- 1Nursing Department, The Third People’s Hospital of Henan Province, Zhengzhou, China
- 2School of Nursing, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
- 3Anesthesiology Department, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
- 4School of Rehabilitation Therapy, Henan Vocational College of Tuina, Luoyang, China
- 5School of Nursing, North Henan Medical University, Xinxiang, China
- 6The Seventh Clinical Medicine College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen, China
- 7Nursing Department, Nanjing Central Hospital, Nanjing, China
- 8Department of Oncology, School of Medicine, Zhongda Hospital, Southeast University, Nanjing, China
Objectives: The present study aimed to investigate the levels of illness stigma in patients with Meige syndrome and to determine the association of socio-demographic characteristics, positive coping style, and resilience with illness stigma in patients with Meige syndrome.
Method: A cross-sectional survey using convenience sampling was conducted in four hospitals in China from March 2025 to May 2025. A total of 280 patients clinically diagnosed with Meige syndrome were recruited. A socio-demographic characteristic questionnaire, the Chinese version of the Stigma Scale for Chronic Illness, the Chinese version of the simplified coping style questionnaire, and the Chinese version of the 10-item Connor–Davidson resilience scale were used to perform this research. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 27.0.
Result: A high level of illness stigma was observed among 280 participants, as reflected by a mean score of 90.40 ± 25.59. The present study identified a negative correlation between illness stigma, positive coping style, and resilience. Multiple linear regression analysis showed that living arrangement (β = −0.16, p = 0.007), self-care ability (β = 0.13, p = 0.026), positive coping style (β = −0.15, p = 0.012), and resilience (β = −0.18, p = 0.002) were significant factors associated with illness stigma in Meige syndrome patients.
Conclusion: This study reveals that patients with Meige syndrome experience high levels of illness stigma, which is associated with factors including living arrangement, self-care ability, positive coping style, and resilience. Healthcare professionals should prioritize stigma reduction in individuals with Meige syndrome, particularly those living alone or with limited self-care abilities, through targeted psychological support that enhances positive coping and resilience.
1 Introduction
Meige syndrome, also known as cranial dystonia, is a rare neurological disorder characterized by involuntary and often severe muscle contractions that primarily affect the orbicularis oculi and lower facial muscles (1). These symptoms can lead to a range of functional impairments, such as problems with vision, speech, and eating, which can severely reduce a patient’s quality of life (2). In addition to its physical manifestations, however, Meige syndrome can have far-reaching psychological effects on its sufferers (3). The reason for this is that the external presentation of Meige syndrome often exposes patients to public misconceptions, social isolation, and discrimination (4).
Illness stigma refers to the negative social labeling and discriminatory perceptions suffered as a result of an illness or health condition (5). It is a social phenomenon in which people are ostracized, discriminated against, and excluded because they are perceived as “abnormal” or “inferior” because of a disease or condition (6). This phenomenon not only affects an individual’s social interactions but can also have far-reaching negative effects on his or her mental health, quality of life, and social integration (7). Studies have shown that illness stigma, both perceived and experienced, contributes to depressive symptoms, low self-esteem, and reduced treatment adherence in a wide range of chronic and neurological conditions (8, 9). In particular, Meige syndrome—although a relatively rare neurological disorder—presents a unique combination of physical symptoms, such as pronounced facial spasms and profound psychosocial challenges. Compared with other well-studied neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease or epilepsy (10, 11), the facial characteristics of Meige syndrome draw more public attention, increasing patients’ exposure to social scrutiny and discrimination. Studies on focal dystonia have shown that visible motor symptoms are significantly associated with social withdrawal and mental distress (12). Moreover, Meige syndrome has been underrepresented in psychosocial research, despite growing qualitative evidence that these patients experience a high psychological burden (13). Therefore, focusing on Meige syndrome fills an important research gap and offers clinical insights for a particularly vulnerable population, as illness stigma in this context is not merely a reflection of social prejudice but a systemic health challenge that compromises patients’ physical and mental well-being, as well as treatment outcomes, through intertwined psychological, behavioral, and social mechanisms.
In order to face these challenges, patients may adopt different psychological mechanisms to cope with the stresses and social pressures associated with the disease (14). Coping style refers to the cognitive and behavioral strategies that individuals use to regulate emotions, reduce psychological burdens, or solve problems when confronted with stress, conflict, or adversity (15). It reflects both how a person appraises a stressful event and how he/she responds on an emotional and behavioral level (16). According to the transactional model of stress and coping (17), coping can be problem-focused (addressing the stressor directly) or emotion-focused (managing the emotional response), and it represents a relatively stable individual characteristic that can nonetheless be adapted to specific situations (18, 19). Prior studies have shown that patients with higher stigma are more likely to adopt negative coping strategies (20) and that coping plays a mediating role in the formation and alleviation of stigma: positive coping styles are protective, while negative coping may reinforce self-stigmatization (21). Importantly, multiple findings have shown that positive coping style demonstrates superior predictive power over negative coping style, particularly in terms of enhancing psychological resilience versus suppressing negative psychological outcomes (e.g., anxiety and fear) (22–24). Therefore, in the present investigation, we focused only on positive coping style. While coping style reflects the immediate responses that patients use to manage stress, long-term adaptation to illness may involve broader psychological resources that extend beyond these momentary strategies.
Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to effectively adapt to and recover from stress, trauma, adversity, tragedy, or significant threats (25). Unlike coping strategies, which reflect situational and short-term responses to stress, resilience represents a more enduring psychological resource that enables individuals to sustain adjustment over time. High levels of psychological resilience are associated with better psychological outcomes (26), improved social functioning (27), and enhanced positive coping style (28) in patients with a variety of diseases. There is also evidence that resilience is beneficial in reducing illness stigma in adolescent psychiatric patients (29). These findings indicate that resilience, together with coping style, may play a central role in shaping how patients experience illness stigma.
