- Department of Child Development and Behavior, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Objective: The present research was conducted to examine whether family functioning is related to affiliate stigma in Chinese caregivers of children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and how positive aspects of caregiving affect this relationship.
Methods: Two hundred and six caregivers of children with ASD were investigated using the Family APGAR scale, the Affiliate Stigma scale, and the Chinese version of the Positive Aspects of Caregiving scale. The statistical methods of Pearson correlation analysis and mediation effect analysis were used to statistically analyze the relationship between family functioning, affiliate stigma and positive aspects of caregiving.
Results: The results indicated that family functioning and positive aspects of caregiving were negatively associated with affiliate stigma and that family functioning was positively correlated with positive aspects of caregiving. Furthermore, positive aspects of caregiving partially mediated family functioning and affiliate stigma.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that family functioning can directly influence the affiliate stigma of caregivers of children with ASD and indirectly influence affiliate stigma through positive aspects of caregiving.
Introduction
Autism spectrum disorders (ASDs), commonly referred to as autism, are neurodevelopmental conditions present at birth that are characterized by significant social deficits, delayed language acquisition, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors (1). The global prevalence of ASD is steadily increasing and is currently estimated to be 1%–2% (2). In China, the prevalence of ASD is 1%, including over 13 million individuals (3, 4). This makes ASD one of the fastest growing neurodevelopment disorders in terms of incidence rate (2, 5). Currently, there is no targeted treatment for ASD, with long-term interventional therapy serving as the primary approach (6, 7). Family caregivers assume a central role in the care and support of individuals with ASD (8, 9). Unfortunately, the focus on ASD often leads to the mental well-being of the caregivers being overlooked. Research indicates that parents of children with autism commonly experience prolonged periods of suboptimal mental health throughout their child’s diagnosis and treatment (10, 11).
Affiliate stigma
Affiliate stigma (AS) linked to ASD significantly affects the physical and mental well-being of primary caregivers (12, 13). This AS, also known as stigmatization, manifests as self-isolation and group avoidance due to the discrimination, slander, and exclusion that result from close associations with stigmatized individuals or communities (14). Public stereotypes (15), a lack of social support (16), financial stress (17), and uncertainty about the effectiveness of treatment (7) make it more difficult for children with ASD to improve over time. All of these factors reinforce stigmas and lead to negative feelings among caregivers. Research indicates that caregivers of children with ASD who experience high levels of stigma tend to exhibit social avoidance and withdrawal behaviors (12, 13, 18), including concealing their child’s condition. Such behavior negatively impacts their attitude toward their child and caregiving practices (19, 20), consequently affecting intervention management (12). Therefore, scholars emphasize the importance of implementing targeted interventions for caregivers of children with ASD to mitigate stigma and improve care quality (21, 22).
Family functioning
Symptom severity in children with ASD is correlated with parents’ mental health, quality of life, and caregiving burden (16, 23–25). Consequently, caregivers of children with ASD commonly seek support, either internally or externally (16, 26). Family support is a readily accessible resource for both patients and caregivers. Previous studies have shown that certain characteristics of the family system are essential for a child’s healthy development (27). Hence, family units are of paramount importance in the context of patients and their caregivers (28, 29). Empirical evidence has demonstrated that a robust family support system can enhance psychological resilience. Family functioning (FF) can enhance caregivers’ self-efficacy and empower them to effectively take on life challenges effectively (30, 31). FF encompasses various forms of support, including physical, financial, emotional, and psychological assistance from family members, which manifests as satisfaction with family dynamics (32). Quality family care not only contributes to patients’ recovery, mental well-being, and healthy habits but also benefits caregivers’ physical, psychological, and overall quality of life (33, 34). Lovell and Wetherell (35) reported that parents of children with ASD who perceived greater familial support tended to report reduced levels of shared stigma. Similarly, as Meulien and Baghdadli (36) noted, caregivers’ perceptions of shared stigma are influenced by the presence of a robust support system for children with ASD. Among them, family, friends, and professional support are important protective factors to prevent stigmatization.
Positive aspects of caregiving
Family caregivers play crucial roles in the treatment and rehabilitation of ASD children. The well-being and health of caregivers, including their quality of life and physical and mental health, are increasingly under scrutiny because of the significant responsibilities and high costs associated with long-term care for children with ASD (25, 37). A substantial care burden often leads to negative emotions and feelings among caregivers (10, 12). Nevertheless, the emergence of positive psychology has shed light on the fact that caregiving is not linked solely to adverse outcomes; caregivers can also derive positive emotions, subjective benefits, and satisfaction from the caregiving process (38). The positive aspects of caregiving (PAC) include the beneficial impact of caregiving on caregivers, including a sense of personal achievement and enhanced family unity (38). Research indicates that the positive aspects experienced by caregivers can enhance their well-being and satisfaction (39), decrease their stress level and depressive symptoms (40), bolster their commitment to caregiving, and enhance the quality of the care provided (41). The literature suggests a link between FF and PAC (42, 43). Effective FF can strengthen family bonds, facilitate caregivers’ receipt of increased care and affection from family members, and provide caregivers with greater support and encouragement. Increased encouragement and support can effectively mitigate internal conflicts resulting from traumatic events, facilitate positive changes, reduce negative emotions, and foster the development of positive aspects (44).
