- 1Faculty of Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao, Macao SAR, China
- 2Faculty of Medicine and Health, The University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 3Faculty of Health, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 4School of Health and Biomedical Sciences, RMIT University, Bundoora, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Background: There has been a notable increase in the utilisation of SWEMWBS as a measure of mental well-being globally. To enhance its interpretability for both healthcare professionals and laypeople, categorising SWEMWBS scores is considered beneficial. Two approaches have been recommended, yet they have not been thoroughly investigated. This study aimed to explore the categorisation of the scores from an epidemiological perspective.
Methods: Adopting PHQ-9 results, as suggested by the original scale author, to be the benchmarking comparator and employing the epidemiological approach, the concordance between SWEMWBS and PHQ-9 was examined using data from a health survey. The scales were categorised following the recommended cutoffs suggested by the authors. An additional cutoff was generated from the Nonparametric Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Analysis and verified using the multiclass ROC analysis. The agreement indicators, including the sensitivity, specificity, Positive Predictive Value, Negative Predictive Value, Likelihood Ratio Positive, Likelihood Ratio Negative, and Receiver Operating Characteristic-Area Under the Curve (ROC AUC), were calculated.
Results: The categorisation of SWEMWBS scores by benchmarking yielded the highest sensitivity, but the smallest specificity with 86.1% (95% C.I. = 84.1%-87.9%) and 56.6% (95% C.I. = 49.1%- 63.9%) respectively. Categorisation using the mean and SD approach resulted in a sensitivity of 81.3% (95% C.I. = 79.1%- 83.4%) and a specificity of 68.1% (95% C.I. = 60.8%-74.8%). In contrast, categorisation using the ROC analysis approach provided a sensitivity of 76.5% (95% C.I. = 73.8%-79.0%) and a specificity of 77.5% (95% C.I. = 70.7%-83.3%). The ROC AUC values were moderately low with the largest being 0.769 (95% C.I. = 0.737-0.802).
Conclusions: The concordance of the Chinese version of the SWEMWBS has been examined using PHQ-9 as the benchmarking comparator. The results indicate moderate sensitivity, specificity, LR+, and LR- values.
Background
The Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale (WEMWBS) and its 7-item Short Form (SWEMWBS) are among the few psychometric instruments specifically designed to assess mental well-being (1). Since the validation of SWEMWBS (2, 3), there has been a notable increase in the translation, validation, and utilisation of SWEMWBS as a measure of mental well-being globally (4–13). To facilitate the use of the scale and enhance its interpretability for both healthcare professionals and laypeople, categorising SWEMWBS scores is considered beneficial (14).
According to information provided by Warwick University, scores can be categorised using statistical and benchmarking approaches (14). The statistical approach is based on the observed characteristic that the scores follow an approximately normal distribution. Guided by the principles of probability theory, the probability density function (PDF) of a normal distribution N(0, σ2) encompasses approximately 68.3% of the area under the curve within one standard deviation (SD) from the mean, both above and below (15). The remaining area under the curve is evenly distributed in the upper and lower tails, with 15.85% each. Based on this concept, cutoff points are suggested to be one SD above and below the mean value, with approximately 15% classified as high/good well-being and 15% classified as low/poor well-being (14). Given a mean value of 23.5, an SD of 3.9, with the possible scores ranged between 7 and 35, found in the UK general population sample (2), it was suggested that scores of 27.5 and 19.5 serve as cutoff points for high/good and low/poor well-being, respectively (14). Benchmarking is a simpler approach based on the high correlation between SWEMWBS scores and the Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) (16). Consequently, SWEMWBS scores are suggested to be benchmarked with the cutoff points of PHQ-9 at 5 and 10, with a SWEMWBS score <18 indicating probable clinical depression and 19–20 indicating possible clinical depression (14). While these approaches have facilitated data analysis and, to some extent, simplified the interpretation of raw and transformed metric scores, further evidence is required to support the utilisation of the categorised scoring in clinically oriented environments, such as mental health services.
An essential type of study in epidemiology is measurement investigation (17). The primary objective of measurement studies is to determine the accuracy and validity of a test or instrument, providing evidence for its utility in an appropriate setting (18). To determine the accuracy of an instrument, such as a psychometric scale, the core of the measurement test study involves comparing the scale under investigation with a well-established comparator (17). Various statistical approaches can be employed to determine the degree of agreement between the instrument under investigation and the comparator, reflecting the accuracy of the studied scale (18). So far, few studies have been found in the literature investigating the properties of SWEMWBS from an epidemiological perspective (2).
Given the growing utilisation of the SWEMWBS in various settings globally, it is prudent to explore the psychometric properties of the scale from an epidemiological perspective. Based on the aforementioned recommended methods of scoring categorisation by Warwick University, this exploratory study aimed to examine the performance of these cutoff scores as to how closely they can align with the categorisation of the PHQ-9 adopted as the benchmarking comparator.
Methods
Sample and data collection
The data for this study was gathered through a population-based cross-sectional health survey, utilising a self-reported online questionnaire. Conducted between April and July 2024, the survey targeted adult residents of Macau. The questionnaire was disseminated via 23 associations and societies that collaborated in the city-wide study, including professional bodies, community associations, and non-government organisations. With the support of these organisations’ management, members were encouraged to participate through public appeals and personal invitations. The potential participant pool exceeded 50,000 individuals, representing nearly 9% of Macau’s adult population. The sample comprised 1,460 respondents, of which 1,001 were females (68.6%), and about 45% fell within the 18–34 age group (n=655, 44.9%). Ethics approval was obtained from the Faculty Ethics Research Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology (MUST-FMD-200402025001).
