mice injected intratracheally with bleomycin | 10, 30, 90 mg/kg, i.p., daily for 14 days | Fibrosis-related markers and suppressed the EMT process expression ↓ | N-Acetylcysteine/DimethylSulfoxide | Liu R. et al. (2025) |
| 39 | ALLF | In vitro | TGF-β1-Induced Alteration of A549 Cell | 0, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1,000 μg/mL for 48 h | αSMA, COL1A1 levels ↓; E-cadherin ↓; Vimentin ↑ | Nintedanib/PhysiologicSaline | Liu R. et al. (2025) |
| 40 | ELLB | In vivo | LPS-induced pneumonia mice | 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg, i.g., for 48 h | Inflammatory cell infiltration, proinflammatory factors (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α) levels ↓; (IL-6, NF-κB P65) in the lung tissue, cilia-related genes (Ttc21a, Cfap45, etc.) proteins levels ↓ | Lipopolysaccharide/PhysiologicSaline | Sun et al. (2024) |
| 41 | MELDB2 | In vivo | mice model exposed to the carbon black nanoparticles | 0.1, 0.5, 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/mL i.g., for 28 days | TNF-α, IL-10, and IL-6 levels ↓ | CarbonBlackNanoparticles/Phosphate-BufferedSaline | Khan et al. (2024) |
| Gastrointestinal protection activity | |||||||
| 42 | ELLF | In vitro | GB medium pre-culture | 10 mg/mL for 24 h | Bifidobacterium longum abundance ↑; Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron abundance ↓ | Simvastatin/DistilledWater | Li Z. et al. (2025) |
| 43 | ALLB | In vivo | Intestinal contents and mucosa of male Kunming mice | 0.15 g/mL, i.g., twice daily for 49 days | Lactobacillus spp. and Bifidobacteria spp growth ↑; Amylase activities in intestine contents ↑; Mucosa lactase activity ↑ | Lactobacillusspp./Bifidobacteriaspp.StandardStrains/SterilizedWater | Wu et al. (2021) |
| Relieve joint pain activity | |||||||
| 44 | ELLB | In vivo | Clinical trial (adults experiencing pain for more than 3 months with pain Visual Analog Scale scores of 30–70 mm) | 1,000 mg; p.o., daily for 12 weeks | IL-6, TNF-α levels ↓; Arthritis-related pain ↓ | StandardSolutions/PlaceboTablets | Jeon et al. (2024) |
| 45 | ELLB | In vivo | Osteoarthritis induction male beagle dogs | 60 mg/kg; p.o., daily for 12 weeks | IL-6, COX-2, LTB-4, PGE-2, and MMP-9 levels ↓ | GlucosamineHydrochloride/EmptyGelatinCapsules | Cho et al. (2022) |
| Myoprotective | |||||||
| 46 | ELLB | In vitro | DEX-induced C2C12 myoblast cells | 0.2 mM DEX for 24 h | C2C12 myo- tubes muscle density ↑ | Resveratrol/Phosphate-BufferedSaline | Kim et al. (2024) |
| 47 | ELLB | In vivo | DEX-induced male C57BL/6 N the mice | 100, 300 mg/kg, i.g., daily for 10 days | Myogenic protein Myod1 promoter activity ↑; Muscle protein degradation ↓ | AscorbicAcid/Dulbecco’sModifiedEagleMedium | Kim et al. (2024) |
| Anti-melanogenesis activity | |||||||
| 48 | ALLR | In vitro | B16F10 cells | 0, 20, 50, 100, and 200 μg/mL for 48 h | Melanin production, core melanogenic enzymes expression ↓; Cellular tyrosinase activity as well as the mRNA and protein levels of tyrosinase, Tyrp1, and Tyrp2 ↓; Melanogenesis by effectively attenuating the CREB/Mitf signaling pathway ↓; Upstream signaling proteins, such as PKA, ERK, and p38 levels ↓ | Arbutin/Dulbecco’sModifiedEagleMedium | Park et al. (2023) |
| Anti-insomnia activity | |||||||
| 49 | MELDB | In vivo | Injected with sodium pentobarbital male SD rats | 5 mg/kg, i.v., for 60 min | sleep latency ↓; sleep time ↑ | Melatonin/NormalSaline | Zhang H. et al. (2022) |
| 50 | EELBB | In vivo | Insomnia model by intraperitoneally injection p-chlorophenylalanine | 598.64 mg/kg, p.o., daily for 7 days | 5-HT, MT↑; 5-HT1AR and GABAAR ↓; kynurenic acid, trimethylamine-N-oxide ↓ | p-Chlorophenylalanine/NormalSaline | Si et al. (2022) |
| Alleviate obesity activity | |||||||
| 51 | MLLB | In vitro | HepG2 cells | 200 and 400 μg/mL for 48 h | Mitochondrial membrane potential, reactive oxygen species production, oxidative stress, and lipid accumulation ↓ | AscorbicAcid/Dulbecco’sModifiedEagleMedium | Kan et al. (2021) |
| 52 | MLLB | In vivo | High-fat diet the mice | 150, 300 mg/kg, i.g., daily for 11 weeks | Body weight gain, lipid levels in serum and liver ↓; amelliorated hepatic steatosis and hepatic-lipogenesis-related genes (SREBP-1c, FAS, ACC1, and SCD-1) expression ↑; Lipolysis genes (SRB1 and HL) and lipid oxidation genes (PPARα and CPT-1) in mice fed a high-fat diet ↑ | OleicAcid/NormalDiet | Kan et al. (2021) |
| Hepato protection activity | |||||||
| 53 | AELDB | In vivo | High-fat diet induced NAFLD mice | 100, 200 mg/kg i.g., daily for 4 weeks | TG, TC, HDL-C and LDL-C levels, hepatic steatosis, TNF-α and IL-1β expression, hepatic proinflammatory cytokines leves ↓ | Simvastatin/NormalDiet | Li Z. et al. (2025) |
Pharmacological effects of crude extracts and bioactive metabolites of Lilium spp.
NM, not mentioned; ELLB, ethanol extract of L. lancifolium Bulbs; MLLR, methanol extract from the L. lancifolium roots; MLLB, methanol extract from the L. lancifolium Bulbs; ELLF, ethanol extract of L. lancifolium flowers; ALLL, aqueous extract from the L. lancifolium leaves; ALLB, aqueous extract from the L. lancifolium Bulbus; ALLR, aqueous extract from the L. lancifolium roots; ALLF, aqueous extract from the L. lancifolium flowers; AELDB, acetone extract of L. davidii Bulbs; MELDB1, acetone extract of L. davidii Bulbs; EELBB, ethanol extract of Lilium brownii Bulbs; MELDB2, methanol extract of Lilium davidii Bulbs; MELLB, Methanol extract of L. ledebourii Bulbs; LLLPS, Longya Lilium lipopolysaccharide (LPS); LLS, Longya L. saponins; AELBB, aqueous extract of L. brownii Bulbs; PELDB, polyethylene glycol extract of Lilium davidii Bulbs; Inos, Inducuble nitric oxide synthase; COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; NGF, nerve growth factor; GDNF, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; MMP-2, matrix metalloproteinase-2; TIMP-1, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1; TLRs, Toll-like receptors family.
FIGURE 3

Sankey diagram of pharmacological activities of the Lilium spp.
FIGURE 4

Main pharmacological activities of the Lilium spp.
5.1 Anti-inflammatory activity
Inflammation can contribute to various diseases, such as autoimmune, neurodegenerative diseases, and even cancer. Available anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin and other NSAIDs may have harmful side effects despite being effective (Ruggiero et al., 2025). So, safer phytopharmaceutical anti-inflammatory metabolites are gaining attention as a better option. Anti-inflammatory activities of dried Korean and Japanese L. lancifolium bulb extracts were examined using RAW 264.7 cells by Sim et al. (2020). Furthermore, the anti-inflammatory effects of the ethanolic extract from Korean L. lancifolium bulbs were found to be mediated through both the MyD88-dependent and TRIF-dependent pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. In particular, pro-inflammatory protein expression through the MyD88 dependent pathway was significantly reduced upon treatment with ethanolic extracts of Korean L. lancifolium bulbs than those of Japanese bulbs. Taken together, Korean L. lancifolium bulbs could be an anti-inflammatory agent (Sim et al., 2020). Concurrently, others were also conducting similar experiments. Han et al. (2018) also investigated the anti-inflammatory activity of Lilium spp. bulbs and the underlying mechanism of action in macrophages using Lilium spp. bulb ethanol extracts (Lb-EE). The study concluded that Lb-EE inhibited the production of nitric oxide (NO) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) in a Dose-dependent manner, without causing significant cytotoxicity. Furthermore, Lb-EE inhibited IKKα/β-induced activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, and IKK inhibition significantly reduced NO production in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. In summary, these results suggest that Lb-EE plays an anti-inflammatory role by targeting IKKα/β-mediated activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway during macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses (Han et al., 2018). In addition, Kwon et al. (2010) investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of methanol extracts of the root of L. lancifolium (LL extracts) in LPS-stimulated Raw264.7 cells. Levels of NO, PGE2, and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α) in the supernatant were quantified using sandwich ELISA. Expression of COX-2 and iNOS, phosphorylation of MAPK subgroups (ERK and JNK), and NF-κB activation in cellular extracts were assessed by Western blotting and immunocytochemistry. The LL extract significantly inhibited the production of NO, PGE2, IL-6, and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated cells and suppressed the expression of iNOS and COX-2. The study concluded that the anti-inflammatory effects of L. lancifolium methanol extract in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells may be mediated by downregulating iNOS and COX-2 by inhibiting NF-κB activation and nuclear translocation, and blocking ERK and JNK signaling (Kwon et al., 2010).
In this study, Ma et al. (2017) made use of the bioassay-guided approach to investigate the potential anti-inflammatory metabolites of LB and macrophage RAW264.7 cell line to explore the molecular mechanisms responsible for its anti-inflammatory activity. These two metabolites significantly decreased the production of nitrite oxide (NO) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 9.12 µM and 12.01 µM, respectively. The study concluded that these metabolites inhibited the production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and several other pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, and exhibited anti-inflammatory activity by acting on the NF-κB and MAPKs pathways (Ma et al., 2017). In another experiment, Hu et al. (2025) creatively established an inflammation model using HaCaT cells to assess the skin-soothing effects of the lily bulbs extract (LBE) and regaloside A. RT-qPCR was conducted to investigate the effects of LBE at 50 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL, and 200 μg/mL and regaloside A at 25 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, and 100 μg/mL on the relative mRNA expression of IL-6 and iNOS in HaCaT cells. The study concluded that each treatment group significantly reduced the relative mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and iNOS in HaCaT cells compared to the model group. This suggests that regaloside A possesses potential anti-inflammatory activity and holds promise as a natural metabolite for developing cosmetics with skin-soothing effects (Hu et al., 2025).
In conclusion, Multiple studies have confirmed the significant anti-inflammatory activity of extracts from Lilium spp. These extracts primarily exert their anti-inflammatory effects by modulating various signaling pathways, including down-regulating pro-inflammatory genes such as COX-2, iNOS, IL-6, and TNF-α through blocking the classical NF-κB pathway (inhibiting IKKα/β phosphorylation, IκB degradation, and p65 nuclear translocation); concurrently suppressing the MAPK cascade (ERK, JNK) to reduce transcription factor AP-1 activation, thereby decreasing PGE2 and NO production; and simultaneously interfering with TLR4 adapter protein MyD88/TRIF-dependent signaling to weaken the initiation of inflammation at its source. These findings provide a scientific basis for developing Lilium spp. extracts as anti-inflammatory agents, suggesting their broad application prospects in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic fields. In summary, the regulatory mechanism of the Lilium genus on the mRNA and protein expression levels of inflammation-related factors is shown in Figure 5.
FIGURE 5
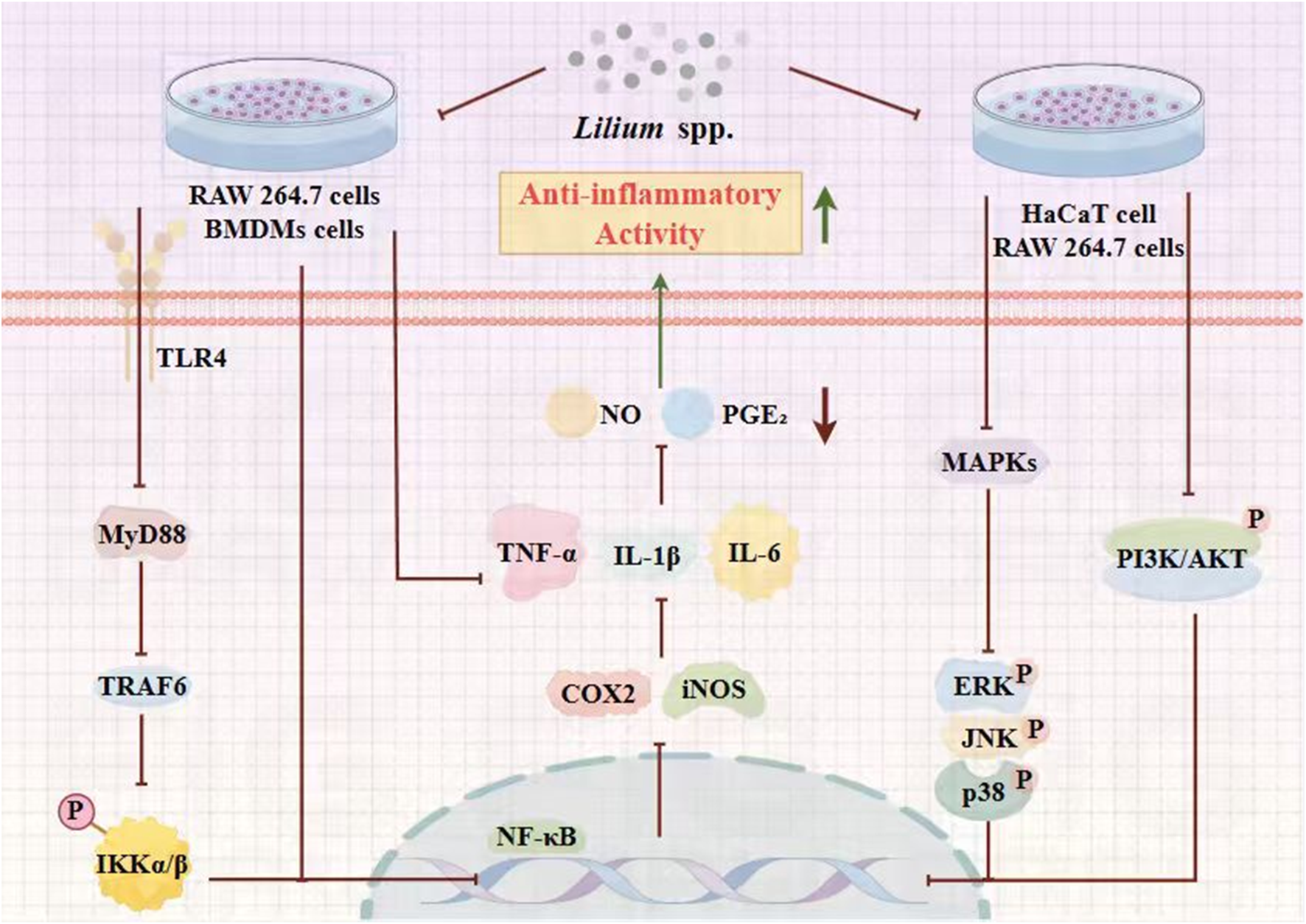
Schematic representation of underlying molecular mechanism displaying the anti-inflammatory activity of the Lilium spp.
