- 1Clinical Medical of Acupuncture, Moxibustion and Rehabilitation, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
- 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
- 3The First Clinical Medical School, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
Background: Depression causes many negative effects and even death to patients; the burden on society is also heavy in terms of economics. The neuroinflammatory mechanism of acupuncture regulating depression is unclear. Thus, this study evaluated the effect of acupuncture on neuroinflammatory responses in depression animals and provided a clinical reference for depression treatment.
Methods: The Web of Science, Embase, the Cochrane Library, PubMed, CNKI, WanFang, CBM, and VIP databases were searched. The SYRCLE Risk of Bias Tool was used to assess bias in the studies. Meta-analysis was performed using Stata 15.0. The sources of heterogeneity were explored using subgroup analysis, and stability was evaluated using sensitivity analysis. Quality of evidence for outcomes was assessed using GDT.
Results: This study included 25 studies and 466 animals. According to meta-analysis, compared with the control group, acupuncture significantly reduced IL-1β (SMD: −1.62, 95% CI: −1.93, −1.31), IL-6 (SMD: −1.89, 95% CI: −2.51, −1.26), and TNF-α in depression animals (SMD: −2.09, 95% CI: −2.83, −1.34) and improved IL-4 (SMD: 1.01, 95% CI:0.35, 1.67), IL-10 (SMD:0.77, 95% CI:0.26, 1.28), body weight (SMD:1.69, 95% CI: 1.23, 2.15), crossing numbers (SMD: 1.74, 95% CI: 1.31, 2.17), and rearing numbers (SMD: 1.77, 95% CI: 1.16, 2.39).
Conclusion: Acupuncture has the potential to alleviate depression by attenuating neuroinflammatory responses, and the mechanism may be related to modulating the release of inflammatory factors as well as regulating the activation of microglia.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42024534237.
1 Introduction
Depression is a common mental health disorder characterized by a persistently low mood, loss of interest, and reduced ability to carry out daily activities. According to data from the Global Health Data Exchange Platform, 34% of adolescents aged 10–19 worldwide are at risk of developing clinical depression, exceeding the prevalence among those aged 18–25 (1, 2). As a mental illness, depression not only causes negative impacts on patients, including death, but also imposes a significant economic burden on society due to its associated clinical symptoms and medical expenses (3).
Treatment for depression typically involves both psychological and pharmacological approaches. Psychological therapy helps patients learn to cope with stress, change negative thought patterns, and modify unhealthy behavioral habits. Pharmacological treatment typically involves antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), as well as other pharmacological treatments (4). However, these medications require long-term use and may cause side effects such as suicidal thoughts, sexual dysfunction, and metabolic syndrome (5, 6). Therefore, finding safe and natural treatment options for depression is of great importance.
The current mainstream view on the pathogenesis of depression suggests that low levels of neurotransmitters such as 5-HT and norepinephrine, dysfunction of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, impaired immune function, and low levels of endocrine hormones play a key role in the development of depression. In terms of immune function, pro-inflammatory factors (IL-6, IFNs, IL-1β, TNF-α, IFNs, etc.) and anti-inflammatory factors (IL-10, IL-8, etc.) regulate the activation of microglia, leading to the sustained release of a series of inflammatory mediators that affect neurons and neurotransmitters, thereby inducing depressive symptoms in the body (7, 8). This chronic neuroinflammation mechanism is the primary mechanism underlying the development of depression. Chronic stress is a major trigger for the onset of depression and an effective method for preparing animal models of depression. Chronic stress can lead to elevated inflammatory cytokines and can cause depression through multiple pathways, including promoting oxidative stress, inducing neurotoxic effects, and inhibiting neurogenesis (9). Additionally, both clinical studies and animal models of depression have observed immune system activation. Persistently activated inflammatory cytokines can directly affect hippocampal function in the brain and indirectly influence depressive behavior and emotional regulation (10, 11). These findings suggest that inflammatory responses are closely associated with depressive disorders and are present throughout the entire process of disease onset, progression, and outcome (12, 13). However, treatment methods and drugs targeting this key point remain relatively scarce at present.
Acupuncture, as a safe, natural, and traditional treatment method, has therapeutic effects on depression (14), but its specific mechanisms of action remain unclear. It has been demonstrated that acupuncture can effectively improve depressive symptoms such as low mood and suicidal tendencies by regulating inflammatory mediators. Studies (15, 16) have shown that acupuncture reduces the levels of pro-inflammatory factors in the serum of depressed patients. Animal studies (17) have also found that acupuncture can downregulate pro-inflammatory factor levels in the prefrontal cortex of chronically stressed depressed rats and upregulate anti-inflammatory factor levels to alleviate brain inflammation. However, the specific regulatory mechanisms of these studies remain unclear, and there is a lack of systematic reviews of the evidence. Therefore, this study was conducted to evaluate the effects of acupuncture on neuroinflammatory responses in depressed animals, providing a reference for future treatments of depression.
2 Methods
This study has been registered with PROSPERO (CRD42024534237) and also follows systematic reviews and meta-analysis according to the latest PRISMA guidelines (18).
2.1 Search strategy
A combination of subject terms and entry terms were mainly used in the search, and the subject terms were mainly “depression,” “animals,” “acupuncture,” “electroacupuncture”, “MDD (Major depressive disorder)”, “CUMS (Chronic unpredictable mild stress)” and “CRS (Chronic restraint stress)”. Search was limited to August 2025. The language was limited to English and Chinese. The detailed search strategy is presented in Supplementary Table 1.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
The retrieved studies were screened independently by two authors for inclusion and exclusion. Here are the criteria for inclusion (1): depression animals (2); the test group included manual acupuncture (MA) or electroacupuncture (EA) (3); the control group included depression animals without any interventions (4); the outcomes included at least one inflammatory indicator (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-4, IL-10).
2.3 Exclusion criteria
(1) Depression combined with other diseases (2); other acupuncture or other therapies were used in the test group (3); review or clinical trial (4); non-Chinese and English studies.
2.4 Studies screening and data extraction
To resolve disputes, the study was reviewed by two independent researchers, the data were extracted, and a third party cross-checked it. We excluded duplicates first and then read the title after excluding studies that were obviously irrelevant, a further reading of the abstract followed, and then the full text was read in order to determine if it was included. Authors of the original studies were contacted by e-mail in order to obtain information that had not yet been identified but was crucial to the study. We extracted data on (1) first author’s name and year of publication (2), basic characteristics of depression animals (3), depression modeling methodology (4), intervention characteristics (5), outcomes (the primary outcome is inflammation, and the secondary outcomes are body weight and behaviors). If only graphical data were provided, GetData Graph Digitizer 2.26 was used to digitize the graphs.
2.5 Risk of bias
We assessed the risk of bias using 10 items of the SYRCLE Risk of Bias Tool, which were rated as “low risk,” “unclear,” and “high risk” (19). Differences in assessments were resolved through discussion between two evaluators, and a third investigator could be consulted if needed for judgment.
2.6 Statistics
Statistical analysis was performed with Stata 15.0. All outcomes variables were continuous. Since the units are not consistent, we used the standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) as the effect indicator, and the difference between the data was statistically significant when P < 0.05. The heterogeneity was determined by I²; if I² ≥ 50%, the heterogeneity was more obvious and the data were analyzed using the random effects model; and if I² < 50%, the heterogeneity was less and the fixed effects model was used to analyze the data. To identify heterogeneity sources, a subgroup analysis was conducted based on different acupuncture methods and modeling in the test group and the random effects model was used to test the differences in effect size between subgroups. Sensitivity analysis was performed using the “one-by-one method” to ensure the robustness of the results. The publication bias was checked using funnel plots and Egger’s test when the number of studies exceeded 10.
2.7 Certainty assessment
In accordance with the grading guidelines, the evidence quality for the primary outcome was assessed using the GDT software. Several factors were taken into account, including study design domain, risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and other considerations such as publication bias, effect size, and potential confounders. Based on the evidence quality, four categories were defined: high, moderate, low, and very low.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search process
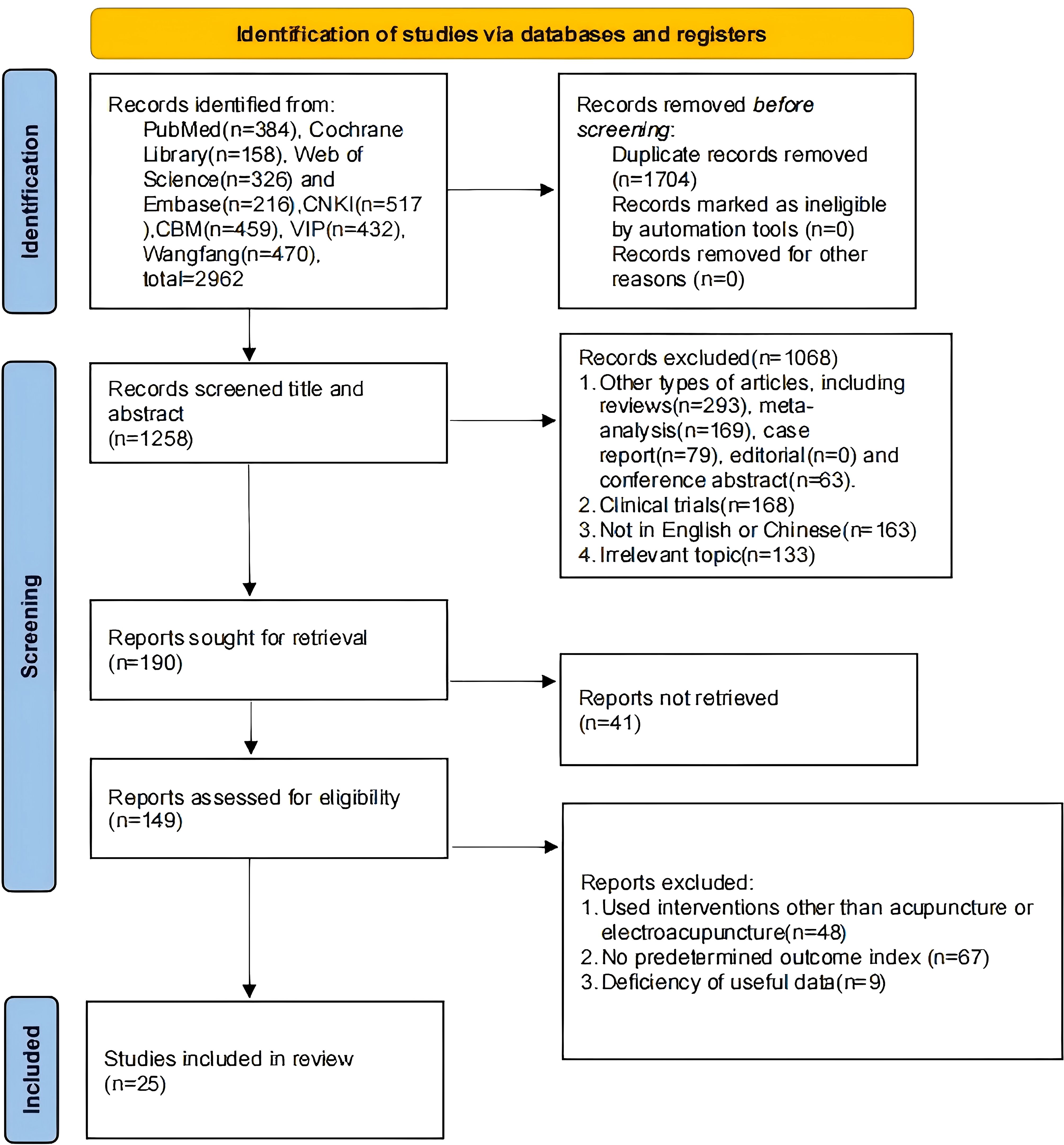
We retrieved 2,962 studies, of which 1,704 duplicates were removed after import into Endnote, and 1,068 studies were eliminated by reading the titles and abstracts, of which 604 were other types of studies, 168 were clinical trials, 163 were non-Chinese and English, and 133 were irrelevant topics. Then, 41 studies were excluded without retrieving the report. By reading the full text, 48 studies using interventions other than MA or EA were excluded, 67 studies without predetermined outcomes, and 9 studies lacking useful data. A total of 25 studies were finally included (17, 20–43) (Figure 1).