Measurements
The Short Form of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale
The 14-item WEMWBS has been validated and is widely utilised in numerous mental well-being studies, demonstrating robust content and structural validity, with a single factor confirmed by Confirmatory Factor Analysis (1). It also exhibits high reliability, with Cronbach’s alpha scores ranging from 0.89 to 0.91. The WEMWBS demonstrates strong correlations with other mental health and well-being scales and lower correlations with scales measuring overall health, with a test-retest reliability of 0.83 at one week (1). The Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (SWEMWBS), derived from the original scale with 7 items by Stewart-Brown et al. in 2009, employs a 5-point frequency Likert response set ranging from 1=rarely to 5=all the time, resulting in a total score range of 7 to 35. More information on the SWEMWBS can be found on the official website (14). The Chinese version of the SWEMWBS, first translated by Ng et al. in 2014, has been used in several studies. A few validation studies employed the classical test theory approach, all using samples from a single location, primarily Hong Kong, except one conducted in China (7, 10, 19–24). Overall, these studies indicated that the scale has good validity and reliability for use in the Chinese population (7, 10). The utilisation of the Chinese version of the instrument, in both traditional and simplified characters, in various studies confirmed that the high psychometric properties of the scale. In this study, the raw scores of the scale were used for the analyses.
Benchmarking comparator
In this study, the Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders Patient Health Questionnaire (PRIME-MD-PHQ) (25) was employed as the benchmarking comparator due to its use by the original authors for cutoff recommendations (14). The reason for adopting PHQ as the quasi comparator, apart from the aforementioned recommendation of the scale authors, was that there is no commonly recognised gold standard of mental well-being. In examining the utility of SWEMWBS, it would be prudent to use a sensitive instrument for assessing common mental disorders as a proxy benchmarking standard. The PHQ-9 is extensively utilised for evaluating mental health issues, particularly depression, among outpatients and the general population (25). This unidimensional scale consists of nine items designed to assess symptoms of depression. Respondents are asked to reflect on their experiences over the past two weeks using a 4-point frequency Likert scale, ranging from 0 (Not at all) to 3 (Nearly every day). An example item is “Feeling down, depressed, and hopeless.” The instrument has undergone validation and standardisation in numerous studies across various countries (25–27). This study will utilise the nine-item version (PHQ-9). The Chinese version of the PHQ-9 has been translated, and validated, and is widely used in Chinese-speaking countries (28). It demonstrates reliability, with an internal consistency Cronbach’s alpha of 0.86 and a two-week test-retest correlation of 0.86. The scale exhibits good convergent validity, with a positive correlation of 0.29 (p<0.001) with the SDS and a negative correlation of -0.47 with the SF-36. The area under the ROC curve is 0.92 (95% confidence interval: 0.86–0.97). A cutoff score of seven or higher on the PHQ-9 has a sensitivity of 0.86 and a specificity of 0.86 (28). For the categorisation of scores, the authors recommended cutoffs of 5, 10, 15, and 20 for mild, moderate, moderately severe, and severe depression, respectively (29).
Data management and analysis
Data management
Data were managed and analysed using STATA statistical software (StataNow 19.0). The categorisation of the SWEMWBS and PHQ-9 scores was conducted following the recommended cutoffs. Hence, the SWEMWBS scores were categorised into three groups by the mean with standard deviation and the benchmarking approaches. Adopting the original meaning suggested by the authors, these groups were labelled as poor, moderate, and well/normal. For the PHQ-9, the scores were categorised into five groups namely normal, mild, moderate, moderately severe, and severe depression. To synchronise the number of groups in both scales, the five groups of PHQ-9 were then regrouped into three normal/mild, moderate, and moderately severe/severe. The two scales were negatively correlated suggesting the response sets were in reversed directions. For ease of data analysis, SWEMWBS scores were reversely coded so that the direction of both scales was unified with a higher-ordered group having a higher risk of poor mental health/wellbeing. In terms of the categorisation of the scale, groups were first generated from the original raw scores following the two categorisation approaches. Then the order of the groups was reversely coded so that the direction of the groups synchronised with the direction of the PHQ-9 (normal/mild, moderate, severe).
Data analysis
Descriptive statistics of the demographic variables, SWEMWBS, and PHQ-9 were generated as means and standard deviations for continuous variables and frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. The values and the 95% Confidence Intervals (95% C.I.) of the concordance or agreement indicators between categorised SWEMWBS, based on the two approaches, and PHQ-9 as the benchmarking comparator were calculated with the severe group as the positive case group. These included the accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), negative likelihood ratio (LR-), and the Receiver Operating Characteristic Area Under the Curve (ROC AUC). To further explore the “cutoff” point of the SWEMWBS for probable cases empirically, the reversed scores were subjected to a Nonparametric ROC Analysis using the same benchmarking comparator and positive case criteria as the two approaches. Once the “cutoff” point of SWEMWBS was identified, it was then used to calculate the values and 95% C.I. of the agreement indicators. For determining the “cutoff” point, the principles regarding the sensitivity and specificity propounded by Power et al. were applied (30). It was emphasised that, for a test to be useful, the sum of the sensitivity and specificity should be 1.5 or 150% (30). The rationale for such criteria was that the true positive and the true negative rates of the test should be at least 75% each with some variations in both rates. To verify the results obtained from the empirical “cutoff”, the multiclass ROC analysis was applied to the data controlling for demographic variables. A type I error rate of 5% was used for all hypothesis tests.
