Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to explore the impacts of social cognition and interaction training (SCIT) on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) levels, and psychosocial function in first-episode, drug-naïve (FEDN) major depressive disorder (MDD) patients.
Methods:
In this 8-week randomized controlled trial (RCT), 45 MDD patients were assigned to SCIT group and 39 to cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) group. The 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale (HDRS-17) and the Functioning Assessment Short Test (FAST) were performed to measure depressive symptoms and functional impairment severity, respectively. We also collected blood samples for serum BDNF/GDNF level detection.
Results:
Compared to CBT, SCIT demonstrated significantly greater improvements in total FAST scores (F (1,82) = 109.21, p < 0.001, ); especially in occupational (F (1,82) = 16.69, p < 0.001, ); cognitive (F (1,82) = 103.51, p < 0.001, ), and interpersonal relationship domains (F (1,82) =65.07, p < 0.001, ). Changes in serum GDNF levels were positively associated with changes in autonomy (r (40) = 0.32, 95% CI = [0.02, 0.57], p = 0.038), and financial domains (r (40) = 0.44, 95% CI = [0.15, 0.65], p = 0.004) in SCIT group.
Conclusion:
Improvements in social function through SCIT can be effectively generalized to MDD patients. Moreover, improved GDNF levels were associated with improvements in specific aspects of social functioning post-SCIT.
1 Introduction
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a prevalent illness, with 12-month and lifetime prevalences of 1.6% and 1.8% in China (1). MDD has a deleterious effect on patients’ daily functioning in various aspects, including but not limited to personal relationships, social life, and vocational efficacy, which significantly impairs psychosocial functioning and diminishes the quality of life (QoL) (2–4). Almost 70% of MDD patients do not achieve long-term functional recovery post-first-line antidepressant intervention (5). Research indicates that the risk of recurrence increases by about 12% for every 1-point increase in functional impairment scores (6). The World Health Organization has projected that depression will become the leading disease burden in high-income countries by 2030. Notably, psychosocial dysfunction represents a pronounced indirect cost to the burden of disease (7). Previous studies have demonstrated that cognitive deficits persist even after improvement and remission of mood symptoms, mediating the relationship between psychosocial deficits and MDD, leading to poor efficacy and disease recurrence (6–8). There is an urgent need to explore clinical interventions that can improve the social functioning of MDD patients (3).
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) participate in specific neuronal growth, differentiation, and synaptic plasticity (9). Of note, accumulated evidence has summarized that BDNF/GDNF might constitute a neurobiological substrate of cognitive dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disorders (10, 11). So far, correlations between social function/cognition impairment and/or BDNF/GDNF levels have been reported in anorexia nervosa, schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) patients (12–14). It appears to be a trend suggesting that higher levels of BDNF/GDNF are associated with better social cognition and/or social functioning in patients with mental illnesses. Unfortunately, when exploring the association between cognitive intervention and changes in BDNF and GDNF concentrations in the MDD population, da Silva et al. failed (15). Psychosocial dysfunction may act as a secondary consequence of cognitive impairment, and both may play a critical role in the prognosis of depression (7, 8). Thus, it is helpful to explore the correlation between social function/cognition and BDNF/GDNF levels, especially for first-episode, drug-naïve (FEDN) MDD patients.
Social cognition and interaction training (SCIT) was primarily developed to improve social functioning through social cognition in schizophrenia individuals, which is feasible and effective in improving QoL, emotion recognition, and social skills in patients with schizophrenia and its spectrum disorders (16). In bipolar disorder (BD) population, SCIT has produced greater improvements in occupational and interpersonal function, as well as in visual-verbal cognitive abilities, compared to psychoeducation interventions (17). In addition, by targeting social cognition, a 14-week SCIT intervention has been proven to improve MDD patients’ emotional perception, theory of mind, and attributional styles (18). Social function, as an urgent problem that needs to be addressed, requires prompt attention (3). Interpersonal and occupational declines, as important components of social functioning, persist even when depression is remitted, posing high-risk factors for MDD recurrence and relapse, and adversely affecting the QoL of MDD patients (19, 20). Given the relationship between social function and social cognition (7), SCIT’s role in social functioning in MDD patients needs further discussion.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has been widely applied to improve depressive symptoms and cognitive deficits in the MDD population (21), while its role in improving social function across various mental illnesses (e.g., bipolar disorder, social anxiety disorder, chronic depression) has also been proven (22–24). It is recognized that both psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy are biological treatments that affect the brain both in similar and different ways (25). The value of neurotrophins in the prognosis of antidepressant treatment has been discussed (11). However, biomarkers capable of predicting the outcomes of psychotherapy remain elusive. As mediators of neuroplasticity, BDNF/GDNF represent promising targets for research in this field. Although BDNF might act as a promising genetic marker for treatment response to CBT intervention in depression has been discussed, BDNF levels post-CBT treatment remain controversial (26, 27). Unfortunately, no study has paid attention to the impacts of SCIT on improving social functioning in FEDN MDD patients, and BDNF or GDNF levels post-SCIT are still unknown (18). Taken together, the investigation of changes in neurotrophic factors following psychotherapy holds significant clinical relevance.
Therefore, our main purpose was to discover whether SCIT intervention is more likely to improve social function and GDNF/BDNF levels compared to CBT intervention, and to explore whether the improvement of FAST including its six domains is related to biomarkers GDNF and BDNF in FEDN MDD patients.
2 Methods and materials
2.1 Subjects
This study was performed at the Tianjin Anding Hospital from December 2018 to June 2019. Ninety outpatients with FEDN MDD aged 18–60 years were enrolled according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed (DSM-5), with a baseline score ≥ 18 on the 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale (HDRS-17). Patients with severe medical conditions, substance abuse disorders, and other severe mental illnesses, i.e., schizophrenia, BD, mental retardation, etc., were excluded. Additionally, patients who received any regular psychotherapy, such as CBT or psychoeducation before enrollment were also ruled out. The study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Tianjin Anding Hospital (Ethics number: 2018-020). Besides, written informed consent was obtained from all participants. This study was registered on http://www.chictr.org.cn/(Identifier number: ChiCTRIIR-17010453).
