Abstract
Background:
This study aims to utilize various machine learning algorithms to construct a risk prediction model for post-stroke Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), select the optimal model, and identify risk factors.
Methods:
A total of 249 stroke patients from two tertiary hospitals in Jiangsu Province and Shandong Province were selected and randomly divided into the training group and the validation group. Based on the results of Logistic regression analysis, a risk prediction model for PTSD after stroke was constructed by using Logistic regression, Random forest (RF) and K-nearest neighbor algorithm, and further verification was conducted according to the best algorithm.
Results:
The incidence of PTSD in stroke patients was 40.56%, and the RF model was the best. Feature importance ranking shows that the factors affecting PTSD in stroke patients are: Stroke type (0.187), Sleep in the last three months (0.152), Way of hospitalization (0.147), Monthly household income (0.133), Hypertension (0.108), Gender (1.104), Marital status (0.079), Physical exercise situation (0.067), and Educational background (0.023).
Conclusion:
The model based on the RF algorithm has the best predictive performance, and the factors affecting PTSD in stroke patients include stroke type, gender, Way of hospitalization, Sleep in the last three months, Physical exercise situation, Hypertension, etc. The results of this study can assist clinical medical staff to screen high-risk groups of PTSD after stroke and provide the basis for early implementation of targeted preventive measures.
Introduction
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder triggered by exposure to traumatic events, characterized by re-experiencing the event, avoidance of reminders, persistent negative emotions and cognitions, and physiological hyperarousal that persists for at least one month after the event (1). Stroke is a severe disease and a leading cause of death and long-term disability, characterized by high incidence, disability, mortality, recurrence, and economic burden, imposing a significant global burden (2). The occurrence of stroke presents substantial risks and negative impacts on patients’ physical and mental health (3), frequently leading to the development of PTSD (4, 5), with an incidence rate ranging from 3% to 37% among stroke patients (1, 6, 7). Following the onset of PTSD in stroke patients, medication compliance typically decreases (8), resulting in elevated levels of tension, fear, sleep disturbances, and the emergence of post-stroke fatigue (PSF), which impairs recovery and reduces the likelihood of returning to work (9),significantly diminishing the quality of life (10).Although conventional statistical methods like regression analysis have identified risk factors and provided foundational insights, their predictive validity is substantially limited in post-stroke PTSD populations (4, 11). This limitation stems from the condition’s complex, multifactorial etiology, which involves substantial heterogeneity and intricate nonlinear interactions that traditional models fail to capture (12). Therefore, developing predictive tools for early screening, identifying risk factors for stroke-related PTSD, and implementing early interventions are crucial to halt PTSD progression and mitigate its harm. Machine learning has emerged as a robust tool for risk prediction modeling, leveraging its powerful data mining and processing capabilities and proficiency in handling nonlinear relationships between complex variables (13). Although machine learning has been applied to identify risk factors for post-stroke PTSD, existing research has predominantly relied on individual models. This approach creates a critical gap, as the absence of a comprehensive comparative analysis prevents the determination of the most effective predictive model. Although machine learning has been applied to identify risk factors for post-stroke PTSD, existing research has predominantly relied on individual models (14, 15). This approach creates a critical gap, as the absence of a comprehensive comparative analysis prevents the determination of the most effective predictive model. In recent years, the random forest (RF) algorithm has been widely used in disease risk prediction, early warning, and prognosis, while logistic regression enables quantitative analysis and intuitive explanation of influencing factors through OR value (16). K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) detects local patterns in demographically similar individuals. This study employed logistic regression, RF, and KNN to analyze the status and influencing factors of PTSD in stroke patients from two tertiary hospitals. The objective was to develop a predictive model to identify high-risk individuals and provide a scientific basis for preventing PTSD in this population.
Methods
Participants
A total of 249 patients diagnosed with stroke from two tertiary hospitals in Jiangsu Province and Shandong Province between October 2023 and December 2023 were selected as the study population. In accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, all subjects gave written informed consent (17). The inclusion criteria for this study were as follows: Patients included in the study met the diagnostic criteria for ischemic stroke (18), with initial confirmation through CT and/or MRI imaging. Additionally, they met the diagnostic criteria for hemorrhagic stroke (19);Inclusion criteria also stipulated an age of ≥18 years, clear consciousness, and voluntary participation in the research. Exclusion criteria were: Patients with severe diseases of the heart, brain, kidneys, or other organ systems were excluded from the study. Additionally, individuals with speech or cognitive impairments, as well as those with psychiatric disorders or intellectual disabilities, were not eligible for participation.
General information and questionnaire data
Our study comprised two main components. Our research consists of two main parts. The first part includes general demographic information, a total of 28 items, including gender, age, living style, place of residence, family income, marital status, hypertension (Meet the diagnostic criteria for hypertension established by the Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension (2024 Revision) (20)), diabetes (meet the diagnostic criteria for diabetes (21)), etc. The Impact of Event Scale-Revised (IES-R) (22) was utilized to assess the intrusiveness, avoidance, or hyperarousal thoughts related to the health event. IES-R was revised by Weiss (23) and Marmar (24) in 1997, and it was translated into Chinese by the Chinese scholar Guo Suran as early as 2007 (25).This scale comprises 22 items, with patients rating the severity of their distress regarding cancer and its treatment over the past week for each item on a scale of 0 (never) to 4 (always), resulting in a total score ranging from 0 to 88. Higher scores indicate more pronounced post-traumatic stress reactions, with a score of ≥35 suggesting a positive PTSD screening (26). In this study, the Cronbach’s α for the sample was 0.953.
Data collection
Prior to commencing the survey, all investigators underwent standardized training via video sessions, covering survey principles, procedural precautions, and guidance on clear explanations. During the survey, investigators engaged patients in face-to-face interactions, presenting paper-based questionnaires to elucidate the survey’s purpose, content, and completion process. Upon obtaining patient consent, questionnaires were distributed, allowing patients to independently complete them. Completed questionnaires were promptly retrieved on-site. In instances where patients were unable to complete the questionnaire due to unique circumstances, investigators impartially presented the questions and assisted in truthful completion. A total of 260 questionnaires were distributed, with 249 effectively collected, yielding a robust retrieval rate of 95.7%.
Statistical analysis
Paper questionnaire was used to collect data, and Excel was used to organize the data. SPSS 27.0 software was used for data analysis. Data that did not meet our study inclusion and exclusion criteria were deleted. Disaggregated data are expressed in frequency and percentage terms. A Python script is used to shuffle the data and distribute it between the training set (70%) and the verification set (30%). Chi-square test and Mann-Whitney U test were used for general data comparison, and logistic regression was used for risk factor screening. Logistic regression, RF and K-nearest neighbor algorithm were used to construct a cognitive impairment risk prediction model for stroke patients in training concentration. The optimal hyperparameters were obtained by grid search and 5-fold cross-validation, and the optimal threshold was determined by Jorden index. Validation sets were used to evaluate the model’s performance, including area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and Jorden index. When the results of each index are inconsistent, the AUC is used as the main reference, and the evaluation results of the validation set are used as the basis for selecting the best model.
