- 1State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China
- 3International Research Center for Animal Disease, Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, Wuhan, China
Introduction: As a prevalent swine pathogen worldwide, Mycoplasma hyorhinis (M. hyorhinis, Mhr) is associated with various diseases, including multiple serositis, pneumonia, arthritis, and otitis media. It is also linked to the porcine respiratory disease complex (PRDC).
Methods: M. hyorhinis prevalence in 2022 Chinese lung samples was assessed by species-specific PCR, followed by isolation and purification of field strains, followed by genetic characterization via multilocus sequence typing (MLST). Pathogenicity evaluation of three isolates (ZZ-1, GD-1 and AH-1) was evaluated using controlled piglet infection trials.
Results: Mhr detection in clinical lung samples showed 31.77% prevalence. Three isolates (ZZ-1/ST166, GD-1/ST167, AH-1/ST144) were characterized by MLST. Piglet infection trials confirmed Mhr-induced polyserositis, pneumonia, and arthritis, with strain-dependent virulence variation observed.
Discussion: This study confirms M. hyorhinis as a high-prevalence pathogen (31.77%) in Chinese swine herds. Animal infection models demonstrated virulence variation among different Mhr strains. These findings contribute to identifying and assessing the threats posed by different strains to pig health, guiding the development of clinical prevention and control strategies.
1 Introduction
Mycoplasma hyorhinis (M. hyorhinis, Mhr) is a globally prevalent swine pathogen that has been largely understudied. While it is a common respiratory bacterium, most pigs colonized with Mhr exhibit no apparent clinical symptoms (1, 2). However, Mhr can cause various diseases, including swine multiple serositis, pneumonia, pericarditis, pleuritis, arthritis, conjunctivitis, and otitis media (3–11). Recent studies have shown that Mhr is also associated with meningitis and endocarditis (12–14). It is also recognized as a contributing pathogen in the porcine respiratory disease complex (PRDC) (15, 16). The prevalence of Mhr varies geographically and between herds. In this respect, in Switzerland, 10% of lung tissues from pigs with pneumonia tested positive for Mhr, while in the United States, PCR testing revealed that up to 98% of weaned piglets were positive (17). Mhr can cause enzootic pneumonia (EP) independently, although Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae is the primary pathogen associated with EP (4, 18–21). Mhr colonizes the ciliated epithelium of the respiratory tract and can typically be isolated from nasal secretions, tonsils, or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) (9, 22, 23). Some researchers have also isolated Mhr from lung tissue (4, 24).
Clinical symptoms typically manifest in piglets between 3 and 10 weeks of age, although older pigs can occasionally be affected (25). In younger piglets, infection can lead to emaciation and reduced daily weight gain (26). Infected pigs may exhibit lethargy, decreased appetite, lameness, and dyspnea (5, 22). The primary anatomical and pathological findings include polyserositis and arthritis, with occasional occurrences of pneumonia (4, 27, 28).
It has been hypothesized that systemic dissemination plays a crucial role in M. hyorhinis-associated diseases (29–31). However, the precise mechanisms underlying the systemic dissemination of Mhr, leading to conditions such as polyserositis and arthritis, remain poorly understood. Some researchers propose that co-infection with other pathogens and stress factors may promote the systemic spread of Mhr (6, 31). Several in vivo infection studies involving various field isolates of Mhr have been conducted (4, 22), indicating that strains with different virulence levels exhibit varying pathogenic potentials.
To investigate the prevalence of Mhr in clinical lung tissue in China, 1,001 lung tissue samples were collected from 25 provinces in 2022 and analyzed using a specific qPCR assay targeting the p37 gene. Three Mhr strains were successfully isolated and purified from these samples. An Mhr infection model was established in piglets through multiple routes of infection to assess the virulence of different strains and to investigate whether all Mhr strains isolated from lung tissue exhibit pathogenicity. This study also provides a foundation for further research into the pathogenic mechanisms of Mhr.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Identification of Mycoplasma hyorhinis in pig lung samples
Clinical samples randomly collected from pig farms across various regions of China in 2022 were processed for DNA extraction using an Automatic total DNA extraction machine (Vazyme, China) and analyzed using specific qPCR to detect Mhr, as described in a previous study (32). Mhr presence in a sample was confirmed when the qPCR results targeting the P37 gene showed a Ct value of ≤35. The primer and probe sequences were as follows: Forward primer 5′-AGAAGGTTCTTTTGCTTGAACACA-3′, Reverse primer 5′-TGCTTCCATCTTTTCATTTGCTT-3′, and Probe 5′-FAM-ATCAGCAACAAAACCTT-MGB-3′. The PCR master mix consisted of 10 μL 2 × Taq Master Mix (Vazyme, China), 0.8 μL of primer, 0.2 μL of probe, and 9 μL of DNA. PCR conditions were as follows: 37°C for 2 min, 95°C for 5 min, and 45 cycles of 95°C for 10 s and 55.9°C for 30 s.
2.2 Isolation and purification of Mycoplasma hyorhinis
2.2.1 Methods for the isolation and purification of Mycoplasma hyorhinis
Sampling was performed at the lesion margins of fresh lung tissue to optimize Mhr isolation. Approximately 2.0 grams of each sample was collected, finely minced in a biosafety cabinet, and placed in a 2.0 mL centrifuge tube with an equal volume of PBS buffer. After grinding at 60 Hz for 5 min, the homogenate was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 3 min. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, transferred to Friis medium, and incubated at 37°C. Once the broth culture changed color, 100 μL of the culture was spread evenly onto a solid medium and incubated at 37°C. Individual colonies were picked and purified by inoculating them into liquid broth. Pure cultures were obtained after three rounds of purification on solid plates.
The isolates were identified using regular PCR targeting the P37 gene and 16S rRNA with Mycoplasma genus-specific primers. The primer sequences were as follows: P37 forward primer 5′-TTGCTCAAAAAATTTAAAAATTT-3′, P37 reverse primer 5′-AACAAAAATTTTATTAATTTCTTTA-3′; 16S rRNA forward primer 5′-GATGAACGCTCGCTGTGTGCCTA-3′, 16S rRNA reverse primer 5′-CTTCACCCCTGTCATCAGTCCT-3′. The PCR master mix consisted of 12.5 μL 2 × Rapid Taq Master Mix (Vazyme, China), 2 μL of each primer, 2 μL of DNA template, and 8.5 μL of ddH2O. PCR conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 s, annealing at 52°C for 15 s, and extension at 72°C for 15 s, with a final extension at 72°C for 5 min.
2.2.2 Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) analysis
To determine the genotypes of Mhr isolates in this study, a PCR-based MLST analysis was employed. Primers for six housekeeping genes (adk, gmk, gltX, rpoB, dnaA, gyrB) were synthesized following established protocols, referencing Jolley et al. (33). Following MLST analysis, the housekeeping gene sequences were uploaded to the same website to obtain allele values and assign sequence types (STs) for the six genes (34). A list of oligonucleotide primers used to amplify and sequence Mhr MLST can be found in Additional File 1.
2.3 Animal experiment
2.3.1 Bacterial strain preparation and animal grouping
To explore the diversity in virulence among different M. hyorhinis strains, three field isolates with high and stable growth titers were selected for virulence evaluation. These isolates were obtained from the lung tissues of pigs in Hunan (ZZ-1 strains), Guangdong (GD-1 strains), and Anhui (AH-1 strains) provinces in China, with titers reaching 1010 to 1011 CCU/mL.
