- The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Hunan, China
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) profoundly impairs patients’ quality of life (QoL), creating a critical gap between symptom remission and holistic functional recovery. This narrative review examines the potential role and conceptual basis of nursing interventions in addressing this gap and improving QoL for individuals with MDD. It explores the evolution of mental health nursing from custodial care to a recovery-oriented, therapeutic practice, emphasizing the nurse’s unique position in providing continuity within fragmented care systems. The review classifies and discusses key nursing strategies—including psychoeducation, cognitive-behavioral techniques, integrated case management, mind-body interventions, and social reintegration support—while critically appraising the strength of the available evidence. A central theme throughout is the methodological challenge that much of the existing literature infers QoL benefits from symptom or functional improvement, rather than consistently employing validated, multidimensional QoL measures as primary outcomes. The review also elucidates proposed mechanistic pathways, such as the therapeutic alliance and self-efficacy development, through which nursing care may enhance QoL. Significant barriers to implementation, including workforce shortages and role ambiguity, are addressed. We conclude that while nursing interventions hold significant potential to improve patient-reported QoL, this potential is not yet fully realized or evidenced. Future work must prioritize the systematic embedding of standardized QoL assessment into intervention research, validate technology-driven solutions, and conduct robust trials to firmly establish the impact of nursing care on the holistic well-being of individuals living with MDD.
1 Introduction
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is a pervasive mental health condition affecting over 280 million people globally, with significant implications for healthcare systems and societal burden (1). MDD profoundly impairs patients’ quality of life (QoL), extending beyond symptom reduction to encompass functional, social, and emotional well-being (2). While pharmacological and psychotherapeutic treatments target symptom remission, the disconnect between clinical recovery and holistic QoL improvement remains a critical challenge (3). Nursing interventions, emphasizing continuity and patient-centered care, potentially bridge this gap (4). However, existing reviews often focus narrowly on specific interventions or outcomes, lacking comprehensive synthesis of how diverse nursing strategies collectively impact QoL in MDD. Despite growing recognition of nursing’s role in mental health, a comprehensive synthesis focusing specifically on how nurse-led interventions influence quality of life in MDD remains limited. This review aims to synthesize evidence on nursing interventions’ impact on QoL in MDD, analyze mechanistic pathways, identify implementation barriers, and propose future directions for research and practice.
Nursing practices, evolved from custodial care to proactive therapeutic models, are uniquely positioned to address these dimensions through psychoeducation, cognitive-behavioral techniques (CBT), and integrated care pathways (5, 6). Nurse-led case management has shown promise in improving treatment adherence and reducing stigma-related isolation, directly influencing QoL outcomes (7, 8). Studies within mental health settings have demonstrated that nurse-delivered psychosocial interventions, including those focusing on structured activity and family support, can enhance emotional regulation and facilitate occupational reengagement, which are key determinants of QoL in MDD (9, 10). However, barriers such as workforce shortages and inconsistent outcome measurement hinder implementation (11). By evaluating mechanistic pathways—such as therapeutic alliance and self-efficacy development—this article underscores nursing’s role in fostering empowerment and resilience (12, 13).
Innovations like digital platforms and standardized nursing protocols offer scalable solutions, yet their integration into MDD care pathways requires further evidence (8). This narrative review highlights the need for interdisciplinary collaboration to optimize QoL-centric interventions. Given the current state of evidence, which often infers QoL improvements through proxy measures rather than consistently employing validated QoL instruments, this article aims to synthesize the conceptual arguments and preliminary evidence that support the potential of nursing care to enhance QoL. Ultimately, we advocate for nursing practices to be systematically embedded in MDD care and for future research to more directly and rigorously evaluate their impact on patient-reported QoL.
2 Methods: literature search strategy for this narrative review
This article is a narrative review. Its primary aim is to provide a comprehensive and critical synthesis of the existing literature on the role of nursing interventions in enhancing the QoL of patients with MDD. The objective is to explore conceptual frameworks, classify interventions, elucidate mechanistic pathways, and discuss implementation challenges, rather than to conduct a systematic aggregation of all available evidence.
The literature search and selection for this review were conducted in a non-systematic manner, focusing on breadth and conceptual relevance to build a coherent narrative. To ensure comprehensive coverage of the topic, the following strategy was employed:
2.1 Electronic databases and search terms
Searches were conducted in the electronic databases PubMed, CINAHL, and PsycINFO for relevant English-language publications. Combinations of key terms were used, including: (“Major Depressive Disorder” OR “depression”) AND (“nursing intervention” OR “nurse-led” OR “psychiatric nursing”) AND (“quality of life” OR “QoL” OR “well-being”).
2.2 Time frame and selection criteria
The search was not restricted by a rigid time to capture both foundational theories and recent advancements. Articles were selected based on their relevance to the core themes of the review, including conceptual models of QoL in MDD, the historical evolution of mental health nursing, specific nursing interventions (psychoeducation, cognitive-behavioral therapy [CBT], case management), and barriers to care. We prioritized peer-reviewed original research, review articles, and clinical guidelines. The selection process was iterative and involved examining the reference lists of key articles (snowballing method) to identify additional relevant publications.
It is important to note that, as a narrative review, this work does not claim to be exhaustive. The synthesis and interpretation of the literature are inherently influenced by the authors’ perspective and the goal of building a thematic narrative. Therefore, some selection bias may be present. The findings and conclusions should be interpreted as a critical analysis and discussion of the existing landscape, intended to highlight key insights, gaps in knowledge, and directions for future research.
2.2.1 Conceptualizing QoL in MDD: beyond symptomatology
MDD is a complex mental health disorder that extends beyond the presence of clinical symptoms such as low mood, anhedonia, and fatigue. QoL in MDD encompasses a broader spectrum of psychological, physical, social, and functional dimensions. While symptom reduction remains a primary treatment goal, it does not always correlate with improved QoL, necessitating a more holistic approach to patient care (14). The WHO defines QoL as an individual’s perception of their position in life within the context of their culture, value systems, and personal goals. This definition underscores the subjective nature of QoL, which may differ significantly among individuals with similar symptom severity (15–17). A patient with mild depressive symptoms may report severe QoL impairment due to occupational dysfunction, whereas another with severe symptoms may adapt better socially, highlighting the need for personalized assessments (18, 19).
