- 1College of Animal Science and Technology, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China
- 2Lanzhou Qilihe District Agricultural Technology Extension Station, Lanzhou, China
This study aimed to investigate the effects of dietary zinc-loaded montmorillonite (Zn-MMT) on performance, Zn transporter expression, metal deposition, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal function in broilers. A total of 144 one-day-old male Cobb broilers were randomly divided into three treatment groups. The broilers in the control group (CK) were fed a corn–soybean meal basal diet, while the experimental groups were fed a basal diet supplemented with 40 mg/kg Zn-MMT and ZnSO4 (in terms of Zn content). The results showed that Zn-MMT had no significant (p > 0.05) effect on average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI), or carcass parameters, but it significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the feed-to-gain (F: G) ratio. Dietary Zn supplementation increased (p < 0.05) the expression of Zn transporter 1 (ZnT-1), Zn transporter 5 (ZnT-5), metallothionein (MT), and MTF-1 mRNA in the jejunum and the Zn content in the tibia and whole blood. In addition, it increased (p < 0.05) total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) and Cu/Zn-SOD while reducing (p < 0.05) malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in the liver and jejunum. However, no significant effect (p > 0.05) was observed on the microbial population in the cecum. Furthermore, compared to the CK and ZnSO4 groups, Zn-MMT significantly (p < 0.05) increased the mRNA expression of MT-3 and divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT-1) in the jejunum and promoted the storage of Zn in the liver and pancreas. It also significantly (p < 0.05) increased villus height (VH) and the villus heightto-crypt depth (VH/CD) ratio in the duodenum and jejunum, increased the VH/CD ratio in the ileum, and reduced CD in the duodenum. In conclusion, supplementation with Zn-MMT in a corn–soybean meal basal diet can increase the expression of metal transporters, promote Zn deposition, enhance antioxidant capacity, improve intestinal tissue parameters, and increase Zn utilization.
Introduction
Zinc (Zn), an essential trace mineral widely utilized in poultry nutrition, plays a critical role in avian physiological processes and survival (1). Functioning as a structural component or enzymatic cofactor, Zn actively participates in over 300 metalloenzymes and functional proteins that regulate fundamental biological processes in broilers (2). From a nutritional perspective, Zn demonstrates multifaceted functionality in poultry systems, including enhanced nutrient assimilation, antioxidant defense mechanisms, and the maintenance of homeostasis (3, 4). As the second most abundant trace mineral in avian organisms, Zn exerts regulatory control over physiological pathways governing growth performance, immune competence, and reproductive efficiency in broilers (5, 6). The significance of this mineral extends to its pivotal role in antioxidant systems and immunomodulatory responses, as evidenced by recent studies on broilers (7–9). Notably, Zn interacts competitively with other trace elements, including copper (Cu), iron (Fe), and manganese (Mn), during intestinal absorption (10). Experimental evidence indicates that Zn serves as the first limiting element in these interactions, with its deficiency significantly impairing the absorption and utilization of Fe, Mn, and Cu (11). Clinical manifestations of Zn deficiency in poultry encompass growth retardation, immunosuppression, and increased susceptibility to disease. However, broilers lack the ability for endogenous Zn synthesis, making them entirely dependent on dietary sources to meet their physiological requirements. Consequently, Zn supplementation in poultry diets is essential to meet nutritional requirements and support optimal growth. Among inorganic Zn sources, zinc sulfate (ZnSO₄) remains the predominant additive in commercial formulations. Nevertheless, studies have demonstrated that inorganic Zn compounds exhibit low bioavailability in broilers (12), potentially limiting their metabolic utilization. Recent studies have reported that organic manganese compounds, such as manganese amino acid chelates, exhibit enhanced manganese utilization efficiency in animal nutrition. However, their industrial application in feed additives remains limited due to stringent production processes and elevated manufacturing costs, which impose significant barriers to widespread adoption. Therefore, structural modification of ZnSO₄ (e.g., through chelation or encapsulation) and the implementation of sustained-release delivery systems targeting distal intestinal segments may offer viable strategies to enhance Zn absorption efficiency.
Montmorillonite (MMT), a naturally abundant silicate clay mineral, is characterized by a 2:1 layered structure, with silica tetrahedral sheets sandwiched between alumina octahedral sheets. This unique configuration endows MMT with exceptional physicochemical properties, including a high specific surface area, strong ion exchange capacity, superior adsorption capability, and excellent colloidal stability. Notably, these attributes, particularly its expansive surface area, remarkable adsorption capacity, and chemical inertness, have established MMT as an effective carrier for the controlled delivery of mineral elements. Compared to traditional metallic supplements, metal-loaded montmorillonite demonstrates superior characteristics in terms of enhanced safety profile, sustained efficacy, and improved biological activity. Substantial evidence suggests that the bioavailability of trace mineral elements in metal-intercalated montmorillonite formulations significantly exceeds that of conventional inorganic mineral sources (13, 14). Controlled studies have shown that dietary supplementation with Zn oxide-modified clay in weaned piglets (15) and broiler chickens (16) enhances growth performance and promotes intestinal functional development. Particularly, Wang et al. (17) demonstrated that Zn-bearing palygorskite and Zn-bearing clinoptilolite effectively inhibit Escherichia coli proliferation while reducing its intestinal colonization density in broilers. Our preliminary investigations have revealed that Zn-loaded montmorillonite (Zn-MMT) exerts more pronounced positive effects on broiler growth parameters compared to inorganic Zn supplements. This experimental observation corroborates previous studies, demonstrating the superior bioavailability of Zn-MMT compared to ZnSO₄ in avian nutritional applications. Therefore, we hypothesized that Zn-MMT could serve as a potential alternative to inorganic Zn in broiler nutrition through multiple mechanisms: (1) enhancing Zn ion transport efficiency; (2) optimizing trace element deposition patterns; (3) improving systemic antioxidant capacity; and (4) reinforcing intestinal barrier function. To validate this hypothesis, the current study was designed to systematically evaluate the impacts of Zn-MMT supplementation on broiler growth performance, zinc transport dynamics, and trace element deposition.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
The animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Gansu Agricultural University (Protocol No. GAU-Eth-AST-2024-026). All procedures involving animals adhered to the National Research Council’s Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, with special confirmation that no specimens from threatened or protected species were employed throughout the study.
Zn-loaded montmorillonite
Zn-MMT was provided by the company, Chifeng and Mingsheng Chemical Co., LTD., and was determined by the testing company, Lanzhou Zhongjike Test Technology Co., LTD. The Zn content was 10,408.80 mg/kg.
Experimental design, animals, and diet groups
A total of 144 one-day-old male Cobb broilers with uniform initial body weight (36.5 ± 0.3 g) were obtained from Huaqin Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Technology Co., Ltd. (Shaanxi, China). The birds were randomly allocated to three dietary treatment groups using a completely randomized design, with six replicates per group and eight birds per replicate. The experiment was conducted over a 42-day period under controlled environmental conditions. All birds were housed in wire-floored cages with continuous access to mash feed and water.
The temperature was maintained at 34–35°C during the first 3 days post-hatching, followed by a gradual weekly reduction of 2–3°C until reaching 22°C by the end of the trial.
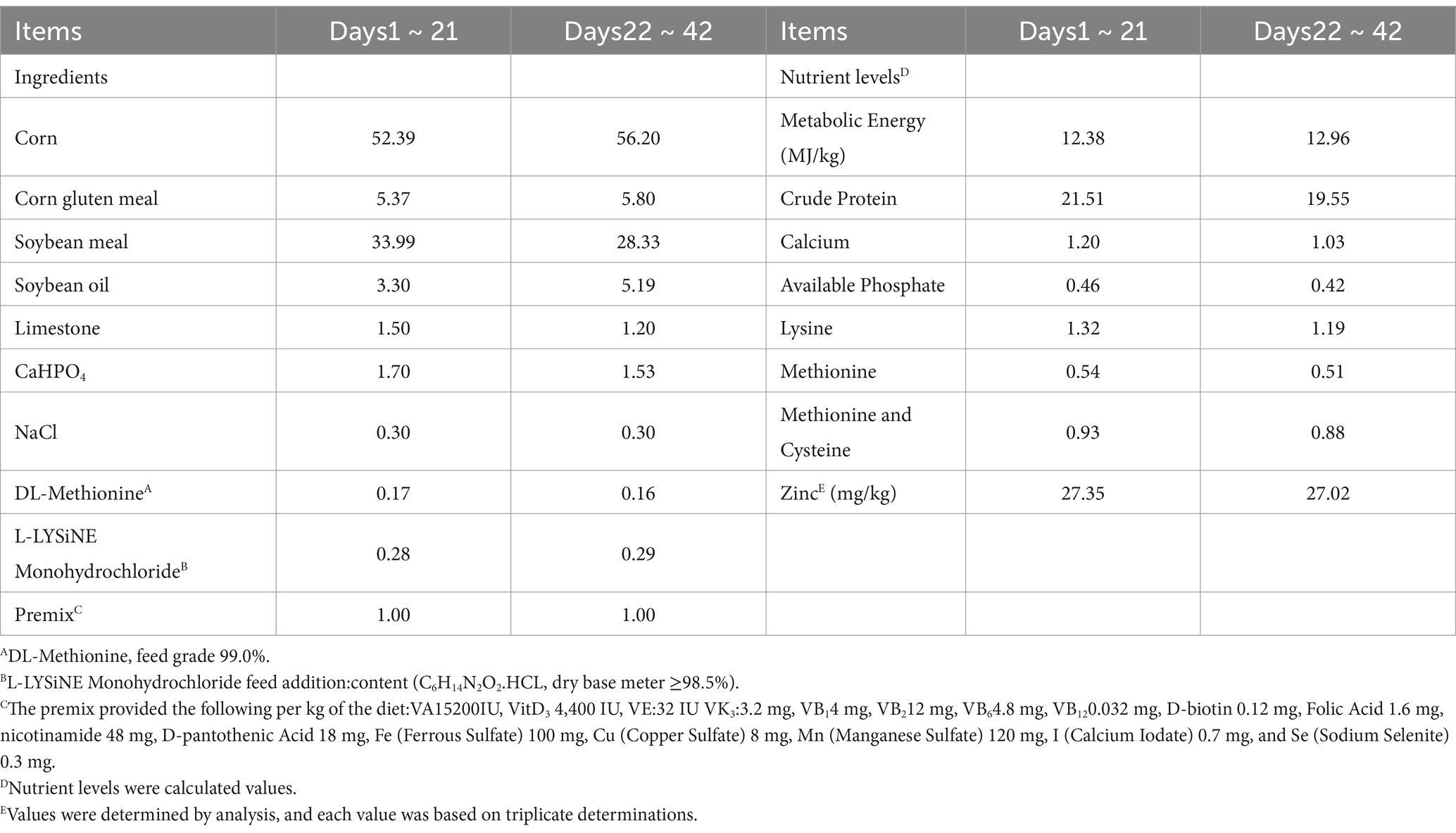
The treatments were as follows: (1) the control, fed a corn–soybean meal basal diet (CK); (2) the basal diet supplemented with 40 mg/kg Zn as Zn-MMT; and (3) the basal diet supplemented with 40 mg/kg Zn as ZnSO4. In both cases, Zn-MMT and ZnSO4 were adjusted to provide the same zinc content by replacing the carrier. The formulation and calculated nutrient levels of the basal diet are shown in Table 1.