2.2 Procedures
To ensure allocation concealment, the sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelope (SNOSE) technique was employed. The envelopes were prepared by people who was not involved in participant recruitment or intervention. After a participant completed the baseline assessment, the psychiatrists would open the next sequentially numbered envelope to reveal the group assignment: SCIT or CBT. Both groups received weekly interventions for a total of 8 weeks, with each training session lasting 1.5 hours. Both at baseline and week 8, all participants were assessed by one experienced psychiatrist who was blind to any intervention conditions. Two psychiatrists who were responsible for SCIT and CBT intervention respectively were also blind to each other’s intervention, and they had to receive strict training provided by senior psychologists.
2.2.1 SCIT intervention
SCIT is a manualized intervention program designed to improve psychiatric patients’ social cognitive dysfunction (28). Chan et al. translated and condensed the original SCIT protocol from a 15- to a 9-week program, which confirmed suitable for Chinese adults (29). We further slightly modified it into an 8-week program by removing the general introduction but integrating its key components into the beginning of the subsequent core sessions. Our previous study has evidenced that modified SCIT programs are effective in improving the total functioning in BD patients (17). Our eight-week training sessions were divided into three phases, to be specific, 3 sessions for understanding emotions, 3 sessions for social cognitive biases, and 2 sessions for operating integration practically. To maintain the quality of the intervention, two therapists accepted the training program of the SCIT by Dr. Chan and passed the training trial.
2.2.2 CBT intervention
The handbook of CBT was structured in agreement with Aaron Beck’s theory (30). According to this model, distorted or dysfunctional thinking—which adversely affects mood and behavior— is common to all psychological disorders. An accurate assessment and modification in thinking is associated with improvements in mood and behavior. Lasting improvements are achieved through the modification of the basic dysfunctional beliefs. Its early effectiveness has been verified in FEDN MDD patients (21). FEDN MDD patients in the CBT group received equal-time training, sessions focused on cognitive reconstruction (3 sessions), emotional transformation (3 sessions), and behavioral training (2 sessions).
2.2.3 Pharmacological interventions
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) with flexible doses were allowed to relieve depressive symptoms, including sertraline, fluoxetine, escitalopram or citalopram, duloxetine and venlafaxine. Non-benzodiazepines such as zopiclone (7.5 mg/day) and zolpidem (5–10 mg/day) were used to improve insomnia, but benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotics were avoided due to their potential for inducing cognitive impairment.
2.3 Materials
2.3.1 Demographic information
Baseline sociodemographic characteristics of enrolled patients, including age, gender, education years, marriage, duration of MDD, and family history were collected.
2.3.2 Depressive symptoms assessment
The HDRS-17 (31) was performed to measure depressive severity. Most items are rated on a 5-point scale of 0-4, and a small number of items are rated on a 3-point scale of 0-2. The more severe the depressive symptoms, the higher the score.
2.3.3 Social function assessment
The Functioning Assessment Short Test (FAST) was used to measure functional impairment across six domains: autonomy, occupational functioning, cognitive functioning, financial issues, interpersonal relationship, and leisure time. It consists of 24 items rated on a 4-point scale ranging from 0 to 3, with a higher total score indicating more severe functional impairment (32). The FAST–Chinese version has been verified for good validity and reliability in BD patients (33). Additionally, the FAST scale has been validated for use with individuals experiencing depression, providing a detailed assessment of daily functioning (34, 35).
2.3.4 Serum BDNF and GDNF concentration
We collected 10 ml of blood samples to detect serum BDNF and GDNF levels both at baseline and week 8 for all participants. Venous blood was collected without anticoagulant between 7 and 8 a.m. and immediately sent to the laboratory for serum preparation. Within 1 hour of collection, blood samples were separated into two parts for BDNF and GDNF testing to minimize variability. Serum samples were separated by centrifugation post 1 hour of incubation and stored at − 80°C for further analysis. The blood samples were analyzed by a commercial ELISA kit (Promega. USA), using the protocol already depicted (36). The intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation were < 4% and < 5%, respectively. Importantly, lab personnel were blinded to group allocation during ELISA testing.
2.4 Statistical analysis
SPSS 26.0 was used to analyze the statistical data, and besides, GPower 3.1 was used to calculate the sample size and verify the statistical power, while GraphPad Prism 9.0 was used to plot graphs. The characteristics of sociodemographic and clinical-related variables (HDRS, FAST including its six domains, and serum BDNF/GDNF levels) between SCIT and CBT groups were analyzed using independent sample t-tests for continuous variables and chi-square tests for categorical variables. Repeated-measures analyses of variances (ANOVA) were performed to detect the effects of the two different interventions on scores of HDRS, FAST including its six domains, as well as serum levels of BDNF and GDNF from pre- to post-treatment. Perform pairwise comparisons on variables with significant intervention * time interaction, all of which have been corrected by Bonferroni or Sidak. Pearson correlations were performed to explore the association between changes in the FAST scale and serum levels of BDNF and/or GDNF both in SCIT and CBT groups. All statistical tests were two-tailed (p < 0.05 is considered significant).
