- 1School of Medicine, Qilu Institute of Technology, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2School of Nursing, Qilu Medical University, Zibo, Shandong, China
- 3Department of Nursing, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University; Shandong Provincial Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
Background: Stroke patients have a high incidence of Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Previous studies on PTSD in stroke patients mainly focus on the risk factors and possible harms caused by PTSD and use the overall score to explain the severity of PTSD. The interconnections and effects of symptoms are ignored. Network analysis is a statistical method that can discover and visualize complex relationships between multiple variables. The purpose of this study was to identify the central and core symptoms in the symptom network of PTSD in stroke patients.
Methods: 315 patients diagnosed with cerebral apoplexy were selected as the study objects. Symptoms of PTSD were assessed using the Event Impact Scale (IES-R). The graph Gaussian model is used to estimate the network model. To clarify the network relationship and core symptoms of PTSD in stroke patients. The network’s stability and accuracy are tested using the discard example method and non-parametric bootstrap method.
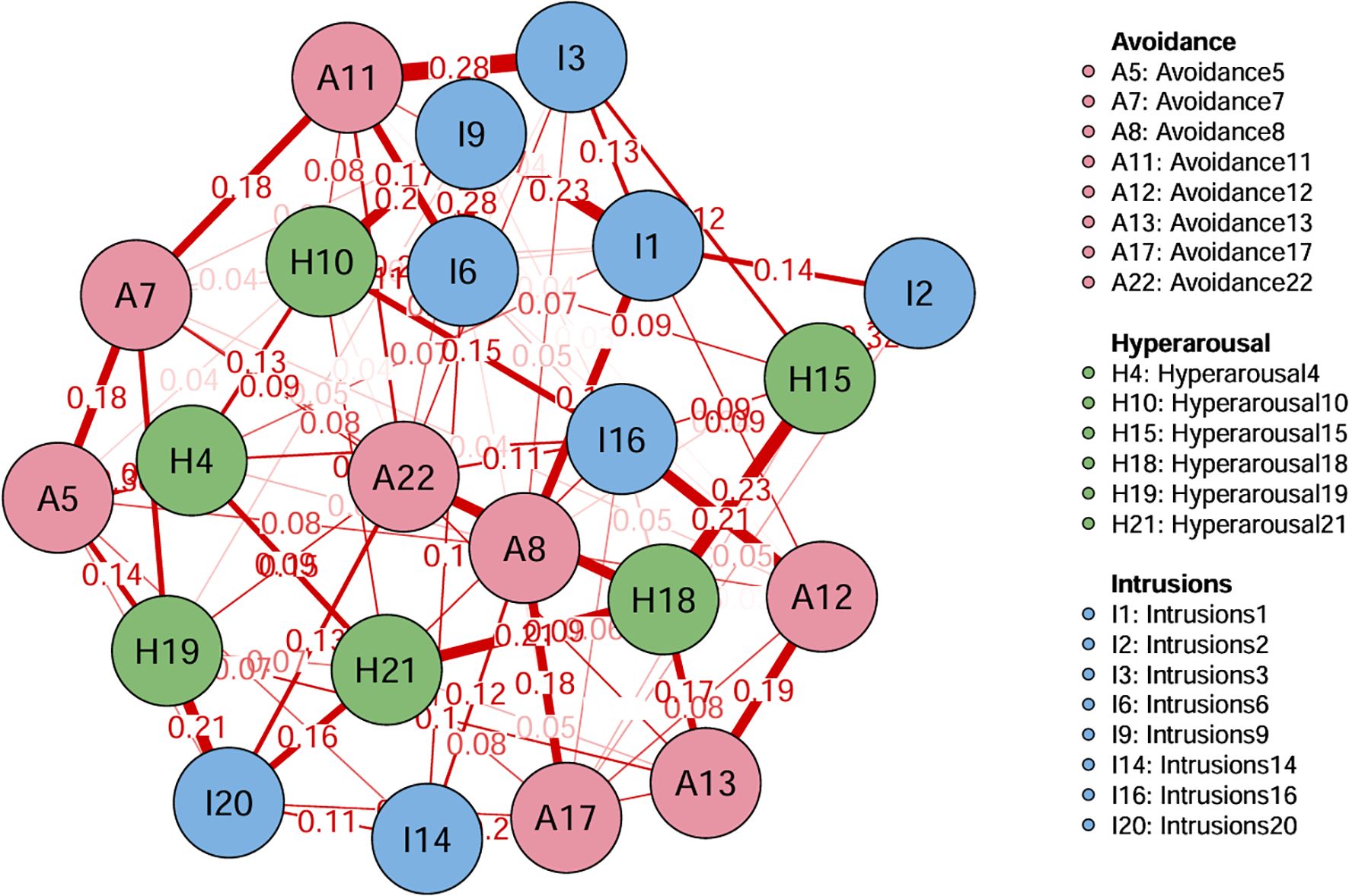
Result: The network analysis found that A11 (I tried not to think about it) has the most substantial relationship with I3 (Other things kept making me think about it). I6 (I thought about it when I didn’t mean to) has the most substantial relationship with I9 (Pictures about it popped into my mind). “I was jumpy and easily startled”(H10) is the core symptom of PTSD in stroke patients. The network structure is suitable for stability and accuracy tests.