Results
Descriptive statistics
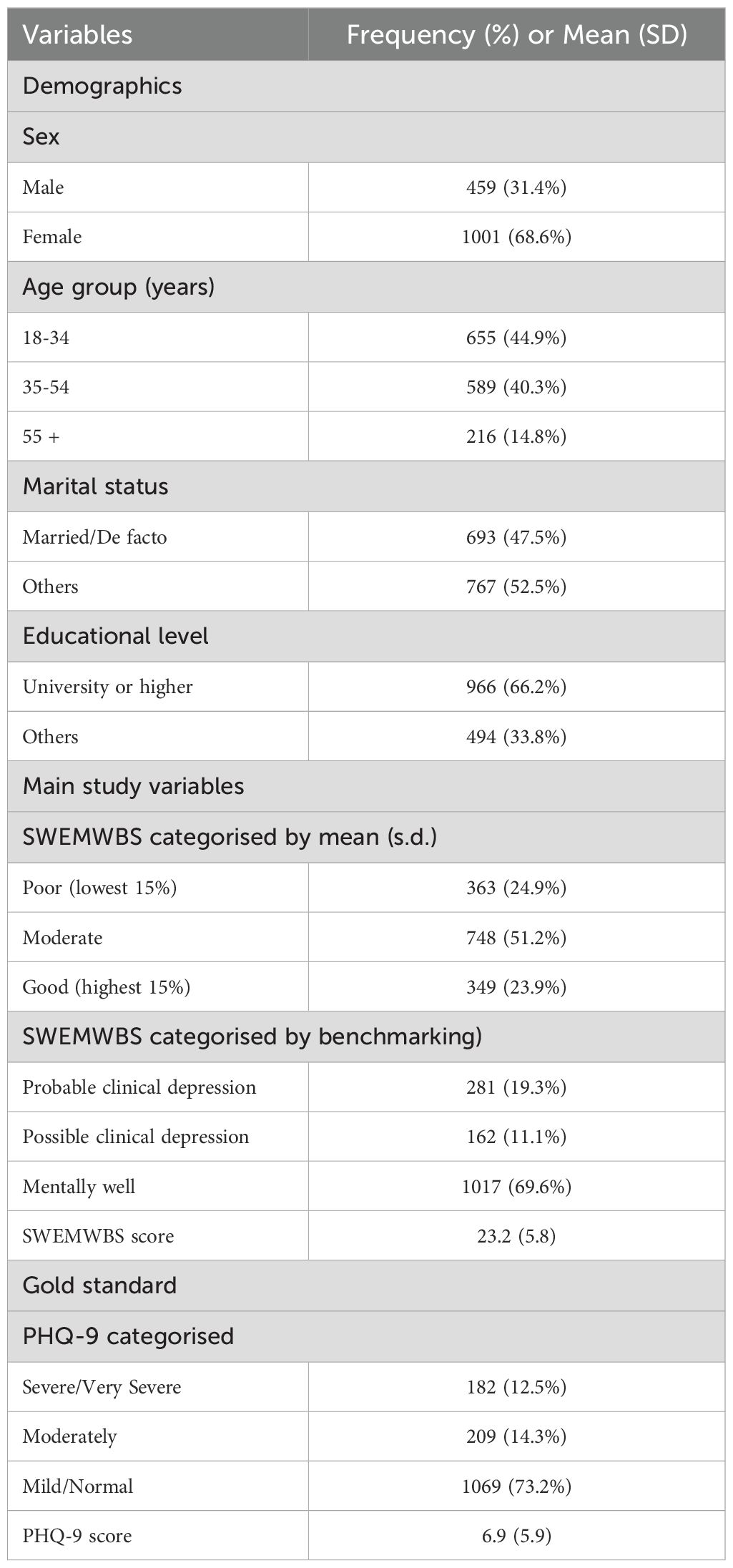
The sample included 1,460 participants, as shown in Table 1. The majority were female (n=1001, 68.6%) and younger, with nearly 45% aged between 18 and 34 years (n=655, 44.9%). Slightly less than half were either married or in a de facto relationship (n=693, 47.5%), and two-thirds had achieved a university-level education or higher (n=966, 66.2%). A total of 672 participants (46%) identified as caregivers. The mean score on the Chinese SWEMWBS was 21.5 (SD = 4.9) out of a possible 35. Of these, 363 (24.9%) were in the lowest 15% of the sample and 281 (19.3%) could be categorised as having probable clinical depression based on the two approaches. For depression, the average scores were 6.9 (SD = 6.0) with 182 (12.5%) classified as severe and very severe depression.