3 Results
3.1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of all participants at baseline
According to Gpower 3.1, a medium level effect size (f = 0.25) (see Cohen’s criteria) was set, with an alpha (α) level set at 0.05 (two-tailed) and a desired power (1-β) of 0.80. A total sample size of N = 34 resulted in a 0.81 actual power. Actually, ninety FEDN MDD patients were recruited at baseline. According to the per-protocol analysis principle, 6 patients (4 for SCIT group, 2 for CBT group) were excluded because they uncompleted all assessments during 8 consecutive weeks. There were no differences in demographics, HDRS, FAST including its six domains, and serum BDNF/GDNF levels between excluded and included patients (all p’s > 0.05). Finally, 84 FEDN MDD patients completed the interventions and all assessments during the 8-week follow-up, including 45 patients for SCIT group and 39 patients for CBT group. There was no significant difference in gender (χ2 = 0.02,φ = 0.02, p = 0.886), age (t = 0.64, Cohen’s d = 0.14, p = 0.524), education years (t = -0.38, Cohen’s d = 0.08, p = 0.709), marriage status (χ2 = 2.35, Cramér’sV = 0.17, p = 0.308), the current duration (t = -1.08, Cohen’s d = 0.24, p = 0.283), and family history (χ2 = 2.76, φ = 0.18, p = 0.096) between SCIT group and CBT group, see Table 1. The type of antidepressants according to flexible dosage was also not significantly different between groups (χ2 = 0.44, Cramér’sV = 0.07, p = 0.994). Moreover, we compared the scores of HDRS, FAST including its six domains, as well as serum BDNF and GDNF levels between groups using baseline data, with results revealing no statistical differences in clinical-related variables (all p’s > 0.05), see Table 1.
Table 1
| Variables | SCIT (n = 45) | CBT (n = 39) | T/χ2 | Effect size | 95%CI for1 2 3 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years)† 1 | 34.9(12.3) | 36.6(12.7) | 0.64 | 0.14 | [-0.28,0.56] | 0.524 |
| Gender (Female)# 2 | 27.0(60.0) | 24.0(61.5) | 0.02 | 0.02 | [-0.22,0.19] | 0.886 |
| Marriage# 3 | 2.35 | 0.17 | [0.00,0.35] | 0.308 | ||
| single | 23.0(51.1) | 14.0(35.9) | —— | —— | ||
| married | 19.0(42.2) | 23.0(59.0) | —— | —— | ||
| divorced | 3.0(6.7) | 2.0(5.1) | —— | —— | ||
| Family history (yes)# 2 | 7.0(15.6) | 12.0(30.8) | 2.76 | 0.18 | [-0.38,0.02] | 0.096 |
| Education (years)† 1 | 13.7(2.7) | 13.5(2.9) | -0.38 | 0.08 | [-0.50,0.34] | 0.709 |
| duration of MDD (months)† 1 | 14.0(15.4) | 10.8(11.6) | -1.08 | 0.24 | [-0.66,0.20] | 0.283 |
| HDRS† 1 | 27.6(6.0) | 26.3(4.9) | -1.06 | 0.23 | [-0.65,0.20] | 0.291 |
| BDNF (ng/ml)† 1 | 40.3(4.8) | 40.3(5.6) | -0.01 | 0.00 | [-0.42,0.42] | 0.994 |
| GDNF (ng/ml)† 1 | 377.2(65.2) | 373.0(68.3) | -0.29 | 0.06 | [-0.48,0.36] | 0.771 |
| FAST total score† 1 | 26.2(10.3) | 26.5(11.4) | 0.13 | 0.03 | [-0.39,0.45] | 0.895 |
| - Autonomy† 1 | 3.0(2.1) | 2.7(1.7) | -0.67 | 0.15 | [-0.57,0.28] | 0.505 |
| - Occupational functioning† 1 | 5.1(3.9) | 4.8(4.0) | -0.39 | 0.09 | [-0.51,0.34] | 0.698 |
| - Cognitive functioning† 1 | 6.8(2.9) | 7.6(3.5) | 1.19 | 0.26 | [-0.17,0.69] | 0.237 |
| - Financial issues† 1 | 1.5(1.6) | 2.1(1.8) | 1.55 | 0.34 | [-0.09,0.77] | 0.125 |
| - Interpersonal relationship† 1 | 7.0(3.3) | 6.9(4.5) | -0.15 | 0.03 | [-0.45,0.39] | 0.885 |
| - Leisure time† 1 | 2.7(1.8) | 2.4(1.7) | -0.91 | 0.20 | [-0.62,0.23] | 0.366 |
Demographic and clinical characteristics between SCIT group and CBT group at baseline.
FAST, Functional Assessment Test Short Form; SCIT, social cognition and interaction training; CBT, cognitive-behavioral therapy; MDD, major depressive disorder; HDRS, 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; †, Mean (SD), p-value corresponds to independent samples t-tests; #, n (%), p-value corresponds to chi-square tests, 1, Effect Size (Cohen’s d); 2, Effect Size(φ); 3, Effect Size (Cramér’sV).
3.2 Changes of clinical-related variables from pre- to post-treatment
Repeated-measures ANOVA was performed to examine within-group, between-group, and interaction effects. Both SCIT and CBT showed a prominent improvement in FAST total scores (SCIT: F (1,82) = 100.78, p < 0.001, vs CBT: (1,82) = 30.70, p < 0.001, ); HDRS scores (SCIT: F (1,82) = 694.85 p < 0.001, vs CBT: (1,82) = 453.08, p < 0.001, ); the levels of serum BDNF (SCIT: F (1,82) = 17.68, p < 0.001, vs CBT: (1,82) = 19.90, p < 0.001, ) and GDNF (SCIT: F (1,82) = 91.80, p < 0.001, vs CBT: (1,82) = 100.91, p < 0.001, ) from pre- to post-treatment over 8 weeks, see Figure 1. The intervention*time interaction was significant, indicating that the two groups exhibited different trends in FAST total scores (F (1,82) = 10.67, p = 0.002, ); occupational functioning (F (1,82) = 5.53, p = 0.021, 0); cognitive functioning (F (1,82) = 4.75, p = 0.032, ); and interpersonal relationship of FAST(F (1,82) = 5.73, p = 0.019, ) over time, see Figure 2.
Figure 1

Changes of clinical-related variables from pre- to post-treatment. FAST, Functional Assessment Test Short Form; SCIT, social cognition and interaction training; CBT, cognitive-behavioral therapy; HDRS, 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; ***: p < 0.001.