Although these associations have been established in other chronic and neurological conditions, little is known about whether similar mechanisms operate in Meige syndrome. So far, there is still a lack of research on illness stigma in patients with Meige syndrome. The specific relationship between resilience, coping strategies, and disease stigma among patients with Meige syndrome remains unclear, and further research is necessary. In light of these gaps, the present study aimed to investigate the level of illness stigma in patients with Meige syndrome and to explore the relationship between socio-demographic characteristics, resilience, positive coping style, and illness stigma. This will help to understand the psychological state of patients with Meige syndrome and provide valuable insights into future intervention strategies for patients with Meige syndrome.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design
The present study was implemented using the method of convenience sampling and a descriptive cross-sectional design (30), which has been widely used to investigate the status of psychological indicators in chronic illness patients. This study was performed according to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines.
2.2 Participants
The sample size for this study was calculated according to the sample size calculation principles used in the Kendall cross-sectional survey, n = independent variable × (5 ~ 10) (31). Four scales with 10 independent variables were used in this study, which were derived from a socio-demographic characteristic questionnaire (including seven questions), the Chinese version of the Stigma Scale for Chronic Illness (including two dimensions), the Chinese version of the simplified coping style questionnaire (only positive coping style scale, including one dimension), and the Chinese version of the 10-item Connor–Davidson resilience scale (including one dimension). Considering the 20% invalid questionnaires, the minimum sample size required for this study was 68 to 138.
Participants were clinically diagnosed with Meige syndrome, aged 18 years or older, and capable of independently completing the questionnaire. Exclusion criteria included patients with medical records of severe mental disorders (such as major depressive disorder or schizophrenia) or cognitive impairments that hindered questionnaire comprehension or response.
2.3 Instruments
2.3.1 Socio-demographic characteristic questionnaire
Based on a preliminary study and review, a socio-demographic characteristic questionnaire was designed to collect participants’ general information, including age, gender, residence, education level, marital status, living arrangement, and self-care ability.
2.3.2 The Chinese version of Stigma Scale for Chronic Illness
The Stigma Scale for Chronic Illness (SSCI) is an instrument developed to measure stigma in chronic illness patients, with demonstrated reliability and validity. In 2009, Rao et al. (11) developed the SSCI based on Corrigan’s definition of stigma, which was initially used to measure the stigma experienced by patients with neurological diseases. This scale consists of 24 items grouped into two domains, namely, enacted stigma (11 items) and self-stigma (13 items). Enacted stigma assesses patients’ actual experiences of discrimination (e.g., people being unfriendly, making fun of, or staring at them), while self-stigma measures the internalization of negative stereotypes related to their condition (e.g., feeling different from others, avoiding new friendships to hide the illness, or blaming themselves for problems). Responses are rated on a 5-point Likert scale, where 1 indicates “never” and 5 indicates “always”. Total scores range from 24 to 120, with higher scores reflecting stronger levels of stigma. In a sample of 511 patients with neurological diseases, Rao et al. (11) demonstrated acceptable internal consistency, and the two domains were significantly correlated (r = 0.81). The Chinese version of the SSCI, translated by Deng et al. (32), demonstrated satisfactory reliability and validity and has been widely employed in diverse studies (33, 34). In the current study, the scale demonstrated excellent internal consistency, with a Cronbach’s α of 0.98.
2.3.3 The Chinese Version of Simplified Coping Style Questionnaire
The Simplified Coping Style Questionnaire (SCSQ) was developed by Xie in 1998 (35), drawing on Lazarus and Folkman’s problem-focused and emotion-focused coping model (17). The simplified scale exhibited excellent reliability. It includes two dimensions: positive coping style (12 items, including asking relatives, friends, or classmates for advice and finding several different ways to solve the problem) and negative coping style (eight items, including reliance on others to solve problems). The scale is self-rated on a 4-point Likert scale with 0 = never and 3 = always. This study used only the Positive Coping Scale, so its score ranged from 0 to 36. The higher the total scores, the more likely the participants are to adopt positive coping style. In the current study, the scale demonstrated excellent internal consistency, with a Cronbach’s α of 0.79.
2.3.4 The Chinese version of 10-item Connor–Davidson resilience scale
The 10-item Connor–Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC-10) scale, originally developed by Campbell-Sills et al. (36), was employed to assess participants’ resilience. The Chinese version, which was translated and validated by Ye et al. (37), has shown satisfactory psychometric properties in terms of reliability and validity. Each item is rated on a 5-point Likert scale from 0 (almost never) to 4 (always). The total score ranged from 0 to 40, with higher total scores indicating greater resilience. In the current study, the scale demonstrated excellent internal consistency, with a Cronbach’s α of 0.95.
2.4 Data collection
A descriptive cross-sectional survey was conducted using convenience sampling. Data collection was conducted from March 2025 to May 2025 in four tertiary hospitals in Henan Province. During the study period (March to May 2025), all patients who met the inclusion criteria and were diagnosed with Meige syndrome at the participating hospitals were approached for participation. Recruitment was conducted through outpatient clinics and inpatient wards. Only those who voluntarily agreed to participate and provided written informed consent were enrolled in the study. Researchers personally distributed paper questionnaires to participants in quiet, private settings (e.g., conference rooms or consultation areas) to ensure confidentiality. The questionnaire comprised four components: a socio-demographic characteristic questionnaire, the SSCI, the positive coping style scale of SCSQ, and the CD-RISC-10. All responses were anonymous, with no collection of personally identifiable information (e.g., names and addresses). After completion, trained staff verified the integrity of each questionnaire. Two researchers independently managed paper questionnaire collection and data entry into a computer system, cross-checking for discrepancies and resolving any inconsistencies promptly. Participants were recruited from outpatient clinics and inpatient wards of the study sites. Eligible participants were provided with verbal and written explanations of the study objectives, their rights as participants, and the confidentiality measures in place. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant prior to questionnaire administration. Ethical approval for the study was granted by the institutional review board before data collection, and all data were securely stored and accessible only to the research team.
