- College of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing, China
Introduction: Soluble corn fiber, a safe dietary fiber with prebiotic properties, has been put to several applications in human daily life. However, studies on its use in pet food are scarce. This study was conducted to investigate the effects of SCF on microbial diversity, SCFAs and fecal quality in canines.
Methods: Twenty adult dogs were divided into four groups, including the control group (CON) and three groups fed diet supplemented with 0.1% (SCF1), 0.5% (SCF2), or 1% (SCF3) SCF for 21 days.
Results: Fecal scores of the group fed 1% SCF were the closest to the ideal state. α-diversity analysis showed the Chao1 index in the SCF2 and SCF3 groups was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than in the CON group, indicating an increase in colony abundance. β-diversity analysis showed no significant structural difference among groups (p > 0.05). Microbial diversity analysis showed the addition of SCF to the diets increased the relative abundance of Bacteroidota and Blautia and decreased the relative abundance of Firmicutes, [Ruminococcus]_gnavus_group, and Prevotellaceae_Ga6A1_group; 1% SCF the relative abundance of Prevotella and Blautia (p < 0.05), and the content of acetic acid, valeric acid, and isobutyric acid (p < 0.05) and significantly decreased the content of butyric acid (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Dietary supplementation with SCF improves the fecal condition, modulates microbiota composition, enhances the levels of acetic acid, valeric acid, and isobutyric acid, and decreases the level of butyric acid in dogs, with optimal effects observed for 1% supplementation.
1 Introduction
With the economic and social development, increasing number of people keep dogs or cats as companion animals. The pet food industry, which accounts for more than two-thirds of the pet economy in China, is witnessing a paradigm shift, with pet owners demanding pet food that not only meets the basic nutrient requirements but also contains health-promoting and disease-preventing ingredients. This change in demand has led to the emergence of functional pet foods, such as prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics. As an important prebiotic, dietary fiber can increase the viscosity of the chyme to delay gastric emptying and enhance satiety (1), and prevent constipation by accelerating intestinal peristalsis and increasing fecal volume (2). Additionally, as a fermentation substrate for intestinal flora, dietary fiber promote the proliferation of fiber-utilizing (e.g., Prevotella and Bacteroides) and beneficial (e.g., Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) bacteria and change the structure of the intestinal flora, the SCFAs produced by their fermentation can reduce intestinal inflammation (3), improve lipid metabolism (4). Soluble corn fiber (SCF), a resistant maltodextrin with prebiotic properties, is a non-viscous, soluble, fermentable dietary fiber prepared from corn starch via thermal and enzymatic treatment under acidic conditions (5). SCF has long been used as a human-edible and safe dietary fiber and has been shown to enhance satiety (6), reduce serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels, improve fecal status, and promote an increase in beneficial intestinal bacteria (7). However, the efficacy of SCF has mostly been investigated in humans, mice, and piglets, and studies on its effects on the microbial diversity in dogs have been scarce. Therefore, this study was aimed at investigating the effects of adding different doses of SCF to canine diets on microbial diversity and short-chain fatty acid production in the intestine of dogs. We hypothesized that (a) SCF would improve fecal conditions and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the canine intestine and (b) high doses of SCF would be more beneficial to canine intestinal health than low doses of SCF.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Ethics statement
All experiments were approved by and conducted according to the guidelines of the Science and Technology Ethics Committee of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University (DWKJXY2023127).
2.2 Experimental design
Twenty adult Pembroke Welsh Corgi, aged 2–6 years, with similar body weights were selected and randomly divided into four groups, with five dogs (3 females and 2 males in each group) in each group. The control group (CON group) was fed only the basal diet, whereas the SCF1, SCF2, and SCF3 groups were fed basal diet supplemented with 0.1, 0.5, and 1% SCF, respectively. The basal ration was provided by Synergistic Biologicals, and its composition and nutrient levels are shown in Supplementary Table S1. SCF was provided by Edymion Biotechnology (Tianjin) Co. The test period was 26 days, of which the pretest period was 5 days, and the main test period was 21 days. The test was carried out at the dog training base of the Jilin Agricultural Science and Technology University. Each dog was kept in a single kennel, fed twice a day, and allowed free access to water.