Agreement analysis
The ROC analysis, using the same “gold” standard and positive diagnosis criteria as the two approaches, resulted in a cutoff point of 22 which provided the highest sensitivity and specificity sum value of 153.9% (Figure 1). This cutoff score corresponded to the score of 20 on the original scale.
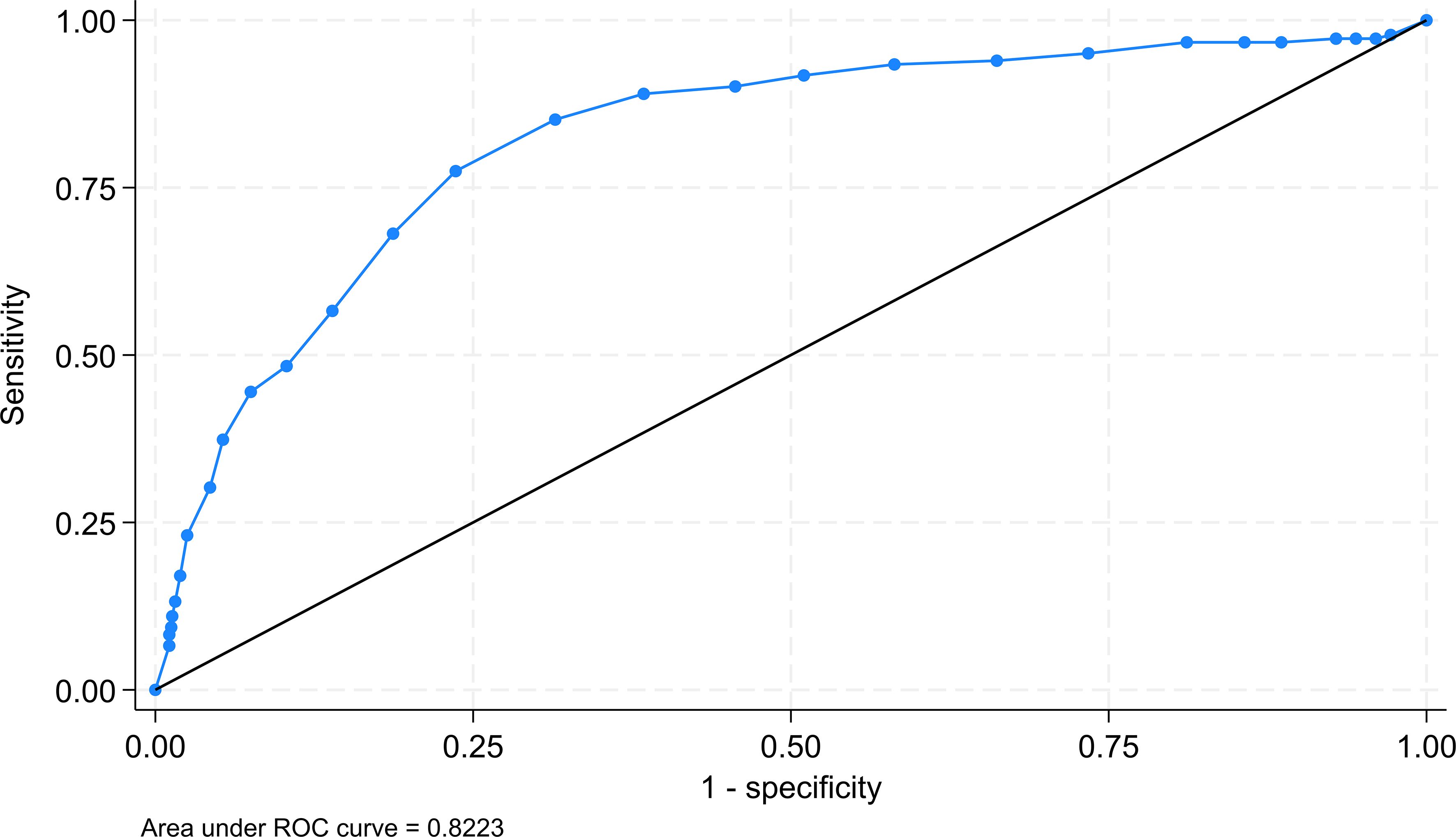
Figure 1. ROC of using the SWEMWBS raw score for determining the cutoff for probable positive cases.
The results of the agreement indicators are summarised in Table 2. As shown, the categorisation of SWEMWBS scores by benchmarking yielded the highest sensitivity, but the smallest specificity with 86.1% (95% C.I. = 84.1%-87.9%) and 56.6% (95% C.I. = 49.1%- 63.9%) respectively. Categorisation using the mean and SD approach resulted in a sensitivity of 81.3% (79.1%- 83.4%) and a specificity of 68.1% (95% C.I. = 60.8%-74.8%). In contrast, categorisation using the ROC analysis approach provided a sensitivity of 77.5% (95% C.I. = 70.7%-83.3%) and a specificity of 76.4% (95% C.I. = 73.9%-78.7%). As expected, the categorisation based on the benchmarking approach provided the largest LR+ value of 4.06 (95% C.I. = 3.37-4.90), but also a large LR- of 0.504 (95% C.I. = 0.427-0.596). On the other hand, categorisation based on ROC analysis had a smaller LR+ value of 3.28 (95% C.I. = 2.89-3.72), but also a smaller LR- value of 0.295 (95% C.I. = 0.225-0.387). In terms of the ROC AUC, the ROC analysis cutoff yielded the largest value of 0.769 (95% C.I. = 0.737-0.802) in comparison to the other two approaches (Table 2). This result suggested the ability of the scores of SWEMWBS in classifying depressive cases based on the definition of PHQ-9 was only moderate. The data were then subjected to the multiclass ROC Analysis by fitting the multinomial logistic regression model. The aforementioned results were also supported by the multiclass ROC analysis resulting in an overall estimated ROC AUC of 0.768 (Figure 2).