3.2 Basic characteristics of the studies
A total of 25 studies and 466 animals were included in this studies, with 233 animals in each of the control and test groups (Supplementary Table 2).
In terms of species and modeling methods, there were four species of rats: 19 SD rats, 3 C57BL/6 mice, 2 Wistar rats, and 1 ICR mouse (Figure 2A). There were 2 modeling methods: 22 rats used CUMS and 3 used CRS (Figure 2B).
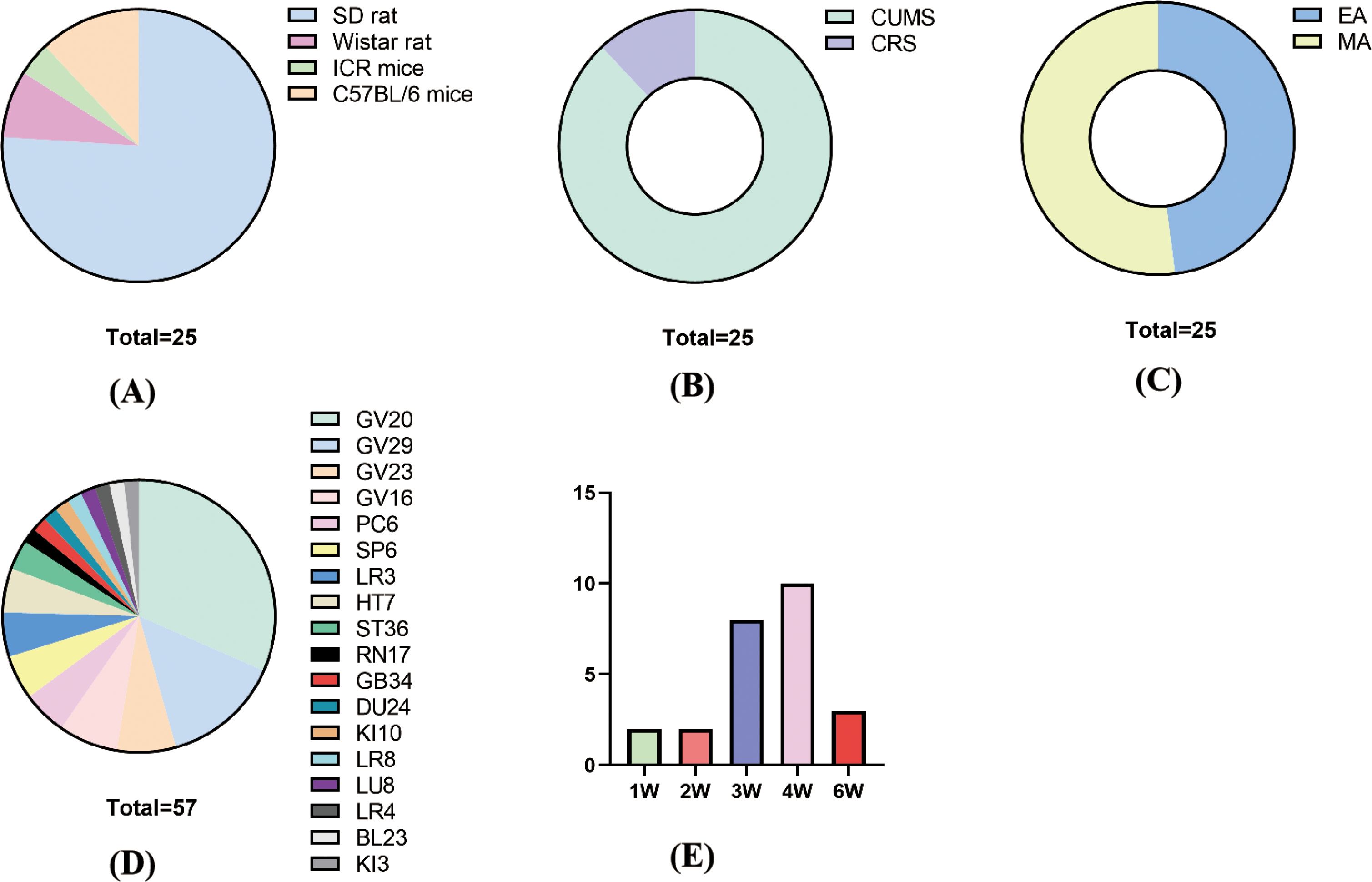
Figure 2. Basic characteristics. (A) Animal species; (B) molding methods; (C) acupuncture methods; (D) acupuncture points; (F) treatment time and course.
For acupuncture methods, 12 studies used EA and 13 studies used MA (Figure 2C). For acupuncture points, the frequency of acupoint use, from largest to smallest, was GV20 (18) GV29 (8) GV23 (4) GV16 (4) PC6 (3) HT7 (3) SP6 (3) LR3 (3) ST36 (2), and the rest of the acupuncture points were used once. In the combination of acupoints, GV20+GC29 and GV23+GV26 were more frequently used (Figure 2D).
For treatment time and course, each treatment time was 10–30 min, with 30 min as the main duration. The course of treatment was 1–6 weeks, with 4 weeks as the main duration (Figure 2E).
For parameters of EA, the frequency used for EA was mainly 2 Hz, and the wave pattern was mainly sparse-dense wave.
Inflammatory indicators (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-4, and IL-10) were used as main outcomes; as secondary outcomes, body weight and open field test.
3.3 Risk of bias
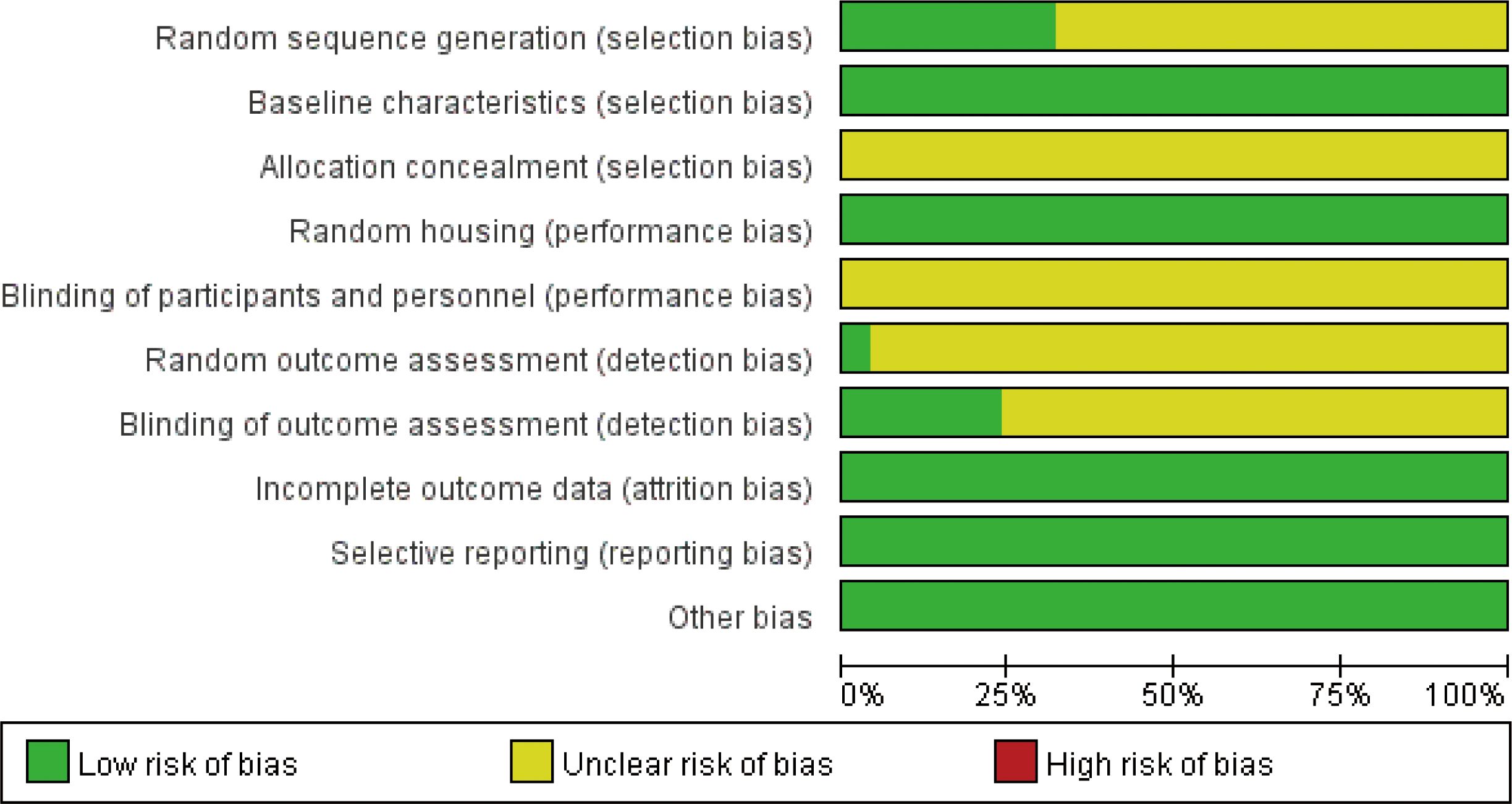
All studies were RCTs; eight studies (22, 25, 27, 29, 30, 35, 40, 41) used the method of random number table, and in the remaining studies, there was no explicit description of the random assignment method. All studies found no significant differences between baseline characteristics of the animals; therefore, they were considered low risk. All studies were referred to the manner in which the animals were allocated concealment. All studies were low risk as there were no significant differences in the animal breeding conditions. Due to the specificity of the intervention, the test group could not use well-implemented blinding. In the randomized outcome assessment, one study (22) used the lottery method for outcome assessment. Six studies (17, 22, 23, 27, 30, 36) used blinding when evaluating the outcome, and the rest were explicitly mentioned. All studies reported complete results without selective reporting, and other sources of bias were not found (Figure 3, Supplementary Figure 1).
