- 1Department of Animal Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 2Department of Physiology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 3Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Srinakharinwirot University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 4Center of Excellence in Animal Fertility Chulalongkorn University (CU-AF), Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
Low birth weight harms growth and immunity in suckling piglets. The effects of chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY)-based product, Globigen® Pig Doser (EW Nutrition GmbH, Visbek, Germany) (GPD), administered at birth on growth performance at weaning were investigated in normal (NBW) and low birth weight (LBW) piglets. The product comprises IgY antibodies against common enteric pathogens in newborn piglets, such as Escherichia spp., antibodies against common enteric pathogens in newborn piglets, such as Escherichia spp., as well as soybean oil, vitamins, and probiotics like Enterococcus faecium. The expression of mRNA and protein related to mucosal innate immunity was measured using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and Western blot in 7-day-old piglets (n = 5 piglets). LBW (0.8–1.0 kg birth weight [BW]) and NBW (1.4–1.6 kg BW) piglets were randomly chosen from different sows. At 6 and 10 h after birth, 1.5 mg of IgY (NBW-IgY or LBW-IgY piglets; n = 32 piglets/group) was orally supplemented. GPD significantly increased the final BW and daily weight gain of NBW-IgY but not LBW-IgY piglets at 24 days after birth compared to the untreated group. The growth performance of LBW-IgY piglets was improved to match NBW piglets. The expressions of antimicrobial peptides, porcine β-defensin (PBD)4, pathogen recognition receptors, toll-like receptor (TLR)1, TLR2, TLR5, TLR6, TLR8, and TLR9, and cytokines IL-6 were enhanced in NBW-IgY. The upregulated expressions of PBD2 and PBD4 were observed in the jejunal mucosa of LBW-IgY piglets. GPD reversed the overexpression of neuropeptides substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptides, and cytokines interleukin 8 (IL-8) that underlie inflammation in the LBW group. The LBW group exhibited elevated expression of tight junction (TJ) barrier proteins, including claudin (CLDN)4, CLDN7, and ZO-1 in the colon, but these levels were reversed by GPD. Our findings indicated that oral GPD supplementation at birth can promote growth by modulating the intestinal barrier system and reducing the incidence of inflammation in pre-weanling piglets.
1 Introduction
The larger litter size of hyperprolific sows is linked to a higher number of low birth weight (LBW) piglets. The variation in body weight of suckling piglets causes management difficulties, such as an irregular start to the finishing period. LBW piglets are linked to pre-weaning mortality, growth retardation, and reduced carcass quality (1). According to Morise et al., LBW piglets weigh 0.8–1 kg, while normal birth weight (NBW) piglets weigh between 1.4 and 1.6 kg (2). Piglets of the LBW group are more vulnerable to pathogens, which can cause long-term negative effects on growth performance during the farrowing and finishing phases (3).
Intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) are crucial for piglet health, including their roles in digestion, absorption, and immunity (4). Intestinal immune systems involve a complex interaction between innate and adaptive components to defend against pathogens, while also tolerating commensal microbes and dietary antigens. The multilayered system of chemical and physical barrier functions, consisting of intestinal epithelium, immune system, and enteric nervous system, serves as the first line of the innate immune response, working to prevent invading pathogens. The most effective chemical barrier is antimicrobial peptides, such as β-defensins (BDs) secreted by IECs and immune cells (5), while the physical barrier is maintained by tight junction (TJ) protein complexes (zona occludin and claudins) (6, 7).
When the host–microbe interaction occurs, IECs initiate the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines (interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α). This represents the second line of the innate immune system, which involves pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), toll-like receptors (TLRs; TLR1-10), and the signaling system expressed by IECs or macrophages and dendritic cells beneath the IECs (7). The recognition of pathogens by PRRs activates intracellular signaling pathways that influence subsequent immune responses, such as the activation of B and T lymphocytes, which provide long-lasting protection against specific pathogens (8). Moreover, regulatory T lymphocytes secrete inhibitory cytokines (transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and IL-10) to prevent overactive immune responses to harmless antigens and to maintain immune tolerance to commensal bacteria and dietary antigens (9).
Various factors, including diet, microbial exposure, and genetic background, influence the development of the intestinal immune system in piglets. Thus, LBW piglets, which may be caused by an inadequate intrauterine nutrients or growth factors, might experience improper GIT development. Moreover, due to the epitheliochorial type of pig placenta, maternal immunity prevents the transfer of antibodies to the fetuses (10). Therefore, maternal immunity through colostrum and milk is the only protection against disease (3).
Maternal colostrum containing antibodies and immune cells is only transferred from the sow to the piglets across the intestinal wall, which is highly effective in the first 24 h after birth (10). Therefore, ingesting colostrum shortly after birth is critical for newborn piglets to receive passive immunity. Nevertheless, the colostrum supply is often insufficient for the number of piglets that exceeds the number of functional teats of the sow, especially for the last-born piglets and the LBW piglets (11).
Animals can receive passive immunity from colostrum, egg yolks, and monoclonal antibodies from various sources (12). Feeding bovine colostrum to piglets has been reported (13). Although bovine colostrum is rich in nutrients and bioactive compounds, the immunoglobulins in bovine colostrum target bovine pathogens (14) and are probably unable to prevent pig-specific infections. Perhaps, passive immunization can enhance the innate immune response to infection, resulting in improved weight gain during the weaning period, especially in LBW piglets.
Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) is a low molecular weight class of immunoglobulin (Ig) present in avian serum and egg yolk of birds, amphibians, and reptiles (15). Similar to mammal IgG, IgY is responsible for the secondary immune response (16). The IgY-based commercial product, Globigen® Pig Doser (EW Nutrition GmbH, Visbek, Germany; GPD), contains high-purity IgY against antigens causing diarrhea, such as enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) F4 and F18, E. coli K88, and Salmonella typhimurium (17). Additionally, preventing the colonization of ETEC E. coli K88 by oral IgY in newly weaned piglets at 10 days of age showed an improvement in weight gain (18). Therefore, IgY-based commercial products are widely used in many applications, including prophylactics, therapeutics, and functional foods to promote growth (19). However, the cellular mechanisms of IgY-based supplementation only at birth on the intestinal barrier system, which may be important targets for improving gut health associated with growth performance, have not been investigated.
In the current study, we aimed to investigate whether oral IgY-based supplementation within 24 h after birth promotes the expression of innate immune system-related genes in connection with growth in weaning piglets. Comparisons between LBW and NBW piglets were also conducted to develop strategies for reducing economic losses from managing or culling weak post-weaned piglets.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Chemicals
The commercially produced IgY, Globigen® Pig Doser, was provided by EW Nutrition GmbH (Visbek, Germany). Radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) reagent and a protease inhibitor cocktail were purchased from Merck Group (Darmstadt, Germany). Reagents used for Western blotting were purchased from Bio-Rad, Inc. (Hercules, CA, United States). The body composition analysis (BCA) test and enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) substrate were purchased from BCA Test Visual Protein (Taipei, Taiwan). All primary antibodies, including CLDN1, rabbit anti-CLDN2, rabbit anti-CLDN4, rabbit anti-CLDN7, and mouse anti-β-actin antibody, were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, United States), and secondary antibodies from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, United States). RNAlater™ solutions and TRIzol® reagent were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, United States). iScript™ Select cDNA Synthesis Kit was purchased from Bio-Rad, Inc. (Hercules, CA, United States). The 2X qPCRBIO SyGreen Mix Lo-ROX was purchased from PCR Biosystems Ltd. (N6 4ER, London, United Kingdom). The specific primer sets were designed and developed by iScience Technology (Bangkok, Thailand).
2.2 Animals and experimental procedures
The animal experiment was conducted in accordance with the animal use protocols approved by the Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol number: 2231047). The basal diets used to meet the requirements for suckling piglets according to the Veterinary Manual: MSD Veterinary Manual (20) as discussed in the following.
A total of 128 piglets [(Landrace × Yorkshire) × Duroc] from 16 sows of the same parity (parity 2) were randomly assigned to four experimental groups (n = 32 piglets/group). The sample size was determined through power analysis (G*Power software (version 3.1.9.2; Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany)) for a two-factor interaction. The input parameters include a medium effect size (Cohen’s d = 0.25) with a significance level of 0.05, a power of 0.8, and a numerator df of 1 to determine the sample size for 4 treatments. The nursing sows and suckling piglets were housed in temperature- and humidity-controlled environments using an evaporative cooling system. During the experiment, the barn maintained a daily temperature of 26.5 ± 0.9°C and relative humidity of 71.0 ± 1.0%. The piglets were separated from their mothers and weighed prior to receiving colostrum. The piglets with a birth weight of 1.4–1.6 kg were assigned to the NBW group, and those with a birth weight of 0.8–1.0 kg were assigned to the LBW piglets. After group allocation, all piglets were returned to their mothers and fed with the sow’s colostrum. Some NBW and LBW piglets (NBW-IgY and LBW-IgY) were orally supplemented with 2 mL of GPD, which is is equivalent to orally pump-fed-IgY (0.3 mg of IgY/ml) (21), administered at 6 and 10 h after birth to simulate the receiving of passive immunity from colostrum. The piglets were cross-fostered according to the farm’s standard practices. Each sow was allotted 13–14 piglets/litter. At 7 days after birth, piglets were cross-fostered again and were further weaned when they were 24 days old. During cross-fostering, the number of piglets per sow per litter and the size of the piglets within each litter will be monitored to ensure that they are similar. Creep feed (with 2.58 Mcal/kg, 20.8% crude protein, 2.5% crude fiber, 0.60% calcium, and 0.45% available phosphorus) and water were provided ad libitum throughout the entire 24-day experimental period, following the farm’s protocol. The piglets were weighed on a pen basis on days 0, 7, 8, and 24 to calculate the average daily gain (ADG).
2.3 Sample collection
Seven-day-old piglets from each experimental group (n = 5 piglets per group) were randomly selected and euthanized to remove the gastrointestinal tract. Immediately after collection, a 1 cm length of intestinal mucosa from the mid-jejunum, ileum, and colon was placed into a 2 mL microcentrifuge tube containing RNAlater and snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. All mucosal samples were kept at −20°C for further analysis.
2.4 RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol® reagent following the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, 1 g of frozen mucosal sample was homogenized on ice in 1 mL of TRIzol® using a homogenizer pestle. After 200 μl of chloroform was added, the mixture was centrifuged at 12,000 g for 15 min. The upper layer containing RNA was transferred into a new microfuge tube and precipitated with 95% isopropanol. The RNA pellet was rinsed with 70% ethanol and air-dried at room temperature. After reconstitution with nuclease-free water, RNA samples with a ratio between 1.8 and 2.0 at a wavelength of 260/280 nm, as determined by NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), were used for the next step.
Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized with iScript™ Select cDNA Synthesis Kit according to the product’s instructions. One microgram of total RNA template was mixed with 5 × reaction mixture, which included 4 μL oligo-(dT)20 primer, 1 μL iScript reverse transcriptase, and nuclease-free water adjusted to 20 μL. The reactions were performed in a thermocycler (Bio-Rad, Inc., Hercules, CA, United States) following steps: denaturation at 65°C for 5 min, primer hybridization at 42°C for 30 min, reverse transcription at 25°C for 5 min, and enzyme inactivation at 85°C for 5 min. The cDNA product was stored at −20°C for the next step.
2.5 Real-time polymerase chain reaction
The mRNA expression of mucosal immunity-related genes, tight junction proteins, and neuropeptides was determined using real-time PCR with a CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) and the 2X (PCR Biosystems Ltd., London, United Kingdom) Lo-ROX as previously described (22). The specific primer sets listed in Table 1, which followed those previously studied (22), were used. The expression of certain genes was normalized as a fold change (2−ΔCt; Ct = the threshold cycle) relative to the reference gene (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GAPDH). Following the equation of the 2−ΔΔCt method (23), semiquantitative of gene expression in all groups was calculated as fold changes from the mean of the NBW group. The amplicons were checked for product specificity by running 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and analyzing the melting curve.
2.6 Semi-quantitative Western blot analysis
The mucosal samples were lysed with RIPA buffer containing 50 mM tris, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N, N, N′, N′-tetraacetic acid (EGTA), 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 1% NP-40, 6.02 mM sodium deoxycholate, 0.01 mg/mL aprotinin, 1 mM NaF, and a cocktail protease inhibitor. After centrifugation, the supernatant was collected, and its protein concentration was measured using the BCA™ protein assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, United States). The lysate sample was incubated with Laemmli buffer containing β-mercaptoethanol (Bio-Rad, Inc., Hercules, CA, United States) at 65°C for 5 min. The denatured protein (30 μg) was separated using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride microporous membrane (Millipore®, St. Louis, MO, United States). After blocking the non-specific binding proteins with 5% non-fat dried milk, the blotted membrane was incubated overnight with primary antibodies, followed by secondary antibodies. The dilution of antibodies was prepared according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. After being developed with an ECL substrate (Santacruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, United States), the immunoreactive band was detected by gel documentation. The band density was analyzed by densitometric Scion Image Software 4.0.3.2 (NIH, Bethesda, MD, United States). The ratio of the target protein band intensity was compared with that of β-actin. All experiments were performed in duplicate to ensure reproducibility.
2.7 Statistical analysis
All data were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of 4 independent experiments from 5 to 32 piglets per group. A comparison of different treatments on varying birth weights was performed using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. One-way ANOVA was used to evaluate gene expression, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. The statistical analysis was done using GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc., CA, USA). A significant difference was considered at a 95% confidence interval (CI; p < 0.05).
3 Results
3.1 Effect of oral GPD on the growth performance of suckling piglets
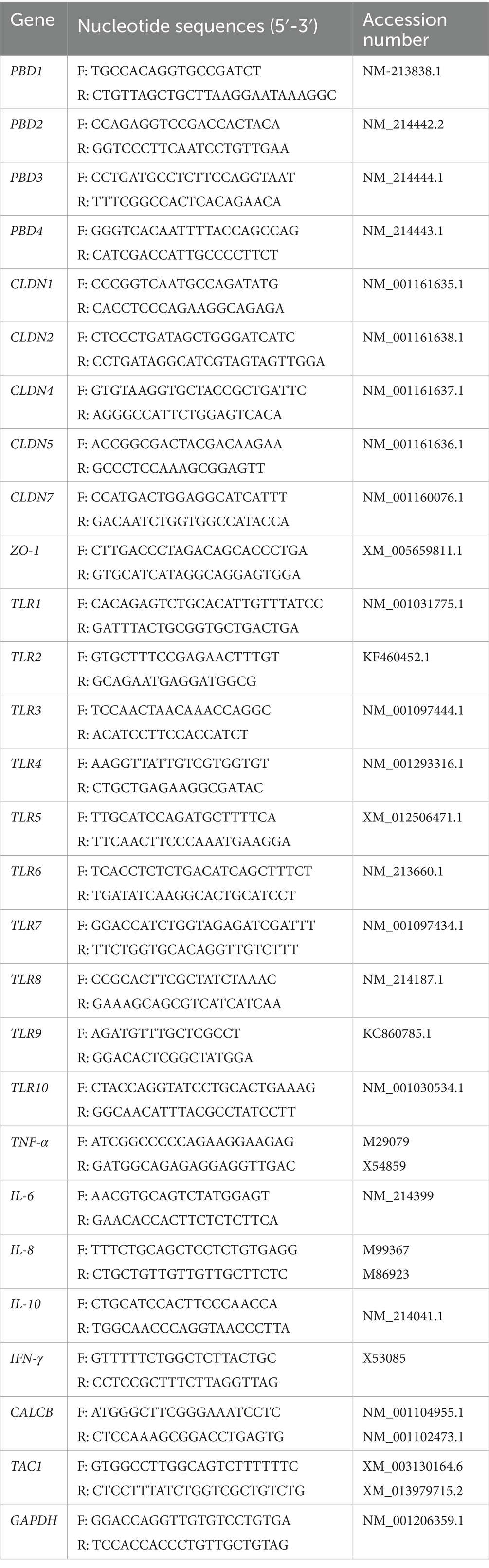
The growth performance of piglets orally administered GPD was demonstrated in two distinct periods: 0–7 and 8–24 days. The average birth weight of NBW piglets was 1.48 ± 0.06, which was significantly higher than LBW piglets (0.95 ± 0.06; p < 0.05; Table 2). During the first week (days 0–7), both NBW and LBW piglets treated with GPD showed significant increases in ADG, despite no difference in the final birth weight (BW) at day 7 compared with the untreated group (p < 0.05; Table 2). During days 8–24, significant increases in both final weight and ADG were also observed in NBW-IgY piglets receiving oral GPD supplementation in relation to NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Table 2). No significant changes in the final weight and ADG were detected between GPD-treated LBW (LBW-IgY) and untreated LBW (Table 2) piglets. Moreover, the final weight of LBW-IgY piglets at 24 days after birth was not different from untreated NBW piglets (Table 2).
3.2 Effect of oral GPD on the mRNA expression of porcine β-defensins in the intestinal mucosa of suckling piglets
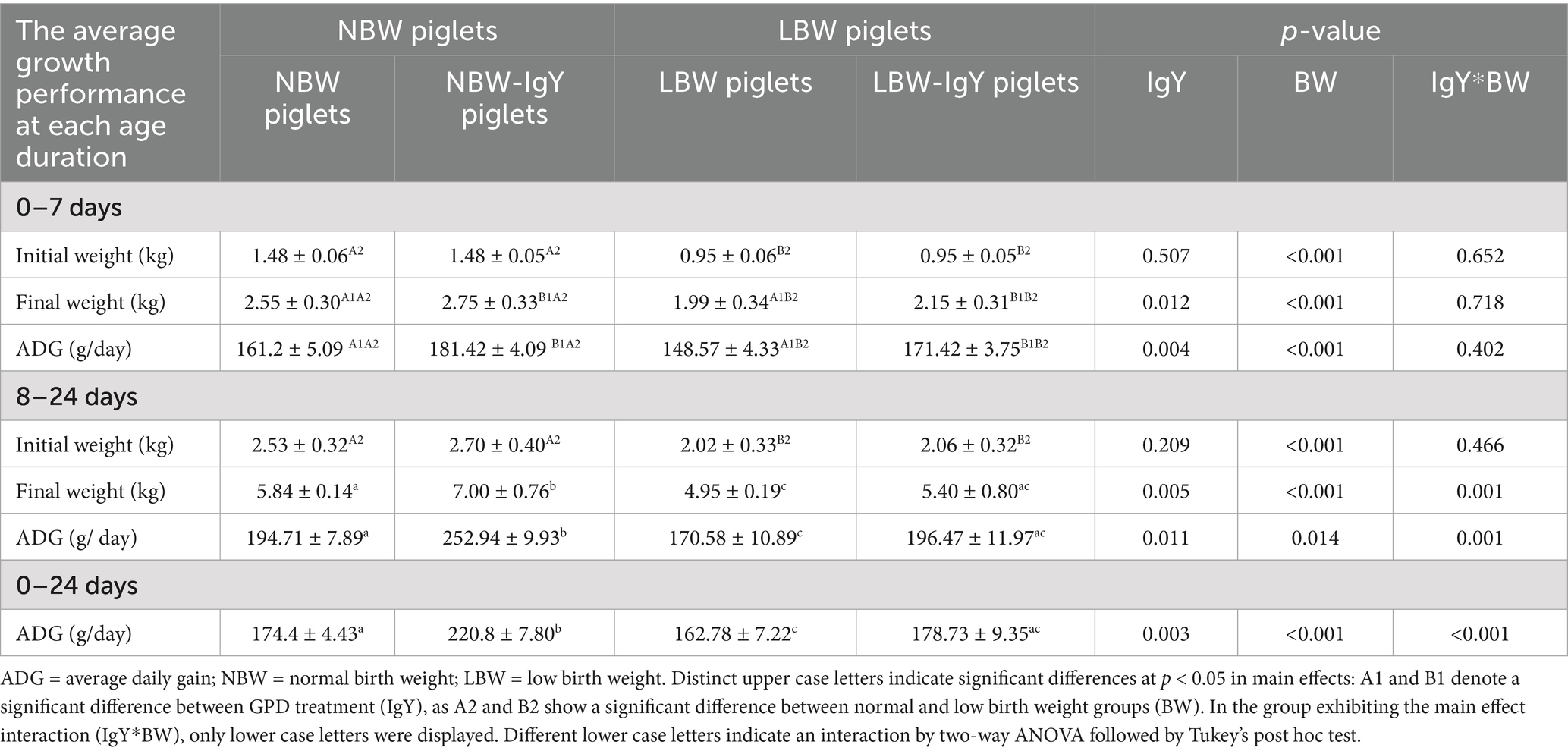
In untreated NBW and LBW piglets, the mRNA expression of PBD1-4 in the intestinal mucosa was detected at a comparable level (1-fold change from NBW piglets; Figure 1), except that PBD1 in the ileal mucosa of LBW piglets was lower than that of NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 1A).