Production performance
On day 42, the body weight and feed consumption of the birds were recorded. Subsequently, the following parameters were calculated: average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI), and the feed-to-gain (F: G) ratio. In addition, slaughter performance indicators and immune organ indices were systematically evaluated.
Sample collection
On day 42 post-hatching, one broiler chicken, approximating the group mean body weight (±5%), was humanely euthanized via cervical dislocation from each replicate group. Immediate postmortem dissection was performed to collect tissue specimens within 3 min of euthanasia, in accordance with the AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals (2020 edition).
Determination of trace element deposition and antioxidant capacity
The collected breast muscle, leg muscle, liver, tibia, and whole blood were stored at −20°C. Subsequently, the trace elements of Fe, Cu, Mn, and Zn in the tissues were determined using a flame atomic absorption spectrometer (Agilent Technology 200 Series AA, Malaysia) according to the NY/T3318-2018 standard recommended method. The liver and jejunum mucosal tissues were collected, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C. Then, they were sent to Bio-company (Gansu Shuolian Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Gansu, China) for the determination of Cu/Zn-SOD activity, malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) in the liver and jejunum using ELISA kits (Shanghai Enzyme Link Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
Intestinal morphometry
After the broilers were slaughtered and dissected, tissue samples of approximately 1 ~ 2 cm were collected from the middle part of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. These samples were rinsed with normal saline and fixed in a paraformaldehyde solution. Then, these tissue blocks were sent to a biological company (Wuhan Seville Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) to make a biopsy. Villus height (VH: from the tip of the villus to the villus–crypt junction) and crypt depth (CD: from the villus–crypt junction to the base of the crypt) were measured using a digital microscope (BA210 Digital, Motic China Group Co., Ltd., China). The ratio of villus height to crypt depth (VH/CD) was calculated at the same time.
Relative mRNA expression levels of zinc-associated metal transporters in the jejunum
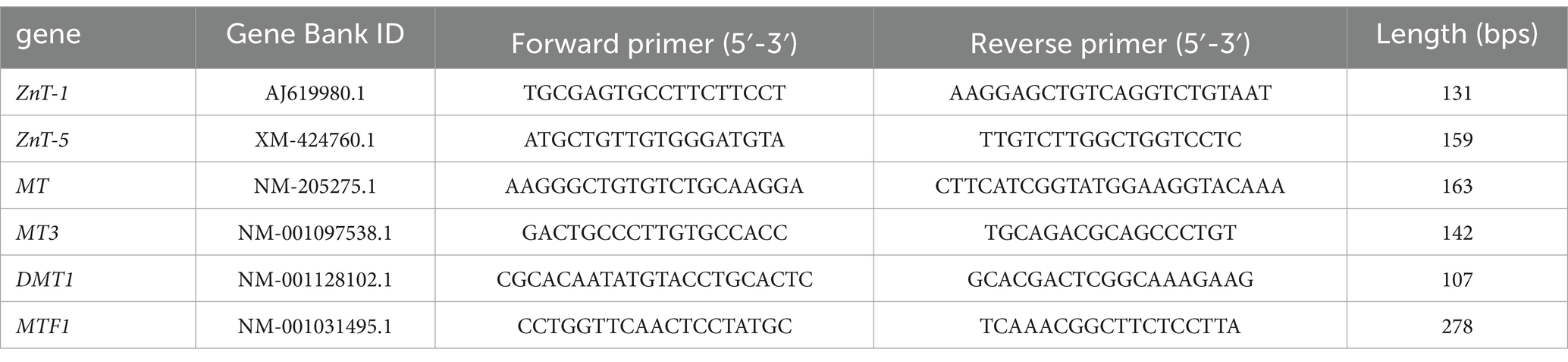
The mRNA expression levels of metal transporters—including Zn transporter 1 (ZnT-1), Zn transporter 5 (ZnT-5), metallothionein (MT), and divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT-1)—in the jejunal mucosa were determined using quantitative real-time PCR. Total RNA was extracted from the jejunal mucosa using TRIzol reagent (TransGen, China). The RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA using the PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (Takara, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Real-time PCR was performed on a LightCycler 480 System (Roche, USA) using a SYBR Green Premix Pro Taq HS qPCR Kit (AG, China). The specific primers for the selected genes, listed in Table 2, were synthesized by Biotech (Suzhou Jin Wei Zhi Biological Technology Co., Ltd., China), with β-actin used as the internal reference. Differential gene expression was calculated using the 2-△△Ct method.
Cecum microorganisms
Sequencing of the 16S rDNA was performed by GENE DENOVO (Guangdong, China). Illumina Novaseq 6,000 sequencing was used to characterize microbial diversity and community composition. Cecal microbial DNA was extracted using the HiPure Stool DNA Kits (Magen, Guangzhou, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. The 16S rDNA target region of the ribosomal RNA gene was amplified using PCR and primers located on both sides of the V3–V4 hypervariable region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene. Related PCR reagents were obtained from TOYOBO (Japan). Amplicons were extracted from 2% agarose gels and purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, U.S.) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The purified amplicons were then quantified using the ABI StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Life Technologies, Foster City, USA).
Raw tags were filtered to obtain clean and high-quality tags, chimera sequences were removed, and sequences with 97% similarity were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) using QIIME2. Alpha diversity indices (Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson) and beta diversity of the cecal microbiota were calculated with QIIME2 and displayed with R software. Beta diversity was determined using the Bray–Curtis index and visualized through principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) and non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using SPSS 26.0 (IBM SPSS Software, Armonk, NY, USA), and statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s new multiple range test. The data were presented as the mean ± SD, and a p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Among them, beta diversity analysis was performed using the Kruskal–Wallis H test and the analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) test.
Results
Production performance
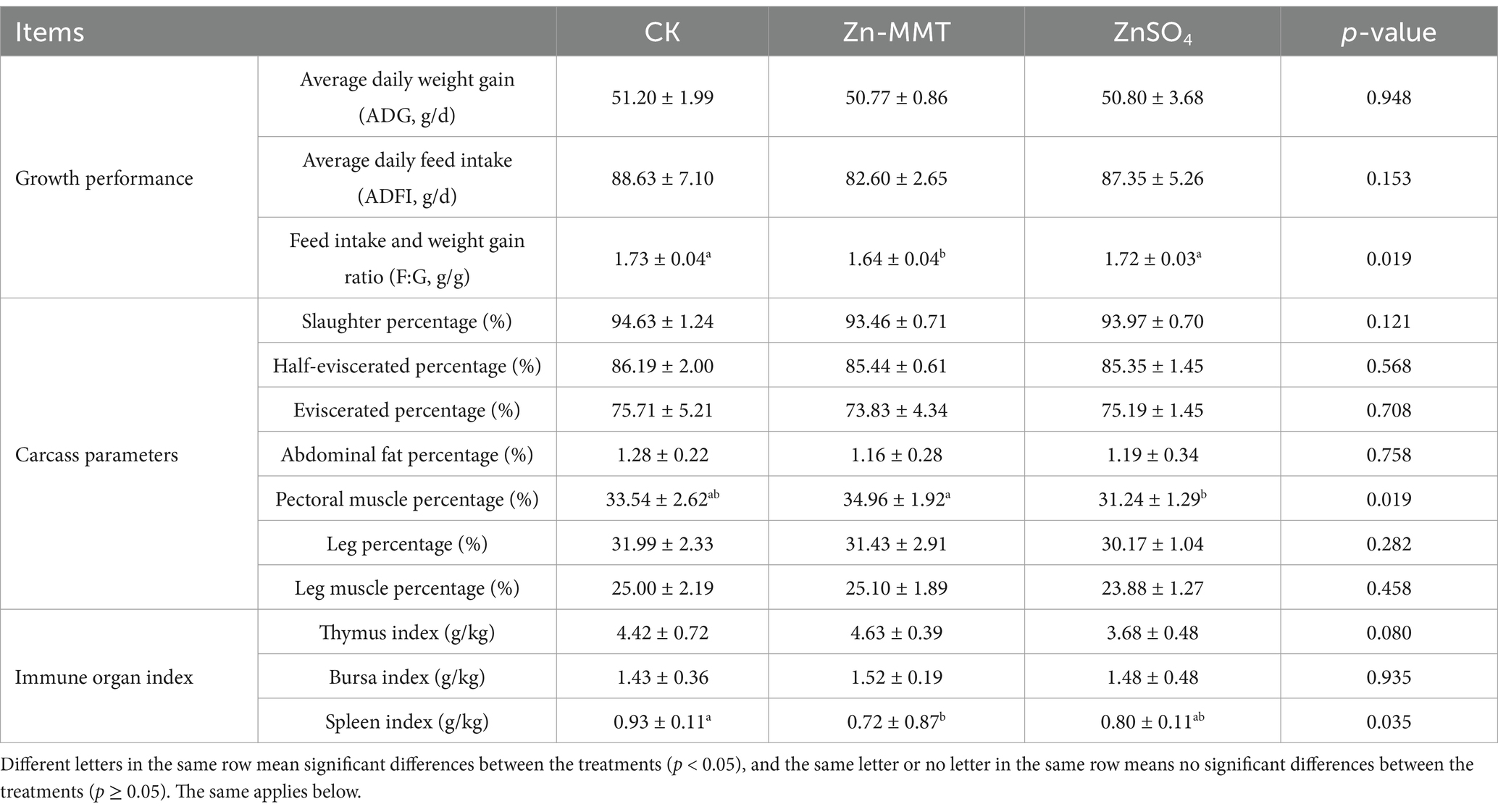
The effects of Zn-MMT on growth performance, carcass parameters, and immune organ indices are shown in Table 3. Compared to the CK group, adding Zn-MMT to the diets did not significantly affect ADG, ADFI, thymus index, bursa index, and the percentages of slaughter, half-eviscerated, eviscerated, abdominal fat, pectoral muscle, leg, or leg muscle rate (p > 0.05). Compared to the CK group, Zn-MMT significantly reduced the F: G ratio and spleen index (p < 0.05).