2.3 Sample collection and indicator measurement
2.3.1 Fecal scores
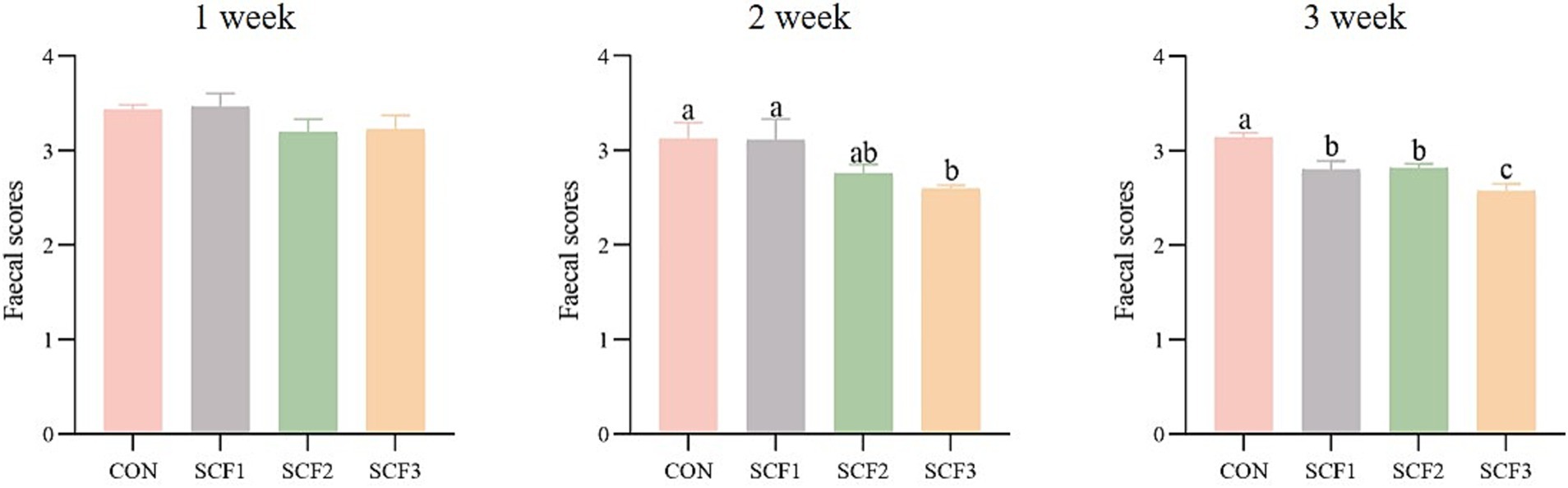
Dogs were observed daily for feces, and scores were recorded, referring the Waltham fecal scoring system in Supplementary Figure S1. Fecal scores on three randomly selected days in weeks 1, 2, and 3 after the formal trial were used for a summary analysis and comparison.
2.3.2 Identification of fecal flora
Fresh feces were collected on day 26 of the experiment and immediately stored in a − 80°C freezer for fecal flora analysis. Fecal DNA was extracted using the MagPure Soil DNA LQ Kit (Magan), the concentration and purity of DNA were measured using a NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) and agarose gel electrophoresis, and the DNA was sequenced by Shanghai Ouyi Biotech Co. (Shanghai Ouyi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) on an Illumina NovaSeq 6,000 sequencing platform. The reads were first trimmed using the Cutadapt software, and then using DADA2 (8), the qualified paired-end raw reads from the previous step were subjected to quality control analyses, such as quality filtering, noise reduction, splicing and de-chimerization in accordance with QIIME 2 (9) (2020.11), to obtain representative sequences and amplicon sequence variant abundance tables, and all the representative sequences were compared with the Silva (version138) database for annotation. The microbial diversity was estimated using the alpha diversity that include Chao1 (10) and Shannon indices (11). The Unifrac distance matrix performed by QIIME software was used for Principal component analysis (PCA).
2.3.3 Determination of short-chain fatty acid content
On Day 26 of the trial, fresh fecal samples were collected and snap-frozen at −80°C for short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) analysis. The concentrations of acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, valeric acid, isobutyric acid, and isovaleric acid were quantified using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (AB Sciex/Waters) following the protocol described by Dobrowolska et al. (12).
2.4 Statistical analyses
Data are expressed as mean ± standard error. Raw data were first sorted using Microsoft Excel 2016 and then analyzed using one-way ANOVA with the SPSS 25.0 statistical software. Graphs were prepared using the Graphpad Prism 8.0 software. A value of p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 Effect of soluble corn fiber on fecal status in dogs
As shown in Figure 1, the SCF3 group exhibited significantly decreased fecal scores than the control and SCF1 groups (p < 0.05) by week 2. By week 3, all treatment groups exhibited significantly lower fecal scores than the control group, and SCF3 groups were significantly lower than SCF1 and SCF2 group (p < 0.05), with fecal scores approaching the ideal benchmark of 2.5.
3.2 Fecal microbiome analysis
3.2.1 Analysis of fecal microbial diversity
The Chao1 index for SCF2 and SCF3 groups was significantly higher than that for the control group (CON group: 159.38 ± 8.52; SCF1 group: 183.26 ± 13.86; SCF2 group: 194.78 ± 2.09; SCF3: 214.29 ± 12.35, p < 0.05), indicating that the addition of higher doses of SCF significantly increased the microbial diversity (Supplementary Table S2). Analysis of the results for β-diversity (Supplementary Figure S2) showed no significant differences in microbial diversity among the four groups.
3.2.2 Analysis of the colony structure at the phylum level
As shown in Figure 2A, the dominant phyla in each group were Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, and Fusobacteriota, with relatively low abundance of Proteobacteria, Actinobacteriota, and Campylobacteria. Figures 2B,C show that the addition of 1% SCF to the diets significantly increased the relative abundance of Bacteroidota (p < 0.05), and that the relative abundance of Firmicutes in the CON group was significantly higher than that in the SCF3 group (p < 0.05).
