- 1School of Nursing, Xinxiang Medical College, Xinxiang, China
- 2Nursing Department, Xinxiang First People’s Hospital, Xinxiang, China
Background: To investigate the prevalence and associated factors of depressive symptoms in middle-aged and elderly stroke patients in China, and to provide reference for improving the mental health of middle-aged and elderly stroke patients in China.
Methods: The data for this study were drawn from the 2020 wave of the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS), and middle-aged and elderly stroke patients aged ≥45 years were considered as study subjects (n=988). A simplified version of the Epidemiological Survey Depression Scale score was used to determine depressive symptoms (≥10 points defined as depression) in the study population, and associated factors were analyzed using binary logistic regression.
Results: Among the 988 middle-aged and elderly stroke patients, 547 (55.4%) had depressive symptoms and 441 (44.6%) did not. The results of binary logistic regression analysis showed that education level, history of alcohol consumption, sleep quality, loneliness, self-rated health status, self-rated memory status, life satisfaction, and ADL were the associated factors of depressive symptom in middle-aged and elderly stroke patients (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The study has shown that depressive symptoms in Chinese middle-aged and elderly stroke patients are associated with a variety of factors, and healthcare professionals should regularly assess with early recognition and take interventions to improve the disease.
Introduction
As the second leading cause of death globally, the post-stroke burden is significant, with studies predicting a 50% increase in stroke mortality—from 66 million in 2020 to 97 million in 2050—and over the same period the disability-adjusted life year (DALY) will increase from 144.8 million in 2020 to 189.3 million in 2050 (1). At the same time, the incidence of stroke is increasing with age, and the number of deaths and disabilities globally is likely to increase significantly in the future. Stroke not only causes complications such as hemiparesis, hemiplegia, aphasia, and ataxia but also leads to emotional and psychiatric disorders in patients with prolonged illness, with post-stroke depression being the most common.
Post-stroke depression (PSD) is one of the most common and serious sequelae of stroke, afflicting approximately one-third of stroke survivors (2), and is the most prevalent neuropsychological disorder among stroke patients, characterized by persistent depressed mood and diminished interest (3). PSD negatively affects the recovery or restoration of motor and cognitive deficits after stroke, and significantly increases the chances of recurrence of neurovascular events (4). Meanwhile, post-stroke depression prevents patients from actively participating in exercise, decreases adherence to rehabilitation exercises, increases stroke recurrence and mortality rates, affects patients’ ability to perform daily living activities, and leads to poor quality of life (5). This brings a heavy burden to today’s society and patients’ families and also has a significant impact on the course, recovery, and prognosis of stroke. The level of mental health of stroke patients seriously affects their functional recovery and cognitive function. Studies have shown that early medication or psychological intervention is beneficial to patients in controlling the progression of the disease (6–8).
Therefore, based on data from the 2020 China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS), this study systematically explored the prevalence of depressive symptoms and their associated factors in middle-aged and elderly Chinese stroke patients. The study’s results will provide a scientific basis for clinical health professionals to identify high-prevalence populations early and implement precise psychological interventions. These findings will also provide valuable insights for guiding the formulation of evidence-based and targeted mental health prevention strategies. The in-depth analysis of the mental health status of this group and its associated factors will help improve the prognosis of middle-aged and elderly stroke patients and provide practical guidance for improving their overall quality of life.
Methods
Study population and design
The data used in this study were sourced from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) 2020, a nationally representative longitudinal survey that collects high-quality microdata on middle-aged and elderly households and individuals aged 45 years and older in China, to address the challenges associated with China’s aging population. CHARLS initiated its nationally representative baseline survey in 2011, covering 150 county-level units and 450 village-level units across the country. Subsequently, follow-up surveys have been conducted every 2–3 years, with four national follow-ups completed in 2013, 2015, 2018, and 2020, respectively. CHARLS surveyed approximately 10,000 households in China using a probability sampling method, and in 2020 completed 19,395 individual questionnaires. Inclusion criteria for participants in this study included: (1) respondents with reported stroke; (2) age 45 years and older; (3) respondents who provided clear answers to the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CESD-10); and (4) no omissions on key variables. Exclusion criteria included (1) lack of information about stroke disease, (2) lack of information about depression, and (3) respondents who refused to participate in the survey or were unable to complete the survey. Based on the above criteria, we finally included and analyzed 988 subjects. CHARLS was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of Peking University (IRB00001052-11015) and informed consent forms were signed by all participants who agreed to take part (9).
Stroke
In the CHARLS 2020 survey, respondents reported stroke events by answering the following questions. (1) Since your last visit, has your stroke condition shown improvement, remained unchanged, or deteriorated? (2) Has a doctor ever told you that you had a stroke? Respondents who answered “yes” to question (1) and question (2) were included in the study.
Depressive symptom
Participants were assessed using the widely used 10-item Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CESD-10). This scale assesses both depressed and positive mood and consists of 10 items. Participants were asked about their depressed mood and behaviors one week prior, such as whether they felt depressed, lonely, or fearful. Each question on the CESD-10 was assessed on a 4-point scale from 0 to 3 [0 = <1 day (never or rarely), 1 = 1–2 days (some days), 2 = 3–4 days (occasionally), and 3 = 5–7 days (always)]. Before calculating the 10-item total score, items 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, and 10 were positively scored, and items 5 and 8 were negatively scored. Scores on the scale range from 0 to 30, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms (10). Depressive symptoms were defined as a binary dependent variable (1 = yes, 0 = no) with a total score of ≥10 indicating the presence of depressive symptoms (11). The CESD-10 scale has been reported to have adequate reliability and validity among Chinese community-dwelling older adults (12).
