Abstract
With the acceleration of urbanization and industrial upgrading in China, vacant industrial buildings in many third-tier cities have gradually emerged as significant resources, playing a crucial role in urban carbon reduction and cultural continuity. This study identified the influencing factors using the fuzzy hierarchical analysis method and ranked them in descending order: market, sustainability, economy, building physics, legal policy, location environment, and public interest. Through expert discussions, it was further clarified that: (1) the adaptive reuse of industrial buildings should prioritize functional transformation, and an accurate customer profile is an important basis for decision-making; (2) green building renovations can leverage government policy benefits while enhancing the competitiveness of the hotel market; and (3) policies and the local environment are not the primary influencing factors in third-tier cities in northern China—which contrasts with findings from previous studies. The research results provide a valuable reference for the adaptive reuse of industrial buildings in third-tier cities of developing countries and offer stakeholders better decision-making insights regarding transformation functions.
1 Introduction
In the past decade, rapid urbanization and industrial upgrading in developing countries have led to the elimination of many original industrial buildings in cities, while some have been integrated into urban development. Consequently, the vacancy rate of industrial buildings has reached an unprecedented level, with estimates indicating that China has approximately 3 billion square meters of idle industrial space (CCID, 2019). On the other hand, the demand for hotels has gradually increased after COVID-19. As China’s economy continues to develop, the number of tourists has risen significantly, leading to a growing demand for diverse hotel options. According to relevant reports, in 2023, the number of domestic tourists in China is projected to reach 675.54 billion USD, an increase of 2.36 billion compared to the same period last year. Additionally, the total expenditure of domestic tourists is expected to reach 0.69 trillion dollars, reflecting a year-on-year increase of 140.3% (The Central Government of the PRC, 2024). With such a substantial influx of tourists, the current hotel bed ratio appears insufficient. Statistics indicate that the ratio of the population to the number of hotel beds in 2019 was 100:2 (China Industry Information, 2019). In comparison, the global average is 100:3.09, indicating room for development (Lair, 2019). Furthermore, economy hotels account for 81.40% of the total, midscale hotels comprise 17.37%, while upscale hotels represent a smaller segment at 1.23% in China (Zero Power Intelligence Group, 2024). Both midscale and upscale hotels exhibit significant growth potential. It is anticipated that the market size of the theme hotel industry will expand to 15.118 billion USD over the next 4 years in China. The housing rental market is expected to serve more than 200 million people, with annual rents exceeding 137.6 billion USD (JLL, 2018). Adaptive reuse (AR) is not only a crucial strategy for achieving the national strategic goal of carbon neutrality (Yu, 2024), but it also plays a significant role in urban regeneration (Liu et al., 2014), Furthermore, adaptive reuse serves as an effective means of preserving the unique cultural characteristics of a city (Huang et al., 2023). Conversely, the demand for hotels and long-term rental apartments in large cities is steadily increasing each year. This creates both market demand and research value in the adaptive reuse of industrial buildings (ARIB) for conversion into hotels and long-term rental apartments.
The ARIB into hotels presents numerous challenges. These buildings are often repurposed into “creative clusters (Tan and Altrock, 2016). Compared to adaptive reuse for museums, cultural and creative centers, and community activity centers, converting industrial buildings into hotels is more complex due to the required functional changes (Ren et al., 2014). Additionally, some industrial buildings must undergo cleaning and safety testing before they can be utilized as hotels, which increases costs and serves as a significant barrier to adaptive reuse (Ihsan and Alshibani, 2018). Furthermore, the operational conditions of the hotel directly influence whether the premises will become vacant again. These conditions include several critical factors, such as site selection, renovation costs, and market competition, all of which collectively determine the hotel’s potential for sustainable operation. Moreover, the ARIB in hotel development offers substantial environmental benefits. Specifically, during urban renewal processes, both new construction and the demolition of old buildings generate significant carbon emissions, exacerbating environmental degradation and climate change impacts. In contrast, ARIB strategies present a sustainable alternative. The renovation and repurposing of buildings represent a relatively low-carbon development approach (Dai and Lai, 2023). ARIB is instrumental in preserving potential industrial architectural heritage and historical memory. ARIB aligns with the policies of industrial transformation in developing countries, reduces construction costs, shortens construction timelines, and enhances social and economic benefits while balancing long-term and short-term interests. In China, there are already a series of supportive policies aimed at transforming the nature of industrial land use and providing favorable conditions for land utilization. Given the expansive nature of industrial buildings, ARIB can transform these spaces into hotels with diverse functionalities, and their unique industrial culture can attract customers (Yang et al., 2012). However, the decision-making process for converting industrial buildings into hotels involves complex advantages and disadvantages, and there is a lack of targeted methodologies applicable to developing countries that integrate multiple disciplines to address practical decision-making challenges.
This study aims to identify the key factors that influence the adoption of ARIB in hotels and to provide decision-making methods suitable for developing countries. It is designed to help stakeholders reasonably estimate the risks and profits associated with ARIB in the hotel sector. The study establishes a model for the transformation of ARIB in hotels through a comprehensive literature review. The Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP) is employed to determine the weights that rank the influencing factors of ARIB in hotels. The key factors identified can serve as a clear and valuable reference for stakeholders involved in refurbishment projects. Additionally, the study offers practical decision-making methods for developers and assists governments in formulating revitalization policies and managing similar projects. Furthermore, it aims to prevent economic losses and the destruction of industrial heritage caused by secondary reconstruction.
2 Literature review
2.1 Research on key influencing factors of industrial building renovation
There are still a significant number of buildings being demolished and redeveloped in China. The average lifespan of a building in China ranges from 25 to 35 years, which is considerably shorter than the intended lifespan of these structures (Wang et al., 2018). ARIB is a direct and effective method for extending the life of buildings, and it is also one of the most efficient strategies for reducing carbon emissions. Therefore, it is practically significant to investigate whether industrial buildings can be converted into accommodation facilities that meet substantial market demand. The key factors influencing ARIB have been extensively studied by scholars worldwide, with Europe and the United States conducting research on ARIB earlier than other regions. The internal factors affecting industrial buildings include the original state of the structure, such as building quality, architectural design, number of floors, floor area, and the presence of pollutants. These factors can pose significant challenges, leading to increased costs and extended construction timelines (Vardopoulos, 2019). According to Bullen and Love, the primary driving forces behind adaptive reuse are life cycle considerations, shifts in building concepts, and government incentives. In the initial stages of adaptive reuse, incentive policies are essential to attract investment and garner public interest (Bullen, 2007). It has been revealed that the primary drivers for adaptive reuse focus on lifecycle issues, changing perceptions of buildings, and governmental incentives. The barriers to reuse include the perception of increased maintenance costs, building regulations, inertia in development criteria, and the inherent risks and uncertainties associated with older building stock (Bullen and Love, 2009; Bullen and Love, 2011). Lanston applied the Adaptive Reuse Potential (ARP) model to assess the adaptive reuse potential of buildings, primarily considering the expected physical lifespan of the building, its current age, and various physical, economic, functional, technical, social, and legal factors. This model further evaluates whether the building has the potential for adaptive reuse (Langston et al., 2007). Wilson points out that the criteria for determining the reusability of applicability encompass five aspects: environment, location, legislation, finance, and market characteristics (Wilson, 2010). Vardopoulos employed the fuzzy DEMATEL method to assess land conservation against urban sprawl and cultural heritage protection (Vardopoulos, 2019). The primary factors considered for suitable reuse include financial, legal, technical, and functional/design aspects (Remoy and van der Voordt, 2014). In the context of Hong Kong, the opportunities and constraints of converting ARIB into residential units were examined with four considerations: planning regulations and government incentives, housing affordability, design and built environment considerations, and outline zoning plan considerations (Kee, 2014). The potential of ARIB in Hong Kong was analyzed, taking into account market needs, developer risks, micro-environment suitability, financial incentives, government guidelines, and regulatory relaxation (Yap, 2014). Tan utilized the Key Success Factors (CSFs) method to identify 33 key factors grouped into eight principal components: sustainability, economics and finance, market dynamics, adaptability, location and neighborhood, cultural and public interests, legal and regulatory matters, and the physical condition of the building (Tan et al., 2018). Considering the context of China, scholars have indicated that external factors such as location conditions, neighborhood characteristics, economic variables, and urban planning are more significant than internal factors. Furthermore, it was noted that policies are a key factor influencing building lifespan (Liu et al., 2014). It was emphasized that the organic integration of architecture, function, aesthetics, economy, and other factors, along with adherence to market demand and customer needs, are crucial for transforming ARIB into homestays (Wang, 2023).
