- 1Department of Human Neuroscience, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
- 2Department of Cardiac, Thoracic, Vascular Sciences and Public Health, University of Padua, Padua, Italy
This structured review critically examines the psychological and neuropsychological effects of MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) use during adolescence, focusing exclusively on human studies. MDMA is a widely consumed psychoactive substance among adolescents, particularly in social and recreational contexts. Drawing on 14 eligible studies identified through a comprehensive literature search in MEDLINE/PubMed and through reference screening, this review synthesizes evidence concerning MDMA’s impact on adolescent mental health and cognitive function. The findings reveal consistent associations between adolescent MDMA use and a range of psychological disturbances, including increased depressive and anxious symptoms, as well as more severe manifestations such as suicidal ideation and attempts. Neuropsychological impairments are also commonly reported, with deficits in memory, attention, and executive functioning linked to early exposure. Neuroimaging evidence indicates that MDMA disrupts serotonergic pathways, potentially leading to persistent alterations in brain function. Although the evidence suggests significant risks, the review highlights several methodological limitations in the current literature, including small sample sizes, high rates of polydrug use, and the lack of longitudinal designs. These factors complicate causal interpretations and underscore the need for further, more robust research. The review emphasizes the urgency of targeted prevention strategies and harm reduction efforts aimed at adolescents. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities of the adolescent brain to MDMA’s neuropsychological effects is essential for clinicians, educators, and policymakers. Overall, this review provides a focused and human-centered perspective on the psychological and neuropsychic consequences of MDMA use in adolescence, reinforcing the call for greater public health awareness and scientific investigation.
1 Introduction
Ecstasy, the common name for MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine), is a popular recreational drug among adolescents (1). Its use is widespread in North America and Europe, particularly in social settings such as raves and dance events. Young people are drawn to MDMA for its ability to enhance feelings of empathy and social connectedness (2, 3). The drug typically induces euphoria, increases energy and heightens the desire for physical contact, such as being touched or hugged. Additionally, it is known to suppress the need for food, drink, and sleep, allowing users to sustain prolonged social activities, sometimes lasting up to two or three days (4).
According to the European Drug Report 2024, MDMA ranks as the second most frequently used illegal stimulant in Europe, following cocaine. Its usage seemed to decrease temporarily during the initial stages of the COVID-19 pandemic but rebounded once social distancing restrictions were eased. Nearly two-thirds of the European cities involved in wastewater monitoring observed a rise in MDMA traces between 2022 and 2023. Furthermore, there are signs of renewed growth in MDMA production across Europe, following a period of apparent decline in manufacturing volumes (5).
In Italy, the 2024 Parliamentary Report on Drug Addiction highlights a growing trend in stimulant use, including MDMA, among students. In 2023, consumption reached its highest recorded levels, with half of the users reporting their first experience between the ages of 15 and 17, and over a third stating they had used the drug before turning 15 (6).
The literature suggests that adolescent exposure to MDMA is associated with a range of neuropsychological impairments, primarily due to its effects on the serotonergic and dopaminergic systems in the brain (7).
Rodent studies indicate that MDMA use during adolescence can lead to cognitive deficits, particularly in learning and memory, with some impairments persisting long after drug cessation (8, 9). Behavioral changes, including increased impulsivity and altered emotional regulation, have also been observed in rodent models of adolescent MDMA exposure (10, 11). At a neurological level, research on rodents has shown that MDMA can affect the serotonergic system, a factor closely linked to the cognitive and behavioral impairments seen in users (12, 13). Additionally, its impact on the dopaminergic system has been demonstrated in rodent studies, leading to long-term reductions in dopamine neurons, exacerbating cognitive dysfunction and promoting neuroinflammatory processes, particularly when combined with other neurotoxic factors (14, 15).
Although these findings mainly derive from animal studies, they raise important concerns regarding potential risks in human adolescents, who may be particularly vulnerable to the neuropsychological effects of MDMA. Indeed, adolescence is a critical developmental phase characterized by profound physical, cognitive, emotional, and social changes (16) During this transitional period toward autonomy and adult decision-making, individuals are especially prone to risk-taking behaviors, including experimentation with psychoactive substances (17). Moreover, neurobiological changes occurring in adolescence may increase vulnerability to the initiation of substance use and to the development of substance use disorders, potentially resulting in long-lasting adverse consequences (16). Considering the problematic nature of substance use in this age group, it is essential to focus on the specific psychological and neuropsychological effects of MDMA during adolescence. At the same time, it is worth noting that MDMA-assisted psychotherapy has shown significant therapeutic benefits for individuals with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (18, 19). These promising results are contributing to growing research interest in MDMA, highlighting the need for a nuanced understanding of both its potential therapeutic uses and its risks, especially among vulnerable populations such as adolescents.
