- 1Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China
- 2School of Management and Economics, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zhengzhou, China
Developing a more innovative industrial and supply chain is crucial for enhancing national selfreliance in innovation capabilities. This study aims to investigate the relationship between corporate ESG performance and innovation within supply chain enterprises, revealing the transmission mechanism of ESG along the supply chain. Utilizing data from Chinese A-share listed companies from 2009 to 2022, this research employs a fixed-effects model to analyze the impact of corporate ESG ratings on the innovation quality of both upstream and downstream firms in the supply chain. To address potential endogeneity concerns, the instrumental variables approach is applied. Mechanism tests are conducted to identify potential mediating channels, followed by heterogeneity analysis to explore the boundary conditions of the ESG impact. The findings indicate that a higher corporate ESG rating is significantly associated with improved innovation quality in customer firms. However, this positive effect is not observed in supplier firms. Mechanism tests suggest that firms primarily enhance their customers’ innovation through pathways such as ESG spillovers, innovation knowledge spillovers, improved supply chain efficiency, alleviated financing constraints, and reduced agency costs. These results imply an asymmetry in the influence of corporate ESG performance, likely shaped by the power structure and direction of knowledge flow within the supply chain. Overall, this study provides a novel perspective for understanding corporate innovation and supply chain collaboration. It offers valuable policy iplications for China’s efforts to enhance supply chain integration and innovation, suggesting that encouraging and supporting stronger corporate ESG practices can help activate innovation vitality across the entire supply network.
1 Introduction
In today’s dynamic market environment, escalating U.S.–China trade tensions and intensified global trade competition, particularly the push by some countries to “decouple” their supply chains from China, have impacted the stability of China’s industrial and supply chains. The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China has placed significant emphasis on enhancing the modernization of these chains, with a focus on improving their resilience, safety, innovation capacity, value-added potential, and overall reliability (Shi et al., 2021; Gopalakrishnan et al., 2021). In recent years, China has faced challenges due to insufficient independent innovation capabilities, particularly in critical areas such as semiconductors and foundational materials, leading to vulnerabilities. Enhancing the innovation and sustainable development capabilities of the industrial and supply chains has thus become a key policy focus, providing new guidance for corporate innovation and introducing a fresh perspective on the supply chain’s critical role. Previous research indicates that core enterprises possess significant informational advantages over upstream suppliers and downstream customers. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) has identified the geographic shift of innovation hubs and the spillover effects within supply chains as critical factors influencing the continuous enhancement of innovation capacity in Chinese enterprises. As key entities within supply chains, these firms can generate substantial spillover effects through their innovation efforts, thereby boosting overall innovation levels. In this context, this study focuses on the innovation spillover effects within intermediary firms in supply chains, which is of significant importance for improving the overall level of innovation in China.
ESG is a concept that comprehensively considers the sustainability of business operations and social values, covering environmental, social, and governance aspects. Recently, the Chinese government has introduced a series of policy measures committed to implementing ESG concepts. More and more entrepreneurs are integrating ESG into corporate strategies, focusing on maximizing stakeholder interests and ESG investment value (Tang, 2022; Zhang and Liu, 2023). In the era of mandatory ESG disclosure, ESG ratings and reports have become an important standard for measuring high-quality enterprises. Global ESG regulation is becoming increasingly stringent. The concretization of China’s “dual carbon” goals subjects firms to stronger policy compliance requirements, incentivizing them to avoid risks through technological innovation, transforming “compliance costs” into “innovation momentum.” For example, Haier Smart Home, as a leading home appliance manufacturer, continuously launches energy-saving and carbon-reducing products, established China’s first green recycling interconnected factory in the home appliance industry, and increased green innovation efforts. Under the synergy of the supply chain, the promoting effect of corporate ESG performance on innovation is amplified. ESG governance practices drive joint technological breakthroughs across the industrial chain upstream and downstream, promoting cross-firm innovation collaboration. Core firms among them can integrate industrial chain resources, promote cross-firm joint R&D and standard coordination, achieving economies of scale in innovation. For example, BYD practices ESG governance concepts, promoting battery product technological innovation, directly facilitating the rapid development of the new energy vehicle industry. Simultaneously, BYD requires green transformation of its supply chain, driving upstream suppliers to carry out low-carbon transformation, forming technology spillover effects. Firms truly transform ESG standards into drivers of corporate innovation and even supply chain innovation.
Existing research on corporate ESG practices, firstly, focuses on the extension of social responsibility and sustainable development, mostly concerning corporate financial performance and growth; secondly, focuses on the role of ESG information disclosure, which can improve the firm’s external environment, thereby promoting high-quality development. However, few studies have researched the impact of ESG on corporate innovation quality from the perspective of supply chain spillovers. Among the most relevant studies, the focus is on the contagion effect of customer firms’ ESG performance; the green innovation concepts of customer firms spill over upward, influencing supplier firms’ innovation. Based on the above analysis, this paper attempts to answer the following questions: Can corporate ESG exert spillover effects within the supply chain? If so, what are the underlying theoretical mechanisms?
The structure of this paper is arranged as follows: Part 1 is the introduction, outlining the research background, research questions, and clarifying the purpose of this study. Part 2 is the literature review, reviewing the research progress on the relationship between corporate ESG performance and innovation quality, as well as supply chain spillover effects. Part 3 is the research design, providing a detailed description of the research sample, variable definitions, and model specification. Part 4 presents the empirical results and analysis, showing the impact of corporate ESG performance on the innovation quality of upstream and downstream firms in the supply chain, and conducting robustness tests. Part 5 is the mechanism test section, empirically testing the theoretical mechanisms through which corporate ESG performance affects supply chain firm innovation. Part 6 is the heterogeneity analysis and extended analysis, conducting heterogeneity tests from perspectives such as client market influence, industry heterogeneity, the number of bank branches in the firm’s location, and further analyzing the moderating effect of geographical distance between the firm and its clients and the divergence effect of corporate ESG. Part 7 is the discussion, summarizing the main findings of this study, comparing them with existing research results, and proposing policy implications. Finally, the conclusion summarizes the main achievements of the research and suggests directions for future research.
2 Literature review and theoretical analysis
2.1 Literature review
2.1.1 The effect of corporate ESG on firms themselves
In the current context where the concept of sustainable development is deeply ingrained, corporate ESG performance has become a focal point of attention from various sectors. Previous research indicates that corporate ESG governance practices can, on the one hand, reduce a firm’s financing costs by improving the quality of information disclosure (Qiu and Yin, 2019), and on the other hand, alleviate principal-agent problems by reducing information asymmetry between managers, shareholders, and stakeholders (Zhu et al., 2025). Furthermore, corporate ESG rating mechanisms, by providing market incentives and prompting stakeholders to play a supervisory role, compel firms to increase R&D investment (Hu et al., 2023), thereby promoting corporate green technology innovation, helping enterprises save energy and reduce emissions, and driving corporate green transformation. Further, good corporate ESG performance enables firms to acquire both non-sunk and unabsorbed redundant resources, transforming them into the firm’s new quality productive forces and enhancing the level of these forces (Zhang et al., 2025). Additionally, the fulfillment of corporate ESG responsibilities helps enterprises achieve simultaneous improvement in existing and potential core competitiveness, fostering corporate development and growth (Liu and Wang, 2024).
2.1.2 The supply chain spillover effects of corporate ESG
Apart from the impact of corporate ESG governance practices on the firm itself, another strand of literature explores the spillover effects of corporate ESG performance on upstream and downstream enterprises in the industrial chain from a supply chain perspective. Relevant research, starting from a firm’s position in the supply chain, suggests that good ESG performance enhances customer relationship stability and strengthens the firm’s bargaining power within the supply chain (Li et al., 2023), enhancing corporate supply chain resilience through mechanisms like increased product differentiation (Chen et al., 2023). Concurrently, studies have also found that the impact of corporate ESG performance on supply chain relationship stability is differentiated; it can enhance customer relationship stability but has a weaker enhancing effect on supplier relationship stability (Xin et al., 2024). Moreover, the default risk mitigation effect of corporate ESG performance also mainly spills over to downstream customer firms. Corporate ESG performance reduces the occurrence of default risk by enhancing customer firms’ ability to obtain long-term bank loans (Su and Zhou, 2024). Research on the impact of corporate ESG performance on upstream supplier firms found that better ESG performance of customer firms leads to more positive annual report tones of supplier firms, primarily due to the mediating effect of supplier innovation investment (Li et al., 2024). The ESG performance advantage of downstream customer firms in the supply chain can incentivize midstream firms to engage in green innovation through channels such as strengthening corporate green awareness, increasing commercial credit support, and green technology spillover, further helping supply chain firms achieve carbon emission reduction and enhance carbon performance (Yan et al., 2024).
2.1.3 Commentary on corporate ESG research
Existing literature has begun to recognize the significance of corporate ESG governance for supply chain security and stability, emphasizing that the outcomes of corporate ESG practices not only have positive effects on the firm’s own development but also generate spillover effects on other firms in the supply chain, enhancing the resilience and security level of the industrial and supply chains. However, against the backdrop of increasingly complex international situations, the coordinated development of industrial and innovation chains has become a crucial measure to address challenges like the blockade of key core technologies. Fundamentally, innovation is a vital means for enterprises to maintain long-term competitive advantages and achieve sustainable growth. Corporate ESG governance practices have a positive impact on the firm’s own innovation (Fang and Hu, 2023), but whether they similarly have positive effects on other firms in the collaboratively developing industrial chain is a question worthy of in-depth exploration. Although a few studies have preliminarily examined the green innovation spillover effects of corporate ESG performance on supply chain firms, there is still a lack of deep analysis on a series of issues: whether similar effects exist for overall innovation performance covering a broader scope, whether there are differences for different types of firms upstream and downstream in the supply chain, and what the core theoretical mechanisms of the corresponding spillover effects are.
2.1.4 The main contributions of this paper
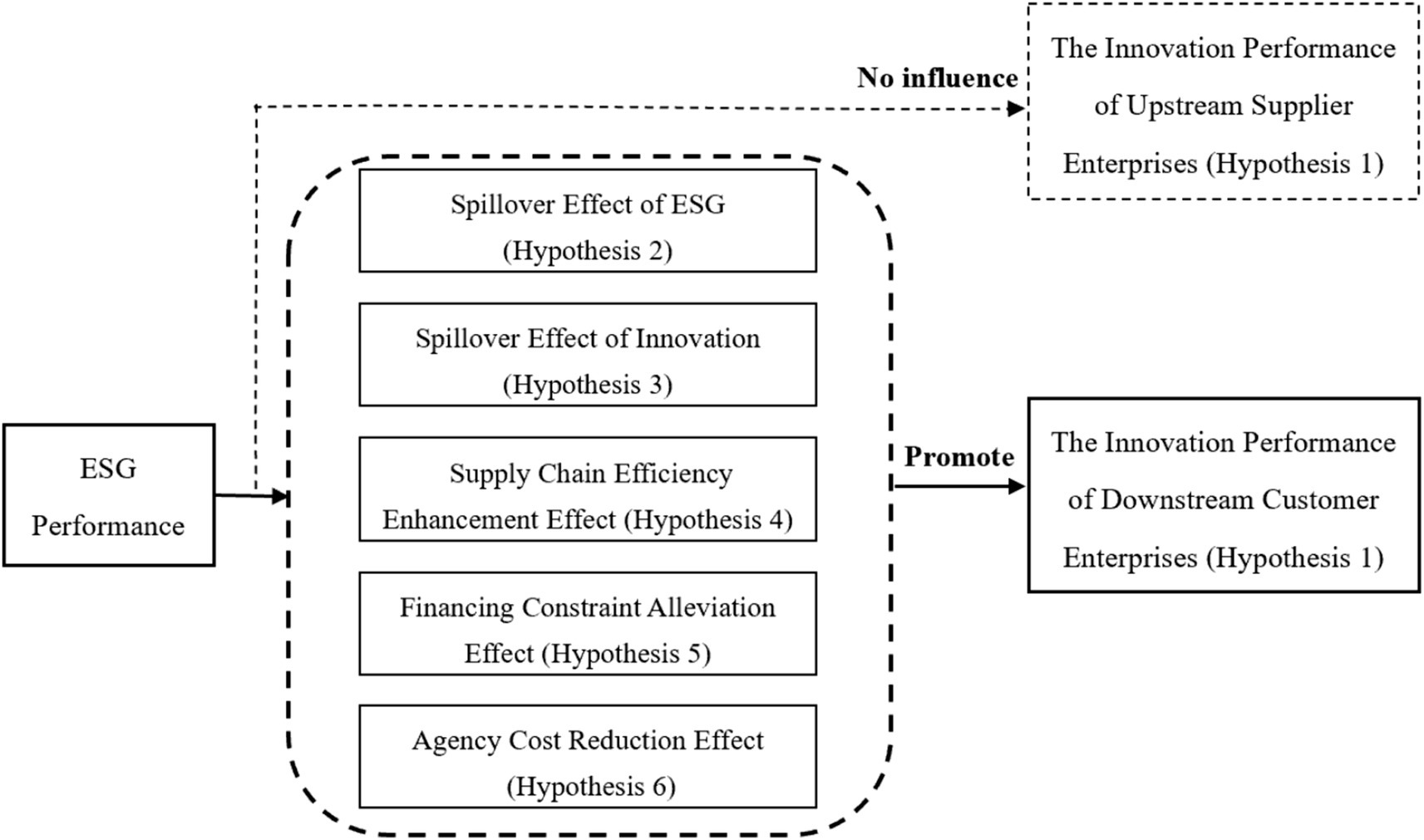
Based on existing research, the potential innovative points of this paper are as follows: First, it enriches the theoretical framework of supply chain relationships from the perspective of corporate ESG. Current research on supply chains mostly focuses on corporate digital transformation and supply chain efficiency. This paper focuses on corporate ESG governance, studying how corporate ESG performance spills over along the industrial chain to suppliers and customers within the industrial and supply chains, and subsequently affects the innovation quality of suppliers and customers. Second, by researching supply chain spillover effects, it expands the research perspective on corporate ESG performance. Past studies have mostly focused on spillover factors such as the herd effect of corporate information disclosure and corporate social responsibility fulfillment. This paper incorporates corporate ESG performance into an analytical framework at the supply chain level, providing new ideas for research on the economic impact of ESG based on supply chain spillover effects. Third, from the perspective of ESG’s positive impact and innovation effects, it reveals the mechanism through which ESG promotes the innovative development of supply chain firms. Unlike existing research, this study finds that corporate ESG ratings have spillover effects within the supply chain, mainly manifested in improving the innovation quality of customer firms, providing a new perspective for exploring how corporate ESG performance drives the innovative development of supply chain firms (Figure 1).