2.2 Literature review factors of adaptive reuse into hotel
2.2.1 Cost and profit
The research on renovating industrial buildings at a low cost has garnered significant attention. Most AR projects typically have shorter construction periods and lower costs compared to demolition and reconstruction projects. However, it is essential to consider not only structural, spatial, equipment, and material changes but also the transformation of public perception. This aspect is vital because when architectural pollution is linked to the building itself, adaptive reuse may necessitate additional investment to shift public attitudes (Teo and Lin, 2011). Furthermore, changes in the plot ratio are a critical factor in the decision-making process for AR, as the potential for increased profitability from a substantial rise in the site plot ratio can significantly influence renovation decisions (Bullen and Love, 2011).
2.2.2 Location and transportation
In the literature on hotel location, the majority of researchers argue that a hotel’s location is the primary factor influencing consumer choice (Mcintosh and Siggs, 2016; Urtasun and Gutiérrez, 2006), Other important determinants include star rating, years since opening, service diversification, ownership, the agglomeration effect, public service infrastructure, road accessibility, subway accessibility, and proximity to tourist sites (Yang et al., 2012). Nevertheless, it is suggested that the significance of hotel location has diminished in contemporary times. Distinctive hotels are compelling enough to attract consumers regardless of their geographical positioning, with some hotels evolving into tourist attractions themselves (Hartesvelt, 2006), This shift is largely due to the increasing demand for experiential accommodations among travelers, who seek more than just a place to sleep (Lim and Endean, 2009). Among social factors, the convenience of public transportation and new energy transportation infrastructure have a significant impact on cultural and creative industrial agglomeration. Location factors play a crucial role in determining the final selection of a business format. Considerations such as transportation, landscape, infrastructure, and the presence of surrounding business formats are essential (Li et al., 2015).
2.2.3 Architectural design
The distinctive design of boutique hotels has been widely recognized as a critical feature (Lim and Endean, 2009; Khosravi et al., 2014). Increasingly, hotels are emphasizing personality and style as essential success factors that differentiate their offerings and attract customers (Milburn and Hall, 2005). In the United Kingdom, the most appealing characteristics of boutique hotels include their location, quality, uniqueness, available services, and the level of personalized attention they provide (Mcintosh and Siggs, 2005). Design has been identified as one of the four most attractive attributes of boutique hotels for guests (Khosravi et al., 2014). The uniqueness of boutique hotels is primarily reflected in the selection of hotel design and building type (Olga, 2009). Furthermore, successful theme hotels are often characterized by their humanization, originality, and experiential qualities (Qin, 2023). Architectural design plays a crucial role in the adaptive reuse of old industrial buildings into cultural and creative spaces, as it directly influences functional use and business development (Yu, 2022).
2.2.4 Recognition of surrounding residents
Qualitative research conducted by various scholars indicates that the AR had both positive and negative effects on the community. On one hand, it can enhance the community environment and improve livability. Additionally, it fosters transformative momentum, creates business opportunities, and encourages greater neighborhood interactions. More than half of the residents expressed a positive view regarding the social value of hotel reuse (Pongsermpol and Upala, 2018). However, drawing on Iranian research that involved semi-structured face-to-face interviews in other developing countries, it was found that reused hotels do not significantly alter the community’s infrastructure or surrounding environment. Furthermore, most community residents are indifferent to whether the reuse is applicable (Ghaderi et al., 2020a). Since hotels are private spaces, compared with cultural and creative buildings, the adaptive reuse of hotels can diminish public access to industrial heritage sites. Consequently, garnering the attention and recognition of local residents is a crucial aspect of ARIB (De Sousa, 2003; Wang et al., 2009).
2.2.5 Policy and law
Scholars have emphasized that national policies and laws are significant factors influencing the implementation of Integrated Building Adaptive Reuse Practices (IBAP) (Ren et al., 2014). For instance, the Los Angeles City Adaptive Reuse Regulations of 1999 represent landmark legislation aimed at encouraging the conversion of historic office buildings into lofts, apartments, and hotels. These regulations apply to non-residential structures, including industrial buildings, and modify numerous regulations typically enforced when repurposing industrial or commercial buildings into residential spaces. Many non-compliant site conditions, such as building height, parking lot requirements, floor area, and setbacks, are permitted, and various neighborhoods are actively encouraged to participate (Cantell, 2005). In the case study of adaptive reuse for hotels in Hong Kong, from 2000 to 2012, more than 70 applications for the redevelopment of hotel commercial zones were approved on various types of land. However, only eight projects have been implemented to date. The ineffective policies and the complicated, unrealistic procedures are the primary reasons for the lack of success in hotel reuse (Ren et al., 2014). The ARIB faces policy risks, including protracted land change procedures and compatibility issues with higher-level urban or district planning (Chan et al., 2015). Additionally, risks associated with policy changes—such as differing specifications, building codes and regulations, and development standards introduced after renovation—pose significant challenges to adaptive reuse (Altes and Tambach, 2008).
2.2.6 Landscape
Last but not least, the hotel’s natural views and environment are also important. Images of natural landscapes may capture more visual attention than those of urban settings, and natural scenes may convey a greater sense of restorative quality to potential customers (Wang et al., 2019). Consequently, customers are willing to pay a higher price for accommodations that feature natural attractions (Mandi and Petri, 2021). Many scholars believe that legacy landscapes associated with industrial culture play a key role in its revitalization, as they embody the heritage of industrial culture. The shaping of landscapes is essential to embodying industrial aesthetics, enhancing land value, and promoting community engagement.
3 Research methods
3.1 Method selection
Currently, there are over 100 Multi-Criteria Decision-Making methods in practice, which include original methods, extensions, variations, and combinations (Nadkarni and Puthuvayi, 2020). The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) has been widely utilized across various fields, particularly for evaluating multiple data points under uncertain conditions. Additionally, it simplifies the decision-making process through pairwise comparisons. Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP) is developed based on AHP and is extensively applied in project risk assessment, multi-criteria decision-making, and site selection, considering multiple influencing factors (Nieto-Morote and Ruz-Vila, 2011; Vahidnia et al., 2009; Mosadeghi et al., 2015). Compared to other methods, FAHP can amplify small differences, align with human cognitive patterns, and more accurately reflect subjective ambiguity and uncertainty (Kabir and Hasin, 2013). Furthermore, in contrast to the AHP method, FAHP mitigates the impact of extreme values. Given the relatively vague relationships among the model’s components and the unclear causal relationships between the factors within each component, FAHP has been selected for this study.
3.2 The methodology of FAHP
Assume, index domain of the evaluation system , and level domain of the evaluation system , where n is the number of evaluation factors and m is the number of evaluation levels. In this case, m = 3. Hence, there are two index domains. Primary index domain where n = 9 and second index domain where n depends on the number of factors included in each component.
