- 1Department of Nursing, The Third People’s Hospital of Henan Province, Zhengzhou, China
- 2School of Nursing, North Henan Medical University, Xinxiang, China
- 3Department of Orthopedics, The Third People’s Hospital of Henan Province, Zhengzhou, China
Background: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a common and effective treatment for advanced knee osteoarthritis, yet it imposes significant demands on primary caregivers throughout the perioperative and rehabilitation phases. Understanding caregivers’ evolving needs is critical for optimizing patient outcomes and sustaining caregiver well-being. This study aimed to explore the dynamic care experiences and changing needs of primary caregivers of TKA patients across three distinct phases: the diagnosis period, discharge transition, and rehabilitation phase, and to construct a comprehensive journey map of caregiving needs.
Methods: A longitudinal qualitative study was conducted using purposive sampling. Sixteen primary caregivers of patients undergoing unilateral TKA were recruited from a tertiary hospital in Henan, China. Semi-structured interviews were conducted at three time points: preoperative (T1), pre-discharge (T2), and one month post-discharge (T3), resulting in 43 interviews. Data were analyzed using content analysis and synchronized temporal mapping to identify themes and subthemes along the caregiving timeline.
Results: Four major themes and 27 subthemes were identified: care tasks, emotional experiences, caregiving barriers, and support systems. Caregivers’ responsibilities evolved from pre-surgical information gathering to intensive post-surgical care and long-term rehabilitation support. Emotional burdens shifted from anxiety and helplessness to fatigue and psychological strain. Major barriers included knowledge deficits, skill limitations, and inadequate systemic support. The caregiver support network transitioned from hospital-based to community and family-based systems over time. A visual journey map was developed to represent these findings.
Conclusion: Primary caregivers of TKA patients face complex and changing needs across different stages of care. A caregiver-centered, multidisciplinary, and phase-specific support framework is essential to improve the quality of postoperative care and reduce caregiver burden.
1 Introduction
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is among the most common degenerative joint diseases in middle-aged and older adults, characterized by progressive cartilage loss and osteophyte formation that lead to persistent pain, functional limitations, and poorer quality of life (1). In China and globally, demographic aging, obesity, and lifestyle-related risks have contributed to steady rise in KOA burden, with older women disproportionately affected (2, 3). These trajectories not only reflect disease prevalence but also foreshadow escalating care needs at the household level.
For patients with advanced KOA, conservative therapies are frequently inadequate, and total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is widely regarded as the standard intervention to relieve pain and restore mobility (4). The procedure's diffusion has been rapid—millions of TKAs are performed worldwide annually, and China has seen double-digit growth since 2010 with continued expansion expected (5). While these trends underscore TKA's clinical value, they also magnify the volume and complexity of postoperative support required after discharge, when patients transition to home-based rehabilitation and rely heavily on informal care (6).
Primary caregivers—most often spouses or adult children—sustain recovery across multiple stages, from preoperative preparation and inpatient rehabilitation to transitional discharge and ongoing home care (7). Their responsibilities span assistance with activities of daily living, symptom monitoring, complication surveillance, facilitation of prescribed exercises, and provision of emotional support. Yet caregivers’ own needs—psychological coping, actionable information, and access to structured resources—are frequently under-recognized in routine care pathways (8).
A substantial body of work links caregiver burden and well-being with patient outcomes such as adherence, functional recovery, and readmission risk (9). However, much of this literature is cross-sectional, providing static snapshots that obscure how caregiving demands, stressors, and coping strategies evolve as patients move through distinct recovery phases. Limited longitudinal evidence illustrates marked temporal fluctuations—e.g., heightened strain in the first month and persistent information gaps thereafter—but the timing, intensity, and persistence of these patterns remain insufficiently resolved (10). Methodologically, heterogeneity in burden measures, follow-up intervals, and contextual factors further constrains synthesis, leaving uncertainty about when and how to intervene most effectively.
The “caregiving journey” framework addresses these limitations by foregrounding the staged, dynamic nature of informal care: responsibilities shift, emotions ebb and flow, and support needs reconfigure across perioperative and rehabilitation milestones (11). Building on this lens, journey mapping can make visible the “pressure points” where unmet needs cluster, thereby guiding the design and timing of targeted interventions and education (12). Nevertheless, systematic longitudinal applications of this approach in TKA remain scarce—particularly in China, where family-based caregiving is central—leaving gaps in culturally and system-specific guidance.