Kramer’s caregiver adaptation model
Kramer’s caregiver adaptation model (45) offers a theoretical framework for examining the interplay between FF, PAC experiences, and AS. This model underscores the significance of caregivers’ external (e.g., FF) and internal resources (e.g., coping strategies) in shaping their caregiving perceptions (e.g., positive aspects and burden). Positive aspects of FF are connected to healthy ways of coping (such as feeling more confident in one’s ability and adjusting to new roles), which affect health and behavior (such as noticing discrimination less frequently and growing as a person). With the help of the caregiver adaptation model, PAC may play a role in the link between FF and AS that caregivers of people with ASD experience. However, to our knowledge, few studies have focused on the relationships among FF, PAC, and AS in patients with ASD.
In summary, this study aimed to examine (a) the relationship between FF and AS and (b) the mediating role of PAC in Chinese caregivers of children with ASD. We used measures to assess the FF, PAC, and AS levels among caregivers of children with ASD and conducted a mediation analysis to examine how PAC mediates the relationship between FF and AS.
Materials and methods
Participants
Two hundred and six caregivers of children with ASD participated in this study. The caregivers were recruited from a hospital in the city of Zhengzhou, China. All of the children were diagnosed with ASD and received rehabilitation at this hospital. Inclusion criteria for participants: 1) the main caregiver of the child, the time of care≥6 months; 2) informed consent, voluntary participation; 3) the child under the care of the U.S. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition of the diagnosis of ASD; 4) literacy, understanding the purpose of the questionnaire survey and the significance. Exclusion criteria: 1) the caregiver has a major physical illness or a history of mental illness; 2) there are other serious negative events in the caregiver’s family; 3) the child suffers from other serious organic diseases. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (2022-391-01).
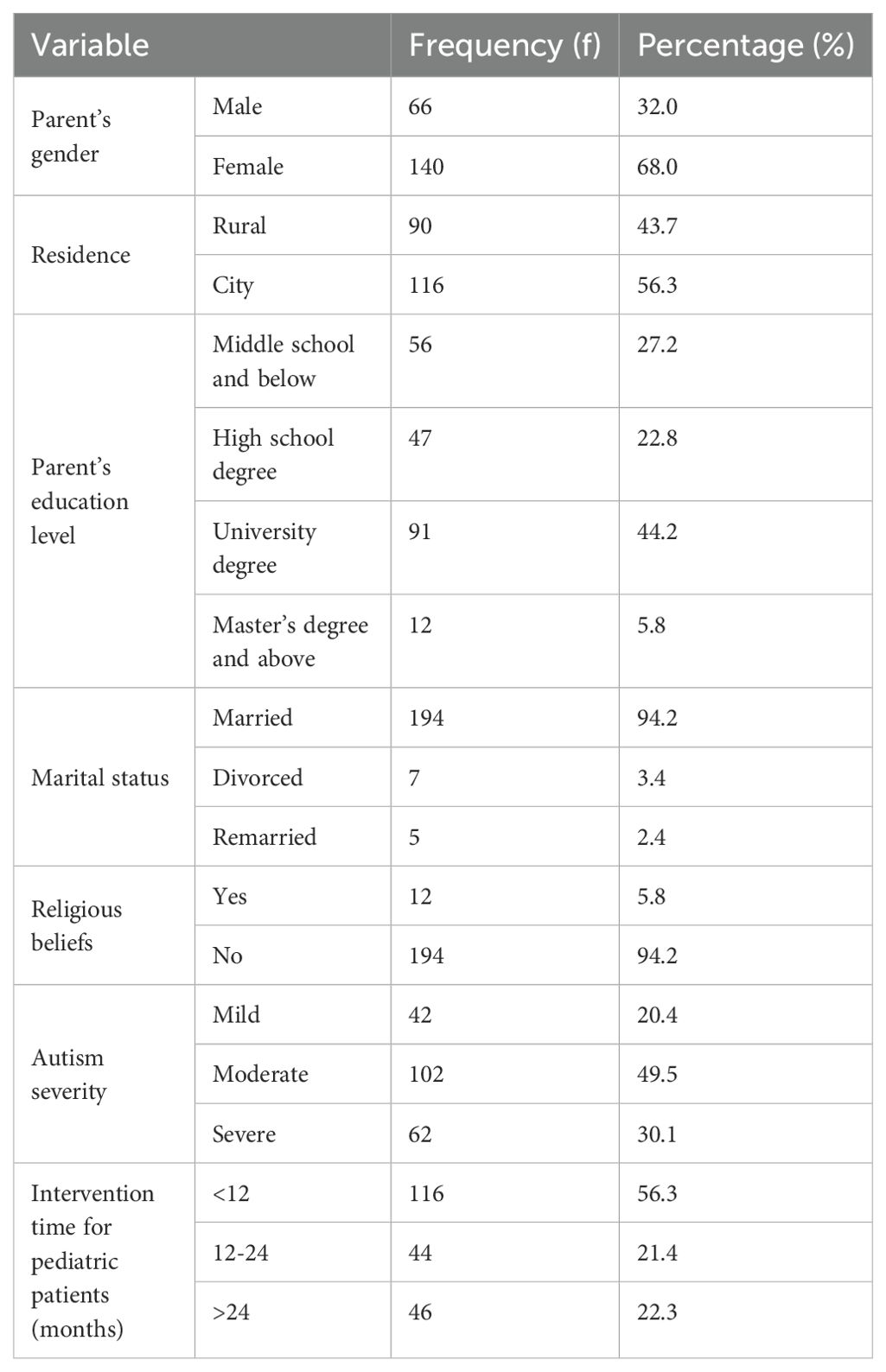
The ages of the caregivers ranged from 20 to 67 years (M = 34.13, SD = 8.15). Most of the caregivers were female (68.0%). Half of the researchers do not have a university degree. The children were between 2 and 9 years of age (Mage = 4.72, SD = 1.54). The patients’ demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Measures
Family APGAR scale
Chinese caregivers for children with ASD use the APGAR scale to measure their FF levels (46). The method includes five items and uses a 3-point scale from 0 (“rarely”) to 2 (“often like this”). Sample items include “When I encounter problems, I can obtain satisfactory help from my family” and “I am happy with the way my family discusses things with me and shares problems.” The total score ranges from 0–10 points, with 0–3 points indicating that family function is severely impaired, (i.e., low family care), 4–6 points indicating that family function is moderately impaired, (i.e., medium family care), and 7–10 points indicating that family function is good, (i.e., high FF). In this study, the Cronbach’s coefficient for this scale was 0.925.
