- Department of Neuropsychiatry, Hyogo Medical University, Nishinomiya, Japan
There is a growing need for widely available, cost-effective, and low-intensity treatments for OCD. Although cognitive–behavioral therapy (CBT) is often the first line of treatment, barriers to providing CBT in OCD patients remain unresolved. In this narrative review, we summarize the current literature on the benefits and challenges of using CBT to treat OCD, review the potential of low-intensity, technology-based CBT programs, and identify issues related to the use of these new approaches. We identified articles to include in this narrative review by entering the following search terms into PubMed, PsychInfo, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: obsessive–compulsive disorder, OCD, cognitive–behavioral therapy, CBT, technolog*, digital. The final literature search was conducted on 13 July 2024, and after checking 68 potentially relevant studies according to our inclusion and exclusion criteria, we included 24 studies (14 review articles and 10 original articles) in the present review. We identified several main factors associated with the accessibility and effectiveness of CBT. Incentives for healthcare practitioners who undergo CBT training may increase the availability of this treatment option. Furthermore, treatment efficacy is related to patient treatment adherence, which may be enhanced by offering low-intensity and convenient treatment options such as digital CBT programs. These findings highlight both the potential and the current limitations of low-intensity and digital CBT approaches for OCD treatment. Although low-intensity and technology-based CBT programs can serve as relatively convenient, effective, and accessible treatment options, further research is needed to examine patient perceptions, and determine the most important characteristics of such programs for optimal treatment efficacy.
1 Introduction
1.1 OCD characteristics and prevalence
Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a psychological condition in which individuals experience obsessive thoughts or urges that are unwanted or intrusive, or engage in compulsive or avoidant behaviors. Obsessions and compulsions are often distressing, disruptive to daily life, and difficult to ignore (1). Compared with the general population, individuals with untreated OCD have an increased mortality rate associated with both natural and unnatural causes, necessitating timely and effective disease management in this population (2). Because OCD onset often occurs in adolescence or early adulthood (1), the disorder is causally associated with a loss of productivity (3).
OCD is a relatively common chronic disorder, with a lifetime prevalence of 2% to 3% (4). Because it is often underdiagnosed, OCD is undertreated in the general population (4, 5). Unfortunately, individuals who develop OCD and remain untreated for prolonged periods of time tend to exhibit more severe symptoms, along with poorer prognosis. In addition, avoidance behaviors can make it difficult for affected individuals to leave their homes or interact socially, and this can lead to reluctance to seek treatment. Thus, the factors influencing treatment responsiveness overlap. Given the above-mentioned factors, early consultation and early initiation of treatment after onset are preferable for individuals with OCD. However, the accessibility of pharmacotherapy and cognitive–behavioral therapy (CBT), which are the first choices of treatment for OCD, can be limited (6, 7).
OCD is often comorbid with other psychiatric disorders, such as depression and anxiety, bipolar disorder, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (1, 8, 9). In particular, depression and social anxiety disorder are considered secondary comorbid symptoms following the onset of OCD. The implementation of standard treatment strategies for OCD could help to prevent the development of these comorbid symptoms.
1.2 Current use of CBT for OCD
Treatments for OCD include both psychological and pharmaceutical approaches. Most guidelines, including those of the American Psychiatric Association (10), recommend CBT, with exposure and response prevention and/or pharmacotherapy, as first-line treatments for OCD (11). Several recent reviews and meta-analyses have examined the effects of CBT on OCD symptoms (12, 13). Although there is strong evidence that CBT reduces OCD symptoms (11) and may increase remission rates (14), the quality and methodology of studies on the use of CBT for OCD has varied, necessitating further research with more standardized methods (15).
CBT is considered the most valuable treatment option for OCD because it is cost-effective compared with other treatment options. Most patients also prefer it to pharmacological therapy because of the potential side effects associated with the latter choice (3, 16). In addition, it can be provided online or via mobile applications, making it a convenient treatment option (17–20). Furthermore, while prescriptions for medication for conditions such as OCD can only be dispensed by psychiatrists in many countries, clinical psychologists and other healthcare practitioners who are unable to prescribe medication are often able to administer CBT. Thus, CBT may be an optimal treatment option for many patients compared with pharmaceutical alternatives. However, there are various challenges in implementing CBT, and a range of strategies have been used to improve CBT introduction and provision, including the use of low-intensity, technology-based approaches. There is currently a need for a narrative review of evidence regarding the benefits of and barriers to CBT for OCD and ways of promoting this treatment modality.
1.3 Aims of the review
In this narrative review, we first describe the importance of timely management of OCD, summarizing various treatment options for those with OCD, and new modalities such as CBT. We then summarize the current literature on the benefits and challenges of using CBT to treat OCD. Moreover, we describe the potential of low-intensity, technology-based CBT programs, providing evidence from literature on its benefits as well as identifying issues that need to be addressed in promoting the use of such approaches. Our aim in this narrative review was to provide a broad conceptual summary of the current status, trends, and evidence gaps in the use of CBT for patients with OCD.
2 Methods
The content of this review article is based on a narrative literature review conducted using online databases; PubMed, PsychInfo, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. In conducting this narrative review, we adhered to the SANRA (Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles) criteria to ensure methodological rigor and transparency (21). In our literature review, we focused on meta-analyses and original studies on the use of CBT and specifically technology-based CBT in the treatment of OCD. Key search terms included; obsessive–compulsive disorder, OCD, cognitive–behavioral therapy, CBT, technolog*, digital. Searches were performed using both US and UK spelling, and also with and without the terms “review” and “meta-analysis”. All key search terms were combined, using Boolean logic, such that one term related to OCD, one term related to CBT, and one term related to technology-based CBT, was searched, and subsequently, narratively reviewed. The final literature search was conducted on 13 July 2024.
The search initially retrieved 56 potentially relevant studies. We also assessed the reference lists of these articles to identify other essential studies (12 additional potentially relevant studies). We then checked those 68 studies against the inclusion and exclusion criteria, as follows. We applied basic inclusion parameters and focused on review articles and meta-analyses, but also considered original studies, on the use of different types of CBT for treating OCD for adults, to ensure relevance. We only examined studies conducted within the last 10 years, and studies of children were excluded. Following the search and exclusion/inclusion processes, 24 studies (14 review articles and 10 original articles) were included in the present narrative review. An overview of the study selection procedure is provided in Figure 1.