In summary, findings from preclinical research suggest that adolescent MDMA use is associated with significant psychological and neuropsychological consequences, including cognitive impairment and neuroalterations, primarily due to its effects on key neurotransmitter systems. However, much of the current evidence stems from studies conducted on animal models. Therefore, this review aims to provide an updated overview of the psychological and neuropsychological effects of MDMA use in adolescents, focusing on human studies, and highlighting both existing knowledge and gaps that require further investigation.
2 Material and methods
The literature search was conducted from March 3 to March 19, 2025, using MEDLINE/PubMed. No time restrictions were applied in the search strategy. The publication dates of the included studies ranged from 1999 to 2022. The following search string was used: ((MDMA[Title/Abstract]) OR (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine[Title/Abstract])) AND ((adolescent[Title/Abstract]) OR (teenager[Title/Abstract])). This search yielded 145 articles.
Given the specific focus of this review on psychological and neuropsychological effects of MDMA use in adolescents, and considering the extensive biomedical coverage of MEDLINE/PubMed, no additional databases were searched. However, to broaden the scope of the search and reduce the risk of missing relevant studies, review articles meeting the eligibility criteria were also included and screened to identify other potential studies to be included.
2.1 Inclusion criteria
Studies meeting both the following criteria were included:
● Cross-sectional, longitudinal, cohort and case-control studies, case series and case reports evaluating psychological and/or neuropsychological effects of MDMA use in adolescents (age ≤ 19 years at the time of exposure);
● Studies conducted on human subjects.
Reviews of studies, conducted on human subjects, evaluating psychological and/or neuropsychological effects of MDMA use in adolescents were also included.
2.2 Exclusion criteria
The following were excluded:
● Preclinical studies on animal models.
● Epidemiological studies focusing exclusively on prevalence of use without analysis of psychological or neurocognitive outcomes.
● Studies focusing on the consequences of MDMA use in adulthood.
● Studies focusing exclusively on effects of MDMA different from psychological or neuropsychological ones (e.g. cardiovascular effects).
Two independent reviewers (R.M. and C.C.) screened titles and abstracts in parallel to identify eligible studies. Disagreements were resolved through discussion or by consultation with a third reviewer (C.T.).
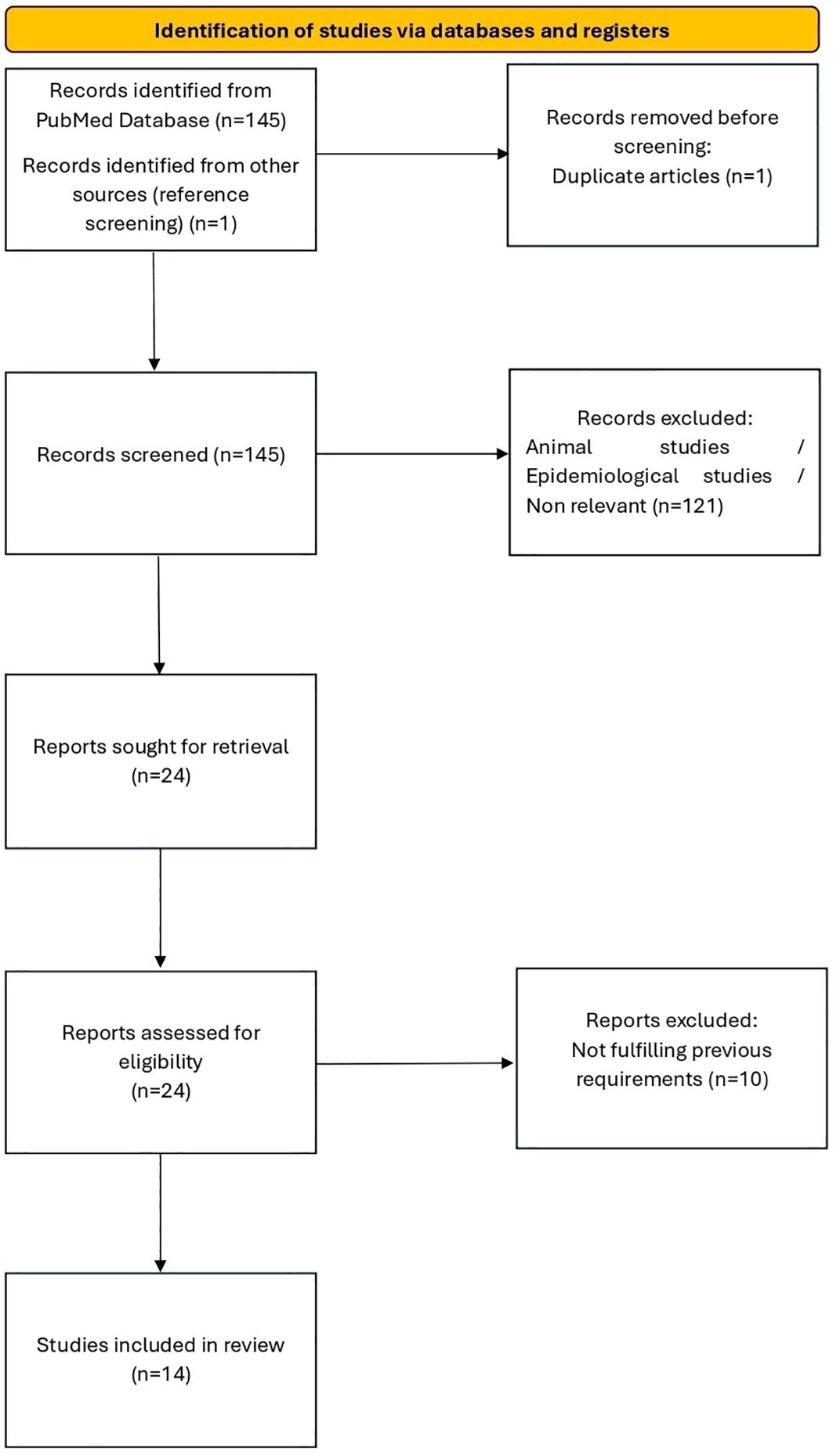
The selection process was documented using a flow diagram in accordance with PRISMA guidelines (Figure 1).