Affiliate stigma scale
Chinese caregivers of children with ASD measure AS using the ASS (47). The ASS includes 18 total items derived from four dimensions: negative emotional cognition, social anxiety avoidance, alienation from the stigma, and discrimination experience. Sample items are as follows: “I was emotionally troubled because I had an autistic child at home” and “Having a child with autism has a negative impact on me.” Items are scored on a 4-point scale from 1 (“strongly disagree”) to 4 (“strongly agree”). The average score of all of the items is determined, and higher average scores indicate higher stigma levels. In this study, the Cronbach’s coefficient of the scale was 0.959.
The Chinese version of the positive aspects of caregiving scale
The Chinese version of the Positive Aspects of Caregiving scale is used to measure PAC in Chinese caregivers of children with ASD (48, 49). Sample items are as follows: “Makes me feel useful” and “Makes me feel needed.” The scale includes two dimensions and nine items. The items are rated on a 5-point scale from 1 (“strongly disagree”) to 5 (“strongly agree”), and higher scores indicate that the caregiver has more positive aspects. The Cronbach’s coefficient of the scale was 0.921.
Procedures
With assistance from the department and the hospital, the research team contacted caregivers of children with ASD who were interested in participating in this study. Before the survey began, members of the research team introduced the study objectives and the participants’ rights to each parent who completed the questionnaire. All of the participants provided informed consent to participate in this study. This study was approved by the hospital ethics committee.
Data analysis
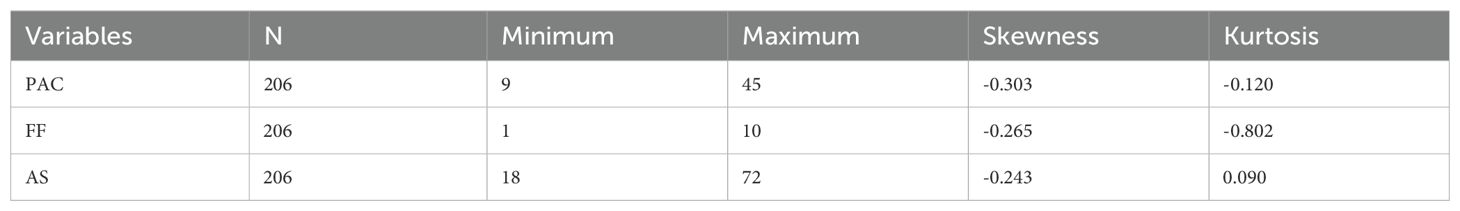
Statistical analyses of the data were conducted using SPSS software (version 23.0). At this stage, first, whether the data complied with normality assumptions was examined. The descriptive statistics and normality values of the data are presented in Table 2. According to the results in Table 2, the skewness and kurtosis values of the data were within acceptable ranges (50). Additionally, the data were examined for multicollinearity. Multicollinearity was assessed using variance inflation factors (VIFs), with all values less than 5, suggesting no significant multicollinearity concerns (51). Next, we conducted Pearson’s correlation analyses to examine the relationships among PAC, FF, and AS in caregivers of children with ASD. The highest value obtained from the correlation analysis between the variables was 0.443. Therefore, it was possible to say that there was no multicollinearity problem between the variables. We then used the PROCESS macro in SPSS to examine the mediating role of PAC in the relationship between FF and AS. The PROCESS macro uses a path analysis modeling tool based on regression to assess the direct and indirect effects of variables (52). In accordance with the relevant literature, we performed mediation analyses using Model 4 with 5000 bias-corrected bootstrap samples.
Results
Descriptive and correlational analyses
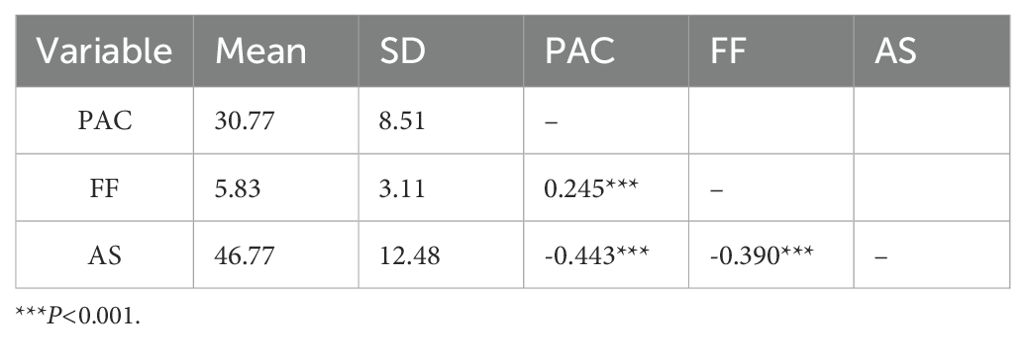
The mean total scores and correlations among the three scales are presented in Table 3. The results indicated that PAC was negatively correlated with AS (r = -0.44, P < 0.001) and positively correlated with FF (r = 0.25, P < 0.001), indicating that caregivers of children with ASD reported high levels of PAC if they had high FF levels and low AS levels. In addition, FF was negatively correlated with AS (r = -0.39, P < 0.001). This result indicates that high FF levels in parents are associated with lower AS levels.