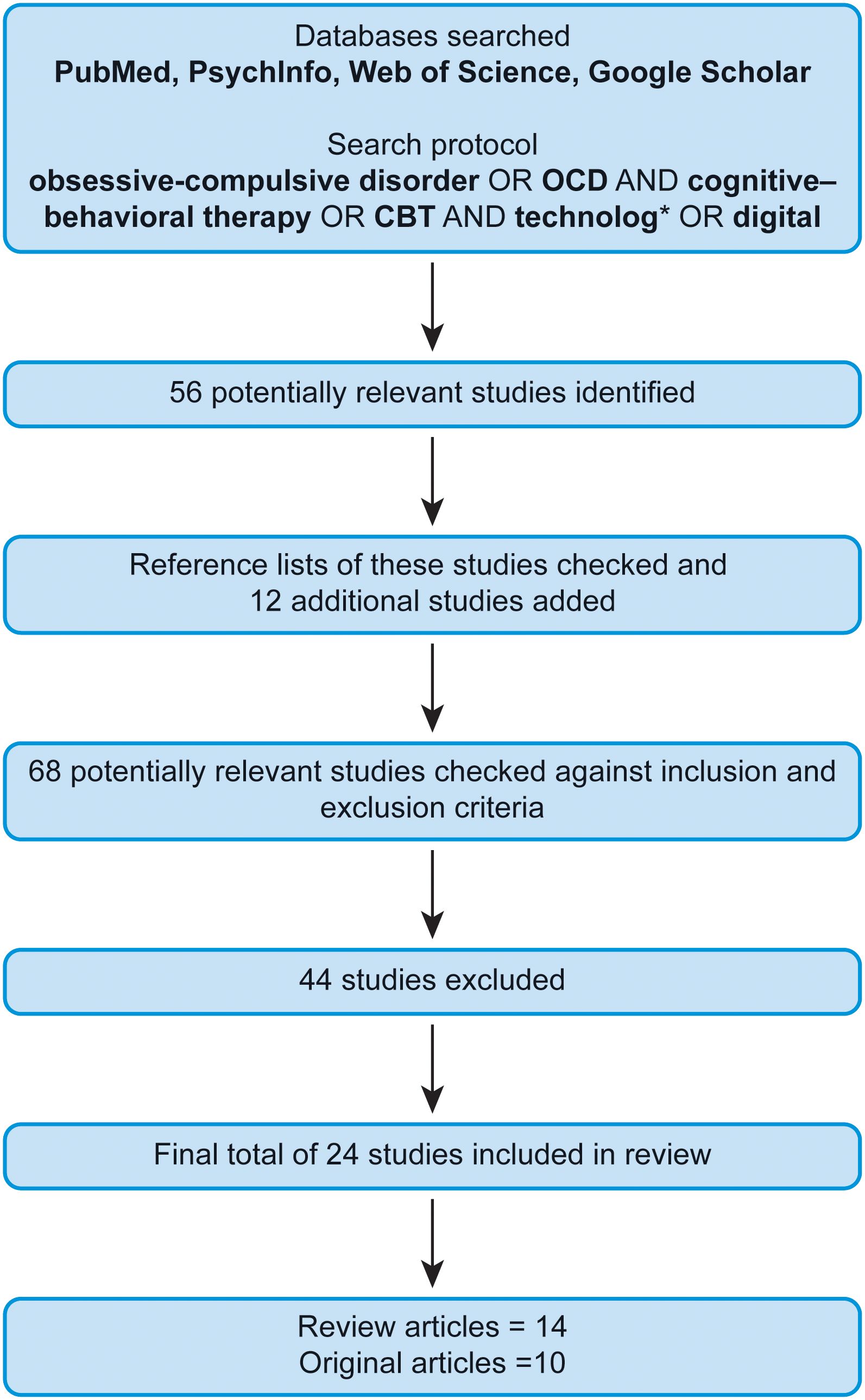
Figure 1. Flowchart of study selection. CBT, cognitive–behavioral therapy; OCD, obsessive–compulsive disorder.
3 Barriers to the use of CBT for treating OCD
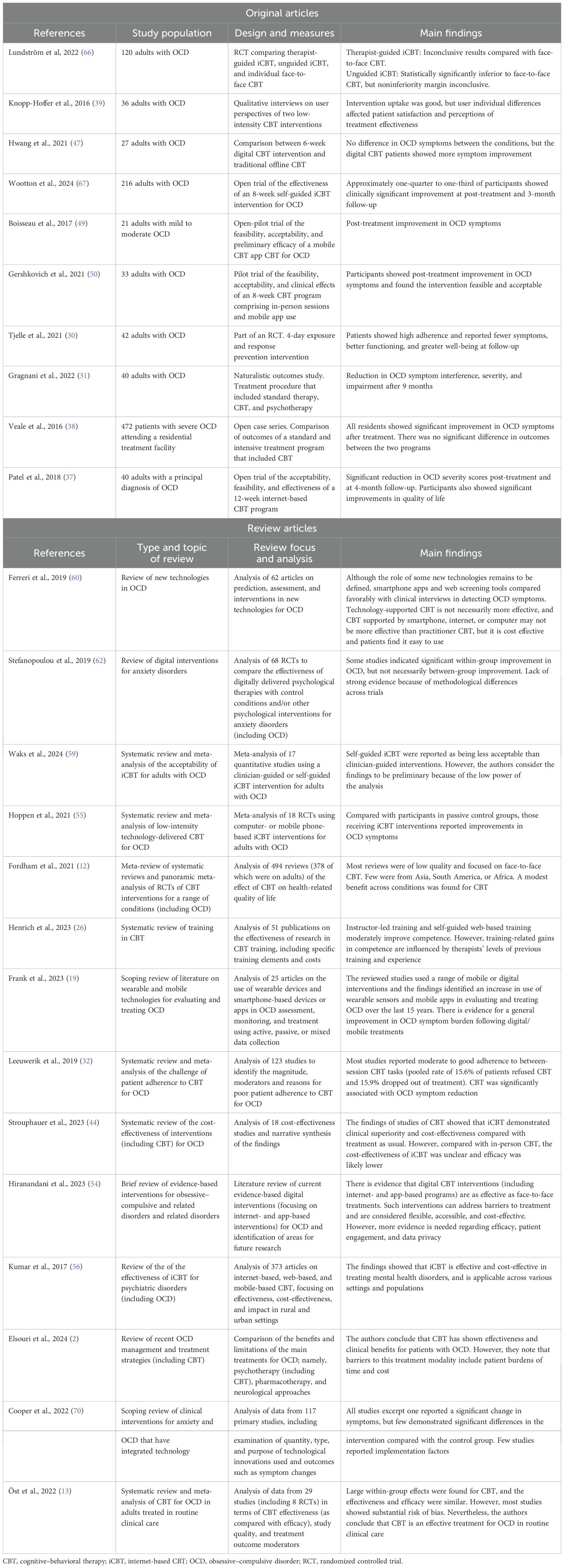
We assessed the included articles with the goal of identifying the main barriers and challenges reported in the use of CBT for treating OCD. We focused on the factors related to treatment participation and effectiveness, along with factors that have limited the widespread use of CBT in this patient population. Table 1 summarizes the main characteristics of the 24 studies included in the review.