5.2 Antioxidant activity
Current evidence strongly indicates that oxidative stress is a key factor in various diseases, including neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Down syndrome, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Luan et al., 2020). Antioxidants that scavenge free radicals are highly valued for their protective properties. The health-promoting effects of antioxidants and their role in reducing disease risk are well-recognized. A wide variety of antioxidants, each with distinct functions, collectively strengthen the body’s defense mechanisms (Liu et al., 2025a). Liu et al. (2025b) isolated metabolites 1 to 10 from the bulbs of L. lancifolium. and investigated their cytotoxicity toward rat adrenal pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells, as well as their antioxidant effects against H2O2-induced oxidative damage in PC12 cells. The results indicated that extracts of L. lancifolium possess potential as antioxidants, and exhibiting varying degrees of antioxidant activity (Liu et al., 2025b). Significant antioxidant activity has also been found in lily polysaccharides. Pectic polysaccharides (WLBP-A3-c) were isolated from traditional Chinese medicines L. brownii by Zhao et al. (2024). Simultaneously, the antioxidant effects of diverse pectin fractions and their structural domains, produced by enzymatic hydrolysis, were assessed for their ability to scavenge different free radicals and protect H2O2-injured HepG2 cells. The study concluded that pectins rich in HG domains from L. brownii exhibit significant antioxidant effects. These findings reveal its potential application in the field of health products (Zhao et al., 2024). In a separate investigation, polysaccharides from Lanzhou Lily (LLPs) were successfully extracted using a polyethylene glycol-based ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic method (PEG-UAEE). The structural features of the purified LLPs were characterized by HPLC, FT-IR, and SEM, and their antioxidant potential was subsequently evaluated. The study found that LLPs have significant in vitro antioxidant effects, indicating their potential as natural antioxidants and food metabolites in functional foods (Gao et al., 2022).
Recently, Sim et al. (2020) aims to confirm the potential of Korean L. lancifolium bulbs as a functional food material by comparing the metabolites and their biological activities with Japanese L. lancifolium bulbs. This study analyzed the efficacy evaluations of dried Korean and Japanese L. lancifolium bulb extracts were performed based on the antioxidant activities. The study concluded that the content of phenolic metabolites in Korean L. lancifolium bulb extracts was higher than that of Japanese L. lancifolium bulb extracts, and the antioxidant activities of Korean L. lancifolium bulb extracts were superior to those of Japanese bulbs (Sim et al., 2020). Subsequently, Xu et al. (2016) extracted polysaccharides from L. lancifolium leaves and successfully prepared three previously undescribed polysaccharide fractions (LLP-1, LLP-2, and LLP-3). DPPH radical scavenging assay, hydroxyl radical scavenging assay, superoxide radical scavenging assay, and ferrous ion chelating assay were used. Within the concentration range of 0.125–5.0 mg/mL, the three polysaccharide fractions all exhibited significant dose-dependent scavenging effects on DPPH radicals, but their overall ability to scavenge DPPH radicals was not as strong as that of Vc. The EC50 values of LLP-1, LLP-2, and LLP-3 were 5.54, 2.34, and 1.43 mg/mL, respectively. Meanwhile, the chelating abilities of the three polysaccharide fractions increased with increasing concentration. At a concentration of 5.0 mg/mL, the chelating activities of LLP-1, LLP-2, and LLP-3 on Fe2+ were 95.21%, 93.57%, and 97.79%, respectively, close to the chelating activity of EDTA-2Na (99.84%). In addition, the EC50 values of LLP-1, LLP-2, and LLP-3 were 0.71, 0.70, and 0.60 mg/mL, respectively. Studies have shown that all three polysaccharide metabolites exhibit strong in vitro free radical scavenging and Fe2+ chelating activities. Therefore, it is evident that the efficiency and potency of L. lancifolium polysaccharide extracts or active metabolites make them a promising natural antioxidant in pharmaceuticals and functional foods (Xu et al., 2016). Simultaneously, A novel polysaccharide fraction (LP2-1) was isolated and purified from the edible bulbs of 16 L. lancifoliumL Thunb by Gao et al. (2015). The study determined the antioxidant activity of LP2-1 through DPPH, Hydroxyl, reducing power, and Fe2+ chelating assays. In addition, LP2-1 had DPPH and hydroxyl radicals scavenging activities, and 25 also had the strong reducing power and chelating activity on ferrous ion. These results suggest that LP2-1 has good antioxidant activity and can be used in food industry (Gao et al., 2015).
Additionally, similar in vitro experiments were conducted, where Jin et al. (2012) homogenized a fine dried L. lancifolium bulb powder sample and extracted it with ultrasonic assistance using an acidified methanol solution (1 M HCl in 80% methanol) at 25 °C for 1 h in an external water bath. Four antioxidant assays, such as DPPH free radical scavenging activity, ABTS radical cation scavenging activity, cupric-reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity (HRSA) were applied. The results indicated that each bulb extract exhibited strong antioxidant activity, which was positively correlated with the total phenolic content and total flavonol content. This reveals that L. lancifolium bulbs can be used as a potential natural antioxidant for food and pharmaceutical applications (Jin et al., 2012). A preparative HSCCC was used to isolate phenylpropanoid glycerides from the bulbs of L. lancifolium by Luo et al. (2012). The antioxidant activities of the obtained metabolites were evaluated using three distinct assays: DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging assays, and the ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay. Studies have demonstrated that these metabolites possess extremely strong antioxidant activities from the bulbs of L. lancifolium (Luo et al., 2012). In other experiments, Liang et al. (2022) studied the relationship between Lilium spp. bulb color and the content of active metabolites, as well as the antioxidant capacity of lilies. Herein, bulbs from 56 wild populations and three cultivars were collected, and their edible characteristics, antioxidant capacities, and pigments were investigated and analyzed. The results showed that phenolic metabolites contributed to the major colors (red, yellow, and white) in Lilium spp. bulbs. Furthermore, Lilium spp. bulbs with darker and redder hues exhibited greater biomass, superior nutritional metabolites, higher active metabolite content, and stronger antioxidant capacity (Liang et al., 2022). Studies have demonstrated that Lilium spp. extracts exhibit remarkable antioxidant properties. Their primary active metabolites, including phenolic metabolites and polysaccharides, are responsible for these effects, which are achieved through mechanisms such as free radical scavenging and metal ion chelation. Notably, Lilium spp. extracts sourced from different origins display variations in antioxidant capacity, and the extent of their antioxidant effects is closely tied to the concentration of these active metabolites. Given these characteristics, Lilium spp. extracts present extensive potential for application in the food and pharmaceutical industries and are anticipated to be developed and utilized as natural antioxidants.
5.3 Antidepressant activity
Depression can manifest physically through symptoms such as fatigue, pain, or sleep disturbances (Wang et al., 2024a). Moreover, newer medications tend to be better tolerated than earlier drugs, leading to better patient compliance with treatment (Wang et al., 2024b). As a chronic illness, depression is marked by an increased likelihood of recurrence with each additional episode (Beton-Mysur and Brożek-Płuska, 2025). This often makes long-term maintenance drug therapy necessary. The antiseizure effects of a water extract of Lilii Bulbus (WELB) in mouse model of pentylenetetrazol (PTZ)-induced seizure was evaluated by Park and Cai (2024). The study found that WELB (The animals were treated orally with 500 mg/kg, once daily for 14 days) treatment could prevent PTZ-induced low seizure threshold and high seizure severity. Furthermore, after WELB treatment, the increased or decreased expression of proteins related to ectopic DGCs (Reelin and Dab-1), MFS (Netrin-1, Sema3A, and Sema3F), and their downstream effectors (ERK, AKT, and CREB) in the hippocampus of PTZ-kindled mice were significantly restored. Overall, our findings suggest that WELB is a potential anti-epileptic drug candidate, including convulsive seizures, ectopic DGCs, and MFS (Park and Cai, 2024). Simultaneously, lily aqueous extract is a potential candidate drug for estradiol. In their experiment, Zhou et al. (2019a) evaluated the ameliorative effects of an aqueous extract of lily bulb (AELB) on menopause-associated psychiatric disorders and its underlying mechanisms relative to estrogen therapy. In their experiment, ovariectomized (OVX) mice were administered AELB (1.8 g/kg) or estradiol (0.3 mg/kg) for 5 weeks. The study concluded that AELB exhibits anti-anxiety, anti-depressant, and cognitive-enhancing effects similar to those of estradiol. AELB reversed the OVX-induced decrease in the expression levels of hippocampal nerve growth factor (NGF) and prefrontal glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). Furthermore, AELB also increased the expression levels of ERβ in the uterus and brain regions. AELB’s efficacy in alleviating menopause-like behaviors is comparable to that of estradiol, suggesting that its metabolites may offer a novel therapeutic avenue for menopause (Zhou et al., 2019a). In another study, Zhou et al. (2019b) sought to further investigate the psychotropic effects of total polysaccharides of lily bulb (TPLB) against anxiety, depression, and cognitive deterioration and the underlying mechanisms in OVX mice using behavioral, neurochemical, molecular, and proteomic approaches in comparison with estrogen therapy. The researchers found that estradiol and TPLB could reduce glutamate levels and NMDAR1 expression in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, and increase the p-CaMKII/CaMKII ratio. These findings suggest that TPLB may exert anti-menopausal effects with improved safety profiles, highlighting its significant potential as a promising drug candidate for menopausal syndrome (Zhou et al., 2019b).
Plants of Lilium spp. can also play a significant role in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, and researchers have begun to explore these applications in recent years. This study by Hui et al. (2024a) aims to investigate the possible mechanism of L. brownii extract in treating PD and to compare the efficacy of ethanol and aqueous extracts of L. brownii. In this study, mice with PD induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine hydrochloride were administered L. brownii extracts for 30 days, after which the effects of both extracts were evaluated. The study concluded that both extracts of L. brownii effectively improved motor dysfunction in MPTP-induced PD mice. Furthermore, they reduced levels of MDA and ferrous ion (Fe2+), while increasing levels of SOD and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) in serum. In summary, L. brownii shows promise as an effective and safe treatment for PD (Hui, C. et al., 2024b). Depression-like behaviors were successfully modeled in mice following exposure to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS). Ma et al. (2024) further explored the underlying potential mechanisms of a combination therapy through both in vitro and in vivo experiments. They analyzed the expression levels of COX-2, PGE2, and IL-22, along with microglial activation and neuronal viability/apoptosis in the hippocampus. These analyses revealed that the combination of Longya Lilium and Fluoxetine synergistically reduced COX-2 expression, thereby alleviating depression-like behaviors and neuroinflammation in mice. Specifically, the downregulation of COX-2 inhibits the activation of BV-2 microglial cells, mitigates inflammation, and reduces neuronal apoptosis by suppressing the PGE2/IL-22 axis. Thus, the combination of Longya Lilium and Fluoxetine inactivates the COX-2/PGE2/IL-22 axis, ultimately relieving neuroinflammatory responses and the associated depression-like behaviors (Ma et al., 2024).
Recently, Yuan et al. (2021) further used Cell Counting Kit-8 assay and Western blotting to evaluate the neuroprotective antidepressant effects of Regaloside A. The results showed the cell survival rate was improved, the phosphorylation levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, tyrosine kinase receptor B, phosphatidylinositol three kinase, protein kinase B, and mammalian target of rapamycin were increased after Regaloside A treatment. It could also alleviate the damage of corticosterone in SH-SY5Y cells. This study revealed that phosphatidylinositol-3kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tyrosine kinase receptor B may play an important role in the neuroprotective antidepressant effects of Regaloside A (Yuan et al., 2021). Additionally, the neuroprotective potential of an aqueous extract of L. lancifoliumL Thunberg (ELL) against corticosterone (CORT)-induced pathophysiology in PC12 cells was reported by Lee et al. (2025). To evaluate the neuroprotective potential of ELL, PC12 cells were pretreated with 50 μg/mL ELL prior to CORT exposure. ELL markedly prevented CORT-induced neuronal death by suppressing the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins, reducing lactate dehydrogenase release, and attenuating reactive oxygen species production while preserving intracellular adenosine triphosphate levels. Moreover, ELL alleviated CORT-triggered endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, as evidenced by diminished unfolded protein responses, stabilized intracellular Ca2+, inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening, and maintenance of mitochondrial membrane potential. Collectively, these findings indicate that ELL confers neuroprotection by blocking apoptosis via suppression of ER stress and preservation of mitochondrial integrity (Lee et al., 2025).