The mediating role of PAC in the relationship between FF and AS
To test whether PAC mediates the relationship between FF and AS, we performed a mediation analysis with FF as a predictor, PAC as a mediator, and AS as the dependent variable. The mediation model is illustrated in Figure 1. The results revealed that the effect of FF on the PAC was -0.68 (SE = 0.18, t = 3.67, P < 0.001, 95% CI: 0.32 to 1.05). Furthermore, the effect of PAC on AS was -0.52 (SE = 0.09, t = -5.68, P < 0.001, 95% CI: -0.69 to -0.34). Importantly, FF had a total effect on AS of -1.56 (SE = 0.26, t = -6.04, P < 0.001, 95% CI: -2.07 to -1.05). Specifically, the indirect effect of FF on AS was -0.35 and significantly different from zero (95% CI: -0.62 to -0.13), whereas the direct effect was -1.21 (SE = 0.24, t = -4.87, P < 0.001, 95% CI: -1.70 to -0.72). This model explained 13.68% of the variance in AS (F = 37.22, P < 0.001). Overall, these results suggest that PAC partially mediates the relationship between FF and AS.
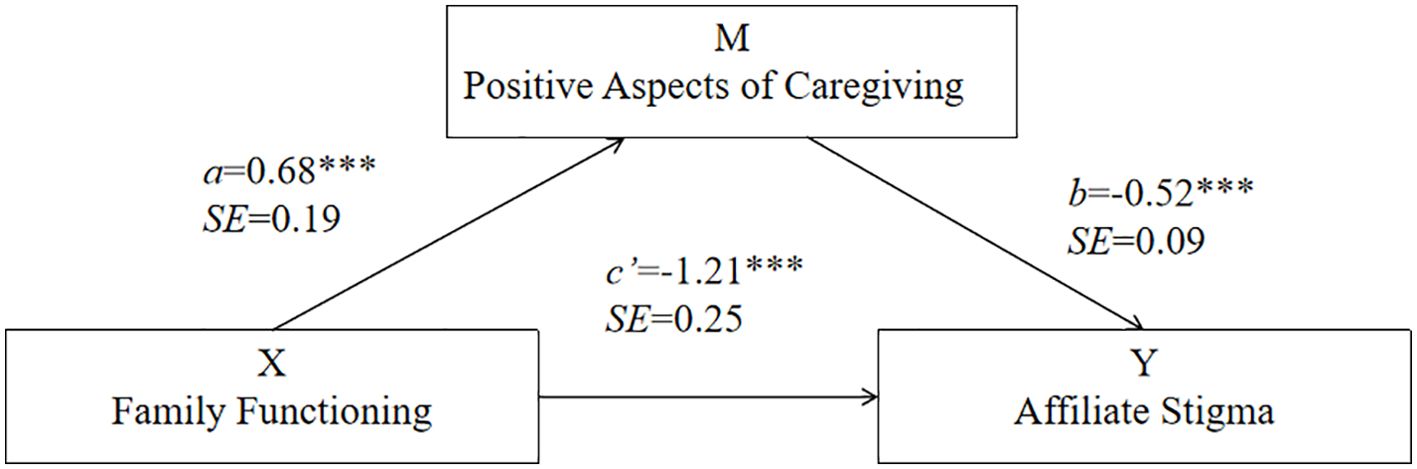
Figure 1. The mediation model for the effect of PAC in the relationship between FF and AS. ***P<0.001.
Discussion
Clinical and intervention implications
This study aimed to investigate the relationship between FF and AS among caregivers of Chinese children with ASD and the mediating role of caregivers’ PAC. First, the study’s results demonstrated a negative relationship between FF and AS. Specifically, caregivers of children with ASD who perceived stronger FF had lower AS, which is consistent with previous research (13, 31, 53). From a theoretical perspective, FF, as an external resource in the caregiver adaptation model, can make important contributions to positive psychological adaptation (42), allowing caregivers to maintain an optimistic psychological state, which reduces their AS (36). FF reflects a caregiver’s access to family support. For caregivers of children with ASD, FF is an important factor in helping them cope with the stress of caring for their children and promoting their children’s recovery, which helps reduce their feelings of AS (28). Clinical staff should monitor family caregivers of children with ASD; encourage family members to maximize the supportive function of the family system; and ensure that caregivers have more emotional, value affirmation, and financial support from the family. Factor et al. (54) reported that research has broadly shifted to focusing on families, highlighting the influence of family support and functioning for families of children with ASD in everyday life and in intervention procedures. There have been intervention studies on the family functioning of caregivers for children with ASD, and the relevant research results can provide a reference for us to conduct similar studies in the future. Peng et al. (55) implemented a family task intervention program to enhance the family functioning of caregivers for children with autism, including (1) medical staff helping caregivers gain relevant health experience, skills, material resources, and services for managing children with autism and (2) by understanding the family structure and general condition of the sick child, medical staff can help caregivers recognize the importance of internal and external support within the family and learn how to cope with illness and emotional problems in daily life. They can provide psychological support and assist in obtaining social assistance. Sabanciogullari and Yildırım (56) conducted a 10-week group counseling and education program (GCEP) for parents with ASD. GCEP can help parents with ASD raise awareness and provide them with social and psychological support, which can help them clarify family relationships, care, and responsibilities for children with ASD. The results showed that GCEP can effectively improve psychological resilience and family functioning.