Results
General characteristics of PTSD in stroke patients
A total of 249 stroke patients were surveyed in this study, comprising 134 males and 115 females. Among them, 101 individuals (40.56%) were diagnosed with PTSD, while 148 individuals (59.44%) did not exhibit PTSD symptoms. Thirty-three potential risk factors were evaluated, and a comparison of general characteristics between the train groups and test groups is presented in Table 1.
Table 1
| Variable | Total | No | Yes | χ²/Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 10.228 | 0.001** | |||
| Male | 134 | 92 | 42 | ||
| Female | 115 | 56 | 59 | ||
| Age(Years) | 1.791 | 0.617 | |||
| ≤60 | 60 | 32 | 28 | ||
| 61-70 | 84 | 54 | 30 | ||
| 71-80 | 87 | 51 | 36 | ||
| ≥81 | 18 | 11 | 7 | ||
| Educational background | 15.519 | <0.001*** | |||
| High school education or below | 221 | 141 | 80 | ||
| College or undergraduate | 28 | 7 | 21 | ||
| Place of Residence | 1.626 | 0.202 | |||
| Countryside | 87 | 47 | 40 | ||
| City | 162 | 101 | 61 | ||
| Living style | 5.705 | 0.127 | |||
| Nursing home | 6 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Live alone | 41 | 19 | 22 | ||
| Live with spouse | 164 | 106 | 58 | ||
| Live with children | 38 | 20 | 18 | ||
| Marital status | 18.077 | <0.001** | |||
| Unmarried | 13 | 5 | 8 | ||
| Married | 196 | 129 | 67 | ||
| Divorce | 24 | 6 | 18 | ||
| Widowed | 16 | 8 | 8 | ||
| Monthly household income | 13.410 | 0.004* | |||
| < 1000 RMB | 28 | 10 | 18 | ||
| 1000–2000 RMB | 59 | 36 | 23 | ||
| 2000–4000 RMB | 93 | 51 | 42 | ||
| ≥4000 RMB | 69 | 51 | 18 | ||
| Type of medical insurance | 7.214 | 0.065 | |||
| Urban medical insurance | 122 | 64 | 58 | ||
| Urban and rural medical insurance | 120 | 80 | 40 | ||
| self-financing | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Other type | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Stroke type | 43.326 | <0.001** | |||
| Hemorrhagic Stroke | 41 | 18 | 23 | ||
| Ischemic Stroke | 155 | 116 | 39 | ||
| Other type | 53 | 14 | 39 | ||
| Cerebrovascular history | 0.978 | 0.323 | |||
| No | 184 | 106 | 78 | ||
| Yes | 65 | 42 | 23 | ||
| Fall history in the last 6 months | |||||
| Yes | 36 | 24 | 12 | 0.912 | 0.340 |
| No | 213 | 124 | 89 | ||
| Physical exercise situation | |||||
| Exercise every day (≥30min per day) | 64 | 39 | 25 | 12.701 | 0.002* |
| Occasionally (1–2 times/week) | 97 | 69 | 28 | ||
| No exercise | 88 | 40 | 48 | ||
| Sleep in the last three months | 13.966 | <0.001** | |||
| Good | 96 | 43 | 53 | ||
| Average | 98 | 68 | 30 | ||
| Poor | 55 | 37 | 18 | ||
| Smoking | 0.008 | 0.927 | |||
| Yes | 166 | 99 | 67 | ||
| No | 83 | 49 | 34 | ||
| Drinking history | 0.012 | 0.914 | |||
| Yes | 184 | 109 | 75 | ||
| No | 65 | 39 | 26 | ||
| Number of lesions | 3.482 | 0.062 | |||
| 2 or less | 244 | 143 | 101 | ||
| 3 or more | 5 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Diabetes | 1.025 | 0.311 | |||
| Yes | 171 | 98 | 73 | ||
| No | 78 | 50 | 28 | ||
| Hypertension | 19.048 | <0.001** | |||
| No | 113 | 84 | 29 | ||
| Yes | 136 | 64 | 72 | ||
| Coronary heart disease | 0.003 | 0.957 | |||
| Yes | 20 | 12 | 8 | ||
| No | 229 | 136 | 93 | ||
| Chronic kidney disease | 0.858 | 0.354 | |||
| Yes | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||
| No | 246 | 147 | 99 | ||
| Cerebral atrophy | 4.288 | 0.038 | |||
| Yes | 225 | 129 | 96 | ||
| No | 24 | 19 | 5 | ||
| Multiple cerebral infarction | 4.202 | 0.040* | |||
| Yes | 216 | 123 | 93 | ||
| No | 33 | 25 | 8 | ||
| Cerebral protein deficiency | 0.430 | 0.512 | |||
| Yes | 242 | 143 | 99 | ||
| No | 7 | 5 | 2 | ||
| Carotid atherosclerotic plaque | 0.599 | 0.439 | |||
| Yes | 184 | 112 | 72 | ||
| No | 65 | 36 | 29 | ||
| Atherosclerosis of the carotid artery | 0.713 | 0.399 | |||
| No | 170 | 98 | 72 | ||
| Yes | 79 | 50 | 29 | ||
| Sleep in the last three months | 13.966 | <0.001*** | |||
| Good | 55 | 37 | 18 | ||
| Average | 98 | 68 | 30 | ||
| Poor | 96 | 43 | 53 | ||
| Way of hospitalization | 27.727 | <0.001*** | |||
| Emergency admission | 115 | 56 | 59 | ||
| Outpatient admission | 107 | 83 | 24 | ||
| Ward transfer | 27 | 9 | 18 | ||
| Physical exercise situation | 12.701 | 0.002** | |||
| Exercise regularly | 64 | 39 | 25 | ||
| Exercise occasionally | 97 | 69 | 28 | ||
| Do not exercise | 88 | 40 | 48 |
Clinical characteristics of patients.
*P<0.05, **P<0.01, P<0.001.
PTSD status in stroke patients
The results of this study revealed that the total score of PTSD in stroke patients was 29.12 ± 15.932, with the intrusion dimension scoring the highest (10.98 ± 5.79) and the hyperarousal dimension scoring the lowest (7.83 ± 4.99). Detailed scores are presented in Table 2.
Table 2
| Items | Score |
|---|---|
| Avoidance Dimension | 10.30 ± 6.11 |
| Intrusion Dimension | 10.98 ± 5.79 |
| Hyperarousal Dimension | 7.83 ± 4.99 |
| Total Score | 29.12 ± 15.93 |
Total PTSD scores and dimensions in stroke patients.