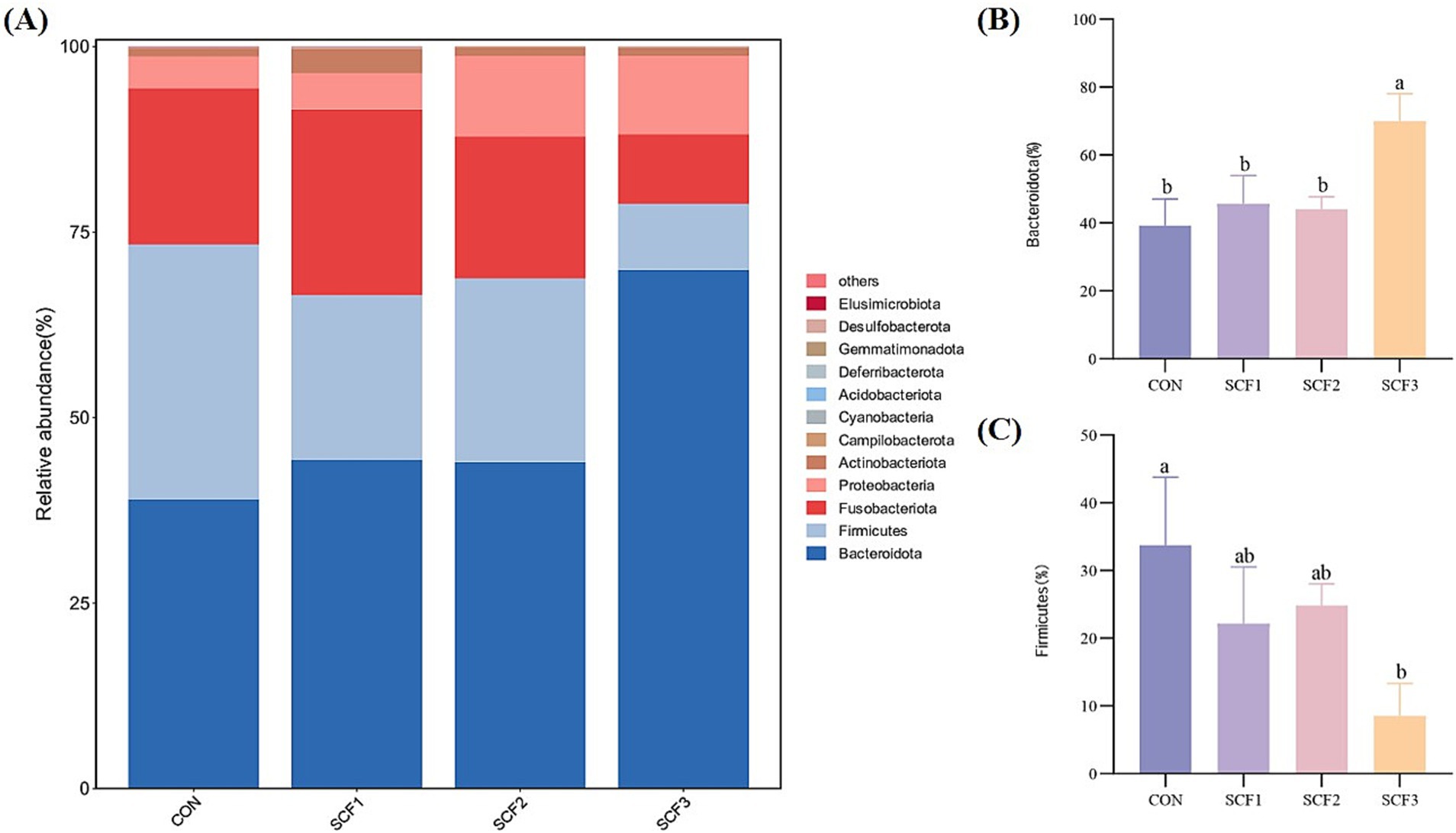
Figure 2. Phylum level analysis of flora. (A) Taxonomic bar plot at the phylum level, (B) The relative abundance of Bacteroidota, (C) The relative abundance of Firmicutes.
3.2.3 Analysis of the colony structure at the genus-level
As shown in Figure 3A, the relative abundances of Prevotella, Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Faecalibacterium, and Alloprevotella, which are the main microbial diversity genera, were higher in the four groups. The addition of 0.5 and 1% SCF to the diets significantly increased the relative abundance of Blautia (p < 0.05); the addition of 1% SCF significantly increased the relative abundance of Prevotella (p < 0.05) and significantly decreased the relative abundance of Bacteroides (p < 0.05); and in the SCF group the abundance of [Ruminococcus]_gnavus_group and Prevotellaceae_Ga6A1_group was significantly lower (p < 0.05) than in the control group (Figures 3B–F).