In terms of the likelihood that patients will seek treatment for OCD, some studies have highlighted the importance of the role of negative stigmatization associated with obtaining a diagnosis of OCD (22, 23), and described a lack of confidence among patients regarding the efficacy of psychiatric treatment in reducing OCD symptoms (6). The studies identified a number of factors that may affect the provision of CBT for OCD patients. For instance, one discussed the prioritization of pharmacotherapy in healthcare and the lack of availability of trained therapists who could deliver CBT (3). A recent literature review of different treatments for OCD showed that although CBT may be more efficacious in reducing the severity of OCD symptoms, pharmacotherapy may be more cost-effective and associated with greater patient adherence (2).
Various approaches developed to increase the number of trained therapists and subsidize the cost of treatment for patients appear to have increased the number of patients seeking CBT. For example, the implementation of the Improving Access to Psychological Therapies (IAPT) program in the UK has provided training for therapists and subsidized the cost of treatment (24–26). This indicates that there is a high demand for CBT and thus an unmet need for treatment for this patient population.
Some psychiatrists may not be familiar with CBT or with the many different types of CBT that have been developed. Additionally, therapists who complete CBT training programs may need to acquire a substantial amount of practical experience before they can offer sufficient quality and effective CBT (27). Accordingly, although they may be challenging to devise, effective strategies are needed to encourage prospective therapists to undergo competency-based training in the implementation of CBT. There is some evidence to suggest that incentives offered to therapists may increase their implementation of CBT. For example, Beidas et al. (28) found that both social incentives and financial rewards were effective in incentivizing community mental health therapists to use CBT. Although there is a dearth of research on this topic, recent studies suggest that the use of more active training strategies (e.g., role play) and online training could help to increase practitioners’ knowledge, and subsequently increase implementation, of CBT (29, 30). Additionally, governmental policies that prioritize training in CBT methods for medical practitioners may facilitate increased access for patients.
The studies included described the following main factors associated with the effectiveness of CBT. First, patient adherence was associated with the effectiveness of CBT for treating OCD (31, 32). However, more research is needed to determine which aspects of patient adherence are most important for treatment success (33). Second, an important factor that affected patient adherence to conventional face-to-face CBT programs was the patient’s ability and willingness to travel to attend a weekly course that may have as many as 10–15 sessions. Geographical and financial constraints can make travel burdensome for patients, particularly those who also have work and family commitments, or who experience avoidance behaviors (34). Therefore, there is a need to develop a greater range of CBT programs that offer different delivery modes and levels of intensity. Finally, some forms of CBT, such as exposure and response prevention, can be challenging for patients because they require them to face the object of their fear or anxiety (32).
4 Strategies for increasing CBT provision and adherence
Several of the studies identified factors that could increase the provision of, and adherence to, CBT for people with OCD (Figure 2). We focused particularly on the use of low-intensity and technology-based CBT approaches. Table 2 provides examples and summarizes the characteristics and findings of several studies (including quantitative and qualitative studies) that focused particularly on these types of approaches.
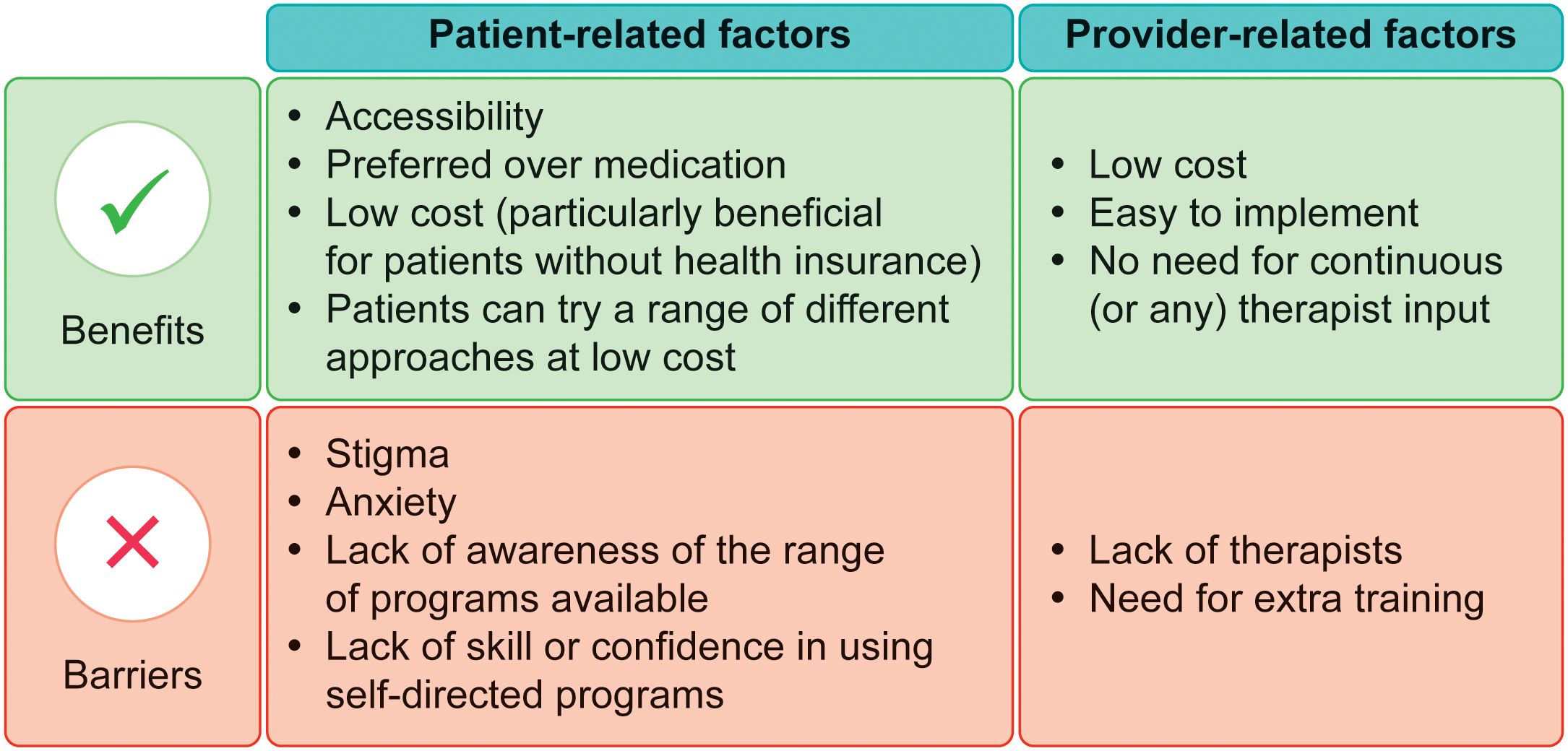
Figure 2. Benefits of, and barriers to, the provision of low-intensity cognitive–behavioral therapy for obsessive–compulsive disorder.