Covariates
Sociodemographic information
Sociodemographic factors included age, gender, education level, marital status, type of residence, smoking history, and drinking history. Age was categorized as 45–59 years, 60–74 years, and ≥75 years. Gender was classified dichotomously as male or female. Educational attainment was categorized into four groups: ‘below primary school,’ ‘primary school,’ ‘junior middle school,’ and ‘high school or above.’ Participants were considered to have a spouse if they were currently married and living with their spouse or if they were married and not living with their spouse temporarily for reasons such as work, or they were considered to have no spouse if they were currently separated, divorced from their spouse, widowed, or never married. The type of residence was categorized as city or rural. History of smoking and alcohol consumption was categorized dichotomously as either yes or no.
Health status and functioning
Health status and functional ability were assessed across several domains, such as hearing, vision, self-rated health, self-rated memory, types of chronic diseases, activities of daily living (ADL), instrumental activities of daily living (IADL), nighttime sleep duration, and sleep quality. Hearing and vision conditions were categorized as “problematic” and “not problematic”. In this study, “problematic” is defined as “yes” and “not problematic” as “no”. Self-rated health status and memory were classified into five categories based on participants’ self-reported responses in the questionnaire: excellent, very good, good, fair, and poor. Chronic diseases were diagnosed as one of the 14 common chronic diseases such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, cancer, liver disease, kidney disease, heart attack, and emotional problems, which were categorized as the presence of one, the presence of two, or the presence of three or more. Respondents’ self-reported activities of daily living (ADL) in the questionnaire comprised six items: dressing, bathing, eating, transferring in and out of bed, toileting, and controlling urination and defecation. Similarly, instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) included six items: performing household chores, preparing meals, shopping, using the telephone, managing medications, and handling household finances. For analytical purposes, responses indicating ‘no difficulty’ for each item were assigned a score of 1 point, while responses such as ‘difficult but still can be completed,’ ‘difficult,’ ‘need help,’ or ‘unable to complete’ were scored as 0 points. The scores for the six items were summed to generate a total score ranging from 0 to 6, with higher scores indicating better functional ability. The higher the score, the better the activity ability. Sleep quality was assessed using participants’ responses to the statement ‘I don’t sleep well,’ with respondents subsequently stratified into four groups based on the frequency of their reported sleep difficulties during the week. Participants were asked to report their average nightly sleep duration over the past month by responding to the question, ‘In the past month, how many hours of actual sleep did you get each night on average?’ Based on their responses, nighttime sleep duration was classified into three categories: less than 6 hours, 6 to 8 hours, and >8 hours.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors include health insurance, pension insurance, employment status, life satisfaction, and social participation. Health insurance, pension insurance, and work status are categorized as “yes” or “no”. Life satisfaction was classified into five levels according to participants’ self-reported responses: extremely satisfied, very satisfied, quite satisfied, not very satisfied, and very dissatisfied. The assessment of social participation was based on participants’ responses to the item, ‘Have you engaged in any of the following social activities in the past month?’ Respondents were stratified into four groups according to their reported level of engagement: no, one type, two types, or three or more types of activities.