Factors associated with PTSD: logistic regression analysis
In the training data set, the occurrence of PTSD after stroke was taken as the dependent variable (No=0, Yes=1). Table 1 shows Gender (Male=0, Female=1), Educational background(High school education or below=0, College or undergraduate=1), Marital status(Married=0, Unmarried=1, Divorce=2, Widowed=3), Monthly household income(≥4000 RMB = 0, 2000–4000 RMB = 1, 1000–2000 RMB = 2, < 1000RMB = 3), Hypertension (No=0, Yes=1), Sleep in the last three months(Good=0, Average =1, Poor=2),Way of hospitalization (Outpatient admission=0, Emergency admission=1, Ward transfer=2), Physical exercise situation(Do not exercise=0, Exercise regularly=1, Exercise occasionally=2), Stroke type(Ischemic Stroke=0, Hemorrhagic Stroke=1, Other type=2), Multiple cerebral infarction(No=0, Yes=1) were independent variables and logistic regression analysis was performed. A total of 9 risk factors were found through analysis (all P < 0.05), as shown in Table 3.
Table 3
| Risk factor | Reference factor | B | SE | Waldx2 | P | OR | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | ||||||
| Female | 0.836 | 0.264 | 10.066 | 0.002 | 2.308 | 1.377 to 3.869 | |
| Educational background | High school education or below | 1.665 | 0.458 | 13.202 | <0.001 | 5.287 | 2.153 to 12.983 |
| College or undergraduate | |||||||
| Marital status | Married | 1.754 | 0.495 | 12.559 | <0.001 | 5.776 | 2.190 to 15.236 |
| Divorce | |||||||
| Monthly household income | ≥4000 RMB | ||||||
| <1000 RMB | 1.629 | 0.480 | 11.505 | <0.001 | 5.100 | 1.989 to 13.075 | |
| Stroke type | Ischemic Stroke | 1.335 | 0.365 | 13.374 | <0.001 | 3.801 | 1.858 to 7.774 |
| Hemorrhagic Stroke | 2.115 | 0.362 | 34.046 | <0.001 | 8.286 | 4.071 to 16.858 | |
| Other type | |||||||
| Hypertension | No | ||||||
| Yes | 1.181 | 0.276 | 18.385 | <0.001 | 3.259 | 1.899 to 5.592 | |
| Sleep in the last three months | Good | ||||||
| Poor | 0.930 | 0.353 | 6.930 | 0.008 | 2.534 | 1.268 to 5.062 | |
| Way of hospitalization | Outpatient admission | ||||||
| Ward transfer | 1.293 | 0.298 | 18.886 | <0.001 | 3.644 | 2.034 to 6.528 | |
| Emergency admission | 1.934 | 0.469 | 16.971 | <0.001 | 6.917 | 2.756 to 17.358 | |
| Physical exercise situation | Do not exercise | ||||||
| Exercise regularly | -1.084 | 0.310 | 12.240 | <0.001 | 0.338 | 0.184 to 0.620 |
Logistic regression analysis of post-stroke PTSD.
Construction and validation of a predictive model for PTSD risk in stroke patients
The predictive model for PTSD risk in stroke patients was constructed and validated in this study. Utilizing the PyCharm software, the scikit-learn library was employed to implement logistic regression, RF, and k-nearest neighbor algorithms. Data from both the training and validation sets were imported, with six influencing factors as independent variables and the occurrence of PTSD as the dependent variable. The models were trained, and optimal parameters were determined through grid search and 5-fold cross-validation. Subsequently, the models were validated using the validation set, and metrics including AUC, sensitivity, specificity, and Youden’s index were calculated for each model. Results indicated that the logistic regression model had the lowest AUC, while the RF model exhibited the highest AUC. Additionally, the RF model demonstrated optimal sensitivity and precision, whereas the logistic regression model showed the lowest sensitivity and precision. Detailed results are presented in Table 4. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for the training and validation group are illustrated in Figures 1, 2.
Table 4
| Prediction model | AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Recall | Precision | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random forest model training group | 0.93 | 0.800 | 0.966 | 0.795 | 0.885 | 0.905 | 0.885 |
| Random forest model validation group | 0.84 | 0.895 | 0.875 | 0.667 | 0.775 | 0.785 | 0.78 |
| Logistic model training group | 0.84 | 0.76 | 0.844 | 0.611 | 0.80 | 0.815 | 0.81 |
| Logistic model testing group | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.667 | 0.844 | 0.775 | 0,74 | 0.78 |
| k-nearest neighbor training group | 0.90 | 0.74 | 0.667 | 0.931 | 0.810 | 0.835 | 0.815 |
| k-nearest neighbor testing group | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.556 | 0.844 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.71 |
Comparison of prediction models.
Figure 1
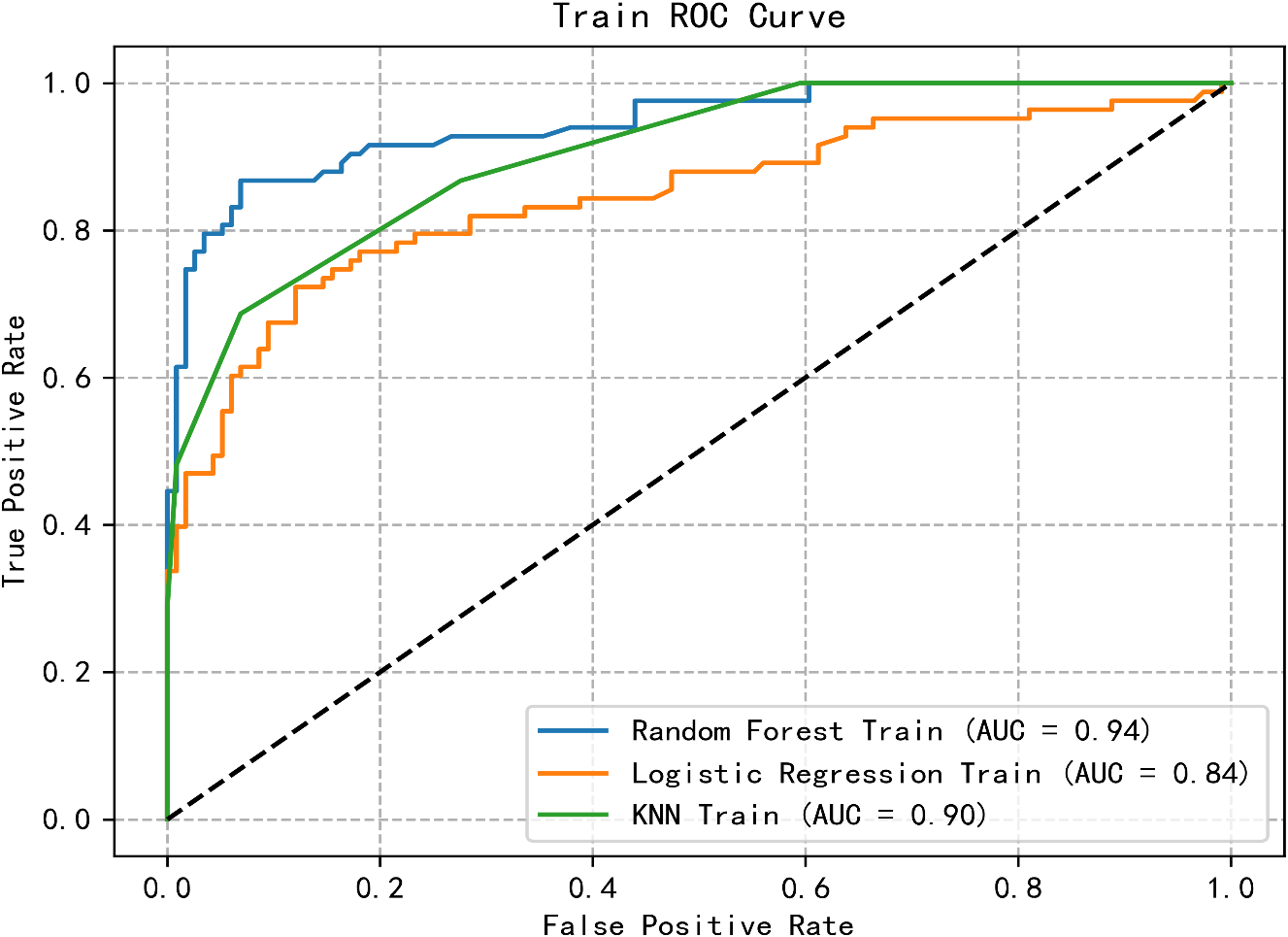
ROC curve of the training group of three machine learning algorithms.
