- 1Research Institute of Highway, Ministry of Transport, Beijing, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Technology on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Ministry of Transport, Beijing, China
The time series data in many applications, for example, wind power and vehicle trajectory, show significant uncertainty. Using a single prediction value of wind power as feedback information for wind turbine control or unit commitment is not enough since the uncertainty of the prediction is not described. This paper addresses the uncertainty issue in time series data forecasting by proposing the novel interval reservoir computing method. The proposed interval reservoir computing can capture the underlying evolution of the stochastic dynamical system for time series data using the recurrent neural network (RNN). On the other hand, by formulating a chance-constrained optimization problem, interval reservoir computing outputs a set of parameters in the RNN, which maps to an interval of prediction values. The capacity of the interval is the smallest one satisfying the condition that the probability of having a prediction inside the interval is lower than the required level. The scenario approach solves the formulated chance-constrained optimization problem. We implemented an experimental data-based validation to evaluate the proposed method. The validation results show that the proposed interval reservoir computing can give a tight interval of time series data forecasting values for wind power and traffic trajectory. In addition, the confidence probability over the feasibility goes to 1 very quickly as the sample number increases.
1 Introduction
Time series data prediction is vital in many applications for pursuing better control or decision-making performance toward achieving a better society or quality of life. For example, to accomplish the net-zero carbon goal, it is vital to establish a reliable power system with renewable energy for energy supplement instead of high-carbon power generation (Evans et al., 2021). Wind energy is one of the best choices among different kinds of renewable energy resources. However, wind power has a stochastic nature, which makes it challenging to realize the optimal wind power supplementation with high reliability (Zhao et al., 2018; Ge et al., 2022). It is necessary to provide a reliable wind power prediction for the security-constrained unit commitment (SCUC) problem to improve the optimality and reliability of wind power supplementation (Hu and Wu, 2016). Instead of using one single wind power prediction, the SCUC problem involved with wind power often considers the uncertain nature of wind power. It is formulated as a stochastic program (Chen et al., 2015). The random variables, such as wind power, are assumed to be within a bounded set in the formulated stochastic program (Hu et al., 2014; Dai et al., 2016). Only with a reliable set for the random variable will the solution of the stochastic program be faithful. Another critical application scene is safety control in complex traffic environments. It is crucial to give reliable sets for the trajectories of traffic participants surrounding the self-vehicle (Liu et al, 2022; Shen and Raksincharoensak, 2022). For example, Liu et al. (2022) proposed a dynamic lane-changing trajectory generator based on the uncertain evaluation of other vehicle trajectories. Yu et al. (2022) proposed a robust and safe trajectory planning method, considering a bounded uncertainty for the other vehicle trajectories. Lyu et al. (2022) improved the vehicle trajectory prediction accuracy using the information from the connected environment. Thus, a reliable set for the random variable’s prediction is vital for robust control and decision-making.
However, giving a reliable set for the random variable’s prediction is challenging due to the computational complexity issue. Conformal prediction is a method to provide scores on confidence in the prediction value and then gives a confidence interval (Wang et al., 2021). It can also be applied to deep neural networks (Wen et al., 2021). However, it suffers from the “curse of dimensionality.” The computational complexity becomes impractical for applications as the dimension of parameters in the model increases. The Bayesian neural network is an alternative way to provide the confidence interval of the predictions (Neal, 2012; Chen et al., 2021; Xue et al., 2022). The uncertainty is represented by giving the weights on the parameters of the neural network. However, the Bayesian neural network needs many assumptions for practical implementation. A neural network that maps an input to an interval of the predictions is called an interval neural network (INN), first proposed in Ishibuki et al. (1993). Compared to the Bayesian neural network, the INN requires fewer assumptions and can provide probabilistic guarantees on the reliability of the obtained neural network (Ak et al., 2015). Recently, a machine learning-based method, called interval predictor models, was proposed in Campi et al. (2009) and Garattia et al. (2019). The problem of constructing an interval predictor model can be formulated as a chance-constrained optimization problem (Shen et al., 2023). The above methods do not consider the neural networks for dynamic systems. In this paper, we extend the above method to recurrent neural networks combining reservoir computing (Jaeger and Haas, 2004) to address the uncertain quantification problem for predictions in dynamic systems. We call the proposed method “interval reservoir computing.” The proposed interval reservoir computing can capture the underlying evolution of the stochastic dynamical system for time series data using the recurrent neural network (RNN). On the other hand, by formulating a chance-constrained optimization problem, interval reservoir computing outputs a set of parameters in the RNN, which maps to an interval of wind power prediction values. The capacity of the interval is the smallest one satisfying the condition that the probability of having a prediction inside the interval is lower than the required level. The scenario approach solves the formulated chance-constrained optimization problem. We implemented experimental data-based validation to evaluate the proposed method.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 gives a general problem formulation of interval prediction in dynamical systems; Section 3 presents the proposed interval reservoir after briefly introducing reservoir computing and the scenario approach; Section 4 gives the experimental data-based validation; Section 5 concludes the whole paper and discusses future work.