Tissue trace element deposition
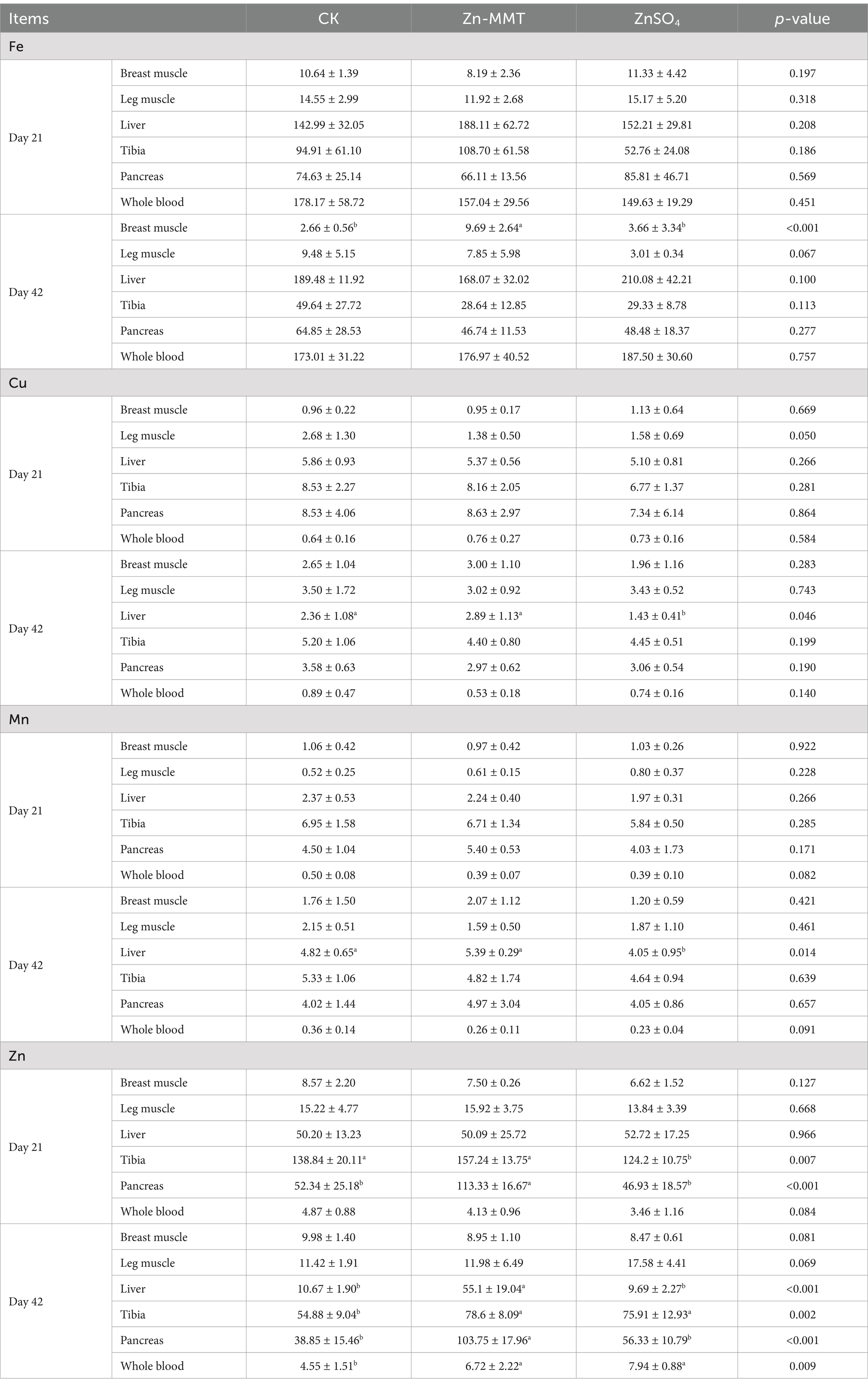
The effect of Zn-MMT on the deposition of the trace elements in the tissues is summarized in Table 4.
In terms of the Fe content, throughout the entire experimental period, except for the Fe content in the breast muscle at 42 days of age, the addition of Zn had no significant (p > 0.05) impact on the iron content in the pectoral muscle, leg muscle, liver, tibia, pancreas, and whole blood. Compared to the CK and ZnSO4 groups, adding Zn-MMT to the diets significantly increased (p < 0.05) the Fe content in the breast muscle at 42 days of age, and there was no significant difference between the CK group and the ZnSO4 group (p > 0.05). In terms of the content of Cu and Mn, similar trends were observed. Compared to the CK group, the addition of Zn had no effect (p > 0.05) on the content of Cu and Mn in all tissues and blood, except in the liver at 42 days of age. Compared to the CK group, ZnSO4 significantly decreased (p < 0.05) the levels of Cu and Mn in the liver at 42 days of age. As for the content of Zn, at 21 days of age, compared to the CK and ZnSO4 groups, the addition of Zn-MMT to the diet significantly increased (p < 0.05) the pancreatic Zn content. However, dietary ZnSO4 supplementation decreased (p < 0 0.05) the tibia Zn content compared to the CK and Zn-MMT groups. At 42 days of age, Zn-MMT supplementation significantly (p < 0.05) affected the pancreatic and liver Zn levels, compared to the CK group, and Zn-MMT notably increased (p < 0.05) the pancreatic Zn content. Compared to the CK group, Zn supplementation significantly increased (p < 0.05) the Zn content in the tibia and whole blood.
Antioxidant capacity
The effects of Zn-MMT on antioxidant capacity are summarized in Table 5. Compared to the CK group, adding Zn-MMT and ZnSO4 to the diets significantly increased (p < 0.05) T-AOC and Cu/Zn-SOD in the liver and jejunum. In contrast, Zn could significantly reduce the MDA content in the liver and jejunum (p < 0.05). Simultaneously, ZnSO4 was more effective than Zn-MMT in reducing the MDA content in the liver and jejunal mucosa (p < 0.05).
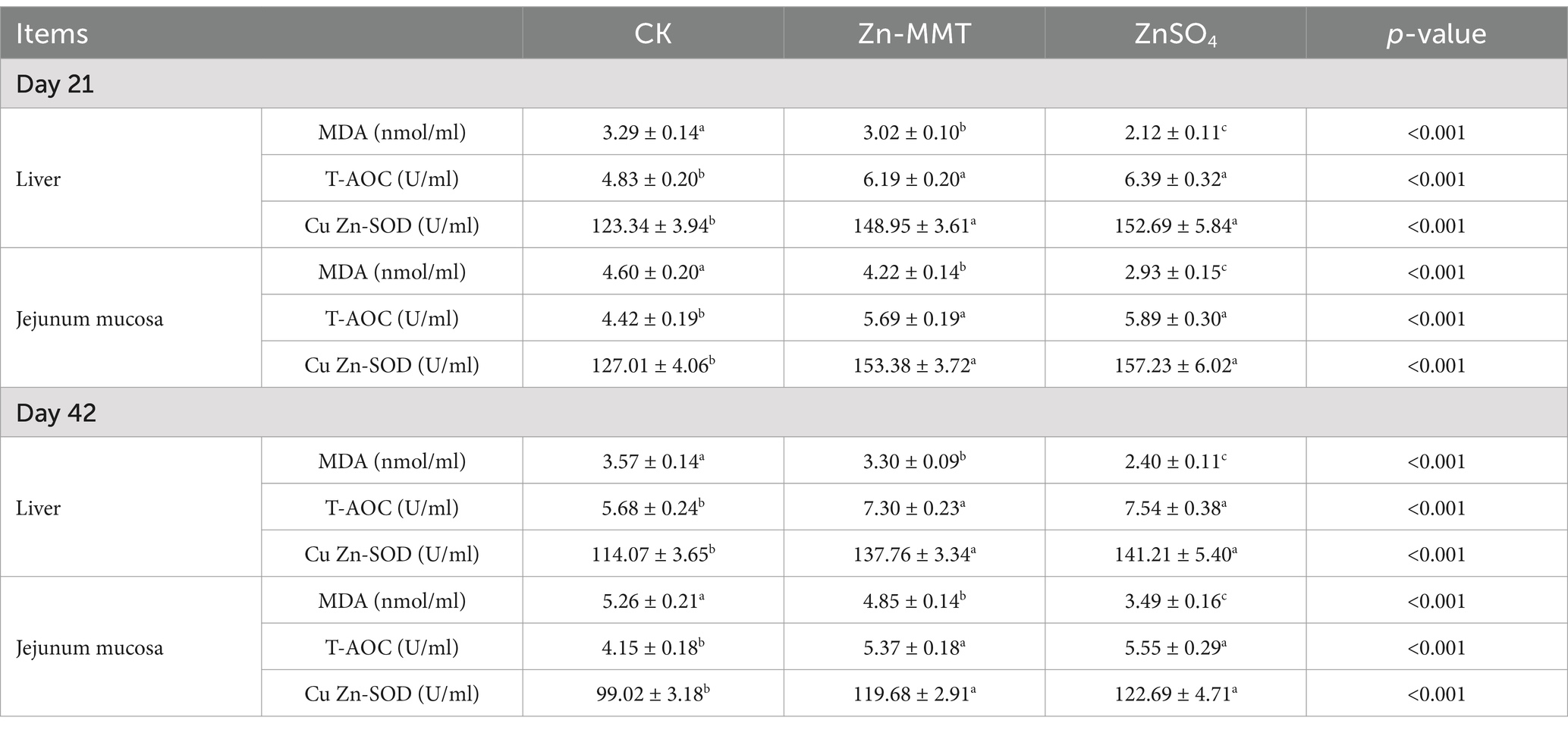
Table 5. The effects of Zn-MMT on the antioxidant capacity of the liver and jejunal mucosa in the broilers.