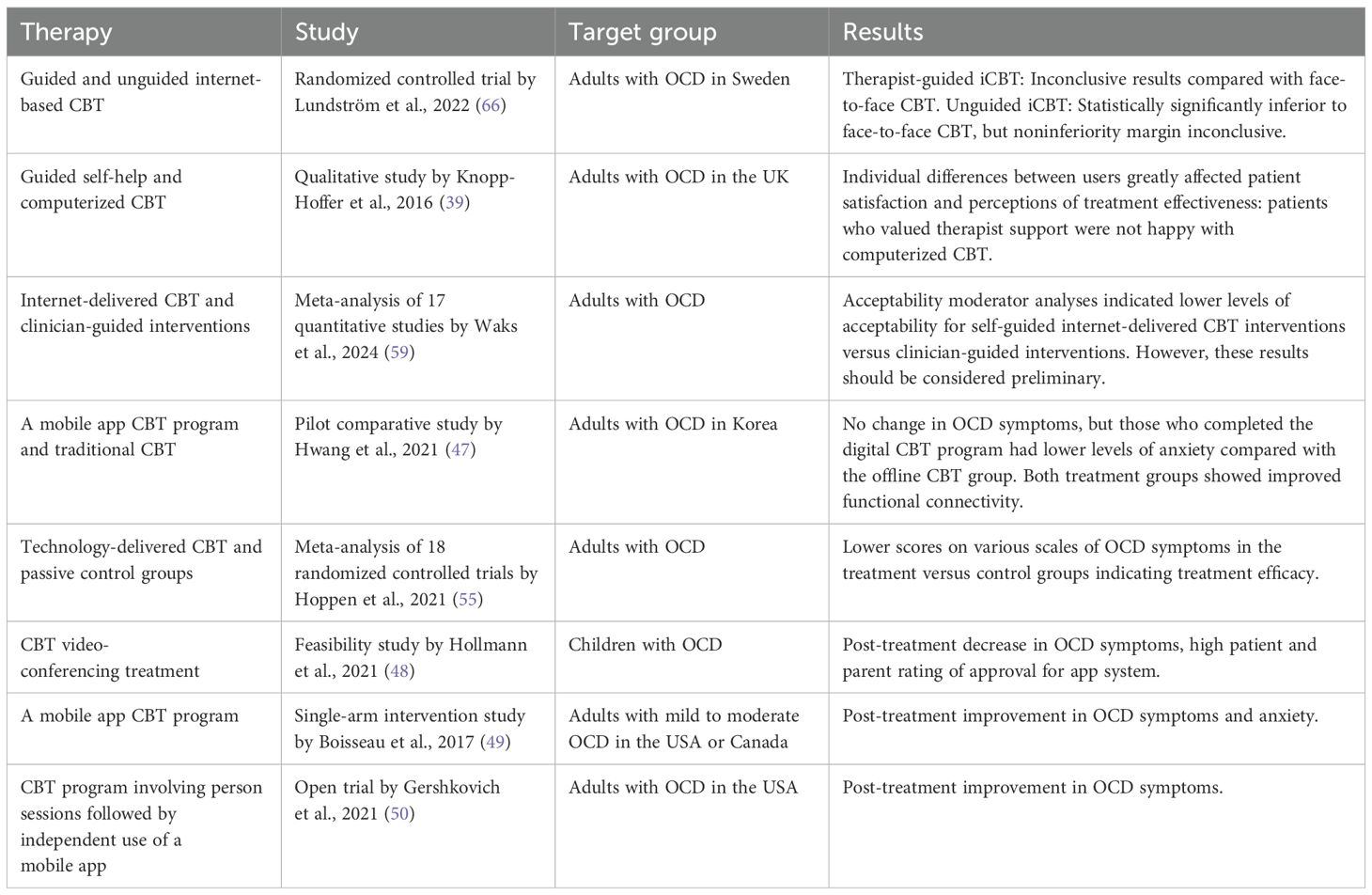
Table 2. Examples of studies on low-intensity, technology-based cognitive–behavioral therapies (CBT) for obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD).
4.1 Low-intensity CBT approaches
New low-intensity CBT approaches have been developed and studied since the late 2000s (35). They offer treatment characterized by low clinical contact or contact with non-specialists, and/or the use of technology-based materials (36). Such programs appear to correspond with the UK NICE Guidelines for OCD, which recommend the use of low-intensity CBT for patients with milder forms of OCD (37). However, these programs do not appear to be widespread, meaning that targeted efforts are needed to increase the availability and attractiveness of low-intensity CBT approaches for people with OCD (38).
The articles examined indicated that the use of low-intensity CBT approaches could help to address cost- and geographic-related constraints experienced by some patients by providing alternatives to conventional CBT formats. Although residential or inpatient high-intensive CBT programs may be more effective for patients with severe OCD symptoms (39), low-intensity CBT is well suited to patients with moderate to mild OCD (40). Because of the lower frequency of treatment, low-intensity approaches can lessen the burden on patients to attend sessions, thus increasing the accessibility and sustainability of CBT for a more diverse range of patients.
Low-intensity CBT programs may also be advantageous compared with alternative treatment options within the context of human resource costs. Conventional face-to-face CBT programs delivered by specialists typically involve 10–15 weekly sessions that are approximately 30–60 minutes in duration (1). Accordingly, the high human resource cost involved in this type of delivery impedes the nationwide implementation of easily accessible standard CBT programs (41). Low-intensity CBT, particularly technology-based programs, can be delivered by qualified healthcare workers or support workers instead of mental health professionals. Furthermore, these programs can be shorter and more accessible than traditional CBT. For instance, one study found that low-intensity CBT programs were typically completed in approximately half the time of conventional programs (36). Indeed, the provision of CBT could be increased if more cost-effective methods were used, such as with the MindSpot program in Australia (42). However, a sound rationale for such methods is needed. While several treatment modalities are available for treating OCD, these must be developed according to the specific context of the medical system, clinical settings, and geographical factors. Some emerging evidence has begun to address this. In Japan, for instance, Matsumoto et al. (2022, 2024) reported favorable clinical and economic outcomes for guided internet-based CBT in OCD (20, 43). While these interventions were not delivered within Japan’s formal insurance-based medical system—given that psychologists are not yet fully reimbursed as providers—they still offer meaningful regional data. Several studies have reported on the cost-effectiveness of CBT interventions, including low-intensity and digital formats (44, 45). However, few studies have directly compared the cost-effectiveness of different CBT delivery methods, such as face-to-face versus internet-based programs (46). Therefore, more research is needed regarding the cost-effectiveness of low-intensity CBT in diverse healthcare settings.