3.4 Meta-analysis
3.4.1 IL-1β
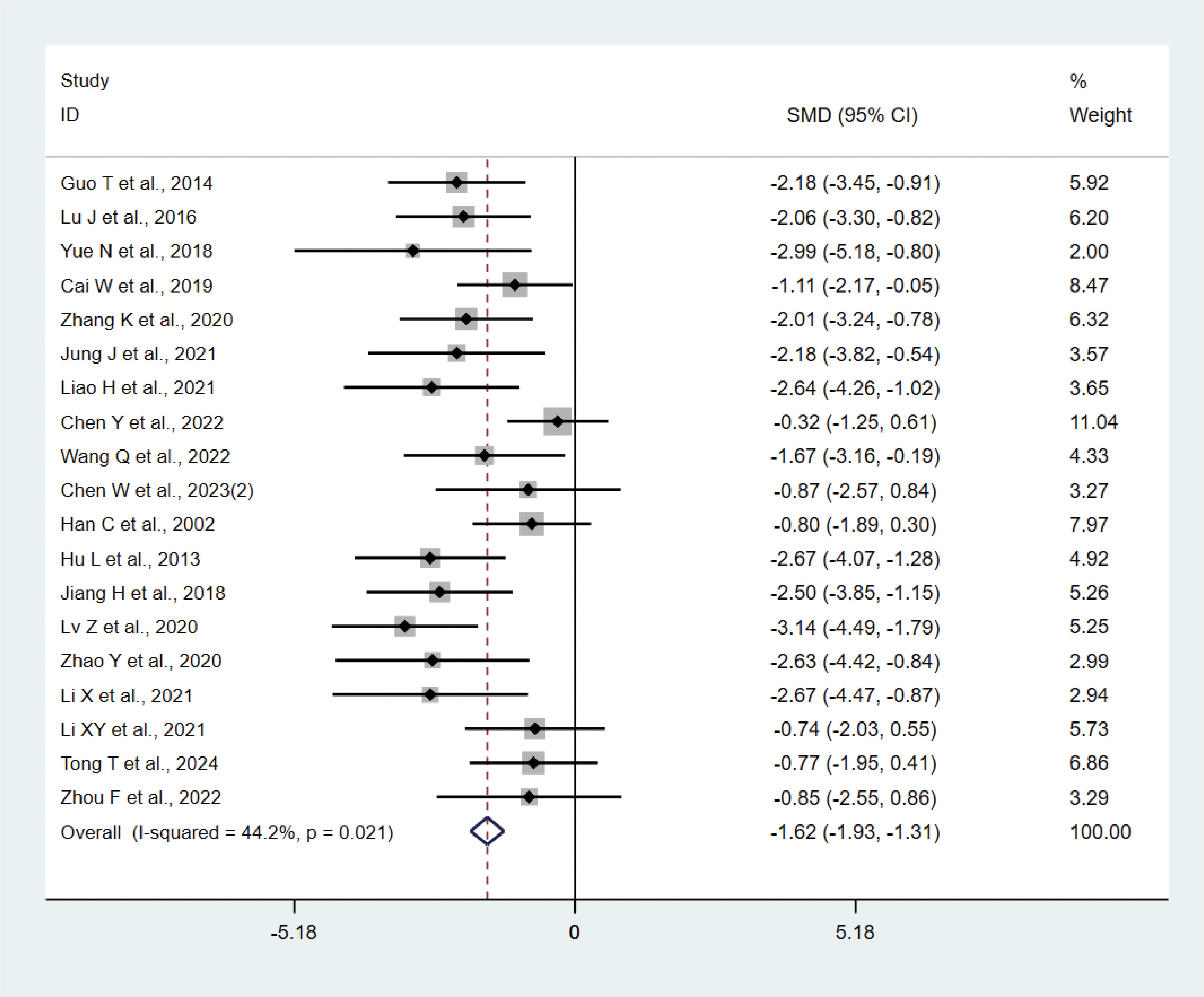
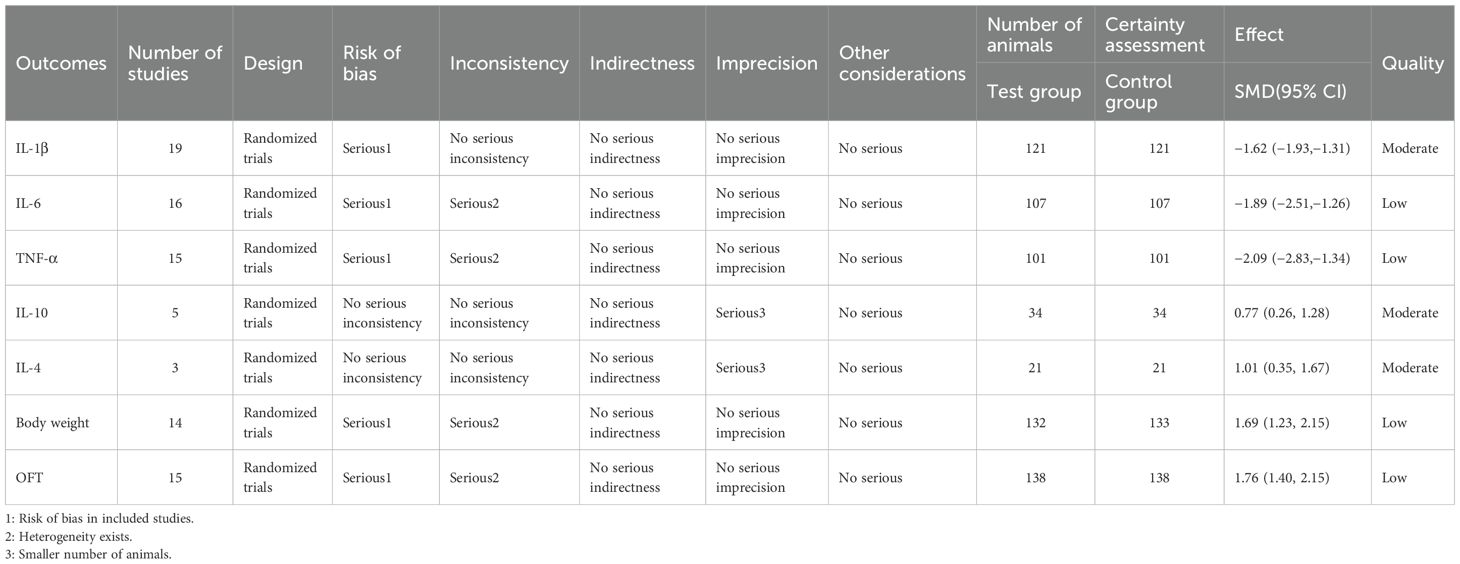
A total of 19 studies (17, 20–22, 24, 25, 31, 36, 39, 43) with 242 animals involved IL-1β. Heterogeneity test showed that I²=44.2%, suggesting less heterogeneity, which was analyzed using a fixed-effect model. Meta-analysis showed that IL-1β was significantly lower in the test group than in the control group (SMD: −1.62, 95% CI: −1.93, −1.31), indicating that depression animals treated with acupuncture had significantly lower levels of IL-1β (P<0.05) (Figure 4). Sensitivity analysis showed stable results of meta-analysis (Supplementary Figure 2).
3.4.2 IL-6
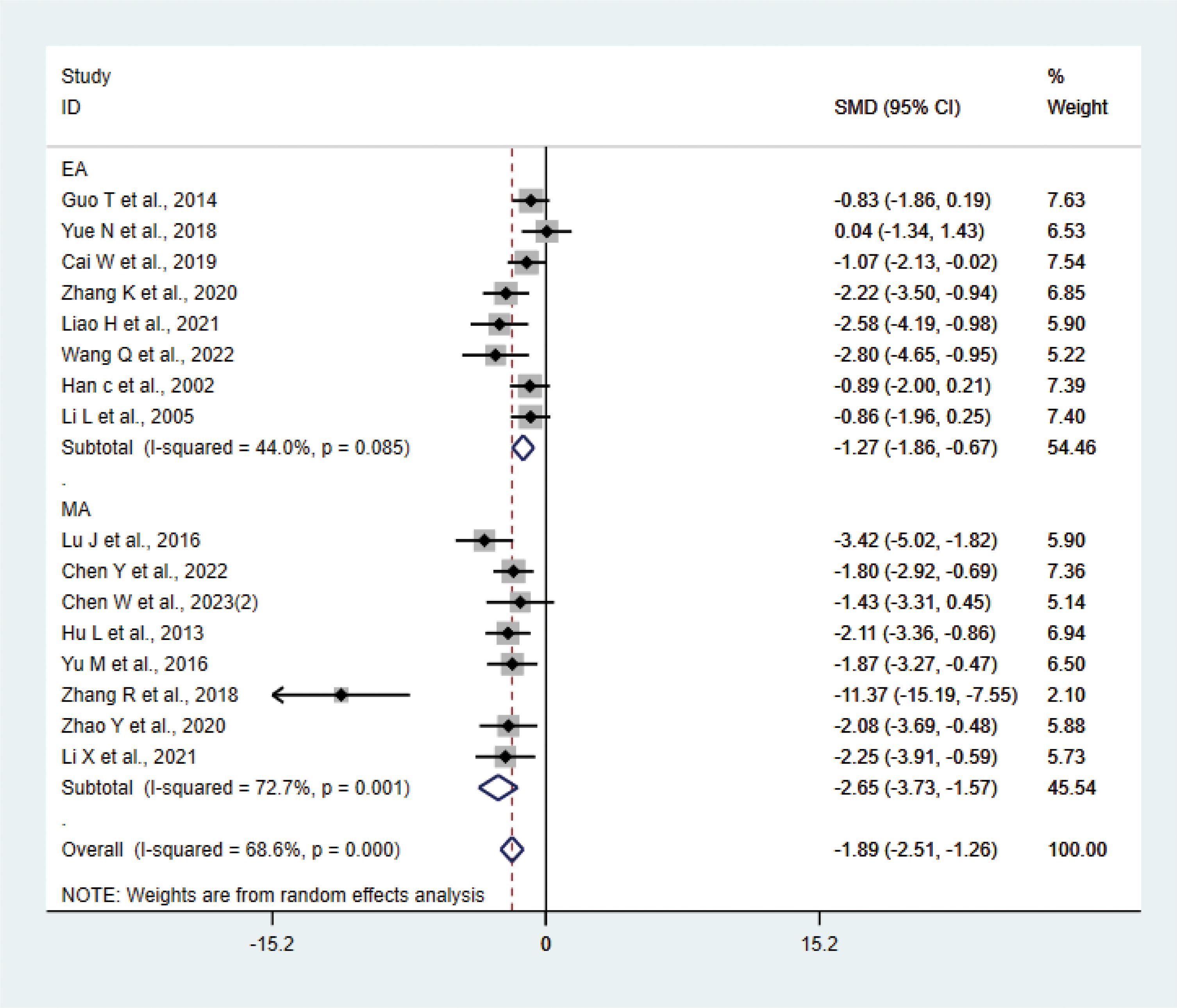
A total of 16 studies (17, 20, 21, 23, 27–29, 31, 33, 34, 36–38, 40–42) with 214 animals involved IL-6. Heterogeneity test showed that I²=68.6% suggesting moderate heterogeneity, which was analyzed using a random-effects model. Meta-analysis showed that IL-6 was significantly lower in the test group compared with the control group (SMD: −1.89, 95% CI: −2.51, −1.26), indicating that depression animals treated with acupuncture had significantly lower levels of IL-6 (P<0.05) (Figure 5). Sensitivity analysis showed stable results of meta-analysis (Supplementary Figure 3). We performed subgroup meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods to investigate heterogeneity (MA EA). Subgroup analysis showed that IL-6 was lower in the EA group than the control group (SMD: −1.27, 95% CI: −1.86, −0.67, I²=44.0%), and IL-6 was lower in the MA than in the control group (SMD: −2.65, 95% CI: −3.73, −1.57, I²=72.7%), P<0.05. The heterogeneity was decreased compared with the previous one, suggesting that the acupuncture methods might be the source of heterogeneity.