2.2 Theoretical analysis
2.2.1 The impact of ESG on supply chain firm innovation performance
Facing complex, volatile, and fiercely competitive market environments, firms increasingly tend to engage in collaborative cooperation to reduce production transaction costs and avoid operational risks. Inter-firm competition has evolved from the game of individual firms in the past to a comprehensive contest involving the integration of upstream and downstream external resources, manifesting as competition among supply chains (Wu and Yao, 2023). The coordinated linkage of upstream and downstream enterprises is key for firms to maintain competitiveness, and their interconnected innovation is the core of corporate development. Corporate ESG performance consists of three aspects: participation in environmental governance, undertaking social responsibility, and improving corporate governance. As a complex evaluation system for enterprises, corporate ESG performance encompasses many aspects of corporate development. For firms embedded in supply chains, their own development significantly influences upstream and downstream firms in the industrial chain through supply chain linkages.
This paper argues that corporate ESG performance positively impacts downstream firms’ innovation performance along the supply chain. Specifically, corporate ESG performance has spillover effects, influencing not only the firm’s own development status but also, through product and service linkages, promoting the enthusiasm and capability of downstream firms to carry out innovation activities. Intuitively, when a firm supplies greener, lower-carbon, and more efficient intermediate products to downstream firms, customer firms can directly utilize the innovation achievements of the upstream firm and, based on this, improve their own production and operations, driving corporate innovation and development. For downstream firms, when innovative changes occur in upstream suppliers’ products or services, they need to adaptively adjust production processes and business models to meet the new demands and technological changes of the upstream firm (Yang et al., 2022). From the perspective of supply chain transmission direction, the influence of ESG performance exhibits a distinct “downward radiation” characteristic. Downstream firms directly face the end market and consumers; their ESG practices are more easily driven by market demand, policies, regulations, and public opinion. When a core firm demonstrates good ESG performance, downstream firms, in order to maintain cooperative relationships and meet the end market’s demand for sustainable products, often proactively adjust their business strategies and increase innovation investment.
This paper argues that it is more difficult for corporate ESG performance to generate positive effects on upstream firms’ innovation performance along the supply chain. Specifically, innovation projects typically have characteristics such as long cycles, high costs, and strong uncertainty. Managers, considering their own reputation or performance evaluations centered on short-term profits, often tend to favor risk-averse conventional investments, lacking sufficient incentive for innovation projects that contribute to long-term firm development but carry greater risks (Zheng et al., 2021). Although upstream firms may be forced by a green forcing mechanism to conduct green process innovations to maintain cooperative relationships—including downstream customers’ ESG advantages incentivizing midstream firms for green innovation through channels like strengthening corporate green awareness, increasing commercial credit support, and green technology spillover (Yan et al., 2024)—in terms of overall innovation performance, the firm’s impact on supplier firms’ innovation performance is not significant. On the one hand, upstream firms occupy a relatively passive position in the supply chain; their production and operations revolve more around the order demands of the core firm. The innovation direction of upstream firms is often determined by the procurement standards of the core firm. The direct impact of the core firm’s ESG performance on upstream firms is more reflected in the compliance of raw material supply rather than innovation incentives. On the other hand, the primary role of upstream firms is to provide raw materials or components to the core firm; their innovation focuses more on reducing production costs and improving production efficiency, with relatively weaker demand for ESG-related innovation. The impact of the core firm’s ESG performance on upstream firms is more at the level of supply chain management, such as requiring upstream firms to comply with labor regulations and reduce environmental pollution. However, these requirements do not directly translate into innovation motivation for upstream firms. Conversely, upstream firms may incur additional costs to meet these compliance requirements, thereby squeezing the space for innovation investment.
Hypothesis 1: Corporate ESG performance can promote the improvement of innovation performance in downstream firms in the supply chain, but has no significant effect on the innovation performance of upstream firms in the supply chain.
2.2.2 Spillover effect of ESG
The spillover effect of corporate ESG refers to the phenomenon whereby a firm’s improved ESG performance drives enhancements in the ESG performance of its downstream supply chain partners. This spillover primarily operates through consciousness alignment and resource synergy. Within the supply chain, enterprises tend to converge in environmental awareness. Firms with high ESG standards elevate the environmental and social responsibility consciousness of downstream customer enterprises through the products and services they supply, thereby enhancing the sustainability attributes of downstream offerings. Furthermore, companies often provide green technologies—such as emission-reduction processes—to downstream partners, reducing the latter’s environmental compliance costs through technology sharing.
The ESG rating of a firm can propagate through the supply chain, influencing the ESG governance of downstream customers. This transmission mechanism elevates the ESG ratings of downstream enterprises and subsequently fosters improvements in their innovation quality. By stimulating human capital vitality, mitigating agency problems, and enhancing brand image, strong ESG performance significantly augments corporate value. In this process, stakeholders including employees, suppliers, and customers play crucial roles. Within supply chains, firms with high ESG ratings not only bolster their own reputation but also generate positive reputational externalities for their downstream partners, thereby elevating overall ESG performance across the chain. According to stakeholder theory, the objective of ESG investment is to maximize the interests of all relevant parties (Huang et al., 2023). Existing research indicates that ESG performance provides incremental non-financial information that reduces corporate debt costs and enhances brand value. As such, it is closely monitored by other firms in the supply chain. Improved ESG performance in one firm can lead to improved ESG performance in others, allowing downstream customers to achieve higher performance and competitive advantage as a result (Tang et al., 2023).
Hypothesis 2: Corporate ESG performance enhances the innovation quality of customer enterprises by improving their ESG performance.
2.2.3 Spillover effect of innovation
The corporate innovation spillover effect refers to the spillover of corporate innovation within the supply chain, especially the direct impact of upstream firm innovation on downstream customer innovation. The innovation spillover effect is primarily based on knowledge spillover and collaborative innovation. Due to the strong externality of knowledge, corporate innovation achievements spill over to supply chain firms through technology purchases and personnel exchanges, prompting them to improve production and operational activities and promoting technology diffusion. Collaborative R&D behaviors exist among firms in the supply chain; customers and suppliers may form innovation networks through industrial chain cooperation, promoting the improvement of overall innovation performance.
Existing literature has demonstrated that ESG ratings promote the firm’s own innovation (Fang and Hu, 2023). Simultaneously, research on innovation suggests that supplier innovation performance in the supply chain has spillover effects on downstream firms (Jiao, 2021; Wei and Wei, 2024). That is, corporate innovation has spillover effects within the supply chain, especially the direct impact of upstream firm innovation on downstream customer innovation. On the one hand, innovation involves knowledge spillover. Arrow’s (1962) pioneering research posited that firms regard new knowledge as a core input for innovation activities. This not only helps the firm develop unique products but also allows knowledge to spill over to other firms, thereby promoting their innovation activities. Knowledge spillover and innovation spatial distribution theory hold that due to the lag, decay, and distortion of knowledge and technology during spatial dissemination, knowledge spillover exhibits the characteristic of decaying with increasing geographical distance, especially for sticky knowledge that is difficult to codify. Geographical distance becomes a significant barrier to knowledge spillover. Supply chain firms are geographically closer and have closer ties than general firms, making knowledge spillover more likely.
On the other hand, supply chain firms enhance their innovation performance through collaborative innovation. Social network theory emphasizes the importance of firms embedding themselves in external networks to achieve innovation advantages, among which close cooperation with suppliers is considered a strategic way to obtain innovation resources. The network structure of suppliers consists of member nodes and their interconnections. The innovation resources possessed by each node member will significantly impact corporate innovation performance. The spillover effects brought by the vertically linked division of labor model between upstream and downstream can transmit the innovation capabilities of upstream suppliers to downstream customer firms through chain conduction (Liu, 2019).
Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 3: Corporate ESG performance improves customer firms’ innovation quality by promoting corporate innovation, forming innovation spillovers.
2.2.4 Supply chain efficiency enhancement effect
Firms with higher ESG performance possess scarce resources and a foundation of trust, enabling them to build stable cooperative relationships with upstream and downstream firms (Xin et al., 2024), improving supply chain efficiency, and thereby enhancing the innovation level of downstream customer firms. Supply chain efficiency refers to solving potential bottlenecks and blockages under the premise of ensuring stable supply chain relationships, further strengthening weak links and leveraging strengths to achieve efficient and smooth operation. Facing increasingly fierce competition, product cost fluctuations, and market demand uncertainty, firms in the supply chain seek to enhance their competitive advantages and overall performance by establishing robust supply chain relationships and improving supply chain efficiency. However, in most industries where firms operate, supply chain efficiency is not high due to their own development cycles or industry averages. When upstream and downstream firms communicate, they cannot connect efficiently, leading to a certain degree of supply–demand mismatch, often resulting in inventory backlog and resource waste (Chen, 2021). Firms with higher supply chain efficiency can often fully utilize idle resources, driving downstream firms through supply chain linkages to utilize idle resources, release operational pressure, and thus have more resources and time for innovation and R&D activities, promoting the improvement of innovation levels.
Corporate ESG ratings enhance the stability, resilience, and efficiency level of the supply chain through internal operation optimization and external relationship strengthening. In terms of internal operation optimization, good corporate ESG performance can increase the likelihood of firms obtaining long-term credit resources through triple mechanisms: information increment, signal release, and reputation guarantee, alleviating corporate financial pressure, optimizing corporate financial conditions, further ensuring the supply of products and services to customer firms, safeguarding supply chain stability, and enhancing supply chain operational efficiency. In terms of external relationship strengthening, corporate ESG governance requires firms to disclose as much corporate information as possible, enhancing information transparency. This helps customer firms grasp more comprehensive and detailed information in a timely manner, promotes cooperation between the firm and its customers, reduces friction, ultimately enhances customer relationship stability, and strengthens supply chain resilience. Firms with higher ESG ratings have a higher foundation of trust within the supply chain, making them more favored by downstream customer firms. To a certain extent, this can enhance the stability and matching degree of supply–demand relationships and improve supply quality, thereby achieving an improvement in supply chain efficiency.
Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 4: Corporate ESG performance improves customer firms’ innovation quality by enhancing supply chain efficiency.
2.2.5 Financing constraint alleviation effect
Corporate ESG ratings alleviate customer firms’ financing constraints, thereby increasing their innovation investment. Corporate ESG ratings primarily alleviate downstream customer firms’ financing constraints through supply chain finance and external financial credit. On the one hand, ESG improves supply chain finance, providing funding relief for downstream customers. Supply chain finance influences supply chain firms through positive externalities in economic, environmental, and social aspects. Corporate ESG ratings comprehensively cover the core elements of sustainability and ethical impact in corporate investment. Their connotation is broad, involving elements such as labor rights, board governance, and management diversity. ESG ratings create a relatively complete core evaluation system for firms, helping investors and society accurately identify potential risks and guiding financial institutions to optimize investments. Therefore, firms with higher ESG ratings also have more developed supply chain finance, helping SMEs obtain financing through means like credit transmission and risk-sharing awareness.
On the other hand, ESG ratings alleviate customer firms’ financing constraints by enhancing access to external financial credit. Firstly, the good reputation of high-rated ESG firms has a certain radiating effect on downstream firms, making it easier for customer firms to obtain preferential bank loans. Secondly, because the Chinese government has significant influence over the allocation of financial resources, especially the supply of bank credit. Firms with high ESG ratings will be more conducive to strengthening their political connections with the government, thereby playing a more important role in the supply chain and gaining government support. Finally, information about the environmental performance and technological innovation of downstream firms in the supply chain may be opaque, leading to information asymmetry in the risk assessment and credit decision-making processes of financial institutions. The disclosure of upstream firms’ ESG alleviates the problem of information blockage in supply chain firms, thereby reducing corporate credit constraints. Alleviating financing constraints can effectively promote firms to engage in innovation activities. When a firm’s own financing constraints are eased, it obtains sufficient funds to invest in R&D and innovation activities, enhancing innovation quality.
Hypothesis 5: Corporate ESG performance improves customer firms’ innovation quality by alleviating their financing constraints.
2.2.6 Agency cost reduction effect
Better corporate ESG performance can reduce customer firms’ agency costs, thereby promoting their innovation performance. In high-rated firms, the cost borne by supply chain managers due to fear of risk is lower, and corporate innovation behavior is stronger. Currently, the professional scoring mechanism of ESG ratings has been recognized and favored by most investment institutions in the market. Professional investor institutions also widely pay attention to corporate ESG performance. Based on this, investors in upstream and downstream firms will improve governance mechanisms, strengthening the supervision of corporate governance bodies to reduce behaviors that pursue personal interests while neglecting the overall development of the firm. Institutional investors effectively supervise the operating decisions of controlling shareholders and management, preventing them from abusing company resources and curbing their encroachment on corporate interests. For customer firms, a higher ESG rating of the supplying firm means stricter scrutiny and supervision by social media. Downstream customer firms in the supply chain are similarly subject to social regulation and media supervision. To safeguard their professional reputation, the management team will actively take corrective actions against misconduct and optimize capital allocation decisions. Such measures help ensure the stable operation of the firm and maintain its good image within the supply chain, also contributing to alleviating principal-agent problems in downstream customer firms.