4.2 The potential of technology-based approaches in delivering low-intensity CBT
Internet-based and mobile app CBT programs generally include text, audio, and video components, and often have homework, along with feedback for completed homework assignments (47, 48). A number of these types of CBT programs have been reviewed by researchers (49–52). Additionally, the International OCD Foundation has reviewed several apps for the treatment of OCD (53). The clinical effectiveness of technology-based CBT approaches has also been demonstrated in several randomized controlled trials. For example, Wootton et al. (2013) demonstrated that therapist-guided internet-based CBT (iCBT) led to large reductions in OCD symptoms compared with a waitlist control (44). Building on these findings, Matsumoto et al. (2022) conducted a cost-effectiveness analysis of guided internet-based CBT in Japan, demonstrating both clinical efficacy and economic efficiency (20). Furthermore, a 24-month follow-up study by the same group confirmed the long-term effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of this intervention, underscoring its sustained clinical utility and viability (43). Herbst et al. (2014) found that an internet-based writing intervention was beneficial in reducing the severity of OCD symptoms (54). More recently, Wu et al. (2023) showed that iCBT was non-inferior to group CBT in terms of both symptom improvement and treatment adherence (45). In parallel with these research-based interventions, a growing number of publicly available CBT apps have emerged (55). Most of these apps are free or very low cost, are self-directed, and use exercises and strategies to train users to change maladaptive thoughts and behaviors. Accordingly, the number of programs is growing rapidly, and although some have been reviewed (and are evidence-based), others have yet to be reviewed. CBT programs delivered via mobile apps are generally lower in intensity than iCBT, with minimal reliance on human resources. Mobile app CBT programs also have fewer time restrictions, as treatment sessions do not have to be scheduled. Additionally, features unique to mobile phones, such as reminder functions, may be useful for supporting adherence. These advantages should be considered in future research.
Recent reviews of digital mental health apps and interventions have found that, although digital and mobile treatments vary, they generally lead to a decrease in symptom burden (19). Furthermore, they may address existing gaps in healthcare by offering scalable, low-stigma, and cost-effective solutions (56). Although there is evidence for the effectiveness of these approaches (56–58), user preferences can affect patient satisfaction and engagement (40). Furthermore, the effectiveness of some technology-based applications has not been validated (59). Another challenge with the use of technology-based CBT approaches is ensuring equality of access to technological resources. Some patients may not have easy access to technology, and older patients in particular may find it more difficult to access digital interventions (60). Furthermore, collaboration between developers and healthcare professionals has been insufficient to lead to optimal design choices for technology-based CBT programs (59).
Despite the above-mentioned challenges, there are a number of additional benefits to using technology-based CBT programs. For instance, technology-based CBT programs seem to be well accepted by OCD patients (61) and may be especially attractive to patients who are reluctant to engage in face-to-face therapy (57) or who live a long distance from a therapist. Given the challenges associated with effecting the widespread adoption of in-person CBT programs, digital approaches are likely to offer feasible alternatives. Therefore, there is a need for research regarding the equivalency of interpersonal CBT and digital treatments, as well as approaches for mitigating potential differences. Compared with face-to-face interventions, digital treatment strategies are easier to implement and are well accepted by patients (62) and healthcare personnel (63). Given the advantages of iCBT in terms of cost and accessibility (46, 58), the value of such digital approaches should not be overlooked. Challenges to the assessment of digital approaches to treating OCD and other disorders include determining the influence of a range of factors (such as therapist involvement level and patient characteristics) on the effectiveness of these methods (64). Therefore, better assessment techniques for determining the effectiveness of digital approaches to OCD are needed. These include determining the influence of various factors, such as therapist involvement level and patient characteristics, on treatment outcome (64).
The relatively recent upsurge in low-intensity digital treatments for psychiatric conditions has highlighted the need for common standards and consensus regarding evaluations of the effectiveness of such treatments (65). Several factors (e.g., the influence of the therapist–patient relationship and a lack of clarity regarding the mechanisms underlying the treatment effect) make it difficult to design control conditions for psychological interventions (including digital interventions) such as CBT (65). Despite these factors, the US Food and Drug Administration recommends the use of randomized controlled trials with sham devices to assess the effectiveness of digital treatments (65, 66). However, the definition of a sham device is ambiguous (65, 67), and the design and validation of appropriate sham devices that are not detectable by patients remains a challenge. Accordingly, it is difficult to blind participants in trials of digital CBT devices to their trial condition, thus limiting the unbiased assessment of the treatment effect. To address this, new applications should be tailored to address the unmet medical needs of patients with OCD, and assessed by comparing them with programs that use different therapeutic styles implemented in various medical settings.
OCD is a heterogeneous psychiatric condition (1) with symptoms that vary according to severity and other factors such as comorbidity with other disorders. Therefore, when developing novel CBT approaches, it is important to understand the unique characteristics of specific patient populations. This would facilitate the tailoring of interventions to specific subsets of patients (40), and make it easier to generate clear protocols for the assessment and validation of the clinical utility of different low-intensity CBT programs. The examined studies indicate that substantial challenges remain in implementing digital CBT programs, such as providing incentives to encourage therapists to engage in further training and determining user competence to complete self-guided programs (40).
5 Future directions
Further research is needed to address the gaps in the literature regarding the use of low-intensity, technology-based CBT approaches for treating OCD. For instance, research is needed regarding the potential differences in the costs and efficacy of self-guided and guided digital therapies for OCD (68). There is a gap in the literature with respect to the specific predictors of the outcomes of digital OCD therapies (69). Additionally, research on patient preferences for self-guided vs. guided treatment is lacking (69, 70). Addressing this issue could help researchers design treatment programs that are more attractive to patients. In particular, there is a need for more qualitative studies on various aspects of user perspectives of technology-based CBT approaches (40, 71), including overall user satisfaction.
Individual differences may play an important role in determining the selection and effectiveness of low-intensity digital approaches. Evidence suggests that users vary in terms of the value they place on aspects such as professional support in self-guided programs (40, 72). Accordingly, more research is needed to understand the requirements and expectations regarding therapy in OCD patients, along with the desirability of tailored approaches. Finally, there is a dearth of research regarding the appropriate use of sham devices in randomized controlled trials of technology-based CBT. Accordingly, further investigations are needed to determine the optimal ways to use sham devices in treatments for psychiatric problems, and to determine the effects of sham controls on psychiatric outcomes (67).