The need for PAC support
Second, the results indicate a significant negative correlation between caregivers’ PAC and AS. Specifically, high PAC levels can lessen the negative feelings associated with AS. This finding is consistent with those from previous studies (57, 58). PAC is the positive experience that caregiving brings to the caregiver’s life, which is reflected mainly in having a strong ability to cope with stress and an improved subjective health status (38, 59). For Chinese families in which a member has ASD, the prejudice and stereotyping of autism by social groups, along with the discrimination and rejection of children with autism and their caregivers, leads to a strong sense of AS among caregivers (12, 13, 21). Most caregivers adopt ineffective coping strategies (e.g., reducing socialization and avoiding interpersonal interactions) to cope with AS (35, 36). However, some studies have shown that caregivers of children with ASD seek supportive resources in the process of caring for their children and derive benefits from their children’s recovery, such as knowledge about autism recovery; improved caregiving skills; and positive feelings, such as perceived value, meaning of life, and self-growth (60, 61). Therefore, providing a multitude of support resources to caregivers of children with ASD can increase PAC and reduce AS. A literature review found that, at present, there are few intervention studies on the positive feelings of caregivers for children with ASD, mainly through qualitative research to understand the positive aspects of caregivers raising ASD children (62). With respect to relevant research results, we can gradually explore the role of positive psychological intervention, focused solution model intervention and caregiver network intervention models based on PAC models in improving the positive feelings of caregivers for children with ASD (63–66).
Theoretical implications
Third, and most importantly, the results suggest that PAC mediates the relationship between FF and AS. These findings support the caregiving adaptation model. FF is an important external resource for caregivers in caring for children with ASD, enabling them to receive more support and encouragement, which alleviates negative emotions, enhances PAC formation, and buffers caregiver stress (28). In addition, the caregivers’ PAC indicates an individual’s optimistic view of life events, and PAC in the caregiving process can reduce caregiver stress, making caregivers more inclined to adopt a positive and optimistic attitude toward parenting children with autism (37). A previous study indicated that the enhancement of positive feelings in caregivers prevents the accumulation of internalized negative experiences and emotions and reduces AS (57). Therefore, in order to better alleviate the AS associated with caring for children with ASD, it is necessary to give full play to the role of FF, help caregivers discover PAC in the caregiving process, and thereby weaken negative emotions.
Limitations
In conclusion, the present study validated the relationships among FF, PAC, and AS among caregivers of children with ASD, but these results should be interpreted with caution. This study has several limitations. First, the participants in this study were recruited from only one hospital, and the sample size was relatively small; therefore, the generalizability of the findings must be validated by increasing the sample size. Second, this was a cross-sectional survey study and all of the data were based on caregivers’ self-reports, which precluded us from interpreting the causal relationships among FF, PAC, and AS among caregivers of children with ASD. Third, the ages of the children with ASD included in this study ranged from 2 to 9 years old. Given the changes in social demands and needs as children enter adolescence and adulthood, future studies should examine whether the same relationships are observed in older age groups.
Therefore, in the future, we can perform more qualitative and longitudinal studies to better confirm the links among FF, PAC, and AS. We can also identify scientifically sound ways to help caregivers of children with ASD improve their FF and PAC, which will lower their AS. Furthermore, children with ASD of different age groups should be selected and included in the sample, and the current status of their caregivers’ FF, PAC and AS, influencing factors and the relationships among the three, should be investigated to formulate targeted intervention plans. Future research should address these issues.