From the selected studies, the following data were extracted:
● Author and year of publication
● Population characteristics (age, sex)
● Study design
● Definition and mode of MDMA exposure
● Measures of psychological and neuropsychological outcomes
● Main findings
3 Results
Our literature search initially identified 145 articles from the PubMed database (including one duplicate, which was removed). Of these, 94 were excluded as they were preclinical studies on animal models, 16 were excluded because they were epidemiological studies focusing exclusively on the prevalence of use without analysis of psychological or neuropsychological outcomes, 6 were excluded as they addressed the consequences of MDMA use in adulthood, and 15 were excluded because they focused exclusively on effects of MDMA other than psychological or neuropsychological ones (e.g., cardiovascular effects). 23 studies deemed relevant were retrieved in full-text format from the PubMed search for further evaluation. By screening the review articles that met the eligibility criteria, another eligible study was identified and, after evaluation, was included in the present review.
Therefore, following the removal of duplicates and the exclusion of studies that did not meet the eligibility criteria upon full-text review, a total of 14 studies were included.
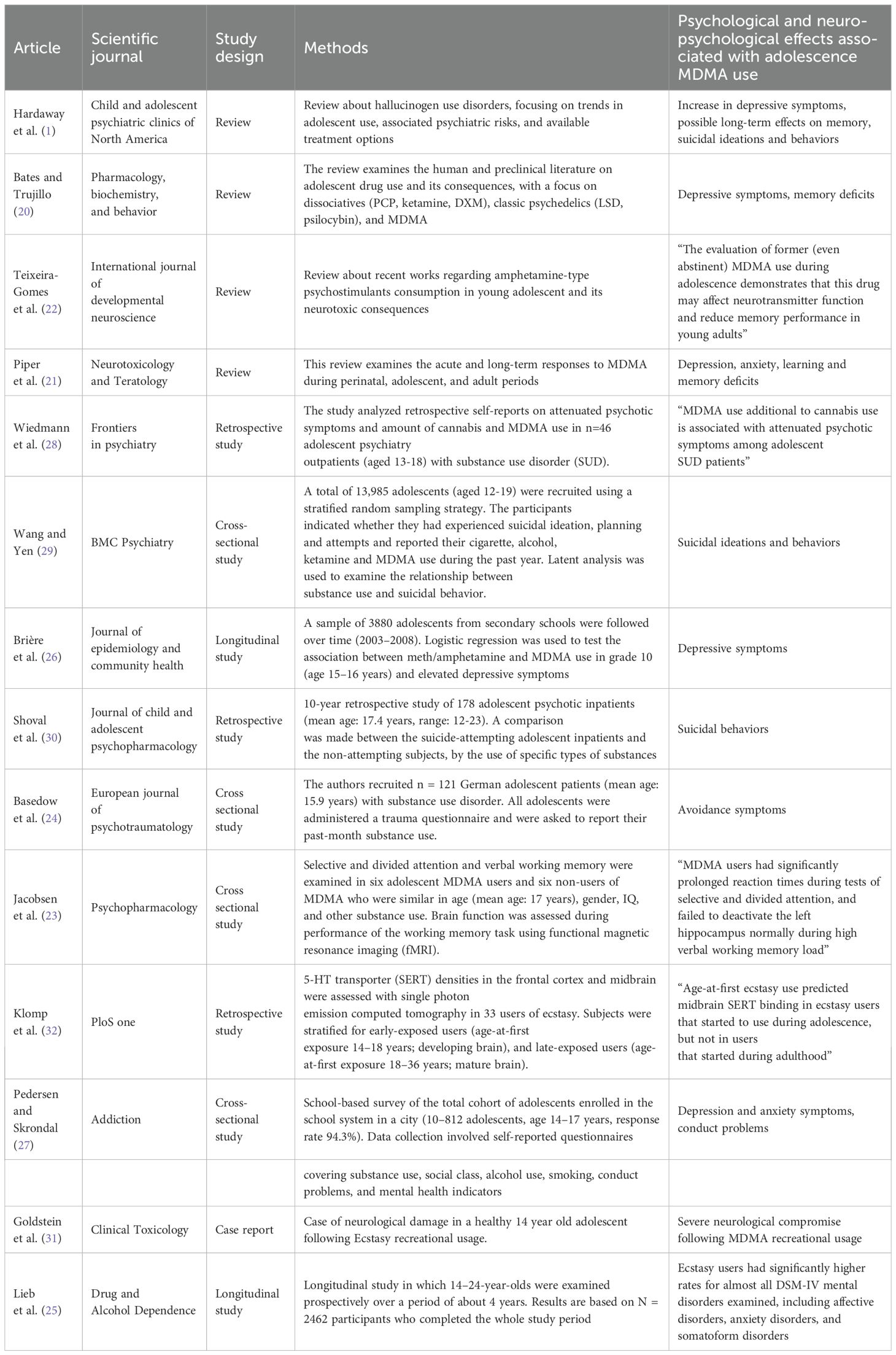
Table 1 summarizes the methodological approaches and findings of the reviewed studies.