Fuzzy Component Matrix for the primary index domain () is shown below,
Data is obtained by online questionnaires and face-to-face interviews with experts. Each expert does not need to give the rank of all factors, only need to compare the relative importance of the two, namely, Ci and Cj. Then experts score based on the following system, as shown in Table 1. They need to evaluate the range of differences between Ci and Cj which is . is the lower bound, is the middle value, and is the upper bound. Assume, there are k experts, then establish the triangular ambiguity scoring matrix of each expert separately.
Table 1
| Scale | Representative meaning |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | Indicates that factor i is as important as factor j |
| 0.6 | Indicates that factor i is slightly more important than factor j |
| 0.7 | Indicates that factor i is obviously more important than factor j |
| 0.8 | Indicates that factor i is much more important than factor j |
| 0.9 | Indicates that factor i is extremely important than factor j |
| 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 | The opposite meaning of the0.9,0.8,0.7,0.6, respectively. |
Scoring standards.
Scoring standards are explained in Table 1.
The questions in questionnaire are shown in Table 2 and Table 3.
Table 2
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2 Sustainability | C1 Market | |||||||||
| C3 Economics | C1 Market | |||||||||
| C4 Location and Surroundings | C1 Market | |||||||||
| C5 Physical condition of industrial building | C1 Market | |||||||||
| C6 Public Interests | C1 Market | |||||||||
| C7 Legal and policy | C1 Market |
The question of component.
Table 3
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risks and difficulties in the procedures for changing the use of land | Difficulties in building codes after changes in building functions |
The question of factors.
Please make 3 scores, the middle value is the most confident score of scorer. Left and right scores are fluctuating scores. Comparing the two elements, they are equally important by 5 points. Which element is more important can be scored near the element’s position. And you can type two repeated numbers out of the 3 numbers, like (2,2,3).
Please make 3 scores, the middle value is the most confident score of you. Left and right scores are fluctuating scores. Comparing the two elements, they are equally important by 5 points. Which element is more important can be scored near the element’s position. And you can type two repeated numbers out of the 3 numbers, like (2,2,3).
Next, calculate the average score of among K experts for the P index domain level, .
where
The Equation 1 is used to calculate each pair of Ci and Cj. Therefore, fuzzy matrix of P index domain is established.
The next step is to calculate the initialize weight for each component, i in the index domain p based on the mentioned before.
Calculate the initial weight according to Equation 2, and establish the initial weight matrix, consisting of .
W is the evaluation weight vector and P is the level of the evaluation, . is calculated as the following method.
Taking two fuzzy number as an example. Assume, and means the degree of possibility Equation 3
Make
In the same way, all the weights of the p-layer are obtained and normalized.
Assume p = 1, the weight of Primary index domain is calculated. Using the same method, the second index domain could be evaluated when p = 2.
The weight of factor i from component m can be evaluated by the following formula:
3.3 Consistency test
The fuzzy consistency is tested by the compatibility CR index. If the CR<0.1, it is considered to pass the fuzzy consistency test; otherwise, it is not passed. And its calculation formula is as follows:
A represents the fuzzy complementary matrix, W is the eigenmatrix, and n is the order.
The above calculations are implemented based on Python (Figure 1).
Figure 1
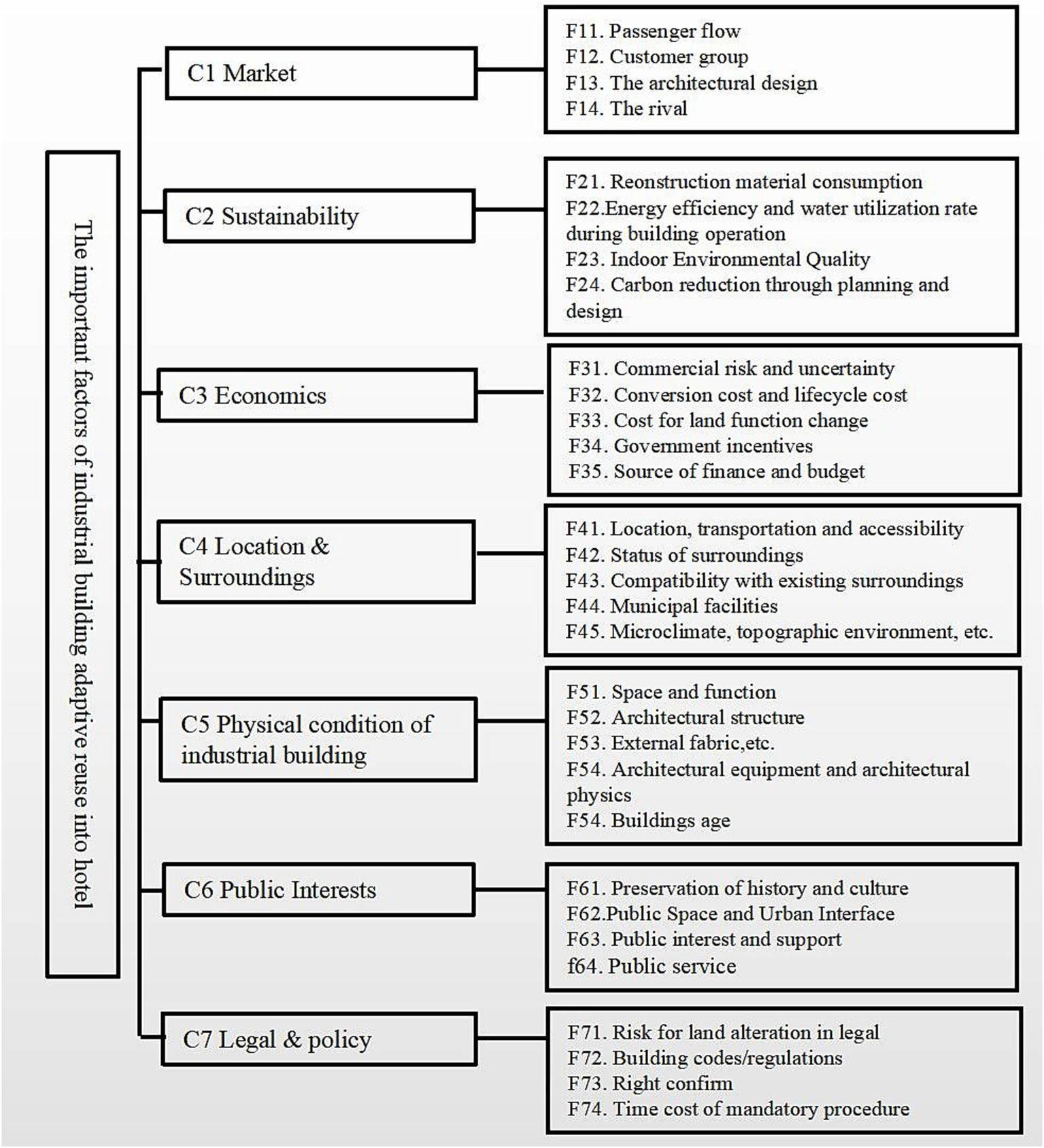
The evaluation framework.
3.4 The evaluation framework
Based on the research content, a hierarchical evaluation index system has been constructed. This system comprises three levels: the target hierarchy, the composition hierarchy, and the factor hierarchy. Each factor is considered uniquely, without repetition or overlap, ensuring that they are mutually comparable.
Based on urban renewal theory, sustainable theory, and research on the adaptive reuse of Chinese industrial buildings, combined with the development characteristics of third-tier cities, this paper focuses on the most current ARIB—cultural-creative building and hotel. Therefore, the factors that are applicable to hotels and cultural and creative buildings are selected in order to construct an evaluation framework (Figure 1).