Statistical analysis
Stata/SE 16.0 was used to clean the CHARLS 2020 data. IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0 was used for statistical analysis. For measures that conformed to normal distribution, they were described using mean ± standard deviation, and those that did not conform to normal distribution were described using median and interquartile spacing. Count data were described by frequency and percentage. One-way analysis was performed using a t-test, χ2 test and rank sum test. Variables that were statistically significant in the one-way analysis were included in the binary Logistic regression analysis. The test level was α = 0.05, and P < 0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
Results
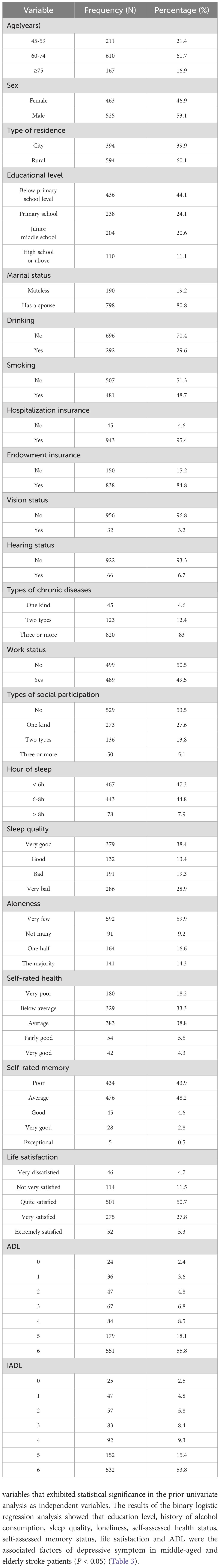
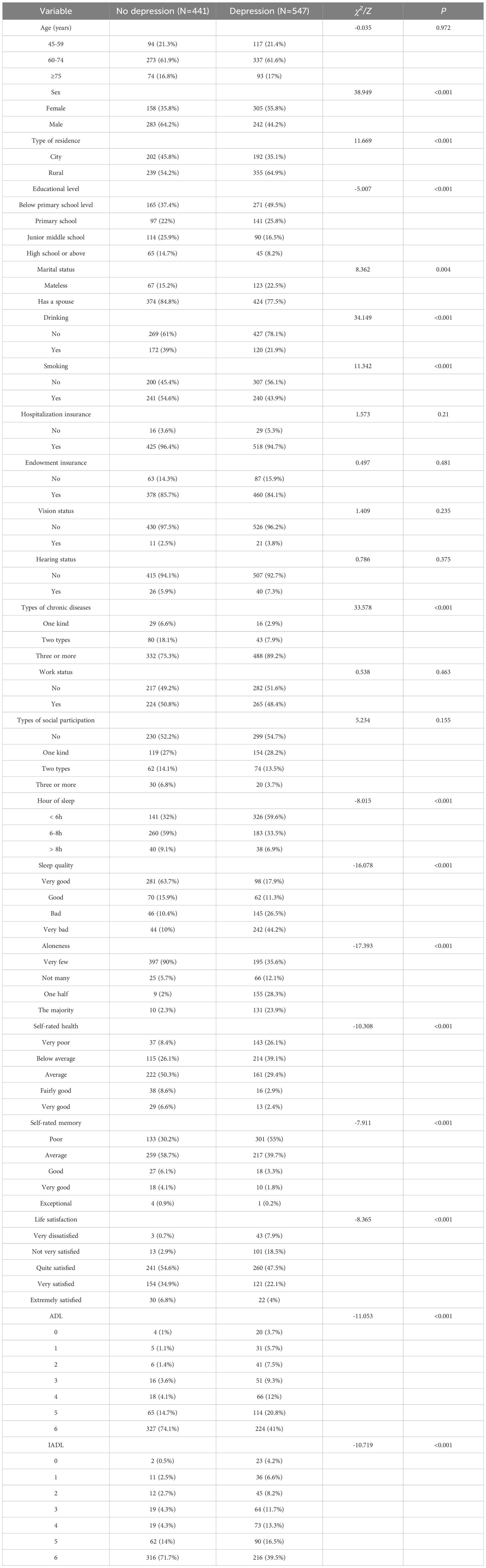
Among 988 middle-aged and elderly stroke patients, 547 (55.4%) exhibited depressive symptoms, while 441 (44.6%) showed no signs of depression. Of the patients with depressive symptoms, 242 (44.2%) were male and 305 (55.8%) were female. In terms of age distribution, 117 (21.4%) were aged 45–59 years, 337 (61.6%) were aged 60–74 years, and 93 (17%) were 75 years or older. Other general data information is shown in Table 1.
Univariate analysis of the occurrence of depressive symptoms in middle-aged and elderly stroke patients
There was statistical significance between stroke patients with and without depressive symptoms in terms of gender, type of residence, education level, marital status, history of alcohol consumption, history of smoking, type of chronic disease, sleep duration, sleep quality, loneliness, self-assessed health status, self-assessed memory status, life satisfaction, ADL and IADL (P < 0.05) (Table 2).
Binary logistic regression analysis of the occurrence of depressive symptoms in middle-aged and elderly stroke patients
A binary logistic regression model was constructed, using depression status (present or absent) among middle-aged and elderly stroke patients as the dependent variable and incorporating variables that exhibited statistical significance in the prior univariate analysis as independent variables. The results of the binary logistic regression analysis showed that education level, history of alcohol consumption, sleep quality, loneliness, self-assessed health status, self-assessed memory status, life satisfaction and ADL were the associated factors of depressive symptom in middle-aged and elderly stroke patients (P < 0.05) (Table 3).
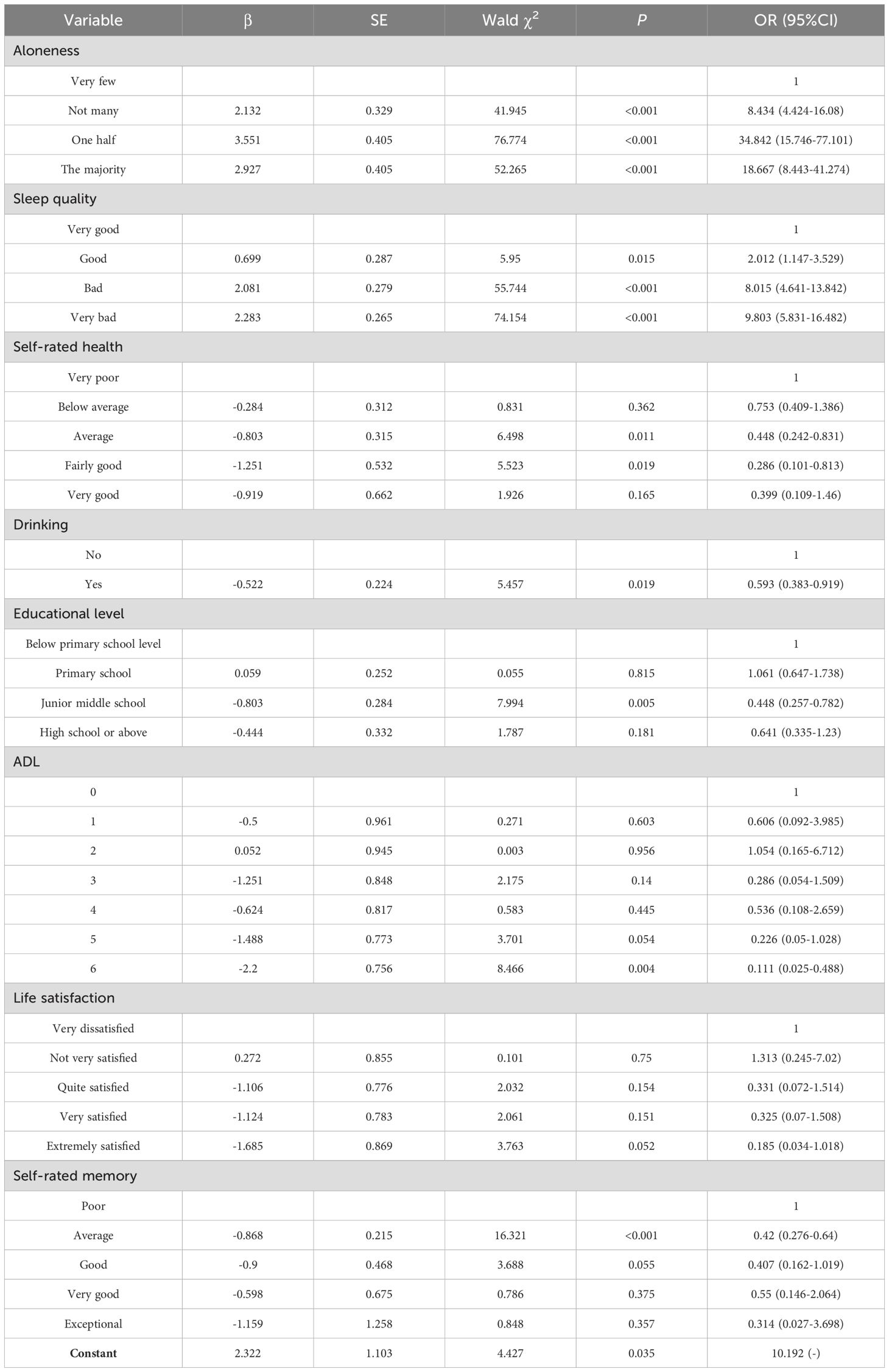
Table 3. Binary logistic regression analysis of depressive symptoms in middle-aged and elderly stroke patients.
Discussion
In this study, the prevalence of depression in stroke patients was 55.4%, which is higher than the prevalence of post-stroke depression in global statistics. Some studies have statistically found that the prevalence of depression in stroke patients ranges from 11% to 41% over 2 years (2). The reasons for the different prevalence rates may include diagnostic criteria, sample size, and ethnic differences (13). The main population in this study was middle-aged and elderly Chinese stroke patients, and the data were obtained from a long-term longitudinal cohort study in China. The differences in prevalence may be related to the different diagnostic criteria for depression in stroke patients. Follow-up studies can adopt standardized diagnostic criteria to ensure consistency and accuracy of diagnosis; and conduct a multidimensional comprehensive analysis by combining relevant examinations, thus improving the reliability and scientificity of the study results. Stroke severity affects post-stroke depression (14). Patients with severe strokes tend to have higher depression scores. However, the CHARLS database lacks indicators to distinguish between stroke severity and type (e.g., hemorrhagic versus ischemic), which may lead to overestimation of prevalence.Finally, the CHARLS database has a limited number of variables. There may be omissions in variable selection. For example, lack of social support and untreated factors may have contributed to higher prevalence (15, 16). We can address this issue by including more variables in future studies.