2.5 Data analysis
The data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics version 27.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). Normality of continuous data was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Since all data were normally distributed, continuous data were presented as mean (standard deviation). Outliers were checked by boxplots and descriptive statistics; extreme values were examined but retained if clinically plausible. Standardization procedures (e.g., z-scores) were not performed because analyses were based on validated raw scale scores. Categorical data were presented as percentages (38). To examine whether illness stigma in patients with Meige syndrome varied across different socio-demographic variables, independent-samples t-tests and one-way ANOVA were conducted (39). To assess the relationships among SSCI scores, positive coping style scores, and CD-RISC-10 scores, Pearson’s correlation analysis was conducted. Multi-collinearity was evaluated through the calculation of tolerance and the variance inflation factor (VIF). The absence of multi-collinearity was confirmed when tolerance exceeded 0.1 and the VIF remained below 10. Variables found to be statistically significant in the t-test, ANOVA, and Pearson’s correlation analyses were identified as potential predictors for inclusion in the regression analysis. Finally, multiple linear regression was conducted with potential predictors as independent variables and illness stigma as the dependent variable to confirm the relationship between Meige syndrome patients’ socio-demographic characteristics, resilience, and coping style. In addition, an additional post-hoc power analysis for each of the two phases was performed. A two-tailed p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.6 Ethical considerations
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Third People’s Hospital of Henan Province in Zhengzhou, China (Ethical Review No. 2025SZSYLCYJ0302), based on the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All eligible participants were informed of the study and its ethical principles (e.g., voluntary participation, withdrawal, anonymity, and confidentiality). All participants were fully informed about the study objectives, procedures, rights, and confidentiality protections, and all provided written informed consent prior to participation. After completing the survey, participants were thanked and provided with general health education materials; no individual results were disclosed to ensure confidentiality. All data were securely stored and accessible only to the research team.
3 Results
3.1 Socio-demographic characteristics of participants and comparison of different variables on stigma in Meige syndrome patients
A total of 400 participants were invited to participate in this study, and 280 valid questionnaires were collected, resulting in an effective response rate of 70.0%. The results of the study found that the total illness stigma score of the 280 participants was 90.40 ± 25.59. Among the 280 participants, the gender distribution was relatively balanced, with two-thirds of the participants residing in the city. In terms of education, about two-thirds had completed at least junior high school. Most participants were married, and more than half lived alone. In terms of self-care ability, the largest proportion of patients were partially dependent, with fewer being fully independent or fully dependent. t-Tests and ANOVA revealed that illness stigma in Meige syndrome patients showed statistically significant differences in residence, living arrangement, and self-care ability (p < 0.05). Specifically, patients residing in city areas, those living alone, and those who are fully dependent exhibited higher illness stigma scores. Conversely, no statistically significant differences in stigma were observed based on gender, education level, or marital status (p > 0.05). See Table 1 for details.
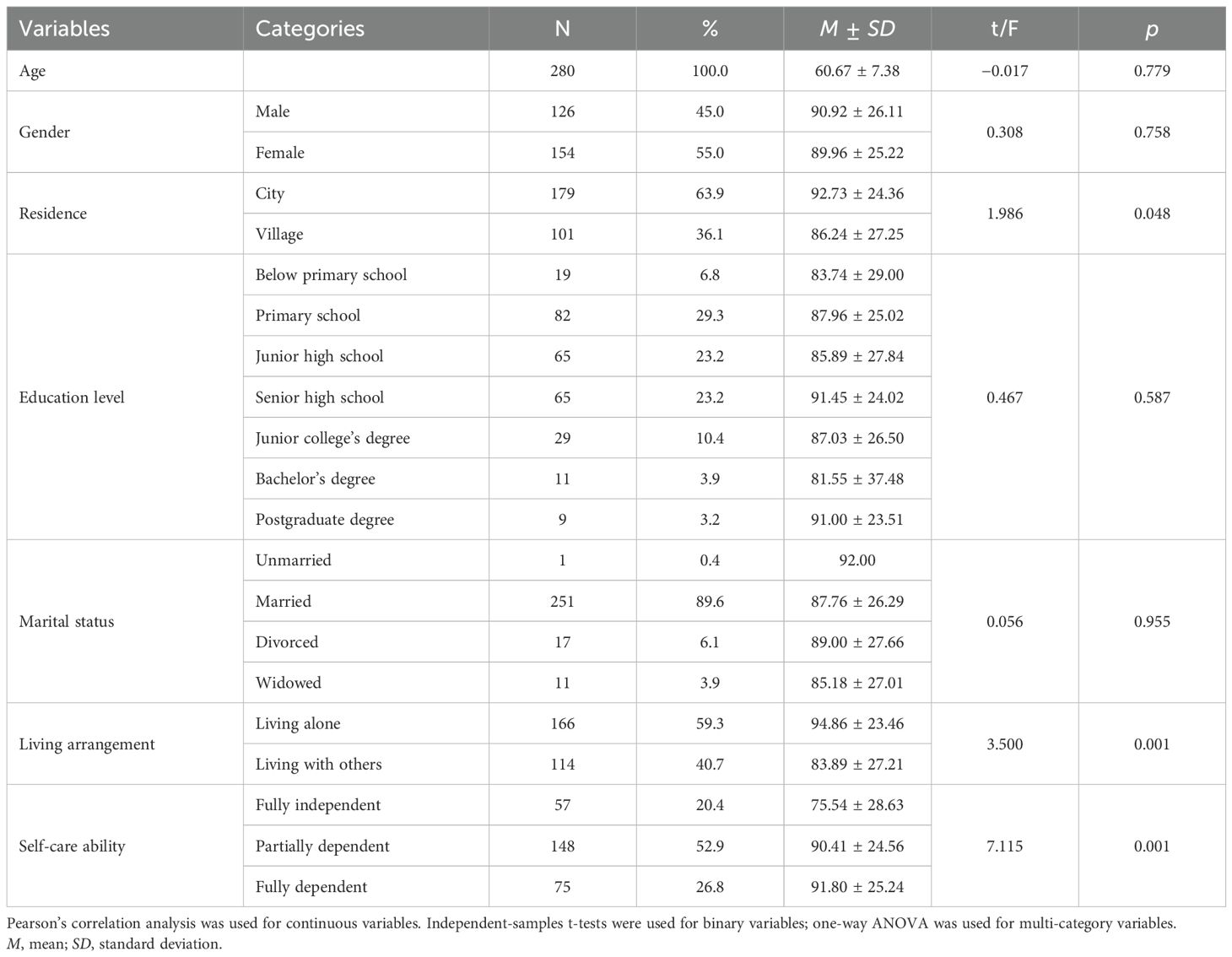
Table 1. Socio-demographic characteristics and comparison of participants’ different variables regarding illness stigma in Meige syndrome (N = 280).