Regarding the relationship between corporate innovation and agency costs, scholars generally agree that principal-agent problems are detrimental to firms engaging in long-term innovation and R&D activities. High agency costs are a key factor hindering corporate innovation (Fang and Hu, 2023). When making innovation decisions, corporate managers often weigh the risks and potential benefits of innovation, considering the potential impact of innovation activities on corporate performance and their own reputation. Simultaneously, due to the complexity and uncertainty inherent in the innovation process, supervising managerial behavior becomes particularly difficult, which is unfavorable for corporate innovation activities. Reducing corporate agency costs can effectively support the long-term development of the firm, incentivizing managers to invest effort in innovation and promoting corporate innovation.
Hypothesis 6: Corporate ESG performance improves customer firms’ innovation quality by reducing their agency costs.
3 Research design
3.1 Sample and data sources
This study primarily investigates the spillover effects of ESG ratings within a firm’s supply chain. The key data used in the research come from three main sources: supply chain information (including upstream suppliers and downstream customers) is extracted from the annual reports of listed companies, patent data and other control variables are obtained from the China Research Data Service Platform (CNRDS), and ESG rating data is sourced from the Wind database.
First, in terms of data organization, this study follows the methodology of Yang et al. (2022) by constructing a dataset that includes information on suppliers, firms, customers, and annual data. Specifically, the study extracts data on the top five customers of Chinese listed companies from the CNRDS database. Considering that Huazheng ESG only began publishing ESG rating data in 2009, the study period is set from 2009 to 2022 to ensure the timeliness and relevance of the data. This results in a dataset comprising year-firm ESG-supply chain innovation observations.
Next, by constructing multi-level innovation quality indicators, we matched supplier and customer names with patent application and authorization information from the Chinese Patent Information Database. In the process of constructing the research sample, in addition to supply chain data, patent data, and ESG data, we also obtained key firm-level control variables from the China Stock Market & Accounting Research (CSMAR) database. The final dataset excludes samples from ST and PT companies, and all continuous variables were winsorized at the 1% level to mitigate the influence of outliers. Through this careful selection and integration process, the study constructs a dataset covering 5,796 firms from 2009 to 2022, which aligns with the findings of existing literature (Di et al., 2020).
3.2 Model specification and variable definitions
In the model, i denotes the firm itself, j denotes upstream/downstream firms in the supply chain, and t denotes the year. The explanatory variable represents the ESG score of firm i itself in year t. The Huazheng ESG rating is used for measurement in the baseline regression, and the rating data published by Wind is used for robustness tests. The explained variable represents the innovation performance of the corresponding supply chain firm j in year t, including patent quality (Know), green patents (Green), and patent citations (Cite). The model does not distinguish whether the supply chain firm j is an upstream or downstream firm of firm i. During the empirical process, suffix symbols are added to the explained variable to distinguish: “-cus” denotes downstream customer firms, “-sup” denotes upstream supplier firms. Represents a set of control variables related to corporate innovation for supply chain firm j in year t. denotes the individual fixed effect of supply chain firm j, denotes the time fixed effect for year t, and denotes the random disturbance term.
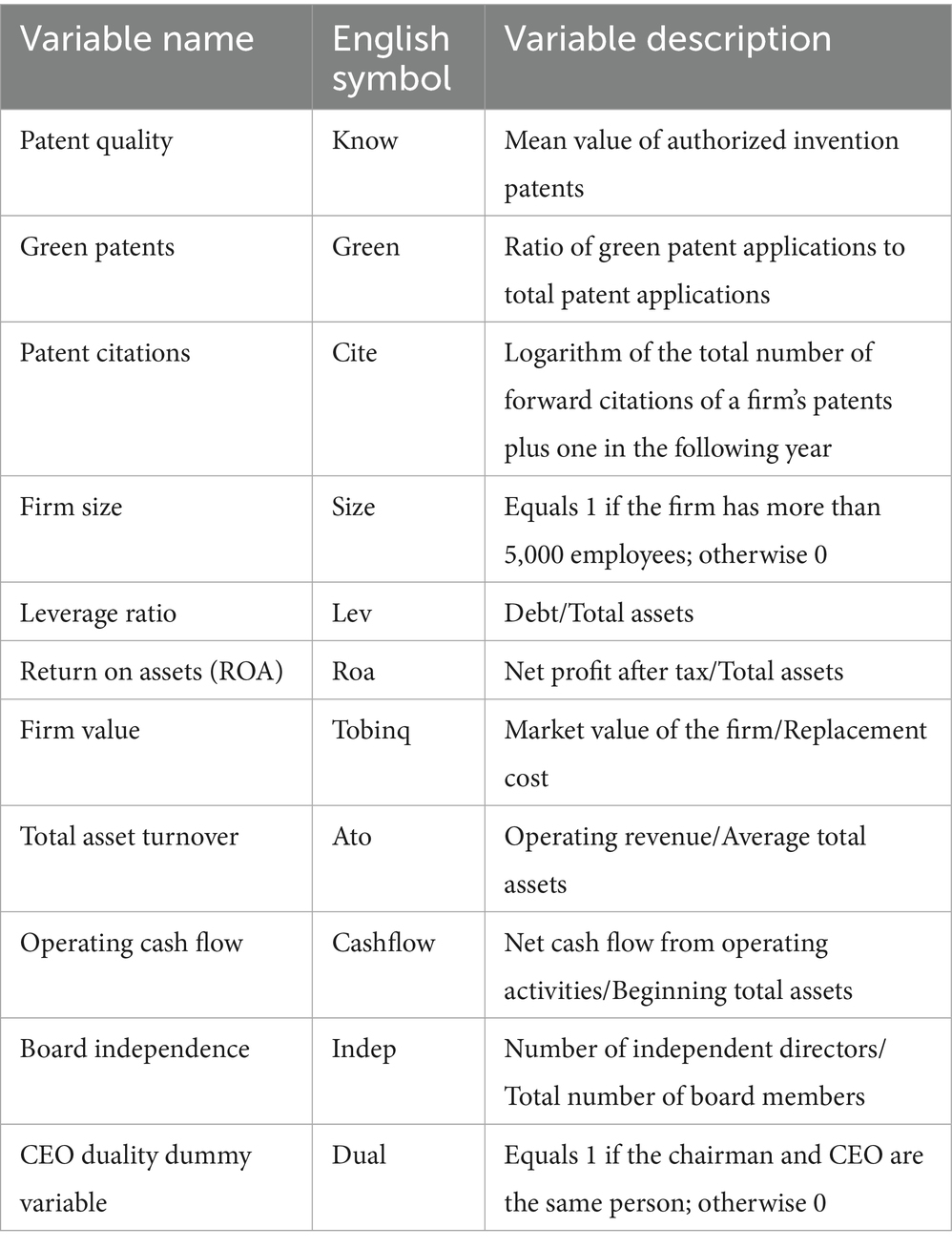
Innovation Performance, measured from three aspects: patent quality, green patents, and patent citations. First, Patent Quality (Know): Measured using the average method of invention authorized patents of listed companies calculated by the knowledge width method (Zhang and Zheng, 2018). The average method of invention application patents is used for robustness tests. Second, Green Patents (Green): The ratio of green patent applications to total patent applications is used as a proxy variable. The natural logarithm of the number of green patent applications plus one is used for robustness tests. Third, Patent Citations (Cite): This paper uses overall innovation quality (Meng et al., 2019), specifically the natural logarithm of the sum of the number of citations by others of patents applied for by the firm in the following year plus 1, as the proxy variable. Table 1 reports the main variables and their definitions.
Corporate ESG performance is an important indicator for evaluating its sustainable development capability, encompassing its friendliness to the environment (E), responsibility to society (S), and the soundness of internal governance (G). The Huazheng ESG rating system conducts in-depth analysis of 16 core themes (e.g., climate change, resource utilization, human capital), breaking them down into 44 key indicators (e.g., greenhouse gas emissions, carbon reduction pathways, employee relations), ultimately forming 9 grades (from AAA to C), fully demonstrating the comprehensive performance of firms in the ESG field. To accurately assess corporate ESG performance, this paper adopts Huazheng ESG rating data as the basis. During the rating process, a scale of 1–9 is used (higher values represent better performance) to reflect the overall quality of the firm in environmental, social, and governance aspects. Considering that Huazheng publishes corporate ESG comprehensive scores quarterly, to ensure evaluation accuracy and stability, this paper uses the average value of a firm’s quarterly ESG comprehensive scores in the current year as the evaluation benchmark.
Referring to the practices of previous literature (Yang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022), this paper selects corporate characteristic variables such as firm size (Size), corporate debt-to-asset ratio (Lev), return on assets (Roa), Tobin’s Q (TobinQ), return on total assets (Ato), operating cash flow (Cashflow), as well as corporate governance structure variables like board independence (Indep) and a dummy variable for CEO-Chair duality (Dual). Meanwhile, this paper controls for individual and year fixed effects to exclude the influence of unobservable factors on the estimation results. Table 1 reports the main variables and their definitions.
3.3 Descriptive statistics
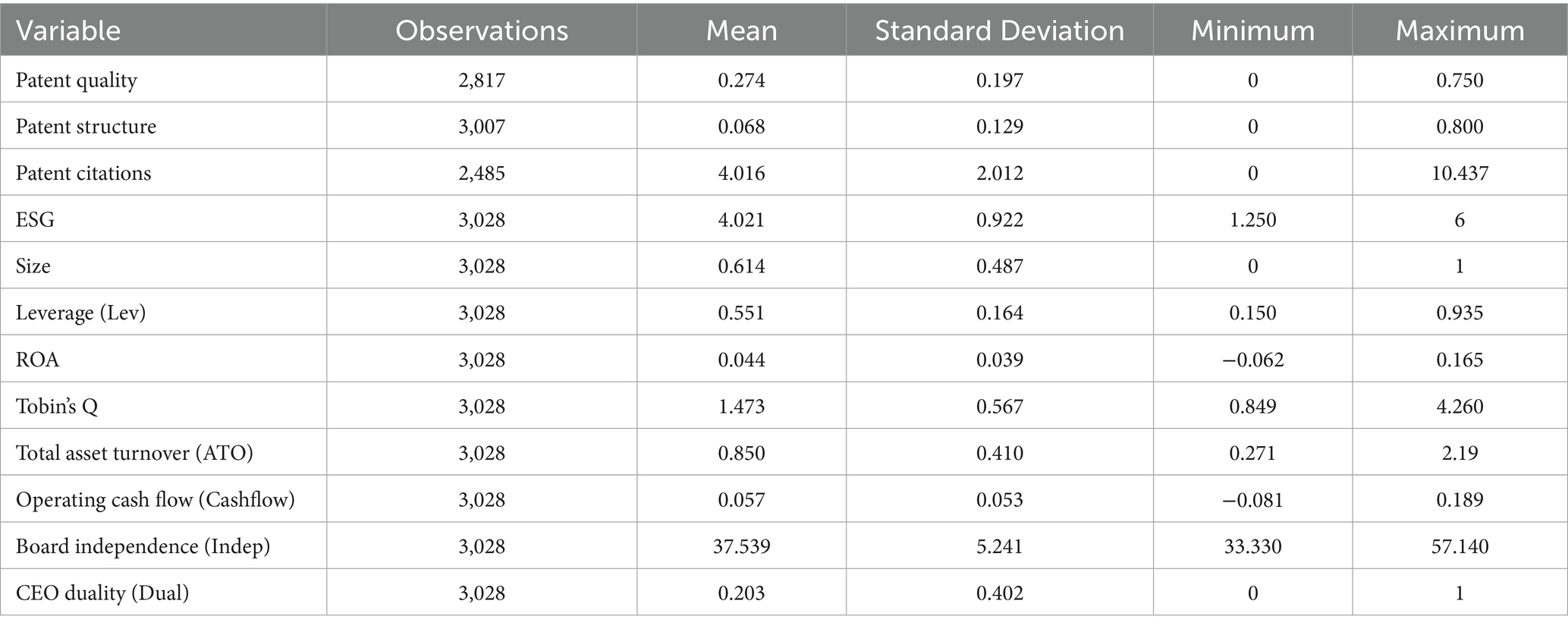
Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics for the main variables in this study. The minimum value for patent citations is 0, while the maximum value is 10.437, with a standard deviation of 2, indicating significant variation in patent citations among supply chain firms. In contrast, the data for patent quality and patent structure, as measured by the knowledge breadth method, are more concentrated. Overall, the distribution of the other financial variables and control variables falls within a reasonable range.