2 Problem formulation: prediction in dynamical systems
In wind power or vehicle trajectory forecasting applications, time series data are generated by an underlying stochastic dynamical system. The stochastic dynamical system has system inputs, hidden states which cannot be observed, and observations that sensors can measure. A graphical model of the addressed stochastic dynamical system is illustrated by Figure 1. Let
where
where
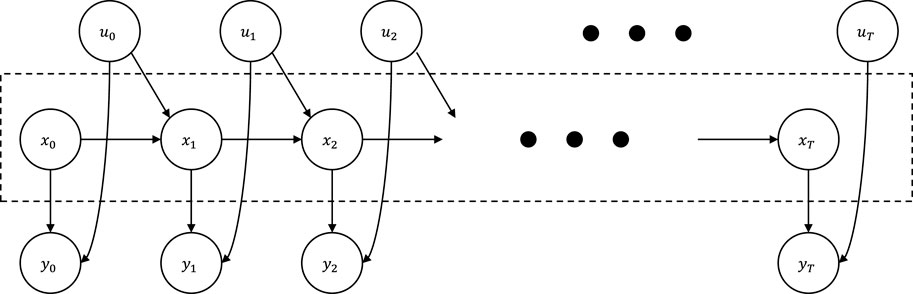
FIGURE 1. Probabilistic graphical model for stochastic dynamical systems with hidden states xt, inputs ut, and observations yt.
The information on f(⋅), g(⋅), r(w), and q(v) is unavailable. In this study, the available information is the dataset UT = {u0, u1, …, uT} of system inputs and the dataset YT = {y0, y1, …, yT} of observations. We want to learn models
Definition 1. Let
where
where
The problem is formally summarized in Problem 1.
Problem 1. Given the system input set UT = {u0, u1, …, uT} and observation set UT = {y0, y1, …, yT}, to obtain
3 Proposed method
In this section, we briefly review the reservoir computing and scenario approach. Then, we give the concept of interval reservoir computing, combining reservoir computing and a scenario approach. The probabilistic reliability of interval reservoir computing to Problem 1 is also given.
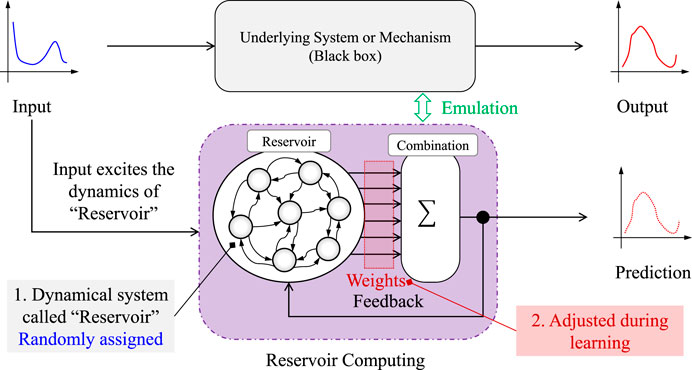
3.1 Brief introduction to reservoir computing
Reservoir computing is a novel algorithm to train a RNN. This study uses the echo state network (ESN) method presented in Jaeger and Haas (2004) to construct RNN. Let
where
On the other hand, the output is computed as
where
• Design of a reservoir vector: a reservoir vector
• Randomly generating
• Determining the output layer by
Figure 2 illustrates the reservoir computing concept.
