- Department of Psychiatry, School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Objective: To investigate the psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the Severity of Dependence Scale for stimulant (C-SDS-S) in screening for the DSM-5-defined Stimulant Use Disorder (SUD).
Design: Retrospective chart review.
Methods: A total of 227 Chinese-speaking stimulant (methamphetamine and cocaine) users were identified from four previous studies conducted in Hong Kong. Their demographic data, frequency of stimulant use within the past 30 days, scorings for C-SDS-S and the severity of SUD at baseline were extracted and synthesized. In addition, test-retest reliability of C-SDS-S was assessed in 101 subjects who reported C-SDS-S scorings 4 weeks after baseline.
Findings: The C-SDS-S demonstrated an acceptable internal consistency with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.736. C-SDS-S scorings were associated with the severity of SUD (ρ = 0.292, p <.001) and with the frequency of stimulant use within the past 30 days (ρ = 0.196, p = .003). All items loaded into one factor which accounted for 50.21% of the variance. Receiver operating characteristic analysis demonstrated that a C-SDS-S cut-off score of ≥ 5 provided optimal discrimination for moderate-to-severe SUD among Chinese-speaking individuals using stimulants. Total scores and individual items of the C-SDS-S demonstrated fair to moderate 30-day test-retest reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient = 0.49; weighted Kappa’s = 0.25-0.46).
Conclusion: The C-SDS-S is a valid and reliable screening instrument to identify stimulant users with DSM-5 defined moderate-to-severe SUD in the Chinese-speaking population.
1 Introduction
Amphetamine-type stimulants (ATS) and cocaine are commonly misused drugs globally (1). Not only is ATS the commonest primary drug of misuse in Asia, it also contributes to more than half of its treatment-seeking drug users (1). Among Chinese-speaking countries and regions, including mainland China, Hong Kong, Malaysia, Singapore, and Taiwan, methamphetamine and cocaine account for the highest number of documented cases who come into a formal contact with authorities, more than that of heroin or cannabis (2). Individuals with stimulant use disorder (SUD) are prone to develop a myriad of psychiatric disorders, encompassing mood, bipolar, and psychotic disorders (3–8). Therefore, developing a reliable and valid screening instrument in Chinese for early detection of SUD in Chinese-speaking stimulant users is of paramount importance to administer timely intervention.
The Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) is a five-item, self-administered scale that measures the psychological dependence of drug users on impaired control, anxiety and preoccupation towards their substance use (9). Rating each item on a Likert scale from 0 to 3 with a maximum score of 15, SDS is designed to contextualize psychological dependence under a dimensional construct with higher scores suggesting more severe dependence. SDS has a single-factor structure with high internal consistency in measuring the construct of substance dependence. It also has a high test-retest reliability and has demonstrated strong associations with the amount and frequency of use across various substances (9–12).
The original English version of SDS had been validated in heroin, cocaine, and amphetamine users (9). Later studies have also translated and validated SDS into various languages, and found different diagnostic cut-offs that allow for the optimal discrimination for substance dependence in accordance with the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) for alcohol, amphetamines, benzodiazepines, cannabis, cocaine, and heroin (10, 12–20). While the Chinese version of the SDS (C-SDS) has been validated for benzodiazepines, cannabis, heroin, and ketamine (13, 20–22), the psychometric properties of C-SDS for stimulant use have not yet been validated, nor its diagnostic cut-offs for DSM-5 defined SUD established.
The present study aims to establish the diagnostic utility of the C-SDS for stimulant (C-SDS-S) in screening for DSM-5 defined SUD. This study also focuses on determining the cut-off scores that provide optimal discrimination for mild and moderate-to-severe SUD, thus allowing the C-SDS-S to be adopted as a rapid screening instrument in routine clinical practice.
2 Methods
2.1 Participants
Chinese-speaking stimulant users resided in Hong Kong were retrospectively identified from four previous studies. These studies (UW 18-094, UW 18-095, UW 19–228 and UW 20-189) were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong/Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster (HKU/HA HKW IRB). Details of studies UW 18-094, UW 18–095 and UW 20–189 can be reviewed at www.clinicaltrials.gov with study identifiers NCT03485417, NCT03485274 and NCT04373525, respectively. For study UW 19-228, details can be found at www.hkuctr.com with study identifier HKUCTR-2690. In short, these four studies focused on commonly misused drugs in Hong Kong. All the participants included in the present study joined these four studies between August 2018 and October 2023. They were recruited through random sampling from the substance misuse treatment clinics and the community. All these studies were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
For the current study, we included those participants from these four studies who reported using cocaine and/or methamphetamine for at least six times in the past six months and had completed the C-SDS-S and the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 (SCID-5) on stimulant use disorders at baseline. Cocaine and methamphetamine were pre-selected as the major types of stimulants of concern as these were the two major stimulants of misuse over the past decade in Hong Kong (23). Participants who did not specify the type of stimulants used in their SDS questionnaires, did not use separate SDS questionnaire for different stimulants, had not completed rating on all items, nor completed the SCID-5 assessments would be excluded from the current study.