4 Empirical results analysis
4.1 Baseline estimation results
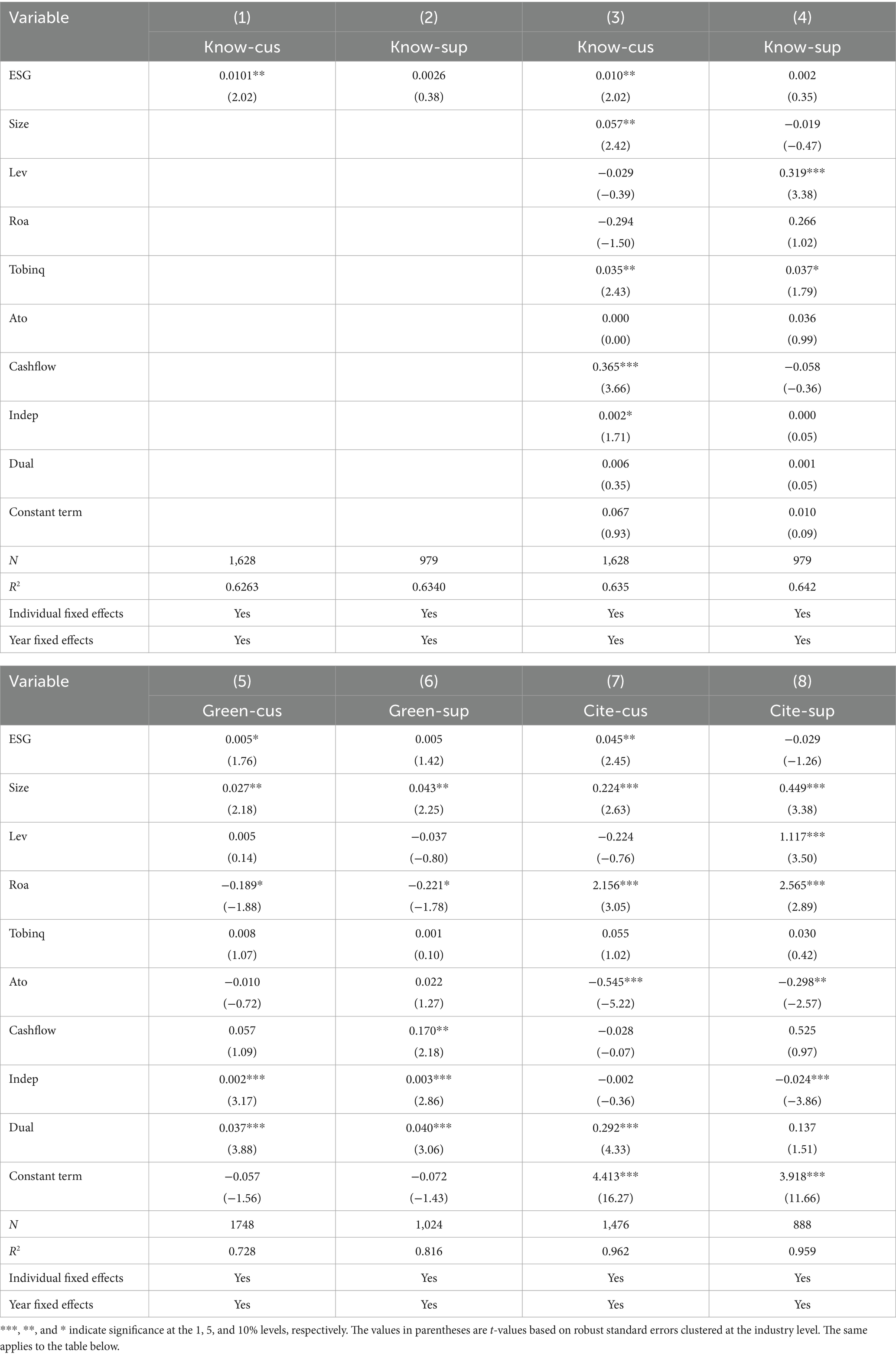
Table 3 reports the baseline regression results of the impact of ESG on the innovation levels of supplier and customer firms. In the table, X-cus refers to downstream customer firms, and X-sup refers to upstream supplier firms. Columns (1) and (2) show the regression results of customer and supplier innovation on corporate ESG without including control variables. The results indicate that customer innovation quality is significant at the 5% level. We then add control variables, and Columns (3), (5), and (7) show that in the downstream customer segment of the supply chain, the coefficients for patent quality represented by the patent breadth method, patent citations represented by average citation counts, and patent structure represented by the proportion of green patents are all positive and significant to varying degrees. In contrast, Columns (4), (6), and (8) show that the three innovation indicators for the supply chain’s upstream suppliers do not exhibit significant improvement effects, providing preliminary empirical evidence for the theoretical hypotheses of this study. Overall, the results in Table 3 indicate that corporate ESG has a spillover effect within the supply chain, particularly showing a significant positive impact on the innovation of downstream customer firms. Hypothesis 1 is partially validated.
4.2 Robustness checks
4.2.1 Considering potential endogeneity
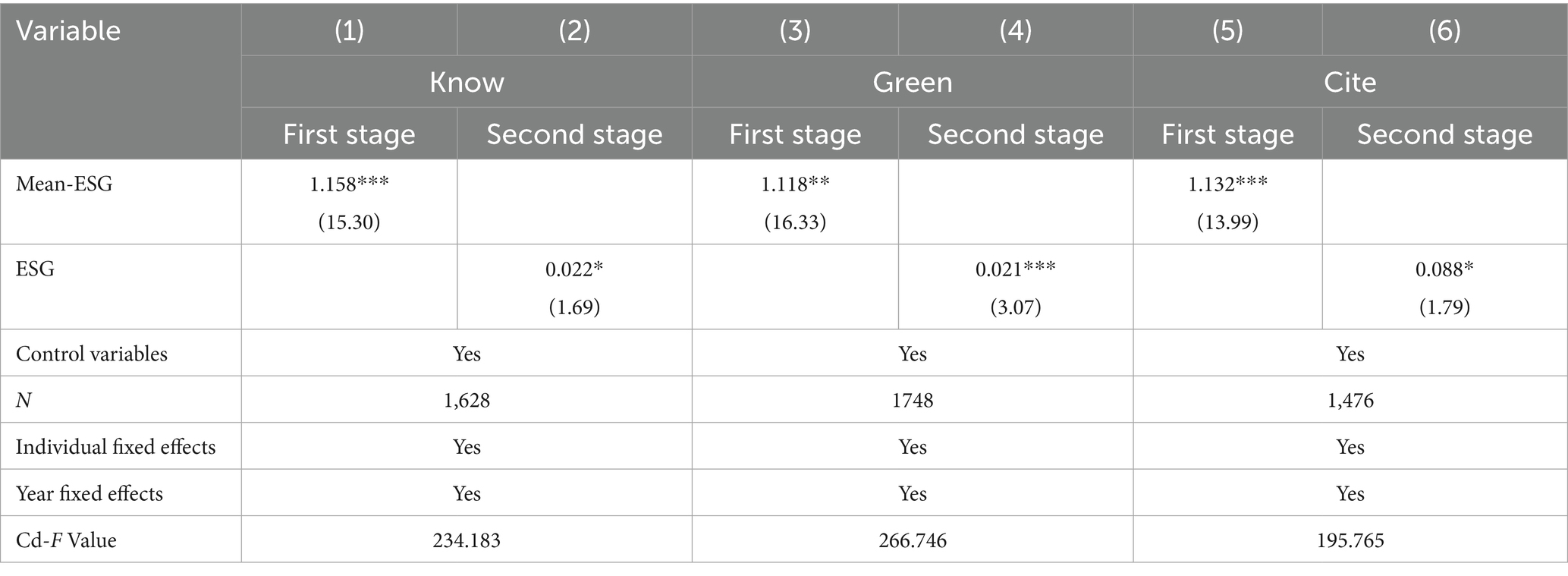
Since there may be a bidirectional causal relationship between corporate ESG ratings and innovation, this study employs the instrumental variable (IV) approach to address endogeneity concerns. Given the baseline conclusion that corporate ESG has a spillover effect on downstream customer innovation, the following analysis focuses primarily on downstream customers. Following the approach of Fang and Hu (2023), the mean ESG rating of other firms in the same industry and year (Mean-ESG) is used as an instrumental variable to test for endogeneity. Columns (1), (2), and (3) of Table 4 present the first-stage regression results of the instrumental variable approach. On one hand, the coefficient of Mean-ESG is significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating a strong correlation. On the other hand, the Cragg-Donald Wald F-statistic exceeds the critical value at the 5% level, suggesting that there is no weak instrument problem, thus rejecting the null hypothesis of weak instruments and confirming the reliability of the results. Columns (2), (4), and (6) show the second-stage regression results, where the coefficients of the mean ESG are 0.022, 0.021, and 0.088, respectively, all of which are significantly positive and consistent with the baseline regression results.
4.2.2 Alternative measurement of the independent variable
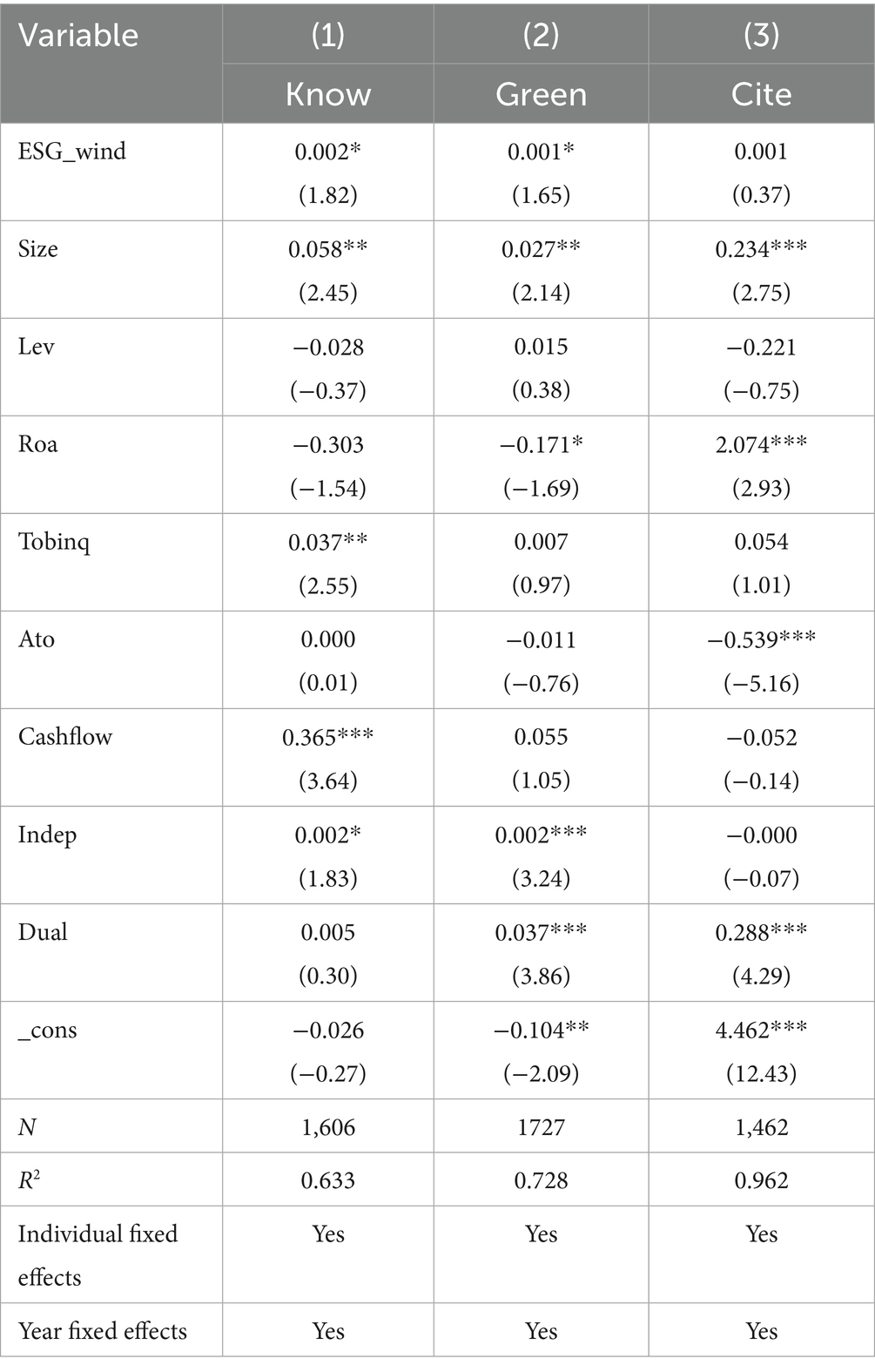
To enhance the reliability of the conclusion that ESG ratings can promote corporate green transformation, this study adopts an alternative method for the core explanatory variable. Considering that the Wind database began an in-depth study of ESG standards and their framework in 2018 and subsequently released comprehensive ESG rating scores, this study uses this new evaluation method to verify the robustness of the research findings. Specifically, the study reassesses ESG performance using the comprehensive ESG rating scores published by the Wind database. The regression results are presented in Columns (1), (2), and (3) of Table 5. The regression coefficients of ESG_wind are 0.002, 0.0001, and 0.001, with the first two coefficients being significant at the 10% level. These results indicate that ESG ratings can improve the innovation quality and the proportion of green patents among downstream customer firms, suggesting a certain spillover effect within the industrial chain. The conclusions drawn are thus considered reliable.
4.2.3 Alternative measurement of innovation
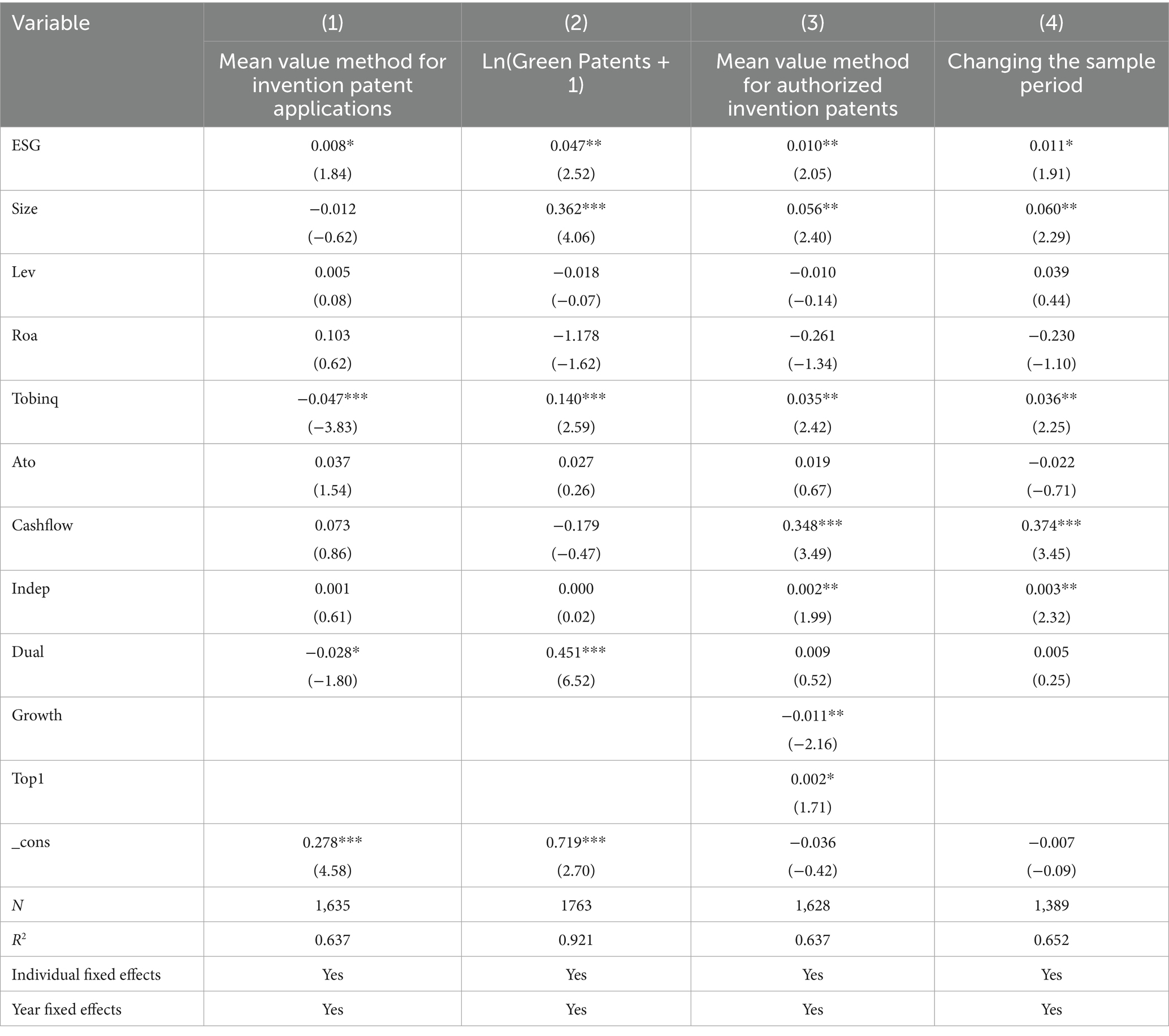
In terms of patent quality, the number of authorized patents measured by the knowledge breadth method is used as an innovation indicator. For green patents, the natural logarithm of the number of green patent applications plus one is used as a proxy variable. The results, as shown in Columns (1) and (2) of Table 6, indicate that the coefficients of ESG are both significantly positive, consistent with the baseline regression results.