2.2.1.1 Multidimensional constructs of QoL in chronic mental illness
MDD often leads to persistent QoL deficits that persist beyond acute symptomatic episodes. The WHOQOL-Bref instrument captures four key domains—physical health, psychological well-being, social relationships, and environment—providing a comprehensive framework for evaluating QoL in MDD (17, 20). Evidence shows that individuals with MDD often place greater value on psychological and social aspects than on physical health when rating their QoL (18, 21). Depressive states tend to shift the interpretation of WHOQOL-Bref items toward emotional rather than physical priorities (18). The primacy of psychosocial factors in determining QoL is also observed in other chronic conditions with high rates of comorbid depression. For instance, in end-stage renal disease, the strength of social support can be a more powerful predictor of QoL than some biological markers (22, 23). This reinforces the broader principle that in chronic illness states—including chronic mental illness like MDD—psychosocial variables often dominate the subjective lived experience of well-being.
2.2.1.2 The discrepancy between symptom remission and functional recovery
Symptom remission, as measured by instruments such as the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD), does not inherently equate to a return to full functional capacity. Between 30% and 50% of individuals who reach remission continue to face limitations in daily activities, work performance, and social interaction (24, 25). In outpatient MDD populations, somatic complaints—including chronic pain—correlate more strongly with QoL impairment than mood disturbances alone (25). This aligns with findings from stroke rehabilitation, where post-stroke MDD was the primary determinant of QoL decline, surpassing physical disability (26). Longitudinal observations confirm that improvement in QoL early in the course of treatment is a predictor of eventual symptom remission, irrespective of initial severity (19). This suggests that interventions targeting functional and psychosocial outcomes may enhance long-term recovery, even in patients with residual symptoms (27, 28).
2.2.1.2 Relevance of the WHOQOL model in evaluating holistic outcomes in MDD
The WHOQOL-Bref’s bifactor structure—validated across diverse populations, including psychiatric patients—makes it particularly suited for MDD care (17, 20). Its emphasis on subjective perception aligns with recovery-oriented models, which prioritize patient-defined goals over clinician-rated metrics (21, 28). Critically, the tool’s mental health recovery module (WHOQOL-MHR) addresses gaps in assessing hope, empowerment, and autonomy—key themes in MDD recovery (21). Achieving QoL parity with the general population in primary care MDD settings appears possible only when both depressive and anxiety symptoms are addressed, reinforcing the need for a multidimensional and integrated approach to assessment and treatment (29). Circadian rhythm disturbances, commonly observed in MDD, significantly impact sleep quality and daily functioning (30). Nursing interventions addressing sleep-wake cycles may thus represent an important pathway to QoL improvement.
2.2.2 Historical and professional evolution of mental health nursing
The transformation of mental health nursing mirrors the broader evolution in psychiatric care, shifting from institutional models to recovery-oriented, community-based approaches. This paradigm shift has fundamentally redefined the role of nurses, propelling them from passive observers to active participants in therapeutic engagement, while concurrently addressing the systemic fragmentation that characterizes mental healthcare delivery.
2.2.2.1 Transition from custodial care to therapeutic engagement in psychiatric nursing
In the early 20th century, psychiatric nursing was largely centered on custodial care, focusing on patient supervision and the fulfillment of basic needs within the confines of asylum settings. The deinstitutionalization movement of the 1960s–1980s marked a pivotal shift, placing a new emphasis on rehabilitation and community integration (31). This era saw the emergence of nursing practices that integrated biopsychosocial assessments, a stark contrast to the historic symptom-focused checklists (32). Contemporary protocols now routinely incorporate the screening of social determinants of health, addressing aspects of care that were previously overlooked (31).
2.2.2.2 Core competencies defining modern mental health nursing practice
Modern mental health nursing practice is defined by the mastery of six core competencies, as validated by the American Psychiatric Nurses Association (APNA) and WHO guidelines. These competencies are operationalized through frameworks such as the Mental Health Nursing Competency Framework, which links skill acquisition directly to patient outcomes (31).
2.2.2.3 The nurse as a continuity provider in fragmented mental health systems
The fragmentation of mental health services, characterized by isolated service delivery and frequent care transitions, poses a significant barrier to effective management of MDD. Nurses play a crucial role in bridging these gaps through three key mechanisms of continuity: Longitudinal Relationship-Building, Crisis Stabilization, and Care Coordination. Nurses often maintain contact with patients across various settings, including inpatient, outpatient, and community environments. Additionally, nurse-led crisis plans have been shown to shorten emergency response times compared to ad-hoc interventions (33).
2.2.3 Classification and application of nursing interventions in depressive disorders
It is important to note that many studies investigating the nursing interventions described below primarily report outcomes such as symptom reduction, treatment adherence, or functional improvement. While these are crucial determinants of QoL, direct evidence from studies using validated, multidimensional QoL instruments as a primary endpoint in MDD-specific populations is more limited. The following sections present these interventions and their observed effects with the understanding that they represent a critical, though incomplete, evidence base for concluding a direct, measured impact on QoL.
The multifaceted nature of depressive disorders necessitates nursing interventions that go beyond pharmacotherapy to address the psychological, social, and functional impairments experienced by patients. Evidence-based nursing strategies are essential for enhancing patient outcomes, targeting the underlying causes of disability in MDD and promoting autonomy and resilience (34, 35).
2.2.3.1 Psychoeducational strategies enhancing patient autonomy and treatment adherence
Psychoeducation is a powerful tool for empowering patients with MDD by providing them with a clear understanding of their condition, its treatment, and self-management techniques. Nurses are instrumental in delivering structured psychoeducational programs that significantly improve medication adherence and reduce the risk of relapse. The evidence supporting these benefits often comes from randomized controlled trials or pre-post studies that primarily use symptom severity and medication adherence rates as their main outcomes (36, 37). However, the direct use of validated QoL scales as a primary endpoint is less common in these studies. Furthermore, limitations such as small sample sizes and insufficient follow-up duration in some trials hinder a robust assessment of the long-term impact of psychoeducation on QoL. Additionally, integrating psychoeducation into routine nursing care has been found to enhance patients’ self-efficacy, particularly when the education is tailored to their cultural and literacy levels (38).