4 Research subjects and data quality
4.1 Research subjects
The large machinery repair factory is situated in the western part of Hohhot, northern China. Hohhot serves as a central hub for the Belt and Road Initiative and the China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor. It is just two and a half hours from the capital, Beijing, via China’s high-speed rail, drawing tourists with its rich grassland culture and historical sites (Figure 2).
The large machinery repair factory was established in the 1990s and holds significant importance in the industrial history of Hohhot and its surrounding cities. It retains its original layout and architectural features. The facility spans over 7 hectares and is located adjacent to the Zadagai River in the northwest, offering a pleasant environment, low community density, convenient transportation, and comprehensive amenities. The factory is situated 1.9 kilometers from the Prince’s Palace, 3.7 kilometers from the Jokhang Temple, 4.5 kilometers from the General Affairs Office, and 4.7 kilometers from the Baoerhan Tower. Its strategic location allows for easy access to the main attractions.
The large machinery maintenance workshop is a brick-concrete structure. The auto repair workshop in the north is one floor with a high clearance height of about 7 meters. The second floor on the south side is an auxiliary room, with a floor height of about 4.5 meters on the first floor and 3 meters on the second floor. It has the conditions for transformation into a cultural and creative building to arrange large exhibits, a hotel lobby, or a loft apartment hotel.
The thickness of the outer wall is 370 mm, and the maintenance structure is solid brick masonry. Some walls are weathered and peeling. The windows are made of red brick window frames with ordinary glass. The window frames are rusted, the glass has poor light transmittance and poor sealing, and the thermal insulation and sound insulation effects are not good, which does not meet the current green energy-saving requirements. The overall structural framework remains relatively intact. The municipal situation is intact, water and electricity are available, and the roads inside and outside the site are flat. The large machinery maintenance workshop is in generally excellent transformation conditions (Figures 2–4).
Figure 2
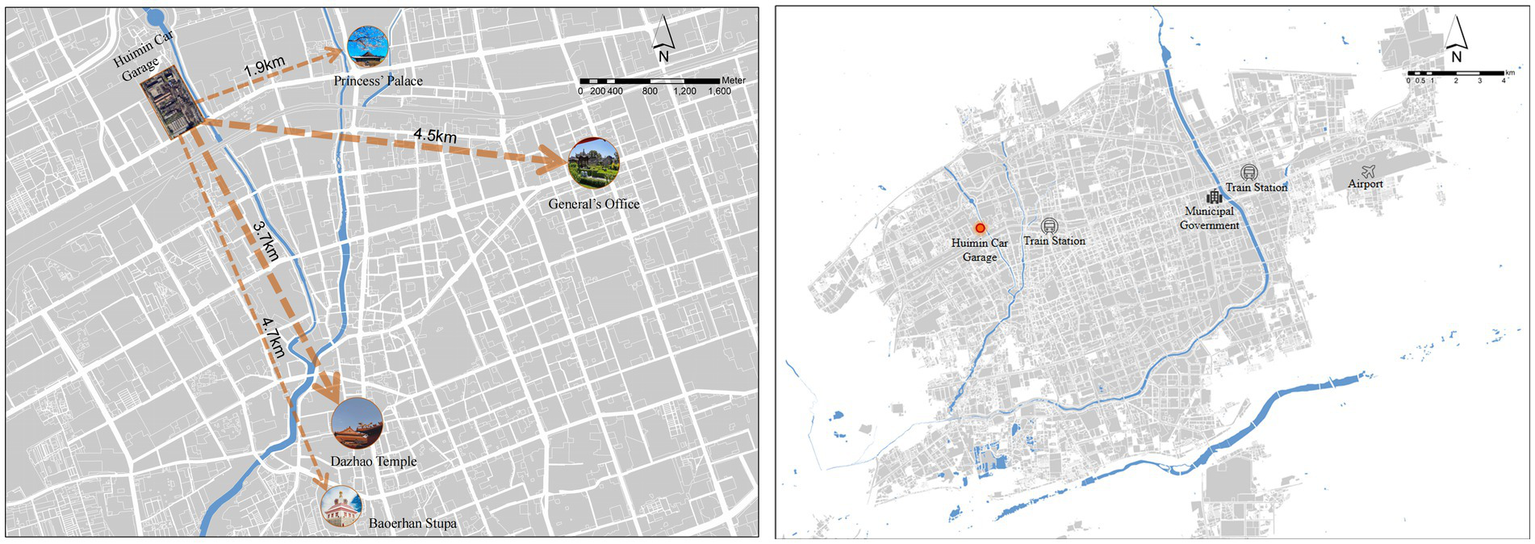
Diagram of distances of the Huimin Car Garage from major attractions (left); Location of Huimin Garage in Hohhot (right) (self-drawn by the authors).
Figure 3
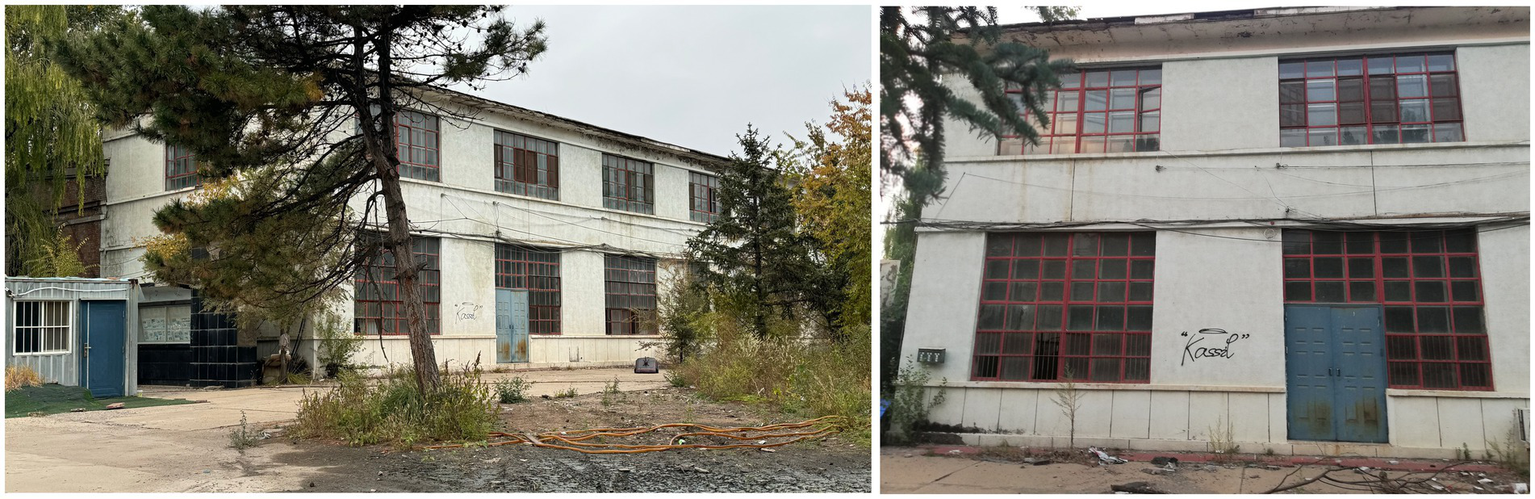

Current status of the large machinery maintenance workshop (photographed by the authors).
Figure 4

Main street scenes and landscapes of the large machinery maintenance workshop (photographed by the authors).
4.2 Data quality
The index system was discussed and verified by numerous universities, planning and design companies, architectural design companies, and local residents, and it underwent two revisions. The final index system received approval from the selected experts.