2.2 Design
This was a retrospective data review study. Demographic information, frequency of stimulant use within the past 30 days, scorings on the C-SDS-S, and the severity of SUD verified by board-certified psychiatrists using SCID-5, were retrieved from the study records of participants meeting the inclusion criteria. All participants self-reported their stimulant use over the past 30 days at the time of assessment.
Participants filled in the same C-SDS which was previously translated into traditional Chinese and was validated by Tung et al. (22) and by Chung and Tse (13) in ketamine and cannabis users, respectively. C-SDS-S comprised the same five items from the English version of the SDS: (1) “Did you think your use of (stimulant) was out of control?”; (2) “Did the prospect of missing a smoke/snort make you anxious or worried?”; (3) “Did you worry about your use of the drug?”; (4) “Did you wish you could stop?”; and (5) “How difficult did you find to stop or go without (stimulant)?”. Each item anchored on a 4-point scale. Participants scored the first four items among “0: never/almost never”, “1: sometimes”, “2: often”, and “3: always/nearly always”; while the last item among “0: not difficult”, “1: quite difficult”, “2: very difficult” and “3: impossible”. The total C-SDS-S score ranged from 0 to 15 where a higher score indicates a greater degree of dependence.
This study was approved by HKU/HA HKW IRB (UW 23-267). No external funding sponsored this study.
2.3 Statistical analysis
Demographic data, the mean C-SDS-S scores for different severity of SUD, and the frequency of stimulant use in the past 30 days were presented with descriptive statistics. Baseline differences were assessed using one-way ANOVA or the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables, and the Chi-squared test or the Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables. Reliability of the C-SDS-S was assessed by the Cronbach’s alpha. Test-retest reliability of the C-SDS-S was assessed in participants who repeated C-SDS-S scorings 4 weeks after baseline by the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for total scores and Cohen’s weighted Kappa for individual items. Correlations of the scorings on the C-SDS-S with the severity of SUD and the frequency of stimulant use in the past 30 days were assessed for its concurrent validity. Factor analysis using principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted to investigate the construct validity of C-SDS-S. Lastly, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to determine the area under curve (AUC) and the diagnostic cut-offs on C-SDS-S for DSM-5 defined mild SUD and moderate-to-severe SUD, respectively. Subgroup analyses were performed for cocaine and methamphetamine. All analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 29.0, with a significance of alpha = .05.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of participants
Two hundred and twenty-seven participants (36.9%) fulfilling the inclusion criteria were identified from 615 records from the four studies. Table 1 described their demographics and baseline information of stimulants and other drugs used. Majority of the participants were male (70.9%) and their mean age was 39.8 years old (SD = 10.0). Most of participants (93.8%) had lifetime history of drug use other than stimulants, but less than half of these participants (45.4%) had recent use of other non-stimulant drug within the past 30 days. On average, these poly-drug users had used fewer than one non-stimulant drug in the past 30 days. Eighteen (7.9%) stimulant users did not meet the diagnosis of SUD. A total of 54 users (23.8%) had mild SUD and 155 users (68.3%) had moderate-to-severe SUD. The mean C-SDS-S score for all stimulant users was 5.84 (SD = 3.25), where the average frequency of stimulant use within the past 30 days was 7.7 days (SD = 10.1). A total of 192 participants reported methamphetamine use (84.6%) and 52 participants reported cocaine use (22.9%). Of the 192 methamphetamine users, only one administered methamphetamine via injection with the rest used via smoking. Of the 52 cocaine users, only four used intranasally with powder cocaine and the rest (92.3%) smoked with crack cocaine. Among those methamphetamine users, 13 (6.8%) did not meet the diagnosis of SUD, 52 (27.1%) had mild SUD and 127 (66.1%) had moderate-to-severe SUD; whereas for cocaine users, 8 (15.4%) had no SUD, 9 (17.3%) had mild and 35 (67.3%) had moderate-to-severe SUD. Overall, the age and gender of the participants, their duration of stimulant use, the total number of non-stimulant drug lifetime use and recent use within the past 30 days were similar across different severities of SUD as compared to those with no SUD. Participants with SUD who used methamphetamine had consistently significantly more frequent use than those without SUD (all p’s < 0.05).

Table 1. Demographics, C-SDS-S scores, frequency of stimulant use, and substance use history for all participants (N=227).