Figure 2
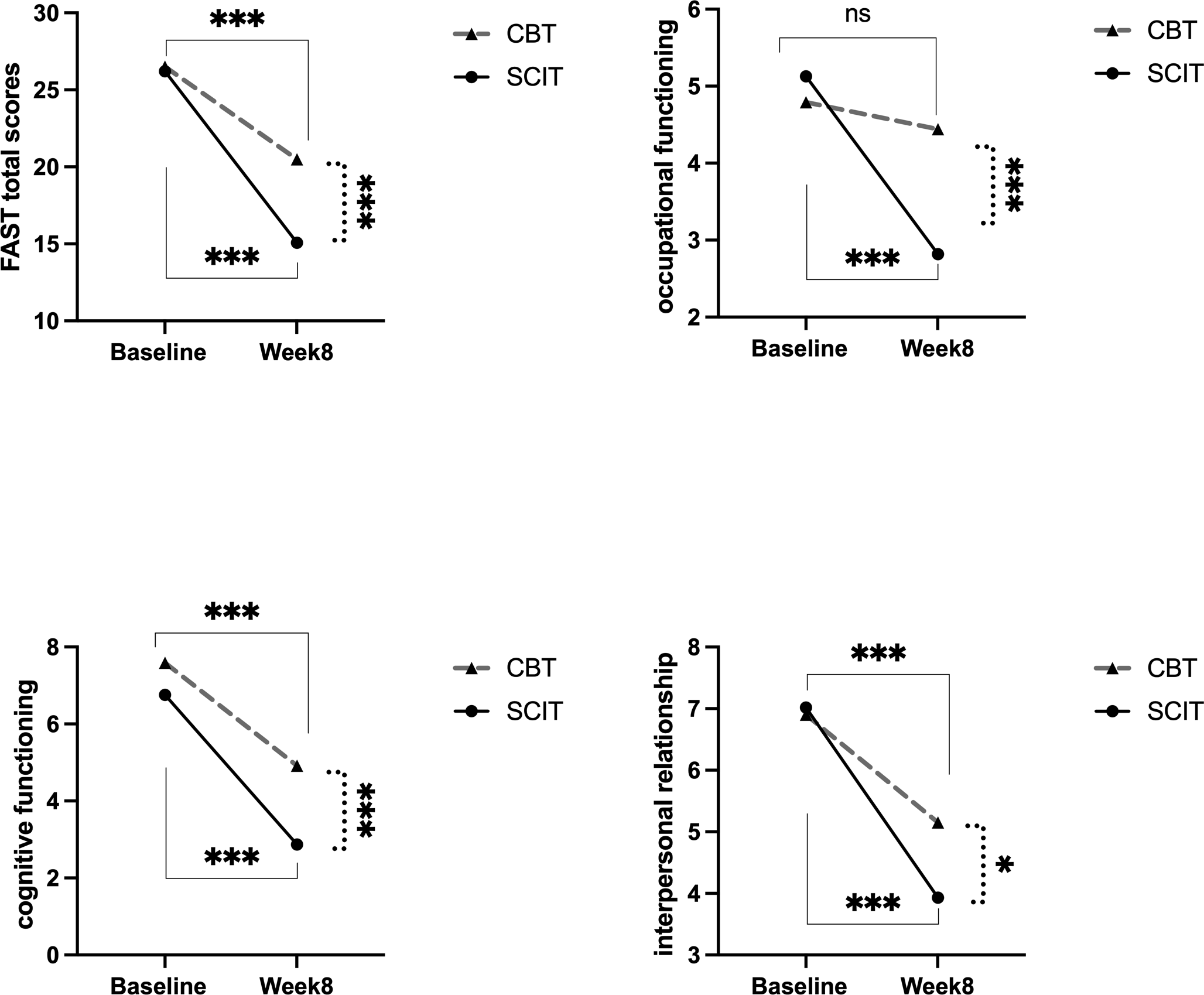
The intervention*time interaction effects on FAST and occupational, cognitive, interpersonal domains pre to post 8-week intervention in SCIT and CBT group. SCIT, social cognition and interaction training; CBT, cognitive-behavioral therapy; FAST, Functional Assessment Test Short Form; solid lines represent the time effect within groups;dashed lines indicate the between-group comparison at week 8;***: p < 0.001; *: p < 0.05.
After post-hoc pairwise comparisons, the SCIT group showed a more pronounced decrease in FAST total scores (SCIT: F (1, 82) = 109.21, p < 0.001, vs CBT: F (1, 82) = 27.72, p < 0.001, ); occupational functioning (SCIT: F (1, 82) = 16.69, p < 0.001, vs CBT: F (1, 82) = 0.35, p = 0.556, ); cognitive functioning (SCIT: F (1, 82) =103.51, p < 0.001, vs CBT: F (1, 82) = 42.18, p < 0.001, ); and interpersonal relationship (SCIT: F (1, 82) = 65.07, p < 0.001, vs CBT: F (1, 82) =17.97, p < 0.001, ) of FAST than the CBT group. There were no differences between the two groups in the above variables at baseline (all p’s > 0.05) after pairwise comparisons. However, at Week 8, the SCIT group’s FAST total scores (F (1, 82) = 24.38, p < 0.001, ); occupational functioning (F (1, 82) = 23.96, p < 0.001, ); cognitive functioning (F (1,82) = 46.45, p < 0.001, ); and interpersonal relationship (F (1, 82) = 6.79, p = 0.011, ) of FAST was significantly lower than that of the CBT group, see Figure 2. All pairwise comparisons were Bonferroni/Sidak-corrected. There were no different trends and statistical differences in HDRS scores, BDNF, and GDNF levels between the two groups from pre- to post-intervention over 8 weeks (all p’s > 0.05).