3.2 Correlation analysis of stigma, coping style, and psychological resilience
In this study, illness stigma was found to be correlated with positive coping style and resilience. Specifically, the total illness stigma score showed a negative correlation with the total score of positive coping style (r = −0.225, p < 0.001), indicating that higher illness stigma was associated with less frequent use of positive coping style. Similarly, the total stigma score was significantly negatively correlated with resilience (r = −0.176, p = 0.003), suggesting that higher stigma was associated with lower levels of resilience. However, positive coping style scores were positively correlated with resilience (r = 0.163, p < 0.001), indicating that individuals who employed positive coping strategies tended to have higher levels of resilience. See Table 2 for details.
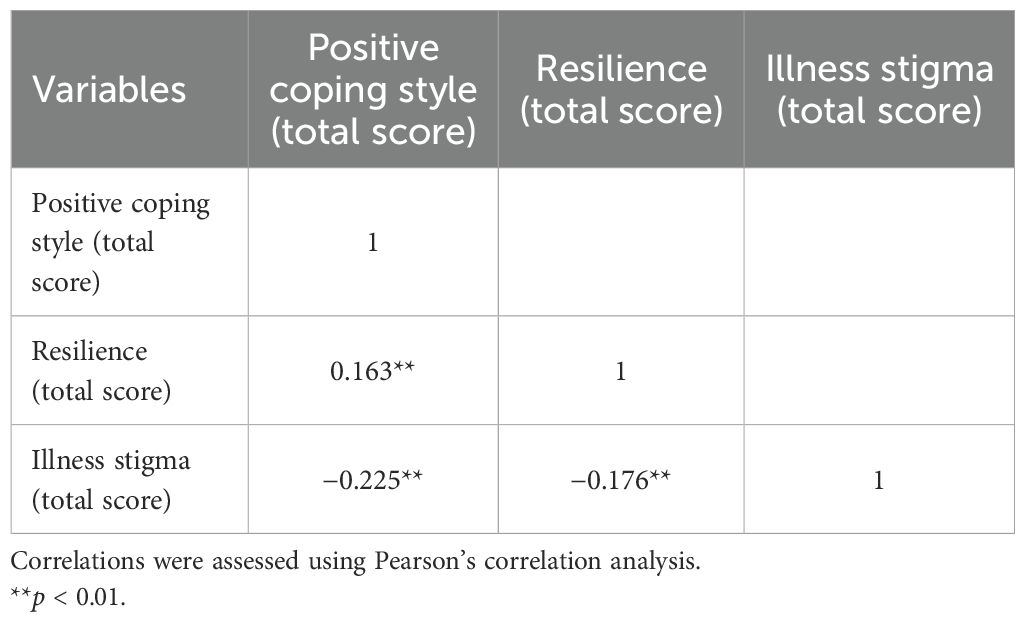
Table 2. Pearson’s correlation of positive coping style, resilience, and stigma in patients with Meige syndrome.
3.3 Multiple linear regression analysis of factors associated with illness stigma in Meige syndrome patients
Multi-collinearity among the independent variables was assessed to verify the basic assumptions of the regression model. Given that the VIF was 10 or less and the tolerance was 0.1 or above, no significant multi-collinearity issues were identified. The Durbin–Watson statistic was 1.818, close to 2.0, indicating no autocorrelation and suggesting that the error terms were independent of each other. Based on univariate analysis of t-test, ANOVA, and Pearson’s analysis, variables with statistical significance (p < 0.05) were selected as independent variables, with illness stigma as the dependent variable for multiple linear regression analysis. As shown in Table 3, the model explained a significant proportion of the variance in stigma among Meige syndrome patients. The results indicated that living arrangement (β = −0.16, p = 0.007), self-care ability (β = 0.13, p = 0.026), positive coping style (β = −0.15, p = 0.012), and resilience (β = −0.18, p = 0.002) were significant factors associated with illness stigma in Meige syndrome patients.
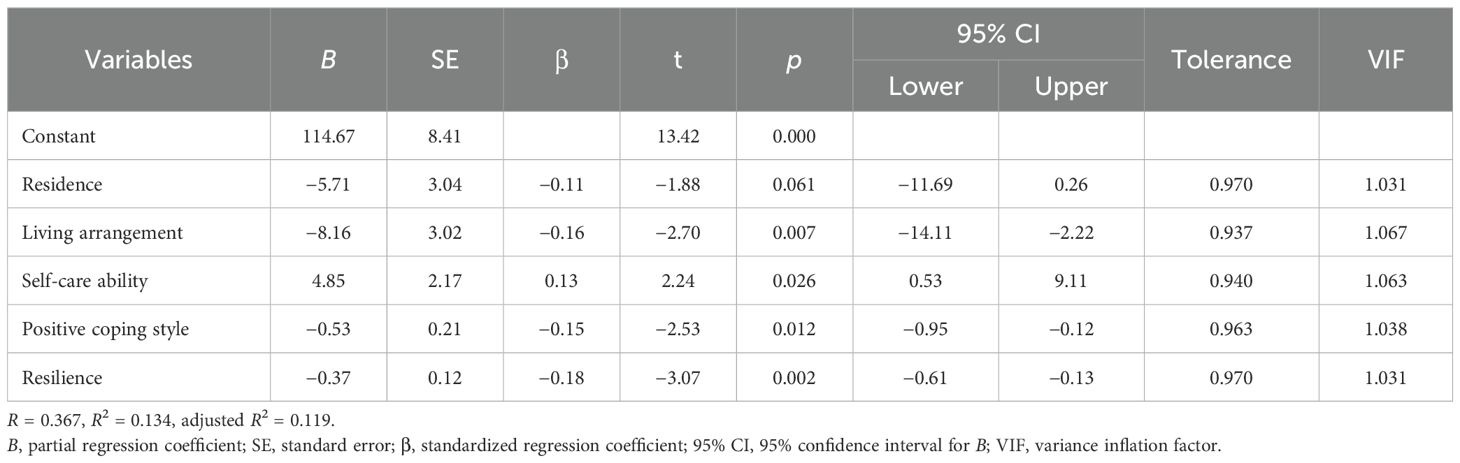
Table 3. Multiple linear regression analysis for factors associated with illness stigma in patients with Meige syndrome.