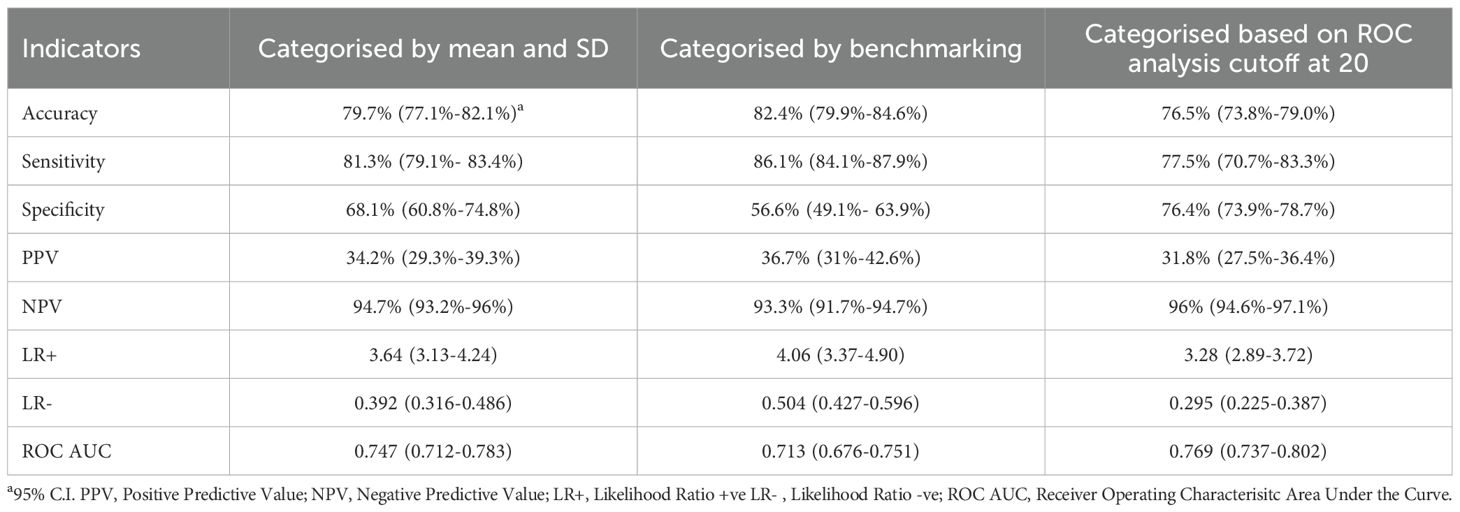
Table 2. Results of the agreement indicators for SWEMWBS measured against the gold standard for probable clinical depression.
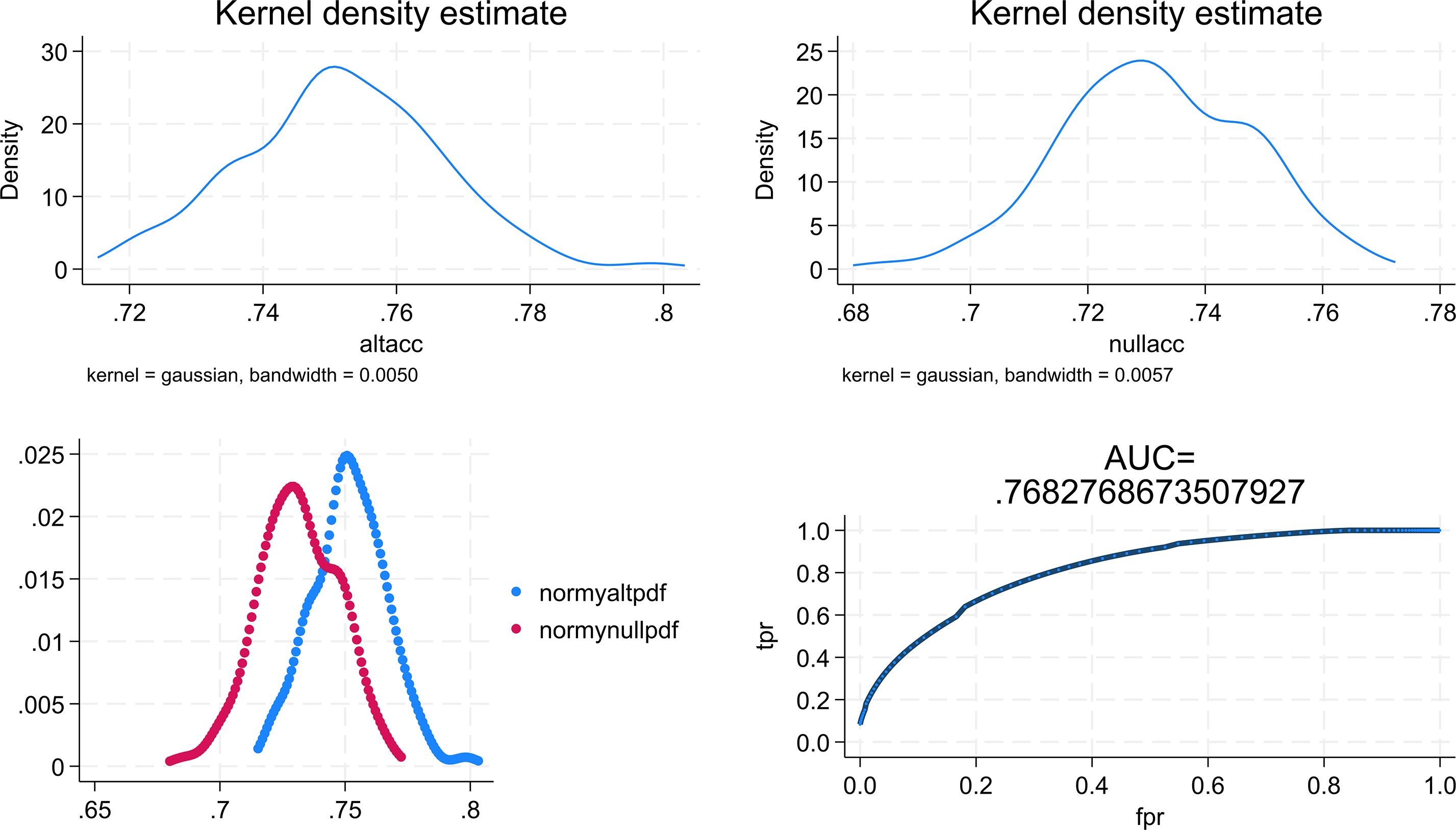
Figure 2. Graphical results obtained from the multiclass ROC analysis. altacc, alternative accuracy; nullacc, null accuracy; mormy nullpdf =estimated probability density function for the null class; normy altpdf, estimated probability density function for the alternative class; tpr, true probability; fpr, false probability.
Discussion
The SWEMWBS was initially designed to provide a theoretically driven and validated means for evaluating mental well-being, a concept that reflects the positive aspects of mental health (31–33). The increasing utilisation of the SWEMWBS as a mental health-related measure calls for more studies from an epidemiological perspective (34, 35). However, the scarcity of studies in the literature indicates a significant knowledge gap in the field of mental well-being research. Consequently, the author is motivated to further explore the scale’s psychometric properties from the epidemiological perspective, focusing on the issue of accuracy while adopting PHQ-9 as the benchmarking comparator.
The results suggested that both recommended approaches for categorising scale scores yielded a sensitivity of greater than 80% (86.1% for benchmarking and 81.3% for using mean and standard deviation). Conversely, the specificity was much weaker, with only 56.6% and 68.1% for the benchmarking and mean with standard deviation approaches, respectively. Using the cutoff provided by the ROC analysis resulted in a sensitivity of 77.5% and a specificity of 76.4%. The ROC AUC of all three approaches were also moderate. As such, these results did not differ significantly, suggesting no single approach for categorisation is superior to the others. This suggested that SWEMWBS would be better utilised as a screening measure than other purposes. Given the absence of comparable studies in the existing literature, a comparison of results is shown to be difficult. The results obtained are considered to be novel and unique.
There could be various reasons for the results obtained. One possible reason is the use of PHQ-9 as the comparator on which the benchmarking approach has been based. PHQ-9 is a highly sensitive instrument with good psychometric properties for assessing depression in both clinical settings and the general population (29). However, the instrument was designed for assessing depression, and the underlying construct that the items attempt to capture is clinical depression reflected through the symptoms described in the items. On the other hand, SWEMWBS aims to evaluate mental well-being, with the underlying constructs involving two different dimensions: the hedonic and eudaimonic aspects (36). The hedonic aspect refers to the individual subjective feeling of happiness and satisfaction in life, whereas the eudaimonic aspect is related to psychological functioning and the actualization of the individual’s