To summarize, Lilium species extracts appear highly promising as neuroprotective agents and as therapeutics for neuropsychiatric conditions. They regulate the BDNF/TrkB/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to enhance neurotrophy and anti-apoptosis effects; inhibit the COX-2/PGE2/IL-22 inflammation axis to alleviate neuritis and microglial activation; regulate the NMDAR1/CaMKII pathway to balance glutamic acidergic neurotransmission; upregulate the expression of neurotrophic factors such as NGF and GDNF through ERβ-mediated Estrogens-like effects; and exert anti-Depression and neuroprotective effects by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum Stress, maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP levels, and blocking the apoptosis pathway. These different mechanisms make Lilium extracts promising for the development of new therapeutic drugs or adjuvant therapies. The regulatory mechanism of the Lilium genus governing the mRNA and protein expression levels of antidepressant associated factors are illustrated in Figure 6.
FIGURE 6

Schematic representation of underlying molecular mechanism displaying the antidepressant activity of the Lilium spp.
5.4 Antitumor activity
Chemotherapy is a traditional approach that has long played a vital role in tumor treatment. However, current clinical anti-tumor drugs are often plagued by drawbacks such as limited efficacy and significant side effects (Lei et al., 2025). Moreover, the development of new anti-tumor drugs is a lengthy process that demands substantial resources. In contrast, the active metabolites in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) are increasingly recognized for their potential anti-tumor effects, which are often characterized by fewer side effects (Ren et al., 2026). Zhou J. et al. (2024) firstly isolated four unprecedented steroidal saponins from lily bulbs, together with five known congeners. Evaluation of their cytotoxic potential against MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, HepG2, and A549 cell lines revealed that metabolite 9 selectively inhibited MCF-7 cells with an IC50 of 15.2 μM. Moreover, metabolite 6 was found to trigger G2/M-phase arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 cells (Zhou J. et al., 2024). In another study, Zhang et al. (2020) investigate the effects of total saponins from L. lancifoliumL (TSLL) on proliferation, apoptosis and migration of human gastric carcinoma cells lines SGC-7901 and HGC-27 and its underlying mechanism. The study concludes that TSLL inhibits the proliferation of stomach cancer cells by inhibiting the level of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and increasing the level of p21. TSLL induces apoptosis by up-regulating the expression of pro-apoptotic protein Bax and down-regulating the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Meanwhile, TSLL significantly inhibits cell migration and invasion, reduces the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), and increases the expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1). In summary, TSLL can be used as an alternative or adjuvant to chemotherapeutic drugs for cancer treatment, revealing that TSLL may be a promising candidate for preventing and inhibiting the growth of stomach cancer cells (Zhang et al., 2020).
In addition, a water-soluble polysaccharide LP60-1 was isolated and purified from L. davidii var. unicolor Cotton by Zhang M. et al. (2022). Furthermore, the anti-tumor activity was assessed by MTT method. The study concluded that LP60-1 has significant anti-tumor activity against MDA-MB-231, A549, HepG2, and MCF7 cells. In summary, LP60-1 can be studied and developed as a potential novel anti-cancer drug (Zhang M. et al., 2022). Concurrently, Partovi et al. (2023) aimed to evaluate the anti-proliferative activity of Lonicera nummularifolia, Lilium ledebourii, Campsis radicans, and Parthenocissus quinquefolia extracts. These extracts were obtained from fresh leaves and bulbs of the plants through maceration in the dark. Following solvent separation, the extracts were introduced into a culture medium containing G292, A431, and KB cancer cells, along with HGF-1 normal cells, for cytotoxicity, cell cycle, and apoptosis assays. The study concluded that the methanol extract activated p53 protein-induced apoptosis by upregulating the expression of BID/MAPK14 and downregulating the expression of MDM2/BCL2/MYC (Partovi et al., 2023). Research indicates that steroidal saponins, structural polysaccharides, and other active metabolites of Lilium spp. arrest the cell cycle at the G2/M phase and upregulate p21. They also block PCNA-mediated proliferation signals and MMP-2-dependent migration and invasion. Furthermore, these metabolites suppress anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2 and MDM2, activate the p53-Bax-caspase pathway to induce apoptosis, synergistically increase ROS and MAPK14 stress signals, and enhance immune recognition. These actions demonstrate their potential as candidates for novel anticancer therapies.
5.5 Hypoglycemic activity
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic disorders defined by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The chronic hyperglycemia in diabetes is associated with long-term damage, dysfunction, and failure of various organs, particularly the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, and blood vessels (Haider et al., 2025). The Caco-2 cell was used to study the glucose absorption regulation and mechanism of kaempferol, caffeic acid and quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactoside in L. lancifoliumL Thunb in vitro. Glucose oxidase-peroxidase (GOD-POD) method was used to measure glucose consumption in supernatant. Western blotting and quantitative real-time PCR were used to detect the protein expression and mRNA transcription. The results showed that caffeic acid and quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactoside could significantly promote the absorption of glucose by normal Caco-2 cells. It can also significantly promote the uptake of glucose tracer 2-NBDG by Caco-2 cells, as well as the protein expression levels and mRNA transcription of SGLT1 and GLUT2. The study reveals that its mechanism of action may be related to promoting the protein expression levels and mRNA transcription of SGLT1 and GLUT2 (Xu et al., 2021). In other in vitro studies, Zhu et al. (2014) used a bioassay-guided approach to explore the potential anti-hyperglycaemic L. brownii fraction (s). Their anti-hyperglycaemic activities were further confirmed in human hepatoma HepG2 cells and murine 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. The study concluded that L. brownii fraction (SGL) could increase glucose consumption in HepG2 cells and 3T3L1 adipocytes by 1.61- and 2.13-fold, respectively, and enhance 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation (Zhu et al., 2014).
In another study, Hui et al. (2024c) sought to elucidate the fine structure, morphology, and thermal properties of a galactoglucan (BHP-2) derived from Lanzhou lily bulbs. The in vitro hypoglycemic potential of BHP-2 was evaluated by assessing its inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase and α-amylase. The results indicated that BHP-2 exerted competitive inhibition against α-amylase and mixed non-competitive inhibition against α-glucosidase, with respective IC50 values of 0.31 mg/mL and 0.18 mg/mL. These values were comparable to those of acarbose (0.27 mg/mL for α-amylase and 0.12 mg/mL for α-glucosidase). Overall, BHP-2 demonstrated favorable thermal stability and a significant hypoglycemic effect (Hui, H. et al., 2024c). Similar investigations have previously been carried out. In one such study, Hui et al. (2024d) assessed the hypoglycemic effects of O-acetyl mannoglucan (BHP-1) obtained from Lanzhou lily bulbs. The findings indicated that BHP-1 demonstrated substantial inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase and moderate inhibitory activity against α-amylase within the tested concentration range. These results underscore the significant potential of BHP-1 in reducing blood sugar levels (Hui, H. et al., 2024d).
Additionally, the protective effect of L. lancifoliumL polysaccharides (LLP) on streptozotocin (STZ, Dose of 200 mg/kg, gavage, for 28 days)-induced diabetic mice and possible mechanism were investigated by Zhang et al. (2014). The activities of antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase (CAT) in serum, liver, and kidney of STZ-induced diabetic mice were measured, and the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) was reduced. It was concluded that oral administration of LLP could significantly reduce blood glucose levels in STZ-induced diabetic mice, increase body weight, significantly increase the activities of SOD, GPx, and CAT in serum, liver, and kidney of STZ-induced diabetic mice, and reduce MDA levels. At the same time, after LLP administration, pancreatic damage was significantly repaired, and the integrity of islet cells and tissues was improved. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that LLP exerts hypoglycemic and protective effects on STZ-induced diabetic mice by reducing oxidative stress and maintaining pancreatic islet integrity (Zhang et al., 2014). In conclusion, Lilium spp. extracts hold considerable promise for modulating blood glucose via a multi-targeted mode of action. They upregulate SGLT1/GLUT2 expression in Caco-2 cells, promoting intestinal glucose absorption; competitively inhibit α-amylase and non-competitively inhibit α-glucosidase, delaying carbohydrate breakdown; increase SOD, GPx, and CAT activity and decrease MDA, mitigating pancreatic islet oxidative damage and maintaining β-cell integrity; and enhance 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation, improving insulin sensitivity. These mechanisms indicate that Lilium spp. extracts could be promising candidates for developing hypoglycemic drugs or functional foods.
5.6 Immune enhancement activity
Innate immunity forms the host’s first - line of defense against infectious agents, providing a rapid response to pathogen invasion. Key cellular metabolites of this arm of the immune system include neutrophils and macrophages. These cells are equipped to perform phagocytosis, engulfing and eliminating invading pathogens. Simultaneously, they release inflammatory mediators and cytokines to signal the presence of infection and orchestrate the immune response. Macrophages, in particular, serve as critical mediators in both innate and adaptive immunity. They are capable of secreting a diverse array of molecules such as inflammatory mediators, cytokines, chemokines, as well as stress response and anti - apoptotic proteins, thus playing a multifaceted role in immune regulation (Brooks et al., 2026). In a recent study, Pan et al. (2017) explored the in vitro immune-enhancing activity of the water-soluble polysaccharide fraction (LLP-1A) in macrophages and the underlying molecular mechanism. The study found that in terms of the effect on macrophages, LLP-1A enhanced the phagocytic activity of macrophages, induced the production of NO, and was dose-dependent. In addition, it also induced the expression of cytokines interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β. In terms of molecular mechanism, LLP-1A increased the protein expression of toll-like receptor 4 in RAW 264.7 cells, as well as the phosphorylation of nuclear factor κB kinase inhibitor, NF-κB inhibitor, and nuclear factor κB. This study suggests that LLP-1A may have immunomodulatory functions and warrants further investigation to clarify its potential utility in immunization-related diseases (Pan et al., 2017). Simultaneously, in study, crude polysaccharides were extracted from bulblet of L. brownii by aqueous alcoholic precipita-tion, and eluted on a DEAE-52 column to obtain L. brownii polysaccharide (LBP) by Li X. J. et al. (2024). In vitro experimental results showed that LBP has good biocompatibility, and a low dose of 5 μg/mL LBP can significantly upregulate the expression of TNF-α, iNOS, IL-6, IL-1β, and toll-like receptor family (TLRs) mRNA in RAW 264.7 cells. In summary, LBP plays an important role in immunomodulation, and it may exert its immunisation activity through TLRs family receptors (Li X. J. et al., 2024).
In addition, Li et al. (2021) delved into the immunoregulatory potential of selenized polysaccharides from lily bulb (sLP). In vitro experiments revealed that sLP significantly enhanced the phagocytic activity of RAW 264.7 cells, elevated the levels of interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-2, boosted acid phosphatase activity, and upregulated the surface expression of CD86 and CD80 molecules. In vivo studies further demonstrated that sLP positively influenced the immune system by improving the indices of immune organs, increasing the serum levels of interferon-γ, IL-6, immunoglobulin (Ig)G, and IgM, and stimulating lymphocyte proliferation (Li et al., 2021). In summary, Lilium spp. species extracts display remarkable immunomodulatory activity. They engage and activate macrophage TLR4/TLR family receptors, inducing IKK-NF-κB axis phosphorylation, upregulating CD80/CD86 co-stimulatory molecules, and significantly boosting phagocytic capacity and the expression of key inflammatory mediators, including NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and iNOS. Furthermore, they promote dendritic cell maturation, increase serum levels of IFN-γ, IL-2, IgG, and IgM, and enhance antigen presentation. Ultimately, they increase the immune organ index and lymphocyte proliferation rate, synergistically enhance acid phosphatase activity, and establish a positive immunomodulatory feedback loop. Overall, Lilium spp. species extracts are highly promising for developing new immunomodulatory agents.
5.7 Maintain lung function activity
Pneumonia, a prevalent lower respiratory tract infection, primarily affects the alveoli and distal bronchioles, and can progress to severe complications such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and sepsis (Garvey, 2024; Han and Mallampalli, 2015). Current treatment strategies mainly revolve around anti - infective therapy and prevention of complications, with common medications including antitussives, antipyretic analgesics, and antibiotics. However, the growing concern of drug resistance caused by the overuse of these medications (Li et al., 2023), coupled with their potential adverse effects, has highlighted the urgent need for novel therapeutic approaches. In this context, the extraction of natural bioactive metabolites from plants, which are safe, effective, and free from undesirable side effects, offers a promising alternative for the treatment and rehabilitation of pneumonia patients. In this study, the effect of L. lancifolium Extract on Pulmonary Inflammatory Response in CS-Exposed Mouse Model by Lee et al. (2013). Water extract of L. lancifolium root was fed to C57BL/6 mice prior CS exposure every day for 3 weeks. The study used real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, ELISA, or Western blot to detect relevant inflammatory factors, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12). In the CS-exposed mouse model, we found that L. lancifolium extract could reduce inflammatory cells (macrophages and neutrophils), pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β), chemokines (MCP-1), and proteases (MMP-12). It also reduced airway dilation in CS-exposed mice. The above studies conclude that L. lancifolium extract may be a candidate drug for the treatment of CS-induced lung inflammation and emphysema (Lee et al., 2013). Meanwhile, Eom et al. (2023) investigated the protective effect of Lilium longiflorum Thunb (LLT) bulb extract fermented with Lactobacillus acidophilus 803 in COPD mouse models induced by cigarette smoke extract (CSE) and porcine pancreas elastase (PPE). The study showed that oral administration of the fermentation product (LS803) (at a Dose of 100 and 200 mg/kg, gavage, for 22 days) could inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators and the infiltration of immune cells (including neutrophils and macrophages), thereby exerting a protective effect on lung injury. Furthermore, LS803 significantly inhibited the increased production of IL-6 and MIP-2 after CSE and LPS stimulation by inhibiting the activity of NF-κB in mouse peritoneal macrophages. In summary, the fermentation product LS803 demonstrated preventive and alleviating effects on pulmonary inflammation in this model, providing preliminary evidence that warrants further studies to clarify its potential for managing pulmonary inflammatory diseases (Eom et al., 2023).