Conclusion: It is possible to reduce the severity of PTSD in stroke patients and promote their personal growth by taking timely intervention measures according to the identified central symptoms of PTSD.
Introduction
Stroke is the leading cause of death worldwide (1), accounting for 11.8% of deaths worldwide (2), and is the leading cause of long-term physical, cognitive or psychological disability. Psychological complications of stroke include depression and anxiety in 29-33% of stroke survivors (3–5). Due to the sudden onset of stroke, it is difficult to predict and uncontrollable, which seriously affects the physical and mental health of patients and causes post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (6). PTSD is a form of mental trauma that is delayed or persists for a long time after an individual experiences sudden, threatening, or even catastrophic events (7). The main manifestations are that the content or scenes related to trauma repeatedly surface in the mind uncontrollably. Individuals often resist participating in activities related to the traumatic event and try to avoid places and people related to the traumatic event (7). In addition, patients may also experience emotional reactions such as irritability and excessive alertness. Some people may even show somatization symptoms of anxiety (8). The prevalence rate of PTSD after stroke is up to 18% (9). PTSD not only affects patients’ interpersonal communication, work, and life but also comorbidities such as anxiety, depression, drug abuse, and fear, which seriously affect patients’ quality of life and mental health. Research shows that most people with PTSD are not detected and treated in time and that this traumatic event causes widespread suffering for almost everyone (10, 11). Foreign studies have shown that PTSD significantly affects patients’ cognitive problems and adaptation problems (12), and the more severe the PTSD symptoms, the worse the cognitive function (13).There are various clinical symptoms of PTSD, and the interaction between symptoms will affect the progression of the disease (14). Previous studies on PTSD in stroke patients mainly focus on the risk factors of PTSD and the possible harm caused by PTSD, using the overall score. To explain the severity of PTSD, it is assumed that each symptom or item is of equal importance, ignoring the correlation and function of the symptoms (15).
Borsboom proposed the network theory of mental disorder (NTMD) in 2017 (16). This theory holds that mental disorders are complex network systems formed by the interactions among symptoms, and the direct interactions among symptoms lead to the emergence of mental disorders (16). Specifically, a certain stimulus may activate a certain symptom, and the emergence of this symptom will further activate other related symptoms (17). Thus, a continuous activation cycle is formed. When the activated symptom cluster reaches a certain diagnostic criterion, mental disorders occur. Network analysis is a data analysis method based on network theory (17). It is a statistical approach capable of discovering and visualizing complex relationships among multiple variables and identifying potential influencing factors (18). An essential goal of network analysis methods is identifying central and bridging symptoms in a network and analyzing the mechanisms affecting its connectivity (19). A network diagram visually represents a system consisting of nodes and edges. Nodes represent variables, and edges represent connections between nodes. The centrality index is used to identify the most critical nodes in the network, including strength, tightness, and intermediateness (20). Strength centrality determines the strength of the relationship between a node and its neighbors. Proximity centrality represents the average distance between a node and other nodes. Intermediate centrality represents the frequency at which a node is connected between two nodes (21). Researchers can better understand the mechanisms underpinning component-to-symptom interaction and provide more accurate intervention targets at a finer level with the use of NA (22).
The central symptoms vary from person to person. Therefore, based on NA, this study attaches importance to the interaction of PTSD symptoms in stroke patients and constructs PTSD symptom networks through symptom network analysis. Driven by data, this study presents the connection between symptoms and symptom interactions through network maps, intuitively identifies network features and core symptoms, and proposes corresponding nursing countermeasures. It provides the basis for exploring the target of psychological rehabilitation intervention and accurate symptom management.
Measurement
Participants
This is a cross-sectional study conducted from May 2024 to May 2025 in Shandong Province, China. Clinical staff recruited participants on site, and after obtaining informed consent from eligible individuals, they quickly distributed paper versions of the questionnaire. Participants were selected based on the following criteria: (1) they were at least 18 years of age; (2) they had been diagnosed as stroke by a clinician and confirmed as stroke by neuroimaging tests such as CT or MRI; (3) Clear consciousness, able to cooperate with research; (4) Express willingness to participate in this study. Exclusion criteria: (1) a history of significant anxiety, depression, mental retardation or other serious mental illness; (2) Patients with various serious physical diseases or malignant tumors; (3) recent use of antidepressants or sedatives; (4) Experienced heavy family changes or trauma in the past six months. Ultimately, 350 stroke patients participated in the study. A total of 315 people successfully completed the questionnaire, with an effective response rate of 90%.
Sociodemographic characteristics
Participants self-reported their information, providing details of age, educational background, marital status, whether they were co-diabetics, whether they were co-hypertensive, etc.