Twenty experts with over 10 years work experience in the building industry were selected. Experts include designers, urban planners who are key person in charge of urban renewal projects, real estate developers, college teachers in adaptive reuse, landscape designers with experience in industrial heritage park design, project managers, and technical consultants for construction.
5 Results and discussion
Twenty experts in related fields were selected to provide evaluations, and the results from these experts are presented in Table 4 and Table 5.
Table 4
| C1 Market | C2 Sustainability | C3 Economy | C4 Location and Surroundings | C5 Physical condition of industrial building | C6 Public Interests | C7 Legal and policy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 Market | 0.50 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.70 | 0.48 | 0.70 | 0.62 |
| C2 Sustainability | 0.24 | 0.50 | 0.64 | 0.46 | 0.68 | 0.54 | 0.58 |
| C3 Economy | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.50 | 0.70 | 0.56 | 0.60 | 0.64 |
| C4 Location and Surroundings | 0.30 | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.50 | 0.38 | 0.74 | 0.42 |
| C5 Physical condition of industrial building | 0.52 | 0.32 | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| C6 Public Interests | 0.30 | 0.46 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.42 | 0.50 | 0.42 |
| C7 Legal and policy | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.58 | 0.50 |
Fuzzy complementary matrix.
Table 5
| C1 Market | C2 Sustainability | C3 Economy | C4 Location and Surroundings | C5 Physical condition of industrial building | C6 Public Interests | C7 Legal and policy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 Market | 0.5000 | 0.5341 | 0.5366 | 0.5535 | 0.5374 | 0.5724 | 0.5509 |
| C2 Sustainability | 0.4659 | 0.5000 | 0.5025 | 0.5195 | 0.5033 | 0.5386 | 0.5168 |
| C3 Economy | 0.4634 | 0.4975 | 0.5000 | 0.5170 | 0.5008 | 0.5362 | 0.5144 |
| C4 Location and Surroundings | 0.4465 | 0.4805 | 0.4830 | 0.5000 | 0.4838 | 0.5192 | 0.4974 |
| C5 Physical condition of industrial building | 0.4626 | 0.4967 | 0.4992 | 0.5162 | 0.5000 | 0.5353 | 0.5136 |
| C6 Public Interests | 0.4276 | 0.4614 | 0.4638 | 0.4808 | 0.4647 | 0.5000 | 0.4782 |
| C7 Legal and policy | 0.4491 | 0.4832 | 0.4856 | 0.5026 | 0.4864 | 0.5218 | 0.5000 |
Feature matrix.
The calculated values of Wc1, Wc3, Wc4, Wc5, Wc6, Wc7 are 0.1676, 0.1462, 0.1448, 0.1352, 0.1443, 0.1252, 0.1367.
After calculations, the consistency ratio (cr) is found to be 0.09433, which is less than 0.1, indicating that it passes the consistency test. Similarly, the weights of the indicator layer are calculated, as shown in Table 6. Usually, industrial buildings are transformed into cultural and creative spaces, so AP is selected to be converted into cultural and creative public buildings and hotels as options 1 and 2. The scoring results of 10 stakeholders are shown in Table 6. The final score of conversion to public buildings is 2.4622, and the score of conversion to hotels is 3.7765.
Table 6
| Indicator | Weight (Rank) | Score of Plan 1 | Final score | Score of Plan 1 | Final score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.1676 | Cultural and creative buildings | Hotels | |||
| Market | F11. Passenger flow | 0.0332 | 1 | 0.0332 | 5 | 0.1659 |
| F12. Customer group | 0.0513 (1) | 1.5 | 0.0770 | 6 | 0.3080 | |
| F13. The architectural design | 0.0426 (3) | 2 | 0.0852 | 3 | 0.1278 | |
| F14. The rival | 0.0405 (4) | 3 | 0.1215 | 1 | 0.0405 | |
| C2 | 0.1462 | |||||
| Sustainability | F21. Reonstruction material consumption | 0.0279 | 1 | 0.0279 | 5 | 0.1394 |
| F22. Energy efficiency and water utilization rate during building operation | 0.0341 | 3 | 0.1024 | 3 | 0.1024 | |
| F23. Indoor Environmental Quality | 0.0451 (2) | 4 | 0.1803 | 3 | 0.1352 | |
| F24. Carbon reduction through planning and design | 0.0391 (5) | 2 | 0.0782 | 1 | 0.0391 | |
| C3 | 0.1448 | |||||
| Economic | F31. Commercial risk and uncertainty | 0.0229 | 1 | 0.0229 | 4 | 0.0917 |
| F32. Conversion cost and lifecycle cost | 0.0355 | 2 | 0.0709 | 5 | 0.1773 | |
| F33. Cost for land function change | 0.0302 | 1 | 0.0302 | 5 | 0.1508 | |
| F34. Government incentives | 0.0331 | 2 | 0.0661 | 4 | 0.1322 | |
| F35. Source of finance and budget | 0.0232 | 1 | 0.0232 | 4 | 0.0926 | |
| C4 | 0.1443 | |||||
| Location and Surrounding | F41. Location, transportation and accessibility | 0.0291 | 2 | 0.0582 | 5 | 0.1455 |
| F42. Status of surroundings | 0.0317 | 1 | 0.0317 | 4 | 0.1270 | |
| F43. Compatibility with existing surroundings | 0.0255 | 2 | 0.0510 | 4.5 | 0.1147 | |
| F44. Municipal facilities | 0.0337 | 5 | 0.1683 | 5 | 0.1683 | |
| F45. Microclimate, topographic environment, etc. | 0.0243 | 3 | 0.0729 | 1 | 0.0243 | |
| C5 | 0.1367 | |||||
| Physical condition of industrial building | F51. Space and function | 0.0317 | 1 | 0.0317 | 5 | 0.1583 |
| F52. Architectural structure | 0.0255 | 1 | 0.0255 | 4 | 0.1020 | |
| F53. External fabric, etc. | 0.0296 | 2 | 0.0592 | 3 | 0.0888 | |
| F54. Architectural equipment and architectural physics | 0.0269 | 5 | 0.1344 | 5 | 0.1344 | |
| F54. Buildings age | 0.0230 | 4 | 0.0920 | 3 | 0.0690 | |
| C6 | 0.1352 | |||||
| Public Interests | F61. Preservation of history and culture | 0.0376 | 4 | 0.1503 | 3 | 0.1127 |
| F62. Public Space and Urban Interface | 0.0289 | 4 | 0.1157 | 3 | 0.0868 | |
| F63. Public interest and support | 0.0381 | 4 | 0.1525 | 4 | 0.1525 | |
| f64. Public service | 0.0306 | 4 | 0.1225 | 2 | 0.0612 | |
| C7 | 0.1252 | |||||
| Legal and policy | F71. Risk for land alteration in legal | 0.0337 | 2 | 0.0675 | 4 | 0.1350 |
| F72. Building codes/regulations | 0.0269 | 3 | 0.0806 | 5 | 0.1344 | |
| F73. Right confirm | 0.0300 | 2 | 0.0600 | 4 | 0.1200 | |
| F74. Time cost of mandatory procedure | 0.0346 | 2 | 0.0692 | 4 | 0.1385 | |
| 2.4622 | 3.7765 |
Weight distribution and scheme scoring table at different levels.
Similarly, the weights of the indicator layer have been calculated, as shown in Table 6. Typically, industrial buildings are repurposed into cultural and creative spaces; therefore, option 1 is to convert the asset into cultural and creative public buildings, while option 2 is to transform it into hotels. The scoring results from 10 stakeholders are presented in Table 6. The final score for the conversion to public buildings is 2.4622, whereas the score for the conversion to hotels is 3.7765.
