- Department of Mathematics, School of Advanced Sciences, Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, India
Effective waste management is essential for smart cities, but fixed collection schedules frequently result in missed pickups, overflow events, and inefficient fuel consumption. This study introduces a framework that integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and graph-theoretic optimization. A simulated dataset of 500 bins across five zones was used to train an XGBoost classifier for overflow prediction, combined with spatial risk mapping and routing optimization on a weighted bin network. The AI model achieved high predictive accuracy (94.1%) and recall (95.8%), ensuring reliable identification of overflow-prone bins. Compared to a static collection model, the smart system reduced overflow events by 50%, missed pickups by 72.7%, and fuel usage by 15.5%, while improving bin utilization efficiency by 35.5%. These findings demonstrate that integrating AI, IoT, and graph-theoretic methods can significantly enhance operational efficiency and environmental sustainability in urban waste logistics. The framework provides a scalable solution that adheres to Industry 4.0 principles and serves as a foundation for future smart city infrastructures. The system’s modular architecture allows seamless integration with existing municipal platforms, enabling in real-time responsiveness and adaptive service delivery. By bridging operational decision-making with simulation-driven insights, the framework sets a precedent for data-driven governance in urban infrastructure.
1 Introduction
One of the 21st century’s most urgent problems is the exponential increase in urban waste output. According to the World Bank, the amount of MSW generated worldwide is predicted to reach 3.4 billion tonnes per year by 2050, a 70% increase from 2016 levels (World Bank, 2018). As a result, cities are facing increasing challenges related to public health, infrastructural strain, and environmental degradation. In India, almost 32% of the more than 160,000 tonnes of waste produced daily in cities goes unaccounted for, due to deficiencies in collection, treatment, and monitoring (Central Pollution Control Board, 2021). Outdated waste logistics strategies, jurisdictional differences, and rapid urbanization all contribute to these inefficiencies (Joshi and Ahmed, 2016).
Traditional waste management systems-characterized by static routing, manual bin monitoring, and centralized dispatching-are increasingly ineffective in dynamic urban environments. These systems lead to wasteful fuel consumption, missed pickups, and overflowing bins, which not only compromise service reliability but also exacerbate greenhouse gas emissions, vector-borne illnesses, and public dissatisfaction (UN-Habitat, 2024; Gupta et al., 2022). There has never been a greater demand for decentralized, data-driven, and adaptive waste infrastructure. Urban waste systems are undergoing a transformation through Industry 4.0 technologies, which enable cities to shift from reactive to predictive, intelligent, and sustainable operations. By integrating AI, IoT, graph-theoretic modeling, and spatial analytics, cities can implement SWMS that support geographic prioritization, overflow forecasting, route optimization, and real-time bin telemetry (Mudannayake et al., 2022).
Recent studies have shown that machine learning algorithms like XGBoost, LSTM, and Random Forest are effective in forecasting bin overflow and waste generation patterns (Kodihal and Akhtar, 2024; Spiridonova, 2025). Simultaneously, graph-theoretic techniques have been used to model bin networks as weighted graphs, enabling multi-objective routing based on bin priority, congestion, and distance (Mondal et al., 2024). Spatial intelligence tools-such as risk scoring, zone grouping, and heatmaps-translate predictive outputs into actionable geographic insights, enhancing decision-making (Cui et al., 2025; Agrawal et al., 2025). Despite these advances, current smart waste models often operate in silos, focusing on either spatial risk mapping, routing optimization, or overflow prediction, without offering a unified architecture. To bridge this gap, the present study proposes a hybrid architecture that integrates AI, IoT, and graph theory into a cohesive decision-support system. The framework employs XGBoost-based overflow prediction trained on simulated smart bin data to estimate bin fill levels. Concurrently, geospatial risk mapping identifies temporal accumulation trends and high-risk zones, enabling proactive intervention. Finally, graph-theoretic decision optimization guides dynamic routing based on geographic distance, congestion, and bin priority.
This integrated system uses multi-objective cost functions, zone-specific simulation, and clustering algorithms to ensure operational feasibility in real-world urban settings. The framework aligns with circular economy principles, supports resource recovery, and contributes to SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities. Moreover, it advances the Waste 4.0 paradigm, which emphasizes the convergence of robotics, AI, and geospatial intelligence for infrastructure resilience and emissions reduction (GIZ India, 2023; Zhang et al., 2023). This work lays the foundation for future research in multi-stream waste optimization, real-time dispatching, and citizen-centric service design, by embedding predictive analytics into graph-based routing and spatial prioritization. The proposed framework is validated through simulation using synthetic smart bin data and zone-specific routing scenarios to demonstrate its operational feasibility in urban contexts.
In the subsequent subsections, important aspects that influence the development of intelligent waste systems are examined to place the suggested framework within larger urban, technological, and policy contexts. Global waste issues, social and behavioral factors, governance structures, technical preparedness, and the demands of the circular economy are a few of these. When taken as a whole, they highlight how urgent and pertinent integrated, AI-powered waste management solutions are.
1.1 The global waste epidemic and urban intricacy
The waste epidemic is now a global problem rather than just a problem in underdeveloped countries. Smart waste solutions have been used by cities such as Singapore, New York, and Amsterdam to address inefficient routing, unlawful dumping, and overflow; nevertheless, many metropolitan centers still face challenges related to pricing and scalability. Diverse waste streams, varying generation rates, and jurisdictional overlaps contribute to the complexity of urban waste systems, making centralized planning challenging in the absence of real-time intelligence. An unsustainable rate of urban waste output is creating serious logistical, financial, and environmental problems. Rapidly urbanizing regions in Asia and Africa are projected to experience the steepest increases in waste generation, placing disproportionate pressure on cities with limited infrastructure and fragmented governance (Zhang et al., 2024). Large cities like Delhi, Tokyo, and New York are already feeling the strain of overloaded landfills, ineffective waste collection systems, and disjointed jurisdictional regulations. Some EU member states continue to dispose of more than 60% of household waste in landfills, indicating the need for more environmentally friendly waste management practices (European Environment Agency, 2024b). Many cities throughout the world have responded by developing novel approaches to deal with this issue. By 2050, Amsterdam wants to achieve the lofty aim of becoming a zero-waste city. Japan enforces strict waste categorization laws, with some municipalities managing over 45 distinct waste categories to improve recycling and material recovery (Ministry of the Environment, 2023). Barcelona has also adopted IoT sensor technologies to optimize bin collection and reduce fuel consumption by 20%. These illustrations demonstrate the pressing need for integrated, intelligent, and scalable waste management systems that can keep up with the expanding needs of metropolitan areas.
1.2 The social and behavioral aspects
Smart waste management is not solely a technological challenge-it is deeply influenced by human behavior. Studies consistently show that recycling practices, community participation, and digital engagement significantly affect the performance and sustainability of waste systems. For instance, the implementation of door-to-door recycling programs in Italy, supported by tax incentives, led to a 35% increase in public involvement, demonstrating the effectiveness of financial incentives in promoting behavioral change (Gilli et al., 2018). In Greece, the Bitter Orange Project used mobile applications and reward-based mechanisms to encourage organic waste collection and foster environmental responsibility. Similarly, a study in Slovenia found that installing smart bins with emotional feedback screens improved waste sorting behavior by 22%, highlighting the positive impact of interactive technologies on daily routines (Guna et al., 2022). These examples illustrate that integrating behavioral analytics and citizen engagement strategies is essential for achieving long-term impact in intelligent waste systems.
1.3 Significance of policy and governance
Waste infrastructure is being matched by governments around the world with SDG targets, zero-waste roadmaps, and climate action plans. In India, decentralized waste management and digital transformation are key components of the National Action Plan for Climate Change and the Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban). The proposed AI-IoT-graph framework facilitates data-driven decision-making, emissions reduction, and equitable service delivery, directly supporting these sustainability objectives. Globally, efficient waste management is becoming increasingly acknowledged as a governmental priority and an environmental requirement. National and international sustainability goals are closely aligned with the suggested AI-IoT-graph framework. Over 7,800 projects in India have been mapped to 51 SDG targets by the Smart Cities Mission, while waste reduction and circularity are highlighted by the CSCAF (Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, 2023; Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs and National Institute of Urban Affairs, 2022). Cities around the world are being pushed toward more intelligent waste systems by the EU Waste Framework Directive, which requires the separate collection of textiles and organics by 2025 (European Environment Agency, 2024a). SDGs 11 (Sustainable Cities) and 12 (Responsible Consumption) are advanced by the suggested framework, which makes predictive, zone-aware, and resource-efficient waste logistics possible. However, the success of such frameworks depends on municipal capacity, inter-agency coordination, and the availability of interoperable digital infrastructure. Technological preparedness helps realize this goal. Over 18,000 IoT sensors have been installed in cities like Barcelona, which has saved €555,000 a year in waste management; Amsterdam’s AI-powered smart grid has also decreased energy use by 15% (Madakam and Ramachandran, 2015; Angry Nerds, 2024). Pilot programs for smart bins have decreased fuel use by 30% and public complaints by 60% in India (Agrawal et al., 2025). The modular design of the suggested system makes it simple to integrate with GIS platforms and municipal dashboards, increasing the likelihood that it will be adopted in practice. Despite being historically disregarded, textile waste is becoming a significant urban stream, particularly in areas like Tamil Nadu where volume, potential for reuse, and socioeconomic consequences all come together. The suggested AI-IoT-graph framework’s modular design enables zone-specific diversion and resource recovery techniques by adapting it beyond general MSW to specialized categories like organics and textiles. Circular economy principles are promoted via anticipatory waste management, which goes beyond logistics. With the use of precise overflow forecasts, organic waste may be promptly diverted to compost and hotspots for textile waste can be identified for upcycling and reuse. Such models have been shown to divert thousands of tonnes of waste while creating jobs in Tamil Nadu (Härri and Levänen, 2024; GIZ India, 2023). In this way, the suggested paradigm helps cities transition from linear disposal models to sustainable, circular urban systems.
1.4 Technological development and integration capabilities
Cloud-based analytics, edge computing, and the maturity of IoT sensors have made smart waste systems more practical than ever. Current platforms provide features like predicting maintenance needs, adjusting routes on the fly, and monitoring containers, which have shown in tests to cut emissions by up to 60% and lower operational costs by 40% (Idoko et al., 2024). Despite these advancements, challenges such as legacy system compatibility, data standardization, and cybersecurity must be addressed to ensure seamless integration. AI and IoT technologies have advanced past the experimental stage and are now prepared for deployment, with shown advantages in urban settings. Barcelona’s Sentilo platform, for example, incorporates more than 18,000 IoT sensors, which lowers waste collection expenses by €555,000 annually (Angry Nerds, 2024). To illustrate the observable benefits of intelligent infrastructure, Amsterdam’s AI-enabled smart grids have reduced energy consumption by 15%. According to preliminary research, installing smart bin networks in India can save fuel use by 30% and citizen complaints by 60%. To improve its practicality and scalability for real-world application, the proposed AI-IoT waste management system’s modular architecture enables seamless interaction with current GIS, urban innovation labs, and municipal dashboards. The modular architecture of the proposed AI-IoT waste management system enables seamless integration with existing GIS, urban innovation labs, and municipal dashboards, enhancing its practicality and scalability for real-world application.
1.5 Circular economy and resource recovery
AI-enabled smart waste systems facilitate resource recovery by enabling real-time diversion of organics, recyclables, and residuals to appropriate treatment streams. AI-enabled smart waste systems facilitate resource recovery by enabling real-time diversion of organics, recyclables, and residuals to appropriate treatment streams. Cities can reduce their reliance on landfills by rerouting organics to composting, recyclables to sorting centers, and residuals to energy conversion by mapping waste hotspots and forecasting overflow (Soni et al., 2025). In addition to being a tool for bettering waste collection, overflow prediction is an essential component of resource recovery and circular economy strategies. Methane emissions from landfills can be greatly decreased by towns utilizing predictive mapping to redirect organic waste to composting facilities. Finding hotspots for textile waste can also help direct upcycling and reuse projects, especially in low-income areas where they benefit the environment and society. To divert more than 20,000 tonnes of waste yearly and create almost 400,000 person-days of work, for instance, inclusive textile waste models are being implemented in Tamil Nadu (GIZ India, 2023). Technologies such as RFID tagging and blockchain-based traceability can further enhance material tracking and accountability across the waste value chain. To assist urban systems in moving from linear disposal models toward circular resource loops that put sustainability and local economic development first, the suggested AI-IoT-graph framework facilitates these waste-to-value transformations.
1.6 Related works
The capabilities of smart waste systems have been greatly enhanced by the integration of AI and IoT technology, making automated decision-making, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics possible. According to recent research, dynamic routing algorithms in conjunction with IoT-enabled smart bins can optimize bin placement in urban settings, decrease overflow events, and increase collection efficiency (Alaoui et al., 2025). Deep learning models such as CNNs and YOLO have been applied for real-time waste classification, improving sorting accuracy and reducing manual labor (Gaikwad et al., 2025). By reducing needless travel and emissions, these solutions not only increase operational efficiency but also support environmental sustainability.