Due to the heterogeneity of study designs and outcome measures, data were synthesized narratively. The results are presented in terms of the psychological and neuropsychological effects associated with adolescent MDMA use, including depressive symptoms, memory deficits, and neuroalterations. A subsection is dedicated to suicidal behaviors related to MDMA consumption during adolescence.
3.1 Psychological and neuropsychological effects of adolescent MDMA use
Several studies reported an association between MDMA use during adolescence and increased depressive symptoms, as well as potential long-term memory impairments. Hardaway et al. (1) highlighted an increase in depressive symptoms among adolescent MDMA users and suggested possible enduring effects on cognitive function. Similarly, Bates and Trujillo (20) reviewed human and preclinical literature, finding consistent evidence of depressive symptoms and memory deficits. Piper et al. (21) also reported a correlation between adolescent MDMA exposure and an increased risk of depression and anxiety, along with deficits in learning and memory.
Teixeira-Gomes et al. (22) explored the neuropsychological consequences of MDMA consumption in young adolescents, emphasizing alterations in neurotransmitter function and reduced memory performance. A study by Jacobsen et al. (23) employing functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) found significant impairments in selective and divided attention among adolescent MDMA users, along with abnormal hippocampal activity during high verbal working memory load (p<0.01).
Moreover, studies assessing the relationship between MDMA use and psychological distress have provided additional insights. Basedow et al. (24) reported an association between MDMA use and PTSD-related avoidance symptoms (e.g., emotional detachment or restricted range of affect) in adolescents with substance use disorders (p=0.008).
The longitudinal investigation by Lieb et al. (25) followed 2462 participants from two age cohorts (aged 14–17 and 18–24 years) over a 4-year period and found that Ecstasy users had significantly higher rates of almost all DSM-IV mental disorders examined (including affective disorders, anxiety disorders, and somatoform disorders) compared with non-users (OR 3.1, 95% CI 2.1–4.4), and with users of other illicit drugs (OR 1.8, 95% CI 1.2–2.6); furthermore, the results were reported in aggregated form, and in the majority of cases, the onset of psychiatric disorders preceded first Ecstasy use.
The longitudinal study by Brière et al. (26), found that adolescent MDMA use is associated with depressive symptoms (OR 1.7, 95% CI 1.1-2.6), particularly in cases of concurrent meth/amphetamine use (OR 1.9, 95% CI 1.2-2.9). Similarly, Pedersen and Skrondal (27) conducted a school-based survey of 10,812 adolescents in Oslo, identifying associations between MDMA use and conduct problems, as well as depressive and anxious symptoms. These associations were more pronounced when MDMA was used alongside amphetamines. Additionally, Wiedmann et al. (28) analyzed self-reports from 46 adolescent psychiatric outpatients with substance use disorders, finding that MDMA use, in conjunction with cannabis, was linked to prodromal symptoms of psychosis (with a regression coefficient B = 4.88 and p = 0.001).
3.2 Suicidal behaviors associated with adolescent MDMA use
A concerning finding among the reviewed literature is the association between adolescent MDMA use and suicidal ideation and behaviors. Wang and Yen (29), in a large-scale cross-sectional study of 13,985 adolescents, found statistically significant associations between MDMA use and increased rates of suicidal ideation, planning, and attempts (all p-values < 0.05). These associations were consistent across genders, though stronger in males.
In a retrospective study, Shoval et al. (30) examined a cohort of 178 adolescent psychiatric inpatients, comparing those with and without a history of suicide attempts. They found a notable association between MDMA use and suicidal behaviors, particularly among individuals with preexisting psychiatric conditions (p<0.05). Overall, these findings point to a consistent relationship between adolescent MDMA use and suicidal behaviors, especially in clinical populations.