Conclusion
This study explored the relationships among FF, PAC, and AS among caregivers of children with ASD in China. These findings support a relationship between FF and AS. In addition, caregivers’ PAC mediated this relationship. The study results emphasize the critical role of FF and PAC in enhancing psychological resources and alleviating AS associated with caregivers of children with ASD. These findings suggest that interventions aimed at strengthening FF and enhancing PAC may be effective strategies for alleviating AS associated with caregivers of children with ASD. Healthcare professionals should consider incorporating FF and PAC into support programs for these caregivers. These findings may provide valuable information on how to reduce AS among caregivers of children with autism in China. Healthcare professionals should adopt family-centered interventions with the participation of family members to help caregivers of children with ASD establish a good family support system, promote PAC enhancement, and reduce AS so parents can adjust their mindsets to actively participate in the rehabilitation process of their children and better integrate into society.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
XD: Investigation, Funding acquisition, Software, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Validation, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. XS: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Formal Analysis, Validation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Data curation. DD: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. YZ: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology. YS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MW: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. YX: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HX: Resources, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Formal Analysis, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Medical Science and Technology Research Program of Henan Province (LHGJ20210435).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank our participants, who devoted their time to supporting this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Hodges H, Fealko C, and Soares N. Autism spectrum disorder: definition, epidemiology, causes, and clinical evaluation. Transl Pediatr. (2020) 9:S55–65. doi: 10.21037/tp.2019.09.09
2. Zeidan J, Fombonne E, Scorah J, Ibrahim A, Durkin MS, Saxena S, et al. Global prevalence of autism: A systematic review update. Autism Res. (2022) 15:778–90. doi: 10.1002/aur.2696
3. Salari N, Rasoulpoor S, Rasoulpoor S, Shohaimi S, Jafarpour S, Abdoli N, et al. The global prevalence of autism spectrum disorder: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Ital J Pediatr. (2022) 48:112. doi: 10.1186/s13052-022-01310-w
4. Zhao YN, Li ZW, Li L, Guan CR, Yin YF, Yang YF, et al. Screening prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in children aged 0–6 years in China. Chin J Reprod Health. (2023) 34:423–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-878X.2023.05.005
5. Qiu S, Lu Y, Li Y, Shi J, Cui H, Gu Y, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in Asia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. (2020) 284:112679. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112679
6. Kodak T and Bergmann S. Autism spectrum disorder: characteristics, associated behaviors, and early intervention. Pediatr Clin North Am. (2020) 67:525–35. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2020.02.007
7. Jing J. Current status and recommendations for treatment and intervention of autism spectrum disorder. Chin J Child Health Care. (2023) 31:939–44. doi: 10.11852/zgetbjzz2023-0680
8. Crowell JA, Keluskar J, and Gorecki A. Parenting behavior and the development of children with autism spectrum disorder. Compr Psychiatry. (2019) 90:21–9. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2018.11.007
9. Tint A and Weiss JA. Family wellbeing of individuals with autism spectrum disorder: A scoping review. Autism. (2016) 20:262–75. doi: 10.1177/1362361315580442
10. Bonfim TA, Giacon-Arruda B, Hermes-Uliana C, Galera S, and Marcheti MA. Family experiences in discovering Autism Spectrum Disorder: implications for family nursing. Rev Bras Enferm. (2020) 73:e20190489. doi: 10.1590/0034-7167-2019-0489
11. Magalhães JM, Rodrigues TA, Neta M, Damasceno C, and Sousa K. Experiences of family members of children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. Rev Gaucha Enferm. (2021) 42:e20200437. doi: 10.1590/1983-1447.2021.20200437
12. Salleh NS, Abdullah KL, Yoong TL, Jayanath S, and Husain M. Parents’ Experiences of affiliate stigma when caring for a child with autism spectrum disorder (ASD): A meta-synthesis of qualitative studies. J Pediatr Nurs. (2020) 55:174–83. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2020.09.002
13. Zhou T, Wang Y, and Yi C. Affiliate stigma and depression in caregivers of children with Autism Spectrum Disorders in China: Effects of self-esteem, shame and family functioning. Psychiatry Res. (2018) 264:260–5. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.03.071
14. Farrugia D. Exploring stigma: medical knowledge and the stigmatisation of parents of children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder. Sociol Health Illn. (2009) 31:1011–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9566.2009.01174.x
15. Westby C, Chen KM, Cheng L, Jithavech P, and Maroonroge S. Autism in Taiwan and Thailand: influences of culture. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2024) 20:1523–38. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S462864
16. Lei X and Kantor J. Social support and family quality of life in Chinese families of children with autism spectrum disorder: the mediating role of family cohesion and adaptability. Int J Dev Disabil. (2022) 68:454–61. doi: 10.1080/20473869.2020.1803706
17. Rogge N and Janssen J. The economic costs of autism spectrum disorder: A literature review. J Autism Dev Disord. (2019) 49:2873–900. doi: 10.1007/s10803-019-04014-z
18. Wang W, Yang Y, Song C, Liu Q, Mu R, and Yu D. Suicidal risk among Chinese parents of autistic children and its association with perceived discrimination, affiliate stigma and social alienation. BMC Psychiatry. (2024) 24:784. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06252-7
19. Ni LP, Ailipata TLT, Wang MN, and Rena MMT. Correlation analysis of stigma, coping styles, and social support among parents of children with autism spectrum disorder. Sichuan Ment Health. (2023) 36:354–8. doi: 10.11886/scjsws20230129001
20. Chan K, Yip C, and Leung D. Longitudinal impact of self-stigma content and process on parental warmth and hostility among parents of children with autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. (2023) 53:2728–36. doi: 10.1007/s10803-022-05529-8
21. Ng C and Ng S. A qualitative study on the experience of stigma for Chinese parents of children with autism spectrum disorder. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:19550. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23978-0
22. Chen X, Tong J, Jiang B, Ma S, Wang X, Sun X, et al. Courtesy stigma among primary caregivers of children with autism spectrum disorder in eastern China. Front Psychiatry. (2023) 14:1236025. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1236025