PTSD symptoms
Weiss and Marmar (23) revised Horowitz’s Impact of Events Scale in 1979 (24), a total of 22 items. Domestic scholars such as Guo (25) divided the scale into three factors, arousal, escape, and intrusion, according to the original text, and revised the scale. The severity of PTSD was evaluated according to the total score. When the total score was 0-8, it was subclinical without PTSD. A score of 9 to 25 is mild PTSD, 26 to 43 is moderate PTSD, and 44 to 88 is severe PTSD. The IES-R has been widely used among Chinese populations (26, 27), demonstrating good reliability and validity in this study. The Cronbach’s α coefficient of this scale was 0.95 in the study.
Data analysis
First, the data were analyzed in the SPSS 26.0 package program. We conducted a descriptive analysis to analyze the characteristics of the participants (continuous variables: means and standard deviations (SD); categorical variables: frequencies and percentages). We computed polychoric correlations between all nodes to examine the edges of the network. Polychoric, EBIC and glasso jointly calculated the edge weight. Then, we estimated the Graphical Gaussian Model (GGM) using the graphical least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) in combination with the Extended Bayesian Information Criterion (EBIC) model (20). In the network model, each symptom is represented as a “node” and the association between symptoms is defined as an “edge.” Nodes with high EI values can activate other nodes within the network, making them essential components of their own network (28). To identify bridge nodes that connect PTSD, we calculated the bridge expected influence (BEI). A higher positive value of the BEI for a node indicates a greater activation capacity toward nodes in another cluster. In contrast, a higher negative value signifies a more substantial deactivation capacity toward nodes in another cluster (28, 29). Bootstrapping approaches were adopted through the R package botnet to guarantee the networks’ accuracy and stability. We applied non-parametric bootstrapping (with 2,000 samples) to estimate the 95% confidence interval for all edges within the network to verify the accuracy of edge weights (20). To ensure the stability of BEI centrality, the correlation stability (CS) coefficient was obtained by a case-dropping subset bootstrap method (with 2,000 bootstrap samples) (20). It is recommended that the CS-coefficient is preferably above 0.5 and should not fall below 0.25 (20). Bootstrap difference tests (2,000 samples) were conducted to determine if there are significant differences between edge weights or between node BEIs. Bootstrap difference testing (2,000 samples) was run to determine whether significant differences exist between edge weights or node BEIs (20).
Results
Characteristics of the participants