3.3 Associations of FAST and serum BDNF/GDNF levels
Using baseline data, after controlling for age, educational years, and duration of MDD, partial correlation analysis yielded that occupational functioning was negatively associated with serum GDNF levels (r (79) = -0.24, 95% CI = [–0.43, –0.02], p = 0.033) in all FEDN MDD patients, see Figure3A. Further analyses based on intervention measures revealed that changes in serum GDNF levels were significantly associated with changes in domains of autonomy (r (40) = 0.32, 95% CI = [0.02, 0.57], p = 0.038), and financial issues (r (40) = 0.44, 95% CI = [0.15, 0.65], p = 0.004) in SCIT group, see Figure 3B. To account for multiple comparisons across the examined serum biomarkers and social functioning, false discovery rate (FDR) correction was applied using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure, significant results were considered at an FDR-adjusted p-value threshold of < 0.05. However, after correction, only the correlation between GDNF difference and financial issues difference still holds statistical significance (FDR-adjusted p = 0.49). Besides, there was no correlation between changes in FAST (including its six domains) and changes in serum GDNF or BDNF level were found in CBT group.
Figure 3

Associations between domains of FAST and serum levels of BDNF/GDNF from pre- to post-intervention. GDNF, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; (A) contains all samples at baseline, (B) contains only SCIT group samples from pre- to post-intervention.
4 Discussion
This was an 8-week randomized controlled trial (RCT), which aimed to examine the impacts of SCIT on improvements in psychosocial function, depressive symptoms, and serum BDNF/GDNF levels in FEDN MDD patients. Our findings indicated that both SCIT and CBT interventions could significantly enhance scores of HDRS and total FAST, and levels of serum BDNF and GDNF in FEDN MDD patients. Notably, the SCIT group demonstrated more substantial improvements in overall social functionality, especially in interpersonal relationship, occupational capacity, and cognitive function domains compared to the CBT group. Intriguingly, enhancements in serum GDNF levels following SCIT intervention were correlated with changes in autonomy and financial issue domains of FAST. These findings support our initial hypotheses, highlighting the superior effectiveness of SCIT intervention in improving social function compared to CBT intervention. Furthermore, although preliminary exploration, our study appears to establish a potential link between elevated levels of the serum biomarker GDNF and improvements in specific aspects of social functioning.
The current research found that both SCIT and CBT exerted a positive effect on social functioning. Besides, our findings revealed that CBT had a significant improvement in depressive symptoms, demonstrating its strong efficacy in the enhancement of emotional regulation. SCIT’s role in relieving depressive symptoms in schizophrenia and BD populations has been discussed (17, 37), and we verified improved depressive symptoms in MDD population. However, our study did not find any differences in depression improvement between SCIT and CBT intervention. CBT’s role in improving depression has been verified (38). Our findings can be interpreted as a positive outcome, demonstrating that SCIT is an effective therapy to alleviate depressive symptoms that is no less effective than CBT. It is possibly due to the fact that both interventions could improve cognitive dysfunction and, in turn, depressed mood and social function. SCIT was initially designed to improve social cognitive dysfunction, and its role in schizophrenia, BD, and MDD patients has been proven (16–18, 28). In light of the association between cognitive dysfunction and subsequent functional deficits in everyday life has been explored in mental illnesses (39), there appears to be a trend that social functioning will be improved post-SCIT, and this viewpoint has been validated in schizophrenia and BD patients (16, 17). Our findings further substantiate this evidence in the MDD population. Thus, we hypothesize that SCIT could improve social cognitive capacities to support social function measured by FAST in the MDD population. However, this hypothesis needs to be validated with further cognitive function measurement.
Although previous studies have confirmed that CBT intervention could improve cognitive impairment and social dysfunction (23, 40). A strength in our findings is that SCIT has been shown to be superior to CBT in enhancing interpersonal relationship, occupational function, and cognitive function in FEDN MDD patients. In short, our research extends Zhu et al’s findings that SCIT could improve interpersonal and occupational capacities among depressed individuals (18). Interestingly, our previous study elaborated that compared to psychoeducation, SCIT exhibited greater improvements in the aforementioned domains in the BD group (11). Taken together, it appeared that SCIT benefits interpersonal and occupational function in mental illness patients. A cross-sectional analysis has proved that interpersonal interaction could reverse the effects of functional disabilities on the QoL for serious mental illness, highlighting the important role of interpersonal relationship in social function (41). Another study focused on work-targeted psychotherapy proved to remediate occupational impairment (42). We considered that SCIT not only targets to promote interpersonal interactions by ameliorating judgmental ambiguities and difficulties in work and social settings (28, 33), but also encourages patients to interact with other members to learn more social skills, which may obviously promote interpersonal activity, further boost the work skills and cognitive abilities, while CBT mainly focuses on automatic and maladaptive thought patterns (40).
To date, BDNF levels in MDD patients following psychotherapy remain controversial (26). Distinct from da Silva et al.’ finding that no changes in neurotrophic concentrations were found after psychotherapy, our study showed that both SCIT and CBT intervention can elevate serum BDNF and GDNF levels in MDD patients (15). Zhou et al. confirmed that CBT intervention could restore aberrant dynamic functional connectivity within the dorsolateral frontal anterior cortex, which may play a pivotal role in regulating both emotion and cognition in MDD patients (40). Intriguingly, BDNF and GDNF are associated with emotion and cognition, which might possess a remarkable capability to repair brain damage (9, 43). Taken together, BDNF/GDNF could be indicators of the efficacy of CBT (26). However, the present study did not find a difference between CBT and SCIT intervention in the extent of improvement in BDNF and GDNF levels, suggesting psychotherapy may have a similar mechanism of action, or that an 8-week intervention was too short to observe such variability (26, 44). Besides, the smaller sample size means that though there may be subtle differences between SCIT and CBT, this study was unlikely to identify them. Thus, our findings indicated that larger-scale, longer-term intervention should be considered to explore differences in biomarkers and functioning between SCIT and CBT intervention.