In their study, Liu R. et al. (2025) isolated a novel polysaccharide (L005-B) from L. lancifolium and characterized its Anti-pulmonary fibrosis properties. In vitro experiments demonstrated that L005-B effectively counteracted TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in A549 alveolar epithelial cells, as evidenced by reversal of E-cadherin downregulation, and suppression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and vimentin overexpression. Using a bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mouse model, the team further observed that L005-B (doses ranging from 0 to 1,000 μg/mL for 48 h) administration significantly reduced fibrotic markers (α-SMA, COL1A1, and fibronectin) while restoring E-cadherin expression in vivo. These findings collectively position L005-B as a promising therapeutic candidate for pulmonary fibrosis (Liu R. et al., 2025). In addition, the biological effects and mechanisms of Lily extract on LPS-induced pneumonia mice were explored by Sun et al. (2024). In the experiment, LPS was used to construct a mouse pneumonia model, and L. brownii var. viridulum extract was extracted via ultrasonic alcohol extraction. The study concluded that treatment with low-dose and high-dose Lily extract (100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg) for 48 h significantly reduced lung tissue inflammatory cell infiltration, pro-inflammatory factor (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α) mRNA expression levels, and inflammation-related protein (IL-6, NF-κB P65) protein levels. Furthermore, Lily extract significantly improved the assembly and motor function of cilia, and the expression levels of cilia-related genes (Ttc21a, Cfap45, etc.) and proteins were significantly upregulated (Sun et al., 2024).
In other experiments, Khan et al. (2024) explored enhancing the active metabolites in L. davidii (Lanzhou Lily) bulbs by fermenting them with Limosilactobacillus fermentum GR-3, a strain isolated from Jiangshui. The fermented lily bulb fraction (LFB + GR-3) was used to treat mice exposed to carbon black nanoparticles (CBNPs). Results showed that CBNP deposition and lung tissue damage were markedly reduced in the LFB + GR-3 group. Meanwhile, TNF-α, IL-10, and IL-6 levels increased by 6.9, 4.3, and 7 times, respectively, in the CBNP-exposed group. Additionally, probiotic-fermented lily bulbs may aid in treating lung infections (Khan et al., 2024).
Research indicates that extracts from Lilium spp. species hold significant potential for mitigating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. These block the NF-κB signaling cascade, significantly downregulate pro-inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and MMP-12, and reduce neutrophil and macrophage count infiltration; inhibit TGF-β1-driven epithelium-mesenchymal transition (EMT), reverse E-cadherin downregulation, and reduce α-SMA, COL1A1, and Fibronectin expression, thereby alleviating the pulmonary fibrosis process; meanwhile, upregulate cilia-related genes such as Ttc21a and Cfap45, and repair airway epithelium cilia structure and motor function. Thus, Lilium spp. extracts show promise as therapeutic candidates for pulmonary inflammatory diseases, including COPD, pneumonia, and pulmonary fibrosis, and merit further exploration of their clinical applications. The regulatory mechanism of the Lilium genus governing the mRNA and protein expression levels of maintain lung function associated factors are illustrated in Figure 7.
FIGURE 7

Schematic representation of underlying molecular mechanism displaying the maintain lung function activity of the Lilium spp.
5.8 Gastrointestinal protection activity
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are among the most widely used medications currently available. Their use is associated with gastrointestinal toxicity, affecting both the upper gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer disease) and the lower gastrointestinal tract (NSAID-induced enteropathy). Therefore, clinicians should avoid prescribing NSAIDs for long-term therapy or at high doses (Hijos-Mallada et al., 2022). In this study, Li and co-workers (2025) isolated a novel RG-I like pectin, L01-B1, with an average molecular weight of 43.9 kDa from the flowers of L. lancifolium. They elucidated its macromolecular structure and function in the human gut microbiota, revealing that the backbone of L01-B1 consists of 1,6-β-galactan and RG-I pectin. In vitro evaluation of its effects on human gut microbiota demonstrated that L01-B1 altered microbial composition and increased the abundance of Bifidobacterium longum. Additionally, L01-B1 may be degraded by two types of enzymes, potentially altering gut microbiota metabolism (Li M. et al., 2025). Moreover, The results of this study suggest that L01-B1 may be beneficial to human gut health by modulating Bifidobacterium longum.
The effect of lily bulbs on the microecological characteristics of intestinal microbiota and enzyme activities in normal micewere investigated by Wu and co-workers (2021). In the experiment, the administration group mice were given 0.15 g/mL lily bulb solution, intragastrically administered twice daily, and the control group mice were given the same volume of sterile water. After 49 days, intestinal contents and mucosa of each group of mice were collected to analyze the characteristics of intestinal flora and enzyme activity. The experiment proved that lily bulb can significantly increase the activity of amylase in intestinal contents and improve the digestion and absorption of food. In addition, lily bulb stimulates intestinal epithelial cells to secrete lactase, increases mucosal lactase activity, and maintains intestinal mucosal immunity. At the same time, it can promote the growth of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in the intestine of normal mice, inhibit the growth of total bacteria in the intestine, and maintain the intestinal mucosal barrier. In summary, this study may help reveal the potential of lily bulb as a functional food and further strengthen the research on its active metabolites for improving intestinal microecology (Wu et al., 2021). In summary, an aqueous solution of lily bulb significantly enhances the activity of amylase and lactase, improving nutrient digestion and absorption while maintaining mucosal immunity. Furthermore, it promotes the colonization of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, inhibits the overgrowth of opportunistic pathogens, and strengthens the intestinal mucosal barrier function. This multi-target regulatory mechanism provides a theoretical basis for developing lily-derived functional foods or microbial agents as alternatives to NSAIDs and their associated damage.
5.9 Relieve joint pain activity
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic chronic inflammatory disease characterized by widespread synovitis, which leads to the erosion of articular cartilage and marginal bone, and ultimately joint destruction (Hussein et al., 2025; Jeon et al., 2024). NSAIDs are currently commonly used to treat Osteoarthritis (OA) (Dixit et al., 2025). However, some studies have found that long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can cause various health problems, including nephrotoxicity (Baker and Perazella, 2020) and gastrointestinal diseases (Domper Arnal et al., 2022). Arthritis is a common geriatric disease characterized by joint pain, limited mobility, and significantly reduced quality of life. HY-LL was prepared by (Jeon et al., 2024) using 50% ethanol extraction from the Dried L. lancifoliumL bulbs. Several subjects were recruited for this trial and randomly assigned to the HY-LL group or the placebo control group, with oral administration of tablets twice daily for 12 weeks. The effects of HY-LL on the degree of joint pain and quality of life were systematically evaluated during the study. The results showed that continuous administration of HY-LL for 12 weeks significantly improved the overall quality of life of the subjects. This confirms that 12 weeks of HY-LL intervention can relieve joint pain and improve quality of life, suggesting the potential value of L. lancifoliumL bulbs ethanol extract in the treatment of arthritis pain (Jeon et al., 2024).
In this study, OA was induced by experimenters in 2-year-old dogs through resection of cranial cruciate ligament and lateral collateral ligament. Inflammatory cytokines, enzymes, lameness score, radiology, and histological changes were assessed. The experiment concluded that long-term oral therapy with L. lancifolium (dosage of 60 mg/kg, administered orally once daily for 12 weeks) alleviated inflammation and increased histological damage. L. lancifolium treatment effectively reduced cytokines, such as interleukin-6, metalloproteinase-9, leukotriene-4, prostaglandin, and cyclo-oxygenase, suggesting the potential to minimize inflammatory reactions in OA (Cho et al., 2022).
In conclusion, Lilium extract alleviates joint pain and dysfunction by downregulating inflammatory mediators and improving joint function. It suppresses the expression of key inflammatory factors, including IL-6, MMP-9, LTB4, PGE2, and COX-2, thereby reducing synovitis and cartilage degradation, with no significant adverse effects observed. This study provides robust clinical and animal evidence supporting the development of Lilium plants into long-acting, safe interventions for arthritis, potentially replacing or complementing traditional NSAID therapies.
5.10 Other effects
5.10.1 Myoprotective
Myalgia is a common symptom of various neuromuscular diseases. It is observed in metabolic muscle diseases, inflammatory muscle diseases, muscular dystrophies, and myotonic disorders. Myalgia can lead to a significant decline in the patient’s quality of life (Vasvit et al., 2025). Kim et al. (2024) evaluated the effectiveness of L. brownii ethanol extract (LBE) in a dexamethasone (DEX)-induced muscle atrophy model and elucidated its mechanism of action through muscle transcriptome analysis. The effects of citric acid on the viability of C2C12 myoblasts and the density of myotubes, as well as the effects of DEX treatment with or without on C2C12 myotube differentiation, were also investigated. The study concluded that LBE (The animals were administered doses of 100 and 300 mg/kg via gavage, once daily for 10 days) pretreatment had a protective effect on rat C2C12 myoblasts and increased the muscle density of rat C2C12 myotubes. LBE exhibited strong free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity in C2C12 myoblasts. In summary, LBE inhibited muscle protein degradation, preserved the muscle tissue microenvironment, reduced skeletal muscle loss, and maintained muscle function caused by DEX chronic toxicity by protecting muscle cells from various stress conditions and the effects of DEX itself. Research indicates that LBE shows preliminary promise for mitigating glucocorticoid-induced muscle atrophy, although confirmatory studies are still needed (Kim et al., 2024).
5.10.2 Anti-melanogenesis activity
Melanin is synthesized within oval-shaped organelles called melanosomes. These melanosomes are produced by dendritic melanocytes in the epidermal basal layer, representing only 1% of the total cellular composition (Ning et al., 2025). Several in vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated the significant anti-Melanogenic Effects of L. lancifoliumL Root. Park et al. (2023) studied the anti-melanogenic effects of L. lancifoliumL extract (LRE) on B16F10 cells, and concluded that LRE effectively reduced melanin production in a dose-dependent manner without causing cytotoxicity. Meanwhile, LRE decreased cellular tyrosinase activity and the mRNA and protein levels of tyrosinase, Tyrp1, and Tyrp2 in a dose-dependent manner, revealing the potential of LRE to effectively exert anti-melanin effects by inhibiting the expression of core melanogenic enzymes in B16F10 cells (Park et al., 2023).
5.10.3 Anti-insomnia activity
Insomnia is defined as difficulty in sleeping. As a highly prevalent and chronic disabling disease, it places a significant health and economic burden on both individuals and society. Consequently, medicinal plants are receiving increased attention as potential sedative agents, due to their diverse array of natural bioactive metabolites and comparatively fewer side effects (Yan et al., 2025). Twenty-five water-soluble metabolites were isolated from the bulbs of L. davidii var. unicolor, including two metabolites termed Liliumtides A and B (155–156) by Zhang H. et al. (2022). Compared with the blank control group, the Liliumtide A decreased sleep latency and significantly increased the sleep time. In conclusion, Liliumtide A could be investigated as a natural anti-insomnia lead metabolite in the pharmaceutical and food industries (Zhang H. et al., 2022). Simultaneously, Si et al. (2022) delved into the molecular mechanism underlying the insomnia-alleviating effects of L. brownii (LB) bulb. An insomnia model was established by administering p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA) to rats via intraperitoneal injection, alongside oral treatment for 7 days at a dose of 598.64 mg/kg. The research team assessed the levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), and melatonin (MT), examined the expression of GABAA, 5-HT1A, and MT receptors, and analyzed pathological changes within the hypothalamus. The findings revealed that LB treatment significantly counteracted the adverse effects induced by PCPA in the rats. Notably, it enhanced the abundance and diversity of intestinal flora and modulated the fecal metabolic phenotype. Specifically, LB administration led to increased levels of 5-HT (8.14 ng/mL) and MT (16.16 pg/mL), upregulated 5-HT1A and GABAA receptors, reduced NE levels (0.47 ng/mL), and improved the pathological conditions of hypothalamic cells. Overall, the study highlights the promising potential of LB as a health food for insomnia treatment (Si et al., 2022).
5.10.4 Alleviate obesity activity
Obesity, particularly when characterized by excessive visceral fat distribution, is associated with multiple alterations in hormone, inflammation, and endothelial levels. These changes stimulate several other mechanisms, ultimately leading to hypertension and, consequently, increased cardiovascular morbidity (Kar et al., 2025). Park et al. (2023) explore the effects of lily bulbs’ polyphenols (LBPs) on oxidative stress and lipid metabolism. In vitro studies revealed that LBPs mitigated the disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential, inhibited the production of reactive oxygen species, reduced oxidative stress, and decreased lipid accumulation in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells. In vivo studies showed that LBPs (doses of 150 and 300 mg/kg via gavage for 11 weeks) significantly inhibited weight gain in mice, reduced serum and liver lipid levels, and improved oxidative damage in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, LBPs also ameliorated hepatic steatosis, inhibited the expression of hepatic lipogenesis-related genes (SREBP-1c, FAS, ACC1, and SCD-1), and promoted the expression of lipolysis genes (SRB1 and HL) and lipid oxidation genes (PPARα and CPT-1), highlighting the significant potential of LBPs in the prevention and treatment of obesity and obesity-related diseases (Kan et al., 2021).