A total of 315 stroke participants were investigated, of which 174 (55.2%) were male stroke participants and 141 (44.8%) were female. In terms of comorbidities, 86 (27.3%) stroke participants had diabetes, and 144 (45.7%) stroke participants had hypertension. Further demographic information on the participants is shown in Table 1. The total score of PTSD was 32.05 ± 15.472. The mean and standard deviation of the PTSD program are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
Network structure
Figure 1 shows the network structure of PTSD. Two hundred thirty-one edge numbers were constructed in the whole network, and 22 symptoms in 3 dimensions were included in the entire network. Among them, the two groups with the most significant edge weight, A11 (I tried not to think about it) and I3 (Other things kept making me think about it), have an edge weight value of 0.28. I6 (I thought about it when I didn’t mean to) and I9 (Pictures about it popped into my mind) have an edge weight of 0.28. The correlation matrix for PTSD items is presented in Supplementary Table S2.
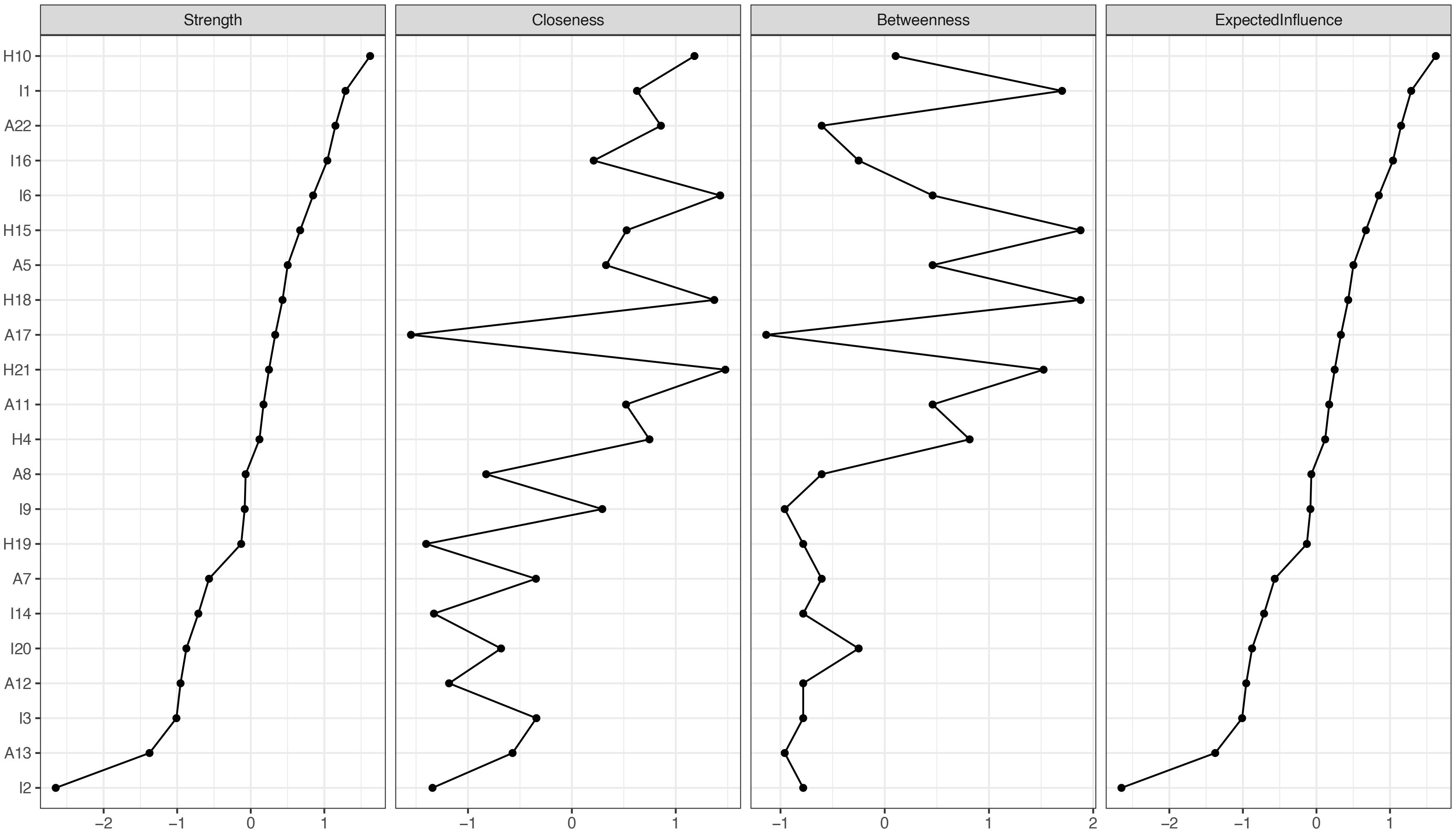
In terms of EI centrality, network node H10 (“I was jumpy and easily startled”) has the highest EI value (1.622). This is followed by I1 (“Any reminder brought back feelings about it”) (EI value 1.288) and A22 (“ I tried not to talk about it”) (EI value 1.151). The PTSD values for each node are illustrated in Figures 2, 3. The bootstrapped 95% CIs for most edge weights were relatively narrow, indicating an accurate network structure (see Supplementary Figure S1). In addition, the non-parametric bootstrap difference test showed significant differences between partial edge weights and node EIS (see Supplementary Figures S2, S3).
Network stability and accuracy
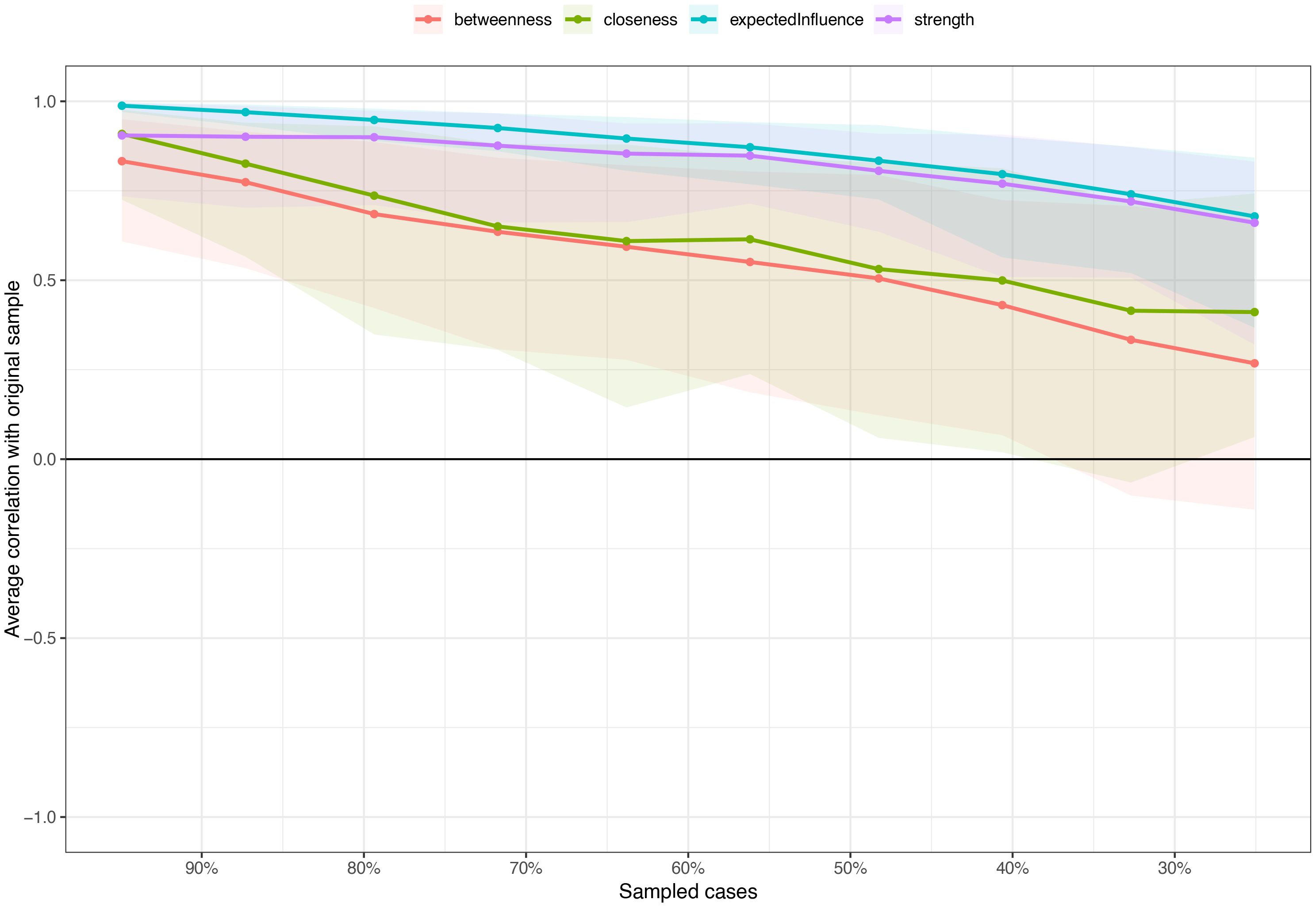
Network stability and accuracy Figure 4 shows the results of the case-dropping bootstrap test. In terms of network stability, the CS coefficient of the centrality EI is 0.517. The centrality index will change significantly only after the network samples decrease by 51.7%. Additionally, nonparametric bootstrapped difference tests revealed significant differences among most edge weights and node EIs (see Supplementary Figures S2, Supplementary Figures S3).
Discussion
In our study, we found that the PTSD score of stroke patients was 32.05 (SD 15.472), which was at a moderate level. Stroke patients with sudden onset and severe disease, easy to cause the body’s nervous, endocrine and immune system dysfunction. The suddenness, unpredictability, uncontrollability and severity of stroke have caused severe blows to patients both physically and psychologically, which can easily lead to PTSD in patients. We suggest conducting PTSD assessment for stroke patients at an early stage, promptly formulating and implementing care plans. Additionally, through interdisciplinary collaboration, integrating professional knowledge from fields such as psychology, neuroscience, and rehabilitation medicine, we aim to further promote research and practice on PTSD in stroke patients, thereby facilitating their mental health and overall recovery.