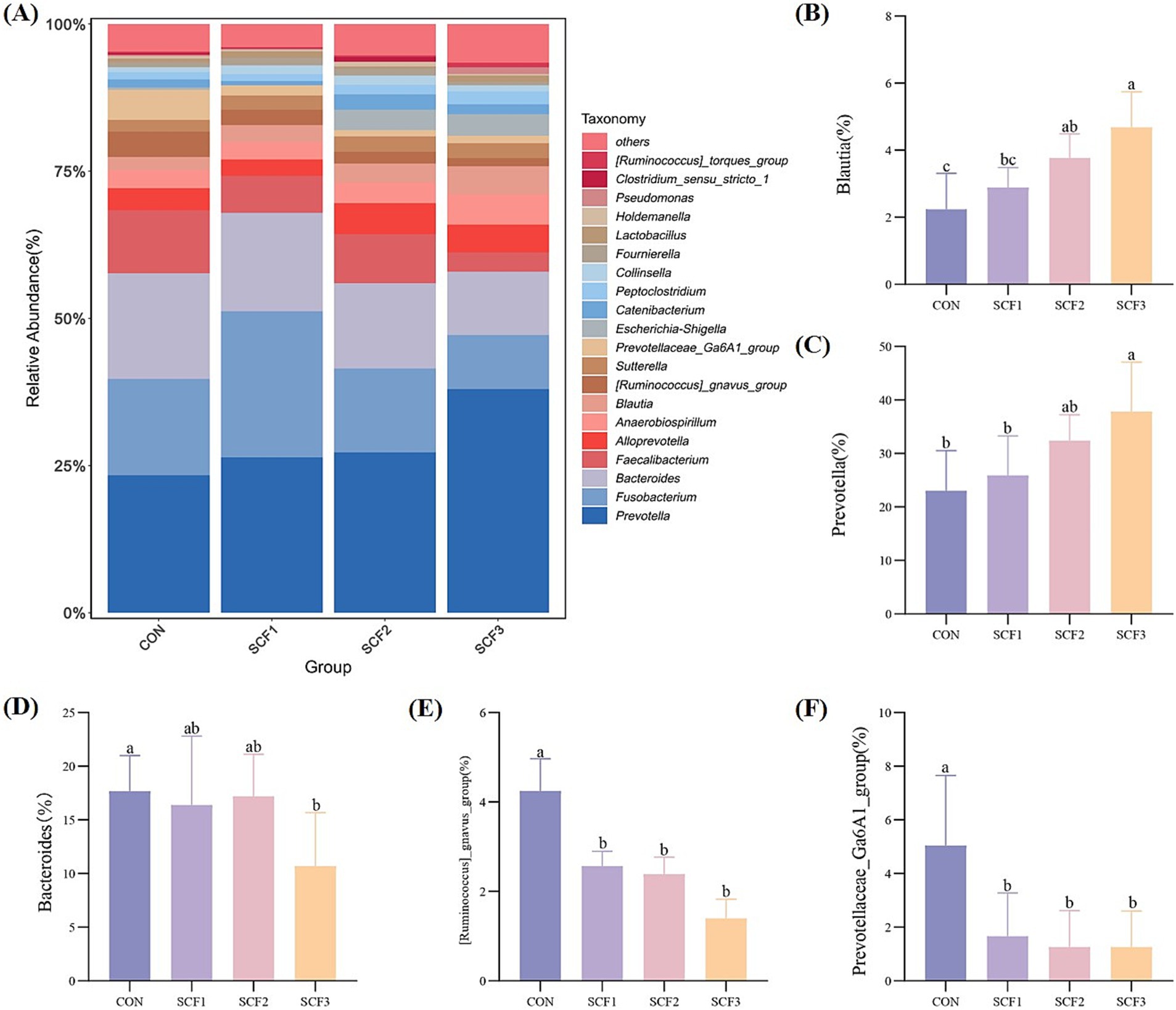
Figure 3. Genus level analysis of flora. (A) Taxonomic bar plot at the genus level, (B) The relative abundance of Blautia, (C) The relative abundance of Prevotella, (D) The relative abundance of Bacteroides, (E) The relative abundance of [Ruminococcus]_gnavus_group, (F) The relative abundance of Prevotellaceae_Ga6A1_group.
3.3 Effect of soluble corn fiber on short-chain fatty acids in dog feces
As shown in Figures 4A–D, the addition of 1% SCF to the diets significantly increased the concentrations of valeric acids in the feces (p < 0.05) and significantly decreased the concentration of butyric acid (p < 0.05) compared with that in the control group. The concentration of acetic and isobutyric acid in both the SCF2 and SCF3 groups were significantly higher than that in the CON group (p < 0.05).