5.10.5 Hepato protection activity
Long-term ethanol consumption can lead to liver damage and unfavorable blood lipid profiles in humans. Toxic acetaldehyde, which is formed from alcohol under the catalysis of alcohol dehydrogenase, causes various adverse reactions such as thirst, vomiting, fatigue, headache, and abdominal pain (Zhao et al., 2021). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is intricately connected to the gut microbiota. Recent advancements highlight that leveraging natural polysaccharides as prebiotics is emerging as a highly promising therapeutic avenue for alleviating NAFLD (Younossi, 2019). In this study, Li Z. et al. (2025) explored the therapeutic potential of Lanzhou Lily polysaccharides (LLP) for high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The findings showed that LLP administration significantly attenuated NAFLD, as evidenced by substantial reductions in lipid accumulation and liver function markers in HFD-induced NAFLD mice. Specifically, LLP treatment led to decreased serum levels of TG, TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C. Moreover, histological analysis using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Oil Red O staining demonstrated that LLP effectively alleviated hepatic steatosis. Additionally, LLP suppressed the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β, reducing hepatic inflammation. Overall, LLP exhibited potential therapeutic effects on NAFLD and may hold promise for its clinical application (Li Z. et al., 2025).
6 Toxicological studies
The genus Lilium spp. has a medicinal and edible history of over two thousand years, and modern research has also confirmed its multi-target pharmacological activity, but the label of food-drug homology is not equivalent to absolute safety. With the expansion of clinical doses of Lilium preparations and the increase in the application population, systematically sorting out its toxicological profile, clarifying species differences and long-term exposure risks has become an unavoidable part of ensuring rational drug use and functional food development. Toxicological studies of Lilium plants began as early as the Eastern Han Dynasty. The “Shen Nong’s Herbal Classic” has listed L. brownii var. viridulum and L. brownii F.E.Br. ex Miellezis as “none-toxic” top grade, and later generations of Materia Medica followed this statement. The current “Chinese Pharmacopoeia” stipulates that the clinical dose of dried Lilium is 6–12 g/d; comprehensive ancient and modern literature shows that the oral safety window can reach 5.55–60 g, and external use does not exceed 65 g, and no acute toxicity record has been found within this range (Wang et al., 2020). In modern research, there are few toxicological studies on Lilium, and no cases of Lilium poisoning have been found so far, but the possibility of Lilium causing chronic poisoning cannot be ruled out (Song et al., 2023). At the same time, Lilium plants have species differences in animal toxicity, and rodents and rabbits are highly tolerant to Lilium: no toxicity renal or death occurred in mice and rats with gavage equivalent dose ≥1.5 times the weight; dogs and cats showed obvious sensitivity. Fitzgerald et al. reported that dogs developed vomiting and gastrointestinal hemorrhage after accidental ingestion (Fitzgerald, 2010); Langston et al. recorded a case of a cat that died of acute kidney failure within 48 h after eating L. tigrinum (Langston, 2002).
In summary, Lilium has no significant acute toxicity to humans and has good safety within the dose and course of treatment specified in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia; however, it has toxicity renal to cats and dogs, and clinical attention should be paid to pet contact. Long-term excessive use may pose potential colchicine-like risks, and systematic toxicology data are urgently needed to support its wider clinical application.
7 Potential applications
As mentioned above, Lilium spp., an important plant resource, is mainly distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, including Asia, North America, and Europe (Zhou N. et al., 2024). The east coast of Asia, the west coast of North America, and the Mediterranean region are particularly rich in Lilium spp. resources. Furthermore, this plant commands a large market and possesses significant economic and medicinal value (Munafo and Gianfagna, 2015). Lilium spp. is rich in bioactive metabolites and possesses significant bioactivities. It holds considerable potential for applications in functional food, health products, and the pharmaceutical industry. Hence, developing nutritious and more stable Lilium-related products is of great significance.
In the realm of food technology, a study explored how natural flower extracts from Prunus persica, Rosa chinensis, and Lilium davidii could enhance the aroma of dealcoholized Chardonnay wine, aiming to tackle the common sensory drawbacks of dealcoholized wine beverages. Results showed that these extracts significantly enriched the wine’s aromatic profile, marked by increased levels of alcohols, esters, and terpenes, all while keeping the physicochemical properties intact. This research not only offers new strategies for improving non-alcoholic wines but also promises to drive innovation in the beverage industry (Ma and Sam, 2024). In the pharmaceutical field, Baihe Zhimu Decoction (LBRAD), which contains Lilium lancifolium bulb and Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizome, is the first prescription for “Lily Disease” recorded in ancient medical texts. It is also a specific remedy for “Lily Disease” following sweating. The classic LBRAD recipe combines fresh Lilium lancifolium bulbs and dried Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizome slices. It is known for supplementing nutrition, clearing heat, nourishing Yin, and providing moisture (Pan et al., 2024).
In other fields, the sulfuric acid acidification method has been used to make periodic mesoporous organosilica hydrophilic microspheres. PMO aqueous microspheres were made by a co-condensation reaction, using sulfated Lentinus edodes polysaccharide-bridged silane (SLLTPBS) and polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) as silicon sources. This method solves the problem of using large amounts of acetonitrile in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) columns. Compared to ordinary C18 columns, the PMO (SLLTP-POSS) column has much better acid and alkali resistance. At the same time, this stationary phase shows high separation efficiency and selectivity for mixtures of organic acids, sugars, sugar alcohols, amino acids, and sweeteners (Chen et al., 2023). Lily-related cosmetics offer a wide array of functions such as skin care, whitening, antioxidation, anti-aging, wrinkle removal, spot fading, acne treatment, moisturizing, anti-radiation, skin repair, heat clearing, as well as promotion of hair growth and hair blackening. Lilium spp. plants are rich in health-beneficial metabolites. Phenolic acids and flavonoids contained in these plants exhibit strong antioxidant, anti-ultraviolet radiation and antibacterial properties. Polysaccharides possess excellent skin moisturizing, antibacterial and skin-repairing capabilities. Other metabolites such as saponins, alkaloids, carotenoids and anthocyanins also offer potential health benefits. These metabolic metabolites provide the material and functional basis for the application of lilies in cosmetics (Tang et al., 2022). Bulb macerates were obtained using 70% and 96% ethanol. The total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), condensed tannins (CTC), mineral composition, and antioxidant activity (DPPH assay) were evaluated. Additionally, spectroscopic (FTIR) and antibacterial analyses were performed to further characterize the bulb macerates. Stable hydrogel formulations containing LD-70 and LA-70 were developed, showing excellent pH stability, favorable rheological properties, and sustained antioxidant activity over 60 days. These results support the use of lily-derived macerates in dermocosmetic formulations for skin protection and microbial defense (Lupşor et al., 2025). Yeast-derived biosurfactants, prized for their low toxicity, unique action, and versatility, have broad applications in food, medicine, and cosmeceuticals. We isolated a highly surface-active yeast strain, L3-GPY, from Lilium lancifolium Thunb., and identified it as Aureobasidium pullulans. From its culture supernatant, we extracted glycerol-liamocin, a novel low-surface-tension metabolite with potent biosurfactant activity (31 mN/m). Our findings indicate glycerol-liamocin holds great promise as a new biosurfactant for various industrial uses (Kim et al., 2015).
Patent activity related to Lilium spp. is experiencing significant growth. Current Status of Patent Filings Related to the Genus Lilium, with Patent Utilization Illustrated in Figure 8 and Table 4, the past 2 decades have witnessed a substantial increase in patent applications, reflecting growing interest in its potential. To date, 2,517 patents concerning Lilium spp. have been granted globally, with 211 issued in 2024 alone. These patents originate primarily from China, the United States, Brazil, Canada, and Australia. The technological scope of these patents is diverse, encompassing preparation and production methods, applications involving animal tissues, and uses with Bacillus. Primarily, the reported application potential focuses on areas such as antidiabetic, antidepressant, anti-insomnia, and analgesic effects, alongside immune enhancement, lung-moistening and cough-relieving properties, and health food applications. Table 4 summarizes a list of specific Lilium spp.-containing product patents and their claimed biological properties. As research delves deeper into the unique nutritional and medicinal properties of Lilium spp., the application of related functional products is expanding. This trend exhibits diversification, broadening the market to better cater to diverse population needs. Consequently, Lilium spp. is playing a significant role in pharmaceuticals and nutritional health products. The applications of Lilium spp. extend to every aspect of our lives, potential applications in health and medicine are shown in Figure 9.
FIGURE 8

Current situation of patent related to Lilium spp. (A) Document numbers; (B) Patents distribution; (C) Patents use.
TABLE 4
| Application | Main composition | Pharmacological properties | Publish number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Poria, lily bulb, Gordon euryale seed, lotus seed, wolfberry, black date, and vine tea | Antidiabetic | CN120392904A |
| Pharmaceutical | Lily bulb powder | Improve sleep | CN120392948A |
| Pharmaceutical | Poria, Radix Pseudostellariae, Semen Euryales, Radix Puerariae Lobatae, Celery, Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae, Capsella bursa-pastoris, Fructus Crataegi, Luffa, Bulbus Lilii | Enhance pancreatic function | CN120360258A |
| Pharmaceutical | Zaocys dhumnades, Spatholobus suberectus Dunn, Astragalus propinquus Schischkin, Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, Scutellaria barbata D. Don, Lilium brownii F.E. Brown var. viridulum Baker, Trichosanthes peel, and Platycladus orientalis (L.) Franco | Analgesia | CN120324536A |
| Pharmaceutical | Lilial A | Anti-inflammatory | CN117105946B |
| Pharmaceutical | Lily polysaccharide | Anti-enteritis | CN116650517B |
| Pharmaceutical | Radix Ophiopogonis, Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma, Fructus Mume, Bulbus Lilii, and Rhizoma Phragmitis | Antidiabetic | CN120204326A |
| Pharmaceutical | Lily, lotus seed | Antidiabetic | CN120053556A |
| Pharmaceutical | Concentrated pear juice, lily bulb, Polygonatum odoratum, Siraitia grosvenorii fruit, almond, Semen Sterculiae Lychnophorae, Flos Lonicerae Japonicae, Platycodon grandiflorus root, Chrysanthemum morifolium flower, tangerine peel, Chinese date, Polygonatum sibiricum rhizome, loquat leaf, Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizome, Gnaphalium affine, crystal sugar | Moisten the lung and relieve cough | CN120053558A |
| Pharmaceutical | Lily, Coptis chinensis, cinnamon | Anti-heart failure | CN119770577A |
| Pharmaceutical | Lilium longiflorum bulbifera polysaccharide | Immunological activity | CN119638862A |
| Pharmaceutical | Rhizoma Coptidis, Prepared Fructus Evodiae, Cortex Cinnamomi, Bulbus Lilii, Sclerotium Poriae Paradicis, Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii, Prepared Radix Polygalae, and Mentha | Anti-insomnia | CN119157965A |
| Health product | American ginseng slices, lily bulb, wolfberry, Polygonatum sibiricum, peppermint, and jasmine green tea | Invigorate | CN120323540A |
| Health product | Pueraria powder, natto powder, turmeric powder, inulin, lily bulb powder, Semen Ziziphi Spinosae powder, and Poria cocos powder | Antidepressant | CN120304514A |
| Health product | Lotus Seeds, Coix Seeds, Erythritol, Lilies | Sedative | CN120113771A |
| Health product | Fructus Canarii, Fructus Canarii, Semen Sterculiae Lychnophorae, Radix Glycyrrhizae, Bulbus Lilii, and Mentha Haplocalyx | Soothing the throat and moistening the lungs | CN119867229A |
| Ecological conservation | Lily Bulb | Water purification | CN120328738A |
| Plant research | Carotenoid | Regulation of lily colour | CN119685353A |
Patents list of products containing the Lilium spp. and their claimed beneficial effects for improving human health.
FIGURE 9

Potential applications of Lilium spp. in health and medicine.
8 Future outlooks
This review synthesizes recent advances in Lilium spp. research, integrating botanical characterization, ethnobotanical records, nutritional value, phytochemical profiles, pharmacological activities, patent landscapes, and commercial applications. Bulbs of the genus, rich in edible starch, have long served as both food and medicine, while selected species additionally provide aromatic oils for perfumery. The growing recognition of their nutritional assets and broad health benefits has intensified interest from the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors. To date, 123 distinct metabolites have been identified, comprising 68 saponins, 23 phenolics, 13 phenylpropanoids, 17 polysaccharides, and 2 additional metabolites. Among these, saponins, phenolics, and phenylpropanoids underpin a spectrum of bioactivities, including hypoglycaemic, anti-obesity, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumour, antidepressant, sleep-promoting, and immunomodulatory effects. Accumulating evidence positions Lilium spp. as a promising therapeutic resource for depression, insomnia, diabetes, and disorders driven by inflammation and oxidative stress. Collectively, the genus emerges as a dual-purpose functional food and medicinal plant with considerable health-promoting potential and expanding commercial relevance.
Despite the growing body of evidence, several critical knowledge gaps continue to impede the translation of Lilium spp. bioactivities into health-promoting applications: (1) Although numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Lilium spp. extracts, the specific metabolites responsible for these effects remain largely unidentified. Systematic isolation, structural elucidation, and mechanism-of-action studies of active monomers are therefore urgently required. Such investigations will clarify structure–activity relationships, enable precise dosing, and accelerate the discovery of novel bioactive scaffolds; (2) Over the past 2 decades, Lilium spp. preparations have shown promise in preventing depression, insomnia, and diabetes, as well as in promoting general health. Historical and documentary records also indicate their use as functional foods for managing depression, diabetes, tumors, pulmonary disorders, and other oxidative stress–related chronic diseases. Future research should thus prioritize the development of standardized Lilium-based products for dietary therapy, medicine, and cosmetology; (3) Despite centuries of culinary and medicinal use, the nutritional composition and patent landscape of Lilium spp. remain insufficiently explored. The bulbs are rich in polysaccharides, saponins, vitamins (B1, B2, B3, and C), amino acids, starch, calcium, iron, and other micronutrients. In traditional Chinese medicine, the bulbs are believed to resolve phlegm, relieve cough, nourish Yin, and moisten the lungs, whereas modern studies emphasize their antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and antihyperglycemic properties. These attributes highlight the potential of Lilium spp. as a dual-purpose functional food and pharmaceutical resource, warranting expanded nutritional and intellectual property investigations; (4) Finally, before pharmaceutical formulation can proceed, comprehensive studies of the pharmacokinetic properties of bioactive metabolites—including absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) processes—are required to elucidate their in vivo behavior and inform toxicity assessment. Concurrently, detailed evaluations of both acute and chronic toxicity, as well as analyses of metabolite-related biological effects, are essential to ensure drug safety and efficacy. Moreover, pharmacokinetic insights can facilitate the rational design of dosing regimens and guide the structural optimization of active substances, thereby enhancing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing toxicity.