3.2 Validity, reliability, and factor analysis
C-SDS-S demonstrated a weak correlation with the severity of SUD (ρ = 0.292, p <.001) and with the frequency of stimulant use within the past 30 days (ρ = 0.196, p = .003). Subgroup analyses of the C-SDS-S scorings among methamphetamine users showed similar positive correlations with the severity of SUD (ρ = 0.260, p <.001) and the frequency of methamphetamine use (ρ = 0.201, p = .005). However, C-SDS-S scorings among cocaine users was only correlated with the severity of SUD (ρ = 0.356, p = .011) but not the frequency of cocaine use (ρ = 0.144, p = .308). The magnitude of the correlations of C-SDS-S scorings with the degree of severity in SUD suggested that it had better concurrent validity for cocaine than methamphetamine.
The internal consistency of C-SDS-S as measured by the Cronbach’s alpha for all stimulants, methamphetamine alone and cocaine alone were 0.736, 0.738 and 0.744, respectively. Overall, the total score of C-SDS-S has fair test-retest reliability with an ICC of 0.49. Subgroup analyses for methamphetamine and cocaine revealed similar levels of reliability with the corresponding ICCs of 0.52 and 0.50, respectively. For individual items, Item 5 recorded the largest weighted Kappa statistic, followed by Item 2, 4, 3, and 1. Subgroup analyses revealed identical trends among methamphetamine users but not cocaine users, where Item 1 recorded the highest and Item 2 the lowest weighted Kappa statistic (Table 2).
Regarding factor analysis, the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin measures of sampling adequacy for all stimulants, methamphetamine alone and cocaine alone were 0.743, 0.754, and 0.727, respectively. PCA identified one factor for stimulants and for the methamphetamine subgroup, but two factors for the cocaine subgroup. Factor 1 explained roughly 50% of the variance in all stimulant users and methamphetamine users, while Factors 1 and 2 accounted for over 70% of the variance in cocaine users (Table 3). Most items possessed strong factor loading characteristics (> 0.6) except for Item 4 that had weak factor loadings on Factor 1 (0.38-0.55) (Table 4). The C-SDS-S would be more consistent if Item 4 was removed, resulting in Cronbach’s alpha of 0.756, 0.747, and 0.797 for all stimulants, methamphetamine alone and cocaine alone, respectively.
3.3 ROC analysis