The decision-making weights are ranked in descending order as follows: market, sustainability, economy, building physics, legal policy, location environment, and public interest. The top five factors influencing decision-making are customer groups, indoor environmental quality, building design, competitors, and planning strategies for carbon reduction. Market demand serves as the primary driving force behind the adaptive reuse of industrial buildings, aligning with existing research findings (Tan et al., 2018), that underscore the critical role of market demand in third-tier cities in northern China. The study conducted by Tan has demonstrated that the five most influential factors are sustainability, construction cost, market, and variability (Tan et al., 2018). Among these factors, the market represents the third element, distinct from the first factor discussed in this study. This distinction arises from the fact that, in contrast to Hong Kong, where urbanization approaches 100% and the population density is 7,060 people per square kilometer, Hohhot has an urbanization rate of 81.91% and a population density of only 209 people per square kilometer. Due to the extreme scarcity of land in Hong Kong, the region has long faced a shortage of housing land, and the market mechanism is highly developed. Industrial buildings do not encounter a lack of clientele when converted into hotels or long-term rental apartments. The primary concern of the adaptive reuse is the optimization of efficiency. However, Hohhot remains in the phase of population and industrial agglomeration, while the ARIB is at the phase that requires government support and guidance, as well as multi-party cooperation and exploration. Consequently, the impact weights vary. Expert discussions further revealed two core findings: (1) The current applicability of buildings in third-tier cities primarily focuses on revitalizing these structures through functional transformation, emphasizing the creation of sustainable spaces rather than short-term attractions for social media. Compared to creating an Instagrammable spot that generates temporary excitement, the renovation of industrial buildings in third-tier cities must take into account the unique characteristics of the community, the city, and the surrounding areas. It is essential to leverage regional attributes to foster community attention and enhance operational capabilities following the renovation. This aligns with the strategic research on real cases of industrial buildings in third-tier cities (Chen, 2015). (2) Accurate customer profiles are fundamental to decision-making and rank first among the 31 influencing factors. This is because differentiated functional adaptations must align with specific user groups, which is crucial for ensuring the long-term vitality of the transformed community. Due to the limited consumption capacity of third-tier cities, it is essential to achieve precise transformation positioning by targeting specific demographic groups. Even in third-tier cities like Hohhot, which attracts more tourists than Hong Kong, the consumption characteristics of its customer base differ significantly from those in Hong Kong. This disparity is evident in terms of consumption destinations, spending levels, urban consumption patterns, and the age structure of customers. Hohhot should focus on the mass supply of seasonal grassland tourism, while Hong Kong must cater to the quality demands of high-end clientele. Establishing hotel positioning based on customer profiles, followed by subsequent development decisions, is a fundamental principle for third-tier cities in northern to avoid resource wastage and achieve low-carbon sustainable development.
Sustainable development ranks second in priority, Compared to the first factor in Hong Kong, the essence lies in the differing stages of development. The scarcity of land in Hong Kong necessitates the highly sustainable utilization of resources. Elevated sustainability requirements have emerged as a threshold for transformation. Furthermore, as Hong Kong consumers become increasingly aware of sustainability, it has gradually evolved into a significant selling point in market competition. In the third-tier cities in the north, the indoor air quality and carbon reduction in planning and design are the most crucial factors for sustainability. This emphasis arises not only from relevant national requirements and standards but also from the Hohhot Municipal Government’s issuance of the “Implementation Plan for Building Energy Conservation and Green Building Development in Hohhot. clearly states that projects eligible for transformation must achieve a minimum of two-star certification and proposes incentives such as exemptions from municipal supporting fees (ranging from 30 to 50%), increased volume ratios (up to 10%), bonuses, and evaluations for green buildings (Hohhot Municipal Government, 2021).
Some experts have noted that transforming industrial buildings into green buildings with corresponding star ratings is often challenging. There exists a fundamental contradiction between the structural system and the optimization of its green performance. Due to the large span commonly used in industrial buildings, it is challenging to ensure that the buildings complies with current energy efficiency standards once it is converted into a hotel. Therefore, compared with the transformation of cultural and creative spaces, the transformation into a hotel is more suitable for the temperate continental monsoon climate of Hohhot, because the transformation typically involves dividing the space into smaller areas, which can lead to slower air circulation, rapid temperature increases, and the insulation is energy-saving. At the same time, the transformation of functions will bring challenges to the layout of space and equipment pipelines. At the same time, the transformation of abandoned industrial buildings needs to focus on addressing the public’s cognitive bias regarding the potential environmental pollution legacy of industrial heritage (Teo and Lin, 2011). Budget experts have pointed out that sustainable transformation faces many difficulties and challenges. However, from the perspective of the entire life cycle, sustainable transformation is still of great significance. This is not only because of the green building policy benefits provided by the government, but also because sustainability can enhance the attractiveness of hotels in the competitive mark.
Architectural design is the third influencing factor because excellent design reduces the cost and construction cycle of the entire life cycle (Paulson, 1976), spatial aesthetics forms brand premium through social media communication, prolongs customer stay time (Rong et al., 2025), has spatial attractiveness converted into commercial value (Sheppard et al., 2023), and enhances regional competitiveness with innovative spatial experience. Well-designed industrial renovation hotels actively enhance the industrial character and historical significance of the building, transforming it into a distinctive brand symbol that attracts customers eager to explore local culture (Ji and Luo, 2023). The adaptability of the design can also reduce operational costs in the long term and indirectly improve the return on investment. Analysis of 53 cases of industrial building renovation hotels reveals that poor design has led some establishments to deliberately downplay their renovation attributes, resulting in a lack of the cultural value associated with industrial buildings. Some hotels have been swiftly eliminated from the market due to a mediocre spatial experience and subpar living environment (Gong and Bridnia, 2021). This corroborates Ren’s study on hotels, which indicates that any compromise, even a minor concession in architectural design, can have a detrimental impact on their competitiveness (Ren et al., 2014). This further underscores the crucial role of exceptional design in the sustainability of ARIB.
There is a significant difference between the legal policy of Ghaderi in Iran, which is also a developing country (Ghaderi et al., 2020b). Because the Iranian government does not allocate sufficient funds to support the preservation of industrial buildings, and given that certain areas are designated as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, there are numerous policy restrictions on the conversion of hotels. Consequently, legal policies are central to the development of adaptive reuse hotels. In contrast, mainly due to the fact that the urban renewal and industrial architectural heritage protection policies have been transmitted to cities and counties in China. Since 2021, the national level has successively issued programmatic documents, and provincial governments have formed differentiated policy toolboxes through pilot projects and the promulgation of urban renewal models, which has encouraged the advancement of urban renewal projects.
It is noteworthy that location ranks as the second-to-last influencing factor, which contradicts relevant research conducted in Hong Kong. Some industrial buildings in Hong Kong are located in areas with inadequate traffic conditions and limited surrounding facilities. Furthermore, industrial land is often situated far from tourist attractions, contributing to an overall unfavorable environment in these regions (Ren et al., 2014). In contrast, in third-tier northern cities like Hohhot, the vacant industrial buildings in the central urban area, the transportation and infrastructure conditions are convenient, and the accessibility to major urban attractions and important public buildings is similar. As a result, the significance and influence of the urban locational environment are relatively diminished.
Public interests are often overlooked. While some scholars focus on public spaces and urban interfaces following transformation, the residents of Hohhot show limited concern for the conversion of industrial buildings. The community is generally indifferent to changes in the environment that do not directly affect their personal interests. Additionally, the influence of community residents has historically been relatively weak.