In conclusion, Lilium spp. have drawn broad attention for their plentiful benefits, showcasing significant potential in functional foods, modern medicine, and cosmetics. They serve as a bridge for the internationalization of traditional Chinese medicine, providing developed nations with innovative pathways to enhance human health and contribute to a shared future via modern medical advancements. Despite facing opportunities and challenges in development and applications, Lilium spp. are expected to hold vast market prospects in medicine, functional foods, and cosmetics.
Statements
Author contributions
YW: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Validation. HC: Visualization, Validation, Software, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Methodology. PF: Validation, Writing – review and editing, Resources, Investigation. DW: Resources, Project administration, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Software. XD: Supervision, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Project administration.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was finically supported by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment of Refractory Gastrointestinal Diseases: Inheritance and Innovation Team Project (Grant No. ZYYCXTD-C-202010), the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Project for Building Evidence-Based Capacity in Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant No. 2019XZZX-XH011), and the Third Session of the Shaanxi Province Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Practitioners’ Inheritance Studio Construction Project (Grant No. 2019021).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1713957/full#supplementary-material
Glossary
- AELBB
aqueous extract of L. brownii Bulbs
- AELDB
Acetone extract of L. davidii Bulbs
- AI
atherogenic index
- AIP
atherogenic index of plasma
- AKP
alkaline phosphatase
- ALLB
aqueous extract from the L. lancifolium Bulbus
- ALLF
aqueous extract from the L. lancifolium flowers
- ALLL
aqueous extract from the L. lancifolium leaves
- ALLR
aqueous extract from the L. lancifolium roots
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- ALP
alkaline phosphatase
- AMPK α
AMP-activated protein kinase α
- Ang II
angiotensin II
- AST
aspartate aminotransferase
- BAMBI
BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor
- Bax
Bcl-associated X protein
- BUN
blood urea nitrogen
- CAT
catalase
- C/EBPα
CCAAT-enhancer binding protein α
- COX2
cyclooxygenase-2
- Col Ⅲ
collagen type Ⅲ
- Col Ⅳ
collagen type Ⅳ
- cAMP
cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- CTGF
connective tissue growth factor
- CVF
collagen volume fraction
- CVDs
cardiovascular diseases
- CysC
cystatin C
- DENA
diethylnitrosamine
- DMDD
2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione
- DPPH
2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging activity
- ECE
endothelin-converting enzyme
- EELBB
Ethanol extract of Lilium brownii Bulbs
- ELLB
Ethanol extract of L. lancifolium Bulbs
- ELLF
Ethanol extract of L. lancifolium flowers
- ET-1
endothelin-1
- FAS
fatty acid synthase
- FBG
fasting blood glucose
- FINS
fasting insulin
- FFA
free fatty acids
- FRAP
ferric reducing antioxidant power
- G-6-Pase
glucose-6-phosphatase
- GDNF
glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor
- GHb
glucosylated hemoglobin
- GSH
reduced glutathione
- GSH-Px
glutathione peroxidase
- HA
hyaluronic acid
- HDL-C
high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- Hyp
hydroxyproline
- IL-6
interleukin-6
- iNOS
inducible NO synthase
- Inos
inducible nitric oxide synthase
- ISI
insulin sensitivity index
- LDL-C
low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LLLBPS
Longya Lilium lipopolysaccharide
- LLS
Longya Lilium saponins
- LN
laminin
- LPO
lipid peroxidation
- MDA
malondialdehyde
- MAPKs
mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MELLB
methanol extract of L. ledebourii Bulbs
- MELDB1
methanol extract of L. davidii Bulbs
- MELDB2
methanol extract of L. davidii Bulbs
- MLLB
methanol extract from the L. lancifolium Bulbs
- MLLR
methanol extract from the L. lancifolium roots
- MMP-2
matrix metalloproteinase-2
- MPO
myeloperoxidase
- Myd88
myeloid differentiation factor 88
- NEFA
non-esterified fatty acid
- NF-κB
nuclear factor-κB
- NGF
nerve growth factor
- NM
not mentioned
- PCNA
proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- PELDB
polyethylene glycol extract of L. davidii Bulbs
- p-AMPK α
phospho-AMPK α
- PPAR-α/γ
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α/γ
- Scr
serum creatinine
- SCD1
stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1
- SDH
sorbitol dehydrogenase
- SGOT
serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase
- SGPT
serum pyruvate transaminase
- SOD
superoxide dismutase
- SREBP-1c
sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c
- STZ
streptozotocin
- TAA
total ascorbic acid
- TC
total cholesterol
- TEAC
trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity
- TGF-β
transforming growth factor-β
- TGF-β1
transforming growth factor beta 1
- TIMP-1
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1
- TL
total lipids
- TLR4
Toll-like receptor four
- TLRs
Toll-like receptor family
- TNF-α
tumor necrosis factor-α
- TNOS
total NO synthase
- TQ
triglyceride
- TG
triglycerides
- VLDL-C
very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
References
1
An Z. Jin J. Tan Z. Wang Y. Wang T. Dong Z. et al (2025). Lanzhou lily as nutraceuticals: identification of active metabolites via the UHPLC-Q-exactive orbitrap mass spectrometer. Microchem. J.213, 113626. 10.1016/j.microc.2025.113626
2
Bai G. Ye M. Yu L. Yang M. Wang Y. Chen S. (2024). Purification, characterization, simulated gastrointestinal digestion and gut microbiota fermentation of a Bifidobacterium-directed mannoglucan from Lilium brownii Var. viridulum. Food Chem. X23, 101671. 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101671
3
Baker M. Perazella M. A. (2020). NSAIDs in CKD: are they safe?Am. J. Kidney Dis.76 (4), 546–557. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.03.023
4
Bao G. Tian Y. Wang K. Chang Z. Jiang Y. Wang J. (2024). Mechanistic understanding of the improved drying characteristics and quality attributes of lily (Lilium lancifolium thunb.) by modified microstructure after pulsed electric field (PEF) pretreatment. Food Res. Int.190, 114660. 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114660
5
Beton-Mysur K. Brożek-Płuska B. (2025). Exploring the impact of citalopram on human Colon cells: insights into antidepressant action beyond the brain. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.343, 126464. 10.1016/j.saa.2025.126464
6
Brooks N. A. H. Riar I. Klegeris A. (2026). Mitochondrial damage-associated molecular patterns: neuroimmunomodulators in central nervous system pathophysiology. Neural Regen. Res.21 (4), 1322–1338. 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01459
7
Bruni A. Ballero M. Poli F. (1997). Quantitative ethnopharmacological study of the campidano valley and urzulei district, Sardinia, Italy. J. Ethnopharmacol.57 (2), 97–124. 10.1016/s0378-8741(97)00055-x
8
Chen Z. Ding L. W. (2012). Clinical observation on treating 40 cases of depression with the Chaihu plus Longgu Muli decoction and lily anemarrhena decoction. Clin. J. Chin. Med.4 (03), 38–39.
9
Chen Z. G. Zhang D. N. Zhu Q. Yang Q. H. Han Y. B. (2014). Purification, preliminary characterization and in vitro immunomodulatory activity of tiger lily polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Polym.106, 217–222. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.02.004
10
Chen T. Wang S. Zong X. Li B. Shu Y. Di X. et al (2023). Preparation and application of sulfated lily polysaccharide bridged polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane hybrid organosilicas as stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A1691, 463822. 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.463822
11
Chen M. Yang Y. Han X. Nie G. Li X. Wang Z. et al (2024). Metabolomics integrated with transcriptomics provides insights into the phenylpropanoids biosynthesis pathway in Lilium davidii Var. unicolor and L. lancifolium thunb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.279 (Pt 1), 135103. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135103
12
Chen L. Zhu L. Cao Y. (2025). Effects and the mechanism of pine pollen polysaccharides on diabetic wound healing in vitro and in vivo. Regen. Ther.30, 241–251. 10.1016/j.reth.2025.06.009
13
Chen X. Yuan Y. Gao Y. (2025). Lilium pseudonanum (liliaceae), a rare and cryptic species from southeast Xizang, China. Ecol. Evol.15 (7), e71738. 10.1002/ece3.71738
14
Cho J. H. Park Y. G. Choi J. Adam G. O. Ju E. M. Park H. et al (2022). Long-term intake of Lilium lancifolium mitigated osteoarthritic effects by suppressing inflammatory cytokines in a dog model. Vet. World15 (8), 2012–2020. 10.14202/vetworld.2022.2012-2020
15
Ding G. P. Yuan J. X. Li L. D. Mi X. L. Chen H. S. (2004). Lily, a food-drug homology plant. Food Nutr. China(09), 52–53.
16
Dixit T. Vaidya A. Ravindran S. (2025). Polymeric nanoparticles-based targeted delivery of drugs and bioactive compounds for arthritis management. Future Sci. OA11 (1), 2467591. 10.1080/20565623.2025.2467591
17
Djafarou S. Alves E. Amine Khodja I. Seyhan G. Barut B. Harakat D. et al (2025). Design, synthesis and evaluation of anticancer and antioxidant properties of phenolic derivatives incorporating 4H-pyran/1,4-dihydropyridine/1,3-dihydropyrimidinone scaffolds. Eur. J. Med. Chem.295, 117803. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117803
18
Domper Arnal M. J. Hijos-Mallada G. Lanas A. (2022). Gastrointestinal and cardiovascular adverse events associated with NSAIDs. Expert Opin. Drug Saf.21 (3), 373–384. 10.1080/14740338.2021.1965988
19
Eom J. E. Kim G. D. Kim Y. I. Lim K. M. Song J. H. Kim Y. et al (2023). Bulb of Lilium longiflorum thunb extract fermented with Lactobacillus acidophilus reduces inflammation in a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.33 (5), 634–643. 10.4014/jmb.2301.01022
20
Fiorito S. Preziuso F. Sharifi-Rad M. Marchetti L. Epifano F. Genovese S. (2020). Auraptene and umbelliprenin: a review on their latest literature acquisitions. Phytochem. Rev.21 (2), 317–326. 10.1007/s11101-020-09713-5
21
Fitzgerald K. T. (2010). Lily toxicity in the cat. Top. Companion Anim. Med.25 (4), 213–217. 10.1053/j.tcam.2010.09.006
22
Gao J. Zhang T. Jin Z. Y. Xu X. M. Wang J. H. Zha X. Q. et al (2015). Structural characterisation, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Lilium lancifolium thunb. Food Chem.169, 430–438. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.016
23
Gao D. Chen H. Liu H. Yang X. Guo P. Cao X. et al (2022). Structure characterization and antioxidant activity analysis of polysaccharides from lanzhou lily. Front. Nutr.9, 976607. 10.3389/fnut.2022.976607
24
Garvey M. (2024). Hospital acquired sepsis, disease prevalence, and recent advances in sepsis mitigation. Pathogens13 (6), 461. 10.3390/pathogens13060461
25
Guclu-Ustundag O. Mazza G. (2007). Saponins: properties, applications and processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.47 (3), 231–258. 10.1080/10408390600698197
26
Haider A. S. Ambatwar R. Khatik G. L. (2025). Insights into PTP1B inhibitors as antidiabetic agents: current research and future perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem.295, 117791. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117791
27
Haladová M. Eisenreichová E. Mučaji P. Buděšínský M. Ubik K. (1998). Steroidal saponins from Lilium candidum L. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun.63 (2), 205–210. 10.1135/cccc19980205
28
Haladova M. Mucaji P. Budesinsky M. Vokac K. Cvacka J. Grancai D. et al (2011). Spirostanol saponins from the bulbs of Lilium candidum. Chem. Nat. Compd.46 (6), 1004–1005. 10.1007/s10600-011-9812-9
29
Han S. Mallampalli R. K. (2015). The acute respiratory distress syndrome: from mechanism to translation. J. Immunol.194 (3), 855–860. 10.4049/jimmunol.1402513
30
Han S. Y. Yi Y. S. Jeong S. G. Hong Y. H. Choi K. J. Hossain M. A. et al (2018). Ethanol extract of lilium Bulbs plays an anti-inflammatory role by targeting the IKKalpha/beta-mediated NF-kappaB pathway in macrophages. Am. J. Chin. Med.46 (6), 1281–1296. 10.1142/S0192415X18500672
31
Hijos-Mallada G. Sostres C. Gomollón F. (2022). NSAIDs, gastrointestinal toxicity and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.45 (3), 215–222. 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2021.06.003
32
Hu M. Zhang S. Luo F. Hu Z. Chen Y. (2025). Potential mechanisms underlying the protective effects of lily bulbs extract and characteristic ingredients against LPS-Induced inflammation in HaCaT cells. Food Biosci.66, 106142. 10.1016/j.fbio.2025.106142
33
Hui H. Jin H. Li X. Yang X. Cui H. Xin A. et al (2019a). Purification, characterization and antioxidant activities of a polysaccharide from the roots of Lilium davidii Var. unicolor cotton. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.135, 1208–1216. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.030
34
Hui H. Li X. Jin H. Yang X. Xin A. Zhao R. et al (2019b). Structural characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of two heteropolysaccharides purified from the bulbs of Lilium davidii Var. unicolor cotton. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.133, 306–315. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.082
35
Hui C. He S. Ji M. Zhang Y. Wang H. Wang X. et al (2024a). Two new phenylpropanoid compounds from Lilium brownii and their anti-monoamine oxidase activity. Chem. Biodivers.21 (6), e202400524. 10.1002/cbdv.202400524
36
Hui C. Jin J. Ji M. Wang H. Wang X. Ma J. et al (2024b). Neuroprotective properties of the Lilium brownii extracts in the experimental model of parkinson's disease. Metab. Brain Dis.39 (6), 1085–1097. 10.1007/s11011-024-01397-6
37
Hui H. Jin H. Yang X. Wang X. Qin B. (2024c). Fine structure and hypoglycemic effect of a galactoglucan from the bulbs of lanzhou lily. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.254 (Pt 1), 127774. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127774
38
Hui H. Jin H. Yang X. Wang X. Qin B. (2024d). The structure elucidation, anti-aging and hypoglycemic effects of an O-acetyl mannoglucan from the bulbs of lanzhou lily. Fitoterapia179, 106240. 10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106240
39
Hussein A. A. Aldosari B. N. Zaki R. M. Afzal O. Ali A. A. Aboud H. M. et al (2025). Repurposing losartan potassium against rheumatoid arthritis via transdermally-delivered leciplexes: accentuated efficacy through modulation of angiotensin II/AT1R/AT2R axis. Int. J. Pharm. X10, 100354. 10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100354
40
Hutskalova V. Sparr C. (2025). Aromatic ring-opening metathesis. Nature638 (8051), 697–703. 10.1038/s41586-024-08472-z
41
Jeon S. Lee H. Lee J. H. Lee K. Hong D. Park S. D. et al (2024). The effects of Lilium lancifolium thunb. On the alleviation of joint pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Life (Basel)14 (9), 1136. 10.3390/life14091136
42
Ji H. W. Ding X. L. (2003). GC/MS analysis of steroidal sapogenins from bulbs of Lilium brownii var.colchesteri and their identification. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. (03), 84–88.