The AUC for users with mild SUD was 0.377 (95% CI 0.290 to 0.464), whereas for users with moderate-to-severe SUD was 0.632 (95% CI 0.552 to 0.711) (Figure 1). The cut-off score of ≥ 5 yielded the highest Youden Index of 0.27 with a sensitivity of 71.0% and a specificity of 55.6% (Table 5). It follows that the C-SDS-S had the greatest diagnostic utility for moderate-to-severe SUD but not mild SUD, and stimulant users scoring 5 points or higher on the C-SDS-S would likely be suffering from a moderate-to-severe SUD.
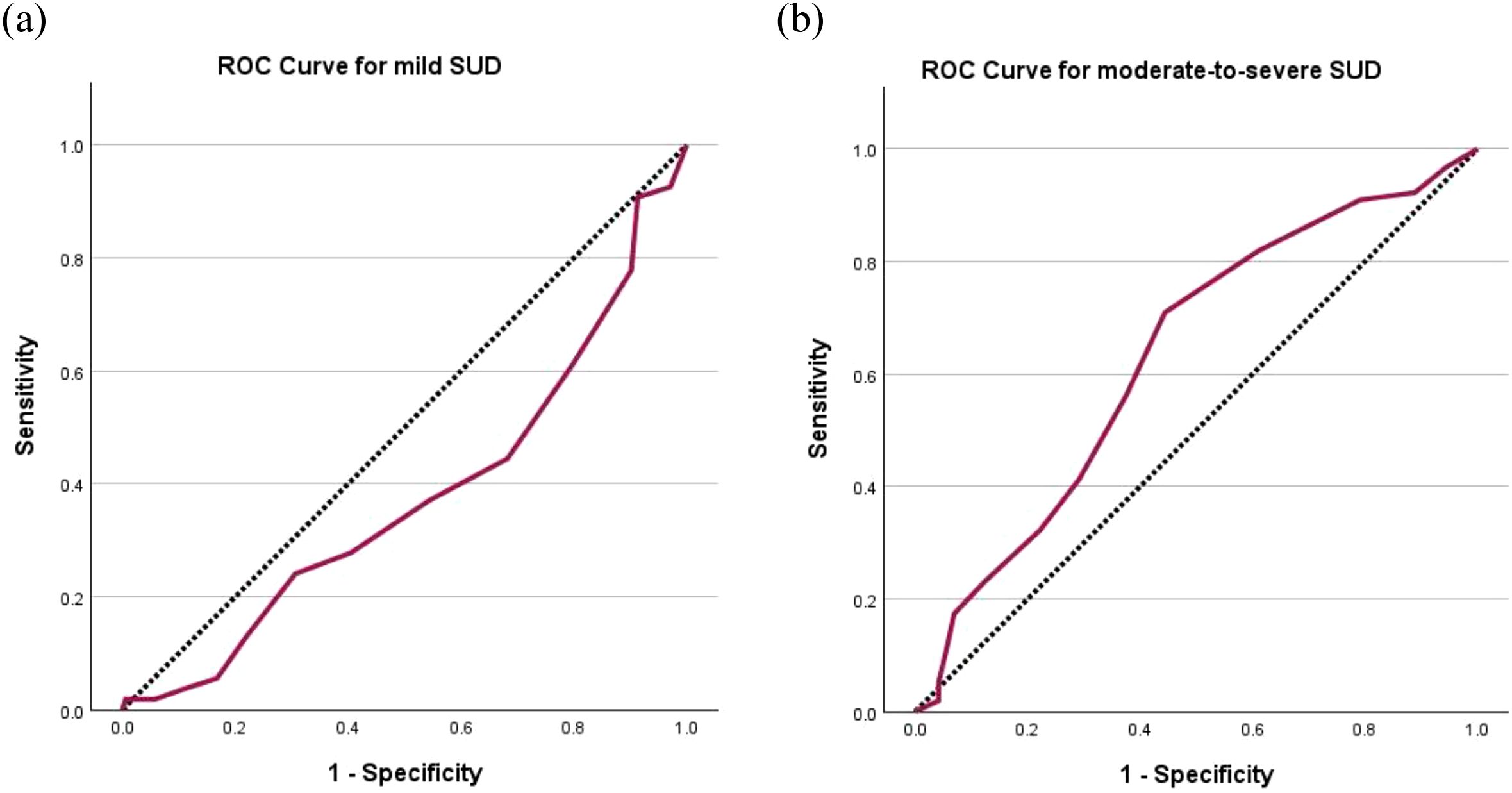
Figure 1. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of C-SDS-S for (a) mild SUD with area under curve (AUC) = 0.377 and (b) moderate-to-severe SUD with AUC = 0.632. The diagonal segments were produced by ties. C-SDS-S, Chinese version of the Severity of Dependence Scale for stimulant; SUD, stimulant use disorder.

Table 5. Criterion validity of C-SDS-S at each successive cut-off score on the optimal discrimination for DSM-5 moderate-to-severe SUD in stimulant users (N=155).
Subgroup analyses demonstrated low AUCs for both mild SUD of methamphetamine (0.401, 95% CI 0.309 to 0.493) and cocaine (0.208, 95% CI 0.060 to 0.356), but those for moderate-to-severe SUD of methamphetamine and cocaine were as high as 0.618 (95% CI 0.533 to 0.703) and 0.712 (95% CI 0.555 to 0.869), respectively (Figure 2). The same cut-off scores of ≥ 5 identified moderate-to-severe SUD for both methamphetamine (sensitivity = 66.9%, specificity = 56.9%, Youden Index = 0.24) and cocaine (sensitivity = 85.7%, specificity = 52.9%, Youden Index = 0.39) (Table 5).
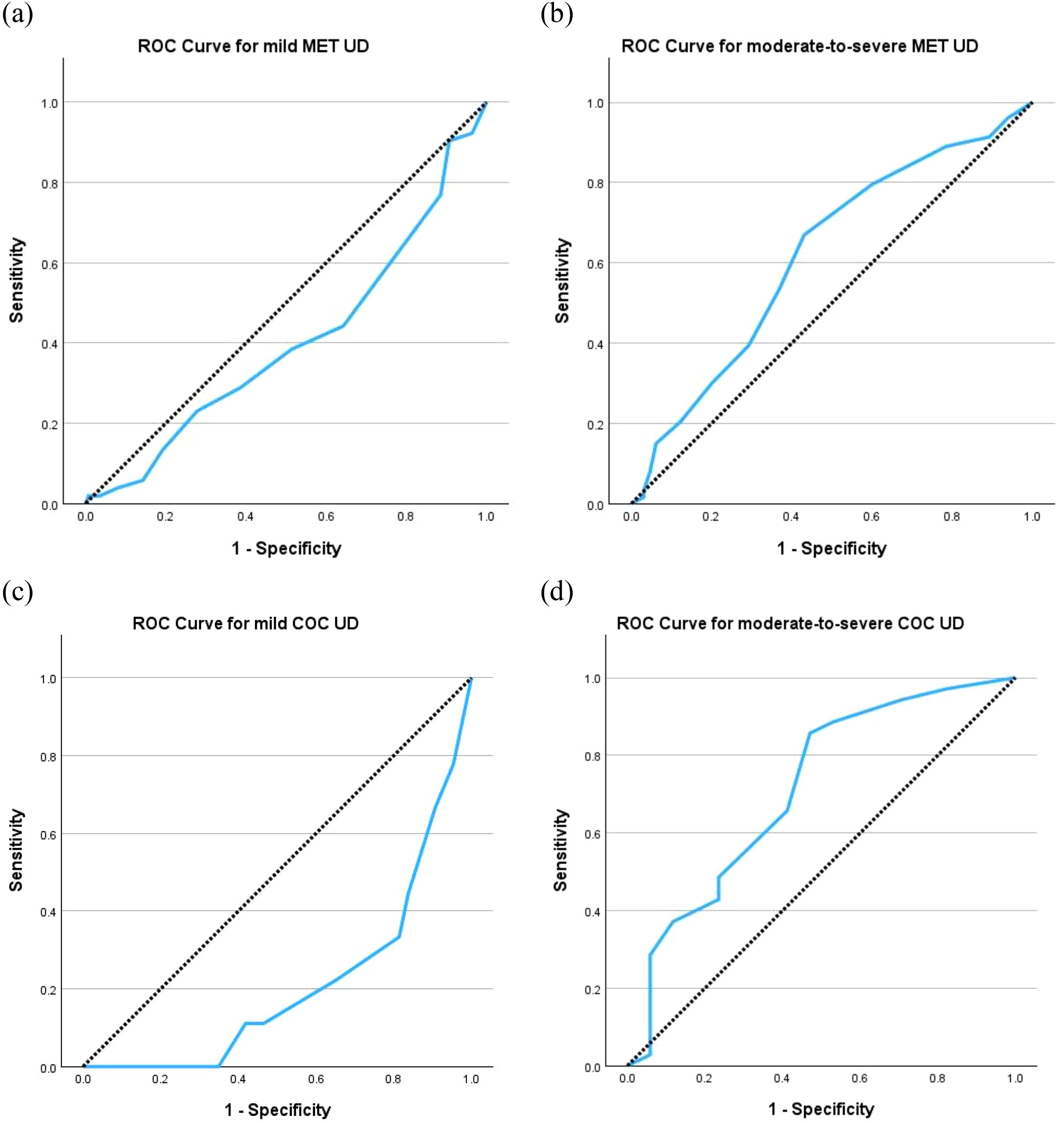
Figure 2. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of C-SDS-S for (a) mild UD for methamphetamine (MET) with area under curve (AUC) = 0.401, (b) moderate-to-severe UD for MET with AUC = 0.618, (c) mild UD for cocaine (COC) with AUC = 0.208, and (d) moderate-to-severe UD for COC with AUC = 0.712. The diagonal segments were produced by ties. C-SDS-S, Chinese version of the Severity of Dependence Scale for stimulant; UD, use disorder.
4 Discussion