Accordingly, this study employs a longitudinal qualitative design to capture the evolving experience of primary caregivers for TKA patients (13). Repeated, in-depth interviews across preoperative, early postoperative, and home-rehabilitation stages allow us to trace temporal patterns in needs, stressors, and adaptive strategies beyond what cross-sectional snapshots can reveal. Guided by the gaps identified above, the objectives of this study are twofold: (1) to explore and interpret how caregivers’ needs, challenges, and coping processes evolve across the perioperative and rehabilitation stages of TKA; and (2) to construct an in-depth understanding of the critical moments where informational, practical, and psychosocial support needs become most salient, thereby providing a nuanced foundation for context-sensitive, stage-specific interventions. By prioritizing caregivers’ narratives and experiences, this study aims to generate empirically grounded insights for nursing practice, caregiver education, and health service planning.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design
This study adopted a longitudinal qualitative design grounded in the interpretivist paradigm, using the journey mapping method combined with conventional content analysis (14). This approach was selected to capture caregivers’ evolving experiences and to interpret the contextual meanings of caregiving practices over time. The design was further informed by SRQR (Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research) and COREQ (Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research) guidelines, to enhance transparency and methodological rigor (15).
2.2 Participants and sampling
Participants were the primary caregivers of patients who underwent TKA at Henan Provincial Third People's Hospital. A purposive sampling method, guided by the principle of maximum variation, was used to ensure diversity in age, gender, educational background, and socio-economic status. Inclusion criteria for patients were: (1) first-time recipients of unilateral TKA; (2) a Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia (TSK) score >37, indicating moderate to severe kinesiophobia; (3) clear consciousness, normal cognitive and hearing function, and the ability to communicate verbally or in writing; (4) provision of informed consent and willingness to participate in longitudinal follow-up. Exclusion criteria included: (1) severe dysfunction of vital organs such as the heart, liver, lungs, or kidneys; (2) diagnosed anxiety, depression, or current use of psychiatric medications; (3) mental illness or cognitive impairments impairing communication; (4) simultaneous participation in other similar studies.
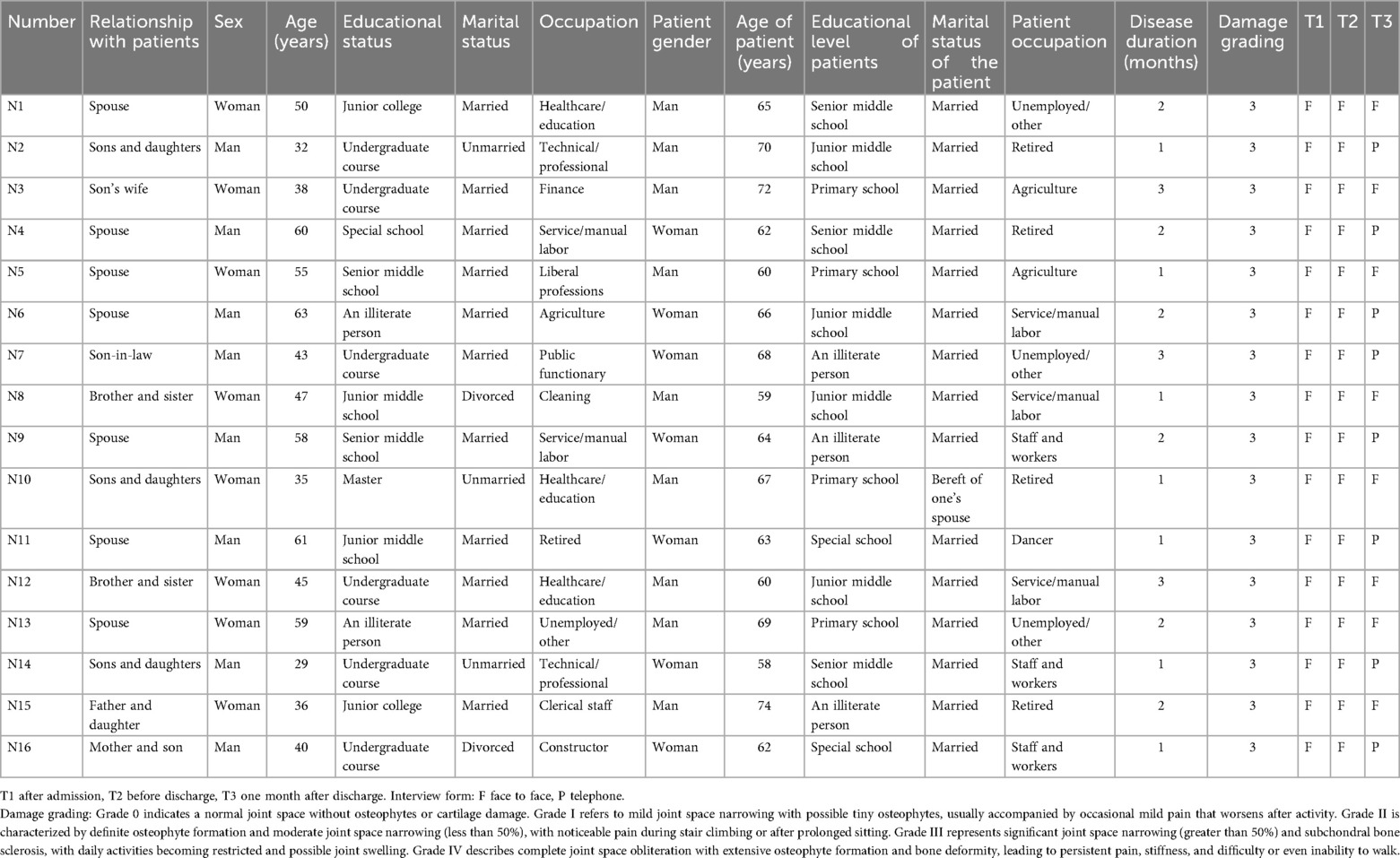
Inclusion criteria for caregivers were: (1) the primary caregiver providing ≥4 h of daily care; (2) unpaid caregiving role; (3) adequate communication and comprehension ability. Exclusion criteria included: (1) caregivers with a professional healthcare background; (2) patients’ death or caregiver withdrawal during the study. Sample size was determined according to the principle of data saturation, defined as the point at which no new codes or themes emerged during successive interviews (16). Saturation was reached after 16 caregivers were recruited, resulting in 43 interviews across three time points. The mean age of caregivers was 47.3 years (SD = 8.6). Ethical approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Henan Provincial Third People's Hospital (Approval No. 2025-126).
2.3 Interview timing and guide
To reduce recall bias and ensure the authenticity of data, interviews were conducted at three key time points identified through literature review and clinical practice, and aligned with the structure of the caregiver journey map:
T1 (Preoperative phase): Within the first 2 days of hospitalization
T2 (Discharge transition phase): One day before discharge
T3 (Rehabilitation phase): One month post-discharge
Although these three time points may seem limited, they were chosen to balance participant burden with feasibility, and to capture phases shown by prior research to involve the most significant caregiving challenges. The relatively short interview duration (15–20 min) reflected participants’ time constraints and fatigue during hospital stays, but repeated interviews allowed for cumulative depth.
A semi-structured interview guide was used consistently, refined iteratively during data collection to accommodate emerging themes. Sample questions included: “What is your biggest current difficulty as a caregiver?” and “How has this experience affected your own life and health?” A pilot interview with two caregivers was conducted to refine question wording and flow.
2.4 Data collection
All interviews were conducted by two researchers trained in qualitative methods. One served as interviewer and reflexive facilitator, while the second took observational notes on non-verbal cues. The researchers positioned themselves as clinical nurses with prior experience in perioperative care, which facilitated rapport but also necessitated reflexive journaling to manage potential bias.
T1 and T2 interviews were face-to-face in a private hospital room, while T3 interviews were conducted in person or by telephone, depending on caregiver preference. All interviews were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim within 24 h. Participants were anonymized using codes (N1–N16).
2.5 Data analysis
All interviews were transcribed verbatim within 24 h and independently verified by two researchers. Data were analyzed using conventional content analysis (17), supported by NVivo 12 software for coding and data management. The analysis proceeded iteratively: transcripts were read repeatedly for immersion, and open coding was conducted to generate initial codes. Codes with similar meanings were then grouped into subthemes and further synthesized into broader themes. These themes were subsequently mapped onto a temporal framework corresponding to the caregiving journey (T1–T3), enabling both synchronic and longitudinal interpretation. To ensure credibility, coding decisions and theme development were discussed in regular peer debriefing sessions, and an audit trail was maintained throughout. The interview guide was refined iteratively to incorporate emerging insights, and data collection continued until thematic saturation, defined as the absence of new codes in successive interviews, was achieved.
2.6 Rigor and quality control
To ensure methodological rigor, multiple strategies were implemented throughout the study. First, trust was established between researchers and participants through long-term engagement in inpatient nursing care, fostering an environment conducive to open and honest dialogue. Second, reflexive journaling was used by all researchers to document potential biases, emotional reactions, and decision-making during data collection and analysis. This practice helped minimize the influence of subjectivity and maintained analytical transparency. Third, member checking was employed by revisiting selected participants to verify the accuracy of thematic interpretations and confirm that the findings reflected their lived experiences. Lastly, to ensure technical integrity, dual-device recording was used during telephone interviews—one for communication and the other for audio capture—to prevent data loss and maintain recording quality. These quality assurance measures collectively contributed to the credibility, dependability, and confirmability of the study findings.