3.4.3 TNF-α
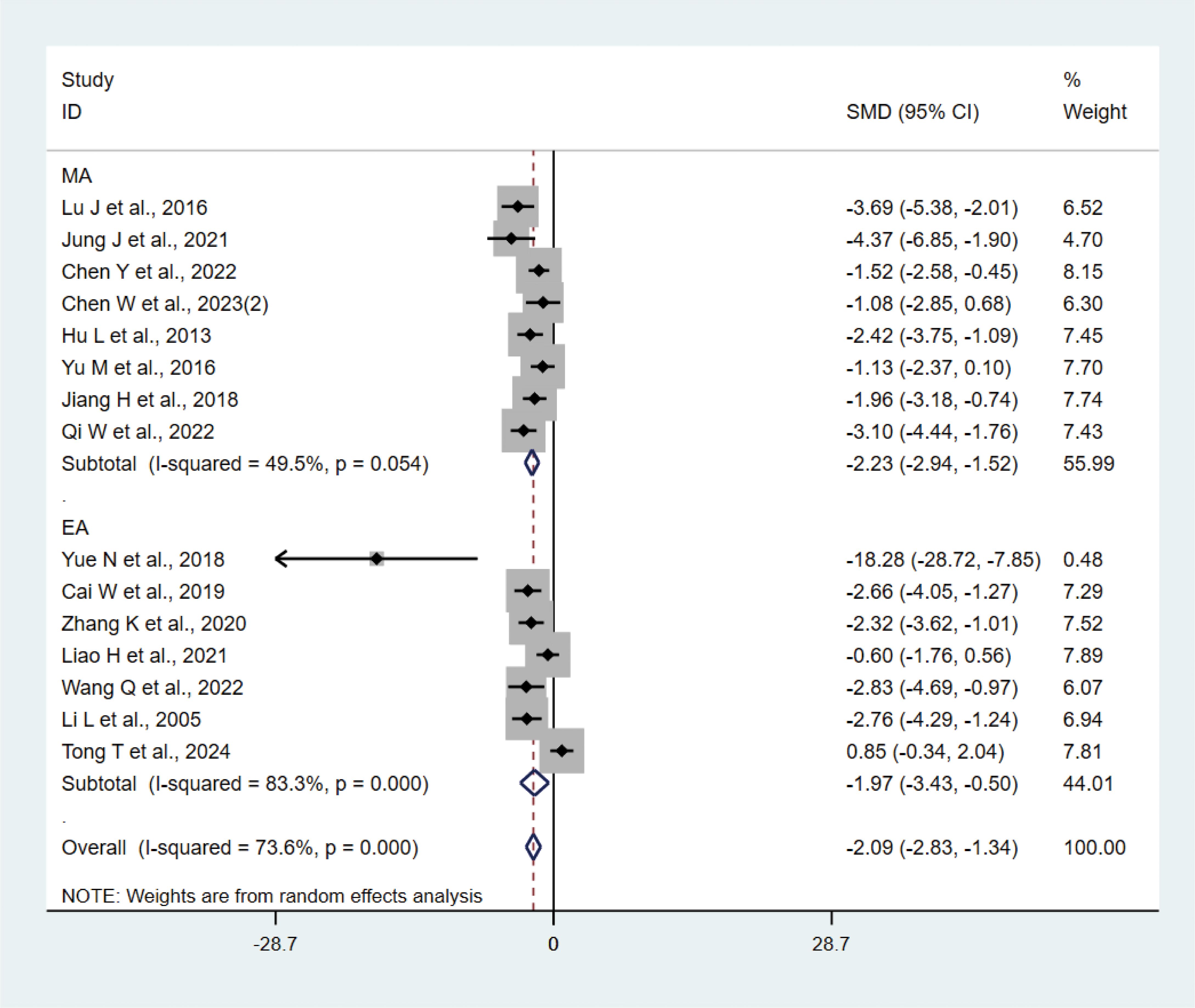
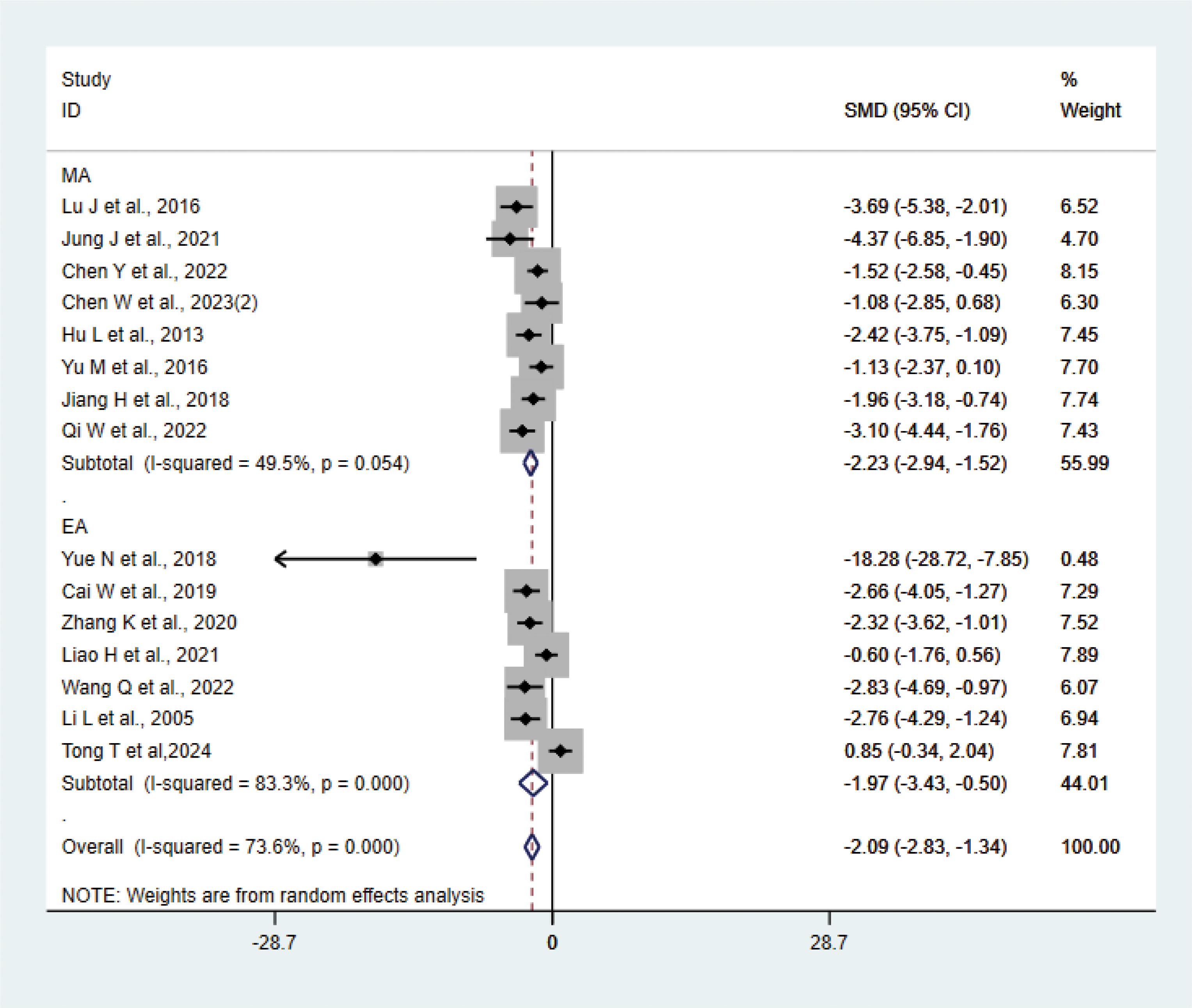
A total of 15 studies (21–23, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 38, 40–42) with 202 animals involved TNF-α. Heterogeneity test showed that I²=73.6%, suggesting moderate heterogeneity, which was analyzed using a random-effects model. Meta-analysis showed that TNF-α was lower in the test group compared with the control group (SMD: −2.09, 95% CI: −2.83, −1.34), indicating that depression animals treated with acupuncture had significantly lower levels of TNF-α (P<0.05) (Figure 6). Sensitivity analyses showed stable results from the meta-analysis (Supplementary Figure 4). To explore the source of heterogeneity, we performed subgroup meta-analysis of the different acupuncture methods (MA EA), and the results of the subgroup analysis showed that the MA had lower TNF-α than the control group (SMD: −2.23, 95% CI: −2.94, −1.52, I²=49.5%) and lower TNF-α in the EA than the control group (SMD: −1.97, 95% CI: −3.43, −0.50, I²=83.3%), P<0.05, with a decrease in heterogeneity compared with the previous one, suggesting that the acupuncture method may be the source of heterogeneity.