The present study explored the validity and reliability of the C-SDS-S as a clinical tool to screen for mild and moderate-to-severe DSM-5 SUD in Chinese-speaking stimulant users. We showed that a higher total score on the C-SDS-S is associated with greater SUD severity and the frequency of stimulant use, especially among methamphetamine users. Overall, a single-factor structure was observed for the C-SDS-S and when used among methamphetamine users, consistent with other studies that demonstrated a one-dimensional structure of the SDS when administered in different languages and for various substances (9, 12, 13, 16, 17, 21, 22, 24, 25). The two-factor structure identified among our cocaine samples who are predominantly crack cocaine users corroborated with the previous study by Ferri et al. (24). Overall, our findings suggest that C-SDS-S may serve as a preliminary screening instrument in selected clinical contexts, particularly for moderate-to-severe stimulant use disorders, although its diagnostic performance remains limited.
Our study also established a cut-off score of five for DSM-5 defined moderate-to-severe SUD, regardless if the stimulant used was methamphetamine or cocaine. These cut-off scores were both higher than those established in Australia and Spain two decades ago, which were four for methamphetamine and three or four for cocaine (15, 19). It follows that the diagnostic utility of SDS is highly contextual. For the same substance, the diagnostic cut-off for the optimal discrimination of SDS-defined dependence might be gender- and ethnic-specific, in which the difference could be as large as 2 points between male and female, and between Westerners and non-Westerners (12). Cabana-Dominguez et al. revealed that cocaine dependence is a highly heritable disorder within the European ancestry, though little is known among the Asian-ancestry cocaine users (26). On the other hand, recent genome wide association studies demonstrated the significant loci for methamphetamine dependence might be different between the European-, African- and Chinese- ancestries (27, 28). Such genetic variabilities could result in different single nucleotide polymorphism-based expression on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activity at the reward circuitry, axonal pruning in hippocampus, and might potentially lead to diverse trajectories in the development of methamphetamine use disorder. These variations suggest that different SDS cut-off scores may be necessary, in particular for different population across ancestries. We did not perform subgroup analyses for male and female participants due to the small number of female participants.