3 Results
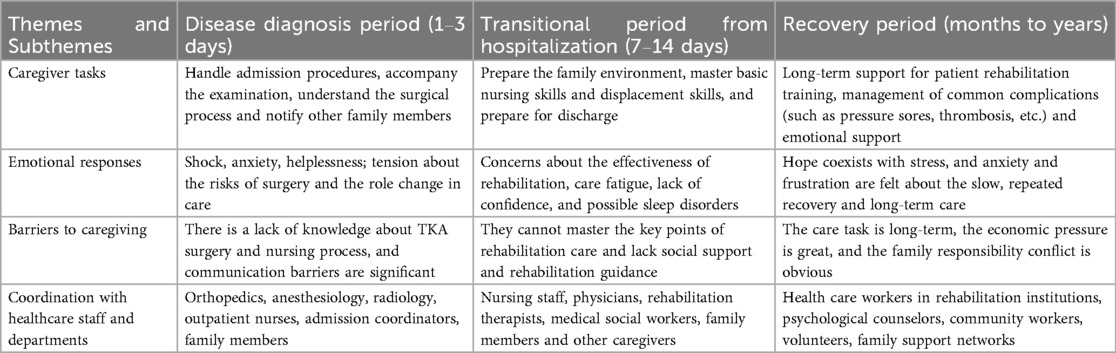
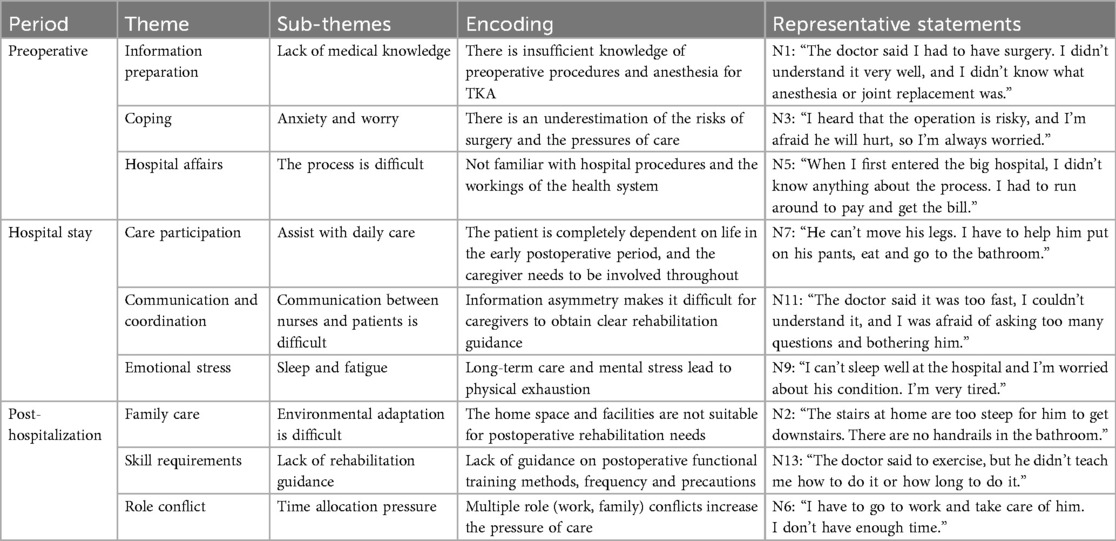
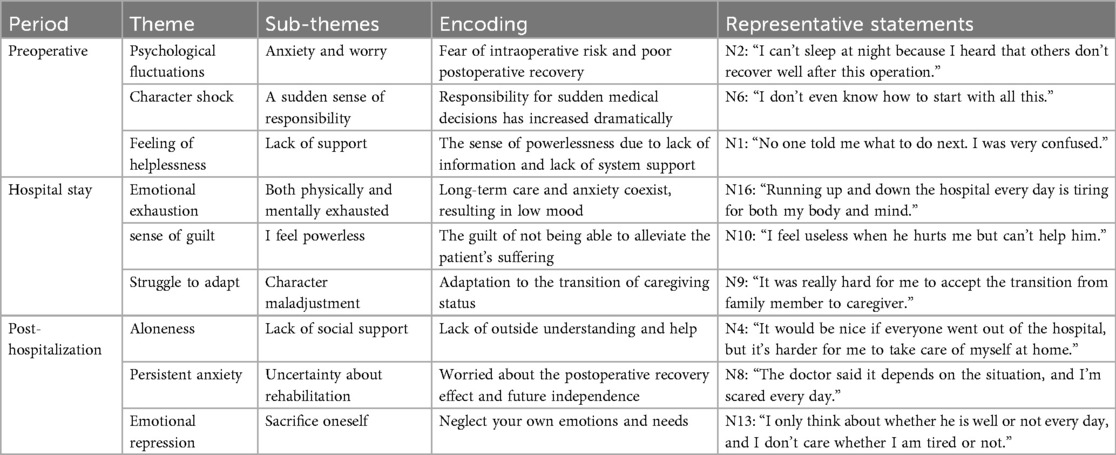
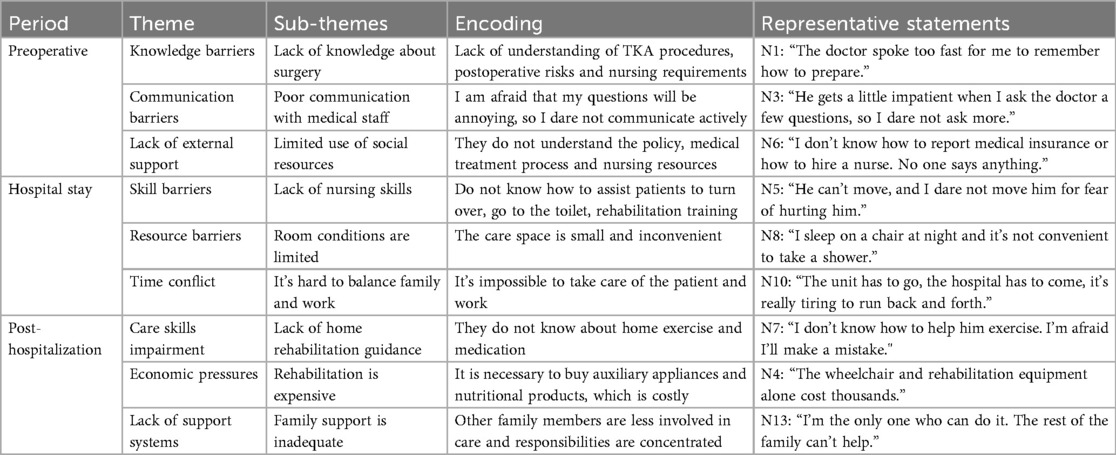
This longitudinal qualitative study traced caregivers’ dynamic experiences across the preoperative (diagnosis), discharge transition, and rehabilitation phases (Table 1). The thematic analysis identified caregivers’ experiences and captured both barriers and facilitators (Table 2). The analysis yielded four main themes—care tasks, emotional experiences, caregiving barriers, and support systems—and 27 subthemes, which were integrated into a comprehensive caregiving journey map. This map visually demonstrated how caregivers’ roles evolved from performing basic organizational tasks to assuming a more complex “quasi-professional” function, accompanied by fluctuating emotions and shifting support needs.
3.1 Participant characteristics
A total of 16 dyads of TKA patients and their primary caregivers participated in this study. Caregivers ranged in age from 29 to 63 years, with a mean age of 47.3 years (SD = 8.6). The majority were female (68.8%), and most were either spouses (43.8%) or adult children (31.3%), with smaller proportions of in-laws (12.5%), siblings (12.5%), and parents of patients (6.3%). Educational attainment varied considerably, from illiteracy (12.5%) to postgraduate training (6.3%), though most caregivers had completed at least junior middle school (62.5%). Marital status was predominantly married (81.3%), with a minority unmarried (12.5%) or divorced (6.3%). Caregivers occupations were grouped into broader categories, including agriculture, healthcare and education, public service, technical or professional work, service and manual labor, and unemployed/retired, reflecting broad socio-economic heterogeneity.