3.4.4 IL-10
Five studies (17, 22, 25, 35, 37) with 68 animals involved IL-10. Heterogeneity test showed that I²=49.8%, suggesting less heterogeneity, which was analyzed using a fixed effect model. Meta-analysis showed that IL-10 was higher in the test group compared with the control group (SMD: 0.77, 95% CI:0.26, 1.28), indicating that depression animals treated with acupuncture had significantly higher levels of IL-10 (P < 0.05) (Figure 7). Sensitivity analysis showed stable results of meta-analysis (Supplementary Figure 5).
3.4.5 IL-4
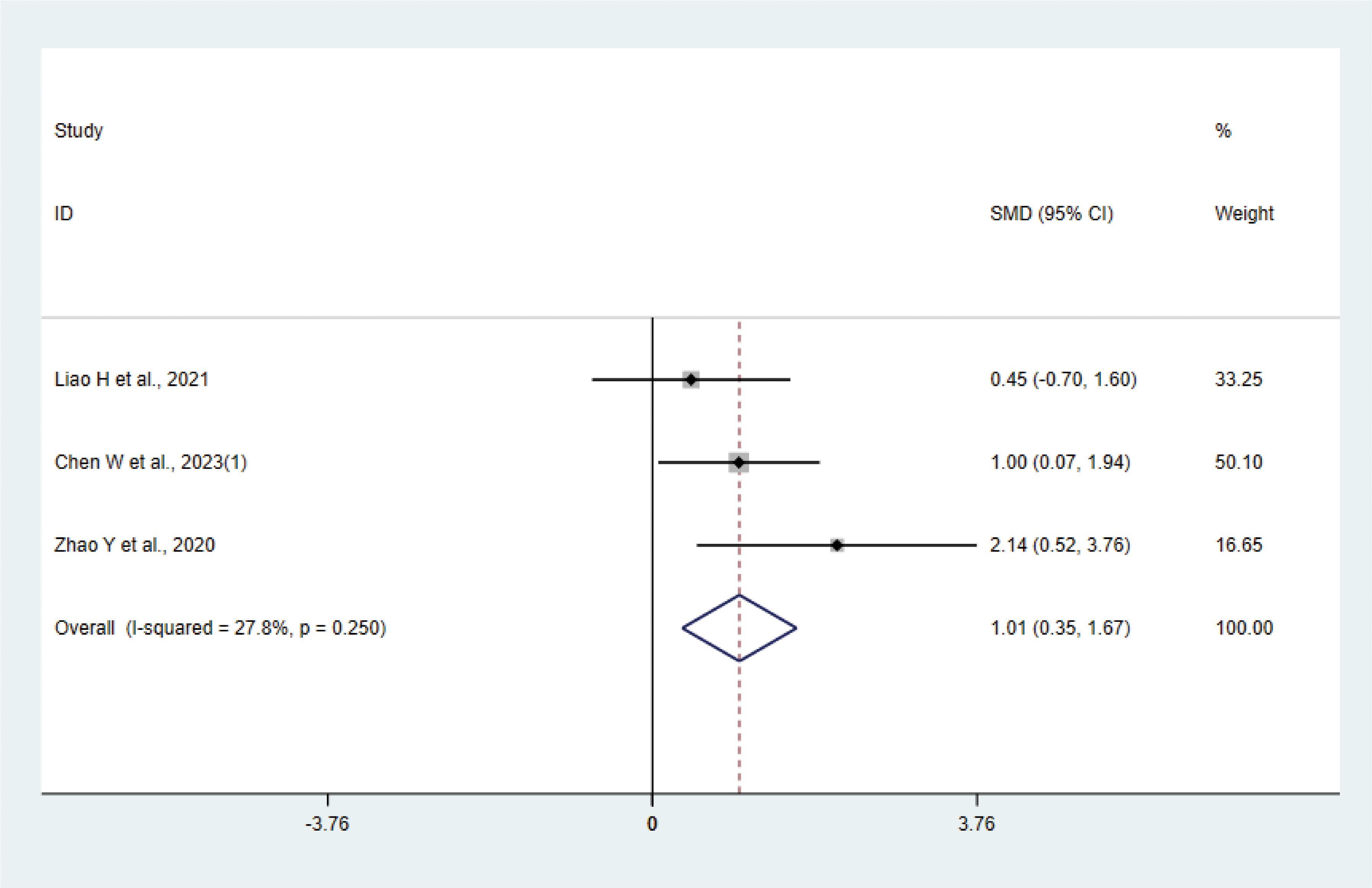
Three studies (17, 31, 37) with 42 animals involved IL-4. Heterogeneity test showed that I²=27.8% suggesting low heterogeneity, which was analyzed using a fixed effect model. Meta-analysis showed that IL-4 was higher in the test group than in the control group (SMD: 1.01, 95% CI: 0.35, 1.67), indicating that depression animals treated with acupuncture had significantly higher levels of IL-4 (P < 0.05) (Figure 8). Sensitivity analysis showed stable results of meta-analysis (Supplementary Figure 6).
3.4.6 Body weight
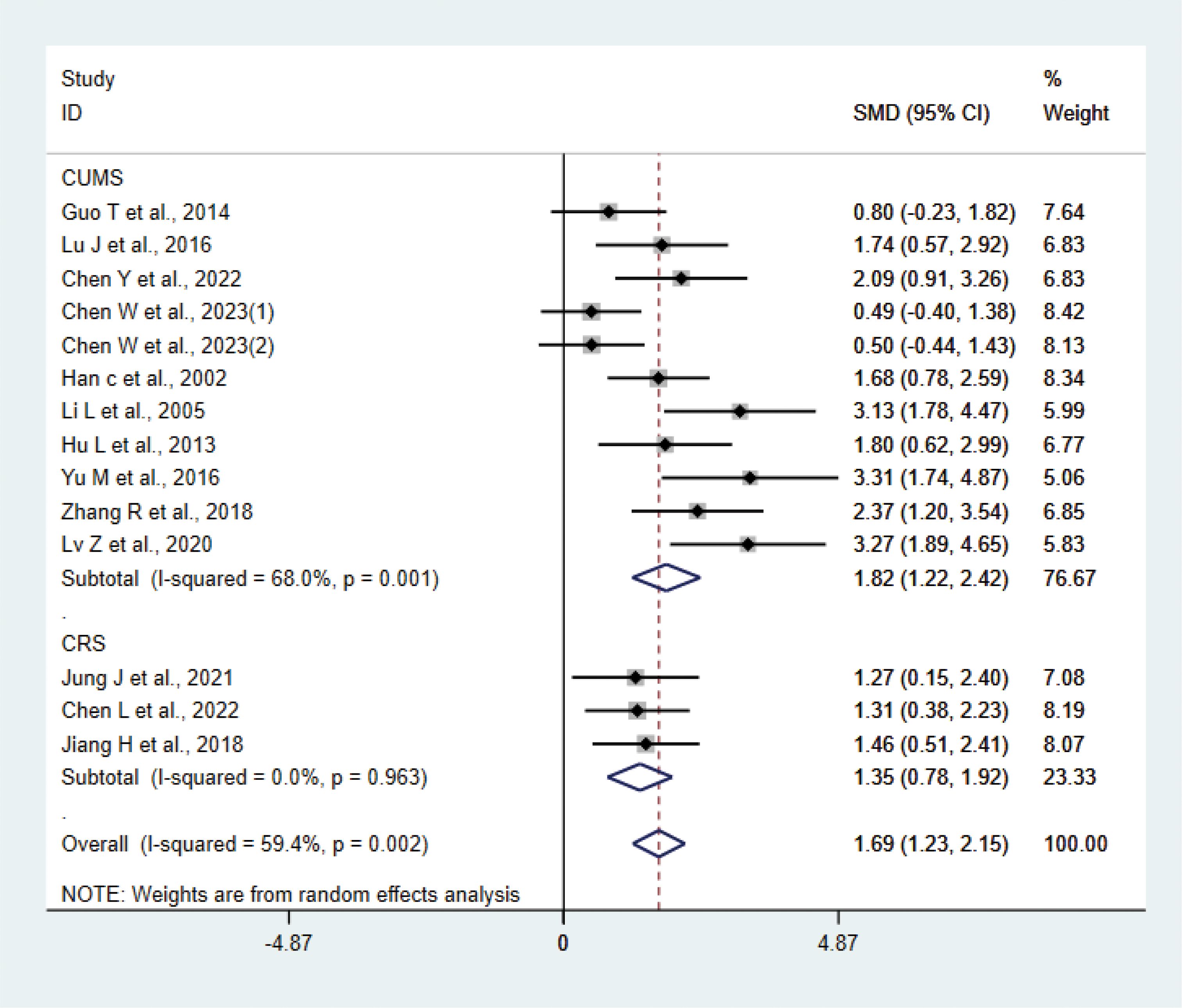
A total of 14 studies (20–23, 25–28, 30, 31, 33, 34, 38, 39) with 265 animals involved body weight. The test for heterogeneity showed that I² = 59.4%, suggesting moderate heterogeneity, and was analyzed using a random effects model. Meta-analysis showed that the test group had heavier body weights than the control group (SMD: 1.69, 95% CI: 1.23, 2.15), suggesting that acupuncture significantly increased body weights of the depression animals (P < 0.05) (Figure 9). The results of the meta-analysis were stable according to sensitivity analysis (Supplementary Figure 7). To explore the source of heterogeneity, we performed subgroup meta-analysis of different modeling methods (CUMS CRS), and according to subgroup analysis, the test group in CRS was heavier than the control group in CRS (SMD: 1.35, 95% CI: 0.78, 1.92, I²=0.0%), and the test group was heavier than the control group in CUMS (SMD: 1.82, 95% CI: 1.22, 2.42, I²=68.0%), P<0.05. Heterogeneity was reduced compared with before, suggesting that the modeling methods may be the source of heterogeneity.