3.3 Neurobiological and functional implications
The neuroalterative effects of MDMA appear to be strongly linked to its impact on the serotoninergic system. Goldstein et al. (31) provided a compelling case study demonstrating severe neurological compromise following recreational MDMA use in an adolescent. The study highlighted that MDMA-induced central nervous system (CNS) abnormalities are partly due to serotonin depletion and damage to serotoninergic nerve endings. Furthermore, the authors noted that serotoninergic nerve damage has been linked to the long-term memory deficits observed in chronic MDMA users.
Neuroimaging studies have provided further evidence supporting the negative impact of adolescent MDMA use on brain function. Klomp et al. (32) examined serotonin transporter (SERT) densities in 33 MDMA users and found that age-at-first ecstasy use predicted midbrain SERT binding in ecstasy users who started during adolescence (p<0.01), suggesting that early exposure to MDMA may have a distinct and lasting impact on serotonergic function. These findings indicate that MDMA use during adolescence can lead to persistent neurobiological changes with significant cognitive and functional consequences.
4 Discussion
This review aimed to critically analyze evidence from human studies to understand the psychological and neuropsychological consequences of MDMA use during adolescence.
Differently from previous reviews examining a broad range of substances (e.g., hallucinogens, amphetamines) or considering MDMA’s effects regardless of the user’s age, this review exclusively focus on MDMA use during adolescence: this targeted perspective allows for a more specific understanding of the risks associated with MDMA consumption during this particularly vulnerable phase of maturation. Moreover, unlike the more common reliance on animal models, this review draws exclusively on human research to explore the nuanced effects of MDMA during a critical developmental window. By privileging this human-focused, age-specific lens, the analysis offers insights directly applicable to real-world adolescent populations.
The findings discussed in this review acquire particular relevance when considered within the broader context of adolescence as a developmental phase marked by significant cognitive, emotional, and social changes. During this period, individuals show an increased tendency toward risk-taking and experimentation with psychoactive substances (33), which may heighten their susceptibility to the negative psychological and neuropsychological consequences of MDMA use. In this sense, the evidence reviewed here does not simply describe isolated effects, but rather reflects how MDMA may interact with the specific vulnerabilities of the adolescent brain, potentially amplifying risks for mental health and cognitive development.
Although one considers MDMA a “safe” drug (34), the included studies reveal a broad spectrum of adverse outcomes associated with adolescent MDMA use. Key psychological effects include an increase in depressive and anxious symptoms (1, 21, 25–27). Moreover, findings from clinical populations, such as those reported by Wiedmann et al. (28) and Basedow et al. (24), emphasized the link between MDMA use and broader psychological distress, including attenuated psychotic symptoms and avoidance behaviors that could interfere with daily functioning. Neuropsychological impairments such as memory deficits and attentional problems were also observed, along with evidence of dysfunction in inhibitory circuits within the hippocampus (23). Additionally, as highlighted by Goldstein et al. (31) and Klomp et al. (32), neurobiological alterations -particularly involving serotonergic dysfunction- may underlie these mood and cognitive impairments. It is worth noting that Klomp et al. (32) found that age at first ecstasy use predicted midbrain SERT binding in individuals who began using during adolescence, but not in those who initiated use during adulthood. This suggests that the heightened neuroplasticity characteristic of the adolescent brain may amplify MDMA’s neurobiological impact during this sensitive developmental period.
Viewed from this perspective, the synthesis of findings presented here highlights that MDMA’s effects may be especially disruptive during adolescence, when the brain is still undergoing complex processes of maturation. The cognitive and emotional alterations associated with MDMA use may, therefore, not only represent temporary disruptions but could interfere with critical trajectories of development, potentially leading to longer-term consequences (4, 22).
Finally, studies investigating suicidal behaviors, notably Wang and Yen (29) and Shoval et al. (30), identified a significant association between MDMA use and increased risk of suicidal ideation and attempts, raising concerns about a possible relationship between MDMA use and underlying psychological vulnerabilities in susceptible adolescents.
These findings could be important especially for clinicians, educators, and policymakers, highlighting the need for targeted early intervention and prevention strategies. Even moderate MDMA use during adolescence appears to carry disproportionate and potentially lasting consequences. The observed alterations in serotonergic function may contribute to persistent psychological and cognitive difficulties, warranting further investigation into adolescent neurobiological vulnerabilities. The evidence also underscores the importance of reinforcing harm reduction initiatives and public health campaigns aimed at reducing MDMA use among youth. In this light, the current review not only provides a synthesis of available evidence but also underlines the importance of addressing MDMA use within the broader developmental framework of adolescence, where neurobiological immaturity may magnify the drug’s harmful effects.
Despite these concerning findings, the current evidence base is subject to several limitations. Research involving human adolescents remains relatively limited, especially when compared to the more extensive body of animal studies (22). Many studies use animal models to infer potential human outcomes, which may fail to fully capture the complexity of human MDMA use and its effects on the developing adolescent brain.