23. Pardo-Salamanca A, Rosa-Martínez E, Gómez S, Santamarina-Siurana C, and Berenguer C. Parenting stress in autistic and ADHD children: implications of social support and child characteristics. J Autism Dev Disord. (2024) 55(7):2284–93. doi: 10.1007/s10803-024-06377-4
24. Wang Y, Xiao L, Chen RS, Chen C, Xun GL, Lu XZ, et al. Social impairment of children with autism spectrum disorder affects parental quality of life in different ways. Psychiatry Res. (2018) 266:168–74. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.05.057
25. Turnage D and Conner N. Quality of life of parents of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An integrative literature review. J Spec Pediatr Nurs. (2022) 27:e12391. doi: 10.1111/jspn.12391
26. Ault S, Breitenstein SM, Tucker S, Havercamp SM, and Ford JL. Caregivers of children with autism spectrum disorder in rural areas: A literature review of mental health and social support. J Pediatr Nurs. (2021) 61:229–39. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2021.06.009
27. Flenik T, Bara TS, and Cordeiro ML. Family functioning and emotional aspects of children with autism spectrum disorder in southern Brazil. J Autism Dev Disord. (2023) 53:2306–13. doi: 10.1007/s10803-022-05497-z
28. He B, Wongpakaran T, Wongpakaran N, and Wedding D. Marital satisfaction and perceived family support in families of children with autistic spectrum disorder: dyadic analysis. Healthcare (Basel). (2022) 10(7):1227. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10071227
29. Losada-Puente L, Baña M, and Asorey M. Family quality of life and autism spectrum disorder: Comparative diagnosis of needs and impact on family life. Res Dev Disabil. (2022) 124:104211. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2022.104211
30. Wang J, Duan Y, Geng L, Li X, Yue S, and Liu H. Trajectory of caregiver burden and associated factors in family caregivers of individuals with colorectal cancer: A longitudinal, observational multicenter study. Patient Prefer Adherence. (2024) 18:879–92. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S451487
31. Lyu QY, Yu XX, Wang JL, Wang XY, Ke QQ, Liu D, et al. Self-esteem and family functioning mediates the association of symptom severity and parental affiliate stigma among families with children with ASD. J Pediatr Nurs. (2022) 66:e122–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2022.04.019
32. Zhang Y, Hu DY, Liu YL, Xie JZ, Ding XP, Zhang YY, et al. The mediating role of medical coping and negative emotions between family care and psychological resilience in gynecological cancer patients. J Nurs Sci. (2023) 38:89–92. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2023.12.089
33. Kim EY and Yeom HE. Influence of home care services on caregivers’ burden and satisfaction. J Clin Nurs. (2016) 25:1683–92. doi: 10.1111/jocn.13188
34. Milberger S, Marsack-Topolewski C, Janks E, Anderson N, Bray M, and Samuel PS. Evaluating the benefits of a family support program on the health and well-being of aging family caregivers of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities. J Gerontol Soc Work. (2023) 66:413–32. doi: 10.1080/01634372.2022.2110347
35. Lovell B and Wetherell MA. Affiliate stigma, perceived social support and perceived stress in caregivers of children with autism spectrum disorder: A multiple mediation study. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. (2019) 33:31–5. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2019.08.012
36. Meulien C and Baghdadli A. A systematic review of the stigma experienced by people with autism spectrum disorder associated with intellectual disabilities and by their family caregivers. J Autism Dev Disord. (2024) 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s10803-024-06435-x
37. Warreman EB, Lloyd SE, Nooteboom LA, Leenen P, Terry MB, Hoek HW, et al. Psychological, behavioural, and physical aspects of caregiver strain in autism-caregivers: a cohort study. EClinicalMedicine. (2023) 64:102211. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102211
38. Wang J, Li X, Liu W, Yang B, Zhao Q, Lü Y, et al. The positive aspects of caregiving in dementia: A scoping review and bibliometric analysis. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:985391. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.985391
39. Quinn C, Nelis SM, Martyr A, Victor C, Morris RG, Clare L, et al. Influence of positive and negative dimensions of dementia caregiving on caregiver well-being and satisfaction with life: findings from the IDEAL study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2019) 27:838–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2019.02.005
40. Cheng ST. Positive aspects of caregiving attenuate the relationship between behavioral bother and anxiety and depressive symptoms in dementia family caregivers. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2023) 23:366–70. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14581
41. Fang N, Deng H, Fu T, Zhang Z, Long X, Wang X, et al. Association between caregiver ability and quality of life for people with inflammatory bowel disease: The mediation effect of positive feelings of caregivers. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:988150. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.988150
42. Zhou CT, Wu HS, Li YN, Zhou ZN, and Xie JF. The impact of family function on positive feelings among caregivers of children with autism. Chin J Nursing. (2015) 50:1479–84. doi: 10376/j.issn.0254-1796.2015.12.013
43. Zhang YZ, Zhong FX, and Huang ST. Correlation between family function and positive feelings among caregivers of liver cancer patients. Chin J Modern Drug Application. (2024) 18:161–6. doi: 10.14164/j.cnki.cn11-5581/r.2024.21.043
44. Zhang Y, Tang R, Bi L, Wang D, Li X, Gu F, et al. Effects of family-centered positive psychological intervention on psychological health and quality of life in patients with breast cancer and their caregivers. Support Care Cancer. (2023) 31:592. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-08053-2
45. Kramer BJ. Gain in the caregiving experience: where are we? What next? Gerontologist. (1997) 37:218–32. doi: 10.1093/geront/37.2.218
46. Smilkstein G. The family APGAR: a proposal for a family function test and its use by physicians. J Fam Pract. (1978) 6:1231–9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/
47. Zhang J, Lin XF, Zhang Y, Gao W, Qin WY, and Zhang MY. The mediating role of rumination between affiliate stigma and post-traumatic growth in parents of children with autism. Chin Ment Health J. (2023) 37:1085–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6729.2023.12.014
48. Tarlow BJ, Wisniewski SR, Belle SH, Rubert M, Ory MG, and Gallagher-Thompson D. Positive aspects of caregiving - Contributions of the REACH project to the development of new measures for Alzheimer’s caregiving. Res Aging. (2004) 26:429–53. doi: 10.1177/0164027504264493
49. Zhang R and Li Z. Reliability and validity of the chinese version of the caregiver positive feelings scale. Chin J Nursing. (2007) 12):1068–71. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZHHL.0.2007-12-005
50. George D and Mallery P. SPSS for windows step by step: A simple guide and reference 17.0 update. Boston: Pearson (2010).