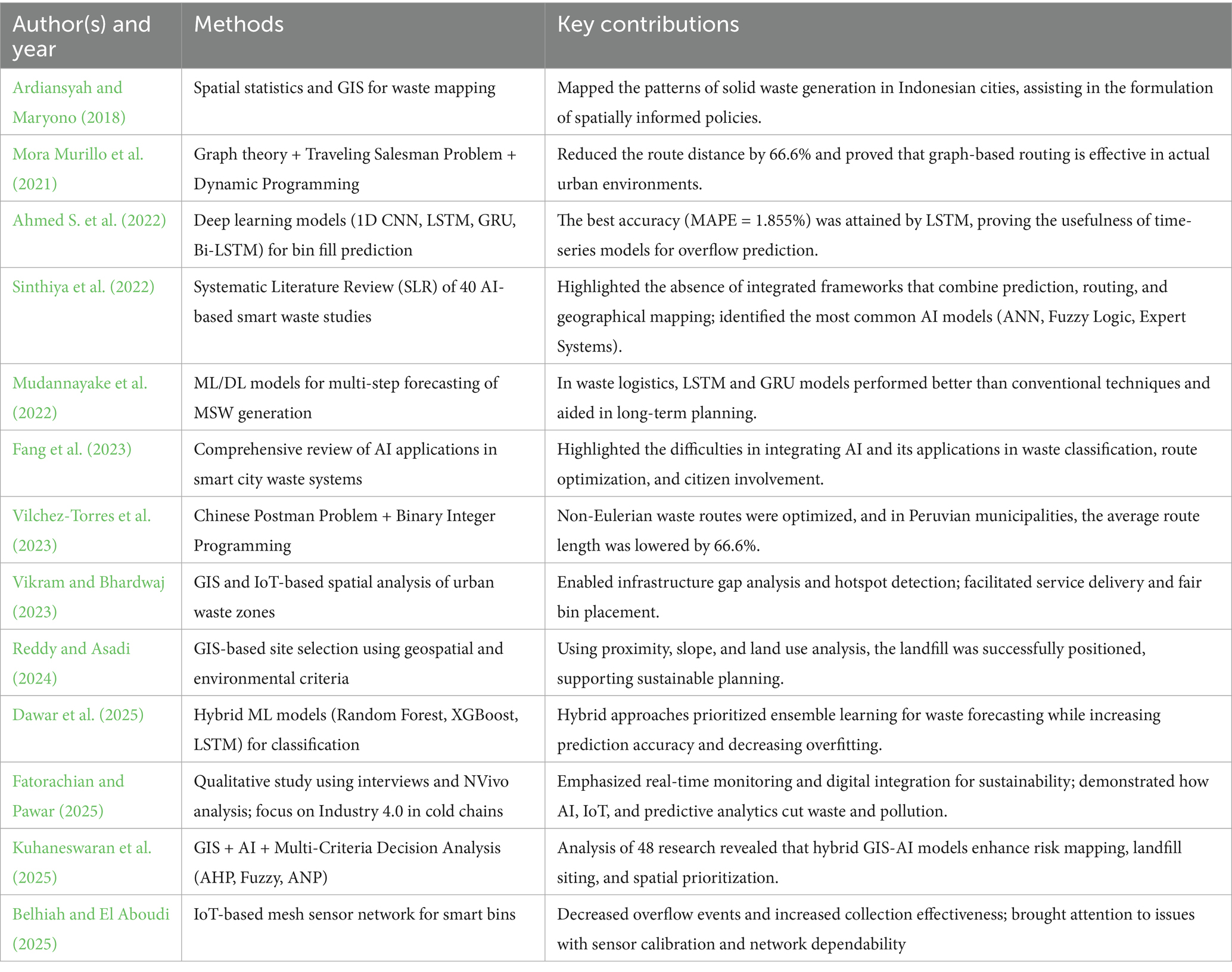
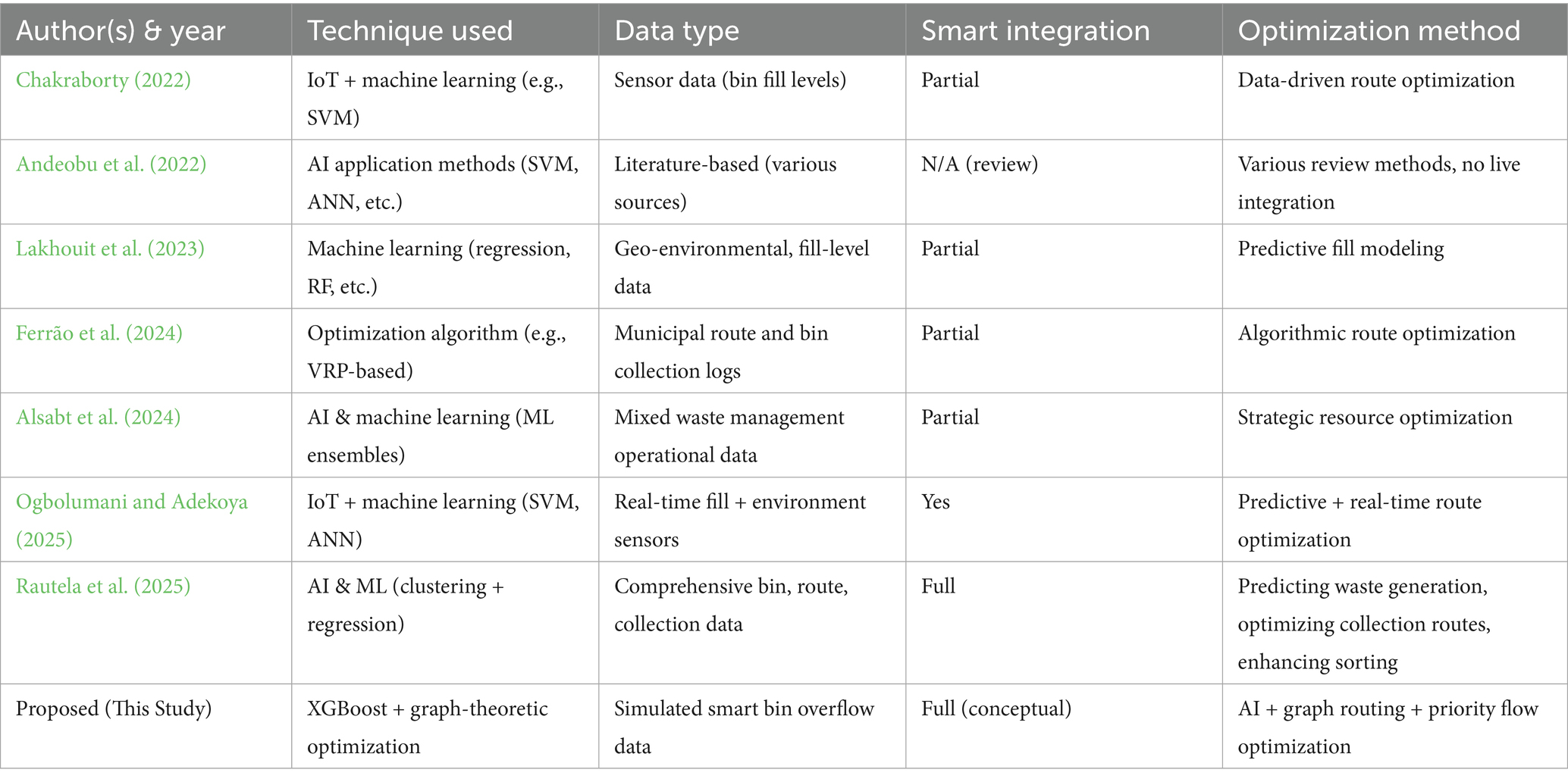
Forecasting waste generation and assisting with long-term planning have both been successfully accomplished using machine learning models. In predicting residential and non-residential waste patterns, a recent study showed that ANNs performed better than SVMs and MLR, with (coefficient of determination) values as high as 99.9% (Billal and Kumar, 2025). Reduced travel distances and increased service dependability have been achieved by integrating waste volume forecast into route planning using graph-theoretic models to optimize waste sorting and transportation networks (Cui et al., 2025). Adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies-including AI, IoT, and predictive analytics-has been shown to enhance waste efficiency in supply chains, aligning smart waste systems with broader sustainability goals such as SDG 11 and Net Zero targets (Gaur et al., 2025). The primary themes in the literature are listed in Table 1 below, which synthesizes important contributions from various fields. However, many of these models operate in isolation-focusing on either prediction, routing, or spatial mapping-without offering a unified operational framework.
The studies included in Table 1 were chosen based on two main criteria: (i) methodological relevance, which included AI models for prediction, IoT-enabled sensing, graph-theoretic routing, and GIS-based spatial mapping; and (ii) representativeness, which highlighted recent and influential contributions from 2018 to 2025 that collectively illustrate the evolution of smart waste research. These studies were selected because they exhibit either unique techniques or common constraints (e.g., focussing solely on prediction, routing, or spatial mapping), highlighting the necessity for an integrated AI-IoT-graph framework.
This corpus of work demonstrates the growing convergence of AI, IoT, spatial intelligence, and graph theory in advancing intelligent waste systems. However, most existing approaches remain fragmented focusing narrowly on routing, spatial mapping, or prediction in isolation. Few studies provide a comprehensive operational framework that combines these dimensions into a coherent decision-support system. To address this gap, the present study develops an AI-IoT-graph framework that blends overflow prediction, spatial risk mapping, and graph-theoretic optimization into a scalable architecture for sustainable urban waste logistics.
2 Problem statement
Traditional MSW collection practices-characterized by static schedules and reactive maintenance-often lead to missed pickups, bin overflow, excessive fuel consumption, and increased labor costs. These inefficiencies are particularly pronounced in rapidly urbanizing areas, where waste generation patterns vary significantly by zone, time, and consumption behavior. Despite technological advancements, most urban waste systems lack integration with real-time data sources such as smart bins and do not possess predictive intelligence. Additionally, current models frequently overlook the complex spatial relationships between collection points, resulting in suboptimal routing and delayed responses. There is a pressing need for an intelligent, adaptive, and graph-aware framework that can anticipate overflow risks and optimize waste collection in a scalable and sustainable manner. Figure 1 illustrates the rationale for this study, highlighting existing inefficiencies, the proposed AI-IoT-graph-theoretic approach, and its anticipated operational and environmental benefits within the Industry 4.0 paradigm. Addressing these challenges is essential for building resilient, data-driven waste systems aligned with smart city and sustainability goals.
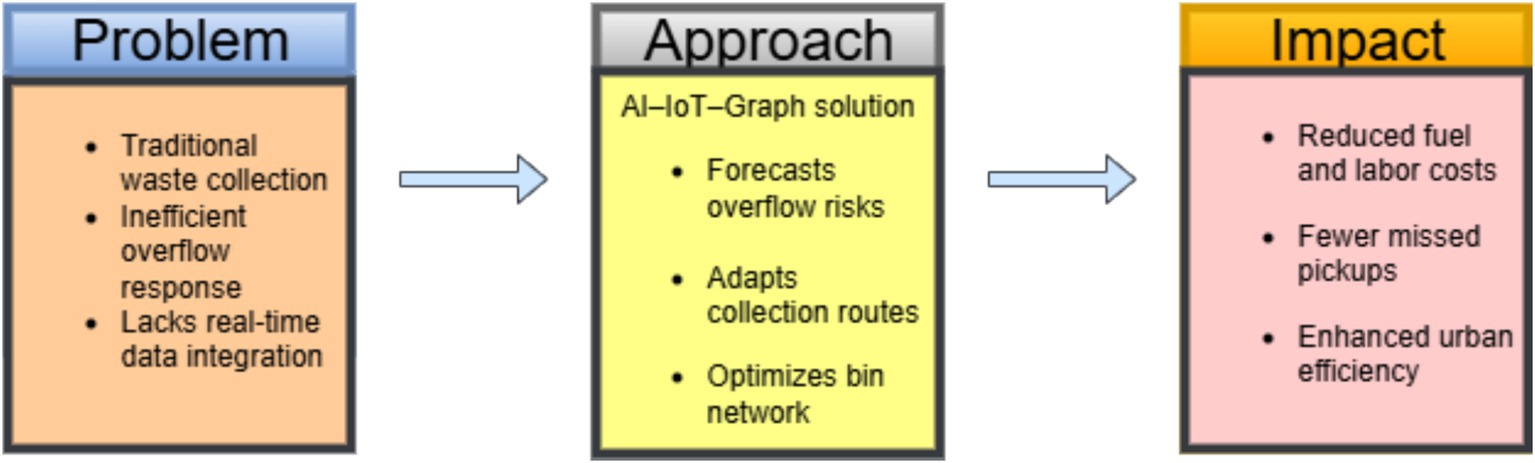
Figure 1. Problem-approach-impact framework illustrating the AI-IoT-graph-based solution for smart waste management.
3 Research significance
This study presents a novel AI-IoT-Graph-Theoretic framework aimed at transforming traditional waste collection systems into responsive, efficient, and predictive networks. To bridge the gap between intelligent forecasting and structural design, the study combines machine learning, smart IoT bin data, and graph-based optimization algorithms. Grounded in Industry 4.0 principles-such as cyber-physical infrastructure, real-time sensing, and system-wide optimization-the approach is highly relevant to the evolving needs of smart cities. The methodological innovation of this work contributes to academic discourse while offering practical value for municipalities seeking to reduce operational costs, lower environmental impact, and enhance service delivery. The proposed framework not only addresses current inefficiencies in waste systems but also offers a scalable model adaptable to other critical urban infrastructures such as energy grids, water distribution, and traffic management.
4 Methodology
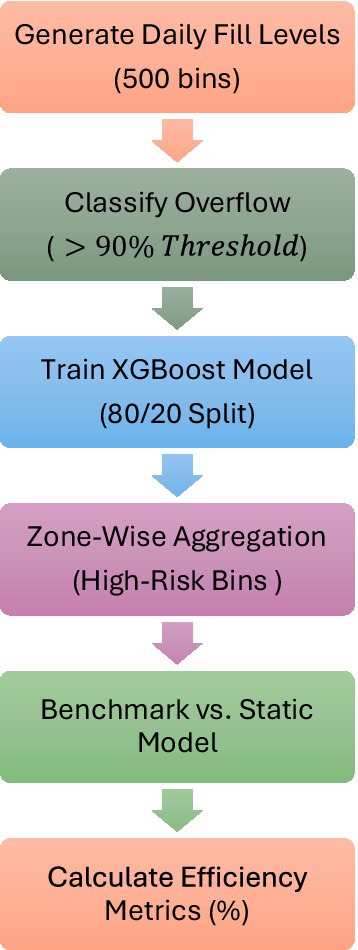
This project creates a single smart waste management system by combining AI, IoT, and graph-theoretic modeling. The system begins with simulated smart bin data, which includes temporal fill levels, geospatial positions, and overflow events. The simulation pipeline followed a structured sequence: (i) daily fill levels were generated for 500 bins across five zones using zone-specific growth functions; (ii) overflow risk was assigned based on the >90% threshold; (iii) XGBoost was trained on 80% of the data and validated on 20%; (iv) predictions were aggregated zone-wise to calculate percentages of high-risk bins (Table 2); (v) comparative benchmarking against a static model yielded efficiency percentages (Table 3). This step-by-step approach, illustrated in Figure 2, avoids uncertainty in percentage computation and ensures reproducibility.
These data points are used as approximations for real-time sensor inputs in urban deployment scenarios. The predicted scores provided by XGBoost are integrated in a directed, weighted graph of the city’s waste collection network, with nodes representing bins and edges representing accessible routes weighted by distance. Clustering methods and centrality measures (such as betweenness and degree) are used to discover high-priority nodes and optimize route construction.
