- 1Mycobacteria Research Laboratories, Microbiology, Immunology and Pathology, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, United States
- 2Consortium for Applied Microbial Metrics, Aurora, CO, United States
- 3Division of Pulmonary Sciences and Critical Care Medicine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, CO, United States
- 4Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center, Aurora, CO, United States
by Cummings JE, Woolhiser LK, Guglielmi V, Wernsman M, Romano A, Pauly S, Belisle JT, Walter ND, Robertson GT and Slayden RA (2025). Front. Pharmacol. 16:1667592. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1667592
There was a mistake in Figure 1 as published. Figure S1 was published in place of the true Figure 1. The corrected Figure 1 appears below.
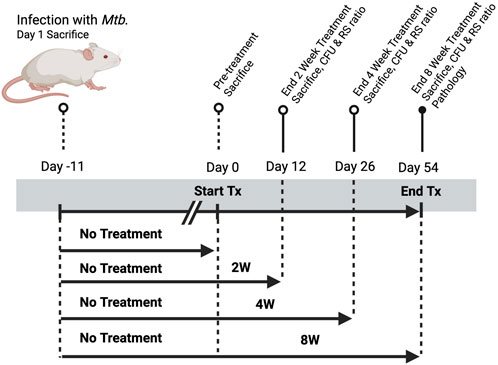
Figure 1. Study design for evaluating treatment duration-dependent responses to standard HRZE therapy in a murine model of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Mice were aerosol-infected with M. tuberculosis on Day−11 and one group was sacrificed at Day 1 post-infection to establish baseline lung bacterial burden. All remaining animals remained untreated until Day 0, at which point treatment (Tx) was initiated. Groups received treatment for 2, 4, or 8 weeks, with corresponding sacrifices on Days 12, 26, and 54 to assess treatment efficacy. Endpoints included colony-forming unit (CFU) enumeration and determination of RS Ratio. Day 54 mice were also evaluated for histopathological changes and PK analysis. A parallel untreated control group was maintained through the full 8-week period.
Supplemental material Figure S1 was omitted. The file has now been published.
The original article has been updated.
Generative AI statement
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: high-burden aerosol BALB/c model, high burden, tuberculosis, mycobacteria, drug discovery
Citation: Cummings JE, Woolhiser LK, Guglielmi V, Wernsman M, Romano A, Pauly S, Belisle JT, Walter ND, Robertson GT and Slayden RA (2025) Correction: Evaluating the efficacy of HRZE-based regimens in a high-burden murine model: a back-translational assessment of rifamycins and moxifloxacin substitutions in tuberculosis treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1733648. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1733648
Received: 27 October 2025; Accepted: 28 October 2025;
Published: 18 November 2025.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2025 Cummings, Woolhiser, Guglielmi, Wernsman, Romano, Pauly, Belisle, Walter, Robertson and Slayden. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Richard A. Slayden, cmljaGFyZC5zbGF5ZGVuQGNvbG9zdGF0ZS5lZHU=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jason E. Cummings1†
Jason E. Cummings1† Vincent Guglielmi
Vincent Guglielmi John T. Belisle
John T. Belisle Gregory T. Robertson
Gregory T. Robertson Richard A. Slayden
Richard A. Slayden