Intestinal morphology
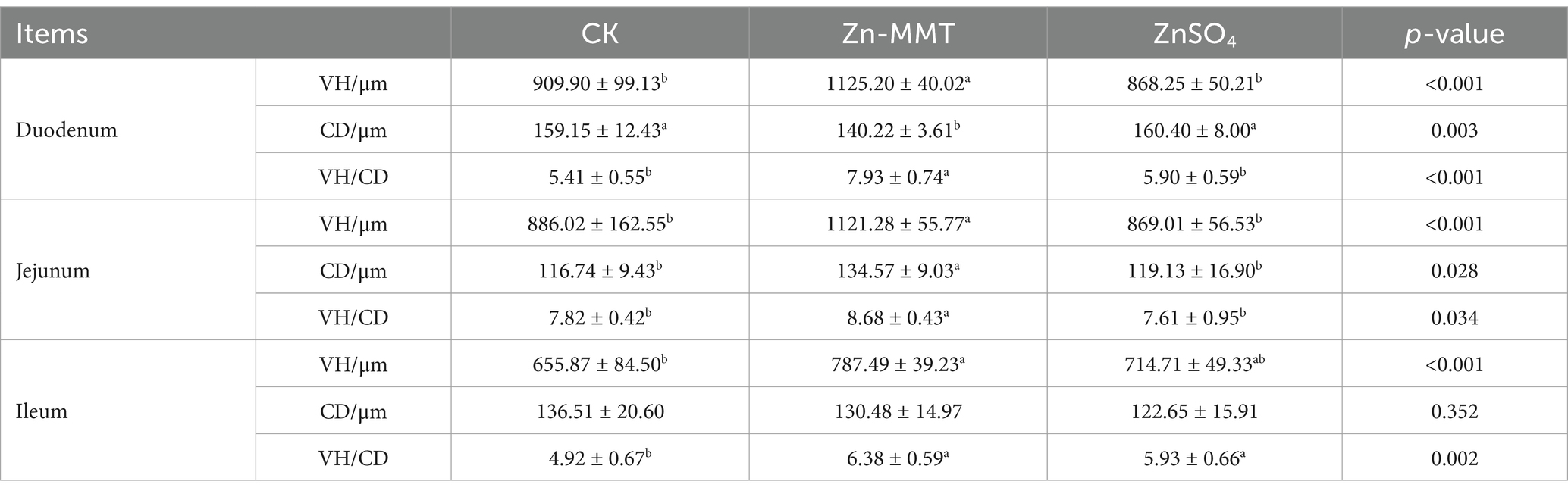
The effects of Zn-MMT on intestinal morphology are summarized in Table 6. Compared to the CK group, adding Zn-MMT to the diets significantly (p < 0.05) increased VH and the VH/CD ratio in the duodenum and jejunum, as well as increased CD in the jejunum. Simultaneously, compared to the CK group, Zn-MMT decreased CD in the duodenum. Compared to the CK group, dietary supplementation with Zn-MMT or ZnSO4 significantly (p < 0.05) increased VH and the VH/CD ratio in the ileum. Ileum CD was not significantly (p > 0.05) affected by the addition of Zn from different sources.
Relative mRNA expression of metal transporters in the jejunum
The effects of Zn-MMT on jejunum metal transporter relative mRNA expression are summarized in Figure 1. Compared to the CK group, adding Zn-MMT and ZnSO4 to the diets significantly (p < 0.05) increased the mRNA relative expression of ZnT-1, ZnT-5, MT, and MTF-1 in the jejunum. Compared to the CK group, adding Zn-MMT and ZnSO4 to the diets significantly increased the mRNA relative expression of MT-3 and DMT-1. As for the mRNA expression of MT-3 and DMT-1 in the jejunum, the addition of Zn-MMT was significantly greater than that of ZnSO4 (p < 0.05).
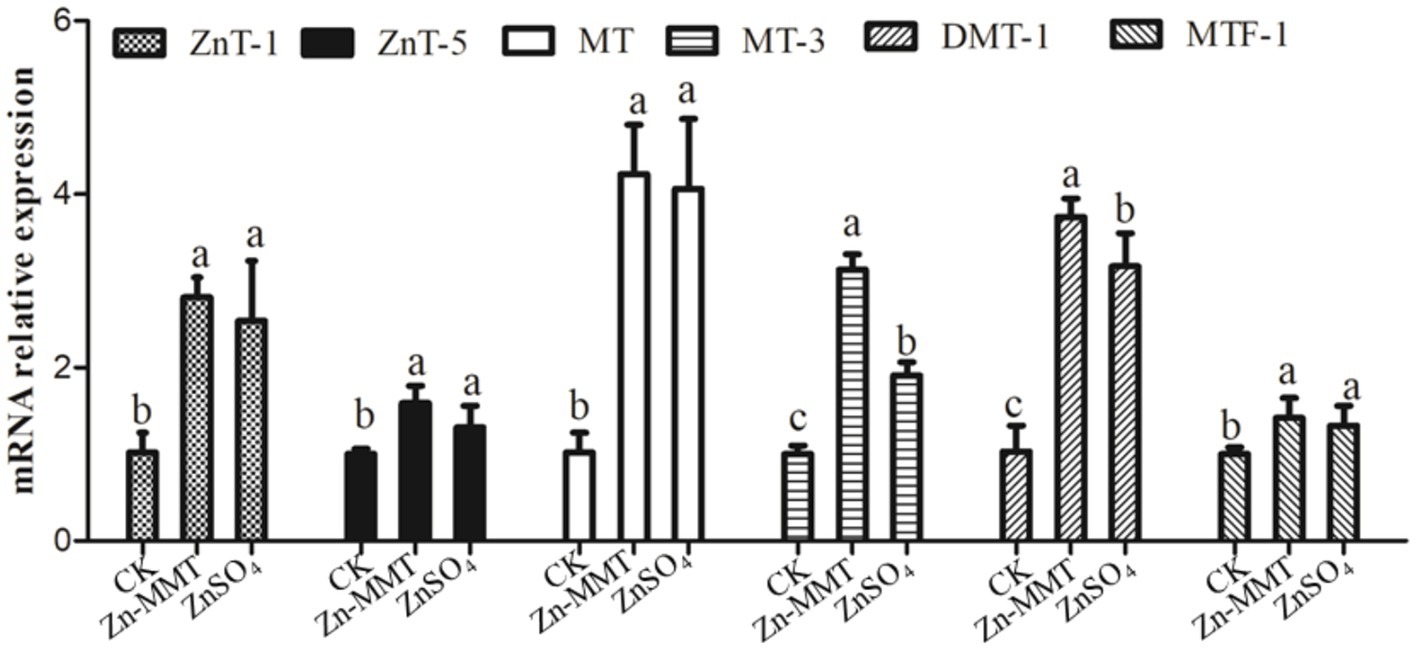
Figure 1. Effects of Zn-MMT on metal transport carriers in the jejunum of the broilers. The data shown represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments, and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
Cecum microbiome
The effects of Zn-MMT on the alpha and beta diversity of the cecum microbiome in the broilers are shown in Figures 2, 3, respectively. As shown in Figure 2, Zn-MMT had no significant effect on the observed species, Shannon index, Simpson index, ACE index, or Chao1 index (p > 0.05). The results of PCOA, NMDS, and ANOSIM were consistent, and there was no independent distribution among the treatment groups, indicating that there was no significant difference in the structure and diversity of the cecal bacteria in the broilers. A total of 17 phyla and 214 genera were identified in the cecum microorganisms. The 10 most abundant phyla and genera are presented in Figure 4. At the phylum level (Figure 4A) and at the genus level (Figure 4B), the top 10 bacterial genera in the CK, Zn-MMT, and ZnSO4 groups accounted for more than 75.58% of the annotated genera. However, at the phylum and genus levels, the abundance of the top 10 bacterial genera among the treatment groups was not significantly different.
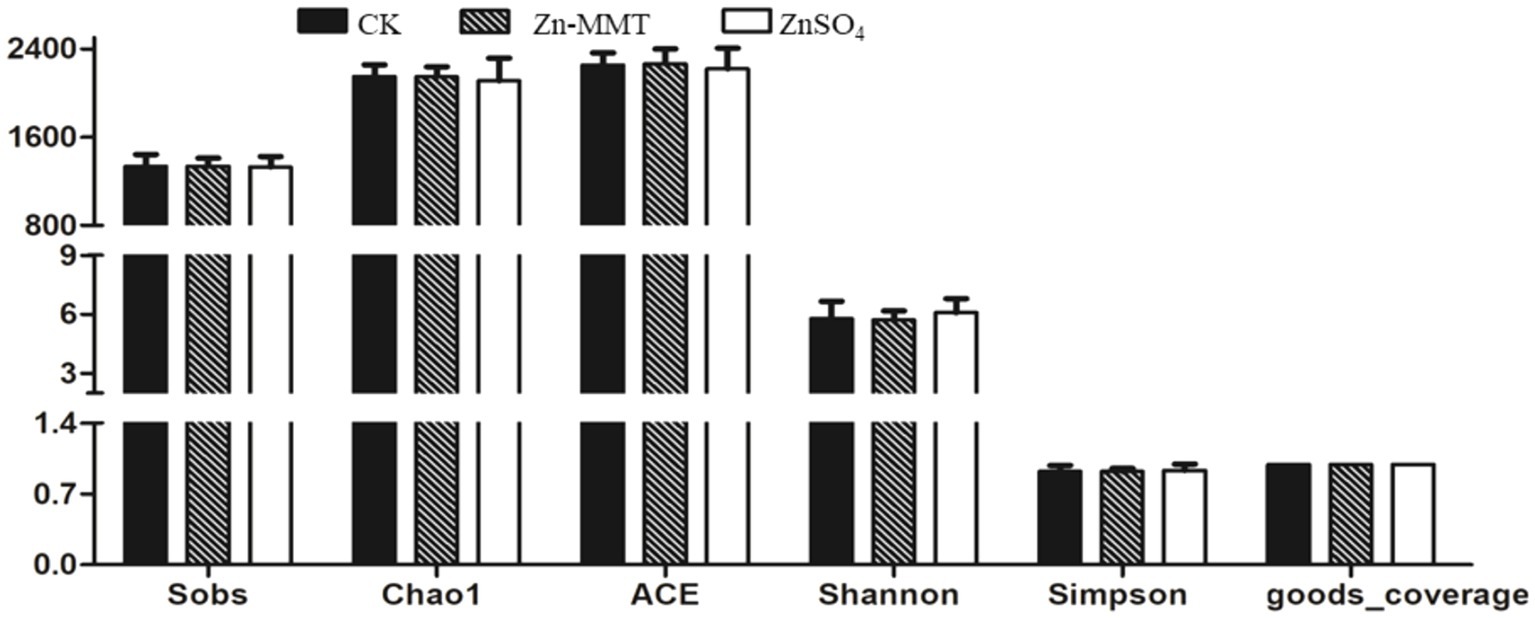
Figure 2. Determination of bacterial community α-diversity in the cecum of the broilers. The figure includes the Observed species, Chao1 index, ACE index, Shannon index, Simpson index, and Goods_coverage, with the CK, Zn-MMT, and ZnSO₄ groups representing the control, Zn-MMT, and ZnSO₄ treatments, respectively. Unmarked letters on the bar chart indicate no significant difference between the groups.