4.2.4 Adding control variables
To account for potentially omitted variables that might affect the innovation quality of supply chain firms, additional control variables are included. Considering that a firm’s innovation quality might be related to its own characteristics, this study includes variables such as company growth (growth, measured as total assets/market value) and the shareholding ratio of the largest shareholder (top1) in Model (1). The results, shown in Column (3) of Table 6, indicate that the regression of ESG on downstream customer innovation is significantly positive at the 5% level, consistent with the baseline regression results.
4.2.5 Changing the sample period
At the end of 2019, the unexpected outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic caused unprecedented disruptions to the global economic landscape. The pandemic not only destabilized global supply chains but also had a significant negative impact on market enterprises, leading many firms to face operational difficulties and challenges in innovation. To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the study and to avoid potential interference from the pandemic on corporate innovation efficiency, the sample data were carefully handled by excluding data from 2019 onwards. This was done to reassess the impact of corporate ESG ratings on downstream customer innovation.
Column (4) of Table 6 presents the detailed results of this reassessment. After excluding the 2019 data and rerunning the regression analysis, the coefficient of ESG is 0.011, which is significant at the 10% level. This further confirms the positive impact of ESG ratings on the innovation quality of downstream customer firms.
5 Mechanism testing
5.1 Testing the spillover effect of corporate ESG
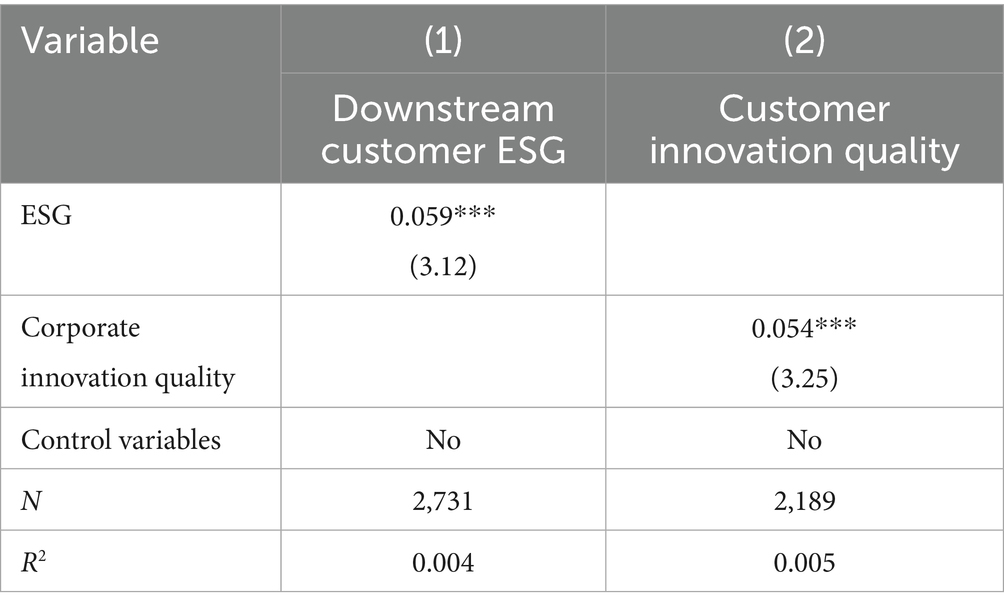
Column (1) of Table 7 presents the results of testing the spillover effect of corporate ESG within the supply chain. The regression coefficient of corporate ESG on downstream customer ESG is 0.059, which is significantly positive at the 1% level. This supports Hypothesis 1, indicating that corporate ESG performance exhibits contagion within the supply chain. In other words, when the primary firm’s ESG performance is strong, the downstream customer firms’ ESG ratings also tend to improve. This finding aligns with existing research, such as the study by Li et al. (2024), which used the ESG performance of the top five customers of Chinese supplier firms as a sample. They found that corporate ESG practices can strengthen the relationship between firms and their suppliers, with customer ESG performance exhibiting a contagion effect. For downstream customers, a high ESG rating in the primary firm reflects high reputation and trust. The spillover effect of ESG suggests that when rating a firm, institutions consider environmental governance, social performance, and corporate governance dimensions. Upstream firms can influence the ESG ratings of downstream customers, thereby improving the overall ESG ratings within the supply chain and solidifying their competitive position in the market.
5.2 Testing the spillover effect of corporate innovation
Midstream firms within the supply chain hold rich resources and information, with suppliers upstream and customers downstream. Their innovation has the potential to generate significant spillover effects, playing a crucial role in enhancing overall innovation capacity (An et al., 2023). From the previous analysis, it is evident that corporate ESG performance effectively promotes the firm’s own innovation quality. Next, we test whether corporate innovation exhibits contagion effects within the supply chain. Column (2) of Table 7 presents the results, showing that the coefficient for corporate innovation quality on downstream customer innovation is 0.0542, which is significantly positive at the 1% level. This finding is consistent with existing research. Yuan and Sun (2023) found that in their study of the impact of digital transformation on supply chain firm innovation, the innovation outcomes of core firms effectively diffuse along the supply chain network to upstream and downstream SMEs. This process enables SMEs to build on the innovation outcomes of core firms, further achieving secondary innovation, thereby significantly improving their innovation efficiency. Compared to complete independent innovation, SMEs tend to prefer leveraging external resources to achieve innovation through learning and emulation, which is more cost-effective and efficient. On one hand, firms with higher ESG ratings tend to have higher innovation quality, and the costs of information disclosure decrease, making it easier for SMEs to access the innovation experiences of core firms. On the other hand, firms with higher ESG ratings have lower supply chain network risks. This shared risk within the supply chain network includes, but is not limited to, optimizing resource allocation between upstream and downstream firms, altering the distribution of supply network risks, and incentivizing firms to increase their efforts. Therefore, whether through collaborative innovation or by integrating external innovations with their own efforts, downstream customers can reduce their innovation risks and enhance R&D efficiency.
5.3 ESG ratings and supply chain efficiency
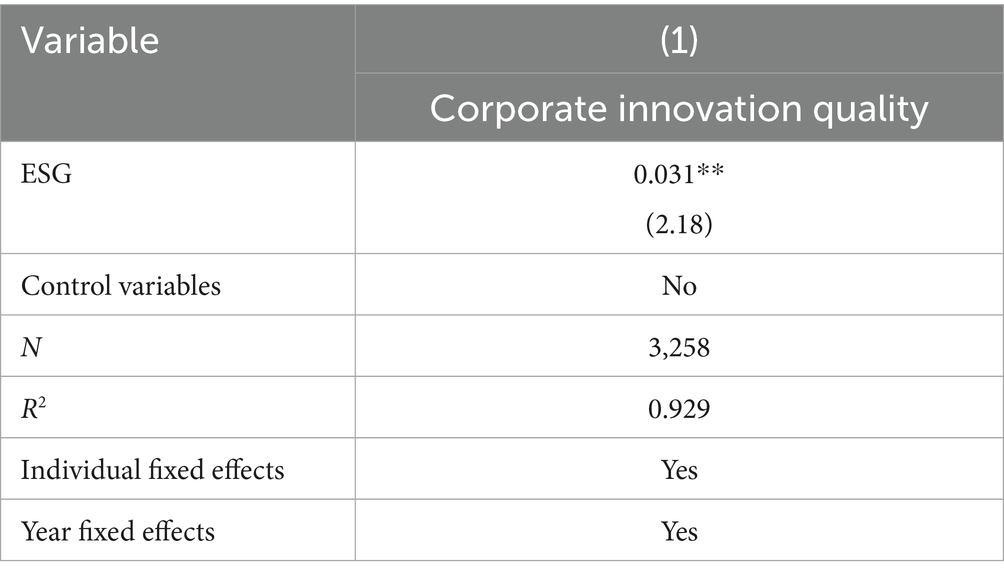
Supply chain efficiency emphasizes enhancing the frequency of dialogue and trade between upstream and downstream firms, resulting in smooth circulation of products and services. This study follows the approach of Zhang et al. (2023) by using inventory turnover days to represent supply chain efficiency, calculated as ln(365/Inventory Turnover Ratio). For a typical firm, fewer product turnover days indicate faster inventory liquidation, leading to higher efficiency in the product chain. This creates a virtuous cycle, where all aspects of the supply chain, including logistics, information flow, and capital flow, are positively impacted, thereby improving supply chain efficiency. Table 8 presents the empirical results of the impact of ESG on supply chain efficiency. The coefficient is 0.031, which is significantly positive at the 5% level, indicating that higher corporate ESG ratings can enhance supply chain efficiency. This supports Hypothesis 4.
5.4 ESG ratings and financing constraints
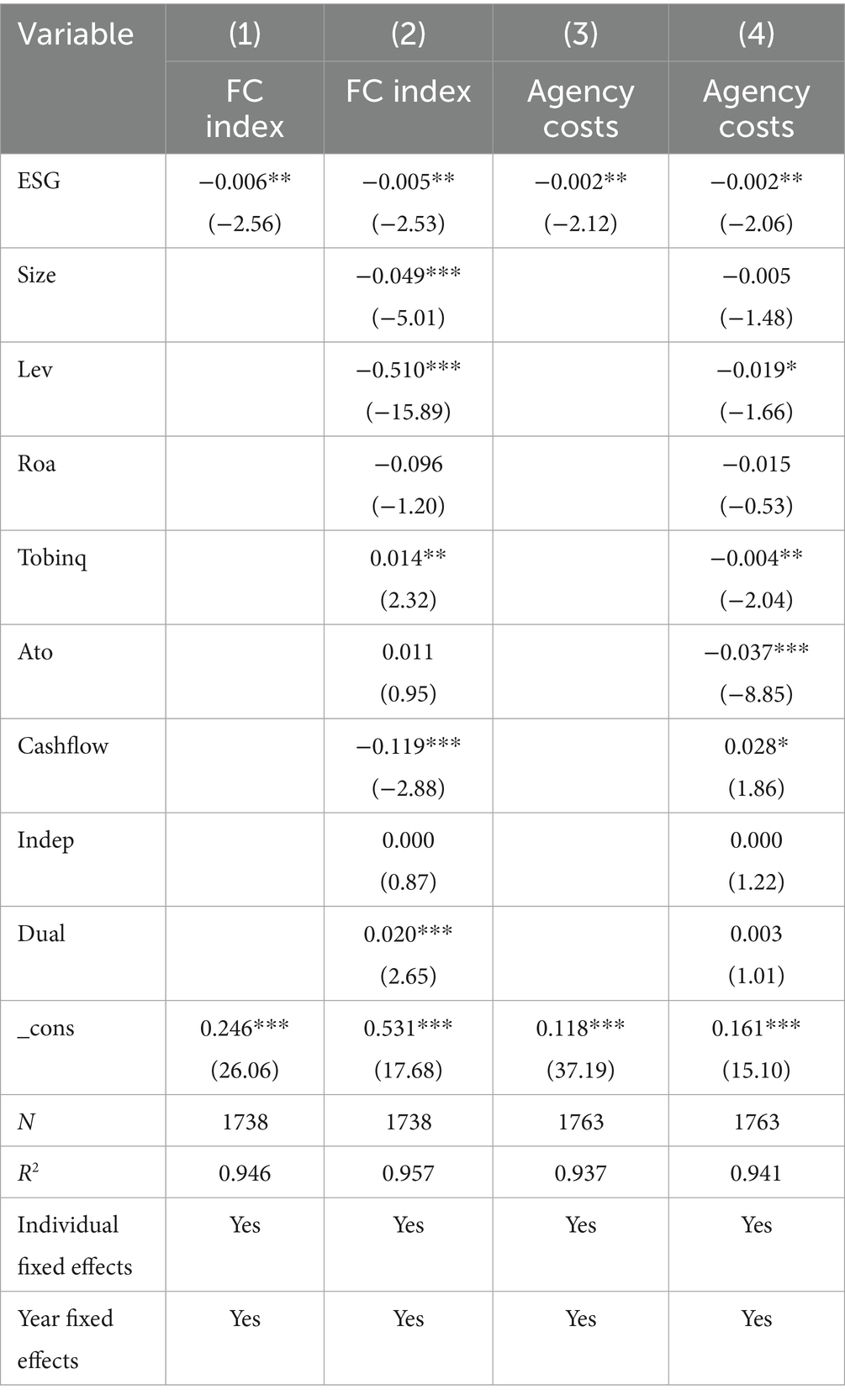
As previously discussed, corporate ESG performance exhibits a spillover effect within the supply chain, enhancing the ESG ratings of downstream customers and thereby improving the innovation quality of supply chain firms. The following section examines the mechanism through which ESG spillovers alleviate financing constraints for customer firms. ESG provides financial institutions with a framework for assessing the overall performance of firms, helping to identify risks and optimize investment portfolios. This, in turn, alleviates financing difficulties through supply chain finance and external credit. By emphasizing credit transmission and risk-sharing—where large firms provide credit guarantees—supply chain optimization is achieved, assisting downstream firms in securing financing and supporting innovation. This study uses the FC index to measure financing constraints. Index-based metrics, including the KZ index, WW index, SA index, and FC index, are widely used to assess the degree of financing constraints. Following the approaches of Gu et al. (2020) and Yuan et al. (2022), the FC index is selected as the measurement variable for financing constraints. A higher FC index indicates more severe financing constraints for the firm. Columns (1) and (2) of Table 9 report the regression results of financing constraints on ESG, with the coefficients significantly negative at the 1% level. This indicates that higher ESG ratings can alleviate financing constraints, reducing corporate financing costs. Overall, the financing constraint mechanism is validated.