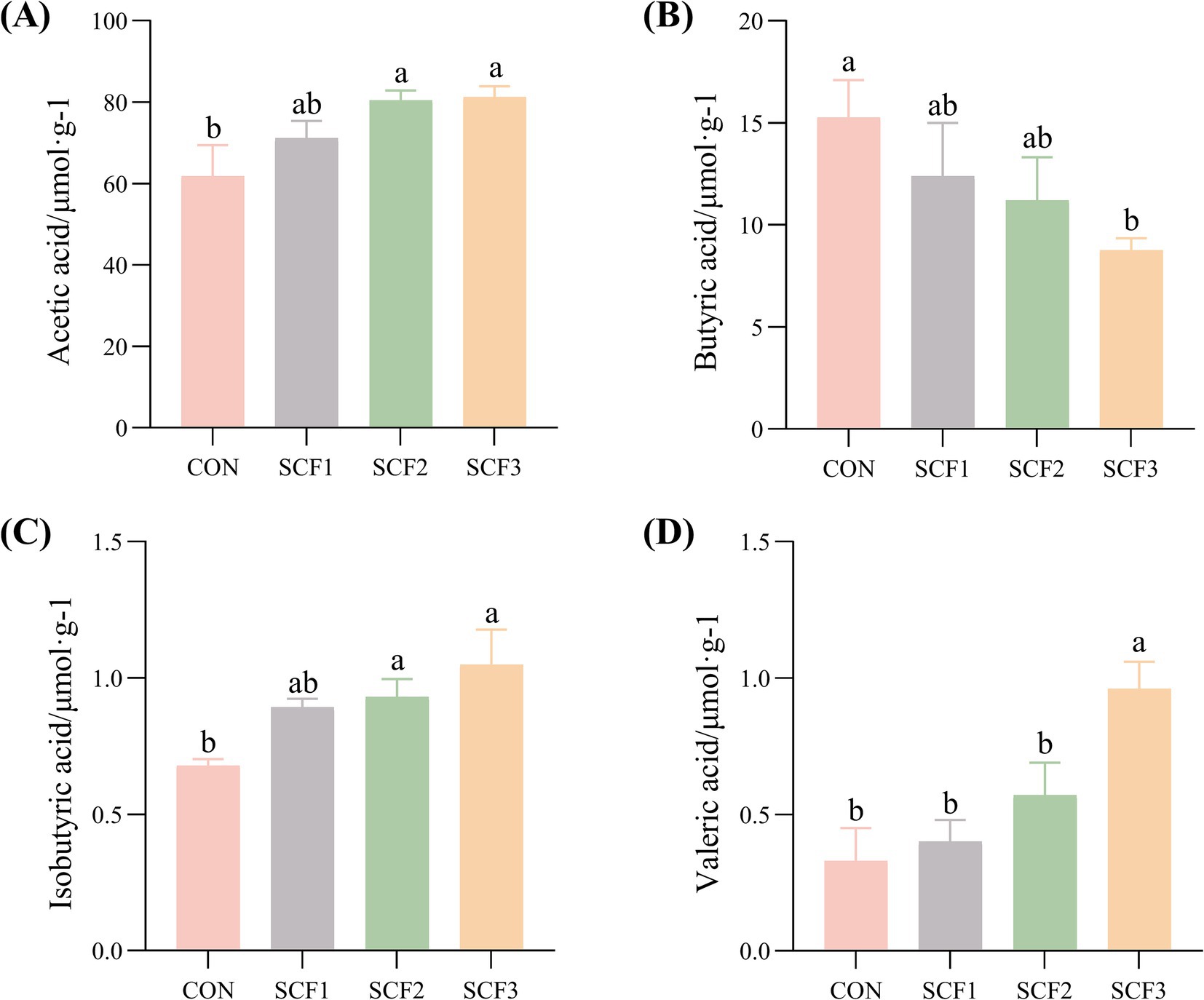
Figure 4. Effect of soluble corn fiber on canine fecal short-chain fatty acid content. (A) Acetic acid concentration, (B) Butyric acid concentration, (C) Isobutyric acid concentration, (D) Valeric acid concentration. Different small letters in the same column indicated significant differences between groups (p < 0.05).