Using baseline data, we also found that serum GDNF levels exhibited a negative correlation with the impairment of occupational function. Although the association is no longer significant after FDR correction, it still suggests a trend that lower serum GDNF levels might be a risk factor for psychosocial dysfunction in MDD patients. Similarly, Okuno et al. proved that social adaptation positively correlates with plasma BDNF levels in healthy controls (45). Another study suggests that a healthy population carrying the BDNF Val Val genotype might show a better ability for social interactions (46), which could facilitate work ability (47). Accumulated human and animal experiments have shown that increased levels of BDNF and GDNF were associated with better cognitive function, including but not limited to learning and memory domains (10, 48, 49). Considering that functional disability can be a result of cognitive dysfunction (7, 8), it can be inferred that the long-term effects of higher BDNF and GDNF concentrations are advantageous for enhancing social functioning. However, we failed to replicate the correlation between BDNF and social function in the MDD population. The small sample size and eight-week duration of the study may have weakened this correlation. Moreover, this separation may provide a novel insight, suggesting that BDNF and GDNF may play distinct roles in functional recovery from MDD.
Taking SCIT intervention into further consideration, changes in serum GDNF levels correlated with improved autonomy and financial ability, with the financial aspect remaining statistically significant even after FDR correction. Unfortunately, we found no correlations between changes in BDNF and FAST including its six domains post-SCIT. The supplementary motor area is a crucial area for linking cognition to action (50), and its abnormal neural activities correlated with cognitive functioning and financial issue ability have been validated in FEDN MDD patients (51). It raises a question about whether SCIT like CBT, can act on specific brain regions, promote the secretion of GDNF, and subsequently lead to a series of social cognitive and functional changes, as we hypothesized. This inference needs to be further confirmed by future research on brain imaging combined with neurocognitive. However, we could not find these correlations in the CBT group, even though recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have emphasized the effects of CBT on decreased dorsal anterior cingulate cortex activity which mainly involved in emotional and cognitive functions (52, 53). So far, the association between biomarkers and social function has received less attention, our study preliminarily shows a tendency that higher serum GDNF levels might be related to better social function.
Some limitations of our research should be stated. Firstly, although flexible doses of antidepressants were more suitable for clinical situations, they also introduce confounding effects that may obscure the isolated impact of psychosocial interventions. Conducting only different psychological interventions in the future will make our conclusion more convincing. Besides, enrolling a control group (e.g., waiting list, TAU) would benefit the interpretation of natural symptom trajectories. Secondly, the absence of social cognitive assessments may limit the explanation for how SCIT enhances social functioning. Previous research has suggested that SCIT might exert its positive effects on social functioning by modifying theory of mind abilities (54). Thirdly, the limited sample size, the current 8-week intervention, and absence of follow-up data limit understanding of the long-term effects of SCIT and CBT (55, 56). Lastly, the assessment was limited to the FAST scale, which may not fully capture social functioning domains in MDD patients. Future studies could incorporate broader instruments, such as the Social Disability Screening Schedule (SDSS), to explore a wider range of correlations. Considering future large-scale, long-term interventions, combined with social cognition and brain imaging techniques such as fMRI, to more precisely detect the similarities and differences in neural networks and molecular levels under the two therapies.
5 Conclusion
Improvements in social function through SCIT can be effectively generalized to MDD patients. Moreover, improved GDNF levels were associated with improvements in specific aspects of social functioning post-SCIT.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committees of Tianjin Anding Hospital (Ethics number: 2018-020). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
JL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SJ: Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Validation. XL: Software, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. YZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Tianjin Key Medical Discipline Construction Project (grant number (TJYXZDXK-3-015B and (ADYKHT2020004)).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Chan and his team for providing SCIT manual and training program. The authors would like to thank all nurses and patients in Tianjin Anding Hospital for their contributions to our study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
SCIT, Social cognition and interaction training; BDNF, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF, Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; FEDN, First-episode, drug-naïve; MDD, Major depressive disorder; RCT, Randomized controlled trial; CBT, Cognitive-behavioral therapy; HDRS-17, 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale; FAST, Functioning Assessment Short Test; QoL, Quality of life; OCD, Obsessive-compulsive disorder; BD, Bipolar disorder; TAU, Treatment-as-usual; DSM-IV, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV; SSRIs, Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; SNRIs, Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors; ANOVA, Analyses of variances; False discovery rate (FDR).