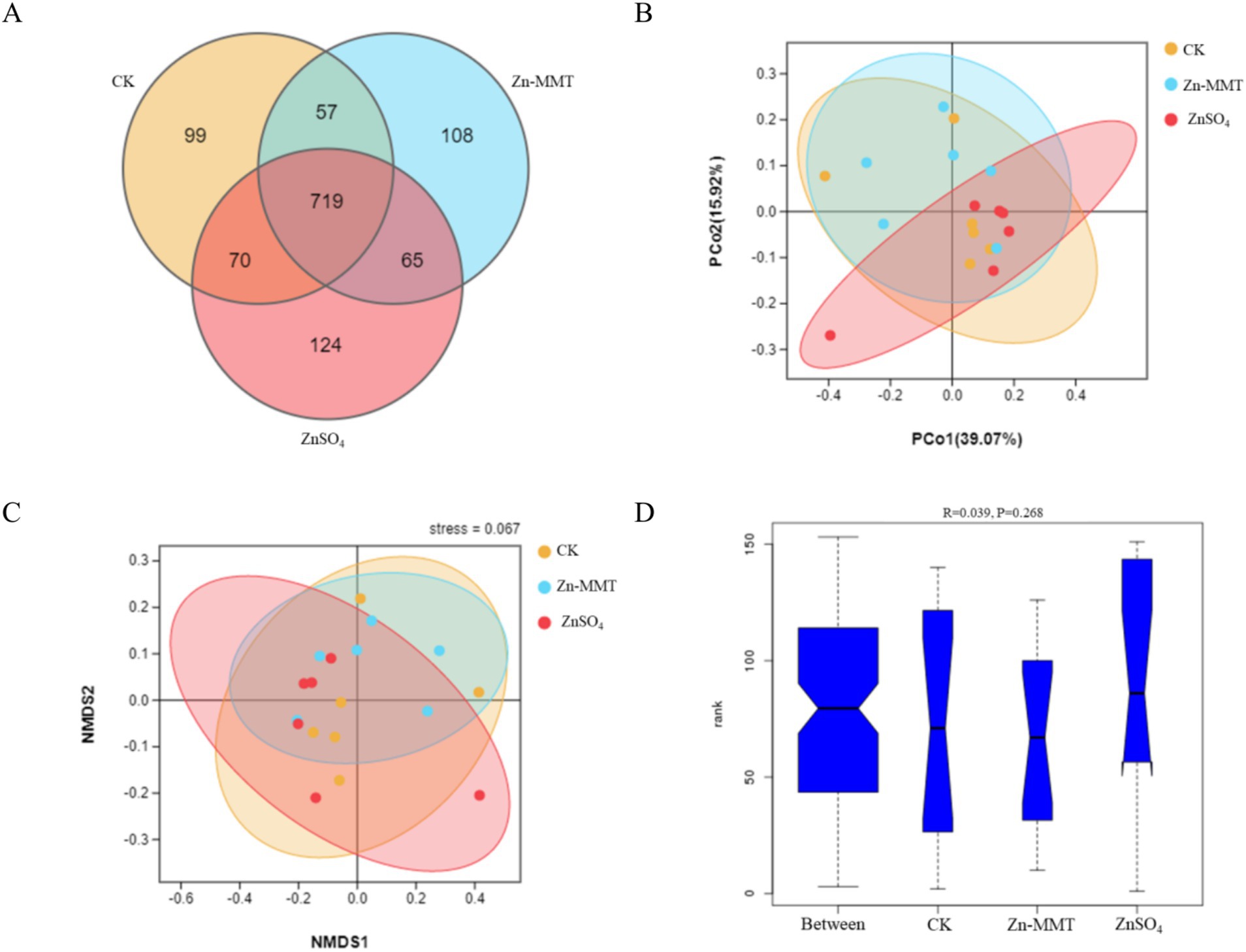
Figure 3. Comparison of gut bacterial communities among the CK, MMT, and Zn groups. The Venn diagram shows the shared operational taxonomic units (OTUs) in each group. The overlapping part refers to the amount of OTUs shared between the groups, while the non-overlapping part refers to the only amount of OTUs in the group (A). Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) (B), Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis (C), and analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) (D). CK = control group; MMT = Zn-loaded MMT group; Zn = ZnSO4 group.
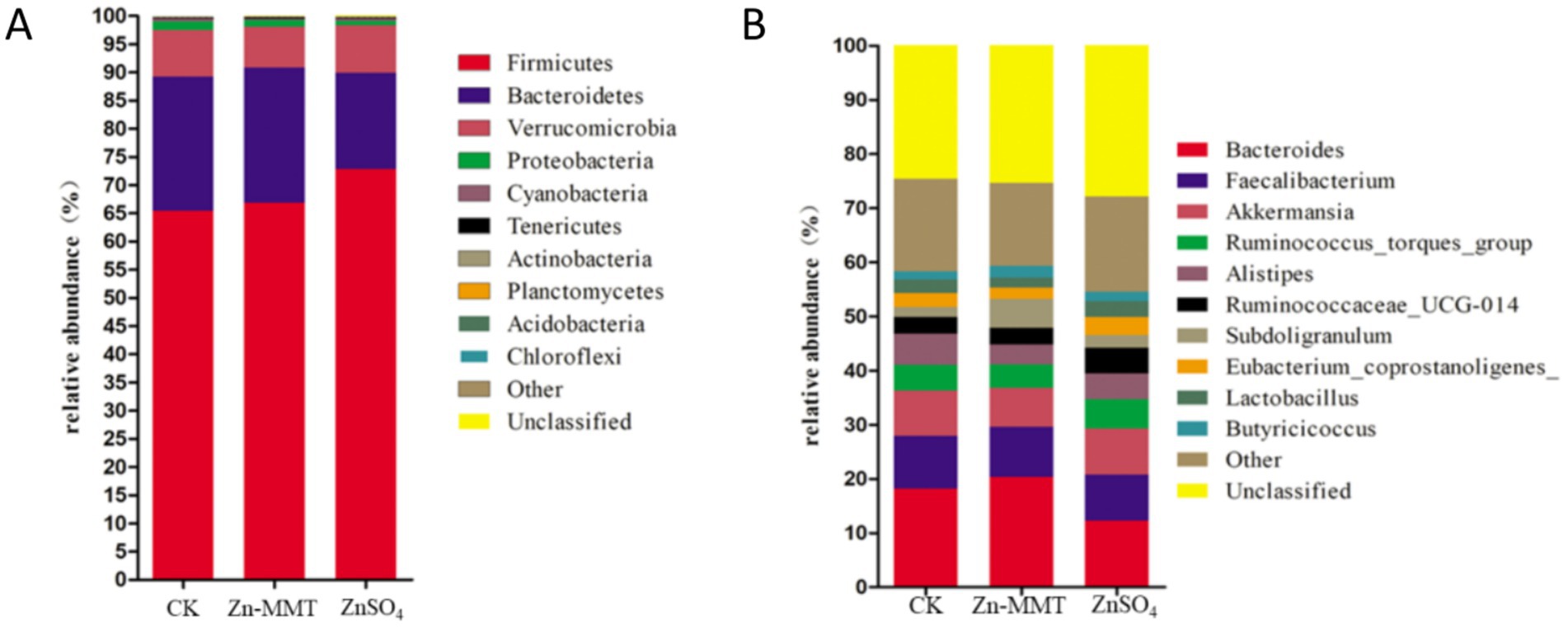
Figure 4. The relative abundance of the top 10 phyla (A) and the top 10 genera (B) of the gut bacteria.
Discussion
Effects of Zn-MMT on growth performance
The chemical form of Zn plays a critical role in determining its bioavailability and biological functions in broilers, thereby significantly influencing growth performance (18–20). Among various mineral delivery systems, MMT-intercalated trace elements have emerged as a promising strategy. As an efficient nutrient carrier, MMT offers unique advantages in sustained nutrient release. Hu et al. (16) reported that ZnO-MMT significantly enhanced broiler growth compared to conventional ZnO supplementation. Similarly, Jiao et al. (21) demonstrated that dietary supplementation with 150 mg/kg Zn in the form of Zn-MMT improved production performance in weaned pigs. Building on this approach, Jiao et al. (22) further revealed that Cu/Zn-MMT supplementation in weaned piglet diets resulted in superior growth performance compared to inorganic Cu and Zn sources. Notably, Eckhardt et al. (23) documented that the administration of calcium-modified MMT (Ca-MMT) not only increased body weight but also enhanced daily feed intake and feed conversion efficiency in poultry. In the present study, neither the ADG nor ADFI of the broilers showed significant differences among the experimental groups supplemented with Zn-MMT or ZnSO₄. The NRC set the Zn requirement at a level of 40 mg/kg for broilers. Corn–soybean meal-based diets typically contain Zn concentrations exceeding 40 mg/kg (20), which may adequately satisfy the growth demands of chicks and thereby explain the absence of significant effects on weight gain.