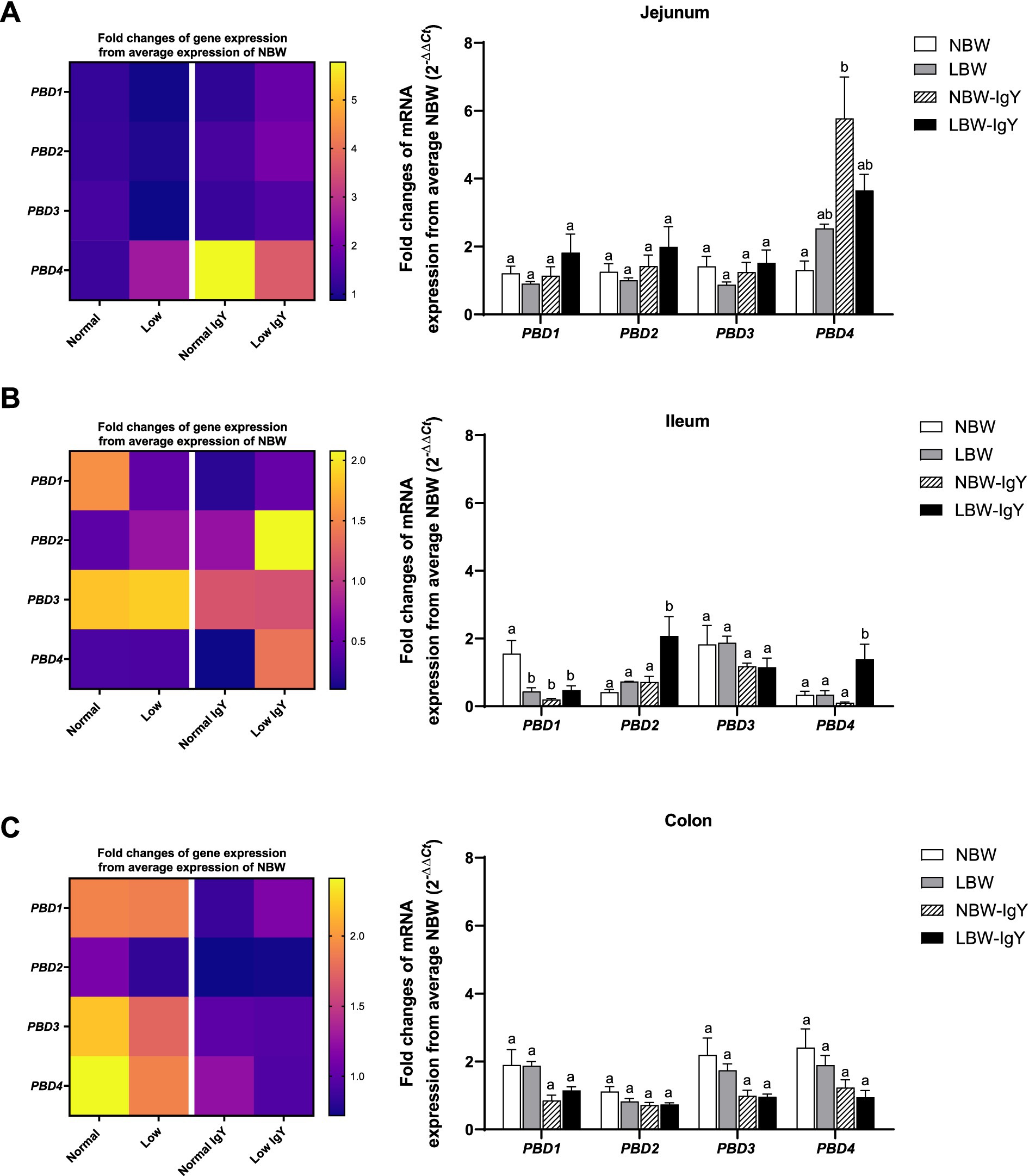
Figure 1. Effect of oral GPD supplementation on the porcine β-defensins (PBD) mRNA expression in (A) jejunal, (B) ileal, and (C) colonic mucosa of suckling piglets with normal birth weight (NBW) piglets vs. low birth weight (LBW) piglets. GPD was orally administered to NBW (NBW-IgY) and LBW (LBW-IgY) piglets at 6 and 10 h after birth. Total RNA was extracted from the intestinal mucosa of 7-day-old piglets. Expressions of PBD1, PBD2, PBD3, and PBD4 were determined by real-time RT-PCR as relative fold changes from the mean of NBW piglets using 2 −∆∆Ct calculation. The heat map represents the mean, and the bar represents the mean ± SEM of individual gene expression conducted in duplicated run (n = 5 piglets). The colors ranging from purple to yellow in the heat map for each gene reflect the fold changes in gene expression from lower to higher than in NBW piglets. Bar graphs with different letters (a or b) indicate significant differences among groups at p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
PBD1-4 expression of NBW-IgY piglets did not differ from that of NBW piglets except that PBD4 was upregulated (>6-fold p < 0.05; Figure 1A) in the jejunal mucosa, and PBD1 was downregulated in the ileal mucosa (2-fold; p < 0.05; Figure 1B).
LBW-IgY piglets showed the highest levels of PBD2 and PBD4 expression in the ileal mucosa among all groups (p < 0.05; Figure 1A). Nevertheless, GPD treatment could not reverse the low-level expression of PBD1 in the ileal mucosa of LBW piglets to the same level as NBW piglets (Figure 1B). Notably, no significant changes in all PBD expressions were detected in the colonic mucosa of untreated or GPD-treated NBW and LBW piglets (Figure 1C).
3.3 Effect of oral GPD on the mRNA expression of toll-like receptors in the intestinal mucosa of suckling piglets
The expression of TLR1-10 mRNA in the intestinal mucosa is shown in Figure 2. In the jejunal mucosa, all TLR types were expressed in NBW piglets at the same levels as LBW piglets (Figure 2A). However, LBW piglets had higher expression of TLR2 in the ileal mucosa and TLR8, TLR9, and TLR10 in colonic mucosa (p < 0.05; Figures 2B,C) but had lower expression of TLR9 in the ileal mucosa as compared with NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 2B).
Figure 2. Effect of oral GPD on the toll-like receptors (TLRs) mRNA expression in (A) jejunal, (B) ileal, and (C) colonic mucosa of suckling piglets with normal birth weight (NBW) piglets vs. low birth weight (LBW) piglets. GPD was orally administered to NBW (NBW-IgY) and LBW (LBW-IgY) piglets at 6 and 10 h after birth. Total RNA was extracted from the intestinal mucosa of 7-day-old piglets. Expressions of TLRs (TLR1 to TLR10) were determined by real-time RT-PCR as relative fold changes from the mean of NBW piglets using 2 −∆∆Ct calculation. The heat map represents the mean, and the bar represents the mean ± SEM of individual gene expression conducted in duplicated run (n = 5 piglets). The colors ranging from purple to yellow in the heat map for each gene reflect the fold changes in gene expression from lower to higher than NBW piglets. Bar graphs with different letters (a or b) indicate significant differences among groups at p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
In the jejunal mucosa of NBW-IgY piglets, the upregulated TLR1, TLR2, and TLR6 expression (>3-fold; p < 0.05; Figure 2A) and the downregulated TLR4 expression were seen as compared with NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 2A). Likely, LBW-IgY piglets showed only upregulated TLR1 and TLR2 expression (>3-fold; p < 0.05; Figure 2A) in the jejunal mucosa.
In the ileal mucosa, GPD treatment downregulated only TLR6 in NBW-IgY and LBW-IgY piglets compared to NBW (p < 0.05; Figure 2B). Treatment with GPD enhanced the TLR2 upregulation in the ileal mucosa of LBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 2B). However, TLR1, TLR3, TLR4, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, and TLR10 mRNA expressions were not modulated by GPD in the ileal mucosa of both LBW and NBW piglets (p > 0.05; Figure 2B).
The colonic mucosa of both NBW and LBW piglets treated with GPD demonstrated the elevated TLR4, TLR5, TLR8, and TLR9 expression (>2-fold; p < 0.05; Figure 2C). The upregulated TLR6, TLR7, and TLR10 were additionally observed in LBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 2C) as compared with NBW piglets. Nonetheless, the level of the increased TLR8, TLR9, and TLR10 expression in LBW-IgY piglets was not different from that of LBW piglets (Figure 2C). Markedly, in the colonic mucosa, GPD treatment could not alter TLR1, TLR2, and TLR3 expression in NBW and LBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 2C).
3.4 Effect of oral GPD on the growth performance and mRNA expression of cytokines in the intestinal mucosa of suckling piglets
The mRNA expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α), chemokines (IL-8), and anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10), but not interferons (IFN-γ), were detected in the intestinal mucosa of both NBW and LBW piglets. In all untreated intestinal mucosa, TNF-α and IL-6 expression in NBW piglets did not differ from LBW piglets (Figures 3A–C). Compared with NBW piglets, LBW piglets revealed a significantly higher IL-8 expression in the colonic mucosa (>5-fold; p < 0.05; Figure 3C) but not in the ileal or jejunal mucosa. Interestingly, the IL-10 mRNA expression of LBW piglets was lower in the jejunal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 3A), but higher in the colonic mucosa than that of NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3C).