While psychoeducation demonstrates benefits for treatment adherence, the evidence for direct QoL improvement is constrained by methodological limitations. Many studies employ small samples and brief follow-up periods, with QoL measures as secondary outcomes rather than primary endpoints.
2.2.3.2 Nurse-delivered CBT in routine clinical practice
Preliminary evidence from some trials suggests that trained nurses can effectively deliver CBT for depression, with some studies reporting reductions in depressive symptoms that are comparable to those achieved by specialist therapists in specific, often supervised, settings (39, 40). However, the generalizability of these findings is constrained by factors such as variability in nurse training, the level of psychological supervision, and a predominant focus on symptom reduction rather than QoL or functional outcomes.
Common components of nurse-delivered CBT include:
Behavioral activation: Structured scheduling of pleasurable activities to counteract anhedonia.
Cognitive restructuring: Identifying and challenging negative automatic thoughts.
Problem-solving training: Enhancing coping skills for daily stressors.
Despite challenges such as time constraints and limited training, brief, protocol-driven CBT sessions conducted during routine nursing visits have proven to be a feasible approach in reducing symptom severity (38, 40).
The comparative effectiveness of nurse-delivered CBT remains uncertain due to variability in training protocols and supervision. Future trials should prioritize standardized competency frameworks and direct QoL assessment.
2.2.3.3 Integrated care models utilizing nursing-led case management
Nurse-led case management plays a vital role in bridging the gaps within fragmented mental health systems by coordinating multidisciplinary care. For patients with comorbid MDD and chronic illness, nurse case managers have successfully reduced emergency department visits through regular follow-ups and adjustments to care plans (41, 42). The critical functions of nurse case managers include:
Comprehensive assessment: Monitoring both physical and mental health status.
Care coordination: Facilitating communication between psychiatrists, primary care providers, and social workers.
Crisis intervention: Providing immediate support during acute episodes.
Evidence supporting the effectiveness of nurse-led case management on QoL is currently derived mainly from prospective cohort studies or non-randomized trials involving patients with comorbid medical conditions (e.g., cardiovascular disease, cancer) and depressive symptoms (43, 44). For instance, improvements in WHOQOL-Bref scores have been observed in populations like hemodialysis patients with MDD (45, 46). However, these findings must be interpreted with caution. The study designs (often lacking control groups) and the specific nature of the populations (where the physical comorbidity heavily influences QoL) limit the direct applicability of this evidence to primary care populations with standalone MDD. The evidence for case management directly improving QoL in primary MDD populations requires further strengthening through dedicated RCTs.
2.2.3.4 Mind-body interventions administered by nurses to improve daily functioning
Mind-body interventions, including mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and progressive muscle relaxation, have proven effective in mitigating the somatic symptoms associated with MDD. Nurse-guided MBSR has been found to reduce fatigue and sleep disturbances in participants (47, 48). It is important to note, however, that many supporting studies are pilot feasibility studies that primarily targeted the reduction of anxiety or improvement of sleep as their main outcome. These studies often have small sample sizes and do not exclusively enroll participants with a primary MDD diagnosis. Therefore, the specific effect of these mind-body interventions on the multidimensional QoL of individuals with MDD needs further validation through larger, robust trials that use QoL as a primary endpoint.
Breathing exercises: Taught during bedside care to alleviate acute anxiety.
Guided imagery: Utilized in group settings to enhance emotional regulation.
Yoga therapy: Incorporated into outpatient rehabilitation programs.
In the administration of ketamine, nurses’ monitoring of QTc intervals during infusion ensures patient safety while maximizing the therapeutic benefits of the treatment (49).
2.2.3.5 Family and social reintegration interventions
Beyond individual-focused therapies, nursing interventions that engage the patient’s social environment and functional roles are critical for holistic QoL improvement in MDD. As noted in the conceptualization of QoL, deficits in social relationships and occupational functioning often persist even after symptomatic remission (50). Mental health nurses are uniquely positioned to address these gaps through structured family engagement and community reintegration strategies.
Family Psychoeducation and Support. Involving family members in care is a cornerstone of psychiatric nursing practice. Structured family psychoeducation programs, often nurse-led, aim to improve family understanding of MDD, enhance communication patterns, reduce expressed emotion, and build a more supportive home environment (51). While the primary outcome in many studies has been patient relapse rates or caregiver burden, the improvement in family dynamics and reduction in interpersonal stress are direct contributors to the patient’s perceived social QoL. For instance, programs that equip families with problem-solving skills have been associated with improved patient well-being and family functioning, which are key dimensions of the WHOQOL’s social relationships domain (52).
A summary of the evidence for key nursing interventions discussed in this section, including the target populations, QoL instruments used, nature of findings, and study limitations, is provided in Table 1. This table synthesizes the current state of the evidence and highlights the variability in how QoL impacts have been assessed across different intervention types and study designs.