The feed conversion ratio (F: G) was significantly influenced by Zn-MMT supplementation. The superior performance associated with Zn-MMT could be attributed to synergistic interactions between the montmorillonite matrix and Zn ions, which may enhance nutrient utilization efficiency through improved mineral bioavailability and intestinal absorption capacity (16, 18). The intestinal mucosal protective mechanisms of montmorillonite (MMT) operate through two primary pathways: (1) MMT exhibits selective adsorption capacity through its layered nanostructure and cation exchange properties (24), and (2) MMT interacts with mucin glycoproteins to enhance the physicochemical properties of the mucus layer (25). As an essential cofactor for over 300 metalloenzymes, including alkaline phosphatase, carbonic anhydrase, and matrix metalloproteinases, Zn orchestrates critical biological processes, ranging from nucleic acid metabolism to antioxidant defense systems (26). Its bacteriostatic activity arises from the competitive inhibition of microbial magnesium uptake and the disruption of bacterial membrane potential, particularly against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. (1). The interlayer spacing and high specific surface area render MMT an exceptional controlled-release carrier (13, 15, 16). Zn ions can be intercalated into MMT’s octahedral sheets through ion-exchange reactions, achieving sustained release kinetics that correlate with gastrointestinal pH variations. This pH-responsive release profile optimizes Zn bioavailability while minimizing ionic oversaturation toxicity. It has been hypothesized that the clinoptilolite component in Zn-MMT functions as a sustained-release carrier, potentially modulating the temporal and spatial release kinetics of Zn within the gastrointestinal tract. This controlled-release mechanism may enhance Zn bioavailability by prolonging its intestinal retention time and facilitating targeted delivery to the hindgut region, thereby amplifying its biological efficacy and antimicrobial activity (16, 27). Subsequent studies have further demonstrated that the MMT matrix in Zn-MMT creates ion-exchange channels that regulate Zn dissolution rates while protecting against premature degradation in the proximal gut (28, 29). Such optimized Zn delivery characteristics not only improve intestinal zinc absorption but also potentiate its bacteriostatic effects in the colonic environment. Collectively, these mechanisms contribute to enhanced gastrointestinal homeostasis and improved growth performance in broilers. Notably, the supplementation of Zn-MMT reduced the spleen index in the present trial, which contrasts with previous findings (30). As the largest immune organ, the spleen serves as a central hub for both cellular and humoral immunity, playing a crucial role in immune regulation. The precise mechanisms underlying this phenomenon warrant further investigation.
Effects of Zn-MMT on mineral retention in the tissues
In the study, the supplementation of Zn-MMT increased the Zn concentration in the liver, tibia, pancreas, and whole blood. It is well established that the deposition of trace minerals in various tissues and organs is an important parameter for the normal growth and development of broilers. The above results are consistent with the observed growth performance of the broilers in this experiment, suggesting that Zn-MMT can be used as a Zn supplement in broiler feed and that it may be better than ZnSO4. Research has reported that Zn in Zn-MMT has superior bioavailability, which may be related to the controlled-release properties of MMT. MMT can adsorb nutrients and gradually control their release, thereby increasing their duration of action or biological effects. These results indicate that Zn-MMT may alter the rate, timing, or location of Zn release, thereby improving the biological effects of Zn. This modulation is beneficial for Zn accumulation, tissue or organ development, and overall growth performance in broilers. The dietary inclusion of Zn-MMT significantly increased Zn concentrations in key metabolic tissues, including the liver, tibia, pancreas, and whole blood, compared to the control group. Tissue-specific Zn deposition serves as a critical biomarker for evaluating trace mineral bioavailability and metabolic homeostasis in broilers (31). These findings align with the observed improvements in growth performance parameters, suggesting that Zn-MMT functions as an effective zinc supplement in broiler nutrition. Notably, the enhanced bioavailability of Zn-MMT compared to conventional ZnSO4 may be attributed to montmorillonite’s unique cation-exchange capacity and layered structure (16). As demonstrated by Tang et al. (32), the interlamellar spaces of MMT enable the controlled release of adsorbed Zn ions through a pH-dependent mechanism, prolonging nutrient retention time in the gastrointestinal tract. This sustained-release property reduces ionic competition with dietary antagonists, thereby improving Zn absorption efficiency compared to ZnSO4 (33, 34). Similar findings were reported by Huang et al. (20), who demonstrated that dietary Zn-MMT supplementation elevated Zn concentrations in biological specimens. This observation was corroborated by Tang et al. (18), whose investigation revealed that Zn-loaded zeolite supplementation significantly enhanced Zn deposition in the pancreas, liver, and tibia of broilers. Jiao et al. (22) reported that the inclusion of Cu/Zn-MMT increased Zn concentrations in the jejunal and ileal mucosa compared to controls, suggesting that the Zn release in vivo was prolonged. Current research on the impact of Zn-MMT on Fe, Mn, and Cu homeostasis remains limited. In laying hens, Li et al. (34) observed that Zn-bearing zeolite supplementation increased serum Fe levels. Furthermore, Yang et al. (33) identified a linear increase in the Fe content with dietary supplementation of Zn-palygorskite. In the current study, dietary Zn-MMT supplementation significantly influenced the Fe content in the breast muscle of the broilers, which aligns with previous observations in avian species. However, this finding contrasts with data from Jiao et al. (22), who reported no alterations in the Fe concentration across tissues and feces when supplementing Cu/Zn-MMT in weaned piglets. In this study, we observed that dietary ZnSO4 supplementation significantly reduced Mn and Cu concentrations in the liver compared to the CK and Zn-MMT groups. Notably, synergistic and antagonistic interactions between trace elements are reported to directly influence the absorption and metabolism of essential minerals in animals (35). Given the conflicting reports regarding the effects of Zn supplementation on trace element concentrations in biological matrices, further investigation is required to elucidate how different dietary Zn sources affect trace element absorption, metabolism, and accumulation in animals.
Effects of Zn-MMT on antioxidant capacity and intestinal morphology
Certain trace elements (Cu, Zn, and Mn) serve as structural components of metalloenzymes that scavenge reactive oxygen species and mitigate oxidative damage. Zn is constitutively required for maintaining the structural integrity and catalytic activity of Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn SOD). As the predominant SOD isoform, accounting for 90% of total SOD activity, Cu/Zn SOD provides essential protection against oxidative injury in vulnerable tissues such as the nervous and pulmonary systems (36). This biochemical dependency suggests that modulation of tissue Zn concentrations may directly influence antioxidant capacity. The experimental results demonstrated that dietary Zn-MMT supplementation significantly enhanced antioxidant capacity in the broilers compared to conventional ZnSO₄ supplementation. Notably, the broilers receiving Zn-MMT showed substantial improvements in antioxidant parameters: total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) increased by 28.5% in the liver and 29.4% in the jejunal mucosal tissue, while Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD) activity exhibited significant elevation. These observations align with previous reports by Yang et al. (33) and Xie et al. (37) on Zn’s antioxidant properties. This effect was further corroborated by Dukare et al. (38), who documented increased serum SOD levels following 80 mg/kg Zn supplementation. Interestingly, we observed that dietary supplementation with Zn-MMT and ZnSO₄ significantly reduced the MDA content in the liver and jejunum, with the ZnSO₄ group showing significantly lower levels than the Zn-MMT group. This phenomenon may be attributed to the aldehyde and carbonyl groups in MDA forming stable complexes with Zn2+ ions from ZnSO₄, thereby reducing MDA accumulation. The distinct efficacy of ZnSO₄ compared to Zn-MMT likely stems from differences in zinc bioavailability or chemical interactions. ZnSO₄ dissociates more readily in vivo, releasing free Zn2+ for chelation with MDA, whereas Zn-MMT may exhibit slower ion release kinetics, partially limiting its capacity to neutralize MDA. These findings indicate that dietary Zn supplementation enhances the antioxidant capacity of broilers, with Zn-MMT demonstrating superior efficacy in activating antioxidant enzyme systems compared to ZnSO4 and thereby alleviating oxidative stress-induced cellular damage.
Oxidative stress has been extensively documented to exert significant interactions with intestinal morphology. As a critical organ system, the intestinal tract plays an essential role in nutrient digestion, absorption, and immune regulation. VH, CD, and their ratio (VH/CD) serve as key morphological indicators for assessing intestinal integrity and nutrient assimilation capacity. Zn, an essential trace mineral, has been shown to modulate intestinal morphology, improve nutrient absorption efficiency, and enhance growth performance through multiple physiological mechanisms. Previous studies have demonstrated that dietary Zn supplementation enhances VH and the VH/CD ratio in the small intestine of broilers, although the efficacy varies significantly depending on the Zn source (1, 5). Our study demonstrated that dietary supplementation with Zn-MMT significantly increased VH and the VH/CD ratio in the intestinal mucosa by an average of 23.4 and 25.8%, respectively. These findings align with the observations reported by Tang et al. (31) in chicks and Jiao et al. (21) in weaned piglets. Zn-MMT demonstrated superior efficacy compared to ZnSO4 in improving VH and the VH/CD ratio while also significantly reducing crypt depth. Emerging evidence indicates that Zn plays a pivotal role in intestinal epithelial repair and the maintenance of mucosal integrity through three primary mechanisms (1): stabilization of tight junction proteins (2); modulation of inflammatory cytokine expression (3); enhancement of antioxidant enzyme activity. The potential mechanism may involve Zn’s regulatory effects on DNA and protein synthesis, inhibition of cellular apoptosis, and modulation of cell proliferation (39). MMT interacts with gastrointestinal mucus proteins through selective binding, which enhances mucus secretion while improving its cohesive and elastic properties, ultimately promoting mucosal integrity protection and repair (40). This suggests that Zn-MMT’s protective effects on the intestinal barrier likely result from synergistic interactions between Zn and the components of MMT.