Symptom network analysis results of this study showed that symptoms “I tried not to think about it (A11)” and symptoms “Other things kept making me think about it (I3)”, The strongest association was found between symptoms such as “I thought about it when I didn’t mean to (I6)” and “Pictures about it popped into my mind” (I9). Avoidance is a common behavior in mental illness (30). People who experience trauma often avoid thoughts, feelings, and places that remind them of the traumatic experience. In fact, individuals who have experienced trauma often distort attribution about themselves and the world, forming negative cognitive styles (31, 32). In order to avoid having this negative experience, they will shift their attention away from the thoughts and feelings associated with the traumatic event, i.e. show symptoms of thoughts avoidance. Recalling the thoughts and feelings of stroke may cause pain to patients. In order to reduce the pain, some patients will choose to avoid recalling the thoughts and feelings related to stroke experience (33), such as the feeling of numbness and dizziness during stroke attack, and the dialogue and scenes during stroke attack will also remind patients of stroke. Stroke is a sudden, significant physical and psychological traumatic event. When a patient experiences an episode of stroke, it is often accompanied by intense physical pain, fear, confusion, or a sense of death. Emotionally intense events tend to leave deep memory traces in the brain, especially those that are physically or psychologically extremely upsetting or frightening. These memories are reinforced and stored by the brain’s amygdala (emotional processing center), causing the patient’s mind to repeatedly reproduce images, situations or fragments associated with stroke. Active psychological care should be given to patients with cerebral stroke to guide them in understanding stroke and coping with trauma. Nurses should achieve precise positioning in clinical practice, help patients understand the nature of stroke and the rehabilitation process, and alleviate patients’ mental stress through measures such as cognitive therapy (34). On the basis of routine care, psychological care should be provided, and patients should be guided to correctly deal with trauma. In future research, the above symptoms should be closely monitored, and symptoms with strong preventive identification should be identified. Taking this as the entry point, a combination of early psychological intervention and drug treatment is adopted to weaken the interaction between symptoms (35), cut off the strong connection between symptoms, improve the efficiency and effect of intervention (35), and control the progression of PTSD.