Patients ranged in age from 52 to 74 years, with a mean age of 63.1 years (SD = 5.9), and an equal distribution of men and women. Educational attainment was generally lower than that of caregivers: nearly half (43.8%) had only primary schooling or were illiterate, while a minority reached junior middle school (37.5%) or higher education (18.7%). The majority were married (87.5%), and most were retiredd, agricultures, or manual workers. The primary causes of injury were falls from heights (31.3%), traffic accidents (25.0%), and slips (18.7%), with disease durations concentrated between one and three months (68.8%). Injury severity was most often classified as Grade B (31.3%) or Grade D (25.0%), while the remainder were Grade F as shown in Table 3.
3.2 Theme 1: care tasks
Caregiving tasks expanded over time from logistical coordination to complex, quasi-clinical responsibilities. In the diagnosis stage, caregivers focused on obtaining medical information, organizing hospital admission, and negotiating treatment decisions. During discharge transition, tasks shifted toward facilitating functional training, modifying the home environment, and acquiring practical caregiving skills. In rehabilitation, responsibilities included preventing complications, managing long-term functional recovery, and sustaining patients’ psychological adaptation. Differences between subgroups emerged: spouses more often engaged in continuous physical assistance, whereas adult children were more likely to coordinate external resources and financial support. This transition illustrates a trajectory of increasing technical and psychosocial complexity (Table 2).