Figure 2
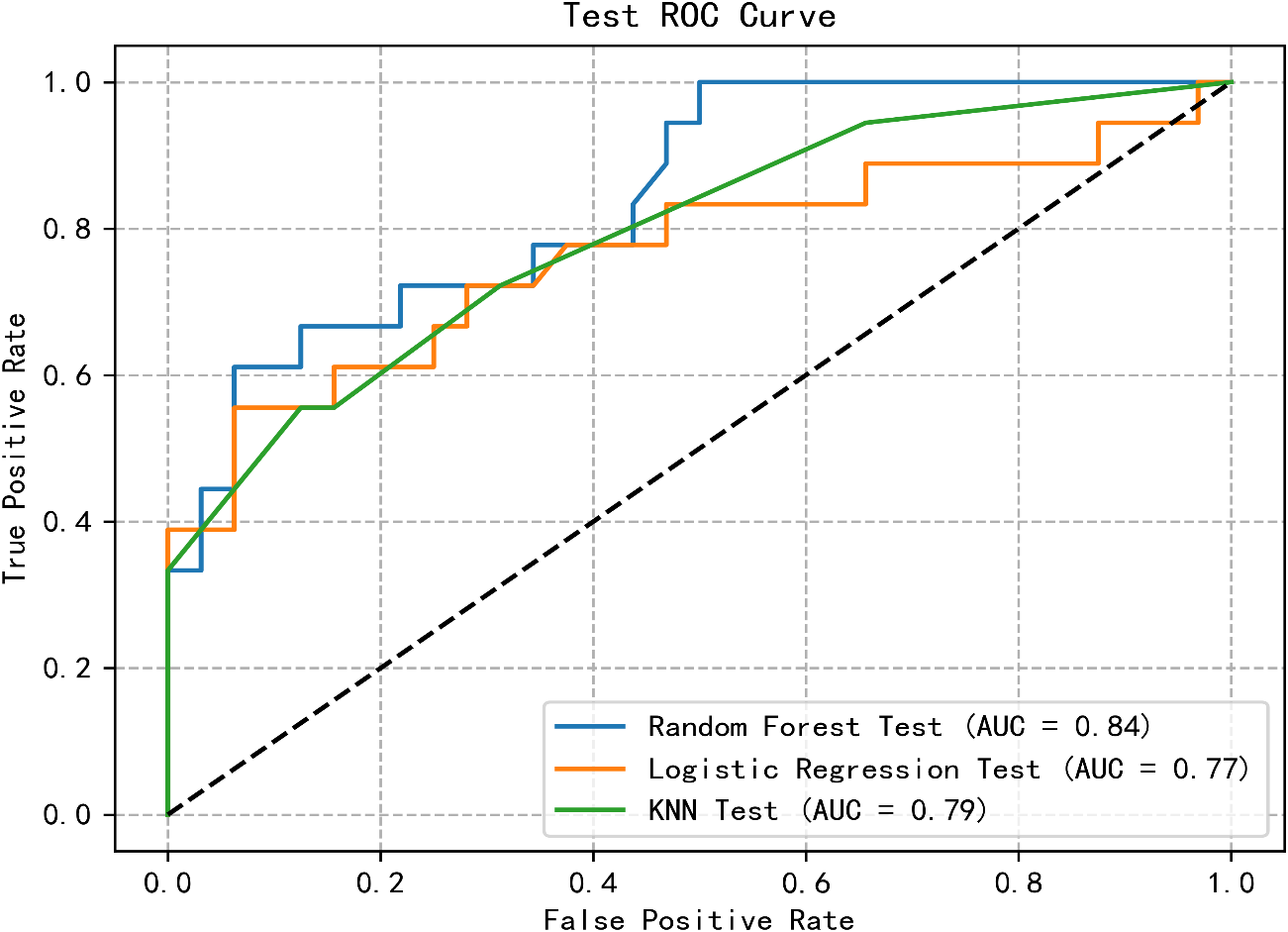
ROC curve of test group of three machine learning algorithms.
Feature importance ranking
The factors affecting PTSD in patients with stroke are as follows: Stroke type (0.187), Sleep in the last three months (0.152), Way of hospitalization (0.147), Monthly household income (0.133), Hypertension (0.108), Gender (1.104), Marital status (0.079), Physical exercise situation (0.067), and Educational background (0.023) (Figure 3). The Brier scores of RF, Logistic, and KNN were 0.157, 0.179, and 0.179, respectively. At the same time, we also conducted further verification through Partial Dependency Plots (PDPs) (Supplementary Figures 1-5).