Twelve four-week-old hybrid piglets, free of Mhr and M. hyopneumoniae (Mhp) infection, were randomly divided into four groups: three infection groups (n = 3 each) and one negative control group (n = 3). Pigs in the infection groups were inoculated with one of three Mhr strains, while the control group received Friis medium. To ensure fresh infection material, purified Mhr isolates were prepared 24 h before inoculation. The medium was used directly for inoculation once its color turned orange-yellow, and the viable cell count of Mhr was determined using the color-changing unit (CCU) method (26).
2.3.2 Infection procedure
A simultaneous inoculation strategy through multiple routes was employed for 4-week-old piglets. Each pig in the infection groups received a total of 10 mL of Mhr broth (4 mL intrapulmonary, 4 mL intraperitoneal, and 2 mL intranasal), with the viable cell count determined on the inoculation day. The negative-control group received the same volume of Friis medium administered via the same routes. Twenty-eight days post-infection, all pigs were euthanized and necropsied.
2.3.3 Clinical symptom observation
Daily clinical observations were conducted from 3 days before inoculation (−3 dpi) to 28 days post-infection (28 dpi) to monitor signs of abnormal respirations, cough, and lameness. A clinical scoring system, adapted from the literature (26) (Additional File 2), was used to assess clinical severity. Body temperatures and weights were monitored throughout the observation period to assess the pigs’ overall health and response to infection.
2.3.4 Histopathological observation
At 28 dpi, all pigs were euthanized via intramuscular injection of Xylazine Hydrochloride (0.2 mg/kg) followed by exsanguination until cardiac arrest. Limb joints were examined for signs of arthritis, while abdominal and thoracic cavities, including the pericardium, were inspected for serositis. Lung tissues were assessed for lesions, and lesion severity was scored based on criteria established in previous studies (22, 26, 35), as detailed in Additional File 3. Lung tissue samples with lobulated or patchy consolidation were collected for tissue fixation, sectioning, and hematoxylin–eosin (HE) staining. Pathological histological changes were observed microscopically.
Tissue samples, including myocardium, pericardial membrane, pericardial fluid, pleural effusion, lung, hilar lymph nodes, tonsils, abdominal effusion, and joint fluid, were tested for Mhr using PCR targeting the P37 gene (550 bp). Mhr was re-isolated from positive tissue samples, and the isolates were subjected to MLST typing to confirm strain identity.
The experiment was approved by the Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection of the Laboratory Animal Centre, Huazhong Agriculture University, under reference number HZAUSW-2024-0079.