5.5 ESG ratings and agency problems
In modern corporations, agency conflicts between owners and managers often lead to short-sighted behavior by corporate managers, which is detrimental to innovation. Introducing ESG ratings can mitigate short-sighted behavior in the supply chain and effectively reduce agency costs. ESG ratings are increasingly valued and recognized by investors. For client enterprises, a higher ESG rating of the supply side enterprises means that they receive stricter attention and supervision from social media. The management teams of downstream client enterprises in the supply chain will actively take actions to correct improper behaviors and ensure the stable operation of the enterprises. This study uses the operating expense ratio to measure agency costs, calculated as the ratio of management and selling expenses to operating revenue. The operating expense ratio reflects the efficiency of management in controlling the agency costs associated with actual consumption, including perks (Li, 2007). Lower agency costs indicate that managers are more effectively utilizing corporate resources, leading to improved overall operating efficiency and reduced agency costs between shareholders and management. Columns (3) and (4) of Table 9 report the regression results of the agency cost mechanism. The results show that the regression coefficients for agency costs on ESG are significantly negative both before and after adding control variables, indicating that ESG ratings can mitigate agency problems among downstream customers in the supply chain, thereby enhancing corporate innovation efficiency.
6 Heterogeneity analysis and extended analysis
6.1 Client market influence
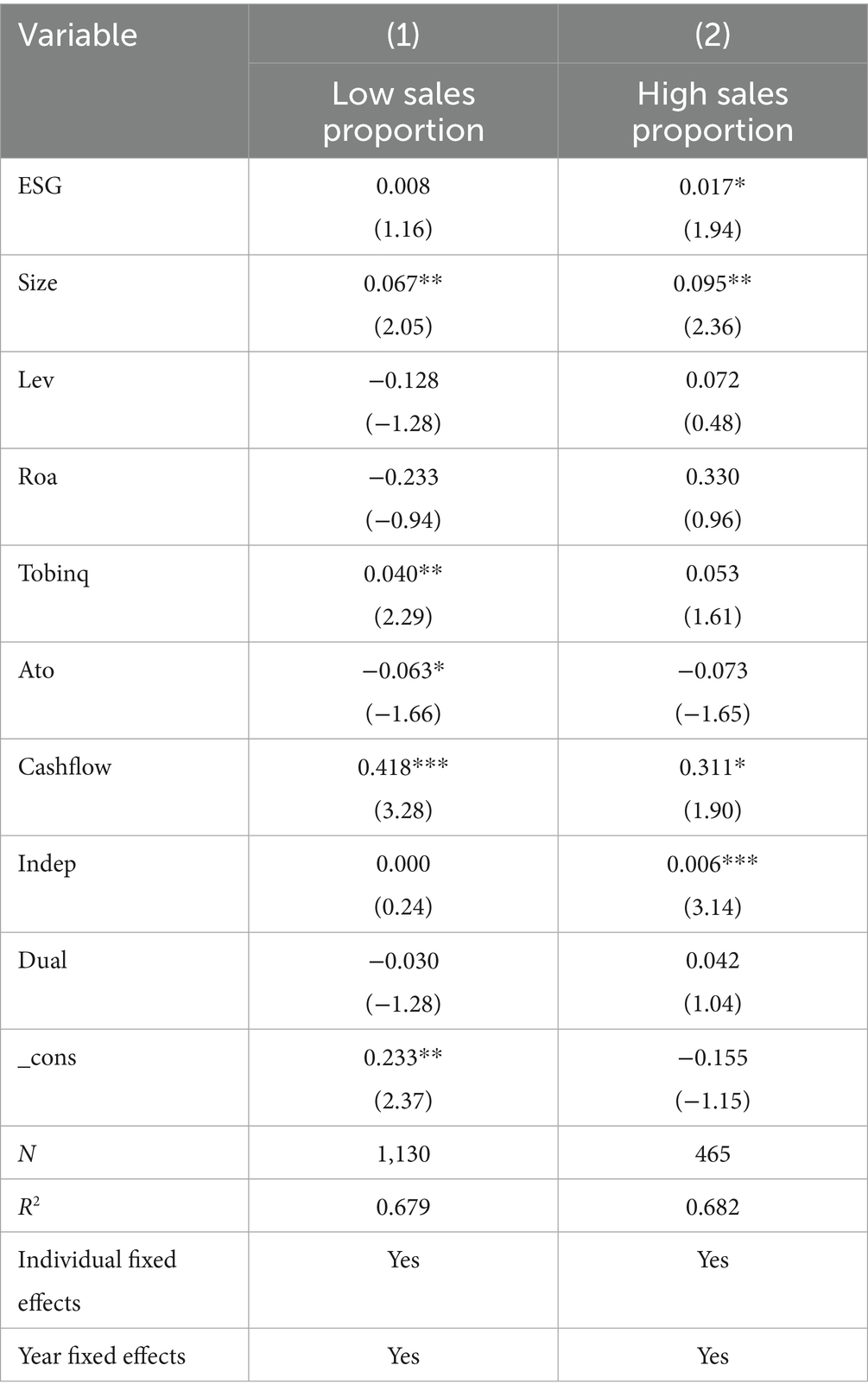
In the digital age, the industrial and supply chains exhibit a clear “demand-driven, order-driven” characteristic, with major clients who have strong market influence serving as key representatives of market demand and primary sources of suppliers’ sales revenue (Yang et al., 2020). As the digital wave sweeps across the globe, the operational mechanisms of industrial and supply chains have undergone profound changes, highlighting the “demand-driven, order-driven” nature. Particularly, clients with strong market influence not only lead market demand but also become crucial pillars of suppliers’ sales revenue. Firms’ dependence on downstream customers has increasingly grown, especially when customers demonstrate strong market influence. To delve deeper into the mechanisms behind this phenomenon, this study employs a grouping method based on the median share of customer revenue in supplier sales, dividing the sample into two groups: firms significantly influenced by client market power and those less influenced. Comparative analysis reveals that when downstream clients possess strong market influence, the ESG ratings of midstream firms have a significant positive effect on these downstream clients. This positive effect is strongly supported by the regression results in Table 10. Conversely, when client market influence is weaker, the impact is not significant. This finding reinforces the notion that under the backdrop of promoting high-quality development in global industrial and supply chains, downstream firms with greater market influence experience more pronounced spillover effects from the productivity growth of upstream firms. This strongly supports the demand-driven nature of the ESG spillover effect, which extends along the industrial chain to downstream firms under strong market demand. Conversely, when client market influence is lower, this coefficient is not significant.
6.2 High-tech vs. non-high-tech firms
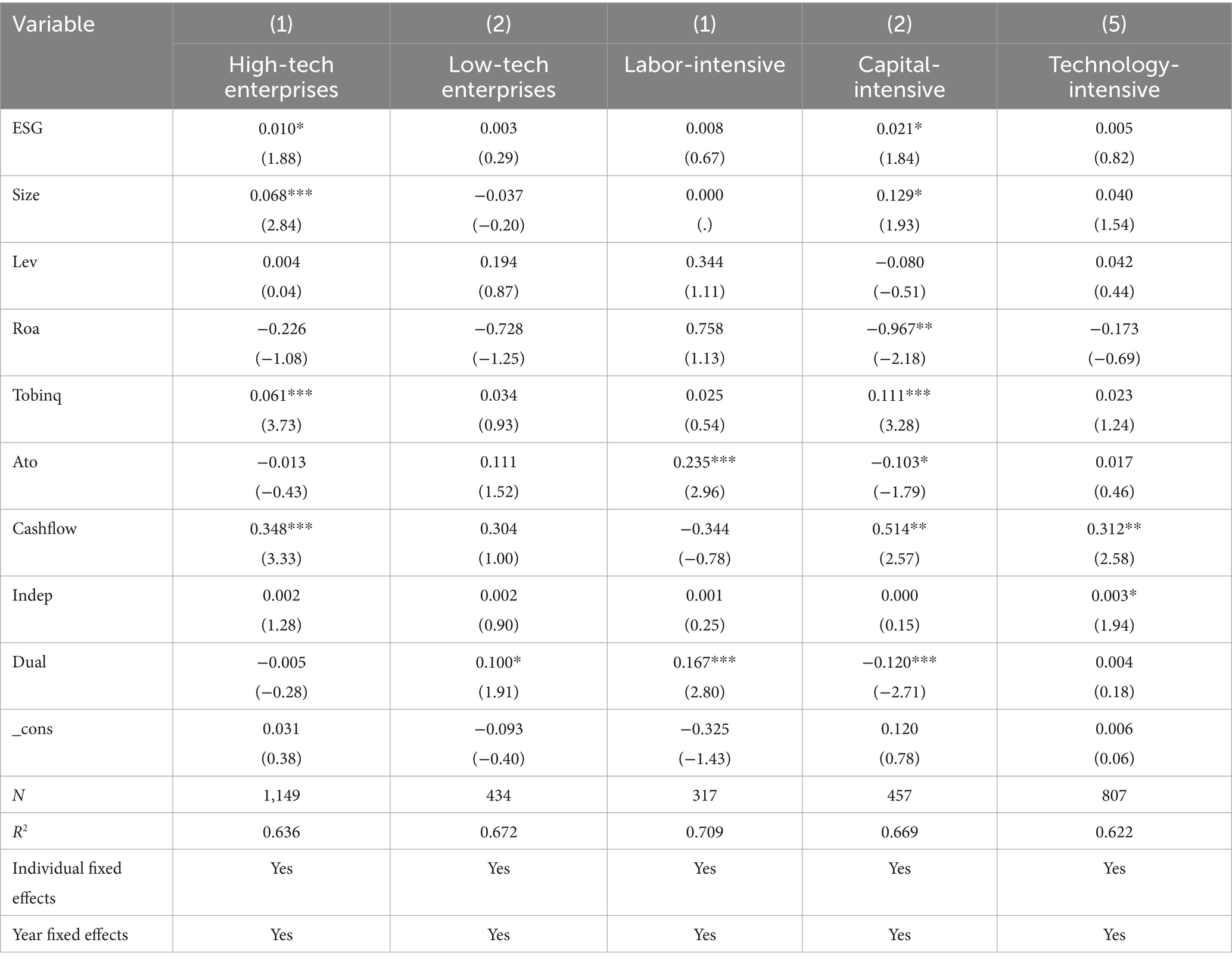
To further explore the differential impact of digital transformation on corporate innovation, this study categorizes industries into high-tech and non-high-tech sectors. High-tech industries are characterized by long investment return periods and high product barriers, which provide strong support for creating long-term value. Compared to traditional industries, high-tech firms often face greater financing constraints, but their valuation metrics are generally higher, indicating a higher sensitivity to the relationship between ESG performance and corporate value (Chen and Zhang, 2023). This gives high-tech industries an advantage in seizing development opportunities and efficiently transforming knowledge and information into innovation output. On the other hand, the competitive landscape in high-tech industries is more intense. To survive, these firms may focus more on breakthrough and exploratory innovation. As emerging industries, high-tech sectors emphasize cutting-edge innovation and foster a substantive innovation environment. They are more likely to acquire resources through various means, such as innovation spillover and knowledge spillover, aiming to maximize their innovation capabilities to meet the innovation demands of customer firms and maintain their competitive edge (Tao et al., 2023). Therefore, this study hypothesizes that the positive impact of corporate ESG on the innovation of high-tech customer firms will be more pronounced. The results, as shown in Columns (1) and (2) of Table 11, indicate that the regression coefficient for high-tech firms is 0.01, significant at the 10% level. This suggests that corporate ESG has a more significant impact on the innovation performance of high-tech customer firms compared to non-high-tech firms.
6.3 Factor-intensive industry classification
Following the approach of Lu and Dang (2014), which clusters industries based on factor intensity, the industries are classified into three types: labor-intensive, capital-intensive, and technology intensive. The empirical results are presented in Columns (3)–(5) of Table 11. Among these, the regression coefficient for capital-intensive firms is significant at the 10% level, indicating that capital-intensive firms are more significantly affected by corporate ESG in the supply chain, leading to a notable improvement in innovation quality, which aligns with practical logic. Firms with higher ESG ratings tend to have a better reputation within the supply chain, and capital gravitates toward firms with high social credibility and responsibility. Consequently, capital-intensive firms receive more funding and resources, leading to increased innovation investment and output.