Figure 3
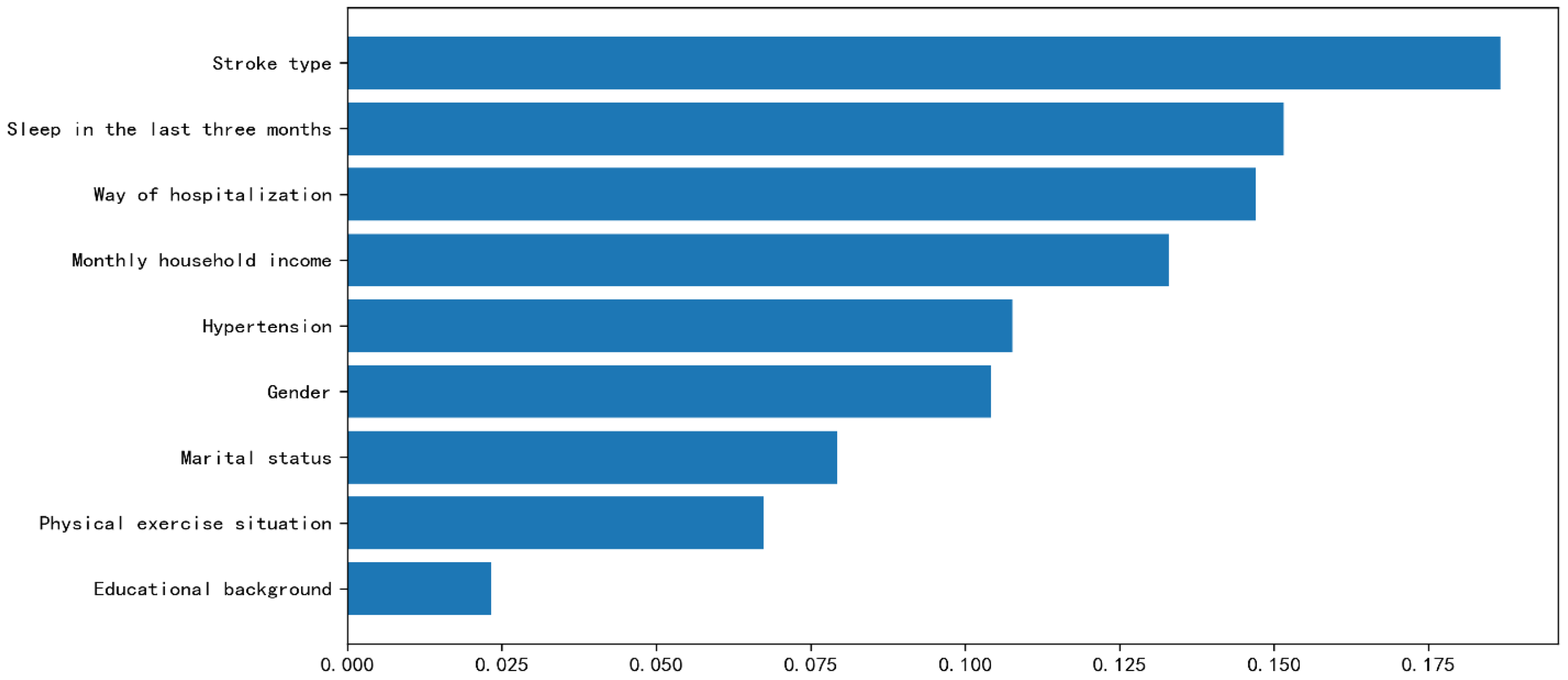
Feature importance ranking.
Discussion
In this study, three machine learning algorithms—logistic regression, RF, and KNN—were employed to construct predictive models for PTSD symptoms. The results revealed that the RF model exhibited the highest values for the area under the ROC, specificity, sensitivity, and F1 score, indicating its superiority over the other models. The findings indicate that the RF model represents the optimal choice, while logistic regression demonstrated the least favorable overall performance among the models. Compared to alternative models, RF aggregates classification decisions from multiple trees, selecting the most frequently occurring class as the final output (27). Its ensemble-based nature provides a substantial advantage over traditional regression methods when handling nonlinear data. The RF model effectively addresses classification and regression tasks (28). The inherent randomness in the RF algorithm enhances its data fitting capability and provides robustness against noise and overfitting (29). To optimize the RF model’s performance, grid search was employed to optimize its hyperparameters, evaluating model performance through cross-validation of different hyperparameter combinations to select the optimal configuration. Feature importance analysis revealed each feature’s contribution to the classification process, identifying key factors affecting prediction results. Our RF model demonstrated favorable performance in screening for post-traumatic stress disorder among stroke survivors, achieving an area under the curve of 0.84. This represents a competitive advantage compared to prior studies (30), complemented by its satisfactory sensitivity, accuracy, and F1-score on internal validation. By identifying key predictor variables, the model also provides clinically interpretable insights, establishing a foundation for early detection and targeted interventions. Its balanced performance in case identification and false-positive reduction positions it as a suitable initial screener within a stepped-care framework. This approach allows for optimized resource allocation by focusing comprehensive diagnostic assessments on a pre-identified high-risk subgroup, while future clinical translation could involve calibrating the decision threshold to accommodate local healthcare needs.
The research findings indicate a post-stroke PTSD incidence of 40.56%, exceeding previous studies (31, 32). These discrepancies may stem from variations in geographical settings, diagnostic tools, ethnic demographics, and healthcare disparities (33). Post-stroke PTSD significantly impacts patients’ occupational and daily functioning, manifesting in severe somatic symptoms (34) and increased comorbidity and suicide risks (35). The study revealed the highest scores in the intrusion dimension (10.98 ± 5.79) and lowest in hyperarousal (7.83 ± 4.99). Intrusion dimension encompasses patients’ impressions and recollections of disease onset, progression, and treatment (36). Elevated intrusion scores correlate with increased anxiety tendencies, as patients exhibit disease-related apprehension and hypervigilance (37). Evidence indicates that PTSD not only increases cardiovascular disease risk (38) but also serves as an independent risk factor for stroke occurrence (39).Risk factor screening through logistic and RF model analysis revealed the following hierarchy of risk factors: Stroke type, Sleep in the last three months, Way of hospitalization, Monthly household income, Hypertension, Gender, Marital status, Physical exercise situation, and Educational background.
While existing research has explored risk factors for PTSD in stroke patients, the relationship between stroke type and PTSD remains largely unexplored (40). This study demonstrates that stroke type significantly influences PTSD development. Ischemic stroke occurs when blood supply to brain tissue is compromised due to vascular obstruction, while hemorrhagic stroke involves blood vessel rupture into the cerebral parenchyma or ventricle (41). Although hemorrhagic stroke has a lower incidence rate, it presents greater severity, mortality, disability rates, and economic burden compared to ischemic stroke. The distinct treatment and rehabilitation protocols for hemorrhagic stroke (42) may intensify patients’ psychological distress, potentially contributing to PTSD development. The study reveals that stroke patients with hypertension demonstrate increased PTSD risk compared to those without hypertension. The chronic nature and fluctuations of hypertension-induced intracerebral hemorrhage (43) heighten stroke patients’ anxiety. Furthermore, hypertension imposes substantial economic and medical burdens on patients’ families. Post-stroke activity restrictions and medication side effects compound patients’ psychological burden, potentially exacerbating PTSD symptoms.