43
Jiang X. N. Chen C. Wang X. Feng Y. Song Y. M. (2019). Study of baihe dihuang decoction. J. Changchun Univ. Chin.35 (05), 987–990.
44
Jin L. Zhang Y. Yan L. Guo Y. Niu L. (2012). Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of bulb extracts of six lilium species native to China. Molecules17 (8), 9361–9378. 10.3390/molecules17089361
45
Kan J. Hui Y. Xie W. Chen C. Liu Y. Jin C. (2021). Lily bulbs' polyphenols extract ameliorates oxidative stress and lipid accumulation in vitro and in vivo. J. Sci. Food Agric.101 (12), 5038–5048. 10.1002/jsfa.11148
46
Kar R. Das P. Panchali T. Dutta A. Phoujdar M. Ghosh K. et al (2025). Anti-obese potentiality of marine topse (Polynemus paradiseus) fish oil by inhibiting the expression of SREBP-1c and promoting β-oxidation of fat through upregulating PPAR-α. Adipocyte14 (1), 2524640. 10.1080/21623945.2025.2524640
47
Khan A. Wang W. Ji J. Ling Z. Liu P. Xiao S. et al (2024). Fermented lily bulbs by “jiangshui” probiotics improves lung health in mice. Food Chem.440, 138270. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.138270
48
Kim J. S. Lee I. K. Yun B. S. (2015). A novel biosurfactant produced by Aureobasidium pullulans L3-GPY from a tiger lily wild flower, Lilium lancifolium thunb. PLoS One10 (4), e0122917. 10.1371/journal.pone.0122917
49
Kim A. Kim J. Kim B. Y. Seo C. S. Kim Y. R. Song K. H. et al (2024). Aquo-ethanolic extract of lilii Bulbus attenuates dexamethasone-induced muscle loss and enhances muscle strength in experimental mice. Biomed. Pharmacother.181, 117658. 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117658
50
Kwon O. K. Lee M. Y. Yuk J. E. Oh S. R. Chin Y. W. Lee H. K. et al (2010). Anti-inflammatory effects of methanol extracts of the root of Lilium lancifolium on LPS-Stimulated Raw264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol.130 (1), 28–34. 10.1016/j.jep.2010.04.002
51
Langston C. E. (2002). Acute renal failure caused by lily ingestion in six cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc.220 (1), 49–52. 10.2460/javma.2002.220.49
52
Lee E. Yun N. Jang Y. P. Kim J. (2013). Lilium lancifolium thunb. extract attenuates pulmonary inflammation and air space enlargement in a cigarette smoke-exposed mouse model. J. Ethnopharmacol.149 (1), 148–156. 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.014
53
Lee J. Choi J. Yun H. Y. Jang H. Cho M. Ha J. H. et al (2025). Neuroprotective effects of Lilium lancifolium thunberg extract against corticosterone-induced dysfunctions in PC12 cells. J. Med. Food28 (4), 366–376. 10.1089/jmf.2024.k.0241
54
Lei Z. Luan F. Zou J. Zhang X. Zhai B. Xin B. et al (2025). Traditional uses, phytochemical constituents, pharmacological properties, and quality control of Pseudostellaria heterophylla (miq.) pax. J. Ethnopharmacol.337 (Pt 2), 118871. 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118871
55
Li Z. Q. Liu Z. H. (2025). Lily: a good health product with the same origin as medicine and food. China Food (10), 86–87.
56
Li C. H. Zhu Z. M. Cheng L. Zheng J. M. Liu W. H. Lin Y. et al (2024). Extraction, purification, characteristics, bioactivities, prospects, and toxicity Of lilium spp. polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.259, 128532. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128532
57
Li S. Bao F. Cui Y. (2021). Immunoregulatory activities of the selenylated polysaccharides of Lilium davidii Var. unicolor Salisb in vitro and in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol.94, 107445. 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107445
58
Li L. Ma J. Yu Z. Li M. Zhang W. Sun H. (2023). Epidemiological characteristics and antibiotic resistance mechanisms of streptococcus pneumoniae: an updated review. Microbiol. Res.266, 127221. 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127221
59
Li M. Liu R. Wang T. Duo L. Chen G. Mao M. et al (2025). Human gut Bifidobacterium longum subsp. suillum is enriched in vitro by a pectic polysaccharide isolated from the flowers of Lilium lancifolium. Carbohydr. Polym.364, 123772. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.123772
60
Li X. J. Yin Y. Xiao S. J. Chen J. Zhang R. Yang T. et al (2024). Extraction, structural characterization and immunoactivity of glucomannan type polysaccahrides from Lilium brownii var. viridulum baker. Carbohydr. Res.536, 109046. 10.1016/j.carres.2024.109046
61
Li Z. Wang X. Li X. Chen X. Wang C. Mao Y. et al (2025). Polysaccharides from lanzhou lily attenuate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease modifying the gut microbiota and metabolite profile. Chem. Biodivers.22 (1), e202401538. 10.1002/cbdv.202401538
62
Liang Z.-X. Zhang J.-Z. Xin C. Li D. Sun M.-Y. Shi L. (2022). Analysis of edible characteristics, antioxidant capacities, and phenolic pigment monomers in lilium bulbs native to China. Food Res. Int.151, 110854. 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110854
63
Liu Y. L. Kang W. Y. (2025). Lily: the “Yunshang Fairy” with the same origin as medicine and food. China Food(01)66.
64
Liu S. Gao Y. Luo J. Chen Y. Cao H. Guo Z. et al (2025a). Dietary baking soda (NaHCO(3)) therapy recovered urolithiasis-induced kidney injury in mice by inhibition of oxidative stress, pyroptosis, and inflammation through gut-kidney axis. Ren. Fail47 (1), 2521456. 10.1080/0886022x.2025.2521456
65
Liu S. Luo Y. Jiang P. Zhang Z. Wang Y. Hao Z. et al (2025b). Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of Lilium lancifolium thunb. and their antioxidant effects. Phytochemistry237, 114521. 10.1016/j.phytochem.2025.114521
66
Liu R. Wu T. Zhou W. Zhu A. Liao W. Ding K. (2025). A novel polysaccharide from the flowers of Lilium lancifolium alleviates pulmonary fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem.73 (13), 7774–7787. 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c11703
67
Liu X. Y. Chen M. M. Luo J. R. Han F. F. Cai X. Y. Zhang Y. C. (2025). Evaluation of major nutritional and functional components in different genotypes of lilies. J. Northwest A and F Univ. Sci. Ed.53 (06), 127–136.
68
Luan F. Zeng J. Yang Y. He X. Wang B. Gao Y. et al (2020). Recent advances in Camellia oleifera abel: a review of nutritional constituents, biofunctional properties, and potential industrial applications. J. Funct. Foods75, 104242. 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104242
69
Luo J. Li L. Kong L. (2012). Preparative separation of phenylpropenoid glycerides from the bulbs of Lilium lancifolium by high-speed counter-current chromatography and evaluation of their antioxidant activities. Food Chem.131 (3), 1056–1062. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.112
70
Lupşor S. Stanciu G. Cristache R. E. Pănuş E. Radulescu C. Olteanu R. L. et al (2025). Phytochemical evaluation and antioxidant-antimicrobial potential of lilium spp. bulbs: therapeutic and dermatocosmetic applications. Plants (Basel)14 (13), 1917. 10.3390/plants14131917
71
Ma T. Sam F. E. (2024). Floral infusions: elevating the bouquet of non-alcoholic chardonnay wine beverage. Food Chem. X24, 102015. 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.102015
72
Ma T. Wang Z. Zhang Y. M. Luo J. G. Kong L. Y. (2017). Bioassay-guided isolation of anti-inflammatory components from the bulbs of Lilium brownii var. viridulum and identifying the underlying mechanism through acting on the NF-κB/MAPKs pathway. Molecules22 (4), 506. 10.3390/molecules22040506
73
Ma H. Huang H. Li C. Li S. Gan J. Lian C. et al (2024). The antidepressive mechanism of longya lilium combined with fluoxetine in mice with depression-like behaviors. Syst. Biol. Appl.10 (1), 5. 10.1038/s41540-024-00329-5
74
Matsuo Y. Takaku R. Mimaki Y. (2015). Novel steroidal glycosides from the bulbs of Lilium pumilum. Molecules20 (9), 16255–16265. 10.3390/molecules200916255
75
Mimaki Y. Sashida Y. (1990). Steroidal saponins and alkaloids from the bulbs of Lilium brownii Var. colchesteri. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo)38 (11), 3055–3059. 10.1248/cpb.38.3055
76
Mimaki Y. Ishibashi N. Ori K. Sashida Y. (1992). Steroidal glycosides from the bulbs of Lilium dauricum. Phytochemistry31 (5), 1753–1758. 10.1016/0031-9422(92)83141-k
77
Mimaki Y. Sashida Y. Nakamura O. Nikaido T. Ohmoto T. (1993). Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of Lilium regale and L. henryi. Phytochemistry33 (3), 675–682. 10.1016/0031-9422(93)85472-4
78
Mimaki Y. Nakamura O. Sashida Y. Satomi Y. Nishino A. Nishino H. (1994). Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of Lilium longiflorum and their antitumour-promoter activity. Phytochemistry37 (1), 227–232. 10.1016/0031-9422(94)85030-5
79
Mimaki Y. Satou T. Kuroda M. Sashida Y. Hatakeyama Y. (1998). New steroidal constituents from the bulbs of Lilium candidum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo)46 (11), 1829–1832. 10.1248/cpb.46.1829
80
Mimaki Y. Satou T. Kuroda M. Sashida Y. Hatakeyama Y. (1999). Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of Lilium candidum. Phytochemistry51 (4), 567–573. 10.1016/s0031-9422(99)00022-9
81
Munafo J. P. Jr. Gianfagna T. J. (2015). Chemistry and biological activity of steroidal glycosides from the lilium genus. Nat. Prod. Rep.32 (3), 454–477. 10.1039/c4np00063c
82
Munafo J. P. Ramanathan A. Jimenez L. S. Gianfagna T. J. (2010). Isolation and structural determination of steroidal glycosides from the bulbs of easter lily (Lilium longiflorum thunb.). J. Agric. Food Chem.58 (15), 8806–8813. 10.1021/jf101410d
83
Neelam K. Khatkar A. Sharma K. K. (2019). Phenylpropanoids and its derivatives: biological activities and its role in food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.60 (16), 2655–2675. 10.1080/10408398.2019.1653822
84
Ning M. Liu X. C. He M. Peng X. R. Qiu M. H. (2025). 2,5-Dihydroxyphenylethanone: an anti-melanogenic bioactive compound isolated from Ganoderma cochlear. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem.40 (1), 2495364. 10.1080/14756366.2025.2495364
85
Pan G. Xie Z. Huang S. Tai Y. Cai Q. Jiang W. et al (2017). Immune-enhancing effects of polysaccharides extracted from Lilium lancifolium Thunb. Int. Immunopharmacol.52, 119–126. 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.030
86
Pan W. Shi H. Zang Z. Meng Q. Cheng Y. Liang L. et al (2024). Research progress on classical traditional Chinese medicine formula baihe zhimu (Lilium lancifolium bulb and Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizome) decoction in the treatment of depression. Heliyon10 (3), e25171. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25171
87
Park H. R. Cai M. (2024). Antiseizure effects of lilii bulbus on pentylenetetrazol kindling-induced seizures in mice: involvement of Reelin, Netrin-1, and semaphorin. Biomed. Pharmacother.173, 116385. 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116385
88
Park S. Han N. Lee J. Lee J. N. An S. Bae S. (2023). Anti-Melanogenic effects of Lilium lancifolium root extract via downregulation of PKA/CREB and MAPK/CREB signaling pathways in B16F10 cells. Plants (Basel)12 (21), 3666. 10.3390/plants12213666
89
Partovi N. Hassani Kumleh H. Mirzajani E. Farhadpour M. (2023). Identification of Lilium ledebourii antiproliferative compounds against skin, bone and oral cancer cells. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 13 (6), 626–640. 10.22038/AJP.2023.22875
90
Pieroni A. (2000). Medicinal plants and food medicines in the folk traditions of the upper Lucca province, Italy. J. Ethnopharmacol.70 (3), 235–273. 10.1016/s0378-8741(99)00207-x
91
Ren Y. Fan Q. Yao X. Zhang J. Wen K. Qu X. et al (2026). A phosphatidylserine-targeted self-amplifying nanosystem improves tumor accumulation and enables efficient tumor therapy by modulating anticancer immunity. Biomaterials324, 123526. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2025.123526
92
Ruggiero N. Ciuciu A. Sedigh A. Rajpar I. Shelton D. Belanger P. et al (2025). The effect of celecoxib and muMab911 on strain adaptive bone remodeling and fracture repair in female mice: implications for rapidly progressive osteoarthritis. Bone198, 117542. 10.1016/j.bone.2025.117542
93
Satou T. Mimaki Y. Kuroda M. Sashida Y. Hatakeyama Y. (1996). A pyrroline glucoside ester and steroidal saponins from Lilium martagon. Phytochemistry41 (4), 1225–1230. 10.1016/0031-9422(95)00723-7
94
Seo C. S. Kim N. S. Song K. H. (2024). The HPLC-PDA method for simultaneous determination of regalosides from bulbs of Lilium lancifolium thunb. And their antioxidant effects. Plants (Basel)13 (19), 2793. 10.3390/plants13192793
95
Sharifi Rad J. Hoseini Alfatemi S. M. Sharifi Rad M. Iriti M. (2014). Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activities of different parts ofNitraria schoberiL. J. Biol. Act. Prod. Nat.4 (1), 44–51. 10.1080/22311866.2014.890070
96
Sharifi-Rad J. Quispe C. Zam W. Kumar M. Cardoso S. M. Pereira O. R. et al (2021). Phenolic bioactives as antiplatelet aggregation factors: the pivotal ingredients in maintaining cardiovascular health. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2021, 2195902. 10.1155/2021/2195902
97
Sharifi-Rad M. Mohanta Y. K. Pohl P. Jaradat N. Aboul-Soud M. A. M. Zengin G. (2022). Variation of phytochemical constituents, antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties of Grantia aucheri (boiss.) at different growth stages. Microb. Pathog.172, 105805. 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105805
98
Sharifi-Rad J. Seidel V. Izabela M. Monserrat-Mequida M. Sureda A. Ormazabal V. et al (2023). Phenolic compounds as Nrf2 inhibitors: potential applications in cancer therapy. Cell Commun. Signal21 (1), 89. 10.1186/s12964-023-01109-0
99
Si Y. Wei W. Chen X. Xie X. Guo T. Sasaki Y. et al (2022). A comprehensive study on the relieving effect of Lilium brownii on the intestinal flora and metabolic disorder in p-chlorphenylalanine induced insomnia rats. Pharm. Biol.60 (1), 131–143. 10.1080/13880209.2021.2019283
100
Sim W. S. Choi S. I. Jung T. D. Cho B. Y. Choi S. H. Park S. M. et al (2020). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Lilium lancifolium bulbs extract. J. Food Biochem.44 (5), e13176. 10.1111/jfbc.13176
101
Song Y. Li L. X. Zhao K. W. Zhang Y. H. Zhang M. (2023). Study on medicinal edibility of lily and relationship between medicine and food. J. Basic Chin. Med.29 (02), 276–279.