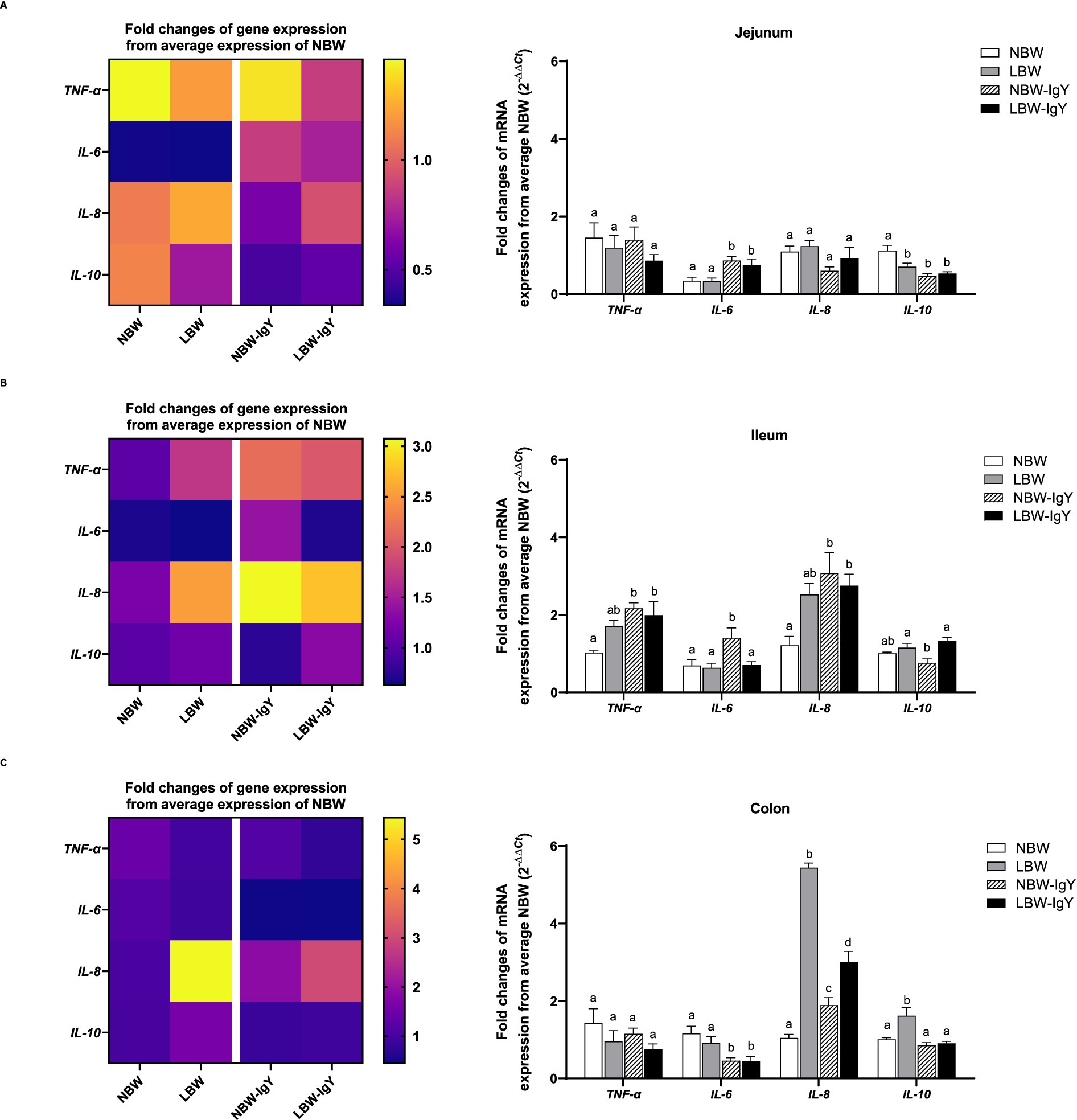
Figure 3. Effect of oral GPD on interleukin (IL)-6, −8, and −10 and tumor necrotic factor (TNF)-α mRNA expression in (A) jejunal, (B) ileal, and (C) colonic mucosa of suckling piglets with normal birth weight (NBW) piglets vs. low birth weight (LBW) piglets. GPD was orally administered to NBW (NBW-IgY) and LBW (LBW-IgY) piglets at 6 and 10 h after birth. Total RNA was extracted from the intestinal mucosa of 7-day-old piglets. Expressions of related cytokines IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10, and TNF-α were determined by real-time RT-PCR as relative fold changes from the mean of NBW piglets using 2 −∆∆Ct calculation. The heat map represents the mean, and the bars represent the mean ± SEM of individual gene expression conducted in a duplicated run (n = 5 piglets). The colors ranging from purple to yellow in the heat map for each gene reflect the fold changes of gene expression from lower to higher than NBW piglets. Bar graphs with different letters (a, b, c, or d) indicate significant differences among groups at p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
GPD elevated TNF-α expression only in the ileal tissue (p < 0.05; Figure 3A) but not in the jejunal or colonic mucosa of both NBW and LBW piglet groups (Figures 3B,C). Additionally, IL-6 was upregulated in the jejunal mucosa of both NBW-IgY and LBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3A), as well as in the ileal mucosa of NBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3B). Unlikely, GPD downregulated IL-6 expression in all colonic mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 3C). In the ileal mucosa, GPD upregulated IL-8 in both NBW-IgY and LBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3B); however, the increased IL-8 expression was not significantly different from untreated LBW piglets (Figure 3B). In the colonic mucosa, LBW piglets showed upregulated IL-8 expression compared to NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3B). The GPD treatment could reverse the upregulated IL-8 expression in LBW-IgY piglets to below that of LBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3C), but the IL-8 level in LBW-IgY piglets still remained higher than in NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3C). GPD increased IL-8 expression in NBW-IgY piglets compared to NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3C); however, the level of increased IL-8 expression was lower than in LBW or LBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3C).
In the LBW piglets, IL-10 expression was lower in duodenal mucosa but higher in colonic mucosa than NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figures 3A,C). GPD could not reverse the downregulated IL-10 expression in the duodenal mucosa; moreover, it suppressed IL-10 in NBW-IgY (p < 0.05; Figure 3A). In contrast, in the colonic mucosa, GPD significantly reversed the upregulated IL-10 expression caused by LBW-IgY piglets to the same level as NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3C). In the jejunal mucosa, the level of IL-10 expression in NBW and LBW piglets was similar (p > 0.05; Figure 3B); however, GPD treatment downregulated the IL-10 in NBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 3B).
3.5 Effect of oral GPD on the mRNA expression of neuropeptides related to inflammation in the intestinal mucosa of suckling piglets
The level of calcitonin-related polypeptide beta (CALCB) expression in jejunal and colonic mucosa in LBW piglets was higher than in other groups (>3-fold; p < 0.05; Figures 4A,C). Unlikely, LBW piglets had lower tachykinin precursor 1 (TAC1) expression in the ileal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 4B), but its TAC1 expression in the colonic mucosa was higher than that of NBW piglets (2–4 fold; p < 0.05; Figure 4C).
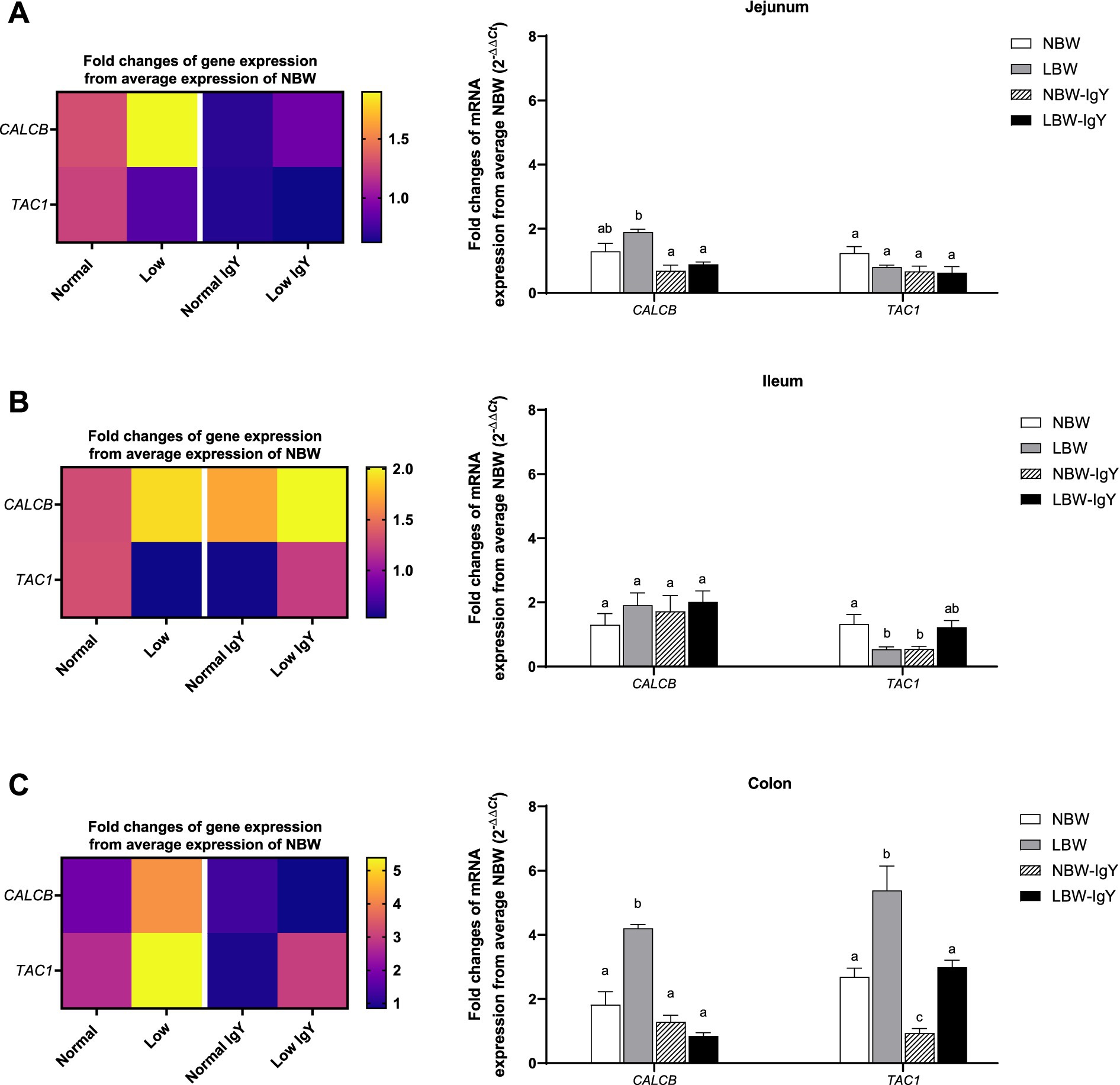
Figure 4. Effect of oral GPD on the mRNA expression of neuropeptides related to inflammation, calcitonin-related polypeptide beta (CALCB) and tachykinin precursor 1 (TAC1) mRNA expression in (A) jejunal, (B) ileal, and (C) colonic mucosa of suckling piglets with normal birth weight (NBW) piglets vs. low birth weight (LBW) piglets. GPD was orally administered to NBW (NBW-IgY) and LBW (LBW-IgY) piglets at 6 and 10 h after birth. Total RNA was extracted from the intestinal mucosa of 7-day-old piglets. Expression of CALB and TAC1 was determined by real-time RT-PCR as relative fold changes from the mean of NBW piglets using 2 −∆∆Ct calculation. The heat map represents the mean, and the bar represents the mean ± SEM of individual gene expression conducted in duplicated run (n = 5 piglets). The colors ranging from purple to yellow in the heat map for each gene reflect the fold changes of gene expression from lower to higher than NBW piglets. Bar graphs with different letters (a, b, or c) indicate significant differences among groups at p value < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
GPD did not alter the CALB expression in any intestinal mucosa (Figure 4), whereas it downregulated TAC1 expression in the ileal and colonic mucosa of NBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figures 4B,C). However, GPD reversed the upregulated CALB expression in the jejunal and colonic mucosa to the same level as NBW piglets (p > 0.05; Figures 4A,C). GPD also reversed the upregulated TAC1 expression in the colonic mucosa of LBW-IgY piglets to the same level as in NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 4C).