Our study found a correlation between sleep quality and post-stroke depression, with stroke patients with poor sleep quality more likely to develop depressive symptoms. A meta-analysis showed a prevalence of insomnia in 38.2% of patients after stroke and an association between sleep and post-stroke depression (17). Sleep disorders were also found to be associated with increased odds of post-stroke depression in a national survey based on a US population (18). Sleep status not only contributes to the diagnosis of post-stroke depression but is also an easily observed clinical manifestation (19). As a risk factor for depression, sleep disorders may occur before or after stroke, affecting patients’ functional recovery after stroke and increasing the risk of post-stroke depression through neurobiological mechanisms (20, 21). In addition to this, impaired cerebral hemodynamics and sympathetic hyperactivity due to sleep disorders (e.g., obstructive sleep apnea) lead to poorer neurological and functional recovery, affecting the quality of sleep and increasing the risk rate of cerebrovascular disease recurrence and death (22). Stroke patients are prone to sleep difficulties that affect sleep quality (23), and changes in sleep quality can lead to changes in mental health. One study found that implementing interventions to improve sleep quality reduced depressive symptoms (24), so assessing and improving sleep quality may help in the early identification and reduce the probability of developing depressive symptoms after stroke. Clinical staff should pay adequate attention to sleep quality in stroke patients and provide effective interventions to improve patients’ prognosis and quality of life.
Loneliness is associated with depressive symptoms after stroke. A Canadian longitudinal study of aging also found that stroke victims who often felt lonely were more likely to be depressed than their peers who did not feel lonely as often (25).Huang H et al (26) scholars found that loneliness is a common phenomenon among stroke patients, adversely affecting the recovery of neurological, psychological, and physical functions while increasing the likelihood of stroke recurrence, disability, and even mortality. Loneliness can negatively affect stroke patients who participate in rehabilitation and other daily activities, leading to poor functional outcomes and social isolation (27), further increasing their risk of depression. Patients who do not have a partner or friends at the time of their stroke feel lonely and are prone to develop depressive symptoms; stroke patients who become less lonely and receive more help develop fewer depressive symptoms (28). Living alone is an important risk factor for depression after stroke (29). Living alone increases the likelihood of loneliness among older adults, which is closely linked to diminished well-being. Reduced well-being leads to a higher prevalence of mental health problems, and a clear association between living alone and depressive symptoms has been observed (30). Therefore reducing loneliness and increasing well-being is essential to promote physical and psychological recovery and improve the mental health of stroke patients. Interventions targeting loneliness in stroke patients may reduce post-stroke psychological sequelae and enhance their overall quality of life (31).In clinical practice, it is essential to not only monitor changes in patients’ clinical conditions but also address the impact of loneliness on the psychological well-being of stroke patients, and implement timely and effective interventions to alleviate loneliness and enhance overall quality of life.