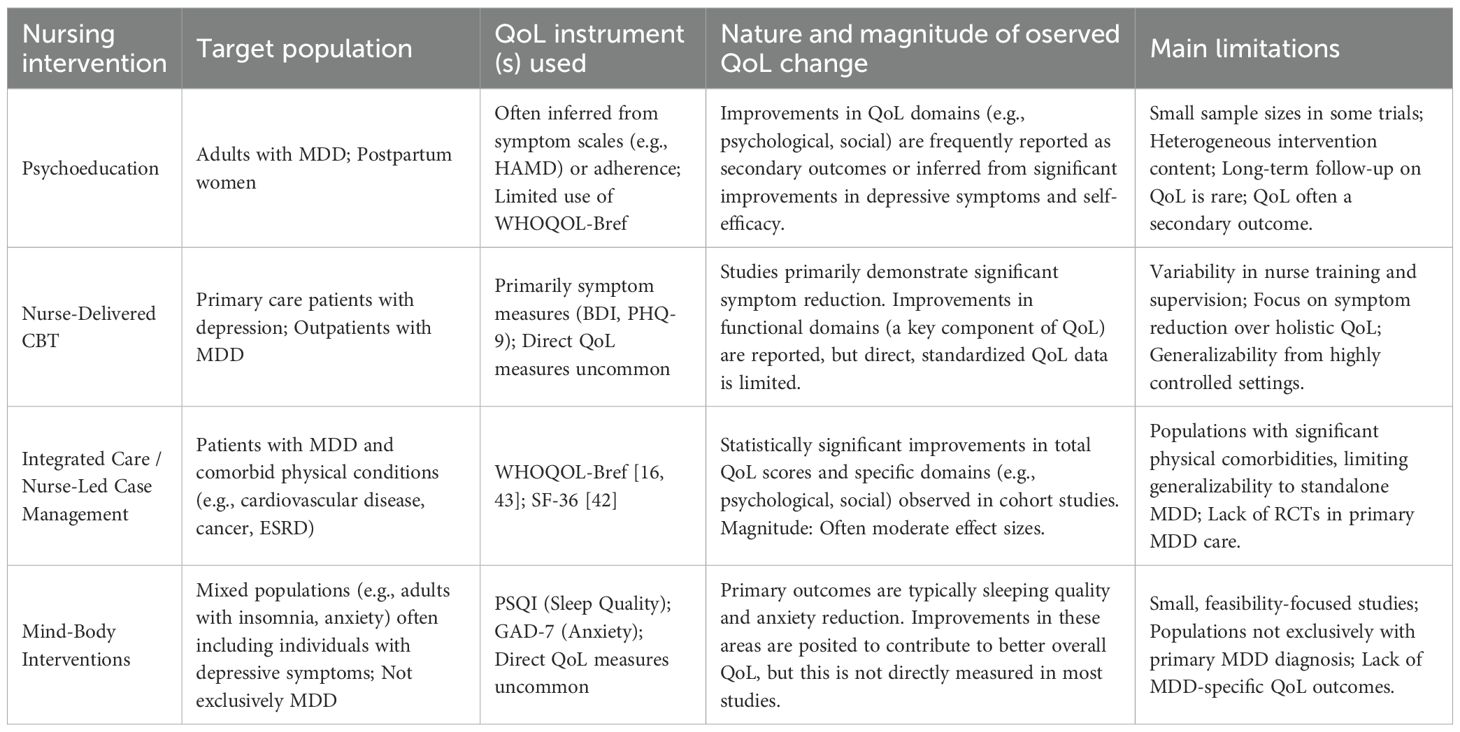
Table 1. Summary of evidence on nursing interventions and quality of life (QoL) in Major Depressive Disorder (MDD).
2.2.4 Mechanistic pathways linking nursing care to enhanced QoL
The benefits of nursing interventions in MDD extend beyond the alleviation of symptoms to promote fundamental changes in patients’ cognitive processes, behavioral patterns, and social functioning. Three interconnected mechanisms—therapeutic alliance, self-efficacy development, and resilience building—help explain how nurse-led care produces sustained improvements in quality of life.
2.2.4.1 The therapeutic alliance as a catalyst for patient empowerment
The therapeutic alliance between nurse and patient is a foundational component of effective MDD care. It is built on trust, empathy, and shared goal-setting, and distinguishes itself from brief, episodic clinician-patient encounters through the continuity and depth of engagement nurses are able to provide. Observational studies and qualitative research suggest that strong therapeutic alliances are directly associated with higher levels of patient empowerment (39, 53). Within this dynamic, structured psychoeducational interventions illustrate how relationship-building supports recovery. Nurses who provide clear, accessible education about MDD and its underlying mechanisms enable patients to reconceptualize their condition as both understandable and manageable. Programs delivered over a series of structured sessions have been shown to increase patients’ perceived control over their symptoms compared with standard care approaches (54).
2.2.4.2 Development of self-efficacy through sustained nurse-patient interaction
Nurse-delivered CBT, with its emphasis on applied skill-building, is theorized to strengthen self-efficacy. Nurse-delivered CBT, with its emphasis on applied skill-building, actively strengthens self-efficacy more effectively than pharmacotherapy alone. Techniques such as behavioral activation guide patients to reengage in meaningful activities, while systematic cognitive restructuring targets negative thought processes that undermine confidence (55, 56). While these studies primarily demonstrate efficacy for symptom and functional improvement, they provide indirect support for the role of self-efficacy as an underlying mechanism.
Graded task assignments: Breaking larger objectives into achievable steps to maintain momentum and reduce overwhelm.
Mastery experiences: Tracking small but meaningful accomplishments to counteract negative self-perceptions (57).
Verbal persuasion: Offering consistent encouragement, particularly during periods of medication adjustment or challenges with adherence (58).
2.2.5 Barriers to implementation and methodological challenges in current evidence
Despite the demonstrated efficacy of nursing interventions in improving QoL for patients with MDD, several systemic and methodological barriers hinder their widespread adoption. These challenges range from workforce limitations to inconsistencies in outcome measurement, ultimately affecting the scalability and reproducibility of evidence-based practices (59).
2.2.5.1 Systemic constraints including workforce shortages and role ambiguity
Mental health nursing faces chronic workforce shortages, with a scoping review revealing that psychiatric-mental health nurses account for less than the global nursing workforce (60). This deficit is compounded by role ambiguity, where nurses in general medical settings report inadequate training to address complex depressive symptoms, leading to task avoidance or delegation to other specialists (61).
Nurses in psychosocial care networks often perceive mental health interventions as bureaucratic obligations rather than therapeutic opportunities, further reducing implementation fidelity. This systemic undervaluation contrasts with evidence showing nurse-led interventions improve remission rates compared to standard care in primary settings. Role clarification through interdisciplinary care models—such as embedding psychiatric nurses in primary care teams—has shown promise in overcoming these barriers (62).