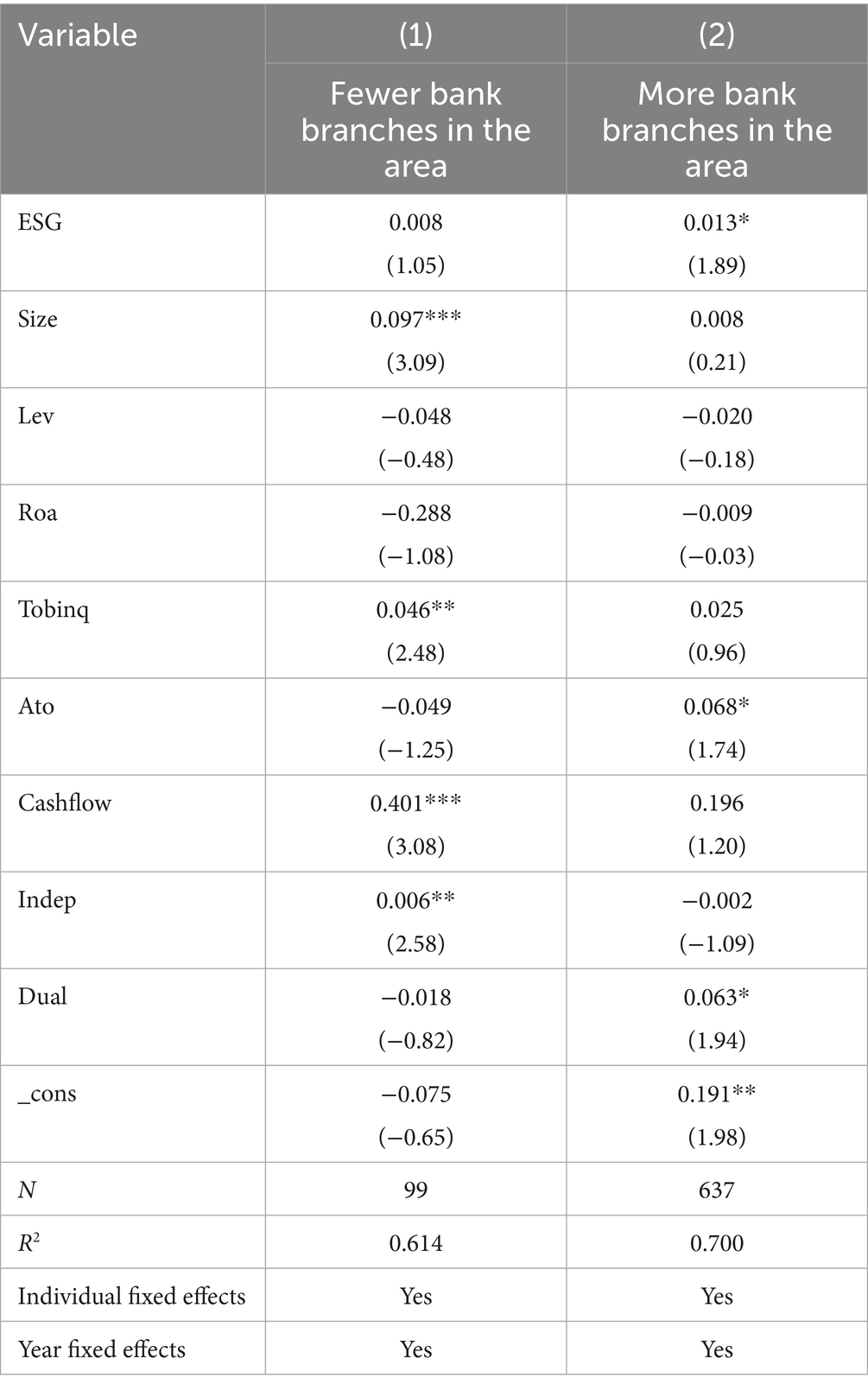
6.4 Bank branch density
The impact of ESG performance on corporate innovation should also take into account the heterogeneity in the number of local bank branches. Bank branches, as operating entities, are at the forefront of providing products and services to participate in market competition. The efficiency, service quality, and profitability of these branches are closely related. Beyond their commercial attributes, the effective extension of bank branch functions can create significant social benefits, greatly aiding banks in practicing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles and achieving ESG goals (Huang and Wang, 2021). Currently, to enhance transparency and promote the robust development of green credit, commercial banks regularly publish comprehensive reports that include not only financial information but also extensive disclosures on ESG information related to both the bank and the enterprises they serve, helping to mitigate issues of environmental information asymmetry. To study this, we conducted an in-depth analysis of the national banking and economic statistics from 2009 to 2022 as published by the China Banking Regulatory Commission (CBRC) on its official website. We aggregated the number of bank branches in each prefecture-level city and divided them into two groups: regions with dense bank branches and those with sparse bank branches, based on the median number of branches. Table 12 reports the heterogeneity results related to the number of bank branches. The empirical results show a regression coefficient of 0.013, which is significantly positive at the 10% level. This indicates that in regions with a higher number of bank branches, the innovation spillover effect of corporate ESG ratings is more pronounced for downstream firms.
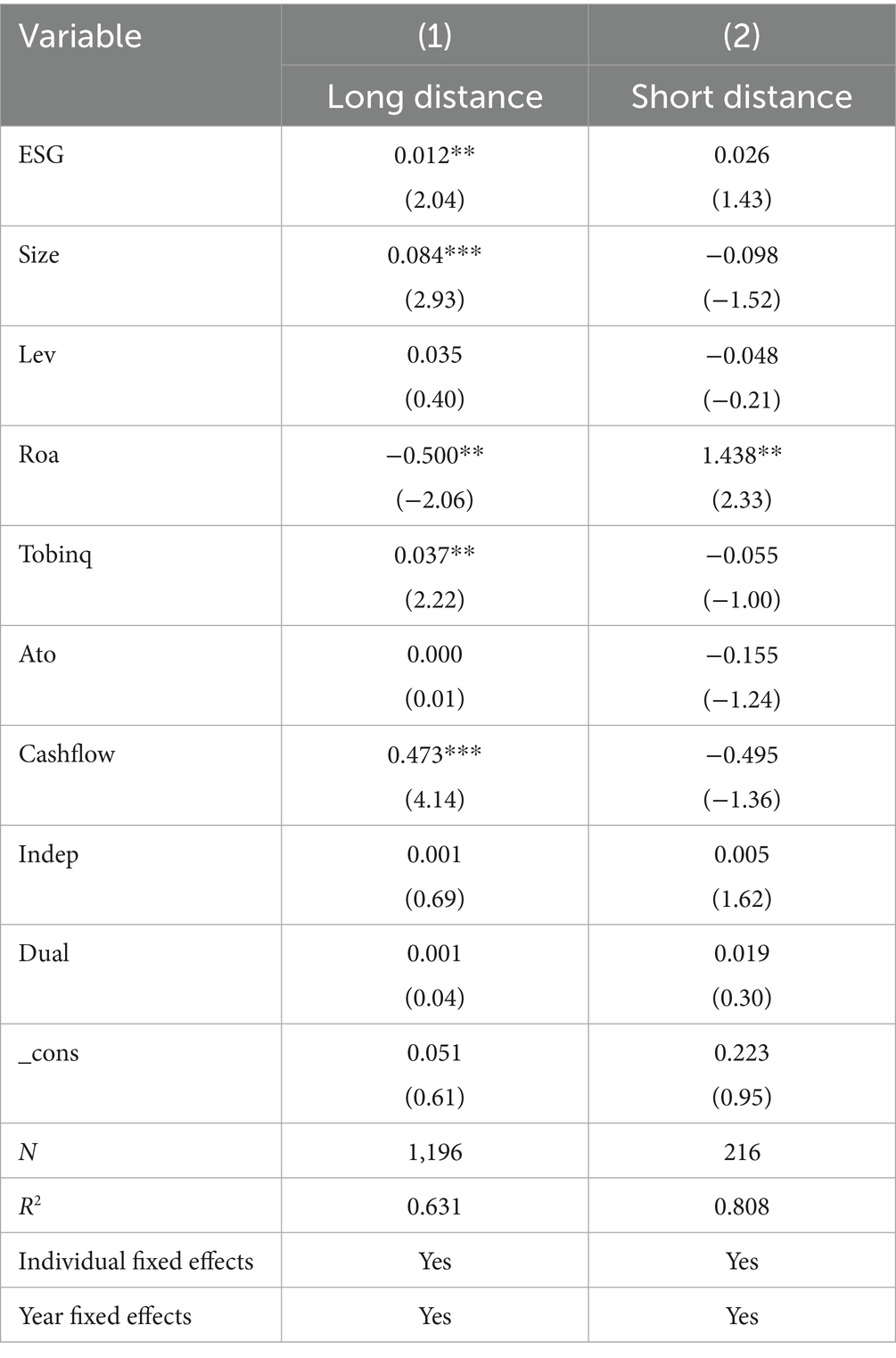
6.5 Heterogeneity analysis of geographic distance
This study delves into the impact of geographic distance between firms and their suppliers and customers on the relationship between firms and their clients. Numerous studies have shown that the spillover and feedback effects of resources are characterized by geographic proximity, with knowledge and information spillovers being more pronounced over shorter distances. Existing research suggests that proximity in the supply chain can enhance a firm’s innovation capability through various channels, such as feedback, demand, agglomeration, and social connections. However, when considering ESG performance as the core independent variable, the impact of geographic distance may change. Specifically, when the geographic distance between suppliers and customers is greater, customers and their stakeholders face higher supervision costs, which hinders the establishment of stable cooperative relationships between firms and customers. Therefore, we hypothesize that if a firm’s ESG performance can effectively convey informational advantages to customers and help the firm gain customer recognition and legitimacy, the mechanism by which ESG performance enhances customer relationship stability should be more significant in firms that are geographically distant from their customers. To further investigate this issue, we follow the approach of Tang and Li (2019) and use the spatial distance between firms and their customers as a measure of customer distance. The higher the value of this metric, the farther the customer is from the firm. We determine this based on the registered addresses of the listed company and its customers or suppliers; if the spatial distance between them is within 100 km, the value is set to 1; otherwise, it is 0. The regression results in Table 13 show that the innovation spillover effect is stronger for firms with distant customers, with a coefficient of 0.012, which is significantly positive at the 5% level, while the coefficient for firms with closer customers is not significant. The conclusion indicates that ESG ratings effectively reduce the information asymmetry caused by greater geographic distances, thereby promoting the innovation quality of firms that are geographically distant within the supply chain.
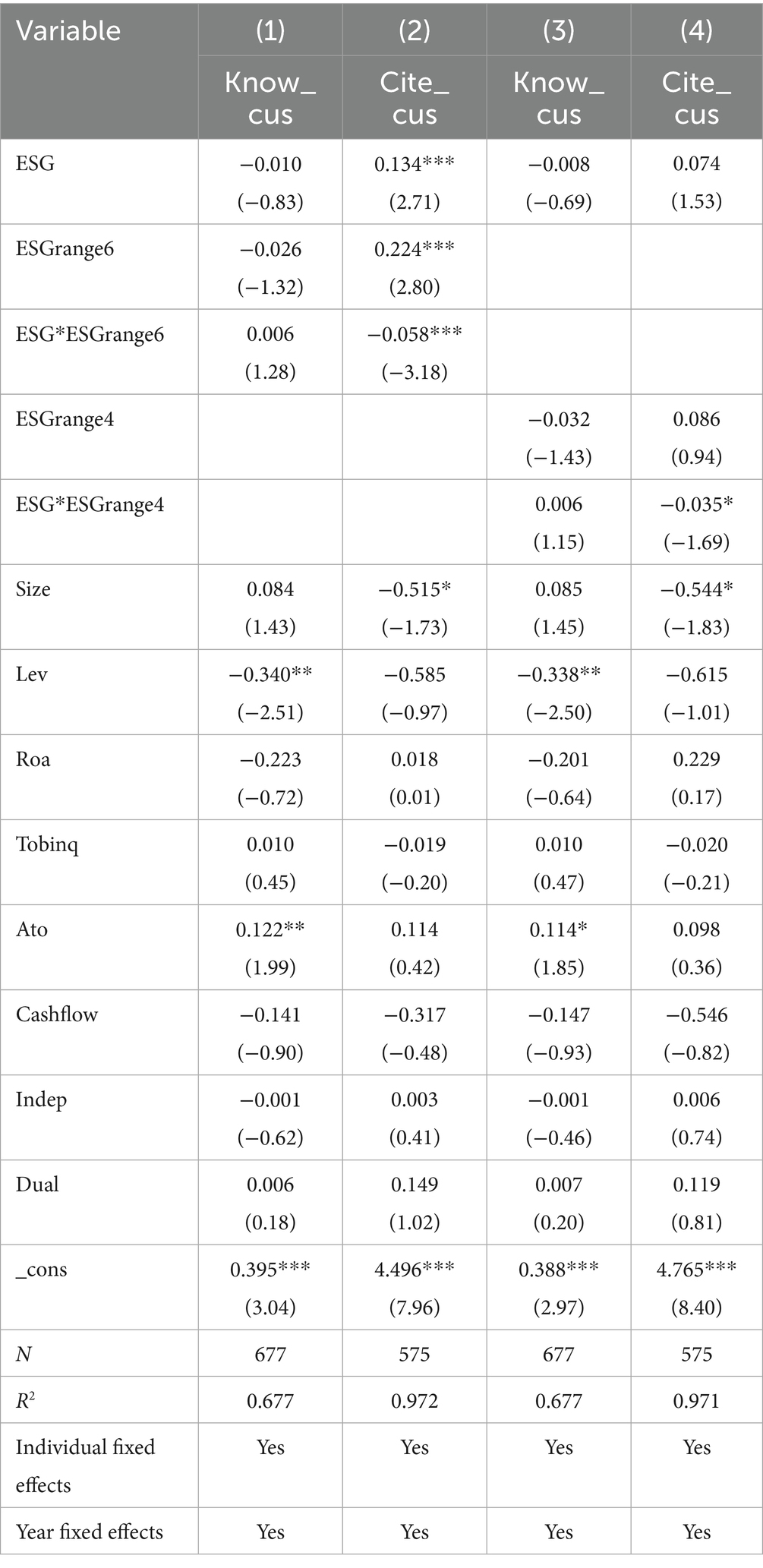
6.6 Moderating effect of ESG rating discrepancies
This study examines the innovation spillover effect of ESG ratings within the supply chain, relying on ESG ratings for assessment. However, a widely recognized issue is that different ESG rating agencies often provide divergent ratings, leading to inconsistent conclusions.