4 Discussion
This study investigated illness stigma in patients with Meige syndrome and examined its associations with socio-demographic characteristics, coping style, and resilience. The findings revealed three main points. First, patients with Meige syndrome experienced a markedly high level of illness stigma, with mean scores significantly exceeding those reported in other chronic and neurological conditions. Second, socio-demographic variables, particularly living alone and low self-care ability, were associated with higher levels of stigma. Third, psychological resources such as positive coping style and resilience were negatively associated with stigma, suggesting their protective role. To better understand these findings, the following sections discuss each aspect in detail.
Our study revealed that patients with Meige syndrome experienced a high level of illness stigma, with a mean score of 90.40 ± 25.59. This value is significantly higher than those reported in previous studies of chronic disease populations (40). Moreover, in research involving multiple neurological disorders such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke, the average stigma score was 42.7 ± 19.7 (11), which is less than half of the mean observed in our sample. These comparisons highlight that individuals with Meige syndrome are subject to exceptionally high levels of stigmatization, likely due to the visibility and uncontrollability of their facial and motor symptoms. Such manifestations may draw unwanted social attention, foster misinterpretations, and intensify experiences of discrimination, thereby exacerbating internalized stigma. This finding underscores the urgent need for greater clinical and social interventions to reduce stigma in this patient group, as well as the importance of public education to improve awareness and reduce misconceptions about Meige syndrome.
Our findings showed that the patients’ illness stigma score for living alone was significantly higher than that of patients living with family. On the one side, the reason may be that living with family members offers a close‐knit, supportive community that could reduce stigma. One possible explanation is that cohabiting with family provides a supportive environment that buffers against social alienation and reduces perceived stigma, a notion supported by studies showing that stronger family and social bonds are associated with lower stigmatization (41, 42). On the other side, living alone has been associated with poor mental health conditions (43–45). Stahl et al. (1) found that living alone was associated with elevated levels of depressive symptoms compared to living with a family member. Similar findings were also noted in the elderly population (46). In a qualitative meta-analysis, Hu et al. (47) found that older people living alone had a higher risk of depression than those not living alone (47). Consistent with our results, the relationship between living alone and anxiety has also been discussed in previous research; for example, Hunt et al. (48) and Yu et al. (49) found that people living alone had a significantly higher risk of generalized anxiety disorder than those living with their families. These findings suggest that social support—especially from family members—plays a crucial role in protecting patients with Meige syndrome from the psychological burden of stigma. Interventions that strengthen family involvement and foster broader social support networks may therefore be effective strategies to mitigate stigma in this population.
Our study found that higher self-care ability is associated with lower stigma. Consistent with our findings, Asuka Katoo et al. (50) demonstrated in a cohort of 209 type 2 diabetes patients that self-stigma was significantly and inversely associated with self-care behaviors (β = −0.23, p = 0.001), independent of self-efficacy and depressive symptoms. A possible explanation is that self-care enhances patients’ sense of autonomy and competence, which may counteract internalized stigma. Conversely, diminished self-care capacity can erode self-efficacy, increase dependence on others, and heighten vulnerability to stigmatization, a pattern also observed in disability-related research (51, 52). These findings suggest that self-care capability may reduce stigma by fostering autonomy and competence, whereas loss of independence can erode self-worth and increase vulnerability to stigmatization. Moreover, inadequate self-care often manifests in visible neglect, which can trigger negative social judgments and marginalization (53, 54). Although the correlation observed in our study was relatively weak (|r| < 0.3) and should be interpreted with caution, it nevertheless suggests that strengthening patients’ ability to manage their daily health could serve as a practical strategy for stigma reduction. Interventions that foster self-care skills and incorporate cognitive reframing or acceptance-based approaches may help patients maintain autonomy, mitigate feelings of worthlessness, and better cope with the visible symptoms of Meige syndrome (55).
We also observed a significant negative correlation between the total positive coping style score and the illness stigma score among patients with Meige syndrome (r = −0.225, p < 0.01). Although the effect size was relatively small (|r| < 0.3) and should be interpreted with caution, the finding aligns with coping theory, which highlights the protective role of adaptive coping strategies in reducing stress and stigma (17). Positive coping behaviors—such as seeking social support, reframing the meaning of illness, regulating emotions, and adopting problem-solving orientations—may help patients reinterpret their condition as a manageable challenge rather than a personal failure, thereby reducing internalized stigma (21). In addition, positive coping tends to promote social engagement and help-seeking, counteracting the avoidance and isolation that often characterize stigmatized individuals. Li et al. (13) pointed out that those Meige syndrome patients who actively sought external support perceived significantly lower levels of stigmatization. Nevertheless, cultivating positive coping habits may still help patients mobilize internal resources and enhance their self-efficacy in dealing with disease-related challenges, thereby contributing to the development of a more resilient psychological defense system.