Based on the scoring results from 20 experts, the functional selection preferences for the transformation of industrial buildings in northern third-tier cities have been identified. The data indicates that the comprehensive score for transformed hotels (3.7765) is significantly higher than that for cultural and creative public buildings (2.4622). Experts noted that in non-city center areas, cultural and creative spaces face dual challenges: uncertainty regarding long-term rental income and intensified market competition, whereas the hotel industry demonstrates greater market adaptability. Architects particularly emphasized that the development of cultural and creative spaces must address three core challenges: first, the cost of transformation is increasing in order to create a differentiated spatial experience; second, achieving deep coordination among architectural design, interior design, and operational planning is essential, which generally extends the project cycle; third, market demand imposes higher requirements on the flexibility of design solutions, significantly increasing project risks. The customer demographics of hotels converted from other uses are more diverse than those in the cultural and creative industries. Additionally, the market demand for these hotels is stable, making it easier to maintain operations. Furthermore, the investment costs and revenue associated with hotel conversions are more predictable due to the established experience in hotel investment. In contrast, the costs associated with cultural and creative spaces can vary significantly, making it challenging to estimate potential income.
6 Conclusion
With urbanization and industrial upgrading, many third-tier cities have vacated numerous vacancy industrial buildings. The adaptive reuse of these buildings not only preserves historical memory of cities, but also significantly reduces urban carbon emissions. While the government encourages the adaptive reuse of industrial buildings, various factors contribute to the controversy surrounding these transformations. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the key factors influencing industrial building transformation in the third-tier market. This study uses the fuzzy hierarchical analysis method to identify the influencing factors in descending order: market, sustainability, economy, building physics, legal policy, location environment, and public interest. The research findings offer valuable insights for industrial building adaptive reuse in third-tier cities of developing countries and assist stakeholders in making informed decisions regarding transformation functions. Future studies can provide cultural and creative building and hotel design plans within a cost range, and then conduct comparative studies using the evaluation framework, the results will be more viable. And it is meaningful to further study the post-construction evaluation of hotels after industrial building transformation.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
ZG: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Software, Methodology. YS: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – original draft. QZ: Writing – review & editing, Validation. XR: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. JL: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Conceptualization, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the [Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Land and Space Planning Institute] under Grant Exploration of Utilization Models for Underutilized Urban Land in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region [number GTKJGHY2024-002].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AR, Adaptive reuse; ARIB, Adaptive reuse of industrial buildings; FAHP, Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process.
References
1
Altes W. Tambach M. (2008). Municipal strategies for introducing housing on industrial estates as part of compact-city policies in the Netherlands. Cities25, 218–229. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2008.04.005
2
Bullen P. A. (2007). Adaptive reuse and sustainability of commercial buildings. Facilities25, 287–302. doi: 10.1108/0263277071071691
3
Bullen P. A. Love P. E. D. (2009). The rhetoric of adaptive reuse or reality of demolition: views from the field. Cities27, 215–224.doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2009.12.005
4
Bullen P. Love P. (2011). Factors influencing the adaptive re‐use of buildings. J. Engin. Design Technol.9, 32–46. doi: 10.1108/17260531111121459
5
Cantell S. F. (2005). The adaptive reuse of historic industrial buildings: regulation barriers, best practices and case studies. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
6
CCID (2019). White paper on reuse paths and typical cases of China’s industrial relics. Beijing: CCID consulting company limited.
7
Chan A. Cheung E. Wong I. (2015). Recommended measures on the revitalizing industrial buildings scheme in Hong Kong. Sustain. Cities Soc.17, 46–55. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2015.03.012
8
Chen Z . (2015) The activation and renewal of the old industrial Building-Baseon the study of the transform of the architecture building in Inner Mongolia University of Technology. Annual conference and academic seminar of the Chinese Society of Architectural History, 2015 Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. 8.
9
China Industry Information . (2019). Analysis of the current situation of the Chinese hotel industry market in 2019 and prediction of the development trend of the Chinese hotel industry in 2019. Available online at: http://www.chyxx.com/industry/201909/787493.html. (Accessed September 26, 2019).
10
Dai R. Lai S. (2023). Research on comprehensive benefit evaluation of industrial building renovation based on C-Owa operator. Real Estate World20, 9–13. Available at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=wOuTVkq58NnsZ-wa1bpdgx1S3O0f4oAzH1niTmtuOjyTExNV3cecWv8UtSFmb4gNL-ykMCAM94uNU3VjKTRjnQxDCLcCKM99I8DL_De2HJzCRmZM46r4vMNZWeh8TmM-V7lmbe5ZsHiDXEiCU_UvAFvJJE_Uvr_hGF4_S6dW4039Gj2d3oV-0SlkFXotq4f6&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS%WCNKI
11
De Sousa C. A. (2003). Turning brownfields into green space in the City of Toronto. Landsc. Urban Plan.62, 181–198. doi: 10.1016/S0169-2046(02)00149-4
12
Ghaderi Z. Farashah M. D. P. Aslani E. Hemati B. (2020). Managers’ perceptions of the adaptive reuse of heritage buildings as boutique hotels: insights from Iran. J. Herit. Tour.15, 696–708. doi: 10.1080/1743873X.2020.1756834
13
Gong Z. Bridnia L. (2021). Analysis of the experience of renovating industrial enterprises into hotels in China. E3S Web of Conferences.
14
Hartesvelt M. V. (2006). Building a better boutique hotel. Lodg. Hosp.62, 32–44.
15
Hohhot Municipal Government . (2021). Hohhot City building energy saving and green building development implementation plan. Hohhot Municipal Government.
16
Huang Y. Liu Z. Zhang D. (2023). Research on reconstruction and regeneration strategy of industrial building heritage. Journal of. Archit. Technol.7:1-3+7. Available at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=wOuTVkq58NkcCgI8-J3PeN8_znHhgyr5hIKGxy0oI9tWUWcAtM6HzFb7ewxziOsrR83QP5W4EgYMFGZHP5lCBrzHl3CYYubJlr1f1-hZ-iQWe14dPYkax_B66cObhvQE1YLT8YooGQjZTM3H7ShzM6IEe0Qz7mXBzqRbVweg4CS9KZS6Wa-spMV-poi5tpF&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS%WCNKI
17
Ihsan B. Alshibani A. (2018). Factors affecting operation and maintenance cost of hotels. Prop. Manag.36, 296–313. doi: 10.1108/PM-04-2017-0023
18
Ji Q. Luo C. (2023). Research on the renewal of hotel industrial heritage under the guidance of“ConsumerSociety”: a case of Suzhou no. 3 textile machinery factory. Urban. Architect.20, 41–45. doi: 10.19892/j.cnki.csjz.2023.10.12
19
JLL . (2018). The rise of China’s rental housing market. Available online at: https://www.joneslanglasalle.com.cn/en/newsroom/china-rental-housing-market (Accessed 11 December 2018).
20
Kabir G. Hasin M. A. A. (2013). Multi-criteria inventory classification through integration of fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and artificial neural network. Int. J. Industr. Syst. Engin.14, 74–103. doi: 10.1504/IJISE.2013.052922
21
Kee T. (2014). Adaptive reuse of industrial buildings for affordable housing in Hong Kong. Journal of design and. Built Environ.14, 45–60.
22
Khosravi S. Malek A. Ekiz E. (2014). Why tourists are attracted to boutique hotels: case of Penang Island, Malaysia. J. Hospital. Tourism12, 26–41.