3.6 Effect of oral GPD on the mRNA and protein expression of tight junction proteins of suckling piglets
There was no difference in mRNA expression of all examined claudins (CLDNs), CLDN1, CLDN2, CLDN4, and CLDN7, and scaffold proteins Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1) in the jejunal mucosa of NBW and LBW piglets (Figure 5A). Unlikely, CLDN7 expression in LBW piglets was lower in the ileal mucosa but higher in the colonic mucosa compared with those in NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figures 5B,C, respectively). Additionally, the colonic mucosa of LBW piglets expressed a lower level of CLDN1 than that of NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 5C).
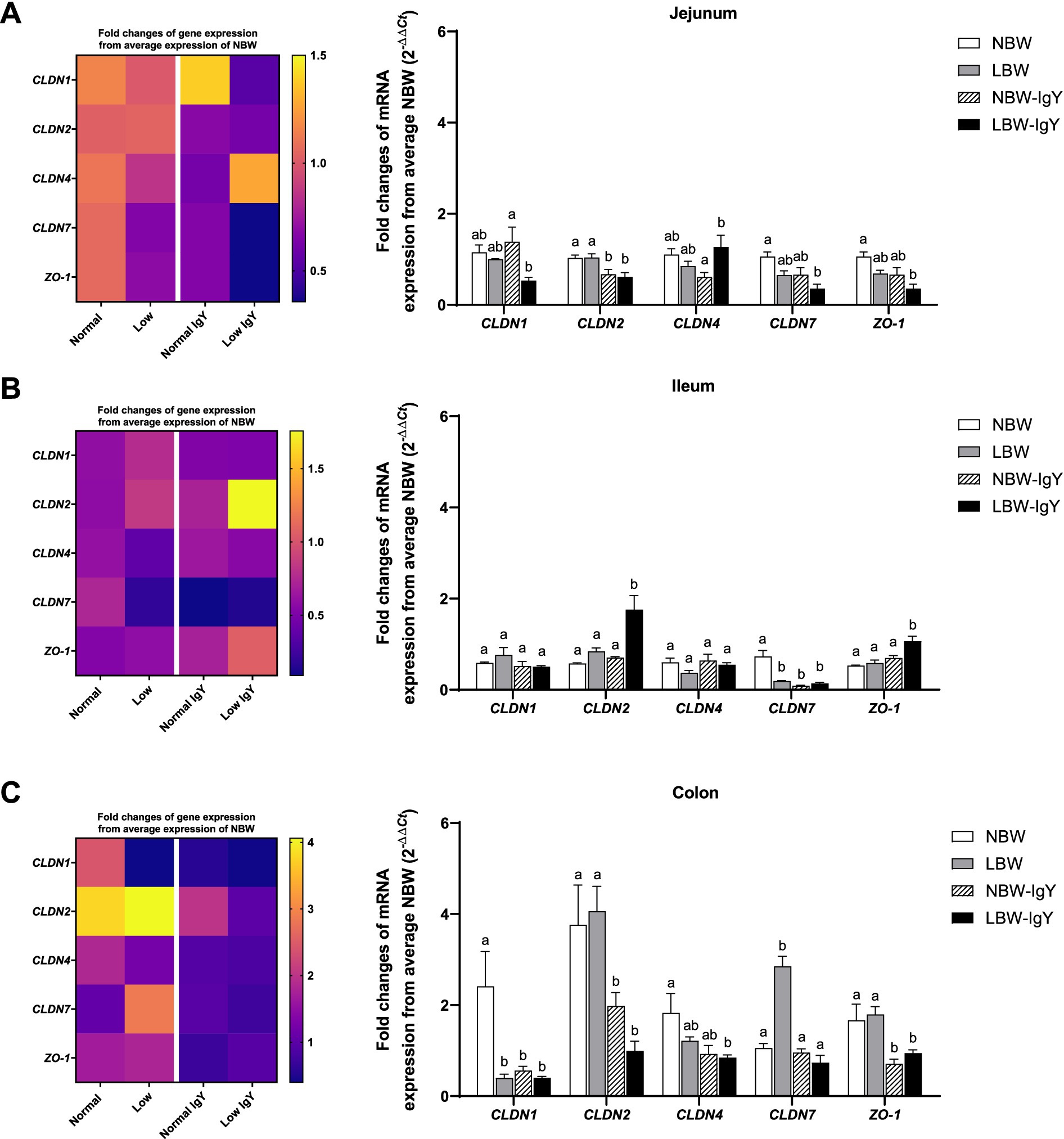
Figure 5. Effect of oral GPD on the mRNA expression of tight junction proteins in (A) jejunal, (B) ileal, and (C) colonic mucosa of suckling piglets with normal birth weight (NBW) piglets vs. low birth weight (LBW) piglets. GPD was orally administered to NBW (NBW-IgY) and LBW (LBW-IgY) piglets at 6 and 10 h after birth. Total RNA was extracted from the intestinal mucosa of 7-day-old piglets. Expressions of claudin, CLDN1, CLDN2, CLDN4, CLDN7, and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) were determined by real-time RT-PCR as relative fold changes from the mean of NBW piglets using 2 −∆∆Ct calculation. The heat map represents the mean, and the bar represents the mean ± SEM of individual gene expression conducted in duplicated run (n = 5 piglets). The colors ranging from purple to yellow in the heat map for each gene reflect the fold changes of gene expression from lower to higher than NBW piglets. Bar graphs with different letters (a or b) indicate significant differences among groups at p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
GPD supplementation suppressed CLDN2 in the jejunal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 5A), CLDN7 in the ileal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 5B), as well as CLDN1 and CLDN2 in the colonic mucosa of NBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 5C).
In the LBW-IgY piglets, CLDN2 was downregulated in the jejunal and colonic mucosa, respectively (p < 0.05; Figures 5A,C). GPD increased CLDN4 of LBW-IgY piglets in the jejunal mucosa compared with NBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 5A), but it did not significantly differ from NBW and LBW piglets (Figure 5A).
Interestingly, GPD downregulated CLDN7 in the ileal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 5B) and downregulated CLDN1 in the colonic mucosa of NBW piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 5C). Nonetheless, the downregulated CLDN7 and CLDN1 in LBW-IgY piglets could not be reversed by GPD treatment (p > 0.05; Figures 5B,C).
In addition to CLDNs expression, GPD upregulated ZO-1 only in the ileal mucosa of LBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 5B) but downregulated ZO-1 expression in the colonic mucosa of NBW-IgY and LBW-IgY piglets (p < 0.05; Figure 5C).
Relative protein expressions of the above CLDNs and ZO-1in the intestinal mucosa were further evaluated using Western blot analysis. LBW piglets upregulated ZO-1 in the jejunal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 6A), CLDN4 in the ileal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 6B), and CLDN2, CLDN4, and CLDN7 in the colonic mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 6C) when compared with NBW piglets. Notably, GPD-treated LBW piglets reversed upregulation of ZO-1 in the jejunal mucosa and reversed the upregulation of CLDN2, CLDN4, and CLDN7 in the colonic mucosa to the same level as in the NBW piglets (p > 0.05; Figures 6A,C).
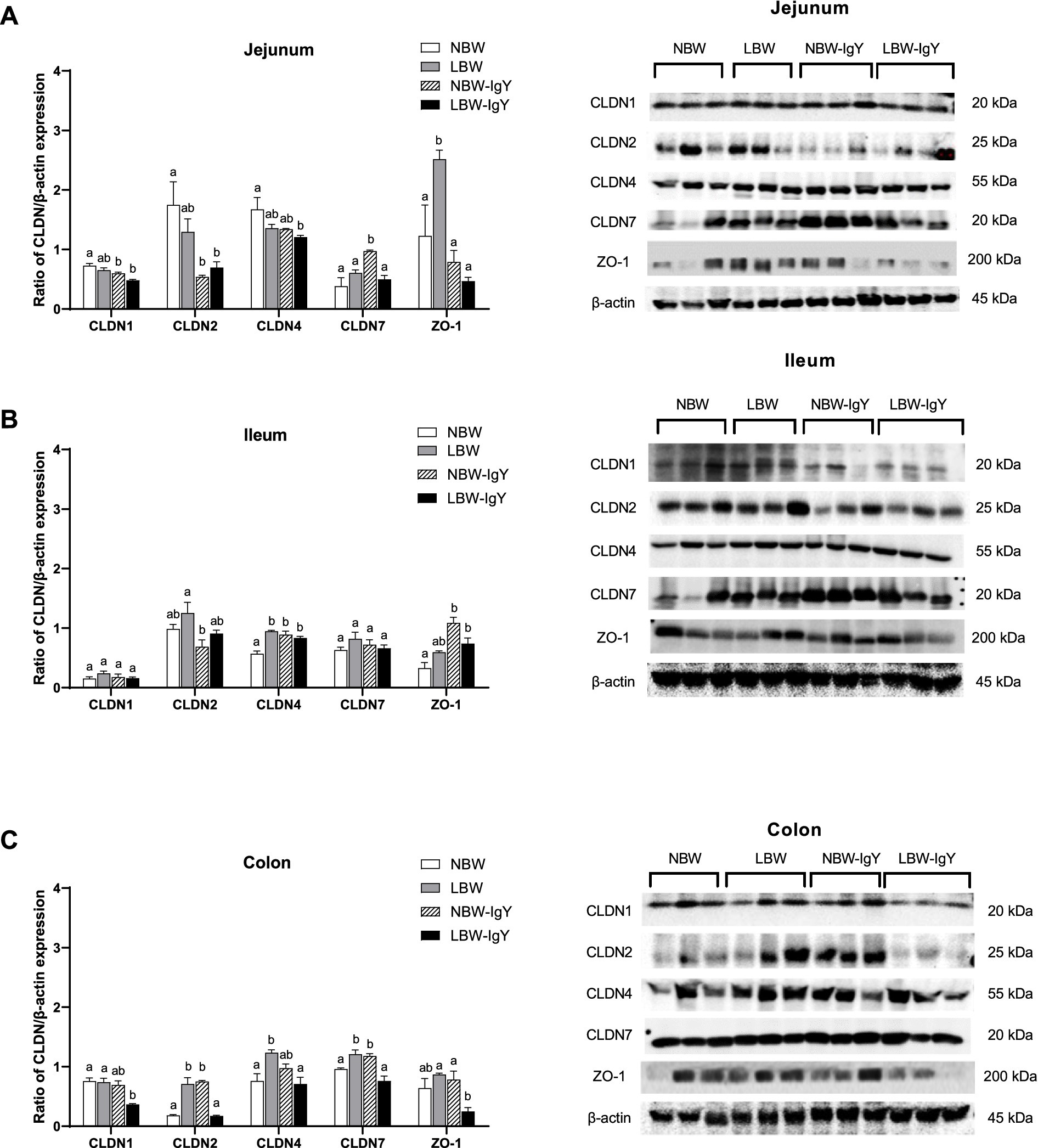
Figure 6. Effect of oral GPD on tight junction proteins expression in (A) jejunal, (B) ileal, and (C) colonic mucosa of suckling piglets with normal birth weight (NBW) piglets vs. low birth weight (LBW) piglets. GPD was orally administered to NBW (NBW-IgY) and LBW (LBW-IgY) piglets at 6 and 10 h after birth. Semi-quantitative Western blot analysis of tight junction proteins, claudins (CLDNs), CLDN1, CLDN2, CLDN4, and CLDN7, and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) were compared with β-actin. Representative protein bands of Western blot contributed to the quantitative analysis at 7 days after supplementation were presented in the right panel. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of experiments conducted in duplicated run (n = 5 piglets). Bar graphs with different letters (a, b, or c) indicate significant differences among groups at p 0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
Nevertheless, GPD treatment in NBW piglets significantly upregulated CLDN7 in the jejunal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 6A). In addition, CLDN4 and ZO-1 in the ileal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 6B) and CLDN2 and CLDN7 in the colonic mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 6C) were upregulated, but CLDN1 and CLDN2 were downregulated in the jejunal mucosa (p < 0.05; Figure 6A).