In addition, a significant negative correlation was observed between resilience and illness stigma (r = −0.176, p < 0.01). Although the effect size was weak (|r| < 0.3) and should be interpreted with caution in terms of clinical significance, the direction of the association suggests that resilience may serve as a protective factor against stigmatization. This interpretation is consistent with previous studies showing that resilience fosters psychological adjustment and buffers stigma (24, 28). Other research has shown that individuals with higher resilience are often better able to manage emotions, maintain a positive mindset, and demonstrate greater psychological stability in the face of adversity (56, 57). Importantly, recent research also suggests a bidirectional link, whereby perceived stigma can erode resilience and, in turn, amplify social anxiety symptoms (58, 59). Such findings point to an interactive process between stigma and resilience that may exacerbate psychosocial vulnerability in patients with visible conditions like Meige syndrome. Clinically, these findings highlight the value of resilience as a protective factor, suggesting that interventions aiming to foster resilience should be prioritized to improve psychological well-being and reduce stigma in patients with Meige syndrome.
In addition, individuals with higher resilience typically possess more mature cognitive and physiological regulatory mechanisms, which enhance their capacity to adopt positive coping strategies when facing stress and challenges. For example, Yu Wu et al. (60) found that undergraduates with greater resilience and better emotion regulation demonstrated more flexible and adaptive coping styles. In the context of Meige syndrome, this interplay between resilience and coping may be especially important: stronger resilience facilitates positive coping, which in turn alleviates the physical and psychological burden of the disease and improves overall quality of life. This reciprocal relationship suggests a potential “virtuous cycle”, where resilience and coping mutually reinforce each other to buffer against stigma. These findings imply that psychological interventions should not only aim to enhance resilience but also incorporate structured coping skills training, enabling patients to build a more solid psychological defense system and adapt more effectively to the challenges of their illness and daily life.
In conclusion, this study found that people with Meige syndrome experience high levels of stigmatization. It comprehensively revealed that living alone, low self-care ability, and poor positive coping style are risk factors exacerbating illness stigma among Meige syndrome patients, while resilience and positive coping style act as protective factors. The significant correlations uncovered positive coping with psychological resilience, and both coping style and resilience with stigma underscored the intricate interplay of these factors. These findings highlight the need for multi-dimensional clinical interventions that focus on fostering positive coping mechanisms, enhancing psychological resilience, and addressing the unique social pressures faced by patients. By targeting these aspects, healthcare providers can effectively reduce stigma, improve mental well-being, and facilitate better adaptation to the challenges posed by Meige syndrome, ultimately promoting a more positive quality of life for patients.
5 Limitations
Despite efforts to enhance the methodological rigor of this study, several limitations should be noted. First, the demographic representativeness of the sample is limited, as participants were primarily drawn from specific geographic regions, potentially restricting the generalizability of the findings. Second, the cross-sectional design limited causal inferences regarding the associations among stigma, psychological resilience, and positive coping style. Third, the study focused predominantly on individual-level psychological variables, without extensive examination of broader contextual factors such as community support networks or healthcare accessibility.
6 Conclusion
This study reveals that patients with Meige syndrome experience high levels of illness stigma, which is associated with factors including living arrangement, self-care ability, positive coping style, and resilience. The findings indicated that patients who demonstrated higher resilience and adopted positive coping strategies experienced lower levels of perceived stigma, highlighting the need for targeted interventions that address the specific challenges faced by Meige syndrome patients, particularly in terms of reducing stigma and enhancing psychological resilience. Healthcare professionals should focus on the level of stigma in people with Meige syndrome who live alone or have low self-care abilities. Targeted psychological support measures focusing on positive coping style and resilience should be implemented for all patients with Meige syndrome. Future research should consider longitudinal designs to capture temporal changes in stigma and resilience and investigate the influence of external support systems in mitigating stigma among individuals with Meige syndrome.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Third People’s Hospital of Henan Province. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
ML: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. MTL: Methodology, Writing – original draft. NZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. KY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. FL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. CG: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Hao Q, Wang D, OuYang J, Ding H, Wu G, Liu Z, et al. Pallidal deep brain stimulation in primary Meige syndrome: clinical outcomes and psychiatric features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2020) 91:1343–8. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2020-323701
2. Aires A, Gomes T, Linhares P, Cunha F, Rosas MJ, and Vaz R. The impact of deep brain stimulation on health related quality of life and disease-specific disability in Meige Syndrome (MS). Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2018) 171:53–7. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2018.05.012
3. Yi M, Li J, Liu G, Ou Z, Liu Y, Li J, et al. Mental health and quality of life in patients with craniofacial movement disorders: A cross-sectional study. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:938632. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.938632
4. Fabbrini G, Berardelli I, Moretti G, Pasquini M, Bloise M, Colosimo C, et al. Psychiatric disorders in adult-onset focal dystonia: a case-control study. Mov Disord. (2010) 25:459–65. doi: 10.1002/mds.22983
5. Liamputtong P and Rice ZS. Stigma, discrimination, and social exclusion, Handbook of social inclusion: Research and practices in health and social sciences. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG (2022) p. 113–28.