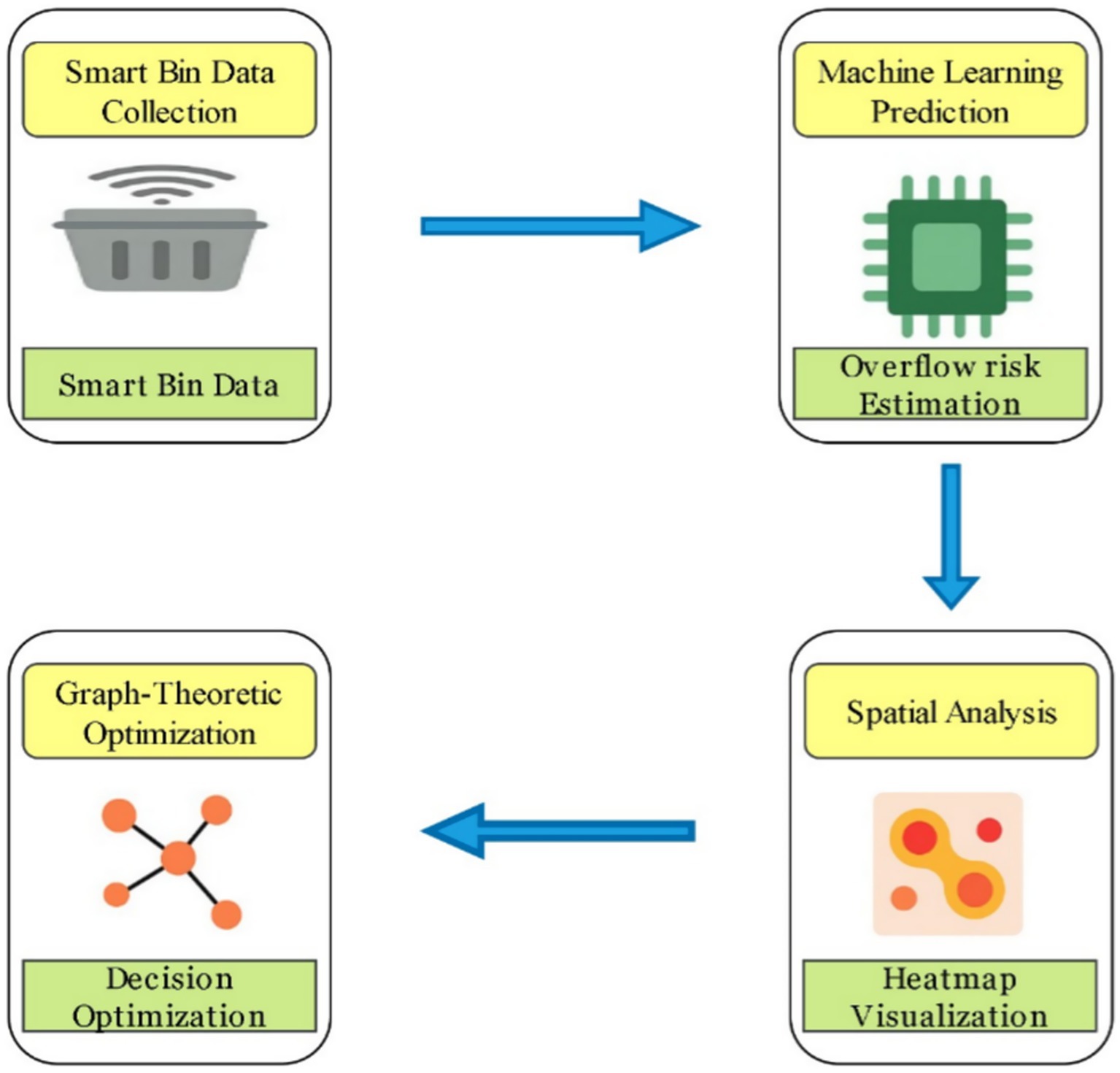
To support spatial decision-making, heatmaps are generated using spatial interpolation techniques to visualize zone-wise accumulation trends and overflow risk. These visual tools help municipal planners detect service shortages and high-risk zones. The framework models an Industry 4.0 infrastructure in which routing decisions are dynamically informed by predictive analytics and spatial intelligence. To determine its effectiveness, the suggested system is compared to a traditional static model utilizing performance measure such as fuel consumption, bin utilization efficiency, and overflow occurrence frequency. As shown in Figure 3, the system design is divided into four stages: smart bin data simulation, overflow prediction, geographical risk mapping, and graph-based routing optimization.
5 Materials and methods
This section outlines the technological components and experimental setup employed in the study. The framework integrates spatial mapping, machine learning-based overflow prediction, synthetic data generation, and graph-based optimization to simulate a smart waste monitoring system grounded in AI, IoT, and network theory.
5.1 Data simulation and smart bin configuration
A realistically structured simulation approach was chosen, simulating 500 smart bins across five urban zones (A–E), each with distinct waste generation patterns because there were no fine-grained smart bin datasets available to the public at the metropolitan scale. This approach is in line with procedures in recently developed smart infrastructure research, which use simulated datasets for system benchmarking and pilot-scale validation (Ahmed A. K. A. et al., 2022). Each of the five urban zones (A–E) with different waste generation rates and behavioral patterns was represented by 100 smart bins in the simulation.
Each smart bin was configured with the following attributes:
• Fill levels every day (in %).
• Co-ordinates of a geospatial location (for mapping purposes).
• Overflow risk labels (classification in binary: Yes, if anticipated fill is greater than 90%, else No).
• Timestamped updates (to record patterns over a period of 7 days).
Using design ideas from current IoT-based smart waste deployments, this simulation model was created. Sensor characteristics, such as GPS transmitters, ultrasonic fill sensors, and ambient context, were digitally incorporated into the dataset structure to align with smart bin telemetry in the actual world (Kumar et al., 2021).
With this method, we were able to account for zone-specific variances and peak accumulation times (such weekends) while training and testing prediction models under operational conditions that were almost realistic. The simulated dataset preserved waste buildup variability impacted by proxy variables such as residential clustering and commercial density (Abba and Light, 2020). Using simulated data was primarily done to allow for a controlled examination of the suggested AI-IoT-Graph architecture without the biases or gaps in data that are frequently present in public repositories. This also facilitated downstream interface with graph-based routing modules, providing optimization workflows in line with clustering-based graph-theoretic waste collection techniques (Balaga, 2020).
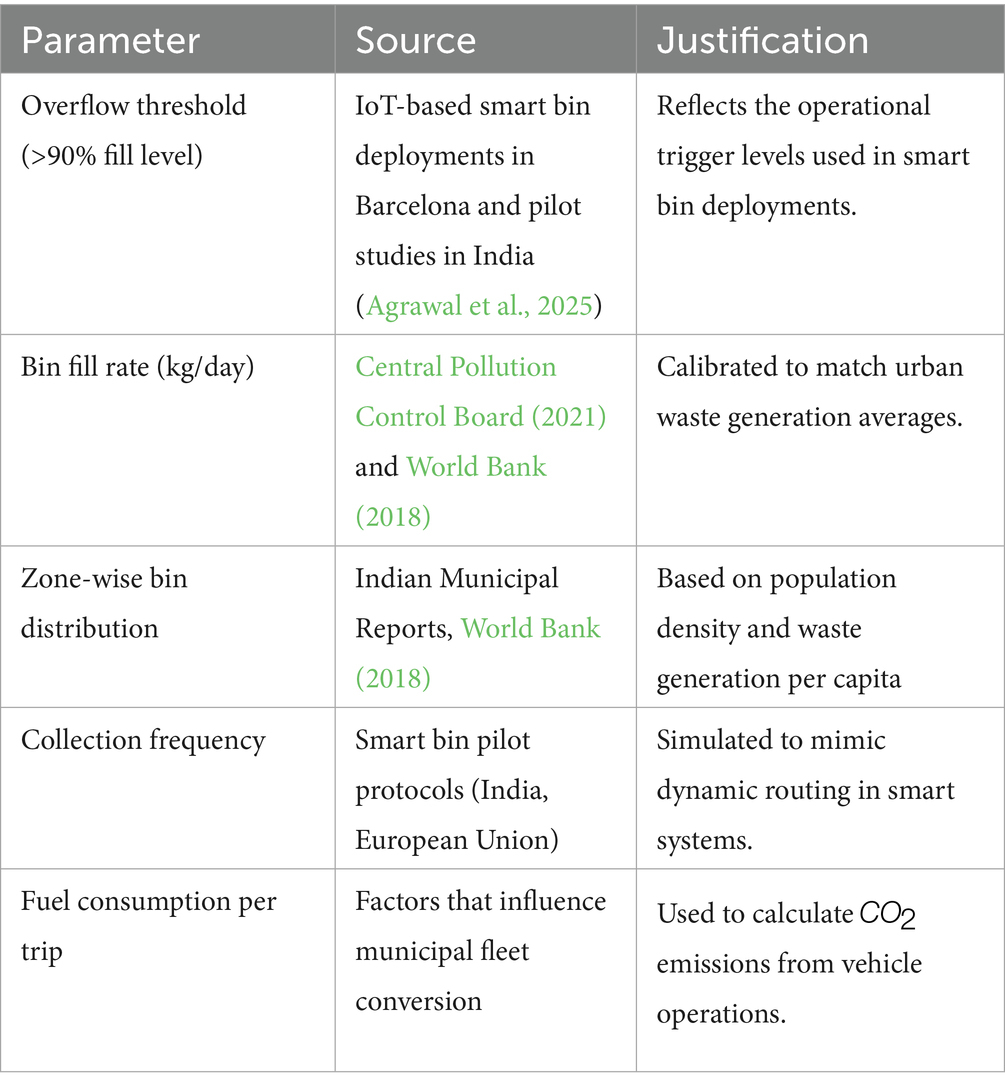
The simulation monitors daily fill levels over a 7-day period, and the model forecasts overflow on day 8 based on historical data. Although simulated data were used, the design was evidence-based. Overflow criteria (>90% fill level) were derived from IoT-based smart bin experiments conducted in Barcelona and pilot implementations in Indian cities (Agrawal et al., 2025). Zone-level waste generation rates were benchmarked against urban averages reported by the World Bank (2018) and the Central Pollution Control Board (2021), confirming that the synthetic dataset accurately represents fill-level dynamics and operational constraints. These design choices enhance the credibility of the simulation and support the validity of the predictive analysis. Table 4 presents a summary of the benchmarking parameters and their sources.
5.2 AI-based overflow prediction
Utilizing XGBoost, we developed a machine learning-based prediction module to foresee possible bin overflow incidents and proactively schedule waste pickup. Based on recent waste analytics research, this supervised learning technique was chosen for its demonstrated efficacy in binary classification problems with high-dimensional, tabular data and temporal dependencies (Chen and Guestrin, 2016; Vaisharma, 2023).
An overflow condition was labeled “Yes” if the anticipated fill level for the following day was greater than 90%; if not, it was labeled “No.” The goal variable was a binary overflow status (Yes/No). From every smart bin record, a few essential features were taken out to properly train the model. A categorical encoding of the Bin ID was used to capture bin-specific usage patterns, the daily growth trend in fill level (ΔFill/day) was used to capture trajectory, the average fill percentage at the zone level was used to contextualize accumulation behavior, and historical fill levels from Days 1 through 3 of the previous 3 days were included. For supervised training and performance assessment, these manufactured characteristics were organized and supplied into the XGBoost classifier. The model was implemented using Python 3.10 and the Scikit-learn and XGBoost libraries.
Model evaluation metrics:
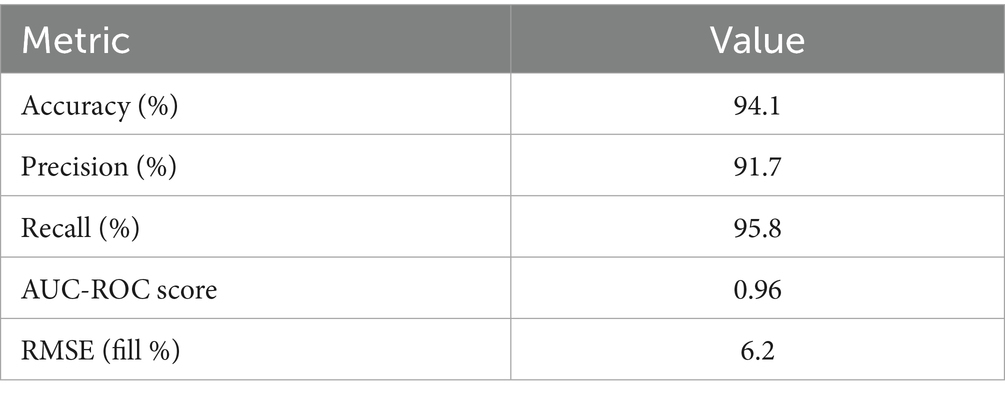
Key classification metrics were used to assess the model after it was trained using a stratified 80–20 train-test split:
• Accuracy: 94.1%.
• Precision: 91.7%.
• Recall (sensitivity): 95.8%.
• AUC-ROC Score: 0.96.
• Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of fill level prediction: 6.2%.
The high recall rate guarantees that overflow-prone bins are not overlooked, which is essential in urban waste environments where even a single overflow incident can compromise service dependability and public health.
XGBoost was well-suited to the bin network due to its scalability and robustness to sparse inputs. Additionally, it facilitates feature importance extraction, which makes it possible to determine which variables have the greatest impact on overflow prediction in a transparent and interpretable manner. XGBoost consistently outperformed other classification models, including logistic regression and decision trees, in terms of precision and recall. This strategy aligns with recent research that tested several prediction models and discovered that deep learning models like LSTM and XGBoost surpassed traditional classifiers in smart waste bin forecasting tasks (Liu et al., 2025). Furthermore, the 90% threshold for defining overflow was adopted in accordance with prior smart bin studies (e.g., Fang et al., 2023), ensuring timely intervention before spillage occurs and aligning with operational standards in IoT-enabled waste systems.