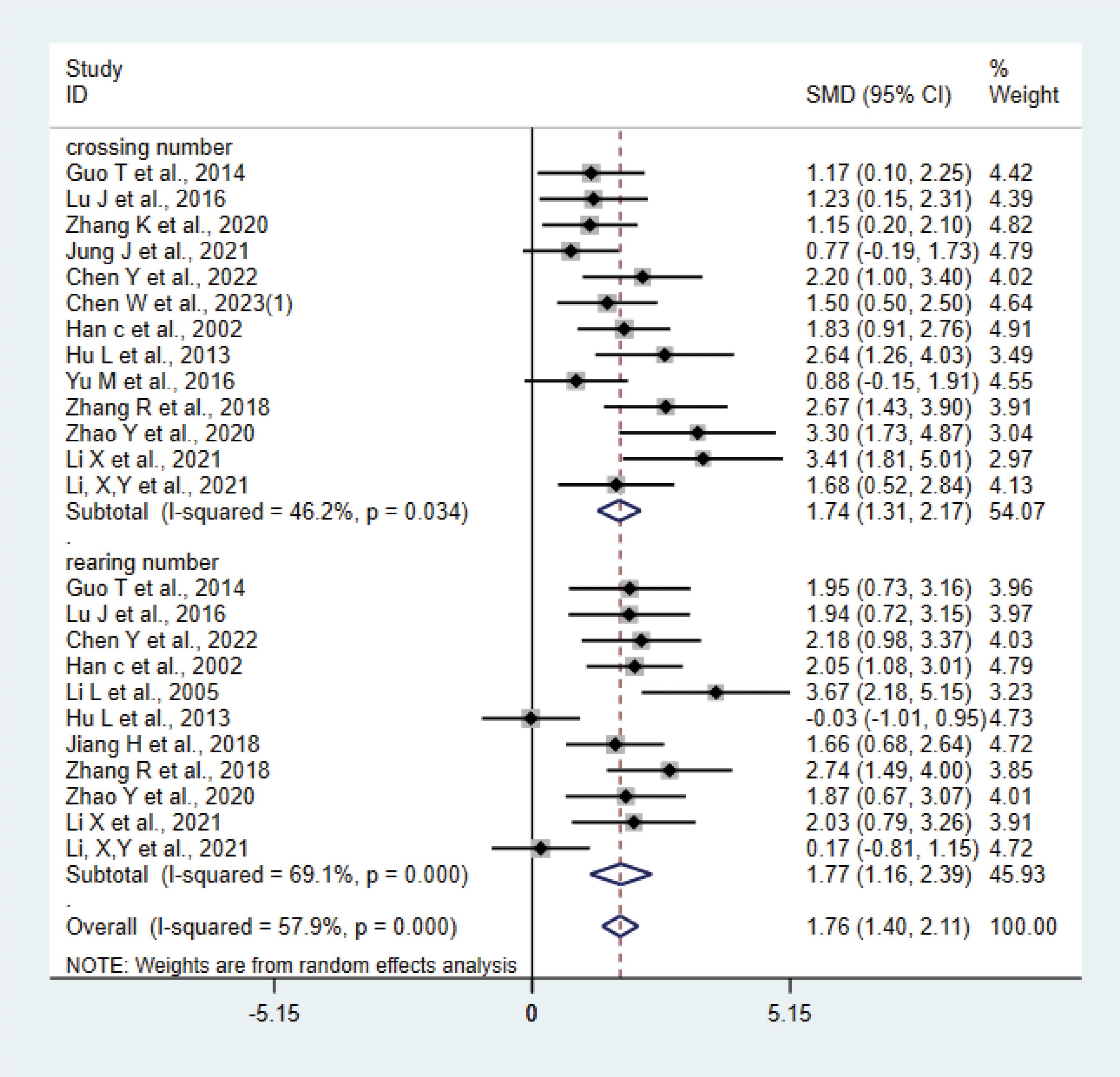
3.4.7 OFT
A total of 15 studies (17, 20–24, 27, 28, 31, 33–36, 38, 42) with 276 animals were involved in OFT. The test for heterogeneity showed that I²=57.9% suggesting moderate heterogeneity, which was analyzed using a random-effects model. Based on the meta-analysis, it was found that the test group had a greater number of crossing numbers than the control group (SMD: 1.74, 95% CI: 1.31,2.17), indicating that acupuncture significantly increased the crossing number of depression animals (P<0.05) (Figure 10). The rearing numbers of the test group were more than those of the control group (SMD: 1.77, 95% CI: 1.16,2.39), indicating that acupuncture significantly increased the rearing number of depression animals (P < 0.05) (Figure 10). Sensitivity analysis showed stable results of meta-analysis (Supplementary Figure 8). Subgroup analysis of different acupuncture methods was conducted to explore the source of heterogeneity in rearing numbers (MA EA) (Supplementary Figure 9); as a result of subgroup meta-analysis, the EA rearing numbers were higher than those of the control group (SMD: 2.48, 95% CI: 1.77,3.18, I²=27.3%), and the MA rearing numbers were higher than those of the control group (SMD: 1.35, 95% CI: 0.63, 2.07, I²=66.5%), P<0.05. The heterogeneity was decreased compared with the previous one, suggesting that the acupuncture method may be the source of heterogeneity.
3.5 Publication bias
Inverted funnel plots and Egger’s test were used to detect publication bias for outcomes involving more than 10 studies. According to the Egger’s test, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, body weight, and OFT showed a statistically significant publication bias (P<0.05), which indicated that these studies might have been biased by publication (Supplementary Figure 10). To assess the impact of publication bias (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, body weight, and OFT) on the results, we applied the trimming and filling method. The results showed that the robustness of body weight and OFT was not significantly affected by publication bias (Supplementary Table 3). After trimming and filling, no studies were added to IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. This may be because Egger’s test assumes publication bias as the sole cause of funnel plot asymmetry, overlooking other potential factors (differences in study design, sample selection bias). The trimming and filling method assumes that funnel chart asymmetry stems from publication bias, with missing studies symmetrically distributed around existing research. If actual asymmetry arises from causes other than publication bias, this method may fail to effectively fill gaps, resulting in no additional studies being incorporated.
3.6 Certainty assessment
Evidence quality was evaluated using GRADE (Table 1). Due to bias risks, IL-1 was assessed moderate; IL-6, TNF-α, body weight, and OFT were assessed as low due to the presence of risk of bias and heterogeneity. IL-10 and IL-4 were assessed as moderate because of small sample sizes.
4 Discussion
The meta-analysis showed that acupuncture significantly reduced IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels; increased IL-4 and IL-10 levels; improved depressive-like behavior (OFT); and increased body weight in depressive animal models compared with the control group.
Statistical analysis revealed that most of the inflammatory markers measured in the included studies were derived from brain tissues such as the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala, with a small portion originating from serum. Some studies have shown that both serum inflammatory factors and central nervous system inflammatory factors are important contributors to depression (44), and serum inflammatory factors can disrupt the blood–brain barrier, entering the central nervous system and inducing or exacerbating inflammatory responses (45). Therefore, investigating changes in central nervous system inflammatory responses during depression is highly meaningful. Based on previous research, a meta-analysis validated the efficacy and mechanisms of acupuncture in depressive animal models, suggesting that acupuncture may treat depression by reducing central nervous system inflammation (46); however, the study did not comprehensively examine all relevant inflammatory markers nor did it delve deeply into their underlying mechanisms. Therefore, we explored a more comprehensive set of neuroinflammatory markers of depression animal models to analyze the effects of acupuncture on neuroinflammation and its potential mechanisms.
4.1 Possible mechanisms
Our findings indicate that acupuncture can reduce TNF-α and IL-1β levels while increasing IL-10 and IL-4 levels in depression animals. Recent studies have shown that excessive activation of microglia leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines is considered an important mechanism in depression (47). Based on the different inflammatory mediators they secrete, microglia can be classified into two polarized phenotypes: M1-type (pro-inflammatory) and M2-type (anti-inflammatory). In the M1 phenotype, activated microglia secrete superoxide free radicals and pro-inflammatory factors (such as TNF-α, IL-1β), thereby damaging neurons; in the M2 phenotype, upon activation, MG secretes anti-inflammatory factors (such as IL-10 and IL-4) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), which promote the repair of neuronal damage (48). Previous studies have reported that microglia in the brains of depression patients exhibit abnormal activation, with significantly elevated expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α (49).
An increasing number of studies have confirmed that acupuncture can inhibit the excessive activation of microglia during the depression process, reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines, and increase anti-inflammatory factor levels, thereby alleviating depression-like behavior in animal models. Studies have found that acupuncture at the Baihui and Yintang acupoints can reduce Iba-1 (a microglial marker) levels of CUMS-induced depressed rats and decrease the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6, thereby inhibiting microglial activation and alleviating depressive-like behavior (24). This is consistent with our findings on the effects of acupuncture on pro-inflammatory factors. Electroacupuncture can also regulate the activation of microglia in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, reducing the expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β genes (50). Another study (51) showed that acupuncture can upregulate the expression of Arg-1 protein (a marker of M2-type microglia) in perimenopausal depressive rats, promote the polarization of microglia toward the M2 type, and simultaneously increase the levels of IL-4 and IL-10, thereby improving depressive-like behavior. Acupuncture can also downregulate the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 in the hippocampus of CUMS-induced depressed rats and increase the level of the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 (52). This is consistent with our findings on the effects of acupuncture on anti-inflammatory factors.
Our findings indicate that acupuncture reduces TNF-α and IL-1β levels in the brain tissue of depression animals; it may be due to the fact that acupuncture can regulate inflammatory cell signaling pathways. Specifically, acupuncture can alleviate central inflammatory damage by regulating the activation of inflammatory cell signaling pathways and reducing the release of inflammatory factors. Several studies support this view: Electroacupuncture can inhibit the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in the hippocampus of CUMS rats, reducing the expression of IL-6, IL-1β, IL-18, and TNF-α (40); acupuncture can reduce the expression of TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB, and TNF-α proteins in the hippocampus of rats subjected to chronic restraint stress, alleviating depressive behavior (53); and acupuncture can also reduce the expression of HMGB-1, Iba-1, and TNF-α in the hippocampus of rats with chronic restraint stress-induced depression, alleviating HMGB-1-mediated neuroinflammation (30). Additionally, Yue et al. (41) found that electroacupuncture intervention in CUMS rats led to reduced expression of P2X7R, IL-1β, TNF-α, and Iba-1 proteins in the hippocampus, suggesting that electroacupuncture may alleviate neuroinflammation through P2X7R-mediated signaling pathways and exert antidepressant effects.
In summary, acupuncture influences the polarization of microglia, inhibits the polarization of MG toward the M1 type, reduces the release of pro-inflammatory factors, promotes the polarization of MG toward the M2 type, increases the release of anti-inflammatory factors, and dynamically rebalances inflammatory cytokines, thereby alleviating central inflammatory responses and protecting neurons. This may be a potential mechanism for acupuncture treatment of depression (Figure 11).