In addition, changes in the diagnostic criteria for substance use disorder might have attributed to the disparity in diagnostic cut-offs across multiple substances. In most validation studies, the 4th edition of the DSM (DSM-IV) was adopted as the “gold standard”. According to DSM-IV, substance abuse and dependence were independently categorized using two separate sets of diagnostic criteria. Under DSM-5, however, substance use disorder was defined using a set of diagnostic criteria primarily adopted from that of DSM-IV abuse and DSM-IV dependence (29). The change from a dichotomous to a continuous diagnostic construct warrants the validation of the C-SDS-S against the DSM-5 criteria to ascertain its criterion validity. Also, similar to our previous work in cannabis (13), we established the diagnostic cut-off on C-SDS for moderate-to-severe SUD but not for mild SUD (13). While the original SDS was developed with a single factor structure under a unidimensional construct for dependence, such single-factor solution might not hold equally valid for non-dependent low-level drug users (30, 31). Therefore, its diagnostic utility in detecting milder states as in abuse or harmful use might be low. Given the clinical significance of timely identification of mild SUD for early intervention, the generalizability of the C-SDS-S in detecting mild SUD warrants further investigation.
While most validation studies on SDS to date identified a unidimensional structure, PCA revealed a two-factor structure for cocaine with Item 4 contributing to the second factor. This is consistent with the validation study of C-SDS in benzodiazepines in Taiwan (20), which also showed the scorings on Item 4 were similar between dependent and non-dependent users. Factor loading for Item 4 is consistently and substantially lower than all other items of the C-SDS-S in the present study, and the internal consistency of the C-SDS-S would improve if Item 4 was removed. Although repeated attempts to quit or reduce stimulant use is one of the diagnostic criteria for DSM-5 SUD, the lower factor loadings of Item 4 suggested that those with stimulant dependence might not have adequate motivation to alter their drug use behavior. Stimulant-dependent users might also hesitate in the prospect of withdrawal symptoms, hence are ambivalent to quit or reduce stimulant use despite its myriad of consequences. In fact, repeated exposure to stimulants reinforces the negative state manifested as craving, withdrawal symptoms, and/or emotional distress (32). This upregulated negative state following prolonged stimulant exposure in dependent users might supersede their desire to quit or reduce stimulant use. Besides, cyclothymic and irritable temperaments have been associated with cocaine and stimulant abuse and heavy uses (33). These temperamental predispositions in stimulant users may heighten their vulnerability to emotional dysregulation during such negative state and contribute to their motivational ambivalence, as reflected by a lower factor loading for Item 4 (“wish to stop”) in the C-SDS-S.
One of the limitations of the present study is the small sample size of cocaine users, which could have attributed to the disparity between the results from the subgroup analyses on cocaine and existing literature, as well as the methamphetamine subgroup and the overall model in the present study. For instance, Item 1 had the lowest test-retest reliability in methamphetamine users and the entire cohort, but was the highest in cocaine users. Among the 101 participants who had repeated C-SDS-S scorings within four weeks, only 16 were cocaine users. Such sample imbalance in particular for the cocaine subgroup may also affect the ROC analysis and the subsequent skewed AUC. All these can inevitably undermine the certainty of the results. As opposed to previous validation studies (9, 11), the small number of cocaine users in the present study might also explain the independence between C-SDS-S scorings and frequency of use within this subgroup where no statistical difference was observed despite showing patterns similar to the methamphetamine subgroup. An early epidemiological study in the United States found that the number of days of stimulant use over the past 12 months was higher in dependent users than those with abuse (34). A different relationship between C-SDS-S scores and frequency of use in cocaine users might be observed if more users could be included. Furthermore, the unique pharmacodynamics of cocaine as a predominant dopamine-reuptake inhibitors as opposed to methamphetamine as a dopamine “releaser”, along with their differing pharmacokinetics, may lead to the distinct use pattern and dependence model specific to cocaine. All these suggest that a single version of C-SDS-S might not fit all stimulant types equally well.
Another limitation of our study is that we were only able to access data in a single locality. Whether the results can be generalized to other Chinese-speaking communities warrants further investigation. Moreover, the cross-sectional design of this study limits the predictive validity of using the C-SDS-S. In addition, our study only assessed the use disorders of methamphetamine and cocaine, both being the predominantly misused stimulants in our locality. Further investigations targeting novel stimulants and psychoactive substances such as khat is warranted.