2.4 Statistical analysis
To compare the virulence of three Mhr isolates, statistical analysis was performed on body temperature, average daily weight gain (ADWG), clinical observation scores (abnormal respirations, cough, lameness, and summary score), and postmortem observation scores (peritonitis, pleuritis, pericarditis, arthritis, pneumonia, and summary score). Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). ADWG data were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with effect size analysis for selected pairs. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 The positivity rate of Mycoplasma hyorhinis in clinical lung samples
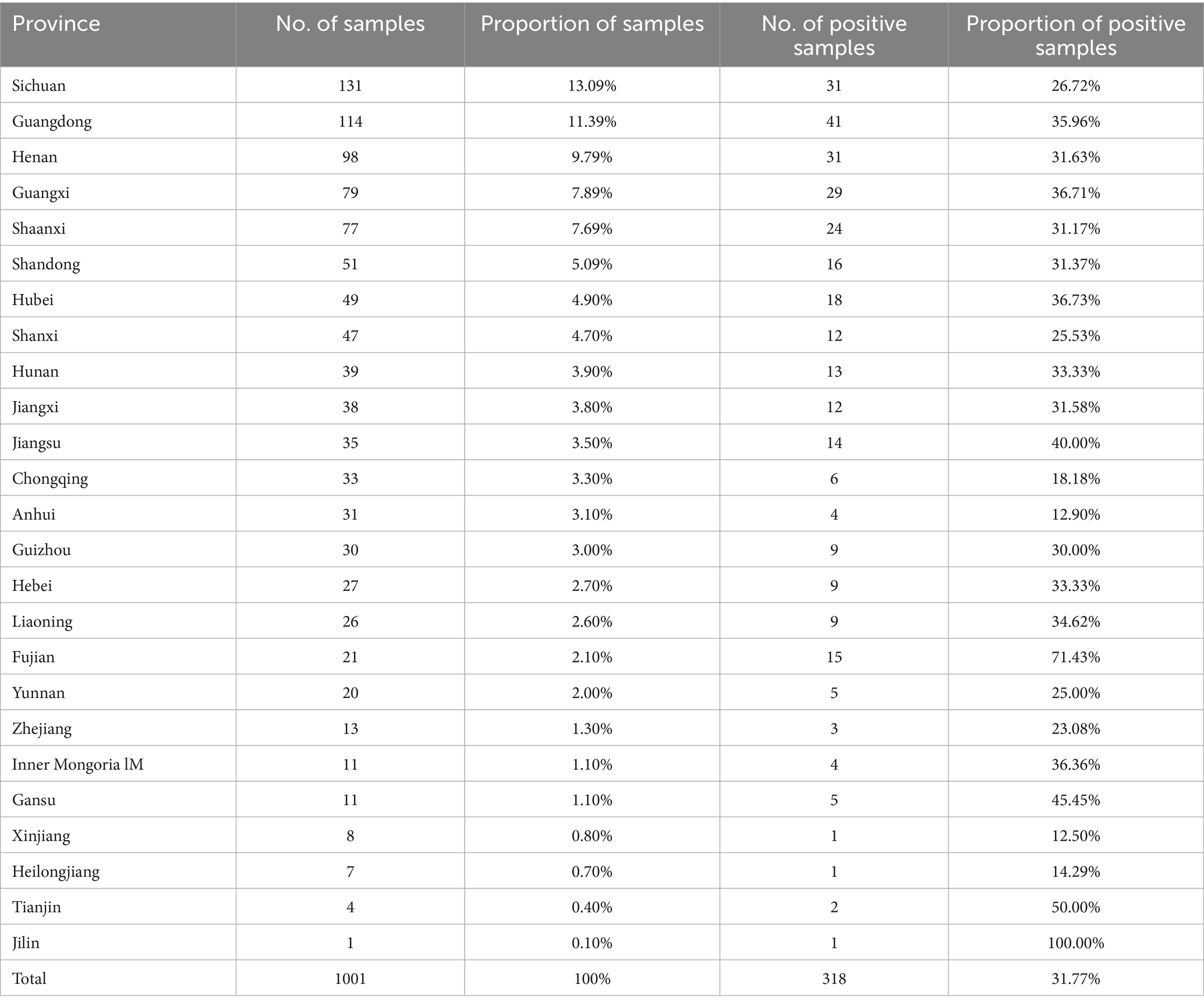
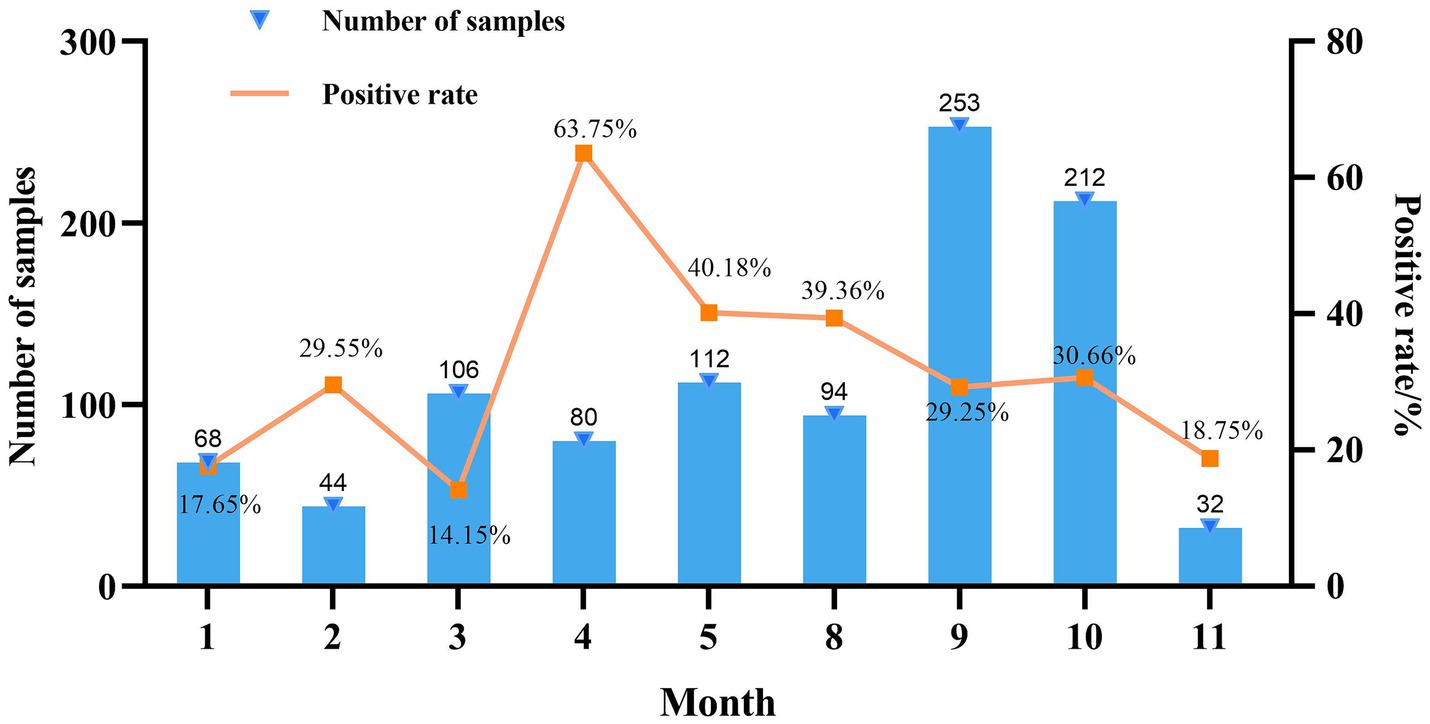
Mycoplasma hyorhinis-specific qPCR was performed on 1,001 clinical lung tissue samples collected from 25 provinces in China during 2022. Among these, 13.1% were from Sichuan, 11.4% from Guangdong, 9.8% from Henan, 7.9% from Guangxi, 7.7% from Shaanxi, and 5.1% from Shandong, with the remaining 45.1% originating from 19 other provinces. Among provinces with over 30 samples, Jiangsu exhibited the highest positivity rate for Mhr (40.00%), followed by Hubei (36.73%). Conversely, Anhui and Chongqing had the lowest positivity rates (12.90 and 18.18%, respectively) (Table 1). The highest number of samples were collected in September (253) and October (212), while the fewest were collected in November (32). The positivity rate of Mhr peaked in April (63.75%), May (40.18%), and August (39.36%), and was lowest in January (17.65%), February (29.55%), March (14.15%), and November (18.75%) (Figure 1).
3.2 Isolation, purification, and sequence typing (ST) of Mycoplasma hyorhinis
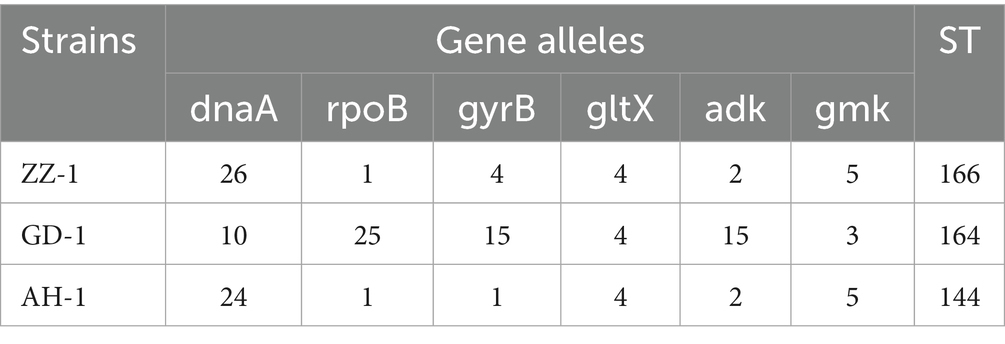
Three strains of M. hyorhinis were isolated and purified: ZZ-1, GD-1, and AH-1. After 12–20 h of incubation, the isolates turned the liquid media from red to yellow without visible turbidity. The titers of the three strains reached 1 × 109 to 1 × 1011 CCU/ml. On solid media, all strains formed characteristic “fried egg” colonies (Figure 2A). PCR amplification confirmed the presence of the Mhr-specific P37 gene (550 bp) and 16S rRNA gene (1,450 bp) in all three strains (Figure 2B). No exact matches were found for all loci of the ZZ-1 strain in the PubMLST database. New sequences were submitted to the database, and new allele profiles were created, assigning novel ST numbers to their respective allele combinations. Ultimately, the three isolated strains were identified as ST 166 (ZZ-1), ST 167 (GD-1), and ST 144 (AH-1), respectively, which were used in subsequent experiments (Table 2).