Gender has been identified as a risk factor influencing PTSD in stroke patients, with females exhibiting a higher risk compared to males, consistent with previous research findings (44). Studies have shown that females tend to engage in more emotional expression behaviors than males. When faced with the same event, males typically express themselves in a cognitive-focused manner, while females tend to employ an emotion-focused approach (45, 46). The onset of stroke is often sudden and severe, leading patients to experience sudden changes in physical condition, bodily pain, functional impairments, and other stressors (47), Consequently, patients often resort to negative coping strategies such as refusal to comply with treatment, venting, and irritability, which predisposes females to a higher risk of developing PTSD (48). Additionally, differences in hippocampal structure between males and females are also cited as one of the factors contributing to the increased vulnerability of females to PTSD (49). Multiple studies have indicated that low educational background is a contributing factor to PTSD following stroke (47, 49, 50).Sufficient cultural literacy provides crucial support for interpersonal relationships, offering patients effective internal resources for problem-solving (51). Higher education levels typically correlate with better economic conditions and health literacy (52), enabling more effective utilization of social resources and support systems. These patients generally demonstrate better disease comprehension, reducing illness-related fears and facilitating psychological adaptation (53), thus lowering PTSD risk. Conversely, patients with limited education often struggle with disease understanding, emotional management, and problem-solving, increasing their PTSD susceptibility. Healthcare professionals should therefore consider patients’ information processing capabilities, particularly for female stroke patients and those with lower educational levels. They should provide guidance for appropriate disease understanding, minimize knowledge-related anxieties, and assist with emotional management to reduce PTSD incidence. Additionally, this study identifies marital status as an influential factor in stroke-related PTSD, ranking seventh in feature importance. These findings differ from Stela’s research (54). Studies indicate that interpersonal-oriented therapies, including couple and family interventions, may ameliorate PTSD symptoms, with positive intimate relationships serving as protective factors (55). Married individuals often benefit from partner support, enabling better psychological pressure management and emotional regulation, leading to improved overall health status and reduced post-stroke psychological distress (56). Divorced patients, experiencing emotional disconnection and lacking partner support, typically demonstrate poorer psychological states and increased susceptibility to post-stroke PTSD.
The findings of this study demonstrate that the mode of admission significantly influences PTSD occurrence in stroke patients, with emergency department admissions showing higher susceptibility to PTSD. Patients admitted through the emergency department typically experience acute onset stroke, in which severe cerebrovascular dysfunction develops suddenly, inducing substantial psychological distress manifested through anxiety, fear, and helplessness. The abrupt onset of illness provides these patients with limited time for adaptation and coping, thus elevating their PTSD risk. Additionally, the trauma-induced tension and panic activate the amygdala within the brain’s limbic system, a region crucial for forming conditioned fear memories, which constitute core PTSD symptoms (57). Healthcare providers treating stroke patients admitted through emergency departments should strengthen patient and family communication, implement proactive psychological counseling, and assist patients in developing positive attitudes and effective coping strategies.
Research identifies low household income as a risk factor for PTSD (58), aligning with previous study findings. The extended medical and rehabilitative care required by stroke patients creates financial pressure, potentially increasing anxiety and concern, thereby elevating the risk of stress disorders. Additionally, the prolonged recovery period following severe trauma reduces patients’ capacity, confidence, and motivation to resume work, intensifying economic challenges and exacerbating PTSD symptoms (59).For stroke patients with lower household incomes, clinical healthcare providers should actively monitor their psychological well-being, offer psychological support and care, assist them in facing their illness positively, alleviate psychological stress, and reduce the occurrence of PTSD.
Physical exercise demonstrates multiple beneficial effects: reducing stress and anxiety, facilitating neurological changes, activating neurotransmitters while regulating brain function, promoting neuronal growth (60), maintaining neuroplasticity, and enhancing mitochondrial activity in the brain, consequently improving PTSD symptoms (61). The research indicates that regular physical activity serves as a protective factor against PTSD in stroke patients. Physical inactivity among stroke patients may result in diminished physical function, substantially affecting their daily living capabilities and quality of life, while increasing future uncertainty, thereby elevating risks of anxiety, depression, and PTSD onset. This study also found that poor (or very poor) sleep quality among stroke patients is a risk factor for PTSD. Sleep quality issues are prevalent among stroke patients, with sleep disturbances being a common problem affecting their sleep quality (62). Sleep disturbances are crucial predictors for the development of PTSD, with both pre- and post-traumatic sleep disturbances increasing the risk of PTSD (63, 64). Additionally, research has found that sleep disturbances mediate the relationship between PTSD and suicidal ideation among hospitalized patients (65). The sleep condition of stroke patients should not be overlooked, and healthcare professionals should actively create a conducive sleep environment during hospitalization, assist patients in developing good sleep habits, avoid stimulating substances, and improve sleep quality to reduce the occurrence of PTSD.
Strengths and limitations
This study constructed prediction models for PTSD in stroke patients using RF algorithm, logistic regression, and KNN machine learning approaches. The analysis demonstrated that the RF model exhibited superior predictive performance, providing valuable insights for clinical diagnosis, treatment, and nursing protocols. However, several limitations warrant consideration. First, as the study relied on patient self-reported data, certain potentially influential factors affecting PTSD incidence may be missing or incomplete, particularly physiological and biochemical parameters. Second, the absence of genomic information may limit mechanistic insights. Furthermore, the cross-sectional nature of the study and its relatively small sample size may impact the generalizability of the results. Future research would benefit from multi-center, large-scale studies, establishing comprehensive follow-up cohorts, and investigating additional objective and quantifiable predictors to validate these findings.
Conclusion
This investigation employed three machine learning algorithms to develop a risk prediction model for post-traumatic stress disorder in stroke patients, with the RF model emerging as the most effective predictor. The study identified several risk factors for PTSD in stroke patients, including stroke type, physical exercise, sleep quality, gender, education level, and family economic status. These findings enable clinical medical staff to monitor risk factors for post-traumatic stress disorder in stroke patients and develop tailored intervention strategies to mitigate its impact. Given the cross-sectional design and limited sample size, which may not fully represent patients across different healthcare facilities and geographical regions, future large-scale, multi-center, longitudinal studies are essential. Furthermore, as machine learning continues to advance as a core technology in artificial intelligence, its robust data mining and processing capabilities show increasing promise in disease risk prediction. Future research should explore additional machine learning algorithms to enhance PTSD risk prediction models for stroke patients, thereby strengthening the foundation for effective screening and intervention strategies.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Research Ethics Committee of Jishou University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Ethics approval number (JSDX-2023-0084).
Author contributions
YL: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CP: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YG: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the 2025 Annual Research Basic Ability Enhancement Program for Young and Middle-Aged Teachers in Guangxi Universities (2025KY0521).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1694654/full#supplementary-material.
Abbreviations
PTSD, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder; PSF, Post-stroke fatigue; KNN, K-Nearest Neighbors; AUC, Area under the curve; ROC, Receiver operating characteristic.