6. Rüsch N, Angermeyer MC, and Corrigan PW. Mental illness stigma: Concepts, consequences, and initiatives to reduce stigma. Eur Psychiatry. (2005) 20:529–39. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2005.04.004
7. El-Badri S and Mellsop G. Stigma and quality of life as experienced by people with mental illness. Australas Psychiatry. (2007) 15:195–200. doi: 10.1080/10398560701320089
8. Meca-Lallana JE, Prefasi D, Pérez-Miralles F, Forero L, Sepúlveda M, Calles C, et al. Perception of stigma in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Patient Prefer Adherence. (2021) 15:713–9. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S305707
9. Brooks BD, Job SA, Kaniuka AR, Kolb R, Unda Charvel P, and Araújo F. Healthcare discrimination and treatment adherence among sexual and gender minority individuals living with chronic illness: the mediating effects of anticipated discrimination and depressive symptoms. Psychol Health. (2025) 40:304–20. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2023.2220008
10. Rasing NB, van de Geest-Buit W, Chan OYA, Mul K, Lanser A, Erasmus CE, et al. Psychosocial functioning in patients with altered facial expression: a scoping review in five neurological diseases. Disabil Rehabil. (2024) 46:3772–91. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2023.2259310
11. Rao D, Choi SW, Victorson D, Bode R, Peterman A, Heinemann A, et al. Measuring stigma across neurological conditions: the development of the stigma scale for chronic illness (SSCI). Qual Life Res. (2009) 18:585–95. doi: 10.1007/s11136-009-9475-1
12. Lencer R, Steinlechner S, Stahlberg J, Rehling H, Orth M, Baeumer T, et al. Primary focal dystonia: evidence for distinct neuropsychiatric and personality profiles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2009) 80:1176–9. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2008.170191
13. Li M, Li Q, Wei J, Li Y, Liu F, Li S, et al. Qualitative study on the real experiences of patients with meige syndrome based on the individual and family self-management theory. Patient Prefer Adherence. (2024) 18:2681–96. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S484296
14. Gowling H, O'Keeffe F, and Eccles FJR. Stigma, coping strategies, distress and wellbeing in individuals with cervical dystonia: a cross-sectional study. Psychol Health Med. (2024) 29:1313–30. doi: 10.1080/13548506.2024.2305172
16. Cummings EM and Kouros CD. Stress and Coping. In: Haith MM and Benson JB, editors. Encyclopedia of Infant and Early Childhood Development. Academic Press, San Diego (2008). p. 267–81.
17. Folkman S, Lazarus RS, Gruen RJ, and DeLongis A. Appraisal, coping, health status, and psychological symptoms. J Pers Soc Psychol. (1986) 50:571–9. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.50.3.571
18. Kato T. Examination of the coping flexibility hypothesis using the coping flexibility scale-revised. Front Psychol. (2020) 11:561731. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.561731
19. Carver CS, Scheier MF, and Weintraub JK. Assessing coping strategies: a theoretically based approach. J Pers Soc Psychol. (1989) 56:267–83. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.56.2.267
20. Misra S, Jackson VW, Chong J, Choe K, Tay C, Wong J, et al. Systematic review of cultural aspects of stigma and mental illness among racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States: implications for interventions. Am J Community Psychol. (2021) 68:486–512. doi: 10.1002/ajcp.v68.3-4
21. Zulu JM. Experiences and coping strategies of adolescents living with HIV at community level in Zambia. Edorium J Public Health. (2017) 4:48–57. doi: 10.5348/P16-2017-15-OA-7
22. Liu S, Xiao H, Qi P, Song M, Gao Y, Pi H, et al. The relationships among positive coping style, psychological resilience, and fear of falling in older adults. BMC Geriatr. (2025) 25:51. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-05682-6
23. Hasimi L, Ahmadi M, Hovyzian SA, and Ahmadi A. Sense of Coherence or resilience as predictors of psychological distress in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1233298. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1233298
24. Kurtses Gürsoy B and Köseoğlu Toksoy C. Psychological resilience and stress coping styles in migraine patients. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2023) 19:63–72. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S398838
25. Schäfer SK, Kunzler AM, Kalisch R, Tüscher O, and Lieb K. Trajectories of resilience and mental distress to global major disruptions. Trends Cognit Sci. (2022) 26:1171–89. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2022.09.017
26. Tao TJ, Liang L, Liu H, Hobfoll SE, Hou WK, and Bonanno GA. The interrelations between psychological outcome trajectories and resource changes amid large-scale disasters: A growth mixture modeling analysis. Transl Psychiatry. (2023) 13:57. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02350-4
27. Kashdan TB and Rottenberg J. Psychological flexibility as a fundamental aspect of health. Clin Psychol Rev. (2010) 30:865–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.03.001
28. Zhou J, Zhang Z, Li S, Chen H, Chen X, Tang H, et al. Childhood maltreatment influences coping in youths with major depression and bipolar depression through resilience and impulsivity. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:11441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96021-7
29. Moses T. What helps or undermines adolescents' anticipated capacity to cope with mental illness stigma following psychiatric hospitalization. Int J Soc Psychiatry. (2015) 61:215–24. doi: 10.1177/0020764014540147
30. Wang X and Cheng Z. Cross-sectional studies: strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations. Chest. (2020) 158:S65–s71. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.012
31. Zhang W, Pan Z, Zhu Y, Lv D, Zhang H, Li S, et al. Illness uncertainty, resilience, and perceived social support among patients with moyamoya disease: a cross-sectional study. Front Psychiatry. (2024) 15:1405594. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1405594
32. Lu Q, Deng C, Fu L, Wu R, Chang L, Qi H, et al. Reliability and validity of a Chinese version of the Stigma Scale for Chronic Illness (SSCI) in patients with stroke. Topics Stroke Rehabil. (2019) 26:1–6. doi: 10.1080/10749357.2019.1592306
33. Martínez-Fernández A, Vega MR, Quintas S, Heras MDT, and Gago-Veiga AB. Psychosocial repercussion of migraine: is it a stigmatized disease? Neurological Sci. (2020) 41:2207–13. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04332-6
34. Tan H. A cross-sectional study of the impact of stigma on quality of life in hemiplegic stroke patients following suicide attempts in nursing homes. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:26953. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75131-8
