- 1Tuberculosis Research Laboratory, Vaccine and Infectious Disease Research Centre, Translational Health Science and Technology Institute, Faridabad, India
- 2Symbiosis School of Biological Sciences, Symbiosis International University, Lavale, India
- 3Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, India
- 4Department of Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee, India
A Corrigendum on
CitE Enzymes Are Essential for Mycobacterium tuberculosis to Establish Infection in Macrophages and Guinea Pigs
by Arora, G., Chaudhary, D., Kidwai, S., Sharma, D., and Singh, R. (2018). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 8:385. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00385
Due to an oversight by the authors, there was a mistake in the Figure 7 as published. The wild type H&E stained section at 8 weeks post-infection (56 days) were replaced with the sections obtained from another animal in the same experiment. The correct Figure 7 appears below.
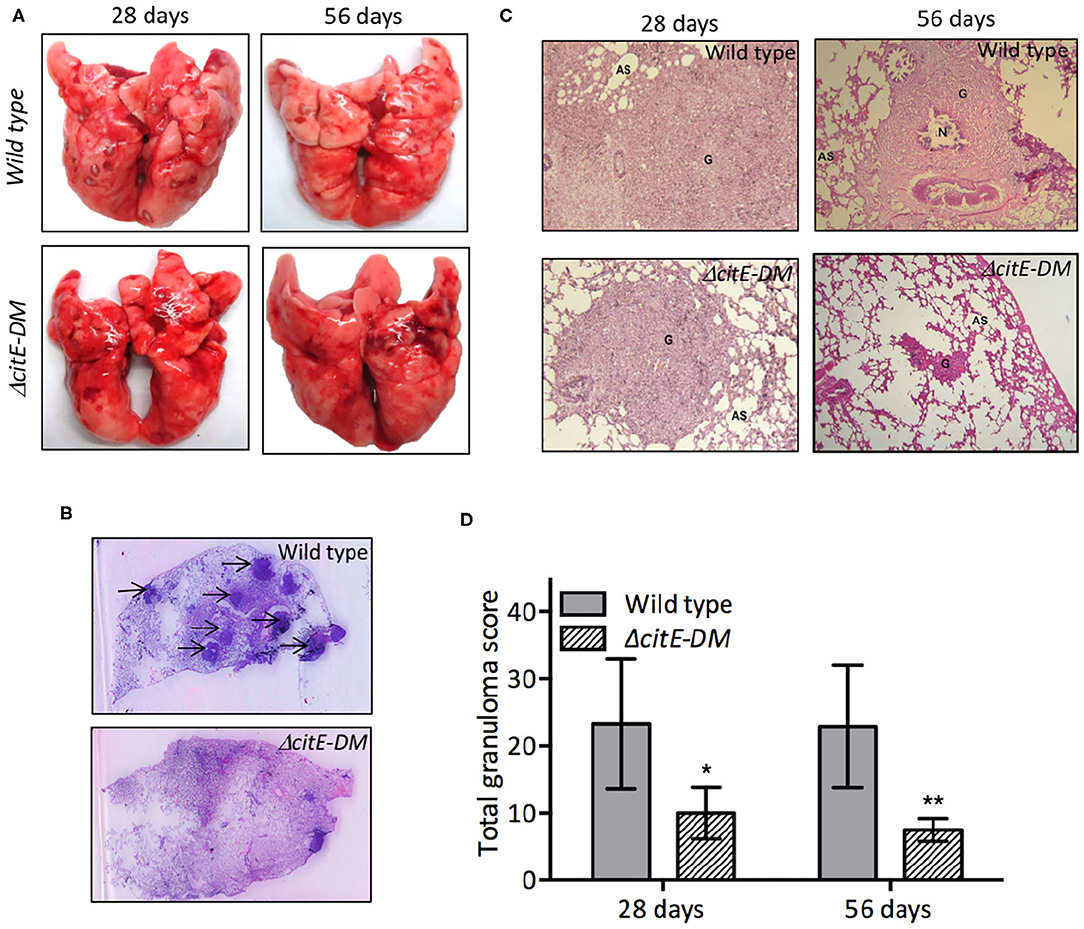
Figure 7. Gross pathological and histopathological analysis of lungs of infected guinea pigs. (A) This panel depicts representative photographs of lungs showing granulomatous lesions from guinea pigs infected with various strains at 4 or 8 weeks post-infection. (B) High-resolution scans (2,400 dpi) of lung sections from infected guinea pigs were performed at 8 weeks post-infection. A representative high-resolution photomicrograph for each group is shown and granulomas are marked by arrows. (C) Images of H & E stained lung sections from guinea pigs at day 28 and 56 post-infection. These images were taken at 40× magnification and show granulomas (G), areas of necrosis (N) and alveolar spaces (AS). (D) Total granuloma score in H&E-stained lung sections of animals infected with wild type or ΔcitE-DM at both 4 and 8 weeks post-infection. Significant differences were observed for the indicated groups (paired two-tailed t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, reverse TCA, β-subunit of citrate lyase, virulence, oxidative stress
Citation: Arora G, Chaudhary D, Kidwai S, Sharma D and Singh R (2020) Corrigendum: CitE Enzymes Are Essential for Mycobacterium tuberculosis to Establish Infection in Macrophages and Guinea Pigs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 10:587907. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.587907
Received: 27 July 2020; Accepted: 09 September 2020;
Published: 30 October 2020.
Edited and reviewed by: John S. Gunn, The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital, United States
Copyright © 2020 Arora, Chaudhary, Kidwai, Sharma and Singh. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ramandeep Singh, cmFtYW5kZWVwQHRoc3RpLnJlcy5pbg==
 Garima Arora1,2
Garima Arora1,2 Deepika Chaudhary
Deepika Chaudhary Deepak Sharma
Deepak Sharma Ramandeep Singh
Ramandeep Singh