4 Discussion
Prebiotics, including oligosaccharides and dietary fibers, are substances that cannot be digested and absorbed by animals; however, their selective utilization by gut microbes improves the intestinal health (13). In present study showed that dietary supplementation with SCF for 2 weeks can improve the fecal condition of dogs, with the SCF3 group exhibiting a fecal score closest to the ideal score of 2.5. This may be attributed to the high viscous and water-holding capacity of SCF, which absorbs water and swells expands in the large intestine, increasing stool bulk and promoting stool formation to improve diarrhea symptoms (14). microbial fermentation of SCF into organic acids help regulate intestinal motility, which could relieve constipation (15). However, a previous study investigating cellulose and prebiotic mixtures studied reported no effect on canine fecal scores (16). This discrepancy may be attributed to the differences in physicochemical properties caused by the structural differences among dietary fibers (such as glycosidic bond and molecular weight). SCF is a dietary fiber that cannot be digested and metabolized by digestive enzymes in the gut, but can only be metabolized by certain species of gut microbiota via anaerobic fermentation, the main products of which are SCFAs. The Chao1 index of alpha diversity was significantly higher in the SCF group, indicating that SCF significantly affected the diversity and abundance of microbes, which is consistent with the findings of Wang et al. (16). At the phylum level, the dominant flora in all groups were mainly Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, Fusobacteriota, and Proteobacteria, consistent with the results of a previous study (17, 18). This may be attributed to the fact that the modulation of dietary fiber on bacterial phyla was relatively stable, while more pronounced compositional changes occur at the family, genus or species level. The Bacteroidota is involved in the metabolism of a variety of soluble polysaccharides and upregulates the expression of soluble polysaccharide-degrading enzymes (19, 20). The Firmicutes have a system for degrading dietary fiber, which tends to transport the fibers into the cell for degradation, which is different from that in Bacteroidota (21). In this study, the addition of SCF significantly increased Bacteroidota and decreased the abundance of Firmicutes, which is in general agreement with the results of Miyazato et al. (22). Some Blautia strains can utilize CO, H2/CO2, and carbohydrates as energy sources (23). Several studies on the utilization of carbohydrates have shown that all strains of the genus Blautia can utilize glucose, but different strains differ in their ability to utilize sucrose, fructose, lactose, maltose, and rhamnose, and that they ferment SCFAs, namely acetic, succinic, and lactic acids (24–27). In this study, the addition of a slightly higher dose of SCF to the diet not only significantly increased the relative abundance of Blautia but also the level of acetic acid, suggesting that SCF may increase the level of acetic acid in the intestinal tract by promoting the growth of Blautia and thus maintain the intestinal health of dogs. Studies showed that acetic acid could modulate adipose tissue inflammation by elevating IL-17 and IL-10 (28), and improve lipid homeostasis via reduction of free fatty acids (e.g., triglyceride and cholesterol) (29). In this study, the addition of 1% SCF increased the relative abundance of Prevotella and decreased the relative abundance of Bacteroides This finding is consistent with that of Kovatcheva-Datchary et al. (30). Prevotella exhibits more superior fiber utilization efficiency than Bacteroides, and correlating with enhanced SCFAs production (31). Several enzymes produced by Prevotella are involved in polysaccharide degradation and play an important role in the decomposition of polysaccharides and the formation of SCFAs. It has also been demonstrated that Prevotellaceae_UCG-003 elevate isobutyric acid levels to alleviate diarrhea in piglets (32). In present study, the concentration of isobutyric acid in SCF group increased and the quality of feces were improved. The significantly lower abundance of Bacteroides was possibly due to substrate competition with Prevotella. The abundance of [Ruminococcus]_gnavus_group is positively correlated with chronic inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn’s disease (33), In the present study, the abundance of [Ruminococcus]_gnavus_group in the dog groups supplemented with SCF was significantly lower than that in the control group, suggesting that consumption of SCF can potentially reduce the risk of inflammatory bowel disease in dogs. The abundance of the Prevotellaceae_Ga6A1_group was significantly lower in the SCF group than in the control group, which is consistent with the findings of Thunyaporn et al. (34). In present study, isobutyric and valeric acids concentrations were elevated and butyrate acids concentration was reduced in the 1% SCF group than in the control group. Butyrate acids is the primary energy substrate for colonic epithelial cells. Butyric acid produced by the fermentation of resistant starch can promote intestinal peristalsis (35). The decrease in butyric acid concentration in present study might be related to the accelerated utilization of intestinal epithelial cells. Several studies have shown that the addition of dietary fibers with prebiotic potential to the diet promotes the production of isobutyric and valeric acids (36–38), which is consistent with the findings of the present study. As energy substrates for colonic epithelial cells, isobutyric and valeric acids regulate intestinal motility and fecal excretion (39). The addition of valeric acid derivatives also showed positively effects on the mucosa (40). In this study, the optimal addition amount of SCF could not be determined because only three gradients of SCF addition were set, which failed to fully cover its dose-effect relationship. In addition, the experimental results showed that the abundance of Proteobacteria increased significantly after the addition of SCF, and the specific mechanism of this phenomenon is not clear, which may be related to the dose-dependent flora response or individual differences. In order to further validate this result and explore the potential mechanism, it is recommended to expand the sample size and set a wider dose gradient in subsequent studies to comprehensively evaluate the effects of SCF on intestinal flora and host metabolism.
5 Conclusion
Adding SCF to the diet for 3 weeks improved the fecal condition, modulated microbiota composition and enhanced SCFA production in dogs, with optimal effects observed at 1% inclusion level. These findings provide a supporting basis for the application of SCF in pet food.