potential, capacity, and positive relationship with self and others (36). There are similarities between these two scales, particularly the hedonic domain of the SWEMWBS, since both consist of items on happiness, personal satisfaction in life, and psychological functioning. However, they differ on the eudaimonic aspect that PHQ-9 does not cover much. While these constructs are highly and significantly correlated with depression, they do not assess the same phenomena. Therefore, there arises a question as to whether PHQ-9 could be used as a “gold” standard for benchmarking or examining the accuracy of SWEMWBS. This calls for further studies on the accuracy of the scale using other appropriate instruments as the “gold” standard. Unfortunately, as aforementioned, there is no commonly recognised gold standard of mental well-being so far. As such, a possible solution is to use a set of well-validated instruments as comparators for different aspects of SWEMWBS. Another possible reason is sampling biases. As aforementioned, the majority, nearly 69%, of the respondents were females, and nearly 45% were in the 18–34 year group. The sex and age imbalance characteristics might have affected the respondents’ responses to the two scales. It has been demonstrated that the overall prevalence of depression in males is lower than that of females, with 6.6% and 9.3%, respectively, before the COVID-19 pandemic (37). On the other hand, the performance of the SWEMWBS as a scale has been demonstrated to be better in males than in females (38). This might help explain the issue of moderate sensitivity and specificity. Further research is warranted to explore the sex and age-specific accuracy of SWEMWBS.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the SWEMWBS have been further examined using the epidemiological approach, specifically the concordance with PHQ-9 as the benchmarking comparator. The results indicate moderate sensitivity and specificity without outstanding LR+ and LR- values. It is noteworthy that SWEMWBS is a validated instrument of assessing mental well-being, not depression. Hence, caution should be taken when applying the results as an indicator of mental health.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article is not publicly available a protect participant confidentiality and privacy. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Faculty Ethics Research Committee of the Faculty of Medicine (MUST-FMD-200402025001), Macau University of Science and Technology. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
LL: Project administration, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization. ML: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AUC, Area Under the Curve; LR-, Negative Likelihood Ratio; LR+, Positive likelihood ratio; NPV, Negative predictive value; PHQ-9, Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders Patient Health Questionnaire; PPV, Positive Predictive Value; ROC, Receiver Operating Characteristic; SWEMWBS, Short Warwick Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale.