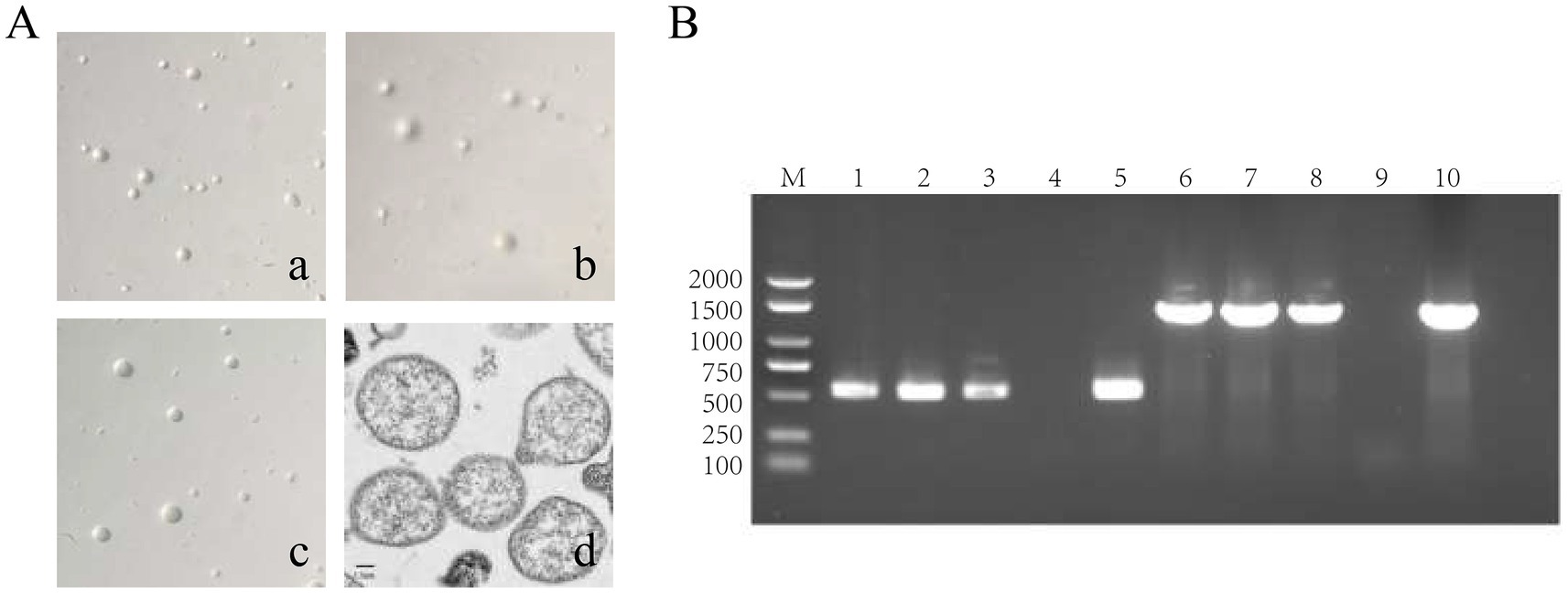
Figure 2. Identification of M. hyorhinis isolates. (A) Colony morphology of the three Mhr strains on solid media (40×), exhibiting similar “fried egg” colonies. (a) ZZ-1 strains; (b) GD-1 strains; (c) AH-1 strains; (d) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of Mhr ZZ-1 strain (Scale bar: 1 μm). The image reveals the typical pleomorphic structure of the Mycoplasma genus, with the cell wall-lacking structures with a granular interior. (B) PCR identification of Mhr targeting the P37 gene (550 bp) and 16S rRNA gene (1450 bp). M, DNA marker; lane 1–3, ZZ-1 strain, GD-1 strains and AH-1 strains’ P37 gene amplification; lane 4, negative control; lane 5, positive control (P37 gene); lane 6–8, ZZ-1 strain, GD-1 strains and AH-1 strains’ 16S rRNA gene amplification; lane 9, negative control; lane 10, positive control (16S rRNA gene).
3.3 Clinical symptom observations
The viable cell counts of three fresh Mhr strains were determined using the CCU method, and piglets were infected with a total dose of 5 × 108 CCU/pig for the ZZ-1 strain and 5 × 109 CCU/pig for the GD-1 and AH-1 strains. Following infection, all three groups exhibited a transient increase in body temperature. The AH-1 strain group peaked at 40.5°C at 2 dpi, the ZZ-1 strain group reached 40.8°C at 2 or 5 dpi, and the GD-1 strain group peaked at 40.7°C at 2 dpi. By 7 dpi, body temperatures in all groups had returned to normal, with no fluctuations exceeding 1.0°C thereafter. In contrast, the control group showed only one piglet reaching 40°C at 5 dpi, with no other temperature abnormalities observed throughout the study (Figure 3A).

Figure 3. Clinical symptom observation. (A) Body temperature of piglets after infection. Temperatures were monitored daily, with peak temperatures at 2 dpi for all infection groups. At 7 dpi, body temperatures in all groups returned to below 40°C. The control group exhibited no significant temperature abnormalities throughout the study. (B) Average daily weight gain (ADWG) during the 28-day experimental period. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). The ZZ-1 strain and AH-1 strain groups showed lower ADWG than the control group, while the GD-1 strain group displayed no significant difference in ADWG compared to the control group. (C) Total clinical observation scores of each group. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Total scores in ZZ-1 and AH-1 strain groups were significantly increased compared to that in the control group, for which no signs of pathological changes were detected (*p < 0.05). (D) Abnormal respiration, cough, and lameness scores of each group. (E) Swollen joints observed in the ZZ-1 strain group. (F) Persistent and pronounced lameness in the ZZ-1 strain group.
During the 28-day experimental period, the ADWG was 0.07 ± 0.0694 kg for the ZZ-1 strain group, 0.18 ± 0.0082 kg for the GD-1 strain group, 0.08 ± 0.0478 kg for the AH-1 strain group, and 0.17 ± 0.0478 kg for the control group. The ADWG in the ZZ-1 and AH-1 strain groups was lower than that of the control group. However, no significant difference in ADWG was observed between the GD-1 strain group and the control group (Figure 3B). Notably, both the ZZ-1 and AH-1 strain groups included one piglet (Z3 and A2, respectively) whose ADWG did not meet expectations. This discrepancy may be attributed to a relatively large initial age, leading to a faster growth rate, or individual differences in pathogen tolerance, resulting in abnormal weight gain compared to group peers. Although the ANOVA p-value did not indicate statistical significance (p-value > 0.05), effect size analysis revealed a relatively high effect size (η2 = 0.507), suggesting that group differences account for 50.7% of the total variance.
No clinical signs of Mycoplasma hyorhinis infection, such as respiratory distress, coughing, or lameness, were observed in the control group. In contrast, all three infection groups exhibited abnormal respiration, with at least two piglets affected in each group. The ZZ-1 and AH-1 strain groups displayed more severe respiratory symptoms than the GD-1 strain group (Figure 3D). Moderate coughing was observed in one piglet from each infection group (Figure 3D). Coughing began at 14 dpi and persisted until euthanasia in four piglets (Z1, G2, A1, A2).
All piglets in the ZZ-1 and AH-1 strain groups exhibited varying degrees of lameness, with the ZZ-1 strain group displaying higher lameness scores (Figure 3D). Joint swelling, particularly in the tarsal joints, was a common observation (Figure 3E). One piglet (Z1) from the ZZ-1 strain group displayed joint swelling in three limbs, while two piglets (G7, G8) from the GD-1 strain group also exhibited swollen joints. Joint swelling was first detected as early as 5 dpi (Z3, A8) and as late as 21 dpi (Z2). Notably, one piglet (Z3) from the ZZ-1 strain group developed severe lameness, characterized by an inability to stand or walk normally, bearing no weight on both hind limbs, and adopting a dog-sitting posture. This piglet could only walk a few steps with manual assistance, and the lameness remained visibly severe (Figure 3F). No lameness was observed in the GD-1 strain group.
During the entire monitoring period, the ZZ-1 and AH-1 strain groups (5.00 ± 1.41 and 4.00 ± 1.63, respectively) exhibited significantly higher clinical scores than the control group (0.00 ± 0.00, p < 0.05) (Figure 3C). The GD-1 strain group (1.33 ± 1.25) did not show a significant difference in clinical scores compared to the control group.
3.4 Histopathological observation
No postmortem signs of disease were observed in the control group. In contrast, pigs in the infection groups exhibited pleuritis, pericarditis, peritonitis, arthritis, and pneumonia, which were documented and scored (Figures 4A–F). The number of animals exhibiting pathological manifestations was quantified (Figure 4G).