5.3 Spatial risk mapping
As part of the smart waste monitoring system, a spatial mapping module was created to convert AI-predicted overflow concerns into useful geographic intelligence. This element was essential in helping municipal planners with proactive action, visualizing high-risk areas, and streamlining collection routes. Five simulated metropolitan zones (A through E) were used to spatially distribute the fill-level and overflow probability outputs produced by the AI algorithm. Coordinates that were in line with proxies for urban density were used to map the position of each smart bin. High-risk nodes were defined as bins having an overflow probability of within the following 24 h. After that, these were combined zone-by-zone and plotted using a heatmap visualization approach that was created using the folium and seaborn libraries in Python. These libraries enabled both static and dynamic mapping of overflow risk across time and space.
Under resource constraints, it has been demonstrated that spatial clustering enhances service prioritization and improves the interpretability of bin-level predictions (Borase et al., 2024). Together with static heatmaps, the system also included dynamic temporal mapping, which allowed for the detection of patterns by observing risk intensity over a series of days (e.g., frequent overflows near transport hubs or commercial zones). For example, in accordance with the simulation’s population density assumptions, Zones A and B continuously showed higher concentrations of anticipated overflow accidents. This allowed adaptive dispatching techniques to be simulated in addition to validating the predictive structure of the AI model.
The average overflow probability, total bins, and forecasted high-risk bins were reported in zone-wise summaries to further include spatial intelligence into decision-making. Using the following formula, a zone-priority score was determined:
By measuring spatial urgency, this metric made it easier for the routing engine to schedule order. These zone-priority scores were then used to adjust edge weights in the graph-based routing module, ensuring that high-risk areas received prioritized service. Recent research on smart cities has accelerated the application of geospatial mapping in urban waste systems because it can connect physical infrastructure planning and predictive analytics (Singh, 2021). In summary, the spatial risk mapping module served as more than just visual assistance; it was a fundamental decision-support layer that made it possible to implement risk-aware routing, zone-based prioritization, and real-time situational awareness-all essential components of an urban infrastructure that is in line with Industry 4.0. In summary, the spatial risk mapping module functioned not only as a visualization tool but as a core decision-support layer, enabling zone-based prioritization, risk-aware routing, and real-time situational awareness-key features of an Industry 4.0-aligned urban infrastructure.
5.4 Graph-theoretic decision optimization
A graph-theoretic optimization framework was developed to enhance waste collection efficiency by modeling the urban bin network as a directed, weighted graph that prioritizes high-risk bins and minimizes resource usage.
The urban waste network was represented by the graph , where is the set of vertices that stand in for smart bins and is the set of directed edges that provide potential routes for traversing between bins. A weight is assigned to each edge . This weight is increased by overflow priority or congestion penalties and corresponds to the Euclidean or route-based distance between bins and . Edges were annotated with distance, static or simulated congestion penalties, and optional zone weights, while nodes were annotated with degree centrality, historical fill patterns, and overflow risk ratings (derived from the XGBoost model). The goal of the optimization objective, which was presented as a multi-objective shortest path problem, was to minimize the overall distance, minimize missed pickups, and maximize bin prioritization based on estimated overflow risk. This was formulated as a weighted decision function:
where is the congestion factor for edge is the overflow risk score for bin , and is the distance between bins and . The coefficients α, β, and γ were calibrated through iterative tuning based on domain knowledge and preliminary simulations to ensure a balanced prioritization of distance, overflow risk, and congestion. To improve computational scalability and adapt to urban complexity, a two-stage optimization strategy was adopted according to geolocation and overflow risk to increase scalability and routing efficiency in congested urban layouts. Anchor bins were then identified inside each cluster using centrality measures including degree and closeness. This method combines real-time predictive bin status with the underlying network structure, which enables dynamic, context-aware route selection, in contrast to traditional vehicle routing problems (Balaga, 2020; Cui et al., 2025). This hybrid methodology is well-suited for smart city logistics, where scalability, adaptability, and real-time responsiveness are critical (Li et al., 2024).
5.5 System architecture and workflow
The proposed system connects real-time sensing, predictive analytics, and graph-theoretic decision-making through a modular, layered architecture. IoT-enabled smart bins, equipped with LPWAN technologies such as NB-IoT and LoRaWAN, continuously transmit data on fill levels, timestamps, and geolocation. Although simulated data was employed in this study, live data integration is supported by the system’s design. After being gathered, bin data is pre-processed and normalized before being entered into an overflow risk prediction XGBoost model. The prediction output is then used to assign risk scores to each bin, which are passed to the graph-based decision layer for route optimization. Priority risk zones are simultaneously identified throughout the urban landscape using spatial grouping logic. The bin network is abstracted as a directed weighted graph by the decision layer, with nodes standing in for bins and edges for collecting pathways that are weighted by proximity and overflow risk. Graph-theoretic methods, such as cluster discovery and centrality measures, are used to optimize routing and find important collection locations. Making decisions quickly and with few resources is made possible by this organized workflow. As seen in Figure 4, the architecture serves as a practical tool for intelligent municipal waste logistics, supporting interoperability, scalability, and real-world deployment readiness. The modular design ensures compatibility with existing municipal dashboards, GIS platforms, and cloud-based analytics systems.
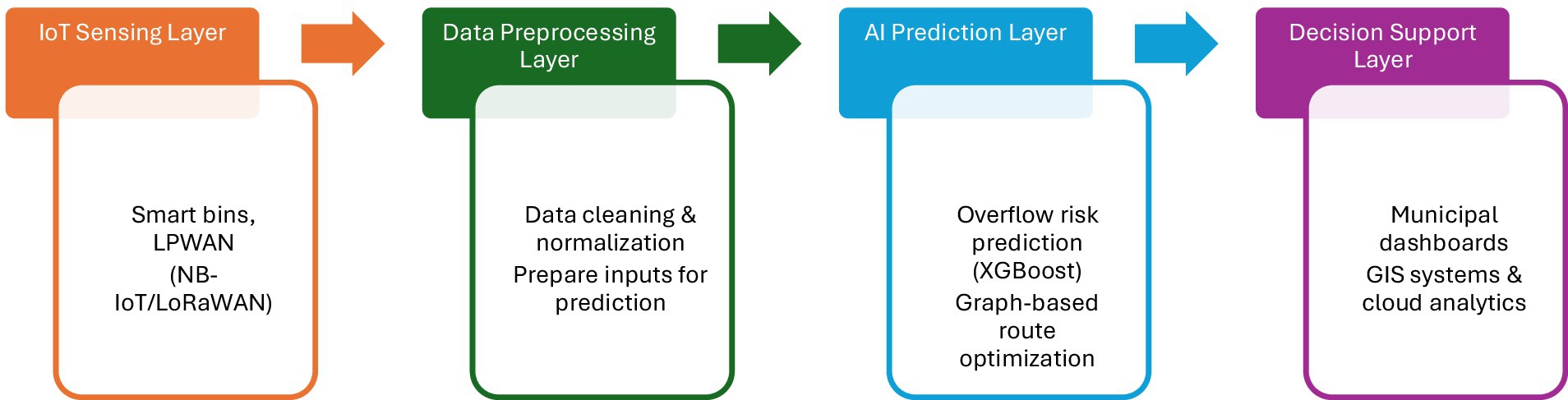
Figure 4. System architecture and workflow illustrating the layered design of the proposed solution.
6 Results
This section presents the results of the proposed AI-IoT-graph-based smart waste monitoring system, focusing on overflow prediction accuracy, spatial risk distribution, graph-theoretic clustering, and comparative performance evaluation. The simulated data used to represent 100 smart bins spread throughout five city zones (A–E) over a week is the source of all results. The rising use of AI and IoT in smart waste systems is supported by recent research. According to studies, sensors built inside bins may track fill levels in real time and transmit data via Internet of Things systems, enabling waste collection decision-making that is responsive and predictive. Additionally, in line with Industry 4.0 objectives, graph-theoretic study of bin networks aids in the strategic construction of optimal collection paths.
6.1 Accuracy of AI prediction for bin overflow
Using XGBoost classification, the model predicted the likelihood of bin overflow based on historical fill level patterns. In Table 5, an example of the simulated input data is presented.
The XGBoost classifier showed a high degree of predictive power in predicting bin overflow incidents using fill-level data from the past. With an overall accuracy of 94.1%, precision of 91.7%, and recall of 95.8%, as shown in Table 2, the model demonstrated its efficacy in reducing false positives and false negatives. It is further confirmed that the model is robust in differentiating between bins that overflow and those that do not by the strong AUC-ROC score of 0.96. The model’s low margin of error, as indicated by its fill-level forecast RMSE of 6.2%, further qualifies it for real-time deployment in intelligent waste systems. These findings support the notion that XGBoost is a dependable engine for anticipatory waste monitoring in urban settings. These outcomes demonstrate that the AI model can accurately forecast bins that are prone to overflow within a 24-h period.
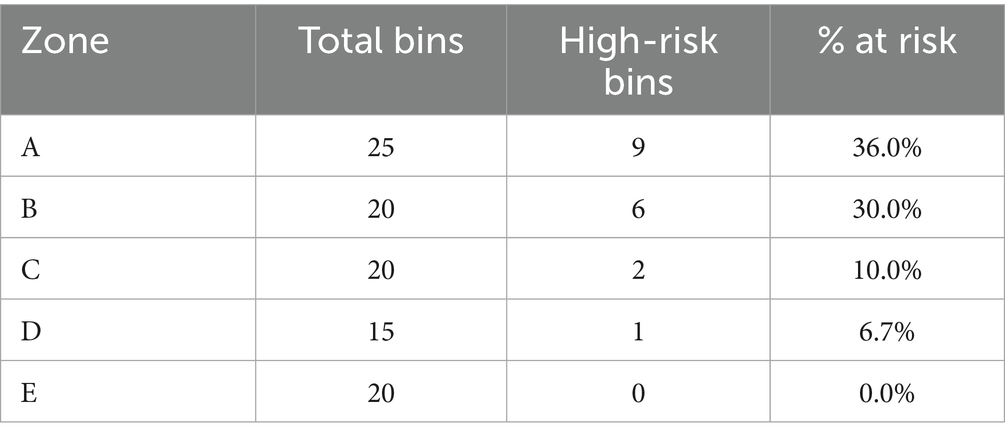
6.2 Overflow risk mapping by zone
As anticipated, the proportion of high-risk bins (fill level 90%) each zone was determined. Real-time sensor input-based dynamic routing techniques are justified by this spatial risk analysis. As seen in Figure 5, the heatmap identifies places with a higher risk of overflow, supporting the use of dynamic routing techniques in high-density regions and confirming the distribution patterns.
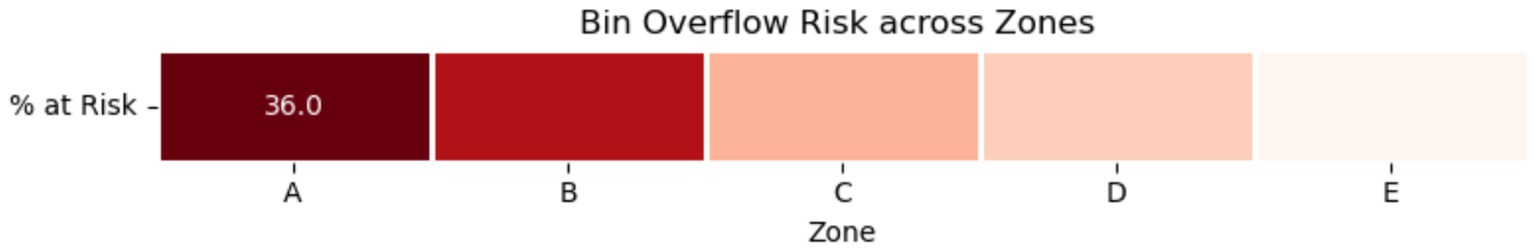
Figure 5. Overflow risk intensity across zones A–E. Darker shades indicate higher concentrations of high-risk bins.
Zone-priority scores calculated using the methodology’s formula were consistent with the percentages shown in Table 6. Zones A and B, for example, had the highest priority rankings due to a higher percentage of high-risk bins and higher average overflow probability.
6.3 Graph-theoretic analysis of bin clusters
Inter-bin relationships were analyzed using a graph-based methodology. Edges indicate proximity or route dependency, whereas each node represents a bin. Metrics of centrality and clustering identified areas for strategic intervention.
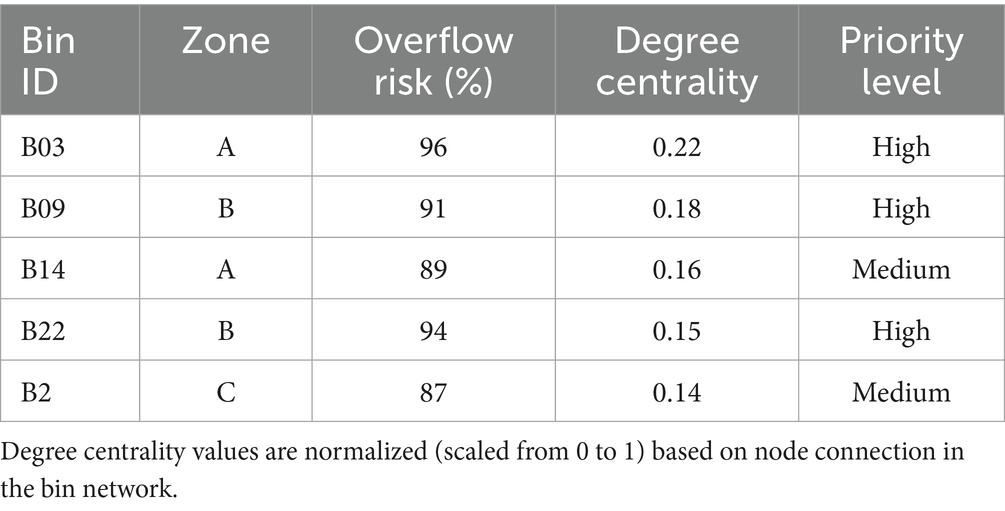
Due to their high centrality and overflow risk, bins B03, B09, and B22 emerged as high-priority nodes, as identified in Table 3, underscoring the need for targeted interventions. Localized actions are supported by the graph-theoretic paradigm, particularly in densely connected, high-risk zones. As illustrated in Figure 6, the smart bin network is represented as a graph where nodes indicate bins and edges reflect route proximity-thicker edges denoting shorter or more critical paths. High-risk bins are visually emphasized through red nodes, highlighting structurally important collection points. This visualization reinforces the analytic findings and confirms the utility of graph-theoretic routing strategies in optimizing waste collection.