23
Lair A. R. (2019). How many rooms is too many?: per-capita demand and the hotel cycle. Available online at: https://www.hvs.com/article/8587-How-Many-Rooms-Is-Too-Many-Per-capita-Demand-and-the-Hotel-Cycle (Accessed September 3, 2019)
24
Langston C. Wong F. K. W. Hui E. C. M. Shen L.-Y. (2007). Strategic assessment of building adaptive reuse opportunities in Hong Kong. Build. Environ.43, 1709–1718. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2007.10.017
25
Li X. Hu L. Wang L. Xu S. (2015). Analysis of main factors influencing on industrial heritage’s reuse——cases study on the textile industrial heritage in Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai And Suzhou. Architect. Cult.6, 96–100.
26
Lim W. M. Endean M. (2009). Elucidating the aesthetic and operational characteristics of Uk boutique hotels. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag.21, 38–51. doi: 10.1108/09596110910930179
27
Liu Y. Oort F. V. Geertman S. Lin Y. (2014). Institutional determinants of brownfield formation in Chinese cities and urban villages. Habitat Int.44, 72–78. doi: 10.1016/j.habitatint.2014.05.005
28
Luo X. Gao N. Yuan X. (2025). Locational drivers of China’s digital creative industries: unveiling regional concentration and sectoral differences. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res.20:123. doi: 10.3390/jtaer20020123
29
Mandi A. Petri L. (2021). The impacts of location and attributes of protected natural areas on hotel prices: Implications for sustainable tourism development. Environment, development and sustainability, 23, 833–863.
30
Mcintosh A. J. Siggs A. (2005). An exploration of the experiential nature of boutique accommodation. J. Travel Res.44, 74–81. doi: 10.1177/0047287505276593
31
Mcintosh A. J. Siggs A. (2016). An exploration of the experiential nature of boutique accommodation. J. Travel Res.44, 74–81
32
Milburn R. Hall L. (2005). The secret of lifestyle hotels' popularity is simple: they are in tune with the needs of the new, complex consumer. Analysis Maternity Histories. 12, 1–11. Available at: http://www.pwc.com/hospitalitydirections
33
Mosadeghi R. Warnken J. Tomlinson R. Mirfenderesk H. (2015). Comparison of fuzzy-Ahp and Ahp in a spatial multi-criteria decision making model for urban land-use planning. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst.49, 54–65. doi: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2014.10.001
34
Nadkarni R. R. Puthuvayi B. (2020). A comprehensive literature review of multi-criteria decision making methods in heritage buildings. J. Build. Engin.32, 101814. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101814
35
Nieto-Morote A. Ruz-Vila F. (2011). A fuzzy approach to construction project risk assessment. Int. J. Proj. Manag.29, 220–231. doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2010.02.002
36
Olga A. (2009) The alternative hotel market. 2009 international conference on management science and engineering, 2009. Ieee, 2021-2025.
37
Paulson B. C. (1976). Designing to reduce construction costs. J. Constr. Div.102, 587–592. doi: 10.1061/JCCEAZ.0000639
38
Pongsermpol C. Upala P. (2018). Impacts of adaptive reuse of heritage buildings converted to small Hotels in Bangkok. Asian J. Quality Life (AjQoL)3, 69–79. doi: 10.21834/ajqol.v3i13.163
39
Qin Y. (2023). Research on theme hotel design based on Adaptive transformation of OldBuildings——Taking the Design of Theme Hotelin Chengdu International Youth Culture andArt community as an example. Master.
40
Remoy H. Van Der Voordt D. (2014). Adaptive reuse of office buildings into housing: opportunities and risks. Build. Res. Inform.42, 381–390. doi: 10.1080/09613218.2014.865922
41
Ren L. Shih L. Mckercher B. (2014). Revitalization of industrial buildings into hotels: anatomy of a policy failure. Int. J. Hosp. Manag.42, 32–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2014.06.007
42
Rong M. Chun Y. Ying L. (2025). Space aesthetics "into the game" stretch the new texture of Dongqian Lake. 2025-01-18.
43
Sheppard B. Kouyoumjian G. Sarrazin H. Dore F. (2023). The business value of design. (Mckinsey Company).
44
Tan X. Altrock U. (2016). Struggling for an adaptive strategy? Discourse analysis of urban regeneration processes–a case study of Enning road in Guangzhou City. Habitat Int.56, 245–257. doi: 10.1016/j.habitatint.2016.06.006
45
Tan Y. Shuai C. Wang T. (2018). Critical success factors (Csfs) for the adaptive reuse of industrial buildings in Hong Kong. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health15:1546. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15071546
46
Teo E. A. L. Lin G. (2011). Building adaption model in assessing adaption potential of public housing in Singapore. Build. Environ.46, 1370–1379. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2011.01.003
47
The Central Government of the PRC . (2024). Domestic tourism data in 2023. Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/bumen/202402/content_6931178.htm. (Accessed January 24, 2025)
48
Urtasun A. Gutiérrez I. (2006). Hotel location in tourism cities: Madrid 1936-1998. Ann. Tour. Res.33, 382–402. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2005.12.008
49
Vahidnia M. H. Alesheikh A. A. Alimohammadi A. (2009). Hospital site selection using fuzzy Ahp and its derivatives. J. Environ. Manag.90, 3048–3056. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.04.010
50
Vardopoulos I. (2019). Critical sustainable development factors in the adaptive reuse of urban industrial buildings. A fuzzy Dematel approach. Sustain. Cities Soc.50:101684. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101684
51
Wang W. (2023). The application of industrial elements in interior decoration -- a case study of the urban B&B hotel renovation project of "safe with apartments" Master: Changchun Normal University.
52
Wang T. C. Tsai C. L. Tang T. W. (2019). Restorative quality in tourist hotel marketing pictures: natural and built characteristics. Curr. Issue Tour.22, 1679–1685. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2018.1471051
53
Wang Y. P. Wang Y. Wu J. (2009). Urbanization and informal development in China: urban villages in Shenzhen. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res.33, 957–973. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2427.2009.00891.x
54
Wang J. Zhang Y. Wang Y. (2018). Environmental impacts of short building lifespans in China considering time value. J. Clean. Prod.203, 696–707. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.314
55
Wilson C. (2010). Adaptive reuse of industrial buildings in Toronto. Ontario: Evaluating Criteria for Determining Building Selection.
56
Yang Y. Wong K. K. F. Wang T. (2012). How do hotels choose their location? Evidence from hotels in Beijing. Int. J. Hosp. Manag.31, 675–685. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2011.09.003
57
Yap K. K. K. (2014). Industrial building - exploring its potential in adaptive reuse in Hong Kong. Karlsruhe, Germany:Iccrem.
58
Yu X. (2022). Research on key influencing factors and Configurationof old industrial building reconstruction: Master Yangzhou University.
59
Yu Q. (2024). Research on the reconstruction strategy of industrial relic buildings from the perspective of low carbon: Master Shandong Jianzhu University.
60
Zero Power Intelligence Group . (2024). Annual research and consultation report of panorama survey and investment strategy on China industry.
Summary
Keywords
FAHP, adaptive reuse, reuse, industrial buildings, hotels, factor
Citation
Gong Z, Si Y, Zhang Q, Rong X and Lyv J (2025) Research on key factors and decision-making in the adaptive reuse of industrial buildings as hotels in third-tier cities in northern China: the large machinery maintenance workshop in Hohhot. Front. Sustain. Cities 7:1642816. doi: 10.3389/frsc.2025.1642816
Received
07 June 2025
Accepted
31 July 2025
Published
11 September 2025
Volume
7 - 2025
Edited by
Charles Chen, University of Hawaii–West Oahu, United States
Reviewed by
Xiao Ding, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao SAR, China
Qingshan Yang, Northeast Normal University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Gong, Si, Zhang, Rong X and Lyv.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Si, 245953238@qq.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.