Effects of Zn-MMT on relative mRNA expression of metal transporters in the jejunum
Zn homeostasis is predominantly regulated through the coordinated modulation of intestinal Zn absorption, transport, and excretion. Studies have demonstrated that Zn absorption in the animal intestine occurs via two distinct mechanisms: passive diffusion and saturable, carrier-mediated transport. The latter represents an energy-dependent process facilitated by specific Zn-binding transporter proteins. The carrier-mediated Zn absorption pathway in the intestinal epithelium can be categorized into three sequential steps: (1) Apical uptake: Zn ions traverse the apical membrane of enterocytes from the intestinal lumen into the cytoplasm, mediated by transporters such as Zrt-/Irt-like protein. (2) Intracellular trafficking: Zn undergoes cytosolic redistribution from the apical to the basolateral membrane, involving metallothionein buffering and vesicular transport mechanisms. (3) Basolateral efflux: Zn is extruded across the basolateral membrane into systemic circulation via ZnT, completing its transcellular translocation. Zn homeostasis in animals is regulated by multiple transport carriers, including ZnT, DMT-1, MT, and MTF-1 (41). Current evidence demonstrates that ZnT-1 and ZnT-5 primarily mediate Zn ion absorption and transport in the duodenal and jejunal epithelia, facilitating the translocation of Zn2+ from the cytoplasm to peripheral circulation or intracellular organelles (42, 43). MT, a cysteine-rich, low-molecular-weight protein, exhibits a high binding affinity for both zinc and heavy metals (44). Although DMT-1 participates in the transport of divalent cations, its Zn translocation capacity operates independently of other cation transport systems (45–47). In broilers, Cao et al. (48) demonstrated that Zn-enriched diets upregulated MT mRNA levels in both pancreatic and hepatic tissues. This finding supports earlier observations in rats, where MT expression in the liver increased in a dose-dependent manner in response to dietary Zn intake (44). Similar regulatory patterns have been documented in weaned piglets (49) and poultry (50), confirming the evolutionary conservation of Zn-mediated MT modulation. These coordinated responses in MT and ZnT-1 expression highlight their synergistic roles in Zn absorption and detoxification, although the precise molecular mechanisms warrant further investigation. In this study, dietary supplementation with 40 mg/kg Zn, either as Zn-MMT or ZnSO4, in the corn–soybean meal diets elicited significant upregulation of jejunal Zn transport machinery. Both treatments increased the mRNA levels of Zn-specific transporters (ZnT-1: 2.8-fold, ZnT-5: 1.6-fold) and metallothionein isoforms (MT: 4.1-fold, MT-3: 3.1-fold) compared to the control group. Notably, Zn-MMT supplementation demonstrated 18% greater induction efficacy for DMT-1 expression and 63.4% higher MT-3 levels compared to the ZnSO4 treatment. The coordinated upregulation of MTF-1 (1.42-fold) suggests enhanced metal-responsive element binding activity under Zn-MMT exposure. The observed discrepancy may be attributed to differential absorption and transport regulation mechanisms between ZnSO4 and Zn-MMT in the intestine. The sustained-release properties of Zn-MMT enable gradual Zn liberation within the intestinal tract, effectively maintaining stable luminal Zn concentrations while enhancing the expression of Zn transport-related proteins. However, the specific underlying mechanisms warrant further systematic investigation to elucidate the precise regulatory pathways involved. These findings provide a mechanistic basis for the observed improvements in Zn accumulation in the tibia and whole blood of 42-day-old broilers. The enhanced mineral retention may be attributed to the unique properties of metal-modified clays, as prior studies have reported that palygorskite (51), clinoptilolite (52), Ca-MMT (53), and Cu-MMT (14) can optimize intestinal morphology, modulate metal transporter expression, and consequently improve nutrient absorption and transport efficiency.
Effects of Zn-MMT on the cecum microbiome
Through comprehensive α- and β-diversity analyses, we observed that key microbial community parameters—including total species richness (α-diversity), between-sample diversity patterns (β-diversity), and species distribution evenness—remained comparable across all treatment groups. The Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Verrucomicrobia phyla collectively accounted for over 97% of the cecal microbial community in the broilers. At the genus level, this phylum-level dominance was further reflected in the prevalence of three core microbial taxa: Bacteroides (Bacteroidetes phylum), Faecalibacterium (Firmicutes phylum), and Akkermansia (Verrucomicrobia phylum). Furthermore, no significant differences were observed in the relative abundance of the top 10 bacterial genera at both phylum and genus levels. A previous study by Hu et al. (16) demonstrated that ZnO-MMT significantly reduced Clostridium spp. populations in both the small intestine and the cecum of broilers. In contrast to these findings, our study revealed no significant differences in cecal microbial composition between the broilers who received Zn-MMT and those supplemented with ZnSO4. These findings align with the established patterns of dominant gastrointestinal microbiota composition in terrestrial vertebrates (54). Although MMT exhibits adsorption capacity toward certain intestinal bacteria, its interaction may not induce substantial alterations in gut microbiota composition at higher taxonomic levels (phylum and genus), which could be attributed to the resilient symbiotic equilibrium maintained between the host and gut microbiota (55).
Conclusion
In conclusion, Zn-MMT supplementation showed multifaceted beneficial effects in the broilers. Specifically, it enhanced intestinal morphological development by improving the VH/CD ratio and epithelial integrity. Furthermore, Zn-MMT upregulated the expression of key metal transporters (ZnT-1 and ZnT-5) in duodenal enterocytes, thereby promoting systemic Zn deposition and utilization efficiency. Notably, the intervention group exhibited enhanced antioxidant defense mechanisms through increased SOD activity, along with reduced MDA levels in the intestinal tissues. These findings collectively suggest that Zn-MMT serves as an effective Zn supplement that synergistically improves intestinal health parameters, optimizes Zn metabolic pathways, and reinforces antioxidant capacity in commercial broiler production.
Data availability statement
Sequence data that support the findings of this study have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the accession number: PRJNA1267805, access link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA1267805.
Ethics statement
The animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Gansu Agricultural University (Protocol No. GAU-Eth-AST-2024-026). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
ShizQ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HW: Writing – review & editing. ShijQ: Software, Writing – review & editing. JL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. DT: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32360848); the Fuxi youth talent training program of Gansu Agricultural University, China (Grant No. Gaufx-05Y01); the Lanzhou Youth Science and Technology Talent Innovation Project, Gansu, China (Grant No. 2023-QN-139).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Khan, MI, Chand, N, Naz, S, Alonaizan, R, Hu, H, Shamsi, S, et al. Effects of zinc supplementation from organic and inorganic sources on growth, blood biochemical indices, and intestinal microarchitecture in broilers. Vet Q. (2024) 44:1–7. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2023.2298491
2. Qin, S, Zhang, L, Ma, F, Che, Y, and Shi, Z. Dietary zinc and growth, carcass characteristics, immune responses, and serum biochemistry of broilers. Anim Prod Sci. (2020) 60:815–22. doi: 10.1071/AN18763
3. Saeeda, K, Chand, N, Khan, NU, Saeed, M, and Khan, RU. Dietary organic zinc and probiotic alleviate induced Eimeria tenella infection in Japanese quails model of coccidiosis. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2023) 55:37. doi: 10.1007/s11250-022-03449-4
4. Naz, S, Idris, M, Khalique, MA, Ur-Rahman, Z, Alhidary, IA, Abdelrahman, MM, et al. The activity and use of zinc in poultry diets. Worlds Poult Sci J. (2016) 72:159–67. doi: 10.1017/S0043933915002755
5. De Grande, A, Leleu, S, Delezie, E, Rapp, C, De Smet, S, Goossens, E, et al. Dietary zinc source impacts intestinal morphology and oxidative stress in young broilers. Poult Sci. (2020) 99:441–53. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez525
6. Besong, EE, Ashonibare, PJ, Obembe, OO, Folawiyo, MA, Adeyemi, DH, Hamed, MA, et al. Zinc protects against lead-induced testicular damage via modulation of steroidogenic and xanthine oxidase/uric acid/caspase 3-mediated apoptotic signaling in male Wistar rats. Aging Male. (2023) 26:2224428. doi: 10.1080/13685538.2023.2224428
7. Shao, Y, Wang, Y, Li, X, Zhao, D, Qin, S, Shi, Z, et al. Dietary zinc supplementation in breeding pigeons improves the carcass traits of squabs through regulating antioxidant capacity and myogenic regulatory factor expression. Poult Sci. (2023) 102:102809. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102809
8. Chand, N, Ali, P, Alhidary, IA, Abdelrahman, MA, Albadani, H, Khan, MA, et al. Protective effect of grape (Vitis vinifera) seed powder and zinc-glycine complex on growth traits and gut health of broilers following Eimeria tenella challenge. Antibiotics (Basel). (2021) 10:186. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10020186
9. Chand, N, Zahirullah, KRU, Shah, M, Naz, S, and Tinelli, A. Zinc source modulates zootechnical characteristics, intestinal features, humoral response, and paraoxonase (PON1) activity in broilers. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2020) 52:511–5. doi: 10.1007/s11250-019-02036-4
10. Macdonald, RS. The role of zinc in growth and cell proliferation. J Nutr. (2000) 130:1500S–8S. doi: 10.1093/jn/130.5.1500S
11. Bao, YM, Choct, M, Iji, PA, and Bruerton, K. Trace mineral interactions in broiler chicken diets. Br Poult. (2010) 51:109–17. doi: 10.1080/00071660903571904
12. Zhao, CY, Tan, SX, Xiao, XY, Qiu, XS, Pan, JQ, and Tang, ZX. Effects of dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth performance and antioxidative status in broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2014) 160:361–7. doi: 10.1007/s12011-014-0052-2
13. Hu, CH, Gu, LY, Luan, ZS, Song, J, and Zhu, K. Effects of montmorillonite–zinc oxide hybrid on performance, diarrhea, intestinal permeability and morphology of weanling pigs. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2012) 177:108–15. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2012.07.028
14. Xia, MS, Hu, CH, and Xu, ZR. Effects of copper-bearing montmorillonite on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities, and intestinal microflora and morphology of male broilers. Poult Sci. (2004) 83:1868–75. doi: 10.1093/ps/83.11.1868
15. Hu, C, Song, J, You, Z, Luan, Z, and Li, W. Zinc oxide-montmorillonite hybrid influences diarrhea, intestinal mucosal integrity, and digestive enzyme activity in weaned pigs. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2012) 149:190–6. doi: 10.1007/s12011-012-9422-9