3.2 Scenario approach
The scenario approach has been applied to obtain the probabilistic boundary for a given nonlinear state space model (Shen et al., 2020a). The theory of the scenario approach has been presented in Calafiore and Campi (2005) for solving robust optimization with the convex objective function and constraint functions. The result has been extended to non-convex cases in Campi et al. (2015). This paper reviews the method of Campi et al. (2015).
The decision variable is
where
Problem Eq. 9 is NP-hard and cannot be solved by any algorithms for a general optimization problem. An approximate problem of that in Eq. 9 is obtained by sampling a dataset δ(1), …, δ(N), which is written by
Let
It is natural to doubt whether
Definition 2. The violation probability of any decision θ ∈ Θ is written as
where
For a given probability level ɛ ∈ (0, 1) and a given confidence bound 1 − β ∈ (0, 1), we want to get a bound of sample number
Theorem 1 of Campi et al. (2015) is stated as follows:
Lemma 1. Let ɛ : {0, …, N} → [0, 1] be a function such that
and
It holds that
where
3.3 Interval reservoir computing
In this study, compared to obtain
Note that the set
The interval output of the RNN obtained via Eq. 15 is explicitly written as
Then, the problem of obtaining a spherical INN is written as
where η is a positive number. Let
Defining the optimal solution set of Problem
Suppose that the dataset
Let
Defining the optimal solution set of Problem
By adapting Lemma 1, we have the following theorem on the probabilistic feasibility of
Theorem 1. Let
where
and
Proof. Since
where
By Theorem 1, we know that it can adjust the sample number T to regulate the violation probability. Using the scenario approach directly, it cannot regulate the violation probability to the desired one. We leave this issue for future work. Based on the theoretical analysis, the algorithm for interval reservoir computing is designed, and the pseudo-code is written in Algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1.Algorithm for interval reservoir computing.
Inputs: data set
1: design of reservoir vector and function according to Eqs 6, 7
2: randomly generate
3: solve Problem
Output:
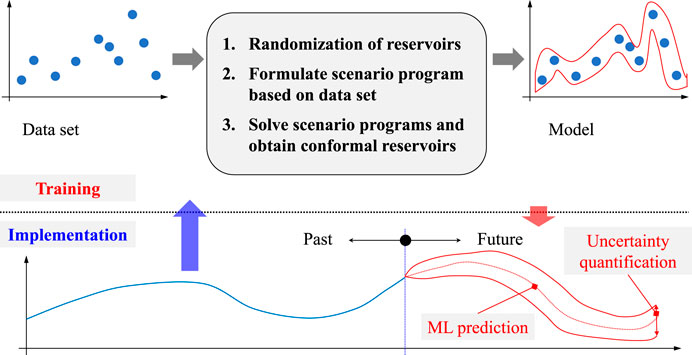
Figure 3 illustrates the proposed framework for implementing the interval reservoir computing method. It follows the general framework widely used to validate the time series model (Shen et al., 2020b). The online obtained history data range from the blue line (not the whole line). Then, the data are used to give the future maximum likelihood prediction (the red dotted line) and the confidence region (the red line) by the model trained by the training dataset.
4 Validations
4.1 Wind power prediction
Let
Here, both
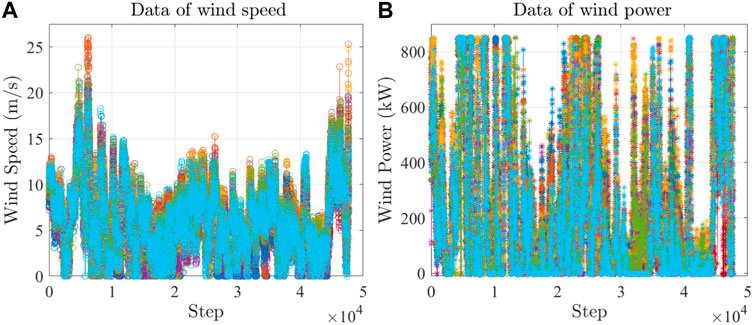
The experimental dataset shown in Figure 4 is used in this validation. Figure 4A plots the time series data on wind speed, and Figure 4B plots the time series data on the wind power at the same time. There are a total of 13 groups of data. Eight groups are used as training datasets; the other groups are used as test datasets.