Finally, low-intensity CBT is well suited for initial treatments and in mild cases of mental health disorders, providing an accessible form of therapy that can effectively manage symptoms without intensive intervention. However, traditional CBT, which involves more frequent and intensive sessions, may be more appropriate for moderate cases, patients with comorbid psychiatric conditions, or those receiving concurrent pharmacotherapy. This differentiation in therapeutic intensity highlights the importance of developing a range of therapeutic approaches, such as stepped care models, that match treatment modalities to patient groups based on severity and specific needs. To maximize the use of medical resources and provide tailored treatment pathways that enhance patient outcomes, it is essential to implement such frameworks in healthcare systems and develop appropriate guidelines.
6 Conclusions
The studies examined in this narrative review indicate that there is a growing demand for widely accessible, cost-effective, and low-intensity treatments for OCD. However, there are several diverse barriers to the provision of in-person CBT in OCD patients. Low-intensity, technology-based CBT programs hold promise as accessible and affordable treatment options. However, more research is needed, with a focus on the differences between guided and self-guided programs, patient perceptions of treatment options, strategies for controlled trials, and the influence of individual patient differences, to realize the potential of such approaches.
Author contributions
KM: Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Project administration. YK: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SO: Writing – original draft, Investigation. YH: Writing – original draft, Investigation. KH: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. HM: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study received partial funding from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development under Grant Number JP24hma322035 and JP25hma322035. No additional financial support was provided for the conduct of this research or the preparation of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Diane Williams, PhD. and Sydney Koke, BSc., of Edanz, for providing medical writing support in accordance with Good Publication Practice guidelines (https://www.ismpp.org/gpp-2022).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Janardhan Reddy YC, Sundar AS, Narayanaswamy JC, and Math SB. Clinical practice guidelines for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Indian J Psychiatry. (2017) 59:S74–90. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.196976
2. Elsouri KN, Heiser SE, Cabrera D, Alqurneh S, Hawat J, and Demory ML. Management and treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): a literature review. Cureus. (2024) 16:e60496. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60496
3. Laynard R, Clark D, Knapp M, and Mayraz G. Cost-benefit analysis of psychological therapy. Natl Inst Econ Rev. (2007) 202:90–8. doi: 10.1177/0027950107086171
4. Stein DJ, Costa DLC, Lochner C, Miguel EC, Reddy YCJ, Shavitt RG, et al. Obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2019) 5:52. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0102-3
5. Dell’osso B and Altamura AC. Duration of untreated psychosis and duration of untreated illness: new vistas. CNS Spectr. (2010) 15:238–46. doi: 10.1017/s1092852900000079
6. Marques L, LeBlanc NJ, Weingarden HM, Timpano KR, Jenike M, and Wilhelm S. Barriers to treatment and service utilization in an internet sample of individuals with obsessive-compulsive symptoms. Depress Anxiety. (2010) 27:470–5. doi: 10.1002/da.20694
7. Lattie EG, Stiles-Shields C, and Graham AK. An overview of and recommendations for more accessible digital mental health services. Nat Rev Psychol. (2022) 1:87–100. doi: 10.1038/s44159-021-00003-1
8. Carrasco JL, Hollander E, Schneier FR, and Liebowitz MR. Treatment outcome of obsessive compulsive disorder with comorbid social phobia. J Clin Psychiatry. (1992) 53:387–91.
9. Diniz JB, Rosario-Campos MC, Shavitt RG, Curi M, Hounie AG, Brotto SA, et al. Impact of age at onset and duration of illness on the expression of comorbidities in obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. (2004) 65:22–7. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v65n0104
10. Koran LM, Hanna GL, Hollander E, Nestadt G, Simpson HB, and American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. (2007) 164:5–53.
11. Swierkosz-Lenart K, Dos Santos JFA, Elowe J, Clair AH, Bally JF, Riquier F, et al. Therapies for obsessive-compulsive disorder: current state of the art and perspectives for approaching treatment-resistant patients. Front Psychiatry. (2023) 14:1065812. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1065812
12. Fordham B, Sugavanam T, Edwards K, Stallard P, Howard R, das Nair R, et al. The evidence for cognitive behavioural therapy in any condition, population or context: a meta-review of systematic reviews and panoramic meta-analysis. Psychol Med. (2021) 51:21–9. doi: 10.1017/S0033291720005292
13. Öst LG, Enebrink P, Finnes A, Ghaderi A, Havnen A, Kvale G, et al. Cognitive behavior therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder in routine clinical care: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Res Ther. (2022) 159:104170. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2022.104170
14. Nakajima A, Matsuura N, Mukai K, Yamanishi K, Yamada H, Maebayashi K, et al. Ten-year follow-up study of Japanese patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2018) 72:502–12. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12661
15. Reid JE, Laws KR, Drummond L, Vismara M, Grancini B, Mpavaenda D, et al. Cognitive behavioural therapy with exposure and response prevention in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Compr Psychiatry. (2021) 106:152223. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2021.152223
16. McHugh RK, Whitton SW, Peckham AD, Welge JA, and Otto MW. Patient preference for psychological vs pharmacologic treatment of psychiatric disorders: a meta-analytic review. J Clin Psychiatry. (2013) 74:595–602. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12r07757
17. Crino RD. Psychological treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder: an update. Australas Psychiatry. (2015) 23:347–9. doi: 10.1177/1039856215590030
18. Himle JA, Fischer DJ, Muroff JR, Van Etten ML, Lokers LM, Abelson JL, et al. Videoconferencing-based cognitive-behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Behav Res Ther. (2006) 44:1821–9. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2005.12.010
19. Frank AC, Li R, Peterson BS, and Narayanan SS. Wearable and mobile technologies for the evaluation and treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder: scoping review. JMIR Ment Health. (2023) 10:e45572. doi: 10.2196/45572
20. Matsumoto K, Hamatani S, Makino T, Takahashi J, Suzuki F, Ida T, et al. Guided internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: a multicenter randomized controlled trial in Japan. Internet Interv. (2022) 28:100515. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2022.100515
21. Baethge C, Goldbeck-Wood S, and Mertens S. SANRA—a scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res Integrity Peer Review. (2019) 4:5. doi: 10.1186/s41073-019-0064-8
22. Ociskova M, Prasko J, Cerna M, Jelenova D, Kamaradova D, Latalova K, et al. Obsessive compulsive disorder and stigmatization. Act Nerv Super Rediviva. (2013) 55:19–26.