Whether or not alcohol is consumed is one of the factors associated with depressive symptoms in stroke patients. A meta-analysis assessing risk factors for post-stroke depression found a correlation between post-stroke depression and alcohol (32). Moderate drinkers have also been previously shown to be a protective factor for depression after stroke (33). Non-drinkers had higher levels of psychological distress and more cases of anxiety and depression than moderate drinkers (34). Moderate drinkers are more likely to have improved mental health; drinking is often associated with social activities and social support is an important factor in alleviating depression, which gives them more opportunities to engage in social activities and be more satisfied with their lives (35). Stroke patients who consume alcohol may receive more emotional support through social activities, which can lead to fewer depressive symptoms. Alcohol consumption may help to relax and relieve stress. For stroke patients, alcohol consumption may help them cope with the psychological stress of the disease to some extent, thus reducing the occurrence of depression, but this does not mean excessive alcohol consumption. Although moderate alcohol consumption may have a positive effect on depression risk in some cases (36), excessive alcohol consumption can have serious negative health consequences, including an increased risk of depression (37).
A significant association exists between educational attainment and the prevalence of depressive symptoms among stroke patients. This is consistent with the findings of a cross-sectional study from China, which noted a significant difference in educational attainment, with high rates of post-stroke depression in patients with low levels of education (13). A study from South Africa noted that low educational level was a negative factor in the occurrence of depression in stroke patients, which may be due to cognitive biases, life stress, and social roles of the patients (38). Individuals with a high educational background are more likely to be aware of knowledge related to their condition and utilize relevant health education resources in order to improve their health literacy and reduce the development of negative emotions such as anxiety and depression. In contrast, patients with lower levels of education tend to have less knowledge about stroke and its consequences, lack the knowledge to cope with it, and ignore changes in symptoms and functioning, failing to intervene promptly in the progression of complications, which ultimately leads to more serious health consequences (39). Less educated patients tend to have limited social resources, less emotional, financial, and medical support, greater isolation and stress, and are prone to depression (2). Therefore, less educated patients are also at higher risk of developing post-stroke depression or developing depressive symptoms (40, 41). During the treatment period, healthcare professionals should provide tailored health education to stroke patients with lower educational attainment, utilizing clear and accessible language to explain disease-related knowledge. This approach can enhance patients’ understanding of their condition, alleviate fear and misconceptions, and improve their ability to cope with the disease.
Poor self-reported health status is strongly associated with an increased prevalence of depression among stroke patients. A Brazilian study showed that stroke patients who rated their self-rated health as good had fewer depressive symptoms than those who rated their self-rated health as poor (42). Individuals who report poor self-rated health are more likely to develop negative cognitions regarding their physical functioning. Such negative self-perceptions can contribute to emotional distress, heightened concerns about future health outcomes, and exacerbate depressive symptoms (43). It is essential to assist patients in identifying and modifying negative cognitive patterns, fostering the development of positive thought processes, and ultimately improving their emotional well-being. Studies have shown that there is a correlation between depression scores and physical functional status at 6 months after stroke, with depression scores significantly higher in patients with poor physical health than in patients with good health (44). Stroke has a high rate of disability, and when patients’ physical health is affected, the quality of life cannot be ensured, individual self-assessed health will decline, and patients who are physically and mentally traumatized are prone to adverse emotions. High depressive symptom trajectories in stroke patients are associated with severe disability, and patients with severe disability are more likely to be in the moderate and high depressive symptom groups (45). Rehabilitation should be undertaken as early as possible after a stroke to improve the patient’s health and reduce disability, thereby reducing the prevalence of depressive symptoms. In addition, this study found that the memory status of stroke patients also affects their ability to develop depressive symptoms. Acute stroke patients are often accompanied by cognitive dysfunction (46), and this neurocognitive impairment may be a prominent feature of acute stroke, which is mainly manifested by impaired cognitive function such as memory loss and inattention. This cognitive dysfunction not only affects the neurological recovery of patients but also has a significant correlation with the occurrence of post-stroke depression (19). Patients with cognitive impairment after stroke are prone to depression (47, 48). Clinical staff should perform a comprehensive assessment of patients’ cognitive function and implement targeted cognitive training interventions for those with identified impairments. This enhances the memory and cognitive level of stroke patients and increases self-confidence, reducing depressive symptoms.
The relationship between life satisfaction and post-stroke depression was negatively correlated. This is consistent with the findings of a study that specifically examined the factors influencing the depressive status of middle-aged and elderly patients with stroke, heart disease, and other chronic diseases in China, which showed that depression was negatively correlated with subjective satisfaction, and in particular, with life satisfaction (49). Stroke may lead to functional impairments such as limb paralysis, speech disorders, and dysphagia, and patients may feel a reduced quality of life and dissatisfaction with their current life status due to the loss or limitation of physical function (35), which in turn leads to depression. Poor stroke outcomes are associated with poorer quality of life and affect stroke recovery (31). Life satisfaction has been shown to be a negative predictor of depressive symptoms, and interventions to improve life satisfaction can be effective in reducing or preventing depressive symptoms (50). Rehabilitation training, such as physical therapy or speech therapy, can be performed to help stroke patients restore or improve their physical function, increase life satisfaction, and improve their mental health.