5 Conclusion
The present study supports the application of the C-SDS-S as a valid and reliable screening instrument for moderate-to-severe SUD in Chinese-speaking stimulant users. A cut-off score of 5 provides optimal discrimination for both methamphetamine and cocaine and should prompt further diagnostic assessments by broad-certified psychiatrists. Additionally, revising Item 4 of the C-SDS-S may enhance its accuracy for screening purposes in Chinese-speaking stimulant users. Notwithstanding its high validity and reliability, we urge the validation of the SDS in accordance with the updated diagnostic criteria defined in DSM-5 to maximize its diagnostic utility in screening for both mild and moderate-to-severe substance use disorders in routine clinical settings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong/Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster (HKU/HA HKW IRB) (UW 23-267). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
AC: Project administration, Data curation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis. WL: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Data curation, Methodology, Validation. CT: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, U. N. World drug report 2024 (2024). Available online at: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/world-drug-report-2024.html (Accessed March 31, 2025).
2. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, U. N. Synthetic Drugs in East and Southeast Asia - Latest developments and challenges. (2023). Available online at: https://www.unodc.org/roseap/uploads/documents/Publications/2023/Synthetic_Drugs_in_East_and_Southeast_Asia_2023.pdf (Accessed March 31, 2025).
3. Conway KP, Compton W, Stinson FS, and Grant BF. Lifetime comorbidity of DSM-IV mood and anxiety disorders and specific drug use disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J Clin Psychiatry. (2006) 67:247–57. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v67n0211
4. Hunt GE, Malhi GS, Cleary M, Lai HM, and Sitharthan T. Comorbidity of bipolar and substance use disorders in national surveys of general populations 1990-2015: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2016) 206:321–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.051
5. Kandel DB, Huang FY, and Davies M. Comorbidity between patterns of substance use dependence and psychiatric syndromes. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2001) 64:233–41. doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(01)00126-0
6. Rounsaville BJ, Anton SF, Carroll K, Budde D, Prusoff BA, and Gawin F. Psychiatric diagnoses of treatment-seeking cocaine abusers. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (1991) 48:43–51. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810250045005
7. Sara G, Burgess P, Harris M, Malhi GS, Whiteford H, and Hall W. Stimulant use disorders: characteristics and comorbidity in an Australian population sample. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. (2012) 46:1173–81. doi: 10.1177/0004867412461057
8. Vergara-Moragues E, Gonzalez-Saiz F, Lozano OM, Betanzos Espinosa P, Fernandez Calderon F, Bilbao-Acebos I, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity in cocaine users treated in therapeutic community: substance-induced versus independent disorders. Psychiatry Res. (2012) 200:734–41. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.07.043
9. Gossop M, Darke S, Griffiths P, Hando J, Powis B, Hall W, et al. The Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS): psychometric properties of the SDS in English and Australian samples of heroin, cocaine and amphetamine users. Addiction. (1995) 90:607–14. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.1995.9056072.x
10. de las Cuevas C, Sanz EJ, de la Fuente JA, Padilla J, and Berenguer JC. The Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) as screening test for benzodiazepine dependence: SDS validation study. Addiction. (2000) 95:245–50. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.2000.95224511.x
11. Gonzalez-Saiz F, Domingo-Salvany A, Barrio G, Sanchez-Niubo A, Brugal MT, de la Fuente L, et al. Severity of dependence scale as a diagnostic tool for heroin and cocaine dependence. Eur Addict Res. (2009) 15:87–93. doi: 10.1159/000189787
12. van der Pol P, Liebregts N, de Graaf R, Korf DJ, van den Brink W, and van Laar M. Reliability and validity of the Severity of Dependence Scale for detecting cannabis dependence in frequent cannabis users. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. (2013) 22:138–43. doi: 10.1002/mpr.1385
13. Chung AKK and Tse CY. Determining the diagnostic cut-off on the Chinese version of severity of dependence scale for cannabis. Front Psychiatry. (2025) 15:1495119. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1495119
14. Iraurgi Castillo I, Gonzalez Saiz F, Lozano Rojas O, Landabaso Vazquez MA, and Jimenez Lerma JM. Estimation of cutoff for the Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) for opiate dependence by ROC analysis. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. (2010) 38:270–7. Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21117001.