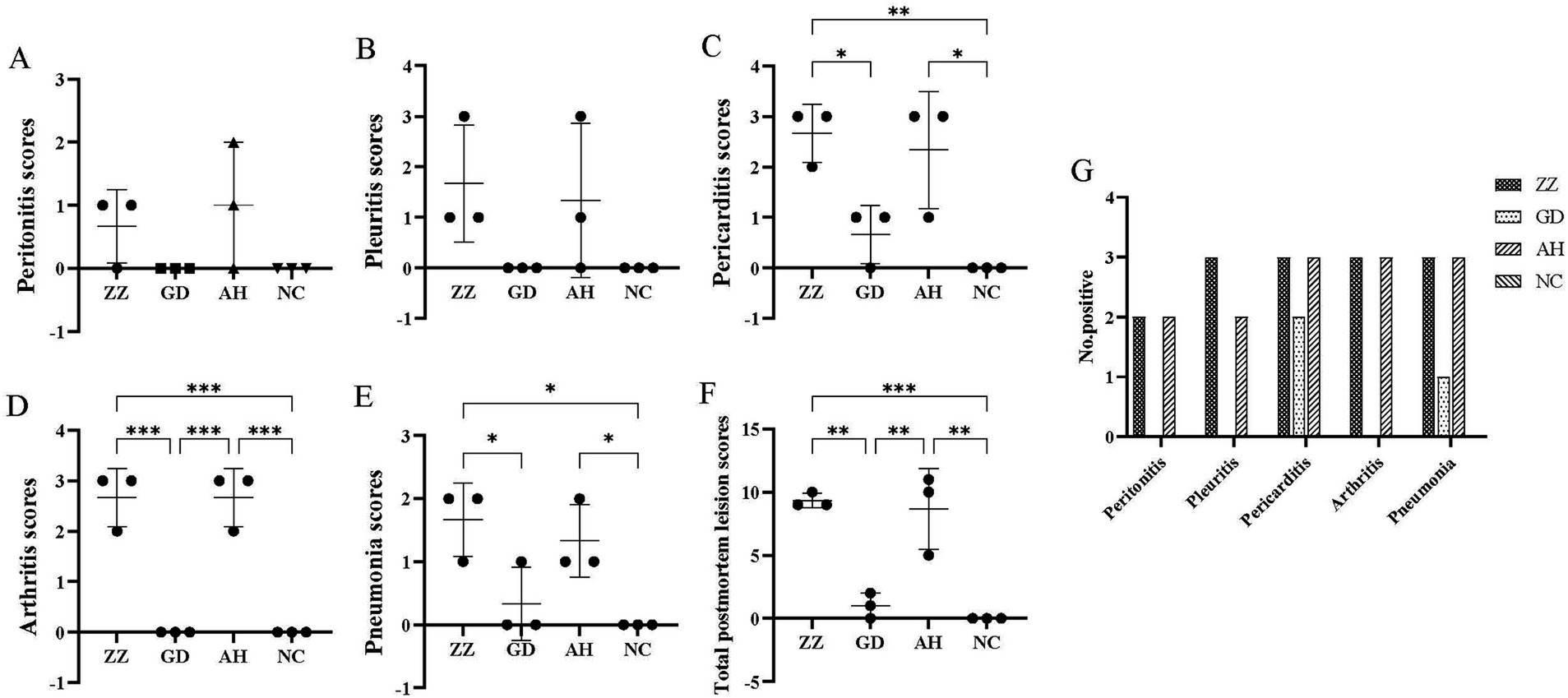
Figure 4. Postmortem observation scores of each group. (A) Peritonitis scores of each group. (B) Pleuritis scores of each group. (C) Pericarditis scores of each group. (D) Arthritis scores of each group. (E) Pneumonia scores of each group. (F) Total Postmortem observation scores of each Group. 9.33 ± 0.47, 1.00 ± 0.82, 8.67 ± 2.62, 0.00 ± 0.00 in ZZ-1, GD-1, AH-1 strain groups and control group, respectively. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. (G) Number of positive animals.
All pigs in the ZZ-1 strain group exhibited varying degrees of pericarditis and arthritis, ranging from moderate to severe. The pericarditis was characterized by diffuse, severe fibrinous inflammation, pericardial exudate between the heart and pericardium, and significant pericardial thickening. Additionally, increased pericardial effusion was observed (Figures 5A–C). All pigs in this group also displayed moderate to severe arthritis, marked by significant swelling and enlargement of the joint capsule, increased joint fluid, and, in one case (Z2), cheese-like exudate (Figure 5F). One pig (Z1) developed severe pleuritis characterized by diffuse, severe fibrinous pleuritis with thoracic exudate, with most lung lobes adhered to the parietal pleura and interlobar adhesions (Figure 5D). One pig in the ZZ-1 strain group also developed peritonitis, manifesting as a few fibrinous adhesions and yellow cheese-like material in the abdominal cavity (Figure 5E).
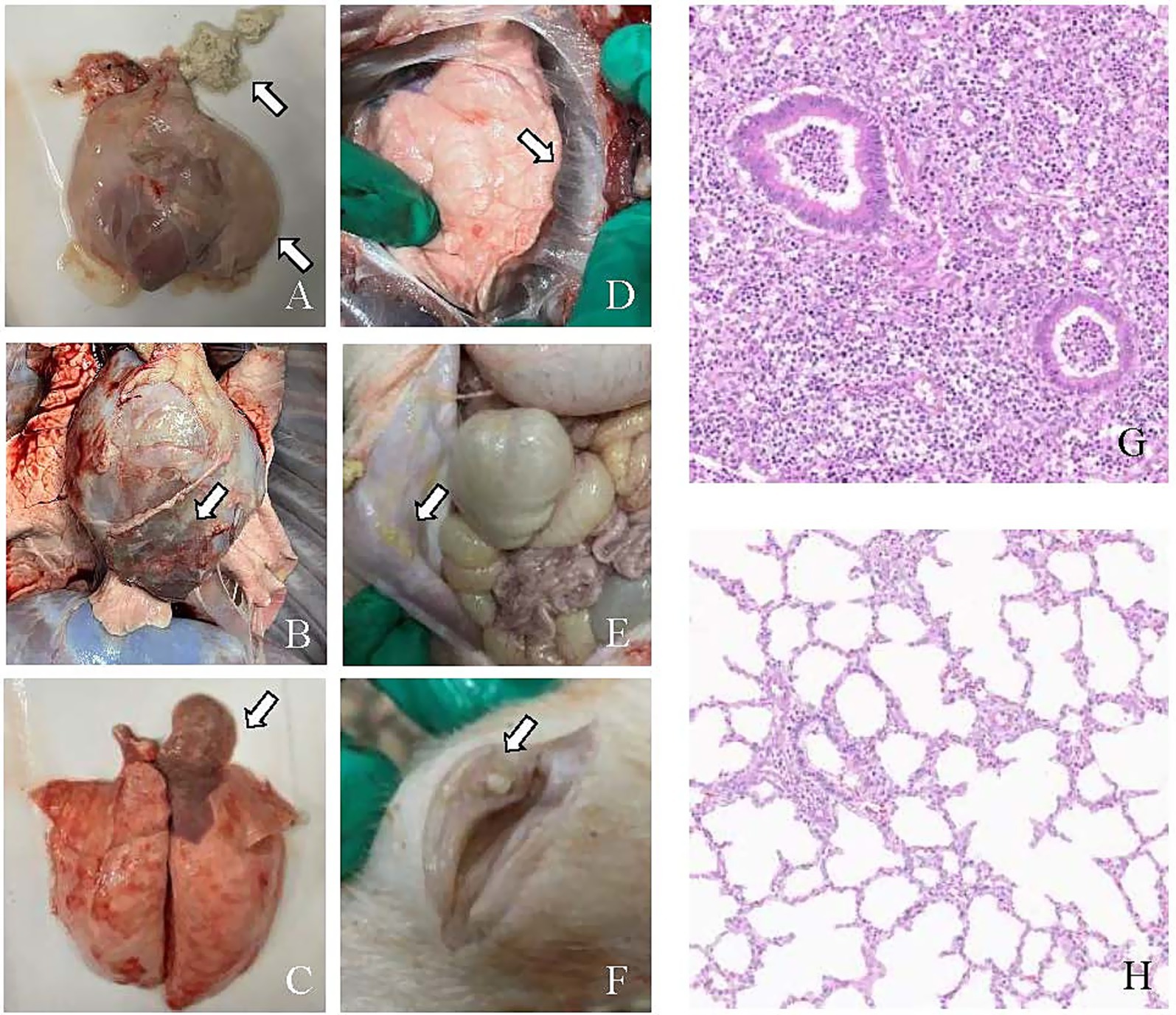
Figure 5. Pathological changes caused by M. hyorhinis infection. (A) Pericarditis: the arrow indicates the thickening of the pericardium, increased pericardial effusion, and cheese-like exudate between the heart and pericardium. (B) Pericarditis: the arrow highlights a close adhesion between the pericardium and the heart. (C) Pneumonia: the arrow highlights the shrimp-like lung lesions observed on the dorsal side. (D) Pleuritis: the arrow shows fibrinous adhesions between the lung lobes and pleura. (E) Peritonitis: the arrow highlighting the cheese-like exudate in the abdominal cavity. (F) Arthritis: the arrow points to the abnormal synovial membrane with cheese-like exudate in the articular cavity. (G) H&E-stained hepatization-lung tissue of ZZ-1 strain group (Z1), showing obscured or absent alveolar structure, alveolar spaces filled with fibrinous exudates, accompanied by extensive inflammatory cell infiltration and thickened alveolar septa. (H) Lung tissue of control group (C11), showing intact alveolar structure, clear alveolar spaces, thin alveolar septa, and minimal inflammatory cell presence.
In the AH-1 strain group, one pig developed moderate to severe polyserositis (including pleuritis, pericarditis, and peritonitis) and arthritis (A7), another developed moderate pericarditis and severe arthritis (A8), and a third developed severe pericarditis and arthritis (A9). The GD-1 strain group exhibited significantly lower severity scores than the other two infection groups, although increased pericardial fluid accumulation was observed. Notably, pneumonia symptoms were found in at least one pig from each of the three infection groups. Moderate pulmonary consolidation was observed in two pigs from the ZZ-1 strain group (Z1, Z2) and one from the AH-1 strain group (A9). Additionally, pigs Z3, G4, A7, and A8 showed slight consolidation of lung injury.
Histopathological examination of hepatized pig lung tissue, stained with H&E, revealed significant deviations from normal lung architecture. The alveolar spaces were extensively filled with fibrinous exudate, obscuring or destroying the normal structure and creating a solid, liver-like appearance. A pronounced inflammatory response was evident, characterized by heavy infiltration of inflammatory cells, primarily neutrophils and macrophages, within both the alveolar spaces and septa. The alveolar septa were thickened due to interstitial edema, and blood vessels were often dilated and congested. Additionally, extravasated erythrocytes were observed within the alveoli. These findings collectively indicate severe lung tissue inflammation and damage (Figures 5G,H).
Mhr was detected in various tissue samples, including myocardium, pericardial membrane, pericardial fluid, pleural effusion, lung, hilar lymph nodes, tonsil, abdominal effusion, and joint fluid, from the infected groups. The bacteria were successfully re-isolated from all three infection groups (Additional File 4). MLST analysis confirmed that the re-isolated strains had the same sequence types as the original infection strains.
Significant differences in postmortem observations and scores were observed between the three infection groups (p < 0.05), indicating varying virulence among the strains. The ZZ-1 strain was the most virulent, consistent with clinical observations.
4 Discussion