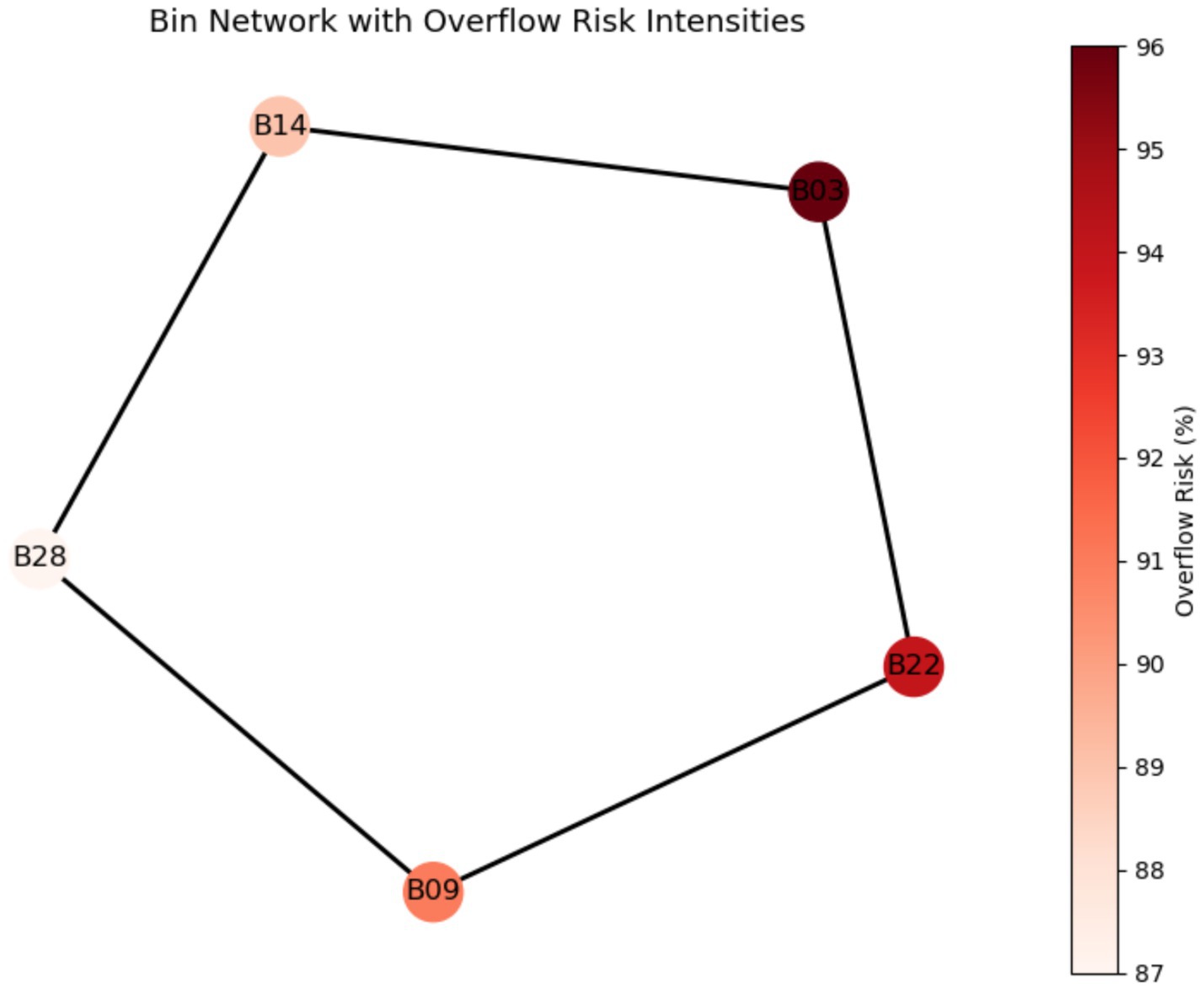
Figure 6. Graph visualization of smart bin network. Edge thickness denotes route weight, whereas node color intensity indicates overflow risk.
These results align with the methodology’s multi-objective decision function, where distance , overflow risk as well as congestion fines were considered together during the process of setting priorities. Due to their higher overflow probabilities, bins B03, B09, and B22 had the highest ranking under the term, and their strategic value was further bolstered by their network centrality. This shows how structural position and prediction risk are operationally translated into practical collection priorities by the weighted function.
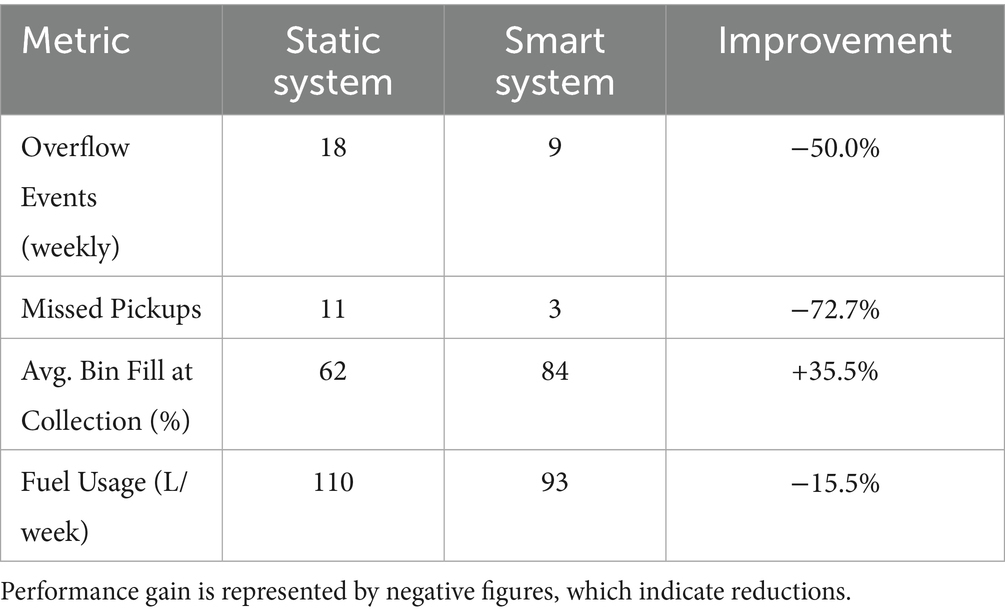
6.4 Comparative analysis of smart and static monitoring systems
A conventional static scheduling system was used as a benchmark for the intelligent AI–IoT paradigm. Table 7 provides a summary of the findings.
As illustrated in Figure 7, these performance metrics are derived from the simulation results of the proposed model. The results highlight the operational and environmental advantages of intelligent waste systems, including improved collection efficiency, reduced fuel consumption, and enhanced service reliability.
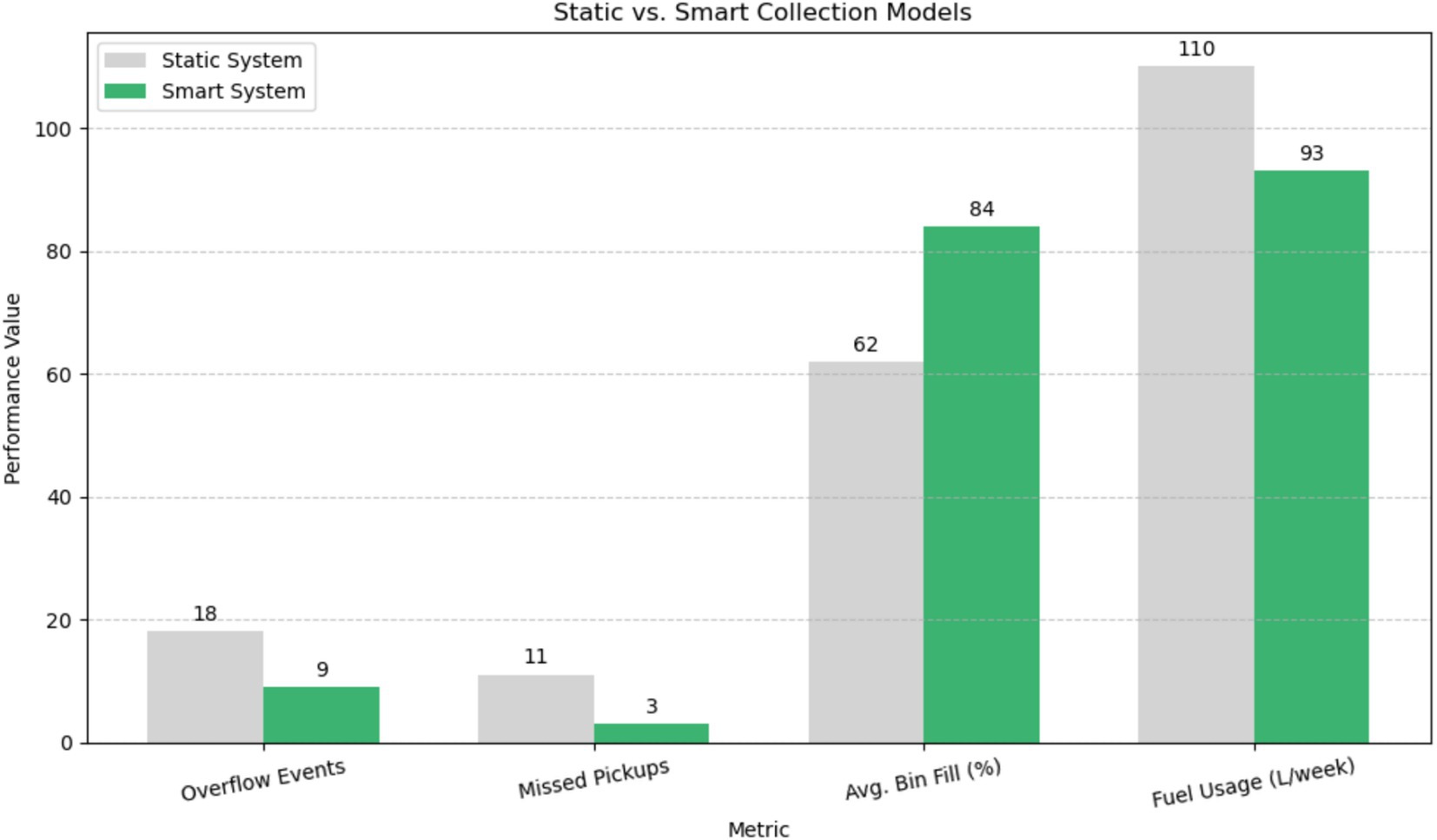
Figure 7. Comparative performance metrics between AI-IoT-based smart waste system and traditional static scheduling.
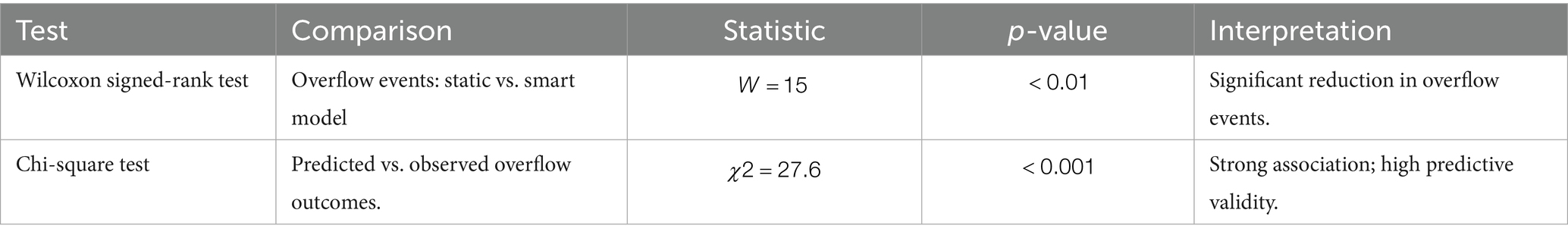
6.5 Statistical validation
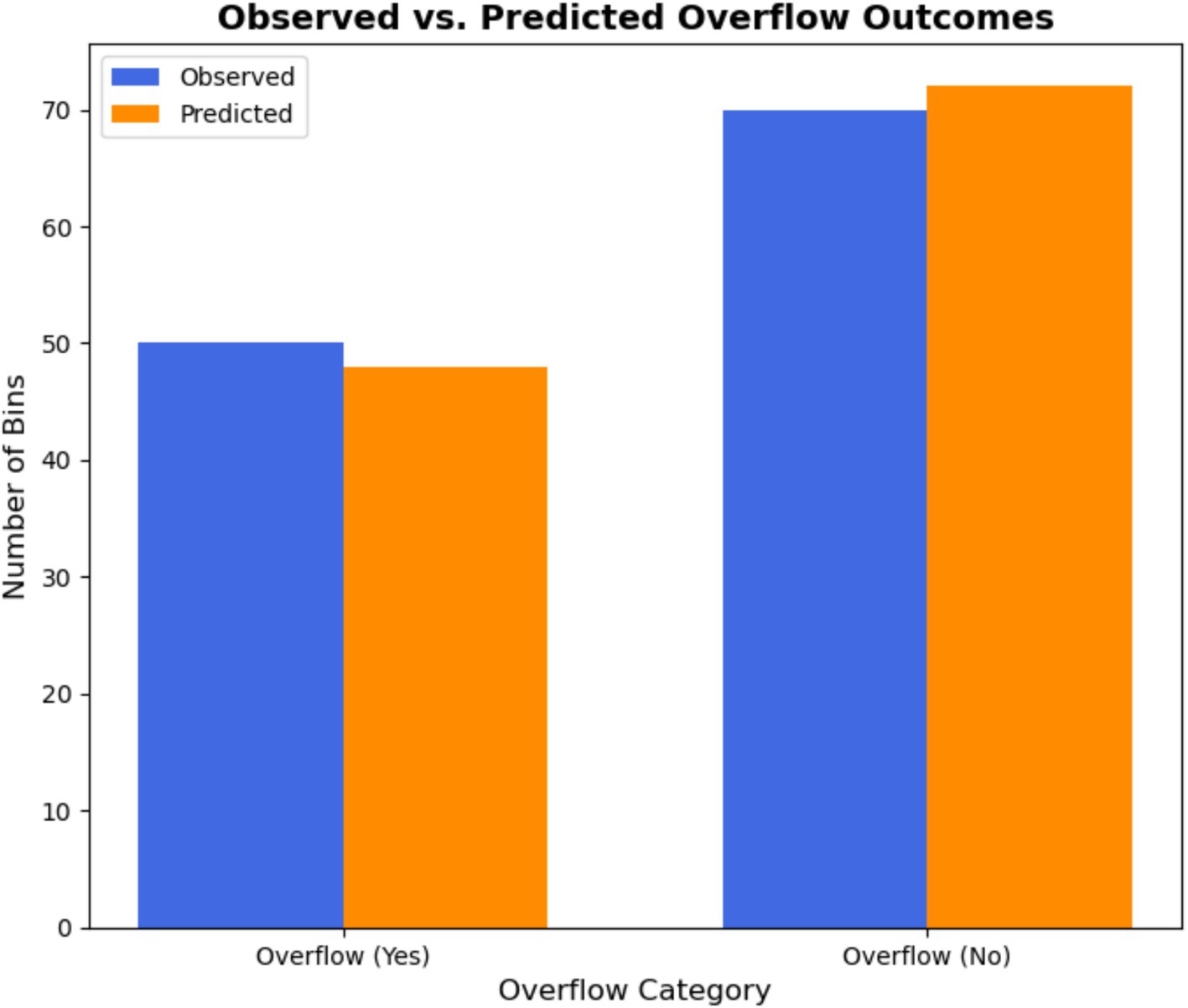
Statistical tests were carried out to ensure that the findings were reliable. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test comparing overflow incidents across static and smart models revealed a significant difference (), indicating that the observed reductions were not caused by random variation. A Chi-square test showed a significant correlation between anticipated and observed overflow labels, indicating the AI model’s predictive validity. The detailed results of these tests are summarized in Table 8. As shown in Figure 8, the predicted overflow closely aligns with observed outcomes across the simulation period. Figure 9 depicts the performance of overflow classification by comparing the number of bins predicted to overflow with actual observations. The model correctly recognizes both overflow and non-overflow bins, with small differences between predicted and observed numbers. This agreement strengthens the validity of threshold-based classification and promotes the use of predictive analytics in operational planning.