2.2.5.2 Inconsistencies in QoL measurement tools across clinical studies
The lack of standardized QoL assessment in MDD research obscures comparative effectiveness analyses. While the WHOQOL-Bref is validated for psychiatric populations (17). Methodological advancements are needed to harmonize QoL measurement while preserving patient-centeredness. Initiatives such as the NIH Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) offer a modular approach to standardized assessment, allowing for customization while maintaining comparability across studies (62). Future studies should prioritize the use of core outcome sets (COS) to align nursing research with international MDD care standards and facilitate evidence synthesis.
2.2.6 Innovative technologies and nursing interventions
Digital health technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing the field of mental health care, offering innovative solutions to enhance nursing interventions for patients with MDD (63, 64). These technologies have the potential to improve patient engagement, treatment adherence, and overall quality of life. Additionally, AI algorithms can assist in optimizing resource allocation and tailoring interventions to individual preferences. These advancements in digital health and AI offer promising avenues for improving nursing care and outcomes for patients with MDD (65).
2.2.6.1 Digital health in MDD care
Digital health technologies, including mobile health applications and remote monitoring systems, are increasingly recognized for their potential to enhance nursing interventions in MDD (66). Mobile applications can facilitate symptom tracking, medication reminders, and psychoeducational content delivery, empowering patients to engage actively in self-management between clinical visits (67). These tools also allow nurses to monitor mood fluctuations and treatment adherence in real time, enabling prompt intervention when signs of relapse or deterioration are detected. Remote monitoring platforms can be integrated with wearable devices to track sleep quality, activity levels, and physiological parameters, which provide valuable contextual data for tailoring nursing care plans. Evidence from chronic disease management suggests that digitally supported nursing interventions improve patient engagement and treatment outcomes, which can be translated to mental health care (68).
2.2.6.2 Artificial intelligence for personalized care
AI has the potential to transform nursing interventions in MDD by enabling highly individualized care plans (69). AI-driven predictive models can analyze large datasets — including electronic health records, patient-reported outcomes, and behavioral data from digital health tools — to identify patients at high risk of relapse, non-adherence, or severe symptom exacerbation (70). This predictive capability allows nurses to proactively adjust interventions, such as intensifying psychoeducation, modifying CBT session frequency, or initiating crisis stabilization protocols. AI algorithms can also assist in optimizing resource allocation, matching patients with appropriate community resources, and tailoring interventions to cultural and individual preferences (71). Moreover, natural language processing can be used to analyze patient communication patterns in telehealth or digital platforms to detect subtle mood changes, providing nurses with early warning signals for intervention (72).
2.2.7 Future directions and recommendations
Several evidence gaps and systemic barriers hinder the optimal implementation and evaluation of nursing interventions for QoL improvement in MDD. To address these, a multi-faceted approach is required. We recommend: (1) integrating standardized QoL assessment into nursing education curricula to equip future practitioners with the necessary skills; (2) developing policy frameworks that recognize nurse-led QoL interventions as billable services, thereby ensuring sustainable funding and institutional support; and (3) establishing clear competency pathways for advanced practice mental health nursing to formalize roles in QoL-focused care.
The integration of AI and digital technologies, while promising, presents both opportunities and ethical challenges. Future implementation must carefully consider data privacy, algorithmic bias, and equitable access. Particularly in underserved populations, technology-driven solutions risk exacerbating existing healthcare disparities if not implemented with careful attention to digital literacy and resource availability.
Future research should also prioritize the cultural adaptation and validation of QoL assessment tools, such as the WHOQOL-BREF and PROMIS, for diverse patient populations to ensure their relevance and accuracy. Furthermore, as treatment-resistant depression (TRD) represents a particularly challenging subgroup with severe QoL impairment (73), the development and evaluation of specialized nursing protocols—addressing both novel pharmacological augmentation strategies (74–77)—are urgently needed.
3 Conclusion
This review has articulated the pivotal potential and proposed role of nursing interventions in improving the QoL of patients with MDD. However, the evidence base would be strengthened by more studies that employ validated QoL measures as primary outcomes. Moving forward, the integration of innovative technologies offers a promising path ahead. Future research must focus on validating these approaches through robust clinical trials that prioritize standardized QoL measures to firmly establish the holistic impact of nursing care and transform long-term outcomes for individuals living with MDD.
Mechanistic pathways, including the therapeutic alliance, self-efficacy enhancement, and resilience building, provide insight into how nurse-led interventions translate into sustained QoL improvements. However, systemic constraints such as workforce shortages, role ambiguity, variability in intervention fidelity, and inconsistent QoL measurement tools inhibit wider implementation.
The integration of innovative technologies is discussed as a potentially promising path forward. Digital health platforms can extend the reach and continuity of nursing care, while AI can facilitate precision in intervention design and prediction of patient outcomes, supporting timely and personalized care delivery19. Future work must focus on validating these approaches in robust clinical trials while ensuring cultural adaptability. A parallel priority is embedding standardized quality of life (QoL) measures into all intervention protocols. The synthesis of literature presented here suggests that by combining evidence-based therapeutic strategies with technology-driven solutions, nursing practice has the potential to play a more transformative role in achieving holistic recovery and improving long-term outcomes for individuals living with MDD.