3.3 Theme 2: emotional experiences
Emotional states varied across phases, with acute anxiety and helplessness dominating the diagnosis stage. During discharge transition, caregivers reported fatigue, tension, and insecurity regarding recovery. By the rehabilitation phase, emotions became ambivalent, combining hope with frustration at slow progress, and in some cases, role-related self-sacrifice. Female caregivers more frequently expressed emotional exhaustion and feelings of isolation, whereas male caregivers emphasized financial pressure and role strain. This heterogeneity underscores how caregiver identity shapes psychological vulnerability and coping strategies (Table 4).
3.4 Theme 3: caregiving barriers
Three categories of barriers were identified: (1) knowledge barriers, such as limited understanding of perioperative information; (2) skill barriers, including difficulties with mobility support, wound care, and complication prevention; and (3) systemic barriers, encompassing financial stress, fragmented care coordination, and insufficient community resources. These barriers intensified in rehabilitation, when institutional support diminished while care demands persisted. The findings reflect the uniqueness of the post-TKA context in China, where the family remains the primary care provider in the absence of structured community-based rehabilitation pathways (Table 5).
3.5 Theme 4: support systems
Support sources shifted from hospital-based professionals (orthopedics, anesthesiology, inpatient nurses) during the diagnosis and hospitalization phases to rehabilitation therapists and discharge planners in the transition phase, and finally to community services, counselors, and family networks in the rehabilitation phase. However, this transition also revealed fragmentation between hospital and community care, leaving caregivers without continuous professional guidance (Table 1).
4 Discussion
4.1 Dynamic evolution of care tasks and role transformation
This study used longitudinal qualitative interviews to systematically depict how caregiving tasks for TKA patients evolved across the diagnosis, discharge transition, and rehabilitation stages. The findings confirm that caregiving is not static but develops in a staged and accumulative manner. Caregivers began as logistical coordinators—responsible for admission, paperwork, and information gathering—and then shifted toward performing quasi-clinical duties, such as monitoring rehabilitation training, preventing complications, and supporting psychological recovery. By the rehabilitation phase, their roles increasingly resembled those of paraprofessionals, combining physical, technical, and emotional responsibilities.
This trajectory can be interpreted through role adaptation theory, which posits that individuals gradually reconstruct their roles in response to prolonged exposure to stressors and expectations. The evidence from this study enriches existing cross-sectional findings (18, 19) by demonstrating how caregivers actively adapt their roles over time. In particular, spousal caregivers were more consistently engaged in hands-on tasks, whereas adult children often took on resource coordination and financial responsibilities, illustrating how family role structures influence caregiving dynamics.
4.2 Stage-based emotional fluctuations interpreted through stress–coping models
Caregivers’ emotional responses shifted significantly across the three phases, reflecting the appraisal and coping processes described in Lazarus and Folkman's stress–coping model. In the diagnosis stage, anxiety and helplessness reflected primary appraisal of uncertain events, while the discharge transition period was characterized by secondary appraisal under conditions of insufficient coping resources, leading to fatigue and diminished confidence. By the rehabilitation stage, caregivers reported ambivalent emotions: hope and optimism about patient recovery, but also frustration with slow progress, psychological suppression, and even self-sacrifice.
The gender differences observed add cultural nuance. Female caregivers frequently emphasized emotional exhaustion and loneliness, while male caregivers reported financial pressure and role strain. Such differences are consistent with gendered expectations in Chinese families, where women are often expected to engage in emotional labor and men in financial support. Compared with Western studies (20, 21), our participants reported more emotional suppression and acceptance of sacrifice, suggesting the influence of filial piety and spousal duty in shaping emotional coping strategies in the Chinese context.
4.3 Theoretical and analytical considerations: framing caregiver burden
Beyond descriptive findings, the analysis benefits from a theoretical integration of the caregiver burden framework. This framework conceptualizes stress across informational, physical, and systemic domains, and our data highlight how these burdens accumulate longitudinally. Early deficits in medical information limited caregivers’ ability to make informed decisions. Skill-related challenges in patient transfer and complication prevention became most salient during discharge and early rehabilitation, when institutional guidance diminished. Systemic barriers—financial strain, lack of community rehabilitation services, and fragmented continuity of care—were most pronounced during long-term recovery.
These findings extend prior work (22, 23) by showing that caregiver burden is not simply a static condition but an escalating process tied to the temporal trajectory of recovery. Importantly, the theoretical framing underscores the need for stage-specific interventions. Structured preoperative education could address informational gaps, while community-based rehabilitation services and caregiver training programs could alleviate long-term skill deficits.
4.4 Evolution of support networks and cultural specificity
Support networks shifted from professional, hospital-based providers during admission and hospitalization to family and community resources during rehabilitation. This transition revealed fragmentation in the healthcare–community–home continuum, with caregivers often left unsupported after discharge. While similar patterns of fragmentation have been described internationally (24), the findings in this study reflect the particular reliance on family caregiving in China, where community rehabilitation and formal long-term care systems remain underdeveloped.