15. Kaye S and Darke S. Determining a diagnostic cut-off on the Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) for cocaine dependence. Addiction. (2002) 97:727–31. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00121.x
16. Lawrinson P, Copeland J, Gerber S, and Gilmour S. Determining a cut-off on the Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) for alcohol dependence. Addict Behav. (2007) 32:1474–9. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2006.09.005
17. Martin G, Copeland J, Gates P, and Gilmour S. The Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) in an adolescent population of cannabis users: reliability, validity and diagnostic cut-off. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2006) 83:90–3. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2005.10.014
18. Swift W, Copeland J, and Hall W. Choosing a diagnostic cut-off for cannabis dependence. Addiction. (1998) 93:1681–92. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.1998.931116816.x
19. Topp L and Mattick RP. Choosing a cut-off on the Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) for amphetamine users. Addiction. (1997) 92:839–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1997.tb02953.x
20. Tsai JH, Tang TC, Yeh YC, Yang YH, Yeung TH, Wang SY, et al. The Chinese version of the Severity of Dependence Scale as a screening tool for benzodiazepine dependence in Taiwan. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2012) 28:225–30. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2011.06.023
21. Chen VC, Chen H, Lin TY, Chou HH, Lai TJ, Ferri CP, et al. Severity of heroin dependence in Taiwan: reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS[Ch]). Addict Behav. (2008) 33:1590–3. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2008.06.001
22. Tung CK, Yeung SW, Chiang TP, Xu K, and Lam M. Reliability and validity of the Severity of Dependence Scale in a Chinese sample of treatment-seeking ketamine users. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. (2014) 24:156–64.
23. Narcotics Division H. K. S. A. R. Central registry of drug abuse seventy-third report. (2024). Available online at: https://www.nd.gov.hk/pdf/report/crda_73rd/CRDA_73rd_Report_Full_Version.pdf (Accessed March 31, 2025).
24. Ferri CP, Marsden J, M DEA, Laranjeira RR, and Gossop M. Validity and reliability of the Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) in a Brazilian sample of drug users. Drug Alcohol Rev. (2000) 19:451–5. doi: 10.1080/713659418
25. Ozaki S and Wada K. A validation of the applicability of the Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS) in a nationwide mental hospital survey on substance-related psychiatric disorders. Japanese J Alcohol Stud Drug Depend. (2005) 40:126–36. Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15912744.
26. Cabana-Dominguez J, Shivalikanjli A, Fernandez-Castillo N, and Cormand B. Genome-wide association meta-analysis of cocaine dependence: Shared genetics with comorbid conditions. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2019) 94:109667. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109667
27. Cox J, Sherva R, Wetherill L, Foroud T, Edenberg HJ, Kranzler HR, et al. Genome-wide association study of stimulant dependence. Transl Psychiatry. (2021) 11:363. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01440-5
28. Hao L, Luo T, Dong H, Tang A, and Hao W. CHN2 promoter methylation change may be associated with methamphetamine dependence. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. (2017) 29:357–64. doi: 10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.217100
29. Hasin DS, O’Brien CP, Auriacombe M, Borges G, Bucholz K, Budney A, et al. DSM-5 criteria for substance use disorders: recommendations and rationale. Am J Psychiatry. (2013) 170:834–51. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12060782
30. Helzer JE, Bucholz KK, and Gossop M. A dimensional option for the diagnosis of substance dependence in DSM-V. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. (2007) 16:S24–33. doi: 10.1002/mpr.210
31. Nelson CB, Rehm J, Ustün TB, Grant B, and Chatterji S. Factor structures for DSM-IV substance disorder criteria endorsed by alcohol, cannabis, cocaine and opiate users: results from the WHO reliability and validity study. Addiction. (1999) 94:843–55. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.1999.9468438.x
32. Robinson TE and Berridge KC. The incentive-sensitization theory of addiction 30 years on. Annu Rev Psychol. (2025) 76:29–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-011624-024031
33. Favaretto E, Bedani F, Brancati GE, De Berardis D, Giovannini S, Scarcella L, et al. Synthesising 30 years of clinical experience and scientific insight on affective temperaments in psychiatric disorders: State of the art. J Affect Disord. (2024) 362:406–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.07.011
Keywords: SUD: stimulant use disorder, severity of dependence scale, cocaine, methamphetamine, psychometrics, Chinese-speaking
Citation: Chung AKK, Leung W and Tse CY (2025) Determining the diagnostic cut-off on the Chinese version of severity of dependence scale for DSM-5 stimulant use disorder. Front. Psychiatry 16:1622306. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1622306
Received: 03 May 2025; Accepted: 11 August 2025;
Published: 05 September 2025.
Edited by:
Liana Fattore, CNR Neuroscience Institute (IN), ItalyReviewed by:
Vassilis Martiadis, Asl Napoli 1 Centro, ItalyMichiel Van Kernebeek, Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Belgium
Ana Filošević Vujnović, University of Rijeka, Croatia
Copyright © 2025 Chung, Leung and Tse. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Albert Kar Kin Chung, Y2h1bmdra2FAaGt1Lmhr
 Albert Kar Kin Chung
Albert Kar Kin Chung Welton Leung
Welton Leung