Author contributions
ZL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. WL: Methodology, Writing – original draft. LY: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by The Hunan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Key Area R&D Program Project (2023SK2050).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Ortega MA, Fraile-Martínez Ó, García-Montero C, Alvarez-Mon MA, Lahera G, Monserrat J, et al. Nutrition, epigenetics, and major depressive disorder: understanding the connection. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:867150. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.867150
2. Marx W, Penninx B, Solmi M, Furukawa TA, Firth J, Carvalho AF, et al. Major depressive disorder. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2023) 9:44. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00454-1
3. Qaseem A, Owens DK, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, Tufte J, Cross JT Jr., Wilt TJ, et al. Nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatments of adults in the acute phase of major depressive disorder: A living clinical guideline from the american college of physicians. Ann Intern Med. (2023) 176:239–52. doi: 10.7326/M22-2056
4. Meng J, Du J, Diao X, and Zou Y. Effects of an evidence-based nursing intervention on prevention of anxiety and depression in the postpartum period. Stress Health. (2022) 38:435–42. doi: 10.1002/smi.3104
5. Wilhelm S, Bernstein EE, Bentley KH, Snorrason I, Hoeppner SS, Klare D, et al. Feasibility, acceptability, and preliminary efficacy of a smartphone app-led cognitive behavioral therapy for depression under therapist supervision: open trial. JMIR Ment Health. (2024) 11:e53998. doi: 10.2196/53998
6. Ediz Ç and Kavak Budak F. Effects of psychosocial support-based psychoeducation for Turkish pregnant adolescents on anxiety, depression and perceived social support: a randomized controlled study. Rural Remote Health. (2023) 23:7553. doi: 10.22605/RRH7553
7. Mattila E, Leino K, Paavilainen E, and Astedt-Kurki P. Nursing intervention studies on patients and family members: a systematic literature review. Scand J Caring Sci. (2009) 23:611–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-6712.2008.00652.x
8. McKenzie KJ, Fletcher SL, Pierce D, and Gunn JM. Moving from “let’s fix them” to “actually listen”: the development of a primary care intervention for mental-physical multimorbidity. BMC Health Serv Res. (2021) 21:301. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06307-5
9. Zhang H and Dator WL. Toward a comprehensive understanding of nurses’ Compassion fatigue: A meta-integrative qualitative synthesis. J Adv Nurs. (2025). doi: 10.1111/jan.16785
10. Foster K, Shochet I, Shakespeare-Finch J, Maybery D, Bui MV, Gordon I, et al. Promoting resilience in mental health nurses: A partially clustered randomised controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. (2024) 159:104865. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2024.104865
11. Chen SY, Bian C, Cheng Y, Zhao WW, Yan SR, and Zhang YH. A randomized controlled trial of a nurse-led psychological pain solution-focused intervention for depressed inpatients: study protocol. BMC Nurs. (2023) 22:111. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01252-6
12. Tang JL, Yang WW, and Yang XY. Optimization of nursing interventions for postoperative mental status recovery in patients with cerebral hemorrhage. World J Psychiatry. (2024) 14:434–44. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i3.434
13. Temel M and Kutlu FY. Gordon’s model applied to nursing care of people with depression. Int Nurs Rev. (2015) 62:563–72. doi: 10.1111/inr.12217
14. Knight MJ, Lyrtzis E, and Baune BT. The association of cognitive deficits with mental and physical Quality of Life in Major Depressive Disorder. Compr Psychiatry. (2020) 97:152147. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2019.152147
15. ten Doesschate MC, Koeter MW, Bockting CL, and Schene AH. Health related quality of life in recurrent depression: a comparison with a general population sample. J Affect Disord. (2010) 120:126–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.04.026
16. Zimmermann JJ, Tiellet Nunes ML, and Fleck MP. How do depressed patients evaluate their quality of life? A qualitative study. J Patient Rep Outcomes. (2018) 2:52. doi: 10.1186/s41687-018-0076-z
17. Oliveira SE, Carvalho H, and Esteves F. Toward an understanding of the quality of life construct: Validity and reliability of the WHOQOL-Bref in a psychiatric sample. Psychiatry Res. (2016) 244:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.07.007
18. Zimmerman M, McGlinchey JB, Posternak MA, Friedman M, Boerescu D, and Attiullah N. Remission in depressed outpatients: more than just symptom resolution? J Psychiatr Res. (2008) 42:797–801. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.09.004
19. Jha MK, Greer TL, Grannemann BD, Carmody T, Rush AJ, and Trivedi MH. Early normalization of Quality of Life predicts later remission in depression: Findings from the CO-MED trial. J Affect Disord. (2016) 206:17–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.07.012
20. Perera HN, Izadikhah Z, O’Connor P, and McIlveen P. Resolving dimensionality problems with WHOQOL-BREF item responses. Assessment. (2018) 25:1014–25. doi: 10.1177/1073191116678925
21. Rowthorn MJ, Billington DR, Krägeloh CU, Landon J, and Medvedev ON. Development of a mental health recovery module for the WHOQOL. Qual Life Res. (2019) 28:3363–74. doi: 10.1007/s11136-019-02265-y
22. Barros A, Costa BE, Mottin CC, and d’Avila DO. Depression, quality of life, and body composition in patients with end-stage renal disease: a cohort study. Braz J Psychiatry. (2016) 38:301–6. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2015-1681
23. Jeon HJ, Park HC, Park JI, Lee JP, Oh KH, Chin HJ, et al. The effect of depression and health-related quality of life on the outcome of hemodialysis patients. Kidney Res Clin Pract. (2012) 31:54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.krcp.2012.01.001
24. Schwarz R, Munkholm K, Christensen MS, Kessing LV, and Vinberg M. Functioning in patients with major depressive disorder in remission: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2024) 363:112–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.07.054
25. Woo JM, Jeon HJ, Noh E, Kim HJ, Lee SW, Lee KK, et al. Importance of remission and residual somatic symptoms in health-related quality of life among outpatients with major depressive disorder: a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2014) 12:188. doi: 10.1186/s12955-014-0188-y
26. Pan JH, Song XY, Lee SY, and Kwok T. Longitudinal analysis of quality of life for stroke survivors using latent curve models. Stroke. (2008) 39:2795–802. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.515460
27. van Grieken RA, Kirkenier AC, Koeter MW, Nabitz UW, and Schene AH. Patients’ perspective on self-management in the recovery from depression. Health Expect. (2015) 18:1339–48. doi: 10.1111/hex.12112
28. IsHak WW, Bonifay W, Collison K, Reid M, Youssef H, Parisi T, et al. The recovery index: A novel approach to measuring recovery and predicting remission in major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. (2017) 208:369–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.08.081
29. Riihimäki K, Sintonen H, Vuorilehto M, and Isometsä E. Health-related quality of life-based definition of remission from depression among primary care patients. Front Psychiatry. (2023) 14:926410. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.926410
30. Monteleone P, Martiadis V, and Maj M. Circadian rhythms and treatment implications in depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2011) 35:1569–74. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.07.028
31. Storr B, Peiris CL, and Snowdon DA. Community reintegration after rehabilitation for hip fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2022) 103:1638–1650.e1637. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2021.12.007
32. Longoria KD, Nguyen TC, Franco-Rocha O, Garcia SR, Lewis KA, Gandra S, et al. A sum of its parts: A systematic review evaluating biopsychosocial and behavioral determinants of perinatal depression. PloS One. (2024) 19:e0290059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290059
33. Choi KR, Omery AK, and Watkins AM. An integrative literature review of psychiatric rapid response teams and their implementation for de-escalating behavioral crises in nonpsychiatric hospital settings. J Nurs Adm. (2019) 49:297–302. doi: 10.1097/NNA.0000000000000756
34. Sharrock J and Happell B. Competence in providing mental health care: a grounded theory analysis of nurses’ experiences. Aust J Adv Nurs. (2006) 24:9–15.