In this validation, we set the threshold for violation probability as α = 0.05. The number of samples, N, is from {100, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10,000}. Figures 5, 6 show two examples of the one-step-ahead prediction by the proposed interval reservoir computing. The parts (a), (b), (c), and (d) of each figure provide the results with N = 500, N = 1000, N = 2000, and N = 5000, respectively. As the sample number N increases, the size of the interval also increases, while the center of the interval does not change significantly. In particular, as N surpluses 2,000, the probability of having the data inside the interval is less than the required value α = 0.05, implying that the proposed method gives a more conservative interval than we expect.
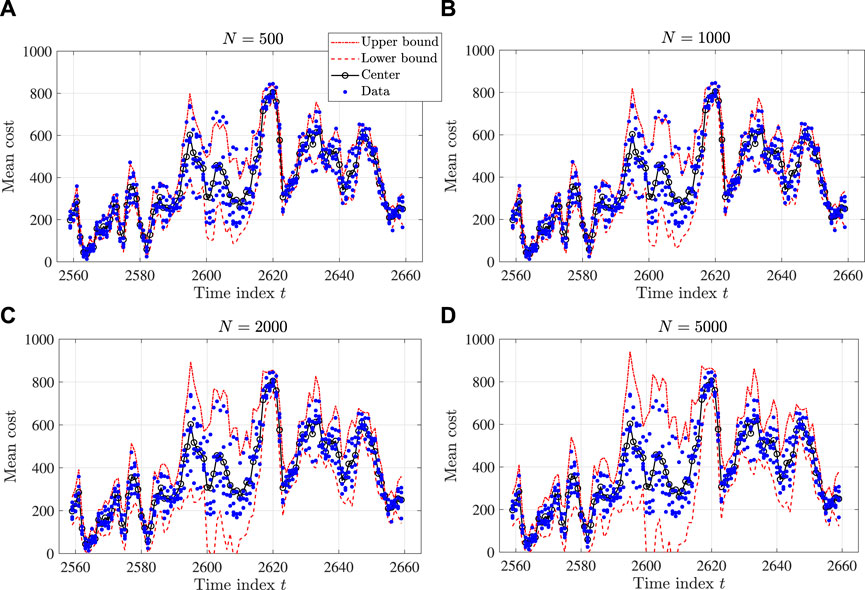
FIGURE 5. Results of a one-step-ahead prediction by the proposed interval reservoir computing (from t = 2560 to t = 2660): (A) N = 500, (B) N = 1000, (C) N = 2000, and (D) N =5000.
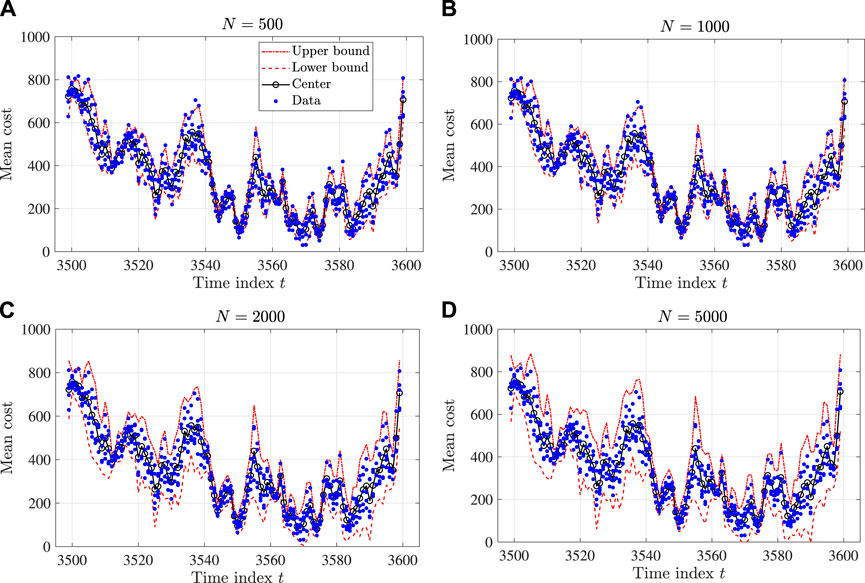
FIGURE 6. Results of a one-step-ahead prediction by the proposed interval reservoir computing (from t = 2560 to t = 2660): (A) N = 500, (B) N = 1000, (C) N = 2000, and (D) N = 5000.