References
1. Tennant R, Hiller L, Fishwick R, Platt S, Joseph S, Weich S, et al. The Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS): development and UK validation. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2007) 5:63. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-5-63
2. Ng Fat L, Scholes S, Boniface S, Mindell J, and Stewart-Brown S. Evaluating and establishing national norms for mental wellbeing using the short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (SWEMWBS): findings from the Health Survey for England. Qual Life Res. (2017) 26:1129–44. doi: 10.1007/s11136-016-1454-8
3. McKay MT and Andretta JR. Evidence for the psychometric validity, internal consistency and measurement invariance of warwick edinburgh mental well-being scale scores in scottish and irish adolescents. Psychiatry Res. (2017) 255:382–6. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.06.071
4. Haver A, Akerjordet K, Caputi P, Furunes T, and Magee C. Measuring mental well-being: A validation of the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale in Norwegian and Swedish. Scand J Public Health. (2015) 43:721–7. doi: 10.1177/1403494815588862
5. Ringdal R, Bradley Eilertsen ME, Bjørnsen HN, Espnes GA, and Moksnes UK. Validation of two versions of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale among Norwegian adolescents. Scand J Public Health. (2018) 46:718–25. doi: 10.1177/1403494817735391
6. Koushede V, Lasgaard M, Hinrichsen C, Meilstrup C, Nielsen L, Rayce SB, et al. Measuring mental well-being in Denmark: Validation of the original and short version of the Warwick-Edinburgh mental well-being scale (WEMWBS and SWEMWBS) and cross-cultural comparison across four European settings. Psychiatry Res. (2019) 271:502–9. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.003
7. Sun Y, Luk TT, Wang MP, Shen C, Ho SY, Viswanath K, et al. The reliability and validity of the Chinese Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale in the general population of Hong Kong. Qual Life Res. (2019) 28:2813–20. doi: 10.1007/s11136-019-02218-5
8. Melendez-Torres GJ, Hewitt G, Hallingberg B, Anthony R, Collishaw S, Hall J, et al. Measurement invariance properties and external construct validity of the short Warwick-Edinburgh mental wellbeing scale in a large national sample of secondary school students in Wales. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2019) 17:139. doi: 10.1186/s12955-019-1204-z
9. Anthony R, Moore G, Page N, Hewitt G, Murphy S, and Melendez-Torres GJ. Measurement invariance of the short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale and latent mean differences (SWEMWBS) in young people by current care status. Qual Life Res. (2022) 31:205–13. doi: 10.1007/s11136-021-02896-0
10. Hong Y, Jiang X, Zhang T, Luo N, and Yang Z. Examining the relationship between the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (SWEMWBS) and EQ-5D-5L and comparing their psychometric properties. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2023) 21:25. doi: 10.1186/s12955-023-02108-y
11. Hauch D, Fjorback LO, and Juul L. Psychometric properties of the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale in a sample of Danish schoolchildren. Scand J Public Health. (2023) 51:1214–21. doi: 10.1177/14034948221110002
12. Hanzlová R and Kudrnáč A. Validation and psychometric evaluation of the Short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale (SWEMWBS) among Czech adolescents using Item Response Theory. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2024) 2 2:66. doi: 10.1186/s12955-024-02280-9
13. Stewart-Brown S, Tennant A, Tennant R, Platt S, Parkinson J, and Weich S. Internal construct validity of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS): a Rasch analysis using data from the Scottish Health Education Population Survey. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2009) 7:15. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-7-15
14. Warwick Medical School. Collect, score, analyse and interpret WEMWBS (2023). Available online at: https://warwick.ac.uk/fac/sci/med/research/platform/wemwbs/using/howto/ (Accessed June 17, 2025).