Among the symptoms, “I was jumpy and easily startled”(H10) showed the highest EI value. This is an effective target for the prevention, treatment and intervention of PTSD in stroke patients. Individuals who experience trauma become more sensitive to similar stimuli or triggering events, and with a heightened panic response, the patient exhibits a heightened state of alertness (36). Studies have found that patients with PTSD have apparent abnormal changes in brain function in the amygdala, ventromedial prefrontal cortex, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex and hippocampus (37, 38). The amygdala and dorsal anterior cingulate gyrus are essential brain regions for cognitive function and emotional generation and regulation, and enhancing activation will cause hypervigilance in patients (39). Thus, intensive interventions by caregivers targeting the symptom “I was jumpy and easily startled”(H10) “may be more effective in reducing the overall level of PTSD than interventions targeting the remaining symptoms, which may have the greatest clinical significance at the moment.” Psychological interventions can be implemented to reduce the symptoms (40). At present, the common psychological interventions include cognitive behavioral therapy (41), cognitive processing therapy, exposure therapy (42), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy (43). However, it is important to note that each patient’s situation is unique, and it is important to choose treatment options individually. This study provides several important implications for addressing mental disorders in stroke patients. First, the prevalence of PTSD in patients with brain stroke (3-37%) remains alarmingly high (5, 44–48), and our study also found moderate levels of PTSD in stroke patients. This demonstrates the urgent need for timely screening and targeted mental health interventions, the implementation of which is essential to maintain the well-being of stroke patients and maintain quality of life. Second, our study not only provides a detailed understanding of PTSD in stroke patients, but also lays the foundation for future psychological interventions aimed at reducing PTSD in stroke patients. Third, “I was jumpy and easily startled”(H10) is considered to be the core symptom of PTSD in patients with brain stroke. This suggests that in future research, more attention should be paid to whether patients will show negative emotional manifestations after stroke. During health education and nursing intervention, patients should be guided to have a correct understanding of the occurrence of stroke. At the same time, psychological counseling should be provided to patients in a timely manner, encouraging them to express and vent their emotions. Emphasis should be placed on improving patients’ understanding of the disease and eliminating their fears. Reduce the physiological responses caused by fright (49), provide precise rehabilitation guidance, improve the patient’s psychological cognition, avoid emotional imbalance, accelerate the progression of PTSD, and at the same time tell the patient to maintain healthy behaviors and lifestyles. Moreover, in future research, it is necessary to further understand the influencing factors of this symptom, so as to achieve more precise intervention effects, promote the psychological rehabilitation of patients, and more widely reduce the overall level of PTSD.
Limitations
Current research on NA of PTSD symptoms has primarily focused on populations such as veterans (50) and firefighters (51), while studies examining NA in relation to PTSD among stroke patients remain limited. Our study provides a novel and systematic perspective on the core maintaining factors and potential intervention targets of post-stroke PTSD, thereby offering evidence to support healthcare providers in improving PTSD symptoms in stroke survivors. However, our research still has limitations. First, with the cross-sectional design used in this study, we could not assess PTSD dynamics. A longitudinal investigation of these variables using NA is required. Second, the sample is entirely from the city of Dalian in northern China, so extending the findings to more developed cities remains to be considered. Finally, our study does not empirically confirm the proposed intervention goals and further research is needed to validate them before they can be applied in the real world.
Conclusion
In summary, this study found the symptom network characteristics and key symptoms of PTSD in stroke patients through symptom network analysis. In future studies, preventive identification of strongly linked and key symptoms should be considered, and scientific psychological intervention measures should be developed to promote the improvement of the mental health status of stroke patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Shandong First Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YiL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YaL: Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all participants and medical staff involved in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1663366/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Katan M and Luft A. Global burden of stroke. Semin Neurol. (2018) 38:208–11. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1649503
2. Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. (2014) 383:245–54. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61953-4
3. Hackett ML, Yapa C, Parag V, and Anderson CS. Frequency of depression after stroke: a systematic review of observational studies. Stroke. (2005) 36:1330–40. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000165928.19135.35
4. Ayerbe L, Ayis S, Wolfe CD, and Rudd AG. Natural history, predictors and outcomes of depression after stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. (2013) 202:14–21. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.111.107664
5. Merriman C, Norman P, and Barton J. Psychological correlates of PTSD symptoms following stroke. Psychol Health Med. (2007) 12:592–602. doi: 10.1080/13548500601162747
6. Duan CM, Wang YY, and Wang LL. Application effect of multi module rehabilitation nursing model in intelligent follow-up of stroke patients. Chin J Nurs. (2023) 58:276–82. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.03.003
7. Pausch MJ, Matten SJ, Pausch MJ, and Matten SJ. Trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)—Definition, classification, epidemiology and history. In: Trauma and trauma consequence disorder: in media, management and public. Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, Wiesbaden (2022). p. 3–12.