4 Discussion
Our study demonstrates that commercial oral IgY Globigen® Pig Doser (EW Nutrition GmbH, Visbek, Germany; GPD) supplementation has a positive effect on growth in NBW piglets, significantly increasing the final weight at weaning. Although the GPD supplementation could not increase the final weight of LBW piglets to the same degree as NBW-IgY piglets, the final weight and ADG of LBW-IgY piglets were comparable to those of NBW piglets. These results indicate that the use of GPD supplementation can increase postpartum body weight and weaning weight of both NBW and LBW piglets.
Indeed, the control NBW group that was not treated also showed an increase in final weight and weight gain at 7 days. However, the results of the NBW-IgY group assessed at 24 days were higher than those of the untreated NBW group. Our study highlighted that GPD supplementation improves the local intestinal innate immunity, which is associated with the growth performance-enhancing potential of GPD in pre-weaned piglets. Globigen® Jump Start (EW Nutrition GmbH, Visbek, Germany) supplementation provides passive immunity against multiple common pathogens challenged piglets during the first weeks of life, that is, E. coli (ETEC) F4 and F18, E. coli K88, Clostridium perfringens, rotavirus, and S. typhimurium (17, 24), but not a direct effect on growth performance.
Pathogenic E. coli strains, the most common pathogens on the first day, particularly ETEC, utilize fimbriae (also known as pili) to adhere to the intestinal mucosa of piglets. This adherence is crucial for colonization and subsequent infection (25). Once attached, these bacteria produce enterotoxins, such as heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) and heat-stable enterotoxin (ST), which disrupt the normal fluid balance in the intestines, leading to diarrhea (26).
Possibly, administering GPD blocked bacterial adhesion to intestinal mucus, reduced colonic bacterial loads, and stabilized inflammatory cytokine levels, thereby improving gut health and potentially supporting better growth performance (18). Even though the commercial oral GPD improved growth performance in LBW-IgY to NBW piglets, the results were not significantly different from LBW piglets.
In addition to IgY against specific pathogens, as in Globigen® Jump Start (EW Nutrition GmbH, Visbek, Germany), Globigen® Pig Doser (EW Nutrition GmbH, Visbek, Germany) contains other active gradients, including soybean oil, vitamins A, D3, and E, and probiotics Enterococcus faecium (24), aiming to reduce diarrhea and intestinal inflammation in piglets. The anti-inflammatory effect of commercial oral GPD supplementation may protect physiological processes in terms of energy conservation against fever and anorexia, thereby causing a reduction in pig performance. Interestingly, soybean oil not only facilitates the delivery of IgY but also provides additional nutritional benefits (27). It appears that the potential immunity effects of oral IgY supplementation depend on proper epithelial integrity. Since LBW piglets were indicated to have lower small intestine development and function than NBW piglets (28), the response of LBW-IgY piglets was not comparable to that of NBW-IgY piglets. However, vitamin A, D, and E are essential vitamins for growth and development, promoting the expression of barrier TJs protein, such as Cldn-1 and Occludin1 expression in jejunum and ileum (29, 30). In addition, the expressions of inhibitory cytokines, such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10, are upregulated, while the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, is downregulated by these essential vitamins (29, 30). E. faecium is a beneficial bacterium that promotes intestinal health (31). It raised the possibility that GPD reduces gastrointestinal infections during supplementation and may have a long-term effect promoting the cellular target of mucosal immunity in all post-weaned piglets.
The cellular target of GPD in distinct intestinal tissues was of interest since each intestinal site has a specific gut health responsibility. The jejunum is the primary region to absorb most nutrients, the ileum, consisting of Peyer’s patch, exerts immunity and barrier function, and the colon is mainly involved in water reabsorption (32) is colonized by a large microbial population (59). Our current results indicate that the expression of tight junction genes and proteins, as well as the expression of genes related to mucosal barrier and immunity, in the jejunal, ileal, and colonic mucosa was most considered and found to be modulated by GPD supplementation to varying degrees.
Porcine β-defensins (PBDs) are antimicrobial peptides (AMP) that play an important role in the innate immune response in the intestine (33, 34). In the present study, using the ileal mucosa of LBW piglets, GPD supplementation was found to upregulate PBD2 and PBD4 without affecting the low level of PBD1 expression. The low constitutive PBD1 expression may be of less significance since PBD2 and PBD3, rather than PBD1, are inducible subtypes in response to invasive microorganisms (35). As the pig PBD2 or human BD4 has antimicrobial activity against S. typhimurium, E. coli, C. perfringens, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa (36, 37). Our data indicate that GPD supplementation increases the expression of PBDs, notably in the intestinal mucosa of LBW piglets, where the gut immune system may be underdeveloped or impaired. Improving PBD expression through GPD supplementation may be especially effective in providing antibacterial protection.
The induction of PBD synthesis by both microbial and chemical stimuli is mediated by hormonal receptors, including the epidermal growth factor receptor (EFGR) (38–40). Chicken egg powder-based immunoglobulin, Globigen® Pig Doser (EW Nutrition GmbH, Visbek, Germany), contains specific antibodies raised against pathogens in piglets, that is, enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) (24). Hyperimmunized IgY and critical proteins in egg yolks may enhance intestinal immune system development, notably innate immune system PRRs and signaling system to trigger all epithelial pathogen responses.
TLRs are one of the major PRRs that are expressed by immune and non-immune cells, including intestinal epithelial cells (41). All TLR1-10 subtypes were identified in the intestinal tissues used in the present study. These TLRs play significant roles in promoting both adaptive and regulatory immunity. For example, TLR8 and TLR9 are responsible for the production of antiviral molecules such as type I interferons (60), whereas TLR2, TLR4, and TLR6 stimulate an inflammatory response against pathogenic bacteria and probiotics (42). Moreover, TLR2 and TLR4 simultaneously stimulate the production of IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, which inhibits the overresponse from inflammation (61).
In the present results, the TLR1, TLR2, and TLR6 in NBW-IgY and LBW-IgY piglets’ jejunum, as well as the TLR2 in LBW-IgY piglets’ ileum, were upregulated. Even though the evidence does not seem significant in the small intestinal tissues, which have the principal function in nutrient absorption, the upregulated TLRs may help the small intestine mucosa respond to microorganisms during food transit in the lumen. In colonic mucosa, the upregulation of several TLRs, TLR4, TLR5, TLR8, and TLR9 in NBW-IgY piglets and TLR4, TLR5, and TLR10 in LBW-IgY piglets indicates that GPD may help promote microbial recognition at the colonic mucosa. Conversely, the upregulation of TLR2, TLR8, TLR9, and TLR10, especially in the colonic mucosa of LBW piglets, may cause undesired effects. In the stress weaning piglets, pathogenic bacteria, including E. coli, a diarrhea-causing bacterium directly binds cell-surface molecules such as gangliosides GM1 (43), inducing the cellular response including the expression of many genes associated with intestinal mucosal immunity, that is, TLRs, pro-inflammatory cytokines or tight junction proteins (44). High levels of colonic TLRs expression may cause the over-response of LBW piglets to all microorganisms, including residential microflora in the colon resulting in chronic inflammation. The evidence may be associated with poor growth performance in LBW piglets.
Cytokines play crucial roles in the pig intestinal system by mediating immune responses, regulating inflammation, and affecting overall gut health. In the present study, the expression of relevant cytokines was detected except for IFN-γ. The primer sets used in this study were tested and reported in our previous study (22). However, the level of IFN-γ. expression in intestinal mucosa was undetectable. Thus, the result of IFN-γ expression was not demonstrated in the figure. The expression level of cytokine genes TNF-α and IL-6 by the intestinal mucosa of LBW piglets was similar to that of NBW piglets. In contrast, the expression of IL-8 in in the colonic mucosa of LBW piglets was generally greater than in NBW piglets. The increased TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-8 in the hindgut mucosa of LBW piglets has been previously reported (45). IL-8 plays a key role in the early inflammatory response by activating monocytes and recruiting neutrophils to the site of inflammation (46). Therefore, high expression of IL-8 in the colonic mucosa of LBW piglets indicated a proneness to low-grade inflammation (45). However, upregulated TNF-α and IL-6 coincided with downregulated IL-10 contributes to intestinal inflammation and barrier dysfunction (47). Perhaps, our finding of the upregulation of inhibitory cytokines IL-10 in the colonic mucosa may help in managing the inflammation in LBW piglets. Even though the downregulated IL-10 was found in the jejunal mucosa of LBW piglets, it did not coincide with the upregulated pro-inflammatory cytokines. Thereby, gastrointestinal disorders or enteritis were not shown in all LBW piglets during the suckling period. Nonetheless, the long-term effects of the changes in cytokine levels need to be monitored.