A statistical analysis has been conducted to check the performance of the proposed interval reservoir computing. Monte Carlo tests have been repeated 5,000 times for each choice of sample number N = 100, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10,000. We check the violation probability and CPU time in this Monte Carlo simulation. The metric for checking the performance of the violation probability is
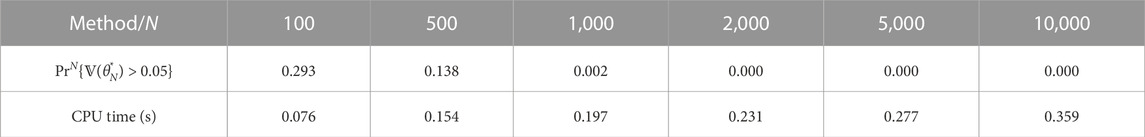
TABLE 1. Statistical performance of the proposed method with different sample numbers N. Mean values of 5,000 Monte Carlo trials are presented.
4.2 Vehicle trajectory prediction
In another example, we have applied the proposed interval reservoir computing to vehicle trajectory prediction. The experimental data are the public dataset “US Highway 101 Dataset.” As in the example of wind power prediction, the number of samples is chosen from {100, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10,000}, and the violation probability threshold is α = 0.05. Figure 7 shows one example of a one-step-ahead prediction for the vehicle trajectory prediction with N = 500 and N = 5000 results.
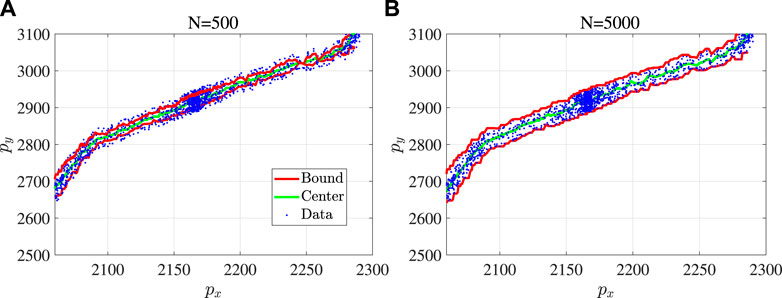
FIGURE 7. One example of a one-step-ahead prediction by the proposed interval reservoir computing for vehicle trajectory prediction: (A) N = 500 and (B) N = 5000.
Statistical analysis has also been conducted in this example of vehicle trajectory prediction. The settings of Monte Carlo tests are the same as the example of wind power prediction. As shown in Table 2, the results are consistent with the results of wind power prediction.
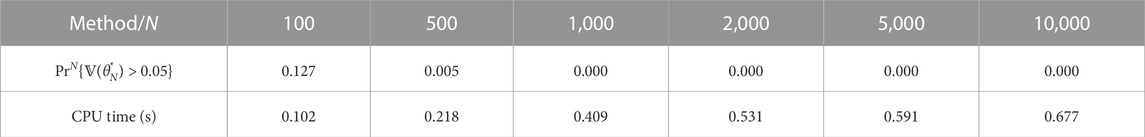
TABLE 2. Statistical performance of the proposed method with different sample numbers N. Mean values of 5,000 Monte Carlo trials are presented.
4.3 Discussion
In this validation, we mainly check the performance of the proposed method with different sample numbers. Indeed, it is necessary to compare the proposed method with other uncertainty quantification methods, such as conformal prediction and Bayesian neural networks. We will further research on this as future work.