References
1
Zhao YJ Jin Y Rao WW Zhang QE Zhang L Jackson T et al . Prevalence of major depressive disorder among adults in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:659470. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.659470
2
Sheehan DV Nakagome K Asami Y Pappadopulos EA Boucher M . Restoring function in major depressive disorder: A systematic review. J Affect Disord. (2017) 215:299–313. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.02.029
3
Malhi GS Mann JJ . Depression. Lancet. (2018) 392:2299–312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31948-2
4
Christensen MC Grande I Rieckmann A Chokka P . Efficacy of vortioxetine versus desvenlafaxine in the treatment of functional impairment in patients with major depressive disorder: Results from the multinational VIVRE study. CNS Spectr. (2024) 1-10. doi: 10.1017/s1092852924000610
5
Carvalho AF Berk M Hyphantis TN McIntyre RS . The integrative management of treatment-resistant depression: a comprehensive review and perspectives. Psychother Psychosom. (2014) 83:70–88. doi: 10.1159/000357500
6
Solomon DA Leon AC Endicott J Mueller TI Coryell W Shea MT et al . Psychosocial impairment and recurrence of major depression. Compr Psychiatry. (2004) 45:423–30. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2004.07.002
7
McIntyre RS Cha DS Soczynska JK Woldeyohannes HO Gallaugher LA Kudlow P et al . Cognitive deficits and functional outcomes in major depressive disorder: determinants, substrates, and treatment interventions. Dep Anxiety. (2013) 30:515–27. doi: 10.1002/da.22063
8
Bortolato B Carvalho AF McIntyre RS . Cognitive dysfunction in major depressive disorder: a state-of-the-art clinical review. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. (2014) 13:1804–18. doi: 10.2174/1871527313666141130203823
9
Popova NK Ilchibaeva TV Naumenko VS . Neurotrophic factors (BDNF and GDNF) and the serotonergic system of the brain. Biochem (Mosc). (2017) 82:308–17. doi: 10.1134/s0006297917030099
10
Chiavellini P Canatelli-Mallat M Lehmann M Goya RG Morel GR . Therapeutic potential of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and cell reprogramming for hippocampal-related neurological disorders. Neural Regener Res. (2022) 17:469–76. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.320966
11
Liu X Li P Ma X Zhang J Sun X Luo X et al . Association between plasma levels of BDNF and GDNF and the diagnosis, treatment response in first-episode MDD. J Affect Disord. (2022) 315:190–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.07.041
12
Fontenelle LF Barbosa IG Luna JV Rocha NP Silva Miranda A Teixeira AL . Neurotrophic factors in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res. (2012) 199:195–200. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.03.034
13
Dmitrzak-Weglarz M Skibinska M Slopien A Tyszkiewicz M Pawlak J Maciukiewicz M et al . Serum neurotrophin concentrations in polish adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa. Neuropsychobiology. (2013) 67:25–32. doi: 10.1159/000343500
14
Mosiołek A Mosiołek J . The effects of treatment in psychotic disorders-changes in BDNF levels and clinical outcomes: systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2023) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20032111
15
da Silva SK Wiener C Ghisleni G Oses JP Jansen K Molina ML et al . Effects of cognitive-behavioral therapy on neurotrophic factors in patients with major depressive disorder. Braz J Psychiatry. (2018) 40:361–6. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2017-2357
16
Gordon A Davis PJ Patterson S Pepping CA Scott JG Salter K et al . A randomized waitlist control community study of Social Cognition and Interaction Training for people with schizophrenia. Br J Clin Psychol. (2018) 57:116–30. doi: 10.1111/bjc.12161
17
Zhang Y Ma X Liang S Yu W He Q Zhang J et al . Social cognition and interaction training (SCIT) for partially remitted patients with bipolar disorder in China. Psychiatry Res. (2019) 274:377–82. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2019.03.002
18
Zhu S Zhu K Jiang D Shi J . Social cognition and interaction training for major depression: A preliminary study. Psychiatry Res. (2018) 270:890–4. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.11.008
19
Sheets ES Craighead WE . Comparing chronic interpersonal and noninterpersonal stress domains as predictors of depression recurrence in emerging adults. Behav Res Ther. (2014) 63:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2014.09.001
20
Greer TL Trombello JM Rethorst CD Carmody TJ Jha MK Liao A et al . Improvements in psychosocial functioning and health-related quality of life following exercise augmentation in patients with treatment response but nonremitted major depressive disorder: results from the tread study. Dep Anxiety. (2016) 33:870–81. doi: 10.1002/da.22521
21
Wu Z Wang C Dai Y Xiao C Zhang N Zhong Y . The effect of early cognitive behavior therapy for first-episode treatment-naive major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. (2022) 308:31–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.04.008
22
Patelis-Siotis I Young LT Robb JC Marriott M Bieling PJ Cox LC et al . Group cognitive behavioral therapy for bipolar disorder: a feasibility and effectiveness study. J Affect Disord. (2001) 65:145–53. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0327(00)00277-9
23
Zu S Xiang YT Liu J Zhang L Wang G Ma X et al . A comparison of cognitive-behavioral therapy, antidepressants, their combination and standard treatment for Chinese patients with moderate-severe major depressive disorders. J Affect Disord. (2014) 152–154:262–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.09.022
24
Yoshinaga N Matsuki S Niitsu T Sato Y Tanaka M Ibuki H et al . Cognitive behavioral therapy for patients with social anxiety disorder who remain symptomatic following antidepressant treatment: A randomized, assessor-blinded, controlled trial. Psychother Psychosom. (2016) 85:208–17. doi: 10.1159/000444221
25
Martinez-Aran A Vieta E . Precision psychotherapy. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2022) 55:20–1. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2021.10.771
26
Claudino FCA Gonçalves L Schuch FB Martins HRS da Rocha NS . The effects of individual psychotherapy in BDNF levels of patients with mental disorders: A systematic review. Front Psychiatry. (2020) 11:445. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00445
27
Schosser A Fischer-Hansal D Swoboda MM Ludwig B Carlberg L Swoboda P et al . BDNF gene polymorphisms predicting treatment response to CBT-based rehabilitation of depression: to be submitted to: European Neuropsychopharmacology. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2022) 58:103–8. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.03.005
28
Penn D Roberts DL Munt ED Silverstein E Jones N Sheitman B . A pilot study of social cognition and interaction training (SCIT) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. (2005) 80:357–9. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2005.07.011
29
Chan RC Gao XJ Li XY Li HH Cui JF Deng YY et al . The Social Cognition and Interaction Training (SCIT): an extension to individuals with schizotypal personality features. Psychiatry Res. (2010) 178:208–10. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2010.03.017
30
Beck AT Rush AJ Shaw B Emery G . Cognitive Therapy of Depression. New York: The Guilford Press. (1979).