23. Stengler-Wenzke K, Trosbach J, Dietrich S, and Angermeyer MC. Experience of stigmatization by relatives of patients with obsessive compulsive disorder. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. (2004) 18:88–96. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2004.03.004
24. NHS Digital. Psychological therapies: reports on the use of IAPT services, England August 2020 Final including reports on the IAPT pilots (2021). Available online at: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/psychological-therapies-report-on-the-use-of-iapt-services/august-2020-final-including-reports-on-the-iapt-pilots (Accessed July 13, 2024).
25. OCD UK. Improving access to psychological therapies – IAPT (2022). Available online at: https://www.ocduk.org/overcoming-ocd/accessing-ocd-treatment/accessing-ocd-treatment-through-the-nhs/iapt/:~:text=The%20Improving%20Access%20to%20Psychological%20Therapies%20or%20IAPT%20for%20short (Accessed July 13, 2024).
26. Wakefield S, Kellett S, Simmonds-Buckley M, Stockton D, Bradbury A, and Delgadillo J. Improving Access to Psychological Therapies (IAPT) in the United Kingdom: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 10-years of practice-based evidence. Br J Clin Psychol. (2021) 60:1–37. doi: 10.1111/bjc.12259
27. Henrich D, Glombiewski JA, and Scholten S. Systematic review of training in cognitive-behavioral therapy: summarizing effects, costs and techniques. Clin Psychol Rev. (2023) 101:102266. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2023.102266
28. Beidas RS, Becker-Haimes EM, Adams DR, Skriner L, Stewart RE, Wolk CB, et al. Feasibility and acceptability of two incentive-based implementation strategies for mental health therapists implementing cognitive-behavioral therapy: a pilot study to inform a randomized controlled trial. Implement Sci. (2017) 12:148. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0684-7
29. Frank HE, Becker-Haimes EM, and Kendall PC. Therapist training in evidence-based interventions for mental health: a systematic review of training approaches and outcomes. Clin Psychol (New York). (2020) 27:e12330. doi: 10.1111/cpsp.12330
30. Marriott BR, Kliethermes MD, McMillen JC, Proctor EK, and Hawley KM. Implementation of a low-cost, multi-component, web-based training for trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy. Adm Policy Ment Health. (2023) 50:392–9. doi: 10.1007/s10488-022-01246-7
31. Tjelle K, Opstad HB, Solem S, Launes G, Hansen B, Kvale G, et al. Treatment adherence as predictor of outcome in concentrated exposure treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:667167. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.667167
32. Gragnani A, Zaccari V, Femia G, Pellegrini V, Tenore K, Fadda S, et al. Cognitive-behavioral treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder: the results of a naturalistic outcomes study. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:2762. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102762
33. Leeuwerik T, Cavanagh K, and Strauss C. Patient adherence to cognitive behavioural therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Anxiety Disord. (2019) 68:102135. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2019.102135
34. Mancebo MC, Eisen JL, Sibrava NJ, Dyck IR, and Rasmussen SA. Patient utilization of cognitive-behavioral therapy for OCD. Behav Ther. (2011) 42:399–412. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2010.10.002
35. Andersson E, Enander J, Andrén P, Hedman E, Ljótsson B, Hursti T, et al. Internet-based cognitive behaviour therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Psychol Med. (2012) 42:2193–203. doi: 10.1017/S0033291712000244
36. Shafran R, Myles-Hooton P, Bennett S, and Öst LG. The concept and definition of low intensity cognitive behaviour therapy. Behav Res Ther. (2021) 138:103803. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2021.103803
37. National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (UK). Obsessive-compulsive disorder: core interventions in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder and body dysmorphic disorder. Leicester (UK: British Psychological Society (UK (2006).
38. Patel SR, Wheaton MG, Andersson E, Rück C, Schmidt AB, La Lima CN, et al. Acceptability, feasibility, and effectiveness of internet-based cognitive-behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder in New York. Behav Ther. (2018) 49:631–41. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2017.09.003
39. Veale D, Naismith I, Miles S, Childs G, Ball J, Muccio F, et al. Outcome of intensive cognitive behaviour therapy in a residential setting for people with severe obsessive compulsive disorder: a large open case series. Behav Cognit Psychother. (2016) 44:331–46. doi: 10.1017/S1352465815000259
40. Knopp-Hoffer J, Knowles S, Bower P, Lovell K, and Bee PE. ‘One man’s medicine is another man’s poison’: a qualitative study of user perspectives on low intensity interventions for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). BMC Health Serv Res. (2016) 16:188. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1433-3
41. Antle BF, Owen JJ, Eells TD, Wells MJ, Harris LM, Cappiccie A, et al. Dissemination of computer-assisted cognitive-behavior therapy for depression in primary care. Contemp Clin Trials. (2019) 78:46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2018.11.001
42. Lee YC, Gao L, Dear BF, Titov N, and Mihalopoulos C. The cost-effectiveness of the online MindSpot clinic for the treatment of depression and anxiety in Australia. J Ment Health Policy Econ. (2017) 20:155–66.
43. Matsumoto K, Hamatani S, and Shimizu E. Long-term effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of guided internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: 24-month follow-up. Internet Interv. (2024) 35:100725. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2024.100725
44. Wootton BM, Dear BF, Johnston L, Terides MD, and Titov N. Remote treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized controlled trial (2013). J Obsessive Compuls Relat Disord. (2013) 2:375–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jocrd.2013.07.002
45. Wu MS, Li X, Zhou Y, Gao R, Wang K, Ye H, et al. Efficacy and cost-effectiveness analysis of Internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e41283. doi: 10.2196/41283
46. Strouphauer ER, Morris OJ, Soileau KJ, Wiese AD, Quast T, Goodman WK, et al. Economic analyses of obsessive-compulsive disorder interventions: a systematic review. Pharmacoeconomics. (2023) 41:499–527. doi: 10.1007/s40273-023-01250-1
47. Andersson G, Carlbring P, Ljótsson B, and Hedman E. Guided internet-based CBT for common mental disorders. J Contemp Psychother. (2012) 43:223–33. doi: 10.1007/s10879-013-9237-9
48. Edge D, Watkins ER, Limond J, and Mugadza J. The efficacy of self-guided internet and mobile-based interventions for preventing anxiety and depression – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Res Ther. (2023) 164:104292. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2023.104292
49. Hwang H, Bae S, Hong JS, and Han DH. Comparing effectiveness between a mobile app program and traditional cognitive behavior therapy in obsessive-compulsive disorder: evaluation study. JMIR Ment Health. (2021) 8:e23778. doi: 10.2196/23778
50. Hollmann K, Allgaier K, Hohnecker CS, Lautenbacher H, Bizu V, Nickola M, et al. Internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy in children and adolescents with obsessive compulsive disorder: a feasibility study. J Neural Transm (Vienna). (2021) 128:1445–59. doi: 10.1007/s00702-021-02409-w
51. Boisseau CL, Schwartzman CM, Lawton J, and Mancebo MC. App-guided exposure and response prevention for obsessive compulsive disorder: an open pilot trial. Cognit Behav Ther. (2017) 46:447–58. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2017.1321683
52. Gershkovich M, Middleton R, Hezel DM, Grimaldi S, Renna M, Basaraba C, et al. Integrating exposure and response prevention with a mobile app to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder: feasibility, acceptability, and preliminary effects. Behav Ther. (2021) 52:394–405. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2020.05.001