Moreover, human studies face several important methodological flaws. A major challenge lies in isolating the specific effects of MDMA, as many participants report concurrent use of other substances such as alcohol or cannabis (35). This co-use introduces confounding variables that complicate the attribution of psychological or cognitive impairments solely to MDMA. Such studies are often further confounded by uncertainty regarding the quantity and purity of the MDMA consumed, limited reliability of self-reported drug histories, and the absence of baseline assessments prior to MDMA exposure (4, 23). In this regard, hair analysis has been proposed as a useful tool to objectively assess recent MDMA exposure and may help improve the accuracy of substance use measurements in future studies (36).
Sample sizes in human studies are often small, limiting the generalizability of their findings. It is also worth emphasizing that habitual ecstasy users do not reflect the general population, and cross-sectional studies comparing them to control groups may lead to misleading conclusions due to differences in polydrug use, lifestyle variables, and pre-existing mental health conditions (21, 25).
Another important limitation concerns the demographic variability among the adolescent samples included. There are inconsistencies in how adolescence is defined across studies, with participant ages ranging from early to late adolescence. This heterogeneity complicates the interpretation of findings, as neurodevelopmental and psychological responses to MDMA may vary significantly depending on the age subgroup. Notably, the study by Lieb et al. (25)—which included participants aged 14–24 years—revealed no systematic cohort effects in psychopathological outcomes. This suggests that, despite the broader age range, the associations between MDMA use and mental disorders were consistent across younger and older subgroups, reinforcing the relevance of its findings for adolescent populations. Nevertheless, the inclusion of young adults in some studies underscores the need for future research with stricter age stratification.
Furthermore, there is a notable absence of longitudinal studies capable of tracking the long-term trajectory of cognitive and psychological impairments (21, 28). As a result, it remains unclear whether observed deficits are transient or indicative of enduring neurodevelopmental disruption.
Some previous longitudinal studies investigated whether pre-existing psychological vulnerabilities predispose individuals to MDMA use. Huizink et al. (37) prospectively demonstrated that childhood anxiety/depression symptoms (assessed before MDMA availability) significantly predicted later MDMA initiation, supporting the self-medication hypothesis whereby adolescents may seek MDMA’s euphoric or bonding effects to alleviate distress. Conversely, de Win et al. (38) found that baseline depression/impulsivity did not predict future MDMA use in high-risk youth, though pre-existing cannabis use did—highlighting polydrug contexts as confounding pathways. Daumann et al. (39) observed that psychopathology in MDMA users remitted with cannabis abstinence but not MDMA cessation, suggesting cannabis may drive symptoms often misattributed to MDMA. This bidirectional complexity—where pre-existing vulnerabilities may facilitate use, but polysubstance exposure complicates attribution—underscores that the long-term psychiatric impact of MDMA itself remains an open question that requires further investigation (40).
Future research should prioritize large-scale longitudinal studies with better control of confounding variables to more clearly define the causal links between adolescent MDMA use and its psychological and neurocognitive effects. Such studies would not only clarify the extent and duration of these deficits but also inform the development of more effective interventions.
An additional limitation of the present review concerns the absence of quantitative statistical analyses, such as meta-analysis. While meta-analytic approaches can strengthen the rigor and interpretability of findings, they were deemed unsuitable in this case due to the high heterogeneity among the included studies—particularly in terms of sample characteristics, study designs, and outcome measures. This work was intentionally conducted as a narrative synthesis, aiming to provide a thorough and critical overview of the available literature while capturing the specific contexts and methodological nuances of each study. Despite the lack of a meta-analysis, the review maintains its academic contribution by offering a focused perspective on human adolescent MDMA users—an area that remains relatively underexplored—thereby generating insights directly relevant to clinical practice and prevention efforts. Nonetheless, future systematic reviews including meta-analyses would be highly valuable to better quantify the effects of MDMA use during adolescence, particularly regarding the severity and duration of use and their relationship with neuropsychological outcomes.
Lastly, as the literature search for this review was only conducted in one database, the adoption of a broader search strategy could be useful to ensure more comprehensive coverage of available evidence.
In conclusion, while the current literature underscores significant risks associated with adolescent MDMA use, the evidence is tempered by methodological limitations. This review contributes uniquely by narrowing its scope to adolescent users of MDMA, thereby providing more specific insights than broader, substance-inclusive reviews. The findings clearly indicate that MDMA may contribute to a range of adverse outcomes, from mood and cognitive impairments to alterations in brain function. However, the limited scope of human research and the aforementioned methodological issues call for more comprehensive, longitudinal studies. By addressing these gaps, future research can better delineate the long-term impacts of MDMA on adolescent brain development and psychological health, ultimately guiding more effective intervention and prevention strategies.