This cultural specificity is crucial: in China, caregiving remains deeply embedded in family structures, guided by norms of filial piety and collective responsibility. Unlike in some Western contexts where professional caregivers supplement family roles, Chinese families are often the sole source of support. This reliance underscores the importance of building multidisciplinary and community-integrated support systems that can bridge hospital discharge with ongoing rehabilitation.
4.5 The novelty of this study
An important contribution of this study lies in its methodological design. Previous research on TKA caregiving has been largely cross-sectional, providing valuable but static insights into caregiver burden, emotional distress, or support needs. By adopting a longitudinal design, this study captured temporal trajectories of caregiving tasks, emotional states, and barriers, revealing not only what caregivers experience but also when these challenges emerge and how they evolve.
For example, anxiety peaked during the diagnosis and discharge phases, while frustration and fatigue accumulated during rehabilitation. Similarly, systemic barriers were less visible during hospitalization but became acute once institutional support receded. Such insights are possible only with longitudinal observation, highlighting the added value of this approach for developing time-sensitive interventions.
4.6 Study limitations and future directions
This study has several limitations. First, participants were recruited from a single hospital, limiting generalizability to other regions. Second, although purposive sampling with maximum variation was employed, selection bias cannot be excluded; caregivers under extreme burden may have declined participation. Third, data were self-reported, and despite triangulation with non-verbal observations, recall and desirability bias may still have influenced findings. Fourth, the positionality of the researchers as clinical nurses may have affected interview dynamics, despite the use of reflexive journaling and peer debriefing to mitigate this risk. Fifth, the interview duration was relatively short (15–20 min) due to time constraints in clinical environments, which may have limited narrative depth.
Future studies should expand to multiple sites and diverse cultural settings, adopt mixed-methods approaches to triangulate qualitative findings with quantitative measures of caregiver burden, and extend follow-up periods to capture long-term trajectories beyond the first month of rehabilitation.
5 Conclusion
This longitudinal qualitative study mapped the evolving care journey of primary caregivers of TKA patients across the diagnosis, discharge transition, and rehabilitation stages. The findings revealed that caregivers encountered cumulative burdens, emotional fluctuations, knowledge and skill gaps, and insufficient systemic support at each stage, with their roles continuously shifting and intensifying. These insights underscore the need for stage-specific interventions. In the preoperative phase, structured caregiver education programs should be established to provide accurate medical knowledge, set realistic expectations, and prepare caregivers for their roles. During the discharge transition, multidisciplinary discharge planning combined with short-term psychological counseling is critical to reduce anxiety, enhance confidence, and ensure effective continuity of care. In the rehabilitation stage, caregivers would benefit most from community-based rehabilitation services, peer-support groups, and digital training platforms, which can sustain skill development, alleviate long-term burden, and prevent social isolation. Overall, a caregiver-centered, culturally sensitive, and multidisciplinary continuum of care should be prioritized to strengthen caregiving quality and mitigate both the physical and emotional strain on TKA caregivers.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the Third People's Hospital of Henan Province, Approval No. 2025-126. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
JH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology, Conceptualization. GD: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. DL: Investigation, Data curation. DW: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Software, Formal analysis, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Hall M, van der Esch M, Hinman RS, Peat G, de Zwart A, Quicke JG, et al. How does hip osteoarthritis differ from knee osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. (2022) 30(1):32–41. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2021.09.010
2. GBD 2021 Osteoarthritis Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990–2020 and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5(9):e508–22. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00163-7
3. Shao W, Hou H, Han Q, Cai K. Prevalence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional survey in Nanjing, China. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1441408. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1441408
4. AlShehri Y, Megaloikonomos PD, Neufeld ME, Howard LC, Greidanus NV, Garbuz DS, et al. Cementless total knee arthroplasty: a state-of-the-art review. JBJS Rev. (2024) 12(7):e24.00064. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.24.00064
5. Clement ND. Predicting the risk of needing a total knee arthroplasty. Lancet Rheumatol. (2022) 4(2):e78–9. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00389-1
6. Zomar BO, Bryant DM, Marsh JD, Lanting BA. Assessment of informal caregiver assistance and strain with total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. (2021) 36(7):2424–2430.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2021.02.024