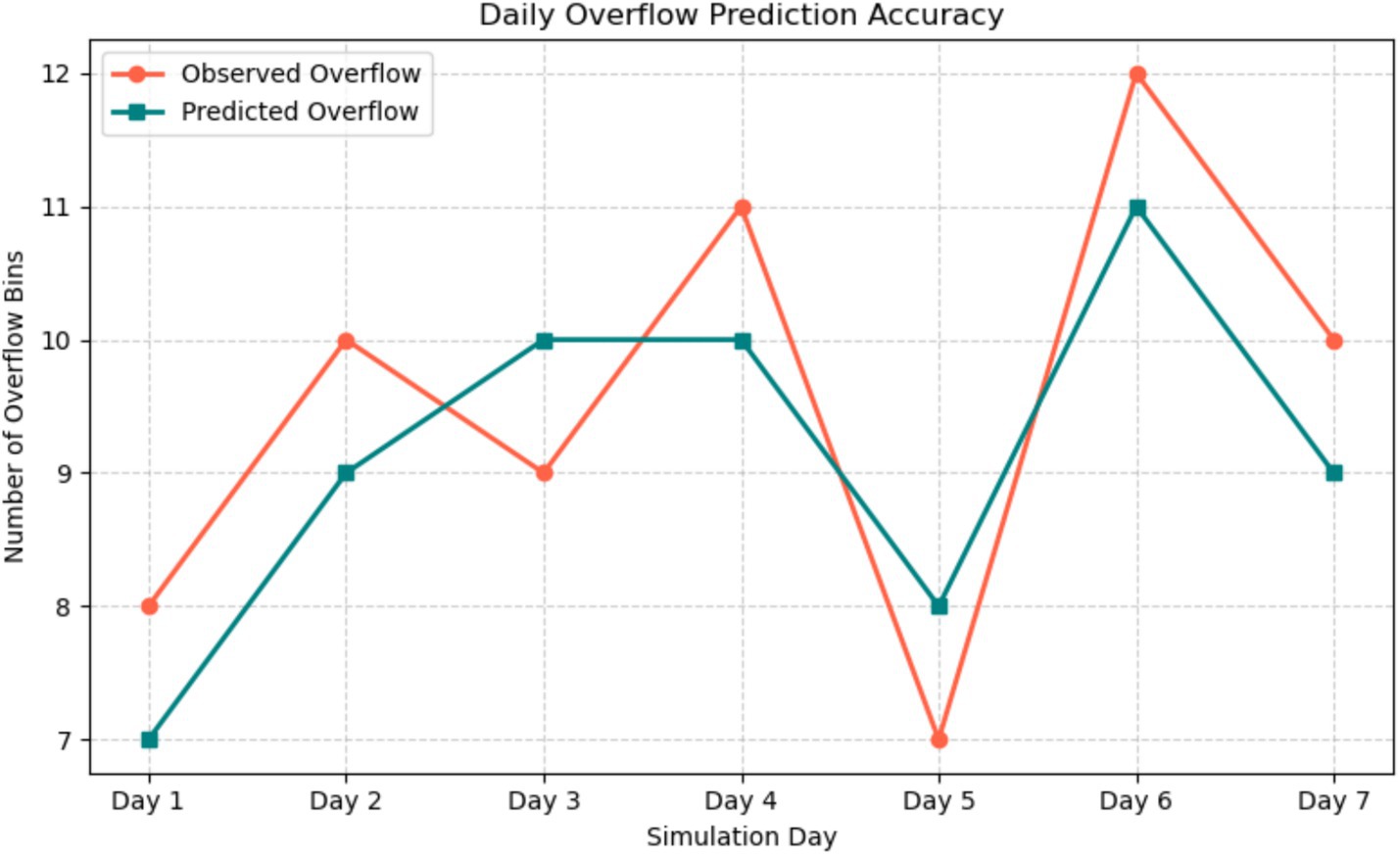
Figure 8. Daily comparison of observed and expected overflow incidents throughout a 7-day simulation period.
These statistical validations underscore the proposed framework’s dependability and scalability. The following section explores its compatibility with Industry 4.0 capabilities, situating the findings within the evolving paradigm of digitally enabled urban systems.
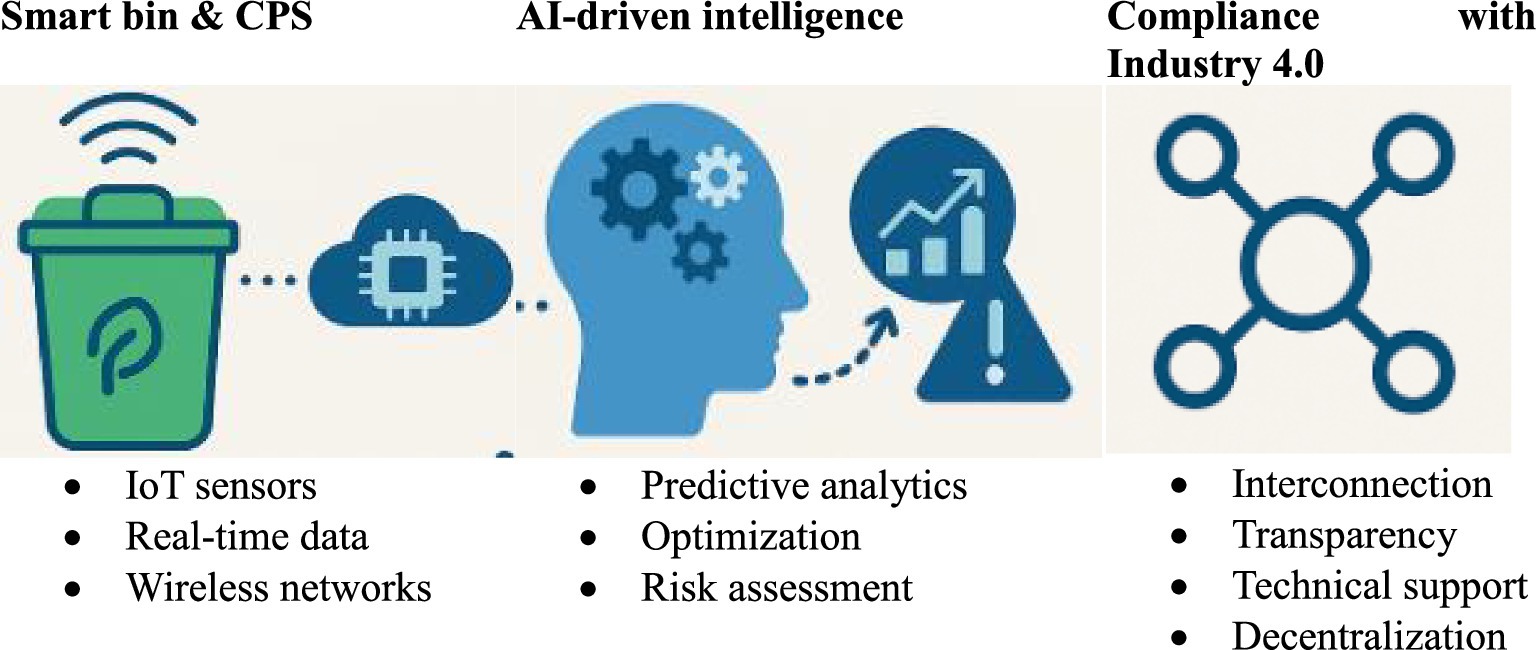
7 Industry 4.0 integration for smart waste management
Intelligent technologies like IoT, AI, CPS, and real-time analytics have transformed traditional urban services with the introduction of Industry 4.0. Waste management is a critical pillar of urban sustainability and is undergoing a paradigm shift toward data-driven, predictive technologies aligned with Industry 4.0 objectives. This section describes the ways in which the suggested AI-IoT-based smart bin monitoring framework supports smarter, more resilient urban settings and is consistent with the fundamental ideas of Industry 4.0.
7.1 Smart bins and cyber-physical systems (CPS)
Industry 4.0 relies heavily on CPS, which allow machines to interface with digital platforms and with one other. In the proposed framework, smart bins function as cyber-physical assets equipped with sensors that monitor fill levels, temperature, and overflow risk in real time. This IoT-enabled physical layer continuously streams data to a cloud-based analytics engine, enabling real-time decision-making. A centralized processing unit receives data from each bin, which acts as a node in a decentralized sensor network, using wireless networks (such as LPWAN, 4G, and 5G). The three main markers of a successful CPS-based smart city system-autonomy, transparency, and scalability are improved by this framework (Rajput and Singh, 2020). A key component of CPS in Industry 4.0 systems, closed-loop feedback control is made possible by the interplay of the physical environment (waste accumulation), digital infrastructure (data processing and AI algorithms), and human interface (municipal operators) (Lee et al., 2015). This continuous feedback loop between physical conditions, digital analytics, and human decision-makers exemplifies the core principles of CPS in Industry 4.0.
7.2 AI-driven intelligence and predictive analytics
The development of Industry 4.0 relies heavily on artificial intelligence (AI), which gives systems the ability to learn from data, forecast results, and suggest the best course of action. Our approach uses historical fill level data and supervised machine learning, specifically XGBoost classification, to predict bin overflow risk. Proactive scheduling, overflow incident reduction, and collection route optimization are made possible by this method. A further layer of structural intelligence is added by the incorporation of graph theory, which models bin interactions and finds priority nodes based on centrality. When these two elements are combined, static waste systems become self-learning, adaptive infrastructures that change based on usage patterns.
In this system, predictive analytics also makes it easier to:
• Forecasting load by zone.
• Prioritization based on risk.
• High-density bin clustering.
• Rerouting possibilities in real time (future extension).
According to Industry 4.0 paradigms, data-driven automation minimizes environmental impact, enhances operational efficiency, and reduces manual intervention-reflecting the core promises of AI in Industry 4.0: automation, intelligence, and sustainability (Wamba et al., 2017).
7.3 Compliance with Industry 4.0 objectives
The four Industry 4.0 design concepts are directly aligned with the proposed framework:
• Interconnection: Made possible by wireless data transfer between the central AI model and smart bins.
• Information transparency: Guaranteed by stakeholder-accessible predictive insights and visual analytics (heatmaps, graphs).
• Technical support: By predicting high-risk bins and suggesting intervention zones, AI supports human decision-making.
• Decentralized decisions: Independent bin-level status reporting and risk assessment are made possible by the distributed design of the system.
Thus, in addition to serving as a monitoring tool, the smart waste system facilitates digital transformation, thereby advancing the long-term objectives of sustainable development, smart governance, and the circular economy. This integration exemplifies how Industry 4.0 can transform public services by embedding intelligence, adaptability, and sustainability into core municipal operations (Lasi et al., 2014). The key components of Industry 4.0 integration in the proposed smart waste management system are summarized in Figure 10.
8 Enhancements to the proposed framework
This section presents a suite of enhancements that address practical implementation, comparative benchmarking, and policy scalability, reinforcing the applicability and transformative potential of the proposed AI-IoT-enabled waste management system. Digital solutions must not only function effectively in simulations but also provide quantifiable socio-economic advantages, outperform current systems, and comply with public infrastructure policies as urban centers transition to Industry 4.0 and Smart City paradigms.
8.1 Cost–benefit evaluation of AI-IoT integration
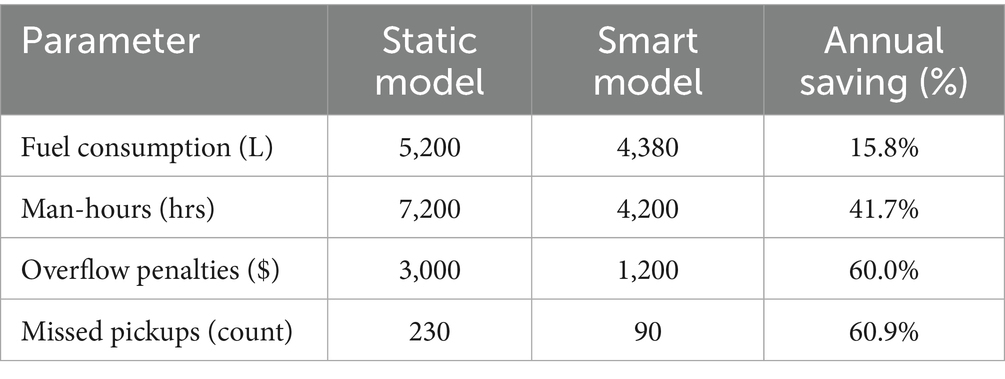
The observable financial and operational advantages of intelligent systems are among the strongest justifications for their adoption. To do this, we compared our AI-enabled system with traditional static waste collecting methods using a simulation-based cost–benefit analysis. Fuel usage, labor hours, fines for overflow, and missing pickups are examples of key performance indicators. Table 9 provides specifics on the expected yearly savings obtained by switching from a static scheduling system to the suggested smart monitoring framework.