16. Hu, CH, Qian, ZC, Song, J, Luan, ZS, and Zuo, AY. Effects of zinc oxide-montmorillonite hybrid on growth performance, intestinal structure, and function of broiler chicken. Poult Sci. (2013) 92:143–50. doi: 10.3382/ps.2012-02250
17. Wang, LC, Zhang, TT, Wen, C, Jiang, ZY, and Zhou, YM. Protective effects of zinc-bearing clinoptilolite on broilers challenged with Salmonella pullorum. Poult Sci. (2012) 91:1838–45. doi: 10.3382/ps.2012-02284
18. Tang, ZG, Chen, GY, Li, LF, Wen, C, Wang, T, and Zhou, YM. Effect of zinc-bearing zeolite clinoptilolite on growth performance, zinc accumulation, and gene expression of zinc transporters in broilers. J Anim Sci. (2015) 93:620–6. doi: 10.2527/jas.2014-8165
19. Star, L, van der Klis, JD, Rapp, C, and Ward, TL. Bioavailability of organic and inorganic zinc sources in male broilers. Poult Sci. (2012) 91:3115–20. doi: 10.3382/ps.2012-02314
20. Huang, YL, Lu, L, Li, SF, Luo, XG, and Liu, B. Relative bioavailabilities of organic zinc sources with different chelation strengths for broilers fed a conventional corn-soybean meal diet. J Anim Sci. (2009) 87:2038–46. doi: 10.2527/jas.2008-1212
21. Jiao, LF, Ke, YL, Xiao, K, Song, ZH, Lu, JJ, and Hu, CH. Effects of zinc-exchanged montmorillonite with different zinc loading capacities on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, morphology and permeability in weaned piglets. Appl Clay Sci. (2015) 112-113:40–3. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.04.012
22. Jiao, LF, Zhang, QH, Wu, H, Wang, CC, Cao, ST, Feng, J, et al. Influences of copper/zinc-loaded montmorillonite on growth performance, mineral retention, intestinal morphology, mucosa antioxidant capacity, and cytokine contents in weaned piglets. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2018) 185:356–63. doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1259-4
23. Eckhardt, JC, Santurio, JM, Zanette, RA, Rosa, AP, Scher, A, Dal Pozzo, M, et al. Efficacy of a Brazilian calcium montmorillonite against toxic effects of dietary aflatoxins on broilers reared to market weight. Br Poult Sci. (2014) 55:215–20. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2014.883065
24. Ramu, J, Clark, K, Woode, GN, Sarr, AB, and Phillips, TD. Adsorption of cholera and heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxins by various adsorbents: an in vitro study. J Food Prot. (1997) 60:358–62. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-60.4.358
25. Wu, QJ, Zhou, YM, Wu, YN, Zhang, LL, and Wang, T. The effects of natural and modified clinoptilolite on intestinal barrier function and immune response to LPS in broiler chickens. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. (2013) 153:70–6. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2013.02.006
26. Ogbuewu, IP, and Mbajiorgu, CA. Potentials of dietary zinc supplementation in improving growth performance, health status, and meat quality of broiler chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2023) 201:1418–31. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03223-5
27. Roselli, M, Finamore, A, Garaguso, I, Britti, MS, and Mengheri, E. Zinc oxide protects cultured enterocytes from the damage induced by Escherichia coli. J Nutr. (2003) 133:4077–82. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.12.4077
28. Liu, JH, Cai, WK, Khatoon, N, Yu, WH, and Zhou, CH. On how montmorillonite as an ingredient in animal feed functions. Appl Clay Sci. (2021) 202:105963–3. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105963
29. Song, J, Li, YL, and Hu, CH. Effects of copper-exchanged montmorillonite, as alternative to antibiotic, on diarrhea, intestinal permeability and proinflammatory cytokine of weanling pigs. Appl Clay Sci. (2013) 77-78:52–5. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2013.01.016
30. Hidayat, C, Sadarman, S, Adli, DN, Rusli, RK, Bakrie, B, Ginting, SP, et al. Comparative effects of dietary zinc nanoparticle and conventional zinc supplementation on broiler chickens: a meta-analysis. Vet World. (2024) 17:1733–47. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.1733-1747
31. Erinle, TJ, and Adewole, DI. Fruit pomaces-their nutrient and bioactive components, effects on growth and health of poultry species, and possible optimization techniques. Anim Nutr. (2022) 9:357–77. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2021.11.011
32. Tang, ZG, Wen, C, Wang, LC, Wang, T, and Zhou, YM. Effects of zinc-bearing clinoptilolite on growth performance, cecal microflora and intestinal mucosal function of broiler chickens. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2014) 189:98–106. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2013.12.014
33. Yang, WL, Chen, YP, Cheng, YF, Li, XH, Zhang, RQ, Wen, C, et al. An evaluation of zinc bearing palygorskite inclusion on the growth performance, mineral content, meat quality, and antioxidant status of broilers. Poult Sci. (2016) 95:878–85. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev445
34. Li, L, Li, P, Chen, Y, Wen, C, Zhuang, S, and Zhou, Y. Zinc-bearing zeolite clinoptilolite improves tissue zinc accumulation in laying hens by enhancing zinc transporter gene mRNA abundance. Anim Sci J. (2015) 86:782–9. doi: 10.1111/asj.12358
35. Chen, X, He, C, Zhang, K, Wang, J, Ding, X, Zeng, Q, et al. Comparison of zinc bioavailability in zinc-glycine and zinc-methionine chelates for broilers fed with a corn-soybean meal diet. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:983954. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.983954
36. Rahimi, G, Mohammad, KS, Zarei, M, Shokoohi, M, Oskoueian, E, Poorbagher, M, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Hyssopus Officinalis L. extract induced oxidative stress and changes the expression of key genes involved in inflammatory and antioxidant systems. Biol Res. (2022) 55:24. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00392-4
37. Xie, S, Li, Y, Suo, Y, Wang, Z, Zhang, B, Li, J, et al. (2024). Effect of organic, nano, and inorganic zinc sources on growth performance, antioxidant function, and intestinal health of young broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04341-y [Epub ahead of print].
38. Dukare, S, Mir, NA, Mandal, AB, Dev, K, Begum, J, Rokade, JJ, et al. A comparative study on the antioxidant status, meat quality, and mineral deposition in broiler chicken fed dietary nano zinc viz-a-viz inorganic zinc. J Food Sci Technol. (2021) 58:834–43. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04597-x
39. Truong-Tran, AQ, Carter, J, Ruffin, RE, and Zalewski, PD. The role of zinc in caspase activation and apoptotic cell death. Biometals. (2001) 14:315–30. doi: 10.1023/A:1012993017026
40. Albengres, E, Urien, S, Tillement, JP, Oury, P, Decourt, S, Flouvat, B, et al. Interactions between smectite, a mucus stabilizer, and acidic and basic drugs. In vitro and in vivo studies. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (1985) 28:601–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00544074
41. Plum, LM, Rink, L, and Haase, H. The essential toxin: impact of zinc on human health. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2010) 7:1342–65. doi: 10.3390/ijerph7041342
42. Lichten, LA, and Cousins, RJ. Mammalian zinc transporters: nutritional and physiologic regulation. Annu Rev Nutr. (2009) 29:153–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-033009-083312
43. Yu, YY, Kirschke, CP, and Huang, L. Immunohistochemical analysis of ZnT1, 4, 5, 6, and 7 in the mouse gastrointestinal tract. J Histochem Cytochem. (2007) 55:223–34. doi: 10.1369/jhc.6A7032.2006
44. Cousins, RJ, and Lee-Ambrose, LM. Nuclear zinc uptake and interactions and metallothionein gene expression are influenced by dietary zinc in rats. J Nutr. (1992) 122:56–64. doi: 10.1093/jn/122.1.56
45. Bressler, JP, Olivi, L, Cheong, JH, Kim, Y, and Bannona, D. Divalent metal transporter 1 in Lead and cadmium transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2010) 1012:142–52. doi: 10.1196/annals.1306.011
46. Arredondo, M, Munoz, P, Mura, CV, and Nunez, MT. DMT1, a physiologically relevant apical Cu1+ transporter of intestinal cells. Am J Phys Cell Physiol. (2003) 284:C1525–30. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00480.2002
47. Hubert, N, and Hentze, MW. Previously uncharacterized isoforms of divalent metal transporter (DMT)-1: implications for regulation and cellular function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2002) 99:12345–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.192423399
48. Cao, J, Henry, PR, Davis, S, Cousins, R, Miles, RD, Littell, R, et al. Relative bioavailability of organic zinc sources based on tissue zinc and metallothionein in chicks fed conventional dietary zinc concentrations. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2002) 101:161–70. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8401(02)00051-2
49. Martinez, MM, Hill, GM, Link, JE, Raney, NE, Tempelman, RJ, and Ernst, CW. Pharmacological zinc and phytase supplementation enhance metallothionein mRNA abundance and protein concentration in newly weaned pigs. J Nutr. (2004) 134:538–44. doi: 10.1093/jn/134.3.538
50. Yu, Y, Lu, L, Luo, XG, and Liu, B. Kinetics of zinc absorption by in situ ligated intestinal loops of broilers involved in zinc transporters. Poult Sci. (2008) 87:1146–55. doi: 10.3382/ps.2007-00430
51. Zhang, J, Lv, Y, Tang, C, and Wang, X. Effects of dietary supplementation with palygorskite on intestinal integrity in weaned piglets. Appl Clay Sci. (2013) 86:185–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2013.10.009
52. Wu, QJ, Zhou, YM, Wu, YN, and Wang, T. Intestinal development and function of broiler chickens on diets supplemented with clinoptilolite. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2013) 26:987–94. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2012.12545
53. Wan, XL, Yang, ZB, Yang, WR, Jiang, SZ, Zhang, GG, Johnston, SL, et al. Toxicity of increasing aflatoxin B1 concentrations from contaminated corn with or without clay adsorbent supplementation in ducklings. Poult Sci. (2013) 92:1244–53. doi: 10.3382/ps.2012-02748
54. Tao, Z, Xu, W, Zhu, C, Zhang, S, Shi, Z, Song, W, et al. Effects of ammonia on intestinal microflora and productive performance of laying ducks. Poult Sci. (2019) 98:1947–59. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey578
Keywords: broilers, Zn-loaded montmorillonite, antioxidant capacity, zinc transporter, intestinal function
Citation: Qin S, Wang H, Qin S, Li J, Tang D and Shi Z (2025) Supplementation with Zn-loaded montmorillonite enhanced Zn ion transport, trace element deposition, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal function in broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1609339. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1609339
Edited by:
Mierlita Daniel, University of Oradea, RomaniaReviewed by:
Kambham Sudharani, Sri Venkateswara Veterinary University, IndiaBram Brahmantiyo, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Qin, Wang, Qin, Li, Tang and Shi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhaoguo Shi, MTk5MTM3ODk4NUBxcS5jb20=
 Shizhen Qin
Shizhen Qin Haibo Wang
Haibo Wang Shijiao Qin2
Shijiao Qin2 Defu Tang
Defu Tang Zhaoguo Shi
Zhaoguo Shi