15. Blitzstein JK and Hwang J. Introduction to Probability. 2nd. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC (2019). doi: 10.1201/9780429428357
16. Shah N, Cader M, Andrews W, Stewart-Brown SL, and Warwick-Edinburgh S. Mental Well-being Scale (SWEMWBS): performance in a clinical sample in relation to PHQ-9 and GAD-7 BMC Health and Quality of Life Outcomes. Health Qual Life Outcomes (2021) 19:260. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01882-x
17. Rothman K and Greenland S. Modern Epidemiology. 2nd. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (1998).
18. Bolboacă SD. Medical diagnostic tests: A review of test anatomy, phases, and statistical treatment of data. Comput Math Methods Med. (2019) 2019:1891569. doi: 10.1155/2019/1891569
19. Ng SS, Lo AW, Leung TK, Chan FS, Wong AT, Lam RW, et al. Translation and validation of the Chinese version of the short Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale for patients with mental illness in Hong Kong. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. (2014) 24:3–9.
20. Guo N, Luk TT, Ho SY, Lee JJ, Shen C, Oliffe J, et al. Problematic smartphone use and mental health in chinese adults: A population-based study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:844. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17030844
21. Lee EK, Wong B, Chan PHS, Zhang DD, Sun W, Chan DC, et al. Effectiveness of a mindfulness intervention for older adults to improve emotional well-being and cognitive function in a Chinese population: A randomized waitlist-controlled trial. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2022) 37. doi: 10.1002/gps.5616
22. Fung SF. Psychometric evaluation of the warwick-edinburgh mental well-being scale (WEMWBS) with chinese university students. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2019) 17:46. doi: 10.1186/s12955-019-1113-1
23. Wong RHK, Wing Cheong Au R, Wai Lan C, Pi Fan C, Chiu FPF, Chu MMK, et al. A randomized controlled trial on the effectiveness of the abridged illness management and recovery program for people with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Hong Kong J Occup Ther. (2023) 36:118–27. doi: 10.1177/15691861231204904
24. Lam LT. Caregiving and mental well-being: the role of caregivers’ age and insomnia. Front Psychiatry. (2025) 16:1482890. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1482890
25. Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, and Williams JB. Validation and utility of a self-report version of PRIME-MD: the PHQ primary care study. Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders. Patient Health Questionnaire. JAMA. (1999) 282:1737–44. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.18.1737
26. Beard C, Hsu KJ, Rifkin LS, Busch AB, and Björgvinsson T. Validation of the PHQ-9 in a psychiatric sample. J Affect Disord. (2016) 193:267–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.12.075
27. Smith ML, Sanchez SE, Rondon M, Gradus JL, and Gelaye B. Validation of the patient health questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for detecting depression among pregnant women in lima, Peru. Curr Psychol. (2022) 41:3797–805. doi: 10.1007/s12144-020-00882-2
28. Wang W, Bian Q, Zhao Y, Li X, Wang W, Du J, et al. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) in the general population. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2014) 36:539–44. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2014.05.021
29. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, and Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. (2001) 16:606–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016009606.x
30. Power M, Fell G, and Wright M. Principles for high-quality, high-value testing. Evid Based Med. (2013) 18:5–10. doi: 10.1136/eb-2012-100645
32. Keyes CL. Mental illness and/or mental health? Investigating axioms of the complete state model of health. J Consult Clin Psychol. (2005) 73:539–48. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.73.3.539
33. Waterman AS. Two conceptions of happiness: Contrasts of personal expressiveness (eudaimonia) and hedonic enjoyment. J Pers Soc Psych. (1993) 64:678–91. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.64.4.678
34. Trousselard M, Steiler D, Dutheil F, Claverie D, Canini F, Fenouillet F, et al. Validation of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale (WEMWBS) in French psychiatric and general populations. Psychiatry Res. (2016) 245:282–90. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.08.050
35. Scior K, Patel M, Goldsmith-Sumner A, Hayden N, Lee JY, Lunsky Y, et al. Development and initial psychometric properties of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale-Intellectual Disability version. J Intellect Disabil Res. (2023) 67:893–900. doi: 10.1111/jir.13039
36. Joshanloo M and Weijers D. A two-dimensional conceptual framework for understanding mental well-being. PloS One. (2019) 14:e0214045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214045
37. Hall BJ, Lam AIF, Wu TL, Hou WK, Latkin C, and Galea S. The epidemiology of current depression in Macau, China: towards a plan for mental health action. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. (2017) 52:1227–35. doi: 10.1007/s00127-017-1415-8
Keywords: SWEMWBS, agreement, sensitivity, specificity, receiver operating characteristic-area under the curve ROC AUC
Citation: Lam LT and Lam MK (2025) The categorisation of the Short Warwick Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale scores: an exploration from an epidemiological perspective. Front. Psychiatry 16:1674009. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1674009
Received: 27 July 2025; Accepted: 03 November 2025;
Published: 28 November 2025.
Edited by:
Wenchao Wang, Beijing Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Kashef N. Zayed, Sultan Qaboos University, OmanChen Jiang, Ningbo Women and Children’s Hospital, China
Wei Deng, University of Pittsburgh, United States
Copyright © 2025 Lam and Lam. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lawrence T. Lam, dG1sYW1AbXVzdC5lZHUubW8=, bGF3cmVuY2UubGFtQHN5ZG5leS5lZHUuYXU=, bGF3cmVuY2UubGFtQHV0cy5lZHUuYXU=
†ORCID: Lawrence T. Lam, orcid.org/0000-0001-6183-6854
Mark K. Lam, orcid.org/0000-0001-9451-8203
 Lawrence T. Lam
Lawrence T. Lam Mary K. Lam4†
Mary K. Lam4†