51. Kim JH. Multicollinearity and misleading statistical results. Korean J Anesthesiol. (2019) 72:558–69. doi: 10.4097/kja.19087
52. Hayes A. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach. 2nd Edn. New York, NY: Guilford Press (2018).
53. Efe F, Aksoy H, Ok F, Kocak E, and Gunes S. Perception of internalized stigma in parents of children with autism spectrum disorder: investigating the effects of depression, anxiety, and family functioning. Cureus. (2024) 16:e73860. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73860
54. Factor RS, Ollendick TH, Cooper LD, Dunsmore JC, Rea HM, and Scarpa A. All in the family: A systematic review of the effect of caregiver-administered autism spectrum disorder interventions on family functioning and relationships. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. (2019) 22:433–57. doi: 10.1007/s10567-019-00297-x
55. Peng GY, Peng XF, Tong TT, Wang Y, Tong P, and Meng EH. The effect of family task intervention on improving family functioning and parental self-efficacy in children with autism spectrum disorder. Chin Gen Practice. (2019) 22(S1):91–4. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=__pNPjlwk1pgRdVRuzdh7b3SVsi8frU_0vmkENzDnKtpoMHTf4o11czYPnnldOv1msBnacKMbUfBdVnDOKORzCCBREU6_nIATAqPE_rP3tijr5xRnvy3Pk3ov-biD1FFtgC1ccSQxWRrB3UirKXo6xjv8m737hy4EycR8wi-4TOvI6fPBCSkcg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS&anchor=citnet.
56. Sabanciogullari S and Yildırım F. Group counseling education program for parents of children with autism spectrum disorder: effect on parents’ Psychological resilience, life satisfaction, and family functioning. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv. (2025), 1–10. doi: 10.3928/02793695-20250304-01
57. Li HX, Wang YX, Ma MY, Du YC, Zhao HF, and Yang QJ. The relationship between affiliate stigma, social support, and general self-efficacy among family caregivers of alzheimer’s disease patients. Evidence-Based Nursing. (2023) 9:1409–13. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.2095-8668.2023.08.015
58. Duangjina T, Hershberger PE, Gruss V, and Fritschi C. Resilience in family caregivers of Asian older people with dementia: An integrative review. J Adv Nurs. (2025) 81:156–70. doi: 10.1111/jan.16272
59. Machaki D, Mutisya AK, Mutinda J, OluChina S, and Gatimu SM. Challenges and coping strategies among caregivers of children with cancer receiving care at a national referral hospital in Kenya. BMC Palliat Care. (2024) 23:242. doi: 10.1186/s12904-024-01573-6
60. Wu SQ, Yang NB, Yuan XQ, Lin RF, Wu SH, Liu LQ, et al. The mediating effect of family resilience between psychological resilience and benefit finding in mothers of preschool children with autism. Chin Nurs Management. (2024) 24:315–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2024.02.029
61. Qin X, Feng Y, Qu F, Luo Y, Chen B, Chen M, et al. Posttraumatic growth among parents of children with autism spectrum disorder in China and its relationship to family function and mental resilience: A cross-sectional study. J Pediatr Nurs. (2021) 57:e59–67. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2020.10.026
62. Curley K, Hughes R, and Kotera Y. Stressful but not unhappy: A review of the positive aspects of parenting a child with autism spectrum disorder. Children (Basel). (2025) 12(1):107. doi: 10.3390/children12010107
63. Paúl C, Teixeira L, Duarte N, Pires CL, and Ribeiro O. Effects of a community intervention program for dementia on mental health: the importance of secondary caregivers in promoting positive aspects and reducing strain. Community Ment Health J. (2019) 55:296–303. doi: 10.1007/s10597-018-0345-6
64. Lü SJ. A Study on the Impact of Positive Psychological Interventions on the Mental Health of Caregivers of Children with Hydrocephalus. Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan Province, China. (2020). doi: 10.27466/d.cnki.gzzdu.2020.004115
65. Jing TT. Current Status of Positive Feelings Among Family Caregivers of Dementia Patients and Intervention Study Based on the Solution-Focused Approach. Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province, China. (2023). doi: 10.27288/d.cnki.gsxyu.2023.000517
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder, parents of children with ASD, caregiver, family functioning, affiliate stigma, positive aspects of caregiving, mediating effect
Citation: Du X, Su X, Ding D, Zhu Y, Sun Y, Wang M, Xiao Y and Xu H (2025) Relationship between family functioning and affiliate stigma in parents of children with autism spectrum disorder in China: the mediating role of positive aspects of caregiving. Front. Psychiatry 16:1613340. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1613340
Received: 17 April 2025; Accepted: 24 June 2025;
Published: 21 July 2025.
Edited by:
Naomi Beth Swiezy, Indiana University, United StatesReviewed by:
Cynde Josol, University of California, Davis, United StatesNoor Shuhada Salleh, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Du, Su, Ding, Zhu, Sun, Wang, Xiao and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiangdan Su, c3hkenp1MjExQDE2My5jb20=; Haiping Xu, eHVoYWlwaW5nMTk4MkAxMjYuY29t
 Xiaoyan Du
Xiaoyan Du Xiangdan Su
Xiangdan Su Dandan Ding
Dandan Ding