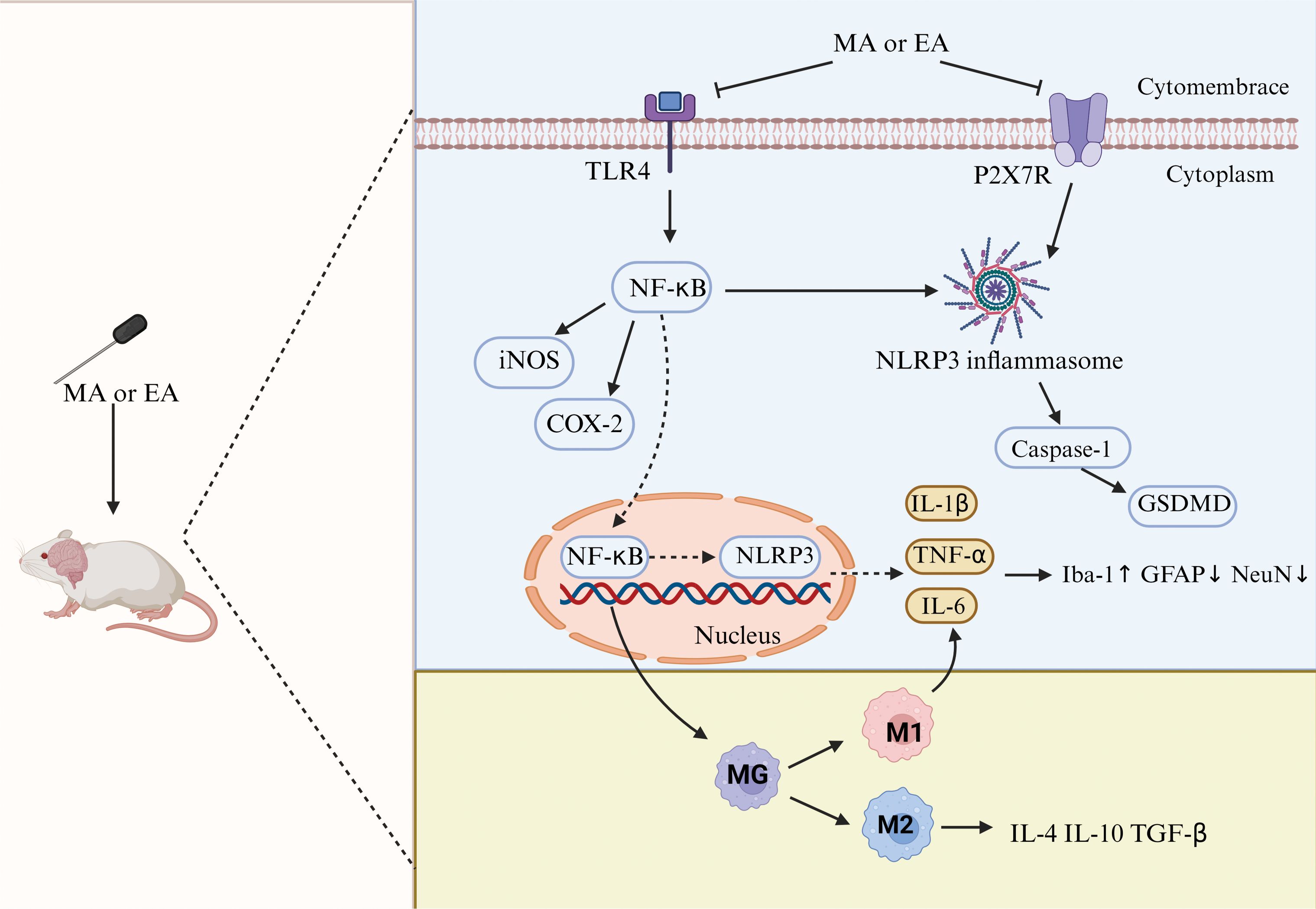
Figure 11. Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of antidepression in acupuncture. TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; NLRP3, NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; GSDMD, gasdermin D; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; NeuN, neuron-specific nuclear protein.
4.2 Clinical application
In this study, we also paid attention to the frequency of the use of different acupoints and EA parameters as well as their effects on inflammatory factors. In terms of the pattern of acupoints selection, we found that GV20 and GV29 were used with the highest frequency, which is consistent with the previous pattern of point selection in the treatment of depression with acupuncture (54). Study found that hippocampal NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β protein expression was significantly reduced in depressed mice after EA GV20. The mechanism may be to downregulate the pro-inflammatory factors by inhibiting the activity of hippocampal NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles, thus reducing the neuroinflammatory responses (55). This suggests that GV20 is quite advantageous in central anti-inflammation; it may be the therapeutic mechanism of CV20 for depression. It is worth noting that we found SP6 and PC6 were also used with high frequency, which is different from the conventional acupoints for depression. It has been shown that acupuncture of SP6 can reduce muscle edema in mice of inflammatory muscle pain model, whereas this phenomenon was not found in IL-10 knockout mice, which is possible that acupuncture promotes IL-10 release and the transformation of macrophages from type M1 to type M2 (56, 57). The above studies have shown that SP6 is also effective in anti-inflammation, and its mechanism may be related to promoting the release of IL-10 to reduce inflammation in the central system. Therefore, in clinical practice, in addition to the conventional matching points of GV20 and GC29, the combination of SP6 may have a better therapeutic effect on the alleviation of depression. In terms of EA parameters, the sparse and dense waves of 2 Hz/100 Hz are used most frequently. Previous studies have found that stimulation of ST36 and ST25 with a frequency of 2 Hz/100 Hz with sparse waves can reduce the expression of local inflammatory factors in the intestinal tissues through the vagus nerve or the sympathetic nerve, respectively, and promote the restoration of gastrointestinal dynamics (58, 59). This suggests that the sparse-dense wave and 2 Hz/100 Hz may be more advantageous in reducing the inflammatory response. Therefore, in the treatment of depression, this frequency may be more effective at reducing neuroinflammatory responses. Furthermore, we have incorporated both EA and MA interventions, with research (60) suggesting that these may possess distinct molecular mechanisms in antidepressant treatment; for instance, EA may tend to alleviate depression by modulating macrophage polarization, whereas MA may tend to alleviate depression by regulating inflammatory pathways. Therefore, caution is warranted when extrapolating these findings to clinical practice. Future studies should compare them as separate interventions to elucidate their respective unique therapeutic mechanisms.
4.3 Limitations
(1) None of the included studies mentioned whether concealed grouping was performed, and none of them explicitly described the blinding method administered by the experimental researchers and animal keepers, which may have an impact on the evaluation of the behavioral outcomes (2); the sample sizes of the indexes about anti-inflammatory factors, such as IL-4 and IL-10, are relatively small, which may have a small-sample effect (3); due to the language limitation, we only included Chinese and English publications, and it was not possible to fully include all the relevant studies.
5 Conclusion
Acupuncture may alleviate depression by attenuating neuroinflammatory responses; its mechanism may be related to regulating the activation of microglia and inflammatory factors. For validation of this conclusion, more high-quality, large-sample, multi-mechanism studies are needed in the future.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
DN: Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. JZ: Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. RQ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft. YH: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Software. ML: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. LD: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 82305383), National TCM Inheritance and Innovation Center Scientific Research Special Youth Project (No. 2022QN06), The Ordinary University Innovation Young Talent Project of Guangdong Province (2023KQNCX017), Scientific Research project of Guangdong Provincial Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine (20241088). The funding source had no role in the design, execution, analysis, data interpretation, or decision to present the results of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1624648/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Park LT and Zarate CA Jr. Depression in the primary care setting. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:559–68. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1712493
2. Shorey S, Ng ED, and Wong CHJ. Global prevalence of depression and elevated depressive symptoms among adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Psychol. (2022) 61:287–305. doi: 10.1111/bjc.12333
4. Gonda X, Petschner P, Eszlari N, Baksa D, Edes A, Antal P, et al. Genetic variants in major depressive disorder: From pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol Ther. (2019) 194:22–43. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.09.002
5. Gibbons RD, Brown CH, Hur K, Marcus SM, Bhaumik DK, and Mann JJ. Relationship between antidepressants and suicide attempts: an analysis of the Veterans Health Administration data sets. Am J Psychiatry. (2007) 164:1044–9. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2007.164.7.1044
6. Reichenpfader U, Gartlehner G, Morgan LC, Greenblatt A, Nussbaumer B, Hansen RA, et al. Sexual dysfunction associated with second-generation antidepressants in patients with major depressive disorder: results from a systematic review with network meta-analysis. Drug Saf. (2014) 37:19–31. doi: 10.1007/s40264-013-0129-4
7. Pan Y, Chen XY, Zhang QY, and Kong LD. Corrigendum to “Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates IL-1beta-related inflammation in prefrontal cortex of depressive rats” [Brain Behav. Immun 41 (2014) 90-100]. Brain Behav Immun. (2021) 97:455. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.08.221
8. Wang YL, Han QQ, Gong WQ, Pan DH, Wang LZ, Hu W, et al. Microglial activation mediates chronic mild stress-induced depressive- and anxiety-like behavior in adult rats. J Neuroinflammation. (2018) 15:21. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1054-3
9. Frost JL and Schafer DP. Microglia: architects of the developing nervous system. Trends Cell Biol. (2016) 26:587–97. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.02.006
10. Yang S, Yi L, Xia X, Chen X, Hou X, Zhang L, et al. Transcriptome comparative analysis of amygdala-hippocampus in depression: A rat model induced by chronic unpredicta ble mild stress (CUMS). J Affect Disord. (2023) 334:258–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.04.074
11. Barnes J, Mondelli V, and Pariante CM. Genetic contributions of inflammation to depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2017) 42:81–98. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.169
12. Nettis MA and Pariante CM. Is there neuroinflammation in depression? Understanding the link between the brain and the peripheral immune system in depression. Int Rev Neurobiol. (2020) 152:23–40. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.12.004
13. Xu G, Lei H, Huang L, Xiao Q, Huang B, Zhou Z, et al. The dose-effect association between acupuncture sessions and its effects on major depressive disorder: A meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. J Affect Disord. (2022) 310:318–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.04.155
14. Yang NN, Lin LL, Li YJ, Li HP, Cao Y, Tan CX, et al. Potential mechanisms and clinical effectiveness of acupuncture in depression. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2022) 20:738–50. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210609162809
15. Song C, Halbreich U, Han C, Leonard BE, and Luo H. Imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and between Th1 and Th2 cytokines in depressed patients: the effect of electroacupuncture or fluoxetine treatment. Pharmacopsychiatry. (2009) 42:182–8. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1202263
16. Ma F, Cao G, Lu L, Zhu Y, Li W, and Chen L. Electroacupuncture versus Escitalopram for mild to moderate Post-Stroke Depression: A randomized non-inferiority trial. Front Psychiatry. (2024) 15:1332107. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1332107
17. Zhao Y. Effect of acupuncture on inflammatory cytokines and microglia in the prefrontal cortex of depressed rats. Beijing, China: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (2020). doi: 10.26973/d.cnki.gbjzu.2020.000574
18. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
19. Hooijmans CR, Rovers MM, de Vries RB, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, and Langendam MW. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-43
20. Han C. Clinical and experimental study of electroacupncture for depression. Beijing, China: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (2002).
21. Hu L. Study of the effect of acupuncture on serum and brain inflammatory cytokines in chronic stress depressed rats. Beijing, China: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (2013).