36. Campbell-Sills L and Stein MB. Psychometric analysis and refinement of the Connor-davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC): Validation of a 10-item measure of resilience. J Trauma Stress. (2007) 20:1019–28. doi: 10.1002/jts.20271
37. Ye ZJ, Qiu HZ, Li PF, Chen P, Liang MZ, Liu ML, et al. Validation and application of the Chinese version of the 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC-10) among parents of children with cancer diagnosis. Eur J Oncol Nurs. (2017) 27:36–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2017.01.004
38. Gilvari T, Babamohamadi H, and Paknazar F. Perceived professional identity and related factors in Iranian nursing students: a cross-sectional study. BMC Nurs. (2022) 21:279. doi: 10.1186/s12912-022-01050-6
39. Feng X, Wang Y, Jia P, Wang Y, Guan Z, and Meng K. Associations between professional identity and turnover intent in prehospital emergency physicians: The mediating effect of burnout. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:1034925. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1034925
40. Ballesteros J, Martínez-Ginés ML, García-Domínguez JM, Forero L, Prefasi D, and Maurino J. Assessing stigma in multiple sclerosis: psychometric properties of the eight-item stigma scale for chronic illness (SSCI-8). Int J MS Care. (2019) 21:195–9. doi: 10.7224/1537-2073.2018-053
41. Polat H, Turan GB, and Tan M. Determining the relationship between stigmatization and social support in tuberculosis patients. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. (2024) 37:100502. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2024.100502
42. Liu X, Wen S, and Wu D. The mediating roles of family care and self-efficacy between stigma and social alienation among colorectal cancer survivors. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:15312. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99852-6
43. Oladele DA, Balogun MR, Odeyemi K, and Salako BL. A comparative study of knowledge, attitude, and determinants of tuberculosis-associated stigma in rural and urban communities of lagos state, Nigeria. Tuberc Res Treat. (2020) 2020:1964759. doi: 10.1155/2020/1964759
44. Schroeder S, Tan CM, Urlacher B, and Heitkamp T. The role of rural and urban geography and gender in community stigma around mental illness. Health Educ Behav. (2021) 48:63–73. doi: 10.1177/1090198120974963
45. Chen TY, Geng JH, Chen SC, and Lee JI. Living alone is associated with a higher prevalence of psychiatric morbidity in a population-based cross-sectional study. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:1054615. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1054615
46. Dean A, Kolody B, Wood P, and Matt GE. The influence of living alone on depression in elderly persons. J Aging Health. (1992) 4:3–18. doi: 10.1177/089826439200400101
47. Xiu-Ying H, Qian C, Xiao-Dong P, Xue-Mei Z, and Chang-Quan H. Living arrangements and risk for late life depression: a meta-analysis of published literature. Int J Psychiatry Med. (2012) 43:19–34. doi: 10.2190/PM.43.1.b
48. Hunt C, Issakidis C, and Andrews G. DSM-IV generalized anxiety disorder in the Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Well-Being. Psychol Med. (2002) 32:649–59. doi: 10.1017/S0033291702005512
49. Yu J, Choe K, and Kang Y. Anxiety of older persons living alone in the community. Healthcare (Basel). (2020) 8. doi: 10.3390/healthcare8030287
50. Kato A, Fujimaki Y, Fujimori S, Isogawa A, Onishi Y, Suzuki R, et al. Association between self-stigma and self-care behaviors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2016) 4:e000156. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2015-000156
51. Pyszkowska A and Stojek MM. Early maladaptive schemas and self-stigma in people with physical disabilities: the role of self-compassion and psychological flexibility. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710854
52. Livneh H and Antonak RF. Psychosocial adaptation to chronic illness and disability: A primer for counselors. J Couns Dev. (2011) 83:12–20. doi: 10.1002/j.1556-6678.2005.tb00575.x
53. Zhang R, Wang MS, Toubiana M, and Greenwood R. Stigma beyond levels: advancing research on stigmatization. Acad Manage Ann. (2021) 15:15. doi: 10.5465/annals.2019.0031
54. Tyerman J, Patovirta AL, and Celestini A. How stigma and discrimination influences nursing care of persons diagnosed with mental illness: A systematic review. Issues Ment Health Nurs. (2020) 42:1–11. doi: 10.1080/01612840.2020.1789788
55. Zhang X, Shao C, Wang B, and Huang S. The impact of COVID-19 on travel mode choice behavior in terms of shared mobility: A case study in beijing, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127130
56. Post F, Buchta M, Kemmler G, Pardeller S, Frajo-Apor B, and Hofer A. Resilience predicts self-stigma and stigma resistance in stabilized patients with bipolar I disorder. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:678807. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.678807
57. Tomás CC, Oliveira E, Sousa D, Uba-Chupel M, Furtado G, Rocha C, et al. Proceedings of the 3rd IPLeiria's international health congress: leiria, Portugal. BMC Health Serv Res. (2016) 16 Suppl 3:200. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1423-5
58. Hahm HC, Ha Y, Scott JC, Wongchai V, Chen JA, and Liu CH. Perceived COVID-19-related anti-Asian discrimination predicts post traumatic stress disorder symptoms among Asian and Asian American young adults. Psychiatry Res. (2021) 303:114084. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114084
59. Chen X, Mao Y, Kong L, Li G, Xin M, Lou F, et al. Resilience moderates the association between stigma and psychological distress among family caregivers of patients with schizophrenia. Pers Individ Dif. (2016) 96:78–82. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2016.02.062
Keywords: Meige syndrome, illness stigma, cross-sectional study, influencing factors, resilience
Citation: Li M, Li M, Zhang N, Zhou L, Zhang W, Yang K, Yang X, Li S, Li Y, Liu F, Li Q, Wei J, Gao C and Li H (2025) The relationships between positive coping style, resilience, and illness stigma in patients with Meige syndrome: a cross-sectional study. Front. Psychiatry 16:1646084. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1646084
Received: 12 June 2025; Accepted: 18 September 2025;
Published: 06 October 2025.
Edited by:
Nida Zahid, Aga Khan University, PakistanReviewed by:
Francesco Monaco, Azienda Sanitaria Locale Salerno, ItalyAndré Luiz Monezi Andrade, Pontifical Catholic University of Campinas, Brazil
Serdar Karakullukçu, Karadeniz Technical University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Li, Li, Zhang, Zhou, Zhang, Yang, Yang, Li, Li, Liu, Li, Wei, Gao and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huawei Li, MTc4MDY1NjQzQHFxLmNvbQ==; Chanchan Gao, Z2FvY2hhbmNoYW4xOTgxQDE2My5jb20=; Junfan Wei, d2VpanVuZmFuMTIzNDU2QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Meng Li
Meng Li Mengtian Li
Mengtian Li Ning Zhang
Ning Zhang Linghan Zhou1
Linghan Zhou1 Wenling Zhang
Wenling Zhang Shen Li
Shen Li Qiong Li
Qiong Li Junfan Wei
Junfan Wei