35. Barker P and Buchanan-Barker P. Myth of mental health nursing and the challenge of recovery. Int J Ment Health Nurs. (2011) 20:337–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0349.2010.00734.x
36. Hurley J, Lakeman R, Linsley P, Ramsay M, and McKenna-Lawson S. Utilizing the mental health nursing workforce: A scoping review of mental health nursing clinical roles and identities. Int J Ment Health Nurs. (2022) 31:796–822. doi: 10.1111/inm.12983
37. Edward KL and Munro I. Nursing considerations for dual diagnosis in mental health. Int J Nurs Pract. (2009) 15:74–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-172X.2009.01731.x
38. Lafontaine S, Rassy J, Duval-Martin AL, Girard A, Marceau M, Gallagher F, et al. Nursing interventions designed to improve healthcare in general healthcare settings for adults living with mental illness: A scoping review. Issues Ment Health Nurs. (2022) 43:955–70. doi: 10.1080/01612840.2022.2083736
39. Halcomb EJ, McInnes S, Patterson C, and Moxham L. Nurse-delivered interventions for mental health in primary care: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Fam Pract. (2019) 36:64–71. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmy101
40. Elias A, Tavares CMM, and Muniz MP. The intersection between being a nurse and being a therapist in Mental Health. Rev Bras Enferm. (2020) 73:e20180134. doi: 10.1590/0034-7167-2018-0134
41. Delaney KR, Robinson KM, and Chafetz L. Development of integrated mental health care: critical workforce competencies. Nurs Outlook. (2013) 61:384–91. doi: 10.1016/j.outlook.2013.03.005
42. Tofthagen R, Talseth AG, and Fagerström L. Mental health nurses’ experiences of caring for patients suffering from self-harm. Nurs Res Pract. (2014) 2014:905741. doi: 10.1155/2014/905741
43. Marcogliese ED and Vandyk A. Mental health nurses’ Knowledge of entry-to-practice competencies in psychiatric care. J Contin Educ Nurs. (2019) 50:325–30. doi: 10.3928/00220124-20190612-08
44. Silva TGD, Santana RF, Dutra VFD, and Souza PA. Nursing process implantation in mental health: a convergent-care research. Rev Bras Enferm. (2020) 73 Suppl 1:e20190579. doi: 10.1590/0034-7167-2019-0579
45. Xu H and Liu D. Nursing interventions in the management of mental illness and alcohol use disorders: A comprehensive review. Galen Med J. (2023) 12:e2999. doi: 10.31661/gmj.v12i.2999
46. Ayar D and Sabanciogullari S. The effect of a solution-oriented approach in depressive patients on social functioning levels and suicide probability. Perspect Psychiatr Care. (2021) 57:235–45. doi: 10.1111/ppc.12554
47. Van der Zweerde T, Lancee J, Slottje P, Bosmans JE, Van Someren EJW, and van Straten A. Nurse-guided internet-delivered cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia in general practice: results from a pragmatic randomized clinical trial. Psychother Psychosom. (2020) 89:174–84. doi: 10.1159/000505600
48. Kim SM, Park JM, Seo HJ, Kim J, Noh JW, and Kim HL. Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction on adults with sleep disturbance: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e058032. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-058032
49. Samalin L, Mekaoui L, De Maricourt P, Sauvaget A, Codet MA, Gaudré-Wattinne É, et al. Real-world demographic and clinical profiles of patients with treatment-resistant depression initiated on esketamine nasal spray. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. (2024) 28:83–93. doi: 10.1080/13651501.2024.2398788
50. Denee T, Kerr C, Eva J, Vincent SA, Young AH, Jacobsen N, et al. The impact of treatment-resistant depression on the lives of carers: A mixed-methods study. J Affect Disord. (2023) 325:194–205. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.12.135
51. Loutfy A, Zoromba MA, Mohamed MA, El-Gazar HE, Andargeery SY, El-Monshed AH, et al. Family-centred care as a mediator in the relationship between parental nurse support and parental stress in neonatal intensive care units. BMC Nurs. (2024) 23:572. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02258-4
52. Waller JM, Silk JS, Stone LB, and Dahl RE. Co-rumination and co-problem solving in the daily lives of adolescents with major depressive disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. (2014) 53:869–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2014.05.004
53. Weber M, Stalder S, Techau A, Centi S, McNair B, and Barton AJ. Behavioral health integration in a nurse-led federally qualified health center: Outcomes of care. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract. (2020) 33:1166–72. doi: 10.1097/JXX.0000000000000506
54. Casañas R, Martín Royo J, Fernandez-San-Martín MI, Raya Tena A, Mendioroz J, Sauch Valmaña G, et al. Effectiveness of a psychoeducation group intervention conducted by primary healthcare nurses in patients with depression and physical comorbidity: study protocol for a randomized, controlled trial. BMC Health Serv Res. (2019) 19:427. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4198-7
55. Hollon SD. The efficacy and acceptability of psychological interventions for depression: where we are now and where we are going. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. (2016) 25:295–300. doi: 10.1017/S2045796015000748
56. Rihmer Z, Dome P, and Katona C. Serotonin and depression - a riposte to Moncrieff et al. (2022). Neuropsychopharmacol Hung. (2022) 24:120–5.