The results show that smart solutions significantly cut down on operational waste and inefficiency. Fuel consumption fell by more than 15% annually, which resulted in lower greenhouse gas emissions and financial savings. The 41.7% reduction in labor hours supports the case for operational streamlining, and the significant 60% decrease in overflow penalties indicates better service delivery and regulatory compliance. These findings align with prior research highlighting the environmental and economic benefits of adopting smart waste technologies (Batty et al., 2012).
8.2 Comparative review of existing methods
To put our approach’s uniqueness into perspective, we conducted a comparative analysis of current smart waste research methodologies. This makes it easier to compare our model to earlier attempts and highlights the degree of integration and optimization expertise of our contribution. The strategies presented in Table 10 show a distinct move toward real-time optimization and predictive analytics in smart waste systems as compared to previous approaches.
Recent studies have demonstrated the expanding use of smart technologies in waste management, particularly in areas such as AI-driven prediction, IoT-enabled monitoring, and optimization algorithms (Fang et al., 2023). However, many of these approaches rely on static optimization techniques or limited data streams. In contrast, the proposed framework in this study integrates AI-based overflow prediction (XGBoost), graph-theoretic routing, and priority-based flow optimization using simulated smart bin data. This combination offers a more comprehensive and scalable solution aligned with Industry 4.0 principles by enabling both predictive accuracy and structural decision-making.
8.3 Recommendations for policy integration
The widespread implementation of smart waste frameworks in urban environments requires strong institutional and governance frameworks to facilitate technological innovation. The following are our multi-level policy recommendations:
• The installation of smart bins with overflow sensors ought to be required by municipalities in densely populated urban areas.
• Real-time dashboards that are open to the public can speed up reaction times, promote citizen participation, and increase transparency.
• Waste contractors should be incentivized through tax credits or performance-based bonuses to adopt AI-driven routing systems.
These policy recommendations support the digital transformation of waste management in alignment with smart city goals. By fostering public–private collaboration and institutional accountability, they ensure that technological innovation translates into sustainable urban outcomes. Collectively, these enhancements demonstrate that the suggested framework is more than just a theoretical idea; rather, it is a scalable, policy-ready solution that uses graph-theoretic intelligence, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics to speed up the digital transformation of urban waste systems.
9 Discussion
9.1 Effectiveness of the proposed framework
The proposed AI-IoT-graph framework demonstrates significant performance improvements over conventional static scheduling systems, confirming its suitability for next-generation urban waste management. With an accuracy of 94.1% and a recall of 95.8%, the machine learning model (XGBoost) demonstrated a high level of predictive performance, indicating its ability to accurately identify bin overflow problems. Pre-emptive collection planning and resource allocation depend on these prognostic insights. Persistent high-risk clusters were identified by the heatmap-based spatial analysis, especially in Zones A and B, where overflow events were more common. With the use of this geographic data, municipalities can substitute responsive methods that are in line with actual waste creation patterns for strict, time-based collection plans by enabling dynamic routing based on real-time risk levels. Graph-theoretic analysis identified critical nodes such as bins B03 and B22, which exhibited high centrality and frequent overflow risk. Because of their high degree of centrality and frequent overflow risk, these bins serve as structural bottlenecks in the network of collections. To reduce cascading inefficiencies throughout the system, their prioritization is crucial. Operationally, the intelligent system beat the static model in every major metric: overflow events were cut in half, missed pickups decreased by 72.7%, and bin fill-level at pickup increased from 62 to 84%. In addition to lowering environmental risks, these efficiency improvements maximize logistical resources including labor deployment and fuel use. Crucially, the report emphasizes how this framework is strategically aligned with Industry 4.0 principles. The three main tenets of smart infrastructure-automation, decentralization, and system-wide intelligence are embodied in the convergence of graph-theoretic optimization, IoT-enabled sensing, and AI-driven forecasts. The system’s modular design enables expansion beyond waste management into other urban domains such as water resource management, energy distribution, and traffic optimization. As such, the proposed framework serves not only as a technological innovation but also as a systemic enabler of data-driven urban governance. By bridging the gap between fragmented waste operations and integrated smart city systems, it contributes meaningfully to both digital transformation and environmental sustainability. These results affirm the framework’s theoretical robustness and practical viability for real-world urban infrastructure deployment.
9.2 Comparative discussion
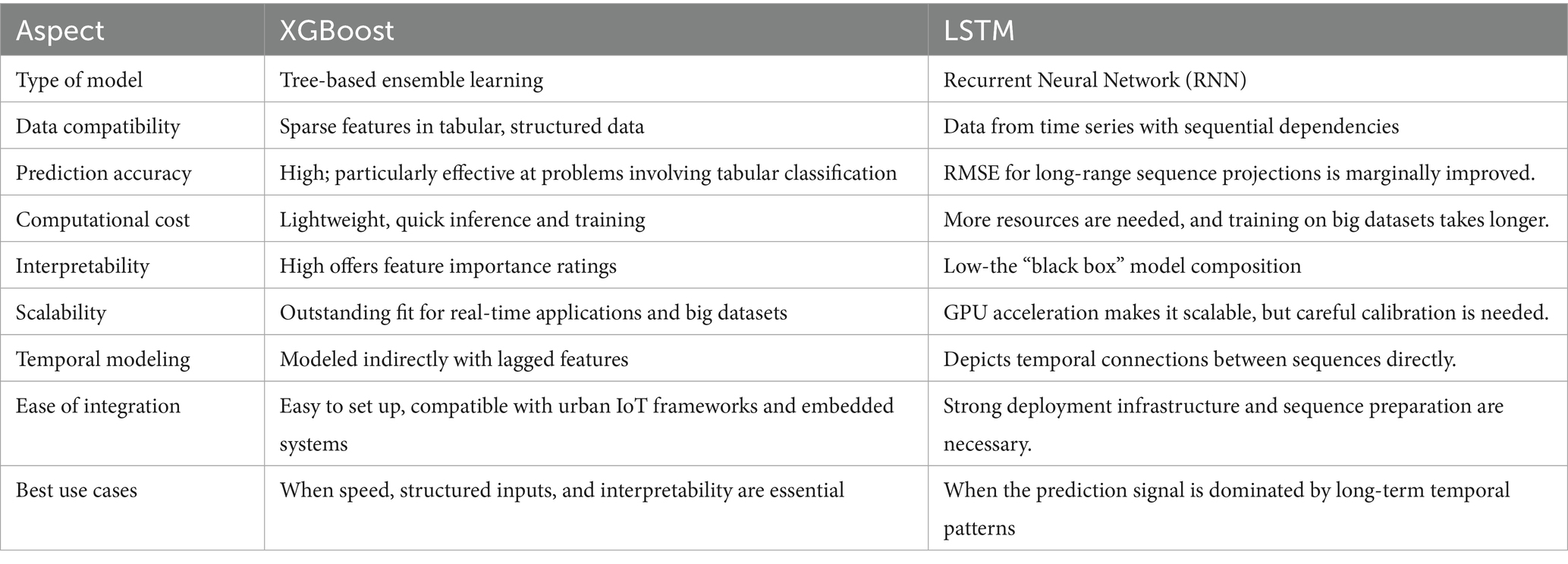
In smart waste monitoring tasks, deep learning models such as LSTM networks offer appealing advantages, even if XGBoost showed remarkable performance in terms of recall, precision, and general resilience. For fill-level progression modeling over long periods of time, LSTM models are perfect because they are especially good at capturing temporal dynamics and long-range dependencies in time-series data. However, they are computationally intensive, often require larger training datasets, and lack the interpretability of tree-based models like XGBoost. On the other hand, XGBoost offers transparent feature importance rankings, efficient gradient-boosting, and the capacity to manage sparse input and nonlinear interactions. This makes it an invaluable tool for smart city stakeholders who want automated judgments to be understandable. According to earlier research, LSTM models may marginally outperform tree-based models in RMSE under optimal data settings, but this advantage frequently comes at the expense of interpretability and training complexity (Ahmed S. et al., 2022). Because our dataset was structured and had a moderate temporal scale, XGBoost was able to achieve a realistic balance between scalability, accuracy, and practicality. Table 11 provides a summary of the main distinctions between XGBoost and LSTM for overflow prediction.
While LSTM and other deep learning models provide better temporal modeling, they are less appropriate for real-time, resource-constrained municipal deployments due to their high computing requirements and low interpretability. On the other hand, XGBoost is an appealing option for AI-driven urban waste monitoring since it achieves a realistic balance between accuracy, transparency, and deployment efficiency. This comparative evaluation underscores the importance of aligning algorithm selection with operational feasibility, stakeholder trust, and predictive performance in critical infrastructure applications.
9.3 Impact assessment
The improvements demonstrated by the proposed system yield tangible socio-environmental benefits. A 50% reduction in weekly overflow events mitigates public health risks such as vector-borne infections and unpleasant odors, while also curbing greenhouse gas emissions from decomposing waste. Likewise, the 35.5% increase in bin utilization ensures optimal resource deployment, reducing unnecessary collection trips, and associated fuel consumption. Based on standard municipal fleet conversion factors, the observed 15.5% decrease in fuel usage corresponds to an estimated annual reduction of approximately 2.3 tonnes of emissions. These operational gains underscore that the framework is not merely a technological enhancement but a strategic enabler of sustainable urban waste services, directly supporting SDG 11 and SDG 12. The integration of predictive analytics with operational efficiency reinforces its potential for real-world deployment and policy alignment.
10 Limitations
Notwithstanding the encouraging results, this study has several limitations that present opportunities for future enhancement:
• Simulated data assumptions: The analysis was based on simulated smart bin data. While the simulation was carefully designed to reflect realistic urban waste dynamics, it may not fully capture the complexity and variability of real-world waste generation behaviors.
• Static zone configurations: The city was divided into predefined zones (A–E) without accounting for dynamic urban factors such as mixed land use, population mobility, or socioeconomic diversity-all of which can significantly influence waste generation patterns.
• Limited predictive features: The overflow prediction model relied solely on historical fill levels. The exclusion of contextual variables such as holidays, public events, and seasonal fluctuations may have constrained the model’s predictive robustness.
• Simplified graph structure: The graph-theoretic model generated edges primarily based on spatial proximity. However, real-world urban routing involves additional constraints such as one-way streets, traffic congestion, and accessibility barriers, which were not incorporated into the current model.
• Lack of real-time IoT integration: Although the framework was designed with IoT compatibility, it does not yet incorporate live sensor data from deployed bins. Real-time data integration is essential for enabling responsive decision-making in operational environments.
Addressing these limitations in future work will enhance the framework’s realism, scalability, and readiness for deployment in complex urban settings.
11 Future work
Future research can address the current limitations and further enhance the proposed framework through the following directions:
• Real-world deployment: Implement the system in a pilot smart city project to validate prediction accuracy, monitor real-time data streams, and evaluate performance under dynamic urban conditions.
• Expanded predictive inputs: Incorporate additional contextual variables-such as traffic patterns, weather forecasts, public events, and demographic data-to improve model accuracy and adaptability.
• Adaptive zoning mechanisms: Develop dynamic zoning strategies using clustering algorithms or geospatial analytics to redefine service zones based on real-time fill trends and urban mobility patterns.
• Advanced graph-based optimization: Extend the graph-theoretic model to include multi-layered constraints such as depot locations, time windows, vehicle capacities, and road hierarchies for more realistic route planning.
• Integration with urban management platforms: Connect the framework with broader smart city ecosystems to enable cross-domain insights across sectors like energy, transportation, and water management.
• Scalability and economic feasibility: Conduct a comprehensive analysis of the system’s scalability, operational costs, and maintenance requirements across cities with varying resource capacities.
By addressing these areas, the proposed AI-IoT-graph framework can evolve into a robust, scalable decision-support system for resilient, data-driven, and circular waste management in smart urban environments.
12 Conclusion
This study presents a novel decision-intelligent framework that integrates machine learning, IoT simulations, and graph-theoretic modeling to optimize municipal solid waste management. By leveraging AI (XGBoost) for accurate bin overflow prediction, spatial heatmap analytics for risk zone identification, and graph-based clustering and centrality for dynamic routing, the framework introduces a transformative approach to waste logistics. Unlike traditional systems that rely on fixed schedules or limited heuristics, the proposed model enables adaptive, data-driven decision-making aligned with Industry 4.0 principles-namely automation, real-time analytics, and cyber-physical integration. The observed improvements in service reliability, resource utilization, and operational cost underscore the viability of intelligent waste management as a foundational element of smart city infrastructure. Beyond its technical contributions, the framework also offers a policy-relevant architecture with clear pathways for integration into municipal systems. Its modular and scalable design opens promising avenues for future research, including uncertainty-aware scheduling, real-time IoT deployment, and multi-layer analytics that incorporate behavioral, environmental, and traffic data. Ultimately, this study lays a robust foundation for transitioning from reactive waste management to intelligent, proactive systems that advance the goals of the circular economy and sustainable urban living.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
RA: Writing – original draft. AP: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The article processing fee for open access is funded by the Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, TamilNadu, India.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abba, S., and Light, C. I. (2020). IoT-based framework for smart waste monitoring and control system: a case study for smart cities. Eng. Proc. 2:90. doi: 10.3390/ecsa-7-08224
Agrawal, S., Oza, P., Patel, S., Oza, H., Sharma, Y., and Patel, T. (2025). IoT-enabled smart waste management: applications, adoption barriers, and mitigation strategies in the Indian scenario. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 27, 2099–2118. doi: 10.1007/s10163-025-02248-x
Ahmed, A. K. A., Ibraheem, A. M., and Abd-Ellah, M. K. (2022). Forecasting of municipal solid waste multi-classification by using time-series deep learning depending on the living standard. Res. Eng. 16:100655. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100655
Ahmed, S., Mubarak, S., Du, J. T., and Wibowo, S. (2022). Forecasting the status of municipal waste in smart bins using deep learning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:16798. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416798
Alaoui, M., Belhiah, M., and Ziti, S. (2025). Smart waste management systems using IoT: a systematic literature review. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 16, 315–324. doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2025.0160415
Alsabt, R., Alkhaldi, W., Adenle, Y. A., and Alshuwaikhat, H. M. (2024). Optimizing waste management strategies through artificial intelligence and machine learning-an economic and environmental impact study. Clean. Waste Sys. 8:100158. doi: 10.1016/j.clwas.2024.100158
Andeobu, L., Wibowo, S., and Grandhi, S. (2022). Artificial intelligence applications for sustainable solid waste management practices in Australia: a systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 834:155389. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155389
Angry Nerds (2024). The future of internet of things in smart cities: Barcelona case study. Poland: Angry Nerds.