Data availability statement
The data presented in this study are deposited in the NCBI repository, with the accession number PRJNA1263151. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
DL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Visualization, Formal analysis. SZ: Formal analysis, Software, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. GY: Supervision, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Formal analysis, Validation, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2025.1599213/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Patra, S, Everhart Nunn, SL, Levent, G, and Chelikani, PK. Prebiotics pectin and resistant starch-type 4 stimulate peptide YY and cholecystokinin to promote satiety, and improve gut microbiota composition. FASEB J. (2025) 39:e70457. doi: 10.1096/fj.202403239R
2. Reis, V, Melo, VX, Silva, MLR, Filho, PSL, Portugal, LC, Sartoratto, A, et al. Insoluble dietary fibers from Hancornia speciosa alleviates chronic constipation on experimental loperamide-induced model. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 306:141215–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.141215
3. Ying, M, Yu, Q, Zheng, B, Wang, H, Wang, J, Chen, S, et al. Cultured Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharides modulate intestinal mucosal immunity and gut microbiota in cyclophosphamide-treated mice. Carbohydr Polym. (2020) 235:115957–7. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115957
4. O'Grady, J, O'Connor, EM, and Shanahan, F. Review article: dietary fibre in the era of microbiome science. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2019) 49:506–15. doi: 10.1111/apt.15129
5. Włodarczyk, M, and Śliżewska, K. Efficiency of resistant starch and Dextrins as prebiotics: a review of the existing evidence and clinical trials. Nutrients. (2021) 13:13. doi: 10.3390/nu13113808
6. Fernández-Raudales, D, Yor-Aguilar, M, Andino-Segura, J, Hernández, A, Egbert, R, and López-Cintrón, JR. Effects of high plant protein and high soluble Fiber beverages on satiety, appetite control and subsequent food intake in healthy men. Food Nutr Sci. (2018) 9:751–62. doi: 10.4236/fns.2018.96057
7. Burns, AM, Solch, RJ, Dennis-Wall, JC, Ukhanova, M, Nieves, C Jr, Mai, V, et al. In healthy adults, resistant maltodextrin produces a greater change in fecal bifidobacteria counts and increases stool wet weight: a double-blind, randomized, controlled crossover study. Nutr Res. (2018) 60:33–42. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.09.007
8. Callahan, BJ, McMurdie, PJ, Rosen, MJ, Han, AW, Johnson, AJ, and Holmes, SP. DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods. (2016) 13:581–3. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869
9. Bolyen, E, Rideout, JR, Dillon, MR, Bokulich, NA, Abnet, CC, Al-Ghalith, GA, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol. (2019) 37:852–7. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
10. Chao, A, and Bunge, J. Estimating the number of species in a stochastic abundance model. Biometrics. (2002) 58:531–9. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2002.00531.x
11. Hill, TC, Walsh, KA, Harris, JA, and Moffett, BF. Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. (2003) 43:1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2003.tb01040.x
12. Dobrowolska-Iwanek, J, Lauterbach, R, Huras, H, Pako, P, Ewelina, P, Michal, W, et al. HPLC-DAD method for the quantitative determination of short-chain fatty acids in meconium samples. Microchem J. (2020) 155:104671. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2020.104671
13. Ojo, O, Feng, QQ, Ojo, OO, and Wang, XH. The role of dietary fibre in modulating gut microbiota Dysbiosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3239. doi: 10.3390/nu12113239
14. McRorie, JW Jr. Evidence-based approach to Fiber supplements and clinically meaningful health benefits, part 2: what to look for and how to recommend an effective Fiber therapy. Nutr Today. (2015) 50:90–7. doi: 10.1097/nt.0000000000000089
15. Wu, L, Tang, C, Chen, L, and Zhao, J. Modified dietary fiber from soybean dregs by fermentation alleviated constipation in mice. Food Chem X. (2023) 19:100810. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100810
16. Wang, F, Gao, S, Peng, Q, Tan, L, Chen, S, and Xia, Z. Effects of heat-treated Bifidobacterium longum CECT-7347 combined with Fibersol-2 on the intestinal health of cats submitted to an abrupt dietary change: a randomized controlled study. Animals. (2024) 14:2668. doi: 10.3390/ani14182668
17. Alessandri, G, Milani, C, Mancabelli, L, Mangifesta, M, Lugli, GA, Viappiani, A, et al. Metagenomic dissection of the canine gut microbiota: insights into taxonomic, metabolic and nutritional features. Environ Microbiol. (2019) 21:1331–43. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14540
18. Yang, Q, and Wu, Z. Gut probiotics and health of dogs and cats: benefits, applications, and underlying mechanisms. Microorganisms. (2023) 11:2452. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11102452
19. Flint, HJ, Bayer, EA, Rincon, MT, Lamed, R, and White, BA. Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2008) 6:121–31. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1817
20. Zafar, H, and Saier, MH Jr. Gut Bacteroides species in health and disease. Gut Microbes. (2021) 13:1–20. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1848158
21. Sun, Y, Zhang, S, Nie, Q, He, H, Tan, H, Geng, F, et al. Gut firmicutes: relationship with dietary fiber and role in host homeostasis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 63:12073–88. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2098249