8. Deja M, Denke C, Weber-Carstens S, Schröder J, Pille CE, Hokema F, et al. Social support during intensive care unit stay might improve mental impairment and consequently health-related quality of life in survivors of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care. (2006) 10:R147. doi: 10.1186/cc5070
9. Kronish IM, Edmondson D, Goldfinger JZ, Fei K, and Horowitz CR. Posttraumatic stress disorder and adherence to medications in survivors of strokes and transient ischemic attacks. Stroke. (2012) 43:2192–7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.655209
10. Tang WK, Wang L, Kk FT, Rutovic S, and Kim JS. Post-traumatic stress disorder after stroke: A systematic review. Neurol India. (2022) 70:1887–95. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.359285
11. Yu S, Alper HE, Nguyen AM, Maqsood J, and Brackbill RM. Stroke hospitalizations, posttraumatic stress disorder, and 9/11-related dust exposure: Results from the World Trade Center Health Registry. Am J Ind Med. (2021) 64:827–36. doi: 10.1002/ajim.23271
12. Bano Z and Naz I. Post-traumatic stress disorder, cognitive function and adjustment problems in women burn survivors: A multi-center study. J Pak Med Assoc. (2020) 70:2102–7. doi: 10.47391/jpma.1260
13. Buodo G, Ghisi M, Novara C, Scozzari S, Di Natale A, Sanavio E, et al. Assessment of cognitive functions in individuals with post-traumatic symptoms after work-related accidents. J Anxiety Disord. (2011) 25:64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2010.08.004
14. Armour C, Fried EI, and Olff M. PTSD symptomics: network analyses in the field of psychotraumatology. Eur J Psychotraumatol. (2017) 8:1398003. doi: 10.1080/20008198.2017.1398003
15. Jin Y, Sha S, Tian T, Wang Q, Liang S, Wang Z, et al. Network analysis of comorbid depression and anxiety and their associations with quality of life among clinicians in public hospitals during the late stage of the COVID-19 pandemic in China. J Affect Disord. (2022) 314:193–200. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.06.051
16. Borsboom D. A network theory of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. (2017) 16:5–13. doi: 10.1002/wps.20375
17. Borsboom D, Cramer AO, and Kalis A. Brain disorders? Not really: Why network structures block reductionism in psychopathology research. Behav Brain Sci. (2018) 42:e2. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X17002266
18. Henneghan A, Wright ML, Bourne G, and Sales AC. A cross-sectional exploration of cytokine-symptom networks in breast cancer survivors using network analysis. Can J Nurs Res. (2021) 53:303–15. doi: 10.1177/0844562120927535
19. Shang B, Chen R, Luo C, Lv F, Wu J, Shao X, et al. The relationship between alexithymia, depression, anxiety, and stress in elderly with multiple chronic conditions in China: a network analysis. Front Psychiatry. (2023) 14:1209936. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1209936
20. Epskamp S, Borsboom D, and Fried EI. Estimating psychological networks and their accuracy: A tutorial paper. Behav Res Methods. (2018) 50:195–212. doi: 10.3758/s13428-017-0862-1
21. Mcnally RJ. Can network analysis transform psychopathology? Behav Res Ther. (2016) 86:95–104. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2016.06.006
22. Zhou Y, Gao W, Li H, Yao X, Wang J, and Zhao X. Network analysis of resilience, anxiety and depression in clinical nurses. BMC Psychiatry. (2024) 24:719. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06138-8
23. Weiss DS and Marmar CR. “The impact of event scale—revised”. In: Wilson JP and Keane TM (Eds.). Assessing psychological trauma and PTSD. The Guilford Press (1997) p. 399–411.
24. Horowitz M, Wilner N, and Alvarez W. Impact of Event Scale: a measure of subjective stress. Psychosom Med. (1979) 41:209–18. doi: 10.1097/00006842-197905000-00004
25. Guosu- R, Zi-Qiang X, and Liu-Na G. Reliability and validity of chinese version of the impact of event scale- revised. Chin J Clin Psychol. (2007) (01):15–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3611.2007.01.006
26. Yang L, Liu Y, Han L, Ao Y, and Yang H. Impact of COVID-19 on mental health of chinese residents in its initial stage. Front Psychol. (2021) 12:722093. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.722093
27. Chen B, Li QX, Zhang H, Zhu JY, Yang X, Wu YH, et al. The psychological impact of COVID-19 outbreak on medical staff and the general public. Curr Psychol. (2022) 41:5631–9. doi: 10.1007/s12144-020-01109-0
28. Mcnally RJ. Network analysis of psychopathology: controversies and challenges. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. (2021) 17:31–53. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-081219-092850
29. Jones PJ, Ma R, and Mcnally RJ. Bridge centrality: A network approach to understanding comorbidity. Multivariate Behav Res. (2021) 56:353–67. doi: 10.1080/00273171.2019.1614898
30. Bishop LS, Ameral VE, and Palm Reed KM. The impact of experiential avoidance and event centrality in trauma-related rumination and posttraumatic stress. Behav Modif. (2018) 42:815–37. doi: 10.1177/0145445517747287
31. Bolger KE, Patterson CJ, and Kupersmidt JB. Peer relationships and self-esteem among children who have been maltreated. Child Dev. (1998) 69:1171–97.