Ardiansyah, S. Y., and Maryono, M. (2018). Spatial statistics for mapping solid waste generation mapping in tembalang, Semarang city. Geoplanning 5, 163–174. doi: 10.14710/geoplanning.5.1.163-174
Balaga, O. N. R. (2020). A graph-theoretic model for optimal collection of municipal solid waste using clustering method. Middle East 400:545.
Batty, M., Axhausen, K. W., Giannotti, F., Pozdnoukhov, A., Bazzani, A., Wachowicz, M., et al. (2012). Smart cities of the future. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 214, 481–518. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2012-01703-3
Belhiah, M., and El Aboudi, M. (2025). An IoT-based sensor mesh network architecture for waste management in smart cities. J. Commun. 20:165. doi: 10.12720/jcm.20.2.153-165
Billal, M. M., and Kumar, A. (2025). Forecasting residential and nonresidential solid waste generation, disposal, and diversion using three machine learning approaches. Biofuels Bioprod. Bior. 7:10. doi: 10.1002/bbb.70010
Borase, A. A., Bokil, S., and Sakhare, V. (2024). Geospatial solution for sustainable waste management: a case study. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 9:218. doi: 10.1007/s41062-024-01539-w
Central Pollution Control Board (2021). Annual report on implementation of solid waste management rules 2020–2021. India: Central Pollution Control Board.
Chakraborty, A. (2022). “Evolution of the internet of things and fundamentals of human-machine interaction” in Human-machine interaction and IoT applications for a smarter world. eds. G. Nishu and K. G. Srinivasa (Boca Raton: CRC Press), 3–14.
Chen, T., and Guestrin, C. (2016). Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 785–794). San Francisco: ACM
Cui, J., Yan, Y., Jiang, L., Zhang, L., and Xu, W. (2025). Research on optimization of waste sorting and transportation network in smart cities based on garbage volume prediction. Disc. Comp. 28, 1–22. doi: 10.1007/s10791-025-09537-x
Dawar, K., Srivastava, A., Singal, M., Dhyani, N., and Rastogi, S. (2025). A systematic literature review on municipal solid waste management using machine learning and deep learning. Artif. Intell. Rev. 58:183. doi: 10.1007/s10462-025-11196-9
European Environment Agency (2024a). Management of used and waste textiles in Europe’s circular economy. Denmark: European Environment Agency.
European Environment Agency (2024b). Diversion of waste from landfill in Europe. Denmark: European Environment Agency.
Fang, B., Yu, J., Chen, Z., Osman, A. I., Farghali, M., Ihara, I., et al. (2023). Artificial intelligence for waste management in smart cities: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 21, 1959–1989. doi: 10.1007/s10311-023-01604-3
Fatorachian, H., and Pawar, K. (2025). Waste efficiency in cold supply chains through industry 4.0-enabled digitalisation. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 18:2461564. doi: 10.1080/19397038.2025.2461564
Ferrão, C. C., Moraes, J. A. R., Fava, L. P., Furtado, J. C., Machado, E., Rodrigues, A., et al. (2024). Optimizing routes of municipal waste collection: an application algorithm. Manag. Environ. Qual. 35, 965–985. doi: 10.1108/MEQ-08-2023-0267
Gaikwad, P. Y., Jawanjal, T. M., Munot, T. R., Bhusari, T. D., and Muddalkar, S. S. (2025). Intelligent waste management: leveraging AI, IoT, and deep learning for sustainability. Int. Res. J. Modern. Eng. Technol. Sci. 7, 122–128.
Gaur, T. S., Yadav, V., Prakash, S., and Panwar, A. (2025). Integration of industry 4.0 and circular economy for sustainable E-waste management. Manag. Environ. Qual. 36, 1304–1325. doi: 10.1108/MEQ-07-2024-0277
Gilli, M., Mancinelli, S., Nicolli, F., Gilli, M., Mancinelli, S., and Nicolli, F. (2018). “Do motivations crowd in recycling policies? Evidence from Italy” in Household waste management: some insights from behavioural economics. eds. M. Gilli, S. Mancinelli, and F. Nicolli (New York: Springer International Publishing), 57–80.
GIZ India (2023). Building an inclusive and circular textile waste value chain in India. Germany: Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH.
Guna, J., Horvat, K. P., and Podjed, D. (2022). People-centred development of a smart waste bin. Sensors 22:1288. doi: 10.3390/s22031288
Gupta, S., Prathipati, B., Dangayach, G. S., Rao, P. N., and Jagtap, S. (2022). Development of a structural model for the adoption of industry 4.0 enabled sustainable operations for operational excellence. Sustainability 14:11103. doi: 10.3390/su141711103
Härri, A., and Levänen, J. (2024). “It should be much faster fashion”—textile industry stakeholders’ perceptions of a just circular transition in Tamil Nadu, India. Discover Sustain. 5:39. doi: 10.1007/s43621-024-00211-8
Idoko, D. O., Imarenakhue, W. U., Olade, A. D., Oppong, R. A., Bah, M. B., Elue, H. C., et al. (2024). Development of smart waste management technologies using IoT solutions for environmental sustainability in urban infrastructure planning. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 9, 1–8. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.14353675
Joshi, R., and Ahmed, S. (2016). Status and challenges of municipal solid waste management in India: a review. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2:1139434. doi: 10.1080/23311843.2016.1139434
Kodihal, S., and Akhtar, M. P. (2024). GIS based multi-criteria decision making to identify regional groundwater potential zones: a critical review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 10:61. doi: 10.1007/s40899-024-01080-9
Kuhaneswaran, B., Chamanee, G., and Kumara, B. T. G. S. (2025). A comprehensive review on the integration of geographic information systems and artificial intelligence for landfill site selection: a systematic mapping perspective. Waste Manag. Res. 43, 137–159. doi: 10.1177/0734242X241237100
Kumar, S., Kaur, M., and Rakesh, N. (2021). IoT-based smart waste management system. In Innovations in information and communication technologies (IICT-2020) proceedings of international conference on ICRIHE-2020 (pp. 133–139). Delhi, India: Springer International Publishing.
Lakhouit, A., Shaban, M., Alatawi, A., Abbas, S. Y., Asiri, E., Al Juhni, T., et al. (2023). Machine-learning approaches in geo-environmental engineering: exploring smart solid waste management. J. Environ. Manag. 330:117174. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117174
Lasi, H., Fettke, P., Kemper, H. G., Feld, T., and Hoffmann, M. (2014). Industry 4.0. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 6, 239–242. doi: 10.1007/s12599-014-0334-4
Lee, J., Bagheri, B., and Kao, H. A. (2015). A cyber-physical systems architecture for industry 4.0-based manufacturing systems. Manufact. Let. 3, 18–23. doi: 10.1016/j.mfglet.2014.12.001
Li, W., Wang, P., Xu, Y., Pan, L., Nie, C., and Yang, B. (2024). Multi-objective optimization of municipal solid waste collection based on adaptive large neighborhood search. Electronics 14:103. doi: 10.3390/electronics14010103
Liu, X., Zhi, W., and Akhundzada, A. (2025). Enhancing performance prediction of municipal solid waste generation: a strategic management. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1553121. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1553121
Madakam, S., and Ramachandran, R. (2015). Barcelona smart city: the heaven on earth (internet of things: technological god). ZTE Commun. 13:3.
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (2023). Smart cities Mission: CSCAF 2.0 booklet. Government of India. India: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs and National Institute of Urban Affairs (2022). ClimateSmart cities assessment framework (CSCAF) 3.0: technical document. India: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs & National Institute of Urban Affairs.
Ministry of the Environment (2023). Waste management in Japan: rules and figures. Japan: Ministry of the Environment.
Mondal, S., Parveen, M. T., Alam, A., Rukhsana, I., and Zhran, M. (2024). Future site suitability for urban waste management in English bazar and old Malda municipalities, West Bengal: a geospatial and machine learning approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 13:388. doi: 10.3390/ijgi13110388
Mora Murillo, M. F., Mora Murillo, W. A., Orbea Hinojosa, L. X., Lastre Aleaga, A. M., Cevallos Uve, G. E., Jorba Cuscó, M., et al. (2021). An efficient route design for solid waste collection using graph theory and the algorithm of the traveling agent in dynamic programming. Environ. Monit. Assess. 193:288. doi: 10.1007/s10661-021-09003-3
Mudannayake, O., Rathnayake, D., Herath, J. D., Fernando, D. K., and Fernando, M. (2022). Exploring machine learning and deep learning approaches for multi-step forecasting in municipal solid waste generation. IEEE Access 10, 122570–122585. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3221941
Ogbolumani, O. A., and Adekoya, M. (2025). Intelligent waste management optimization through machine learning analytics. J. Sci. Res. Rev. 2, 7–26. doi: 10.70882/josrar.2025.v2i1.25
Rajput, S., and Singh, S. P. (2020). Industry 4.0 model for circular economy and cleaner production. J. Clean. Prod. 277:123853. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123853
Rautela, K. S., Goyal, M. K., and Surampalli, R. Y. (2025). AI and machine learning for optimizing waste management and reducing air pollution. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 29:04025014. doi: 10.1061/JHTRBP.HZENG-1483
Reddy, C. M., and Asadi, S. S. (2024). “Solid waste disposal site selection using geospatial technology: a comprehensive study” in International conference on advances in environmental sustainability, energy and earth science. eds. P. Pathak, S. Ilyas, R. R. Srivastava, J. Dar, and S. Kothandaraman (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland), 187–200.
Singh, A. J. (2021). Role of GIS in urban planning in context of Indian smart cities. IJAR 7, 19–21.
Sinthiya, N. J., Chowdhury, T. A., and Haque, A. K. M. B. (2022). “Artificial intelligence based smart waste management—a systematic review” in Computational intelligence techniques for green smart cities. eds. M. Lahby, A. Al-Fuqaha, and Y. Maleh (Cham: Springer), 67–92.
Soni, A., Gupta, S. K., Rajamohan, N., and Yusuf, M. (2025). Waste-to-energy technologies: a sustainable pathway for resource recovery and materials management. Mater. Adv. 6, 4598–4622. doi: 10.1039/D5MA00449G
Spiridonova, E. (2025). “Waste 4.0”: transforming waste management and emissions reduction in the age of industry 4.0. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/387668420 (Accessed June 06, 2025).
UN-Habitat (2024). World cities report 2024: Cities and climate action. Nairobi, Kenya: United Nations Human Settlements Programme.
Vaisharma, V. (2023). Time series forecasting with XGBoost. Available online at: https://github.com/vaisharma16/Time-Series-Forecasting-with-XGBoost (Accessed July 03, 2025).
Vikram, L., and Bhardwaj, M. (2023). Assessment of urban wastelands using GIS and IoT as tools for spatial data analysis. Curr. World Environ. 18, 1–10. doi: 10.12944/CWE.18.2.35
Vilchez-Torres, M., Ramos Castillo, N. L., and Bobadilla Asto, L. E. (2023). Optimization of solid waste collection routes using graph theory and linear program. LACCEI 1:925. doi: 10.18687/LACCEI2023.1.1.925
Wamba, S. F., Gunasekaran, A., Akter, S., Ren, S. J. F., Dubey, R., and Childe, S. J. (2017). Big data analytics and firm performance: effects of dynamic capabilities. J. Bus. Res. 70, 356–365. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.08.009
World Bank (2018). What a waste 2.0: A global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050. Washington DC: World Bank Publications.
Zhang, Z., Chen, Z., Zhang, J., Liu, Y., Chen, L., Yang, M., et al. (2024). Municipal solid waste management challenges in developing regions: a comprehensive review and future perspectives for Asia and Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 930:172794. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172794
Zhang, J., Hu, R., Wang, Y. J., Yang, Y. Y., and Qian, B. (2023) Deep reinforcement learning for solving multi-objective vehicle routing problem. In International conference on intelligent computing (pp. 146–155). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
Glossary
AI - Artificial Intelligence
IoT - Internet of Things
MSW - Municipal Solid Waste
SWMS - Smart Waste Management Systems
XGBoost - Extreme Gradient Boosting
LSTM - Long Short-Term Memory
SDG 11 - Sustainable Cities and Communities
SDGs - Sustainable Development Goals
CSCAF - Climate Smart Cities Assessment Framework
ANP - Analytic Network Process
DL - Deep Learning
RMSE - Root Mean Square Error
AUC-ROC - Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve
NB-IoT - Narrowband Internet of Things
CPS - Cyber-Physical Systems
RNN - Recurrent Neural Network
RF - Random Forest
GIS - Geographic Information Systems
EU - European Union
SVMs - Support Vector Machines
CNNs - Convolutional Neural Networks
ANNs - Artificial Neural Networks
MLR - Multiple Linear Regression
YOLO - You Only Look Once
MAPE - Mean Absolute Percentage Error
AHP - Analytic Hierarchy Process
GRU - Gated Recurrent Unit
ML - Machine Learning
GPS - Global Positioning System
LPWAN - Low-Power Wide-Area Network
LoRaWAN - Long Range Wide Area Network
VRP - Vehicle Routing Problem
GPU - Graphics Processing Unit
SDG 12 - Responsible Consumption and Production
Keywords: smart waste management, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, overflow prediction, graph-theoretic optimization, Industry 4.0, urban waste logistics
Citation: Anitha R and Parthiban A (2025) AI-IoT-graph synergy for smart waste management: a scalable framework for predictive, resilient, and sustainable urban systems. Front. Sustain. 6:1675021. doi: 10.3389/frsus.2025.1675021
Edited by:
Elena Cristina Rada, University of Insubria, ItalyReviewed by:
Ramona Giurea, Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, RomaniaKishori Kasat, Symbiosis School for Liberal Arts, India
Copyright © 2025 Anitha and Parthiban. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: A. Parthiban, cGFydGhpYmFuLmFAdml0LmFjLmlu
 R. Anitha
R. Anitha A. Parthiban
A. Parthiban