References
1
Edmondson D Richardson S Fausett JK Falzon L Howard VJ Kronish IM . Prevalence of PTSD in survivors of stroke and transient ischemic attack: a meta-analytic review. PloS One. (2013) 8:e66435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066435
2
Roth GA Mensah GA Johnson CO Addolorato G Ammirati E Baddour LM et al . Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990-2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010
3
Macfarlane J . Positive psychology and its role within mental health nursing. Br J Ment Health Nursing. (2019) 8:81–7. doi: 10.12968/bjmh.2019.8.2.81
4
Kronish IM Edmondson D Goldfinger JZ Fei K Horowitz CR . Posttraumatic stress disorder and adherence to medications in survivors of strokes and transient ischemic attacks. Stroke. (2012) 43:2192–7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.655209
5
Noble AJ Baisch S Schenk T Mendelow AD Allen L Kane P . Posttraumatic stress disorder explains reduced quality of life in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients in both the short and long term. Neurosurgery. (2008) 63:1095–105. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000327580.91345.78
6
Poulos AM Reger M Mehta N Zhuravka I Sterlace SS Gannam C et al . Amnesia for early life stress does not preclude the adult development of posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in rats. Biol Psychiatry. (2014) 76:306–14. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.10.007
7
Speck V Noble A Kollmar R Schenk T . Diagnosis of spontaneous cervical artery dissection may be associated with increased prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder. J Stroke Cerebrovascular Diseases. (2014) 23:335–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.03.033
8
Edmondson D Horowitz CR Goldfinger JZ Fei K Kronish IM . Concerns about medications mediate the association of posttraumatic stress disorder with adherence to medication in stroke survivors. Br J Health Psychol. (2013) 18:799–813. doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12022
9
Vickrey BG Williams LS . Posttraumatic stress disorder after cerebrovascular events: broadening the landscape of psychological assessment in stroke and transient ischemic attack. Am Heart Assoc;. (2014) p:3182–3. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.006865
10
Hedlund M Zetterling M Ronne-Engström E Carlsson M Ekselius L . Depression and post-traumatic stress disorder after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage in relation to lifetime psychiatric morbidity. Br J neurosurgery. (2011) 25:693–700. doi: 10.3109/02688697.2011.578769
11
Favrole P Jehel L Levy P Descombes S Muresan IP Manifacier MJ et al . Frequency and predictors of post-traumatic stress disorder after stroke: a pilot study. J Neurol Sci. (2013) 327:35–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.02.001
12
Morrow DA Antman EM Charlesworth A Cairns R Murphy SA de Lemos JA et al . TIMI risk score for ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A convenient, bedside, clinical score for risk assessment at presentation: An intravenous nPA for treatment of infarcting myocardium early II trial substudy. Circulation. (2000) 102:2031–7. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.17.2031
13
Handelman GS Kok HK Chandra RV Razavi AH Lee MJ Asadi H . eDoctor: machine learning and the future of medicine. J Intern Med. (2018) 284:603–19. doi: 10.1111/joim.12822
14
Shi S Shi L . Investigation of risk factors and development of a risk prediction nomogram for post-stroke patients with post-traumatic stress disorder. Chin J Integr Med Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease. (2021) 19:1734–8. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2021.10.035
15
Yan X Zeng Z Li F Huo H . Development and validation of a prediction model for post-stroke post-traumatic stress disorder integrating cox regression and decision trees. J Clin Intern Med. (2024) 41:629–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9057.2024.09.013
16
Ganyuan D Zhongting Y Xingmei D Chunyan D Ting S Ruiyu L et al . Exploring the influencing factors of antenatal depression based on random forest algorithm and multivariate logistic regression model. Chin J Dis Control Prev. (2023) 27:1003–9. doi: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2023.09.003
17
Qiu X Miao J Lan Y Sun W Li G Pan C et al . Artificial neural network and decision tree models of post-stroke depression at 3 months after stroke in patients with BMI ≥ 24. J Psychosom Res. (2021) 150:110632. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2021.110632
18
Di Z Shuting Z Bo W . Interpretation of “Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018. ChinJContemp Neurol Neurosurg. (2019) 19:897–901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2019.11.015
19
Deng L Bo W . Update and interpretation of “China’s guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of cerebral hemorrhage 2019. Cardio-Cerebrovasc Dis Prev Treat. (2021) 21:13–7 + 34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-816x.2021.01.002.
20
Chinese Hypertension Prevention and Control Guidelines Revision Committee HAC Chinese Association for the Promotion of International Exchanges in Healthcare Hypertension Branch Chinese Geriatric Society Hypertension Branch Chinese Geriatric Health Care Association Hypertension Branch Chinese Stroke Society, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention of Chronic Noncommunicable Diseases . Chinese guidelines for the prevention and treatment of hypertension (2024 revision). Chin J Hypertens. (2024) 32:603–700. doi: 10.16439/j.issn.1673-7245.2024.07.002.
21
Alberti KG Zimmet PZ . Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetes Med. (1998) 15:539–53. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199807)15:7<539::AID-DIA668>3.0.CO;2-S
22
Miles A McClements PL Steele RJ Redeker C Sevdalis N Wardle J . Perceived diagnostic delay and cancer-related distress: a cross-sectional study of patients with colorectal cancer. Psycho-Oncology. (2017) 26:29–36. doi: 10.1002/pon.4093
23
Weiss DS . The impact of event scale: revised. In: Cross-cultural assessment of psychological trauma and PTSD. Springer US, Boston, MA (2007). p. 219–38.
24
Horowitz M Wilner N Alvarez W . Impact of Event Scale: a measure of subjective stress. Psychosom Med. (1979) 41:209–18. doi: 10.1097/00006842-197905000-00004
25
Guo S-r Zi-qiang X Liu-na G . Reliability and validity of chinese version of the impact of event scale- revised. Chin J Clin Psychol. (2007) 01:15–7. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2007.01.007
26
Guoping H Yalin Z Hui X Yunfei Z . The Chinese Version of the mpact of Event ScaleRevised: Reliab ility and Validity. Chin Ment Health J. (2006), 01:28–31.
27
Xin Z xiuying L Yu Z Sixue C Shuhan Y . Construction and validation of Intraoperative Hypothermia risk prediction model in lung cancer patients. Chin Nurs Manage. (2023) 23:1500–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2023.10.012
28
Minyi WZX Dongfang Y . Comparison on classification performance between random forest and deepForest. Chin J Health Statistics. (2023) 40:349–53. doi: 10.11783/j.issn.1002-3674.2023.03.007
29
Xiao-hui W Yan P Jun Z . Application of artificial neural network in establishing predictive models with infection during chemotherapy for hospitalized elderly patients with lung cancer. Journal North Sichuan Med College. (2017) 32:871–3 + 89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2017.06.018
30
Huang H Jiajia YJ Li S . Influencing factors of post-traumatic stress disorder in stroke patients and construction of risk prediction nomogram model. Cardiac Cereb Pulmonary Vasc Disease. (2021) 29:35–9. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1008-5971.2021.00.272
31
Cumming TB Blomstrand C Skoog I Linden T . The high prevalence of anxiety disorders after stroke. Am J Geriatric Psychiatry. (2016) 24:154–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2015.06.003
32
Maaijwee N Tendolkar I Rutten-Jacobs L Arntz R Schaapsmeerders P Dorresteijn L et al . Long-term depressive symptoms and anxiety after transient ischaemic attack or ischaemic stroke in young adults. Eur J Neurology. (2016) 23:1262–8. doi: 10.1111/ene.13009
33
Singer A Kosowan L Muthumuni D Katz A Zafari H Zulkernine F et al . Characterizing primary care patients with posttraumatic stress disorder using electronic medical records: a retrospective cross-sectional study. Family Pract. (2022) 41(4):434–41. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmac139
34
Lu H-s Hong-bo H Jin F Gui-ling M . Correlation between resilience, acute stress disorder and prognosis of patients with traumatic fracture. Chin Med Front J (electronic edition). (2018) 10:65–9.