Author contributions
RM: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. CC: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. SR: Writing – review & editing. GP: Writing – review & editing. CT: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Hardaway R, Schweitzer J, and Suzuki J. Hallucinogen use disorders. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. (2016) 25:489–96. doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2016.03.006
2. Lake S, Gaddis A, Tupper KW, Nosova E, and DeBeck K. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA; ecstasy) use and transitions to injection drug use among street-involved youth. Subst Abus. (2019) 40:350–5. doi: 10.1080/08897077.2018.1528493
3. Schwartz R and Miller N. MDMA (ecstasy) and the rave: a review. Pediatrics. (1997) 100:705–8. doi: 10.1542/peds.100.4.705
4. Montoya A, Sorrentino R, Lukas S, and Price B. Long-term neuropsychiatric consequences of “ecstasy” (MDMA): a review. Harv Rev Psychiatry. (2002) 10:212–20. doi: 10.1080/hrp.10.4.212.220
5. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. (2024). Available online at: https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/european-drug-report/2024_en (Accessed May 31, 2025).
6. Presidenza del Consiglio dei Ministri – Dipartimento per le Politiche Antidroga. (2024). Available online at: https://www.politicheantidroga.gov.it/it/ (Accessed May 31, 2025).
7. Morgan M. Ecstasy (MDMA): a review of its possible persistent psychological effects. Psychopharmacology. (2000) 152:230–48. doi: 10.1007/s002130000545
8. Compton D, Dietrich K, Esquivel P, and García C. Longitudinal examination of learning and memory in rats following adolescent exposure to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine or 5-methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine. J Behav Brain Sci. (2017) 7:371–98. doi: 10.4236/jbbs.2017.79028
9. Nawata Y, Nishioku T, Yamamoto T, and Yamaguchi T. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) impairs cognitive function during withdrawal via activation of the arachidonic acid cascade in the hippocampus. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2024) 257:111139. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2024.111139
10. Piper B, Fraiman J, and Meyer J. Repeated MDMA (“ecstasy”) exposure in adolescent male rats alters temperature regulation, spontaneous motor activity, attention, and serotonin transporter binding. Dev Psychobiol. (2005) 47:145–57. doi: 10.1002/dev.20085
11. Meyer J, Piper B, and Vancollie V. Development and characterization of a novel animal model of intermittent MDMA (“ecstasy”) exposure during adolescence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2008) 1139:1–13. doi: 10.1196/annals.1432.029
12. Faria R, Magalhães A, Silva R, Oliveira R, Rocha E, and Barbosa F. MDMA in adolescent male rats: decreased serotonin in the amygdala and behavioral effects in the elevated plus-maze test. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2006) 1074:643–9. doi: 10.1196/annals.1369.062
13. Cox BM, Young AB, See RE, and Reichel CM. Behavioral and neurochemical effects of repeated MDMA administration during late adolescence in the rat. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2014) 48:229–35. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.09.021
14. Cadoni C, Pisanu A, Simola N, Frau L, Porceddu P, Corongiu S, et al. Widespread reduction of dopamine cell bodies and terminals in adult rats exposed to a low dose regimen of MDMA during adolescence. Neuropharmacology. (2017) 123:385–94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.06.008
15. Costa G, Simola N, and Morelli M. MDMA administration during adolescence exacerbates MPTP-induced cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology. (2014) 231:4007–18. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3536-z
16. Gray KM and Squeglia LM. Research review: what have we learned about adolescent substance use? J Child Psychol Psychiatry. (2018) 59:618–27. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12783
17. Alderman EM, Breuner CC, and Committee on Adolescence. Unique needs of the adolescent. Pediatrics. (2019) 144:e20193150. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3150
18. Feduccia AA, Jerome L, Yazar-Klosinski B, Emerson A, Mithoefer MC, and Doblin R. MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD: are memory reconsolidation and fear extinction underlying mechanisms? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2018) 84:221–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.03.003
19. Krystal JH, Kelmendi B, Petrakis IL, Krystal AD, Charney DS, and D’Souza DC. Psychotherapy-supported MDMA treatment for PTSD. Cell Rep Med. (2021) 2:100378. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100378
20. Bates MLS and Trujillo KA. Use and abuse of dissociative and psychedelic drugs in adolescence. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. (2021) 203:173129. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2021.173129
21. Piper BJ. A developmental comparison of the neurobehavioral effects of ecstasy (MDMA). Neurotoxicol Teratol. (2007) 29:288–300. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2006.10.002
22. Teixeira-Gomes A, Costa VM, Feio-Azevedo R, Bastos M, Carvalho F, and Capela JP. The neurotoxicity of amphetamines during the adolescent period. Int J Dev Neurosci. (2015) 41:44–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2014.12.001