Mycoplasma hyorhinis has a high prevalence in various countries and regions worldwide. In the United States, approximately 40% of sows tested positive for Mhr and M. hyosynoviae (36). Additionally, a study found Mhr in up to 97% of 2,710 oral fluid and feces samples (37). Silva et al. examined Mhr in pig tissue samples in the United States from 2017 to 2022, finding a positive rate of 57% (4578/8069), primarily in serosal fibrin and joint samples. Mhr-associated serositis increased annually by 4.2% (38). Similarly, in Austria, Renzhammer et al. analyzed 1,975 samples collected between 2016 and 2021, with Mhr having the highest detection rate, reaching 55.1% (39).
Generally, the samples analyzed primarily originate from upper respiratory tract swabs, joint fluid, and serous membranes, while researchers often prioritize examining lung tissues for M. hyopneumoniae. In this study, the positivity rate of Mhr was 31.77% among 1,001 lung samples collected from China in 2022. Additionally, the study observed that the positivity rate of Mhr was highest in April, May, and August (63.75, 40.18, and 39.36%, respectively), while rates were lower in January, February, March, and November (17.65, 29.55, 14.15, and 18.75%, respectively). A province-based analysis revealed that Jiangsu had the highest positivity rate of Mhr (40.00%), followed by Hubei at 36.73%. These findings suggest a correlation between the positivity rate of Mhr and both seasonal factors (or temperature) and geographical regions.
Currently, the full extent of Mhr’s pathogenic potential remains uncertain. Some studies that used intranasal or tonsillar inoculation did not observe clinical symptoms or visible lesions (40, 41). This suggests that a single-dose intranasal inoculation may not be sufficient to induce all typical lesions, and multiple inoculation routes may be more suitable for establishing a challenge model (4, 26, 42–44). This study established piglet infection models by inoculating them via multiple routes and assessed clinical symptoms and histopathological changes. All three strains used in the virulence study were isolated from lung tissue samples. We observed that piglets infected with Mhr experienced transient fever, and piglets infected with highly virulent strains showed a trend toward reduced ADWG, though the difference was not statistically significant. Additionally, some piglets displayed joint swelling, with severe cases leading to lameness. These clinical observations (fever, weight loss, and lameness) are consistent with previous studies (43, 45). The ZZ-1 and AH-1 strains induced typical and extensive symptoms in piglets, including pleuritis, peritonitis, pericarditis, arthritis, and pneumonia, which aligns with findings from Földi D and Martinson B et al. (26, 45). The pericarditis observed in piglets in our study was mainly serous and fibrinous, which aligns with the findings of Földi et al. (45). However, naturally infected piglets at a similar age typically show fibrinous pericarditis (5). This discrepancy may be due to differences in the age at infection or strain virulence. Given the limited number of reports, it is difficult to conclude whether pericarditis induced by coinfection and natural infection follows a consistent pattern. Notably, the three Mhr strains exhibited varying levels of virulence. Based on clinical observations and necropsy results, the ZZ-1 strain demonstrated the highest virulence, while the GD-1 strain exhibited the lowest, offering valuable insights into the pathogenicity of different Mhr strains and their impact on swine health. This study lays the groundwork for a database of high- and low-virulence strains, essential for virulence target screening and precise diagnostic development. Highly virulent strains may serve as ideal candidates for vaccine development, enabling the selection of effective and broadly protective vaccines, while also providing a basis for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Moving forward, it is imperative to intensify our focus on Mhr. Strengthening the study of its pathogenicity and expanding the scope of epidemiological investigations is essential. This study, being a smaller-scale “pilot study,” aims to provide preliminary insights into the pathogenicity and virulence of Mhr strains, which will guide the design of larger, more comprehensive studies in the future. Additionally, establishing infection models with a broader range of strains and animals will deepen our understanding of its pathogenic mechanisms. Investigating the genetic differences between various strains from a molecular biology perspective will shed light on the underlying causes of these differences. Developing methods for the rapid differentiation of highly virulent and less virulent strains, coupled with advancing vaccine research, will be crucial for the effective prevention and control of Mhr-related diseases.