Our findings reveal that GPD treatment altered cytokine profiles relevant to TLR expression in different segments of the intestinal mucosa. GPD increased IL-6 in the jejunal mucosa and TNF-α and IL-8 in the ileal mucosa, but decreased IL-10, especially in the jejunal and ileal mucosa of NBW piglets and LBW piglets. As mentioned earlier, based on cytokines levels, GPD treatment indicates a shift toward a more pro-inflammatory environment, which could improve pathogen clearance but also increase the risk of inflammation-related tissue damage. Coincidentally, GPD-upregulated TLRs improved colonic mucosa responsiveness to recognizing pathogens in all piglets. Meanwhile, GPD reversed IL-8 overexpression in colonic mucosa of LBW piglets, which may improve intestinal immune response by preventing overactive immune response, causing intestinal mucosa damage.
Enteric nervous system neurochemicals CGRP and SP govern secretomotor reflex, motility, and secretory response to modulate bacterial toxin sensing and adherence (48, 49). Early weaning stress causes as long-term reduction in gut barrier function along with increased secretomotor activity. The suggested mechanisms involved corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) signaling pathways and inflammatory cytokine responses to stimulate cholinergic secretory activities (50). However, the increase in cholinergic neurons did not completely explain the increased neurosecretory diarrhea in early weaned piglets (50). Instead, high levels of TAC1 and CALCB, which encode SP and CGRP, are related to several pathologic states, including GI inflammation and nerve damage (51). Our results found the elevated TAC1 and CALCB only in the LBW piglets’ colonic mucosa, which was correlated with a greater level of IL-8. Interestingly, these elevated neuropeptides and IL-8 expression levels were reversed by the GPD supplementation, indicating that GPD may improve gastrointestinal health in LBW piglets by inhibiting the adherence of luminal pathogens to the intestinal mucosa.
TJs are multiprotein complexes crucial for intestinal barrier function, regulating the paracellular permeability of ions, water, and molecules (52). The present study focused on alterations of barrier builder (CLDN1, CLDN4, CLDN7, and ZO-1) and pore forming (CLDN2) TJ mRNA and protein expression in response to birth weight or GPD. Both NBW and LBW piglets showed different TJ mRNA and protein expression in the intestinal mucosa; however, only the increased CLDN7 protein was associated with gene expression in the colonic mucosa. However, the regulation of TJs protein expression should be more thoroughly examined because it exploits functions in gut integrity.
In LBW piglets, the upregulated barrier builder TJs, ZO-1 in the jejunal mucosa, and CLDN4 in the ileal mucosa were found. Additionally, CLDN2, CLDN4, and CLDN7 were upregulated in the colonic mucosa. The increased barrier TJs in the early stage of life in LBW piglets from the “open state” to “close state” or leaky to tight epithelia may be disadvantageous to paracellular permeability for growth factors and immunoglobulins presented in colostrum/milk to be transported (53).
In contrast, overexpression of pore-forming TJs, CLDN2, in the colonic mucosa where the pathogens are colonized may be harmful (54). These findings indicate an adaptive response in LBW piglets to maintain intestinal barrier integrity; however, TJs that mediate epithelial tightening may be overexpressed or imbalanced. GPD treatment modulated TJ expressions in LBW piglets, especially the increased ZO-1 in the jejunal mucosa to levels comparable to NBW piglets. Although the IgY decreased barrier TJs, CLDN1, CLDN4, and ZO-1 and pore-forming TJ, CLDN2, in LBW piglets’ colon, it should be considered as a benefit because the growth retardation of LBW piglets were reversed to normal (Figure 6C; Table 2).
In NBW piglets, GPD promotes growth performance by increasing the characteristics of tight epithelia through upregulation of CLDN4, CLDN7, and ZO-1, while downregulating CLDN2 in jejunal and ileal regions. In addition to maintaining gut integrity, upregulated ZO-1 is involved in cell signaling pathways that regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and repair. Dietary supplement mitigates the effects of enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) infections by modulation of ileal microbiota involving the increase of ZO-1 expression (55). The increased ZO-1 was also widely distributed under conditions of faster cell turnover/proliferation (56).
Moreover, another study found that high dietary calcium and microbial phytase intake enhanced the expression of CLDN4 and CLDN7, promoting paracellular calcium absorption, which is vital for nutrient absorption and gut health (57). IgY treatment downregulated the cation-pore-forming TJ, CLDN2 expression; however, CLDN2 is often associated with inflammation and barrier dysfunction in response to inflammatory signals (58). Perhaps, like other diets, GPD may promote post-birth bacterial colonization by influencing the expression of TJs or directly enhance gut maturation, promoting intestinal health in suckling piglets. Nevertheless, the GPD effect, by improving intestinal morphology and barrier function, promoting beneficial gut microbiota, and improving outcomes in the GIT of piglets, needs to be further confirmed.
5 Conclusion
Application of commercial IgY-based supplement Globigen® Pig Doser (EW Nutrition GmbH, Visbek, Germany) demonstrates a positive effect on growth performance in suckling piglets, whether the piglet has a low or normal birth weight. GPD supplementation also enhances intestinal mucosal immunity by modulating the expression of the innate immune system, that is, TLRs, cytokines, and tight junction genes, particularly in LBW piglets, which have a distorted development from NBW piglets. The study’s findings may serve as an informative tool for interested parties and provide guidelines for management to improve gut health, particularly in LBW piglets, thereby preventing pre-weaning losses.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol number 2231047). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
ML: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft. AK: Conceptulaization, Writing – review & editing. MM: Methodology, Investigation, Data curation. DR: Investigation, Data curation. TS: Investigation, Data curation. ST: Data curation, Conceptualization. CD: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. SP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was partially supported by Faculty of Agriculture, Kasetsart University (Grant numbers: YF9(KU)1.66) and Faculty of Veterinary Science research grants Chulalongkorn University (Basic FF_4709702/2567-HEAF67310017). This work was carried out by means of the collaboration between Faculty of Veterinary Science research grants Chulalongkorn University and Thai Foods Swine Farm Co., Ltd.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Thai Food Research Center, Thai Foods Swine Farm Co., Ltd., for kindly supporting the laboratory animals, and the Faculty of Medicine, Srinakharinwirot University, for providing the equipment used in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2025.1458279/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Beaulieu, AD, Aalhus, JL, Williams, NH, and Patience, JF. Impact of piglet birth weight, birth order, and litter size on subsequent growth performance, carcass quality, muscle composition, and eating quality of pork1. J Anim Sci. (2010) 88:2767–78. doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-2222
2. Morise, A, Louveau, I, and Le Huërou-Luron, I. Growth and development of adipose tissue and gut and related endocrine status during early growth in the pig: impact of low birth weight. Animal. (2008) 2:73–83. doi: 10.1017/S175173110700095X
3. Hurley, WL, and Theil, PK. Perspectives on immunoglobulins in colostrum and milk. Nutrients. (2011) 3:442–74. doi: 10.3390/nu3040442
4. Le Dividich, J, Rooke, J, and Herpin, P. Nutritional and immunological importance of colostrum for the new-born pig. J Agric Sci. (2005) 143:469–85. doi: 10.1017/S0021859605005642
5. Raffaela, P, Brancaccio, M, Laneri, S, De Biasi, M-G, Lombardo, B, and Scudiero, O. A novel view of human Helicobacter pylori infections: interplay between microbiota and beta-defensins. Biomolecules. (2019) 9:237. doi: 10.3390/biom9060237
6. Adewole, DI, Kim, IH, and Nyachoti, CM. Gut health of pigs: challenge models and response criteria with a critical analysis of the effectiveness of selected feed additives – a review. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2016) 29:909–24. doi: 10.5713/ajas.15.0795
7. Turner, JR. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2009) 9:799–809. doi: 10.1038/nri2653
8. Akira, S, Uematsu, S, and Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. (2006) 124:783–801. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.015
9. Izcue, A, Coombes, JL, and Powrie, F. Regulatory T cells suppress systemic and mucosal immune activation to control intestinal inflammation. Immunol Rev. (2006) 212:256–71. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00423.x
10. Furukawa, S, Kuroda, Y, and Sugiyama, A. A comparison of the histological structure of the placenta in experimental animals. J Toxicol Pathol. (2014) 27:11–8. doi: 10.1293/tox.2013-0060
11. Nuntapaitoon, M, Juthamanee, P, Theil, PK, and Tummaruk, P. Impact of sow parity on yield and composition of colostrum and milk in Danish landrace x Yorkshire crossbred sows. Prev Vet Med. (2020) 181:105085. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2020.105085
12. Dubourdieu, D. Colostrum antibodies, egg antibodies and monoclonal antibodies providing passive immunity for animals. In: RC Gupta, A Srivastava, and R Lall, editors. Nutraceuticals in veterinary medicine. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2019). 245–57.
13. Agbokounou, A, Ahounou, S, Youssao Abdou Karim, I, Mensah, G, B, K, and Hornick, J-L. Effect of cow colostrum on the performance and survival rate of local newborn piglets in Benin Republic. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2017) 49:287–94. doi: 10.1007/s11250-016-1191-6
14. Playford, RJ, and Weiser, MJ. Bovine colostrum: its constituents and uses. Nutrients. (2021) 13:265. doi: 10.3390/nu13010265
15. Schade, R, Calzado, EG, Sarmiento, R, Chacana, PA, Porankiewicz-Asplund, J, and Terzolo, HR. Chicken egg yolk antibodies (IgY-technology): a review of Progress in production and use in research and human and veterinary medicine. Altern Lab Anim. (2005) 33:129–54. doi: 10.1177/026119290503300208
16. Lee, L, Samardzic, K, Wallach, M, Frumkin, LR, and Mochly-Rosen, D. Immunoglobulin Y for potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications in infectious diseases. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:696003. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.696003
17. Pozzebon da Rosa, D, de Moraes Vieira, M, Kessler, AM, de Moura, TM, Frazzon, APG, Mcmanus, CM, et al. Efficacy of hyperimmunized hen egg yolks in the control of diarrhea in newly weaned piglets. Food Agric Immunol. (2015) 26:622–34. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2014.998639
18. Wang, Z, Li, J, Li, J, Li, Y, Wang, L, Wang, Q, et al. Protective effect of chicken egg yolk immunoglobulins (IgY) against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 adhesion in weaned piglets. BMC Vet Res. (2019) 15:234. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-1958-x
19. Marcq, C., Théwis, A., Portetelle, D., and Beckers, Y. Keep bacteria under control: dietary modulation of gut microflora in farm animals by use of hen egg yolk antibodies. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. (2010) 94:e2–e10. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01014.x
20. Cromwell, G.L. (2015). Nutritional requirements of pigs. MSD Veterinary Manual: MSD Veterinary Manual. Available online at: https://www.msdvetmanual.com/management-and-nutrition/nutrition-pigs/nutritional-requirements-of-pigs (accessed 2015).
21. Sarandan, M, Ordodi, V, Sisu, I, Sarandan, H, Purcarea, VL, and Penescu, M. Obtaining high purity antibodies with therapeutic potential. Farmacia. (2010) 58:686–94.