23. Jacobsen LK, Mencl WE, Pugh KR, Skudlarski P, and Krystal JH. Preliminary evidence of hippocampal dysfunction in adolescent MDMA (“ecstasy”) users: possible relationship to neurotoxic effects. Psychopharmacology. (2004) 173:383–90. doi: 10.1007/s00213-003-1679-4
24. Basedow LA, Kuitunen-Paul S, Wiedmann MF, Roessner V, and Golub Y. Self-reported PTSD is associated with increased use of MDMA in adolescents with substance use disorders. Eur J Psychotraumatol. (2021) 12:1968140. doi: 10.1080/20008198.2021.1968140
25. Lieb R, Schuetz CG, Pfister H, von Sydow K, and Wittchen HU. Mental disorders in ecstasy users: a prospective-longitudinal investigation. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2002) 68:195–207. doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(02)00190-4
26. Brière FN, Fallu JS, Janosz M, and Pagani LS. Prospective associations between meth/amphetamine (speed) and MDMA (ecstasy) use and depressive symptoms in secondary school students. J Epidemiol Community Health. (2012) 66:990–4. doi: 10.1136/jech-2011-200706
27. Pedersen W and Skrondal A. Ecstasy and new patterns of drug use: a normal population study. Addiction. (1999) 94:1695–706. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.1999.941116957.x
28. Wiedmann M, Kuitunen-Paul S, Basedow LA, Roessner V, and Golub Y. Attenuated psychotic symptoms in adolescents with chronic cannabis and MDMA use. Front Psychiatry. (2022) 12:696133. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.696133
29. Wang PW and Yen CF. Adolescent substance use behavior and suicidal behavior for boys and girls: a cross-sectional study by latent analysis approach. BMC Psychiatry. (2017) 17:392. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1546-1
30. Shoval G, Sever J, Sher L, Diller R, Apter A, Weizman A, et al. Substance use, suicidality, and adolescent-onset schizophrenia: an Israeli 10-year retrospective study. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. (2006) 16:767–75. doi: 10.1089/cap.2006.16.767
31. Goldstein LH, Mordish Y, Abu-Kishak I, Toledano M, and Berkovitch M. Acute paralysis following recreational MDMA (ecstasy) use. Clin Toxicol (Phila). (2006) 44:339–41. doi: 10.1080/15563650600584600
32. Klomp A, den Hollander B, de Bruin K, Booij J, and Reneman L. The effects of ecstasy (MDMA) on brain serotonin transporters are dependent on age-of-first exposure in recreational users and animals. PloS One. (2012) 7:e47524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047524
33. Conrod P, Castellanos-Ryan N, and Strang J. Annual research review: on the developmental neuropsychology of substance use disorders. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. (2016) 57:371–94. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12516
34. Patel MM, Wright DW, Ratcliff JJ, and Miller MA. Shedding new light on the “safe” club drug: methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy)-related fatalities. Acad Emerg Med. (2004) 11:208–10.
35. von Sydow K, Lieb R, Pfister H, Höfler M, and Wittchen HU. Use, abuse and dependence of ecstasy and related drugs in adolescents and young adults—a transient phenomenon? Results from a longitudinal community study. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2002) 66:147–59. doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(01)00195-8
36. Janousch C, Eggenberger L, Steinhoff A, Johnson-Ferguson L, Bechtiger L, Loher M, et al. Words versus strands: reliability and stability of concordance rates of self-reported and hair-analyzed substance use of young adults over time. Eur Addict Res. (2025) 31:60–74. doi: 10.1159/000541713
37. Huizink AC, Ferdinand RF, van der Ende J, and Verhulst FC. Symptoms of anxiety and depression in childhood and use of MDMA: prospective, population based study. BMJ. (2006) 332:825–8. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38743.539398.3A
38. de Win MM, Schilt T, Reneman L, Vervaeke H, Jager G, Dijkink S, et al. Ecstasy use and self-reported depression, impulsivity, and sensation seeking: a prospective cohort study. J Psychopharmacol. (2006) 20:226–35. doi: 10.1177/0269881106063275
39. Daumann J, Hensen G, Thimm B, Rezk M, Till B, and Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E. Self-reported psychopathological symptoms in recreational ecstasy (MDMA) users are mainly associated with regular cannabis use: further evidence from a combined cross-sectional/longitudinal investigation. Psychopharmacology. (2004) 173:398–404. doi: 10.1007/s00213-003-1719-0
Keywords: MDMA, adolescence, substance use, cognitive impairment, neuroimpact
Citation: Miazzi R, Cestonaro C, Righetto S, Petroni G and Terranova C (2025) Psychological and neuropsychological effects of MDMA use during adolescence: a structured review. Front. Psychiatry 16:1644599. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1644599
Received: 10 June 2025; Accepted: 22 August 2025;
Published: 08 September 2025.
Edited by:
Liana Fattore, CNR Neuroscience Institute (IN), ItalyReviewed by:
Boris B. Quednow, University of Zurich, SwitzerlandNoah Chisamore, University of Toronto, Canada
Copyright © 2025 Miazzi, Cestonaro, Righetto, Petroni and Terranova. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Claudio Terranova, Y2xhdWRpby50ZXJyYW5vdmFAdW5pcGQuaXQ=
 Rocco Miazzi
Rocco Miazzi Clara Cestonaro
Clara Cestonaro Silvia Righetto2
Silvia Righetto2 Giulia Petroni
Giulia Petroni Claudio Terranova
Claudio Terranova