22. Jiang HL. Anti-inflammatory effector mechanism of immune/inflammatory activation of acupuncture on hippocampal TLR4 signaling pathway/NLRP 3 inflammasome-induced activation in CRS rats. Beijing, China: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (2018).
23. Li LP. Study on the central regulatory mechanism of acupuncture in the treatment of depression. Heilongjiang, China: Heilongjiang University Of Chinese Medicine (2005).
24. Li XY, Wang HM, Zhao Y, Li C, Lu J, Wu JH, et al. Effect of acupuncture on microglia activation in prefrontal cortex of chronic stress-induced depression rats. Acupuncture Res. (2021) 46:52–7. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200886
25. Lv ZQ. Effect of rat depressive behavior and βCaMKII GluR 1 protein content and their gene expression in the bridle nucleus. Shanxi, China: Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine (2020). doi: 10.27820/d.cnki.gszxy.2020.000105
26. Qi W, Li L, Cao R, Jiang Y, Li T, Wang FC, et al. The influence of zhenjingAnshen acupuncture on inflammPARLatory factors in depression model mice. Lishizhen Med Materia Med Res. (2022) 33:745–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2022.03.69
27. Yu M. “Effect of acupuncture on the cAMP-PKA-CREB pathway in the prefrontal cortex of depression model rats. Beijing, China: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (2016).
28. Zhang R. “Effect of “depression prescription” on the expression of serum IL-1 β, IL-6 and TSH in depressed rats. Shanxi, China: Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine (2018).
29. Cai W, Ma W, Wang GT, Li YJ, and Shen WD. Antidepressant, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects of electroacupuncture through sonic hedgehog-signaling pathway in a rat model of poststroke depression. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2019) 15:1403–11. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S205033
30. Chen L, Jiang H, Bao T, Wang Y, Meng H, Sun Y, et al. Acupuncture ameliorates depressive behaviors by modulating the expression of hippocampal iba-1 and HMGB1 in rats exposed to chronic restraint stress. Front Psychiatry. (2022) 13:903004. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.903004
31. Chen W, Chen Y, Aslam MS, Shen J, Tong T, Yan S, et al. The effect of acupuncture on lateral habenular nucleus and intestinal microflora in depression model rats. Behav Brain Res. (2023) 455:114627. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114627
32. Chen W, Chen Y, Cheng W, Li P, Shen J, Tong T, et al. Acupuncture exerts preventive effects in rats of chronic unpredicta ble mild stress: The involvement of inflammation in amygdala and brain-spleen axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2023) 646:86–95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.01.046
33. Chen Y, Hao C, Chen W, Cheng W, Li P, Shen J, et al. Anti-depressant effects of acupuncture: The insights from NLRP3 mediated pyroptosis and inflammation. Neurosci Lett. (2022) 785:136787. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2022.136787
34. Guo T, Guo Z, Yang X, Sun L, Wang S, Yingge A, et al. The alterations of IL-1Beta, IL-6, and TGF-beta levels in hippocampal CA3 region of chronic restraint stress rats after electroacupuncture (EA) pretreatment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2014) 2014:369158. doi: 10.1155/2014/369158
35. Jung J, Lee SM, Lee MJ, Ryu JS, Song JH, Lee JE, et al. Lipidomics reveals that acupuncture modulates the lipid metabolism and inflammatory interaction in a mouse model of depression. Brain Behav Immun. (2021) 94:424–36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.02.003
36. Li X, Wang H, Li C, Wu J, Lu J, Guo JY, et al. Acupuncture inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the prefrontal cortex of a chronic stress rat model of depression. Anat Rec (Hoboken). (2021) 304:2470–9. doi: 10.1002/ar.24778
37. Liao HY and Lin YW. Electroacupuncture attenuates chronic inflammatory pain and depression comorbidity through transient receptor potential V1 in the brain. Am J Chin Med. (2021) 49:1417–35. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X2150066X
38. Lu J, Shao RH, Hu L, Tu Y, and Guo JY. Potential antiinflammatory effects of acupuncture in a chronic stress model of depression in rats. Neurosci Lett. (2016) 618:31–8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.02.040
39. Tong T, Hao C, Shen J, Liu S, Yan S, Aslam MS, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates chronic unpredicta ble mild stress-induced depression-like behavior and cognitive impairment through suppressing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in rats. Brain Res Bull. (2024) 206:110838. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.110838
40. Wang Q, Bi H, Huang H, Wang Y, Gong L, Qi N, et al. Electroacupuncture prevents the depression-like behavior by inhibiting the NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammatory pathway in hippocampus of mice subjected to chronic mild stress. Neuropsychobiology. (2022) 81:237–45. doi: 10.1159/000521185
41. Yue N, Li B, Yang L, Han QQ, Huang HJ, Wang YL, et al. Electro-acupuncture alleviates chronic unpredicta ble stress-induced depressive- and anxiety-like behavior and hippocampal neuroinflammation in rat model of depression. Front Mol Neurosci. (2018) 11:149. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00149
42. Zhang K, Liu R, Gao Y, Ma W, and Shen W. Electroacupuncture relieves LPS-induced depression-like behaviour in rats through IDO-mediated tryptophan-degrading pathway. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2020) 16:2257–66. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S274778
43. Zhou F, Jiang H, Kong N, Lin J, Zhang F, Mai T, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuated anxiety and depression-like behavior via inhibition of hippocampal inflammatory response and metabolic disorders in TNBS-induced IBD rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:8295580. doi: 10.1155/2022/8295580
44. Shu Y, Xiaolei L, Licong Y, Shaochuan Z, Tianhao B, and Wenlin T. Relationship between depression and serum inflammatory factors and its therapeutic research progress. Med Herald. (2025) 44:906–11. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1004-0781.2025.06.011
45. de Vries HE, Blom-Roosemalen MC, van Oosten M, de Boer AG, van Berkel TJ, Breimer DD, et al. The influence of cytokines on the integrity of the blood-brain barrier in vitro. J Neuroimmunol. (1996) 64:37–43. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(95)00148-4
46. Huang Y, Chen W, Li X, Tan T, Wang T, Qiu S, et al. Efficacy and mechanism of acupuncture in animal models of depressive-like behaviors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurosci. (2024) 18:1330594. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1330594
47. Fenn AM, Gensel JC, Huang Y, Popovich PG, Lifshitz J, and Godbout JP. Immune activation promotes depression 1 month after diffuse brain injury: a role for primed microglia. Biol Psychiatry. (2014) 76:575–84. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.10.014
48. Zhang A, Liu Y, Xu H, Zhang Z, Wang X, Yuan L, et al. CCL17 exerts neuroprotection through activation of CCR4/mTORC2 axis in microglia after subarachnoid haemorrhage in rats. Stroke Vasc Neurol. (2022) 8:4–16. doi: 10.1136/svn-2022-001659
49. Kobayashi N, Shinagawa S, Nagata T, Shigeta M, and Kondo K. Suppressors of cytokine signaling are decreased in major depressive disorder patients. J Pers Med. (2022) 12. doi: 10.3390/jpm12071040
50. Huang WT, Li DD, Bing L, Chen H, and Li W. Effects of electroacupuncture on microglia activation and learning memory capacity in the subgranular region of dentate gyrus of hippocampus in depressed rats. Chin J Lab Anim Science. (2022) 30:513–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2022.04.009
51. Shi LQ, Lu R, Qin L, Chen HY, Mei L, and Xin Z. Effects of acupuncture and moxibustion therapy on the polarization of microglia in rats with PDD by regulating the “kidney-brain-tianjie” system. Liaoning J Chin Med. (2024) 51:170–5 + 223-5. doi: 10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2024.10.044
52. Wei GW, Wu JH, Wang HM, Shao RJ, Jun L, and Ya T. Effects of acupuncture on hippocampal NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles and inflammatory cytokines in chronic stress-depressed rats. J Beijing Univ Chin Med. (2023) 46:427–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2023.03.021
53. Jiang H, Long X, Wang Y, Zhang X, Chen L, Yang X, et al. Acupuncture ameliorates depression-like behaviors through modulating the neuroinflammation mediated by TLR4 signaling pathway in rats exposed to chronic restraint stress. Mol Neurobiol. (2024) 61:2606–19. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03737-6
54. Gong XY, Zhou HF, and Zhang BW. Characteristics of acupuncture point selection and the pattern of acupoint pairing in the treatment of depression. Liaoning J Chin Med. (2024) 51:147–50 + 227. doi: 10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2024.03.039
55. Yang LD and Li HL. Effects of electroacupuncture at Baihui and Shenting on the behavior of lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like mice and hippocampal NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammatory vesicles. Heibei Zhongguo Zhongguo. (2023) 45:1693–7 + 702. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2619.2023.10.026
56. da Silva MD, Bobinski F, Sato KL, Kolker SJ, Sluka KA, and Santos AR. IL-10 cytokine released from M2 macrophages is crucial for analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of acupuncture in a model of inflammatory muscle pain. Mol Neurobiol. (2015) 51:19–31. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8790-x
57. Huang Y, Huang H, Chen Q, Luo Y, Feng J, Deng Y, et al. Efficacy and immune-inflammatory mechanism of acupuncture-related therapy in animal models of knee osteoarthritis: a preclinical systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:177. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04660-9
58. Liu JL, Chen SP, Gao YH, and Meng FY. Comparison of analgesic effects of electroacupuncture of different intensities and frequencies in rats with chronic pain. Acupuncture Res. (2006) 05):280–5. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.2006.05.00
59. Huo R, Han SP, Liu FY, Shou XJ, Liu LY, Song TJ, et al. Responses of primary afferent fibers to acupuncture-like peripheral stimulation at different frequencies: characterization by single-unit recording in rats. Neurosci Bull. (2020) 36:907–18. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00509-3
60. Sun L, Liang J, Lu J, Wang J, Wu Q, Guo Z, et al. Effects of manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture on hippocampal p-JNK, c-jun, and Caspase-3 protein expression in a chronic stress-induced depression rat model. J Beijing Univ Chin Med. (2014) 37:820–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2014.12.007
Keywords: acupuncture, neuroinflammatory, depression, animals, depressive-like behaviors, meta-analysis, systematic review
Citation: Ni D, Zhang J, Qi R, Huang Y, Li M and Duan L (2025) Effect of acupuncture on neuroinflammatory responses in depression animals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 16:1624648. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1624648
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 16 October 2025;
Published: 31 October 2025.
Edited by:
Yueheng Tang, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Jin Xian, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaJiazhen Cao, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Ni, Zhang, Qi, Huang, Li and Duan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lining Duan, MjI4MjM1MTU5MEBxcS5jb20=
 Dongyi Ni
Dongyi Ni Jinbu Zhang
Jinbu Zhang Ruyu Qi1
Ruyu Qi1 Yingjie Huang
Yingjie Huang Min Li
Min Li Lining Duan
Lining Duan