5 Conclusion
Overall, this study assessed the positive rate of Mhr in clinical lung samples from pigs, successfully isolated three wild strains of Mhr, and established infection models to evaluate their virulence. The results indicated that Mhr can cause multiple serositis, pneumonia, and arthritis in piglets, with notable differences in virulence among the various strains.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection of Laboratory Animal Centre, Huazhong Agriculture University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
FY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LY: Writing – original draft. XD: Writing – original draft. YQ: Writing – original draft. HM: Writing – original draft. XJ: Writing – original draft. XH: Writing – original draft. WD: Writing – review & editing. HC: Writing – review & editing. CT: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD1800901), the earmarked fund for CARS (CARS-35).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2025.1542992/full#supplementary-material
ADDITIONAL FILE 1 | Oligonucleotide primers for amplification and sequencing of Mycoplasma hyorhinis MLST.
ADDITIONAL FILE 2 | Description of clinical observation scoring.
ADDITIONAL FILE 3 | Postmortem observations and scores of relative lesion severity.
ADDITIONAL FILE 4 | Detection of M. hyorhinis in postmortem tissues from virulence experiments.
References
1. Siqueira, FM, Thompson, CE, Virginio, VG, Gonchoroski, T, Reolon, L, Almeida, LG, et al. New insights on the biology of swine respiratory tract mycoplasmas from a comparative genome analysis. BMC Genomics. (2013) 14:175. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-175
2. Ferrarini, MG, Siqueira, FM, Mucha, SG, Palama, TL, Jobard, É, Elena-Herrmann, B, et al. Insights on the virulence of swine respiratory tract mycoplasmas through genome-scale metabolic modeling. BMC Genomics. (2016) 17:353. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2644-z
3. Decker, JL, and Barden, JA. Mycoplasma hyorhinis swine arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. (1971) 14:781. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140617
4. Lin, JH, Chen, SP, Yeh, KS, and Weng, CN. Mycoplasma hyorhinis in Taiwan: diagnosis and isolation of swine pneumonia pathogen. Vet Microbiol. (2006) 115:111–6. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2006.02.004
5. Ustulin, M, Rossi, E, and Vio, D. A case of pericarditis caused by Mycoplasma hyorhinis in a weaned piglet. Porcine Health Manag. (2021) 7:32. doi: 10.1186/s40813-021-00211-4
6. Friis, NF, and Feenstra, AA. Mycoplasma hyorhinis in the etiology of serositis among piglets. Acta Vet Scand. (1994) 35:93–8. doi: 10.1186/BF03548359
7. Jansson, E, Backman, A, Hakkarainen, K, Miettinen, A, and Seniusová, B. Mycoplasmas and arthritis. Z Rheumatol. (1983) 42:315–9.
8. Resende, TP, Pieters, M, and Vannucci, FA. Swine conjunctivitis outbreaks associated with Mycoplasma hyorhinis. J Vet Diagnostic Investig. (2019) 31:766–9. doi: 10.1177/1040638719865767
10. Friis, NF, Kokotovic, B, and Svensmark, B. Mycoplasma hyorhinis isolation from cases of otitis media in piglets. Acta Vet Scand. (2002) 43:191–3.
11. Morita, T, Sasaki, A, Kaji, N, Shimada, A, Kazama, S, Yagihashi, T, et al. Induction of temporary otitis media in specific-pathogen-free pigs by intratympanic inoculation of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Am J Vet Res. (1998) 59:869–73.
12. Bünger, M, Brunthaler, R, Unterweger, C, Loncaric, I, Dippel, M, Ruczizka, U, et al. Mycoplasma hyorhinis as a possible cause of fibrinopurulent meningitis in pigs? - a case series. Porcine Health Manag. (2020) 6:38. doi: 10.1186/s40813-020-00178-8
13. Ko, CC, Merodio, MM, Spronk, E, Lehman, JR, Shen, H, Li, G, et al. Diagnostic investigation of Mycoplasma hyorhinis as a potential pathogen associated with neurological clinical signs and central nervous system lesions in pigs. Microb Pathog. (2023) 180:106172. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106172
14. Suk, RN, Helke, KL, Fitzgerald, DC, Hassid, M, McVadon, D, Taylor, CL, et al. Bacteria endocarditis caused by Mycoplasma hyorhinis in a juvenile, immunosuppressed pig (Sus scrofa domesticus) following partial heart transplantation. Comp Med. (2024) 74:295–303. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-23-000090
15. Lee, JA, Oh, YR, Hwang, MA, Lee, JB, Park, SY, Song, CS, et al. Mycoplasma hyorhinis is a potential pathogen of porcine respiratory disease complex that aggravates pneumonia caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. (2016) 177:48–51. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2016.06.008
16. Thakor, JC, Sahoo, M, Karam Pal, S, Rajendra, S, Salauddin, Q, Ajay, K, et al. Porcine respiratory disease complex (PRDC) in Indian pigs: a slaughterhouse survey. Vet Ital. (2023) 59:23–38. doi: 10.12834/VetIt.2935.20591.2
17. Clavijo, MJ, Murray, D, Oliveira, S, and Rovira, A. Infection dynamics of Mycoplasma hyorhinis in three commercial pig populations. Vet Rec. (2017) 181:68. doi: 10.1136/vr.104064
18. Luehrs, A, Siegenthaler, S, Grützner, N, Grosse Beilage, E, Kuhnert, P, and Nathues, H. Occurrence of Mycoplasma hyorhinis infections in fattening pigs and association with clinical signs and pathological lesions of enzootic pneumonia. Vet Microbiol. (2017) 203:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.02.001
19. Fourour, S, Fablet, C, Tocqueville, V, Dorenlor, V, Eono, F, Eveno, E, et al. A new multiplex real-time TaqMan(®) PCR for quantification of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, M. hyorhinis and M. flocculare: exploratory epidemiological investigations to research mycoplasmal association in enzootic pneumonia-like lesions in slaughtered pigs. J Appl Microbiol. (2018) 125:345–55. doi: 10.1111/jam.13770
20. Lobo, E, Poveda, C, Gupta, R, Suarez, A, Hernández, Y, Ramírez, A, et al. Mycoplasmas hyorhinis in different regions of Cuba diagnosis. Braz J Microbiol. (2011) 42:721–5. doi: 10.1590/S1517-838220110002000039
21. L’Ecuyer, C, and Boulanger, P. Enzootic pneumonia in pigs: identification of a causative mycoplasma in infected pigs and in cultures by immunofluorescent staining. Can J Comp Med. (1970) 34:38–46.