53. International OCD Foundation. OCD apps . Available online at: https://iocdf.org/ocd-apps/ (Accessed July 13, 2024).
54. Herbst N, Voderholzer U, Thiel N, Schaub R, Knaevelsrud C, Stracke S, et al. No talking, just writing! Efficacy of an internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy with exposure and response prevention in obsessive compulsive disorder. Psychother Psychosom. (2014) 83:165–75. doi: 10.1159/000357570
55. Firth J, Torous J, Nicholas J, Carney R, Rosenbaum S, and Sarris J. Can smartphone mental health interventions reduce symptoms of anxiety? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Affect Disord. (2017) 218:15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.04.046
56. Hiranandani S, Ipek SI, Wilhelm S, and Greenberg JL. Digital mental health interventions for obsessive compulsive and related disorders: a brief review of evidence-based interventions and future directions. J Obsessive Compuls Relat Disord. (2023) 36:100765. doi: 10.1016/j.jocrd.2022.100765
57. Hoppen LM, Kuck N, Bürkner PC, Karin E, Wootton BM, and Buhlmann U. Low intensity technology-delivered cognitive behavioral therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. (2021) 21:322. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03272-5
58. Kumar V, Sattar Y, Bseiso A, Khan S, and Rutkofsky IH. The effectiveness of internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy in treatment of psychiatric disorders. Cureus. (2017) 9:e1626. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1626
59. Van Ameringen M, Turna J, Khalesi Z, Pullia K, and Patterson B. There is an app for that! The current state of mobile applications (apps) for DSM-5 obsessive-compulsive disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, anxiety and mood disorders. Depress Anxiety. (2017) 34:526–39. doi: 10.1002/da.22657
60. Leukel J, Schehl B, and Sugumaran V. Digital inequality among older adults: explaining differences in the breadth of Internet use. Inf Commun Soc. (2021) 26:139–54. doi: 10.1080/1369118X.2021.1942951
61. Waks S, Moses K, and Wootton BM. Acceptability of internet-delivered cognitive behavioural therapy for adults with symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analysis. Br J Clin Psychol. (2024) 63:315–29. doi: 10.1111/bjc.12462
62. Ferreri F, Bourla A, Peretti CS, Segawa T, Jaafari N, and Mouchabac S. How new technologies can improve prediction, assessment, and intervention in obsessive-compulsive disorder (e-OCD): review. JMIR Ment Health. (2019) 6:e11643. doi: 10.2196/11643
63. Silfee V, Williams K, Leber B, Kogan J, Nikolajski C, Szigethy E, et al. Health care provider perspectives on the use of a digital behavioral health app to support patients: qualitative study. JMIR Form Res. (2021) 5:e28538. doi: 10.2196/28538
64. Stefanopoulou E, Lewis D, Taylor M, Broscombe J, Larkin J, and Psychiatr Q. (2019) 90:197–215. doi: 10.1007/s11126-018-9620-5
65. Lutz J, Offidani E, Taraboanta L, Lakhan SE, and Campellone TR. Appropriate controls for digital therapeutic clinical trials: a narrative review of control conditions in clinical trials of digital therapeutics (DTx) deploying psychosocial, cognitive, or behavioral content. Front Digit Health. (2022) 4:823977. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2022.823977
66. US Food and Drug Administration. Design considerations for pivotal clinical investigations for medical devices guidance for industry, clinical investigators, institutional review boards and food and drug administration staff (2013). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/media/87363/download (Accessed July 13, 2024).
67. Bos E, Preller KH, Kaur G, Malhotra P, Kharawala S, and Motti D. Challenges with the use of digital sham: systematic review and recommendations. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e44764. doi: 10.2196/44764
68. Lundström L, Flygare O, Andersson E, Enander J, Bottai M, Ivanov VZ, et al. Effect of internet-based vs face-to-face cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5:e221967. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.1967
69. Wootton BM, McDonald S, Melkonian M, Karin E, Titov N, and Dear BF. Efficacy and acceptability of a self-guided internet-delivered cognitive-behavioral educational program for obsessive-compulsive symptoms with international recruitment. Cognit Behav Ther. (2024) 53:133–51. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2023.2279492
70. Sapkota RP, Lozinski T, Wilhems A, Nugent M, Schaub MP, Keough MT, et al. Internet-delivered therapy for alcohol misuse: engagement, satisfaction, and outcomes when patients select their preference for therapist- or self-guided treatment. Addict Sci Clin Pract. (2024) 19:30. doi: 10.1186/s13722-024-00456-8
71. Du E, Quayle E, and Macleod H. A qualitative study of patients’ experiences and acceptance of computerised cognitive behavioural therapy in primary care, Scotland. Cognit Behav Ther. (2021) 14:e24. doi: 10.1017/S1754470X21000210
Keywords: cognitive-behavioral therapy, obsessive-compulsive disorder, narrative review, mental health apps, digital healthcare technology, internet interventions
Citation: Mukai K, Kyosuke Y, Ogino S, Hosoi Y, Hayashida K and Matsunaga H (2025) Benefits and barriers associated with using cognitive–behavioral therapy to treat obsessive–compulsive disorder: a narrative review. Front. Psychiatry 16:1593384. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1593384
Received: 14 March 2025; Accepted: 08 July 2025;
Published: 28 July 2025.
Edited by:
Andras Norbert Zsido, University of Pécs, HungaryReviewed by:
Kazuki Matsumoto, Kagoshima University, JapanNoor Ahmed Giasuddin, Dhaka Medical College and Hospital, Bangladesh
Copyright © 2025 Mukai, Kyosuke, Ogino, Hosoi, Hayashida and Matsunaga. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Keiichiro Mukai, ay1tdWthaUBoeW8tbWVkLmFjLmpw
 Keiichiro Mukai
Keiichiro Mukai Yamanishi Kyosuke
Yamanishi Kyosuke Hisato Matsunaga
Hisato Matsunaga