57. Knippenberg IAH, Leontjevas R, Stoyanov S, Persoon A, Verboon P, Vermeulen H, et al. Informal antidepressant strategies for nursing home residents: two group concept mapping studies. Aging Ment Health. (2023) 27:251–62. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2022.2057427
58. Brammer SV. What interventions improve outcomes for the patient who is depressed and in pain? Pain Manag Nurs. (2018) 19:580–4. doi: 10.1016/j.pmn.2018.06.006
59. Bai W, Cai H, Wu S, Zhang L, Feng KX, Li YC, et al. Internet addiction and its association with quality of life in patients with major depressive disorder: a network perspective. Transl Psychiatry. (2022) 12:138. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-01893-2
60. Sevilla Guerra S, Zabalegui A, Comellas Oliva M, Estrem Cuesta M, Martín-Baranera M, and Ferrús Estopà L. Advanced practice nurses: Analysis of their role from a multicentre cross-sectional study. Int Nurs Rev. (2022) 69:30–7. doi: 10.1111/inr.12706
61. Botha E, Gwin T, and Purpora C. The effectiveness of mindfulness based programs in reducing stress experienced by nurses in adult hospital settings: a systematic review of quantitative evidence protocol. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. (2015) 13:21–9. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2380
62. Montano CB, Jackson WC, Vanacore D, and Weisler RH. Practical advice for primary care clinicians on the safe and effective use of vortioxetine for patients with major depressive disorder (MDD). Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2022) 18:867–79. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S337703
63. Lee EE, Torous J, De Choudhury M, Depp CA, Graham SA, Kim HC, et al. Artificial intelligence for mental health care: clinical applications, barriers, facilitators, and artificial wisdom. Biol Psychiatry Cognit Neurosci Neuroimaging. (2021) 6:856–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2021.02.001
64. Sajjadian M, Lam RW, Milev R, Rotzinger S, Frey BN, Soares CN, et al. Machine learning in the prediction of depression treatment outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol Med. (2021) 51:2742–51. doi: 10.1017/S0033291721003871
65. Sadeh-Sharvit S, Camp TD, Horton SE, Hefner JD, Berry JM, Grossman E, et al. Effects of an artificial intelligence platform for behavioral interventions on depression and anxiety symptoms: randomized clinical trial. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e46781. doi: 10.2196/46781
66. McIntyre RS, Greenleaf W, Bulaj G, Taylor ST, Mitsi G, Saliu D, et al. Digital health technologies and major depressive disorder. CNS Spectr. (2023) 28:662–73. doi: 10.1017/S1092852923002225
67. Berk M, Köhler-Forsberg O, Turner M, Penninx B, Wrobel A, Firth J, et al. Comorbidity between major depressive disorder and physical diseases: a comprehensive review of epidemiology, mechanisms and management. World Psychiatry. (2023) 22:366–87. doi: 10.1002/wps.21110
68. Tu Q, Hyun K, Hafiz N, Knight A, Hespe C, Chow CK, et al. Utilisation of chronic disease and mental health management services and cardioprotective medication prescriptions in primary care for patients with cardiovascular diseases and cancer: A cross-sectional study. Heart Lung Circ. (2024) 33:738–46. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2024.01.030
69. Poirot MG, Ruhe HG, Mutsaerts HMM, Maximov II, IR G, Bjørnerud A, et al. Treatment response prediction in major depressive disorder using multimodal MRI and clinical data: secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Am J Psychiatry. (2024) 181:223–33. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.20230206
70. Rathnam S, Hart KL, Sharma A, Verhaak PF, McCoy TH, Doshi-Velez F, et al. Heterogeneity in antidepressant treatment and major depressive disorder outcomes among clinicians. JAMA Psychiatry. (2024) 81:1003–9. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.1778
71. Cui L, Wang C, Wu Z, Peng D, Huang J, Zhang C, et al. Symptomatology differences of major depression in psychiatric versus general hospitals: A machine learning approach. J Affect Disord. (2020) 260:349–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.09.030
72. Wang Z, Niu Z, Yang L, and Cui L. Internet-based management for depressive disorder. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2019) 1180:267–76. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9271-0_14
73. Fiorillo A, Demyttenaere K, Martiadis V, and Martinotti G. Editorial: Treatment resistant depression (TRD): epidemiology, clinic, burden and treatment. Front Psychiatry. (2025) 16:1588902. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1588902
74. Pessina E, Martini A, Raffone F, and Martiadis V. Cariprazine augmentation in patients with treatment resistant unipolar depression who failed to respond to previous atypical antipsychotic add-on. A Case-series Front Psychiatry. (2023) 14:1299368. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1299368
75. Martiadis V, Pessina E, Martini A, Raffone F, Cattaneo CI, De Berardis D, et al. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors augmentation with cariprazine in patients with treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a retrospective observational study. CNS Spectr. (2024) 2024:1–4. doi: 10.1017/S1092852924000348
76. Maina G, Adami M, Ascione G, Bondi E, De Berardis D, Delmonte D, et al. Nationwide consensus on the clinical management of treatment-resistant depression in Italy: a Delphi panel. Ann Gen Psychiatry. (2023) 22:48. doi: 10.1186/s12991-023-00478-7
Keywords: nursing intervention, quality of life, major depressive disorder, psychoeducation, cognitive-behavioral therapy
Citation: Liao Z, Liu W and Yin L (2025) The impact of nursing intervention on the quality of life of patients with major depressive disorder: a narrative review. Front. Psychiatry 16:1689832. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1689832
Received: 21 August 2025; Accepted: 03 November 2025;
Published: 19 November 2025.
Edited by:
Vassilis Martiadis, Department of Mental Health, ItalyReviewed by:
Fabiola Raffone, Asl Napoli 1 Centro, ItalyMiriam Broncano, Institut d’Assistència Sanitària, Spain
Copyright © 2025 Liao, Liu and Yin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Luojuan Yin, eWlsdW9qdWFuQDEyNi5jb20=
 Zhizhen Liao
Zhizhen Liao Luojuan Yin
Luojuan Yin