There is a negative correlation between ADL scores and depressive symptoms in stroke patients. This is consistent with the results of a prospective study that showed that reduced ADL tend to contribute to the development of depression after stroke (51). After a stroke, patients’ ability to perform their own activities decreases, and they may also need help with basic activities of daily living (ADL), which leads to changes in their standard of living (52), negative psychological emotions such as guilt towards family and friends (53), and ultimately to the development of depression or worsening of their condition. A longitudinal study lasting six years also found that post-stroke depressive symptoms were significantly associated with functional limitations in activities of daily living (54). Patients with poor activities of daily living (ADL) functioning develop chronic stressful stimuli, which may also be an influential factor in the emergence of depression (19). Poor activities of daily living (ADL) may prevent stroke patients from actively participating in rehabilitation and having a better life experience, which may have a profound impact on the recovery of stroke patients. Therefore, family members and clinical staff should also pay attention to patients with severe limitations or low activity, provide them with psychological comfort (55), and guide them to adapt to the change of activity ability caused by the disease and carry out appropriate activities according to their conditions, to improve the depressive symptoms of patients with stroke by improving their ability to perform activities of daily living.
There are some limitations to this study. Firstly, The study utilized a self-report survey, and the diagnosis of stroke relied on self-reports provided by the subjects or other informants, which may have some bias in the diagnosis of stroke. Secondly, although the CESD-10 questionnaire is widely used in today’s surveys, it is not representative of studies of people who are ultimately diagnosed with depression. This is because it measures the respondent’s mental state in the past week, which primarily reflects depressive symptoms, and there may still be a diagnostic difference between that and actual depression. Further research is therefore needed to determine the actual clinical level of depression. Finally, this study was a cross-sectional investigation and did not include an analysis of longitudinal changes over time, making it difficult to confirm causality. Therefore, further longitudinal studies are necessary in the future.
Conclusion
This study took middle-aged and elderly stroke patients as research subjects to investigate the prevalence of current depressive symptoms and related factors and found that several factors, such as education level, history of alcohol consumption, sleep quality, loneliness, self-assessed health status, self-assessed memory status, life satisfaction, and ADL were correlated with depressive symptoms. Analyzing the associated factors enables healthcare professionals to more accurately evaluate disease susceptibility and design targeted interventions for the treatment and management of middle-aged and elderly stroke patients. This can effectively reduce the development of depressive symptoms in stroke patients and improve their quality of life and recovery process. Future care strategies should prioritize not only the physical rehabilitation of stroke patients but also their psychological well-being, aiming to provide comprehensive support that enhances their overall quality of life.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: http://charls.pku.edu.cn/en/.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Biomedical Ethics Review Board of Peking University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
YS: Writing – original draft, Data curation. CL: Writing – original draft. XS: Writing – original draft. DL: Writing – original draft. SW: Writing – original draft. XZ: Writing – original draft. KP: Writing – original draft. XC: Writing – review & editing. HZ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project of Henan Province in 2024 (grant number 2024BSH033).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) research and field team, as well as each of the respondents in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1647228.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Feigin VL and Owolabi MO. Pragmatic solutions to reduce the global burden of stroke: a World Stroke Organization-Lancet Neurology Commission. Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:1160–206. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00277-6
2. Guo J, Wang J, Sun W, and Liu X. The advances of post-stroke depression: 2021 update. J Neurol. (2022) 269:1236–49. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10597-4
3. Zhou H, Wei YJ, and Xie GY. Research progress on post-stroke depression. Exp Neurol. (2024) 373:114660. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114660
4. Das J and G K R. Post stroke depression: The sequelae of cerebral stroke. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2018) 90:104–14. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.04.005
5. Gnanaprakasam A, Solomon JM, Roy AK, Deshmukh AS, and Karthikbabu S. Association between depression and adherence to upper limb exercises among community-dwelling stroke survivors: A cross-sectional study. Health Sci Rep. (2024) 7:e70133. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70133
6. Fang Y, Mpofu E, and Athanasou J. Reducing depressive or anxiety symptoms in post-stroke patients: Pilot trial of a constructive integrative psychosocial intervention. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). (2017) 11:53–8.