One drawback of the proposed interval reservoir computing is that it cannot give an exact interval for a given violation probability α. This drawback comes from using a scenario approach to solve the problem
5 Conclusion and future work
This paper proposes an improved version of interval reservoir computing for time series data forecasting, for example, wind power forecasting and vehicle trajectory forecasting. More than giving a maximum likelihood prediction value of wind power or vehicle trajectory, interval reservoir computing provides an interval of the prediction. The future data will be located inside the interval with a probability larger than the required value. To obtain the interval, a chance-constrained optimization has to be solved for obtaining the interval of the parameters in an RNN. We apply a scenario approach to solve the chance-constrained optimization problem. Experimental data-based validations have been conducted to evaluate the proposed interval reservoir computing. Although the results show that the proposed interval reservoir computing can give a tight interval for wind power forecasting and vehicle trajectory forecasting, the following issues remain to be resolved in future work.
• It is necessary to compare the proposed method with other uncertainty quantification methods, such as the conformal prediction and Bayesian neural networks.
• The scenario approach for solving chance-constrained optimization cannot ensure the convergence of the optimality of the approximate solution. Thus, it is necessary to develop a method that ensures the convergence of the optimality to solve the chance-constrained optimization.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
L-DG: methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, data curation, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. Z-HL: conceptualization, methodology, writing–original draft, writing–review and editing, supervision, and funding acquisition. M-YW: conceptualization, methodology, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. Q-LF: methodology, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. LX: data curation. Z-MZ: data curation. Y-YL: data curation. Y-PZ: supervision and funding acquisition. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Technology on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Ministry of Transport, Beijing, China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ak, R., Vitelli, V., and Zio, E. (2015). An interval-valued neural network approach for uncertainty quantification in short-term wind speed prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 26, 2787–2800. doi:10.1109/tnnls.2015.2396933
Calafiore, G., and Campi, M. C. (2005). Uncertain convex programs: randomized solutions and confidence levels. Math. Program. 102, 25–46. doi:10.1007/s10107-003-0499-y
Campi, M., and Garatti, S. (2011). A sampling-and-discarding approach to chance-constrained optimization: feasibility and optimality. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 148, 257–280. doi:10.1007/s10957-010-9754-6
Campi, M., Garatti, S., and Ramponi, F. (2015). A general scenario theory for nonconvex optimization and decision making. IEEE Trans. Automatic Control 63, 4067–4078. doi:10.1109/tac.2018.2808446
Campi, M. C., Calafiore, G., and Garatti, S. (2009). Interval predictor models: identification and reliability. Automatica 45, 382–392. doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2008.09.004
Chen, C., Lu, C., Wang, B., Trigoni, N., and Markham, A. (2021). Dynanet: neural kalman dynamical model for motion estimation and prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32, 5479–5491. doi:10.1109/tnnls.2021.3112460
Chen, Z., Wu, L., and Shahidehpour, M. (2015). Effective load carrying capability evaluation of renewable energy via stochastic long-term hourly based scuc. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 6, 188–197. doi:10.1109/tste.2014.2362291
Dai, C., Wu, L., and Wu, H. (2016). A multi-band uncertainty set based robust scuc with spatial and temporal budget constraints. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 31, 4988–5000. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2016.2525009
Evans, M., Bono, C., and Wang, Y. (2021). Toward net-zero electricity in europe: what are the challenges for the power system? IEEE Power Energy Mag. 20, 44–54. doi:10.1109/mpe.2022.3167575
Garattia, S., Campib, M., and Care, A. (2019). On a class of interval predictor models with universal reliability. Automatica 110, 108542. doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108542