The reasons for ESG rating discrepancies can be summarized in two aspects (Zhang et al., 2023). First, there are differences in private information. Rating agencies rely not only on public information but also on private information during their evaluations. Companies may voluntarily disclose some relevant information, which constitutes public information, while private information needs to be independently collected by the rating agency. Second, current ESG ratings are primarily conducted by private agencies. Due to differing focal points and perspectives among agencies, discrepancies in information collection, data processing, and indicator settings lead to divergent ESG ratings. According to information production theory, there is a substitution effect between the disclosure of public information and the generation of private information. When a company’s information disclosure is not sufficiently transparent and standardized, ESG rating agencies increase their reliance on and collection of private information, thereby exacerbating rating discrepancies. In such cases, the actual performance of firms in terms of operational efficiency, social reputation, moral standards, and policy risks is more likely to diverge from the ratings, which may affect the mechanisms discussed earlier. Based on this analysis, this study posits that the innovation spillover effect in the supply chain will be weaker for companies with larger ESG rating discrepancies.
This study constructs an ESG rating discrepancy index following the approach of Zhang et al. (2023). In the mainstream rating databases, including Wind, Sino-Sustainability, Huazheng, SynTao Green Finance, FTSE Russell, and Bloomberg, the first four are rating forms with scores ranging from 1 to 9, FTSE Russell is multiplied by 200% and rounded, and Bloomberg is multiplied by 10% and rounded. This is the initial data processing step to ensure equal weight for each data point. The ESG rating range across these six ratings from 2015 to 2022 is used to derive the ESG discrepancy index. The data is matched with downstream customer data and interacted with corporate ESG data to create an interaction term. The results of testing the impact of ESG rating discrepancies on innovation spillover effects are shown in Table 14. The results indicate that the interaction term’s effect on patent quality is not significant, while its effect on patent citations is −0.058, significantly negative at the 1% level. Similarly, when using the ESG rating range of the four ratings as a robustness check, the results suggest that the higher the ESG rating discrepancy among downstream firms, the weaker the innovation spillover effect of corporate ESG on downstream customers. This finding is consistent with our theoretical analysis.
7 Discussion and implications
This study explores the spillover effects of corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) performance within supply chains, using panel data from Chinese A-share listed firms between 2009 and 2022. By examining the ESG ratings of focal firms and their top suppliers and customers, we assess the impact of ESG practices on supply chain innovation dynamics.
The empirical results indicate that corporate ESG performance generates significant downstream spillovers. Firms with higher ESG ratings are associated with enhanced innovation quality in their customer firms, as reflected in a statistically significant increase in patent citations (p < 0.05) and a moderate improvement in the proportion of green patents (p < 0.1). However, no comparable effect is observed on the innovation performance of upstream suppliers. Mechanism analyses reveal that these ESG-driven effects operate through channels such as reputation spillovers, knowledge diffusion, improved financing access, and enhanced supply chain efficiency. Heterogeneity tests further show that the strength of spillovers is influenced by contextual factors, including client market power, industry type, input intensity, local banking accessibility, and geographic proximity. Notably, larger discrepancies in ESG ratings among supply chain partners tend to weaken the observed spillover effects.
These findings contribute to the growing literature on ESG and innovation by highlighting the inter-firm transmission mechanisms that extend beyond the focal firm. They underscore the strategic importance of ESG not only as an internal governance tool but also as a relational asset within the supply chain. In particular, ESG-driven firms can play a critical role in catalyzing innovation among downstream partners.
For corporate decision-makers, the findings suggest several practical actions: First, integrate ESG into supply chain governance: Firms should align ESG goals with supplier and customer relationship management to foster innovation synergy and co-create value across the chain. Second, enhance ESG transparency: Clear and credible ESG disclosures can reduce information asymmetry, improve reputational signaling, and strengthen both internal and inter-firm trust mechanisms. Finally, leverage ESG for downstream innovation: High-ESG firms are well-positioned to support customer innovation through joint R&D, technical assistance, and stable long-term contracts—enhancing their own influence and value capture in the supply network.
For policymakers and regulatory institutions, the study offers the following insights: First, standardize ESG evaluation systems: To reduce rating discrepancies and improve reliability, regulators should promote the development of a unified ESG rating framework, integrating international standards with localized criteria. Second, incentivize ESG-aligned collaboration: Targeted incentives—such as tax benefits, green bonds, or innovation grants—can be designed to encourage ESG-based partnerships within supply chains, especially those with demonstrable innovation impact. Finally, support SME ESG capacity building: Governments and industry associations should provide guidance, training, and infrastructure to help small and medium-sized enterprises improve their ESG practices and participate in responsible supply chains.
Besides, future studies may consider extending the analysis to multinational contexts to assess the cross-border generalizability of ESG spillover effects. Additionally, exploring other performance dimensions—such as financial resilience, market valuation, and risk exposure—would offer a more comprehensive view of ESG’s strategic value. Finally, integrating firm-level ESG behavior with broader institutional or regulatory environments could uncover further interaction effects and policy implications.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZJ: Writing – review & editing. XG: Writing – review & editing. LX: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
An, T., Jiang, G., and Wang, D. (2023). Technological measurement and catch-up paths of China's high-tech manufacturing industry: a case study of the lithium battery industry. Econ. Res. J. 1, 192–208.
Arrow, K. J. (1962). Economic welfare and the allocation of resources for invention, the rate and direction of inventive activity: economic and social factor. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Chen, L. H. (2021). Digital construction of the industrial supply chain service system from the perspective of supply-side structural reform. Natl. Govern. 48, 38–45. doi: 10.16619/j.cnki.cn10-1264/d.2021.48.010
Chen, J. J., Ding, H. Y., and Zhang, X. M. (2023). Does ESG performance affect customer relationship stability? Secur. Mark. Her. 3, 13–23.
Chen, H., and Zhang, L. (2023). ESG performance, digital transformation, and enterprise value enhancement. J. Zhongnan Univ. Econ. Law 3, 136–149. doi: 10.19639/j.cnki.issn1003-5230.2023.0030
Di, L. L., Luo, Y. G., Jiang, W., and Chen, C.. (2020). Does customer annual report tone have a supply chain contagion effect?——a perspective of corporate cash holdings. Manage. World 36, 148–163. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2020.0124
Fang, X. M., and Hu, D. (2023). Corporate ESG performance and innovation: evidence from listed companies in China’s a-share market. Econ. Res. J. 2, 91–106.
Gopalakrishnan, B., Chakravarthy, S., Tewary, T., and Jain, V. (2021). Isolating China: deglobalisation and its impact on global value chains. Foreign Trade Rev. 57, 390–407. doi: 10.1177/00157325211045463
Gu, L. L., Guo, J. L., and Wang, H. Y. (2020). Corporate social responsibility, financing constraints, and corporate financialization. J. Financ. Res. 2, 109–127.
Hu, J., Yu, X. R., and Han, Y. M. (2023). Can ESG ratings promote corporate green transformation?——verification based on multi-period did method. J. Quant. Techn. Econ. 40, 90–111. doi: 10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.20230517.002
Huang, S. P., and Wang, S. (2021). Thoughts and suggestions on the implementation of ESG concepts by commercial banks. Rural Financ. Res. 10, 22–29. doi: 10.16127/j.cnki.issn1003-1812.2021.10.005
Huang, J., Wang, Y. H., and Han, F. F. (2023). ESG information disclosure: connotation analysis, evaluation methods, and mechanism of action. Foreign Econ. Manag. 6, 3–18. doi: 10.16538/j.cnki.fem.20221018.202
Jiao, X. J. (2021). The innovation spillover effect of supply chain relationship embedding—from the pesrspective of key customers. Enterprise Econ. 7, 83–93. doi: 10.13529/j.cnki.enterprise.economy.2021.07.009
Li, Y. H., Lan, Q. F., and Wu, W. F. (2022). Research on the diffusion mechanism of customer digital transformation in the supply chain. China Ind. Econ. 12, 146–165. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2022.12.009
Li, Q. Y., Li, Y., Zhang, Y. S. N., and Zheng, H. T. (2023). The information spillover effect of corporate digital transformation——empirical evidence based on the supply chain perspective. China Ind. Econ. 7, 142–159. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2023.07.008
Li, P. L., Wang, J. L., and Qu, G. J. (2024). Contagion effect of customer ESG performance——based on the perspective of supplier firm annual report tone. Econ. Probl. 1, 66–75. doi: 10.16011/j.cnki.jjwt.2024.01.012
Liu, E. (2019). Industrial policies in production networks. Q. J. Econ. 134, 1883–1948. doi: 10.1093/qje/qjz024
Liu, G., and Wang, J. (2024). Does ESG responsibility fulfillment benefit corporate core competitiveness enhancement? Res. Econ. Manag. 45, 18–33. doi: 10.13502/j.cnki.issn1000-7636.2024.07.002
Lu, T., and Dang, Y. (2014). Corporate governance and technological innovation: an industry comparison. Econ. Res. J. 6, 115–128.
Meng, Q. B., Li, X. Y., and Zhang, P. (2019). Can employee stock ownership plans promote corporate innovation?—empirical evidence based on employees' perspectives. Manage. World 11, 209–228. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2019.0158
Qiu, M. Y., and Yin, H. (2019). Corporate ESG performance and financing costs under the background of ecological civilization construction. J. Quant. Techn. Econ. 36, 108–123. doi: 10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2019.03.007
Shi, X., Cheong, T. S., and Zhou, M. (2021). COVID-19 and global supply chain configuration: economic and emissions impacts of Australia-China trade disruptions. Front. Public Health 9:752481. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.752481
Su, J. X., and Zhou, L. G. (2024). Research on the impact of corporate ESG performance on customer default risk from a supply chain perspective. Chinese J. Manag. 21, 1392–1400.
Tang, H. (2022). The effect of ESG performance on corporate innovation in China: the mediating role of financial constraints and agency cost. Sustainability 14:3769. doi: 10.3390/su14073769
Tang, S. Y., and Li, D. (2019). Geographical distance in the supply chain and audit fees of listed companies. Audit. Res. 1, 72–80.
Tang, J. H., Wang, X. M., and Liu, Q. G. (2023). The spillover effect of customers' ESG to suppliers. Pac. Basin Financ. J. 78:101947. doi: 10.1016/j.pacfin.2023.101947
Tao, F., Wang, X. R., and Xu, Y. (2023). Digital transformation, industrial chain and supply chain resilience, and corporate productivity. China Ind. Econ. 5, 118–136. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2023.05.012
Wei, Q. F., and Wei, X. H. (2024). The spillover effect of supplier innovation: a study on the upstream and downstream innovation linkage. Contemp. Finance Econ. 4, 85–98. doi: 10.13676/j.cnki.cn36-1030/f.20240008.002
Wu, Q., and Yao, Y. X. (2023). Corporate digital transformation and supply chain configuration: concentration or diversification. China Ind. Econ. 8, 99–117. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2023.08.005
Xin, C. H., Zhang, X. Y., and Wang, X. Y. (2024). Does corporate ESG performance help stabilize supply chain cooperative relationships? Res. Econ. Manag. 45, 35–54. doi: 10.13502/j.cnki.issn1000-7636.2024.01.003
Yan, B., Cheng, M., and Wang, N. H. (2024). ESG green spillover, supply chain transmission and corporate green innovation. Econ. Res. J. 59, 72–91.
Yang, J. Y., Peng, Q. P., and Ge, Z. T. (2022). Customer contagion effect of digital transformation——supplier innovation perspective. China Ind. Econ. 8, 156–174. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2022.08.009
Yang, Z. Q., Tang, S., and Li, Z. Q. (2020). Capital market information disclosure, relational contracts, and the bullwhip effect—empirical evidence from supply chain information spillover. Manage. World 7, 89–105+217-218. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2020.0105
Yuan, Y. H., and Sun, Y. P. (2023). The impact and mechanism of supply chain core enterprise digital transformation on SME innovation. Sci. Res. Manag. 6, 1–10. doi: 10.19571/j.cnki.1000-2995.2024.06.002
Yuan, Z. M., Yu, X., and Li, M. (2022). How does digital transformation affect corporate financing constraints? Friend Account. 19, 99–108.
Zhang, J., and Liu, Z. (2023). Study on the impact of corporate ESG performance on green innovation performance—evidence from listed companies in China A-shares. Sustainability 15:14750. doi: 10.3390/su152014750
Zhang, B. J., Yang, J. W., Hu, X. Y., Tian, Y. N., and Li, N. N. (2025). Research on the impact mechanism of corporate ESG performance on new quality productive forces——empirical analysis based on resource-based theory. Sci. Decis. Making 4, 104–123.
Zhang, Y. Q., Yang, H. Y., and Zhang, X. Y. (2023). ESG rating divergence and debt capital costs. Financ. Rev. 4, 22–43+124.
Zhang, J., and Zheng, W. P. (2018). Does the innovation catch-up strategy inhibit China's patent quality? Econ. Res. J. 5, 28–41.
Zheng, Z. G., Zhu, G. S., and Li, Q. (2021). Dual-class share structures, sunset clauses, and corporate innovation: evidence from U.S.-listed Chinese firms. Econ. Res. J. 12, 94–110.
Keywords: ESG performance, corporate innovation, supply chain spillover effects, industrial chain, supply chain
Citation: Jian Z, Guanghua X and Xiaodong L (2025) Intersection of ESG performance and corporate innovation: a perspective of vertical linkages within the industrial chain. Front. Sustain. 6:1642317. doi: 10.3389/frsus.2025.1642317
Edited by:
Lipan Feng, South China University of Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Zhiping Lin, Nanchang University, ChinaFen Qin, Taiyuan University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Jian, Guanghua and Xiaodong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li Xiaodong, NjQ1NTc0Nzc0QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Zhu Jian
Zhu Jian Xu Guanghua1
Xu Guanghua1 Li Xiaodong
Li Xiaodong