7. Makimoto K, Fujita K, Konno R. Review and synthesis of the experience of patients following total hip or knee arthroplasty in the era of rapidly decreasing hospital length of stay. Jpn J Nurs Sci. (2020) 17(4):e12361. doi: 10.1111/jjns.12361
8. Page BM, Urbach DR, Wolfstadt JI, Varkul O, Clavel N, Brull R. Impact of outpatient total hip or knee replacement on informal caregivers at home: a scoping review. Can J Surg. (2023) 66(2):E150–5. doi: 10.1503/cjs.010022
9. Fidan Ö, Buker N, Savkin R, Sanlialp Zeyrek A. Does early or late discharge after total knee replacement affect the burden and stress of caregivers? Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. (2024) 52:101036. doi: 10.1016/j.ijotn.2023.101036
10. Joshi R, Joseph A, Mihandoust S, Hoskins L, O'Hara S, Dye CJ, et al. Understanding key home and community environment challenges encountered by older adults undergoing total knee or hip arthroplasty. Gerontologist. (2021) 61(7):1071–84. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnab025
11. Roustán G, Loro M, Rosell Á, Menchen B, Vicente O, Elosua-González M, et al. Development of a patient journey map for improving patient experience and quality of atopic dermatitis care. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). (2024) 14(2):505–19. doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01100-8
12. Saragosa M, Nizzer S, McKay S, Kuluski K. The hospital-to-home care transition experience of home care clients: an exploratory study using patient journey mapping. BMC Health Serv Res. (2023) 23(1):934. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-09899-2
13. Balmer DF, Varpio L, Bennett D, Teunissen PW. Longitudinal qualitative research in medical education: time to conceptualise time. Med Educ. (2021) 55(11):1253–60. doi: 10.1111/medu.14542
14. Bulto LN, Davies E, Kelly J, Hendriks JM. Patient journey mapping: emerging methods for understanding and improving patient experiences of health systems and services. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. (2024) 23(4):429–33. doi: 10.1093/eurjcn/zvae012
15. Dossett LA, Kaji AH, Cochran A. SRQR and COREQ reporting guidelines for qualitative studies. JAMA Surg. (2021) 156(9):875–6. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.0525
16. Hennink M, Kaiser BN. Sample sizes for saturation in qualitative research: a systematic review of empirical tests. Soc Sci Med. (2022) 292:114523. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114523
17. Fatemeh MT, Maryam N, Leila M. The story of staying out of normal routine life in adolescent mothers in marginal areas in Urmia through the lenz of conventional content analysis approach. Midwifery. (2024) 137:104108. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2024.104108
18. Moellenbeck B, Horst F, Gosheger G, Theil C, Seeber L, Kalisch T. Does total hip or knee arthroplasty have an effect on the Patients’ functional or behavioral outcome and health-related quality of life of the affected partners? J Arthroplasty. (2021) 36(3):885–91. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2020.08.066
19. Kunkel ST, Sabatino MJ, Torchia MT, Jevsevar DS, Moschetti WE. Does the impact of joint arthroplasty extend beyond the patient? The effect of total joint arthroplasty on patient’s significant others. J Arthroplasty. (2020) 35(6S):S129–32. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2020.01.028
20. Page BM, Urbach DR, Wolfstadt JI, Clavel N, Brull R. Beast of burden? Understanding the impact of outpatient total hip and knee replacement on caregivers at home. Can J Anaesth. (2022) 69(4):423–6. doi: 10.1007/s12630-021-02140-w
21. Nuevo M, Modrego A, Rodríguez-Rodríguez D, Jauregui R, Fabrellas N, Zabalegui A, et al. The influence of sociodemographic and health factors on adherence to home-based rehabilitation after fast-track total knee arthroplasty: secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil. (2025) 47(18):4728–37. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2025.2458191
22. Wang Q, Hunter S, Lee RL, Chan SW. The effectiveness of a mobile application-based programme for rehabilitation after total hip or knee arthroplasty: a randomised controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. (2023) 140:104455. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2023.104455
23. Li N, Yao X, Ji H. Relationships among disease knowledge, social support, anxiety and self-efficacy in patients after total knee arthroplasty: a chain mediating effect. Nurs Open. (2023) 10(7):4728–36. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1723
Keywords: total knee arthroplasty (TKA), primary caregivers, longitudinal, qualitative research, caregiver burden
Citation: Hu J, Dong G, Liu D and Wang D (2025) A longitudinal qualitative study on the care needs journey map of primary caregivers of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 6:1623623. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2025.1623623
Received: 10 May 2025; Accepted: 7 October 2025;
Published: 23 October 2025.
Edited by:
Jodi L. Southerland, East Tennessee State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Aliya Zhylkybekova, West Kazakhstan Marat Ospanov State Medical University, KazakhstanGulbakit Koshmaganbetova, West Kazakhstan Marat Ospanov State Medical University, Kazakhstan
Copyright: © 2025 Hu, Dong, Liu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dongyang Wang, d2FuZ2Rvbmd5YW5nMTk5NEBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Jingru Hu
Jingru Hu Guanglei Dong2
Guanglei Dong2 Dongyang Wang
Dongyang Wang