7. Woranush W, Moskopp ML, Sedghi A, Stuckart I, Noll T, Barlinn K, et al. Preventive approaches for post-stroke depression: where do we stand? A systematic review. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2021) 17:3359–77. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S337865
8. Mikami K, Jorge RE, Moser DJ, Arndt S, Jang M, Solodkin A, et al. Prevention of post-stroke generalized anxiety disorder, using escitalopram or problem-solving therapy. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2014) 26:323–8. doi: 10.1176/appi.neuropsych.11020047
9. Zhao Y, Hu Y, Smith JP, Strauss J, and Yang G. Cohort profile: the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS). Int J Epidemiol. (2014) 43:61–8. doi: 10.1093/ije/dys203
10. Rong J, Zhang N, Wang Y, Cheng P, and Zhao D. Development and validation of a nomogram to predict the depressive symptoms among older adults: A national survey in China. J Affect Disord. (2024) 361:367–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.06.036
11. Zhou L, Ma X, and Wang W. Relationship between cognitive performance and depressive symptoms in chinese older adults: the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS). J Affect Disord. (2021) 281:454–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.12.059
12. Chen H and Mui AC. Factorial validity of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale short form in older population in China. Int Psychogeriatr. (2014) 26:49–57. doi: 10.1017/S1041610213001701
13. Hu QY, Chen YJ, Liu J, Zhao XP, Feng WY, Tian JB, et al. A cross-sectional study on post-stroke depression and the quality of life. BMC Psychol. (2024) 12:646. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-02143-4
14. Chau JPC, Lo SHS, Zhao J, Choi KC, Lam SKY, Butt L, et al. Factors associated with post-stroke depression in chinese stroke survivors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2021) 30:106076. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.106076
15. Kwon B, Lee EJ, Park S, Lee JS, Lee MH, Jeong D, et al. Long-term changes in post-stroke depression, emotional incontinence, and anger. J Stroke. (2021) 23:263–72. doi: 10.5853/jos.2020.04637
16. Volz M, Möbus J, Letsch C, et al. The influence of early depressive symptoms, social support and decreasing self-efficacy on depression 6 months post-stroke. J Affect Disord. (2016) 206:252–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.07.041
17. Baylan S, Griffiths S, Grant N, Broomfield NM, Evans JJ, Gardani M, et al. Incidence and prevalence of post-stroke insomnia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. (2020) 49:101222. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2019.101222
18. Chen W, Shen Y, Song S, and Li X. Association of sleep duration and sleep disorders with post-stroke depression and all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in US stroke survivors: results from NHANES 2005–2018. Eur J Med Res. (2025) 30:2. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02227-2
19. Liao W, Chen D, Wu J, Liu K, Feng J, Li H, et al. Risk factors for post-stroke depression in patients with mild and moderate strokes. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e34157. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034157
20. Dong L, Brown DL, Chervin RD, Case E, Morgenstern LB, and Lisabeth LD. Pre-stroke sleep duration and post-stroke depression. Sleep Med. (2021) 77:325–9. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2020.04.025
21. Liu F, Yang Y, Wang S, Zhang XL, Wang AX, Liao XL, et al. Impact of sleep duration on depression and anxiety after acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. (2021) 12:630638. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.630638
22. Hale E, Gottlieb E, Usseglio J, and Shechter A. Post-stroke sleep disturbance and recurrent cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. (2023) 104:29–41. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2023.02.019
23. Tan XM, Liao ZX, Zhao YY, Sun XC, and Yi FL. Changes in depressive symptoms before and after the first stroke: A longitudinal study from China Family Panel Study (CFPS). J Affect Disord. (2023) 340:567–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.08.058
24. Scott AJ, Webb TL, Martyn-St James M, Rowse G, and Weich S. Improving sleep quality leads to better mental health: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev. (2021) 60:101556. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101556
25. MacNeil A, Li G, Gulati I, Taunque A, Jiang Y, de Groh M, et al. Depression during the COVID-19 pandemic among older adults with stroke history: Findings from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2024) 39:e6062. doi: 10.1002/gps.v39.2
26. Huang H, Zhang L, Dong W, Tu L, Tang H, Liu S, et al. Stigma and loneliness among young and middle-aged stroke survivors: A moderated mediation model of interpersonal sensitivity and resilience. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. (2024) 31:596–606. doi: 10.1111/jpm.13016
27. Shi Y, Fong MWM, Metts CL, LaVela SL, Bombardier C, Hu L, et al. Dynamics of perceived social isolation, secondary conditions, and daily activity patterns among individuals with stroke: A network analysis of ecological momentary assessment data. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2024) 105:1314–21. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2024.02.733
28. Elayoubi J, Haley WE, Nelson ME, and Hueluer G. How social connection and engagement relate to functional limitations and depressive symptoms outcomes after stroke. Stroke. (2023) 54:1830–8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.042386
29. Wang Z, Zhu M, Su Z, Guan B, Wang A, Wang Y, et al. Post-stroke depression: different characteristics based on follow-up stage and gender-a cohort perspective study from Mainland China. Neurol Res. (2017) 39:996–1005. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2017.1364514
30. Xiao A, Wang R, Liu C, and Wang X. Influencing factors and predictive models of early post-stroke depression in patients with acute ischemic stroke. BMC Neurol. (2025) 25:104. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04090-y
31. Theeke L, Horstman P, Mallow J, Lucke-Wold N, Culp S, Domico J, et al. Quality of life and loneliness in stroke survivors living in Appalachia. J Neurosci Nurs. (2014) 46:E3–15. doi: 10.1097/JNN.0000000000000097
32. Perrain R, Mekaoui L, Calvet D, Mas JL, and Gorwood P. A meta-analysis of poststroke depression risk factors comparing depressive-related factors versus others. Int Psychogeriatr. (2020) 32:1331–44. doi: 10.1017/S1041610219002187