32. Kim J and Cicchetti D. Longitudinal trajectories of self-system processes and depressive symptoms among maltreated and nonmaltreated children. Child Dev. (2006) 77:624–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2006.00894.x
33. Kp Z. Effects of attachment and ruminant thinking on post traumatic stress disorder and drug compliance in stroke patients. (2020).
34. Vuper TC, Philippi Cl, and Bruce SE. Altered resting-state functional connectivity of the default mode and central executive networks following cognitive processing therapy for PTSD. Behav Brain Res. (2021) 409:113312. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113312
35. Sessa B. MDMA and PTSD treatment: “PTSD: From novel pathophysiology to innovative therapeutics. Neurosci Lett. (2017) 649:176–80. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.07.004
36. Armstrong T, Engel M, and Dalmaijer ES. Vigilance: A novel conditioned fear response that resists extinction. Biol Psychol. (2022) 174:108401. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2022.108401
37. Lee MS, Anumagalla P, and Pavuluri MN. Individuals with the post-traumatic stress disorder process emotions in subcortical regions irrespective of cognitive engagement: a meta-analysis of cognitive and emotional interface. Brain Imaging Behav. (2021) 15:941–57. doi: 10.1007/s11682-020-00303-9
38. Harlé KM, Simmons AN, Norman SB, and Spadoni AD. Neural affective mechanisms associated with treatment responsiveness in veterans with PTSD and comorbid alcohol use disorder. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. (2020) 305:111172. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2020.111172
39. Beining Y and Nan C. Advances in neuroimaging research on pathogenesis and diagnosis of post-traumatic stress disorder. J Clin Radiol. (2024) 43:1218–21. doi: 10.13437/j.cnki.jcr.2024.07.032
40. Schrader C and Ross A. A review of PTSD and current treatment strategies. Mo Med. (2021) 118:546–51.
41. Ross SL, Sharma-Patel K, Brown EJ, Huntt JS, and Chaplin WF. Complex trauma and Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: How do trauma chronicity and PTSD presentation affect treatment outcome? Child Abuse Negl. (2021) 111:104734. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104734
42. Mclean CP, Levy HC, Miller ML, and Tolin DF. Exposure therapy for PTSD: A meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. (2022) 91:102115. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2021.102115
43. Arditte Hall KA, Werner KB, Griffin MG, and Galovski TE. The effects of cognitive processing therapy + hypnosis on objective sleep quality in women with posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychol Trauma. (2021) 13:652–6. doi: 10.1037/tra0000970
44. Sembi S, Tarrier N, O’neill P, Burns A, and Faragher B. Does post-traumatic stress disorder occur after stroke: a preliminary study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (1998) 13:315–22. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1166(199805)13:5<315::AID-GPS766>3.0.CO;2-P
45. Bruggimann L, Annoni JM, Staub F, von Steinbüchel N, van der Linden M, and Bogousslavsky J. Chronic posttraumatic stress symptoms after nonsevere stroke. Neurology. (2006) 66:513–6. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000194210.98757.49
46. Field EL, Norman P, and Barton J. Cross-sectional and prospective associations between cognitive appraisals and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms following stroke. Behav Res Ther. (2008) 46:62–70. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2007.10.006
47. Sagen U, Vik TG, Moum T, Mørland T, Finset A, and Dammen T. Screening for anxiety and depression after stroke: comparison of the hospital anxiety and depression scale and the Montgomery and Asberg depression rating scale. J Psychosom Res. (2009) 67:325–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2009.03.007
48. Wang X, Chung MC, Hyland ME, and Bahkeit M. Posttraumatic stress disorder and psychiatric co-morbidity following stroke: the role of alexithymia. Psychiatry Res. (2011) 188:51–7. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2010.10.002
49. Yue HE and Zhang H. Psychological effect and psychological recovery of PTSD. Chin J Clin Rehabi. (2003) 16):2346–7.
50. Duek O, Spiller TR, Pietrzak RH, Fried EI, and Harpaz-Rotem I. Network analysis of PTSD and depressive symptoms in 158,139 treatment-seeking veterans with PTSD. Depress Anxiety. (2021) 38:554–62. doi: 10.1002/da.23112
Keywords: PTSD, stroke, network analysis, post-traumatic stress disorder, symptoms
Citation: Li Y, Li Y and Zhang Z (2025) Network analysis of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in stroke patients. Front. Psychiatry 16:1663366. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1663366
Received: 26 July 2025; Accepted: 28 August 2025;
Published: 18 September 2025.
Edited by:
Ansab Akhtar, Louisiana State University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Li, Li and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenmei Zhang, MzQ0NTA1ODcyOUBxcS5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
 Yingying Li
Yingying Li Yanchun Li2†
Yanchun Li2†