35
Jordan NN Hoge CW Tobler SK Wells J Dydek GJ Egerton WE . Mental health impact of 9/11 Pentagon attack: validation of a rapid assessment tool. Am J Prev Med. (2004) 26:284–93. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2004.01.005
36
Zhenhua Z Yiying L Ling L Desu C . Impact of post-traumatic stress disorder and sleep status on mental health of patients with lung cancer. J Nurs Science. (2020) 35:81–3.
37
Matsuoka Y Nakano T Inagaki M Sugawara Y Akechi T Imoto S et al . Cancer-related intrusive thoughts as an indicator of poor psychological adjustment at 3 or more years after breast surgery: a preliminary study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2002) 76:117–24. doi: 10.1023/A:1020572505095
38
Al Nakhebi OAS Albu-Kalinovic R Neda-Stepan O Giurgi-Oncu C Crișan CA Enatescu VR et al . (2025). Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. 14:7979–7979. doi: 10.3390/jcm14227979
39
Perkins JD Wilkins SS Kamran S Shuaib A . Post-traumatic stress disorder and its association with stroke and stroke risk factors: A literature review. Neurobiol Stress. (2021) 14:100332. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100332
40
Anderson CS . (2024). Stroke advances in 2023: a new horizon for the management of intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 23:12–13. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00451-9. PMID: 38101883
41
Ikenouchi H . (2025). The importance of hypertension awareness and adequate blood pressure control before intracerebral hemorrhage. Hypertens Res. 48:1621–3. doi: 10.1038/s41440-025-02161-8
42
Jiang C . Posttraumatic stress disorder after a first-ever intracerebral hemorrhage in the Chinese population: A pilot study. Appl Neuropsychol Adult. (2020) 27:1–8. doi: 10.1080/23279095.2018.1451334
43
Ikenouchi H . (2025). The importance of hypertension awareness and adequate blood pressure control before intracerebral hemorrhage. Hypertens Res. 48:1621–3. doi: 10.1038/s41440-025-02161-8
44
Goldfinger JZ Edmondson D Kronish IM Fei K Balakrishnan R Tuhrim S et al . (2014). Correlates of post-traumatic stress disorder in stroke survivors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 23(5):1099–5
45
Ayan C Jiemin Y Shuang X Jiajin Y . The male advantage in regulating negative emotion byexpressive suppression: An event-related potentia study. Acta Psychologica Sin. (2016) 48:482–94.
46
Hatch R Young D Barber V Griffiths J Harrison DA Watkinson P . Anxiety, Depression and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder after critical illness: a UK-wide prospective cohort study. Crit Care. (2018) 22:310. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2223-6
47
Fei ZZ . Correlation study of post-traumatic stress disorder, cognitive function and quality of life in stroke patients. (2023).
48
Suo W . Risk factors of post-traumatic stress disorder and the effect of non-pharmacological intervention in ICU survivors. (2017).
49
van der Meer CA Bakker A Smit AS van Buschbach S den Dekker M Westerveld GJ et al . Gender and age differences in trauma and PTSD among Dutch treatment-seeking police officers. J nervous Ment disease. (2017) 205:87–92. doi: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000000562
50
Bruggimann L Annoni JM Staub F von Steinbüchel N van der Linden M Bogousslavsky J . Chronic posttraumatic stress symptoms after nonsevere stroke. Neurology. (2006) 66:513–6. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000194210.98757.49
51
Stubbe DE . (2020). Practicing Cultural Competence and Cultural Humility in the Care of Diverse Patients. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 18(1):49–51. doi: 10.1176/appi.focus.20190041
52
Balasubramanian P Kiss T Tarantini S et al . (2021). Obesity-induced cognitive impairment in older adults: a microvascular perspective. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 320(2):H740–61
53
Wenji L Jia L Lanlan M . (2015). Analysis of the related factors of posttraumatic stress disorder in the hospitalized patients with breast cancer and nursing tactics. Journal of Qilu Nursing. 21(12):1–3
54
Rutovic S Kadojic D Dikanovic M et al . (2021). Prevalence and correlates of post-traumatic stress disorder after ischaemic stroke. Acta Neurol Belg. 121(2):437–42
55
Sijercic I Liebman RE Ip J et al . (2022). A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual and couple therapies for posttraumatic stress disorder: Clinical and intimate relationship outcomes. J Anxiety Disord. 91:102613
56
Huntington C Stanley SM Doss BD Rhoades GK . Happy, healthy, and wedded? How the transition to marriage affects mental and physical health. J Fam Psychol. (2022) 36:608–17. doi: 10.1037/fam0000913
57
Molina CSP Berry S Nielsen A Winfield R . PTSD in civilian populations after hospitalization following traumatic injury: A comprehensive review. Am J Surgery. (2018) 216:745–53. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2018.07.035
58
Wu B Huang X Qian Hu . (2021). Post-traumatic stress disorder level of patients after replantation of amputated finger and the influence factors. CHINESENURSINGRESEARCH. 35(24):4451–5
59
Li Y Zhong Z Li H Deng J Wujing H . (2023). Analysis of the occurrence and influencing factors of post-traumatic stress disorder in patients with severe trauma. J Gen Surg Clin. 11:57–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5308.2023.01.017
60
Alkadhi KA . Exercise as a positive modulator of brain function. Mol neurobiology. (2018) 55:3112–30. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0516-4
61
Hao Z Yihan N . A systematic review of the intervention effect of physical exercise onPost traumatic stress disorder in veterans. Bull Sport Sci Technol. (2023) 31:259–62 + 67.
62
Shuxiao Luo Y Baohua L . Research progress of nursing care for patients with post-stroke sleep disorders. Chin J Cerebrovasc Dis. (2021) 15:422–5.
63
Koren D Arnon I Lavie P Klein E . Sleep complaints as early predictors of posttraumatic stress disorder: a 1-year prospective study of injured survivors of motor vehicle accidents. Am J Psychiatry. (2002) 159:855–7. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.5.855
64
Sandahl H Carlsson J Sonne C Mortensen EL Jennum P Baandrup L . Investigating the link between subjective sleep quality, symptoms of PTSD, and level of functioning in a sample of trauma-affected refugees. Sleep. (2021) 44:zsab063. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab063
65
Rohr JC Rufino KA Alfano CA Patriquin MA . Sleep disturbance in patients in an inpatient hospital mediates relationship between PTSD and suicidal ideation. J Psychiatr Res. (2021) 133:174–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.12.039
Summary
Keywords
stroke, post-traumatic stress disorder, random forest, prediction model, machine learning, risk factors
Citation
Li Y, Pan C and Gu Y (2025) Using machine learning methods to predict post-traumatic stress disorder in stroke patients in China. Front. Psychiatry 16:1694654. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1694654
Received
28 August 2025
Revised
01 November 2025
Accepted
04 November 2025
Published
20 November 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Ansab Akhtar, Louisiana State University, United States
Reviewed by
Filippo Rapisarda, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, Canada
Boluwaji Ade Akinnuwesi, University of Eswatini, Eswatini
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Li, Pan and Gu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yue Gu, 591690454@qq.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.