22. Miyazato, S, Kishimoto, Y, Takahashi, K, Kaminogawa, S, and Hosono, A. Continuous intake of resistant maltodextrin enhanced intestinal immune response through changes in the intestinal environment in mice. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. (2016) 35:1–7. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.2015-009
23. Lorowitz, WH, and Bryant, MP. Peptostreptococcus productus strain that grows rapidly with CO as the energy source. Appl Environ Microbiol. (1984) 47:961–4. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.961-964.1984
24. Kim, JS, Park, JE, Lee, KC, Choi, SH, Oh, BS, Yu, SY, et al. Blautia faecicola sp. nov., isolated from faeces from a healthy human. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. (2020) 70:2059–65. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.004015
25. Ghimire, S, Wongkuna, S, Kumar, R, Nelson, E, Christopher-Hennings, J, and Scaria, J. Genome sequence and description of Blautia brookingsii SG772 sp. nov., a novel bacterial species isolated from human faeces. New Microbes New Infect. (2020) 34:100648. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2019.100648
26. Paek, J, Shin, Y, Kook, JK, and Chang, YH. Blautia argi sp. nov., a new anaerobic bacterium isolated from dog faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. (2019) 69:33–8. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002981
27. Shin, NR, Kang, W, Tak, EJ, Hyun, DW, Kim, PS, Kim, HS, et al. Blautia hominis sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. (2018) 68:1059–64. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002623
28. Park, J, Kim, M, Kang, SG, Jannasch, AH, Cooper, B, Patterson, J, et al. Short-chain fatty acids induce both effector and regulatory T cells by suppression of histone deacetylases and regulation of the mTOR-S6K pathway. Mucosal Immunol. (2015) 8:80–93. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.44
29. Laurent, C, Simoneau, C, Marks, L, Braschi, S, Champ, M, Charbonnel, B, et al. Effect of acetate and propionate on fasting hepatic glucose production in humans. Eur J Clin Nutr. (1995) 49:484–91.
30. Kovatcheva-Datchary, P, Nilsson, A, Akrami, R, Lee, YS, De Vadder, F, Arora, T, et al. Dietary Fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of Prevotella. Cell Metab. (2015) 22:971–82. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.001
31. Chen, T, Long, W, Zhang, C, Liu, S, Zhao, L, and Hamaker, BR. Fiber-utilizing capacity varies in Prevotella- versus Bacteroides-dominated gut microbiota. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:2594. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02995-4
32. Fang, X, Wang, Z, Chen, Q, Du, Y, Sun, H, Liu, H, et al. Protective effect of the branched short-chain fatty acid isobutyrate on intestinal damage in weaned piglets through intestinal microbiota remodeling. J Sci Food Agric. (2025) 105:1556–68. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13930
33. Liu, S, Zhao, W, Lan, P, and Mou, X. The microbiome in inflammatory bowel diseases: from pathogenesis to therapy. Protein Cell. (2021) 12:331–45. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00745-3
34. Phungviwatnikul, T, Lee, AH, Belchik, SE, Suchodolski, JS, and Swanson, KS. Weight loss and high-protein, high-fiber diet consumption impact blood metabolite profiles, body composition, voluntary physical activity, fecal microbiota, and fecal metabolites of adult dogs. J Anim Sci. (2022) 100:100. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab379
35. Lu, D, Pi, Y, Ye, H, Wu, Y, Bai, Y, Lian, S, et al. Consumption of dietary Fiber with different physicochemical properties during late pregnancy alters the gut microbiota and relieves constipation in sow model. Nutrients. (2022) 14:2511. doi: 10.3390/nu14122511
36. Yao, H, Wang, L, Tang, X, Yang, Z, Li, H, Sun, C, et al. Two novel polysaccharides from Solanum nigrum L. exert potential prebiotic effects in an in vitro fermentation model. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 159:648–58. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.121
37. Xu, D, Feng, M, Chu, Y, Wang, S, Shete, V, Tuohy, KM, et al. The prebiotic effects of oats on blood lipids, gut microbiota, and short-chain fatty acids in mildly Hypercholesterolemic subjects compared with Rice: a randomized. Controlled Trial Front Immunol. (2021) 12:787–97. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.787797
38. Wang, K, Wang, Y, Chen, S, Gu, J, and Ni, Y. Insoluble and soluble dietary fibers from kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) modify gut microbiota to alleviate high-fat diet and Streptozotocin-induced TYPE 2 diabetes in rats. Nutrients. (2022) 14:3369. doi: 10.3390/nu14163369
39. Jaskiewicz, J, Zhao, Y, Hawes, JW, Shimomura, Y, Crabb, DW, and Harris, RA. Catabolism of isobutyrate by colonocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. (1996) 327:265–70. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1996.0120
Keywords: soluble corn fiber, microbial diversity, short-chain fatty acids, dogs, pet food
Citation: Liang D, Zhao S and Yin G (2025) Dietary supplementation with soluble corn fiber improved fecal score, microbiota, and SCFAs in dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1599213. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1599213
Edited by:
Bing Dong, China Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Haoyu Liu, Yangzhou University, ChinaSun Baosheng, Shanxi Agricultural University, China
Chengzeng Luo, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), China
Copyright © 2025 Liang, Zhao and Yin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guoan Yin, Z3VvYW55aW5AZm94bWFpbC5jb20=
 Donghui Liang
Donghui Liang Shuai Zhao
Shuai Zhao Guoan Yin
Guoan Yin