22. Lothong, M, Rukarcheep, D, Wattanaphansak, S, Thammacharoen, S, Deachapunya, C, and Poonyachoti, S. Differential innate immune response of endometrial cells to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus type 1 versus type 2. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0284658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284658
23. Livak, KJ, and Schmittgen, TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods. (2001) 25:402–8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
24. Prudyus, T, and Kyryliv, Y. The effectiveness of the use of drugs Globigen pig dozer and Globigen jump start when growing pigs. Sci Mess LNU Vet Med Biotech. (2019) 21:94–7. doi: 10.32718/nvlvet-a9116
25. Luppi, A, Gibellini, M, Gin, T, Vangroenweghe, F, Vandenbroucke, V, Bauerfeind, R, et al. Prevalence of virulence factors in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with post-weaning diarrhoea in Europe. Porcine Health Manag. (2016) 2:20. doi: 10.1186/s40813-016-0039-9
26. Loos, M, Geens, M, Schauvliege, S, Gasthuys, F, Van Der Meulen, J, Dubreuil, JD, et al. Role of heat-stable enterotoxins in the induction of early immune responses in piglets after infection with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e41041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041041
27. Yang, W, Jiang, F, Yu, B, Huang, Z, Luo, Y, Wu, A, et al. Effect of different dietary lipid sources on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and intestinal health in weaned pigs. Animals. (2023) 13:3006. doi: 10.3390/ani13193006
28. Wiyaporn, M, Thongsong, B, and Kalandakanond-Thongsong, S. Growth and small intestine histomorphology of low and normal birth weight piglets during the early suckling period. Livest Sci. (2013) 158:215–22. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2013.10.016
29. Lauridsen, C, Matte, JJ, Lessard, M, Celi, P, and Litta, G. Role of vitamins for gastro-intestinal functionality and health of pigs. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2021) 273:114823. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2021.114823
30. Wu, S, Wang, L, Cui, B, Wen, X, Jiang, Z, and Hu, S. Effects of vitamin a on growth performance, antioxidants, gut inflammation, and microbes in weaned piglets. Antioxidants (Basel). (2023) 12:2049. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122049
31. Hu, C, Xing, W, Liu, X, Zhang, X, Li, K, Liu, J, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of probiotic Enterococcus faecium on growth performance and gut microbiota in weaned piglets. AMB Express. (2019) 9:33. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0755-z
32. Ogobuiro, I, Gonzales, J, Shumway, KR, and Tuma, F. Physiology, gastrointestinal. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing (2023). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537066/
33. Choi, M-K, Le, MT, Nguyen, DT, Choi, H, Kim, W, Kim, J-H, et al. Genome-level identification, gene expression, and comparative analysis of porcine β-defensin genes. BMC Genet. (2012) 13:98. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-13-98
34. Veldhuizen, EJ, Van Dijk, A, Tersteeg, MH, Kalkhove, SI, Van Der Meulen, J, Niewold, TA, et al. Expression of beta-defensins pBD-1 and pBD-2 along the small intestinal tract of the pig: lack of upregulation in vivo upon Salmonella typhimurium infection. Mol Immunol. (2007) 44:276–83. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.03.005
35. Zilbauer, M, Dorrell, N, Boughan, PK, Harris, A, Wren, BW, Klein, NJ, et al. Intestinal innate immunity to Campylobacter jejuni results in induction of bactericidal human beta-defensins 2 and 3. Infect Immun. (2005) 73:7281–9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.11.7281-7289.2005
36. Smiley, AK, Gardner, J, Klingenberg, JM, Neely, AN, and Supp, DM. Expression of human beta defensin 4 in genetically modified keratinocytes enhances antimicrobial activity. J Burn Care Res. (2007) 28:127–32. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013E31802C88FD
37. Veldhuizen, EJ, Rijnders, M, Claassen, EA, Van Dijk, A, and Haagsman, HP. Porcine beta-defensin 2 displays broad antimicrobial activity against pathogenic intestinal bacteria. Mol Immunol. (2008) 45:386–94. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.06.001
38. Nakamura, H, Wang, Y, Kurita, T, Adomat, H, Cunha, GR, and Wang, Y. Genistein increases epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and promotes tumor progression in advanced human prostate cancer. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e20034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020034
39. Sørensen, OE, Thapa, DR, Rosenthal, A, Liu, L, Roberts, AA, and Ganz, T. Differential regulation of β-defensin expression in human skin by microbial stimuli. J Immunol. (2005) 174:4870–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.8.4870
40. Srisomboon, Y, Poonyachoti, S, and Deachapunya, C. Soy isoflavones enhance β-defensin synthesis and secretion in endometrial epithelial cells with exposure to TLR3 agonist polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Am J Reprod Immunol. (2017) 78:e12694. doi: 10.1111/aji.12694
41. Young, SL, Lyddon, TD, Jorgenson, RL, and Misfeldt, ML. Expression of toll-like receptors in human endometrial epithelial cells and cell lines. Am J Reprod Immunol. (2004) 52:67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2004.00189.x
42. Vijay, K. Toll-like receptors in immunity and inflammatory diseases: past, present, and future. Int Immunopharmacol. (2018) 59:391–412. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.03.002
43. Sun, Y, and Kim, SW. Intestinal challenge with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in pigs, and nutritional intervention to prevent postweaning diarrhea. Anim Nutr. (2017) 3:322–30. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2017.10.001
44. Tao, X, Xu, Z, and Wan, J. Intestinal microbiota diversity and expression of pattern recognition receptors in newly weaned piglets. Anaerobe. (2015) 32:51–6. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2014.12.005
45. Tao, S, Bai, Y, Li, T, Li, N, and Wang, J. Original low birth weight deteriorates the hindgut epithelial barrier function in pigs at the growing stage. FASEB J. (2019) 33:9897–912. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900204RR
46. Harada, A. Essential involvement of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in acute inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. (1994) 56:559–64. doi: 10.1002/jlb.56.5.559
47. Lackeyram, D, Young, D, Kim, C, Yang, C, Archbold, T, Mine, Y, et al. Interleukin-10 is differentially expressed in the small intestine and the colon experiencing chronic inflammation and ulcerative colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate in young pigs. Physiol Res. (2017) 66:147–62. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.933259
48. Furness, JB. Types of neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Auton Nerv Syst. (2000) 81:87–96. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1838(00)00127-2
49. Gonkowski, S. Substance P as a neuronal factor in the enteric nervous system of the porcine descending colon in physiological conditions and during selected pathogenic processes. Biofactors. (2013) 39:542–51. doi: 10.1002/biof.1097
50. Medland, JE, Pohl, CS, Edwards, LL, Frandsen, S, Bagley, K, Li, Y, et al. Early life adversity in piglets induces long-term upregulation of the enteric cholinergic nervous system and heightened, sex-specific secretomotor neuron responses. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2016) 28:1317–29. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12828
51. Makowska, K, and Gonkowski, S. The influence of inflammation and nerve damage on the neurochemical characterization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like Immunoreactive (CGRP-LI) neurons in the enteric nervous system of the porcine descending Colon. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:548. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020548
52. Lu, Z, Ding, L, Lu, Q, and Chen, YH. Claudins in intestines: distribution and functional significance in health and diseases. Tissue Barriers. (2013) 1:e24978. doi: 10.4161/tisb.24978
53. Guilloteau, P, Biernat, M, Woliński, J, and Zabielski, R. Chapter 11 gut regulatory peptides and hormones of the small intestine. In: R Zabielski, PC Gregory, B Weström, and E Salek, editors. Biology of the Intestine in Growing Animals, 1st ed. Amsterdam; Boston: Elsevier (2002). 325–62.
54. Luettig, J, Rosenthal, R, Barmeyer, C, and Schulzke, JD. Claudin-2 as a mediator of leaky gut barrier during intestinal inflammation. Tissue Barriers. (2015) 3:e977176. doi: 10.4161/21688370.2014.977176
55. Zhu, C, Le, M, He, Z, Bai, Y, Yang, J, Ye, J, et al. Dietary berberine supplementation improves growth performance and alleviates gut injury in weaned piglets by modulating ileal microbiota and metabolites. Food Funct. (2023) 14:4143–62. doi: 10.1039/D3FO01044A
56. Imafuku, K, Iwata, H, Natsuga, K, Okumura, M, Kobayashi, Y, Kitahata, H, et al. Zonula occludens-1 distribution and barrier functions are affected by epithelial proliferation and turnover rates. Cell Prolif. (2023) 56:e13441. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13441
57. Hu, Y, Van Baal, J, Hendriks, WH, Resink, J-W, Liesegang, A, Van Krimpen, MM, et al. High dietary ca and microbial phytase reduce the expression of ca transporters while enhancing claudins involved in paracellular ca absorption in the porcine jejunum and colon. Br J Nutr. (2023) 129:1127–35. doi: 10.1017/S0007114522002239
58. Capaldo, CT. Claudin barriers on the brink: how conflicting tissue and cellular priorities drive IBD pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:8562. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108562
59. Donaldson, G, Lee, S, and Mazmanian, S. Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2016) 14:20–32. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3552
60. Takeda, K, and Akira, S. TLRs and innate immunity. Semin Immunol. (2004) 16:3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2003.10.003
Keywords: immunoglobulin Y, growth, mucosal innate immunity, low birth weight, pre-weaned piglets, intestinal barrier
Citation: Lothong M, Kayan A, Malison M, Rakarcheep D, Samritwatchasai T, Thammacharoen S, Deachapunya C and Poonyachoti S (2025) Cellular effects of oral egg yolk immunoglobulin-based supplementation at birth on promoting growth and strengthening intestinal mucosal innate immunity in pre-weaned piglets. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1458279. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1458279
Edited by:
Luciana Rossi, University of Milan, ItalyReviewed by:
Kateryna Goncharova Pierzynowska, Lund University, SwedenGeferson Fischer, Federal University of Pelotas, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Lothong, Kayan, Malison, Rakarcheep, Samritwatchasai, Thammacharoen, Deachapunya and Poonyachoti. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sutthasinee Poonyachoti, c3V0dGhhc2luZWUucEBjaHVsYS5hYy50aA==
 Muttarin Lothong
Muttarin Lothong Autchara Kayan
Autchara Kayan Manmueang Malison
Manmueang Malison Dran Rakarcheep
Dran Rakarcheep Theerawat Samritwatchasai
Theerawat Samritwatchasai Sumpun Thammacharoen
Sumpun Thammacharoen Chatsri Deachapunya
Chatsri Deachapunya Sutthasinee Poonyachoti
Sutthasinee Poonyachoti