102
Sun Z. Xu D. Wang X. Zhou J. Xiao N. Jia R. et al (2024). Lily extract ameliorate mouse pneumonia by modulating ciliary function. J. Funct. Foods123, 106603. 10.1016/j.jff.2024.106603
103
Tang L. Li L. Sun X. Q. Xiao W. Z. (2021). A philological study and visual analysis of the historical evolution of lily processing. J. Li-shizhen Traditional Chin.32 (11), 2668–2672.
104
Tang Y. Liu Y. Luo K. Xu L. Yang P. Ming J. (2022). Potential applications of lilium plants in cosmetics: a comprehensive review based on research papers and patents. Antioxidants (Basel)11 (8), 1458. 10.3390/antiox11081458
105
Vasvit P. Klarod K. Sukkho O. Kiatkulanusorn S. Werasirirat P. Wang X. Q. et al (2025). Therapeutic effect of focused-extracorporeal shockwave therapy on muscular and adjacent tissue stiffness and pain changes in myofascial pain syndrome: a randomized controlled trial study. Complement. Ther. Med.92, 103203. 10.1016/j.ctim.2025.103203
106
Wang C. H. Shu Y. Yin F. J. Zhao J. F. Zhang Z. W. Liu X. et al (2018). Textual research on origin and genuine of lilii bulbus. China J. Chin. Materia Medica43 (08), 1732–1736. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20180201.005
107
Wang T. Huang H. Zhang Y. Li X. Li H. Jiang Q. et al (2015). Role of effective composition on antioxidant, anti‐inflammatory, sedative‐hypnotic capacities of 6 common edible lilium varieties. J. Food Sci.80 (4), H857–H868. 10.1111/1750-3841.12787
108
Wang X. M. Xu K. Y. Wu H. R. Wei X. X. Zhang H. Y. Li K. (2020). Clinical application and dosage of lily bulb. J. Changchun Univ. Chin. Med.36 (04), 637–639.
109
Wang Z. Wang X. Mou X. Wang C. Sun Y. Wang J. (2024a). Rehmannia glutinosa DC.-lilium lancifolium thunb. in the treatment of depression: a comprehensive review and perspectives. Front. Pharmacol.15, 1471307. 10.3389/fphar.2024.1471307
110
Wang Z. Zou J. Shi Y. Zhang X. Zhai B. Guo D. et al (2024b). Extraction techniques, structural features and biological functions of Hippophae rhamnoides polysaccharides: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.263 (Pt 1), 130206. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130206
111
Wang F. Wang W. Niu X. Huang Y. Zhang J. (2018). Isolation and structural characterization of a second polysaccharide from bulbs of lanzhou lily. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol.186 (3), 535–546. 10.1007/s12010-018-2750-2
112
Wang M. Tang H. P. Bai Q. X. Yu A. Q. Wang S. Wu L. H. et al (2024). Extraction, purification, structural characteristics, biological activities, and applications of polysaccharides from the genus lilium: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.267 (Pt 1), 131499. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131499
113
Wang Y. F. An Z. Y. Yuan L. Q. Wang T. Jin W. L. (2024). Lilium Brownii/baihe as nutraceuticals: insights into its composition and therapeutic properties. Pharm. (Basel)17 (9), 1242. 10.3390/ph17091242
114
Wei W. Guo T. Fan W. Ji M. Fu Y. Lian C. et al (2024). Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome provides new insights into functional components of lilii bulbus. Chin. Herb. Med.16 (3), 435–448. 10.1016/j.chmed.2023.10.004
115
Wu Y. Zhang C. Shao H. Luo H. Tan Z. (2021). Characteristics of intestinal microbiota and enzyme activities in mice fed with lily bulb. 3 Biotech.11 (1), 17. 10.1007/s13205-020-02597-4
116
Xia X. Zhang J. Wang X. J. Lu Y. Chen D. F. (2022). New phenolic glycosides and lignans from the roots of Lilium dauricum. Planta Med.88 (7), 518–526. 10.1055/a-1527-9602
117
Xu Z. Wang H. Wang B. Fu L. Yuan M. Liu J. et al (2016). Characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from the leaves of Lilium lancifolium thunb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.92, 148–155. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.028
118
Xu X. Wang P. Wang B. Wang M. Wang S. Liu Z. et al (2021). Glucose absorption regulation and mechanism of the compounds in Lilium lancifolium thunb on Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol.149, 112010. 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112010
119
Yan J. Guo W. Zhou L. Guo D. Pei J. Deng Y. et al (2021). Three previously undescribed chlorophenyl glycosides from the bulbs of Lilium regale. Chem. and Biodivers.18 (10), e2100403. 10.1002/cbdv.202100403
120
Yan Z. Xiao L. D. Guo X. Hu Y. Wang N. Wang Y. (2025). The impact of social support and social constraints on sleep disturbances in patients with lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy: serial mediators of sleep cognition and anxiety-depression. Asia Pac J. Oncol. Nurs.12, 100740. 10.1016/j.apjon.2025.100740
121
Yang X. W. Wu Y. S. Cui Y. X. Liu X. H. (2012). New steroidal saponins from the bulbs of Lilium brownii Var. viridulum. Carbohydr. Res.361, 19–26. 10.1016/j.carres.2012.07.027
122
Younossi Z. M. (2019). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease - a global public health perspective. J. Hepatol.70 (3), 531–544. 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.033
123
Yu W. H. Gui M. M. He P. P. Deng X. Y. (2024). Research progress of nutritional value and processing technology of lily. China Food Saf. Mag. (35), 186–189.
124
Yuan T. (2025). Research on the nutritional value and health care effects of lily. Food Ind. (05), 36–38.
125
Yuan Z. Y. Li Z. Y. Zhao H. Q. Gao C. Xiao M. W. Jiang X. M. et al (2021). Effects of different drying methods on the chemical constituents of Lilium lancifolium thunb. based on UHPLC-MS analysis and antidepressant activity of the main chemical component regaloside A. J. Sep. Sci.44 (5), 992–1004. 10.1002/jssc.202000969
126
Zengin G. Uba A. I. Ocal M. Sharifi-Rad M. Caprioli G. Angeloni S. et al (2022). Integration of in vitro and in silico approaches to assess three astragalus species from Turkey flora: a novel spotlight from lab bench to functional applications. Food Biosci.49, 101858. 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101858
127
Zhang J. Gao Y. Zhou X. Hu L. Xie T. (2010). Chemical characterisation of polysaccharides from Lilium davidii. Nat. Prod. Res.24 (4), 357–369. 10.1080/14786410903182212
128
Zhang T. Gao J. Jin Z. Y. Xu X. M. Chen H. Q. (2014). Protective effects of polysaccharides from Lilium lancifolium on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.65, 436–440. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.01.063
129
Zhang W. Wang J. L. Zhang Z. J. Peng H. S. Zhan Z. L. Yang H. J. (2019). Herbal textual research on triditional Chinese medicine “baihe”(lilii bulbus). Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi44 (22), 5007–5011. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190903.101
130
Zhang Y. Y. Luo L. M. Wang Y. X. Zhu N. Zhao T. J. Qin L. (2020). Total saponins from lilium lancifolium: a promising alternative to inhibit the growth of gastric carcinoma cells. J. Cancer11 (14), 4261–4273. 10.7150/jca.42285
131
Zhang H. Jin L. Zhang J. B. Niu T. Guo T. Chang J. (2022). Chemical constituents from the bulbs of Lilium davidii Var. unicolor and anti-insomnia effect. Fitoterapia161, 105252. 10.1016/j.fitote.2022.105252
132
Zhang M. Qin H. An R. Zhang W. Liu J. Yu Q. et al (2022). Isolation, purification, structural characterization and antitumor activities of a polysaccharide from Lilium davidii Var. unicolor cotton. J. Mol. Struct.1261, 132941. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132941
133
Zhao K. H. Yan S. E. He Y. J. Li D. J. Liu D. B. Xie H. Q. (2019). Quantification of phenolics in lilium by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med.41 (06), 1445–1450.
134
Zhao L. Mehmood A. Yuan D. Usman M. Murtaza M. A. Yaqoob S. et al (2021). Protective mechanism of edible food plants against alcoholic liver disease with special mention to polyphenolic compounds. Nutrients13 (5), 1612. 10.3390/nu13051612
135
Zhao X. Meng Y. Liu Y. Sun Z. Cui K. Zhu L. et al (2024). Pectic polysaccharides from Lilium brownii and Polygonatum odoratum exhibit significant antioxidant effects in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.257, 128830. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128830
136
Zhou X. D. Shi D. D. Wang H. N. Tan Q. R. Zhang Z. J. (2019a). Aqueous extract of lily bulb ameliorates menopause-like behavior in ovariectomized mice with novel brain-uterus mechanisms distinct from estrogen therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother.117, 109114. 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109114
137
Zhou X. D. Zheng Y. Sharma R. Zhang Z. J. (2019b). Total polysaccharides of lily bulb ameliorate menopause-like behavior in ovariectomized mice: multiple mechanisms distinct from estrogen therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2019, 6869350. 10.1155/2019/6869350
138
Zhou J. An R. Huang X. (2021). Genus lilium: a review on traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol.270, 113852. 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113852
139
Zhou J. Zhao X. M. An R. F. Li X. R. Wu K. T. Li S. M. et al (2024). Four new steroidal glycosides from Lilium lancifolium thunb. and their antitumor activity. Fitoterapia173, 105808. 10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105808
140
Zhou N. Miao K. Liu C. Jia L. Hu J. Huang Y. et al (2024). Historical biogeography and evolutionary diversification of lilium (liliaceae): new insights from plastome phylogenomics. Plant divers.46 (2), 219–228. 10.1016/j.pld.2023.07.009
141
Zhu M. Luo J. Lv H. Kong L. (2014). Determination of anti-hyperglycaemic activity in steroidal glycoside rich fraction of lily bulbs and characterization of the chemical profiles by LC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. J. Funct. Foods6, 585–597. 10.1016/j.jff.2013.12.002
Summary
Keywords
Lilium spp. , nutritional properties, chemical composition, anti-inflammatory properties, antidepressant effects, patent applications
Citation
Wang Y, Chen H, Feng P, Wang D and Du X (2025) Traditional uses, nutritional properties, phytochemical metabolites, pharmacological properties, and potential applications of Lilium spp.: a systematic review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1713957. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1713957
Received
26 September 2025
Revised
29 October 2025
Accepted
03 November 2025
Published
24 November 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Nunziatina De Tommasi, University of Salerno, Italy
Reviewed by
Majid Sharifi-Rad, Zabol University, Iran
Angela Bisio, University of Genoa, Italy
Wei-Lin Jin, First Hospital of Lanzhou University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wang, Chen, Feng, Wang and Du.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoquan Du, duxiaoquan1997@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.