31
Hamilton M . A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (1960) 23:56–62. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56
32
Rosa AR Sánchez-Moreno J Martínez-Aran A Salamero M Torrent C Reinares M et al . Validity and reliability of the Functioning Assessment Short Test (FAST) in bipolar disorder. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. (2007) 3:5. doi: 10.1186/1745-0179-3-5
33
Zhang Y Long X Ma X He Q Luo X Bian Y et al . Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the Functioning Assessment Short Test (FAST) in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. (2018) 238:156–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.05.019
34
Knight MJ Air T Baune BT . The role of cognitive impairment in psychosocial functioning in remitted depression. J Affect Disord. (2018) 235:129–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.04.051
35
Christensen MC Schmidt SN Grande I . The Functioning Assessment Short Test (FAST): Clinically meaningful response threshold in patients with major depressive disorder receiving antidepressant treatment. J Affect Disord. (2024) 363:634–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.07.018
36
Tunca Z Ozerdem A Ceylan D Yalçın Y Can G Resmi H et al . Alterations in BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor) and GDNF (glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor) serum levels in bipolar disorder: The role of lithium. J Affect Disord. (2014) 166:193–200. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.05.012
37
Tang Y Yu L Zhang D Fang F Yuan Z . The effect of social cognitive interaction training on schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparison with conventional treatment. BioMed Res Int. (2022) 2022:3394978. doi: 10.1155/2022/3394978
38
López-López JA Davies SR Caldwell DM Churchill R Peters TJ Tallon D et al . The process and delivery of CBT for depression in adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. psychol Med. (2019) 49:1937–47. doi: 10.1017/S003329171900120X
39
Cambridge OR Knight MJ Mills N Baune BT . The clinical relationship between cognitive impairment and psychosocial functioning in major depressive disorder: A systematic review. Psychiatry Res. (2018) 269:157–71. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.08.033
40
Zhou W Yuan Z Yingliang D Chaoyong X Ning Z Chun W . Differential patterns of dynamic functional connectivity variability in major depressive disorder treated with cognitive behavioral therapy. J Affect Disord. (2021) 291:322–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.017
41
Sánchez J Muller V Chan F Brooks JM Iwanaga K Tu WM et al . Personal and environmental contextual factors as mediators between functional disability and quality of life in adults with serious mental illness: a cross-sectional analysis. Qual Life Res. (2019) 28:441–50. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-2006-1
42
Hellerstein DJ Erickson G Stewart JW McGrath PJ Hunnicutt-Ferguson K Reynolds SK et al . Behavioral activation therapy for return to work in medication-responsive chronic depression with persistent psychosocial dysfunction. Compr Psychiatry. (2015) 57:140–7. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.10.015
43
Song S Kong X Wang B Sanchez-Ramos J . Administration of Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol following controlled cortical impact restores hippocampal-dependent working memory and locomotor function. Cannabis Cannabin Res. (2022) 7:424–35. doi: 10.1089/can.2021.0053
44
Cuijpers P Karyotaki E de Wit L Ebert DD . The effects of fifteen evidence-supported therapies for adult depression: A meta-analytic review. Psychother Res. (2020) 30:279–93. doi: 10.1080/10503307.2019.1649732
45
Okuno K Yoshimura R Ueda N Ikenouchi-Sugita A Umene-Nakano W Hori H et al . Relationships between stress, social adaptation, personality traits, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol plasma concentrations in employees at a publishing company in Japan. Psychiatry Res. (2011) 186:326–32. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2010.07.023
46
Taschereau-Dumouchel V Hétu S Bagramian A Labrecque A Racine M Chagnon YC et al . BDNF val66Met polymorphism is associated with self-reported empathy. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0149911. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149911
47
Okamoto Y Takanashi R Sutoh C Domon Y Yamada M Baba Y et al . Improvement in social anxiety following a return-to-work intervention for patients with depression. Medicine. (2022) 101:e28845. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028845
48
Valvassori SS Varela RB Arent CO Dal-Pont GC Bobsin TS Budni J et al . Sodium butyrate functions as an antidepressant and improves cognition with enhanced neurotrophic expression in models of maternal deprivation and chronic mild stress. Curr Neurovasc Res. (2014) 11:359–66. doi: 10.2174/1567202611666140829162158
49
Kong L Miu L Yao W Shi Z . Effect of regular aerobic exercise on cognitive function, depression level and regulative role of neurotrophic factor: A prospective cohort study in the young and the middle-aged sample. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. (2024) 17:935–43. doi: 10.2147/rmhp.S456765
50
Sarkheil P Odysseos P Bee I Zvyagintsev M Neuner I Mathiak K . Functional connectivity of supplementary motor area during finger-tapping in major depression. Compr Psychiatry. (2020) 99:152166. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2020.152166
51
Liang S Xue K Wang W Yu W Ma X Luo S et al . Altered brain function and clinical features in patients with first-episode, drug naïve major depressive disorder: A resting-state fMRI study. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. (2020) 303:111134. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2020.111134
52
Franklin G Carson AJ Welch KA . Cognitive behavioural therapy for depression: systematic review of imaging studies. Acta Neuropsychiatri. (2016) 28:61–74. doi: 10.1017/neu.2015.41
53
Marwood L Wise T Perkins AM Cleare AJ . Meta-analyses of the neural mechanisms and predictors of response to psychotherapy in depression and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2018) 95:61–72. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.09.022
54
Lahera G Benito A Montes JM Fernández-Liria A Olbert CM Penn DL . Social cognition and interaction training (SCIT) for outpatients with bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. (2013) 146:132–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2012.06.032
55
Cuijpers P van Straten A Schuurmans J van Oppen P Hollon SD Andersson G . Psychotherapy for chronic major depression and dysthymia: a meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. (2010) 30:51–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2009.09.003
56
Cuijpers P Huibers M Ebert DD Koole SL Andersson G . How much psychotherapy is needed to treat depression? A metaregression analysis. J Affect Disord. (2013) 149:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.02.030
Summary
Keywords
BDNF, GDNF, MDD, psychosocial function, SCIT
Citation
Li J, Li R, Li D, Ji SS, Luo X and Zhang Y (2025) Social cognition and interactive training for first-episode, drug-naïve MDD patients. Front. Psychiatry 16:1566811. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1566811
Received
28 January 2025
Accepted
02 October 2025
Published
15 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Francesco Panza, University of Bari Aldo Moro, Italy
Reviewed by
Ali Saffet Gonul, Ege University, Türkiye
Ömer Faruk Uygur, Atatürk University, Türkiye
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Li, Li, Li, Ji, Luo and Zhang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Zhang, zhangyong@tjmhc.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.