33. Qiu X, Miao J, Lan Y, Sun W, Chen Y, Cao Z, et al. Association of cerebral artery stenosis with post-stroke depression at discharge and 3 months after ischemic stroke onset. Front Psychiatry. (2020) 11:585201. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.585201
34. Rodgers B, Parslow R, and Degenhardt L. Affective disorders, anxiety disorders and psychological distress in non-drinkers. J Affect Disord. (2007) 99:165–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2006.09.006
35. Liu Y, Liu J, Zhou S, Xu X, Cheng Y, Yi Y, et al. Life satisfaction and its influencing factors of middle-aged and elderly stroke patients in China: a national cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e059663. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059663
36. Paulson D, Shah M, Herring D, Scott R, Herrera M, Brush D, et al. The relationship between moderate alcohol consumption, depressive symptomatology, and C-reactive protein: the Health and Retirement Study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2018) 33:316–24. doi: 10.1002/gps.v33.2
37. Gea A, Beunza JJ, Estruch R, Sánchez-Villegas A, Salas-Salvadó J, Buil-Cosiales P, et al. Alcohol intake, wine consumption and the development of depression: the PREDIMED study. BMC Med. (2013) 11:192. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-192
38. Ojagbemi A, Akpa O, Elugbadebo F, Owolabi M, and Ovbiagele B. Depression after stroke in sub-saharan africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Neurol. (2017) 2017:4160259. doi: 10.1155/2017/4160259
39. Huang Y, Wang Q, Zou P, He G, Zeng Y, and Yang J. Prevalence and factors influencing cognitive impairment among the older adult stroke survivors: a cross-sectional study. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1254126. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1254126
40. Backhouse EV, Mchutchison CA, Cvoro V, Shenkin SD, and Wardlaw JM. Cognitive ability, education and socioeconomic status in childhood and risk of post-stroke depression in later life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0200525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200525
41. Hirata S, Ovbiagele B, Markovic D, and Towfighi A. Key factors associated with major depression in a national sample of stroke survivors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2016) 25:1090–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.12.042
42. Viana RT, de Freitas Araújo É, Lima LAO, Teixeira-Salmela LF, and de Morais Faria CDC. General and comparative self-rated health in chronic stroke: an important outcome measure for health professionals. BMC Neurol. (2022) 22:78. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02592-7
43. Cai Q, Qian M, and Chen M. Association between socioeconomic status and post-stroke depression in middle-aged and older adults: results from the China health and retirement longitudinal study. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:1007. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18503-z
44. Hu F, Zhang K, Zhou L, and Wang Y. The impact of post-stroke depression and physical fatigue on functional status. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. (2025) 53:315–23. doi: 10.62641/aep.v53i2.1688
45. Liu L, Li X, Marshall IJ, Bhalla A, Wang Y, and O'Connell MDL. Trajectories of depressive symptoms 10 years after stroke and associated risk factors: a prospective cohort study. Lancet. (2023) 402 Suppl 1:S64. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02111-6
46. Girgenti SG, Brunson AO, and Marsh EB. Baseline function and rehabilitation are as important as stroke severity as long-term predictors of cognitive performance post-stroke. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. (2023) 102:S43–s50. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000002125
47. Ojagbemi A, Akinyemi R, and Baiyewu O. Cognitive dysfunction and functional limitations are associated with major depression in stroke survivors attending rehabilitation in Nigeria. NeuroRehabilitation. (2014) 34:455–61. doi: 10.3233/NRE-141061
48. Olibamoyo O, Adewuya A, Ola B, Coker O, and Atilola O. Prevalence and correlates of depression among Nigerian stroke survivors. S Afr J Psychiatr. (2019) 25:1252. doi: 10.4102/sajpsychiatry.v25i0.1252
49. Lin W, Zhang D, Wang Y, Zhang L, and Yang J. Analysis of depression status and influencing factors in middle-aged and elderly patients with chronic diseases. Front Psychol. (2024) 15:1308397. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1308397
50. Liao M, Zhang X, Xie Z, Li L, and Zou L. The mediating effect of life satisfaction between daily living abilities and depressive symptoms in the Chinese older people: evidence from CHARLS 2020. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1393530. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1393530
51. Vojtikiv-Samoilovska D and Arsovska A. Prevalence and predictors of depression after stroke - results from a prospective study. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. (2018) 6:824–8. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.182
52. Li J, Yang L, Lv R, Kuang J, Zhou K, and Xu M. Mediating effect of post-stroke depression between activities of daily living and health-related quality of life: meta-analytic structural equation modeling. Qual Life Res. (2023) 32:331–8. doi: 10.1007/s11136-022-03225-9
53. Feng Z, Li Q, Zhou L, Chen Z, and Yin W. The relationship between depressive symptoms and activity of daily living disability among the elderly: results from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). Public Health. (2021) 198:75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2021.06.023
54. Ytterberg C, Cegrell L, Von Koch L, and Wiklander M. Depression symptoms 6 years after stroke are associated with higher perceived impact of stroke, limitations in ADL and restricted participation. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:7816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11097-9
Keywords: middle-aged and older adults, stroke, depressive symptom, CHARLS, factors
Citation: Shi Y, Liu C, Sun X, Li D, Wang S, Zhu X, Pan K, Chen X and Zhang H (2025) Analysis of the current status and associated factors of depressive symptoms in Chinese middle-aged and elderly stroke patients—based on CHARLS data. Front. Psychiatry 16:1602287. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1602287
Received: 29 March 2025; Accepted: 19 May 2025;
Published: 06 June 2025; Corrected: 02 July 2025.
Edited by:
Vincenzo De Luca, University of Toronto, CanadaCopyright © 2025 Shi, Liu, Sun, Li, Wang, Zhu, Pan, Chen and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huimin Zhang, MzUyOTA5MTVAcXEuY29t
 Yage Shi
Yage Shi Chenjun Liu1
Chenjun Liu1 Xueting Sun
Xueting Sun