22. Wang, J, Hua, L, Gan, Y, Yuan, T, Li, L, Yu, Y, et al. Virulence and inoculation route influence the consequences of Mycoplasma hyorhinis infection in Bama miniature pigs. Microbiol Spectr. (2022) 10:e0249321. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02493-21
23. Yamaguti, M, Oliveira, RC, Marques, LM, Buzinhani, M, Buim, MR, Neto, RL, et al. Molecular characterisation of Mycoplasma hyorhinis isolated from pigs using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and 16S rRNA sequencing. Vet Record Open. (2015) 2:e000093. doi: 10.1136/vetreco-2014-000093
24. Bekő, K, Felde, O, Sulyok, KM, Kreizinger, Z, Hrivnák, V, Kiss, K, et al. Antibiotic susceptibility profiles of Mycoplasma hyorhinis strains isolated from swine in Hungary. Vet Microbiol. (2019) 228:196–201. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.11.027
25. Martinson, B, Minion, FC, Kroll, J, and Hermann, J. Age susceptibility of caesarian derived colostrum deprived pigs to Mycoplasma hyorhinis challenge. Vet Microbiol. (2017) 210:147–52. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.09.005
26. Martinson, B, Zoghby, W, Barrett, K, Bryson, L, Christmas, R, Minion, FC, et al. Efficacy of an inactivated Mycoplasma hyorhinis vaccine in pigs. Vaccine. (2018) 36:408–12. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.11.063
27. Gois, M, Pospisil, Z, Cerny, M, and Mrva, V. Production of pneumonia after intransal inoculation of gnotobiotic piglets with three strains of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. J Comp Pathol. (1971) 81:401–10. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90028-4
28. Zhang, Y, Gan, Y, Wang, J, Feng, Z, Zhong, Z, Bao, H, et al. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and intestinal barrier dysfunction in pigs with pulmonary inflammation induced by Mycoplasma hyorhinis infection. mSystems. (2022) 7:e0028222. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00282-22
29. Wang, J, Yu, Y, Li, Y, Li, S, Wang, L, Wei, Y, et al. A multifunctional enolase mediates cytoadhesion and interaction with host plasminogen and fibronectin in Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Vet Res. (2022) 53:26. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01041-0
30. Wang, J, Li, Y, Pan, L, Li, J, Yu, Y, Liu, B, et al. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) moonlights as an adhesin in Mycoplasma hyorhinis adhesion to epithelial cells as well as a plasminogen receptor mediating extracellular matrix degradation. Vet Res. (2021) 52:80. doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00952-8
31. Palzer, A, Ritzmann, M, Wolf, G, and Heinritzi, K. Associations between pathogens in healthy pigs and pigs with pneumonia. Vet Rec. (2008) 162:267–71. doi: 10.1136/vr.162.9.267
32. Wang, J, Gan, Y, Yuan, T, Huang, Y, Zhang, L, Wei, Y, et al. Protection against Mycoplasma hyorhinis infection in commercial pigs via immunization with inactivated vaccines prepared with homologous or heterologous strains. Vaccine. (2024) 42:126421. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.126421
33. Jolley, KA, Bray, JE, and Maiden, MCJ. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. (2018) 3:124. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.14826.1
34. Trüeb, B, Catelli, E, Luehrs, A, Nathues, H, and Kuhnert, P. Genetic variability and limited clonality of Mycoplasma hyorhinis in pig herds. Vet Microbiol. (2016) 191:9–14. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.05.015
35. Garcia-Morante, B, Segalés, J, Fraile, L, Pérez de Rozas, A, Maiti, H, Coll, T, et al. Assessment of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae-induced pneumonia using different lung lesion scoring systems: a comparative review. J Comp Pathol. (2016) 154:125–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2015.11.003
36. Roos, LR, Surendran Nair, M, Rendahl, AK, and Pieters, M. Mycoplasma hyorhinis and Mycoplasma hyosynoviae dual detection patterns in dams and piglets. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0209975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209975
37. Gerszon, J, Büchse, A, Genz, B, Pollock, Y, Gleeson, B, Morris, A, et al. The use of oral fluids and sock samples for monitoring key pathogens in pig populations for surveillance purposes. Prev Vet Med. (2024) 228:106237
38. Silva, A, Almeida, M, Michael, A, Rahe, MC, Siepker, C, Magstadt, DR, et al. Detection and disease diagnosis trends (2017-2022) for Streptococcus suis, Glaesserella parasuis, Mycoplasma hyorhinis, Actinobacillus suis, and Mycoplasma hyosynoviae at Iowa State University veterinary diagnostic laboratory. BMC Vet Res. (2023) 19:268. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03807-w
39. Renzhammer, R, Auer, A, Loncaric, I, Entenfellner, A, Dimmel, K, Walk, K, et al. Retrospective analysis of the detection of pathogens associated with the porcine respiratory disease complex in routine diagnostic samples from Austrian swine stocks. Vet Sci. (2023) 10:601. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10100601
40. Merodio, M, McDaniel, A, Poonsuk, K, Magtoto, R, Ferreyra, FSM, Meiroz-De-Souza-Almeida, H, et al. Evaluation of colonization, variable lipoprotein-based serological response, and cellular immune response of Mycoplasma hyorhinis in experimentally infected swine. Vet Microbiol. (2021) 260:109162 doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109162
41. Gomes Neto, JC, Strait, EL, Raymond, M, Ramirez, A, and Minion, FC. Antibody responses of swine following infection with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, M. hyorhinis, M. hyosynoviae, and M. flocculare. Vet Microbiol. (2014) 174:163–71. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.08.008
42. Barden, JA, Decker, JL, Dalgard, DW, and Aptekar, RG. Mycoplasma hyorhinis swine arthritis. 3. Modified disease in piney woods swine. Infect Immun. (1973) 8:887–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.887-890.1973
43. Chen, D, Wei, Y, Huang, L, Wang, Y, Sun, J, Du, W, et al. Synergistic pathogenicity in sequential coinfection with Mycoplasma hyorhinis and porcine circovirus type 2. Vet Microbiol. (2016) 182:123–30. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.11.003
44. Gois, M, Kuksa, F, and Sisák, F. Experimental infection of gnotobiotic piglets with Mycoplasma hyorhinis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Zentralblatt fur Veterinarmedizin Reihe B J Vet Med Ser B. (1977) 24:89–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1977.tb00978.x
Keywords: Mycoplasma hyorhinis , positivity rate, isolation, identification, infection
Citation: Yang F, Yang L, Duan X, Qian Y, Ma H, Jia X, Huo X, Dong W, Chen H and Tan C (2025) Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma hyorhinis and virulence evaluation of its field isolates. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1542992. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1542992
Edited by:
Chao-ting Xiao, Hunan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Sukolrat Boonyayatra, Long Island University, United StatesShulin Fu, Wuhan Polytechnic University, China
Moritz Buenger, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna, Austria
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Yang, Duan, Qian, Ma, Jia, Huo, Dong, Chen and Tan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chen Tan, dGFuY2hlbkBtYWlsLmh6YXUuZWR1LmNu
 Fan Yang
Fan Yang Lijun Yang1
,2
Lijun Yang1
,2
 Huanchun Chen
Huanchun Chen Chen Tan
Chen Tan