Ge, X., Qian, J., Fu, Y., Lee, W., and Mi, Y. (2022). Transient stability evaluation criterion of multi-wind farms integrated power system. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 37, 3137–3140. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2022.3156430
Hu, B., and Wu, L. (2016). Robust scuc with multi-band nodal load uncertainty set. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 31, 2491–2492. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2015.2449764
Hu, B., Wu, L., and Marwali, M. (2014). On the robust solution to scuc with load and wind uncertainty correlations. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 29, 2952–2964. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2014.2308637
Ishibuki, H., Tanaka, H., and Okada, H. (1993). An architecture of neural networks with interval weights and its application to fuzzy regression analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 57, 27–39. doi:10.1016/0165-0114(93)90118-2
Jaeger, H., and Haas, H. (2004). Harnessing nonlinearity: predicting chaotic systems and saving energy in wireless communication. Science 304, 78–80. doi:10.1126/science.1091277
Liu, H., Flores, C. E., Spring, J., Shladover, S. E., and Lu, X. Y. (2022a). Field assessment of intersection performance enhanced by traffic signal optimization and vehicle trajectory planning. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transp. Syst. 23, 11549–11561. doi:10.1109/tits.2021.3105329
Liu, Y., Zhou, B., Wang, X., Li, L., Cheng, S., Chen, Z., et al. (2022b). Dynamic lane-changing trajectory planning for autonomous vehicles based on discrete global trajectory. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transp. Syst. 23, 8513–8527. doi:10.1109/tits.2021.3083541
Lyu, N., Wen, J., Duan, Z., and Wu, C. (2022). Vehicle trajectory prediction and cut-in collision warning model in a connected vehicle environment. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transp. Syst. 23, 966–981. doi:10.1109/tits.2020.3019050
Shen, X., Ouyang, T., Yang, N., and Zhuang, J. (2023). Sample-based neural approximation approach for probabilistic constrained programs. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 34, 1058–1065. doi:10.1109/tnnls.2021.3102323
Shen, X., Ouyang, T., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, X. (2020a). Computing probabilistic bounds on state trajectories for uncertain systems. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. early access 7, 285–290. doi:10.1109/TETCI.2020.3019040
Shen, X., and Raksincharoensak, R. (2022). Pedestrian-aware statistical risk assessment. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transp. Syst. 23, 7910–7918. doi:10.1109/tits.2021.3074522
Shen, X., Zhang, Y., Sata, K., and Shen, T. (2020b). Gaussian mixture model clustering-based knock threshold learning in automotive engines. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 25, 2981–2991. doi:10.1109/tmech.2020.3000732
Wang, P., Wang, P., Wang, D., and Xue, B. (2021). A conformal regressor with random forests for tropical cyclone intensity estimation. IEEE Trans. Geoscience Remote Sens. 60, 1–14. doi:10.1109/tgrs.2021.3139930
Wen, H., Gu, J., Ma, J., Yuan, L., and Jin, Z. (2021). Probabilistic load forecasting via neural basis expansion model based prediction intervals. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 12, 3648–3660. doi:10.1109/tsg.2021.3066567
Xue, B., Hu, S., Xu, J., Geng, M., Liu, X., and Meng, H. (2022). Bayesian neural network language modeling for speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, Lang. Process. 30, 2900–2917. doi:10.1109/taslp.2022.3203891
Yu, Y., Shan, D., Benderius, O., Berger, C., and Kang, Y. (2022). Formally robust and safe trajectory planning and tracking for autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transp. Syst. 23, 22971–22987. doi:10.1109/tits.2022.3196623
Keywords: uncertain dynamical systems, probabilistic prediction, time series data, wind power forecasting, vehicle trajectory
Citation: Gao L-D, Li Z-H, Wu M-Y, Fan Q-L, Xu L, Zhang Z-M, Zhang Y-P and Liu Y-Y (2024) Interval reservoir computing: theory and case studies. Front. Energy Res. 11:1239973. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2023.1239973
Received: 14 June 2023; Accepted: 25 July 2023;
Published: 20 February 2024.
Edited by:
Xun Shen, Osaka University, JapanReviewed by:
Shuang Zhao, Hefei University of Technology, ChinaYahui Zhang, Yanshan University, China
Hardeep Singh, University of Windsor, Canada
Copyright © 2024 Gao, Li, Wu, Fan, Xu, Zhang, Zhang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meng-Yi Wu, d215QGl0c2MuY24=
 Lan-Da Gao
Lan-Da Gao Zhen-Hua Li1,2
Zhen-Hua Li1,2 Yan-Yue Liu
Yan-Yue Liu